diff --git a/translated/tech/20140812 How to set up a USB network printer and scanner server on Debian.md b/published/20140812 How to set up a USB network printer and scanner server on Debian.md
similarity index 79%
rename from translated/tech/20140812 How to set up a USB network printer and scanner server on Debian.md
rename to published/20140812 How to set up a USB network printer and scanner server on Debian.md
index 20d69fb363..3783deed01 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20140812 How to set up a USB network printer and scanner server on Debian.md
+++ b/published/20140812 How to set up a USB network printer and scanner server on Debian.md
@@ -25,33 +25,35 @@
然后,编辑原始文件(下面只显示了最为有关联的部分):
- **Listen**:监听指定的地址和端口,或者域套接口路径。
-- **Location /path**:为命名的位置指定访问控制。
+- **Location /path**:为该名字所代表的位置指定访问控制。
- **Order**:指定HTTP访问控制顺序(allow,deny或deny,allow)。Order allow,deny是说允许规则先于(并且优先处理)拒绝规则。
- **DefaultAuthType** (也可以用**AuthType**): 指定默认使用的认证类型。Basic是指使用/etc/passwd文件来认证CUPS中的用户。
-- **DefaultEncryption**:指定认证请求说使用的加密类型。
+- **DefaultEncryption**:指定认证请求所使用的加密类型。
- **WebInterface**:指定是否启用网页接口。
- # Listen for connections from the local machine
- Listen 192.168.0.15:631
+---
+
+ # Listen for connections from the local machine
+ Listen 192.168.0.15:631
- # Restrict access to the server
-
- Order allow,deny
- Allo 192.168.0.0/24
-
+ # Restrict access to the server
+
+ Order allow,deny
+ Allow 192.168.0.0/24
+
- # Default authentication type, when authentication is required
- DefaultAuthType Basic
- DefaultEncryption IfRequested
+ # Default authentication type, when authentication is required
+ DefaultAuthType Basic
+ DefaultEncryption IfRequested
- # Web interface setting
- WebInterface Yes
+ # Web interface setting
+ WebInterface Yes
- # Restrict access to the admin pages
-
- Order allow,deny
- Allow 192.168.0.0/24
-
+ # Restrict access to the admin pages
+
+ Order allow,deny
+ Allow 192.168.0.0/24
+
现在,让我们重启CUPS来应用修改:
@@ -66,27 +68,27 @@
### 通过网页接口配置网络打印机 ###
-1. 启动网页浏览器,并打开CUPS接口http://:Port,这里在我们的例子中是http://192.168.0.15:631:
+1、 启动网页浏览器,并打开CUPS接口http://:Port,这里在我们的例子中是http://192.168.0.15:631:

-2. 转到**管理**标签,然后点击*添加打印机*:
+2、 转到**管理**标签,然后点击*添加打印机*:

-3. 选择你的打印机;在本例中,**EPSON Stylus CX3900 @ debian (Inkjet Inkjet Printer)**,然后点击**继续**:
+3、 选择你的打印机;在本例中,**EPSON Stylus CX3900 @ debian (Inkjet Inkjet Printer)**,然后点击**继续**:

-4. 是时候为打印机取个名字,并指定我们是否想要从当前工作站共享它:
+4、 是时候为打印机取个名字,并指定我们是否想要从当前工作站共享它:

-5. 安装驱动——选择品牌并点击**继续**。
+5、 安装驱动——选择品牌并点击**继续**。

-6. 如果打印机如果不被CUPS支持(没有在下一页中列出来),我们必须从生产厂家的网站上下载驱动(如[http://download.ebz.epson.net/dsc/search/01/search/?OSC=LX][2]),安装完后回到该页。
+6、 如果打印机如果不被CUPS支持(没有在下一页中列出来),我们必须从生产厂家的网站上下载驱动(如[http://download.ebz.epson.net/dsc/search/01/search/?OSC=LX][2]),安装完后回到该页。

@@ -94,11 +96,11 @@

-7. 注意,预编译的.deb文件必须从我们使用的机器上发送(例如,通过sftp或scp)到打印服务器(当然,如果我们有一个直接的下载链接就更加简单了,而不用下载按钮了):
+7、 注意,预编译的.deb文件必须从我们使用的机器上发送(例如,通过sftp或scp)到打印服务器(当然,如果我们有一个直接的下载链接就更加简单了,而不用下载按钮了):

-8. 在将.deb文件放到服务器上后,我们就可以安装了:
+8、 在将.deb文件放到服务器上后,我们就可以安装了:
# dpkg -i epson-inkjet-printer-escpr_1.4.1-1lsb3.2_i386.deb
@@ -111,7 +113,7 @@
# aptitude install lsb
# dpkg -i epson-inkjet-printer-escpr_1.4.1-1lsb3.2_i386.deb
-9. 现在,我们可以返回到第五步并安装打印机:
+9、 现在,我们可以返回到第五步并安装打印机:

@@ -161,7 +163,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/usb-network-printer-and-scanner-server-debian.ht
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140818 How to Take 'Snapshot of Logical Volume and Restore' in LVM--Part III.md b/published/20140818 How to Take 'Snapshot of Logical Volume and Restore' in LVM--Part III.md
similarity index 64%
rename from translated/tech/20140818 How to Take 'Snapshot of Logical Volume and Restore' in LVM--Part III.md
rename to published/20140818 How to Take 'Snapshot of Logical Volume and Restore' in LVM--Part III.md
index 6213ea22d4..5f34b81685 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20140818 How to Take 'Snapshot of Logical Volume and Restore' in LVM--Part III.md
+++ b/published/20140818 How to Take 'Snapshot of Logical Volume and Restore' in LVM--Part III.md
@@ -1,20 +1,19 @@
-在LVM中“录制逻辑卷快照并恢复”——第三部分
+在 LVM中 录制逻辑卷快照并恢复(第三部分)
================================================================================
-**LVM快照**是空间有效指向时间的lvm卷副本。它只在lvm中工作,并只在源逻辑卷发生改变时消耗快照卷的空间。如果源卷的变化达到1GB这么大,快照卷同样也会产生这样大的改变。因而,对于空间有效利用的最佳途径,就是总是进行小的修改。如果快照将存储空间消耗殆尽,我们可以使用lvextend来扩容。而如果我们需要缩减快照,可以使用lvreduce。
+**LVM快照**是以空间换时间时间的方式制作的lvm卷副本。它只在lvm中工作,并只在源逻辑卷发生改变时占用快照卷的空间。如果源卷的变化达到1GB这么大,快照卷同样也会产生这样大的改变。因而,对于空间有效利用的最佳途径,就是总是进行小的修改。如果快照将存储空间消耗殆尽,我们可以使用lvextend来扩容。而如果我们需要缩减快照所占用卷的大小,可以使用lvreduce。

-在LVM中录制快照
-如果我们在创建快照后意外地删除了无论什么文件,我们没有必要担心,因为快照里包含了我们所删除的文件的原始文件。创建快照时,很有可能文件每次都在那。不要改变快照卷,保持创建时的样子,因为它用于快速恢复。
+*在LVM中录制快照*
+
+如果我们在创建快照后意外地删除了无论什么文件,我们没有必要担心,因为快照里包含了我们所删除的文件的原始文件。创建快照时,很有可能文件已经存在了。不要改变快照卷,保持创建时的样子,因为它用于快速恢复。
快照不可以用于备份选项。备份是某些数据的基础副本,因此我们不能使用快照作为备份的一个选择。
-#### 需求 ####
+#### 前置阅读 ####
-注:此两篇文章如果发布后可换成发布后链接,原文在前几天更新中
-
-- [在Linux中使用LVM创建磁盘存储 — 第一部分][1]
-- [在Linux中扩展/缩减LVM — 第二部分][2]
+- [在Linux中使用LVM构建灵活的磁盘存储(第一部分)][1]
+- [在Linux中扩展/缩减LVM(第二部分)][2]
### 我的服务器设置 ###
@@ -29,9 +28,10 @@
# lvs
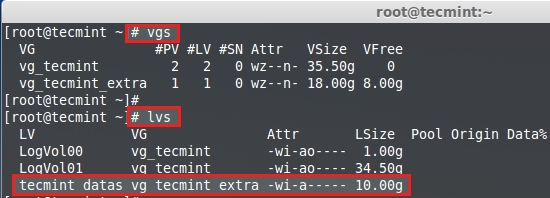
-检查LVM磁盘空间
-正如你所见,在**vgs**命令输出中,我们可以看到有8GB的剩余空闲空间。所以,让我们为我的名为**tecmint_datas**的卷之一创建快照。处于演示的目的,我将会使用以下命令来创建1GB的快照卷。
+*检查LVM磁盘空间*
+
+正如你所见,在**vgs**命令输出中,我们可以看到有8GB的剩余空闲空间。所以,让我们为我的名为**tecmint_datas**的卷创建快照。处于演示的目的,我将会使用以下命令来创建1GB的快照卷。
# lvcreate -L 1GB -s -n tecmint_datas_snap /dev/vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_datas
@@ -45,79 +45,87 @@
- **-n** – 为快照命名

-创建LVM快照
+
+*创建LVM快照*
此处,是对上面高亮要点的说明。
-- 我在此创建的快照的大小。
-- 创建快照。
-- 创建快照名。
-- 新的快照名。
-- 要创建快照的卷。
+1. 我在此创建的快照的大小。
+2. 创建快照。
+3. 创建快照名。
+4. 新的快照名。
+5. 要创建快照的卷。
如果你想要移除快照,可以使用‘**lvremove**’命令。
-# lvremove /dev/vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_datas_snap
+ # lvremove /dev/vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_datas_snap

-移除LVM快照
+
+*移除LVM快照*
现在,使用以下命令列出新创建的快照。
- # lvs
+ # lvs

-验证LVM快照
+
+*验证LVM快照*
上面的你看到了吧,成功创建了一个快照。上面我用箭头标出了快照创建的源,它就是**tecmint_datas**。是的,因为我已经为**tecmint_datas l-volume**创建了一个快照。

-检查LVM快照空间
+
+*检查LVM快照空间*
让我们添加一些新文件到**tecmint_datas**里头。现在卷里大概有650MB左右的数据,而我我们的快照有1GB大。因此,有足够的空间在快照卷里备份我们的修改。这里我们可以使用下面的命令来查看到,我们的快照当前的状态。
# lvs

-检查快照状态
+
+*检查快照状态*
你看到了,现在已经用掉了**51%**的快照卷,你要对你的文件作更多的修改都没有问题。使用下面的命令来查看更多详细信息。
# lvdisplay vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_data_snap

-查看快照信息
+
+*查看快照信息*
再来对上面图片中高亮的要点作个清楚的说明。
-- 快照逻辑卷名称。
-- 当前使用的卷组名。
-- 读写模式下的快照卷,我们甚至可以挂载并使用该卷。
-- 快照创建时间。这个很重要,因为快照将跟踪此时间之后的每个改变。
-- 该快照属于tecmint_datas逻辑卷。
-- 逻辑卷在线并可用。
-- 我们录制快照的源卷大小。
-- 写时复制表大小,Cow = copy on Write,这是说对tecmint_data卷所作的任何改变都会写入此快照。
-- 当前使用的快照大小,我们的tecmint_data有10GB,而我们的快照大小是1GB,这就意味着我们的数据大概有650MB。所以,如果tecmint_datas中的文件增长到2GB,现在的51%中的内容将增加到超过所分配的快照的大小,当然,我们在创建快照时会出现问题。这就意味着我们需要扩展逻辑卷大小(快照逻辑卷)
-- 给出快照组块的大小。
+1. 快照逻辑卷名称。
+2. 当前使用的卷组名。
+3. 读写模式下的快照卷,我们甚至可以挂载并使用该卷。
+4. 快照创建时间。这个很重要,因为快照将跟踪此时间之后的每个改变。
+5. 该快照属于tecmint_datas逻辑卷。
+6. 逻辑卷在线并可用。
+7. 我们录制快照的源卷大小。
+8. 写时复制表大小,Cow = copy on Write,这是说对tecmint_data卷所作的任何改变都会写入此快照。
+9. 当前使用的快照大小,我们的tecmint_data有10GB,而我们的快照大小是1GB,这就意味着我们的数据大概有650MB。所以,如果tecmint_datas中的文件增长到2GB,现在的51%中的内容将增加到超过所分配的快照的大小,当然,我们在创建快照时会出现问题。这就意味着我们需要扩展逻辑卷大小(快照逻辑卷)
+10. 给出快照组块的大小。
现在,让我们复制超过1GB的文件到**tecmint_datas**。让我们看看会发生什么。如果你那么做了,你将会见到‘**Input/output error**’这样的错误信息,它告诉你快照超出空间大小了。

-添加文件到快照
-如果逻辑卷满了,它就会自动下线,我们就不能再使用了,就算我们去扩展快照卷的大小也不行。最好的方法就是在创建快照时,创建一个和源一样大小的快照卷。**tecmint_datas**的大小是10GB,如果我们创建一个10GB大小的快照,它就永远都不会像上面那样超载,因为它有足够的空间来录制你的逻辑卷的快照。
+*添加文件到快照*
+
+如果该逻辑卷满了,它就会自动丢失新的数据,我们就不能再使用了,就算我们去扩展快照卷的大小也不行。最好的方法就是在创建快照时,创建一个和源一样大小的快照卷。**tecmint_datas**的大小是10GB,如果我们创建一个10GB大小的快照,它就永远都不会像上面那样超载,因为它有足够的空间来录制你的逻辑卷的快照。
#### 步骤2: 在LVM中扩展快照 ####
-如果我们需要在超载前扩展快照大小,我们可以使用以下命令来完成此项任务。
+如果我们需要在超过容量前扩展快照卷的大小,我们可以使用以下命令来完成此项任务。
# lvextend -L +1G /dev/vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_data_snap
现在,那里有总计2GB大小的快照空间。

-扩展LVM快照
+
+*扩展LVM快照*
接下来,使用以下命令来验证新的大小和写时复制表。
@@ -128,7 +136,8 @@
# lvs

-检查快照大小
+
+*检查快照大小*
然而,如果你的快照大小和源卷一样,我们就没有必要担心这些问题了。
@@ -139,21 +148,24 @@
# unmount /mnt/tecmint_datas/

-卸载文件系统
-只想检查挂载点是否卸载,可以使用下面的命令。
+*卸载文件系统*
+
+只想检查挂载点是否卸载成功,可以使用下面的命令。
# df -h

-检查文件系统挂载点
+
+*检查文件系统挂载点*
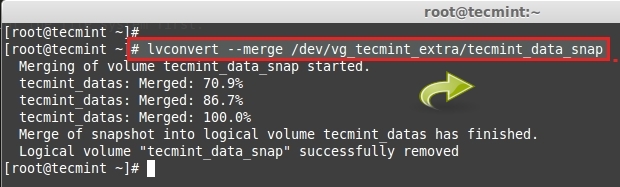
这里,我们的挂载已经被卸载,所以我们可以继续恢复快照。要恢复快照,可以使用**lvconvert**命令。
# lvconvert --merge /dev/vg_tecmint_extra/tecmint_data_snap
-恢复LVM快照
+
+*恢复LVM快照*
在合并完成后,快照卷将被自动移除。现在我们可以使用**df**命令来查看分区大小。
@@ -166,7 +178,8 @@
# lvs
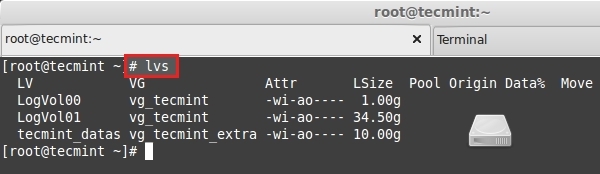
-检查逻辑卷大小
+
+*检查逻辑卷大小*
**重要**:要自动扩展快照,我们可以通过修改配置文件来进行。对于手动扩展,我们可以使用lvextend。
@@ -177,13 +190,14 @@
搜索单词autoextend。默认情况下,该值和下图中的类似。
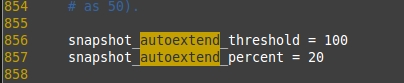
-LVM配置
+
+*LVM配置*
修改此处的**100**为**75**,这样自动扩展的起始点就是**75**,而自动扩展百分比为20,它将自动扩容**百分之20**。
如果快照卷达到**75%**,它会自动为快照卷扩容**20%**。这样,我们可以自动扩容了。使用**wq!**来保存并退出。
-这将把快照从超载下线中拯救出来,这也会帮助你节省更多时间。LVM是我们扩容以及获得其它众多特性如精简资源调配、拆卸、虚拟卷和使用精简池的唯一方法,让我们在下一个话题中来讨论吧。
+这将把快照从超载导致下线事故中拯救出来,这也会帮助你节省更多时间。LVM是我们扩容以及获得其它众多特性如精简资源调配、拆卸、虚拟卷和使用精简池的唯一方法,让我们在下一个话题中来讨论吧。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -191,10 +205,10 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/take-snapshot-of-logical-volume-and-restore-in-lvm/
作者:[Babin Lonston][a]
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/babinlonston/
-[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/create-lvm-storage-in-linux/
-[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/extend-and-reduce-lvms-in-linux/
+[1]:http://linux.cn/article-3965-1.html
+[2]:http://linux.cn/article-3974-1.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/[翻译完成]20140821 How to configure a network printer and scanner on Ubuntu desktop.md b/published/20140821 How to configure a network printer and scanner on Ubuntu desktop.md
similarity index 92%
rename from translated/tech/[翻译完成]20140821 How to configure a network printer and scanner on Ubuntu desktop.md
rename to published/20140821 How to configure a network printer and scanner on Ubuntu desktop.md
index c4218936dd..d405588726 100644
--- a/translated/tech/[翻译完成]20140821 How to configure a network printer and scanner on Ubuntu desktop.md
+++ b/published/20140821 How to configure a network printer and scanner on Ubuntu desktop.md
@@ -2,8 +2,7 @@
如何在ubuntu桌面配置一个网络打印机和扫描仪
================================================================================
-
-在[之前的文章中](注:这篇文章在2014年8月12号的原文里做过,不知道翻译了没有,如果翻译发布了,发布此文章的时候可改成翻译后的链接), 我们讨论过如何在Linux服务器安装各种各样的打印机(当然也包括网络扫描仪)。今天我们将来处理另一端:如何通过桌面客户端来访问网络打印机/扫描仪。
+在[之前的文章中][1], 我们讨论过如何在Linux服务器安装各种各样的打印机(当然也包括网络扫描仪)。今天我们将来处理另一端:如何通过桌面客户端来访问网络打印机/扫描仪。
### 网络环境 ###
@@ -31,49 +30,39 @@

-
-
### 在Ubuntu桌面安装网络打印机 ###
-
在我们的Ubuntu 12.04的客户端,我们将打开"Printing"菜单(Dash -> Printing).你会注意到在其它发行版中,这个名字也许会有一点差别(例如会叫做"Printers" 或者 "Print & Fax"):

-
还没有打印机添加到我们的客户端:

下面是在Ubuntu桌面客户端安装一台网络打印机的一些步骤。
-
-**1)** “Add”按钮将弹出New Printer" 菜单。我们将选择"Network printer" -> "Find Network Printer"并输入我们服务器的IP地址,接着点击"Find":
+**1)** “Add”按钮将弹出 "New Printer" 菜单。我们将选择"Network printer" -> "Find Network Printer"并输入我们服务器的IP地址,接着点击"Find":

-
**2)** 在最下面我们将会看到可使用的打印机的名称。我们来选择这台三星打印机并按"Forward":

-
**3)** 我们将会被要求填写一些关于我们打印机的信息。当我们输入完成时,将点击 "Apply"按钮。

-
**4)** 我们接下来将被询问是否打印一张测试页。让我们点击"Print test page"吧:

-
这个打印任务将被创建为本地id 2:

-
5)适用我们服务器上的CUPS网络借口,我们可以观察到打印任务已经提交成功了(打印机 -> SamsungML1640系列 -> 显示完成任务):

@@ -91,7 +80,6 @@
这个page_log日志显示每一页被打印过的信息,只包括哪些用户发送这些打印任务,打印日期&时间,以及客户端的IPv4地址。
-
要安装Epson喷墨和PDF打印机,我们只需重复第1-5的步骤即可,并每一次选择左边的打印队列。例如,在下图中选择PDF打印机:

@@ -112,17 +100,12 @@
#### 实例 #1 ####
-
-
从Ubuntu12.04中打印,通常在本地用gacanepa(具有相同名字存在打印机服务器上)。

-
打印到PDF打印机之后,让我们来检查打印机服务器上的/home/gacanepa/PDF目录下的内容:
-
-
root@debian:~# ls -l /home/gacanepa/PDF
----------
@@ -133,7 +116,6 @@
-rw------- 1 gacanepa gacanepa 74911 Aug 18 14:36 Welcome_to_Conference_-_Thomas_S__Monson.pdf
-
这个PDF文件被创建时的,权限已经设置为600(-rw-------),这意味着只有打印任务的所有者(在这个例子中是gacanepa )可以访问它们。我们可以通过修改the /etc/cups/cups-pdf.conf文件**UserUMask**变量的值来改变这种行为。例如,0033的umask值将可以使PDF打印者以及其它所有者拥有创建文件的权限,但是只读权限也会赋予给其它所有者。
root@debian:~# grep -i UserUMask /etc/cups/cups-pdf.conf
@@ -190,7 +172,8 @@
**2)** 现在我们需要启用saned进程,用来预装Ubuntu桌面。要启用它,我们需要编辑/etc/default/saned文件,并设置RUN变量为yes:
- $ sudo vim /etc/default/saned
+
+ $ sudo vim /etc/default/saned
----------
@@ -205,7 +188,8 @@
**4)** 重启saned进程:
- $ sudo service saned restart
+
+ $ sudo service saned restart
@@ -235,11 +219,11 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/configure-network-printer-scanner-ubuntu-desktop
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
译者:[disylee](https://github.com/disylee)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/gabriel
-[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/usb-network-printer-and-scanner-server-debian.html
+[1]:http://linux.cn/article-4139-1.html
[2]:http://www.cups-pdf.de/documentation.shtml
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/usb-network-printer-and-scanner-server-debian.html#scanner
diff --git a/published/201410/20140610 How does the cloud affect the everyday linux user.md b/published/201409/20140610 How does the cloud affect the everyday linux user.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140610 How does the cloud affect the everyday linux user.md
rename to published/201409/20140610 How does the cloud affect the everyday linux user.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140624 Staying free--should GCC allow non-free plug ins.md b/published/201409/20140624 Staying free--should GCC allow non-free plug ins.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140624 Staying free--should GCC allow non-free plug ins.md
rename to published/201409/20140624 Staying free--should GCC allow non-free plug ins.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140716 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to define PATH environment variable for sudo commands.md b/published/201409/20140716 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to define PATH environment variable for sudo commands.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140716 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to define PATH environment variable for sudo commands.md
rename to published/201409/20140716 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to define PATH environment variable for sudo commands.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140718 Need Microsoft Office on Ubuntu--Install the Official Webapps.md b/published/201409/20140718 Need Microsoft Office on Ubuntu--Install the Official Webapps.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140718 Need Microsoft Office on Ubuntu--Install the Official Webapps.md
rename to published/201409/20140718 Need Microsoft Office on Ubuntu--Install the Official Webapps.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140722 How to manage DigitalOcean VPS droplets from the command line on Linux.md b/published/201409/20140722 How to manage DigitalOcean VPS droplets from the command line on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140722 How to manage DigitalOcean VPS droplets from the command line on Linux.md
rename to published/201409/20140722 How to manage DigitalOcean VPS droplets from the command line on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140723 How to access SoundCloud from the command line in Linux.md b/published/201409/20140723 How to access SoundCloud from the command line in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140723 How to access SoundCloud from the command line in Linux.md
rename to published/201409/20140723 How to access SoundCloud from the command line in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140723 Top 10 Fun On The Command Line.md b/published/201409/20140723 Top 10 Fun On The Command Line.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140723 Top 10 Fun On The Command Line.md
rename to published/201409/20140723 Top 10 Fun On The Command Line.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140724 diff -u--What is New in Kernel Development.md b/published/201409/20140724 diff -u--What is New in Kernel Development.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140724 diff -u--What is New in Kernel Development.md
rename to published/201409/20140724 diff -u--What is New in Kernel Development.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140729 10 Useful 'Squid Proxy Server' Interview Questions and Answers in Linux.md b/published/201409/20140729 10 Useful 'Squid Proxy Server' Interview Questions and Answers in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140729 10 Useful 'Squid Proxy Server' Interview Questions and Answers in Linux.md
rename to published/201409/20140729 10 Useful 'Squid Proxy Server' Interview Questions and Answers in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140729 How to access Linux command cheat sheets from the command line.md b/published/201409/20140729 How to access Linux command cheat sheets from the command line.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140729 How to access Linux command cheat sheets from the command line.md
rename to published/201409/20140729 How to access Linux command cheat sheets from the command line.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140730 How to use variables in shell Scripting.md b/published/201409/20140730 How to use variables in shell Scripting.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140730 How to use variables in shell Scripting.md
rename to published/201409/20140730 How to use variables in shell Scripting.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140731 Easy Steps to Make GNOME 3 More Efficient.md b/published/201409/20140731 Easy Steps to Make GNOME 3 More Efficient.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140731 Easy Steps to Make GNOME 3 More Efficient.md
rename to published/201409/20140731 Easy Steps to Make GNOME 3 More Efficient.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140801 How To Install Java On Ubuntu 14.04.md b/published/201409/20140801 How To Install Java On Ubuntu 14.04.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140801 How To Install Java On Ubuntu 14.04.md
rename to published/201409/20140801 How To Install Java On Ubuntu 14.04.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140801 How to Create an Ubuntu Kiosk Computer.md b/published/201409/20140801 How to Create an Ubuntu Kiosk Computer.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140801 How to Create an Ubuntu Kiosk Computer.md
rename to published/201409/20140801 How to Create an Ubuntu Kiosk Computer.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140804 Cheat--An Ultimate Command Line 'Cheat-Sheet' for Linux Beginners and Administrators.md b/published/201409/20140804 Cheat--An Ultimate Command Line 'Cheat-Sheet' for Linux Beginners and Administrators.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140804 Cheat--An Ultimate Command Line 'Cheat-Sheet' for Linux Beginners and Administrators.md
rename to published/201409/20140804 Cheat--An Ultimate Command Line 'Cheat-Sheet' for Linux Beginners and Administrators.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140808 When Linux Was Perfect Enough.md b/published/201409/20140808 When Linux Was Perfect Enough.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140808 When Linux Was Perfect Enough.md
rename to published/201409/20140808 When Linux Was Perfect Enough.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140811 Disable or Password Protect Single User Mode or RHEL ro CentOS ro 5.x ro 6.x.md b/published/201409/20140811 Disable or Password Protect Single User Mode or RHEL ro CentOS ro 5.x ro 6.x.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140811 Disable or Password Protect Single User Mode or RHEL ro CentOS ro 5.x ro 6.x.md
rename to published/201409/20140811 Disable or Password Protect Single User Mode or RHEL ro CentOS ro 5.x ro 6.x.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140811 How to Image and Clone Hard Drives with Clonezilla.md b/published/201409/20140811 How to Image and Clone Hard Drives with Clonezilla.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140811 How to Image and Clone Hard Drives with Clonezilla.md
rename to published/201409/20140811 How to Image and Clone Hard Drives with Clonezilla.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140811 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to check the last time system was rebooted on Linux.md b/published/201409/20140811 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to check the last time system was rebooted on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140811 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to check the last time system was rebooted on Linux.md
rename to published/201409/20140811 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to check the last time system was rebooted on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140818 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to set a static MAC address on VMware ESXi virtual machine.md b/published/201409/20140818 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to set a static MAC address on VMware ESXi virtual machine.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140818 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to set a static MAC address on VMware ESXi virtual machine.md
rename to published/201409/20140818 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to set a static MAC address on VMware ESXi virtual machine.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140818 Where And How To Code--Choosing The Best Free Code Editor.md b/published/201409/20140818 Where And How To Code--Choosing The Best Free Code Editor.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140818 Where And How To Code--Choosing The Best Free Code Editor.md
rename to published/201409/20140818 Where And How To Code--Choosing The Best Free Code Editor.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140819 8 Options to Trace or Debug Programs using Linux strace Command.md b/published/201409/20140819 8 Options to Trace or Debug Programs using Linux strace Command.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140819 8 Options to Trace or Debug Programs using Linux strace Command.md
rename to published/201409/20140819 8 Options to Trace or Debug Programs using Linux strace Command.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140819 A Pocket Guide for Linux ssh Command with Examples.md b/published/201409/20140819 A Pocket Guide for Linux ssh Command with Examples.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140819 A Pocket Guide for Linux ssh Command with Examples.md
rename to published/201409/20140819 A Pocket Guide for Linux ssh Command with Examples.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140819 KDE Plasma 5--For those Linux users undecided on the kernel' s future.md b/published/201409/20140819 KDE Plasma 5--For those Linux users undecided on the kernel' s future.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140819 KDE Plasma 5--For those Linux users undecided on the kernel' s future.md
rename to published/201409/20140819 KDE Plasma 5--For those Linux users undecided on the kernel' s future.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140819 Linux Systemd--Start or Stop or Restart Services in RHEL or CentOS 7.md b/published/201409/20140819 Linux Systemd--Start or Stop or Restart Services in RHEL or CentOS 7.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140819 Linux Systemd--Start or Stop or Restart Services in RHEL or CentOS 7.md
rename to published/201409/20140819 Linux Systemd--Start or Stop or Restart Services in RHEL or CentOS 7.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140822 15 Practical Examples of 'cd' Command in Linux.md b/published/201409/20140822 15 Practical Examples of 'cd' Command in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140822 15 Practical Examples of 'cd' Command in Linux.md
rename to published/201409/20140822 15 Practical Examples of 'cd' Command in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140825 China Will Change The Way All Software Is Bought And Sold.md b/published/201409/20140825 China Will Change The Way All Software Is Bought And Sold.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140825 China Will Change The Way All Software Is Bought And Sold.md
rename to published/201409/20140825 China Will Change The Way All Software Is Bought And Sold.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to enable Nux Dextop repository on CentOS or RHEL.md b/published/201409/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to enable Nux Dextop repository on CentOS or RHEL.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to enable Nux Dextop repository on CentOS or RHEL.md
rename to published/201409/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to enable Nux Dextop repository on CentOS or RHEL.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'failed to run aclocal--No such file or directory'.md b/published/201409/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'failed to run aclocal--No such file or directory'.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'failed to run aclocal--No such file or directory'.md
rename to published/201409/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'failed to run aclocal--No such file or directory'.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140825 Linux Terminal--speedtest_cli checks your real bandwidth speed.md b/published/201409/20140825 Linux Terminal--speedtest_cli checks your real bandwidth speed.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140825 Linux Terminal--speedtest_cli checks your real bandwidth speed.md
rename to published/201409/20140825 Linux Terminal--speedtest_cli checks your real bandwidth speed.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140826 Linus Torvalds is my hero, says 13 year old Zachary DuPont.md b/published/201409/20140826 Linus Torvalds is my hero, says 13 year old Zachary DuPont.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140826 Linus Torvalds is my hero, says 13 year old Zachary DuPont.md
rename to published/201409/20140826 Linus Torvalds is my hero, says 13 year old Zachary DuPont.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140828 GIMP 2.8.12 Released--Here' s How to Install it on Ubuntu.md b/published/201409/20140828 GIMP 2.8.12 Released--Here' s How to Install it on Ubuntu.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140828 GIMP 2.8.12 Released--Here' s How to Install it on Ubuntu.md
rename to published/201409/20140828 GIMP 2.8.12 Released--Here' s How to Install it on Ubuntu.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140829 Linux Doesn't Need to Own the Desktop.md b/published/201409/20140829 Linux Doesn't Need to Own the Desktop.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140829 Linux Doesn't Need to Own the Desktop.md
rename to published/201409/20140829 Linux Doesn't Need to Own the Desktop.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140901 Awesome systemd Commands to Manage Linux System.md b/published/201409/20140901 Awesome systemd Commands to Manage Linux System.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140901 Awesome systemd Commands to Manage Linux System.md
rename to published/201409/20140901 Awesome systemd Commands to Manage Linux System.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140901 Remarkable--A New MarkDown Editor For Linux.md b/published/201409/20140901 Remarkable--A New MarkDown Editor For Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140901 Remarkable--A New MarkDown Editor For Linux.md
rename to published/201409/20140901 Remarkable--A New MarkDown Editor For Linux.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140901 Ubuntu Wallpaper Contest Closes, These Are Our 8 Faves.md b/published/201409/20140901 Ubuntu Wallpaper Contest Closes, These Are Our 8 Faves.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140901 Ubuntu Wallpaper Contest Closes, These Are Our 8 Faves.md
rename to published/201409/20140901 Ubuntu Wallpaper Contest Closes, These Are Our 8 Faves.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140902 Happy Birthday Email.md b/published/201409/20140902 Happy Birthday Email.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140902 Happy Birthday Email.md
rename to published/201409/20140902 Happy Birthday Email.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140902 How to share on linux the output of your shell commands.md b/published/201409/20140902 How to share on linux the output of your shell commands.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140902 How to share on linux the output of your shell commands.md
rename to published/201409/20140902 How to share on linux the output of your shell commands.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140902 Use SearchMonkey To Search Text In All Files Within A Directory In Ubuntu.md b/published/201409/20140902 Use SearchMonkey To Search Text In All Files Within A Directory In Ubuntu.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140902 Use SearchMonkey To Search Text In All Files Within A Directory In Ubuntu.md
rename to published/201409/20140902 Use SearchMonkey To Search Text In All Files Within A Directory In Ubuntu.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140904 The Masked Avengers.md b/published/201409/20140904 The Masked Avengers.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140904 The Masked Avengers.md
rename to published/201409/20140904 The Masked Avengers.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140905 Ubuntu Touch Now Has a Torrent Client in the Ubuntu Store.md b/published/201409/20140905 Ubuntu Touch Now Has a Torrent Client in the Ubuntu Store.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140905 Ubuntu Touch Now Has a Torrent Client in the Ubuntu Store.md
rename to published/201409/20140905 Ubuntu Touch Now Has a Torrent Client in the Ubuntu Store.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140910 Colourful systemd vs sysVinit Linux Cheatsheet.md b/published/201409/20140910 Colourful systemd vs sysVinit Linux Cheatsheet.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140910 Colourful systemd vs sysVinit Linux Cheatsheet.md
rename to published/201409/20140910 Colourful systemd vs sysVinit Linux Cheatsheet.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140910 Jelly Conky Adds Simple, Stylish Stats To Your Linux Desktop.md b/published/201409/20140910 Jelly Conky Adds Simple, Stylish Stats To Your Linux Desktop.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140910 Jelly Conky Adds Simple, Stylish Stats To Your Linux Desktop.md
rename to published/201409/20140910 Jelly Conky Adds Simple, Stylish Stats To Your Linux Desktop.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140910 Meet the 12 Ubuntu 14.10 Wallpaper Contest Winners (So Far).md b/published/201409/20140910 Meet the 12 Ubuntu 14.10 Wallpaper Contest Winners (So Far).md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140910 Meet the 12 Ubuntu 14.10 Wallpaper Contest Winners (So Far).md
rename to published/201409/20140910 Meet the 12 Ubuntu 14.10 Wallpaper Contest Winners (So Far).md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140910 [Quick Tip] How To List All Installed Packages On Linux Distributions.md b/published/201409/20140910 [Quick Tip] How To List All Installed Packages On Linux Distributions.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140910 [Quick Tip] How To List All Installed Packages On Linux Distributions.md
rename to published/201409/20140910 [Quick Tip] How To List All Installed Packages On Linux Distributions.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140911 Install UberWriter Markdown Editor In Ubuntu 14.04.md b/published/201409/20140911 Install UberWriter Markdown Editor In Ubuntu 14.04.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140911 Install UberWriter Markdown Editor In Ubuntu 14.04.md
rename to published/201409/20140911 Install UberWriter Markdown Editor In Ubuntu 14.04.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140912 How to Go Hands On With the Utopic Unicorn--Literally.md b/published/201409/20140912 How to Go Hands On With the Utopic Unicorn--Literally.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140912 How to Go Hands On With the Utopic Unicorn--Literally.md
rename to published/201409/20140912 How to Go Hands On With the Utopic Unicorn--Literally.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140912 QuiteRSS--RSS Reader For Desktop Linux.md b/published/201409/20140912 QuiteRSS--RSS Reader For Desktop Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140912 QuiteRSS--RSS Reader For Desktop Linux.md
rename to published/201409/20140912 QuiteRSS--RSS Reader For Desktop Linux.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140915 How To Uninstall Ubuntu Linux From Windows 8 Dual Boot.md b/published/201409/20140915 How To Uninstall Ubuntu Linux From Windows 8 Dual Boot.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140915 How To Uninstall Ubuntu Linux From Windows 8 Dual Boot.md
rename to published/201409/20140915 How To Uninstall Ubuntu Linux From Windows 8 Dual Boot.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to find and remove obsolete PPA repositories on Ubuntu.md b/published/201409/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to find and remove obsolete PPA repositories on Ubuntu.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to find and remove obsolete PPA repositories on Ubuntu.md
rename to published/201409/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to find and remove obsolete PPA repositories on Ubuntu.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140915 One of the Smallest Distros in the World, Tiny Core, Gets a Fresh Update.md b/published/201409/20140915 One of the Smallest Distros in the World, Tiny Core, Gets a Fresh Update.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140915 One of the Smallest Distros in the World, Tiny Core, Gets a Fresh Update.md
rename to published/201409/20140915 One of the Smallest Distros in the World, Tiny Core, Gets a Fresh Update.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140915 Potenza Icon Themes 2.0 Available For Download.md b/published/201409/20140915 Potenza Icon Themes 2.0 Available For Download.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140915 Potenza Icon Themes 2.0 Available For Download.md
rename to published/201409/20140915 Potenza Icon Themes 2.0 Available For Download.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140917 GNOME Control Center 3.14 RC1 Corrects Lots of Potential Crashes.md b/published/201409/20140917 GNOME Control Center 3.14 RC1 Corrects Lots of Potential Crashes.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140917 GNOME Control Center 3.14 RC1 Corrects Lots of Potential Crashes.md
rename to published/201409/20140917 GNOME Control Center 3.14 RC1 Corrects Lots of Potential Crashes.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140919 Another Italian City Says Goodbye To Microsoft Office, Will Switch To OpenOffice Soon.md b/published/201409/20140919 Another Italian City Says Goodbye To Microsoft Office, Will Switch To OpenOffice Soon.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140919 Another Italian City Says Goodbye To Microsoft Office, Will Switch To OpenOffice Soon.md
rename to published/201409/20140919 Another Italian City Says Goodbye To Microsoft Office, Will Switch To OpenOffice Soon.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140919 Mir and Unity 8 Status Update Arrives from Ubuntu Devs.md b/published/201409/20140919 Mir and Unity 8 Status Update Arrives from Ubuntu Devs.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140919 Mir and Unity 8 Status Update Arrives from Ubuntu Devs.md
rename to published/201409/20140919 Mir and Unity 8 Status Update Arrives from Ubuntu Devs.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140919 Netflix Offers to Work with Ubuntu to Bring Native Playback to All.md b/published/201409/20140919 Netflix Offers to Work with Ubuntu to Bring Native Playback to All.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140919 Netflix Offers to Work with Ubuntu to Bring Native Playback to All.md
rename to published/201409/20140919 Netflix Offers to Work with Ubuntu to Bring Native Playback to All.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140919 Red Hat Acquires FeedHenry for $82 Million to Advance Mobile Development.md b/published/201409/20140919 Red Hat Acquires FeedHenry for $82 Million to Advance Mobile Development.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140919 Red Hat Acquires FeedHenry for $82 Million to Advance Mobile Development.md
rename to published/201409/20140919 Red Hat Acquires FeedHenry for $82 Million to Advance Mobile Development.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140922 Ten Blogs Every Ubuntu User Must Follow.md b/published/201409/20140922 Ten Blogs Every Ubuntu User Must Follow.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140922 Ten Blogs Every Ubuntu User Must Follow.md
rename to published/201409/20140922 Ten Blogs Every Ubuntu User Must Follow.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140924 Canonical Closes nginx Exploit in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS.md b/published/201409/20140924 Canonical Closes nginx Exploit in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140924 Canonical Closes nginx Exploit in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS.md
rename to published/201409/20140924 Canonical Closes nginx Exploit in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140924 Debian 8 Jessie to Have GNOME as the Default Desktop.md b/published/201409/20140924 Debian 8 Jessie to Have GNOME as the Default Desktop.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140924 Debian 8 Jessie to Have GNOME as the Default Desktop.md
rename to published/201409/20140924 Debian 8 Jessie to Have GNOME as the Default Desktop.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140924 End of the Line for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.md b/published/201409/20140924 End of the Line for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140924 End of the Line for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.md
rename to published/201409/20140924 End of the Line for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140924 Second Bugfix Release for KDE Plasma 5 Arrives with Lots of Changes.md b/published/201409/20140924 Second Bugfix Release for KDE Plasma 5 Arrives with Lots of Changes.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140924 Second Bugfix Release for KDE Plasma 5 Arrives with Lots of Changes.md
rename to published/201409/20140924 Second Bugfix Release for KDE Plasma 5 Arrives with Lots of Changes.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20140924 Wal Commander GitHub Edition 0.17 released.md b/published/201409/20140924 Wal Commander GitHub Edition 0.17 released.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/20140924 Wal Commander GitHub Edition 0.17 released.md
rename to published/201409/20140924 Wal Commander GitHub Edition 0.17 released.md
diff --git a/published/201410/How to listen to Internet radio from the command line on Linux.md b/published/201409/How to listen to Internet radio from the command line on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/How to listen to Internet radio from the command line on Linux.md
rename to published/201409/How to listen to Internet radio from the command line on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/201410/The Open Source Witch Hunts Have Returned.md b/published/201409/The Open Source Witch Hunts Have Returned.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/201410/The Open Source Witch Hunts Have Returned.md
rename to published/201409/The Open Source Witch Hunts Have Returned.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140910 How to monitor server memory usage with Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE).md b/published/20140910 How to monitor server memory usage with Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE).md
similarity index 85%
rename from translated/tech/20140910 How to monitor server memory usage with Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE).md
rename to published/20140910 How to monitor server memory usage with Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE).md
index d0ace6a56b..f6707b0080 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20140910 How to monitor server memory usage with Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE).md
+++ b/published/20140910 How to monitor server memory usage with Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE).md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
如何用Nagios远程执行插件(NRPE)来检测服务器内存使用率
================================================================================
-在[先前的教程中][1]注:此篇文章在同一个更新中,如果也翻译了,发布的时候可修改相应的链接,我们已经见到了如何在Nagios设置中设置Nagios远程执行插件(NRPE)。然而,监控内存使用率的脚本和插件并没有在原生的Nagios中。本篇中,我们会看到如何配置NRPE来监控远程服务器上的内存使用率。
+在[先前的教程中][1],我们已经见到了如何在Nagios设置中设置Nagios远程执行插件(NRPE)。然而,监控内存使用率的脚本和插件并没有在原生的Nagios中。本篇中,我们会看到如何配置NRPE来监控远程服务器上的内存使用率。
-我们要用的监控内存的脚本在[Nagios 市场][2]上,也在创建者的[Github仓库][3]中。
+我们要用的监控内存的脚本在[Nagios 市场][2]上,在创建者的[Github仓库][3]中也可以找到。
假设我们已经安装了NRPE,我们首先在我们想要监控的服务器上下载脚本。
@@ -133,8 +133,8 @@ Nagios应该开始在使用NRPE的远程服务器上检查内存使用率了。
- 确保NRPE的端口在远程主机上是总是允许的。默认NRPE的端口是TCP 5666。
-- 你可以尝试通过执行check_nrpe 命令: /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H remote-server 手工检查NRPE操作。
-- 你同样可以尝试运行check_mem 命令:/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H remote-server –c check_mem
+- 你可以尝试通过执行check\_nrpe 命令: /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check\_nrpe -H remote-server 手工检查NRPE操作。
+- 你同样可以尝试运行check\_mem 命令:/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check\_nrpe -H remote-server –c check\_mem
- 在远程服务器上,在/etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg中设置debug=1。重启NRPE服务并检查这些日志文件,/var/log/messages (RHEL/CentOS)或者/var/log/syslog (Debain/Ubuntu)。如果有任何的配置或者权限错误,日志中应该包含了相关的信息。如果日志中没有反映出什么,很有可能是由于请求在某些端口上有过滤而没有到达远程服务器上。
总结一下,这边教程描述了我们该如何调试NRPE来监控远程服务器的内存使用率。过程只需要下载脚本、定义命令和重启服务就行了。希望这对你们有帮助。
@@ -145,11 +145,11 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/monitor-server-memory-usage-nagios-remote-plugin
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
-[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2014/03/nagios-remote-plugin-executor-nrpe-linux.html
+[1]:http://linux.cn/article-4101-1.html
[2]:http://exchange.nagios.org/directory/Plugins/Operating-Systems/Solaris/check_mem-2Epl/details
[3]:https://github.com/justintime/nagios-plugins/blob/master/check_mem/check_mem.pl
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140919 Network Installation of Debian 7 (Whezzy) on Client Machines using DNSMASQ Network Boot Server.md b/published/20140919 Network Installation of Debian 7 (Whezzy) on Client Machines using DNSMASQ Network Boot Server.md
similarity index 89%
rename from translated/tech/20140919 Network Installation of Debian 7 (Whezzy) on Client Machines using DNSMASQ Network Boot Server.md
rename to published/20140919 Network Installation of Debian 7 (Whezzy) on Client Machines using DNSMASQ Network Boot Server.md
index 1d7ac429a0..684dd87fbd 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20140919 Network Installation of Debian 7 (Whezzy) on Client Machines using DNSMASQ Network Boot Server.md
+++ b/published/20140919 Network Installation of Debian 7 (Whezzy) on Client Machines using DNSMASQ Network Boot Server.md
@@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
-客户机通过DNSMASQ网络启动服务器网络安装“Debian 7(Wheezy)”
+通过网络方式安装 Debian 7(Wheezy)
================================================================================
-本教程将指引你直接通过使用**DNSMASQ**作为**PXE服务器(预启动执行环境)**的网络位置安装**Debian 7(Wheezy)**,此种情况是假定你的服务器不提供任何CD/DVD/USB介质驱动器,或者它只能通过相连的监视器、键盘和鼠标操作。
+本教程将指引你直接通过使用**DNSMASQ**作为**PXE服务器(预启动执行环境)**,以网络方式安装**Debian 7(Wheezy)**,此种情况是假定你的服务器不提供任何CD/DVD/USB介质驱动器,或者它只能通过相连的监视器、键盘和鼠标操作。

-客户机上的Debian 7网络安装
+*客户机上的Debian 7网络安装*
**DNSMASQ**是一个轻量级网络基础架构服务器,它可以通过内建的DNS、DHCP和TFTP服务器提供如DNS、DHCP和网络启动等关键服务。
一旦PXE服务器启动并运行,你可以指示你所有的客户机直接从网络启动,前提是你的客户机必须拥有一张支持网络启动的网卡,网络启动可以从BIOS的网络启动或启动服务选项中启用。
-### 需求 ###
+### 前置阅读 ###
- [Debian 7 (Wheezy)安装指南][1]
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@
-安装Dnsmasq包
+*安装Dnsmasq包*
**2.** 安装好DNSMASQ包后,你可以开始编辑配置文件。首先创建一个主配置文件的备份,然后使用下面的命令对**dnsmasq.conf**文件进行编辑。
@@ -31,9 +31,9 @@

-备份Dnsmasq配置
+*备份Dnsmasq配置*
-**3.** 上面的备份过程适合重命名配置文件,所以新的文件应该是空,你可以使用以下下面描述的**DNSMASQ**配置文件节录。
+**3.** 上面的备份过程适合重命名配置文件,所以新的文件应该是空,你可以使用以下描述的**DNSMASQ**配置文件节录。
interface=eth0
domain=debian.lan
@@ -47,7 +47,7 @@

-Dnsmasq配置
+*Dnsmasq配置*
- **interface** – 服务器监听的网络接口。
- **domain** – 用你自己的域名替换。
@@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ Dnsmasq配置

-下载Debian网络启动文件
+*下载Debian网络启动文件*
使用以下变量用于**Debian网络安装**镜像和架构。
@@ -95,9 +95,10 @@ Dnsmasq配置

-启动Dnsmasq服务
+*启动Dnsmasq服务*
**6.** 基于Debian的发行版通常附带了**UFW防火墙**包。使用以下命令来打开需要的**DNSMASQ**端口号:**67**(Bootps),**69**(TFTP),**53**(DNS)**4011**(代理DHCP)udp和**53** tcp(DNS)。
+
# ufw allow 69/udp
# ufw allow 4011/udp ## Only if you have a ProxyDHCP on the network
# ufw allow 67/udp
@@ -106,9 +107,8 @@ Dnsmasq配置

-开启Dnsmasq端口
+*开启Dnsmasq端口*
-Now, the PXE loader located on your client network interface will load **pxelinux** configuration files from **/srv/tftp/pxelinux.cfg** directory using this order.
现在,位于你的客户机网络接口上的PXE加载器将使用按以下顺序从**/srv/tftp/pxelinux.cfg**目录加载**pxelinux**配置文件。
- GUID文件
@@ -123,7 +123,7 @@ Now, the PXE loader located on your client network interface will load **pxelinu

-选择BIOS设置
+*选择BIOS设置*
**8。** 在编辑启动顺序后,通常按**F10**来保存BIOS设置。重启后,你的客户端计算机应该可以直接从网络启动了,应该会出第一个**PXE**提示,要求你按**F8**键进入菜单。
@@ -131,15 +131,15 @@ Now, the PXE loader located on your client network interface will load **pxelinu

-启动菜单选择
+*启动菜单选择*

-选择Debian安装器启动
+*选择Debian安装器启动*

-选择Debian安装
+*选择Debian安装*
从这里开始,你可以使用Debian 7 Wheezy安装进程将Debian安装到你的机器上了(安装链接见上面)。然而,为了能够完成安装进程,你也需要确保你的机器上互联网连接已经激活。
@@ -151,7 +151,7 @@ Now, the PXE loader located on your client network interface will load **pxelinu

-DNSMASQ服务器排障
+*DNSMASQ服务器排障*
**10.** 如果服务器测试中已一切就绪,你现在可以在**sysv-rc-conf**包的帮助下,启用**DNSMASQ**守护进程自启动,以使该进程在系统重启后自动启动。
@@ -160,11 +160,11 @@ DNSMASQ服务器排障

-启用DNSMASQ守护进程
+*启用DNSMASQ守护进程*
到此为止吧!现在你的**PXE**服务器已经整装待发,随时准备好分配IP地址了(**DHCP**),并为你所有网段中的客户端提供需要的启动信息,这些信息配置用来从网络启动并安装Debian Wheezy。
-使用PXE网络启动安装在服务器主机数量增长时很有优势,因为你可以在短时间内火同时设置整个网络基础架构,为版本升级提供了方便,也可以通过kickstart文件使整个安装的全自动化。
+使用PXE网络启动安装在服务器主机数量很多时很有优势,因为你可以在短时间内火同时设置整个网络基础架构,为版本升级提供了方便,也可以通过kickstart文件使整个安装的全自动化。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -172,7 +172,7 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/network-installation-of-debian-7-on-client-machines/
作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20 Useful Commands of ‘Sysstat’ Utilities (mpstat, pidstat, iostat and sar) for Linux Performance Monitoring.md b/published/201410/20 Useful Commands of ‘Sysstat’ Utilities (mpstat, pidstat, iostat and sar) for Linux Performance Monitoring.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20 Useful Commands of ‘Sysstat’ Utilities (mpstat, pidstat, iostat and sar) for Linux Performance Monitoring.md
rename to published/201410/20 Useful Commands of ‘Sysstat’ Utilities (mpstat, pidstat, iostat and sar) for Linux Performance Monitoring.md
diff --git a/published/20140711 How to use systemd for system administration on Debian.md b/published/201410/20140711 How to use systemd for system administration on Debian.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140711 How to use systemd for system administration on Debian.md
rename to published/201410/20140711 How to use systemd for system administration on Debian.md
diff --git a/published/20140724 Camicri Cube--An Offline And Portable Package Management System.md b/published/201410/20140724 Camicri Cube--An Offline And Portable Package Management System.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140724 Camicri Cube--An Offline And Portable Package Management System.md
rename to published/201410/20140724 Camicri Cube--An Offline And Portable Package Management System.md
diff --git a/published/20140724 What are useful online tools for Linux.md b/published/201410/20140724 What are useful online tools for Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140724 What are useful online tools for Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20140724 What are useful online tools for Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20140729 How to use awk command in Linux.md b/published/201410/20140729 How to use awk command in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140729 How to use awk command in Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20140729 How to use awk command in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20140801 What are better alternatives to basic command line utilities.md b/published/201410/20140801 What are better alternatives to basic command line utilities.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140801 What are better alternatives to basic command line utilities.md
rename to published/201410/20140801 What are better alternatives to basic command line utilities.md
diff --git a/published/20140804 How to install and configure Nvidia Optimus driver on Ubuntu.md b/published/201410/20140804 How to install and configure Nvidia Optimus driver on Ubuntu.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140804 How to install and configure Nvidia Optimus driver on Ubuntu.md
rename to published/201410/20140804 How to install and configure Nvidia Optimus driver on Ubuntu.md
diff --git a/published/20140808 How to install Puppet server and client on CentOS and RHEL.md b/published/201410/20140808 How to install Puppet server and client on CentOS and RHEL.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140808 How to install Puppet server and client on CentOS and RHEL.md
rename to published/201410/20140808 How to install Puppet server and client on CentOS and RHEL.md
diff --git a/published/20140811 Check how much do you type with WhatPulse on Linux.md b/published/201410/20140811 Check how much do you type with WhatPulse on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140811 Check how much do you type with WhatPulse on Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20140811 Check how much do you type with WhatPulse on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20140811 How to improve your productivity in terminal environment with Tmux.md b/published/201410/20140811 How to improve your productivity in terminal environment with Tmux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140811 How to improve your productivity in terminal environment with Tmux.md
rename to published/201410/20140811 How to improve your productivity in terminal environment with Tmux.md
diff --git a/published/20140813 How to Extend or Reduce LVM' s (Logical Volume Management) in Linux--Part II.md b/published/201410/20140813 How to Extend or Reduce LVM' s (Logical Volume Management) in Linux--Part II.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140813 How to Extend or Reduce LVM' s (Logical Volume Management) in Linux--Part II.md
rename to published/201410/20140813 How to Extend or Reduce LVM' s (Logical Volume Management) in Linux--Part II.md
diff --git a/published/20140813 How to remove file metadata on Linux.md b/published/201410/20140813 How to remove file metadata on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140813 How to remove file metadata on Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20140813 How to remove file metadata on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20140813 Setup Flexible Disk Storage with Logical Volume Management (LVM) in Linux--PART 1.md b/published/201410/20140813 Setup Flexible Disk Storage with Logical Volume Management (LVM) in Linux--PART 1.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140813 Setup Flexible Disk Storage with Logical Volume Management (LVM) in Linux--PART 1.md
rename to published/201410/20140813 Setup Flexible Disk Storage with Logical Volume Management (LVM) in Linux--PART 1.md
diff --git a/published/20140815 How to manage a WiFi connection from the command line.md b/published/201410/20140815 How to manage a WiFi connection from the command line.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140815 How to manage a WiFi connection from the command line.md
rename to published/201410/20140815 How to manage a WiFi connection from the command line.md
diff --git a/published/20140818 Can Ubuntu Do This--Answers to The 4 Questions New Users Ask Most.md b/published/201410/20140818 Can Ubuntu Do This--Answers to The 4 Questions New Users Ask Most.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140818 Can Ubuntu Do This--Answers to The 4 Questions New Users Ask Most.md
rename to published/201410/20140818 Can Ubuntu Do This--Answers to The 4 Questions New Users Ask Most.md
diff --git a/published/20140818 Disable reboot using Ctrl-Alt-Del Keys in RHEL or CentOS.md b/published/201410/20140818 Disable reboot using Ctrl-Alt-Del Keys in RHEL or CentOS.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140818 Disable reboot using Ctrl-Alt-Del Keys in RHEL or CentOS.md
rename to published/201410/20140818 Disable reboot using Ctrl-Alt-Del Keys in RHEL or CentOS.md
diff --git a/published/20140818 How to configure Access Control Lists (ACLs) on Linux.md b/published/201410/20140818 How to configure Access Control Lists (ACLs) on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140818 How to configure Access Control Lists (ACLs) on Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20140818 How to configure Access Control Lists (ACLs) on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20140818 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'X11 forwarding request failed on channel 0'.md b/published/201410/20140818 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'X11 forwarding request failed on channel 0'.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140818 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'X11 forwarding request failed on channel 0'.md
rename to published/201410/20140818 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix 'X11 forwarding request failed on channel 0'.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140819 How to Encrypt Email in Linux.md b/published/201410/20140819 How to Encrypt Email in Linux.md
similarity index 79%
rename from translated/tech/20140819 How to Encrypt Email in Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20140819 How to Encrypt Email in Linux.md
index 9dadd06e8f..6996d816ea 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20140819 How to Encrypt Email in Linux.md
+++ b/published/201410/20140819 How to Encrypt Email in Linux.md
@@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
在Linux中加密邮件
================================================================================
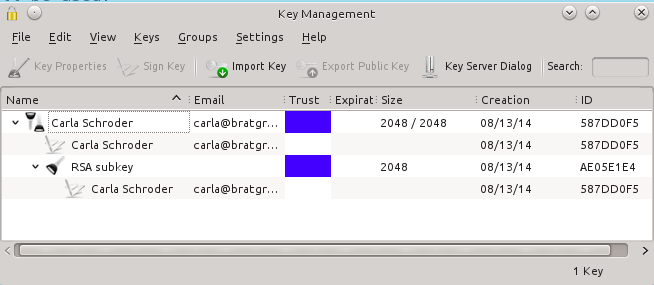
-Kgpg为了创建了管理加密秘钥提供了一个很好的GUI界面.
+*Kgpg为了创建了管理加密秘钥提供了一个很好的GUI界面.*
-如果你一直在考虑如何加密电子邮件,那么在众多的邮件服务和邮件客户端中挑来挑去一定是件头痛的事情.可以考虑两种加密方法:SSL或TLS加密会保护发送到邮件服务器的登录名和密码.[Gunpg][1]是一款标准有用的Linux加密工具,可以加密和认证消息.如果你可以管理自己的GPG加密,并不考虑第三方工具,那它就够了,其它的我们将在稍后讨论.
+如果你一直在考虑如何加密电子邮件,那么在众多的邮件服务和邮件客户端中挑来挑去一定是件头痛的事情.可以考虑两种加密方法:SSL或TLS加密会保护发送到邮件服务器的登录名和密码.[Gunpg][1]是一款标准的、强大的Linux加密工具,可以加密和认证消息.如果你可以管理自己的GPG加密,并不考虑第三方工具,那它就够了,其它的我们将在稍后讨论.
即便加密了消息,你仍然会暴露在流量分析中,因为消息头部必须是明文形式.所以需要另一款比如[Tor network][2]来隐藏你在互联网上的足迹.我们会看看各种邮件服务和客户端,以及其中的利弊.
@@ -11,27 +11,27 @@ Kgpg为了创建了管理加密秘钥提供了一个很好的GUI界面.
如果你使用过GMail, Yahoo,Hotmail或者其它Web邮件提供商的邮件服务,那就忘掉它们吧.你在Web浏览器里输入的任何信息都会暴露在JavaScript攻击中,而且无论服务提供商提供什么保障都是过眼云烟(译者注:此说法靠谱否?).GMail,Yahoo和Hotmail均提供SSL/TLS加密来防止消息被窃听.但是它们不会提供任何保护来阻碍它们自己的数据挖掘,因此并不会提供端到端的加密.Yahoo和Google都声称将在明年推出端到端的加密.对此我持怀疑态度,因为如果一旦它们的核心业务数据挖掘受到干预,它们就什么都干不了了.
-市面上也有各式各样的声称可以为所有类型的电子邮件都能提供安全加密的第三方邮件加密服务,比如[Virtru][3]和[SafeMess][4].对此我依旧表示怀疑,因为无论是谁,只要持有加密秘钥就可以访问你的消息,所以你还是要依赖于可信而不是技术.
+市面上也有各式各样的声称可以为所有类型的电子邮件都能提供安全加密的第三方邮件加密服务,比如[Virtru][3]和[SafeMess][4].对此我依旧表示怀疑,因为无论是谁,只要持有加密秘钥就可以访问你的消息,所以你还是要依赖于对他们的信任而不是技术.
-对等消息可以避免许多使用集中化服务中的缺陷.[RetroShare][5]和[Bitmessage][6]是两种流行的范例.我不知道它们是否如实所述,但这么说肯定由可取之处.
+对等消息可以避免许多使用集中化服务中的缺陷.[RetroShare][5]和[Bitmessage][6]是两种流行的范例.我不知道它们是否如实所述,但这么说肯定有其可取之处.
那Anddroid和iOS又如何呢?假设大部分的Android和iOS应用都没有权限获取你的消息的话,那就是最安全的.不要照搬我说的 -- 在应用将要安装到你的设备上时麻烦读读相关的服务条款并检查所要求的权限.即便在初次安装时它们的条款是可接受的,也记得单方面的条款改变是行业的标准,所以做最坏的打算是最安全的.
-### 零基础知识 ###
+### 零知识(Zero Knowledge) ###
-[Proton Mail][7]是一款全新的邮件服务,声称无需任何基础就可以实现消息加密.认证和消息加密分为两个单独的步骤,Proton受到Swiss隐私条款的保护,它们不会通过日志记录用户的活动.零基础知识加密提供真正的安全.这代表只有你拥有你的加密秘钥,如果你丢了它们,你的消息就无法恢复了.
+[Proton Mail][7]是一款全新的邮件服务,声称采用零知识就可以实现消息加密.认证和消息加密分为两个单独的步骤,Proton遵照Swiss隐私条款,它们不会通过日志记录用户的活动.零知识加密提供真正的安全.这代表只有你拥有你的加密秘钥,如果你丢了它们,你的消息就无法恢复了.
也有许多加密电子邮件服务声称可以保护你的隐私.认真阅读细则,查看红色标注的地方,比如受限的用户数据采集,与好友分享,与执法部门的合作等.这些条款暗示它们会收集和共享用户数据,拥有权限获取你的加密秘钥,并读取你的消息.
### Linux邮件客户端 ###
-一款独立的开源邮件客户端,比如, Mutt, Claws, Evolution, Sylpheed和Alpine,可建立你自己控制的GnuPG秘钥,给你大部分的保护.(建立更安全的电子邮件和Web浏览的最容易的方式是运行TAILS live的Linux发行版.详情查看[Protect Yourself Online With Tor, TAILS, and Debian][8].)
+一款独立的开源邮件客户端,比如, Mutt, Claws, Evolution, Sylpheed和Alpine,可建立你自己控制的GnuPG秘钥,给你大部分的保护.(建立更安全的电子邮件和Web浏览的最容易的方式是运行TAILS live的Linux发行版.详情查看[通过 Tor、TAILS 和 Debian 在网上保护你自己][8]。)
无论你使用的是TAILS还是一款标准Linux发行版,管理GnuPG的方法是相同的,所以下面来学习如何使用GnuPG加密消息.
### 使用GnuPG ###
-首先,熟悉一下相关术语。OpenPGP是一种开放的电子邮件加密和认证协议,基于菲利普·齐默曼的Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)。GNU Privacy Guard (GnuPG or GPG)是OpenPGP的GPL实现。GnuPG使用对称公钥加密算法,也就是说会生成一堆密钥:一个任何人都可以用来加密发送给你的消息的公钥和一个只有你自己拥有用来解密消息的的私钥。GnuPG执行两个分开的函数:数字化签名消息以证明消息来自你和加密消息。任何人都可以读到你的数字签名消息,但只有那些与你交换密钥的人才可以读取加密消息。切记千万不要与他人分享你的密钥!只能分享公钥。
+首先,熟悉一下相关术语。OpenPGP是一种开放的电子邮件加密和认证协议,基于菲利普·齐默曼的Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)。GNU Privacy Guard (GnuPG or GPG)是OpenPGP的GPL实现。GnuPG使用对称公钥加密算法,也就是说会生成一对密钥:一个任何人都可以用来加密发送给你的消息的公钥和一个只有你自己拥有用来解密消息的的私钥。GnuPG执行两个分开的函数:数字化签名消息以证明消息来自你和加密消息。任何人都可以读到你的数字签名消息,但只有那些与你交换密钥的人才可以读取加密消息。切记千万不要与他人分享你的密钥!只能分享公钥。
Seahorse是GnuPG对应的GNOME图形化前端,KGpg是KDE图形化的GnuPG工具。
@@ -39,7 +39,7 @@ Seahorse是GnuPG对应的GNOME图形化前端,KGpg是KDE图形化的GnuPG工
$ gpg --gen-key
-这个过程有许多步骤;对于大部分人来说,只需要回答所有的问题,遵循默认设置就好。当你生成你的密钥时,记下来并将其保存在一个安全的地方,因为如果你丢掉了它,你就不能解密任何消息了。任何关于不要写下密码的建议都是错误的。我们中的大部分人要记住许多登录名和密码,包括那些我们几乎从来不会用到的,所以全部记住它们是不现实的。你知道当人们不写下他们的密码时会发生什么吗?他们会选择生成简单的密码并不断重复使用。你存储在电脑里的任何东西都潜在地会被攻击窃取;一个保存在上锁的柜子里的小本是无法通过渗透获取的,除了物理的入侵,当然入侵者要知道如何去寻找它。
+这个过程有许多步骤;对于大部分人来说,只需要回答所有的问题,遵循默认设置就好。当你生成你的密钥时,记下来并将其保存在一个安全的地方,因为如果你丢掉了它,你就不能解密任何消息了。**任何关于不要写下密码的建议都是错误的。**我们中的大部分人要记住许多登录名和密码,包括那些我们几乎从来不会用到的,所以全部记住它们是不现实的。你知道当人们不写下他们的密码时会发生什么吗?**他们会选择生成简单的密码并不断重复使用。**你存储在电脑里的任何东西都潜在地会被攻击窃取;一个保存在上锁的柜子里的小本是无法通过渗透获取的,除了物理的入侵,当然入侵者要知道如何去寻找它。
我必须叮嘱你们去弄清楚如何使用新密钥去配置邮件客户端,因为每一个都不同。你可以按照如下操作列出你的密钥:
@@ -54,11 +54,11 @@ Seahorse是GnuPG对应的GNOME图形化前端,KGpg是KDE图形化的GnuPG工
$ gpg --send-keys 'Carla Schroder' --keyserver http://example.com
-当你为上传到公钥服务器生成了一个新的密钥,你也应该生成一个撤销证书。不要推迟到以后做———当你生成新密钥时就生成它。你可以给它取任意的名称,比如使用一个像mycodeproject.asc的描述性名称来代替revoke.asc:
+当你生成了一个新的密钥要上传到公钥服务器,你也应该生成一个撤销证书。不要推迟到以后做———当你生成新密钥时就生成它。你可以给它取任意的名称,比如使用一个像mycodeproject.asc的描述性名称来代替revoke.asc:
$ gpg --output revoke.asc --gen-revoke 'Carla Schroder'
-如果你的密钥缺乏抵抗力,你可以通过向keyring导入撤销证书来撤销它:
+如果你的密钥变得不可靠了,你可以通过向keyring导入撤销证书来撤销它:
$ gpg --import ~/.gnupg/revoke.asc
@@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ via: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/784165-how-to-encrypt-email-in-linux
作者:[Carla Schroder][a]
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20140822 15 Practical Examples of 'echo' command in Linux.md b/published/201410/20140822 15 Practical Examples of 'echo' command in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140822 15 Practical Examples of 'echo' command in Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20140822 15 Practical Examples of 'echo' command in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20140822 Want To Start An Open Source Project--Here's How.md b/published/201410/20140822 Want To Start An Open Source Project--Here's How.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140822 Want To Start An Open Source Project--Here's How.md
rename to published/201410/20140822 Want To Start An Open Source Project--Here's How.md
diff --git a/published/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Shutter on CentOS.md b/published/201410/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Shutter on CentOS.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Shutter on CentOS.md
rename to published/201410/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Shutter on CentOS.md
diff --git a/published/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to show a MAC learning table of Linux bridge.md b/published/201410/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to show a MAC learning table of Linux bridge.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to show a MAC learning table of Linux bridge.md
rename to published/201410/20140825 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to show a MAC learning table of Linux bridge.md
diff --git a/published/20140826 Linus Torvalds Promotes Linux for Desktops, Embedded Computing.md b/published/201410/20140826 Linus Torvalds Promotes Linux for Desktops, Embedded Computing.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140826 Linus Torvalds Promotes Linux for Desktops, Embedded Computing.md
rename to published/201410/20140826 Linus Torvalds Promotes Linux for Desktops, Embedded Computing.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140829 6 Interesting Funny Commands of Linux (Fun in Terminal) – Part II.md b/published/201410/20140829 6 Interesting Funny Commands of Linux (Fun in Terminal) – Part II.md
similarity index 89%
rename from translated/tech/20140829 6 Interesting Funny Commands of Linux (Fun in Terminal) – Part II.md
rename to published/201410/20140829 6 Interesting Funny Commands of Linux (Fun in Terminal) – Part II.md
index 84dc635d0d..8cce36ecbb 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20140829 6 Interesting Funny Commands of Linux (Fun in Terminal) – Part II.md
+++ b/published/201410/20140829 6 Interesting Funny Commands of Linux (Fun in Terminal) – Part II.md
@@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
-6个有趣的Linux命令行工具(终端中的乐趣)—— 第二部分
+终端中的乐趣:6个有趣的Linux命令行工具
================================================================================
之前, 我们展示了一些有关有趣的 Linux 命令行命令的文章, 这些文章告诉我们, Linux 并不像看起来那样复杂, 如果我们知道如何使用的话, 反而会非常有趣. Linux 命令行可以简洁而完美地执行一些复杂的任务, 并且十分有趣.
- [Linux命令及Linux终端的20个趣事][3]
-- [Fun in Linux Terminal – Play with Word and Character Counts][2]
+- [Linux终端的乐趣之把玩字词计数][2]

-有趣的 Linux 命令
+
+*有趣的 Linux 命令*
前者包含了20个有趣的 Linux 命令/脚本(和子命令), 得到了读者的高度赞扬. 而另一篇文章虽然没有之前那篇文章那么受欢迎,包含了一些命令/脚本和改进,让你能够玩儿转文本文件、单词和字符串.
@@ -27,9 +28,10 @@
$ echo "Tecmint[dot]com is a community of Linux Nerds and Geeks" | pv -qL 10

-正在运行的 pv 命令
-**注意**: '**q**' 选项表示'安静',没有其他输出信息, '**L**' 选项表示每秒转化的字节数上限. 数字变量可以调整任何一个方向(必须是整数) 来获得所需的模拟文本.
+*正在运行的 pv 命令*
+
+**注意**: '**q**' 选项表示'安静',没有其他输出信息, '**L**' 选项表示每秒转化的字节数上限. 调整数字的值(必须是整数)可以以另外的方向显示文字效果。
### 2. toilet 命令 ###
@@ -38,7 +40,8 @@
$ while true; do echo “$(date | toilet -f term -F border –Tecmint)”; sleep 1; done

-正在运行的 toilet 命令
+
+*正在运行的 toilet 命令*
**注意**: 上面的脚本需要使用 **ctrl+z** 键来暂停.
@@ -49,7 +52,8 @@
# rig

-正在运行的 rig 命令
+
+*正在运行的 rig 命令*
### 4. aview 命令 ###
@@ -58,7 +62,8 @@
$ asciiview elephant.jpg -driver curses

-正在运行的 aview 命令
+
+*正在运行的 aview 命令*
### 5. xeyes 命令 ###
@@ -67,7 +72,8 @@
$ xeyes

-正在运行的 xeyes 命令
+
+*正在运行的 xeyes 命令*
### 6. cowsay 命令 ###
@@ -80,14 +86,16 @@
$ cowsay -f elephant-in-snake Tecmint is Best

-正在运行的 cowsay 命令
+
+*正在运行的 cowsay 命令*
换作山羊又会怎样?
$ cowsay -f gnu Tecmint is Best

-正在运行的 山羊cowsay 命令
+
+*正在运行的 山羊cowsay 命令*
今天就到这里吧. 我将带着另一篇有趣的文章回来. 不要忘记在下面留下您的评论.
@@ -103,6 +111,6 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-funny-commands/
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-funny-commands-of-linux-or-linux-is-fun-in-terminal/
-[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/play-with-word-and-character-counts-in-linux/
+[2]:http://linux.cn/article-4088-1.html
[3]:http://linux.cn/article-2831-1.html
[4]:http://aa-project.sourceforge.net/aview/
diff --git a/published/20140829 Fun in Linux Terminal--Play with Word and Character Counts.md b/published/201410/20140829 Fun in Linux Terminal--Play with Word and Character Counts.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140829 Fun in Linux Terminal--Play with Word and Character Counts.md
rename to published/201410/20140829 Fun in Linux Terminal--Play with Word and Character Counts.md
diff --git a/published/20140902 Mount Google drive in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS.md b/published/201410/20140902 Mount Google drive in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140902 Mount Google drive in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS.md
rename to published/201410/20140902 Mount Google drive in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS.md
diff --git a/published/20140902 Photo Editing on Linux with Krita.md b/published/201410/20140902 Photo Editing on Linux with Krita.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140902 Photo Editing on Linux with Krita.md
rename to published/201410/20140902 Photo Editing on Linux with Krita.md
diff --git a/published/20140904 Making MySQL Better at GitHub.md b/published/201410/20140904 Making MySQL Better at GitHub.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140904 Making MySQL Better at GitHub.md
rename to published/201410/20140904 Making MySQL Better at GitHub.md
diff --git a/published/20140904 Use LaTeX In Ubuntu 14.04 and Linux Mint 17 With Texmaker.md b/published/201410/20140904 Use LaTeX In Ubuntu 14.04 and Linux Mint 17 With Texmaker.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140904 Use LaTeX In Ubuntu 14.04 and Linux Mint 17 With Texmaker.md
rename to published/201410/20140904 Use LaTeX In Ubuntu 14.04 and Linux Mint 17 With Texmaker.md
diff --git a/published/20140910 How To Recover Default Openbox Config Files On Crunchbang.md b/published/201410/20140910 How To Recover Default Openbox Config Files On Crunchbang.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140910 How To Recover Default Openbox Config Files On Crunchbang.md
rename to published/201410/20140910 How To Recover Default Openbox Config Files On Crunchbang.md
diff --git a/published/20140910 How to download GOG games from the command line on Linux.md b/published/201410/20140910 How to download GOG games from the command line on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140910 How to download GOG games from the command line on Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20140910 How to download GOG games from the command line on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20140910 How to set up Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE) in Linux.md b/published/201410/20140910 How to set up Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE) in Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140910 How to set up Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE) in Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20140910 How to set up Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE) in Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to capture TCP SYN, ACK and FIN packets with tcpdump.md b/published/201410/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to capture TCP SYN, ACK and FIN packets with tcpdump.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to capture TCP SYN, ACK and FIN packets with tcpdump.md
rename to published/201410/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to capture TCP SYN, ACK and FIN packets with tcpdump.md
diff --git a/published/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change hostname on CentOS or RHEL 7.md b/published/201410/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change hostname on CentOS or RHEL 7.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change hostname on CentOS or RHEL 7.md
rename to published/201410/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change hostname on CentOS or RHEL 7.md
diff --git a/published/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a new Amazon AWS access key.md b/published/201410/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a new Amazon AWS access key.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a new Amazon AWS access key.md
rename to published/201410/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a new Amazon AWS access key.md
diff --git a/published/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to expand an XFS file system.md b/published/201410/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to expand an XFS file system.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to expand an XFS file system.md
rename to published/201410/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to expand an XFS file system.md
diff --git a/published/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to remove PPA repository from command line on Ubuntu.md b/published/201410/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to remove PPA repository from command line on Ubuntu.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to remove PPA repository from command line on Ubuntu.md
rename to published/201410/20140915 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to remove PPA repository from command line on Ubuntu.md
diff --git a/published/20140919 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a MySQL database from the command line.md b/published/201410/20140919 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a MySQL database from the command line.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140919 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a MySQL database from the command line.md
rename to published/201410/20140919 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a MySQL database from the command line.md
diff --git a/published/20140922 How to Run Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon.md b/published/201410/20140922 How to Run Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140922 How to Run Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon.md
rename to published/201410/20140922 How to Run Android Apps on Ubuntu using ARChon.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140922 How to use logrotate to manage log files in Linux.md b/published/201410/20140922 How to use logrotate to manage log files in Linux.md
similarity index 90%
rename from translated/tech/20140922 How to use logrotate to manage log files in Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20140922 How to use logrotate to manage log files in Linux.md
index c4f03e9dcc..abe0d52984 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20140922 How to use logrotate to manage log files in Linux.md
+++ b/published/201410/20140922 How to use logrotate to manage log files in Linux.md
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
Linux日志文件总管——logrotate
================================================================================
-日志文件包含了关于系统中发生的事件的有用信息,在排障过程中或者系统性能分析时经常被用到。对于忙碌的服务器,日志文件大小会快速增长,服务器会很快消耗磁盘空间,这成了个问题。除此之外,处理一个单个的庞大日志文件也常常是件十分棘手的事。
+日志文件包含了关于系统中发生的事件的有用信息,在排障过程中或者系统性能分析时经常被用到。对于忙碌的服务器,日志文件大小会增长极快,服务器会很快消耗磁盘空间,这成了个问题。除此之外,处理一个单个的庞大日志文件也常常是件十分棘手的事。
-logrotate是个十分有用的工具,它可以自动对日志进行分解(或轮循)、压缩以及删除旧日志文件。例如,你可以设置logrotate,让/var/log/foo日志文件每30天轮循,并删除超过6个月的日志。配置完后,logrotate的运作完全自动化,不必进行任何进一步的认为干预。另外,旧日志也可以通过电子邮件发送,不过该选项超出了本教程的讨论范围。
+logrotate是个十分有用的工具,它可以自动对日志进行截断(或轮循)、压缩以及删除旧的日志文件。例如,你可以设置logrotate,让/var/log/foo日志文件每30天轮循,并删除超过6个月的日志。配置完后,logrotate的运作完全自动化,不必进行任何进一步的人为干预。另外,旧日志也可以通过电子邮件发送,不过该选项超出了本教程的讨论范围。
主流Linux发行版上都默认安装有logrotate包,如果出于某种原因,logrotate没有出现在里头,你可以使用apt-get或yum命令来安装。
@@ -50,16 +50,16 @@ logrotate的配置文件是/etc/logrotate.conf,通常不需要对它进行修
- **rotate 5**: 一次将存储5个归档日志。对于第六个归档,时间最久的归档将被删除。
- **compress**: 在轮循任务完成后,已轮循的归档将使用gzip进行压缩。
- **delaycompress**: 总是与compress选项一起用,delaycompress选项指示logrotate不要将最近的归档压缩,压缩将在下一次轮循周期进行。这在你或任何软件仍然需要读取最新归档时很有用。
-- **missingok**: 在日志轮循其间,任何错误将被忽略,例如“文件无法找到”之类的错误。
+- **missingok**: 在日志轮循期间,任何错误将被忽略,例如“文件无法找到”之类的错误。
- **notifempty**: 如果日志文件为空,轮循不会进行。
- **create 644 root root**: 以指定的权限创建全新的日志文件,同时logrotate也会重命名原始日志文件。
-- **postrotate/endscript**: 在所有其它指令完成后,postrotate和endscript之间指定的命令将被执行。在这种情况下,rsyslogd 进程将立即再次读取其配置并继续运行。
+- **postrotate/endscript**: 在所有其它指令完成后,postrotate和endscript里面指定的命令将被执行。在这种情况下,rsyslogd 进程将立即再次读取其配置并继续运行。
上面的模板是通用的,而配置参数则根据你的需求进行调整,不是所有的参数都是必要的。
### 样例二 ###
-在本例中,我们只想要轮循一个日志文件,然而日志文件大小会增长到50MB。
+在本例中,我们只想要轮循一个日志文件,然而日志文件大小可以增长到50MB。
# vim /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
@@ -92,7 +92,7 @@ logrotate的配置文件是/etc/logrotate.conf,通常不需要对它进行修
endscript
}
-这将导致归档文件在它们的文件名中包含日期信息。
+这将让归档文件在它们的文件名中包含日期信息。
### 排障 ###
@@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ logrotate的配置文件是/etc/logrotate.conf,通常不需要对它进行修
正如我们从上面的输出结果可以看到的,logrotate判断该轮循是不必要的。如果文件的时间小于一天,这就会发生了。
-#### 3. 强制运行 ####
+#### 3. 强制轮循 ####
即使轮循条件没有满足,我们也可以通过使用‘-f’选项来强制logrotate轮循日志文件,‘-v’参数提供了详细的输出。
@@ -153,7 +153,7 @@ logrotate的配置文件是/etc/logrotate.conf,通常不需要对它进行修
running postrotate script
compressing log with: /bin/gzip
-#### 4. Logrotate记录日志 ####
+#### 4. Logrotate的记录日志 ####
logrotate自身的日志通常存放于/var/lib/logrotate/status目录。如果处于排障目的,我们想要logrotate记录到任何指定的文件,我们可以指定像下面这样从命令行指定。
@@ -192,7 +192,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/logrotate-manage-log-files-linux.html
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20140922 Reset Unity and Compiz Settings in Ubuntu 14.04.md b/published/201410/20140922 Reset Unity and Compiz Settings in Ubuntu 14.04.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140922 Reset Unity and Compiz Settings in Ubuntu 14.04.md
rename to published/201410/20140922 Reset Unity and Compiz Settings in Ubuntu 14.04.md
diff --git a/published/20140924 How To Install Vmware 10 On CentOS 7.md b/published/201410/20140924 How To Install Vmware 10 On CentOS 7.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140924 How To Install Vmware 10 On CentOS 7.md
rename to published/201410/20140924 How To Install Vmware 10 On CentOS 7.md
diff --git a/published/20140924 How to delete recently opened files history in ubuntu 14.04.md b/published/201410/20140924 How to delete recently opened files history in ubuntu 14.04.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140924 How to delete recently opened files history in ubuntu 14.04.md
rename to published/201410/20140924 How to delete recently opened files history in ubuntu 14.04.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/20140924 How to use CloudFlare as a ddclient provider under Ubuntu.md b/published/201410/20140924 How to use CloudFlare as a ddclient provider under Ubuntu.md
similarity index 78%
rename from translated/tech/20140924 How to use CloudFlare as a ddclient provider under Ubuntu.md
rename to published/201410/20140924 How to use CloudFlare as a ddclient provider under Ubuntu.md
index bd5f5a49ea..fb78dd7867 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20140924 How to use CloudFlare as a ddclient provider under Ubuntu.md
+++ b/published/201410/20140924 How to use CloudFlare as a ddclient provider under Ubuntu.md
@@ -1,15 +1,16 @@
-Ubuntu下使用CloudFlare作为ddclient提供商
+Ubuntu下使用CloudFlare 动态域名
================================================================================
-DDclient是一个Perl客户端,用于更新动态DNS网络服务提供商帐号下的动态DNS条目。它最初是由保罗·巴利编写的,现在大多数是由维姆潘科在做。它能做的不仅仅是动态DNS,也可以通过几种不同的方式获取你的WAN口IP地址。
-
-CloudFlare有一点已知的功能,它允许你通过API或叫做ddclient的命令行脚本更新你的DNS记录。不管哪一个,结果都一样,而且它是个免费软件。
-
-不幸的是,ddclient并不能在CloudFlare中即开即用。它需要打补丁,这里就是要介绍怎样在Debian或Ubuntu上破解它,它也能在带有Raspberry Pi的Raspbian上工作。
### 需求 ###
首先保证你有一个自有域名,然后登录到CloudFlare,添加你的域名。遵循指令操作,使用它给出的默认值就行了。你将让CloudFlare来托管你的域,所以你需要调整你的注册机构的设置。如果你想要使用子域名,请为它添加一条‘A’记录。目前,任何IP地址都可以。
+DDclient是一个Perl客户端,用于更新动态DNS网络服务提供商帐号下的动态DNS条目。它最初是由保罗·巴利编写的,现在大多数是由维姆潘科在做。它能做的不仅仅是动态DNS,也可以通过几种不同的方式获取你的WAN口IP地址。
+
+CloudFlare 的一个功能是它允许你通过API或叫做ddclient的命令行脚本更新你的DNS记录。不管哪一个,结果都一样,而且它是个免费软件。
+
+不幸的是,ddclient并不能在CloudFlare中即开即用。它需要打补丁,这里就是要介绍怎样在Debian或Ubuntu上破解它,它也能在带有Raspberry Pi的Raspbian上工作。
+
### 在Ubuntu上安装ddclient ###
打开终端,并运行以下命令
@@ -50,15 +51,11 @@ CloudFlare有一点已知的功能,它允许你通过API或叫做ddclient的
#daemon=300
-来自CloudFlare帐号页面的api密钥
+你的 api-key 可以从 CloudFlare帐号页面找到,ssl=yes 可能已经设置,use=web, web=dyndns 表示使用 dyndns 来确定 IP(用于 NAT)。
-ssl=yes might already be in that file
+你已经搞定了。登录到 https://www.cloudflare.com 并检查列出的与你域名对应的IP地址是否与 http://checkip.dyndns.com 列出的相匹配。
-use=web, web=dyndns will use dyndns to check IP (useful for NAT)
-
-你已经搞定了。登录到https://www.cloudflare.com并检查列出的与你域名对应的IP地址是否匹配到了http://checkip.dyndns.com。
-
-使用以下命令来验证你的设置
+使用以下命令来验证你的设置:
sudo ddclient -daemon=0 -debug -verbose -noquiet
@@ -67,6 +64,6 @@ use=web, web=dyndns will use dyndns to check IP (useful for NAT)
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/how-to-use-cloudflare-as-a-ddclient-provider-under-ubuntu.html
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20140924 Unix----stat -- more than ls.md b/published/201410/20140924 Unix----stat -- more than ls.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140924 Unix----stat -- more than ls.md
rename to published/201410/20140924 Unix----stat -- more than ls.md
diff --git a/published/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to catch and handle a signal in Perl.md b/published/201410/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to catch and handle a signal in Perl.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to catch and handle a signal in Perl.md
rename to published/201410/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to catch and handle a signal in Perl.md
diff --git a/published/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change a network interface name on CentOS 7.md b/published/201410/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change a network interface name on CentOS 7.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change a network interface name on CentOS 7.md
rename to published/201410/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to change a network interface name on CentOS 7.md
diff --git a/published/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure a static IP address on CentOS 7.md b/published/201410/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure a static IP address on CentOS 7.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure a static IP address on CentOS 7.md
rename to published/201410/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to configure a static IP address on CentOS 7.md
diff --git a/published/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect a Linux distribution in Perl.md b/published/201410/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect a Linux distribution in Perl.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect a Linux distribution in Perl.md
rename to published/201410/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect a Linux distribution in Perl.md
diff --git a/published/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to embed all fonts in a PDF document generated with LaTex.md b/published/201410/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to embed all fonts in a PDF document generated with LaTex.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to embed all fonts in a PDF document generated with LaTex.md
rename to published/201410/20140925 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to embed all fonts in a PDF document generated with LaTex.md
diff --git a/published/20140926 How To Reset Root Password On CentOS 7.md b/published/201410/20140926 How To Reset Root Password On CentOS 7.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140926 How To Reset Root Password On CentOS 7.md
rename to published/201410/20140926 How To Reset Root Password On CentOS 7.md
diff --git a/published/20140928 How to Use Systemd Timers.md b/published/201410/20140928 How to Use Systemd Timers.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140928 How to Use Systemd Timers.md
rename to published/201410/20140928 How to Use Systemd Timers.md
diff --git a/published/20140928 Oracle Linux 5.11 Features Updated Unbreakable Linux Kernel.md b/published/201410/20140928 Oracle Linux 5.11 Features Updated Unbreakable Linux Kernel.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140928 Oracle Linux 5.11 Features Updated Unbreakable Linux Kernel.md
rename to published/201410/20140928 Oracle Linux 5.11 Features Updated Unbreakable Linux Kernel.md
diff --git a/published/20140929 Git Rebase Tutorial--Going Back in Time with Git Rebase.md b/published/201410/20140929 Git Rebase Tutorial--Going Back in Time with Git Rebase.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140929 Git Rebase Tutorial--Going Back in Time with Git Rebase.md
rename to published/201410/20140929 Git Rebase Tutorial--Going Back in Time with Git Rebase.md
diff --git a/published/20140929 Learning Vim in 2014--Working with Files.md b/published/201410/20140929 Learning Vim in 2014--Working with Files.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140929 Learning Vim in 2014--Working with Files.md
rename to published/201410/20140929 Learning Vim in 2014--Working with Files.md
diff --git a/published/20140929 Using GIT to backup your website files on linux.md b/published/201410/20140929 Using GIT to backup your website files on linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140929 Using GIT to backup your website files on linux.md
rename to published/201410/20140929 Using GIT to backup your website files on linux.md
diff --git a/published/20140930 Check If Your Linux System Is Vulnerable To Shellshock And Fix It.md b/published/201410/20140930 Check If Your Linux System Is Vulnerable To Shellshock And Fix It.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140930 Check If Your Linux System Is Vulnerable To Shellshock And Fix It.md
rename to published/201410/20140930 Check If Your Linux System Is Vulnerable To Shellshock And Fix It.md
diff --git a/published/20140930 How to Boot Linux ISO Images Directly From Your Hard Drive.md b/published/201410/20140930 How to Boot Linux ISO Images Directly From Your Hard Drive.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20140930 How to Boot Linux ISO Images Directly From Your Hard Drive.md
rename to published/201410/20140930 How to Boot Linux ISO Images Directly From Your Hard Drive.md
diff --git a/published/20141008 Adobe Pulls Linux PDF Reader Downloads From Website.md b/published/201410/20141008 Adobe Pulls Linux PDF Reader Downloads From Website.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141008 Adobe Pulls Linux PDF Reader Downloads From Website.md
rename to published/201410/20141008 Adobe Pulls Linux PDF Reader Downloads From Website.md
diff --git a/published/20141008 Linux Calendar App California 0.2 Released.md b/published/201410/20141008 Linux Calendar App California 0.2 Released.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141008 Linux Calendar App California 0.2 Released.md
rename to published/201410/20141008 Linux Calendar App California 0.2 Released.md
diff --git a/published/20141008 Linux Kernel 3.17 Is Out With Plenty of New Features.md b/published/201410/20141008 Linux Kernel 3.17 Is Out With Plenty of New Features.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141008 Linux Kernel 3.17 Is Out With Plenty of New Features.md
rename to published/201410/20141008 Linux Kernel 3.17 Is Out With Plenty of New Features.md
diff --git a/published/20141009 Linux Terminal--An lsof Primer.md b/published/201410/20141009 Linux Terminal--An lsof Primer.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141009 Linux Terminal--An lsof Primer.md
rename to published/201410/20141009 Linux Terminal--An lsof Primer.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/20141009 Linux or UNIX wget command with practical examples.md b/published/201410/20141009 Linux or UNIX wget command with practical examples.md
similarity index 85%
rename from translated/tech/20141009 Linux or UNIX wget command with practical examples.md
rename to published/201410/20141009 Linux or UNIX wget command with practical examples.md
index 7a720c725b..429e997c1d 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20141009 Linux or UNIX wget command with practical examples.md
+++ b/published/201410/20141009 Linux or UNIX wget command with practical examples.md
@@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
-Linux/Unix wget命令实例
+wget 命令实例
================================================================================
wget是Linux/Unix命令行**文件下载器**,它是下载网站上文件的免费的非交互下载工具,它支持**HTTP**、**HTTPS**和**FTP**协议,也支持通过HTTP代理检索。Wget是非交互的,这就是说它可以在用户没有登录到系统时在后台工作。
在本帖中,我们将讨论wget命令的一些不同使用实例。
-### 实例:1 下载单个文件 ###
+### 实例1 :下载单个文件 ###
# wget http://mirror.nbrc.ac.in/centos/7.0.1406/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7.0-1406-x86_64-DVD.iso
该命令会下载CentOS 7 ISO文件到用户当前工作目录中。
-### 实例:2 续传分段下载文件 ###
+### 实例2:续传分段下载文件 ###
总有那么一些场景,当我们开始下载一个大文件时,中途互联网却断开了。那样的话,我们可以使用wget命令的‘**-c**’选项,让下载从断点续传。
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ wget是Linux/Unix命令行**文件下载器**,它是下载网站上文件的
-### 实例:3 后台下载文件 ###
+### 实例3:后台下载文件 ###
我们可以通过在wget命令中使用‘-b’选项来让它在后台下载文件。
@@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ wget是Linux/Unix命令行**文件下载器**,它是下载网站上文件的
2800K ………. ………. ………. ………. ………. 0% 58.2K 18h16m
2850K ………. ………. ………. ………. ………. 0% 52.2K 18h20m
-### 实例:4 限制下载速率 ###
+### 实例4:限制下载速率 ###
默认情况下,wget命令尝试以全速下载,但是有时候你可能使用的是共享互联网,那么如果你尝试使用wget来下载庞大的文件时,就会把其它用户的网络拖慢。这时,你如果使用‘-limit-rate’选项来限制下载速率,就可以避免这种情况的发生。
@@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ wget是Linux/Unix命令行**文件下载器**,它是下载网站上文件的
在上例中,下载速率被限制到了100k。
-### 实例:5 使用‘-i’选项来下载多个文件 ###
+### 实例5:使用‘-i’选项来下载多个文件 ###
如果你想要使用wget命令来下载多个文件,那么首先要创建一个文本文件,并将所有的URL添加到该文件中。
@@ -65,15 +65,15 @@ wget是Linux/Unix命令行**文件下载器**,它是下载网站上文件的
# wget -i download-list.txt
-### 实例:6 增加重试次数 ###
+### 实例6:增加重试次数 ###
-我们可以使用‘-tries’选项来增加重试次数。默认情况下,wget命令会重试20次以使下载成功。
+我们可以使用‘-tries’选项来增加重试次数。默认情况下,wget命令会重试20次,直到下载成功。
该选项在你下载一个大文件的过程中互联网连接发生问题时十分有用,因为在那种情况下,会增加下载失败的几率。
# wget --tries=75 http://mirror.nbrc.ac.in/centos/7.0.1406/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7.0-1406-x86_64-DVD.iso
-### 实例:7 使用-o选项来重定向wget日志到文件 ###
+### 实例7:使用-o选项来重定向wget日志到文件 ###
我们可以使用‘-o’选项来重定向wget命令的日志到一个日志文件。
@@ -81,7 +81,7 @@ wget是Linux/Unix命令行**文件下载器**,它是下载网站上文件的
上面的命令会在用户当前目录下创建download.log文件。
-### 实例:8 下载整个网站用于本地查看 ###
+### 实例8:下载整个网站用于本地查看 ###
# wget --mirror -p --convert-links -P ./ website-url
@@ -92,21 +92,21 @@ wget是Linux/Unix命令行**文件下载器**,它是下载网站上文件的
- **–convert-links** : 下载完成后,转换文档中的链接以用于本地查看。
- -**P ./Local-Folder** : 保存所有文件和目录到指定的目录。
-### 实例:9 下载过程中拒绝文件类型 ###
+### 实例9:下载过程中拒绝文件类型 ###
当你正打算下载整个网站时,我们可以使用‘-reject’选项来强制wget不下载图片。
# wget --reject=png Website-To-Be-Downloaded
-### 实例:10 使用wget -Q设置下载配额 ###
+### 实例10:使用wget -Q设置下载配额 ###
我们可以使用‘-Q’选项强制wget命令在下载大小超过特定大小时退出下载。
# wget -Q10m -i download-list.txt
-注意,配额不会对单个文件的下载产生影响。所以,如果你指定wget -Q10m ftp://wuarchive.wustl.edu/ls-lR.gz,ls-lR的全部内容都会被下载。这在下载命令行指定的多个URL时也一样。然而,在递归或从一个输入文件检索时,还是值得一用。因此,你可以安全地输入‘wget -Q10m -i download-list.txt’,在超过配额时,下载会退出。
+注意,配额不会对单个文件的下载产生影响。所以,如果你指定wget -Q10m ftp://wuarchive.wustl.edu/ls-lR.gz,ls-lR.gz的全部内容都会被下载。这在下载命令行指定的多个URL时也一样。然而,在递归或从一个输入文件检索时,还是值得一用。因此,你可以安全地输入‘wget -Q10m -i download-list.txt’,在超过配额时,下载会退出。
-### 实例:11 从密码保护的网站下载文件 ###
+### 实例11:从密码保护的网站下载文件 ###
# wget --ftp-user= --ftp-password= Download-URL
@@ -120,7 +120,7 @@ via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/wget-command-practical-examples/
作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20141013 UbuTricks 14.10.08.md b/published/201410/20141013 UbuTricks 14.10.08.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141013 UbuTricks 14.10.08.md
rename to published/201410/20141013 UbuTricks 14.10.08.md
diff --git a/published/20141013 Ubuntu's Unity Turns 4 Happy Birthday.md b/published/201410/20141013 Ubuntu's Unity Turns 4 Happy Birthday.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141013 Ubuntu's Unity Turns 4 Happy Birthday.md
rename to published/201410/20141013 Ubuntu's Unity Turns 4 Happy Birthday.md
diff --git a/published/20141013 What is good reference management software on Linux.md b/published/201410/20141013 What is good reference management software on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141013 What is good reference management software on Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20141013 What is good reference management software on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20141014 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to burn an ISO or NRG image to a DVD from the command line on Linux.md b/published/201410/20141014 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to burn an ISO or NRG image to a DVD from the command line on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141014 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to burn an ISO or NRG image to a DVD from the command line on Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20141014 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to burn an ISO or NRG image to a DVD from the command line on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20141014 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect DVD writer' s device name and its writing speed from the command line on Linux.md b/published/201410/20141014 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect DVD writer' s device name and its writing speed from the command line on Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141014 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect DVD writer' s device name and its writing speed from the command line on Linux.md
rename to published/201410/20141014 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect DVD writer' s device name and its writing speed from the command line on Linux.md
diff --git a/published/20141014 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect and patch Shellshock vulnerability in bash.md b/published/201410/20141014 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect and patch Shellshock vulnerability in bash.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141014 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect and patch Shellshock vulnerability in bash.md
rename to published/201410/20141014 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to detect and patch Shellshock vulnerability in bash.md
diff --git a/published/201410/20141017 Linus Torvalds Regrets Alienating Developers with Strong Language.md b/published/201410/20141017 Linus Torvalds Regrets Alienating Developers with Strong Language.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a99457b834
--- /dev/null
+++ b/published/201410/20141017 Linus Torvalds Regrets Alienating Developers with Strong Language.md
@@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
+Linus Torvalds 对于向那些开发者说粗话而感到遗憾
+================================================================================
+> 他没有提到任何人的名字,但是这像一次道歉
+
+**Linus Torvalds在前几天的欧洲LinuxCon和CloudOpen大会上做了讲话,这次大会由Linux基金会组织并且汇聚了开源世界的所有大佬。他回答了很多问题,也谈到了他在邮件发送清单里使用粗话的事情。**
+
+Linus Torvalds被认为是Linux内核的创造者和Linux最新的开发版本的维护者。他给我们几乎每个星期都带来一个新的内核RC 版本,并且会在邮件列表里面进行大量的讨论。在这些讨论中,他经常口不择言地用粗话大骂一些开发者们。
+
+最近又出现了一个这种事情,就像我们在新闻里报道过的一样,他在做了一些苛刻的评论之后,[决定砍掉一些他认定的开发者的代码][1]。大家都知道Linus很招人厌烦,尤其是当内核开发者为了修复内核中的一些问题而破坏了用户空间。这次又发生了同样的事情,他基本上已经把那个家伙给气疯了。
+
+### 这是他最接近道歉意味的一次谈话 ###
+
+以前Linus Torvalds从不真正去特地谈论这些事情,大家也习惯了。但是最近一个[systemd开发者谈到了在开源社区充斥着粗话,并且点名提到了Linus Torvalds][3]。他不太习惯于道歉,所以这次在LinuxCon大会上的这次“认错”是他跨出的一大步。
+
+主持人询问他在过去的23年里所做过的决定有什么最后悔的吗?
+
+"从技术角度来看,没有哪个决定重要到这个程度...有个问题是慢慢地疏远了用户和开发者,而我却恰恰很擅长这个。我说了粗话,但是这不是我想要改变的某一个决定,这些粗话应该有所限制。"
+
+"其中一个原因是我们有说粗话的传统,很多人觉得倒胃口,特别是当有强烈的意愿和推动力的技术人员要做一些技术上的进步时,你就需要用一些强烈的语言来表达你的意愿。" Linus Torvalds [如是说][2] 。
+
+他没提到任何人或者任何事件的名字,但很像是对于一位[名为Leonart Pottering的systemd开发者挑起事端][3]的回应,看上去就是针对这起事件。
+
+Linux内核3.18 RC1也在上周发布了,我们又有新东西玩了。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Linus-Torvalds-Regrets-Alienating-Developers-with-Strong-Language-462191.shtml
+
+作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
+译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
+[1]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Linus-Torvalds-Block-All-Code-from-Systemd-Developer-for-the-Linux-Kernel-435714.shtml
+[2]:http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/791788-linus-torvalds-best-quotes-from-linuxcon-europe-2014
+[3]:http://linux.cn/article-3978-1.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20141017 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a video DVD on Linux desktop.md b/published/201410/20141017 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a video DVD on Linux desktop.md
similarity index 98%
rename from translated/tech/20141017 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a video DVD on Linux desktop.md
rename to published/201410/20141017 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a video DVD on Linux desktop.md
index f95827799e..169c19171b 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20141017 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a video DVD on Linux desktop.md
+++ b/published/201410/20141017 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a video DVD on Linux desktop.md
@@ -67,7 +67,7 @@
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/create-video-dvd-linux-desktop.html
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/published/20141017 Munich sheds light on the cost of dropping Linux and returning to Windows.md b/published/201410/20141017 Munich sheds light on the cost of dropping Linux and returning to Windows.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141017 Munich sheds light on the cost of dropping Linux and returning to Windows.md
rename to published/201410/20141017 Munich sheds light on the cost of dropping Linux and returning to Windows.md
diff --git a/published/20141021 Debian 7.7 Is Out with Security Fixes.md b/published/201410/20141021 Debian 7.7 Is Out with Security Fixes.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141021 Debian 7.7 Is Out with Security Fixes.md
rename to published/201410/20141021 Debian 7.7 Is Out with Security Fixes.md
diff --git a/published/20141021 Nifty Free Image Viewers.md b/published/201410/20141021 Nifty Free Image Viewers.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141021 Nifty Free Image Viewers.md
rename to published/201410/20141021 Nifty Free Image Viewers.md
diff --git a/published/20141023 Claws Mail 3.11.0 Brings a Ton of Changes and Fixes for POODLE Exploit.md b/published/201410/20141023 Claws Mail 3.11.0 Brings a Ton of Changes and Fixes for POODLE Exploit.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/20141023 Claws Mail 3.11.0 Brings a Ton of Changes and Fixes for POODLE Exploit.md
rename to published/201410/20141023 Claws Mail 3.11.0 Brings a Ton of Changes and Fixes for POODLE Exploit.md
diff --git a/published/How to Achieve Better Security With Proper Management of Open Source.md b/published/201410/How to Achieve Better Security With Proper Management of Open Source.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/How to Achieve Better Security With Proper Management of Open Source.md
rename to published/201410/How to Achieve Better Security With Proper Management of Open Source.md
diff --git a/published/How to configure SNMPv3 on ubuntu 14.04 server.md b/published/201410/How to configure SNMPv3 on ubuntu 14.04 server.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/How to configure SNMPv3 on ubuntu 14.04 server.md
rename to published/201410/How to configure SNMPv3 on ubuntu 14.04 server.md
diff --git a/published/Linux FAQs with Answers--How to build a RPM or DEB package from the source with CheckInstall.md b/published/201410/Linux FAQs with Answers--How to build a RPM or DEB package from the source with CheckInstall.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/Linux FAQs with Answers--How to build a RPM or DEB package from the source with CheckInstall.md
rename to published/201410/Linux FAQs with Answers--How to build a RPM or DEB package from the source with CheckInstall.md
diff --git a/published/Linux Performance Monitoring with Vmstat and Iostat Commands.md b/published/201410/Linux Performance Monitoring with Vmstat and Iostat Commands.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/Linux Performance Monitoring with Vmstat and Iostat Commands.md
rename to published/201410/Linux Performance Monitoring with Vmstat and Iostat Commands.md
diff --git a/published/Sysstat – All-in-One System Performance and Usage Activity Monitoring Tool For Linux.md b/published/201410/Sysstat – All-in-One System Performance and Usage Activity Monitoring Tool For Linux.md
similarity index 100%
rename from published/Sysstat – All-in-One System Performance and Usage Activity Monitoring Tool For Linux.md
rename to published/201410/Sysstat – All-in-One System Performance and Usage Activity Monitoring Tool For Linux.md
diff --git a/translated/tech/Wine 1.7.29 (Development Version) Released – Install in RedHat and Debian Based Systems.md b/published/201410/Wine 1.7.29 (Development Version) Released – Install in RedHat and Debian Based Systems.md
similarity index 92%
rename from translated/tech/Wine 1.7.29 (Development Version) Released – Install in RedHat and Debian Based Systems.md
rename to published/201410/Wine 1.7.29 (Development Version) Released – Install in RedHat and Debian Based Systems.md
index 322ce30076..6c5720bd9b 100644
--- a/translated/tech/Wine 1.7.29 (Development Version) Released – Install in RedHat and Debian Based Systems.md
+++ b/published/201410/Wine 1.7.29 (Development Version) Released – Install in RedHat and Debian Based Systems.md
@@ -1,10 +1,11 @@
-Wine 1.7.29(开发版本)已发布-在基于RedHat与Debian的系统上安装
+在基于RedHat与Debian的系统上安装Wine 最新的开发版本
=========================
+
**Wine**,一个在Linux平台上非常受欢迎并且强大的开源应用,有了它,我们可以在Linux平台上完美运行Windows应用与游戏。

-在Linux上安装Wine(开发版本)
+*在Linux上安装Wine(开发版本)*
WineHQ团队,近期宣布了一个新的开发版本**Wine1.7.29**。这个版本带来了诸多重要的特性,并且修复了**44**个bug。
@@ -19,7 +20,7 @@ Wine团队几乎每周都会发布新的开发版本,并且加入许多新特
在官方的 [变更日志][1] 中可以找到关于这个版本更多更深入的细节。
-这篇文章指导你在基于**RedHat**与**Debian**的系统,如CentOS,Fedora,Ubuntu,Linux Mint以及其他的发型版中安装最新的开发版本**Wine 1.7.29**。
+这篇文章指导你在基于**RedHat**与**Debian**的系统,如CentOS,Fedora,Ubuntu,Linux Mint以及其他的发行版中安装最新的开发版本**Wine 1.7.29**。
##在Linux中安装 Wine 1.7.29 开发版本##
@@ -32,8 +33,8 @@ Wine团队几乎每周都会发布新的开发版本,并且加入许多新特
然后,使用如下命令下载Wine最新的开发版本(**1.7.29**)以及解压源码包。
- $cd /tmp
- $wget http://citylan.dl.sourceforge.net/project/wine/Source/wine-1.7.29.tar.bz2
+ $ cd /tmp
+ $ wget http://citylan.dl.sourceforge.net/project/wine/Source/wine-1.7.29.tar.bz2
$ tar -xvf wine-1.7.29.tar.bz2 -C /tmp/
接下来,使用下列命令编译及安装Wine。
@@ -85,7 +86,7 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-wine-in-linux/
作者:[Ravi Saive][a]
译者:[SPccman](https://github.com/SPccman)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/translated/tech/20141022 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix fatal error--openssl or aes.h--No such file or directory.md b/published/20141022 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix fatal error--openssl or aes.h--No such file or directory.md
similarity index 86%
rename from translated/tech/20141022 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix fatal error--openssl or aes.h--No such file or directory.md
rename to published/20141022 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix fatal error--openssl or aes.h--No such file or directory.md
index 99d2cc28c6..c91b027cb7 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20141022 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix fatal error--openssl or aes.h--No such file or directory.md
+++ b/published/20141022 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix fatal error--openssl or aes.h--No such file or directory.md
@@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
-Linux 有问必答 -- 如何修复“fatal error: openssl/aes.h: No such file or directory”
+Linux 有问必答:如何修复“fatal error: openssl/aes.h: No such file or directory”
================================================================================
> **Question**:我尝试在Linux编译一个程序,但是编译失败并报了一个错,“fatal error: openssl/aes.h: No such file or directory”。我该怎样安装要求的头文件并在我的Linux上解决这个问题?
fatal error: openssl/aes.h: No such file or directory
-如果你在编译时遇到这个错误,这可能是下面的原因:你尝试编译的程序使用OpenSSL,但是需要和OpenSSL链接的文件(库和头文件)在你Linux平台上缺少。
+如果你在编译时遇到这个错误,这可能是下面的原因:你尝试编译的程序使用OpenSSL,但是需要和OpenSSL链接的文件(库和头文件)在你Linux平台上缺少。(LCTT 译注:其它类似的错误也可以照此处理)
要解决这个问题,你需要安装**OpenSSL 开发包**,这在所有的现代Linux发行版的标准软件仓库中都有。
@@ -22,8 +22,7 @@ Linux 有问必答 -- 如何修复“fatal error: openssl/aes.h: No such file or
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/fix-fatal-error-openssl.html
-作者:[作者名][a]
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/How to sniff HTTP traffic from the command line on Linux.md b/published/How to sniff HTTP traffic from the command line on Linux.md
similarity index 73%
rename from translated/tech/How to sniff HTTP traffic from the command line on Linux.md
rename to published/How to sniff HTTP traffic from the command line on Linux.md
index 7b8ba77878..849ed9e86d 100644
--- a/translated/tech/How to sniff HTTP traffic from the command line on Linux.md
+++ b/published/How to sniff HTTP traffic from the command line on Linux.md
@@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
-使用Linux命令行嗅探HTTP流量
+Linux 命令行下嗅探 HTTP 流量的工具:httpry
================================================================================
假设由于某种原因,你需要嗅探HTTP站点的流量(如HTTP请求与响应)。举个例子,你可能在测试一个web服务器的实验性功能,或者你在为某个web应用或RESTful服务排错,又或者你正在为PAC(proxy auto config)排错或寻找某个站点下载的恶意软件。不论什么原因,在这些情况下,进行HTTP流量嗅探对于系统管理、开发者、甚至最终用户来说都是很有帮助的。
-数据包嗅工具tcpdump被广泛用于实时数据包的导出,但是你需要设置过滤规则来捕获HTTP流量,甚至它的原始输出通常不能方便的停在HTTP协议层。实时web服务器日志解析器如[ngxtop][3]提供可读的实时web流量跟踪痕迹,但这仅适用于可完全访问live web服务器日志的情况。
+数据包嗅工具tcpdump被广泛用于实时数据包的导出,但是你需要设置过滤规则来捕获HTTP流量,甚至它的原始输出通常不能方便的停在HTTP协议层。实时web服务器日志解析器如[ngxtop][3]可以提供可读的实时web流量跟踪痕迹,但这仅适用于可完全访问live web服务器日志的情况。
-要是有一个仅用于抓取HTTP流量的类tcpdump的数据包嗅探工具就非常好了。事实上,[httpry][4]就是:**HTTP包嗅探工具**。httpry捕获HTTP数据包,并且将HTTP协议层的数据内容以可读形式列举出来。通过这篇指文章,让我们了解如何使用httpry工具嗅探HTTP流量。
+要是有一个仅用于抓取HTTP流量的类似tcpdump的数据包嗅探工具就非常好了。事实上,[httpry][4]就是:**HTTP包嗅探工具**。httpry捕获HTTP数据包,并且将HTTP协议层的数据内容以可读形式列举出来。通过这篇指文章,让我们了解如何使用httpry工具嗅探HTTP流量。
###在Linux上安装httpry###
-基于Debian系统(Ubuntu 或 LinuxMint),基础仓库中没有httpry安装包(译者注:本人ubuntu14.04,仓库中已有包,可直接安装)。所以我们需要通过源码安装:
+基于Debian系统(Ubuntu 或 LinuxMint),基础仓库中没有httpry安装包(译者注:本人ubuntu14.04,仓库中已有包,可直接安装)。所以我们需要通过源码安装:
$ sudo apt-get install gcc make git libpcap0.8-dev
$ git clone https://github.com/jbittel/httpry.git
@@ -16,7 +16,7 @@
$ make
$ sudo make install
-在Fedora,CentOS 或 RHEL系统,可以使用如下yum命令安装httpry。在CentOS/RHEL系统上,运行yum之前使齐能够[EPEL repo][5]。
+在Fedora,CentOS 或 RHEL系统,可以使用如下yum命令安装httpry。在CentOS/RHEL系统上,运行yum之前使其能够访问[EPEL repo][5]。
$ sudo yum install httpry
@@ -62,11 +62,11 @@ httpry就会监听指定的网络接口,并且实时的显示捕获到的HTTP
-如果你下载了httpry的源码,你会发现源码下有一系Perl脚本,这些脚本用于分析httpry输出。脚本位于目录httpry/scripts/plugins。如果你想写一个定制的httpry输出分析器,则这些脚可以作为很好的例子。其中一些有如下的功能:
+如果你下载了httpry的源码,你会发现源码下有一些Perl脚本,这些脚本用于分析httpry输出。脚本位于目录httpry/scripts/plugins。如果你想写一个定制的httpry输出分析器,则这些脚可以作为很好的例子。其中一些有如下的功能:
-- **hostnames**: 显示唯一主机名列表.
-- **find_proxies**: 探测web代理.
-- **search_terms**: 查找及计算在搜索服务里面的搜索词。
+- **hostnames**: 显示唯一主机名列表。
+- **find_proxies**: 探测web代理。
+- **search_terms**: 查找及统计在搜索服务里面的搜索词。
- **content_analysis**: 查找含有指定关键的URL。
- **xml_output**: 将输出转换为XML形式。
- **log_summary**: 生成日志汇总。
@@ -77,9 +77,9 @@ httpry就会监听指定的网络接口,并且实时的显示捕获到的HTTP
$ cd httpry/scripts
$ perl parse_log.pl -d ./plugins
-你可能在使用插件的时候遇到警告。比如,如果你没有安装带有DBI接口的MySQL数据库那么使用db_dump插件时可能会失败。如果一个插件初始化失败的话,那么这个插件不能使用。所以你可以忽略那些警告。
+你可能在使用插件的时候遇到警告。比如,如果你没有安装带有DBI接口的MySQL数据库,那么使用db\_dump插件时可能会失败。如果一个插件初始化失败的话,那么只是这个插件不能使用,所以你可以忽略那些警告。
-当parse_log.pl完成后,你将在httpry/scripts 目录下看到数个分析结果。例如,log_summary.txt 与如下内容类似。
+当parse\_log.pl完成后,你将在httpry/scripts 目录下看到数个分析结果。例如,log\_summary.txt 与如下内容类似。

@@ -91,7 +91,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/sniff-http-traffic-command-line-linux.html
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
译者:[DoubleC](https://github.com/DoubleC)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
diff --git a/sources/news/20141017 Linus Torvalds' Best Quotes from LinuxCon Europe 2014.md b/sources/news/20141017 Linus Torvalds' Best Quotes from LinuxCon Europe 2014.md
deleted file mode 100644
index a2434e23bb..0000000000
--- a/sources/news/20141017 Linus Torvalds' Best Quotes from LinuxCon Europe 2014.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,60 +0,0 @@
-Linus Torvalds' Best Quotes from LinuxCon Europe 2014
-================================================================================
-
-
-Linux creator Linus Torvalds answered questions from Dirk Hohndel, Intel's chief Linux and open source technologist, on Wednesday, Oct. 15, 2014 at LinuxCon and CloudOpen Europe.
-
-Linus Torvalds doesn't regret any of the technical decisions he's made over the past 23 years since he first created Linux, he said Wednesday at [LinuxCon and CloudOpen Europe][1].
-
-“Technical issues, even when they're completely wrong, and they have been, you can fix them later,” said Torvalds, a Linux Foundation fellow.
-
-
-
-Despite these personal issues and disagreements the community has thrived, and created the best technology they possibly can, said Linus Torvalds at LinuxCon Europe 2014.
-
-He does, however, regret the times he has alienated developers and users with his use of strong language on the kernel mailing list, he said. Relationships can't be so easily fixed.
-
-Despite these personal issues and disagreements the community has thrived, and created the best technology they possibly can. This is, Torvalds said, the ultimate goal.
-
-In a Q&A on stage with Dirk Hohndel, Intel's chief Linux and open source technologist, Torvalds spoke about the state of the community, the kernel development process, what it takes to be a kernel developer, and the future of Linux. Here are some highlights of the discussion.
-
-**1.** “The speed of development has not really slowed down the last few years. We have had around 10,000 patches every release from more than 1,000 people and the end result has been very good.”
-
-**2.** Dirk Hohndel: “You said you wanted subsystem maintainers to consider following the x86 model and have more than one maintainer share the role. How about applying your own advice at the top?
-
-Torvalds: “I'll probably have to do that someday. Right now I'm not getting a lot of complaints for not being responsive. Being responsive is one of the most important things a kernel developer at any level can be... So far, partly thanks to Git, I've been able to keep up.”
-
-**3.** “A lot of people want to have market share numbers, lots of users, because that's how they view their self worth. For me, one of the most important things for Linux is having a big community that is actively testing new kernels; it's the only way to support the absolute insane amount of different hardware we deal with.”
-
-**4.** Hohndel: “If you could change a single decision you've made in the last 23 years, what would you do differently?”
-
-Torvalds: “From a technical standpoint, no single decision has ever been that important... The problems tend to be around alienating users or developers and I'm pretty good at that. I use strong language. But again there's not a single instance I'd like to fix. There's a metric shitload of those.”
-
-**5.** “Most people even if though they don't always necessarily like each other, do tend to respect the code they generate. For Linux that's the important part. What really matters is people are very involved in generating the best technology we can.”
-
-**6.** “On the internet nobody can hear you being subtle.”
-
-**7.** “One of the reasons we have this culture of strong language, that admittedly many people find off-putting, is that when it comes to technical people with strong opinions and with a strong drive to do something technically superior, you end up having these opinions show up as sometimes pretty strong language.”
-
-**8.** Hohndel: What will you tell a student who wants to become the next Linus?
-
-Torvalds: “Find something that you're passionate about and just do it.”
-
-**9.** “Becoming a maintainer is easy; you just need an infinite amount of time and respond to email from random people.”
-
-**10.** Hohndel: “Make a bold prediction about the future of Linux.”
-
-Torvalds: “The boldest prediction I can say is, I will probably release rc1 in about a week.”
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/791788-linus-torvalds-best-quotes-from-linuxcon-europe-2014
-
-作者:[Libby Clark][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/41373/catid/200-libby-clark
-[1]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/events/linuxcon-europe
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/news/20141030 Suse enterprise Linux can take your system back in time.md b/sources/news/20141030 Suse enterprise Linux can take your system back in time.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5615c8a7d0
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/news/20141030 Suse enterprise Linux can take your system back in time.md
@@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
+Suse enterprise Linux can take your system back in time
+================================================================================
+> Suse Linux Enterprise Server 12 features a new system snapshot and rollback capability
+
+The newest enterprise edition of the Suse Linux distribution allows administrators to go back in time, for instance, to immediately before they made that fatal system-crippling mistake.
+
+Suse Linux Enterprise Server 12 (SLES 12) features a system snapshot and rollback capability that allows the user to boot the system to an earlier configuration, should the latest one unexpectedly fail.
+
+Such a capability can be handy for undoing a system configuration change that did not turn out as expected. For instance, an administrator might have the SLES computer in a perfectly fine running state, but then install a botched software update, or make a change that destroys the kernel. Typically, Unix systems have been unforgiving about such mistakes, forcing the administrator to reinstall the system software from scratch, should they not know how to undo the unfortunate change.
+
+"This stuff happens, for whatever reason," said Matthias Eckermann, Suse senior product manager. "So the admin has an emergency exit, so to speak."
+
+Users of Microsoft Windows and Apple Macintosh systems have long enjoyed rollback functionality within their respective OSes, but this capability had been missing in Unix-based systems such as Linux, at least as a native function of the OS.
+
+For this functionality, the Suse team used the [Btrfs][1] file system (B-tree file system, often pronounced as "Butter FS"), an open-source file system developed by Oracle engineer Chris Mason ([now at Facebook][2]). Mason created Btrfs to address emerging enterprise requirements such as the ability to make snapshots and to scale across multiple storage nodes.
+
+Although Btrfs is supported in the mainline Linux kernel, SLES is the first major Linux distribution to use Btrfs as the default file system. "Over the last five years, we specifically focused on making Btrfs enterprise-ready," Eckermann said.
+
+The rollback capability also relies on the open-source tool [Snapper][3], first developed by Suse, to manage the snapshots.
+
+The Suse team integrated Snapper with SLES so that users now have the ability, when the OS is first being loaded, to boot into an earlier snapshot of the system. "Whoever installs SLES 12 gets this capability by default," Eckermann said.
+
+SLES also integrated Btrfs with the [Samba Windows file server][4], which makes Linux files accessible to Windows machines. For Windows users, SLES can now make multiple snapshots of a file appear as different versions of a file, which are all accessible.
+
+Initially, Enterprise Suse supports rollbacks for only system changes, though users can also deploy it to handle changes in a user's home directory, in which data is typically kept. "We already have it running, but it is not supported," Eckermann said. Users can continue to use ext3, ext4 or some other traditional Linux file system as their default.
+
+SLES 12, released Monday, comes with a number of other features as well. Like other distributions, SLES has [caught the fever for Docker containers][5] and now comes with a built-in framework to run this virtualization technology. For the first time, the package also provides geo-clustering, which allows the user to build replicate clusters across different geographic regions.
+
+An organization could use geo-clustering, for instance, to set up multiple copies of a single cluster in data centers around the world, so if one or more regions go offline, the others can continue operations unabated, Eckermann said.
+
+Suse [is among the world's most widely used distributions][6] of Linux, along with Ubuntu/Debian, and Red Hat Enterprise Linux. A free version is available under OpenSuse and Suse Linux offers a commercial edition packaged for enterprise usage.
+
+Suse Linux's parent company, Attachmate, is in the process of merging with Micro Focus. Eckermann expects no major changes in the operations of Suse Linux resulting from the new ownership.
+
+SLES 12 is [offered at an annual subscription][7] of US$349 per server. A free 60-day trial is also available.
+
+
+
+Through the combined powers of the Btrfs file system and the Snapper utility, SUSE Enterprise Linux can now take snapshots of the system, and roll back to an earlier configuration if necessary.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.computerworld.com/article/2838950/suse-enterprise-linux-can-take-your-system-back-in-time.html
+
+作者:[Joab Jackson][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.computerworld.com/author/Joab-Jackson/
+[1]:https://btrfs.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/Main_Page
+[2]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTUzNTE
+[3]:http://snapper.io/
+[4]:http://www.samba.org/
+[5]:http://www.pcworld.com/article/2838452/canonical-celebrates-cloud-freedoms-with-new-ubuntu.html
+[6]:http://distrowatch.com/table.php?distribution=suse
+[7]:https://www.suse.com/products/server/how-to-buy/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/news/20141030 Ubuntu Could Give a Fatal Blow to Windows in China.md b/sources/news/20141030 Ubuntu Could Give a Fatal Blow to Windows in China.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4e3c4ceb21
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/news/20141030 Ubuntu Could Give a Fatal Blow to Windows in China.md
@@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
+Ubuntu Could Give a Fatal Blow to Windows in China
+================================================================================
+> Ubuntu Kylin might be able to replace Windows in China
+
+**The Windows operating systems is going out the front door in China and its place will be taken by a Linux distribution that will be used by the authorities and the governing body. The problem is that there is no real alternative, although at least one OS might be ready for the task, and that is Ubuntu Kylin.**
+
+The Chinese government and Microsoft now have a rocky relationship, to say the least. [As detailed in today's news][1], a plan to replace Windows gradually throughout the country with a Linux counterpart is in the works. It's unclear what system will be used to take over, especially since this a very complex situation and a very big country.
+
+Usually, there is no size-fits-all solution to this kind of problem and the Chinese approach does seem to be a little too blunt. In any case, this opens up a great window of opportunity for Ubuntu Kylin, a distribution based on Ubuntu and developed by Chinese devs and Canonical. It's been stable for quite some time and they already had a few consecutive launches.
+
+### Ubuntu Kylin is knocking on Windows' door ###
+
+It's interesting to see that in the same day that this piece of news about the Chinese intentions surfaces, an interview with Dr. Jonas Zhang, vice professor of the National University of Defense Technology (NUDT), about the [recent launch of the 14.10 branch][2] has been published.
+
+"In our 14.10 release, there are some sweet new features. For example, beginners can find a replacement of Windows software via Ubuntu Kylin Software Center easily; users can login to Ubuntu Kylin applications and community via the SSO of Ubuntu Kylin (Single Sign-On System of Ubuntu Kylin, we call it UKID); Sogou IM (one of the most famous Chinese input method in the world, which has been launched on Apple’s App Store since last month) reduces 40% of the CPU and memory usage."
+
+"More than 50 project managers, engineers and community managers from CSIP (one service agency of China government), Canonical and NUDT (National University of Defense Technology) are working on Ubuntu Kylin. Most of the full-time engineers are from NUDT. Many developers from Ubuntu, Debian and other communities also take part in the development of Ubuntu Kylin," [said][2] Dr. Jonas Zhang.
+
+The Chinese government might be looking to build yet another Linux distro by itself (not their first attempt), but it looks like they could already have a very good candidate to take over Windows. This would also be very good business for Canonical, at least in terms of recognition.
+
+If Ubuntu, through its Kylin connection, manages to replace Windows in a country as big as China, it would be a huge boost for the company. It remains to be seen if the developers' efforts to make Ubuntu Kylin a competitive OS were not in vain.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Ubuntu-Could-Give-a-Fatal-Blow-to-Windows-in-China-463500.shtml
+
+作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
+[1]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/China-Starts-Windows-Eradication-15-of-Govt-PCs-to-Switch-to-Linux-Every-Year-463393.shtml
+[2]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Ubuntu-Kylin-14-10-Utopic-Unicorn-Consolidates-Its-Position-in-China-463068.shtml
+[3]:https://insights.ubuntu.com/2014/10/29/interview-nudt-talks-ubuntu-kylin-and-its-14-10-release/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/share/20141027 Handy Disk Image Tools.md b/sources/share/20141027 Handy Disk Image Tools.md
deleted file mode 100644
index b69a0962b0..0000000000
--- a/sources/share/20141027 Handy Disk Image Tools.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,170 +0,0 @@
-Handy Disk Image Tools
-================================================================================
-Disk images are computer files of a disk volume or an entire data storage device, such as a hard drive, optical disk (e.g. DVD, CD, Blu-ray), tape drive, USB flash drive, or floppy disk. A disk image represents the content exactly as it is on the original storage device, including both data and structure information.
-
-Disk image file formats can be open standards, such as the ISO image format for optical disk images, or proprietary to particular software applications. The name "ISO" is taken from the ISO 9660 file system used with CD-ROM media. Converting from a proprietary image format to an open format often crops up as an issue when users migrate to Linux.
-
-Disk images have many different uses such as burning optical media, system backup, data recovery, disk cloning, computer forensics, and operating systems (as Live CD/DVDs).
-
-There are a number of different ways of mounting an ISO image under Linux. The venerable mount command offers an easy solution. But if you need tools that offer more functionality for working with disk images, try some of the following excellent open source tools.
-
-Most of the tools have not seen a recent release, so if you are looking to get involved with a good open source tool, you could pitch in.
-
-----------
-
-
-
-
-
-Furius ISO Mount is a simple open source application for mounting .iso, .img, .bin, .mdf and .nrg image files without burning them to disk.
-
-Features include:
-
-- Automatically mounts ISO, IMG, BIN, MDF and NRG image files
-- Supports mounting UDF images through loop
-- Automatically creates a mount point in your home directory
-- Automatically unmounts the Image files
-- Automatically removes the mount directory to return your home directory to its previous state
-- Automatically saves the history of the last 10 images mounted
-- Mounts multiple images
-- Burn ISO and IMG Files to optical disk
-- Generate MD5 and SHA1 checksums
-- Automatically retrieves any previously unmounted images
-- Automatically generates a log file of all commands needed to mount and unmount images manually
-- Language support (currently Bulgarian, Chinese (Simplified), Czech, Dutch, French, German, Hungarian, Italian, Greek, Italian, Japanese, Polish, Portuguese, Russian, Slovenian, Spanish, Swedish and Turkish)
-
-- Website: [launchpad.net/furiusisomount/][1]
-- Developer: Dean Harris (Marcus Furius)
-- License: GNU GPL v3
-- Version Number: 0.11.3.1
-
-
-----------
-
-
-
-
-
-fuseiso is an open source FUSE module to mount ISO filesystem images.
-
-With FUSE it is possible to implement a fully functional filesystem in a userspace program.
-
-Features include:
-
-- Read ISO, BIN and NRG images containing ISO9660 filesystems
-- Supports plain ISO9660 Level 1 and 2
-- Supports some common extensions, like Joliet, RockRidge and zisofs
-- Supports non-standard images, like CloneCD's IMGs and Alcohol 120%'s MDFs, as their format looks exactly like BIN images
-
-- Website: [sourceforge.net/projects/fuseiso][2]
-- Developer: Dmitry Morozhnikov
-- License: GNU GPL v2
-- Version Number: 20070708
-
-----------
-
-
-
-
-
-iat (Iso9660 Analyzer Tool) is a versatile, open source tool for detecting the structure of many types of image file formats, such as BIN, MDF, PDI, CDI, NRG, and B5I, and converting them into ISO-9660.
-
-Features include:
-
-- Supports reading (input) NRG, MDF, PDI, CDI, BIN, CUE and B5I images
-- Burn disc images directly using cdrecord
-- Outputs information including a progress-bar, Block size, ECC sector (size), header sector (size), image offset start and more
-
-- Website: [sourceforge.net/projects/iat.berlios][3]
-- Developer: Salvatore Santagati
-- License: GNU GPL v2
-- Version Number: 0.1.3
-
-----------
-
-
-
-
-
-AcetoneISO is a feature-rich open source graphical application to mount and manage CD/DVD images.
-
-The utility opens a graphical file manager to mount image formats, including proprietary image formats, including ISO, BIN, NRG, MDF, IMG etc, and lets you perform a number of actions.
-
-AcetoneISO is written with Qt 4, which means that it integrates well in Qt-based desktop environments like KDE, LXQt or Razor-qt.
-
-This software is meant for all those people looking for a "Daemon Tools for Linux".
-
-Features include:
-
-- Mount most common Windows images in a clean and easy GUI
-- Convert all known images to ISO or extract the contents to a folder
-- Encrypt, compress, split any type of image
-- Convert DVD video to xvid avi and any generic video to xvid avi
-- Extract audio from a video
-- Extract images content to a folder: bin mdf nrg img daa dmg cdi b5i bwi pdi
-- Play a DVD Movie Image with Kaffeine / VLC / SMplayer with auto-cover download from Amazon
-- Generate an ISO from a Folder or CD/DVD
-- Check MD5 file of an image and/or generate it to a text file
-- Calculate ShaSums of images in 128, 256, and 384 bit
-- Encrypt / Decrypt an image
-- Split / Merge image in X megabyte
-- Compress with high ratio an image in 7z format
-- Rip a PSX CD to *.bin to make it work with ePSXe/pSX emulators
-- Restore a lost CUE file of *.bin *.img
-- Convert Mac OS *.dmg to a mountable image
-- Mount an image in a specified folder from the user
-- Create a database of images to manage big collections
-- Extract the Boot Image file of a CD/DVD or ISO
-- Backup a CD-Audio to a *.bin image
-- Quick and simple utility to rip a DVD to Xvid AVI
-- Quick and simple utility to convert a generic video (avi, mpeg, mov, wmv, asf) to Xvid AVI
-- Quick and simple utility to convert a FLV video to AVI
-- Utility to download videos from YouTube and Metacafe
-- Extract audio from a video file
-- Extract a *.rar archive that has a password
-- Utility to convert any video for Sony PSP PlayStation Portable
-- Internationalization support English, Italian, Polish, Spanish, Romanian, Hungarian, German, Czech, and Russian
-
-- Website: [sourceforge.net/projects/acetoneiso][4]
-- Developer: Marco Di Antonio
-- License: GNU GPL v3
-- Version Number: 2.3
-
-----------
-
-
-
-
-
-ISO Master is an open-source, easy to use, graphical CD image editor for Linux and BSD. This tool extracts files from an ISO, add files to an ISO, and create bootable ISOs - all in a graphical user interface. It can open ISO, NRG, and some MDF files but can only save as ISO.
-
-ISO Master is based on bkisofs, a simple and stable library for reading, modifying and writing ISO images which supports the Joliet, RockRidge, and EL Torito extensions.
-
-Features include:
-
-- Reads .ISO files (ISO9660, Joliet, RockRidge, and El Torito), most .NRG files, and some single-track .MDF files; it can save only as .ISO
-- Create or customise CD/DVD images
-- Add or remove files and directories to/from a CD image
-- Make bootable CDs/DVDs
-- Internationalization support
-
-- Website: [www.littlesvr.ca/isomaster/][5]
-- Developer: Andrew Smith
-- License: GNU GPL v2
-- Version Number: 1.3.11
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20141025082352476/DiskImageTools.html
-
-作者:Frazer Kline
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[1]:https://launchpad.net/furiusisomount/
-[2]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/fuseiso/
-[3]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/iat.berlios/
-[4]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/acetoneiso/
-[5]:http://www.littlesvr.ca/isomaster/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/talk/20141030 Debian's Civil War--Has It Really Come to This.md b/sources/talk/20141030 Debian's Civil War--Has It Really Come to This.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..090ffb1f03
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/talk/20141030 Debian's Civil War--Has It Really Come to This.md
@@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
+Debian's Civil War: Has It Really Come to This?
+================================================================================
+
+
+**"The 'new' Debian would be rather weak," said blogger Robert Pogson. "Would it have the hundreds of mirrors that make Debian wonderful? I doubt that. Debian is a great distro. Disemboweling it out of spite is just wrong. Why can't we come to some amicable agreement? Why do we have to race at full speed to the edge of a cliff when we don't know if we can stop?"**
+
+Well it seems no matter how loudly we here in the Linux blogosphere try to hum a happy tune or discuss [cheerful FOSS matters][1], we just can't seem to drown out the shouts and screams coming from those standing too close to the Systemd Inferno.
+
+Stand back, people! It's dangerous!
+
+The embers, of course, [had been hot][2] for some time already before the blaze [flared sky-high][3] a few months ago. Now, the conflagration appears to be completely out of control.
+
+Need proof? Two words: [Debian fork][4].
+
+That's right: Debian, the granddaddy of Linux distributions and embodiment of everything so many FOSS fans hold dear, may be forked, and it's apparently all because of Systemd.
+
+A more upsetting development would be hard to conceive.
+
+### 'Roll Up Your Sleeves' ###
+
+
+
+"Debian today is haunted by the tendency to betray its own mandate, a base principle of the Free Software movement: put the user's rights first," explained the anonymous developers behind the Debian Fork site. "What is happening now instead is that through a so-called 'do-ocracy,' developers and package maintainers are imposing their choices on users."
+
+Their conclusion: "Roll up your sleeves, we may need to fork Debian."
+
+Quick as a flash, [word traveled][5] to [Slashdot][6], [LXer][7] and beyond.
+
+Down at the Linux blogosphere's Punchy Penguin Saloon, a profound hush fell as soon as the news arrived. Fortunately, it lasted only a fraction of a second.
+
+### 'I Say Go for It' ###
+
+"Freedom of choice implies the freedom to be a complete idiot, and clearly Free Software has its share," Google+ blogger Kevin O'Brien said.
+
+"I have been skeptical about Systemd, but I have trouble believing there are enough people this crazy to actually pull off a fork of Debian," O'Brien added. "I predict a year from now we won't remember what this was all about."
+
+On the other hand: "I say go for it if you're that passionate about it," offered [Linux Rants][8] blogger Mike Stone. "This is Linux we're talking about, after all, and Linux is open source. Anybody should always feel free to do what they want with Linux, as long as they're willing to share.
+
+"The fact that SysVinit will still be available on standard Debian kind of makes forking it over Systemd seem a little silly, but I'm not going to stand in the way of anybody that wants to fork any FOSS for their own use," Stone added.
+
+Indeed, "Linux's strength is also its Achilles' Heel," Google+ blogger Rodolfo Saenz opined. 'In the Linux world, forking is inevitable. It is part of Linux's evolution."
+
+### 'A Lot of Misinformation' ###
+
+At the same time, "I think if they were likely to actually fork Debian, they would have just gone and done it rather than throw a massive public temper tantrum," consultant and Slashdot blogger Gerhard Mack suggested.
+
+"Secondly, I think there is a lot of misinformation out there about what Systemd does and how it works," Mack added. 'At the beginning of all of this I was very worried about the stability and security of the systems I maintain after reading the nerd rage on Slashdot, The Register, and sites like [Boycott Systemd][9], so I looked into Systemd for myself.
+
+"What I have discovered is that they seem to be confusing Systemd with things that are bundled with Systemd but run separately using a 'least privilege needed for the task' type design," he explained. "There are things I don't like, such as the binary logs, but then I can just configure it to run through syslogd as usual and ignore the binary logs."
+
+Particularly "hilarious," Mack added, is that people "suggest that only desktops need to boot quickly," he said. "I have seen some automated systems that load VMs on demand, and they would be much more effective if they booted faster."
+
+### 'I'm Really Confused' ###
+
+It will be "a sad day if Debian forks over this Systemd thing," longtime Debian user [Robert Pogson][10] told Linux Girl.
+
+"I am one of the haters, I guess," Pogson said. "I see adopting Systemd as something that kept Jessie's bug count high for months. I just don't see the need for it. I've read that some desktop users complain that Systemd is all for server users and I've read that some server users complain that Systemd is all for desktop users. I'm both and I'm really confused."
+
+Meanwhile, "do I need to learn a lot about Systemd to use it?" Pogson wondered. "I'm too old to learn too many new tricks. Does it give me any benefits, or is it just a nuisance?
+
+"I see faster booting as a rather small benefit for a lot of nuisance value like binary logs... what's with that?" he added. "I've learned to use grep on current logs to get what I need. Hiding them is just making GNU/Linux more like that other OS. Yuck!"
+
+### 'Nonfree Software Is the Real Enemy' ###
+
+Debian is an organization of roughly a thousand developers, Pogson pointed out.
+
+"They work hard and make the world a better place," he said. "Forcing them to choose which fork to take is really cruel and unusual punishment for such generous people. If the fork is 50/50, Debian might take years of recruitment to recover. That does no one any good.
+
+"The 'new' Debian would be rather weak," Pogson added. "Would it have the hundreds of mirrors that make Debian wonderful? I doubt that. Debian is a great distro. Disemboweling it out of spite is just wrong. Why can't we come to some amicable agreement? Why do we have to race at full speed to the edge of a cliff when we don't know if we can stop?"
+
+Bottom line: "If this civil war gets any worse, I may switch back to Debian Stable/Wheezy, my 'bomb shelter,' in the hope that I can wait for peace to break out," he concluded. "I don't need the drama. Bill Gates must be laughing at this waste of energy. Nonfree software is the real enemy -- not folks building/using Debian GNU/Linux."
+
+### 'It Is What Happens' ###
+
+It is a sad development, Google+ blogger Gonzalo Velasco C. agreed.
+
+At the same time, "it is what happens in the FLOSS world when you don't listen to your peers and users and listen to others that have their own (commercial) agenda and 'suggest' you use a tool as hungry as Systemd, regardless of its merits and modernism comparing to old sisVinit," he said.
+
+"There are a lot of technical discussions and arguments out there, and Debian must show it is neither deaf nor blind and re-discuss the issue," he added.
+
+### Red Hat's Influence ###
+
+"Do the users wish to be beholden to [Red Hat's][11] corporate roadmap? If the answer is 'no,' then a fork is the only choice left open, as it's pretty plain to see that Debian will go Systemd whether their users like it or not," SoylentNews blogger hairyfeet said.
+
+"It all comes down to cloud computing, and RH intends to foist its version of SVCHOSTS for Linux onto Debian and Ubuntu," he added. "The reason why is obvious: it gives them pretty much every major Linux distro, as they are nearly all built on RH, Debian or Ubuntu."
+
+So, the answer is simple, hairyfeet said: "If you want RH calling the shots, then stay; if not, fork."
+
+### 'Seems Like a Lot of Work' ###
+
+Of course, there's nothing to prevent a fork, Google+ blogger Brett Legree pointed out.
+
+"If someone wants to do it, that's their choice," he noted.
+
+"Seems like a lot of work, though," Legree added. "I mean, I figure that most people wouldn't care either way what init system is being used, and those who do know can probably figure out how to configure Debian (or whatever) to use a different init system. That's been possible up to now, and I'd expect it will continue to be so."
+
+Forks are a lot of work to maintain, agreed Chris Travers, a [blogger][12] who works on the [LedgerSMB][13] project.
+
+"Trust me -- I know from experience, as LedgerSMB began life as a fork of SQL-Ledger," Travers said.
+
+Still, "there are huge differences in philosophy between init scripts and Systemd, and this is an area where there is probably room for a good Unix-like distro to keep the old ways," Travers said. "There are certainly worse things than forks developing. This being said, I wonder if people who really want Unix should instead switch to the BSDs."
+
+### 'Like Killing Mosquitoes With Shotguns' ###
+
+The Debian community was not aware of everything the changes in the init system would bring, Google+ blogger Alessandro Ebersol suggested. "They thought it was a non-issue."
+
+Now that "a large number of Debian sysadmins are not pleased," however, forking would be "an extreme measure," he said, "and a last resort. There are still a lot of things that can be done."
+
+After all, Debian is "the GNU/Linux that runs on anything, in any *nix setup -- remember the Debian BSD flavor, and that Debian BSD will have to be accommodated to work with the new init system," Ebersol pointed out.
+
+"So, I believe all is not lost for Debian, but a fork, right now, is too extreme, like killing mosquitoes with shotguns," he concluded. "There's still time and place to make peace and amendments in the Debian community."
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/81262.html
+
+作者:[Katherine Noyes][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://twitter.com/noyesk
+[1]:http://www.reglue.org/
+[2]:http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/80472.html
+[3]:http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/80980.html
+[4]:http://debianfork.org/
+[5]:http://linux.slashdot.org/story/14/10/20/1944226/debians-systemd-adoption-inspires-threat-of-fork
+[6]:http://slashdot.org/
+[7]:http://lxer.com/module/forums/t/35625/
+[8]:http://linuxrants.com/
+[9]:http://boycottsystemd.org/
+[10]:http://mrpogson.com/
+[11]:http://www.redhat.com/
+[12]:http://ledgersmbdev.blogspot.com/
+[13]:http://www.ledgersmb.org/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141008 The Why and How of Ansible and Docker.md b/sources/tech/20141008 The Why and How of Ansible and Docker.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 59bbc0ea2e..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20141008 The Why and How of Ansible and Docker.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
-[bazz222222222222222222222]
-The Why and How of Ansible and Docker
-================================================================================
-There is a lot of interest from the tech community in both [Docker][1] and [Ansible][2], I am hoping that after reading this article you will share our enthusiasm. You will also gain a practical insight into using Ansible and Docker for setting up a complete server environment for a Rails application.
-
-Many reading this might be asking, “Why don’t you just use Heroku?”. First of all, I can run Docker and Ansible on any host, with any provider. Secondly, I prefer flexibility over convenience. I can run anything in this manner, not just web applications. Last but not least, because I am a tinkerer at heart, I get a kick from understanding how all the pieces fit together. The fundamental building block of Heroku is the Linux Container. The same technology lies at the heart of Docker’s versatility. As a matter of fact, one of Docker’s mottoes is: “Containerization is the new virtualization”.
-
-### Why Ansible? ###
-
-After 4 years of heavy Chef usage, the **infrastructure as code** mentality becomes really tedious. I was spending most of my time with the code that was managing my infrastructure, not with the infrastructure itself. Any change, regardless how small, would require a considerable amount of effort for a relatively small gain. With [Ansible][3], there’s data describing infrastructure on one hand, and the constraints of the interactions between various components on the other hand. It’s a much simpler model that enables me to move quicker by letting me focus on what makes my infrastructure personal. Similar to the Unix model, Ansible provides simple modules with a single responsibility that can be combined in endless ways.
-
-Ansible has no dependencies other than Python and SSH. It doesn’t require any agents to be set up on the remote hosts and it doesn’t leave any traces after it runs either. What’s more, it comes with an extensive, built-in library of modules for controlling everything from package managers to cloud providers, to databases and everything else in between.
-
-### Why Docker? ###
-
-[Docker][4] is establishing itself as the most reliable and convenient way of deploying a process on a host. This can be anything from mysqld to redis, to a Rails application. Just like git snapshots and distributes code in the most efficient way, Docker does the same with processes. It guarantees that everything required to run that process will be available regardless of the host that it runs on.
-
-A common but understandable mistake is to treat a Docker container as a VM. The [Single Responsibility Principle][5] still applies, running a single process per container will give it a single reason to change, it will make it re-usable and easy to reason about. This model has stood the test of time in the form of the Unix philosophy, it makes for a solid foundation to build on.
-
-### The Setup ###
-
-Without leaving my terminal, I can have Ansible provision a new instance for me with any of the following: Amazon Web Services, Linode, Rackspace or DigitalOcean. To be more specific, I can have Ansible create a new DigitalOcean 2GB droplet in Amsterdam 2 region in precisely 1 minute and 25 seconds. In a further 1 minute and 50 seconds I can have the system setup with Docker and a few other personal preferences. Once I have this base system in place, I can deploy my application. Notice that I didn’t setup any database or programming language. Docker will handle all application dependencies.
-
-Ansible runs all remote commands via SSH. My SSH keys stored in the local ssh-agent will be shared remotely during Ansible’s SSH sessions. When my application code will be cloned or updated on remote hosts, no git credentials will be required, the forwarded ssh-agent will be used to authenticate with the git host.
-
-### Docker and application dependencies ###
-
-I find it amusing that most developers are specific about the version of the programming language which their application needs, the version of the dependencies in the form of Python packages, Ruby gems or node.js modules, but when it comes to something as important as the database or the message queue, they just use whatever is available in the environment that the application runs. I believe this is one of the reasons behind the devops movement, developers taking responsibility for the application’s environment. Docker makes this task easier and more straightforward by adding a layer of pragmatism and confidence to the existing practices.
-
-My application defines dependencies on processes such as MySQL 5.5 and Redis 2.8 by including the following `.docker_container_dependencies` file:
-
- gerhard/mysql:5.5
- gerhard/redis:2.8
-
-The Ansible playbook will notice this file and will instruct Docker to pull the correct images from the Docker index and start them as containers. It also links these service containers to my application container. If you want to find out how Docker container linking works, refer to the [Docker 0.6.5 announcement][6].
-
-My application also comes with a Dockerfile which is specific about the Ruby Docker image that is required. As this is already built, the steps in my Dockerfile will have the guarantee that the correct Ruby version will be available to them.
-
- FROM howareyou/ruby:2.0.0-p353
-
- ADD ./ /terrabox
-
- RUN \
- . /.profile ;\
- rm -fr /terrabox/.git ;\
- cd /terrabox ;\
- bundle install --local ;\
- echo '. /.profile && cd /terrabox && RAILS_ENV=test bundle exec rake db:create db:migrate && bundle exec rspec' > /test-terrabox ;\
- echo '. /.profile && cd /terrabox && export RAILS_ENV=production && rake db:create db:migrate && bundle exec unicorn -c config/unicorn.rails.conf.rb' > /run-terrabox ;\
- # END RUN
-
- ENTRYPOINT ["/bin/bash"]
- CMD ["/run-terrabox"]
-
- EXPOSE 3000
-
-The first step is to copy all my application’s code into the Docker image and load the global environment variables added by previous images. The Ruby Docker image for example will append PATH configuration which ensures that the correct Ruby version gets loaded.
-
-Next, I remove the git history as this is not useful in the context of a Docker container. I install all the gems and then create a `/test-terrabox` command which will be run by the test-only container. The purpose of this is to have a “canary” which ensures that the application and all its dependencies are properly resolved, that the Docker containers are linked correctly and all tests pass before the actual application container will be started.
-
-The command that gets run when a new web application container gets started is defined in the CMD step. The `/run-terrabox` command was defined part of the build process, right after the test one.
-
-The last instruction in this application’s Dockerfile maps port 3000 from inside the container to an automatically allocated port on the host that runs Docker. This is the port that the reverse proxy or load balancer will use when proxying public requests to my application running inside the Docker container.
-
-### Running a Rails application inside a Docker container ###
-
-For a medium-sized Rails application, with about 100 gems and just as many integration tests running under Rails, this takes 8 minutes and 16 seconds on a 2GB and 2 core instance, without any local Docker images. If I already had Ruby, MySQL & Redis Docker images on that host, this would take 4 minutes and 45 seconds. Furthermore, if I had a master application image to base a new Docker image build of the same application, this would take a mere 2 minutes and 23 seconds. To put this into perspective, it takes me just over 2 minutes to deploy a new version of my Rails application, including dependent services such as MySQL and Redis.
-
-I would like to point out that my application deploys also run a full test suite which alone takes about a minute end-to-end. Without intending, Docker became a simple Continuous Integration environment that leaves test-only containers behind for inspection when tests fail, or starts a new application container with the latest version of my application when the test suite passes. All of a sudden, I can validate new code with my customers in minutes, with the guarantee that different versions of my application are isolated from one another, all the way to the operating system. Unlike traditional VMs which take minutes to boot, a Docker container will take under a second. Furthermore, once a Docker image is built and tests pass for a specific version of my application, I can have this image pushed into a private Docker registry, waiting to be pulled by other Docker hosts and started as a new Docker container, all within seconds.
-
-### Conclusion ###
-
-Ansible made me re-discover the joy of managing infrastructures. Docker gives me confidence and stability when dealing with the most important step of application development, the delivery phase. In combination, they are unmatched.
-
-To go from no server to a fully deployed Rails application in just under 12 minutes is impressive by any standard. To get a very basic Continuous Integration system for free and be able to preview different versions of an application side-by-side, without affecting the “live” version which runs on the same hosts in any way, is incredibly powerful. This makes me very excited, and having reached the end of the article, I can only hope that you share my excitement.
-
-I gave a talk at the January 2014 London Docker meetup on this subject, [I have shared the slides on Speakerdeck][7].
-
-For more Ansible and Docker content, subscribe to [The Changelog Weekly][8] — it ships every Saturday and regularly includes the week’s best links for both topics.
-
-[Use the Draft repo][9] if you’d like to write a post like this for The Changelog. They’ll work with you through the process too.
-
-Until next time, [Gerhard][a].
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://thechangelog.com/ansible-docker/
-
-作者:[Gerhard Lazu][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://twitter.com/gerhardlazu
-[1]:https://www.docker.io/
-[2]:https://github.com/ansible/ansible
-[3]:http://ansible.com/
-[4]:http://docker.io/
-[5]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_responsibility_principle
-[6]:http://blog.docker.io/2013/10/docker-0-6-5-links-container-naming-advanced-port-redirects-host-integration/
-[7]:https://speakerdeck.com/gerhardlazu/ansible-and-docker-the-path-to-continuous-delivery-part-1
-[8]:http://thechangelog.com/weekly/
-[9]:https://github.com/thechangelog/draft
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141009 How to convert image audio and video formats on Ubuntu.md b/sources/tech/20141009 How to convert image audio and video formats on Ubuntu.md
index a3571253fd..b60bd11479 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20141009 How to convert image audio and video formats on Ubuntu.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20141009 How to convert image audio and video formats on Ubuntu.md
@@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
-2q1w2007翻译中
How to convert image, audio and video formats on Ubuntu
================================================================================
If you need to work with a variety of image, audio and video files encoded in all sorts of different formats, you are probably using more than one tools to convert among all those heterogeneous media formats. If there is a versatile all-in-one media conversion tool that is capable of dealing with all different image/audio/video formats, that will be awesome.
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141023 How to turn your CentOS box into a BGP router using Quagga.md b/sources/tech/20141023 How to turn your CentOS box into a BGP router using Quagga.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 63bda4a215..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20141023 How to turn your CentOS box into a BGP router using Quagga.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,312 +0,0 @@
-How to turn your CentOS box into a BGP router using Quagga
-================================================================================
-In a [previous tutorial][1](注:此文原文做过,文件名:“20140928 How to turn your CentOS box into an OSPF router using Quagga.md”,如果前面翻译发布了,可以修改此链接), I described how we can easily turn a Linux box into a fully-fledged OPSF router using Quagga, an open source routing software suite. In this tutorial, I will focus on **converting a Linux box into a BGP router, again using Quagga**, and demonstrate how to set up BGP peering with other BGP routers.
-
-Before we get into details, a little background on BGP may be useful. Border Gateway Protocol (or BGP) is the de-facto standard inter-domain routing protocol of the Internet. In BGP terminology, the global Internet is a collection of tens of thousands of interconnected Autonomous Systems (ASes), where each AS represents an administrative domain of networks managed by a particular provider.
-
-To make its networks globally routable, each AS needs to know how to reach all other ASes in the Internet. That is when BGP comes into play. BGP is the language used by an AS to exchange route information with other neighboring ASes. The route information, often called BGP routes or BGP prefixes, contains AS number (ASN; a globally unique number) and its associated IP address block(s). Once all BGP routes are learned and populated in local BGP routing tables, each AS will know how to reach any public IP addresses on the Internet.
-
-The ability to route across different domains (ASes) is the primary reason why BGP is called an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) or inter-domain protocol. Whereas routing protocols such as OSPF, IS-IS, RIP and EIGRP are all Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs) or intra-domain routing protocols.
-
-### Test Scenarios ###
-
-For this tutorial, let us consider the following topology.
-
-
-
-We assume that service provider A wants to establish a BGP peering with service provider B to exchange routes. The details of their AS and IP address spaces are like the following.
-
-- **Service provider A**: ASN (100), IP address space (100.100.0.0/22), IP address assigned to eth1 of a BGP router (100.100.1.1)
-- **Service provider B**: ASN (200), IP address space (200.200.0.0/22), IP address assigned to eth1 of a BGP router (200.200.1.1)
-
-Router A and router B will be using the 100.100.0.0/30 subnet for connecting to each other. In theory, any subnet reachable from both service providers can be used for interconnection. In real life, it is advisable to use a /30 subnet from service provider A or service provider B's public IP address space.
-
-### Installing Quagga on CentOS ###
-
-If Quagga is not already installed, we install Quagga using yum.
-
- # yum install quagga
-
-If you are using CentOS 7, you need to apply the following policy change for SELinux. Otherwise, SELinux will prevent Zebra daemon from writing to its configuration directory. You can skip this step if you are using CentOS 6.
-
- # setsebool -P zebra_write_config 1
-
-The Quagga software suite contains several daemons that work together. For BGP routing, we will focus on setting up the following two daemons.
-
-- **Zebra**: a core daemon responsible for kernel interfaces and static routes.
-- **BGPd**: a BGP daemon.
-
-### Configuring Logging ###
-
-After Quagga is installed, the next step is to configure Zebra to manage network interfaces of BGP routers. We start by creating a Zebra configuration file and enabling logging.
-
- # cp /usr/share/doc/quagga-XXXXX/zebra.conf.sample /etc/quagga/zebra.conf
-
-On CentOS 6:
-
- # service zebra start
- # chkconfig zebra on
-
-For CentOS 7:
-
- # systemctl start zebra
- # systemctl enable zebra
-
-Quagga offers a dedicated command-line shell called vtysh, where you can type commands which are compatible with those supported by router vendors such as Cisco and Juniper. We will be using vtysh shell to configure BGP routers in the rest of the tutorial.
-
-To launch vtysh command shell, type:
-
- # vtysh
-
-The prompt will be changed to hostname, which indicates that you are inside vtysh shell.
-
- Router-A#
-
-Now we specify the log file for Zebra by using the following commands:
-
- Router-A# configure terminal
- Router-A(config)# log file /var/log/quagga/quagga.log
- Router-A(config)# exit
-
-Save Zebra configuration permanently:
-
- Router-A# write
-
-Repeat this process on Router-B as well.
-
-### Configuring Peering IP Addresses ###
-
-Next, we configure peering IP addresses on available interfaces.
-
- Router-A# show interface
-
-----------
-
- Interface eth0 is up, line protocol detection is disabled
- . . . . .
- Interface eth1 is up, line protocol detection is disabled
- . . . . .
-
-Configure eth0 interface's parameters:
-
- site-A-RTR# configure terminal
- site-A-RTR(config)# interface eth0
- site-A-RTR(config-if)# ip address 100.100.0.1/30
- site-A-RTR(config-if)# description "to Router-B"
- site-A-RTR(config-if)# no shutdown
- site-A-RTR(config-if)# exit
-
-Go ahead and configure eth1 interface's parameters:
-
- site-A-RTR(config)# interface eth1
- site-A-RTR(config-if)# ip address 100.100.1.1/24
- site-A-RTR(config-if)# description "test ip from provider A network"
- site-A-RTR(config-if)# no shutdown
- site-A-RTR(config-if)# exit
-
-Now verify configuration:
-
- Router-A# show interface
-
-----------
-
- Interface eth0 is up, line protocol detection is disabled
- Description: "to Router-B"
- inet 100.100.0.1/30 broadcast 100.100.0.3
- Interface eth1 is up, line protocol detection is disabled
- Description: "test ip from provider A network"
- inet 100.100.1.1/24 broadcast 100.100.1.255
-
-----------
-
- Router-A# show interface description
-
-----------
-
- Interface Status Protocol Description
- eth0 up unknown "to Router-B"
- eth1 up unknown "test ip from provider A network"
-
-If everything looks alright, don't forget to save.
-
- Router-A# write
-
-Repeat to configure interfaces on Router-B as well.
-
-Before moving forward, verify that you can ping each other's IP address.
-
- Router-A# ping 100.100.0.2
-
-----------
-
- PING 100.100.0.2 (100.100.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
- 64 bytes from 100.100.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.616 ms
-
-Next, we will move on to configure BGP peering and prefix advertisement settings.
-
-### Configuring BGP Peering ###
-
-The Quagga daemon responsible for BGP is called bgpd. First, we will prepare its configuration file.
-
- # cp /usr/share/doc/quagga-XXXXXXX/bgpd.conf.sample /etc/quagga/bgpd.conf
-
-On CentOS 6:
-
- # service bgpd start
- # chkconfig bgpd on
-
-For CentOS 7
-
- # systemctl start bgpd
- # systemctl enable bgpd
-
-Now, let's enter Quagga shell.
-
- # vtysh
-
-First verify that there are no configured BGP sessions. In some versions, you may find a BGP session with AS 7675. We will remove it as we don't need it.
-
- Router-A# show running-config
-
-----------
-
- ... ... ...
- router bgp 7675
- bgp router-id 200.200.1.1
- ... ... ...
-
-We will remove any pre-configured BPG session, and replace it with our own.
-
- Router-A# configure terminal
- Router-A(config)# no router bgp 7675
- Router-A(config)# router bgp 100
- Router-A(config)# no auto-summary
- Router-A(config)# no synchronizaiton
- Router-A(config-router)# neighbor 100.100.0.2 remote-as 200
- Router-A(config-router)# neighbor 100.100.0.2 description "provider B"
- Router-A(config-router)# exit
- Router-A(config)# exit
- Router-A# write
-
-Router-B should be configured in a similar way. The following configuration is provided as reference.
-
- Router-B# configure terminal
- Router-B(config)# no router bgp 7675
- Router-B(config)# router bgp 200
- Router-B(config)# no auto-summary
- Router-B(config)# no synchronizaiton
- Router-B(config-router)# neighbor 100.100.0.1 remote-as 100
- Router-B(config-router)# neighbor 100.100.0.1 description "provider A"
- Router-B(config-router)# exit
- Router-B(config)# exit
- Router-B# write
-
-When both routers are configured, a BGP peering between the two should be established. Let's verify that by running:
-
- Router-A# show ip bgp summary
-
-
-
-In the output, we should look at the section "State/PfxRcd." If the peering is down, the output will show 'Idle' or 'Active'. Remember, the word 'Active' inside a router is always bad. It means that the router is actively seeking for a neighbor, prefix or route. When the peering is up, the output under "State/PfxRcd" should show the number of prefixes received from this particular neighbor.
-
-In this example output, the BGP peering is just up between AS 100 and AS 200. Thus no prefixes are being exchanged, and the number in the rightmost column is 0.
-
-### Configuring Prefix Advertisements ###
-
-As specified at the beginning, AS 100 will advertise a prefix 100.100.0.0/22, and AS 200 will advertise a prefix 200.200.0.0/22 in our example. Those prefixes need to be added to BGP configuration as follows.
-
-On Router-A:
-
- Router-A# configure terminal
- Router-A(config)# router bgp 100
- Router-A(config)# network 100.100.0.0/22
- Router-A(config)# exit
- Router-A# write
-
-On Router-B:
-
- Router-B# configure terminal
- Router-B(config)# router bgp 200
- Router-B(config)# network 200.200.0.0/22
- Router-B(config)# exit
- Router-B# write
-
-At this point, both routers should start advertising prefixes as required.
-
-### Testing Prefix Advertisements ###
-
-First of all, let's verify whether the number of prefixes has changed now.
-
- Router-A# show ip bgp summary
-
-
-
-To view more details on the prefixes being received, we can use the following command, which shows the total number of prefixes received from neighbor 100.100.0.2.
-
- Router-A# show ip bgp neighbors 100.100.0.2 advertised-routes
-
-
-
-To check which prefixes we are receiving from that neighbor:
-
- Router-A# show ip bgp neighbors 100.100.0.2 routes
-
-
-
-We can also check all the BGP routes:
-
- Router-A# show ip bgp
-
-
-
-These commands below can be used to check which routes in the routing table are learned via BGP.
-
- Router-A# show ip route
-
-----------
-
- Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF,
- I - ISIS, B - BGP, > - selected route, * - FIB route
-
- C>* 100.100.0.0/30 is directly connected, eth0
- C>* 100.100.1.0/24 is directly connected, eth1
- B>* 200.200.0.0/22 [20/0] via 100.100.0.2, eth0, 00:06:45
-
-----------
-
- Router-A# show ip route bgp
-
-----------
-
- B>* 200.200.0.0/22 [20/0] via 100.100.0.2, eth0, 00:08:13
-
-The BGP-learned routes should also be present in the Linux routing table.
-
- [root@Router-A~]# ip route
-
-----------
-
- 100.100.0.0/30 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 100.100.0.1
- 100.100.1.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 100.100.1.1
- 200.200.0.0/22 via 100.100.0.2 dev eth0 proto zebra
-
-Finally, we are going to test with ping command. ping should be successful.
-
- [root@Router-A~]# ping 200.200.1.1 -c 2
-
-To sum up, this tutorial focused on how we can run basic BGP on a CentOS box. While this should get you started with BGP, there are other advanced settings such as prefix filters, BGP attribute tuning such as local preference and path prepend. I will be covering these topics in future tutorials.
-
-Hope this helps.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://xmodulo.com/centos-bgp-router-quagga.html
-
-作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
-[1]:http://xmodulo.com/turn-centos-box-into-ospf-router-quagga.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141024 Amazing 25 Linux Performance Monitoring Tools.md b/sources/tech/20141024 Amazing 25 Linux Performance Monitoring Tools.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9f6f386f33..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20141024 Amazing 25 Linux Performance Monitoring Tools.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,292 +0,0 @@
-andyxue translating
-Amazing ! 25 Linux Performance Monitoring Tools
-================================================================================
-Over the time our website has shown you how to configure various performance tools for Linux and Unix-like operating systems. In this article we have made a list of the most used and most useful tools to monitor the performance for your box. We provided a link for each of them and split them into 2 categories: command lines one and the ones that offer a graphical interface.
-
-### Command line performance monitoring tools ###
-
-#### 1. dstat - Versatile resource statistics tool ####
-
-A versatile combination of **vmstat**, **iostat** and **ifstat**. It adds new features and functionality allowing you to view all the different resources instantly, allowing you to compare and combine the different resource usage. It uses colors and blocks to help you see the information clearly and easily. It also allows you to export the data in **CVS** format to review it in a spreadsheet application or import in a **database**. You can use this application to [monitor cpu, memory, eth0 activity related to time][1].
-
-
-
-#### 2. atop - Improved top with ASCII ####
-
-A command line tool using **ASCII** to display a **performance monitor** that is capable of reporting the activity of all processes. It shows daily logging of system and process activity for long-term analysis and it highlights overloaded system resources by using colors. It includes metrics related to **CPU**, **memory**, **swap**, **disks** and **network layers**. All the functions of atop can be accessed by simply running:
-
- # atop
-
-And you will be able to [use the interactive interface to display][2] and order data.
-
-
-
-#### 3. Nmon - performance monitor for Unix-like systems ####
-
-Nmon stands for **Nigel's Monitor** and it's a system monitor tool originally developed for **AIX**. If features an **Online Mode** that uses curses for efficient screen handling, which updates the terminal frequently for real-time monitoring and a **Capture Mode** where the data is saved in a file in **CSV** format for later processing and graphing.
-
-
-
-**More info** in our [nmon performance track article][3].
-
-#### 4. slabtop - information on kernel slab cache ####
-
-This application will show you how the **caching memory allocator** manages in the Linux kernel caches various type of objects. The command is a top like command but is focused on showing real-time kernel slab cache information. It displays a listing of the top caches sorted by one of the listed sort criteria. It also displays a statistics header filled with slab layer information. Here are a few examples:
-
- # slabtop --sort=a
- # slabtop -s b
- # slabtop -s c
- # slabtop -s l
- # slabtop -s v
- # slabtop -s n
- # slabtop -s o
-
-**More info** is available [kernel slab cache article][4]
-
-#### 5. sar - performance monitoring and bottlenecks check ####
-
-The **sar** command writes to standard output the contents of selected cumulative activity counters in the operating system. The **accounting system**, based on the values in the count and interval parameters, writes information the specified number of times spaced at the specified intervals in seconds. If the interval parameter is set to zero, [the sar command displays the average statistics][5] for the time since the system was started. Useful commands:
-
- # sar -u 2 3
- # sar –u –f /var/log/sa/sa05
- # sar -P ALL 1 1
- # sar -r 1 3
- # sar -W 1 3
-
-#### 6. Saidar - simple stats monitor ####
-
-Saidar is a **simple** and **lightweight** tool for system information. It doesn't have major performance reports but it does show the most useful system metrics in a short and nice way. You can easily see the [**up-time, average load, CPU, memory, processes, disk and network interfaces**][6] stats.
-
- Usage: saidar [-d delay] [-c] [-v] [-h]
-
- -d Sets the update time in seconds
- -c Enables coloured output
- -v Prints version number
- -h Displays this help information.
-
-
-
-#### 7. top - The classical Linux task manager ####
-
-top is one of the best known **Linux** utilities, it's a **task manager** found on most **Unix-like** operating systems. It shows the current list of running processes that the user can order using different criteria. It mainly shows how much **CPU** and **memory** is used by the **system processes**. top is a quick place to go a check what process or **processes** hangs your system. You can also find here a [list of examples of top usage][7] . You can access it by running the top command and entering the interactive mode:
-
- Quick cheat sheet for interactive mode:
-
- GLOBAL_Commands: ?, =, A, B, d, G, h, I, k, q, r, s, W, Z
- SUMMARY_Area_Commands: l, m, t, 1
- TASK_Area_Commands Appearance: b, x, y, z Content: c, f, H, o, S, u Size: #, i, n Sorting: <, >, F, O, R
- COLOR_Mapping: , a, B, b, H, M, q, S, T, w, z, 0 - 7
- COMMANDS_for_Windows: -, _, =, +, A, a, G, g, w
-
-
-
-#### 8. Sysdig - Advanced view of system processes ####
-
-**Sysdig** is a tool that gives admins and developers unprecedented visibility into the behavior of their systems. The team that develops it wants to improve the way system-level **monitoring** and **troubleshooting** is done by offering a unified, coherent, and granular visibility into the **storage**, **processing**, **network**, and **memory** subsystems making it possible to create trace files for system activity so you can easily analyze it at any time.
-
-Quick examples:
-
- # sysdig proc.name=vim
- # sysdig -p"%proc.name %fd.name" "evt.type=accept and proc.name!=httpd"
- # sysdig evt.type=chdir and user.name=root
- # sysdig -l
- # sysdig -L
- # sysdig -c topprocs_net
- # sysdig -c fdcount_by fd.sport "evt.type=accept"
- # sysdig -p"%proc.name %fd.name" "evt.type=accept and proc.name!=httpd"
- # sysdig -c topprocs_file
- # sysdig -c fdcount_by proc.name "fd.type=file"
- # sysdig -p "%12user.name %6proc.pid %12proc.name %3fd.num %fd.typechar %fd.name" evt.type=open
- # sysdig -c topprocs_cpu
- # sysdig -c topprocs_cpu evt.cpu=0
- # sysdig -p"%evt.arg.path" "evt.type=chdir and user.name=root"
- # sysdig evt.type=open and fd.name contains /etc
-
-
-
-**More info** is available in our article on [how to use sysdig for improved system-level monitoring and troubleshooting][8]
-
-#### 9. netstat - Shows open ports and connections ####
-
-Is the tool **Linux administrators** use to show various **network** information, like what ports are open and what network connections are established and what process runs that connection. It also shows various information about the **Unix sockets** that are open between various programs. It is part of most Linux distributions A lot of the commands are explained in the [article on netstat and its various outputs][9]. Most used commands are:
-
- $ netstat | head -20
- $ netstat -r
- $ netstat -rC
- $ netstat -i
- $ netstat -ie
- $ netstat -s
- $ netstat -g
- $ netstat -tapn
-
-### 10. tcpdump - insight on network packets ###
-
-**tcpdump** can be used to see the content of the **packets** on a **network connection**. It shows various information about the packet content that pass. To make the output useful, it allows you to use various filters to only get the information you wish. A few examples on how you can use it:
-
- # tcpdump -i eth0 not port 22
- # tcpdump -c 10 -i eth0
- # tcpdump -ni eth0 -c 10 not port 22
- # tcpdump -w aloft.cap -s 0
- # tcpdump -r aloft.cap
- # tcpdump -i eth0 dst port 80
-
-**You can find them described in** [detail in our article on tcpdump and capturing packets][10]
-
-#### 11. vmstat - virtual memory statistics ####
-
-**vmstat** stands for **virtual memory** statistics and it's a **memory monitoring** tool that collects and displays summary information about **memory**, **processes**, **interrupts**, **paging** and **block I/O**. It is an open source program available on most Linux distributions, Solaris and FreeBSD. It is used to diagnose most memory performance problems and much more.
-
-
-
-**More info** in [our article on vmstat commands][11].
-
-#### 12. free - memory statistics ####
-
-Another **command line** tool that will show to standard output a few stats about **memory** usage and swap usage. Because it's a simple tool it can be used to either find **quick information** about memory usage or it can be used in different scripts and applications. You can see that [this small application has a lot of uses][12] and almost all system admin use this tool daily :-)
-
-
-
-#### 13. Htop - friendlier top ####
-
-**Htop** is basically an improved version of top showing more stats and in a more colorful way allowing you to sort them in different ways as you can see in our article. It provides a more a more **user-friendly** interface.
-
-
-
-You can find **more info** in [our comparison of htop and top][13]
-
-#### 14. ss - the modern net-tools replacement ####
-
-**ss** is part of the **iproute2** package. iproute2 is intended to replace an entire suite of standard **Unix networking tools** that were previously used for the tasks of [configuring network interfaces, routing tables, and managing the ARP table][14]. The ss utility is used to dump socket statistics, it allows showing information similar to **netstat** and its able display more TCP and state information. A few examples:
-
- # ss -tnap
- # ss -tnap6
- # ss -tnap
- # ss -s
- # ss -tn -o state established -p
-
-#### 15. lsof - list open files ####
-
-**lsof** is a command meaning "**list open files**", which is used in many Unix-like systems to report a list of all open files and the processes that opened them. It is used by most Linux distributions and other Unix-like operating systems by **system administrators** to check what files are open by various processes.
-
- # lsof +p process_id
- # lsof | less
- # lsof –u username
- # lsof /etc/passwd
- # lsof –i TCP:ftp
- # lsof –i TCP:80
-
-You can find **more examples** in the [lsof article][15]
-
-#### 16. iftop - top for your network connections ####
-
-**iftop** is yet another top like application that will is based on networking information. It shows various current **network connection** sorted by **bandwidth usage** or the amount of data uploaded or downloaded. It also provides various estimations of the time it will take to download them.
-
-
-
-For **more info** see [article on network traffic with iftop][16]
-
-#### 17. iperf - network performance tool ####
-
-**iperf** is a **network testing** tool that can create **TCP** and **UDP** data connections and measure the **performance** of a network that is carrying them. It supports tuning of various parameters related to timing, protocols, and buffers. For each test it reports the bandwidth, loss, and other parameters.
-
-
-
-If you wish to use the tool check out our article on [how to install and use iperf][17]
-
-#### 18. Smem - advanced memory reporting ####
-
-**Smem** is one of the most advanced tools for **Linux** command line, it offers information about the actual **memory** that is used and shared in the system, attempting to provide a more realistic image of the actual **memory** being used.
-
- $ smem -m
- $ smem -m -p | grep firefox
- $ smem -u -p
- $ smem -w -p
-
-Check out our [article on Smem for more examples][18]
-
-### GUI or Web based performance tools ###
-
-#### 19. Icinga - community fork of Nagios ####
-
-**Icinga** is **free** and **open source** system and network monitoring application. It’s a fork of Nagios retaining most of the existing features of its predecessor and building on them to add many long awaited patches and features requested by the user community.
-
-
-
-**More info** about installing and configuring [can be found in our Icinga article][19].
-
-#### 20. Nagios - the most popular monitoring tool. ####
-
-The most used and popular **monitoring solution** found on Linux. It has a daemon that collects information about various process and has the ability to collect information from remote hosts. All the information is then provided via a nice and powerful **web interface**.
-
-
-
-You can find **information** on [how to install Nagios in our article][20]
-
-#### 21. Linux process explorer - procexp for Linux ####
-
-**Linux process explorer** is a graphical process explorer for **Linux**. It shows various **process information** like the process tree, TCP/IP connections and performance figures for each process. It's a replica of procexp found in Windows and developed by **Sysinternals** and aims to be more user friendly then top and ps.
-
-Check our [linux process explorer article][21] for more info.
-
-#### 22. Collectl - performance monitoring tool ####
-
-This is a **performance monitoring** tool that you can use either in an **interactive mode** or you can have it **write reports** to disk and access them with a web server. It reports statistics on **CPU**, **disk**, **memory**, **network**, **nfs**, **process**, **slabs** and more in easy to read and manage format.
-
-
-
-**More info** in our [Collectl article][22]
-
-#### 23. MRTG - the classic graph tool ####
-
-This is a **network traffic** monitor that will provide you **graphs** using the **rrdtool**. It is one of the oldest tools that provides graphics and is one of the most used on Unix-like operating systems. Check our article on [how to use MRTG][23] for information on the installation and configuration process
-
-
-
-#### 24. Monit - simple and easy to use monitor tool ####
-
-**Monit** is an **open source** small **Linux** utility designed to monitor **processes**, **system load**, **filesystems**, **directories** and **files**. You can have it run automatic maintenance and repair and can execute actions in error situations or send email reports to alert the system administrator. If you wish to use this tool you can check out our [how to use Monit article][24].
-
-
-
-#### 25. Munin - monitoring and alerting services for servers ####
-
-**Munin** is a **networked resource monitoring** tool that can help analyze **resource trends** and see what is the weak point and what caused **performance issues**. The team that develops it wishes it for it to be very easy to use and user-friendly. The application is written in Perl and uses the rrdtool to generate graphs, which are with the web interface. The developers advertise the application "plug and play" capabilities with about 500 monitoring plugins currently available.
-
-**More info** can be found in our [article on Munin][25]
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
-
-作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/adriand/
-[1]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/dstat-monitor-linux-performance/
-[2]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/guide-using-linux-atop/
-[3]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/install-nmon-monitor-linux-performance/
-[4]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/kernel-slab-cache-information/
-[5]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-system-performance-monitoring-using-sar-command/
-[6]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/monitor-linux-saidar-tool/
-[7]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-top-command-examples-screenshots/
-[8]:http://linoxide.com/tools/sysdig-performance-linux-tool/
-[9]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/netstat-commad-with-all-variant-outputs/
-[10]:http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/network-traffic-capture-tcp-dump-command/
-[11]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-vmstat-command-tool-report-virtual-memory-statistics/
-[12]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-free-command/
-[13]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-htop-command/
-[14]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/ss-sockets-network-connection/
-[15]:http://linoxide.com/how-tos/lsof-command-list-process-id-information/
-[16]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/iftop-network-traffic/
-[17]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/install-iperf-test-network-speed-bandwidth/
-[18]:http://linoxide.com/tools/memory-usage-reporting-smem/
-[19]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/install-configure-icinga-linux/
-[20]:http://linoxide.com/how-tos/install-configure-nagios-centos-7/
-[21]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/procexp/
-[22]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/collectl-tool-install-examples/
-[23]:http://linoxide.com/tools/multi-router-traffic-grapher/
-[24]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/monit-linux/
-[25]:http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-munin/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141024 How To Upgrade Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty To Ubuntu 14.10 Utopic.md b/sources/tech/20141024 How To Upgrade Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty To Ubuntu 14.10 Utopic.md
index 78777b46a0..dee546fd1e 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20141024 How To Upgrade Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty To Ubuntu 14.10 Utopic.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20141024 How To Upgrade Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty To Ubuntu 14.10 Utopic.md
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
+johnhoow translating...
How To Upgrade Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty To Ubuntu 14.10 Utopic
================================================================================
Hello all! Greetings! Today, we will discuss about how to upgrade from Ubuntu 14.04 to 14.10 final beta. As you may know, Ubuntu 14.10 final beta has already been released. According to the [Ubuntu release schedule][1], the final stable version will be available today in a couple of hours.
@@ -106,4 +107,4 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/upgrade-ubuntu-14-04-trusty-ubuntu-14-10-utopic/
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-[1]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/UtopicUnicorn/ReleaseSchedule
\ No newline at end of file
+[1]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/UtopicUnicorn/ReleaseSchedule
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141029 How to Install and Setup My Weather Indicator in Ubuntu 14.10.md b/sources/tech/20141029 How to Install and Setup My Weather Indicator in Ubuntu 14.10.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a5e06daef8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20141029 How to Install and Setup My Weather Indicator in Ubuntu 14.10.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+How to Install and Setup ‘My Weather Indicator’ in Ubuntu 14.10
+================================================================================
+
+
+**There’s no drought of ways to be kept abreast of the weather on the Ubuntu desktop, with the Unity Dash and desktop apps like [Typhoon][1] all offering to help.**
+
+But panel applets that offer quick glance condition and temperature stats, with a ream of detailed meteorological data never more than a quick click away, are by far the most popular weather utilities on Linux.
+
+[My Weather Indicator][2] by Atareao is one of this breed, and arguably the best.
+
+It displays current temperature and conditions on the Unity panel, and has a menu stuffed full of stats, including ‘feels like’, cloudiness and sunrise/set times. In addition, there’s a desktop widget, multiple location support, a choice of backend data providers, and plenty of configuration options.
+
+Sounds pretty comprehensive, right? Let’s walk through how to install and set it up on Ubuntu.
+
+### Install My Weather Indicator in Ubuntu ###
+
+My Weather Indicator is not available to install from the Ubuntu Software Center directly, but both a .deb installer and an officially maintained PPA (providing packages for both Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and 14.10) are provided by the developers.
+
+- Download My Weather Indicator (.deb)
+
+To ensure you’re always kept up-to-date with the latest release I recommend adding the [Atareao PPA][3] to your Software Sources and installing from there.
+
+How? **Open a new Terminal** window (Unity Dash > Terminal, or press Ctrl+Alt+T) and **enter the following two commands carefully**, entering your system password when prompted:
+
+ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:atareao/atareao
+
+ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install my-weather-indicator
+
+#### Setting Up My Weather Indicator ####
+
+Regardless of how you install the tool, once you have you can launch it from the Unity Dash by searching for “weather”.
+
+
+
+The first time you open the app the following Preferences window will open. From here you can search for a location manually or set it to auto-detect using geo-ip — the latter of which can sometimes be a little imprecise, but saves the need to faff.
+
+
+
+If you’re travelling (or in need of some small talk fodder) **you can monitor a second locale**, too. This is set up in the same way as the first but in the ‘Second Location’ tab.
+
+Checking the ‘**Show Widget**’ box in the “**Widget Options**” section adds a small forecast desklet to your desktop. There are a number of different skins included, so be sure to play around to find the one you like the most (note: widget changes are applied on clicking ‘Ok’).
+
+
+
+My Weather Indicator uses [Open Weather Map][4] as its forecast backend by default, but other options can be selected from the ‘**Weather Services**’ pane (*require an API key to function):
+
+- Open Weather Map
+- Yahoo! Weather
+- Weather Underground*
+- World Weather Online*
+
+The ‘**Units**’ tab is where you can configure measurements for temperature, pressure, wind speed, etc. These are applied globally to all configured locations; you can’t have one location in Celsius and the other in Fahrenheit.
+
+
+
+Finally, in the ‘General Options‘ section you can set the refresh interval, set autostart preference, and choose from one of two panel icons.
+
+MWI not your thing? Why not try [the nerdy way to view weather forecasts on Linux][5]?
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/10/install-weather-indicator-ubuntu-14-10
+
+作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
+[1]:https://launchpad.net/typhoon
+[2]:https://launchpad.net/my-weather-indicator
+[3]:https://launchpad.net/~atareao/+archive/ubuntu/atareao
+[4]:http://openweathermap.org/
+[5]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/02/get-weather-forecast-terminal-linux
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141029 How to create and manage LXC containers on Ubuntu.md b/sources/tech/20141029 How to create and manage LXC containers on Ubuntu.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..5731a7d737
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20141029 How to create and manage LXC containers on Ubuntu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
+How to create and manage LXC containers on Ubuntu
+================================================================================
+While the concept of containers was introduced more than a decade ago to manage shared hosting environments securely (e.g., FreeBSD jails), Linux containers such as LXC or [Docker][1] have gone mainstream only recently with the rising need to deploy applications for the cloud. While [Docker][2] is getting all the media spotlight these days with strong backing from major cloud providers (e.g., Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure) and distro providers (e.g., Red Hat, Ubuntu), LXC is in fact the original container technology developed for Linux platforms.
+
+If you are an average Linux user, what good does Docker/LXC bring to you? Well, containers are actually a great means to switch between distros literally instantly. Suppose your current desktop is Debian. You want Debian's stability. At the same time, you also want to play the latest Ubuntu games. Then instead of bothering to dual boot into a Ubuntu partition, or boot up a heavyweight Ubuntu VM, simply spin off a Ubuntu container on the spot, and you are done.
+
+Even without all the goodies of Docker, what I like about LXC containers is the fact that LXC can be managed by libvirt interface, which is not the case for Docker. If you have been using libvirt-based management tools (e.g., virt-manager or virsh), you can use those same tools to manage LXC containers.
+
+In this tutorial, I focus on the command-line usage of standard LXC container tools, and demonstrate **how to create and manage LXC containers from the command line on Ubuntu**.
+
+### Install LXC on Ubuntu ###
+
+To use LXC on Ubuntu, install LXC user-space tools as follows.
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install lxc
+
+After that, check the current Linux kernel for LXC support by running lxc-checkconifg tool. If everything is enabled, kernel's LXC support is ready.
+
+ $ lxc-checkconfig
+
+
+
+After installing LXC tools, you will find that an LXC's default bridge interface (lxcbr0) is automatically created (as configured in /etc/lxc/default.conf).
+
+
+
+When you create an LXC container, the container's interface will automatically be attached to this bridge, so the container can communicate with the world.
+
+### Create an LXC Container ###
+
+To be able to create an LXC container of a particular target environment (e.g., Debian Wheezy 64bit), you need a corresponding LXC template. Fortunately, LXC user space tools on Ubuntu come with a collection of ready-made LXC templates. You can find available LXC templates in /usr/share/lxc/templates directory.
+
+ $ ls /usr/share/lxc/templates
+
+
+
+An LXC template is nothing more than a script which builds a container for a particular Linux environment. When you create an LXC container, you need to use one of these templates.
+
+To create a Ubuntu container, for example, use the following command-line:
+
+ $ sudo lxc-create -n -t ubuntu
+
+
+
+By default, it will create a minimal Ubuntu install of the same release version and architecture as the local host, in this case Saucy Salamander (13.10) 64-bit.
+
+If you want, you can create Ubuntu containers of any arbitrary version by passing the release parameter. For example, to create a Ubuntu 14.10 container:
+
+ $ sudo lxc-create -n -t ubuntu -- --release utopic
+
+It will download and validate all the packages needed by a target container environment. The whole process can take a couple of minutes or more depending on the type of container. So be patient.
+
+
+
+After a series of package downloads and validation, an LXC container image are finally created, and you will see a default login credential to use. The container is stored in /var/lib/lxc/. Its root filesystem is found in /var/lib/lxc//rootfs.
+
+All the packages downloaded during LXC creation get cached in /var/cache/lxc, so that creating additional containers with the same LXC template will take no time.
+
+Let's see a list of LXC containers on the host:
+
+ $ sudo lxc-ls --fancy
+
+----------
+
+ NAME STATE IPV4 IPV6 AUTOSTART
+ ------------------------------------
+ test-lxc STOPPED - - NO
+
+To boot up a container, use the command below. The "-d" option launches the container as a daemon. Without this option, you will directly be attached to console right after you launch the container.
+
+ $ sudo lxc-start -n -d
+
+After launching the container, let's check the state of the container again:
+
+ $ sudo lxc-ls --fancy
+
+----------
+
+ NAME STATE IPV4 IPV6 AUTOSTART
+ -----------------------------------------
+ lxc RUNNING 10.0.3.55 - NO
+
+You will see that the container is in "RUNNING" state with an IP address assigned to it.
+
+You can also verify that the container's interface (e.g., vethJ06SFL) is automatically attached to LXC's internal bridge (lxcbr0) as follows.
+
+ $ brctl show lxcbr0
+
+
+
+### Manage an LXC Container ###
+
+Now that we know how to create and start an LXC container, let's see what we can do with a running container.
+
+First of all, we want to access the container's console. For this, type this command:
+
+ $ sudo lxc-console -n
+
+
+
+Type to exit the console.
+
+To stop and destroy a container:
+
+ $ sudo lxc-stop -n
+ $ sudo lxc-destroy -n
+
+To clone an existing container to another, use these commands:
+
+ $ sudo lxc-stop -n
+ $ sudo lxc-clone -o -n
+
+### Troubleshooting ###
+
+For those of you who encounter errors with LXC, here are some troubleshooting tips.
+
+1. You fail to create an LXC container with the following error.
+
+ $ sudo lxc-create -n test-lxc -t ubuntu
+
+----------
+
+ lxc-create: symbol lookup error: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/liblxc.so.1: undefined symbol: cgmanager_get_pid_cgroup_abs_sync
+
+This means that you are running the latest LXC, but with an older libcgmanager. To fix this problem, you need to update libcgmanager.
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install libcgmanager0
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/lxc-containers-ubuntu.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/docker-containers-centos-fedora.html
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/manage-linux-containers-docker-ubuntu.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141029 How to install LEMP stack nginx MariaDB or MySQL and php on CentOS.md b/sources/tech/20141029 How to install LEMP stack nginx MariaDB or MySQL and php on CentOS.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0554534f82
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20141029 How to install LEMP stack nginx MariaDB or MySQL and php on CentOS.md
@@ -0,0 +1,248 @@
+How to install LEMP stack (nginx, MariaDB/MySQL and php) on CentOS
+================================================================================
+The LEMP stack is an increasingly popular web service stack, powering mission-critical web services in many production environments. As the name implies, the LEMP stack is composed of Linux, nginx, MariaDB/MySQL and PHP. nginx is a high performance and lightweight replacement of slow and hard-to-scale Apache HTTP server used in the traditional LAMP stack. MariaDB is a community-driven fork of MySQL, with more features and better performance. PHP, a server-side language for generating dynamic content, is processed by PHP-FPM, an enhanced implementation of PHP FastCGI.
+
+In this tutorial, I demonstrate **how to set up the LEMP stack on CentOS platforms**. I target both CentOS 6 and CentOS 7 platforms, and point out differences where necessary.
+
+### Step One: Nginx ###
+
+As the first step, let's install nginx on CentOS, and do basic configuration for nginx, such as enabling auto-start and [customizing the firewall][1].
+
+#### Install Nginx ####
+
+Let's install a pre-built stable version of nginx package from its official RPM source.
+
+On CentOS 7:
+
+ $ sudo rpm --import http://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
+ $ sudo rpm -ivh http://nginx.org/packages/centos/7/noarch/RPMS/nginx-release-centos-7-0.el7.ngx.noarch.rpm
+ $ sudo yum install nginx
+
+On CentOS 6:
+
+ $ sudo rpm --import http://nginx.org/keys/nginx_signing.key
+ $ sudo rpm -ivh http://nginx.org/packages/centos/6/noarch/RPMS/nginx-release-centos-6-0.el6.ngx.noarch.rpm
+ $ sudo yum install nginx
+
+Note that if you do not import the official nginx GPG key before installing nginx RPM, you will get this warning:
+
+ warning: /var/tmp/rpm-tmp.KttVHD: Header V4 RSA/SHA1 Signature, key ID 7bd9bf62: NOKEY
+
+#### Start Nginx ####
+
+After installation, nginx does not start automatically. Let's start nginx right now, and configure it to auto-start upon boot. Also, we need to open a TCP/80 port in the firewall so that you can access nginx webserver remotely. All of these are achieved by entering the following commands.
+
+On CentOS 7:
+
+ $ sudo systemctl start nginx
+ $ sudo systemctl enable nginx
+ $ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
+ $ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
+
+On CentOS 6:
+
+ $ sudo service nginx start
+ $ sudo chkconfig nginx on
+ $ sudo iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
+ $ sudo service iptables save
+
+#### Test Nginx ####
+
+The default document root directory of nginx is /usr/share/nginx/html. A default index.html file must be already placed in this directory. Let's check if you can access this test web page by going to http:///
+
+
+
+If you see the above page, nginx must be set up correctly. Proceed to the next.
+
+### Step Two: MariaDB/MySQL ###
+
+The next step is to install a database component of the LEMP stack. While CentOS/RHEL 6 or earlier provides MySQL server/client packages, CentOS/RHEL 7 has adopted MariaDB as the default implementation of MySQL. As a drop-in replacement of MySQL, MariaDB ensures maximum compatibility with MySQL in terms of APIs and command-line usages. Here is how to install and configure MariaDB/MySQL on CentOS.
+
+On CentOS 7:
+
+Install MariaDB server/client package and start MariaDB server as follows.
+
+ $ sudo yum install mariadb-server
+ $ sudo systemctl start mariadb
+ $ sudo systemctl enable mariadb
+
+On CentOS 6:
+
+Install MySQL server/client package, and start MySQL server as follows.
+
+ $ sudo yum install mysql-server
+ $ sudo service mysqld start
+ $ sudo chkconfig mysqld on
+
+After launching MariaDB/MySQL server successfully, execute the following add-on script that comes with MariaDB/MySQL server package. This one-time run conducts several security hardening steps for the database server, such as setting the (non-empty) root password, removing anonymous user, and locking down remote access.
+
+ $ sudo mysql_secure_installation
+
+
+
+That's it for the database setup. Now move to the next step.
+
+### Step Three: PHP ###
+
+PHP is an important component of the LEMP stack, which is responsible for generating dynamic content from data stored in a MariaDB/MySQL server. For the LEMP stack, you need, at a minimum, to install PHP-FPM and PHP-MySQL. PHP-FPM (FastCGI Process Manager) implements an interface between nginx and PHP applications which generate dynamic content. The PHP-MySQL module allows PHP programs to access MariaDB/MySQL.
+
+#### Install PHP Modules ####
+
+On CentOS 7:
+
+ $ sudo yum php php-fpm php-mysql
+
+On CentOS 6:
+
+First you need to install REMI repository (refer to [this guide][2]), and install the packages from the repository.
+
+ $ sudo yum --enablerepo=remi install php php-fpm php-mysql
+
+
+
+Two observations worth noting while installing PHP:
+
+On CentOS 6, MySQL server and client packages will automatically be upgraded as part of dependencies of the latest php-mysql in REMI.
+
+On both CentOS 6 and 7, installing the php package will also install Apache web server (i.e., httpd) as part of its dependencies. This can cause conflicts with nginx web server. We will take care of this problem in the next section.
+
+Depending on your use cases, you may want to install any of the following additional PHP module packages with yum command to customize your PHP engine.
+
+- **php-cli**: command-line interface for PHP. Useful for testing PHP from the command line.
+- **php-gd**: image processing support for PHP.
+- **php-bcmath**: arbitrary mathematics support for PHP.
+- **php-mcrypt**: encryption algorithm support for PHP (e.g., DES, Blowfish, CBC, CFB, ECB ciphers).
+- **php-xml**: XML parsing and manipulation support for PHP.
+- **php-dba**: database abstraction layer support for PHP.
+- **php-pecl-apc**: PHP accelerator/caching support.
+
+To see a complete list of available PHP modules to install, run:
+
+ $ sudo yum search php- (CentOS 7)
+ $ sudo yum --enablerepo=remi search php- (CentOS 6)
+
+#### Start PHP-FPM ####
+
+You will need to start PHP-FPM, and add it to auto-start list.
+
+On CentOS 7:
+
+ $ sudo systemctl start php-fpm
+ $ sudo systemctl enable php-fpm
+
+On CentOS 6:
+
+ $ sudo chkconfig php-fpm on
+ $ sudo service php-fpm start
+
+### Step Four: Configure the LEMP Stack ###
+
+The final step of the tutorial is tuning the LEMP stack configuration.
+
+#### Disable Httpd ####
+
+Let's first disable httpd which was installed along with the PHP package earlier.
+
+On CentOS 7:
+
+ $ sudo systemctl disable httpd
+
+On CentOS 6:
+
+ $ sudo chkconfig httpd off
+
+#### Configure Nginx ####
+
+Next, let's configure nginx virtual hosts, so that nginx can process PHP via PHP-FPM. For that, open /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf with a text editor, and change it to the following.
+
+ $ sudo vi /etc/nginx/conf.d/default.conf
+
+----------
+
+ server {
+ listen 80;
+ server_name www.server_domain.com;
+ root /usr/share/nginx/html;
+ index index.php index.html index.htm;
+
+ location / {
+ }
+
+ # redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
+ error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
+ location = /50x.html {
+ }
+
+ # nginx passes PHP scripts to FastCGI server via a TCP/9000 socket
+ # this setting much be consistent with /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
+ # try_files prevents nginx from passing bad scripts to FastCGI server
+ location ~ \.php$ {
+ try_files $uri =404;
+ fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
+ fastcgi_index index.php;
+ fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
+ include fastcgi_params;
+ }
+ }
+
+Also, let's adjust the number of nginx worker threads (specified in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf), which is set to one by default. Typically, we create as many worker threads as the number of CPU cores you have. To check how many CPU core you have, run this command:
+
+ $ grep processor /proc/cpuinfo | wc -l
+
+If you have 4 cores, change /etc/nginx/nginx.conf as follows.
+
+ $ sudo vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
+
+----------
+
+ worker_processes 4;
+
+#### Configure PHP ####
+
+Next, let's customize PHP configuration in /etc/php.ini file. More specifically, add the following lines in /etc/php.ini.
+
+ cgi.fix_pathinfo=0
+ date.timezone = "America/New York"
+
+As a security precaution, we want the PHP interpreter to process only an exact file path, instead of guessing any non-existing file. The first line above achieves this goal.
+
+The second line specifies the default timezone used by date/time related PHP functions. Use [this guide][3] to find out your timezone, and set the value of **date.timezone** accordingly.
+
+#### Test PHP ####
+
+Finally, let's check if nginx can process a PHP page. Before testing, make sure to restart nginx and PHP-FPM.
+
+On CentOS 7:
+
+ $ sudo systemctl restart nginx
+ $ sudo systemctl restart php-fpm
+
+On CentOS 6:
+
+ $ sudo service nginx restart
+ $ sudo service php-fpm restart
+
+Create a PHP file named test.php with the following content, and place it in /var/www/html/
+
+
+
+Open a web browser, and go to http:///test.php.
+
+
+
+If you see the above page, you are all set with the LEMP stack!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/install-lemp-stack-centos.html
+
+作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
+[1]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/open-port-firewall-centos-rhel.html
+[2]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-remi-repository-centos-rhel.html
+[3]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/set-default-timezone-php.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141029 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to open a port in the firewall on CentOS or RHEL.md b/sources/tech/20141029 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to open a port in the firewall on CentOS or RHEL.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c36dcac0e8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20141029 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to open a port in the firewall on CentOS or RHEL.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+[translating by KayGuoWhu]
+Linux FAQs with Answers--How to open a port in the firewall on CentOS or RHEL
+================================================================================
+> **Question**: I am running a web/file server on my CentOS box, and to access the server remotely, I need to modify a firewall to allow access to a TCP port on the box. What is a proper way to open a TCP/UDP port in the firewall of CentOS/RHEL?
+
+Out of the box, enterprise Linux distributions such as CentOS or RHEL come with a powerful firewall built-in, and their default firewall rules are pretty restrictive. Thus if you install any custom services (e.g., web server, NFS, Samba), chances are their traffic will be blocked by the firewall rules. You need to open up necessary ports on the firewall to allow their traffic.
+
+On CentOS/RHEL 6 or earlier, the iptables service allows users to interact with netfilter kernel modules to configure firewall rules in the user space. Starting with CentOS/RHEL 7, however, a new userland interface called firewalld has been introduced to replace iptables service.
+
+To check the current firewall rules, use this command:
+
+ $ sudo iptables -L
+
+
+
+Now let's see how we can update the firewall to open a port on CentOS/RHEL.
+
+### Open a Port on CentOS/RHEL 7 ###
+
+Starting with CentOS and RHEL 7, firewall rule settings are managed by firewalld service daemon. A command-line client called firewall-cmd can talk to this deamon to update firewall rules permanently.
+
+To open up a new port (e.g., TCP/80) permanently, use these commands.
+
+ $ sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
+ $ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
+
+Without "--permanent" flag, the firewall rule would not persist across reboots.
+
+### Open a Port on CentOS/RHEL 6 ###
+
+On CentOS/RHEL 6 or earlier, a iptables service is responsible for maintaining firewall rules.
+
+Use iptables command to open up a new TCP/UDP port in the firewall. To save the updated rule permanently, you need the second command.
+
+ $ sudo iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
+ $ sudo service iptables save
+
+Another way to open up a port on CentOS/RHEL 6 is to use a terminal-user interface (TUI) firewall client, named system-config-firewall-tui.
+
+ $ sudo system-config-firewall-tui
+
+Choose "Customize" button in the middle and press ENTER.
+
+
+
+If you are trying to update the firewall for any well-known service (e.g., web server), you can easily enable the firewall for the service here, and close the tool. If you are trying to open up any arbitrary TCP/UDP port, choose "Forward" button and go to a next window.
+
+
+
+Add a new rule by choosing "Add" button.
+
+
+
+Specify a port (e.g., 80) or port range (e.g., 3000-3030), and protocol (e.g., tcp or udp).
+
+
+
+Finally, save the updated configuration, and close the tool. At this point, the firewall will be saved permanently.
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/open-port-firewall-centos-rhel.html
+
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141029 Shell Scripting--Checking Conditions with if.md b/sources/tech/20141029 Shell Scripting--Checking Conditions with if.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..bcd368b908
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20141029 Shell Scripting--Checking Conditions with if.md
@@ -0,0 +1,147 @@
+>>> Translating by ThomazL
+Shell Scripting – Checking Conditions with if
+================================================================================
+In Bourne Shell if statement checks whether a condition is true or not. If so , the shell executes the block of code associated with the if statement. If the statement is not true , the shell jumps beyond the end of the if statement block & Continues on.
+
+### Syntax of if Statement : ###
+
+ if [ condition_command ]
+ then
+ command1
+ command2
+ ……..
+ last_command
+ fi
+
+#### Example: ####
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+ number=150
+ if [ $number -eq 150 ]
+ then
+ echo "Number is 150"
+ fi
+
+#### if-else Statement : ####
+
+In addition to the normal if statement , we can extend the if statement with an else block. The basic idea is that if the statement is true , then execute the if block. If the statement is false , then execute the else block.
+
+#### Syntax : ####
+
+ if [ condition_command ]
+ then
+ command1
+ command2
+ ……..
+ last_command
+ else
+ command1
+ command2
+ ……..
+ last_command
+ fi
+
+#### Example: ####
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+ number=150
+ if [ $number -gt 250 ]
+ then
+ echo "Number is greater"
+ else
+ echo "Number is smaller"
+ fi
+
+### If..elif..else..fi Statement (Short for else if) ###
+
+The Bourne shell syntax for the if statement allows an else block that gets executed if the test is not true. We can nest if statement , allowing for multiple conditions. As an alternative, we can use the elif construct , shot for else if.
+
+#### Syntax : ####
+
+ if [ condition_command ]
+ then
+ command1
+ command2
+ ……..
+ last_command
+ elif [ condition_command2 ]
+ then
+ command1
+ command2
+ ……..
+ last_command
+ else
+ command1
+ command2
+ ……..
+ last_command
+ fi
+
+#### Example : ####
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+ number=150
+ if [ $number -gt 300 ]
+ then
+ echo "Number is greater"
+ elif [ $number -lt 300 ]
+ then
+ echo "Number is Smaller"
+ else
+ echo "Number is equal to actual value"
+ fi
+
+### Nested if statements : ###
+
+If statement and else statement can be nested in a bash script. The keyword ‘fi’ shows the end of the inner if statement and all if statement should end with the keyword ‘fi’.
+
+Basic **syntax of nested** if is shown below :
+
+ if [ condition_command ]
+ then
+ command1
+ command2
+ ……..
+ last_command
+ else
+ if [ condition_command2 ]
+ then
+ command1
+ command2
+ ……..
+ last_command
+ else
+ command1
+ command2
+ ……..
+ last_command
+ fi
+ fi
+
+#### Example: ####
+
+ #!/bin/bash
+ number=150
+ if [ $number -eq 150 ]
+ then
+ echo "Number is 150"
+ else
+ if [ $number -gt 150 ]
+ then
+ echo "Number is greater"
+ else
+ echo "'Number is smaller"
+ fi
+ fi
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/shell-scripting-checking-conditions-with-if/
+
+作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141030 8 Tips to Solve Linux and Unix Systems Hard Disk Problmes Like Disk Full Or Can't Write to the Disk.md b/sources/tech/20141030 8 Tips to Solve Linux and Unix Systems Hard Disk Problmes Like Disk Full Or Can't Write to the Disk.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..1fbed0ced1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20141030 8 Tips to Solve Linux and Unix Systems Hard Disk Problmes Like Disk Full Or Can't Write to the Disk.md
@@ -0,0 +1,288 @@
+8 Tips to Solve Linux & Unix Systems Hard Disk Problmes Like Disk Full Or Can’t Write to the Disk
+================================================================================
+Can't write to the hard disk on a Linux or Unix-like systems? Want to diagnose corrupt disk issues on a server? Want to find out why you are getting "disk full" messages on screen? Want to learn how to solve full/corrupt and failed disk issues. Try these eight tips to diagnose a Linux and Unix server hard disk drive problems.
+
+
+
+### #1 - Error: No space left on device ###
+
+When the Disk is full on Unix-like system you get an error message on screen. In this example, I'm running [fallocate command][1] and my system run out of disk space:
+
+ $ fallocate -l 1G test4.img
+ fallocate: test4.img: fallocate failed: No space left on device
+
+The first step is to run the df command to find out information about total space and available space on a file system including partitions:
+
+ $ df
+
+OR try human readable output format:
+
+ $ df -h
+
+Sample outputs:
+
+ Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
+ /dev/sda6 117G 54G 57G 49% /
+ udev 993M 4.0K 993M 1% /dev
+ tmpfs 201M 264K 200M 1% /run
+ none 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
+ none 1002M 0 1002M 0% /run/shm
+ /dev/sda1 1.8G 115M 1.6G 7% /boot
+ /dev/sda7 4.7G 145M 4.4G 4% /tmp
+ /dev/sda9 9.4G 628M 8.3G 7% /var
+ /dev/sda8 94G 579M 89G 1% /ftpusers
+ /dev/sda10 4.0G 4.0G 0 100% /ftpusers/tmp
+
+From the df command output it is clear that /dev/sda10 has 4.0Gb of total space of which 4.0Gb is used.
+
+#### Fixing problem when the disk is full ####
+
+1.[Compress uncompressed log and other files][2] using gzip or bzip2 or tar command:
+
+ gzip /ftpusers/tmp/*.log
+ bzip2 /ftpusers/tmp/large.file.name
+
+2.Delete [unwanted files using rm command][3] on a Unix-like system:
+
+ m -rf /ftpusers/tmp/*.bmp
+
+3.Move files to other [system or external hard disk using rsync command][4]:
+
+ rsync --remove-source-files -azv /ftpusers/tmp/*.mov /mnt/usbdisk/
+ rsync --remove-source-files -azv /ftpusers/tmp/*.mov server2:/path/to/dest/dir/
+
+4.[Find out the largest directories or files eating disk space][5] on a Unix-like systesm:
+
+ du -a /ftpusers/tmp | sort -n -r | head -n 10
+ du -cks * | sort -rn | head
+
+5.[Truncate a particular file][6]. This is useful for log file:
+
+ truncate -s 0 /ftpusers/ftp.upload.log
+ ### bash/sh etc ##
+ >/ftpusers/ftp.upload.log
+ ## perl ##
+ perl -e'truncate "filename", LENGTH'
+
+6.Find and remove large files that are open but have been deleted on Linux or Unix:
+
+ ## Works on Linux/Unix/OSX/BSD etc ##
+ lsof -nP | grep '(deleted)'
+
+ ## Only works on Linux ##
+ find /proc/*/fd -ls | grep '(deleted)'
+
+To truncate it:
+
+ ## works on Linux/Unix/BSD/OSX etc all ##
+ > "/path/to/the/deleted/file.name"
+ ## works on Linux only ##
+ > "/proc/PID-HERE/fd/FD-HERE"
+
+### #2 - Is the file system is in read-only mode? ###
+
+You may end up getting an error such as follows when you try to create a file or save a file:
+
+ $ cat > file
+ -bash: file: Read-only file system
+
+Run mount command to find out if the file system is mounted in read-only mode:
+
+ $ mount
+ $ mount | grep '/ftpusers'
+
+To fix this problem, simply remount the file system in read-write mode on a Linux based system:
+
+ # mount -o remount,rw /ftpusers/tmp
+
+Another example, from my [FreeBSD 9.x server to remount / in rw mode][7]:
+
+ # mount -o rw /dev/ad0s1a /
+
+### #3 - Am I running out of inodes? ###
+
+Sometimes, df command reports that there is enough free space but system claims file-system is full. You need to check [for the inode][8] which identifies the file and its attributes on a file systems using the following command:
+
+ $ df -i
+ $ df -i /ftpusers/
+
+Sample outputs:
+
+ Filesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on
+ /dev/sda8 6250496 11568 6238928 1% /ftpusers
+
+So /ftpusers has 62,50,496 total inodes but only 11,568 are used. You are free to create another 62,38,928 files on /ftpusers partition. If 100% of your inodes are used, try the following options:
+
+- Find unwanted files and delete or move to another server.
+- Find unwanted large files and delete or move to another server.
+
+### #4 - Is my hard drive is dying? ###
+
+[I/O errors in log file (such as /var/log/messages) indicates][9] that something is wrong with the hard disk and it may be failing. You can check hard disk for errors using smartctl command, which is control and monitor utility for SMART disks under Linux and UNIX like operating systems. The syntax is:
+
+ smartctl -a /dev/DEVICE
+ # check for /dev/sda on a Linux server
+ smartctl -a /dev/sda
+
+You can also use "Disk Utility" to get the same information
+
+[][10]
+
+Fig. 01: Gnome disk utility (Applications > System Tools > Disk Utility)
+
+> **Note**: Don't expect too much from SMART tool. It may not work in some cases. Make backup on a regular basis.
+
+### #5 - Is my hard drive and server is too hot? ###
+
+High temperatures can cause server to function poorly. So you need to maintain the proper temperature of the server and disk. High temperatures can result into server shutdown or damage to file system and disk. [Use hddtemp or smartctl utility to find out the temperature of your hard on a Linux or Unix based system][11] by reading data from S.M.A.R.T. on drives that support this feature. Only modern hard drives have a temperature sensor. hddtemp supports reading S.M.A.R.T. information from SCSI drives too. hddtemp can work as simple command line tool or as a daemon to get information from all servers:
+
+ hddtemp /dev/DISK
+ hddtemp /dev/sg0
+
+Sample outputs:
+
+[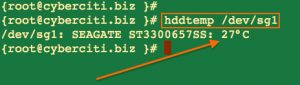][12]
+
+Fig.02: hddtemp in action
+
+You can use the smartctl command as follows too:
+
+ smartctl -d ata -A /dev/sda | grep -i temperature
+
+#### How do I get the CPU temperature? ####
+
+You can use Linux hardware monitoring tool such as [lm_sensor to get the cpu temperature on a Linux based][13] system:
+
+ sensors
+
+Sample outputs from Debian Linux server:
+
+[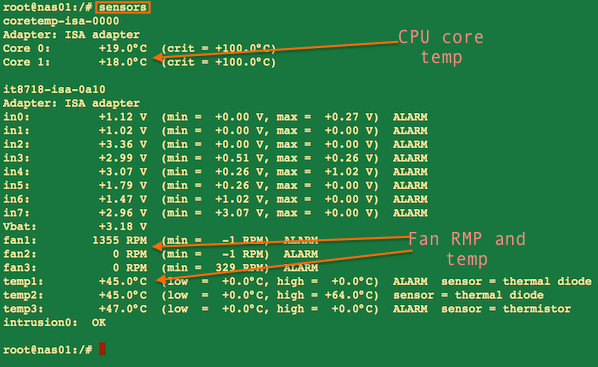][14]
+
+Fig.03: sensors command providing cpu core temperature and other info on a Linux
+
+### #6 - Dealing with corrupted file systems ###
+
+File system on server may be get corrupted due to a hard reboot or some other error such as bad blocks. You can [repair corrupted file systems with the following fsck command][15]:
+
+ umount /ftpusers
+ fsck -y /dev/sda8
+
+See [how to surviving a Linux filesystem failures][16] for more info.
+
+### #7 - Dealing with software RAID on a Linux ###
+
+To find the current status of a Linux software raid type the following command:
+
+ ## get detail on /dev/md0 raid ##
+ mdadm --detail /dev/md0
+
+ ## Find status ##
+ cat /proc/mdstat
+ watch cat /proc/mdstat
+
+Sample outputs:
+
+[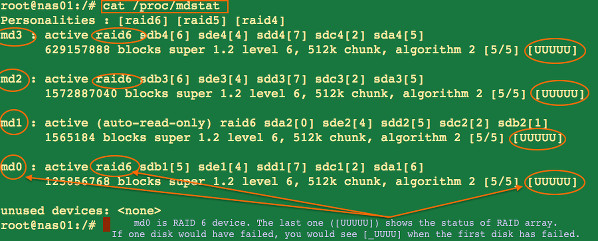][17]
+
+Fig. 04: Find the status of a Linux software raid command
+
+You need to replace a failed hard drive. You must u remove the correct failed drive. In this example, I'm going to replace /dev/sdb (2nd hard drive of RAID 6). It is not necessary to take the storage offline to repair the RAID on Linux. This only works if your server support hot-swappable hard disk:
+
+ ## remove disk from an array md0 ##
+ mdadm --manage /dev/md0 --fail /dev/sdb1
+ mdadm --manage /dev/md0 --remove /dev/sdb1
+
+ # Do the same steps again for rest of /dev/sdbX ##
+ # Power down if not hot-swappable hard disk: ##
+ shutdown -h now
+
+ ## copy partition table from /dev/sda to newly replaced /dev/sdb ##
+ sfdisk -d /dev/sda | sfdisk /dev/sdb
+ fdisk -l
+
+ ## Add it ##
+ mdadm --manage /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb1
+ # do the same steps again for rest of /dev/sdbX ##
+
+ # Now md0 will sync again. See it on screen ##
+ watch cat /proc/mdstat
+
+See our [tips on increasing RAID sync speed on Linux][18] for more information.
+
+### #8 - Dealing with hardware RAID ###
+
+You can use the samrtctl command or vendor specific command to find out the status of RAID and disks in your controller:
+
+ ## SCSI disk
+ smartctl -d scsi --all /dev/sgX
+
+ ## Adaptec RAID array
+ /usr/StorMan/arcconf getconfig 1
+
+ ## 3ware RAID Array
+ tw_cli /c0 show
+
+See your vendor specific documentation to replace a failed disk.
+
+### Monitoring disk health ###
+
+See our previous tutorials:
+
+1. [Monitoring hard disk health with smartd under Linux or UNIX operating systems][19]
+1. [Shell script to watch the disk space][20]
+1. [UNIX get an alert when disk is full][21]
+1. [Monitor UNIX / Linux server disk space with a shell scrip][22]
+1. [Perl script to monitor disk space and send an email][23]
+1. [NAS backup server disk monitoring shell script][24]
+
+### Conclusion ###
+
+I hope these tips will help you troubleshoot system disk issue on a Linux/Unix based server. I also recommend implementing a good backup plan in order to have the ability to recover from disk failure, accidental file deletion, file corruption, or complete server destruction:
+
+- [Debian / Ubuntu: Install Duplicity for encrypted backup in cloud][25]
+- [HowTo: Backup MySQL databases, web server files to a FTP server automatically][26]
+- [How To Set Red hat & CentOS Linux remote backup / snapshot server][27]
+- [Debian / Ubuntu Linux install and configure remote filesystem snapshot with rsnapshot incremental backup utility][28]
+- [Linux Tape backup with mt And tar command tutorial][29]
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/datacenter/linux-unix-bsd-osx-cannot-write-to-hard-disk/
+
+作者:[nixCraft][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/about-us
+[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-create-lage-files-with-dd-command/
+[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/howto/question/general/compress-file-unix-linux-cheat-sheet.php
+[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-linux-unix-delete-remove-file/
+[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-unix-bsd-appleosx-rsync-delete-file-after-transfer/
+[5]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/how-do-i-find-the-largest-filesdirectories-on-a-linuxunixbsd-filesystem/
+[6]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/truncate-large-text-file-in-unix-linux/
+[7]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-freebsd-remount-partition/
+[8]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/understanding-unixlinux-filesystem-inodes.html
+[9]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-find-out-if-harddisk-failing.html
+[10]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-find-out-if-harddisk-failing.html
+[11]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-monitor-hard-drive-temperature.html
+[12]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/datacenter/linux-unix-bsd-osx-cannot-write-to-hard-disk/attachment/hddtemp-on-rhel/
+[13]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-linux-get-sensors-information/
+[14]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/datacenter/linux-unix-bsd-osx-cannot-write-to-hard-disk/attachment/sensors-command-on-debian-server/
+[15]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/repairing-linux-ext2-or-ext3-file-system.html
+[16]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/surviving-a-linux-filesystem-failures.html
+[17]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/datacenter/linux-unix-bsd-osx-cannot-write-to-hard-disk/attachment/linux-mdstat-output/
+[18]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-raid-increase-resync-rebuild-speed.html
+[19]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/monitoring-hard-disk-health-with-smartd-under-linux-or-unix-operating-systems.html
+[20]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/shell-script-to-watch-the-disk-space.html
+[21]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/mac-osx-unix-get-an-alert-when-my-disk-is-full/
+[22]:http://bash.cyberciti.biz/monitoring/shell-script-monitor-unix-linux-diskspace/
+[23]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/howto-write-perl-script-to-monitor-disk-space.html
+[24]:http://bash.cyberciti.biz/backup/monitor-nas-server-unix-linux-shell-script/
+[25]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/duplicity-installation-configuration-on-debian-ubuntu-linux/
+[26]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/how-to-backup-mysql-databases-web-server-files-to-a-ftp-server-automatically.html
+[27]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/redhat-cetos-linux-remote-backup-snapshot-server/
+[28]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-rsnapshot-backup-howto/
+[29]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-tape-backup-with-mt-and-tar-command-howto/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141030 How to run SQL queries against Apache log files on Linux.md b/sources/tech/20141030 How to run SQL queries against Apache log files on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9ae1a5a76b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20141030 How to run SQL queries against Apache log files on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
+How to run SQL queries against Apache log files on Linux
+================================================================================
+One of the distinguishing features of Linux is that, under normal circumstances, you should be able to know what is happening and has happened on your system by analyzing one or more system logs. Indeed, system logs are the first resource a system administrator tends to look to while troubleshooting system or application issues. In this article, we will focus on the Apache access log files generated by Apache HTTP web server. We will explore an alternative way of analyzing Apache access logs using [asql][1], an open-source tool that allows one to run SQL queries against the logs in order to view the same information in a more friendly format.
+
+### Background on Apache Logs ###
+
+There are two kinds of Apache logs:
+
+- **Access log**: Found at /var/log/apache2/access.log (for Debian) or /var/log/httpd/access_log (for Red Hat). Contains records of every request served by an Apache web server.
+- **Error log**: Found at /var/log/apache2/error.log (for Debian) or /var/log/httpd/error_log (for Red Hat). Contains records of all error conditions reported by an Apache web server. Error conditions include, but are not limited to, 403 (Forbidden, usually returned after a valid request missing access credentials or insufficient read permissions), and 404 (Not found, returned when the requested resource does not exist).
+
+Although the verbosity of Apache access log file can be customized through Apache's configuration files, we will assume the default format in this article, which is as follows:
+
+ Remote IP - Request date - Request type - Response code - Requested resource - Remote browser (may also include operating system)
+
+So a typical Apache log entry looks like:
+
+ 192.168.0.101 - - [22/Aug/2014:12:03:36 -0300] "GET /icons/unknown.gif HTTP/1.1" 200 519 "http://192.168.0.10/test/projects/read_json/" "Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Ubuntu; Linux x86_64; rv:30.0) Gecko/20100101 Firefox/30.0"
+
+But what about Apache error log? Since error log entries dealing with particular requests have corresponding entries in the access log (which you can customize), you can use the access log file to obtain more information about error conditions (refer to example 5 for more details).
+
+That being said, please note that access log is a system-wide log file. To find the log files of virtual hosts, you may also need to check their corresponding configuration files (e.g., within /etc/apache2/sites-available/[virtual host name] on Debian).
+
+### Installing asql on Linux ###
+
+asql is written in Perl, and requires two Perl modules: a DBI driver for SQLite and GNU readline.
+
+#### Install asql on Debian, Ubuntu or their derivatives ####
+
+asql and its dependencies will automatically be installed with aptitude on Debian-based distributions.
+
+ # aptitude install asql
+
+#### Install asql on Fedora, CentOS or RHEL ####
+
+On CentOS or RHEL, you will need to enable [EPEL repository][2] first, and then run the commands below. On Fedora, proceed to the following commands directly.
+
+ # sudo yum install perl-DBD-SQLite perl-Term-ReadLine-Gnu
+ # wget http://www.steve.org.uk/Software/asql/asql-1.7.tar.gz
+ # tar xvfvz asql-1.7.tar.gz
+ # cd asql
+ # make install
+
+### How Does asql Work? ###
+
+As you can guess from the dependencies listed above, asql converts unstructured plain-text Apache log files into a structured SQLite database, which can be queried using standard SQL commands. This database can be populated with the contents of current and past log files - including compressed rotated logs such as access.log.X.gz. or access_log.old.
+
+First, launch asql from the command line with the following command
+
+ # asql
+
+You will be entering asql's built-in shell interface.
+
+
+
+Let's type help to list the available commands in the asql shell:
+
+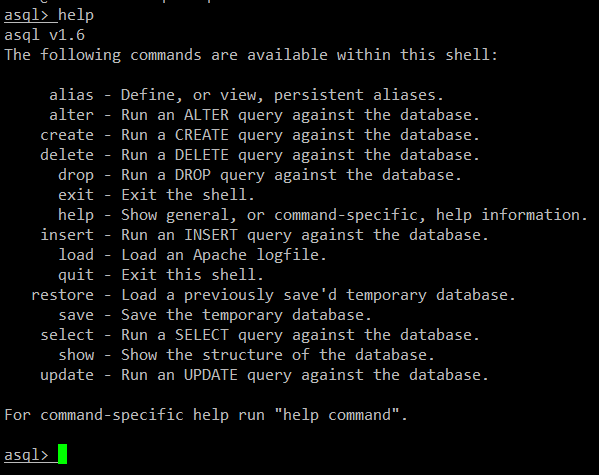
+
+We will begin by loading all the access logs in asql, which can be done with:
+
+ asql> load
+
+In case of Debian, the following command will do:
+
+ asql> load /var/log/apache2/access.*
+
+In case of CentOS/RHEL, use this command instead:
+
+ asql> load /var/log/httpd/access_log*
+
+When asql finishes loading access logs, we can start querying the database. Note that the database created after loading is "temporary," meaning that if you exit the asql shell, the database will be lost. If you want to preserve the database, you have to save it to a file first. We will see how to do that later (refer to examples 3 and 4).
+
+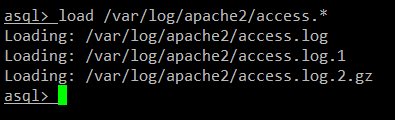
+
+The database contains a table named logs. The available fields in the logs table can be displayed using the show command:
+
+
+
+The .asql hidden file, which is stored in each user's home directory, records the history of the commands that were typed by the user in an asql shell. Thus, you can browse through it using the arrow keys, and repeat previous commands by just pressing ENTER when you find the right one.
+
+### SQL Query Examples with asql ###
+
+Here a few examples of running SQL queries against Apache log files with asql.
+
+**Example 1**: Listing the request sources / dates and HTTP status codes returned during the month of October 2014.
+
+ SELECT source, date, status FROM logs WHERE date >= '2014-10-01T00:00:00' ORDER BY source;
+
+
+
+**Example 2**: Displaying the total size (in bytes) of requests served per client in descending order.
+
+ SELECT source,SUM(size) AS Number FROM logs GROUP BY source ORDER BY Number DESC;
+
+
+
+**Example 3**: Saving the database to [filename] in the current working directory.
+
+ save [filename]
+
+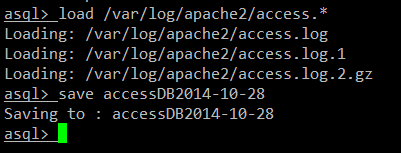
+
+This allows us to avoid the need for waiting while the log parsing is performed with the load command as shown earlier.
+
+**Example 4**: Restoring the database in a new asql session after exiting the current one.
+
+ restore [filename]
+
+
+
+**Example 5**: Returning error conditions logged in the access file. In this example, we will display all the requests that returned a 403 (access forbidden) HTTP code.
+
+ SELECT source,date,status,request FROM logs WHERE status='403' ORDER BY date
+
+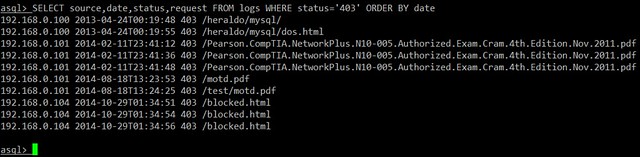
+
+This goes to show that although asql only analyzes access logs, we can use the status field of a request to display requests with error conditions.
+
+### Summary ###
+
+We have seen how asql can help us analyze Apache logs and present the results in a user friendly output format. Although you could obtain similar results by using command line utilities such as cat in conjunction with grep, uniq, sort, and wc (to name a few), in comparison asql represents a Swiss army knife due to the fact that it allows us to use standard SQL syntax to filter the logs according to our needs.
+
+Feel free to leave your questions or comments below. Hope it helps.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/sql-queries-apache-log-files-linux.html
+
+作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/gabriel
+[1]:http://www.steve.org.uk/Software/asql/
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141030 Test drive Linux with nothing but a flash drive.md b/sources/tech/20141030 Test drive Linux with nothing but a flash drive.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..84d5b7a9d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20141030 Test drive Linux with nothing but a flash drive.md
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
+Test drive Linux with nothing but a flash drive
+================================================================================
+
+Image by : Opensource.com
+
+Maybe you’ve heard about Linux and are intrigued by it. So intrigued that you want to give it a try. But you might not know where to begin.
+
+You’ve probably done a bit of research online and have run across terms like dual booting and virtualization. Those terms might mean nothing to you, and you’re definitely not ready to sacrifice the operating system that you’re currently using to give Linux a try. So what can you do?
+
+If you have a USB flash drive lying around, you can test drive Linux by creating a live USB. It’s a USB flash drive that contains an operating system that can start from the flash drive. It doesn’t take much technical ability to create one. Let’s take a look at how to do that and how to run Linux using a live USB.
+
+### What you’ll need ###
+
+Aside from a desktop or laptop computer, you’ll need:
+
+- A blank USB flash drive—preferably one that has a capacity of 4 GB or more.
+- An [ISO image][1] (an archive of the contents of a hard disk) of the Linux distribution that you want to try. More about this in a moment.
+- An application called [Unetbootin][2], an open source tool, cross platform tool that creates a live USB. You don’t need to be running Linux to use it. In the instructions that below, I’m running Unetbootin on a MacBook.
+
+### Getting to work ###
+
+Plug your flash drive into a USB port on your computer and then fire up Unetbootin. You’ll be asked for the password that you use to log into your computer.
+
+
+
+Remember the ISO image that was mentioned a few moments ago? There are two ways you can get one: either by downloading it from the website of the Linux distribution that you want to try, or by having Unetbootin download it for you. To do that latter, click **Select Distribution** at the top of the window, choose the distribution that you want to download, and then click **Select Version** to select the version of the distribution that you want to try.
+
+
+
+Or, you can download the distribution yourself. Usually, the Linux distributions that I want to try aren’t in the list. If you go the second route, click **Disk image** and then click the button to search for the .iso file that you downloaded.
+
+Notice the **Space used to preserve files across reboots (Ubuntu only)** option? If you’re testing Ubuntu or one of its derivatives (like Lubuntu or Xubuntu), you can set aside a few megabytes of space on your flash drive to save files like web browser bookmarks or documents that you create. When you load Ubuntu from the flash drive again, you can reuse those files.
+
+
+
+Once the ISO image is loaded, click **OK**. It takes anywhere from a couple of minutes to 10 minutes for Unetbootin to create the live USB.
+
+
+
+### Testing out the live USB ###
+
+This is the point where you have to embrace your inner geek a bit. Not too much, but you will be taking a peek into the innards of your computer by going into the [BIOS][3]. Your computer’s BIOS starts various bits of hardware and controls where the computer’s operating system starts, or boots, from.
+
+The BIOS usually looks for the operating system in this order (or something like it): hard drive, then CD-ROM or DVD drive, and then an external drive. You’ll want to change that order so that the external drive (in this case, your live USB) is the one that the BIOS checks first.
+
+To do that, restart your computer with the flash drive plugged into a USB port. When you see the message **Press F2 to enter setup**, do just that. On some computers, the key might be F10.
+
+In the BIOS, use the right arrow key on your keyboard to navigate to the **Boot** menu. You’ll see a list of drives on your computer. Use the down arrow key on your keyboard to navigate to the item labeled **USB HDD** and then press **F6** to move that item to the top of the list.
+
+Once you’ve done that, press **F10** to save the changes. You’ll be kicked out of the BIOS and your computer will start up. After a short amount of time, you’ll be presented with a menu listing the options for starting the Linux distribution you’re trying out. Select **Run without installing** (or the menu item closest to it).
+
+Once the desktop loads, you can connect to a wireless or wired network, browse the web, and give the pre-installed software a whirl. You can also check to see if, for example, your printer or scanner works with the Linux distribution you’re testing. If you really, really want to you can also fiddle at the command line.
+
+### What to expect ###
+
+Depending on the Linux distribution you’re testing and the speed of the flash drive you’re using, the operating system might take longer to load and it might run a bit slower than it would if it was installed on your hard drive.
+
+As well, you’ll only have the basic software that the Linux distribution packs out of the box. You generally get a web browser, a word processor, a text editor, a media player, an image viewer, and a set of utilities. That should be enough to give you a feel for what it’s like to use Linux.
+
+If you decide that you like using Linux, you can install it from the flash drive by double clicking on the installer.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/life/14/10/test-drive-linux-nothing-flash-drive
+
+作者:[Scott Nesbitt][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/scottnesbitt
+[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_image
+[2]:http://unetbootin.sourceforge.net/
+[3]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BIOS
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/sources/tech/20141030 rsync Command to Exclude a List of Files and Directories in Linux.md b/sources/tech/20141030 rsync Command to Exclude a List of Files and Directories in Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..23bec502f8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20141030 rsync Command to Exclude a List of Files and Directories in Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
+rsync Command to Exclude a List of Files and Directories in Linux
+================================================================================
+**rsync** is a very useful and popular linux tool being used for backup and restoring files, but also for comparing and syncing them. We already shown you in the past [how to use rsync command in linux with examples][1] and today we will add a few more useful tricks you can use rsync at.
+
+### Exclude a list of files and directories ###
+
+Sometimes when we do large syncs we may wish to exclude a list of files and directories from syncing, in general files that can't by synced like device files and some system files, or files that would take up unnecessary disk space like temporary or cache files.
+
+First let's make a file called "excluded" (you can name it whatever you wish) and write each folder or file we would like to exclude on a separate line like this. For our example if you wish to do a full backup of your root partition you should exclude devices directories that get created at boot time and directories that hold temporary files, your list may look like this:
+
+
+
+Then you can run the following command to backup your system:
+
+ $ sudo rsync -aAXhv --exclude-from=excluded / /mnt/backup
+
+
+
+### Exclude files from the command line ###
+
+You can also exclude files directly from the command line, this is useful when you have a smaller number of files to exclude and you wish to include this in a script or crontab and don't want your script or cron to depend on another file to run successful.
+
+For example if you wish to sync /var to a backup directory but you don't wish to include cache and tmp folder that usualy don't hold important content between restarts you can use the following command:
+
+ $ sudo rsync -aAXhv --exclude={"/var/cache","/var/tmp"} /var /home/adrian/var
+
+
+
+This command will be easy to use in any script or cron and will not depend on another file.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/exclude-files-rsync-examples/
+
+作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/adriand/
+[1]:http://linoxide.com/how-tos/rsync-copy/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/news/20141017 Linus Torvalds Regrets Alienating Developers with Strong Language.md b/translated/news/20141017 Linus Torvalds Regrets Alienating Developers with Strong Language.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 09d4a7d831..0000000000
--- a/translated/news/20141017 Linus Torvalds Regrets Alienating Developers with Strong Language.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
-Linus Torvalds对于骂那些开发者感到后悔
-================================================================================
-> 他没有提到任何人的名字,但是这像一次道歉
-
-**Linus Torvalds在前几天的欧洲LinuxCon和CloudOpen大会上做了讲话,这次大会由Linux基金会组织并且汇聚了开源世界的所有大佬。他回答了很多问题,也谈到了他在邮件发送清单里使用粗话的事情。**
-
-Linus Torvalds被认为是Linux内核的创造者和最新的Linux开发版的维护者。他确保我们几乎每个星期都会得到一个新的RC内核并且涉及发生在邮件发送清单中的对话里,他口不择言地用粗话大骂一些开发者们。
-
-最近出现了一个问题,就是他在做了一些苛刻的评论之后[决定从指定的开发者的手中阉割掉一些代码][1],这种事件在新闻里也报道过。大家都知道Linus很招人厌烦,尤其是当内核开发者为了修复内核中的一些问题而破坏了用户空间。同样的事情就发生在这种情况下,他基本上已经把那个家伙给气疯了。
-
-### 这是他最接近道歉意味的一次谈话 ###
-
-以前Linus Torvalds从不真正去特地谈论一些事情,大家也在稳步地前进。但是最近一个systemd开发者谈到了在开源社区充斥着粗话并且点名提到了Linus Torvalds。他不太知道去道歉,所以这次在LinuxCon大会上的这次“认错”是他跨出的一大步。主持人询问他在过去的23年里所做过的单一的决定。
-
-"从技术角度来看,没有一个单一的决定向来就是重要的...这个问题慢慢地疏远用户和开发者而我却恰恰很擅长这个。我说了粗话。但是我不想再修复单独实例了,都是一坨坨狗X一样的东西。"
-
-"其中一个原因是我们有说粗话的传统,很多人觉得倒胃口,当有强烈提议欲的技术人员和在技术上拥有巨大推动力的上级时,你就会把这些建议想成了一堆堆粗话了。" Linus Torvalds [如是说][2] 。
-
-他没提到任何人或者任何事件的名字,但很像是对于一位名为Leonart Pottering的systemd开发者挑起事端的回应,看上去就是针对这起事件。
-
-Linux内核3.18 RC1也在上周发布了,我们又有新东西玩了。
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Linus-Torvalds-Regrets-Alienating-Developers-with-Strong-Language-462191.shtml
-
-作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
-译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
-[1]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Linus-Torvalds-Block-All-Code-from-Systemd-Developer-for-the-Linux-Kernel-435714.shtml
-[2]:http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/791788-linus-torvalds-best-quotes-from-linuxcon-europe-2014
diff --git a/translated/news/20141017 Linus Torvalds' Best Quotes from LinuxCon Europe 2014.md b/translated/news/20141017 Linus Torvalds' Best Quotes from LinuxCon Europe 2014.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..986f5a3730
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/news/20141017 Linus Torvalds' Best Quotes from LinuxCon Europe 2014.md
@@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
+2014年欧洲LinuxCon大会Linus Torvalds的最佳语录
+================================================================================
+
+
+在今年的10月15日星期三,Linux的创造者Linus Torvalds出席了欧洲LinuxCon和CloudOpen大会并回答了英特尔的Linux及开源技术专家Dirk Hohndel提出的问题。
+
+Linus Torvalds在那天的 [欧洲LinuxCon和CloudOpen大会][1] 上说,从他首次创造出Linux操作系统到现在的23年里,他没后悔过任何他做过的技术决策。
+
+“技术问题,甚至是完全错误的技术问题,你也可以之后再去修复它。” Torvalds说。
+
+
+
+他还说,尽管这些个人问题和异议在社区里“日益繁荣”,但是这些人或许能创造出最好的技术。
+
+他本人就是这样的,然而,他对他在内核邮件列表中用粗话对待开发者和用户的事情感到遗憾。但是彼此间的关系不可能那么轻易就缓和。
+
+社区里的那些人能创造出最好的技术同样也是Torvalds的终极目标和期望。
+
+在英特尔的Linux及开源技术专家Dirk Hohndel的问答环节里,Torvalds 谈了社区里的一些现状和内核开发进展,谈了怎么成为一名内核开发者以及Linux的未来。以下是对话中的一些闪光点。
+
+**1.** “在过去的几年里,我们开发的速度真的没有慢下来。每个版本我们都能从超过1000个人中得到大约100000个补丁,最终效果自然是非常好的。”
+
+**2.** Dirk Hohndel: “你说你希望不只一个子系统的维护人员考虑对x86模型产生兴趣,你是怎么把自己的建议应用到实际中的?
+
+Torvalds: “某一天我可能不得不这么做。目前我还没有收到关于不主动的任何投诉。主动是一个内核开发者最重要的东西,不论水平档次...迄今为止,一定程度上要感谢Git,我才能一直保持着前进的动力。”
+
+**3.** “很多人都想要得到市场份额数,包括很多用户,因为那是体现自我价值的一种方式。就我来说,对Linux最重要的事情之一,就是拥有一个一直在不停测试新内核的大社区,这是支持我们处理大量硬件问题的唯一办法。”
+
+**4.** Hohndel: “如果你能改变在过去23年里尼做过的一个决策,你会怎么做?”
+
+Torvalds: “从技术角度来看,没有哪个决定重要到这个程度...有个问题是慢慢地疏远了用户和开发者,而我却恰恰很擅长这个。我说了粗话,但是这不是我想要改变的某一个决定,这些粗话应该有所限制。”
+
+**5.** “大多数人即使他们不一定彼此喜欢,但会尊重他们写出的代码。对于Linux来说这是很重要的一部分。真正重要的是大家都在尽自己所能产出最佳的代码。”
+
+**6.** “在互联网上没人能察觉到渺小的你。”
+
+**7.** “我们说粗话这个传统导致很多人倒胃口,其中有一个原因是当有强烈的意愿和推动力的技术人员要做一些技术上的进步时,你就需要用一些强烈的语言来表达你的意愿。”
+
+**8.** Hohndel: “你跟那个想成为下一个Linus的学生是怎么说的?”
+
+Torvalds: “寻找能让你充满热情的事情并去完成它。”
+
+**9.** “成为一个维护人员很容易,你只需要无限的时间并且回复人们的邮件就行。”
+
+**10.** Hohndel: “给Linux的未来做个大胆的预测吧。”
+
+Torvalds: “我能做的一个最大的猜测,就是我可能会一周更新一次RC1版本。”
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/791788-linus-torvalds-best-quotes-from-linuxcon-europe-2014
+
+作者:[Libby Clark][a]
+译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/41373/catid/200-libby-clark
+[1]:http://events.linuxfoundation.org/events/linuxcon-europe
diff --git a/translated/share/20141027 Handy Disk Image Tools.md b/translated/share/20141027 Handy Disk Image Tools.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4f96bccede
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/share/20141027 Handy Disk Image Tools.md
@@ -0,0 +1,168 @@
+不得不说的磁盘镜像工具
+================================================================================
+磁盘镜像包括整个磁盘卷的文件或者是全部的存储设备的数据,比如说硬盘,光盘(DVD,CD,蓝光光碟),磁带机,USB闪存,软盘。一个完整的磁盘镜像应该像在原来的存储设备上一样完整、准确,包括数据和结构信息。
+
+磁盘镜像文件格式可以是开放的标准,像ISO格式的光盘镜像,或者是专有的特别的软件应用程序。"ISO"这个名字来源于用CD存储的ISO 9660文件系统。但是,当用户转向Linux的时候,经常遇到这样的问题,需要把专有的的镜像格式转换为开放的格式。
+
+磁盘镜像有很多不同的用处,像烧录光盘,系统备份,数据恢复,硬盘克隆,电子取证和提供操作系统(即LiveCD/DVDs)。
+
+有很多不同非方法可以把ISO镜像挂载到Linux系统下。强大的mount 命令给我们提供了一个简单的解决方案。但是如果你需要很多工具来操作磁盘镜像,你可以试一试下面的这些完美的开源工具。
+
+很多工具还没有看到最新的版本,所以如果你正在寻找一个很好用的开源工具,你也可以加入,一起来为开源做出一点贡献。
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+Furius ISO Mount是一个简单易用的开源应用程序用来挂载镜像文件,它支持直接打开ISO,IMG,BIN,MDF和NRG格式的镜像而不用把他们烧录到磁盘。
+
+特性:
+
+- 支持自动挂载ISO, IMG, BIN, MDF and NRG镜像文件
+- 支持通过loop 挂载 UDF 镜像
+- 自动在根目录创建挂载点
+- 自动解挂镜像文件
+- 自动删除挂载目录,并返回到主目录之前的状态
+- 自动存档最近10次挂载历史
+- 支持挂载多个镜像文件
+- 支持烧录ISO文件及IMG文件到光盘
+- 支持MD5校验和SHA1校验
+- 自动检索之前解挂的镜像
+- 自动创建手动挂载和解挂的日志文件
+- 语言支持(目前支持保加利亚语,中文(简体),捷克语,荷兰语,法语,德语,匈牙利语,意大利语,希腊语,日语,波兰语,葡萄牙语,俄语,斯洛文尼亚语,西班牙语,瑞典语和土耳其语)
+
+- 项目网址: [launchpad.net/furiusisomount/][1]
+- 开发者: Dean Harris (Marcus Furius)
+- 许可: GNU GPL v3
+- 版本号: 0.11.3.1
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+fuseiso 是用来挂载ISO文件系统的一个开源的安全模块。
+
+使用FUSE,我们完全可以在用户空间里运行一个完整的文件系统。
+
+特性:
+
+- 支持读ISO,BIN和NRG镜像,包括ISO9660文件系统
+- 支持普通的ISO9660级别1和级别2
+- 支持一些常用的扩展,想Joliet,RockRidge和zisofs
+- 支持非标准的镜像,包括CloneCD's IMGs 、Alcohol 120%'s MDFs 因为他们的格式看起来恰好像BIN镜像一样
+
+- 项目网址: [sourceforge.net/projects/fuseiso][2]
+- 开发者: Dmitry Morozhnikov
+- 许可: GNU GPL v2
+- 版本号: 20070708
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+iat(Iso9660分析工具)是一个通用的开源工具,能够检测很多不同镜像格式文件的结构,包括BIN,MDF,PDI,CDI,NRG和B5I,并转化成ISO-9660格式.
+
+特性:
+
+- 支持读(输入)NRG,MDF,PDI,CDI,BIN,CUE 和B5I镜像
+- 支持用cd 刻录机直接烧录光盘镜像
+- 输出信息包括:进度条,块大小,ECC扇形分区(大小),头分区(大小),镜像偏移地址等等
+
+- 项目网址: [sourceforge.net/projects/iat.berlios][3]
+- 开发者: Salvatore Santagati
+- 许可: GNU GPL v2
+- 版本号: 0.1.3
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+AcetoneISO 是一个功能丰富的开源图形化应用程序,用来挂载和管理CD/DVD镜像。
+
+当你打开这个程序,你就会看到一个图形化的文件管理器用来挂载镜像文件,包括专有的镜像格式,也包括像ISO, BIN, NRG, MDF, IMG 等等,并且允许您执行一系列的动作。
+
+AcetoneISO是用QT 4写的,也就是说,对于基于QT的桌面环境能很好的兼容,像KDE,LXQT或是Razor-qt。
+
+这个软件适用于所有正在寻找Linux版本的Daemon Tools的人。
+
+特性:
+
+- 支持挂载大多数windowns 镜像,在一个简洁易用的界面
+- 支持所有镜像格式转换到ISO,或者是从中提取内容。
+- 支持加密,压缩,解压任何类型的镜像
+- 支持转换DVD成xvid avi,支持任何格式的转换成xvid avi
+- 支持从录像里提取声音
+- 支持从不同格式中提取镜像文件,包括bin mdf nrg img daa dmg cdi b5i bwi pdi
+- 支持用Kaffeine / VLC / SMplayer播放DVD镜像,可以从Amazon 自动下载。
+- 支持从文件夹或者是CD/DVD生成ISO镜像
+- 支持文件MD5校验,或者是生成一个MD5校验码
+- 支持计算镜像的ShaSums,以128,256和384位的速度
+- 支持加密,解密一个镜像文件
+- 支持以M字节的速度,分开、合并镜像
+- 支持高比例压缩镜像成7z 格式
+- 支持翻录PSX CD成BIN格式,以便在ePSXe/pSX模拟器里运行
+- 支持修复CUE文件为BIN和IMG格式
+- 支持把MAC OS的DMG镜像转换成可挂载的镜像
+- 支持从指定的文件夹中挂载镜像
+- 支持创建数据库来管理一个大的镜像集合
+- 支持从CD/DVD 或者是ISO镜像中提取启动文件
+- 支持备份CD成BIN镜像
+- 支持简单快速的把DVD翻录成Xvid AVI
+- 支持简单快速的把常见的视频(avi, mpeg, mov, wmv, asf)转换成Xvid AVI
+- 支持简单快速的把FLV 换换成AVI 格式
+- 支持从YouTube和一些视频网站下载视频
+- 支持提取一个有密码的RAR存档
+- 支持转换任何的视频到索尼便携式PSP上
+- 国际化的语言支持支持(英语,意大利语,波兰语,西班牙语,罗马尼亚语,匈牙利语,德语,捷克语和俄语)
+
+- 项目网址: [sourceforge.net/projects/acetoneiso][4]
+- 开发者: Marco Di Antonio
+- 许可: GNU GPL v3
+- 版本号: 2.3
+
+----------
+
+
+
+
+
+ISO Master是一个开源、易用的、图形化CD 镜像编辑器,适用于Linux 和BSD 。可以从ISO 里提取文件,给ISO 添加文件,创建一个可引导的ISO,这些都是在一个可视化的用户界面完成的。可以打开ISO,NRG 和一些MDF文件,但是只能保存成ISO 格式。
+
+ISO Master 是基于bkisofs 创建的,一个简单、稳定的阅读库,修改和编写ISO 镜像,支持Joliet, RockRidge 和EL Torito扩展,
+
+特性:
+
+- 支持读ISO 格式文件(ISO9660, Joliet, RockRidge 和 El Torito),大多数的NRG 格式文件和一些单向的MDF文件,但是,只能保存成ISO 格式
+- 创建和修改一个CD/DVD 格式文件
+- 支持CD 格式文件的添加或删除文件和目录
+- 支持创建可引导的CD/DVD
+- 国际化的支持
+
+- 项目网址: [www.littlesvr.ca/isomaster/][5]
+- 开发者: Andrew Smith
+- 许可: GNU GPL v2
+- 版本号: 1.3.11
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20141025082352476/DiskImageTools.html
+
+作者:Frazer Kline
+译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:https://launchpad.net/furiusisomount/
+[2]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/fuseiso/
+[3]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/iat.berlios/
+[4]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/acetoneiso/
+[5]:http://www.littlesvr.ca/isomaster/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/talk/20140915 10 Open Source Cloning Software For Linux Users.md b/translated/talk/20140915 10 Open Source Cloning Software For Linux Users.md
index 9dddef3570..1fef50289f 100644
--- a/translated/talk/20140915 10 Open Source Cloning Software For Linux Users.md
+++ b/translated/talk/20140915 10 Open Source Cloning Software For Linux Users.md
@@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ Clonezilla 是一个基于 Ubuntu 和 Debian 的 Live CD。它可以像 Windows

-### 2. [Redo Backup][2]:###
+### 2. [Redo Backup][2]:###
Redo Backup 是另一个用来方便地克隆磁盘的 Live CD。它是自由和开源的软件,使用 GPL 3 许可协议授权。它的主要功能和特点包括从 CD 引导的简单易用的 GUI、无需安装,可以恢复 Linux 和 Windows 等系统、无需登陆访问文件,以及已删除的文件等。
diff --git a/translated/tech/20141008 The Why and How of Ansible and Docker.md b/translated/tech/20141008 The Why and How of Ansible and Docker.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..748d7eb15b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20141008 The Why and How of Ansible and Docker.md
@@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
+Ansible和Docker的作用和用法
+================================================================================
+在 [Docker][1] 和 [Ansible][2] 的技术社区内存在着很多好玩的东西,我希望在你阅读完这篇文章后也能获取到我们对它们的那种热爱。当然,你也会收获一些实践知识,那就是如何通过部署 Ansible 和 Docker 来为 Rails 应用搭建一个完整的服务器环境。
+
+也许有人会问:你怎么不去用 Heroku?首先,我可以在任何供应商提供的主机上运行 Docker 和 Ansible;其次,相比于方便性,我更偏向于喜欢灵活性。我可以在这种组合中运行任何程序,而不仅仅是 web 应用。最后,我骨子里是一个工匠,我非常理解如何把零件拼凑在一起工作。Heroku 的基础模块是 Linux Container,而 Docker 表现出来的多功能性也是基于这种技术。事实上,Docker 的其中一个座右铭是:容器化是新虚拟化技术。
+
+### 为什么使用 Ansible? ###
+
+我重度使用 Chef 已经有4年了(LCTT:Chef 是与 puppet 类似的配置管理工具),**基础设施即代码**的观念让我觉得非常无聊。我花费大量时间来管理代码,而不是管理基础设施本身。不论多小的改变,都需要相当大的努力来实现它。使用 [Ansible][3],你可以一手掌握拥有可描述性数据的基础架构,另一只手掌握不同组件之间的交互作用。这种更简单的操作模式让我把精力集中在如何将我的技术设施私有化,提高了我的工作效率。与 Unix 的模式一样,Ansible 提供大量功能简单的模块,我们可以组合这些模块,达到不同的工作要求。
+
+除了 Python 和 SSH,Ansible 不再依赖其他软件,在它的远端主机上不需要部署代理,也不会留下任何运行痕迹。更厉害的是,它提供一套内建的、可扩展的模块库文件,通过它你可以控制所有:包管理器、云服务供应商、数据库等等等等。
+
+### 为什么要使用 Docker? ###
+
+[Docker][4] 的定位是:提供最可靠、最方便的方式来部署服务。这些服务可以是 mysqld,可以是 redis,可以是 Rails 应用。先聊聊 git,它的快照功能让它可以以最有效的方式发布代码,Docker 的处理方法与它类似。它保证应用可以无视主机环境,随心所欲地跑起来。
+
+一种最普遍的误解是人们总是把 Docker 容器看成是一个虚拟机,当然,我表示理解你们的误解。Docker 满足[单一功能原则][5],在一个容器里面只跑一个进程,所以一次修改只会影响一个进程,而这些进程可以被重用。这种模型参考了 Unix 的哲学思想,当前还处于试验阶段,并且正变得越来越稳定。
+
+### 设置选项 ###
+
+不需要离开终端,我就可以使用 Ansible 来生成以下实例:Amazon Web Services,Linode,Rackspace 以及 DigitalOcean。如果想要更详细的信息,我于1分25秒内在位于阿姆斯特丹的2号数据中心上创建了一个 2GB 的 DigitalOcean 虚拟机。另外的1分50秒用于系统配置,包括设置 Docker 和其他个人选项。当我完成这些基本设定后,就可以部署我的应用了。值得一提的是这个过程中我没有配置任何数据库或程序开发语言,Docker 已经帮我把应用所需要的事情都安排好了。
+
+Ansible 通过 SSH 为远端主机发送命令。我保存在本地 ssh 代理上面的 SSH 密钥会通过 Ansible 提供的 SSH 会话分享到远端主机。当我把应用代码从远端 clone 下来,或者上传到远端时,我就不再需要提供 git 所需的证书了,我的 ssh 代理会帮我通过 git 主机的身份验证程序的。
+
+### Docker 和应用的依赖性 ###
+
+我发现有一点挺有意思的:大部分开发者非常了解他们的应用需要什么版本的编程语言,这些语言依赖关系有多种形式:Python 的包、Ruby 的打包系统 gems、node.js 的模块等等,但与数据库或消息队列这种重要的概念相比起来,这些语言就处于很随便的境地了——随便给我个编程语言环境,我都能把数据库和消息队列系统跑起来。我认为这是 DevOps 运动(它旨在促进开发与运维团队的和谐相处)的动机之一,开发者负责搭建应用所需要的环境。Docker 使这个任务变得简单明了直截了当,它为现有环境加了实用的一层配置。
+
+我的应用依赖于 MySQL 5.5和 Redis 2.8,依赖关系放在“.docker_container_dependencies”文件里面:
+
+ gerhard/mysql:5.5
+ gerhard/redis:2.8
+
+Ansible 会查看这个文件,并且通知 Docker 加载正确的镜像,然后在容器中启动。它还会把这些服务容器链接到应用容器。如果你想知道 Docker 容器的链接功能是怎么工作的,可以参考[Docker 0.6.5 发布通知][6].
+
+我的应用包括一个 Dockerfile,它详细指定了 Ruby Docker 镜像的信息,这里面的步骤能够保证把正确的 Ruby 版本加载到镜像中。
+
+ FROM howareyou/ruby:2.0.0-p353
+
+ ADD ./ /terrabox
+
+ RUN \
+ . /.profile ;\
+ rm -fr /terrabox/.git ;\
+ cd /terrabox ;\
+ bundle install --local ;\
+ echo '. /.profile && cd /terrabox && RAILS_ENV=test bundle exec rake db:create db:migrate && bundle exec rspec' > /test-terrabox ;\
+ echo '. /.profile && cd /terrabox && export RAILS_ENV=production && rake db:create db:migrate && bundle exec unicorn -c config/unicorn.rails.conf.rb' > /run-terrabox ;\
+ # END RUN
+
+ ENTRYPOINT ["/bin/bash"]
+ CMD ["/run-terrabox"]
+
+ EXPOSE 3000
+
+第一步是复制应用的所有代码到 Docker 镜像,加载上一个镜像的全局环境变量。这个例子中的 Ruby Docker 镜像会加载 PATH 配置,这个配置能确保镜像加载正确的 Ruby 版本。
+
+接下来,删除 git 历史,Docker 容器不需要它们。我安装了所有 Ruby 的 gems,创建一个名为“/test-terrabox”的命令,这个命令会被名为“test-only”的容器执行。这个步骤的目的是能正确解决应用和它的依赖关系,让 Docker 容器正确链接起来,保证在真正的应用容器启动前能通过所有测试项目。
+
+CMD 这个步骤是在新的 web 应用容器启动后执行的。在测试环节结束后马上就执行`/run-terrabox`命令进行编译。
+
+最后,Dockerfile 为应用指定了一个端口号,将容器内部端口号为3000的端口映射到主机(运行着 Docker 的机器)的一个随机分配的端口上。当 Docker 容器里面的应用需要响应来自外界的请求时,这个端口可用于反向代理或负载均衡。
+
+### Docker 容器内运行 Rails 应用 ###
+
+没有本地 Docker 镜像,从零开始部署一个中级规模的 Rails 应用大概需要100个 gems,进行100次整体测试,在使用2个核心实例和2GB内存的情况下,这些操作需要花费8分16秒。装上 Ruby、MySQL 和 Redis Docker 镜像后,部署应用花费了4分45秒。另外,如果从一个已存在的主应用镜像编译出一个新的 Docker 应用镜像出来,只需花费2分23秒。综上所述,部署一套新的 Rails 应用,解决其所有依赖关系(包括 MySQL 和 Redis),只需花我2分钟多一点的时间就够了。
+
+需要指出的一点是,我的应用上运行着一套完全测试套件,跑完测试需要花费额外1分钟时间。尽管是无意的,Docker 可以变成一套简单的持续集成环境,当测试失败后,Docker 会把“test-only”这个容器保留下来,用于分析出错原因。我可以在1分钟之内和我的客户一起验证新代码,保证不同版本的应用之间是完全隔离的,同操作系统也是隔离的。传统虚拟机启动系统时需要花费好几分钟,Docker 容器只花几秒。另外,一旦一个 Dockedr 镜像编译出来,并且针对我的某个版本的应用的测试都被通过,我就可以把这个镜像提交到 Docker 私服 Registry 上,可以被其他 Docker 主机下载下来并启动一个新的 Docker 容器,而这不过需要几秒钟时间。
+
+### 总结 ###
+
+Ansible 让我重新看到管理基础设施的乐趣。Docker 让我有充分的信心能稳定处理应用部署过程中最重要的步骤——交付环节。双剑合璧,威力无穷。
+
+从无到有搭建一个完整的 Rails 应用可以在12分钟内完成,这种速度放在任何场合都是令人印象深刻的。能获得一个免费的持续集成环境,可以查看不同版本的应用之间的区别,不会影响到同主机上已经在运行的应用,这些功能强大到难以置信,让我感到很兴奋。在文章的最后,我只希望你能感受到我的兴奋。
+
+我在2014年1月伦敦 Docker 会议上讲过这个主题,[已经分享到 Speakerdeck][7]了。
+
+如果想获得更多的关于 Ansible 和 Docker 的内容,请订阅 [changlog 周报][8],它会在每周六推送一周最有价值的关于这两个主题的新闻链接。
+
+如果你想为我们的 Changlog 写一篇文章,请[使用 Draft repo][9],他们会帮到你的。
+
+下次见,[Gerhard][a]。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://thechangelog.com/ansible-docker/
+
+作者:[Gerhard Lazu][a]
+译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://twitter.com/gerhardlazu
+[1]:https://www.docker.io/
+[2]:https://github.com/ansible/ansible
+[3]:http://ansible.com/
+[4]:http://docker.io/
+[5]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single_responsibility_principle
+[6]:http://blog.docker.io/2013/10/docker-0-6-5-links-container-naming-advanced-port-redirects-host-integration/
+[7]:https://speakerdeck.com/gerhardlazu/ansible-and-docker-the-path-to-continuous-delivery-part-1
+[8]:http://thechangelog.com/weekly/
+[9]:https://github.com/thechangelog/draft
diff --git a/translated/tech/20141023 How to turn your CentOS box into a BGP router using Quagga.md b/translated/tech/20141023 How to turn your CentOS box into a BGP router using Quagga.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..261abb7767
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20141023 How to turn your CentOS box into a BGP router using Quagga.md
@@ -0,0 +1,365 @@
+How to turn your CentOS box into a BGP router using Quagga
+如何使用Quagga把你的CentOS系统变成一个BGP路由器?
+================================================================================
+
+
+在[之前的教程中][1](注:此文原文做过,文件名:“20140928 How to turn your CentOS box into an OSPF router using Quagga.md”,如果前面翻译发布了,可以修改此链接),我对如何简单地使用Quagga把CentOS系统变成一个不折不扣地OSPF路由器做了一些描述,Quagga是一个开源路由软件套件.在这个教程中,我将会着重**把一个Linux系统变成一个BGP路由器,又是使用Quagga**,演示如何建立BGP与其它BGP路由器对等.
+
+
+在我们进入细节之前,一些BGP的背景知识还是必要的.边界网关协议(或者BGP)是互联网的域间路由协议的实际标准。在BGP术语中,全球互联网是由成千上万相关联的自治系统(ASE)组成,其中每一个AS代表每一个特定运营商提供的一个网络管理域.
+
+
+
+为了使其网络在全球范围内路由可达,每一个AS需要知道如何在英特网中到达其它的AS.这时候BGP出来取代这个角色了.BGP作为一种语言用于一个AS去与相邻的AS交换路由信息的一种工具.这些路由信息通常被称为BGP线路或者BGP前缀,包括AS号(ASN;全球唯一号码)以及相关的IP地址块.一旦所有的BGP线路被当地的BGP路由表学习和填充,每一个AS将会知道如何到达互联网的任何公网IP.
+
+
+路由在不同域(ASes)的能力是BGP被称为外部网关协议(EGP)或者域间协议的主要原因.就如一些路由协议例如OSPF,IS-IS,RIP和EIGRP都是内部网关协议(IGPs)或者域内路由协议.
+
+
+### 测试方案 ###
+
+
+在这个教程中,让我们来关注以下拓扑.
+
+
+
+
+我们假设运营商A想要建立一个BGP来与运营商B对等交换路由.它们的AS号和IP地址空间登细节如下所示.
+
+- **运营商 A**: ASN (100), IP地址空间 (100.100.0.0/22), 分配给BGP路由器eth1网卡的IP地址(100.100.1.1)
+
+
+- **运营商 B**: ASN (200), IP地址空间 (200.200.0.0/22), 分配给BGP路由器eth1网卡的IP地址(200.200.1.1)
+
+
+路由器A和路由器B使用100.100.0.0/30子网来连接到对方.从理论上来说,任何子网从运营商那里都是可达的,可互连的.在真实场景中,建议使用掩码为30位的公网IP地址空间来实现运营商A和运营商B之间的连通.
+
+
+### 在 CentOS中安装Quagga ###
+
+如果Quagga还没被安装,我们可以使用yum来安装Quagga.
+
+ # yum install quagga
+
+
+如果你正在使用的是CentOS7系统,你需要应用一下策略来设置SELinux.否则,SElinux将会阻止Zebra守护进程写入它的配置目录.如果你正在使用的是CentOS6,你可以跳过这一步.
+
+ # setsebool -P zebra_write_config 1
+
+
+
+Quagga软件套件包含几个守护进程,这些进程可以一起工作.关于BGP路由,我们将把重点放在建立一下2个守护进程.
+
+
+- **Zebra**:一个核心守护进程用于内核接口和静态路由.
+- **BGPd**:一个BGP守护进程.
+
+
+### 配置日志记录 ###
+
+在Quagga被安装猴,下一步就是配置Zebra来管理BGP路由器的网络接口.我们通过创建一个Zebra配置文件和启用日志记录来开始第一步.
+
+ # cp /usr/share/doc/quagga-XXXXX/zebra.conf.sample /etc/quagga/zebra.conf
+
+
+在CentOS6系统中:
+
+ # service zebra start
+ # chkconfig zebra on
+
+
+在CentOS7系统中:
+ # systemctl start zebra
+ # systemctl enable zebra
+
+
+Quagga提供了一个叫做vtysh特有的命令行工具,你可以输入路由器厂商(例如Cisco和Juniper)兼容和支持的命令.我们将使用vtysh shell来配置BGP路由在教程的其余部分.
+
+启动vtysh shell 命令,输入:
+
+ # vtysh
+
+
+提示将被改成主机名,这表明你是在vtysh shell中.
+
+
+ Router-A#
+
+现在我们将使用以下命令来为Zebra配置日志文件:
+
+ Router-A# configure terminal
+ Router-A(config)# log file /var/log/quagga/quagga.log
+ Router-A(config)# exit
+
+永久保存Zebra配置:
+
+ Router-A# write
+
+在路由器B操作同样的步骤.
+
+
+### 配置对等的IP地址 ###
+
+
+下一步,我们将在可用的接口上配置对等的IP地址.
+
+ Router-A# show interface #显示接口信息
+
+----------
+
+ Interface eth0 is up, line protocol detection is disabled
+ . . . . .
+ Interface eth1 is up, line protocol detection is disabled
+ . . . . .
+
+配置eth0接口的参数:
+
+ site-A-RTR# configure terminal
+ site-A-RTR(config)# interface eth0
+ site-A-RTR(config-if)# ip address 100.100.0.1/30
+ site-A-RTR(config-if)# description "to Router-B"
+ site-A-RTR(config-if)# no shutdown
+ site-A-RTR(config-if)# exit
+
+
+继续配置eth1接口的参数:
+
+ site-A-RTR(config)# interface eth1
+ site-A-RTR(config-if)# ip address 100.100.1.1/24
+ site-A-RTR(config-if)# description "test ip from provider A network"
+ site-A-RTR(config-if)# no shutdown
+ site-A-RTR(config-if)# exit
+
+现在确认配置:
+
+ Router-A# show interface
+
+----------
+
+ Interface eth0 is up, line protocol detection is disabled
+ Description: "to Router-B"
+ inet 100.100.0.1/30 broadcast 100.100.0.3
+ Interface eth1 is up, line protocol detection is disabled
+ Description: "test ip from provider A network"
+ inet 100.100.1.1/24 broadcast 100.100.1.255
+
+----------
+
+ Router-A# show interface description #现实接口描述
+
+----------
+
+ Interface Status Protocol Description
+ eth0 up unknown "to Router-B"
+ eth1 up unknown "test ip from provider A network"
+
+
+如果一切看起来正常,别忘记保存配置.
+
+ Router-A# write
+
+同样地,在路由器B重复一次配置.
+
+
+在我们继续下一步之前,确认下彼此的IP是可以ping通的.
+
+ Router-A# ping 100.100.0.2
+
+----------
+
+ PING 100.100.0.2 (100.100.0.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
+ 64 bytes from 100.100.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.616 ms
+
+下一步,我们将继续配置BGP对等和前缀设置.
+
+
+### 配置BGP对等 ###
+
+
+
+Quagga守护进程负责BGP的服务叫bgpd.首先我们来准备它的配置文件.
+
+ # cp /usr/share/doc/quagga-XXXXXXX/bgpd.conf.sample /etc/quagga/bgpd.conf
+
+
+在CentOS6系统中:
+
+ # service bgpd start
+ # chkconfig bgpd on
+
+
+在CentOS7中
+
+ # systemctl start bgpd
+ # systemctl enable bgpd
+
+现在,让我们来进入Quagga 的shell.
+
+ # vtysh
+
+
+第一步,我们要确认当前没有已经配置的BGP会话.在一些版本,我们可能会发现一个AS号为7675的BGP会话.由于我们不需要这个会话,所以把它移除.
+
+ Router-A# show running-config
+
+----------
+
+ ... ... ...
+ router bgp 7675
+ bgp router-id 200.200.1.1
+ ... ... ...
+
+
+我们将移除一些预先配置好的BGP会话,并建立我们所需的会话取而代之.
+
+ Router-A# configure terminal
+ Router-A(config)# no router bgp 7675
+ Router-A(config)# router bgp 100
+ Router-A(config)# no auto-summary
+ Router-A(config)# no synchronizaiton
+ Router-A(config-router)# neighbor 100.100.0.2 remote-as 200
+ Router-A(config-router)# neighbor 100.100.0.2 description "provider B"
+ Router-A(config-router)# exit
+ Router-A(config)# exit
+ Router-A# write
+
+
+
+路由器B将用同样的方式来进行配置,以下配置提供作为参考.
+
+ Router-B# configure terminal
+ Router-B(config)# no router bgp 7675
+ Router-B(config)# router bgp 200
+ Router-B(config)# no auto-summary
+ Router-B(config)# no synchronizaiton
+ Router-B(config-router)# neighbor 100.100.0.1 remote-as 100
+ Router-B(config-router)# neighbor 100.100.0.1 description "provider A"
+ Router-B(config-router)# exit
+ Router-B(config)# exit
+ Router-B# write
+
+
+当相关的路由器都被配置好,两台路由器之间的对等将被建立.现在让我们通过运行下面的命令来确认:
+
+ Router-A# show ip bgp summary
+
+
+
+
+从输出中,我们可以看到"State/PfxRcd"部分.如果对等关闭,输出将会现实"空闲"或者"活动'.请记住,单词'Active'这个词在路由器中总是不好的意思.它意味着路由器正在积极地寻找邻居,前缀或者路由.当对等是up状态,"State/PfxRcd"下的输出状态将会从特殊邻居接收到前缀号.
+
+在这个例子的输出中,BGP对等知识在AS100和AS200之间呈up状态.因此,没有前缀被更改,所以最右边列的数值是0.
+
+
+### 配置前缀通告 ###
+
+正如一开始提到,AS 100将以100.100.0.0/22作为通告,在我们的例子中AS 200将同样以200.200.0.0/22作为通告.这些前缀需要被添加到BGP配置如下.
+
+在路由器-A中:
+
+ Router-A# configure terminal
+ Router-A(config)# router bgp 100
+ Router-A(config)# network 100.100.0.0/22
+ Router-A(config)# exit
+ Router-A# write
+
+
+在路由器-B中:
+ Router-B# configure terminal
+ Router-B(config)# router bgp 200
+ Router-B(config)# network 200.200.0.0/22
+ Router-B(config)# exit
+ Router-B# write
+
+
+在这一点上,两个路由器会根据需要开始通告前缀.
+
+
+### 测试前缀通告 ###
+
+首先,让我们来确认前缀的数量是否被改变了.
+
+ Router-A# show ip bgp summary
+
+
+
+
+
+为了查看所接收的更多前缀细节,我们可以使用一下命令,这个命令用于显示邻居100.100.0.2所接收到的前缀总数.
+
+ Router-A# show ip bgp neighbors 100.100.0.2 advertised-routes
+
+
+
+
+查看哪一个前缀是我们从邻居接收到的:
+
+ Router-A# show ip bgp neighbors 100.100.0.2 routes
+
+
+
+
+我们也可以查看所有的BGP路由器:
+
+ Router-A# show ip bgp
+
+
+
+
+以上的命令都可以被用于检查哪个路由器通过BGP在路由器表中被学习到.
+
+ Router-A# show ip route
+
+----------
+
+
+ 代码: K - 内核路由, C - 已链接 , S - 静态 , R - 路由信息协议 , O - 开放式最短路径优先协议,
+
+
+ I - 中间系统到中间系统的路由选择协议, B - 边界网关协议, > - 选择路由, * - FIB 路由
+
+ C>* 100.100.0.0/30 is directly connected, eth0
+ C>* 100.100.1.0/24 is directly connected, eth1
+ B>* 200.200.0.0/22 [20/0] via 100.100.0.2, eth0, 00:06:45
+
+----------
+
+ Router-A# show ip route bgp
+
+----------
+
+ B>* 200.200.0.0/22 [20/0] via 100.100.0.2, eth0, 00:08:13
+
+
+BGP学习到的路由也将会在Linux路由表中出现.
+
+ [root@Router-A~]# ip route
+
+----------
+
+ 100.100.0.0/30 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 100.100.0.1
+ 100.100.1.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 100.100.1.1
+ 200.200.0.0/22 via 100.100.0.2 dev eth0 proto zebra
+
+
+最后,我们将使用ping命令来测试连通.结果将成功ping通.
+
+ [root@Router-A~]# ping 200.200.1.1 -c 2
+
+
+总而言之,该教程将重点放在如何运行一个基本的BGP在CentOS系统中.当这个教程让你开始BGP的配置,那么一些更高级的设置例如设置过滤器,BGP属性调整,本地优先级和预先路径准备等.我将会在后续的教程中覆盖这些主题.
+
+希望这篇教程能给大家一些帮助.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://xmodulo.com/centos-bgp-router-quagga.html
+
+作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
+译者:[disylee](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
+[1]:http://xmodulo.com/turn-centos-box-into-ospf-router-quagga.html
diff --git a/translated/tech/20141024 Amazing 25 Linux Performance Monitoring Tools.md b/translated/tech/20141024 Amazing 25 Linux Performance Monitoring Tools.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..05b4b00e5c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20141024 Amazing 25 Linux Performance Monitoring Tools.md
@@ -0,0 +1,290 @@
+25个linux性能监控工具
+================================================================================
+一段时间以来,我们在网上向读者介绍了如何为Linux以及类Linux操作系统配置多种不同的性能监控工具。在这篇文章中我们将罗列一系列使用最频繁的性能监控工具,并对介绍到的每一个工具提供了相应的简介链接,大致将其划分为两类,基于命令行的和提供图形化接口的。
+
+### 基于命令行的性能监控工具 ###
+
+#### 1. dstat - 多类型资源统计工具 ####
+
+该命令整合了**vmstat**,**iostat**和**ifstat**三种命令。同时增加了新的特性和功能允许你能够看到及时的不同的资源使用情况,从而能够使你对比和整合不同的资源使用情况。通过不同颜色和代码块布局的界面帮助你能够更加清晰容易的获取信息。它同时支持将信息数据导出到**cvs**格式文件中,从而用其他应用程序打开,或者导入到数据库中。你可以用该命令来[监控cpu,内存和网络状态随着时间的变化][1]。
+
+
+
+#### 2. atop - 相比top更好的ASCII码体验 ####
+
+使用**ASCII**码的命令行工具来显示一个性能监控工具能够记录显示所有进程活动。它不但能够展示每日的系统日志,也能够进行长期的进程活动分析,同时也能够高亮过载的系统使用资源。它包含了CPU,内存,交换空间,磁盘和网络层的度量指标。使用所用的功能只需在终端运行**atop**即可。当然你也可以使用[交互接口来显示][2]数据并进行排序。
+
+ # atop
+
+
+
+
+#### 3. Nmon - 类Unix系统的性能监控 ####
+
+Nmon为**Nigel's Monitor**缩写,它最早开发用来作为**AIX**的系统监控工具。它的特征是**在线模式**,该模式在终端中实时更新监控信息,同时使用光标操作来提高屏幕事件处理效率。使用**捕捉模式**能够将数据保存为**CSV**格式,方便进一步的处理和图形化展示。
+
+
+
+更多的信息参考我们的[nmon性能监控文章][3]。
+
+#### 4. slabtop - 显示内核slab缓存信息 ####
+
+个应用能够显示**缓存分配器**是如何管理Linux内核缓存不同类型的对象的。这个命令类似于top命令,区别是它重点实时显示内核slab缓存信息。它能够显示按照不同排序条件来显示最靠前的缓存列表。它同时也能够显示一个以slab层信息填充的统计题头。举例如下:
+
+ # slabtop --sort=a
+ # slabtop -s b
+ # slabtop -s c
+ # slabtop -s l
+ # slabtop -s v
+ # slabtop -s n
+ # slabtop -s o
+
+**更多信息参阅**[内核slab缓存文章][4]。
+
+#### 5. sar - 性能监控和瓶颈检查 ####
+
+**sar** 命令是为了标准输出在操作系统上所选的累积活动计数器内容信息。该基于计数值和时间间隔参数的**审计系统**,会按照指定的时间间隔输出指定次数的监控信息。如果时间间隔参数为设置为0,那么[sar命令将会显示系统从开机到当时时刻的平均统计信息][5]。有用的命令如下:
+
+ # sar -u 2 3
+ # sar –u –f /var/log/sa/sa05
+ # sar -P ALL 1 1
+ # sar -r 1 3
+ # sar -W 1 3
+
+#### 6. Saidar - 简单的统计监控工具 ####
+
+Saidar是一个**简单**且**轻量**的系统信息监控工具。虽然它无法提供大多性能报表,但是它能够通过一个简短友好的方式显示最有用的系统运行状况数据。你可以很容易地看到[up-time, average load,CPU,内存,进程,磁盘和网络接口][6]统计信息。
+
+ Usage: saidar [-d delay] [-c] [-v] [-h]
+
+ -d Sets the update time in seconds
+ -c Enables coloured output
+ -v Prints version number
+ -h Displays this help information.
+
+
+
+#### 7. top - 经典的Linux任务管理工具 ####
+
+作为一个广为认知的**Linux**工具,**top**出现在大多数的类Unix操作系统任务管理中。它可以显示当前正在运行的进程的列表,同时用户可以按照不同的查询条件对该列表进行排序。它主要显示了系统进程对**CPU**和内存的使用状况。top可以快速检查是哪个或哪几个进程挂起了你的系统。你可以在[这里][7]看到top使用的例子。 你可以在终端输入top来运行它并进入到交互模式:
+
+ Quick cheat sheet for interactive mode:
+
+ GLOBAL_Commands: ?, =, A, B, d, G, h, I, k, q, r, s, W, Z
+ SUMMARY_Area_Commands: l, m, t, 1
+ TASK_Area_Commands Appearance: b, x, y, z Content: c, f, H, o, S, u Size: #, i, n Sorting: <, >, F, O, R
+ COLOR_Mapping: , a, B, b, H, M, q, S, T, w, z, 0 - 7
+ COMMANDS_for_Windows: -, _, =, +, A, a, G, g, w
+
+
+
+#### 8. Sysdig - 系统进程的高级视图 ####
+
+**Sasdig**是一个能够让系统管理员和开发人员前所未有的洞察其系统行为的监控工具。其开发团队出于改善系统层次的监控方式以及通过提供关于**存储,进程,网络和内存**子系统的**统一有序**以及**粒度可见**的方式来进行错误排查,通过创建系统活动记录文件使得你可以在任何时间轻松分析。
+
+简单例子:
+
+ # sysdig proc.name=vim
+ # sysdig -p"%proc.name %fd.name" "evt.type=accept and proc.name!=httpd"
+ # sysdig evt.type=chdir and user.name=root
+ # sysdig -l
+ # sysdig -L
+ # sysdig -c topprocs_net
+ # sysdig -c fdcount_by fd.sport "evt.type=accept"
+ # sysdig -p"%proc.name %fd.name" "evt.type=accept and proc.name!=httpd"
+ # sysdig -c topprocs_file
+ # sysdig -c fdcount_by proc.name "fd.type=file"
+ # sysdig -p "%12user.name %6proc.pid %12proc.name %3fd.num %fd.typechar %fd.name" evt.type=open
+ # sysdig -c topprocs_cpu
+ # sysdig -c topprocs_cpu evt.cpu=0
+ # sysdig -p"%evt.arg.path" "evt.type=chdir and user.name=root"
+ # sysdig evt.type=open and fd.name contains /etc
+
+
+
+**更多信息** 可以在 [如何利用sysdig改善系统层次的监控和错误排查][8]
+
+#### 9. netstat - 显示开放的端口和连接 ####
+
+它是**Linux管理员**使用来显示不同网络信息的工具,如查看什么端口开放和什么网络连接已经建立以及何种进程运行在这种连接之上。同时它也显示了**Unix套接**字的信息,这些套接字在不同的程序中为打开状态。作为大多数Linux发行版本的一部分,netstat的许多命令在 [netstat和它的不同输出][9]中有详细的描述。最为常用的如下:
+
+ $ netstat | head -20
+ $ netstat -r
+ $ netstat -rC
+ $ netstat -i
+ $ netstat -ie
+ $ netstat -s
+ $ netstat -g
+ $ netstat -tapn
+
+### 10. tcpdump - 洞察网络包 ###
+
+**tcpdump**可以用来查看**网络连接**包的内容。它显示了传输过程中包内容的各种信息。为了使得输出信息更为有用,它允许使用者通过不同的过滤器获取自己想要的信息。可以参照的例子如下:
+
+ # tcpdump -i eth0 not port 22
+ # tcpdump -c 10 -i eth0
+ # tcpdump -ni eth0 -c 10 not port 22
+ # tcpdump -w aloft.cap -s 0
+ # tcpdump -r aloft.cap
+ # tcpdump -i eth0 dst port 80
+
+你可以找到详细的[描述在topdump和捕捉包][10]文章中。
+
+#### 11. vmstat - 虚拟内存统计信息 ####
+
+**vmstat**是虚拟内存(**virtual memory** statistics)的缩写,作为一个**内存监控**工具,它收集和显示概括关于**内存**,**进程**,**终端**和**分页**和**I/O阻塞**的信息。作为一个开源程序,它可以再大部分Linux发行版本中找到,包括Solaris和FreeBSD。它用来诊断大部分的内存性能问题和其他相关问题
+
+
+
+**M更多信息** 参考 [vmstat命令文章][11]。
+
+#### 12. free - 内存统计信息 ####
+
+free是另一个能够在终端中标准输出内存和交换空间使用的命令行工具。由于它的简易,它经常用于快速查看内存使用或者是应用于不同的脚本和应用程序中。在这里你可以看到[这个小程序的许多应用][12]。几乎所有的系统管理员日常都会用这个工具。:-)
+
+
+
+#### 13. Htop - 更加友好的top ####
+
+**Htop**基本上是一个top改善版本,它能够显示更多的统计信息和更加多彩的方式,同时允许你采用不同的方式进行排序,它提供了一个**用户友好**的接口。
+
+
+
+你可以找到 **更多的信息** 在 [关于htop和top的比较][13]文章中。
+
+#### 14. ss - 更现代感的网络管理替代工具 ####
+
+**ss**是**iproute2**包的一部分。iproute2趋向于替代一整套标准的**Unix网络**工具组件,它曾经用来完成[网络接口配置,路由表和管理ARP表][14]任务。ss工具用来存储套接字统计信息,也能够类似netstat一样显示信息,同时也能显示更多TCP和状态信息。一些例子如下:
+
+ # ss -tnap
+ # ss -tnap6
+ # ss -tnap
+ # ss -s
+ # ss -tn -o state established -p
+
+#### 15. lsof - 列表显示打开的文件 ####
+
+**lsof**命令,意为“**list open files**”, 用于在许多类Unix系统中显示所有打开状态的文件和打开它们的进程。在大部分Linux发行版和其他类Linux操作系统中系统管理员用它来检查不同的进程打开了哪些文件。你可以在这里找到更多的例子。
+
+ # lsof +p process_id
+ # lsof | less
+ # lsof –u username
+ # lsof /etc/passwd
+ # lsof –i TCP:ftp
+ # lsof –i TCP:80
+
+你可以找到 **更多例子** 在[lsof 文章][15]
+
+#### 16. iftop - 类似top的了网络连接工具 ####
+
+**iftop**是一个基于网络信息的类似top的程序。它能够显示当前时刻按照**带宽使用**量或者上传或者下载量排序的**网络连接**状况。它同事提供了下载文件的预估完成时间。
+
+
+
+**更多信息**可以参考[网络流量iftop文章][16]
+
+#### 17. iperf - 网络性能工具 ####
+
+**iperf**是一个**网络测试**工具,能够创建**TCP**和**UDP**数据连接和测量该网络能够传输它们的**性能**。它支持调节关于时间,协议和缓冲等不同的参数。对于每一个测试,它会报告带宽,丢包和其他的一些参数。
+
+
+
+如果你想用使用这个工具,可以参考这篇文章: [如何安装和使用iperf][17]
+
+#### 18. Smem - 高级内存报表工具 ####
+
+**Smem**是一个比较高级的**Linux**命令行工具,它提供关于系统中已经使用的和共享的实际内存,试图提供一个更为可靠地当前**内存**使用数据。
+
+ $ smem -m
+ $ smem -m -p | grep firefox
+ $ smem -u -p
+ $ smem -w -p
+
+参考我们的文章:[Smem更多的例子][18]
+
+### 图形化或基于Web的性能工具 ###
+
+#### 19. Icinga - Nagios的社区分支版本 ####
+
+**Icinga**是一个**开源免费**的网络监控程序,作为Nagios的分支,它获取了前者现存的大部分功能,同时基于这些功能又增加了社区用户要求已久的功能和补丁。
+
+
+
+**更多信息**参考[安装和配置lcinga文章][19].
+
+#### 20. Nagios - 最为流行的监控工具. ####
+
+作为在Linux上使用最为广泛和流行的**监控方案**,它有一个守护程序用来收集不同进程和远程主机的信息,这些收集到的信息都通过功能强大**的web界面**进行呈现。
+
+
+
+你可以在 **找到更多的信息** 在[如何安装nagios][20]
+
+#### 21. Linux process explorer - Linux下的procexp ####
+
+**Linux process explorer**是一个Linux下的图形化进程浏览工具。它能够显示不同的进程信息,如进程数,TCP/IP连接和每一个进程的性能指标。作为**Windows**下**procexp**在Linux的替代品,是由**Sysinternals**开发的,其目标是相比**top**和**ps**用户体验更加的友好。
+
+查看 [linux process explorer 文章][21]获取更多信息。
+
+#### 22. Collectl - 性能监控工具 ####
+
+你可以既可以通过交互的方式使用这个**性能监控**工具,也可以用它产生**报表**,并通过web服务器来访问它在磁盘上的数据。它以一种**易读易管理**的文件格式,记录了**CPU,磁盘,内存,网络,网络文件系统,进程,slabs**等统计信息于。
+
+
+
+**更多** 关于[Collectl的文章][22]。
+
+#### 23. MRTG - 经典网络流量监控图形工具 ####
+
+这是一个采用**rrdtool**的提供给用户图形化流量监控工具。作为**最早**的提供**图形化界面**的工具,它被广泛应用在类Unix的操作系统中。查看我们关于[如何使用MRTG][23]的文章获取更多关于安装和配置的信息。
+
+
+
+#### 24. Monit - 简单易用的监控工具 ####
+
+**Monit**是一个用来**监控进程**,**系统加载**,**文件系统**和**目录文件**等的开源的Linux工具。你能够让它自动化维护和修复,也能够在运行错误的情景下执行动作或者发邮件报告提醒系统管理员。如果你想要用这个工具,你可以查看[如何使用Monit的文章][24]。
+
+
+
+#### 25. Munin - 为服务器提供监控和提醒服务 ####
+
+作为一个网络资源监控工具,*Munin**能够帮助分析**资源趋势**和**查看弱节点**以及导致产生**性能问题**的原因。开发此软件的团队系统它能够易用和用户体验友好。该软件是用Perl开发的同时采用**rrdtool**来绘制图形,使用了**web接口**进行呈现。开发人员推广此应用时声称“**插件化和易用**”,目前已有500多个监控插件可结合使用。
+
+**更多信息**可以在[关于Munin的文章][25]。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
+
+作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/andyxue)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/adriand/
+[1]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/dstat-monitor-linux-performance/
+[2]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/guide-using-linux-atop/
+[3]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/install-nmon-monitor-linux-performance/
+[4]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/kernel-slab-cache-information/
+[5]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-system-performance-monitoring-using-sar-command/
+[6]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/monitor-linux-saidar-tool/
+[7]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-top-command-examples-screenshots/
+[8]:http://linoxide.com/tools/sysdig-performance-linux-tool/
+[9]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/netstat-commad-with-all-variant-outputs/
+[10]:http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/network-traffic-capture-tcp-dump-command/
+[11]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-vmstat-command-tool-report-virtual-memory-statistics/
+[12]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-free-command/
+[13]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-htop-command/
+[14]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/ss-sockets-network-connection/
+[15]:http://linoxide.com/how-tos/lsof-command-list-process-id-information/
+[16]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/iftop-network-traffic/
+[17]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/install-iperf-test-network-speed-bandwidth/
+[18]:http://linoxide.com/tools/memory-usage-reporting-smem/
+[19]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/install-configure-icinga-linux/
+[20]:http://linoxide.com/how-tos/install-configure-nagios-centos-7/
+[21]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/procexp/
+[22]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/collectl-tool-install-examples/
+[23]:http://linoxide.com/tools/multi-router-traffic-grapher/
+[24]:http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/monit-linux/
+[25]:http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-munin/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20141024 How To Upgrade Ubuntu 14.04 To Ubuntu 14.10.md b/translated/tech/20141024 How To Upgrade Ubuntu 14.04 To Ubuntu 14.10.md
index 1fd579521d..0283522090 100644
--- a/translated/tech/20141024 How To Upgrade Ubuntu 14.04 To Ubuntu 14.10.md
+++ b/translated/tech/20141024 How To Upgrade Ubuntu 14.04 To Ubuntu 14.10.md
@@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
-如何升级Ubuntu 14.04 到Ubuntu 14.10
+如何从 Ubuntu 14.04 升级到 Ubuntu 14.10
================================================================================

-Ubuntu 14.10已于昨日发布。想知道**如何从Ubuntu 14.04升级到Ubuntu 14.10**么?别担心,这很容易升级到Ubuntu 14.10。事实上,它只是点击几下和有良好的互联网连接的事情而已。
+Ubuntu 14.10已于前段时间发布。想知道**如何从 Ubuntu 14.04 升级到 Ubuntu 14.10 **么?别担心,这很容易做到。事实上,只要网络连接速度好,升级只是点击几下鼠标的事情而已。
-### 你需要从Ubuntu 14.04 切换到Ubuntu 14.10么? ###
+### 你需要从 Ubuntu 14.04 切换到 Ubuntu 14.10 么? ###
-在你升级到Ubuntu 14.10之前,请确保你真的想为14.10抛弃Ubuntu14.04。一个很重要的原因是你不能从Ubuntu 14.10 降级到14.04。 你需要完全重新安装。
+在你升级到Ubuntu 14.10之前,请确定你真的想为升级 14.10 而抛弃 Ubuntu 14.04。一个很重要的原因是你不能从Ubuntu 14.10 回归到14.04。 你需要完全重新安装。
-Ubuntu 14.04是长期支持(LTS)版本。这意味着更长的支持周期和更稳定和支持。如果升级到14.10,你将被迫在9个月后从Ubuntu 14.10 升级到15.04,而14.04将会持续3年以上。
+Ubuntu 14.04是长期支持(LTS)版本。这意味着有更多的稳定性和更长的支持周期。如果升级到14.10,你将被迫在9个月后从Ubuntu 14.10 升级到15.04,而14.04将会持续3年以上。
-此外,目前Ubuntu的14.10没有很多使用户迫切切换到14.10 的新功能。但是,你肯定会得到最前沿的操作系统。所以,在这之前是否升级到Ubuntu 14.10是你自己的决定。
+此外,目前Ubuntu 14.10没有很多的新功能使吸引用户切换到14.10。当然了,你肯定会得到最前沿的操作系统。所以,在这之前是否升级到Ubuntu 14.10是你自己的决定。
### 从Ubuntu 14.04 升级到 Ubuntu 14.10 ###
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ Ubuntu 14.04是长期支持(LTS)版本。这意味着更长的支持周期

-进入**更新**选项卡。这里要确保**Ubuntu新版本通知我** 设置成**对于任何新版本**。默认Ubuntu只会在另一个LTS发布时通知你。你必须要把它改成在任何中间版本都升级。
+进入**更新**选项卡。这里要确保**Ubuntu有新版本时通知我** 设置成**对于任何新版本**。默认Ubuntu只会在另一个LTS发布时通知你。你必须要把它改成在任何中间版本都升级。

@@ -36,16 +36,16 @@ Ubuntu 14.04是长期支持(LTS)版本。这意味着更长的支持周期

-我希望本篇可以帮助你**从Ubuntu 14.04 升级到 Ubuntu 14.10**。虽然本教程是为Ubuntu写的,但是你可以用同样的步骤升级到Xubuntu 14.10和Kubuntu 14.10或者Lubuntu。敬请期待下一篇Ubuntu 14.10相关文章。
+我希望本篇教程可以帮助你**从 Ubuntu 14.04 升级到 Ubuntu 14.10**。虽然本教程是为Ubuntu写的,但是你可以用同样的步骤升级到 Xubuntu 14.10、Kubuntu 14.10 或者Lubuntu。敬请期待下一篇Ubuntu 14.10相关文章。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
via: http://itsfoss.com/upgrade-ubuntu-14-04-to-14-10/
作者:[Abhishek][a]
-译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
\ No newline at end of file
+[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20141029 How to Install MariaDB in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS.md b/translated/tech/20141029 How to Install MariaDB in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cbc1f4bd69
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20141029 How to Install MariaDB in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+如何在Ubuntu 14.04 LTS上安装MariaDB
+================================================================================
+MariaDB是一个开源数据库且100%与MySQL兼容,目标是替代MySQL数据库。
+
+### MariaDB的背景 : ###
+
+2008年,MySQL被后来被Oracle在2010年收购的**Sun Microsystems**收购了。 最初被Sun公司的收购由于符合项目的需要受到MySQL社区的欢呼,但是这种情绪并没有持续他热爱就,接下来被Oracle的收购不幸期望远远低于预期。许多MySql的开发者离开了Sun和Oracle公司开始新的项目。在他们中间就有MySQL的创建者以及项目长期技术带头人之一的**Michael ‘Monty’ Widenius**。Monty和他的团队创建了MySQL的一个fork版本并且命名它为**MariaDB**。
+
+本篇我们会讨论如何在Ubuntu上安装MariaDB。默认上MariaDB的包并没有在Ubuntu仓库中。要安装MariaDB,我们首先要设置MariaDB仓库。
+
+#### 设置 MariaDB 仓库 ####
+
+ $ sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
+ $ sudo apt-key adv --recv-keys --keyserver hkp://keyserver.ubuntu.com:80 0xcbcb082a1bb943db
+ $ sudo add-apt-repository 'deb http://sfo1.mirrors.digitalocean.com/mariadb/repo/10.0/ubuntu trusty main'
+
+#### 安装 MariaDB : ####
+
+ $ sudo apt-get update
+ $ sudo apt-get install mariadb-server
+
+在安装中,你会被要求设置MariaDB的root密码。
+
+
+
+#### 从命令行连接到MariaDB : ####
+
+ linuxtechi@mail:~$ mysql -uroot -p
+ Enter password:
+ Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
+ Your MariaDB connection id is 40
+ Server version: 10.0.14-MariaDB-1~trusty-log mariadb.org binary distribution
+ Copyright (c) 2000, 2014, Oracle, SkySQL Ab and others.
+ Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
+ MariaDB [(none)]>
+
+#### Maria DB 服务 ####
+
+ $ sudo /etc/init.d/mysql stop
+ $ sudo /etc/init.d/mysql start
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/install-mariadb-in-ubuntu/
+
+作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:http://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20141029 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix hda-duplex not supported in this QEMU binary.md b/translated/tech/20141029 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix hda-duplex not supported in this QEMU binary.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..e3a6f3b4af
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20141029 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to fix hda-duplex not supported in this QEMU binary.md
@@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
+Linux 有问必答 -- 如何修复“hda-duplex not supported in this QEMU binary”(hda-duplex在此QEMU文件中不支持)
+================================================================================
+> **提问**: 当我尝试在虚拟机中安装一个新的Linux时,虚拟机不能启动且报了下面这个错误:“不支持的配置:hda-duplex在此QEMU文件中不支持。” 我该如何修复?
+
+这个错误可能来自一个当默认声卡型号不能被识别时的一个qemu bug。
+
+
+
+ 无法完成安装:‘不支持的配置:hda-duplex在此QEMU文件中不支持’
+
+要解决这个问题,按照下面的做。
+
+### 方案一: virt-manager ###
+
+在**virt-manager**中,打开虚拟机的虚拟硬件详细菜单,进入声卡选项,改变默认的设备型号为ac97。
+
+
+
+点击“应用”按钮并保存设置。看一下虚拟机现在是否可以启动了。
+
+### 方案二: Virsh ###
+
+如果你使用的是**virt-manager** 而不是**virt-manager**, 你可以编辑VM相应的配置文件。在节点中查找**sound**节点,并按照下面的默认声卡型号改成**ac97**。
+
+
+ . . .
+
+
+
+ . . .
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/hda-duplex-not-supported-in-this-qemu-binary.html
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/translated/tech/20141029 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install REMI repository on CentOS or RHEL.md b/translated/tech/20141029 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install REMI repository on CentOS or RHEL.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..66ed92b64d
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20141029 Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install REMI repository on CentOS or RHEL.md
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
+Linux 有问必答 -- 如何在CentOS或者RHEL上安装REMI仓库
+================================================================================
+> **Question**:我该如何在CentOS或者RHEL中配置REMI仓库,并在其中安装包?
+
+[REMI 仓库][1] 提供了核心CentOS和RHEL包的更新版本,尤其是最新的PHP/MySQL系列。
+
+安装REMI仓库要记住的一件事是不要在REMI仓库中运行yum update。因为REMI仓库的包名RHEL/CentOS中的相同,运行yum update可能会触发意外的更新。一个好办法是禁用REMI仓库,在你需要安装RMEI仓库中独有的包时再启用。
+
+### 预备工作 ###
+
+安装REMI仓库之前,你首先需要启用EPEL仓库,因为REMI中的一些包依赖与EPEL。按照[这份指南][2]在CentOS或者RHEL中设置EPEL仓库。
+
+### 安装REMI仓库 ###
+
+现在按照下面的步骤安装REMI仓库。
+
+在CentOS 7上:
+
+ $ sudo rpm --import http://rpms.famillecollet.com/RPM-GPG-KEY-remi
+ $ sudo rpm -ivh http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/remi-release-7.rpm
+
+在CentOS 6上:
+
+ $ sudo rpm --import http://rpms.famillecollet.com/RPM-GPG-KEY-remi
+ $ sudo rpm -ivh http://rpms.famillecollet.com/enterprise/remi-release-6.rpm
+
+默认上,REMI是禁用的。要检查REMI是否已经成功安装,使用这个命令。你会看到几个REMI仓库,比如remi、remi-php55和remi-php56。
+
+ $ yum repolist disabled | grep remi
+
+
+
+### 从REMI仓库中安装一个包 ###
+
+如上所述,最好保持禁用REMI仓库,只有在需要的时候再启用。
+
+要搜索或安装REMI仓库中的包,使用这些命令:
+
+ $ sudo yum --enablerepo=remi search
+ $ sudo yum --enablerepo=remi install
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-remi-repository-centos-rhel.html
+
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[1]:http://rpms.famillecollet.com/
+[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
\ No newline at end of file