
In the previous tutorials, we demonstrated how we can set up a [full-fledged BGP router][1] and configure [prefix filtering][2] with Quagga. In this tutorial, we are going to show you how we can set up IPv6 BGP peering and advertise IPv6 prefixes through BGP. We will also demonstrate how we can filter IPv6 prefixes advertised or received by using prefix-list and route-map features.
The other day when I [installed Elementary OS in dual boot with Windows][1], I encountered a Grub error at the reboot time. I was presented with command line with error message:
**Minimal BASH like line editing is supported. For the first word, TAB lists possible command completions. anywhere else TAB lists possible device or file completions.**
Indeed this is not an error specific to Elementary OS. It is a common [Grub][2] error that could occur with any Linux OS be it Ubuntu, Fedora, Linux Mint etc.
In this post we shall see **how to fix this “minimal BASH like line editing is supported” Grub error in Ubuntu** based Linux systems.
> You can read this tutorial to fix similar and more frequent issue, [error: no such partition grub rescue in Linux][3].
### Prerequisites ###
To fix this issue, you would need the followings:
- A live USB or disk of the same OS and same version
- A working internet connection in the live session
Once you make sure that you have the prerequisites, let’s see how to fix the black screen of death for Linux (if I can call it that ;)).
### How to fix this “minimal BASH like line editing is supported” Grub error in Ubuntu based Linux ###
I know that you might point out that this Grub error is not exclusive to Ubuntu or Ubuntu based Linux distributions, then why am I putting emphasis on the world Ubuntu? The reason is, here we will take an easy way out and use a tool called **Boot Repair** to fix our problem. I am not sure if this tool is available for other distributions like Fedora. Without wasting anymore time, let’s see how to solve minimal BASH like line editing is supported Grub error.
### Step 1: Boot in lives session ###
Plug in the live USB and boot in to the live session.
### Step 2: Install Boot Repair ###
Once you are in the lives session, open the terminal and use the following commands to install Boot Repair:
Note: Follow this tutorial to [fix failed to fetch cdrom apt-get update cannot be used to add new CD-ROMs error][4], if you encounter it while running the above command.
### Step 3: Repair boot with Boot Repair ###
Once you installed Boot Repair, run it from the command line using the following command:
boot-repair &
Actually things are pretty straight forward from here. You just need to follow the instructions provided by Boot Repair tool. First, click on **Recommended repair** option in the Boot Repair.
It will take couple of minutes for Boot Repair to analyze the problem with boot and Grub. Afterwards, it will provide you some commands to use in the command line. Copy the commands one by one in terminal. For me it showed me a screen like this:
Once the process finishes, it will provide you a URL which consists of the logs of the boot repair. If your boot issue is not fixed even now, you can go to the forum or mail to the dev team and provide them the URL as a reference. Cool, isn’t it?
After the boot repair finishes successfully, shutdown your computer, remove the USB and boot again. For me it booted successfully but added two additional lines in the Grub screen. Something which was not of importance to me as I was happy to see the system booting normally again.
So this is how I fixed **minimal BASH like line editing is supported Grub error in Elementary OS Freya**. How about you? Did it work for you? Feel free to ask a question or drop a suggestion in the comment box below.
In this article, we'll learn about the installating Kitematic in Windows Operating System and deploying a Hello World Nginx Web Server. Kitematic is a free and open source software which is a modern designed GUI software that allows us to interactively perform tasks with docker. Kitematic has a beautiful design and pretty good interface. It is pretty fast and easy to setup our containers out of the box without needing to enter commands for it, we can deploy our apps it in just a click with its GUI inteface. Kitematic has Docker Hub Intergration which allows us to search any required image, pull and deploy our apps with it. It also has a beautiful feature to switch to CUI mode simultaneously. Currently, it includes some features like automatically map ports, visually change environment variables, configuring volumes, streamline logs and many more.
RHCSA (Red Hat Certified System Administrator) is a certification exam from Red Hat company, which provides an open source operating system and software to the enterprise community, It also provides support, training and consulting services for the organizations.
RHCSA exam is the certification obtained from Red Hat Inc, after passing the exam (codename EX200). RHCSA exam is an upgrade to the RHCT (Red Hat Certified Technician) exam, and this upgrade is compulsory as the Red Hat Enterprise Linux was upgraded. The main variation between RHCT and RHCSA is that RHCT exam based on RHEL 5, whereas RHCSA certification is based on RHEL 6 and 7, the courseware of these two certifications are also vary to a certain level.
RHCSA 考试(考试编号 EX200)通过后可以获取由Red Hat 公司颁发的证书. RHCSA 考试是RHCT(红帽认证技师)的升级版,而且RHCSA必须在新的Red Hat Enterprise Linux(红帽企业版)下完成.RHCT和RHCSA的主要变化就是RHCT基于 RHEL5 , 而RHCSA基于RHEL6或者7, 这两个认证的等级也有所不同.
This Red Hat Certified System Administrator (RHCSA) is essential to perform the following core system administration tasks needed in Red Hat Enterprise Linux environments:
红帽认证管理员所会的最基础的是在红帽企业版的环境下执行如下系统管理任务:
- Understand and use necessary tools for handling files, directories, command-environments line, and system-wide / packages documentation.
- Operate running systems, even in different run levels, identify and control processes, start and stop virtual machines.
- Set up local storage using partitions and logical volumes.
- Create and configure local and network file systems and its attributes (permissions, encryption, and ACLs).
- Setup, configure, and control systems, including installing, updating and removing software.
- Manage system users and groups, along with use of a centralized LDAP directory for authentication.
- Ensure system security, including basic firewall and SELinux configuration.
- 理解并会使用命令管理文件、目录、命令行以及系统/软件包的文档
- 使用不同的启动等级启动系统,认证和控制进程,启动或停止虚拟机
- 使用分区和逻辑卷管理本地存储
- 创建并且配置本地文件系统和网络文件系统,设置他们的属性(许可、加密、访问控制表)
- 部署、配置、并且控制系统,包括安装、升级和卸载软件
- 管理系统用户和组,独立使用集中制的LDAP目录权限控制
- 确保系统安全,包括基础的防火墙规则和SELinux配置
To view fees and register for an exam in your country, check the [RHCSA Certification page][1].
To view fees and register for an exam in your country, check the RHCSA Certification page.
关于你所在国家的考试注册费用参考 [RHCSA Certification page][1].
In this 15-article RHCSA series, titled Preparation for the RHCSA (Red Hat Certified System Administrator) exam, we will going to cover the following topics on the latest releases of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.
关于你所在国家的考试注册费用参考RHCSA 认证页面
- Part 1: Reviewing Essential Commands & System Documentation
- Part 2: How to Perform File and Directory Management in RHEL 7
- Part 3: How to Manage Users and Groups in RHEL 7
- Part 4: Editing Text Files with Nano and Vim / Analyzing text with grep and regexps
- Part 5: Process Management in RHEL 7: boot, shutdown, and everything in between
- Part 6: Using ‘Parted’ and ‘SSM’ to Configure and Encrypt System Storage
- Part 7: Using ACLs (Access Control Lists) and Mounting Samba / NFS Shares
- Part 8: Securing SSH, Setting Hostname and Enabling Network Services
- Part 9: Installing, Configuring and Securing a Web and FTP Server
- Part 10: Yum Package Management, Automating Tasks with Cron and Monitoring System Logs
- Part 11: Firewall Essentials and Control Network Traffic Using FirewallD and Iptables
- Part 12: Automate RHEL 7 Installations Using ‘Kickstart’
- Part 13: RHEL 7: What is SELinux and how it works?
- Part 14: Use LDAP-based authentication in RHEL 7
- Part 15: Virtualization in RHEL 7: KVM and Virtual machine management
In this Part 1 of the RHCSA series, we will explain how to enter and execute commands with the correct syntax in a shell prompt or terminal, and explained how to find, inspect, and use system documentation.

RHCSA: Reviewing Essential Linux Commands – Part 1
RHCSA:回顾必会的Linux命令 - 第一部分
#### Prerequisites: ####
#### 前提: ####
At least a slight degree of familiarity with basic Linux commands such as:
至少你要熟悉如下命令
- [cd command][2] (change directory)
- [ls command][3] (list directory)
- [cp command][4] (copy files)
- [mv command][5] (move or rename files)
- [touch command][6] (create empty files or update the timestamp of existing ones)
- rm command (delete files)
- mkdir command (make directory)
- [cd command][2] (改变目录)
- [ls command][3] (列举文件)
- [cp command][4] (复制文件)
- [mv command][5] (移动或重命名文件)
- [touch command][6] (创建一个新的文件或更新已存在文件的时间表)
- rm command (删除文件)
- mkdir command (创建目录)
The correct usage of some of them are anyway exemplified in this article, and you can find further information about each of them using the suggested methods in this article.
在这篇文章中你将会找到更多的关于如何更好的使用他们的正确用法和特殊用法.
Though not strictly required to start, as we will be discussing general commands and methods for information search in a Linux system, you should try to install RHEL 7 as explained in the following article. It will make things easier down the road.
If we log into a Linux box using a text-mode login screen, chances are we will be dropped directly into our default shell. On the other hand, if we login using a graphical user interface (GUI), we will have to open a shell manually by starting a terminal. Either way, we will be presented with the user prompt and we can start typing and executing commands (a command is executed by pressing the Enter key after we have typed it).
Commands are composed of two parts:
当我们使用文本模式登陆Linux时,
命令是由两个部分组成的:
- the name of the command itself, and
- arguments
- 命令本身
- 参数
Certain arguments, called options (usually preceded by a hyphen), alter the behavior of the command in a particular way while other arguments specify the objects upon which the command operates.
某些参数,称为选项(通常使用一个连字符区分),改变了由其他参数定义的命令操作.
The type command can help us identify whether another certain command is built into the shell or if it is provided by a separate package. The need to make this distinction lies in the place where we will find more information about the command. For shell built-ins we need to look in the shell’s man page, whereas for other binaries we can refer to its own man page.
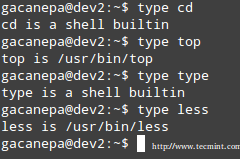
Check Shell built in Commands
检查Shell的内建命令
In the examples above, cd and type are shell built-ins, while top and less are binaries external to the shell itself (in this case, the location of the command executable is returned by type).
在上面的例子中, cd 和 type 是shell内建的命令,top和 less 是由其他的二进制文件提供的(在这种情况下,type将返回命令的位置)
其他的内建命令
Other well-known shell built-ins include:
- [echo command][8]: Displays strings of text.
- [pwd command][9]: Prints the current working directory.
- [echo command][8]: 展示字符串
- [pwd command][9]: 输出当前的工作目录

More Built in Shell Commands
更多内建函数
**exec command**
**exec 命令**
Runs an external program that we specify. Note that in most cases, this is better accomplished by just typing the name of the program we want to run, but the exec command has one special feature: rather than create a new process that runs alongside the shell, the new process replaces the shell, as can verified by subsequent.
# ps -ef | grep [original PID of the shell process]
# ps -ef | grep [shell 进程的PID]
When the new process terminates, the shell terminates with it. Run exec top and then hit the q key to quit top. You will notice that the shell session ends when you do, as shown in the following screencast:
当新的进程注销,Shell也随之注销,运行 exec top 然后按下 q键来退出top,你会注意到shell 会话会结束,如下面的屏幕录像展示的那样:
Exports variables to the environment of subsequently executed commands.
输出之后执行的命令的环境的变量
**history Command**
**history 命令**
Displays the command history list with line numbers. A command in the history list can be repeated by typing the command number preceded by an exclamation sign. If we need to edit a command in history list before executing it, we can press Ctrl + r and start typing the first letters associated with the command. When we see the command completed automatically, we can edit it as per our current need:
展示数行之前的历史命令.在感叹号前输入命令编号可以再次执行这个命令.如果我们需要编辑历史列表中的命令,我们可以按下 Ctrl + r 并输入与命令相关的第一个字符.
This list of commands is kept in our home directory in a file called .bash_history. The history facility is a useful resource for reducing the amount of typing, especially when combined with command line editing. By default, bash stores the last 500 commands you have entered, but this limit can be extended by using the HISTSIZE environment variable:

Linux history Command
Linux history 命令
But this change as performed above, will not be persistent on our next boot. In order to preserve the change in the HISTSIZE variable, we need to edit the .bashrc file by hand:
With no arguments or with the -p option prints the list of aliases in the form alias name=value on standard output. When arguments are provided, an alias is defined for each name whose value is given.
使用alias ,我们可以创建我们自己的命令,或修改现有的命令,包括需要的参数.举个例子,假设我们想别名 ls 到 ls –color=auto ,这样就可以使用不同颜色输出文件、目录、链接
With alias, we can make up our own commands or modify existing ones by including desired options. For example, suppose we want to alias ls to ls –color=auto so that the output will display regular files, directories, symlinks, and so on, in different colors:
# alias ls='ls --color=auto'
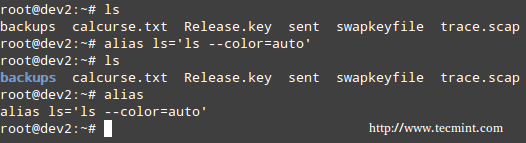
Linux alias Command
Linux 别名命令
**Note**: That you can assign any name to your “new command” and enclose as many commands as desired between single quotes, but in that case you need to separate them by semicolons, as follows:
The exit and logout commands both terminate the shell. The exit command terminates any shell, but the logout command terminates only login shells—that is, those that are launched automatically when you initiate a text-mode login.
If we are ever in doubt as to what a program does, we can refer to its man page, which can be invoked using the man command. In addition, there are also man pages for important files (inittab, fstab, hosts, to name a few), library functions, shells, devices, and other features.
- man uname (print system information, such as kernel name, processor, operating system type, architecture, and so on).
- man inittab (init daemon configuration).
- man uname (输出系统信息,如内核名称、处理器、操作系统类型、架构等).
- man inittab (初始化守护设置).
Another important source of information is provided by the info command, which is used to read info documents. These documents often provide more information than the man page. It is invoked by using the info keyword followed by a command name, such as:
In addition, the /usr/share/doc directory contains several subdirectories where further documentation can be found. They either contain plain-text files or other friendly formats.
Make sure you make it a habit to use these three methods to look up information for commands. Pay special and careful attention to the syntax of each of them, which is explained in detail in the documentation.
**Converting Tabs into Spaces with expand Command**
**使用expand命令把tabs转换为空格**
Sometimes text files contain tabs but programs that need to process the files don’t cope well with tabs. Or maybe we just want to convert tabs into spaces. That’s where the expand tool (provided by the GNU coreutils package) comes in handy.
The unexpand command performs the reverse operation (converts spaces into tabs).
unexpand命令可以实现相反的功能(将空格转为tab)
**Display the first lines of a file with head and the last lines with tail**
**使用head输出文件首行及使用tail输出文件尾行**
By default, the head command followed by a filename, will display the first 10 lines of the said file. This behavior can be changed using the -n option and specifying a certain number of lines.

Linux head and tail Command
Linux 的 head 和 tail 命令
One of the most interesting features of tail is the possibility of displaying data (last lines) as the input file grows (tail -f my.log, where my.log is the file under observation). This is particularly useful when monitoring a log to which data is being continually added.
Read More: [Manage Files Effectively using head and tail Commands][10]
**Merging Lines with paste**
The paste command merges files line by line, separating the lines from each file with tabs (by default), or another delimiter that can be specified (in the following example the fields in the output are separated by an equal sign).
更多: [Manage Files Effectively using head and tail Commands][10]
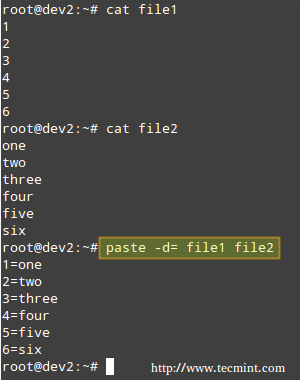
Merge Files in Linux
**Breaking a file into pieces using split command**
**使用split命令将文件分块**
The split command is used split a file into two (or more) separate files, which are named according to a prefix of our choosing. The splitting can be defined by size, chunks, or number of lines, and the resulting files can have a numeric or alphabetic suffixes. In the following example, we will split bash.pdf into files of size 50 KB (-b 50KB), using numeric suffixes (-d):
The tr command can be used to translate (change) characters on a one-by-one basis or using character ranges. In the following example we will use the same file2 as previously, and we will change:
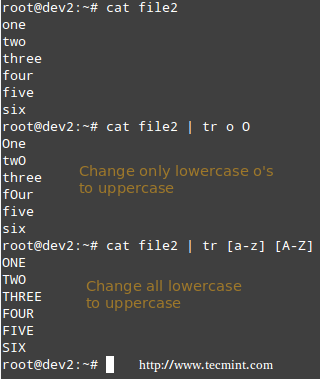
Translate Characters in Linux
在Linux中替换文字
**Reporting or deleting duplicate lines with uniq and sort command**
**使用uniq和sort检查或删除重复的文字**
The uniq command allows us to report or remove duplicate lines in a file, writing to stdout by default. We must note that uniq does not detect repeated lines unless they are adjacent. Thus, uniq is commonly used along with a preceding sort (which is used to sort lines of text files).
By default, sort takes the first field (separated by spaces) as key field. To specify a different key field, we need to use the -k option. Please note how the output returned by sort and uniq change as we change the key field in the following example:
The cut command extracts portions of input lines (from stdin or files) and displays the result on standard output, based on number of bytes (-b), characters (-c), or fields (-f).
Note that the output of the two examples above was truncated for brevity.
**Reformatting files with fmt command**
注意,上方的两个输出的结果是十分简洁的。
fmt is used to “clean up” files with a great amount of content or lines, or with varying degrees of indentation. The new paragraph formatting defaults to no more than 75 characters wide. You can change this with the -w (width) option, which set the line length to the specified number of characters.
**使用fmt命令重新格式化文件**
For example, let’s see what happens when we use fmt to display the /etc/passwd file setting the width of each line to 100 characters. Once again, output has been truncated for brevity.

File Reformatting in Linux
Linux文件重新格式化
**Formatting content for printing with pr command**
**使用pr命令格式化打印内容**
pr paginates and displays in columns one or more files for printing. In other words, pr formats a file to make it look better when printed. For example, the following command:
# ls -a /etc | pr -n --columns=3 -h "Files in /etc"
Shows a listing of all the files found in /etc in a printer-friendly format (3 columns) with a custom header (indicated by the -h option), and numbered lines (-n).

File Formatting in Linux
Linux的文件格式
### Summary ###
### 总结 ###
In this article we have discussed how to enter and execute commands with the correct syntax in a shell prompt or terminal, and explained how to find, inspect, and use system documentation. As simple as it seems, it’s a large first step in your way to becoming a RHCSA.
If you would like to add other commands that you use on a periodic basis and that have proven useful to fulfill your daily responsibilities, feel free to share them with the world by using the comment form below. Questions are also welcome. We look forward to hearing from you!
In this article, RHCSA Part 2: File and directory management, we will review some essential skills that are required in the day-to-day tasks of a system administrator.
### 如何在基于Ubuntu的Linux中修复“minimal BASH like line editing is supported” Grub错误 ###
我知道你一定疑问这种Grub错误并不局限于在基于Ubuntu的Linux发行版上发生,那为什么我要强调在基于Ubuntu的发行版上呢?原因是,在这里我们将采用一个简单的方法并叫作**Boot Repair**的工具来修复我们的问题。我并不确定在其他的诸如Fedora的发行版中是否有这个工具可用。不再浪费时间,我们来看如何修复minimal BASH like line editing is supported Grub错误。
Blocking a user prevents them from interacting with repositories, such as opening or commenting on pull requests or issues. Learn more about blocking a user.