mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
commit
b3f909bad8
@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
Debian GNU/Linux,22 年未完的美妙旅程
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在2015年8月16日, Debian项目组庆祝了 Debian 的22周年纪念日;这也是开源世界历史最悠久、热门的发行版之一。 Debian项目于1993年由Ian Murdock创立。彼时,Slackware 作为最早的 Linux 发行版已经名声在外。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*22岁生日快乐! Debian Linux!*
|
||||
|
||||
Ian Ashly Murdock, 一个美国职业软件工程师, 在他还是普渡大学的学生时构想出了 Debian 项目的计划。他把这个项目命名为 Debian 是由于这个名字组合了他彼时女友的名字 Debra Lynn 和他自己的名字 Ian。 他之后和 Lynn 结婚并在2008年1月离婚。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Debian 创始人:Ian Murdock*
|
||||
|
||||
Ian 目前是 ExactTarget 的平台与开发社区的副总裁。
|
||||
|
||||
Debian (如同Slackware一样) 都是由于当时缺乏满足合乎标准的发行版才应运而生的。 Ian 在一次采访中说:“免费提供一流的产品会是 Debian 项目的唯一使命。 尽管过去的 Linux 发行版均不尽然可靠抑或是优秀。 我印象里...比如在不同的文件系统间移动文件, 处理大型文件经常会导致内核出错。 但是 Linux 其实是很可靠的, 自由的源代码让这个项目本质上很有前途。”
|
||||
|
||||
"我记得过去我像其他想解决问题的人一样, 想在家里运行一个像 UNIX 的东西。 但那是不可能的, 无论是经济上还是法律上或是别的什么角度。 然后我就听闻了 GNU 内核开发项目, 以及这个项目是如何没有任何法律纷争", Ian 补充到。 他早年在开发 Debian 时曾被自由软件基金会(FSF)资助, 这份资助帮助 Debian 取得了长足的发展; 尽管一年后由于学业原因 Ian 退出了 FSF 转而去完成他的学位。
|
||||
|
||||
### Debian开发历史 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- **Debian 0.01 – 0.09** : 发布于 1993 年八月 – 1993 年十二月。
|
||||
- **Debian 0.91** : 发布于 1994 年一月。 有了原始的包管理系统, 没有依赖管理机制。
|
||||
- **Debian 0.93 rc5** : 发布于 1995 年三月。 “现代”意义的 Debian 的第一次发布, 在基础系统安装后会使用dpkg 安装以及管理其他软件包。
|
||||
- **Debian 0.93 rc6**: 发布于 1995 年十一月。 最后一次 a.out 发布, deselect 机制第一次出现, 有60位开发者在彼时维护着软件包。
|
||||
- **Debian 1.1**: 发布于 1996 年六月。 项目代号 – Buzz, 软件包数量 – 474, 包管理器 dpkg, 内核版本 2.0, ELF 二进制。
|
||||
- **Debian 1.2**: 发布于 1996 年十二月。 项目代号 – Rex, 软件包数量 – 848, 开发者数量 – 120。
|
||||
- **Debian 1.3**: 发布于 1997 年七月。 项目代号 – Bo, 软件包数量 974, 开发者数量 – 200。
|
||||
- **Debian 2.0**: 发布于 1998 年七月。 项目代号 - Hamm, 支持构架 – Intel i386 以及 Motorola 68000 系列, 软件包数量: 1500+, 开发者数量: 400+, 内置了 glibc。
|
||||
- **Debian 2.1**: 发布于1999 年三月九日。 项目代号 – slink, 支持构架 - Alpha 和 Sparc, apt 包管理器开始成型, 软件包数量 – 2250。
|
||||
- **Debian 2.2**: 发布于 2000 年八月十五日。 项目代号 – Potato, 支持构架 – Intel i386, Motorola 68000 系列, Alpha, SUN Sparc, PowerPC 以及 ARM 构架。 软件包数量: 3900+ (二进制) 以及 2600+ (源代码), 开发者数量 – 450。 有一群人在那时研究并发表了一篇论文, 论文展示了自由软件是如何在被各种问题包围的情况下依然逐步成长为优秀的现代操作系统的。
|
||||
- **Debian 3.0**: 发布于 2002 年七月十九日。 项目代号 – woody, 支持构架新增 – HP, PA_RISC, IA-64, MIPS 以及 IBM, 首次以DVD的形式发布, 软件包数量 – 8500+, 开发者数量 – 900+, 支持加密。
|
||||
- **Debian 3.1**: 发布于 2005 年六月六日。 项目代号 – sarge, 支持构架 – 新增 AMD64(非官方渠道发布), 内核 – 2.4 以及 2.6 系列, 软件包数量: 15000+, 开发者数量 : 1500+, 增加了诸如 OpenOffice 套件, Firefox 浏览器, Thunderbird, Gnome 2.8, 支持: RAID, XFS, LVM, Modular Installer。
|
||||
- **Debian 4.0**: 发布于 2007 年四月八日。 项目代号 – etch, 支持构架 – 如前,包括 AMD64。 软件包数量: 18,200+ 开发者数量 : 1030+, 图形化安装器。
|
||||
- **Debian 5.0**: 发布于 2009 年二月十四日。 项目代号 – lenny, 支持构架 – 新增 ARM。 软件包数量: 23000+, 开发者数量: 1010+。
|
||||
- **Debian 6.0**: 发布于 2009 年七月二十九日。 项目代号 – squeeze, 包含的软件包: 内核 2.6.32, Gnome 2.3. Xorg 7.5, 同时包含了 DKMS, 基于依赖包支持。 支持构架 : 新增 kfreebsd-i386 以及 kfreebsd-amd64, 基于依赖管理的启动过程。
|
||||
- **Debian 7.0**: 发布于 2013 年五月四日。 项目代号: wheezy, 支持 Multiarch, 私有云工具, 升级了安装器, 移除了第三方软件依赖, 全功能多媒体套件-codec, 内核版本 3.2, Xen Hypervisor 4.1.4 ,软件包数量: 37400+。
|
||||
- **Debian 8.0**: 发布于 2015 年五月二十五日。 项目代号: Jessie, 将 Systemd 作为默认的初始化系统, 内核版本 3.16, 增加了快速启动(fast booting), service进程所依赖的 cgroups 使隔离部分 service 进程成为可能, 43000+ 软件包。 Sysvinit 初始化工具在 Jessie 中可用。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: Linux的内核第一次是在1991 年十月五日被发布, 而 Debian 的首次发布则在1993 年九月十三日。 所以 Debian 已经在只有24岁的 Linux 内核上运行了整整22年了。
|
||||
|
||||
### Debian 的那些事 ###
|
||||
|
||||
1994年管理和重整了 Debian 项目以使得其他开发者能更好地加入,所以在那一年并没有发布面向用户的更新, 当然, 内部版本肯定是有的。
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 1.0 从来就没有被发布过。 一家 CD-ROM 的生产商错误地把某个未发布的版本标注为了 1.0, 为了避免产生混乱, 原本的 Debian 1.0 以1.1的面貌发布了。 从那以后才有了所谓的官方CD-ROM的概念。
|
||||
|
||||
每个 Debian 新版本的代号都是玩具总动员里某个角色的名字哦。
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 有四种可用版本: 旧稳定版(old stable), 稳定版(stable), 测试版(testing) 以及 试验版(experimental)。 始终如此。
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 项目组一直工作在不稳定发行版上, 这个不稳定版本始终被叫做Sid(玩具总动员里那个邪恶的臭小孩)。 Sid是unstable版本的永久名称, 同时Sid也取自'Still In Development"(译者:还在开发中)的首字母。 Sid 将会成为下一个稳定版, 当前的稳定版本代号为 jessie。
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 的官方发行版只包含开源并且自由的软件, 绝无其他东西. 不过 contrib 和非自由软件包使得安装那些本身自由但是其依赖的软件包不自由(contrib)的软件和非自由软件成为了可能。
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 是一堆Linux 发行版之母。 举几个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
- Damn Small Linux
|
||||
- KNOPPIX
|
||||
- Linux Advanced
|
||||
- MEPIS
|
||||
- Ubuntu
|
||||
- 64studio (不再活跃开发)
|
||||
- LMDE
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 是世界上最大的非商业 Linux 发行版。它主要是由C编写的(32.1%), 一并的还有其他70多种语言。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Debian 开发语言贡献表,图片来源: [Xmodulo][1]*
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 项目包含6,850万行代码, 以及 450万行空格和注释。
|
||||
|
||||
国际空间站放弃了 Windows 和红帽子, 进而换成了 Debian - 在上面的宇航员使用落后一个版本的稳定发行版, 目前是 squeeze; 这么做是为了稳定程度以及来自 Debian 社区的雄厚帮助支持。
|
||||
|
||||
感谢上帝! 我们差点就听到来自国际空间宇航员面对 Windows Metro 界面的尖叫了 :P
|
||||
|
||||
#### 黑色星期三 ####
|
||||
|
||||
2002 年十一月二十日, Twente 大学的网络运营中心(NOC)着火。 当地消防部门放弃了服务器区域。 NOC维护着satie.debian.org 的网站服务器, 这个网站包含了安全、非美国相关的存档、新维护者资料、数量报告、数据库等等;这一切都化为了灰烬。 之后这些服务由 Debian 重建了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 未来版本 ####
|
||||
|
||||
下一个待发布版本是 Debian 9, 项目代号 – Stretch, 它会带来什么还是个未知数。 满心期待吧!
|
||||
|
||||
有很多发行版在 Linux 发行版的历史上出现过一瞬间然后很快消失了。 在多数情况下, 维护一个日渐庞大的项目是开发者们面临的挑战。 但这对 Debian 来说不是问题。 Debian 项目有全世界成百上千的开发者、维护者。 它在 Linux 诞生的之初起便一直存在。
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 在 Linux 生态环境中的贡献是难以用语言描述的。 如果 Debian 没有出现过, 那么 Linux 世界将不会像现在这样丰富和用户友好。 Debian 是为数不多可以被认为安全可靠又稳定的发行版,是作为网络服务器完美选择。
|
||||
|
||||
这仅仅是 Debian 的一个开始。 它走过了这么长的征程, 并将一直走下去。 未来即是现在! 世界近在眼前! 如果你到现在还从来没有使用过 Debian, 我只想问, 你还再等什么? 快去下载一份镜像试试吧, 我们会在此守候遇到任何问题的你。
|
||||
|
||||
- [Debian 主页][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/happy-birthday-to-debian-gnu-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[jerryling315](http://moelf.xyz)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/08/interesting-facts-about-debian-linux.html
|
||||
[2]:https://www.debian.org/
|
||||
@ -1,24 +1,24 @@
|
||||
Linux 内核的发展方向
|
||||
对 Linux 内核的发展方向的展望
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**即将到来的 Linux 4.2 内核涉及到史上最多的贡献者数量,内核开发者 Jonathan Corbet 如是说。**
|
||||
** Linux 4.2 内核涉及到史上最多的贡献者数量,内核开发者 Jonathan Corbet 如是说。**
|
||||
|
||||
来自西雅图。Linux 内核持续增长:代码量在增加,代码贡献者数量也在增加。而随之而来的一些挑战需要处理一下。以上是 Jonathan Corbet 在今年的 LinuxCon 的内核年度报告上提出的主要观点。以下是他的主要演讲内容:
|
||||
西雅图报道。Linux 内核持续增长:代码量在增加,代码贡献者数量也在增加。而随之而来的一些挑战需要处理一下。以上是 Jonathan Corbet 在今年的 LinuxCon 的内核年度报告上提出的主要观点。以下是他的主要演讲内容:
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 4.2 内核依然处于开发阶段,预计在8月23号释出。Corbet 强调有 1569 名开发者为这个版本贡献了代码,其中 277 名是第一次提交代码。
|
||||
Linux 4.2 内核已经于上月底释出。Corbet 强调有 1569 名开发者为这个版本贡献了代码,其中 277 名是第一次提交代码。
|
||||
|
||||
越来越多的开发者的加入,内核更新非常快,Corbet 估计现在大概 63 天就能产生一个新的内核里程碑。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 4.2 涉及多方面的更新。其中一个就是引进了 OverLayFS,这是一种只读型文件系统,它可以实现在一个容器之上再放一个容器。
|
||||
|
||||
网络系统对小包传输性能也有了提升,这对于高频传输领域如金融交易而言非常重要。提升的方面主要集中在减小处理数据包的时间的能耗。
|
||||
网络系统对小包传输性能也有了提升,这对于高频金融交易而言非常重要。提升的方面主要集中在减小处理数据包的时间的能耗。
|
||||
|
||||
依然有新的驱动中加入内核。在每个内核发布周期,平均会有 60 到 80 个新增或升级驱动中加入。
|
||||
|
||||
另一个主要更新是实时内核补丁,这个特性在 4.0 版首次引进,好处是系统管理员可以在生产环境中打上内核补丁而不需要重启系统。当补丁所需要的元素都已准备就绪,打补丁的过程会在后台持续而稳定地进行。
|
||||
|
||||
**Linux 安全, IoT 和其他关注点 **
|
||||
**Linux 安全, IoT 和其他关注点**
|
||||
|
||||
过去一年中,安全问题在开源社区是一个很热的话题,这都归因于那些引发高度关注的事件,比如 Heartbleed 和 Shellshock。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,9 +26,9 @@ Linux 4.2 涉及多方面的更新。其中一个就是引进了 OverLayFS,这
|
||||
|
||||
他强调说过去 10 年间有超过 3 百万行代码不再被开发者修改,而产生 Shellshock 漏洞的代码的年龄已经是 20 岁了,近年来更是无人问津。
|
||||
|
||||
另一个关注点是 2038 问题,Linux 界的“千年虫”,如果不解决,2000 年出现过的问题还会重现。2038 问题说的是在 2038 年一些 Linux 和 Unix 机器会死机(LCTT:32 位系统记录的时间,在2038年1月19日星期二晚上03:14:07之后的下一秒,会变成负数)。Corbet 说现在离 2038 年还有 23 年时间,现在部署的系统都会考虑 2038 问题。
|
||||
另一个关注点是 2038 问题,Linux 界的“千年虫”,如果不解决,2000 年出现过的问题还会重现。2038 问题说的是在 2038 年一些 Linux 和 Unix 机器会死机(LCTT译注:32 位系统记录的时间,在2038年1月19日星期二晚上03:14:07之后的下一秒,会变成负数)。Corbet 说现在离 2038 年还有 23 年时间,现在部署的系统都会考虑 2038 问题。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 已经开始一些初步的方案来修复 2038 问题了,但做的还远远不够。“现在就要修复这个问题,而不是等 20 年后把这个头疼的问题留给下一代解决,我们却享受着退休的美好时光”。
|
||||
Linux 已经启动一些初步的方案来修复 2038 问题了,但做的还远远不够。“现在就要修复这个问题,而不是等 20 年后把这个头疼的问题留给下一代解决,我们却享受着退休的美好时光”。
|
||||
|
||||
物联网(IoT)也是 Linux 关注的领域,Linux 是物联网嵌入式操作系统的主要占有者,然而这并没有什么卵用。Corget 认为日渐臃肿的内核对于未来的物联网设备来说肯定过于庞大。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ via: http://www.eweek.com/enterprise-apps/a-look-at-whats-next-for-the-linux-ker
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sean Michael Kerner][a]
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,13 +1,12 @@
|
||||
KevinSJ Translating
|
||||
四大开源版命令行邮件客户端
|
||||
4 个开源的命令行邮件客户端
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
无论你承认与否,email并没有消亡。对依赖命令行的 Linux 高级用户而言,离开 shell 转而使用传统的桌面或网页版邮件客户端并不合适。归根结底,命令行最善于处理文件,特别是文本文件,能使效率倍增。
|
||||
无论你承认与否,email并没有消亡。对那些对命令行至死不渝的 Linux 高级用户而言,离开 shell 转而使用传统的桌面或网页版邮件客户端并不适应。归根结底,命令行最善于处理文件,特别是文本文件,能使效率倍增。
|
||||
|
||||
幸运的是,也有不少的命令行邮件客户端,他们的用户大都乐于帮助你入门并回答你使用中遇到的问题。但别说我没警告过你:一旦你完全掌握了其中一个客户端,要再使用图基于图形界面的客户端将回变得很困难!
|
||||
幸运的是,也有不少的命令行邮件客户端,而它们的用户大都乐于帮助你入门并回答你使用中遇到的问题。但别说我没警告过你:一旦你完全掌握了其中一个客户端,你会发现很难回到基于图形界面的客户端!
|
||||
|
||||
要安装下述四个客户端中的任何一个是非常容易的;主要 Linux 发行版的软件仓库中都提供此类软件,并可通过包管理器进行安装。你也可以再其他的操作系统中寻找并安装这类客户端,但我并未尝试过也没有相关的经验。
|
||||
要安装下述四个客户端中的任何一个是非常容易的;主要的 Linux 发行版的软件仓库中都提供此类软件,并可通过包管理器进行安装。你也可以在其它的操作系统中寻找并安装这类客户端,但我并未尝试过也没有相关的经验。
|
||||
|
||||
### Mutt ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,7 +16,7 @@ KevinSJ Translating
|
||||
|
||||
许多终端爱好者都听说过甚至熟悉 Mutt 和 Alpine, 他们已经存在多年。让我们先看看 Mutt。
|
||||
|
||||
Mutt 支持许多你所期望 email 系统支持的功能:会话,颜色区分,支持多语言,同时还有很多设置选项。它支持 POP3 和 IMAP, 两个主要的邮件传输协议,以及许多邮箱格式。自从1995年诞生以来, Mutt 即拥有一个活跃的开发社区,但最近几年,新版本更多的关注于修复问题和安全更新而非提供新功能。这对大多数 Mutt 用户而言并无大碍,他们钟爱这样的界面,并支持此项目的口号:“所有邮件客户端都很烂,只是这个烂的没那么彻底。”
|
||||
Mutt 支持许多你所期望 email 系统支持的功能:会话,颜色区分,支持多语言,同时还有很多设置选项。它支持 POP3 和 IMAP 这两个主要的邮件传输协议,以及许多邮箱格式。自从1995年诞生以来, Mutt 就拥有了一个活跃的开发社区,但最近几年,新版本更多的关注于修复问题和安全更新而非提供新功能。这对大多数 Mutt 用户而言并无大碍,他们钟爱这样的界面,并支持此项目的口号:“所有邮件客户端都很烂,只是这个烂的没那么彻底。”
|
||||
|
||||
### Alpine ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,13 +24,13 @@ Mutt 支持许多你所期望 email 系统支持的功能:会话,颜色区
|
||||
- [源代码][5]
|
||||
- 授权协议: [Apache 2.0][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Alpine 是另一款知名的终端邮件客户端,它由华盛顿大学开发,初衷是作为 UW 开发的 Pine 的开源,支持unicode的替代版本。
|
||||
Alpine 是另一款知名的终端邮件客户端,它由华盛顿大学开发,设计初衷是作为一个开源的、支持 unicode 的 Pine (也来自华盛顿大学)的替代版本。
|
||||
|
||||
Alpine 不仅容易上手,还为高级用户提供了很多特性,它支持很多协议 —— IMAP, LDAP, NNTP, POP, SMTP 等,同时也支持不同的邮箱格式。Alpine 内置了一款名为 Pico 的可独立使用的简易文本编辑工具,但你也可以使用你常用的文本编辑器: vi, Emacs等。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管Alpine的升级并不频繁,名为re-alpine的分支为不同的开发者提供了开发此项目的机会。
|
||||
尽管 Alpine 的升级并不频繁,不过有个名为 re-alpine 的分支为不同的开发者提供了开发此项目的机会。
|
||||
|
||||
Alpine 支持再屏幕上显示上下文帮助,但一些用户回喜欢 Mutt 式的独立说明手册,但这两种提供了较好的说明。用户可以同时尝试 Mutt 和 Alpine,并由个人喜好作出决定,也可以尝试以下几个比较新颖的选项。
|
||||
Alpine 支持在屏幕上显示上下文帮助,但一些用户会喜欢 Mutt 式的独立说明手册,不过它们两个的文档都很完善。用户可以同时尝试 Mutt 和 Alpine,并由个人喜好作出决定,也可以尝试以下的几个新选择。
|
||||
|
||||
### Sup ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,10 +38,9 @@ Alpine 支持再屏幕上显示上下文帮助,但一些用户回喜欢 Mutt
|
||||
- [源代码][8]
|
||||
- 授权协议: [GPLv2][9]
|
||||
|
||||
Sup 是我们列表中能被称为“大容量邮件客户端”的两个之一。自称“为邮件较多的人设计的命令行客户端”,Sup 的目标是提供一个支持层次化设计并允许再为会话添加标签进行简单整理的界面。
|
||||
Sup 是我们列表中能被称为“大容量邮件客户端”的二者之一。自称“为邮件较多的人设计的命令行客户端”,Sup 的目标是提供一个支持层次化设计并允许为会话添加标签进行简单整理的界面。
|
||||
|
||||
由于采用 Ruby 编写,Sup 能提供十分快速的搜索并能自动管理联系人列表,同时还允许自定义插件。对于使用 Gmail 作为网页邮件客户端的人们,这些功能都是耳熟能详的,这就使得 Sup 成为一种比较现代的命令行邮件管理方式。
|
||||
Written in Ruby, Sup provides exceptionally fast searching, manages your contact list automatically, and allows for custom extensions. For people who are used to Gmail as a webmail interface, these features will seem familiar, and Sup might be seen as a more modern approach to email on the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
### Notmuch ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,16 +50,17 @@ Written in Ruby, Sup provides exceptionally fast searching, manages your contact
|
||||
|
||||
"Sup? Notmuch." Notmuch 作为 Sup 的回应,最初只是重写了 Sup 的一小部分来提高性能。最终,这个项目逐渐变大并成为了一个独立的邮件客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
Notmuch是一款相当精简的软件。它并不能独立的收发邮件,启用 Notmuch 的快速搜索功能的代码实际上是一个需要调用的独立库。但这样的模块化设计也使得你能使用你最爱的工具进行写信,发信和收信,集中精力做好一件事情并有效浏览和管理你的邮件。
|
||||
Notmuch 是一款相当精简的软件。它并不能独立的收发邮件,启用 Notmuch 的快速搜索功能的代码实际上是设计成一个程序可以调用的独立库。但这样的模块化设计也使得你能使用你最爱的工具进行写信,发信和收信,集中精力做好一件事情并有效浏览和管理你的邮件。
|
||||
|
||||
这个列表并不完整,还有很多 email 客户端,它们或许才是你的最佳选择。你喜欢什么客户端呢?
|
||||
|
||||
这个列表并不完整,还有很多 email 客户端,他们或许才是你的最佳选择。你喜欢什么客户端呢?
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://opensource.com/life/15/8/top-4-open-source-command-line-email-clients
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jason Baker][a]
|
||||
译者:[KevinSJ](https://github.com/KevinSj)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu 15.04 下创建一个可供 Android/iOS 连接的 AP
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我成功地在 Ubuntu 15.04 下用 Gnome Network Manager 创建了一个无线AP热点。接下来我要分享一下我的步骤。请注意:你必须要有一个可以用来创建AP热点的无线网卡。如果你不知道如何确认它的话,在终端(Terminal)里输入`iw list`。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有安装`iw`的话, 在Ubuntu下你可以使用`sudo apt-get install iw`进行安装.
|
||||
|
||||
在你键入`iw list`之后, 查看“支持的接口模式”, 你应该会看到类似下面的条目中看到 AP:
|
||||
|
||||
Supported interface modes:
|
||||
|
||||
* IBSS
|
||||
* managed
|
||||
* AP
|
||||
* AP/VLAN
|
||||
* monitor
|
||||
* mesh point
|
||||
|
||||
让我们一步步看:
|
||||
|
||||
1、 断开WIFI连接。使用有线网络接入你的笔记本。
|
||||
|
||||
2、 在顶栏面板里点击网络的图标 -> Edit Connections(编辑连接) -> 在弹出窗口里点击Add(新增)按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
3、 在下拉菜单内选择Wi-Fi。
|
||||
|
||||
4、 接下来:
|
||||
|
||||
a、 输入一个链接名 比如: Hotspot 1
|
||||
|
||||
b、 输入一个 SSID 比如: Hotspot 1
|
||||
|
||||
c、 选择模式(mode): Infrastructure (基础设施)
|
||||
|
||||
d、 设备 MAC 地址: 在下拉菜单里选择你的无线设备
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
5、 进入Wi-Fi安全选项卡,选择 WPA & WPA2 Personal 并且输入密码。
|
||||
6、 进入IPv4设置选项卡,在Method(方法)下拉菜单里,选择Shared to other computers(共享至其他电脑)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
7、 进入IPv6选项卡,在Method(方法)里设置为忽略ignore (只有在你不使用IPv6的情况下这么做)
|
||||
8、 点击 Save(保存) 按钮以保存配置。
|
||||
9、 从 menu/dash 里打开Terminal。
|
||||
10、 修改你刚刚使用 network settings 创建的连接。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 VIM 编辑器:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo vim /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
或使用Gedit 编辑器:
|
||||
|
||||
gksu gedit /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
把名字 Hotspot 用你在第4步里起的连接名替换掉。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
a、 把 `mode=infrastructure` 改成 `mode=ap` 并且保存文件。
|
||||
b、 一旦你保存了这个文件,你应该能在 Wifi 菜单里看到你刚刚建立的AP了。(如果没有的话请再顶栏里 关闭/打开 Wifi 选项一次)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
11、你现在可以把你的设备连上Wifi了。已经过 Android 5.0的小米4测试。(下载了1GB的文件以测试速度与稳定性)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxveda.com/2015/08/23/how-to-create-an-ap-in-ubuntu-15-04-to-connect-to-androidiphone/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sayantan Das][a]
|
||||
译者:[jerryling315](https://github.com/jerryling315)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxveda.com/author/sayantan_das/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
FISH:Linux 的一个智能易用的 Shell
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
FISH(friendly interactive shell)是一个用户友好的命令行 shell,主要是用来进行交互式使用。shell 就是一个用来执行其他程序的程序。
|
||||
|
||||
### FISH 特性 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 自动建议 ####
|
||||
|
||||
fish 会根据你的历史输入和补完来提供命令建议,就像一个网络浏览器一样。注意了,就是Netscape Navigator 4.0!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 漂亮的VGA 色彩 ####
|
||||
|
||||
fish 原生支持 term256, 它就是一个终端技术的艺术国度。 你将可以拥有一个难以置信的、256 色的shell 来使用。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 理智的脚本 ####
|
||||
|
||||
fish 是完全可以通过脚本控制的,而且它的语法又是那么的简单、干净,而且一致。你甚至不需要去重写。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 基于 web 的配置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
对于少数能使用图形计算机的幸运儿, 你们可以在网页上配置你们自己的色彩方案,以及查看函数、变量和历史记录。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 帮助手册补全 ####
|
||||
|
||||
其它的 shell 支持可配置的补全, 但是只有 fish 可以通过自动转换你安装好的 man 手册来实现补全功能。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 开箱即用 ####
|
||||
|
||||
fish 将会通过 tab 补全和语法高亮使你非常愉快的使用shell, 同时不需要太多的学习或者配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在ubuntu 15.04 上安装FISH
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端,运行下列命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:fish-shell/release-2
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install fish
|
||||
|
||||
###使用FISH###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端,运行下列命令来启动FISH:
|
||||
|
||||
fish
|
||||
|
||||
欢迎来到 fish,友好的交互式shell,输入指令 help 来了解怎么使用fish。
|
||||
|
||||
阅读[FISH 文档][1] ,掌握使用方法。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/fish-a-smart-and-user-friendly-command-line-shell-for-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[oska874](https://github.com/oska874)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
|
||||
[1]:http://fishshell.com/docs/current/index.html#introduction
|
||||
@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FISH – A smart and user-friendly command line shell for Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The friendly interactive shell (FISH). fish is a user friendly command line shell intended mostly for interactive use. A shell is a program used to execute other programs.
|
||||
|
||||
### FISH Features ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Autosuggestions ####
|
||||
|
||||
fish suggests commands as you type based on history and completions, just like a web browser. Watch out, Netscape Navigator 4.0!
|
||||
|
||||
#### Glorious VGA Color ####
|
||||
|
||||
fish natively supports term256, the state of the art in terminal technology. You'll have an astonishing 256 colors available for use!
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sane Scripting ####
|
||||
|
||||
fish is fully scriptable, and its syntax is simple, clean, and consistent. You'll never write esac again.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Web Based configuration ####
|
||||
|
||||
For those lucky few with a graphical computer, you can set your colors and view functions, variables, and history all from a web page.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Man Page Completions ####
|
||||
|
||||
Other shells support programmable completions, but only fish generates them automatically by parsing your installed man pages.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Works Out Of The Box ####
|
||||
|
||||
fish will delight you with features like tab completions and syntax highlighting that just work, with nothing new to learn or configure.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install FISH On ubuntu 15.04 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Open the terminal and run the following commands
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:fish-shell/release-2
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install fish
|
||||
|
||||
**Using FISH**
|
||||
|
||||
Open the terminal and run the following command to start FISH
|
||||
|
||||
fish
|
||||
|
||||
Welcome to fish, the friendly interactive shell Type help for instructions on how to use fish
|
||||
|
||||
Check [FISH Documentation][1] How to use.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/fish-a-smart-and-user-friendly-command-line-shell-for-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
|
||||
[1]:http://fishshell.com/docs/current/index.html#introduction
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
ictlyh Translating
|
||||
Do Simple Math In Ubuntu And elementary OS With NaSC
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
ictlyh Translating
|
||||
How To Manage Log Files With Logrotate On Ubuntu 12.10
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
#### About Logrotate ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How To Set Up Your FTP Server In Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In this lesson, I will explain to you how to Set up your FTP server. But first, let me quickly tell you what is FTP.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is FTP? ###
|
||||
|
||||
[FTP][1] is an acronym for File Transfer Protocol. As the name suggests, FTP is used to transfer files between computers on a network. You can use FTP to exchange files between computer accounts, transfer files between an account and a desktop computer, or access online software archives. Keep in mind, however, that many FTP sites are heavily used and require several attempts before connecting.
|
||||
|
||||
An FTP address looks a lot like an HTTP or website address except it uses the prefix ftp:// instead of http://.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is an FTP Server? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Typically, a computer with an FTP address is dedicated to receive an FTP connection. A computer dedicated to receiving an FTP connection is referred to as an FTP server or FTP site.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let’s begin a special adventure. We will make FTP server to share files with friends and family. I will use [vsftpd][2] for this purpose.
|
||||
|
||||
VSFTPD is an FTP server software which claims to be the most secure FTP software. In fact, the first two letters in VSFTPD, stand for “very secure”. The software was built around the vulnerabilities of the FTP protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
Nevertheless, you should always remember that there are better solutions for secure transfer and management of files such as SFTP (uses [OpenSSH][3]). The FTP protocol is particularly useful for sharing non-sensitive data and is very reliable at that.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Installing VSFTPD in rpm distributions: ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can quickly install VSFTPD on your server through the command line interface with:
|
||||
|
||||
dnf -y install vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
#### Installing VSFTPD in deb distributions: ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can quickly install VSFTPD on your server through the command line interface with:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
#### Installing VSFTPD in Arch distribution: ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can quickly install VSFTPD on your server through the command line interface with:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo pacman -S vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
#### Configuring FTP server ####
|
||||
|
||||
Most VSFTPD’s configuration takes place in /etc/vsftpd.conf. The file itself is well-documented, so this section only highlights some important changes you may want to make. For all available options and basic documentation see the man pages:
|
||||
|
||||
man vsftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Files are served by default from /srv/ftp as per the Filesystem Hierarchy Standard.
|
||||
|
||||
**Enable Uploading:**
|
||||
|
||||
The “write_enable” flag must be set to YES in order to allow changes to the filesystem, such as uploading:
|
||||
|
||||
write_enable=YES
|
||||
|
||||
**Allow Local Users to Login:**
|
||||
|
||||
In order to allow users in /etc/passwd to login, the “local_enable” directive must look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
local_enable=YES
|
||||
|
||||
**Anonymous Login**
|
||||
|
||||
The following lines control whether anonymous users can login:
|
||||
|
||||
# Allow anonymous login
|
||||
|
||||
anonymous_enable=YES
|
||||
# No password is required for an anonymous login (Optional)
|
||||
no_anon_password=YES
|
||||
# Maximum transfer rate for an anonymous client in Bytes/second (Optional)
|
||||
anon_max_rate=30000
|
||||
# Directory to be used for an anonymous login (Optional)
|
||||
anon_root=/example/directory/
|
||||
|
||||
**Chroot Jail**
|
||||
|
||||
It is possible to set up a chroot environment, which prevents the user from leaving his home directory. To enable this, add/change the following lines in the configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
chroot_list_enable=YES chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
|
||||
|
||||
The “chroot_list_file” variable specifies the file in which the jailed users are contained to.
|
||||
|
||||
In the end you must restart your ftp server. Type in your command line
|
||||
|
||||
sudo systemctl restart vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. Your FTP server is up and running.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/set-ftp-server-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[alimiracle][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/ali/
|
||||
[1]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File_Transfer_Protocol
|
||||
[2]:https://security.appspot.com/vsftpd.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.openssh.com/
|
||||
@ -1,113 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Install QGit Viewer in Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
QGit is a free and Open Source GUI git viewer written on Qt and C++ by Marco Costalba. It is a better git viewer which provides us the ability to browse revisions history, view commits and patches applied to the files under a simple GUI environment. It utilizes git command line to process execute the commands and to display the output. It has some common features like to view revisions, diffs, files history, files annotation, archive tree. We can format and apply patch series with the selected commits, drag and drop commits between two instances and more with QGit Viewer. It allows us to create custom buttons with which we can add more buttons to execute a specific command when pressed using its builtin Action Builder.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some easy steps on how we can compile and install QGit Viewer from its source code in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS "Trusty".
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Installing QT4 Libraries ###
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, we'll need have QT4 Libraries installed in order to run QGit viewer in our ubuntu machine. As apt is the default package manager of ubuntu and QT4 packages is available in the official repository of ubutnu, we'll gonna install qt4-default using apt-get command as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install qt4-default
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Downloading QGit Tarball ###
|
||||
|
||||
After installing Qt4 libraries, we'll gonna install git so that we can clone the Git repository of QGit Viewer for Qt 4 . To do so, we'll run the following apt-get command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install git
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll clone the repository using git command as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
$ git clone git://repo.or.cz/qgit4/redivivus.git
|
||||
|
||||
Cloning into 'redivivus'...
|
||||
remote: Counting objects: 7128, done.
|
||||
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (2671/2671), done.
|
||||
remote: Total 7128 (delta 5464), reused 5711 (delta 4438)
|
||||
Receiving objects: 100% (7128/7128), 2.39 MiB | 470.00 KiB/s, done.
|
||||
Resolving deltas: 100% (5464/5464), done.
|
||||
Checking connectivity... done.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Compiling QGit ###
|
||||
|
||||
After we have cloned the repository, we'll now enter into the directory named redivivus and create the makefile which we'll require to compile qgit viewer. So, to enter into the directory, we'll run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd redivivus
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we'll run the following command in order to generate a new Makefile from qmake project file ie qgit.pro.
|
||||
|
||||
$ qmake qgit.pro
|
||||
|
||||
After the Makefile has been generated, we'll now finally compile the source codes of qgit and get the binary as output. To do so, first we'll need to install make and g++ package so that we can compile, as it is a program written in C++ .
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install make g++
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll gonna compile the codes using make command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Installing QGit ###
|
||||
|
||||
As we have successfully compiled the source code of QGit viewer, now we'll surely wanna install it in our Ubuntu 14.04 machine so that we can execute it from our system. To do so, we'll run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
cd src/ && make -f Makefile install
|
||||
make[1]: Entering directory `/home/arun/redivivus/src'
|
||||
make -f Makefile.Release install
|
||||
make[2]: Entering directory `/home/arun/redivivus/src'
|
||||
install -m 755 -p "../bin/qgit" "/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qt4/bin/qgit"
|
||||
strip "/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qt4/bin/qgit"
|
||||
make[2]: Leaving directory `/home/arun/redivivus/src'
|
||||
make[1]: Leaving directory `/home/arun/redivivus/src'
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we'll need to copy the built qgit binary file from bin directory to /usr/bin/ directory so that it will be available as global command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp bin/qgit /usr/bin/
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Creating Desktop File ###
|
||||
|
||||
As we have successfully installed qgit in our Ubuntu box, we'll now go for create a desktop file so that QGit will be available under Menu or Launcher of our Desktop Environment. To do so, we'll need to create a new file named qgit.desktop under /usr/share/applications/ directory.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /usr/share/applications/qgit.desktop
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll need to paste the following lines into the file.
|
||||
|
||||
[Desktop Entry]
|
||||
Name=qgit
|
||||
GenericName=git GUI viewer
|
||||
Exec=qgit
|
||||
Icon=qgit
|
||||
Type=Application
|
||||
Comment=git GUI viewer
|
||||
Terminal=false
|
||||
MimeType=inode/directory;
|
||||
Categories=Qt;Development;RevisionControl;
|
||||
|
||||
After done, we'll simply save the file and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Running QGit Viewer ###
|
||||
|
||||
After QGit is installed successfully in our Ubuntu box, we can now run it from any launcher or application menu. In order to run QGit from the terminal, we'll need to run as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ qgit
|
||||
|
||||
This will open the Qt4 Framework based QGit Viewer in GUI mode.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
QGit is really an awesome QT based git viewer. It is available on all three platforms Linux, Mac OSX and Microsoft Windows. It helps us to easily navigate to the history, revisions, branches and more from the available git repository. It reduces the need of running git command line for the common stuffs like viewing revisions, history, diff, etc as graphical interface of it makes easy to do tasks. The latest version of qgit is also available in the default repository of ubuntu which we can install using **apt-get install qgit** command. So, qgit makes our work pretty fast and easy to do with its simple GUI.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-qgit-viewer-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
translation by strugglingyouth
|
||||
Install Qmmp 0.9.0 Winamp-like Audio Player in Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
@ -69,4 +70,4 @@ via: http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/2015/09/qmmp-0-9-0-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/about/
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/~forkotov02/+archive/ubuntu/ppa
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/~forkotov02/+archive/ubuntu/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,5 @@
|
||||
Installing NGINX and NGINX Plus With Ansible
|
||||
translation by strugglingyouth
|
||||
nstalling NGINX and NGINX Plus With Ansible
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Coming from a production operations background, I have learned to love all things related to automation. Why do something by hand if a computer can do it for you? But creating and implementing automation can be a difficult task given an ever-changing infrastructure and the various technologies surrounding your environments. This is why I love [Ansible][1]. Ansible is an open source tool for IT configuration management, deployment, and orchestration that is extremely easy to use.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -447,4 +448,4 @@ via: https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/
|
||||
[33]:http://docs.ansible.com/ansible/shell_module.html
|
||||
[34]:https://www.nginx.com/blog/installing-nginx-nginx-plus-ansible/#deploy-nginx
|
||||
[35]:http://docs.ansible.com/
|
||||
[36]:https://www.nginx.com/nginxconf/
|
||||
[36]:https://www.nginx.com/nginxconf/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
ictlyh Translating
|
||||
Make Math Simple in Ubuntu / Elementary OS via NaSC
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
How to Download, Install, and Configure Plank Dock in Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
It’s a well-known fact that Linux is extremely customizable with users having a lot of options to choose from – be it the operating systems’ various distributions or desktop environments available for a single distro. Like users of any other OS, Linux users also have different tastes and preferences, especially when it comes to desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
While some users aren’t particularly bothered about their desktop, others take special care to make sure that their desktop looks cool and attractive, something for which there are various applications available. One such application that brings life to your desktop – especially if you use a global menu on the top – is the dock. There are many dock applications available for Linux; if you’re looking for the simplest one, then look no further than [Plank][1], which we’ll be discussing in this article.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: the examples and commands mentioned here have been tested on Ubuntu (version 14.10) and Plank version 0.9.1.1383.
|
||||
|
||||
### Plank ###
|
||||
|
||||
The official documentation describes Plank as the “simplest dock on the planet.” The project’s goal is to provide just what a dock needs, although it’s essentially a library which can be extended to create other dock programs with more advanced features.
|
||||
|
||||
What’s worth mentioning here is that Plank, which comes pre-installed in elementary OS, is the underlying technology for Docky, a popular dock application which is very similar in functionality to Mac OS X’s Dock.
|
||||
|
||||
### Download and Install ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can download and install Plank by executing the following commands on your terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:docky-core/stable
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install plank
|
||||
|
||||
Once installed successfully, you can open the application by typing the name Plank in Unity Dash (see image below), or open it from the App Menu if you aren’t using the Unity environment.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Features ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once the Plank dock is enabled, you’ll see it sitting at the center-bottom of your desktop.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see in the image above, the dock contains some application icons with an orange color indication below those which are currently running. Needless to say, you can click an icon to open that application. Also, a right-click on any application icon will produce some more options that you might be interested in. For example, see the screen-shot below:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To access the configuration options, you’ll have to do a right-click on Plank’s icon (which is the first one from the left), and then click the Preferences option. This will produce the following window.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, the preference window consists of two tabs: Appearance and Behavior, with the former being selected by default. The Appearance tab contains settings related to the Plank theme, the dock’s position, and alignment, as well as that related to icons, while the Behavior tab contains settings related to the dock itself.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For example, I changed the position of the dock to Right from within the Appearance tab and locked the icons (which means no “Keep in Dock” option on right-click) from the Behavior tab.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see in the screen-shot above, the changes came into effect. Similarly, you can tweak any available setting as per your requirement.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Like I said in the beginning, having a dock isn’t mandatory. However, using one definitely makes things convenient, especially if you’ve been using Mac and have recently switched over to Linux for whatever reason. For its part, Plank not only offers simplicity, but dependability and stability as well – the project is well-maintained.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/download-install-configure-plank-dock-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Himanshu Arora][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/himanshu/
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/plank
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
How to Run ISO Files Directly From the HDD with GRUB2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Most Linux distros offer a live environment, which you can boot up from a USB drive, for you to test the system without installing. You can either use it to evaluate the distro or as a disposable OS. While it is easy to copy these onto a USB disk, in certain cases one might want to run the same ISO image often or run different ones regularly. GRUB 2 can be configured so that you do not need to burn the ISOs to disk or use a USB drive, but need to run a live environment directly form the boot menu.
|
||||
|
||||
### Obtaining and checking bootable ISO images ###
|
||||
|
||||
To obtain an ISO image, you should usually visit the website of the desired distribution and download any image that is compatible with your setup. If the image can be started from a USB, it should be able to start from the GRUB menu as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the image has finished downloading, you should check its integrity by running a simple md5 check on it. This will output a long combination of numbers and alphanumeric characters
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
which you can compare against the MD5 checksum provided on the download page. The two should be identical.
|
||||
|
||||
### Setting up GRUB 2 ###
|
||||
|
||||
ISO images contain full systems. All you need to do is direct GRUB2 to the appropriate file, and tell it where it can find the kernel and the initramdisk or initram filesystem (depending on which one your distribution uses).
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, a Kubuntu 15.04 live environment will be set up to run on an Ubuntu 14.04 box as a Grub menu item. It should work for most newer Ubuntu-based systems and derivatives. If you have a different system or want to achieve something else, you can get some ideas on how to do this from one of [these files][1], although it will require a little experience with GRUB.
|
||||
|
||||
In this example the file `kubuntu-15.04-desktop-amd64.iso`
|
||||
|
||||
lives in `/home/maketecheasier/TempISOs/` on `/dev/sda1`.
|
||||
|
||||
To make GRUB2 look for it in the right place, you need to edit the
|
||||
|
||||
/etc/grub.d40-custom
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To start Kubuntu from the above location, add the following code (after adjusting it to your needs) below the commented section, without modifying the original content.
|
||||
|
||||
menuentry "Kubuntu 15.04 ISO" {
|
||||
set isofile="/home/maketecheasier/TempISOs/kubuntu-15.04-desktop-amd64.iso"
|
||||
loopback loop (hd0,1)$isofile
|
||||
echo "Starting $isofile..."
|
||||
linux (loop)/casper/vmlinuz.efi boot=casper iso-scan/filename=${isofile} quiet splash
|
||||
initrd (loop)/casper/initrd.lz
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Breaking down the above code ###
|
||||
|
||||
First set up a variable named `$menuentry`. This is where the ISO file is located. If you want to change to a different ISO, you need to change the bit where it says set `isofile="/path/to/file/name-of-iso-file-.iso"`.
|
||||
|
||||
The next line is where you specify the loopback device; you also need to give it the right partition number. This is the bit where it says
|
||||
|
||||
loopback loop (hd0,1)$isofile
|
||||
|
||||
Note the hd0,1 bit; it is important. This means first HDD, first partition (`/dev/sda1`).
|
||||
|
||||
GRUB’s naming here is slightly confusing. For HDDs, it starts counting from “0”, making the first HDD #0, the second one #1, the third one #2, etc. However, for partitions, it will start counting from 1. First partition is #1, second is #2, etc. There might be a good reason for this but not necessarily a sane one (UX-wise it is a disaster, to be sure)..
|
||||
|
||||
This makes fist disk, first partition, which in Linux would usually look something like `/dev/sda1` become `hd0,1` in GRUB2. The second disk, third partition would be `hd1,3`, and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
The next important line is
|
||||
|
||||
linux (loop)/casper/vmlinuz.efi boot=casper iso-scan/filename=${isofile} quiet splash
|
||||
|
||||
It will load the kernel image. On newer Ubuntu Live CDs, this would be in the `/casper` directory and called `vmlinuz.efi`. If you use a different system, your kernel might be missing the `.efi` extension or be located somewhere else entirely (You can easily check this by opening the ISO file with an archive manager and looking inside `/casper.`). The last options, `quiet splash`, would be your regular GRUB options, if you care to change them.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally
|
||||
|
||||
initrd (loop)/casper/initrd.lz
|
||||
|
||||
will load `initrd`, which is responsible to load a RAMDisk into memory for bootup.
|
||||
|
||||
### Booting into your live system ###
|
||||
|
||||
To make it all work, you will only need to update GRUB2
|
||||
|
||||
sudo update-grub
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When you reboot your system, you should be presented with a new GRUB entry which will allow you to load into the ISO image you’ve just set up.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Selecting the new entry should boot you into the live environment, just like booting from a DVD or USB would.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/run-iso-files-hdd-grub2/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
[1]:http://git.marmotte.net/git/glim/tree/grub2
|
||||
186
sources/tech/20150908 List Of 10 Funny Linux Commands.md
Normal file
186
sources/tech/20150908 List Of 10 Funny Linux Commands.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,186 @@
|
||||
translating by tnuoccalanosrep
|
||||
List Of 10 Funny Linux Commands
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Working from the Terminal is really fun. Today, we’ll list really funny Linux commands which will bring smile on your face.**
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. rev ###
|
||||
|
||||
Create a file, type some words in this file, rev command will dump all words written by you in reverse.
|
||||
|
||||
# rev <file name>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. fortune ###
|
||||
|
||||
This command is not install by default, install with apt-get and fortune will display some random sentence.
|
||||
|
||||
crank@crank-System:~$ sudo apt-get install fortune
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Use **-s** option with fortune, it will limit the out to one sentence.
|
||||
|
||||
# fortune -s
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. yes ###
|
||||
|
||||
#yes <string>
|
||||
|
||||
This command will keep displaying the string for infinite time until the process is killed by the user.
|
||||
|
||||
# yes unixmen
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. figlet ###
|
||||
|
||||
This command can be installed with apt-get, comes with some ascii fonts which are located in **/usr/share/figlet**.
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/share/figlet
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
#figlet -f <font> <string>
|
||||
|
||||
e.g.
|
||||
|
||||
#figlet -f big.flf unixmen
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#figlet -f block.flf unixmen
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can try another options also.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. asciiquarium ###
|
||||
|
||||
This command will transform your terminal in to a Sea Aquarium.
|
||||
Download term animator
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://search.cpan.org/CPAN/authors/id/K/KB/KBAUCOM/Term-Animation-2.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Install and Configure above package.
|
||||
|
||||
# tar -zxvf Term-Animation-2.4.tar.gz
|
||||
# cd Term-Animation-2.4/
|
||||
# perl Makefile.PL && make && make test
|
||||
# sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
Install following package:
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install libcurses-perl
|
||||
|
||||
Download and install asciiquarium
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://www.robobunny.com/projects/asciiquarium/asciiquarium.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar -zxvf asciiquarium.tar.gz
|
||||
# cd asciiquarium_1.0/
|
||||
# cp asciiquarium /usr/local/bin/
|
||||
|
||||
Run,
|
||||
|
||||
# /usr/local/bin/asciiquarium
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 6. bb ###
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install bb
|
||||
# bb
|
||||
|
||||
See what comes out:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 7. sl ###
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes you type **sl** instead of **ls** by mistake,actually **sl** is a command and a locomotive engine will start moving if you type sl.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install sl
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# sl
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 8. cowsay ###
|
||||
|
||||
Very common command, is will display in ascii form whatever you wants to say.
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install cowsay
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# cowsay <string>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Or, you can use another character instead of com, such characters are stored in **/usr/share/cowsay/cows**
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /usr/share/cowsay/cows
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
cowsay -f ghostbusters.cow unixmen
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
# cowsay -f bud-frogs.cow Rajneesh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 9. toilet ###
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, this is a command, it dumps ascii strings in colored form to the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install toilet
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# toilet --gay unixmen
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
toilet -F border -F gay unixmen
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
toilet -f mono12 -F metal unixmen
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 10. aafire ###
|
||||
|
||||
Put you terminal on fire with aafire.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install libaa-bin
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# aafire
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
That it, Have fun with Linux Terminal!!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/list-10-funny-linux-commands/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Rajneesh Upadhyay][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/rajneesh/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
|
||||
Linux Server See the Historical and Statistical Uptime of System With tuptime Utility
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
You can use the following tools to see how long system has been running on a Linux or Unix-like system:
|
||||
|
||||
- uptime : Tell how long the server has been running.
|
||||
- lastt : Show the reboot and shutdown time.
|
||||
- tuptime : Report the historical and statistical running time of system, keeping it between restarts. Like uptime command but with more interesting output.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Finding out the system last reboot time and date ####
|
||||
|
||||
You [can use the following commands to get the last reboot and shutdown time and date on a Linux][1] operating system (also works on OSX/Unix-like system):
|
||||
|
||||
## Just show system reboot and shutdown date and time ###
|
||||
who -b
|
||||
last reboot
|
||||
last shutdown
|
||||
## Uptime info ##
|
||||
uptime
|
||||
cat /proc/uptime
|
||||
awk '{ print "up " $1 /60 " minutes"}' /proc/uptime
|
||||
w
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample outputs:**
|
||||
|
||||
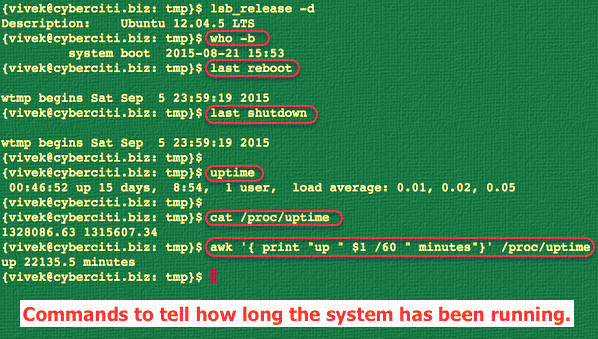
|
||||
|
||||
Fig.01: Various Linux commands in action to find out the server uptime
|
||||
|
||||
**Say hello to tuptime**
|
||||
|
||||
The tuptime command line tool can report the following information on a Linux based system:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Count system startups
|
||||
1. Register first boot time (a.k.a. installation time)
|
||||
1. Count nicely and accidentally shutdowns
|
||||
1. Average uptime and downtime
|
||||
1. Current uptime
|
||||
1. Uptime and downtime rate since first boot time
|
||||
1. Accumulated system uptime, downtime and total
|
||||
1. Report each startup, uptime, shutdown and downtime
|
||||
|
||||
#### Installation ####
|
||||
|
||||
Type the [following command to clone a git repo on a Linux operating system][2]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /tmp
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/rfrail3/tuptime.git
|
||||
$ ls
|
||||
$ cd tuptime
|
||||
$ ls
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample outputs:**
|
||||
|
||||
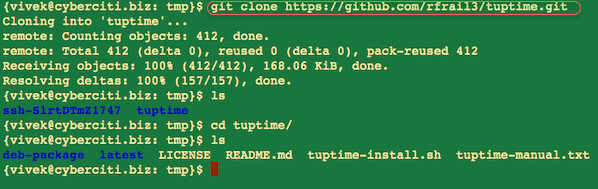
|
||||
|
||||
Fig.02: Cloning a git repo
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you've Python v2.7 installed with sys, optparse, os, re, string, sqlite3, datetime, disutils, and locale modules.
|
||||
|
||||
You can simply install it as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo tuptime-install.sh
|
||||
|
||||
OR do a manual installation (recommended method due to systemd or non-systemd based Linux system):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp /tmp/tuptime/latest/cron.d/tuptime /etc/cron.d/tuptime
|
||||
|
||||
If is a system with systemd, copy service file and enable it:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp /tmp/tuptime/latest/systemd/tuptime.service /lib/systemd/system/
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl enable tuptime.service
|
||||
|
||||
If the systemd don't have systemd, copy init file:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp /tmp/tuptime/latest/init.d/tuptime.init.d-debian7 /etc/init.d/tuptime
|
||||
$ sudo update-rc.d tuptime defaults
|
||||
|
||||
**Run it**
|
||||
|
||||
Simply type the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo tuptime
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample outputs:**
|
||||
|
||||
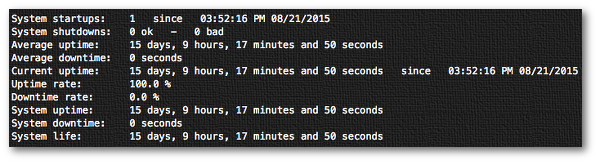
|
||||
|
||||
Fig.03: tuptime in action
|
||||
|
||||
After kernel upgrade I rebooted the box and typed the same command again:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo tuptime
|
||||
System startups: 2 since 03:52:16 PM 08/21/2015
|
||||
System shutdowns: 1 ok - 0 bad
|
||||
Average uptime: 7 days, 16 hours, 48 minutes and 3 seconds
|
||||
Average downtime: 2 hours, 30 minutes and 5 seconds
|
||||
Current uptime: 5 minutes and 28 seconds since 06:23:06 AM 09/06/2015
|
||||
Uptime rate: 98.66 %
|
||||
Downtime rate: 1.34 %
|
||||
System uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 36 minutes and 7 seconds
|
||||
System downtime: 5 hours, 0 minutes and 11 seconds
|
||||
System life: 15 days, 14 hours, 36 minutes and 18 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
You can change date and time format as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo tuptime -d '%H:%M:%S %m-%d-%Y'
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample outputs:**
|
||||
|
||||
System startups: 1 since 15:52:16 08-21-2015
|
||||
System shutdowns: 0 ok - 0 bad
|
||||
Average uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 21 minutes and 19 seconds
|
||||
Average downtime: 0 seconds
|
||||
Current uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 21 minutes and 19 seconds since 15:52:16 08-21-2015
|
||||
Uptime rate: 100.0 %
|
||||
Downtime rate: 0.0 %
|
||||
System uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 21 minutes and 19 seconds
|
||||
System downtime: 0 seconds
|
||||
System life: 15 days, 9 hours, 21 minutes and 19 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
Enumerate each startup, uptime, shutdown and downtime:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo tuptime -e
|
||||
|
||||
**Sample outputs:**
|
||||
|
||||
Startup: 1 at 03:52:16 PM 08/21/2015
|
||||
Uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 22 minutes and 33 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
System startups: 1 since 03:52:16 PM 08/21/2015
|
||||
System shutdowns: 0 ok - 0 bad
|
||||
Average uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 22 minutes and 33 seconds
|
||||
Average downtime: 0 seconds
|
||||
Current uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 22 minutes and 33 seconds since 03:52:16 PM 08/21/2015
|
||||
Uptime rate: 100.0 %
|
||||
Downtime rate: 0.0 %
|
||||
System uptime: 15 days, 9 hours, 22 minutes and 33 seconds
|
||||
System downtime: 0 seconds
|
||||
System life: 15 days, 9 hours, 22 minutes and 33 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/hardware/howto-see-historical-statistical-uptime-on-linux-server/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/hardware/howto-see-historical-statistical-uptime-on-linux-server/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/debian-ubunut-linux-download-a-git-repository/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
|
||||
Learn with Linux: Learning Music
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This article is part of the [Learn with Linux][1] series:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Learning to Type][2]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Physics Simulation][3]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Learning Music][4]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Two Geography Apps][5]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Master Your Math with These Linux Apps][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Linux offers great educational software and many excellent tools to aid students of all grades and ages in learning and practicing a variety of topics, often interactively. The “Learn with Linux” series of articles offers an introduction to a variety of educational apps and software.
|
||||
|
||||
Learning music is a great pastime. Training your ears to identify scales and chords and mastering an instrument or your own voice requires lots of practise and could become difficult. Music theory is extensive. There is much to memorize, and to turn it into a “skill” you will need diligence. Linux offers exceptional software to help you along your musical journey. They will not help you become a professional musician instantly but could ease the process of learning, being a great aide and reference point.
|
||||
|
||||
### Gnu Solfège ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Solfège][7] is a popular music education method that is used in all levels of music education all around the world. Many popular methods (like the Kodály method) use Solfège as their basis. GNU Solfège is a great software aimed more at practising Solfège than learning it. It assumes the student has already acquired the basics and wishes to practise what they have learned.
|
||||
|
||||
As the developer states on the GNU website:
|
||||
|
||||
> “When you study music on high school, college, music conservatory, you usually have to do ear training. Some of the exercises, like sight singing, is easy to do alone [sic]. But often you have to be at least two people, one making questions, the other answering. […] GNU Solfège tries to help out with this. With Solfege you can practise the more simple and mechanical exercises without the need to get others to help you. Just don’t forget that this program only touches a part of the subject.”
|
||||
|
||||
The software delivers its promise; you can practise essentially everything with audible and visual aids.
|
||||
|
||||
GNU solfege is in the Debian (therefore Ubuntu) repositories. To get it just type the following command into a terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install solfege
|
||||
|
||||
When it loads, you find yourself on a simple starting screen/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The number of options is almost overwhelming. Most of the links will open sub-categories
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
from where you can select individual exercises.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There are practice sessions and tests. Both will be able to play the tones through any connected MIDI device or just your sound card’s MIDI player. The exercises often have visual notation and the ability to play back the sequence slowly.
|
||||
|
||||
One important note about Solfège is that under Ubuntu you might not be able to hear anything with the default setup (unless you have a MIDI device connected). If that is the case, head over to “File -> Preferences,” select sound setup and choose the appropriate option for your system (choosing ALSA would probably work in most cases).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Solfège could be very helpful for your daily practise. Use it regularly and you will have trained your ear before you can sing do-re-mi.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tete (ear trainer) ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Tete][8] (This ear trainer ‘ere) is a Java application for simple, yet efficient, [ear training][9]. It helps you identify a variety of scales by playing thhm back under various circumstances, from different roots and on different MIDI sounds. [Download it from SourceForge][10]. You then need to unzip the downloaded file.
|
||||
|
||||
unzip Tete-*
|
||||
|
||||
Enter the unpacked directory:
|
||||
|
||||
cd Tete-*
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming you have Java installed in your system, you can run the java file with
|
||||
|
||||
java -jar Tete-[your version]
|
||||
|
||||
(To autocomplete the above command, just press the Tab key after typing “Tete-“.)
|
||||
|
||||
Tete has a simple, one-page interface with everything on it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can choose to play scales (see above), chords,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
or intervals.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can “fine tune” your experience with various options including the midi instrument’s sound, what note to start from, ascending or descending scales, and how slow/fast the playback should be. Tete’s SourceForge page includes a very useful tutorial that explains most aspects of the software.
|
||||
|
||||
### JalMus ###
|
||||
|
||||
Jalmus is a Java-based keyboard note reading trainer. It works with attached MIDI keyboards or with the on-screen virtual keyboard. It has many simple lessons and exercises to train in music reading. Unfortunately, its development has been discontinued since 2013, but the software appears to still be functional.
|
||||
|
||||
To get Jalmus, head over to the [sourceforge page][11] of its last version (2.3) to get the Java installer, or just type the following command into a terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://garr.dl.sourceforge.net/project/jalmus/Jalmus-2.3/installjalmus23.jar
|
||||
|
||||
Once the download finishes, load the installer with
|
||||
|
||||
java -jar installjalmus23.jar
|
||||
|
||||
You will be guided through a simple Java-based installer that was made for cross-platform installation.
|
||||
|
||||
Jalmus’s main screen is plain.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can find lessons of varying difficulty in the Lessons menu. It ranges from very simple ones, where one notes swims in from the left, and the corresponding key lights up on the on screen keyboard …
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
… to difficult ones with many notes swimming in from the right, and you are required to repeat the sequence on your keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Jalmus also includes exercises of note reading single notes, which are very similar to the lessons, only without the visual hints, where your score will be displayed after you finished. It also aids rhythm reading of varying difficulty, where the rhythm is both audible and visually marked. A metronome (audible and visual) aids in the understanding
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
and score reading where multiple notes will be played
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
All these options are configurable; you can switch features on and off as you like.
|
||||
|
||||
All things considered, Jalmus probably works best for rhythm training. Although it was not necessarily its intended purpose, the software really excelled in this particular use-case.
|
||||
|
||||
### Notable mentions ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### TuxGuitar ####
|
||||
|
||||
For guitarists, [TuxGuitar][12] works much like Guitar Pro on Windows (and it can also read guitar-pro files).
|
||||
PianoBooster
|
||||
|
||||
[Piano Booster][13] can help with piano skills. It is designed to play MIDI files, which you can play along with on an attached keyboard, watching the core roll past on the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux offers many great tools for learning, and if your particular interest is music, your will not be left without software to aid your practice. Surely there are many more excellent software tools available for music students than were mentioned above. Do you know of any? Please let us know in the comments below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/series/learn-with-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-to-type-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-physics-simulation/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-geography-apps/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-linux-maths/
|
||||
[7]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solf%C3%A8ge
|
||||
[8]:http://tete.sourceforge.net/index.shtml
|
||||
[9]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ear_training
|
||||
[10]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/tete/files/latest/download
|
||||
[11]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/jalmus/files/Jalmus-2.3/
|
||||
[12]:http://tuxguitar.herac.com.ar/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20090517041840856/PianoBooster.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
|
||||
Learn with Linux: Learning to Type
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This article is part of the [Learn with Linux][1] series:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Learning to Type][2]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Physics Simulation][3]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Learning Music][4]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Two Geography Apps][5]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Master Your Math with These Linux Apps][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Linux offers great educational software and many excellent tools to aid students of all grades and ages in learning and practicing a variety of topics, often interactively. The “Learn with Linux” series of articles offers an introduction to a variety of educational apps and software.
|
||||
|
||||
Typing is taken for granted by many people; today being keyboard savvy often comes as second nature. Yet how many of us still type with two fingers, even if ever so fast? Once typing was taught in schools, but slowly the art of ten-finger typing is giving way to two thumbs.
|
||||
|
||||
The following two applications can help you master the keyboard so that your next thought does not get lost while your fingers catch up. They were chosen for their simplicity and ease of use. While there are some more flashy or better looking typing apps out there, the following two will get the basics covered and offer the easiest way to start out.
|
||||
|
||||
### TuxType (or TuxTyping) ###
|
||||
|
||||
TuxType is for children. Young students can learn how to type with ten fingers with simple lessons and practice their newly-acquired skills in fun games.
|
||||
|
||||
Debian and derivatives (therefore all Ubuntu derivatives) should have TuxType in their standard repositories. To install simply type
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install tuxtype
|
||||
|
||||
The application starts with a simple menu screen featuring Tux and some really bad midi music (Fortunately the sound can be turned off easily with the icon in the lower left corner.).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The top two choices, “Fish Cascade” and “Comet Zap,” represent typing games, but to start learning you need to head over to the lessons.
|
||||
|
||||
There are forty simple built-in lessons to choose from. Each one of these will take a letter from the keyboard and make the student practice while giving visual hints, such as which finger to use.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For more advanced practice, phrase typing is also available, although for some reason this is hidden under the options menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The games are good for speed and accuracy as the player helps Tux catch falling fish
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
or zap incoming asteroids by typing the words written over them.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Besides being a fun way to practice, these games teach spelling, speed, and eye-to-hand coordination, as you must type while also watching the screen, building a foundation for touch typing, if taken seriously.
|
||||
|
||||
### GNU typist (gtype) ###
|
||||
|
||||
For adults and more experienced typists, there is GNU Typist, a console-based application developed by the GNU project.
|
||||
|
||||
GNU Typist will also be carried by most Debian derivatives’ main repos. Installing it is as easy as typing
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gtype
|
||||
|
||||
You will probably not find it in the Applications menu; insteaad you should start it from a terminal window.
|
||||
|
||||
gtype
|
||||
|
||||
The main menu is simple, no-nonsense and frill-free, yet it is evident how much the software has to offer. Typing lessons of all levels are immediately accessible.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The lessons are straightforward and detailed.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The interactive practice sessions offer little more than highlighting your mistakes. Instead of flashy visuals you have to chance to focus on practising. At the end of each lesson you get some simple statistics of how you’ve been doing. If you make too many mistakes, you cannot proceed until you can pass the level.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
While the basic lessons only require you to repeat some characters, more advanced drills will have the practitioner type either whole sentences,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
where of course the three percent error margin means you are allowed even fewer mistakes,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
or some drills aiming to achieve certain goals, as in the “Balanced keyboard drill.”
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Simple speed drills have you type quotes,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
while more advanced ones will make you write longer texts taken from classics.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you’d prefer a different language, more lessons can also be loaded as command line arguments.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you care to hone your typing skills, Linux has great software to offer. The two basic, yet feature-rich, applications discussed above will cater to most aspiring typists’ needs. If you use or know of another great typing application, please don’t hesitate to let us know below in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-to-type-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/series/learn-with-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-to-type-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-physics-simulation/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-geography-apps/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-linux-maths/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
||||
Learn with Linux: Master Your Math with These Linux Apps
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This article is part of the [Learn with Linux][1] series:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Learning to Type][2]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Physics Simulation][3]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Learning Music][4]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Two Geography Apps][5]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Master Your Math with These Linux Apps][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Linux offers great educational software and many excellent tools to aid students of all grades and ages in learning and practicing a variety of topics, often interactively. The “Learn with Linux” series of articles offers an introduction to a variety of educational apps and software.
|
||||
|
||||
Mathematics is the core of computing. If one would expect a great operating system, such as GNU/Linux, to excel in and discipline, it would be Math. If you seek mathematical applications, you will not be disappointed. Linux offers many excellent tools that will make Mathematics look as intimidating as it ever did, but at least they will simplify your way of using it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Gnuplot ###
|
||||
|
||||
Gnuplot is a command-line scriptable and versatile graphing utility for different platforms. Despite its name, it is not part of the GNU operating system. Although it is not freely licensed, it’s free-ware (meaning it’s copyrighted but free to use).
|
||||
|
||||
To install `gnuplot` on an Ubuntu (or derivative) system, type
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnuplot gnuplot-x11
|
||||
|
||||
into a terminal window. To start the program, type
|
||||
|
||||
gnuplot
|
||||
|
||||
You will be presented with a simple command line interface
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
into which you can start typing functions directly. The plot command will draw a graph.
|
||||
|
||||
Typing, for instance,
|
||||
|
||||
plot sin(x)/x
|
||||
|
||||
into the `gnuplot` prompt, will open another window, wherein the graph is presented.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can also set different attributes of the graphs in-line. For example, specifying “title” will give them just that.
|
||||
|
||||
plot sin(x) title 'Sine Function', tan(x) title 'Tangent'
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can give things a bit more depth and draw 3D graphs with the `splot` command.
|
||||
|
||||
splot sin(x*y/20)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The plot window has a few basic configuration options,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
but the true power of `gnuplot` lies within its command line and scripting capabilities. The extensive full documentation of `gnuplot` can be found [here][7] with a great tutorial for the previous version [on the Duke University’s website][8].
|
||||
|
||||
### Maxima ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Maxima][9] is a computer algebra system developed from the original sources of Macsyma. According to its SourceForge page,
|
||||
|
||||
> “Maxima is a system for the manipulation of symbolic and numerical expressions, including differentiation, integration, Taylor series, Laplace transforms, ordinary differential equations, systems of linear equations, polynomials, sets, lists, vectors, matrices and tensors. Maxima yields high precision numerical results by using exact fractions, arbitrary-precision integers and variable-precision floating-point numbers. Maxima can plot functions and data in two and three dimensions.”
|
||||
|
||||
You will have binary packages for Maxima in most Ubuntu derivatives as well as the Maxima graphical interface. To install them all, type
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install maxima xmaxima wxmaxima
|
||||
|
||||
into a terminal window. Maxima is a command line utility with not much of a UI, but if you start `wxmaxima`, you’ll get into a simple, yet powerful GUI.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can start using this by simply starting to type. (Hint: Enter will add more lines; if you want to evaluate an expression, use “Shift + Enter.”)
|
||||
|
||||
Maxima can be used for very simple problems, as it also acts as a calculator,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
and much more complex ones as well.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It uses `gnuplot` to draw simple
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
and more elaborate graphs.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
(It needs the `gnuplot-x11` package to display them.)
|
||||
|
||||
Besides beautifying the expressions, Maxima makes it possible to export them in latex format, or do some operations on the highlighted functions with a right-click context menu,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
while its main menus offer an overwhelming amount of functionality. Of course, Maxima is capable of much more than this. It has an extensive documentation [available online][10].
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Mathematics is not an easy subject, and the excellent math software on Linux does not make it look easier, yet these applications make using Mathematics much more straightforward and productive. The above two applications are just an introduction to what Linux has to offer. If you are seriously engaged in math and need even more functionality with great documentation, you should check out the [Mathbuntu project][11].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-linux-maths/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/series/learn-with-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-to-type-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-physics-simulation/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-geography-apps/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-linux-maths/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.gnuplot.info/documentation.html
|
||||
[8]:http://people.duke.edu/~hpgavin/gnuplot.html
|
||||
[9]:http://maxima.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[10]:http://maxima.sourceforge.net/documentation.html
|
||||
[11]:http://www.mathbuntu.org/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
Learn with Linux: Physics Simulation
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This article is part of the [Learn with Linux][1] series:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Learning to Type][2]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Physics Simulation][3]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Learning Music][4]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Two Geography Apps][5]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Master Your Math with These Linux Apps][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Linux offers great educational software and many excellent tools to aid students of all grades and ages in learning and practicing a variety of topics, often interactively. The “Learn with Linux” series of articles offers an introduction to a variety of educational apps and software.
|
||||
|
||||
Physics is an interesting subject, and arguably the most enjoyable part of any Physics class/lecture are the demonstrations. It is really nice to see physics in action, yet the experiments do not need to be restricted to the classroom. While Linux offers many great tools for scientists to support or conduct experiments, this article will concern a few that would make learning physics easier or more fun.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Step ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Step][7] is an interactive physics simulator, part of [KDEEdu, the KDE Education Project][8]. Nobody could better describe what Step does than the people who made it. According to the project webpage, “[Step] works like this: you place some bodies on the scene, add some forces such as gravity or springs, then click “Simulate” and Step shows you how your scene will evolve according to the laws of physics. You can change every property of bodies/forces in your experiment (even during simulation) and see how this will change the outcome of the experiment. With Step, you can not only learn but feel how physics works!”
|
||||
|
||||
While of course it requires Qt and loads of KDE-specific dependencies to work, projects like this (and KDEEdu itself) are part of the reason why KDE is such an awesome environment (if you don’t mind running a heavier desktop, of course).
|
||||
|
||||
Step is in the Debian repositories; to install it on derivatives, simply type
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install step
|
||||
|
||||
into a terminal. On a KDE system it should have minimal dependencies and install in seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
Step has a simple interface, and it lets you jump right into simulations.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You will find all available objects on the left-hand side. You can have different particles, gas, shaped objects, springs, and different forces in action. (1) If you select an object, a short description of it will appear on the right-hand side (2). On the right you will also see an overview of the “world” you have created (the objects it contains) (3), the properties of the currently selected object (4), and the steps you have taken so far (5).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once you have placed all you wanted on the canvas, just press “Simulate,” and watch the events unfold as the objects interact with each other.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To get to know Step better you only need to press F1. The KDE Help Center offers a great and detailed Step handbook.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Lightspeed ###
|
||||
|
||||
Lightspeed is a simple GTK+ and OpenGL based simulator that is meant to demonstrate the effect of how one might observe a fast moving object. Lightspeed will simulate these effects based on Einstein’s special relativity. According to [their sourceforge page][9] “When an object accelerates to more than a few million meters per second, it begins to appear warped and discolored in strange and unusual ways, and as it approaches the speed of light (299,792,458 m/s) the effects become more and more bizarre. In addition, the manner in which the object is distorted varies drastically with the viewpoint from which it is observed.”
|
||||
|
||||
These effects which come into play at relative velocities are:
|
||||
|
||||
- **The Lorentz contraction** – causes the object to appear shorter
|
||||
- **The Doppler red/blue shift** – alters the hues of color observed
|
||||
- **The headlight effect** – brightens or darkens the object
|
||||
- **Optical aberration** – deforms the object in unusual ways
|
||||
|
||||
Lightspeed is in the Debian repositories; to install it, simply type:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install lightspeed
|
||||
|
||||
The user interface is very simple. You get a shape (more can be downloaded from sourceforge) which would move along the x-axis (animation can be started by processing “A” or by selecting it from the object menu).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You control the speed of its movement with the right-hand side slider and watch how it deforms.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Some simple controls will allow you to add more visual elements
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The viewing angles can be adjusted by pressing either the left, middle or right button and dragging the mouse or from the Camera menu that also offers some other adjustments like background colour or graphics mode.
|
||||
|
||||
### Notable mention: Physion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Physion looks like an interesting project and a great looking software to simulate physics in a much more colorful and fun way than the above examples would allow. Unfortunately, at the time of writing, the [official website][10] was experiencing problems, and the download page was unavailable.
|
||||
|
||||
Judging from their Youtube videos, Physion must be worth installing once a download line becomes available. Until then we can just enjoy the this video demo.
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
<iframe frameborder="0" src="//www.youtube.com/embed/P32UHa-3BfU?autoplay=1&autohide=2&border=0&wmode=opaque&enablejsapi=1&controls=0&showinfo=0" id="youtube-iframe"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
Do you have another favorite physics simulation/demonstration/learning applications for Linux? Please share with us in the comments below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-physics-simulation/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/series/learn-with-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-to-type-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-physics-simulation/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-geography-apps/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-linux-maths/
|
||||
[7]:https://edu.kde.org/applications/all/step
|
||||
[8]:https://edu.kde.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://lightspeed.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.physion.net/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
|
||||
Learn with Linux: Two Geography Apps
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This article is part of the [Learn with Linux][1] series:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Learning to Type][2]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Physics Simulation][3]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Learning Music][4]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Two Geography Apps][5]
|
||||
- [Learn with Linux: Master Your Math with These Linux Apps][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Linux offers great educational software and many excellent tools to aid students of all grades and ages in learning and practicing a variety of topics, often interactively. The “Learn with Linux” series of articles offers an introduction to a variety of educational apps and software.
|
||||
|
||||
Geography is an interesting subject, used by many of us day to day, often without realizing. But when you fire up GPS, SatNav, or just Google maps, you are using the geographical data provided by this software with the maps drawn by cartographists. When you hear about a certain country in the news or hear financial data being recited, these all fall under the umbrella of geography. And you have some great Linux software to study and practice these, whether it is for school or your own improvement.
|
||||
|
||||
### Kgeography ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are only two geography-related applications readily available in most Linux repositories, and both of these are KDE applications, in fact part of the KDE Educatonal project. Kgeography uses simple color-coded maps of any selected country.
|
||||
|
||||
To install kegeography just type
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install kgeography
|
||||
|
||||
into a terminal window of any Ubuntu-based distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
The interface is very basic. You are first presented with a picker menu that lets you choose an area map.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
On the map you can display the name and capital of any given territory by clicking on it,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
and test your knowledge in different quizzes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It is an interactive way to test your basic geographical knowledge and could be an excellent tool to help you prepare for exams.
|
||||
|
||||
### Marble ###
|
||||
|
||||
Marble is a somewhat more advanced software, offering a global view of the world without the need of 3D acceleration.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To get Marble, type
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install marble
|
||||
|
||||
into a terminal window of any Ubuntu-based distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
Marble focuses on cartography, its main view being that of an atlas.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can have different projections, like Globe or Mercator displayed as defaults, with flat and other exotic views available from a drop-down menu. The surfaces include the basic Atlas view, a full-fledged offline map powered by OpenStreetMap,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
satellite view (by NASA),
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
and political and even historical maps of the world, among others.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Besides providing great offline maps with different skins and varying amount of data, Marble offers other types of information as well. You can switch on and off various offline info-boxes
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
and online services from the menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
An interesting online service is Wikipedia integration. Clicking on the little Wiki logos will bring up a pop-up featuring detailed information about the selected places.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The software also includes options for location tracking, route planning, and searching for locations, among other great and useful features. If you enjoy cartography, Marble offers hours of fun exploring and learning.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux offers many great educational applications, and the subject of geography is no exception. With the above two programs you can learn a lot about our globe and test your knowledge in a fun and interactive manner.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-geography-apps/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/series/learn-with-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-to-type-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-physics-simulation/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-geography-apps/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-linux-maths/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
FSSlc translating
|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA Series: Automate RHEL 7 Installations Using ‘Kickstart’ – Part 12
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux servers are rarely standalone boxes. Whether it is in a datacenter or in a lab environment, chances are that you have had to install several machines that will interact one with another in some way. If you multiply the time that it takes to install Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 manually on a single server by the number of boxes that you need to set up, this can lead to a rather lengthy effort that can be avoided through the use of an unattended installation tool known as kickstart.
|
||||
@ -139,4 +141,4 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/automatic-rhel-installations-using-kickstart/
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:https://access.redhat.com/labs/kickstartconfig/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/multiple-centos-installations-using-kickstart/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/multiple-centos-installations-using-kickstart/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,109 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Debian GNU/Linux 生日: 22年未完的美妙旅程.
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在2015年8月16日, Debian项目组庆祝了 Debian 的22周年纪念日; 这也是开源世界历史最悠久, 热门的发行版之一. Debian项目于1993年由Ian Murdock创立. 彼时, Slackware 作为最早的 Linux 发行版已经名声在外.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
22岁生日快乐! Debian Linux!
|
||||
|
||||
Ian Ashly Murdock, 一个美国职业软件工程师, 在他还是普渡大学的学生时构想出了 Debia n项目的计划. 他把这个项目命名为 Debian 是由于这个名字组合了他彼时女友的名字, Debra Lynn, 和他自己的名字(译者: Ian). 他之后和Lynn顺利结婚并在2008年1月离婚.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Debian 创始人:Ian Murdock
|
||||
|
||||
Ian 目前是 ExactTarget 下 Platform and Development Community 的副总裁.
|
||||
|
||||
Debian (如同Slackware一样) 都是由于当时缺乏满足作者标准的发行版才应运而生的. Ian 在一次采访中说:"免费提供一流的产品会是Debian项目的唯一使命. 尽管过去的 Linux 发行版均不尽然可靠抑或是优秀. 我印象里...比如在不同的文件系统间移动文件, 处理大型文件经常会导致内核出错. 但是 Linux 其实是很可靠的, 免费的源代码让这个项目本质上很有前途.
|
||||
|
||||
"我记得过去我也像其他人一样想解决问题, 想在家里运营一个像 UNIX 的东西. 但那是不可能的, 无论是经济上还是法律上或是别的什么角度. 然后我就听闻了GNU内核开发项目, 以及这个项目是如何没有任何法律纷争", Ian 补充到. 他早年在开发 Debian 时曾被自由软件基金会(FSF)资助, 这份资助帮助 Debian 向前迈了一大步; 尽管一年后由于学业原因 Ian 退出了 FSF 转而去完成他的学位.
|
||||
|
||||
### Debian开发历史 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- **Debian 0.01 – 0.09** : 发布于 1993 八月 – 1993 十二月.
|
||||
- **Debian 0.91 ** – 发布于 1994 一月. 有了原始的包管理系统, 没有依赖管理机制.
|
||||
- **Debian 0.93 rc5** : 发布于 1995 三月. "现代"意义的 Debian 的第一次发布, dpkg 会在系统安装后被用作安装以及管理其他软件包.
|
||||
- **Debian 0.93 rc6**: 发布于1995 十一月. 最后一次a.out发布, deselect机制第一次出现, 有60位开发者在彼时维护着软件包.
|
||||
- **Debian 1.1**: 发布于1996 六月. 项目代号 – Buzz, 软件包数量 – 474, 包管理器 dpkg, 内核版本 2.0, ELF.
|
||||
- **Debian 1.2**: 发布于1996 十二月. 项目代号 – Rex, 软件包数量 – 848, 开发者数量 – 120.
|
||||
- **Debian 1.3**: 发布于1997 七月. 项目代号 – Bo, 软件包数量 974, 开发者数量 – 200.
|
||||
- **Debian 2.0**: 发布于1998 七月. 项目代号 - Hamm, 支持构架 – Intel i386 以及 Motorola 68000 系列, 软件包数量: 1500+, 开发者数量: 400+, 内置了 glibc.
|
||||
- **Debian 2.1**: 发布于1999 三月九日. 项目代号 – slink, 支持构架 - Alpha 和 Sparc, apt 包管理器开始成型, 软件包数量 – 2250.
|
||||
- **Debian 2.2**: 发布于2000 八月十五日. 项目代号 – Potato, 支持构架 – Intel i386, Motorola 68000 系列, Alpha, SUN Sparc, PowerPC 以及 ARM 构架. 软件包数量: 3900+ (二进制) 以及 2600+ (源代码), 开发者数量 – 450. 有一群人在那时研究并发表了一篇论文, 论文展示了自由软件是如何在被各种问题包围的情况下依然逐步成长为优秀的现代操作系统的.
|
||||
- **Debian 3.0**: 发布于2002 七月十九日. 项目代号 – woody, 支持构架新增– HP, PA_RISC, IA-64, MIPS 以及 IBM, 首次以DVD的形式发布, 软件包数量 – 8500+, 开发者数量 – 900+, 支持加密.
|
||||
- **Debian 3.1**: 发布于2005 六月六日. 项目代号 – sarge, 支持构架 – 不变基础上新增 AMD64 – 非官方渠道发布, 内核 – 2.4 以及 2.6 系列, 软件包数量: 15000+, 开发者数量 : 1500+, 增加了诸如 – OpenOffice 套件, Firefox 浏览器, Thunderbird, Gnome 2.8, 内核版本 3.3 先进地支持了: RAID, XFS, LVM, Modular Installer.
|
||||
- **Debian 4.0**: 发布于2007 四月八日. 项目代号 – etch, 支持构架 – 不变基础上新增 AMD64. 软件包数量: 18,200+ 开发者数量 : 1030+, 图形化安装器.
|
||||
- **Debian 5.0**: Released on February 14th, 发布于2009. 项目代号 – lenny, 支持构架 – 保不变基础上新增 ARM. 软件包数量: 23000+, 开发者数量: 1010+.
|
||||
- **Debian 6.0**: 发布于2009 七月二十九日. 项目代号 – squeeze, 包含的软件包: 内核 2.6.32, Gnome 2.3. Xorg 7.5, 同时包含了 DKMS, 基于依赖包支持. 支持构架 : 不变基础上新增 kfreebsd-i386 以及 kfreebsd-amd64, 基于依赖管理的启动过程.
|
||||
- **Debian 7.0**: 发布于2013 五月四日. 项目代号: wheezy, 支持 Multiarch, 私人云工具, 升级了安装器, 移除了第三方软件依赖, 万能的多媒体套件-codec, 内核版本 3.2, Xen Hypervisor 4.1.4 软件包数量: 37400+.
|
||||
- **Debian 8.0**: 发布于2015 五月二十五日. 项目代号: Jessie, 将 Systemd 作为默认的启动加载器, 内核版本 3.16, 增加了快速启动(fast booting), service进程所依赖的 cgroups 使隔离部分 service 进程成为可能, 43000+ packages. Sysvinit 初始化工具首次在 Jessie 中可用.
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: Linux的内核第一次是在1991 十月五日被发布, 而 Debian 的首次发布则在1993 九月十三日. 所以 Debian 已经在只有24岁的 Linux 内核上运行了整整22年了.
|
||||
|
||||
### 有关 Debian 的小知识 ###
|
||||
|
||||
1994年被用来管理和重整 Debian 项目以使得其他开发者能更好地加入. 所以在那一年并没有面向用户的更新被发布, 当然, 内部版本肯定是有的.
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 1.0 从来就没有被发布过. 一家 CD-ROM 的生产商错误地把某个未发布的版本标注为了 1.0, 为了避免产生混乱, 原本的 Debian 1.0 以1.1的面貌发布了. 从那以后才有了所谓的官方CD-ROM的概念.
|
||||
|
||||
每个 Debian 新版本的代号都是玩具总动员里某个角色的名字哦.
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 有四种可用版本: 旧稳定版(old stable), 稳定版, 测试版 以及 试验版(experimental). 始终如此.
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 项目组一直致力于开发写一代发行版的不稳定版本, 这个不稳定版本始终被叫做Sid(玩具总动员里那个邪恶的臭小孩). Sid是unstable版本的永久名称, 同时Sid也取自'Still In Development"(译者:还在开发中)的首字母. Sid 将会成为下一个稳定版, 此时的下一个稳定版本代号为 jessie.
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 的官方发行版只包含开源并且免费的软件, 绝无其他东西. 不过contrib 和 不免费的软件包使得安装那些本身免费但是依赖的软件包不免费的软件成为了可能. 那些依赖包本身的证书可能不属于自由/免费软件.
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 是一堆Linux 发行版的母亲. 举几个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
- Damn Small Linux
|
||||
- KNOPPIX
|
||||
- Linux Advanced
|
||||
- MEPIS
|
||||
- Ubuntu
|
||||
- 64studio (不再活跃开发)
|
||||
- LMDE
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 是世界上最大的非商业Linux 发行版.他主要是由C书写的(32.1%), 一并的还有其他70多种语言.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Debian Contribution
|
||||
|
||||
图片来源: [Xmodulo][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 项目包含6,850万行代码, 以及, 450万行空格和注释.
|
||||
|
||||
国际空间站放弃了 Windows 和红帽子, 进而换成了Debian - 在上面的宇航员使用落后一个版本的稳定发行版, 目前是squeeze; 这么做是为了稳定程度以及来自 Debian 社区的雄厚帮助支持.
|
||||
|
||||
感谢上帝! 我们差点就听到来自国际空间宇航员面对 Windows Metro 界面的尖叫了 :P
|
||||
|
||||
#### 黑色星期三 ####
|
||||
|
||||
2002 十一月而是日, Twente 大学的 Network Operation Center 着火 (NOC). 当地消防部门放弃了服务器区域. NOC维护了satie.debian.org的网站服务器, 这个网站包含了安全, 非美国相关的存档, 新维护者资料, 数量报告, 数据库; 这一切都化为了灰烬. 之后这些服务被使用 Debian 重新实现了.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 未来版本 ####
|
||||
|
||||
下一个待发布版本是 Debian 9, 项目代号 – Stretch, 它会带来什么还是个未知数. 满心期待吧!
|
||||
|
||||
有很多发行版在 Linux 发行版的历史上出现过一瞬然后很快消失了. 在多数情况下, 维护一个日渐庞大的项目是开发者们面临的挑战. 但这对 Debian 来说不是问题. Debian 项目有全世界成百上千的开发者, 维护者. 它在 Linux 诞生的之初起便一直存在.
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 在 Linux 生态环境中的贡献是难以用语言描述的. 如果 Debian 没有出现过, 那么 Linux 世界将不会像现在这样丰富, 用户友好. Debian 是为数不多可以被认为安全可靠又稳定, 是作为网络服务器完美选择的发行版.
|
||||
|
||||
这仅仅是 Debian 的一个开始. 它从远古时代一路走到今天, 并将一直走下去. 未来即是现在! 世界近在眼前! 如果你到现在还从来没有使用过 Debian, 我只想问, 你还再等什么? 快去下载一份镜像试试吧, 我们会在此守候遇到任何问题的你.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Debian 主页][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/happy-birthday-to-debian-gnu-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[jerryling315](http://moelf.xyz)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/08/interesting-facts-about-debian-linux.html
|
||||
[2]:https://www.debian.org/
|
||||
@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu 15.04 下创建连接至 Android/iOS 的 AP
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我成功地在 Ubuntu 15.04 下用 Gnome Network Manager 创建了一个无线AP热点. 接下来我要分享一下我的步骤. 请注意: 你必须要有一个可以用来创建AP热点的无线网卡. 如果你不知道如何找到连上了的设备的话, 在终端(Terminal)里输入`iw list`.
|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有安装`iw`的话, 在Ubuntu下你可以使用`udo apt-get install iw`进行安装.
|
||||
|
||||
在你键入`iw list`之后, 寻找可用的借口, 你应该会看到类似下列的条目:
|
||||
|
||||
Supported interface modes:
|
||||
|
||||
* IBSS
|
||||
* managed
|
||||
* AP
|
||||
* AP/VLAN
|
||||
* monitor
|
||||
* mesh point
|
||||
|
||||
让我们一步步看
|
||||
|
||||
1. 断开WIFI连接. 使用有线网络接入你的笔记本.
|
||||
1. 在顶栏面板里点击网络的图标 -> Edit Connections(编辑连接) -> 在弹出窗口里点击Add(新增)按钮.
|
||||
1. 在下拉菜单内选择Wi-Fi.
|
||||
1. 接下来,
|
||||
|
||||
a. 输入一个链接名 比如: Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
b. 输入一个 SSID 比如: Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
c. 选择模式(mode): Infrastructure
|
||||
|
||||
d. 设备 MAC 地址: 在下拉菜单里选择你的无线设备
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入Wi-Fi安全选项卡, 选择 WPA & WPA2 Personal 并且输入密码.
|
||||
1. 进入IPv4设置选项卡, 在Method(方法)下拉菜单里, 选择Shared to other computers(共享至其他电脑).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入IPv6选项卡, 在Method(方法)里设置为忽略ignore (只有在你不使用IPv6的情况下这么做)
|
||||
1. 点击 Save(保存) 按钮以保存配置.
|
||||
1. 从 menu/dash 里打开Terminal.
|
||||
1. 修改你刚刚使用 network settings 创建的连接.
|
||||
|
||||
使用 VIM 编辑器:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo vim /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
使用Gedit 编辑器:
|
||||
|
||||
gksu gedit /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
把名字 Hotspot 用你在第4步里起的连接名替换掉.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. 把 `mode=infrastructure` 改成 `mode=ap` 并且保存文件
|
||||
1. 一旦你保存了这个文件, 你应该能在 Wifi 菜单里看到你刚刚建立的AP了. (如果没有的话请再顶栏里 关闭/打开 Wifi 选项一次)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. 你现在可以把你的设备连上Wifi了. 已经过 Android 5.0的小米4测试.(下载了1GB的文件以测试速度与稳定性)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxveda.com/2015/08/23/how-to-create-an-ap-in-ubuntu-15-04-to-connect-to-androidiphone/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sayantan Das][a]
|
||||
译者:[jerryling315](https://github.com/jerryling315)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxveda.com/author/sayantan_das/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
如何在linux中搭建FTP服务
|
||||
=====================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我将会解释如何搭建你自己的FTP服务。但是,首先我们应该来的学习一下FTP是什么。
|
||||
|
||||
###FTP是什么?###
|
||||
|
||||
[FTP][1] 是文件传输协议(File Transfer Protocol)的缩写。顾名思义,FTP是用于计算机之间通过网络进行文件传输。你可以通过FTP在计算机账户间进行文件传输,也可以在账户和桌面计算机之间传输文件,或者访问在线软件文档。但是,需要注意的是多数的FTP站点的使用率非常高,并且在连接前需要进行多次尝试。
|
||||
|
||||
FTP地址和HTTP地址(即网页地址)非常相似,只是FTP地址使用ftp://前缀而不是http://
|
||||
|
||||
###FTP服务器是什么?###
|
||||
|
||||
通常,拥有FTP地址的计算机是专用于接收FTP连接请求的。一台专用于接收FTP连接请求的计算机即为FTP服务器或者FTP站点。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们来开始一个特别的冒险,我们将会搭建一个FTP服务用于和家人、朋友进行文件共享。在本教程,我们将以[vsftpd][2]作为ftp服务。
|
||||
|
||||
VSFTPD是一个自称为最安全的FTP服务端软件。事实上VSFTPD的前两个字母表示“非常安全的(very secure)”。该软件的构建绕开了FTP协议的漏洞。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管如此,你应该知道还有更安全的方法进行文件管理和传输,如:SFTP(使用[OpenSSH][3])。FTP协议对于共享非敏感数据是非常有用和可靠的。
|
||||
|
||||
####在rpm distributions中安装VSFTPD:####
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用如下命令在命令行界面中快捷的安装VSFTPD:
|
||||
|
||||
dnf -y install vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
####在deb distributions中安装VSFTPD:####
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用如下命令在命令行界面中快捷的安装VSFTPD:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
####在Arch distribution中安装VSFTPD:####
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用如下命令在命令行界面中快捷的安装VSFTPD:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
####配置FTP服务####
|
||||
|
||||
多数的VSFTPD配置项都在/etc/vsftpd.conf配置文件中。这个文件本身已经有非常良好的文档说明了,因此,在本节中,我只强调一些你可能进行修改的重要选项。使用man页面查看所有可用的选项和基本的 文档说明:
|
||||
|
||||
man vsftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
根据文件系统层级标准,FTP共享文件默认位于/srv/ftp目录中。
|
||||
|
||||
**允许上传:**
|
||||
|
||||
为了允许ftp用户可以修改文件系统的内容,如上传文件等,“write_enable”标志必须设置为 YES。
|
||||
|
||||
write_enable=YES
|
||||
|
||||
**允许本地用户登陆:**
|
||||
|
||||
为了允许文件/etc/passwd中记录的用户可以登陆ftp服务,“local_enable”标记必须设置为YES。
|
||||
|
||||
local_enable=YES
|
||||
|
||||
**匿名用户登陆**
|
||||
|
||||
下面配置内容控制匿名用户是否允许登陆:
|
||||
|
||||
# Allow anonymous login
|
||||
anonymous_enable=YES
|
||||
# No password is required for an anonymous login (Optional)
|
||||
no_anon_password=YES
|
||||
# Maximum transfer rate for an anonymous client in Bytes/second (Optional)
|
||||
anon_max_rate=30000
|
||||
# Directory to be used for an anonymous login (Optional)
|
||||
anon_root=/example/directory/
|
||||
|
||||
**根目录限制(Chroot Jail)**
|
||||
|
||||
(译者注:chroot jail是类unix系统中的一种安全机制,用于修改进程运行的根目录环境,限制该线程不能感知到其根目录树以外的其他目录结构和文件的存在。详情参看[chroot jail][4])
|
||||
|
||||
有时我们需要设置根目录(chroot)环境来禁止用户离开他们的家(home)目录。在配置文件中增加/修改下面配置开启根目录限制(Chroot Jail):
|
||||
|
||||
chroot_list_enable=YES
|
||||
chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
|
||||
|
||||
“chroot_list_file”变量指定根目录监狱所包含的文件/目录(译者注:即用户只能访问这些文件/目录)
|
||||
|
||||
最后你必须重启ftp服务,在命令行中输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo systemctl restart vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
到此为止,你的ftp服务已经搭建完成并且启动了
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/set-ftp-server-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[alimiracle][a]
|
||||
译者:[cvsher](https://github.com/cvsher)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/ali/
|
||||
[1]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File_Transfer_Protocol
|
||||
[2]:https://security.appspot.com/vsftpd.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.openssh.com/
|
||||
[4]:https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chroot
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu中安装QGit浏览器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
QGit是一款Marco Costalba用Qt和C++写的开源GUI Git浏览器。它是一款在GUI环境下更好地提供浏览历史记录、提交记录和文件补丁的浏览器。它利用git命令行来执行并显示输出。它有一些常规的功能像浏览历史、比较、文件历史、文件标注、档案树。我们可以格式化并用选中的提交应用补丁,在两个实例之间拖拽并提交等等。它允许我们创建自定义的按钮来用它内置的生成器来执行特定的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
这里有简单的几步在Ubuntu 14.04 LTS "Trusty"中编译并安装QGit浏览器。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 安装 QT4 库 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先在ubuntu中运行QGit需要先安装QT4库。由于apt是ubuntu默认的包管理器,同时qt4也在官方的仓库中,因此我们直接用下面的apt-get命令来安装qt4。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install qt4-default
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 下载QGit压缩包 ###
|
||||
|
||||
安装完Qt4之后,我们要安装git,这样我们才能在QGit中克隆git仓库。运行下面的apt-get命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install git
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们要使用下面的git命令来克隆仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
$ git clone git://repo.or.cz/qgit4/redivivus.git
|
||||
|
||||
Cloning into 'redivivus'...
|
||||
remote: Counting objects: 7128, done.
|
||||
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (2671/2671), done.
|
||||
remote: Total 7128 (delta 5464), reused 5711 (delta 4438)
|
||||
Receiving objects: 100% (7128/7128), 2.39 MiB | 470.00 KiB/s, done.
|
||||
Resolving deltas: 100% (5464/5464), done.
|
||||
Checking connectivity... done.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 编译 QGit ###
|
||||
|
||||
克隆之后,我们现在进入redivivus的目录,并创建我们编译需要的makefile文件。因此,要进入目录,我们要运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd redivivus
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,我们运行下面的命令从qmake项目也就是qgit.pro来生成新的Makefile。
|
||||
|
||||
$ qmake qgit.pro
|
||||
|
||||
生成Makefile之后,我们现在终于要编译qgit的源代码并得到二进制的输出。首先我们要安装make和g++包用于编译,因为这是一个用C++写的程序。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install make g++
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们要用make命令来编译代码了
|
||||
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 安装 QGit ###
|
||||
|
||||
成功编译QGit的源码之后,我们就要在Ubuntu 14.04中安装它了,这样就可以在系统中执行它。因此我们将运行下面的命令、
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
cd src/ && make -f Makefile install
|
||||
make[1]: Entering directory `/home/arun/redivivus/src'
|
||||
make -f Makefile.Release install
|
||||
make[2]: Entering directory `/home/arun/redivivus/src'
|
||||
install -m 755 -p "../bin/qgit" "/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qt4/bin/qgit"
|
||||
strip "/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/qt4/bin/qgit"
|
||||
make[2]: Leaving directory `/home/arun/redivivus/src'
|
||||
make[1]: Leaving directory `/home/arun/redivivus/src'
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,我们需要从bin目录下复制qgit的二进制文件到/usr/bin/,这样我们就可以全局运行它了。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp bin/qgit /usr/bin/
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 创建桌面文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
既然我们已经在ubuntu中成功安装了qgit,我们来创建一个桌面文件,这样QGit就可以在我们桌面环境中的菜单或者启动器中找到了。要做到这点,我们要在/usr/share/applications/创建一个新文件叫qgit.desktop。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /usr/share/applications/qgit.desktop
|
||||
|
||||
接下来复制下面的行到文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
[Desktop Entry]
|
||||
Name=qgit
|
||||
GenericName=git GUI viewer
|
||||
Exec=qgit
|
||||
Icon=qgit
|
||||
Type=Application
|
||||
Comment=git GUI viewer
|
||||
Terminal=false
|
||||
MimeType=inode/directory;
|
||||
Categories=Qt;Development;RevisionControl;
|
||||
|
||||
完成之后,保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 运行 QGit 浏览器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
QGit安装完成之后,我们现在就可以从任何启动器或者程序菜单中启动它了。要在终端下面运行QGit,我们可以像下面那样。
|
||||
|
||||
$ qgit
|
||||
|
||||
这会打开基于Qt4框架GUI模式的QGit。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
QGit是一个很棒的基于QT的git浏览器。它可以在Linux、MAC OSX和 Microsoft Windows所有这三个平台中运行。它帮助我们很容易地浏览历史、版本、分支等等git仓库提供的信息。它减少了使用命令行的方式去执行诸如浏览版本、历史、比较功能的需求,并用图形化的方式来简化了这些任务。最新的qgit版本也在默认仓库中,你可以使用 **apt-get install qgit** 命令来安装。因此。qgit用它简单的GUI使得我们的工作更加简单和快速。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-qgit-viewer-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user