mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
Translating by ucasFL
This commit is contained in:
parent
54ccefb576
commit
a82b69ddbf
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
ucasFL is Translating
|
||||
pyDash – A Web Based Linux Performance Monitoring Tool
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pydash is a lightweight [web-based monitoring tool for Linux][1] written in Python and [Django][2] plus Chart.js. It has been tested and can run on the following mainstream Linux distributions: CentOS, Fedora, Ubuntu, Debian, Arch Linux, Raspbian as well as Pidora.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use it to keep an eye on your Linux PC/server resources such as CPUs, RAM, network stats, processes including online users and more. The dashboard is developed entirely using Python libraries provided in the main Python distribution, therefore it has a few dependencies; you don’t need to install many packages or libraries to run it.
|
||||
@ -13,9 +13,9 @@ In this article, we will show you how to install pydash to monitor Linux server
|
||||
1. First install required packages: git and Python pip as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
-------------- On Debian/Ubuntu --------------
|
||||
-------------- On Debian/Ubuntu --------------
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install git python-pip
|
||||
-------------- On CentOS/RHEL --------------
|
||||
-------------- On CentOS/RHEL --------------
|
||||
# yum install epel-release
|
||||
# yum install git python-pip
|
||||
-------------- On Fedora 22+ --------------
|
||||
@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ $ sudo pip install virtualenv
|
||||
$ virtualenv pydashtest #give a name for your virtual environment like pydashtest
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Create Virtual Environment
|
||||
@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ Important: Take note the virtual environment’s bin directory path highlighted
|
||||
$ source /home/aaronkilik/pydash/pydashtest/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Active Virtual Environment
|
||||
@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ $ pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
$ vi pydash/settings.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Set Secret Key
|
||||
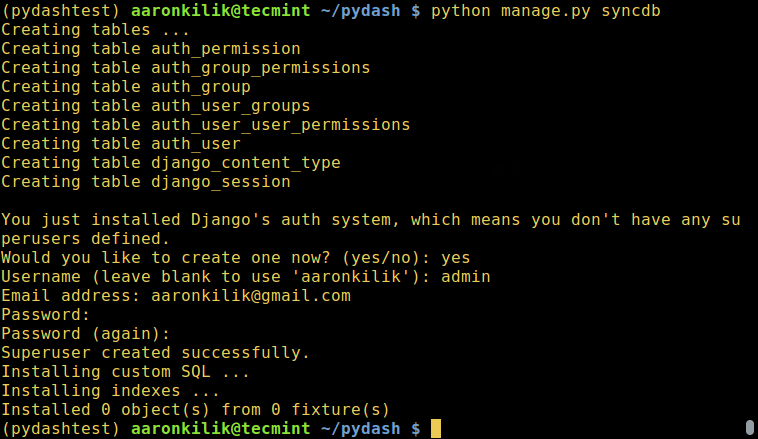
@ -99,7 +99,7 @@ Password: ###########
|
||||
Password (again): ############
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
][7]
|
||||
|
||||
Create Project Database
|
||||
@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ $ python manage.py runserver
|
||||
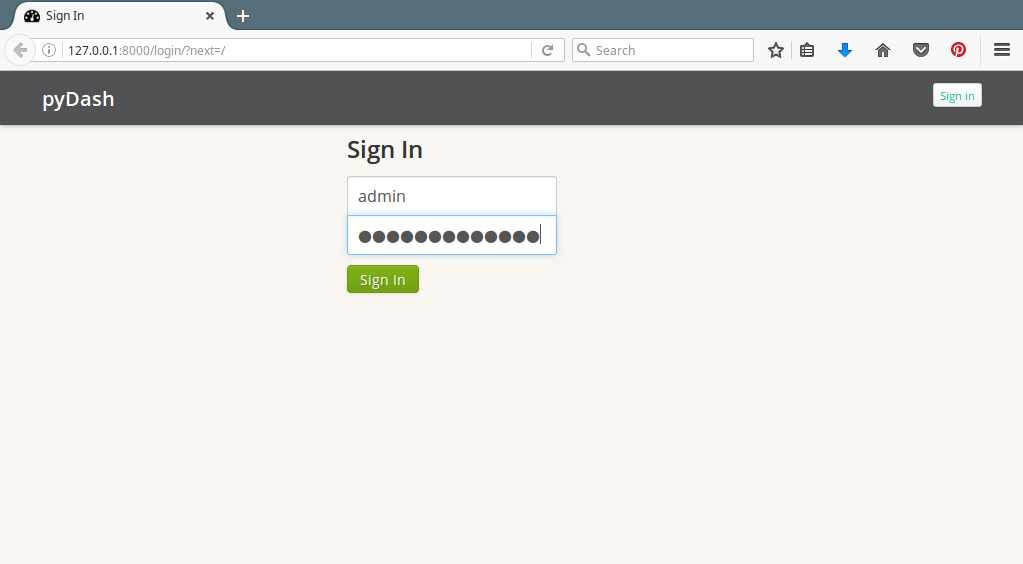
10. Next, open your web browser and type the URL: http://127.0.0.1:8000/ to get the web dashboard login interface. Enter the super user name and password you created while creating the database and installing Django’s auth system in step 8 and click Sign In.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
pyDash Login Interface
|
||||
@ -123,7 +123,7 @@ pyDash Login Interface
|
||||
Simply scroll down to view more sections.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
pyDash Server Performance Overview
|
||||
@ -131,7 +131,7 @@ pyDash Server Performance Overview
|
||||
12. Next, screenshot of the pydash showing a section for keeping track of interfaces, IP addresses, Internet traffic, disk read/writes, online users and netstats.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
][10]
|
||||
|
||||
pyDash Network Overview
|
||||
@ -139,7 +139,7 @@ pyDash Network Overview
|
||||
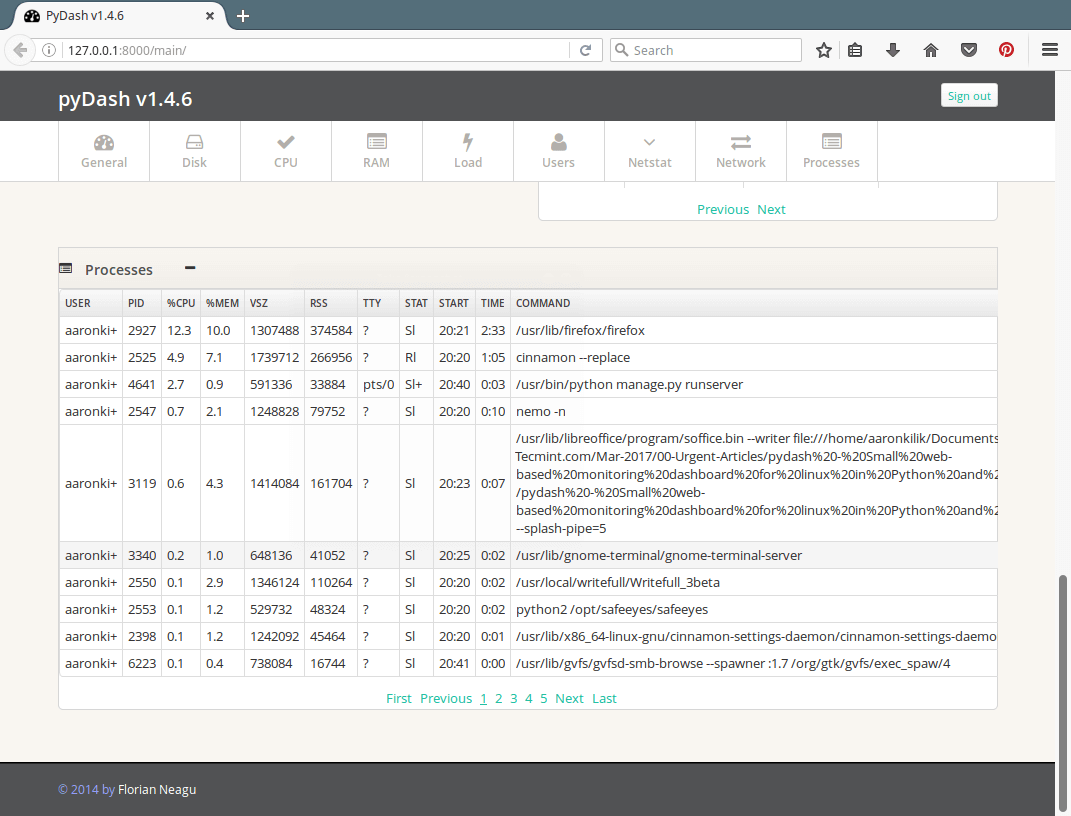
13. Next is a screenshot of the pydash main interface showing a section to keep an eye on active processes on the system.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
pyDash Active Linux Processes
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user