mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-30 02:40:11 +08:00
commit
a830092165
@ -1,38 +1,38 @@
|
||||
Linux LVM简明教程
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
LVM是一个多才多艺的硬盘系统工具。无论在Linux或者其他相似的系统,都是非常的好用。传统分区使用固定大小分区,重新分区十分麻烦。但是,LVM创建和管理从硬盘中分出来的“逻辑”卷,提供管理员弹性管理逻辑卷的扩大缩小,操作简单,还不损坏已存储的数据。附加硬盘可以随意增加到LVM,而且可以直接增加已经存在的逻辑卷。LVM不需要重启而只要内核知道分区的存在。
|
||||
逻辑卷管理LVM是一个多才多艺的硬盘系统工具。无论在Linux或者其他类似的系统,都是非常的好用。传统分区使用固定大小分区,重新调整大小十分麻烦。但是,LVM可以创建和管理“逻辑”卷,而不是直接使用物理硬盘。可以让管理员弹性的管理逻辑卷的扩大缩小,操作简单,而不损坏已存储的数据。可以随意将新的硬盘添加到LVM,以直接扩展已经存在的逻辑卷。LVM并不需要重启就可以让内核知道分区的存在。
|
||||
|
||||
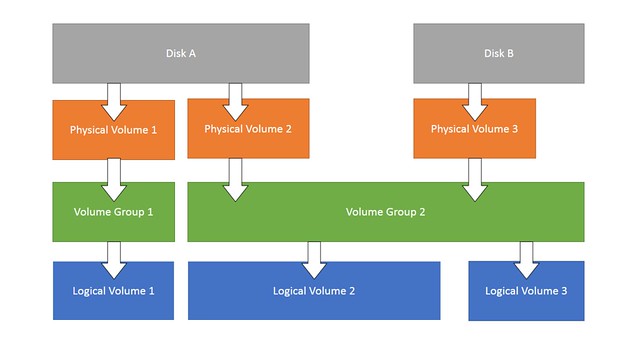
LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
图中顶层,首先是实际的物理卷。下一层,一个或多个物理卷可以用来创建卷组。再下一层,然后逻辑卷的创建基于卷组。只要在卷组中有可用空间,就可以随心所欲的创建逻辑卷。最下面层,文件系统的分区就是从逻辑卷上创建,然后可以在操作系统挂载和访问。
|
||||
图中顶部,首先是实际的物理磁盘及其划分的分区和其上的物理卷(PV)。一个或多个物理卷可以用来创建卷组(VG)。然后基于卷组可以创建逻辑卷(LV)。只要在卷组中有可用空间,就可以随心所欲的创建逻辑卷。文件系统就是在逻辑卷上创建的,然后可以在操作系统挂载和访问。
|
||||
|
||||
### LVM测试说明 ###
|
||||
|
||||
本文将介绍**怎么在linux中创建和管理LVM卷**。我们将会分成两个部分。第一个部分,我们首要要在一个硬盘上创建多个逻辑卷,然后将它们挂载在/lvm-mount目录。然后我们将要对创建好的卷调整大小。而第二部分,我们将会从另外一块硬盘增加额外的卷到LVM中。
|
||||
本文将介绍**怎么在linux中创建和管理LVM卷**。我们将会分成两个部分。第一个部分,我们首先要在一个硬盘上创建多个逻辑卷,然后将它们挂载在/lvm-mount目录。然后我们将要对创建好的卷调整大小。而第二部分,我们将会从另外一块硬盘增加额外的卷到LVM中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 准备磁盘分区 ###
|
||||
|
||||
通过使用fdisk,创建磁盘分区。我们需要创建3个1G分区,注意,相同大小的分区不是强制的。同样,分区需要使用‘8e’类型来使他们兼容LVM。
|
||||
通过使用fdisk,创建磁盘分区。我们需要创建3个1G分区,注意,并不要求分区的大小一致。同样,分区需要使用‘8e’类型来使他们可用于LVM。
|
||||
|
||||
# fdisk /dev/sdb
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Command (m for help): n ## new
|
||||
Command (m for help): n ## 新建
|
||||
Command action
|
||||
e extended
|
||||
p primary partition (1-4)
|
||||
p ## primary
|
||||
p ## 主分区
|
||||
|
||||
Partition number (1-4): 1 ## partition number
|
||||
First cylinder (1-1044, default 1): ## hit enter
|
||||
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-1044, default 1044): +1G ## size
|
||||
Partition number (1-4): 1 ## 分区号
|
||||
First cylinder (1-1044, default 1): ## 回车用默认的1
|
||||
Last cylinder, +cylinders or +size{K,M,G} (1-1044, default 1044): +1G ## 大小
|
||||
|
||||
Command (m for help): t ## change type
|
||||
Command (m for help): t ## 改变类型
|
||||
Selected partition 1
|
||||
Hex code (type L to list codes): 8e ## code for LVM
|
||||
Hex code (type L to list codes): 8e ## LVM 的分区代码
|
||||
Changed system type of partition 1 to 8e (Linux LVM)
|
||||
|
||||
重复上面的操作来创建其他两个分区。分区创建完成后,我们应该有类似如下的输出:
|
||||
@ -46,15 +46,15 @@ LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
/dev/sdb2 133 264 1060290 8e Linux LVM
|
||||
/dev/sdb3 265 396 1060290 8e Linux LVM
|
||||
|
||||
### 准备物理卷 ###
|
||||
### 准备物理卷(PV) ###
|
||||
|
||||
刚创建的分区是用来储存物理卷的。LVM可以在不同大小的物理卷上工作。
|
||||
刚创建的分区是用来储存物理卷的。LVM可以使用不同大小的物理卷。
|
||||
|
||||
# pvcreate /dev/sdb1
|
||||
# pvcreate /dev/sdb2
|
||||
# pvcreate /dev/sdb3
|
||||
|
||||
使用下列命令检查物理卷已经创建。下面截取部分输出。"/dev/sdb2"是一个新的"1.01 GiB"物理卷。
|
||||
使用下列命令检查物理卷的创建情况。下面截取部分输出。"/dev/sdb2"是一个新的"1.01 GiB"物理卷。
|
||||
|
||||
# pvdisplay
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,8 +75,7 @@ LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
# pvremove /dev/sdb1
|
||||
|
||||
### 准备卷组 ###
|
||||
|
||||
### 准备卷组(VG) ###
|
||||
|
||||
下列命令用来创建名为'volume-group1'的卷组,使用/dev/sdb1, /dev/sdb2 和 /dev/sdb3创建。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -109,20 +108,19 @@ LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
Free PE / Size 774 / 3.02 GiB
|
||||
VG UUID bwd2pS-fkAz-lGVZ-qc7C-TaKv-fFUC-IzGNBK
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
从输出中,我们可以看见卷组的使用量/总量。物理卷给卷组提供空间。只要在这个卷组中还有可用空间,我们就可以随意创建逻辑卷。
|
||||
|
||||
使用下列命令删除卷组。
|
||||
|
||||
# vgremove volume-group1
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建逻辑卷 ###
|
||||
### 创建逻辑卷(LV) ###
|
||||
|
||||
下列命令创建一个名为'1v1'、大小为100MB的逻辑卷。我们使用小分区减少执行时间。逻辑卷使用之前创建的卷组的空间。
|
||||
下列命令创建一个名为'1v1'、大小为100MB的逻辑卷。我们使用小分区减少执行时间。这个逻辑卷使用之前创建的卷组的空间。
|
||||
|
||||
# lvcreate -L 100M -n lv1 volume-group1
|
||||
|
||||
逻辑卷使用lvdisplay命令查看。
|
||||
逻辑卷可使用lvdisplay命令查看。
|
||||
|
||||
# lvdisplay
|
||||
|
||||
@ -143,13 +141,13 @@ LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
- currently set to 256
|
||||
Block device 253:2
|
||||
|
||||
现在逻辑卷已经准备好了,我们可以格式化和挂载逻辑卷,就像ext2/3/4分区一样!
|
||||
现在逻辑卷已经准备好了,我们可以格式化和挂载逻辑卷,就像其它ext2/3/4分区一样!
|
||||
|
||||
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/volume-group1/lv1
|
||||
# mkdir /lvm-mount
|
||||
# mount /dev/volume-group1/lv1 /lvm-mount/
|
||||
|
||||
一旦逻辑卷挂载,我们就可以到挂载点/lvm-mount/读取/写入了。为了创建和挂载额外的逻辑卷,我们重复这个过程。
|
||||
一旦逻辑卷挂载,我们就可以到挂载点 /lvm-mount/ 上读写了。要创建和挂载其它的逻辑卷,我们重复这个过程。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,使用lvremove我们可以删除逻辑卷。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -158,9 +156,9 @@ LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
### 扩展一个LVM卷 ###
|
||||
|
||||
调整逻辑卷大小的功能是LVM最好的部分。这个章节会讨论我们怎么样扩展一个存在的逻辑卷。接下来,我们将会扩展先前创建的逻辑卷‘lv1’扩大到200MB。
|
||||
调整逻辑卷大小的功能是LVM最有用的功能。这个部分会讨论我们怎么样扩展一个存在的逻辑卷。下面,我们将会扩展先前创建的逻辑卷‘lv1’扩大到200MB。
|
||||
|
||||
注意,调整逻辑卷大小之后,也需要对文件系统调整大小进行匹配。有个额外的步骤各不相同,这取决于创建文件系统的类型。在本文中,我们使用'lv1'创建了ext4类型的文件系统,所以这里的操作是针对ext4文件系统的。(它也兼容ext2/3文件系统)。命令的执行顺序是很重要的。
|
||||
注意,调整逻辑卷大小之后,也需要对文件系统调整大小进行匹配。这个额外的步骤各不相同,取决于创建文件系统的类型。在本文中,我们使用'lv1'创建了ext4类型的文件系统,所以这里的操作是针对ext4文件系统的。(ext2/3文件系统也类同)。命令的执行顺序是很重要的。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们卸载掉lv1卷
|
||||
|
||||
@ -174,13 +172,12 @@ LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
# e2fsck -f /dev/volume-group1/lv1
|
||||
|
||||
完成以后,ext4信息已经更新。
|
||||
运行以下命令扩展文件系统以后,ext4信息就更新了。
|
||||
|
||||
# resize2fs /dev/volume-group1/lv1
|
||||
|
||||
现在,这个逻辑卷应该已经扩展到200MB了。我们检查LV的状态来验证。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# lvdisplay
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
@ -200,14 +197,13 @@ LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
- currently set to 256
|
||||
Block device 253:2
|
||||
|
||||
现在,这个逻辑卷可以再次挂载,同样这个方法使用其他分区。
|
||||
现在,这个逻辑卷可以再次挂载,同样这个方法也可用于其他分区。
|
||||
|
||||
### 缩减一个LVM卷 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这章节介绍缩减LVM卷大小的方法。命令的顺序同样重要。并且,下列命令对ext2/3/4文件系统同样有效。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
注意减少逻辑卷的大小值若小于储存的数据大小,会出现数据丢失。
|
||||
注意减少逻辑卷的大小值若小于储存的数据大小,存储在后面的数据会丢失。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,卸载掉卷。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -217,7 +213,7 @@ LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
# e2fsck -f /dev/volume-group1/lv1
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,更新ext4信息。
|
||||
接下来缩小文件系统,更新ext4信息。
|
||||
|
||||
# resize2fs /dev/volume-group1/lv1 100M
|
||||
|
||||
@ -254,8 +250,7 @@ LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
### 扩展一个卷组 ###
|
||||
|
||||
本节将讨论扩展卷组的方法,将一个物理卷添加到卷组。让我们假设我们的卷组'volume-group1'已经满了,需要扩大。收上的硬盘(sdb)已经没有其他空闲分区,我们添加了另外一个硬盘(sdc)。我们将看到如何从sdc扩展一个卷组,并增加一个分区。
|
||||
|
||||
本节将讨论扩展卷组的方法,将一个物理卷添加到卷组。让我们假设我们的卷组'volume-group1'已经满了,需要扩大。手上的硬盘(sdb)已经没有其他空闲分区,我们添加了另外一个硬盘(sdc)。我们将看到如何把sdc的分区添加到卷组以扩展。
|
||||
|
||||
检测现在卷组状态
|
||||
|
||||
@ -316,7 +311,7 @@ LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
# vgextend volume-group1 /dev/sdc1
|
||||
|
||||
使用vgdisplay来验证。
|
||||
使用vgdisplay来验证(可以看到卷组大小已经增大)。
|
||||
|
||||
# vgdisplay
|
||||
|
||||
@ -343,7 +338,7 @@ LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
Free PE / Size 1262 / 4.93 GiB
|
||||
VG UUID bwd2pS-fkAz-lGVZ-qc7C-TaKv-fFUC-IzGNBK
|
||||
|
||||
注意,尽管我们使用一个单独的磁盘做示范,其实只要是‘8e’类型的磁盘都可以用来扩展卷组。
|
||||
注意,尽管我们使用一个单独的磁盘做示范,其实只要是‘8e’类型的磁盘分区都可以用来扩展卷组。
|
||||
|
||||
总结一下,LVM是一个非常给力的工具,用来创建和管理可变大小的分区。本文中,我们已经看见了动态分区如何在LVM中创建和使用。我们也看见了扩展/缩小逻辑卷和卷组的方法,和如何增加一个新的磁盘到LVM。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -353,6 +348,6 @@ LVM使用分层结构,如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/use-lvm-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic___](http://www.vicyu.net) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Vic___](http://www.vicyu.net) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
||||
OpenELEC 4.0.4 Now Out, Is Based on XBMC 13.1 “Gotham”
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**OpenELEC 4.0.4, an embedded operating system built specifically to run XBMC, the open source entertainment media hub, is out and uses XBMC 13.1 as a base.**
|
||||
|
||||
The OpenELEC makers are following the XBMC development cycle very closely and they have released a new version of their distribution, 4.0.4. It comes packed with all the goodies from XBMC 13.1 “Gotham” and the devs have made some changes of their own.
|
||||
|
||||
“This release includes some bugfixes, security fixes and improvements since OpenELEC-4.0.3. Besides the usual bugfixes and package updates we updated XBMC with the last fixes to XBMC 13.1 (final) which contains a lot of fixes for issues found after the XBMC-13.0 release (some of them we already shipped with OpenELEC-4.0.0).”
|
||||
|
||||
“We found and fixed with the help of ‘popcornmix’ some RaspberryPi related issues in kernel, firmware and XBMC code. Many thanks to him for the help! OpenELEC-4.0.4 is now the next stable release, which is a bugfix and securityfix release of the OpenELEC-4.0 series,” said the developers on the official website.
|
||||
|
||||
OpenELEC 4.0.3 features some pretty interesting updates and fixes. For example, e2fsprogs has been updated to version 1.42.10, bluez has been updated to version 5.19, fontconfig is now at version 2.11.1, systemd 213 has been integrated by default, gnutls 3.2.12 has been added to fix some security problems, and a new Linux kernel, 3.14.5, has been implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the DVB-T2 support for GeniaTech T220 / August T210 devices has been fixed, support has been added to disable WOL for broken drivers, “e1000e” has been added as broken driver, and the RPi support patch has been updated.
|
||||
|
||||
If you already have an older version of OpenELEC, you might consider upgrading the system instead of installing it from scratch. This can be done safely if the OS is at least at version 3.2.
|
||||
|
||||
If you try to update from an older version of the operating system you might find that some of the plugins and add-ons are no longer working. It's also advisable to back up the system before attempting an upgrade.
|
||||
|
||||
XBMC 13.1 “Gotham,” the distribution used as a base, comes with Android hardware decoding, various Raspberry Pi and Android speed improvements, stereoscopic 3D Rendering, better touchscreen support, improved UPnP capabilities, lots of audio engine improvements, better subtitle searches, extended Python and JSON-RPC API for developers, FFmpeg 1.2, and much more.
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the official [announcement][1] for a complete list of changes and improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
### Download the latest OpenELEC 4.0.4: ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [OpenELEC 4.0.4 (tar.bz2) 64-bit][2][binary] [145 MB]
|
||||
- [OpenELEC 4.0.4 (tar.bz2) 32-bit][3][binary] [142 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/OpenELEC-4-0-4-Is-Out-and-Based-on-XBMC-13-1-quot-Gotham-quot-445802.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://openelec.tv/news/22-releases/129-openelec-4-0-4-released
|
||||
[2]:http://openelec.tv/get-openelec/download/viewdownload/8/339
|
||||
[3]:http://openelec.tv/get-openelec/download/viewdownload/8/338
|
||||
@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Open Source SDN Project OpenDaylight Adds New Members
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The [Linux Foundation][1]'s [OpenDaylight][2] project for promoting open source [software-defined networking][3] (SDN) continues to grow. [Extreme Networks][4] (EXTR), [Flextronics][5] and [Oracle][6] (ORCL) are now among the initiative's members.
|
||||
|
||||
The three companies, which officially joined OpenDaylight June 5, bring the total number of OpenDaylight project members to 39. The project also enjoys the support of 195 developers collaborating to help build an open source SDN platform.
|
||||
|
||||
The new members bring additional expertise in data center and cloud computing design and infrastructure to OpenDaylight's portfolio. Extreme Networks specializes in high-performance networking solutions for enterprises, while Flextronics provides systems design, manufacturing and logistics. Oracle's broad operations, meanwhile, focus on a variety of areas in the cloud and the data center.
|
||||
|
||||
OpenDaylight leaders are celebrating the project's membership growth as a further step toward creating an SDN ecosystem that is centered on open standards and free from domination by particular organizations. "More voices at the table means stronger debate and better code," said Jacques Neela, executive director, OpenDaylight. "We are thrilled to see such a diversity of new members joining who represent an even broader range of perspectives on SDN and NFV."
|
||||
|
||||
The first software release from OpenDaylight, which was itself formed in April 2013, [appeared in February][7] under the name Hydrogen.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/open-source-sdn-project-opendaylight-adds-new-members
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.opendaylight.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://thevarguy.com/sdn
|
||||
[4]:http://www.extremenetworks.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.flextronics.com/
|
||||
[6]:http://oracle.com/
|
||||
[7]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/020514/embargo-until-feb-4-1130-am-est-opendaylight-releases-fir
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu Desktop Next 14.10 Images Available to Download
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
Unity 8′s tablet face
|
||||
|
||||
**Desktop builds of Ubuntu 14.10 using Unity 8 and Mir by default have [been made available][1] to download — not that most users will want to.**
|
||||
|
||||
Plans for a separate Unity 8 desktop flavour were [discussed last month][2]. The aim of the images is to provide developers and testers with a means to identify and document the types of changes needed to tailor both fledgling technologies to traditional desktop usage.
|
||||
|
||||
What these images are not is any sort of stable consumer release ready for production testing. These builds are, and will continue to be, highly unstable, buggy and in a state of feature flux from now up until October — and possibly beyond. Anyone expecting a polished, useable or ‘converged’ desktop will be sorely disappointed as the Unity 8 desktop ISO currently uses the Tablet UI.
|
||||
|
||||
### Work Getting Underway ###
|
||||
|
||||
Work on building competent window management features into Mir and Unity 8 is only just getting underway. Similarly, since desktop-grade graphics chips are yet to add Mir compatible GPU drivers the experience will vary wildly between hardware and users. Virtual machine support is also not a given.
|
||||
|
||||
As Unity 8 on the desktop starts to come together users won’t be presented with a UI too dissimilar to what they’re used to, hinted Ubuntu’s founder Mark Shuttleworth in a recent video Q&A.
|
||||
|
||||
This is good news. Microsoft tried to foist a tablet, touch-orientated UI on desktop users with Windows 8. Reception was mixed and the critical mauling severe. It has had to continually issue “refinements” — ‘concessions’ if you want to be cynical — to counter the complaints.
|
||||
|
||||
### Download Unity 8 Desktop Builds ###
|
||||
|
||||
Regular Ubuntu 14.10, due for release on October 23, will continue to be based on X.Org, Compiz and Unity 7. Unity 8 running on Mir is expected to be made default desktop before the next LTS, due in April 2016.
|
||||
|
||||
Largely unusable at this point, the images linked to below are designed primarily to assist developers test and improve, not help Joe User spin TARDIS-style to Ubuntu’s future.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Ubuntu Desktop Next 14.10 (.iso)][3]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/06/unity-8-daily-build-images-go-live
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://blueprints.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+spec/client-1410-unity8-desktop-iso
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/05/ubuntu-unity-8-desktop-flavour-discussed
|
||||
[3]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-desktop-next/daily-live/current/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
OpenELEC 4.0.4 现已发布, 基于 XBMC 13.1 “Gotham”
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
![] (http://i1-news.softpedia-static.com/images/news2/OpenELEC-4-0-4-Is-Out-and-Based-on-XBMC-13-1-quot-Gotham-quot-445802-2.jpg)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**OpenELEC 4.0.4,一个嵌入式的专门为运行XBMC的操作系统,开放源代码的娱乐媒体中心,已经发布并且使用 XBMC 13.1 作为 基础版本 .**
|
||||
|
||||
OpenELEC 开发商非常密切地关注着 XBMC
|
||||
的产品开发周期而且他们已经发布了他们的最新的 4.0.4 的版本。它来自 XBMC
|
||||
13.1"Gotham"满载着大量的好点子,并且开发者们做了一些了自己的改动。
|
||||
|
||||
"此版本包括一些bug修正、 安全修复和来自于 OpenELEC
|
||||
4.0.3的改进。除了通常的错误修正和软件包更新,我们已经使用最新的补丁文件升级 XBMC 至最新的 XBMC 13.1 (final)
|
||||
这个版本包含了很多已知问题的修复(其中有些我们已附带 OpenELEC 4.0.0中) 在 XBMC 13.0 发布之后 。
|
||||
|
||||
"我们发现并修复了一些和RaspberryPi相关内核问题、 固件和 XBMC 代码中的问题,在 ‘popcornmix’ 的帮助下 ,非常感谢他的帮助 !OpenELEC 4.0.4 现在是下一个稳定版本,这是一款bug修正和 security修复 的 OpenELEC-4.0 系列版本,"开发商的官方网站上如是写道。
|
||||
|
||||
OpenELEC 4.0.3 界面更加美观而且更新和修复了许多问题。例如,e2fsprogs 已更新到版本 1.42.10、 bluez 已更新到版本 5.19、 版本 2.11.1 现在是系统中的字型、 字体设置 213 已被集成并设为默认,gnutls 3.2.12 已被添加用来修复一些安全问题,而且一个新的 Linux 内核,3.14.5,已经来到。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,DVB T2 已经添加了对 GeniaTech T220 / August T210 设备的支持,支持禁用 WOL 由于其破碎的驱动程序、"e1000e"已添加为破碎的驱动程序, RPi 支持补丁已更新。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经有一个旧版的 OpenELEC,你可能需要考虑升级的系统而不是从头开始安装它。如果想顺利地完成安装,至少应该是 3.2 版本。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您尝试从旧版本操作系统的更新,您可能发现一些插件和插件都不再工作。所以最明智的办法就是,在尝试升级之前备份你的系统。
|
||||
|
||||
XBMC 13.1"Gotham,"版本作为一个基础版本,配有 Android 硬件解码、 许多树莓派和 Android 速度方面的改善,立体 3D 渲染,更好的触摸屏支持,改进了 UPnP 功能,很多的音频引擎的改进,更好地字幕搜索、 对开发者友好的扩展如 Python 和 JSON RPC API ,FFmpeg 1.2,还有更多。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
查阅官方 [公告] [1] 的更改和改进的完整列表。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# # # 下载最新的 OpenELEC 4.0.4: # # #
|
||||
- [OpenELEC 4.0.4 (tar.bz2) 64-bit][2][binary] [145 MB]
|
||||
- [OpenELEC 4.0.4 (tar.bz2) 32-bit][3][binary] [142 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/OpenELEC-4-0-4-Is-Out-and-Based-on-XBMC-13-1-quot-Gotham-quot-445802.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[owen-carter](https://github.com/owen-carter) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://openelec.tv/news/22-releases/129-openelec-4-0-4-released
|
||||
[2]:http://openelec.tv/get-openelec/download/viewdownload/8/339
|
||||
[3]:http://openelec.tv/get-openelec/download/viewdownload/8/338
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
开源SDN项目OpenDaylight添加新成员
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Linux基金会][1]的[OpenDaylight][2] 项目促进开源。[软件定义网络][3] (SDN) 继续增长。 [Extreme Networks][4] (EXTR), [Flextronics][5]和[Oracle][6] (ORCL) 现在也是该项目成员了。
|
||||
|
||||
三个公司6月5日正式加入OpenDaylight,成员数达到到39。该项目还有195位合作开发人员,以建立一个开放源码的SDN平台。
|
||||
|
||||
新成员带来在数据中心和云计算的设计和基础设施的知识。Extreme Networks是专业提供高性能网络解决方案的企业,而Flextronics提供系统设计、制作和组织工作。Oracle有广泛的业务,同时专注于各种领域的云计算和数据中心。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
OpenDaylight 领导人正在庆祝项目的会员增长并进一步走向创造一个以开放标准为中心和避免垄断的SDN生态系统。OpenDaylight执行主任Jacques Neela说:"更多的声音意味着更强的辩论和更好的代码,我们很高兴看到这种多样性的新成员加入来加宽探讨SDN和NFV的领域"。
|
||||
|
||||
OpenDaylight的第一款正式软件就是在2013年4月发布的OpenDaylight,该软件首次以Hydrogen的名字在二月出现
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/open-source-sdn-project-opendaylight-adds-new-members
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.opendaylight.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://thevarguy.com/sdn
|
||||
[4]:http://www.extremenetworks.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.flextronics.com/
|
||||
[6]:http://oracle.com/
|
||||
[7]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/020514/embargo-until-feb-4-1130-am-est-opendaylight-releases-fir
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
下一代Ubuntu14.10镜像已开放下载
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 运行在8寸平板上
|
||||
|
||||
**不像大多数用户想得那样,Ubuntu 14.10 的桌面版默认使用Unity 8和Mir([现已可下载][1])**
|
||||
|
||||
根据[上个月的讨论][2]Ubuntu 14.10镜像计划提供单独的Unity 8桌面。 提供此镜像目的是给开发者和测试人员提供一个识别并记录从传统界面到使用两种新技术的界面的变化的手段。
|
||||
|
||||
此镜像并不为为任何稳定的消费者进行生产测试。这个版本会并将会是极不稳定而充满bug的,在十月之前还会不断有变动。所有想要一个完美的、可用的或统一的的桌面的人都会失望,因为Unity 8桌面版镜像用的是平板的UI。
|
||||
|
||||
### 工作进行中 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为Mir和Unity 8建立足够的窗口管理特性的工作正在进行中。同样的,在桌面显卡完全兼容Mir之前,硬件和用户之间发生的经历将会不同,而且不会支持虚拟机。
|
||||
|
||||
桌面Unity 8界面将开始融合平板UI,用户会提出界面与原来相差太大的问题,详见Ubuntu的创始人Mark Shuttleworth最近的视频的问答模块。
|
||||
|
||||
这是个好消息,微软在桌面Windows8上强加了平板界面和为触摸屏设计的UI。结果被骂的不轻,不得不不断地发出"改进"——在你吐槽后让步,来对付投诉。
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载Unity 8桌面版本 ###
|
||||
按计划Ubuntu 14.10预定在10月23日发行稳定版,继续基于 X.Org,Compiz和Unity 7。运行在Mir的Unity8预计将在2016年4月作出下一个 LTS之前成为新的的默认桌面。
|
||||
|
||||
此版本还不具有可用性,下方链接的镜像只是为了协助开发人员测试和完善,不是为了用户适应新的TARDIS样式。
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载下一代Ubuntu14.10 (.iso)][3]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/06/unity-8-daily-build-images-go-live
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://blueprints.launchpad.net/ubuntu/+spec/client-1410-unity8-desktop-iso
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/05/ubuntu-unity-8-desktop-flavour-discussed
|
||||
[3]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-desktop-next/daily-live/current/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user