mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-13 22:30:37 +08:00
Merge pull request #1025 from GOLinux/master
Translated: How to manage ip addresses and subnets with phpIPAM.md
This commit is contained in:
commit
a7b99aaf53
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
|||||||
|
Translating by GOLinux ...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
How to launch applications differently with Gnome-Pie on Linux desktop
|
How to launch applications differently with Gnome-Pie on Linux desktop
|
||||||
================================================================================
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
The biggest complaint you can hear those days about Ubuntu is the new Unity interface. I remember leaving for Archlinux precisely when Unity started to rise, and when it was made clear that it was here to stay. However, Unity indirectly has led to good consequences: it allowed other distributions and other desktop environments to become more prominent as people were unhappy with it. If your system can support it, no one is against a bit of eye candy.
|
The biggest complaint you can hear those days about Ubuntu is the new Unity interface. I remember leaving for Archlinux precisely when Unity started to rise, and when it was made clear that it was here to stay. However, Unity indirectly has led to good consequences: it allowed other distributions and other desktop environments to become more prominent as people were unhappy with it. If your system can support it, no one is against a bit of eye candy.
|
||||||
@ -67,4 +69,4 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/launch-applications-differently-gnome-pie-linux-
|
|||||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[1]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/gnome-pie/
|
[1]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/gnome-pie/
|
||||||
[2]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14247093043/
|
[2]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14247093043/
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -1,195 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
Translating by GOLinux ...
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
How to manage ip addresses and subnets with phpIPAM
|
|
||||||
================================================================================
|
|
||||||
A typical network/system admin is responsible for managing one or more subnets within the network under control. For example, when a LAN segment is assigned a /24 subnet, a total of 254 IP addresses can be used for different purposes. To keep track of what IP addresses are assigned to which hosts, some sort of documentation is needed. The easiest way to do it would be maintaining a single spreadsheet which documents IP address allocation information. This works like a charm for a small network with only one admin. However, relying on a spreadsheet is not convenient and can be error-prone with multiple large networks. Worse, if there are multiple admins involved, updating the spreadsheet could be tricky as each admin could often end up with different versions of the document.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
One way to manage IP address allocations more systematically is using a web based IP address management tool. Not only can the web based tool be accessed from anywhere, but a backend database also ensures that all updates to the database are properly synchronized and applied in real time. While there are many web applications available, we will be focusing on setting up [phpIPAM][1] (IP Address Manager) in this tutorial. phpIPAM is an open source, efficient IP address management application with the following features.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- Support for both IPv4 and IPv6 (unlike many other tools, IPv6 support is very good)
|
|
||||||
- Built in IPv4 and IPv6 calculator
|
|
||||||
- Supports CIDR notations
|
|
||||||
- MySQL support
|
|
||||||
- Nested subnets
|
|
||||||
- User/group based permissions
|
|
||||||
- Visual reporting tool
|
|
||||||
- Import/export using .xls files
|
|
||||||
- Device, VRF, and VLAN support
|
|
||||||
- Powerful search engine
|
|
||||||
- Email notifications
|
|
||||||
- Supports AD/LDAP based authentication
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The demo site for phpIPAM is available at [http://demo.phpipam.net][2].
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In this tutorial, we will be **setting up phpIPAM along with Apache web server in the Ubuntu environment**.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Installing phpIPAM on Ubuntu ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
First of all, install required packages using apt-get.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# apt-get install apache2 mysql-server php5 php5-gmp php-pear php5-mysql php5-ldap wget
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If MySQL has been installed for the first time, please set the root password using the following command.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# mysqladmin -u root password NEWPASSWORD
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
phpIPAM can be set up with any web server directory. We will set it up in the /phpipam/ sub directory under the root directory of Apache web server.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Download phpIPAM package.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# wget http://kent.dl.sourceforge.net/project/phpipam/phpipam-1.0.tar
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Extract the package into the web server directory.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# cp phpipam-1.0.tar /var/www/
|
|
||||||
# cp /var/www/
|
|
||||||
# tar xvf phpipam-1.0.tar
|
|
||||||
# rm phpipam-1.0.tar
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now, specify the MySQL username and password, as well as its base directory.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# vim /var/www/phpipam/config.php
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
----------
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$db['host'] = "localhost";
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## MySQL user for ipam ##
|
|
||||||
$db['user'] = "phpipam";
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## password for the MySQL user ##
|
|
||||||
$db['pass'] = "phpipamadmin";
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## database for MySQL ##
|
|
||||||
$db['name'] = "phpipam";
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## base directory ##
|
|
||||||
define('BASE', "/phpipam/");
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The base directory needs to be defined in the provided .htaccess file.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# vim /var/www/phpipam/.htaccess
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
> RewriteBase /phpipam/
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Preparing Apache Web Server ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
phpIPAM needs the rewrite module for operation. The module can be enabled in an Ubuntu or Debian machine using a2enmod command as follows.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# a2enmod rewrite
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Next, Apache's default configuration needs to be changed as well. Please add/modify your configuration to look like the one below.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# vim /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
----------
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
<Directory /var/www/>
|
|
||||||
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks MultiViews
|
|
||||||
AllowOverride all
|
|
||||||
Order allow,deny
|
|
||||||
allow from all
|
|
||||||
</Directory>
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Finally, restart Apache web service.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# service apache2 restart
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Finalizing Installation ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We can finalize the installation of phpIPAM by using the web browser. Pointing the browser to the URL: http://<serverIP>/phpIPAM will show the following phpIPAM installation page. We can proceed to automatic database installation.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
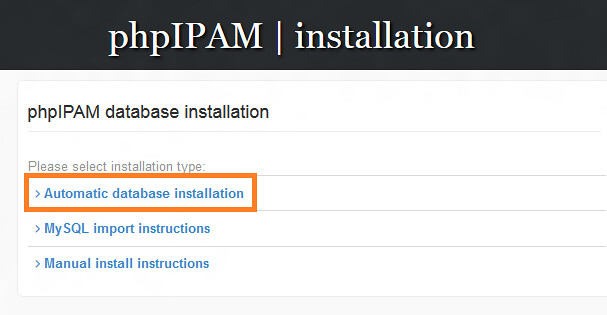
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
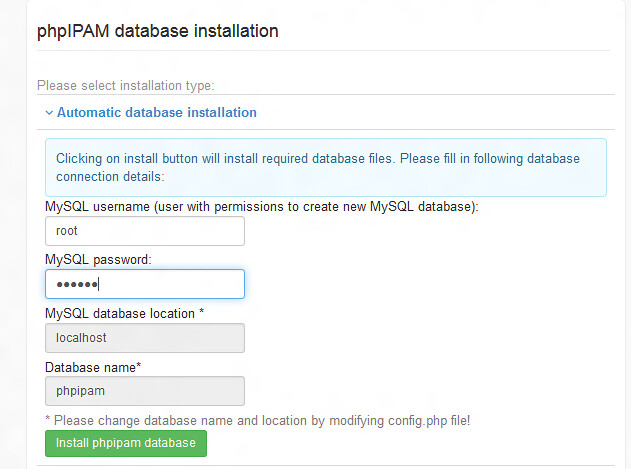
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now phpIPAM should be up and running. We can login using the following default credentials.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- **URL**: http://<serverIP>/phpipam
|
|
||||||
- **User**: Admin
|
|
||||||
- **Pass**: ipamadmin
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Manage IP Addresses with phpIPAM ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In the rest of the tutorial, we will walk you through how to manage subnets and IP addresses with phpIPAM.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Creating a section ####
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Let us start by adding a section for our network. Click on Administration > Sections.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
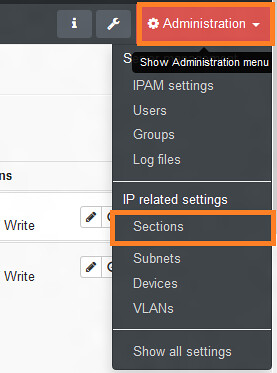
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Click on "Add Section". Now we can name our section as we want it to be displayed. Fill in the details of the section.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[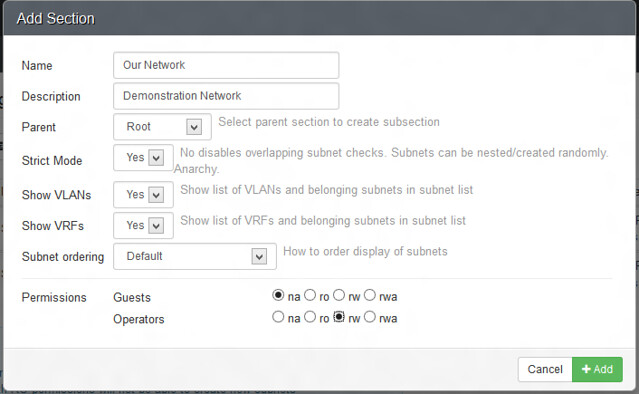][3]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Creating a subnet ####
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
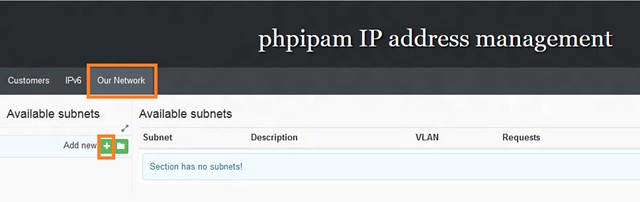
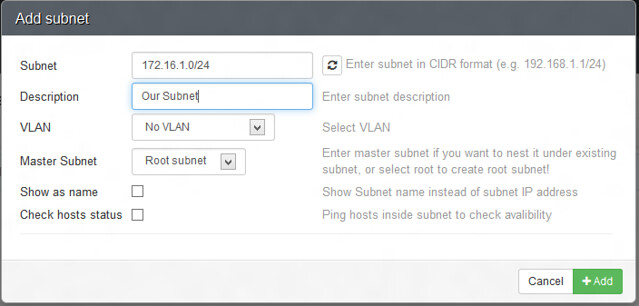
Next, we add a new subnet 172.16.1.0/24 under the section 'Our Network'. Click on Our Network > Add Subnet
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now we can easily add IP addresses in the subnet. One method of adding IP addresses is to add them one by one. phpIPAM provides an alternative method to scan all the hosts and add them automatically without much hassle. It can scan the local subnet located in the same broadcast domain, as well as remote subnets reachable through routing. After selecting a subnet, click on 'scan subnet for new hosts' to scan IP addresses as shown below.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[][4]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
After the scan is performed, the discovered IP addresses can be added into the database by clicking the 'Add discovered hosts' button at the bottom.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Creating an IPv6 subnet ####
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
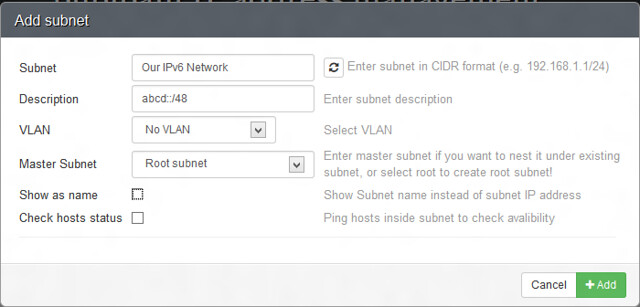
IPv6 subnets can also be created in a similar process. We specify the IPv6 network as showed in the screenshot.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
All the tools available for IPv4 can be used for IPv6 as well.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Creating a nested subnet ####
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
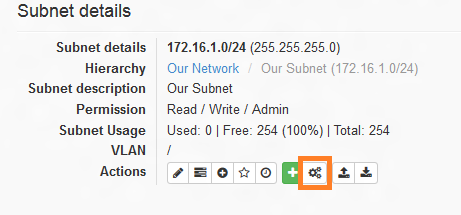
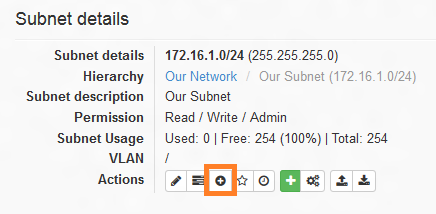
phpIPAM also provides the option of creating nested subnets for both IPv4 and IPv6. For example, we will be dividing our IP block 172.16.1.0/24 into 4 smaller subnets (/26), each for a specific department within the organization. After selecting the /24 subnet, we can create a nested subnet using the 'Add a new nested subnet' button. The screenshot below shows the icon for adding a nested subnet.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[][5]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
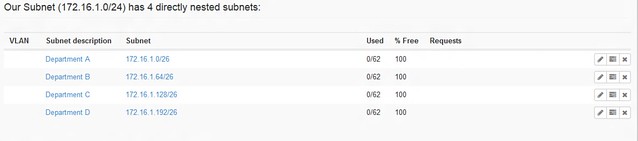
After all the subnets have been created, we should have similar output. Following is a nested subnet preview window.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[][6]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
#### Adding users and groups ####
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
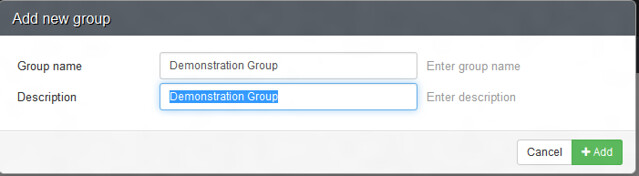
First, we will create a group with READ/WRITE permission to the section 'Our network'. This can be done by selecting Administration > Groups > Create Group.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
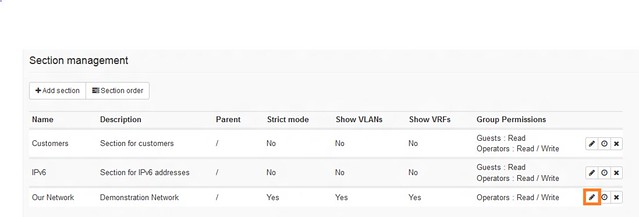
Now that the group has been created, we modify section permission by selecting Administration > Sections, and then editing the section.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[][7]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
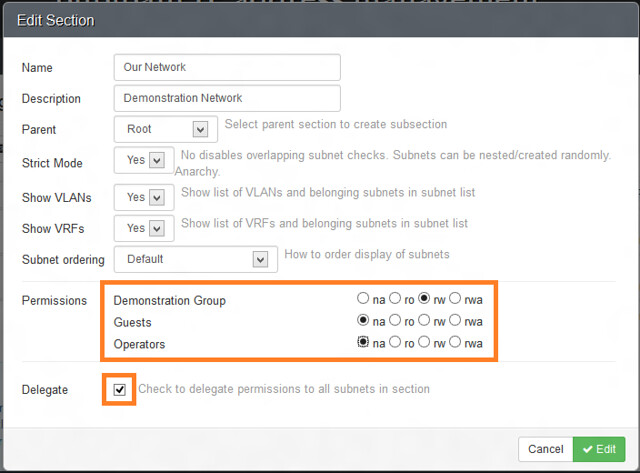
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
We will create a user named 'user1'. We will add the user to the group 'Demonstration group' so that it inherits all necessary permissions from the group. We start by clicking on Administration > Users > Create user.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[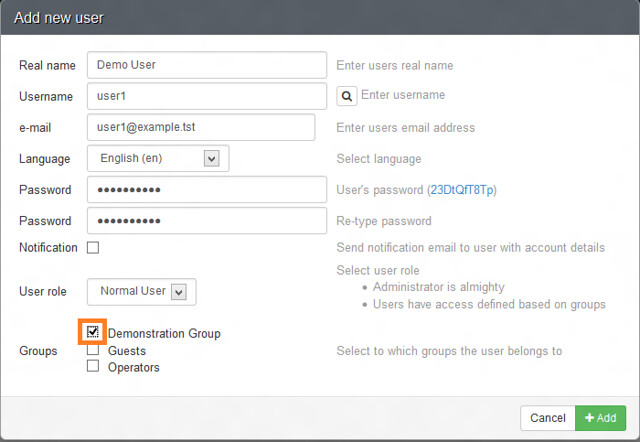][8]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Now we can log in as this user and add/modify IP addresses under the section 'Our network'.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To sum up, phpIPAM is a versatile IP address management tool that can be used for both IPv4 and IPv6. This tutorial focused on the basics that can help you get started. Be sure to test with all the available features like using IP address calculator, adding devices, VLANs and VRFs, and import/export using xls.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Hope this helps.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/manage-ip-addresses-subnets-phpipam.html
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[1]:http://phpipam.net/
|
|
||||||
[2]:http://demo.phpipam.net/
|
|
||||||
[3]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14030287410/
|
|
||||||
[4]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14193740006/
|
|
||||||
[5]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14030318447/
|
|
||||||
[6]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14216904305/
|
|
||||||
[7]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14193739966/
|
|
||||||
[8]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14214506012/
|
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
|
|||||||
|
Translating by GOLinux ...
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
如何使用phpIPAM来管理IP地址和子网
|
||||||
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
|
通常,网络或系统管理员有责任来管理所管理的网络下的一个或多个子网。例如,当一个网段分配了/24子网,那么该子网就有254个IP地址可以用于不同目的。要跟踪某个IP被分配到了哪个主机,就需要某种文件编制。最简单的方法,就是使用一个电子表格来记录IP地址的分配信息。此方法对于只有一个管理员,并且网络很小的情况下比较奏效。然而,对于多个大型网络而言,依赖于电子表格并不方便,而且十分容易出错。更糟糕的是,如果有多个管理员参与管理,更新电子表格就十分麻烦了,因为每个管理员可能生成各种不同版本的文档记录。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
一种系统地管理IP地址分配的方式是使用网络化的IP地址管理工具。不仅仅是因为网络化管理工具能在任何地方访问并管理,而且其后端数据库也能保证所有更新能正确同步并实时生效。尽管有许多可用的网络化应用工具,但我们将在此教程中关注如何来安装[phpIPAM][1](IP地址管理工具)。phpIPAM是一个开源、高效的IP地址管理应用软件,有着以下一些特性。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 同时支持IPv4和IPv6(和其它工具不同,它对IPv6支持得很好)
|
||||||
|
- 内建IPv4和IPv6计算器
|
||||||
|
- 支持无类域间路由(CIDR)标记
|
||||||
|
- 支持MySQL数据库
|
||||||
|
- 子网嵌套
|
||||||
|
- 基于用户/组权限
|
||||||
|
- 可视化报表工具
|
||||||
|
- 使用.xls文件导入/导出
|
||||||
|
- 支持设备、VRF和VLAN
|
||||||
|
- 强大的搜索引擎
|
||||||
|
- 电子邮件标记
|
||||||
|
- 支持基于AD/LDAP的验证
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
可访问[http://demo.phpipam.net][2]查看phpIPAM演示网站。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在本教程中,我们将**在Ubuntu环境中使用Apache来配置phpIPAM**。
|
||||||
|
### 在Ubuntu上安装phpIPAM ###
|
||||||
|
首先,使用apt-get来安装需要的软件包。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# apt-get install apache2 mysql-server php5 php5-gmp php-pear php5-mysql php5-ldap wget
|
||||||
|
如果MySQL是首次安装,请使用以下命令来设置root密码。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# mysqladmin -u root password NEWPASSWORD
|
||||||
|
phpIPAM可以安装在任何Web服务器目录中,我们将会安装到Apache Web服务器的根目录下的/phpipam/子目录中。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
下载phpIPAM软件包。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# wget http://kent.dl.sourceforge.net/project/phpipam/phpipam-1.0.tar
|
||||||
|
将软件包解压到Web服务器相应目录。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# cp phpipam-1.0.tar /var/www/
|
||||||
|
# cp /var/www/
|
||||||
|
# tar xvf phpipam-1.0.tar
|
||||||
|
# rm phpipam-1.0.tar
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
现在来指定MySQL的用户名和密码,同时指定基准目录。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# vim /var/www/phpipam/config.php
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
----------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$db['host'] = "localhost";
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## MySQL user for ipam ##
|
||||||
|
$db['user'] = "phpipam";
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## password for the MySQL user ##
|
||||||
|
$db['pass'] = "phpipamadmin";
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## database for MySQL ##
|
||||||
|
$db['name'] = "phpipam";
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## base directory ##
|
||||||
|
define('BASE', "/phpipam/");
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
需要在提供的.htaccess文件中指定基准目录。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# vim /var/www/phpipam/.htaccess
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
> RewriteBase /phpipam/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 准备Apache Web服务器 ###
|
||||||
|
phpIPAM需要为该操作重写模块,该模块可以在Ubuntu或Debian机器上使用以下命令来启用。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# a2enmod rewrite
|
||||||
|
接下来,需要修改Apache的默认配置。请添加/修改你的配置,使它看起来像下面这样。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# vim /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/000-default
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
----------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
<Directory /var/www/>
|
||||||
|
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks MultiViews
|
||||||
|
AllowOverride all
|
||||||
|
Order allow,deny
|
||||||
|
allow from all
|
||||||
|
</Directory>
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
最后,重启Apache Web服务。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# service apache2 restart
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 完成安装 ###
|
||||||
|
我们可以使用浏览器来完成phpIPAM的安装。将浏览器地址指向URL: http://<serverIP>/phpIPAM,将会显示以下phpIPAM安装页面。我们可以开始自动化数据库安装。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
现在,phpIPAM应该已经起来,并正在运行了,我们可以使用以下默认凭证来登录。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- **URL**: http://<serverIP>/phpipam
|
||||||
|
- **User**: Admin
|
||||||
|
- **Pass**: ipamadmin
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### 使用phpIPAM管理IP地址 ###
|
||||||
|
在本教程的剩下部分,我们将引领你进入phpIPAM的子网和IP地址管理。
|
||||||
|
#### 创建区域 ####
|
||||||
|
让我们从为我们的网络创建区域开始吧。点击“管理” > “区域”。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
点击“添加区域”。现在我们可以为我们的添加的区域取个你想要的名称了,填上区域的详细情况。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
][3]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### 创建子网 ####
|
||||||
|
接下来,在“我们的网络”区域下添加一个新的子网172.16.1.0/24。点击“我们的网络” > “添加子网”
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
现在,我们可以很容易地在子网中添加IP地址了。一种方法是逐个来添加它们,phpIPAM提供了一个可供选择的方法:扫描所有主机并自动添加,这一点都不麻烦。它可以扫描位于同一广播域下的本地子网,也可以通过路由扫描到远程子网。在选择一个子网后,像下面这样点击“扫描子网中的新主机”来扫描IP地址。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
][4]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在扫描完成后,发现的IP地址可以通过点击底部“添加发现的主机”按钮来将IP地址添加到数据库。
|
||||||
|
#### 创建IPv6子网 ####
|
||||||
|
可以通过相似的步骤来创建IPv6子网,像下面截图中展示的那样来指定IPv6网络。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
所有用于IPv4的工具也可以用于IPv6.
|
||||||
|
#### 创建嵌套子网 ####
|
||||||
|
phpIPAM也提供了创建嵌套子网的选项,可以用于IPv4和IPv6。例如,我们将172.16.1.0/24 IP区块划分成4个更小的子网(/26),每个子网用于组织内特定的部门。在选择/24子网后,我们可以使用“添加新的嵌套子网”按钮来创建嵌套子网。截图中展示了添加嵌套子网的图标。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[5]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在所有的子网创建完毕后,我们应该有相同的输出。以下是嵌套子网预览窗口。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[6]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### 添加用户和组 ####
|
||||||
|
首先,我们将为“我们的网络”创建一个具有读/写权限的组。这项工作可以通过选择“管理” > “组” > “创建组”来完成。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
既然组已经被创建完成,那么我们来修改区域权限,选择“管理” > “区域”,然后编辑区域。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[7]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
我们将创建一个名为“user1”的用户,添加该用户到“演示组”,以便该用户能从该组集成有所必要的权限。我们从点击“管理” > “用户” > “创建用户”开始。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[][8]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
现在,我们能以该用户身份登录,并添加/修改“我们的网络”下的IP地址。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
最后小结,phpIPAM是一个多样化的IP地址管理工具,可以用于IPv4和IPv6。本教程仅关注基本内容,以帮助你开始使用该工具。你一定要测试所有可用的特性,如使用IP地址计算器,添加设备,VLAN和VRF,以及使用.xls导入/导出。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
希望本教程对你有所帮助。
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/05/manage-ip-addresses-subnets-phpipam.html
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[1]:http://phpipam.net/
|
||||||
|
[2]:http://demo.phpipam.net/
|
||||||
|
[3]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14030287410/
|
||||||
|
[4]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14193740006/
|
||||||
|
[5]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14030318447/
|
||||||
|
[6]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14216904305/
|
||||||
|
[7]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14193739966/
|
||||||
|
[8]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/14214506012/
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user