mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
commit
a3c55c5583
@ -0,0 +1,345 @@
|
||||
一个八年的 Linux 老用户使用 Windows 10 的体验
|
||||
==========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Windows 10 是2015年7月29日上市的最新一代 Windows NT 系列系统,它是 Windows 8.1 的继任者。Windows 10 支持 Intel 32位平台,AMD64 以及 ARM v7 处理器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*对比:Windows 10与Linux*
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个连续使用 linux 超过8年的用户,我想要去体验一下 Windows 10 ,因为有很多关于它的消息。这篇文章是我观察力的一个重大突破。我将从一个 linux 用户的角度去看待一切,所以这篇文章可能会有些偏向于 linux。尽管如此,本文也绝对不会有任何虚假信息。
|
||||
|
||||
1、用谷歌搜索“download Windows 10”并且点击第一个链接。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*搜索 Windows 10*
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以直接打开: [https://www.microsoft.com/en_us/software-download/Windows10[1]
|
||||
|
||||
2、微软要求我从 Windows 10, Windows 10 KN, Windows 10 N 和 Windows 10 单语言版中选择一个版本。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*选择版本*
|
||||
|
||||
以下是各个版本的简略信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- Windows 10 - 包含微软提供给我们的所有软件
|
||||
- Windows 10N - 此版本不包含媒体播放器
|
||||
- Windows 10KN - 此版本没有媒体播放能力
|
||||
- Windows 10 单语言版 - 仅预装一种语言
|
||||
|
||||
3、我选择了第一个选项“Windows 10”并且单击“确认”。之后我要选择语言,我选择了“英语”。
|
||||
|
||||
微软给我提供了两个下载链接。一个是32位版,另一个是64位版。我单击了64位版--这与我的电脑架构相同。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*下载 Windows 10*
|
||||
|
||||
我的带宽是15M的,下载了整整3个小时。不幸的是微软没有提供系统的种子文件,否则整个过程会更加舒畅。镜像大小为 3.8 GB(LCTT译者注:就我的10M小水管,我使用迅雷下载用时50分钟)。
|
||||
|
||||
我找不到更小的镜像,微软并没有为 Windows 提供网络安装镜像。我也没有办法在下载完成后去校验哈希值。(LCTT 译注:你知道的,这对于 Linux 来说都是常识了)
|
||||
|
||||
我十分惊讶,Windows 在这样的问题上居然如此漫不经心。为了验证这个镜像是否正确下载,我需要把它刻到光盘上或者复制到我的U盘上然后启动它,一直静静的看着它安装直到安装完成。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我用 dd 命令将 win10 的 iso 镜像刻录到U盘上。
|
||||
|
||||
# dd if=/home/avi/Downloads/Win10_English_x64.iso of=/dev/sdb1 bs=512M; sync
|
||||
|
||||
这需要一点时间。在此之后我重启系统并在 UEFI(BIOS)设置中选择从我的U盘启动。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 系统要求 ####
|
||||
|
||||
升级
|
||||
|
||||
- 仅支持从 Windows 7 SP1 或者 Windows 8.1 升级
|
||||
|
||||
全新安装
|
||||
|
||||
- 处理器: 1GHz 以上
|
||||
- 内存: 1GB以上(32位),2GB以上(64位)
|
||||
- 硬盘: 16GB以上(32位),20GB以上(64位)
|
||||
- 显卡: 支持DirectX 9或更新 + WDDM 1.0 驱动
|
||||
|
||||
###Windows 10 安装过程###
|
||||
|
||||
1、Windows 10启动成功了。他们又换了logo,但是仍然没有信息提示我它正在做什么。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Windows 10 Logo*
|
||||
|
||||
2、选择安装语言,时区,键盘,输入法,点击下一步。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*选择语言和时区*
|
||||
|
||||
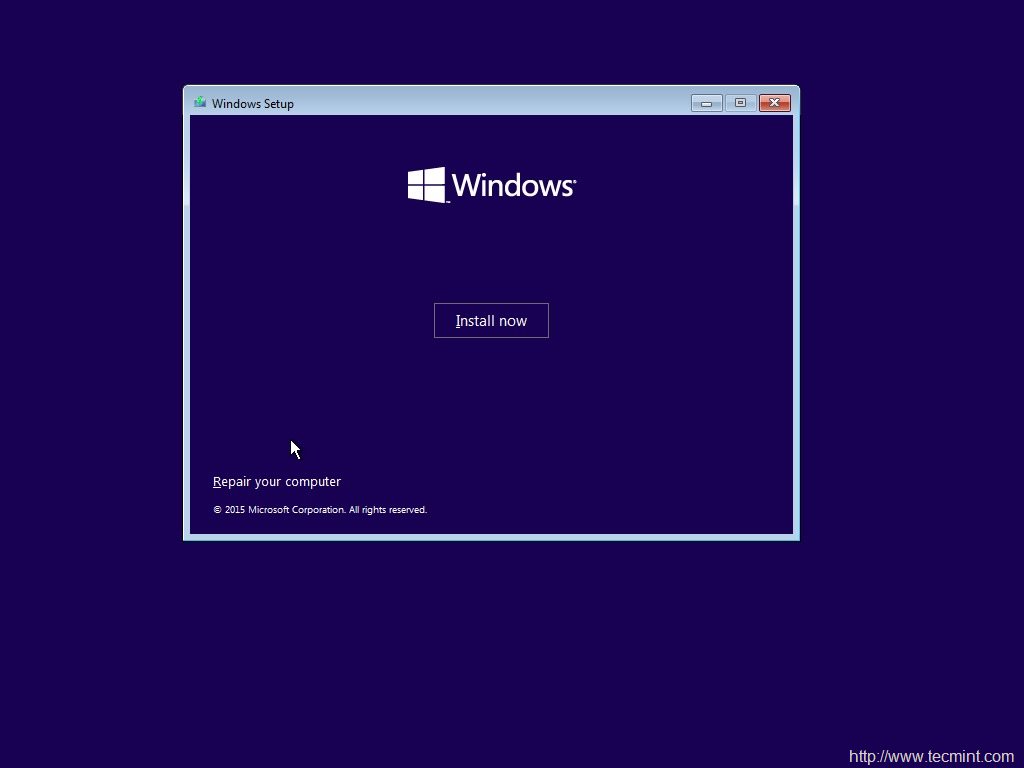
3、点击“现在安装”。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*安装Windows 10*
|
||||
|
||||
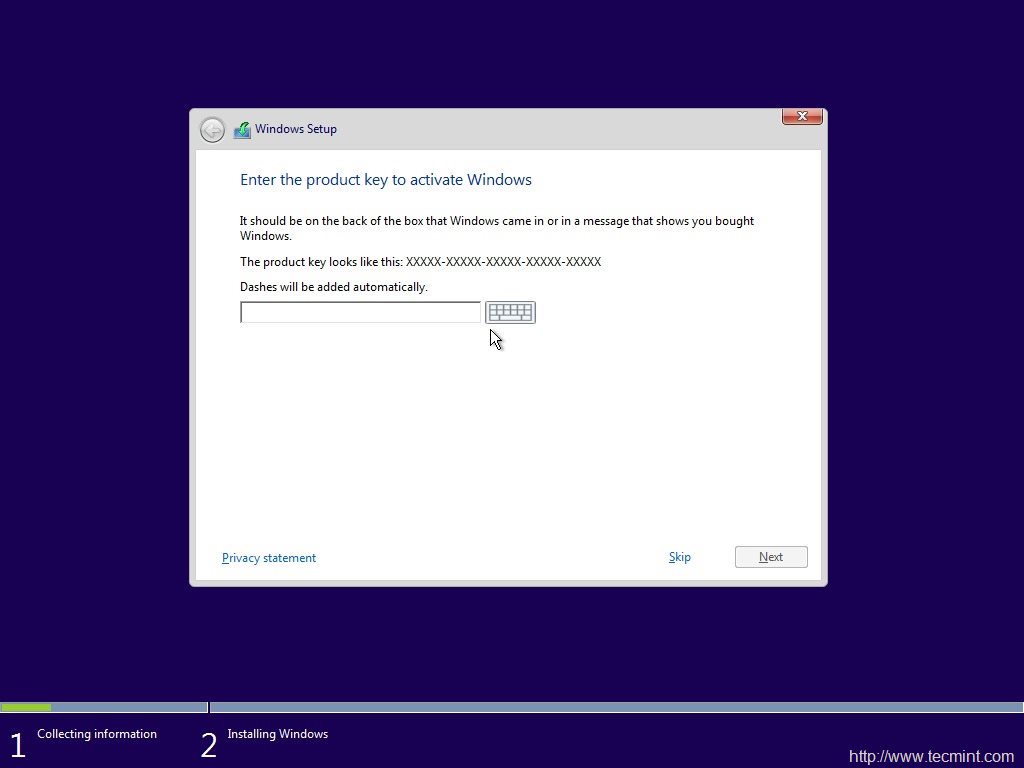
4、下一步是输入密钥,我点击了“跳过”。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Windows 10 产品密钥*
|
||||
|
||||
5、从列表中选择一个系统版本。我选择了 Windows 10专业版。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*选择系统版本*
|
||||
|
||||
6、到了协议部分,选中"我接受"然后点击下一步。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*同意协议*
|
||||
|
||||
7、下一步是选择(从 Windows 的老版本)升级到 Windows 10 或者安装 Windows。我搞不懂为什么微软要让我自己选择:“安装Windows”被微软建议为“高级”选项。但是我还是选择了“安装Windows”。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*选择安装类型*
|
||||
|
||||
8、选择驱动器,点击“下一步”。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*选择安装盘*
|
||||
|
||||
9、安装程序开始复制文件,准备文件,安装更新,之后进行收尾。如果安装程序能在安装时输出一堆字符来表示它在做什么就更好了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*安装 Windows*
|
||||
|
||||
10、在此之后 Windows 重启了。它们说要继续的话,我们需要重启。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*安装进程*
|
||||
|
||||
11、我看到了一个写着“正在准备 Windows”的界面。它停了整整五分多钟!仍然没有说明它正在做什么。没有输出。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*正在准备 Windows*
|
||||
|
||||
12、又到了输入产品密钥的时间。我点击了“以后再说”,并使用快速设置。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*输入产品密钥*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*使用快速设置*
|
||||
|
||||
13、又出现了三个界面,作为 Linux 用户我认为此处应有信息来告诉我安装程序在做什么,但是我想多了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*载入 Windows*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*获取更新*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*还是载入 Windows*
|
||||
|
||||
14、安装程序想要知道谁拥有这台机器,“我的组织”或者我自己。选择我自己并继续。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*选择组织*
|
||||
|
||||
15、在单击继续之前,安装程序提示我加入“Aruze Ad”或者“加入域”。我选择了后者。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*连接网络*
|
||||
|
||||
16、安装程序让我新建一个账户。所以我输入了“user_name”就点击了下一步,我觉得我会收到一个要求我必须输入密码的信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*新建账户*
|
||||
|
||||
17、让我惊讶的是 Windows 甚至都没有显示一个警告或提示信息,告诉我必须创建密码。真粗心。不管怎样,现在我可以体验系统了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Windows 10的桌面环境*
|
||||
|
||||
#### Linux 用户(我)直到现在的体验 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 没有网络安装镜像
|
||||
- 镜像文件太臃肿了
|
||||
- 没有验证 iso 是否为正确的方法(官方没有提供哈希值)
|
||||
- 启动与安装方式仍然与 XP,Win 7,Win 8 相同(可能吧...)
|
||||
- 和以前一样,安装程序没有输出它正在干什么 - 正在复制什么和正在安装什么软件包
|
||||
- 安装程序比 Linux 发行版的更加傻瓜和简单
|
||||
|
||||
####测试 Windows 10####
|
||||
|
||||
18、默认桌面很干净,上面只有一个回收站图标。我们可以直接从桌面搜索网络。底部的快捷方式分别是任务预览、网络、微软应用商店。和以前的版本一样,消息栏在右下角。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*桌面图标*
|
||||
|
||||
19、IE 浏览器被换成了 Edge 浏览器。微软把他们的老IE换成了 Edge (斯巴达计划)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Edge 浏览器*
|
||||
|
||||
测试起来,这个浏览器至少比 IE 要快。他们有相同的用户界面。它的主页包含新闻更新。它还有一个搜索标题栏是“下一步怎么走”。由于浏览器的全面性能提升,它的加载速度非常快。Edge 的内存占用看起来正常。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*性能*
|
||||
|
||||
Edge 也有小娜加成(智能个人助理)、支持 Chrome 扩展、支持笔记(在浏览网页时记笔记)、分享(在选项卡上右击而不必打开其他选项卡)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Linux 用户(我)此时体验 ####
|
||||
|
||||
20、微软确实提升了网页浏览体验。我绝对稳定性和质量还好。现在它并不落后。
|
||||
|
||||
21、对我来说,Edge 的内存占用不算太大。但是有很多用户抱怨它的内存占用太多。
|
||||
|
||||
22、很难说目前 Edge 已经准备好了与火狐或 Chrome竞争。让我们静观其变。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 更多的视觉体验 ####
|
||||
|
||||
23、重新设计的开始菜单 -- 看起来很简洁高效。Merto 磁贴大部分都会动。预先放置了最通用的应用。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Windows*
|
||||
|
||||
而在 Linux 的 Gnome 桌面环境下。我仅仅需要按下 Win 键并输入应用名就可以搜索应用。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*桌面内进行搜索*
|
||||
|
||||
24、文件浏览器 -- 设计的很简洁。左边是进入文件夹的快捷方式。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Windows 文件管理器*
|
||||
|
||||
我们的 Gnome 下的文件管理也同样的简洁高效。从图标上移走了不需要的图形图像是个加分点。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Gnome 的文件管理*
|
||||
|
||||
25、设置 -- 尽管 Windows 10的设置有点精炼,但是我们还是可以把它与 linux 的设置进行对比。
|
||||
|
||||
**Windows 的设置**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Windows 10 设置*
|
||||
|
||||
**Linux Gnome 上的设置**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Gnome 的设置*
|
||||
|
||||
26、应用列表 -- 目前,Linux上的应用列表要好于之前的版本(据我所记,那时我还是一个普通的 Windows 用户),但是 Windows 10 的还比 Gnome 3 的差一点。
|
||||
|
||||
**Windows 的应用列表**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Windows 10 的应用列表*
|
||||
|
||||
**Gnome3 的应用列表**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Gnome3 的应用列表*
|
||||
|
||||
27、虚拟桌面 -- Windows 10 上的虚拟桌面是近来被提及最多的特性之一。
|
||||
|
||||
这是 Windows 10 上的虚拟桌面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Windows 的虚拟桌面*
|
||||
|
||||
这是我们 Linux 用户使用了超过20年的虚拟桌面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Linux 的虚拟桌面*
|
||||
|
||||
#### Windows 10 的其他新特性 ####
|
||||
|
||||
28、Windows 10 自带 wifi 感知。它会把你的 wifi 密码分享给他人。任何在你 wifi 范围内并且曾经通过 Skype, Outlook, Hotmail 或 Facebook与你联系的人都能够获得你的网络接入权。这个特性的本意是让用户可以省时省力的连接网络。
|
||||
|
||||
在微软对于 Tecmint 的问题的回答中,他们说道 -- 用户需要在每次到一个新的网络环境时自己去同意打开 wifi 感知。如果我们考虑到网络安全这将是很不安全的一件事。微软的说法并没有说服我。
|
||||
|
||||
29、从 Windows 7 和 Windows 8.1 升级可以省下买新版的花费。(家庭版 $119 专业版$199)
|
||||
|
||||
30、微软发布了第一个累积更新,这个更新在一小部分设备上会让系统一直重启。Windows可能不知道这个问题或者不知道它发生的原因。
|
||||
|
||||
31、微软内建的“禁用/隐藏我不想要的更新”的功能在我这不起作用。这意味着一旦更新开始推送,你没有方法去禁用/隐藏他们。对不住啦,Windows 用户。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Windows 10 包含的来源于 Linux 的功能 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Windows 10 有很多直接取自 Linux 的功能。如果 Linux 不以 GPL 发布的话,也许以下这些功能永远不会出现在 Windows上。
|
||||
|
||||
32、命令行的包管理器 -- 是的,你没有听错!Windows 10内建了一个包管理器。它只在 Power Shell 下工作。OneGet 是Windows 的官方包管理器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Windows 10的包管理器*
|
||||
|
||||
- 无边窗口
|
||||
- 扁平化图标
|
||||
- 虚拟桌面
|
||||
- 离线/在线搜索一体化
|
||||
- 手机/桌面系统融合
|
||||
|
||||
### 总体印象###
|
||||
|
||||
- 响应速度提升
|
||||
- 动画很好看
|
||||
- 资源占用少
|
||||
- 电池续航提升
|
||||
- Edge 浏览器很稳定
|
||||
- 支持树莓派 2
|
||||
- Windows 10 好的原因是 Windows 8/8.1 没有达到公众预期并且坏的可以
|
||||
- 旧瓶装新酒:Windows 10基本上就是以前的那一套换上新的图标
|
||||
|
||||
测试后我对 Windows 10 的评价是:Windows 10 在视觉和感觉上做了一些更新(就如同 Windows 经常做的那样)。我要为斯巴达计划、虚拟桌面、命令行包管理器、整合在线/离线搜索的搜索栏点赞。这确实是一个更新后的产品 ,但是认为 Windows 10 将是 Linux 的最后一个棺材钉的人错了。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 走在 Windows 前面。它们的做事方法并不相同。在以后的一段时间里 Windows 不会站到 Linux这一旁。也没有什么让 Linux 用户值得去使用 Windows 10。
|
||||
|
||||
这就是我要说的。希望你喜欢本文。如果你们喜欢本篇文章我会再写一些你们喜欢读的有趣的文章。在下方留下你的有价值的评论。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/a-linux-user-using-Windows-10-after-more-than-8-years-see-comparison/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[name1e5s](https://github.com/name1e5s)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/software-download/Windows10ISO
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
|
||||
优秀的开源合作编辑工具
|
||||
六款优秀的开源协作编辑工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
一句话,合作编著就是多个人进行编著。合作有好处也有风险。好处包括更加全面/协调的方式,更好的利用现有资源和一个更加有力的、团结的声音。对于我来说,最大的好处是极大的透明度。那是当我需要采纳同事的观点。同事之间来来回回地传文件效率非常低,导致不必要的延误还让人(比如,我)对整个合作这件事都感到不满意。有个好的合作软件,我就能实时地或异步地分享笔记,数据和文件,并用评论来分享自己的想法。这样在文档、图片、视频、演示文稿上合作就不会那么的琐碎而无聊。
|
||||
|
||||
有很多种方式能在线进行合作,简直不能更简便了。这篇文章表明了我最喜欢的开源实时文档合作编辑工具。
|
||||
简而言之,协作编辑(Collaborative Edit)就是多个人进行编辑。协作有好处也有风险。好处之一是更加全面/协调的方式,更好的利用现有资源和一个更加有力一致的声音。对于我来说,最大的好处是极大的透明度。那是当我需要采纳同事的观点。同事之间来来回回地传文件效率非常低,导致不必要的延误还让人(比如,我)对整个协作这件事都感到不满意。有个好的协作软件,我就能实时地或异步地分享笔记,数据和文件,并用评论来分享自己的想法。这样在文档、图片、视频、演示文稿上协作就不会那么的琐碎而无聊。
|
||||
|
||||
Google Docs 是个非常好的高效应用,有着大部分我所需要的功能。它可以作为一个实时地合作编辑文档的工具提供服务。文档可以被分享、打开并被多位用户同时编辑,用户还能看见其他合作者一个字母一个字母的编辑过程。虽然 Google Docs 对个人是免费的,但并不开源。
|
||||
有很多种方式能在线进行协作,简直不能更简便了。这篇文章展示了我最喜欢的开源的实时文档协作编辑工具。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是我带来的最棒的开源合作编辑器,它们能帮你不被打扰的集中精力进行写作,而且是和其他人协同完成。
|
||||
Google Docs 是个非常好的高效应用,有着大部分我所需要的功能。它可以作为一个实时地协作编辑文档的工具提供服务。文档可以被分享、打开并被多位用户同时编辑,用户还能看见其他协作者一个字母一个字母的编辑过程。虽然 Google Docs 对个人是免费的,但并不开源。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是我带来的最棒的开源协作编辑器,它们能帮你不被打扰的集中精力进行写作,而且是和其他人协同完成。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,17 +15,17 @@ Google Docs 是个非常好的高效应用,有着大部分我所需要的功
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Hackpad 是个开源的基于网页的实时 wiki,基于开源 EtherPad 合作文档编辑器。
|
||||
Hackpad 是个开源的基于网页的实时 wiki,基于开源 EtherPad 协作文档编辑器。
|
||||
|
||||
Hackpad 允许用户实时分享你的文档,它还用彩色编码显示各个作者分别贡献了哪部分。它还允许插入图片、清单,由于提供了语法高亮功能,它还能用来写代码。
|
||||
|
||||
当2014年4月 Dropbox 获得了 Hackpad 后,这款软件就以开源的形式在本月发行。让我们经历的等待非常值得。
|
||||
当2014年4月 Dropbox 收购了 Hackpad 后,就在这个月这款软件以开源的形式发布。让我们经历的等待非常值得。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 有类似 wiki 所提供的,一套非常完善的功能
|
||||
- 实时或者异步地记合作笔记,共享数据和文件,或用评论分享你们的想法
|
||||
- 细致的隐私许可让你可以邀请单个朋友,一个十几人的团队或者上千的 Twitter 粉丝
|
||||
- 实时或者异步地记录协作笔记,共享数据和文件,或用评论分享你们的想法
|
||||
- 细致的隐私许可让你可以邀请单个朋友、一个十几人的团队或者上千的 Twitter 粉丝
|
||||
- 智能执行
|
||||
- 直接从流行的视频分享网站上插入视频
|
||||
- 表格
|
||||
@ -42,9 +43,9 @@ Hackpad 允许用户实时分享你的文档,它还用彩色编码显示各个
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Etherpad 是个基于网页的开源实时合作编辑器,允许多个作者同时编辑一个文本文档,写评论,并与其他作者用群聊方式进行交流。
|
||||
Etherpad 是个基于网页的开源实时协作编辑器,允许多个作者同时编辑一个文本文档,写评论,并与其他作者用群聊方式进行交流。
|
||||
|
||||
Etherpad 是用 JavaScript 运行的,在 AppJet 平台的顶端,通过 Comet 流实现实时的功能。
|
||||
Etherpad 是用 JavaScript 编写的,运行在 AppJet 平台之上,通过 Comet 流实现实时的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -55,9 +56,9 @@ Etherpad 是用 JavaScript 运行的,在 AppJet 平台的顶端,通过 Comet
|
||||
- 每隔一段很短的时间就会自动保存
|
||||
- 可个性化程度高
|
||||
- 有客户端插件可以扩展编辑的功能
|
||||
- 几百个支持 Etherpad 的扩展包括支持 email 提醒,pad 管理,授权
|
||||
- 几百个支持 Etherpad 的扩展,包括支持 email 提醒,pad 管理,授权
|
||||
- 可访问性开启
|
||||
- 可从 Node 里或通过 CLI(命令行界面)和 Pad 目录实时交互
|
||||
- 可从 Node 里或通过 CLI(命令行界面)和 EtherPad 的内容交互
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [etherpad.org][4]
|
||||
- 源代码:[github.com/ether/etherpad-lite][5]
|
||||
@ -71,7 +72,7 @@ Etherpad 是用 JavaScript 运行的,在 AppJet 平台的顶端,通过 Comet
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Firepad 是个开源的合作文本编辑器。它的设计目的是被嵌入到更大的网页应用中对几天内新加入的代码进行批注。
|
||||
Firepad 是个开源的协作文本编辑器。它的设计目的是被嵌入到更大的网页应用中对几天内新加入的代码进行批注。
|
||||
|
||||
Firepad 是个全功能的文本编辑器,有解决冲突,光标同步,用户属性,用户在线状态检测功能。它使用 Firebase 作为后台,而且不需要任何服务器端的代码。他可以被加入到任何网页应用中。Firepad 可以使用 CodeMirror 编辑器或者 Ace 编辑器提交文本,它的操作转换代码是从 ot.js 上借鉴的。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -81,7 +82,7 @@ Firepad 已被多个编辑器使用,包括Atlassian Stash Realtime Editor、Ni
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 纯正的合作编辑
|
||||
- 纯正的协作编辑
|
||||
- 基于 OT 的智能合并及解决冲突
|
||||
- 支持多种格式的文本和代码的编辑
|
||||
- 光标位置同步
|
||||
@ -106,13 +107,13 @@ Firepad 已被多个编辑器使用,包括Atlassian Stash Realtime Editor、Ni
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ownCloud Documents 是个可以单独并/或合作进行办公室文档编辑 ownCloud 应用。它允许最多5个人同时在网页浏览器上合作进行编辑 .odt 和 .doc 文件。
|
||||
ownCloud Documents 是个可以单独并/或协作进行办公室文档编辑 ownCloud 应用。它允许最多5个人同时在网页浏览器上协作进行编辑 .odt 和 .doc 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
ownCloud 是个自托管文件同步和分享服务器。他通过网页界面,同步客户端或 WebDAV 提供你数据的使用权,同时提供一个容易在设备间进行浏览、同步和分享的平台。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 合作编辑,多个用户同时进行文件编辑
|
||||
- 协作编辑,多个用户同时进行文件编辑
|
||||
- 在 ownCloud 里创建文档
|
||||
- 上传文档
|
||||
- 在浏览器里分享和编辑文件,然后在 ownCloud 内部或通过公共链接进行分享这些文件
|
||||
@ -131,16 +132,16 @@ ownCloud 是个自托管文件同步和分享服务器。他通过网页界面
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Gobby 是个支持在一个会话内进行多个用户聊天并打开多个文档的合作编辑器。所有的用户都能同时在文件上进行工作,无需锁定。不同用户编写的部分用不同颜色高亮显示,它还支持多个编程和标记语言的语法高亮。
|
||||
Gobby 是个支持在一个会话内进行多个用户聊天并打开多个文档的协作编辑器。所有的用户都能同时在文件上进行工作,无需锁定。不同用户编写的部分用不同颜色高亮显示,它还支持多个编程和标记语言的语法高亮。
|
||||
|
||||
Gobby 允许多个用户在互联网上实时共同编辑同一个文档。他很好的整合了 GNOME 环境。它拥有一个客户端-服务端结构,这让它能支持一个会话开多个文档,文档同步请求,密码保护和 IRC 式的聊天方式可以在多个频道进行交流。用户可以选择一个颜色对他们在文档中编写的文本进行高亮。
|
||||
Gobby 允许多个用户在互联网上实时共同编辑同一个文档。它很好的整合了 GNOME 环境。它拥有一个客户端-服务端结构,这让它能支持一个会话开多个文档,文档同步请求,密码保护和 IRC 式的聊天方式可以在多个频道进行交流。用户可以选择一个颜色对他们在文档中编写的文本进行高亮。
|
||||
|
||||
还供有一个叫做 infinoted 的专用服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 成熟的文本编辑能力包括使用 GtkSourceView 的语法高亮功能
|
||||
- 实时、无需锁定、通过加密(包括PFS)连接的合作文本编辑
|
||||
- 实时、无需锁定、通过加密(包括PFS)连接的协作文本编辑
|
||||
- 整合了群聊
|
||||
- 本地组撤销:撤销不会影响远程用户的修改
|
||||
- 显示远程用户的光标和选择区域
|
||||
@ -170,9 +171,9 @@ Gobby 允许多个用户在互联网上实时共同编辑同一个文档。他
|
||||
|
||||
ONLYOFFICE(从前叫 Teamlab Office)是个多功能云端在线办公套件,整合了 CRM(客户关系管理)系统、文档和项目管理工具箱、甘特图以及邮件整合器
|
||||
|
||||
它能让你整理商业任务和时间表,保存并分享你的合作或个人文档,使用网络社交工具如博客和论坛,还可以和你的队员通过团队的即时聊天工具进行交流。
|
||||
它能让你整理商业任务和时间表,保存并分享你的协作或个人文档,使用网络社交工具如博客和论坛,还可以和你的队员通过团队的即时聊天工具进行交流。
|
||||
|
||||
能在同一个地方管理文档、项目、团队和顾客关系。OnlyOffice 结合了文本,电子表格和电子幻灯片编辑器,他们的功能跟微软桌面应用(Word、Excel 和 PowerPoint)的功能相同。但是他允许实时进行合作编辑、评论和聊天。
|
||||
能在同一个地方管理文档、项目、团队和顾客关系。OnlyOffice 结合了文本,电子表格和电子幻灯片编辑器,他们的功能跟微软桌面应用(Word、Excel 和 PowerPoint)的功能相同。但是他允许实时进行协作编辑、评论和聊天。
|
||||
|
||||
OnlyOffice 是用 ASP.NET 编写的,基于 HTML5 Canvas 元素,并且被翻译成21种语言。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -182,7 +183,7 @@ OnlyOffice 是用 ASP.NET 编写的,基于 HTML5 Canvas 元素,并且被翻
|
||||
- 文档可以在浏览/编辑模式下分享
|
||||
- 文档嵌入
|
||||
- 电子表格和电子幻灯片编辑器
|
||||
- 合作编辑
|
||||
- 协作编辑
|
||||
- 评论
|
||||
- 群聊
|
||||
- 移动应用
|
||||
@ -209,7 +210,7 @@ via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150823085112605/CollaborativeEditing.ht
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[H-mudcup](https://github.com/H-mudcup)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,198 @@
|
||||
如何在 Linux 系统上安装 Suricata 入侵检测系统
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
随着安全威胁的不断发生,入侵检测系统(IDS)在如今的数据中心环境中显得尤为必要。然而,随着越来越多的服务器将他们的网卡升级到10GB/40GB以太网,对如此线路上的硬件进行计算密集型的入侵检测越来越困难。其中一种提升入侵检测系统性能的途径是**多线程入侵检测系统**,它将 CPU 密集型的深度包检测工作并行的分配给多个并发任务来完成。这样的并行检测可以充分利用多核硬件的优势来轻松提升入侵检测系统的吞吐量。在这方面有两个知名的开源项目,分别是 [Suricata][1] 和 [Bro][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
这个教程里,我会向大家演示**如何在 Linux 服务器上安装和配置 Suricata 入侵检测系统**
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 上安装 Suricata IDS ###
|
||||
|
||||
让我们从源文件来构建 Suricata,但在此之前,需要按如下所示先安装几个依赖包。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Debian, Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint 操作系统上安装依赖包 ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install wget build-essential libpcre3-dev libpcre3-dbg automake autoconf libtool libpcap-dev libnet1-dev libyaml-dev zlib1g-dev libcap-ng-dev libjansson-dev
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 CentOS, Fedora 或者 RHEL 操作系统上安装依赖包 ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install wget libpcap-devel libnet-devel pcre-devel gcc-c++ automake autoconf libtool make libyaml-devel zlib-devel file-devel jansson-devel nss-devel
|
||||
|
||||
一旦将所有依赖包安装完毕,我们就可以继续安装 Suricata 了。
|
||||
|
||||
首先从 [http://suricata-ids.org/download/][3] 下载 Suricata 源代码,然后构建它。撰写这篇文章的时候,其最新版本号为 2.0.8 。
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://www.openinfosecfoundation.org/download/suricata-2.0.8.tar.gz
|
||||
$ tar -xvf suricata-2.0.8.tar.gz
|
||||
$ cd suricata-2.0.8
|
||||
$ ./configure --sysconfdir=/etc --localstatedir=/var
|
||||
|
||||
以下是配置信息的样例。
|
||||
|
||||
Suricata Configuration:
|
||||
AF_PACKET support: yes
|
||||
PF_RING support: no
|
||||
NFQueue support: no
|
||||
NFLOG support: no
|
||||
IPFW support: no
|
||||
DAG enabled: no
|
||||
Napatech enabled: no
|
||||
Unix socket enabled: yes
|
||||
Detection enabled: yes
|
||||
|
||||
libnss support: yes
|
||||
libnspr support: yes
|
||||
libjansson support: yes
|
||||
Prelude support: no
|
||||
PCRE jit: yes
|
||||
LUA support: no
|
||||
libluajit: no
|
||||
libgeoip: no
|
||||
Non-bundled htp: no
|
||||
Old barnyard2 support: no
|
||||
CUDA enabled: no
|
||||
|
||||
现在可以编译、安装了。
|
||||
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
Suricata 源代码带有默认的配置文件。按照如下方法安装这些默认配置文件即可。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make install-conf
|
||||
|
||||
正如你所料,如果没有IDS规则集的话,Suricata 什么用也没有。幸好 Makefile 为我们提供了 IDS 规则集的安装选项。安装方法如下。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make install-rules
|
||||
|
||||
以上的规则安装命令会从 [EmergingThreats.net][4] 上下载可用的社区规则集快照,并且将其存储在 /etc/suricata/rules 目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 首次配置 Suricata IDS ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在到了配置 Suricata 的时候了。配置文件的位置是 **/etc/suricata/suricata.yaml**。参照以下命令,用文本编辑器打开这个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml
|
||||
|
||||
文件中有一些运行所需的基本配置。
|
||||
|
||||
为`default-log-dir`关键字指定 Suricata 日志文件所在的位置。
|
||||
|
||||
default-log-dir: /var/log/suricata/
|
||||
|
||||
在`vars`部分下方,你会发现几项对 Suricata 来说很重要变量。`HOME_NET`变量需要指定 Suricata 检查的网络。被分配给 `EXTERNAL_NET` 变量的 `!$HOME_NET` 代表除本地网络之外的其他网络。`XXX_PORTS`变量用来辨别不同服务所用到的端口号。需要注意的是无论使用什么端口,Suricata 都可以自动检测 HTTP 流量。所以是不是正确指定端口就显得没那么重要了。
|
||||
|
||||
vars:
|
||||
HOME_NET: "[192.168.122.0/24]"
|
||||
EXTERNAL_NET: "!$HOME_NET"
|
||||
HTTP_PORTS: "80"
|
||||
SHELLCODE_PORTS: "!80"
|
||||
SSH_PORTS: 22
|
||||
|
||||
`host-os-policy` 部分用于防御利用操作系统网络栈的自身行为来逃避检测的一些知名攻击手段(例如:TCP reassembly)。作为对策,通过针对目标操作系统而对检测引擎算法进行微调,现代 IDC 提供了“基于目标”的检测手段。因此,如果你知道某台主机运行了什么操作系统的话,将这个信息提供给 Suricata 就可以大幅提高检测的成功率。这就是 `host-os-policy` 存在的意义。本例中,默认的 IDC 策略是 Linux 系统。如果针对某个 IP 地址没有指定操作系统信息,Suricata 会默认应用基于 Linux 系统的检测策略。如下,当捕获到对 192.168.122.0/28 和 192.168.122.155通讯时,Suricata 就会应用基于 Windows 系统的检测策略。
|
||||
|
||||
host-os-policy:
|
||||
# These are Windows machines.
|
||||
windows: [192.168.122.0/28, 192.168.122.155]
|
||||
bsd: []
|
||||
bsd-right: []
|
||||
old-linux: []
|
||||
# Make the default policy Linux.
|
||||
linux: [0.0.0.0/0]
|
||||
old-solaris: []
|
||||
solaris: ["::1"]
|
||||
hpux10: []
|
||||
hpux11: []
|
||||
irix: []
|
||||
macos: []
|
||||
vista: []
|
||||
windows2k3: []
|
||||
|
||||
在 `threading` 部分下,你可以为不同的 Suricata 线程指定 CPU 关联。默认状态下,[CPU 关联][5] 是被禁止使用的 (`set-cpu-affinity: no`),这意味着 Suricata 会分配其线程到所有可用的 CPU 核心上。Suricata 会默认为每一个 CPU 核心创建一个检测线程。你可以通过指定 `detect-thread-ratio: N` 来调整此行为。此处会创建 N*M 个检测线程,M 代表 CPU 核心总数。
|
||||
|
||||
threading:
|
||||
set-cpu-affinity: no
|
||||
detect-thread-ratio: 1.5
|
||||
|
||||
通过以上对线程的设置,Suricata 会创建 1.5*M 个检测线程,M 是系统的 CPU 核心总数。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想对 Suricata 配置有更多的了解,可以去翻阅默认配置文件。里边配有有大量的注释以供你清晰理解。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 Suricata 进行入侵监控 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在是时候让 Suricata 跑起来了,但在这之前还有一个步骤需要去完成。
|
||||
|
||||
当你使用 pcap 捕获模式的时候,强烈建议关闭 Suricata 监听网卡上的任何的包卸载(例如 LRO/GRO)功能。这些功能会干扰包的实时捕获行为。
|
||||
|
||||
按照以下方法关闭 eth0 接口的 LRO/GRO 功能。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ethtool -K eth0 gro off lro off
|
||||
|
||||
这里要注意,在使用某些网卡的情况下,你会看到如下警告信息。忽略它们就行了,这些信息只不过告诉你你的网卡不支持 LRO 功能而已。
|
||||
|
||||
Cannot change large-receive-offload
|
||||
|
||||
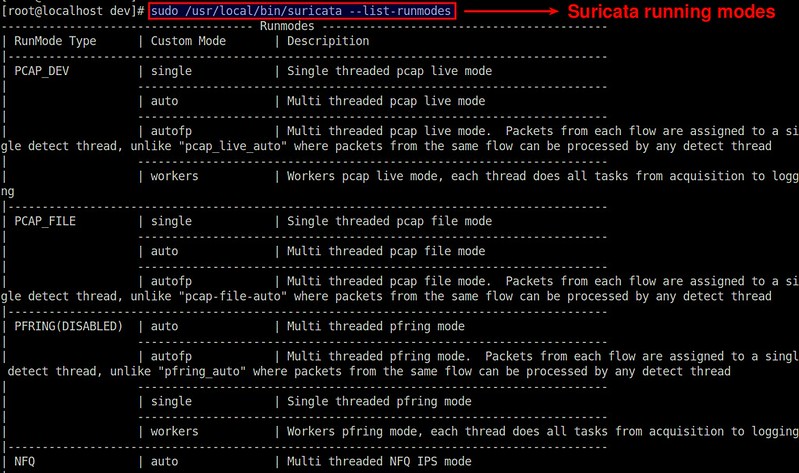
Suricata 支持许多运行模式。运行模式决定着 IDC 会使用何种线程。以下命令可以查看所有 [可用的运行模式][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /usr/local/bin/suricata --list-runmodes
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Suricata 使用的默认运行模式是 autofp("auto flow pinned load balancing"==“自动流绑定负载均衡” 的缩写)。这个模式下,来自某一个流的包会被分配到一个单独的检测线程中。这些流会根据未被处理的包的最低数量来分配相应的线程。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,让我们将 Suricata 运行起来,看看它表现如何。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /usr/local/bin/suricata -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml -i eth0 --init-errors-fatal
|
||||
|
||||
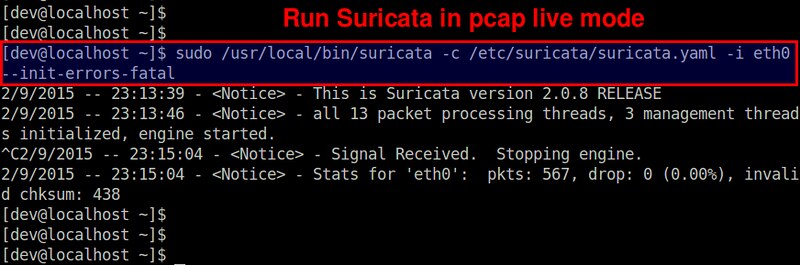
|
||||
|
||||
本例中,我们在一个8核心系统中监控 eth0 网络接口。如上所示,Suricata 创建了13个包处理线程和3个管理线程。包处理线程中包括一个 PCAP 包捕获线程,12个检测线程(由8*1.5得出)。这表示 IDS 内的1个包捕获线程均衡负载到12个检测线程中。管理线程包括1个流管理和2个计数/统计相关线程。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是一个关于Suricata处理的线程截图(由 [htop][7] 绘制)。
|
||||
|
||||
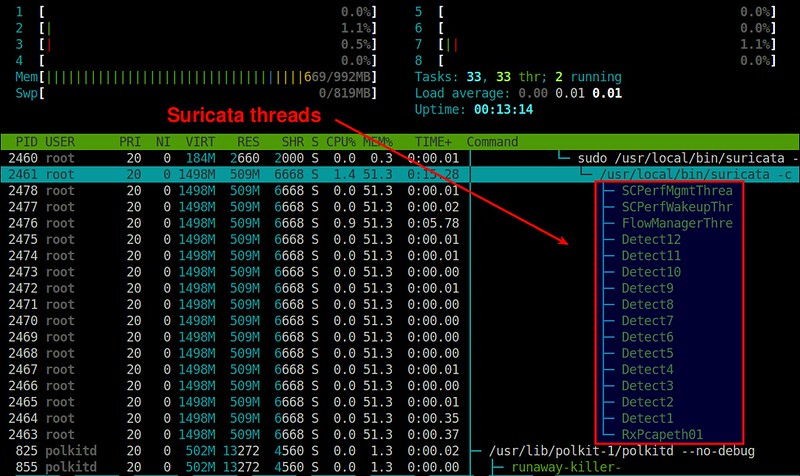
|
||||
|
||||
Suricata 检测日志存储在 /var/log/suricata 目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
$ tail -f /var/log/suricata/fast.log
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
04/01/2015-15:47:12.559075 [**] [1:2200074:1] SURICATA TCPv4 invalid checksum [**] [Classification: (null)] [Priority: 3] {TCP} 172.16.253.158:22 -> 172.16.253.1:46997
|
||||
04/01/2015-15:49:06.565901 [**] [1:2200074:1] SURICATA TCPv4 invalid checksum [**] [Classification: (null)] [Priority: 3] {TCP} 172.16.253.158:22 -> 172.16.253.1:46317
|
||||
04/01/2015-15:49:06.566759 [**] [1:2200074:1] SURICATA TCPv4 invalid checksum [**] [Classification: (null)] [Priority: 3] {TCP} 172.16.253.158:22 -> 172.16.253.1:46317
|
||||
|
||||
日志也可以提供 Json 格式以便导入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ tail -f /var/log/suricata/eve.json
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
{"timestamp":"2015-04-01T15:49:06.565901","event_type":"alert","src_ip":"172.16.253.158","src_port":22,"dest_ip":"172.16.253.1","dest_port":46317,"proto":"TCP","alert":{"action":"allowed","gid":1,"signature_id":2200074,"rev":1,"signature":"SURICATA TCPv4 invalid checksum","category":"","severity":3}}
|
||||
{"timestamp":"2015-04-01T15:49:06.566759","event_type":"alert","src_ip":"172.16.253.158","src_port":22,"dest_ip":"172.16.253.1","dest_port":46317,"proto":"TCP","alert":{"action":"allowed","gid":1,"signature_id":2200074,"rev":1,"signature":"SURICATA TCPv4 invalid checksum","category":"","severity":3}}
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这篇教程中,我为大家演示了如何在一台多核 Linux 服务器上安装 Suricata 入侵检测系统。不同于单线程的 [Snort IDS][8] ,Suricata 可以很容易的从多核硬件的多进程特性所带来的好处中获益。定制 Suricata 来最大化其效能和检测范围是一个很好的主意。Suricata 的粉丝们维护着一个 [在线 Wiki][9],如果你打算将 Suricata 部署到你的环境中,我强烈建议你去那儿取取经。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你现在已经开始使用 Suricata 了的话,把你的经验也分享出来吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/install-suricata-intrusion-detection-system-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[mr-ping](https://github.com/mr-ping)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://suricata-ids.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.bro.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://suricata-ids.org/download/
|
||||
[4]:http://rules.emergingthreats.net/
|
||||
[5]:http://xmodulo.com/run-program-process-specific-cpu-cores-linux.html
|
||||
[6]:https://redmine.openinfosecfoundation.org/projects/suricata/wiki/Runmodes
|
||||
[7]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/view-threads-process-linux.html
|
||||
[8]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-compile-and-install-snort-from-source-code-on-ubuntu.html
|
||||
[9]:https://redmine.openinfosecfoundation.org/projects/suricata/wiki
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,241 @@
|
||||
理查德·斯托曼经典语录集锦
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
<iframe width="660" height="495" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/aIL594DTzH4?feature=oembed" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
**理查德·马修·斯托曼(Richard Matthew Stallman)** (RMS) – 神级程序员之一。他是一名程序员,是 GCC、GDB、Emacs 的构建者,软件自由的传教士,[GNU Project][1] 和 [FSF][2] 的创办人。
|
||||
|
||||
**GNU** 是 “GNU’s Not Unix!”的递归缩写。GNU 是一系列用于基于 Unix 的操作系统的自由软件集合。它能用于 GNU/Hurd 和 Linux 内核。于1983年9月27日公诸于众。常用组件有:
|
||||
|
||||
- GNU Compiler Collection (GCC)
|
||||
- GNU C library (glibc)
|
||||
- GNU Core Utilities (coreutils)
|
||||
- GNU Debugger (GDB)
|
||||
- GNU Binary Utilities (binutils)
|
||||
- GNU Bash shell
|
||||
- GNOME desktop environment
|
||||
|
||||
注:视频
|
||||
<video src="//static.fsf.org/nosvn/FSF30-video/FSF_30_720p.webm" controls="controls" width="640" height="390"></video>
|
||||
|
||||
**自由软件基金会(Free Software Foundation)** (FSF) – 一个自由软件的非营利组织,致力于推进计算机用户的自由和捍卫他们的权力。于 1985年10月4日成立。阅读[更多][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
许多人不理解开源代码(open source code)和自由软件(free software)的区别。每个程序都应该是自由软件:
|
||||
|
||||
- 与目的无关,随心运行程序的自由(自由0)。
|
||||
- 学习程序如何运作,并改变它为你所用的自由(自由1)。可以访问源码是这一条的前提。
|
||||
- 重新发布副本的自由,如此你便可以帮助你周围的人(自由 2)。
|
||||
- 发布自己修改版本给他人的自由(自由 3)。这样能让整个社区有机会从你的改变中受益。可以访问源码是这条的前提。
|
||||
|
||||
以上为自由软件的四项自由原则。
|
||||
|
||||
以下为理查德·斯托曼关于自由、软件、社交、哲学等方面的名言摘引。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于 Facebook:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Facebook is not your friend, it is a surveillance engine.
|
||||
|
||||
Facebook 不是你的朋友,是监控引擎。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于 Android:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Android is very different from the GNU/Linux operating system because it contains very little of GNU. Indeed, just about the only component in common between Android and GNU/Linux is Linux, the kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
Android 和 GNU/Linux 有很大的区别,因为其中几乎没有 GNU。的确,Android 和 GNU/Linux 之间仅有一个共同组件,那就是内核 - Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于计算机行业:**
|
||||
|
||||
> The computer industry is the only industry that is more fashion-driven than women's fashion.
|
||||
|
||||
计算机行业是唯一一个比女性时尚业更容易受潮流影响的行业了。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于云计算:**
|
||||
|
||||
> The interesting thing about cloud computing is that we've redefined cloud computing to include everything that we already do.
|
||||
|
||||
关于云计算,有趣的是我们已经重新定义了云计算来包含我们曾干过的所有事。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于伦理:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Whether gods exist or not, there is no way to get absolute certainty about ethics. Without absolute certainty, what do we do? We do the best we can.
|
||||
|
||||
无论神存在与否,都没有绝对的伦理道德。没有这份理所当然,我们该如何?也唯有尽善吧。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于自由:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Free software is software that respects your freedom and the social solidarity of your community. So it's free as in freedom.
|
||||
|
||||
自由软件是尊重个人自由和社会团结的软件。所以才能如自由般自由自在。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于目标和理想:**
|
||||
|
||||
> If you want to accomplish something in the world, idealism is not enough - you need to choose a method that works to achieve the goal.
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想为这世界做些什么,仅有理想是不够的,你需要找条通往目标的道路并走完。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于分享:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Sharing is good, and with digital technology, sharing is easy.
|
||||
|
||||
分享很棒,而且数字化技术也使分享变得容易。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于 facebook(进阶版):**
|
||||
|
||||
> Facebook mistreats its users. Facebook is not your friend; it is a surveillance engine. For instance, if you browse the Web and you see a 'like' button in some page or some other site that has been displayed from Facebook. Therefore, Facebook knows that your machine visited that page.
|
||||
|
||||
Facebook 蹂躏它们的用户。它不是你们的朋友;它就是个监控引擎。举个例子,你是否曾在一些网页或网站上看到 Facebook 的 “like” 按键。对,Facebook 知道你的电脑曾访问过那些网页。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于 web 应用:**
|
||||
|
||||
> One reason you should not use web applications to do your computing is that you lose control.
|
||||
|
||||
给你个为什么不应该使用 web 应用的理由,因为你失去了计算机的控制权。
|
||||
|
||||
> If you use a proprietary program or somebody else's web server, you're defenceless. You're putty in the hands of whoever developed that software.
|
||||
|
||||
如果你使用私有程序或他人的 web 服务器,那么你只能任人鱼肉。被软件的开发者轻易操纵。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于书:**
|
||||
|
||||
> With paper printed books, you have certain freedoms. You can acquire the book anonymously by paying cash, which is the way I always buy books. I never use a credit card. I don't identify to any database when I buy books. Amazon takes away that freedom.
|
||||
|
||||
印刷出来的书,当然是自由的。你可以付现金匿名买书,这也是我一直买书的方式。我绝不会使用信用卡,我买书时不会被任何数据库记下。是亚马逊把自由夺走了。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于 MPAA:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Officially, MPAA stands for Motion Picture Association of America, but I suggest that MPAA stands for Malicious Power Attacking All.
|
||||
|
||||
MPAA 其实是美国电影协会(Motion Picture Association of America),但我认为叫做攻击万物的邪恶力量(Malicious Power Attacking All)更为合适。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于金钱与职业:**
|
||||
|
||||
> I could have made money this way, and perhaps amused myself writing code. But I knew that at the end of my career, I would look back on years of building walls to divide people, and feel I had spent my life making the world a worse place.
|
||||
|
||||
我可以找份工作赚钱,并沉浸在编码的快乐中。但在职业生涯结束后,回首目睹自己筑就的高墙将人与人分隔开,我会觉得我耗尽毕生精力只换来了一个更糟糕的世界。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于私有软件:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Proprietary software keeps users divided and helpless. Divided because each user is forbidden to redistribute it to others, and helpless because the users can't change it since they don't have the source code. They can't study what it really does. So the proprietary program is a system of unjust power.
|
||||
|
||||
私有软件使用户孤立、无助。因为禁止将软件给他人使用所以孤立,因为无法改变源码所以无助。他们不能学习其中真正的工作方式,所以整个私有软件体系就是一种不公的力量。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于智能手机:**
|
||||
|
||||
> A smartphone is a computer - it's not built using a computer - the job it does is the job of being a computer. So, everything we say about computers, that the software you run should be free - you should insist on that - applies to smart phones just the same. And likewise to those tablets.
|
||||
|
||||
智能手机就是电脑 —— 虽然做的和常用的电脑不同 —— 但是却能干电脑能干的活。所以我们所说的一切有关于电脑上的软件应该能自由运行 —— 必须坚持这一点 —— 在智能手机上也是这样,当然也包括平板。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于 CD 和数字内容:**
|
||||
|
||||
> CD stores have the disadvantage of an expensive inventory, but digital bookshops would need no such thing: they could write copies at the time of sale on to memory sticks, and sell you one if you forgot your own.
|
||||
|
||||
CD 商店有一个弱势就是需要昂贵的库存,但是电子商店就没有这方面的需求:他们只需要将售卖的副本写入记忆棒,并在你忘带自己的记忆棒时卖你一个就是了。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于竞争范式(paradigm of competition):**
|
||||
|
||||
> The paradigm of competition is a race: by rewarding the winner, we encourage everyone to run faster. When capitalism really works this way, it does a good job; but its defenders are wrong in assuming it always works this way.
|
||||
|
||||
竞争范式就像是赛跑:奖励胜者,鼓励每一个跑得更快的人。当资本主义真的这样运作时,当然是件好事;但是维护它的人若是假设它一直这样运作的话那就大错特错了。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于 vi 和 emacs:**
|
||||
|
||||
> People sometimes ask me if it is a sin in the Church of Emacs to use vi. Using a free version of vi is not a sin; it is a penance. So happy hacking.
|
||||
|
||||
有时会有人问我在 Emacs 的阵营使用 vi 是不是一种罪过。使用自由版的 vi 并不是一种罪过;是一种自我惩罚。所以好好享受其中乐趣吧。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于自由和历史:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Value your freedom or you will lose it, teaches history. 'Don't bother us with politics', respond those who don't want to learn.
|
||||
|
||||
历史告诉我们不珍惜自由便失去自由,然而有的人不懂吸取教训,只知道说“别拿政治烦我们”。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于专利:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Fighting patents one by one will never eliminate the danger of software patents, any more than swatting mosquitoes will eliminate malaria.
|
||||
|
||||
和专利一个一个的战斗并不能解决软件专利带来的危害,就像打再多的蚊子也消灭不了疟疾一样。
|
||||
|
||||
> Software patents are dangerous to software developers because they impose monopolies on software ideas.
|
||||
|
||||
软件专利对于软件的开发者来说十分危险,因为它们加剧了对于软件理念的垄断。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于版权:**
|
||||
|
||||
> In practice, the copyright system does a bad job of supporting authors, aside from the most popular ones. Other authors' principal interest is to be better known, so sharing their work benefits them as well as readers.
|
||||
|
||||
其实,版权制度对作者也没有什么好处,撇开最受欢迎的那个,其他作者的主旨可能更好理解,所以分享无论对他们还是你的读者都是一件好事。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于工作与报酬:**
|
||||
|
||||
> There is nothing wrong with wanting pay for work, or seeking to maximize one's income, as long as one does not use means that are destructive.
|
||||
|
||||
劳有所得,或寻求收入的最大化并没有什么错,只要不是不择手段。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于 Chrome OS:**
|
||||
|
||||
> In essence, Chrome OS is the GNU/Linux operating system. However, it is delivered without the usual applications, and rigged up to impede and discourage installing applications.
|
||||
|
||||
Chrome OS 确实是 GNU/Linux 的操作系统。但是,它在发布时没有安装常用应用,并为安装他们设置了阻碍。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于 Linux 用户:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Many users of the GNU/Linux system will not have heard the ideas of free software. They will not be aware that we have ideas, that a system exists because of ethical ideals, which were omitted from ideas associated with the term 'open source.'
|
||||
|
||||
许多的 GNU/Linux 用户并没有听过自由软件。他们并没有意识到,这个系统是因为道德理想才存在的,与此一起被忽视的还有所谓的“开源”。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于 facebook 的隐私:**
|
||||
|
||||
> If there is a Like button in a page, Facebook knows who visited that page. And it can get IP address of the computer visiting the page even if the person is not a Facebook user.
|
||||
|
||||
如果页面上有 “like” 按键,Facebook 就能知道谁访问了页面。即使不是 Facebook 的用户,也可以得到访问该页面电脑的 IP 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于编程:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Programming is not a science. Programming is a craft.
|
||||
|
||||
编程不是科学,编程是手艺。
|
||||
|
||||
> My favorite programming languages are Lisp and C. However, since around 1992 I have worked mainly on free software activism, which means I am too busy to do much programming. Around 2008 I stopped doing programming projects.
|
||||
|
||||
Lisp 和 C 语言是我的最爱。然自 1992 年以来我主要工作在自由软件活动上,导致我太忙了,没法做更多的编程。大概在 2008 年我便停止了做编程项目。
|
||||
|
||||
> C++ is a badly designed and ugly language. It would be a shame to use it in Emacs.
|
||||
|
||||
C++ 设计的真糟糕、真丑陋。在 Emacs 上用它应该觉得羞愧。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于钻研(hacking)和学习编程:**
|
||||
|
||||
> People could no longer learn hacking the way I did, by starting to work on a real operating system, making real improvements. In fact, in the 1980s I often came across newly graduated computer science majors who had never seen a real program in their lives. They had only seen toy exercises, school exercises, because every real program was a trade secret. They never had the experience of writing features for users to really use, and fixing the bugs that real users came across. The things you need to know to do real work.
|
||||
|
||||
(时过境迁,)人们没法再像我当初那样通过改进实实在在的操作系统来学习编程了。上世纪 80 年代,我常遇见计算机专业的毕业生,有生以来没见过真正的程序。他们接触的到的只有小玩意和学校的作业,因为每一个程序都是商业机密。他们没有机会为用户去写真正实用的特性,修复用户真正遭遇的问题。而这些正是真正的工作中你需要掌握的(东西)。
|
||||
|
||||
> It is hard to write a simple definition of something as varied as hacking, but I think what these activities have in common is playfulness, cleverness, and exploration. Thus, hacking means exploring the limits of what is possible, in a spirit of playful cleverness. Activities that display playful cleverness have "hack value".
|
||||
|
||||
对于如“hacking”这般多样化的东西真的很难简单的下定义,不过在我看来诸如此类的行为都会有以下的这些共同点:嬉乐、智慧和探索。因此,hacking 意味着对可能的极限的探索,一颗向往快乐与智慧的心。能带来快乐与智慧的行为就有 “hack 的价值” 。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于浏览网页:**
|
||||
|
||||
> For personal reasons, I do not browse the web from my computer. (I also have no net connection much of the time.) To look at page I send mail to a daemon which runs wget and mails the page back to me. It is very efficient use of my time, but it is slow in real time.
|
||||
|
||||
出于个人原因,我不会在我的电脑上浏览网页。(大部分时间处于没有网络连接的状态。)要浏览网页,我需要给一个守护进程发 mail,然后它会运行 wget 并把页面通过 mail 发还给我。这对我而言已经是最效率了,但那真的比实时慢太多了。
|
||||
|
||||
**关于音乐共享:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Friends share music with each other, they don't allow themselves to be divided by a system that says that nobody is supposed to have copies.
|
||||
|
||||
朋友之间彼此分享音乐,绝不会希望因为系统的一句:“禁止私下拷贝!”而生分。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://tlhp.cf/fsf-richard-stallman/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pavlo Rudyi][a]
|
||||
译者:[martin2011qi](https://github.com/martin2011qi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://tlhp.cf/fsf-richard-stallman/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.gnu.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.fsf.org/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.fsf.org/about/
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 系统管理员必备的80个监控工具
|
||||
最全列表: 80 多个 Linux 系统管理员必备的监控工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
随着行业的不断发展,各种工具多得不可胜数。这里列出网上最全的(工具)。拥有超过80种方式来管理你的机器。在本文中,我们主要讲述以下方面:
|
||||
随着互联网行业的不断发展,各种监控工具多得不可胜数。这里列出网上最全的监控工具。让你可以拥有超过80种方式来管理你的机器。在本文中,我们主要包括以下方面:
|
||||
|
||||
- 命令行工具
|
||||
- 网络相关内容
|
||||
@ -11,51 +11,51 @@ Linux 系统管理员必备的80个监控工具
|
||||
- 日志监控工具
|
||||
- 基础设施监控工具
|
||||
|
||||
监控和调试性能问题非常困难,但用对了正确的工具有时也是很容易的。下面是一些你可能听说过的工具,当你使用它们时可能存在一些问题:
|
||||
监控和调试性能问题是一个艰巨的任务,但用对了正确的工具有时也是很容易的。下面是一些你可能听说过的工具,也有可能没有听说过——何不赶快开始试试?
|
||||
|
||||
### 十大系统监控工具 ###
|
||||
### 八大系统监控工具 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Top ####
|
||||
#### 1. top ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这是一个被预装在许多 UNIX 系统中的小工具。当你想要查看在系统中运行的进程或线程时:top 是一个很好的工具。你可以对这些进程以不同的标准进行排序,默认是以 CPU 进行排序的。
|
||||
这是一个被预装在许多 UNIX 系统中的小工具。当你想要查看在系统中运行的进程或线程时:top 是一个很好的工具。你可以对这些进程以不同的方式进行排序,默认是以 CPU 进行排序的。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. [htop][1] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
HTOP 实质上是 top 的增强版本。它更容易对进程排序。它在视觉上更容易理解并且已经内建了许多通用的命令。它也是完全交互的。
|
||||
htop 实质上是 top 的一个增强版本。它更容易对进程排序。它看起来上更容易理解,并且已经内建了许多通用操作。它也是完全交互式的。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. [atop][2] ####
|
||||
|
||||
Atop 和 top,htop 非常相似,它也能监控所有进程,但不同于 top 和 htop 的是,它会记录进程的日志供以后分析。它也能显示所有进程的资源消耗。它还会高亮显示已经达到临界负载的资源。
|
||||
atop 和 top,htop 非常相似,它也能监控所有进程,但不同于 top 和 htop 的是,它可以按日记录进程的日志供以后分析。它也能显示所有进程的资源消耗。它还会高亮显示已经达到临界负载的资源。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. [apachetop][3] ####
|
||||
|
||||
Apachetop 会监控 apache 网络服务器的整体性能。它主要是基于 mytop。它会显示当前 reads, writes 的数量以及 requests 进程的总数。
|
||||
apachetop 会监控 apache 网络服务器的整体性能。它主要是基于 mytop。它会显示当前的读取进程、写入进程的数量以及请求进程的总数。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. [ftptop][4] ####
|
||||
|
||||
ftptop 给你提供了当前所有连接到 ftp 服务器的基本信息,如会话总数,正在上传和下载的客户端数量以及客户端信息。
|
||||
ftptop 给你提供了当前所有连接到 ftp 服务器的基本信息,如会话总数,正在上传和下载的客户端数量以及客户端是谁。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. [mytop][5] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
mytop 是一个很简洁的工具,用于监控线程和 mysql 的性能。它给了你一个实时的数据库来查询处理结果。
|
||||
mytop 是一个很简洁的工具,用于监控 mysql 的线程和性能。它能让你实时查看数据库以及正在处理哪些查询。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7. [powertop][6] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
powertop 可以帮助你诊断与电量消耗和电源管理相关的问题。它也可以帮你进行电源管理设置,以实现对你服务器最有效的配置。你可以使用 tab 键进行选项切换。
|
||||
powertop 可以帮助你诊断与电量消耗和电源管理相关的问题。它也可以帮你进行电源管理设置,以实现对你服务器最有效的配置。你可以使用 tab 键切换选项卡。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 8. [iotop][7] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
iotop 用于检查 I/O 的使用情况,并为你提供了一个类似 top 的界面来显示。它每列显示读和写的速率,每行代表一个进程。当出现等待 I/O 交换时,它也显示进程消耗时间的百分比。
|
||||
iotop 用于检查 I/O 的使用情况,并为你提供了一个类似 top 的界面来显示。它按列显示读和写的速率,每行代表一个进程。当发生交换或 I/O 等待时,它会显示进程消耗时间的百分比。
|
||||
|
||||
### 与网络相关的监控 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ iotop 用于检查 I/O 的使用情况,并为你提供了一个类似 top 的
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ntopng 是 ntop 的升级版,它提供了一个能使用浏览器进行网络监控的图形用户界面。它还有其他用途,如:定位主机,显示网络流量和 ip 流量分布并能进行分析。
|
||||
ntopng 是 ntop 的升级版,它提供了一个能通过浏览器进行网络监控的图形用户界面。它还有其他用途,如:地理定位主机,显示网络流量和 ip 流量分布并能进行分析。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 10. [iftop][9] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,17 +75,17 @@ iftop 类似于 top,但它主要不是检查 cpu 的使用率而是监听所
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
jnettop 以相同的方式来监测网络流量但比 iftop 更形象。它还支持自定义的文本输出并能以友好的交互方式来深度分析日志。
|
||||
jnettop 以相同的方式来监测网络流量但比 iftop 更形象。它还支持自定义的文本输出,并能以友好的交互方式来深度分析日志。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 12. [bandwidthd][11] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
bandwidthd 可以跟踪 TCP/IP 网络子网的使用情况并能在浏览器中通过 png 图片形象化地构建一个 HTML 页面。它有一个数据库驱动系统,支持搜索、过滤,多传感器和自定义报表。
|
||||
BandwidthD 可以跟踪 TCP/IP 网络子网的使用情况,并能在浏览器中通过 png 图片形象化地构建一个 HTML 页面。它有一个数据库系统,支持搜索、过滤,多传感器和自定义报表。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 13. [EtherApe][12] ####
|
||||
|
||||
EtherApe 以图形化显示网络流量,可以支持更多的节点。它可以捕获实时流量信息,也可以从 tcpdump 进行读取。也可以使用具有 pcap 语法的网络过滤显示特定信息。
|
||||
EtherApe 以图形化显示网络流量,可以支持更多的节点。它可以捕获实时流量信息,也可以从 tcpdump 进行读取。也可以使用 pcap 格式的网络过滤器来显示特定信息。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 14. [ethtool][13] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -97,7 +97,7 @@ ethtool 用于显示和修改网络接口控制器的一些参数。它也可以
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
NetHogs 打破了网络流量按协议或子网进行统计的原理。它以进程组来计算。所以,当网络流量猛增时,你可以使用 NetHogs 查看是由哪个进程造成的。
|
||||
NetHogs 打破了网络流量按协议或子网进行统计的惯例,它以进程来分组。所以,当网络流量猛增时,你可以使用 NetHogs 查看是由哪个进程造成的。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 16. [iptraf][15] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -109,7 +109,7 @@ iptraf 收集的各种指标,如 TCP 连接数据包和字节数,端口统
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果不是网络层的话,ngrep 就是 grep。pcap 意识到后允许其指定扩展规则或十六进制表达式来匹配数据包。
|
||||
ngrep 就是网络层的 grep。它使用 pcap ,允许通过指定扩展正则表达式或十六进制表达式来匹配数据包。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 18. [MRTG][17] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -121,29 +121,29 @@ MRTG 最初被开发来监控路由器的流量,但现在它也能够监控网
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Bmon 能监控并帮助你调试网络。它能捕获网络相关的统计数据,并以友好的方式进行展示。你还可以与 bmon 通过脚本进行交互。
|
||||
bmon 能监控并帮助你调试网络。它能捕获网络相关的统计数据,并以友好的方式进行展示。你还可以与 bmon 通过脚本进行交互。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 20. traceroute ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Traceroute 是一个内置工具,能显示路由和测试数据包在网络中的延迟。
|
||||
traceroute 是一个内置工具,能显示路由和测量数据包在网络中的延迟。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 21. [IPTState][19] ####
|
||||
|
||||
IPTState 可以让你跨越 iptables 来监控流量,并通过你指定的条件来进行排序。该工具还允许你从表中删除状态信息。
|
||||
IPTState 可以让你观察流量是如何通过 iptables,并通过你指定的条件来进行排序。该工具还允许你从 iptables 的表中删除状态信息。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 22. [darkstat][20] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Darkstat 能捕获网络流量并计算使用情况的统计数据。该报告保存在一个简单的HTTP服务器中,它为你提供了一个非常棒的图形用户界面。
|
||||
darkstat 能捕获网络流量并计算使用情况的统计数据。该报告保存在一个简单的 HTTP 服务器中,它为你提供了一个非常棒的图形用户界面。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 23. [vnStat][21] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
vnStat 是一个网络流量监控工具,它的数据统计是由内核进行提供的,其消耗的系统资源非常少。系统重新启动后,它收集的数据仍然存在。它具有颜色选项供系统管理员使用。
|
||||
vnStat 是一个网络流量监控工具,它的数据统计是由内核进行提供的,其消耗的系统资源非常少。系统重新启动后,它收集的数据仍然存在。有艺术感的系统管理员可以使用它的颜色选项。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 24. netstat ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -159,19 +159,19 @@ netstat 是一个内置的工具,它能显示 TCP 网络连接,路由表和
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Nmap 可以扫描你服务器开放的端口并且可以检测正在使用哪个操作系统。但你也可以使用 SQL 注入漏洞,网络发现和渗透测试相关的其他手段。
|
||||
Nmap 可以扫描你服务器开放的端口并且可以检测正在使用哪个操作系统。但你也可以将其用于 SQL 注入漏洞、网络发现和渗透测试相关的其他用途。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 27. [MTR][23] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
MTR 结合了 traceroute 和 ping 的功能到一个网络诊断工具上。当使用该工具时,它会限制单个数据包的跳数,同时也监视它们的到期时间。然后每秒进行重复。
|
||||
MTR 将 traceroute 和 ping 的功能结合到了一个网络诊断工具上。当使用该工具时,它会限制单个数据包的跳数,然后监视它们的到期时到达的位置。然后每秒进行重复。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 28. [Tcpdump][24] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Tcpdump 将输出一个你在命令中匹配并捕获到的数据包的信息。你还可以将此数据保存并进一步分析。
|
||||
Tcpdump 将按照你在命令行中指定的表达式输出匹配捕获到的数据包的信息。你还可以将此数据保存并进一步分析。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 29. [Justniffer][25] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -185,13 +185,13 @@ Justniffer 是 tcp 数据包嗅探器。使用此嗅探器你可以选择收集
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
nmon 将数据输出到屏幕上的,或将其保存在一个以逗号分隔的文件中。你可以查看 CPU,内存,网络,文件系统,top 进程。数据也可以被添加到 RRD 数据库中用于进一步分析。
|
||||
nmon 将数据输出到屏幕上的,或将其保存在一个以逗号分隔的文件中。你可以查看 CPU,内存,网络,文件系统,前列 进程。数据也可以被添加到 RRD 数据库中用于进一步分析。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 31. [conky][27] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Conky 能监视不同操作系统并统计数据。它支持 IMAP 和 POP3, 甚至许多流行的音乐播放器!出于方便不同的人,你可以使用自己的 Lua 脚本或程序来进行扩展。
|
||||
Conky 能监视很多的操作系统数据。它支持 IMAP 和 POP3, 甚至许多流行的音乐播放器!出于方便不同的人,你可以使用自己的 Lua 脚本或程序来进行扩展。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 32. [Glances][28] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -211,17 +211,17 @@ Saidar 是一个非常小的工具,为你提供有关系统资源的基础信
|
||||
|
||||
RRDtool 是用来处理 RRD 数据库的工具。RRDtool 旨在处理时间序列数据,如 CPU 负载,温度等。该工具提供了一种方法来提取 RRD 数据并以图形界面显示。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 35. [monit][31] ####
|
||||
#### 35. [monit][31] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果出现故障时,monit 有发送警报以及重新启动服务的功能。它可以对任何类型进行检查,你可以为 monit 写一个脚本,它有一个 Web 用户界面来分担你眼睛的压力。
|
||||
如果出现故障时,monit 有发送警报以及重新启动服务的功能。它可以对各种数据进行检查,你可以为 monit 写一个脚本,它有一个 Web 用户界面来分担你眼睛的压力。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 36. [Linux process explorer][32] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux process explorer 是类似 OSX 或 Windows 的在线监视器。它比 top 或 ps 的使用范围更广。你可以查看每个进程的内存消耗以及 CPU 的使用情况。
|
||||
Linux process explorer 是类似 OSX 或 Windows 的活动监视器。它比 top 或 ps 的使用范围更广。你可以查看每个进程的内存消耗以及 CPU 的使用情况。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 37. df ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -233,37 +233,37 @@ df 是 disk free 的缩写,它是所有 UNIX 系统预装的程序,用来显
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Discus 类似于 df,它的目的是通过使用更吸引人的特性,如颜色,图形和数字来对 df 进行改进。
|
||||
discus 类似于 df,它的目的是通过使用更吸引人的特性,如颜色,图形和数字来对 df 进行改进。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 39. [xosview][34] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
xosview 是一款经典的系统监控工具,它给你提供包括 IRQ 的各个不同部分的总览。
|
||||
xosview 是一款经典的系统监控工具,它给你提供包括 IRQ 在内的各个不同部分的简单总览。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 40. [Dstat][35] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Dstat 旨在替代 vmstat,iostat,netstat 和 ifstat。它可以让你查实时查看所有的系统资源。这些数据可以导出为 CSV。最重要的是 dstat 允许使用插件,因此其可以扩展到更多领域。
|
||||
dstat 旨在替代 vmstat,iostat,netstat 和 ifstat。它可以让你查实时查看所有的系统资源。这些数据可以导出为 CSV。最重要的是 dstat 允许使用插件,因此其可以扩展到更多领域。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 41. [Net-SNMP][36] ####
|
||||
|
||||
SNMP 是“简单网络管理协议”,Net-SNMP 工具套件使用该协议可帮助你收集服务器的准确信息。
|
||||
SNMP 即“简单网络管理协议”,Net-SNMP 工具套件使用该协议可帮助你收集服务器的准确信息。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 42. [incron][37] ####
|
||||
|
||||
Incron 允许你监控一个目录树,然后对这些变化采取措施。如果你想将目录‘a’中的新文件复制到目录‘b’,这正是 incron 能做的。
|
||||
incron 允许你监控一个目录树,然后对这些变化采取措施。如果你想在目录‘a’中出现新文件时,将其复制到目录‘b’,这正是 incron 能做的。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 43. [monitorix][38] ####
|
||||
|
||||
Monitorix 是轻量级的系统监控工具。它可以帮助你监控一台机器,并为你提供丰富的指标。它也有一个内置的 HTTP 服务器,来查看图表和所有指标的报告。
|
||||
Monitorix 是轻量级的系统监控工具。它可以帮助你监控单独一台机器,并为你提供丰富的指标。它也有一个内置的 HTTP 服务器,来查看图表和所有指标的报告。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 44. vmstat ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
vmstat(virtual memory statistics)是一个小的内置工具,能监控和显示机器的内存。
|
||||
vmstat(virtual memory statistics)是一个小型内置工具,能监控和显示机器的内存。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 45. uptime ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -273,13 +273,13 @@ vmstat(virtual memory statistics)是一个小的内置工具,能监控和
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
mpstat 是一个内置的工具,能监视 cpu 的使用情况。最常见的使用方法是 `mpstat -P ALL`,它给你提供 cpu 的使用情况。你也可以间隔更新 cpu 的使用情况。
|
||||
mpstat 是一个内置的工具,能监视 cpu 的使用情况。最常见的使用方法是 `mpstat -P ALL`,它给你提供 cpu 的使用情况。你也可以间歇性地更新 cpu 的使用情况。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 47. pmap ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
pmap 是一个内置的工具,报告一个进程的内存映射。你可以使用这个命令来找出内存瓶颈的原因。
|
||||
pmap 是一个内置的工具,报告一个进程的内存映射。你可以使用这个命令来找出导致内存瓶颈的原因。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 48. ps ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -291,13 +291,13 @@ pmap 是一个内置的工具,报告一个进程的内存映射。你可以使
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
sar 是 sysstat 包的一部分,可以帮助你收集,报告和保存不同系统的指标。使用不同的参数,它会给你提供 CPU, 内存 和 I/O 使用情况及其他东西。
|
||||
sar 是 sysstat 包的一部分,可以帮助你收集、报告和保存不同系统的指标。使用不同的参数,它会给你提供 CPU、 内存和 I/O 使用情况及其他东西。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 50. [collectl][40] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
类似于 sar,collectl 收集你机器的性能指标。默认情况下,显示 cpu,网络和磁盘统计数据,但它实际收集了很多信息。与 sar 不同的是,collectl 能够处理比秒更小的单位,它可以被直接送入绘图工具并且 collectl 的监控过程更广泛。
|
||||
类似于 sar,collectl 收集你机器的性能指标。默认情况下,显示 cpu、网络和磁盘统计数据,但它实际收集了很多信息。与 sar 不同的是,collectl 能够处理比秒更小的单位,它可以被直接送入绘图工具并且 collectl 的监控过程更广泛。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 51. [iostat][41] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -309,23 +309,23 @@ iostat 也是 sysstat 包的一部分。此命令用于监控系统的输入/输
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这是一个内置的命令用于显示你机器上可用的内存大小以及已使用的内存大小。它还可以显示某时刻内核所使用的缓冲区大小。
|
||||
这是一个内置的命令,用于显示你机器上可用的内存大小以及已使用的内存大小。它还可以显示某时刻内核所使用的缓冲区大小。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 53. /Proc 文件系统 ####
|
||||
#### 53. /proc 文件系统 ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
proc 文件系统可以让你查看内核的统计信息。从这些统计数据可以得到你机器上不同硬件设备的详细信息。看看这个 [ proc文件统计的完整列表 ][42]。
|
||||
proc 文件系统可以让你查看内核的统计信息。从这些统计数据可以得到你机器上不同硬件设备的详细信息。看看这个 [proc 文件统计的完整列表][42]。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 54. [GKrellM][43] ####
|
||||
|
||||
GKrellm 是一个图形应用程序来监控你硬件的状态信息,像CPU,内存,硬盘,网络接口以及其他的。它也可以监视并启动你所选择的邮件阅读器。
|
||||
GKrellm 是一个图形应用程序,用来监控你硬件的状态信息,像CPU,内存,硬盘,网络接口以及其他的。它也可以监视并启动你所选择的邮件阅读器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 55. [Gnome 系统监控器][44] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Gnome 系统监控器是一个基本的系统监控工具,其能通过一个树状结构来查看进程的依赖关系,能杀死及调整进程优先级,还能以图表形式显示所有服务器的指标。
|
||||
Gnome 系统监控器是一个基本的系统监控工具,其能通过一个树状结构来查看进程的依赖关系,能杀死进程及调整进程优先级,还能以图表形式显示所有服务器的指标。
|
||||
|
||||
### 日志监控工具 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -333,11 +333,11 @@ Gnome 系统监控器是一个基本的系统监控工具,其能通过一个
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
GoAccess 是一个实时的网络日志分析器,它能分析 apache, nginx 和 amazon cloudfront 的访问日志。它也可以将数据输出成 HTML,JSON 或 CSV 格式。它会给你一个基本的统计信息,访问量,404页面,访客位置和其他东西。
|
||||
GoAccess 是一个实时的网络日志分析器,它能分析 apache, nginx 和 amazon cloudfront 的访问日志。它也可以将数据输出成 HTML,JSON 或 CSV 格式。它会给你一个基本的统计信息、访问量、404 页面,访客位置和其他东西。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 57. [Logwatch][46] ####
|
||||
|
||||
Logwatch 是一个日志分析系统。它通过分析系统的日志,并为你所指定的区域创建一个分析报告。它每天给你一个报告可以让你花费更少的时间来分析日志。
|
||||
Logwatch 是一个日志分析系统。它通过分析系统的日志,并为你所指定的部分创建一个分析报告。它每天给你一个报告,以便让你花费更少的时间来分析日志。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 58. [Swatch][47] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -349,13 +349,13 @@ Logwatch 是一个日志分析系统。它通过分析系统的日志,并为
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
MultiTail 可帮助你在多窗口下监控日志文件。你可以将这些日志文件合并成一个。它也像正则表达式一样使用不同的颜色来显示日志文件以方便你阅读。
|
||||
MultiTail 可帮助你在多个窗口之下监控日志文件。你可以将这些日志文件合并到一个窗口。它可以通过正则表达式的帮助,使用不同的颜色来显示日志文件以方便你阅读。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 系统工具 ####
|
||||
### 系统工具 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 60. [acct or psacct][49] ####
|
||||
|
||||
acct 也称 psacct(取决于如果你使用 apt-get 还是 yum)可以监控所有用户执行的命令,包括 CPU 和内存在系统内所使用的时间。一旦安装完成后你可以使用命令 ‘sa’ 来查看。
|
||||
acct 也称 psacct(取决于如果你使用 apt-get 还是 yum)可以监控所有用户执行的命令,包括 CPU 时间和内存占用。一旦安装完成后你可以使用命令 `sa` 来查看统计。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 61. [whowatch][50] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -365,31 +365,31 @@ acct 也称 psacct(取决于如果你使用 apt-get 还是 yum)可以监控
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
strace 被用于诊断,调试和监控程序之间的相互调用过程。最常见的做法是用 strace 打印系统调用的程序列表,其可以看出程序是否像预期那样被执行了。
|
||||
strace 被用于诊断、调试和监控程序之间的相互调用过程。最常见的做法是用 strace 打印系统调用的程序列表,其可以看出程序是否像预期那样被执行了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 63. [DTrace][52] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
DTrace 可以说是 strace 的大哥。它动态地跟踪与检测代码实时运行的指令。它允许你深入分析其性能和诊断故障。但是,它并不简单,大约有1200本书中提到过它。
|
||||
DTrace 可以说是 strace 的大哥。它动态地跟踪与检测代码实时运行的指令。它允许你深入分析其性能和诊断故障。但是,它并不简单,关于这个话题有1200本书之多。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 64. [webmin][53] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Webmin 是一个基于 Web 的系统管理工具。它不需要手动编辑 UNIX 配置文件,并允许你远程管理系统。它有一对监控模块用于连接它。
|
||||
Webmin 是一个基于 Web 的系统管理工具。它不需要手动编辑 UNIX 配置文件,可以让你远程管理系统。它有一对监控模块用于连接它。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 65. stat ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Stat 是一个内置的工具,用于显示文件和文件系统的状态信息。它会显示文件被修改,访问或更改的信息。
|
||||
Stat 是一个内置的工具,用于显示文件和文件系统的状态信息。它会显示文件何时被修改、访问或更改。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 66. ifconfig ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ifconfig 是一个内置的工具用于配置网络接口。大多数网络监控工具背后都使用 ifconfig 将其设置成混乱模式来捕获所有的数据包。你可以手动执行 `ifconfig eth0 promisc` 并使用 `ifconfig eth0 -promisc` 返回正常模式。
|
||||
ifconfig 是一个内置的工具,用于配置网络接口。大多数网络监控工具背后都使用 ifconfig 将网卡设置成混乱模式来捕获所有的数据包。你可以手动执行 `ifconfig eth0 promisc` 进入混乱模式,使用 `ifconfig eth0 -promisc` 返回正常模式。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 67. [ulimit][54] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -399,23 +399,23 @@ ulimit 是一个内置的工具,可监控系统资源,并可以限制任何
|
||||
|
||||
#### 68. [cpulimit][55] ####
|
||||
|
||||
CPULimit 是一个小工具用于监控并限制进程对 CPU 的使用率。其特别有用,能限制批处理作业对 CPU 的使用率保持在一定范围。
|
||||
CPULimit 是一个小工具,用于监控并限制进程对 CPU 的使用率。其特别可以用于将批处理作业对 CPU 的使用率保持在一定范围。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 69. lshw ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
lshw 是一个小的内置工具能提取关于本机硬件配置的详细信息。它可以输出 CPU 版本和主板配置。
|
||||
lshw 是一个小的内置工具,能提取关于本机硬件配置的详细信息。它可以输出 CPU 版本和主板配置。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 70. w ####
|
||||
|
||||
w 是一个内置命令用于显示当前登录用户的信息及他们所运行的进程。
|
||||
w 是一个内置命令,用于显示当前登录用户的信息及他们所运行的进程。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 71. lsof ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
lsof 是一个内置的工具可让你列出所有打开的文件和网络连接。从那里你可以看到文件是由哪个进程打开的,基于进程名,可通过一个特定的用户来杀死属于某个用户的所有进程。
|
||||
lsof 是一个内置的工具,可让你列出所有打开的文件和网络连接。从那里你可以看到文件是由哪个进程打开的,基于进程名可找到其特定的用户,或杀死属于某个用户的所有进程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 基础架构监控工具 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -423,13 +423,13 @@ lsof 是一个内置的工具可让你列出所有打开的文件和网络连接
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我们的 [服务器监控工具][56]!它有一个 web 界面,使你可以进行报警设置并可以通过图表来查看所有系统的网络指标。你还可以设置监控的网站,无论是否在线。Server Density 允许你设置用户的权限,你可以根据我们的插件或 api 来扩展你的监控。该服务已经支持 Nagios 的插件了。
|
||||
我们的 [服务器监控工具][56] 它有一个 web 界面,使你可以进行报警设置并可以通过图表来查看所有系统的网络指标。你还可以设置监控的网站,无论是否在线。Server Density 允许你设置用户的权限,你可以根据我们的插件或 api 来扩展你的监控。该服务已经支持 Nagios 的插件了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 73. [OpenNMS][57] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
OpenNMS 主要有四个功能区:事件管理和通知;发现和配置;服务监控和数据收集。其设计可被在多种网络环境中定制。
|
||||
OpenNMS 主要有四个功能区:事件管理和通知;发现和配置;服务监控和数据收集。其设计为可被在多种网络环境中定制。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 74. [SysUsage][58] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -441,19 +441,19 @@ SysUsage 通过 Sar 和其他系统命令持续监控你的系统。一旦达到
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
brainypdm 是一个数据管理和监控工具,它能收集来自 nagios 或其它公共资源的数据并以图表显示。它是跨平台的,其基于 Web 并可自定义图形。
|
||||
brainypdm 是一个数据管理和监控工具,它能收集来自 nagios 或其它常规来源的数据并以图表显示。它是跨平台的,其基于 Web 并可自定义图形。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 76. [PCP][60] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
PCP 可以收集来自多个主机的指标,并且效率很高。它也有一个插件框架,所以你可以把它收集的对你很重要的指标使用插件来管理。你可以通过任何一个 Web 界面或 GUI 访问图形数据。它比较适合大型监控系统。
|
||||
PCP 可以收集来自多个主机的指标,并且效率很高。它也有一个插件框架,所以你可以让它收集对你很重要的指标。你可以通过任何一个 Web 界面或 GUI 访问图形数据。它比较适合大型监控系统。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 77. [KDE 系统保护][61] ####
|
||||
#### 77. [KDE 系统守护][61] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个工具既是一个系统监控器也是一个任务管理器。你可以通过工作表来查看多台机器的服务指标,如果一个进程需要被杀死或者你需要启动一个进程,它可以在 KDE 系统保护中来完成。
|
||||
这个工具既是一个系统监控器也是一个任务管理器。你可以通过工作表来查看多台机器的服务指标,如果需要杀死一个进程或者你需要启动一个进程,它可以在 KDE 系统守护中来完成。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 78. [Munin][62] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -471,7 +471,7 @@ Nagios 是系统和网络监控工具,可帮助你监控多台服务器。当
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Zenoss 提供了一个 Web 界面,使你可以监控所有的系统和网络指标。此外,它能自动发现网络资源和修改网络配置。并且会提醒你采取行动,它也支持 Nagios 的插件。
|
||||
Zenoss 提供了一个 Web 界面,使你可以监控所有的系统及网络指标。此外,它能自动发现网络资源和修改网络配置。并且会提醒你采取行动,它也支持 Nagios 的插件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 81. [Cacti][65] ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -483,7 +483,7 @@ Zenoss 提供了一个 Web 界面,使你可以监控所有的系统和网络
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Zabbix 是一个开源的基础设施监控解决方案。它使用了许多数据库来存放监控统计信息。其核心是用 C 语言编写,并在前端中使用 PHP。如果你不喜欢安装代理,Zabbix 可能是一个最好选择。
|
||||
Zabbix 是一个开源的基础设施监控解决方案。它使用了许多数据库来存放监控统计信息。其核心是用 C 语言编写,并在前端中使用 PHP。如果你不喜欢安装代理端,Zabbix 可能是一个最好选择。
|
||||
|
||||
### 附加部分: ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -491,15 +491,15 @@ Zabbix 是一个开源的基础设施监控解决方案。它使用了许多数
|
||||
|
||||
#### 83. [collectd][67] ####
|
||||
|
||||
Collectd 是一个 Unix 守护进程来收集所有的监控数据。它采用了模块化设计并使用插件来填补一些缺陷。这样能使 collectd 保持轻量级并可进行定制。
|
||||
Collectd 是一个 Unix 守护进程,用来收集所有的监控数据。它采用了模块化设计并使用插件来填补一些缺陷。这样能使 collectd 保持轻量级并可进行定制。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 84. [Observium][68] ####
|
||||
|
||||
Observium 是一个自动发现网络的监控平台,支持普通的硬件平台和操作系统。Observium 专注于提供一个优美,功能强大,简单直观的界面来显示网络的健康和状态。
|
||||
Observium 是一个自动发现网络的监控平台,支持大量硬件平台和操作系统。Observium 专注于提供一个优美、功能强大、简单直观的界面来显示网络的健康和状态。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 85. Nload ####
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个命令行工具来监控网络的吞吐量。它很整洁,因为它使用两个图表和其他一些有用的数据类似传输的数据总量来对进出站流量进行可视化。你可以使用如下方法安装它:
|
||||
这是一个命令行工具来监控网络的吞吐量。它很整洁,因为它使用两个图表和其他一些类似传输的数据总量这样的有用数据来对进出站流量进行可视化。你可以使用如下方法安装它:
|
||||
|
||||
yum install nload
|
||||
|
||||
@ -509,15 +509,15 @@ Observium 是一个自动发现网络的监控平台,支持普通的硬件平
|
||||
|
||||
#### 86. [SmokePing][69] ####
|
||||
|
||||
SmokePing 可以跟踪你网络延迟,并对他们进行可视化。SmokePing 有一个流行的延迟测量插件。如果图形用户界面对你来说非常重要,现在有一个正在开发中的插件来实现此功能。
|
||||
SmokePing 可以跟踪你网络延迟,并对他们进行可视化。有各种为 SmokePing 开发的延迟测量插件。如果图形用户界面对你来说非常重要,现在有一个正在开发中的插件来实现此功能。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 87. [MobaXterm][70] ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果你整天在 windows 环境下工作。你可能会觉得 Windows 下受终端窗口的限制。MobaXterm 正是由此而来的,它允许你使用多个在 Linux 中相似的终端。这将会极大地帮助你在监控方面的需求!
|
||||
如果你整天在 windows 环境下工作。你可能会觉得 Windows 下终端窗口的限制。MobaXterm 正是由此而来的,它允许你使用多个通常出现在 Linux 中的命令。这将会极大地帮助你在监控方面的需求!
|
||||
|
||||
#### 88. [Shinken monitoring][71] ####
|
||||
|
||||
Shinken 是一个监控框架,其是由 python 对 Nagios 进行完全重写的。它的目的是增强灵活性和管理更大环境。但仍保持所有的 nagios 配置和插件。
|
||||
Shinken 是一个监控框架,其是采用 python 对 Nagios 进行了完全重写。它的目的是增强灵活性和管理更大环境。但仍保持所有的 nagios 配置和插件。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -525,7 +525,7 @@ via: https://blog.serverdensity.com/80-linux-monitoring-tools-know/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jonathan Sundqvist][a]
|
||||
译者:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/strugglingyouth)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,57 +1,58 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu 15.04 上安装带JSON 支持的SQLite 3.9.1
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu 15.04 上安装带 JSON 支持的 SQLite 3.9.1
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
欢迎阅读我们关于SQLite 的文章,SQLite 是当今时间上使用最广泛的SQL 数据库引擎,它他基本不需要配置,不需要安装或者管理就可以运行。SQLite 是一个是开放领域的软件,是关系数据库的管理系统,或者说RDBMS,用来在大表存储用户定义的记录。对于数据存储和管理来说,数据库引擎要处理复杂的查询命令,这些命令可能会从多个表获取数据然后生成报告的数据总结。
|
||||
欢迎阅读我们关于SQLite 的文章,SQLite 是当今世界上使用最广泛的 SQL 数据库引擎,它基本不需要配置,不需要设置或管理就可以运行。SQLite 是一个是开放领域(public-domain)的软件,是一个关系型数据库管理系统(RDBMS),用来在一个大数据表中存储用户定义的记录。对于数据存储和管理来说,数据库引擎要处理复杂的查询命令,这些命令可能会从多个表获取数据然后生成报告和数据总结。
|
||||
|
||||
SQLite 是一个非常小、轻量级,不需要分离的服务进程或系统。他可以运行在UNIX,Linux,Mac OS-X,Android,iOS 和Windows 上,已经被大量的软件程序使用,如Opera, Ruby On Rails, Adobe System, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome 和 Skype。
|
||||
SQLite 是一个非常小、轻量级,不需要独立的服务进程或系统。它可以运行在 UNIX,Linux,Mac OS-X,Android,iOS 和 Windows 上,已经被大量的软件程序使用,如 Opera, Ruby On Rails, Adobe System, Mozilla Firefox, Google Chrome 和 Skype。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1) 基本需求: ###
|
||||
|
||||
在几乎全部支持SQLite 的平台上安装SQLite 基本上没有复杂的要求。
|
||||
在绝大部分支持 SQLite 的平台上安装 SQLite 基本上并没有复杂的要求。
|
||||
|
||||
所以让我们在CLI 或者Secure Shell 上使用sudo 或者root 权限登录Ubuntu 服务器。然后更新系统,这样子就可以让操作系统的软件更新到新版本。
|
||||
让我们在 CLI 或者 Secure Shell 上使用 sudo 或者 root 权限登录 Ubuntu 服务器。然后更新系统,这样子就可以让操作系统的软件更新到新版本。
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu 上,下面的命令是用来更新系统的软件源的。
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 上,使用如下的命令来更新系统的软件源。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
如果你要在新安装的Ubuntu 上部署SQLite,那么你需要安装一些基础的系统管理工具,如wget, make, unzip, gcc。
|
||||
如果你要在新安装的 Ubuntu 上部署 SQLite,那么你需要安装一些基础的系统管理工具,如 wget, make, unzip, gcc。
|
||||
|
||||
要安装wget,可以使用下面的命令,然后输入Y 如果系统提示的话:
|
||||
要安装 wget,可以使用下面的命令,如果系统提示的话,输入 Y :
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install wget make gcc
|
||||
|
||||
### 2) 下载 SQLite ###
|
||||
|
||||
要下载SQLite 最好是在[SQLite 官网][1]下载,如下所示
|
||||
要下载 SQLite ,最好是在 [SQLite 官网][1]下载,如下所示
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你也可以直接复制资源的连接然后再命令行使用wget 下载,如下所示:
|
||||
你也可以直接复制资源的连接然后在命令行使用 wget 下载,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
# wget https://www.sqlite.org/2015/sqlite-autoconf-3090100.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下载完成之后,解压缩安装包,切换工作目录到解压缩后的SQLite 目录,使用下面的命令。
|
||||
下载完成之后,解压缩安装包,切换工作目录到解压缩后的 SQLite 目录,使用下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# tar -zxvf sqlite-autoconf-3090100.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
### 3) 安装 SQLite ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们要开始安装、配置刚才下载的SQLite。所以在Ubuntu 上编译、安装SQLite,运行配置脚本。
|
||||
现在我们要开始安装、配置刚才下载的 SQLite。在 Ubuntu 上编译、安装 SQLite,运行配置脚本:
|
||||
|
||||
root@ubuntu-15:~/sqlite-autoconf-3090100# ./configure –prefix=/usr/local
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
配置要上面的prefix 之后,运行下面的命令编译安装包。
|
||||
|
||||
root@ubuntu-15:~/sqlite-autoconf-3090100# make
|
||||
配置要上面的安装位置前缀(prefix)之后,运行下面的命令编译安装包。
|
||||
```
|
||||
root@ubuntu-15:~/sqlite-autoconf-3090100# make
|
||||
source='sqlite3.c' object='sqlite3.lo' libtool=yes \
|
||||
DEPDIR=.deps depmode=none /bin/bash ./depcomp \
|
||||
/bin/bash ./libtool --tag=CC --mode=compile gcc -DPACKAGE_NAME=\"sqlite\" -DPACKAGE_TARNAME=\"sqlite\" -DPACKAGE_VERSION=\"3.9.1\" -DPACKAGE_STRING=\"sqlite\ 3.9.1\" -DPACKAGE_BUGREPORT=\"http://www.sqlite.org\" -DPACKAGE_URL=\"\" -DPACKAGE=\"sqlite\" -DVERSION=\"3.9.1\" -DSTDC_HEADERS=1 -DHAVE_SYS_TYPES_H=1 -DHAVE_SYS_STAT_H=1 -DHAVE_STDLIB_H=1 -DHAVE_STRING_H=1 -DHAVE_MEMORY_H=1 -DHAVE_STRINGS_H=1 -DHAVE_INTTYPES_H=1 -DHAVE_STDINT_H=1 -DHAVE_UNISTD_H=1 -DHAVE_DLFCN_H=1 -DLT_OBJDIR=\".libs/\" -DHAVE_FDATASYNC=1 -DHAVE_USLEEP=1 -DHAVE_LOCALTIME_R=1 -DHAVE_GMTIME_R=1 -DHAVE_DECL_STRERROR_R=1 -DHAVE_STRERROR_R=1 -DHAVE_POSIX_FALLOCATE=1 -I. -D_REENTRANT=1 -DSQLITE_THREADSAFE=1 -DSQLITE_ENABLE_FTS3 -DSQLITE_ENABLE_RTREE -g -O2 -c -o sqlite3.lo sqlite3.c
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行完上面的命令之后,要在Ubuntu 上完成SQLite 的安装得运行下面的命令。
|
||||
运行完上面的命令之后,要在 Ubuntu 上完成 SQLite 的安装得运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# make install
|
||||
|
||||
@ -59,7 +60,7 @@ DEPDIR=.deps depmode=none /bin/bash ./depcomp \
|
||||
|
||||
### 4) 测试 SQLite 安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要保证SQLite 3.9 安装成功了,运行下面的命令。
|
||||
要保证 SQLite 3.9 安装成功了,运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# sqlite3
|
||||
|
||||
@ -77,7 +78,7 @@ SQLite 很容易上手。要获得详细的使用方法,在SQLite 控制台里
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在开始最后一部分,使用一点SQLite 命令创建数据库。
|
||||
现在开始最后一部分,使用一点 SQLite 命令创建数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
要创建一个新的数据库需要运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -103,17 +104,18 @@ SQLite 很容易上手。要获得详细的使用方法,在SQLite 控制台里
|
||||
sqlite> .exit
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
通过本文你可以了解如果安装支持JSON1 的最新版的SQLite,SQLite 从3.9.0 开始支持JSON1。这是一个非常棒的库,可以用来获取内嵌到应用程序,利用它可以很有效而且很轻量的管理资源。我们希望你能觉得本文有所帮助,请自由的像我们反馈你遇到的问题和困难。
|
||||
通过本文你可以了解如果安装支持 JSON1 的最新版的 SQLite,SQLite 从 3.9.0 开始支持 JSON1。这是一个非常棒的库,可以内嵌到应用程序,利用它可以很有效而轻量的管理资源。我们希望你能觉得本文有所帮助,请随意地向我们反馈你遇到的问题和困难。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-sqlite-json-ubuntu-15-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kashif Siddique][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/oska874)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[oska874](https://github.com/oska874)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,237 @@
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 15.04 / CentOS 7 上安装广告服务器 Revive Adserver
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Revive Adserver是一个自由开源的广告管理系统,能使出版商,广告平台和广告商在网页、应用、视频上投放并管理广告的系统。Revive Adserver以前叫做OpenX Source,遵循GNU通用公共授权协议。它集广告管理、网站定位、地理定位和一个用于数据收集的跟踪系统于一体。能使网站站长管理内部的、付费的以及第三方来源的广告,如谷歌的AdSense。本教程中,将会教会你在Ubuntu 15.04或CentOS 7安装并运行Revive Adserver。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 安装LAMP###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,Revive Adserver需要完整的LAMP环境才能运行,所以我们先安装LAMP。LAMP是Apache网页服务器,MySQL/MariaDB数据库和PHP模块的集合。要使Revive正常运行,需要安装PHP的众多模块,如apc, zlib, xml, pcre, mysql和mbstring。在不同的Linux发行版中,我们可以用下列命令进行LAMP的配置:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu 15.04下####
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install apache2 mariadb-server php5 php5-gd php5-mysql php5-curl php-apc zlibc zlib1g zlib1g-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev libapache2-mod-php5 zip
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在CentOS 7下 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install httpd mariadb php php-gd php-mysql php-curl php-mbstring php-xml php-apc zlibc zlib1g zlib1g-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev zip
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 启动Apache Web和MariaDB服务
|
||||
|
||||
可以用下列命令启动刚刚安装好的Apache Web服务和MariaDB数据库服务。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu 15.04下####
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu15.04使用Systemd作为默认初始系统,所以用下列命令启动Apache和MariaDB进程:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start apache2 mysql
|
||||
|
||||
可以用下列命令使其开机自动运行:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable apache2 mysql
|
||||
|
||||
Synchronizing state for apache2.service with sysvinit using update-rc.d...
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d apache2 defaults
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d apache2 enable
|
||||
Synchronizing state for mysql.service with sysvinit using update-rc.d...
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d mysql defaults
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d mysql enable
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在CentOS 7下
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS 7同样是以Systemd作为默认初始系统,可以用下列命令启动:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start httpd mariadb
|
||||
|
||||
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service'
|
||||
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service'
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 配置MariaDB
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在CentOS 7/Ubuntu 15.04下 ####
|
||||
|
||||
当我们第一次启动MariaDB时,MariaDB是没有分配密码的,所以要先设置一个root密码。之后再创建一个新的数据库用来储存Revive Adserver的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令配置MariaDB并设置其root密码:
|
||||
|
||||
# mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
|
||||
这时会要我们输入root密码,但我们之前什么密码都没设置,所以按回车下一步。之后,要求设置root密码,这时我们输入Y,然后输入自己想要的密码。回车继续下一步。
|
||||
|
||||
….
|
||||
so you should just press enter here.
|
||||
|
||||
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
|
||||
OK, successfully used password, moving on…
|
||||
|
||||
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
|
||||
root user without the proper authorisation.
|
||||
|
||||
Set root password? [Y/n] y
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Re-enter new password:
|
||||
Password updated successfully!
|
||||
Reloading privilege tables..
|
||||
… Success!
|
||||
…
|
||||
installation should now be secure.
|
||||
Thanks for using MariaDB!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 创建新的数据库 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为MariaDB的root用户设置了密码之后,就可以创建用来储存Revive Adserver应用数据的数据库。首先通过以下命令登录MariaDB控制台:
|
||||
|
||||
# mysql -u root -p
|
||||
|
||||
这时要求输入root用户的密码,我们只要输入上一步设置好的密码。然后进入MariaDB控制台创建新的数据库,数据库用户及其密码,并且授予其创建、删除、编辑和存储表与数据的全部权限。
|
||||
|
||||
> CREATE DATABASE revivedb;
|
||||
> CREATE USER 'reviveuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Pa$$worD123';
|
||||
> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON revivedb.* TO 'reviveuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
|
||||
> EXIT;
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 下载Revive Adserver
|
||||
|
||||
接下来下载Revive Adserver的最新版本Revive Adserver.3.2.2(写本文时)。可以使用wget命令从Revive Adserverde 官方网站下载压缩包,网址是:[http://www.revive-adserver.com/download/][1] 。命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /tmp/
|
||||
# wget http://download.revive-adserver.com/revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip
|
||||
|
||||
--2015-11-09 17:03:48-- http://download.revive-adserver.com/revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip
|
||||
Resolving download.revive-adserver.com (download.revive-adserver.com)... 54.230.119.219, 54.239.132.177, 54.230.116.214, ...
|
||||
Connecting to download.revive-adserver.com (download.revive-adserver.com)|54.230.119.219|:80... connected.
|
||||
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
|
||||
Length: 11663620 (11M) [application/zip]
|
||||
Saving to: 'revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip'
|
||||
revive-adserver-3.2 100%[=====================>] 11.12M 1.80MB/s in 13s
|
||||
2015-11-09 17:04:02 (906 KB/s) - 'revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip' saved [11663620/11663620]
|
||||
|
||||
解压到临时目录下:
|
||||
|
||||
# unzip revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip
|
||||
|
||||
把解压后的整个文件夹移动到Apache Web服务器的默认根目录/var/www/html/下:
|
||||
|
||||
# mv revive-adserver-3.2.2 /var/www/html/reviveads
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 配置Apache Web服务
|
||||
|
||||
现在配置Apache服务使Revive正常运行。通过创建配置文件reviveads.conf来创建一个新的虚拟主机。这个目录在不同的Linux发行版上有所不同。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu 15.04下
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /etc/apache2/sites-available/reviveads.conf
|
||||
# ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/reviveads.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/reviveads.conf
|
||||
# nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/reviveads.conf
|
||||
|
||||
在这个文件中添加下列几行文本:
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerAdmin info@reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/reviveads/
|
||||
ServerName reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
ServerAlias www.reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
<Directory /var/www/html/reviveads/>
|
||||
Options FollowSymLinks
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/reviveads.linoxide.com-error_log
|
||||
CustomLog /var/log/apache2/reviveads.linoxide.com-access_log common
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出,重启Apache Web服务:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart apache2
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在CentOS 7下 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS下,我们直接在/etc/httpd/conf.d/ 目录下创建reviveads.conf :
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/reviveads.conf
|
||||
|
||||
在这个文件中添加下列几行文本:
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerAdmin info@reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/reviveads/
|
||||
ServerName reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
ServerAlias www.reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
<Directory /var/www/html/reviveads/>
|
||||
Options FollowSymLinks
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/reviveads.linoxide.com-error_log
|
||||
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/reviveads.linoxide.com-access_log common
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出,重启Apache Web服务:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart httpd
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 修复权限和所有权
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们修改安装路径下文件的权限和所有权。把安装目录的所有权改成Apache进程所有,以便Apache Web服务有文件和目录的编辑、创建和删除的完全权限。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu 15.04下####
|
||||
|
||||
# chown www-data: -R /var/www/html/reviveads
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在CentOS 7下
|
||||
|
||||
# chown apache: -R /var/www/html/reviveads
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. 设置防火墙
|
||||
|
||||
现在要配置防火墙,打开80端口使Apache Web服务运行的Revive Adserver能够被网络上的其他机器所访问。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu 15.04/CentOS 7下
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu15.04/CentOS 7都使用Systemd作为默认初始系统,使用firewalld作为其防火墙。要打开80端口(http服务端口),执行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. 网站的安装
|
||||
|
||||
顺利的话我们能够使用浏览器进行交互,并可以将浏览器指向正在运行的网络服务器。只要在浏览器输入http://ip-address/ 或者 http://domain.com 。这里我们要访问 http://reviveads.linoxide.com/
|
||||
|
||||
打开后可以看到Revive Adserver的欢迎页面,上面还有作为它发行许可证的GNU通用公共许可证V2。点击 I agree 继续下一步安装。
|
||||
|
||||
在下一页中,我们要输入数据库信息以便把Revive Adserver和MariaDB数据库服务连接起来。要输入之前设置的数据库名称,用户名以及密码。在本教程中,我们分别输入数据库名称为revivedb,用户名为reviveuser,密码为Pa$$worD123,并且令主机名为localhost,点击continue继续。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
输入要填的信息,如:管理员用户名,密码和邮箱。可以以这些信息登录Adserver的控制界面。然后跳到最后一页,可以看到Revive Adserver已经安装成功了。
|
||||
|
||||
接着,转到Adverstiser页面,添加新的广告管理。在控制界面添加新用户到adserver,为广告库户添加标题,网页,视频
|
||||
广告。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
本文中,我们学习了如何在Ubuntu 15.04和CentOS 7上安装并配置Revive Adserver。尽管Revive Adserver的原始代码是从OpenX那买的,但现在OpenX Enterprise和Revive Adserver已经完全分开了。可以从[http://www.adserverplugins.com/][2] 获得更多插件来扩展新特性。讲真,这个软件确实让网页,应用,视频上的广告管理变得容易了许多。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-revive-adserver-ubuntu-15-04-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[chisper](https://github.com/chisper)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.revive-adserver.com/download/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.adserverplugins.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
没有 Linux 和开源软件的世界会变得怎么样
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Linux 基金会针最近对人们关于 “没有 Linux 的世界” 系列短片所提出的问题做了回应,解答了包括没有 Linux 和其他的开源软件的因特网会变得怎么样等问题。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
假如 Linux —— 这个开源的操作系统内核 —— 不曾出现过,我们现在的世界是否会是另一番景象。会不会没有了因特网,或者没有了电影?这些都是观看 [Linux 基金会][1] 正在连续播出的 “[没有 Linux 的世界][2]” 系列短片的观众提出来的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
假如你错过了观看这些短片也不要紧,“[没有 Linux 的世界][2]” 系列短片是一个搞笑短片的集合,里边描述了没有了 Linux (或者说没有开源软件)的世界发生的事情。这些短片强调了 Linux 在 [电影制作][3] 以及 [因特网服务][4] 中充当的角色。
|
||||
|
||||
为了揭示该系列短片的一些主张、倾向和隐藏元素,Linux 基金会副主席 Jennifer Cloer 最近在 The VAR Guy 上回应了关于该短片的一些问题。以下是她的原话解答。
|
||||
|
||||
### 最新一集短片 —— Sam 和 Annie 一起看电影。假如没有 Linux,我们现在的荧屏是不是也和短片中的一样? ###
|
||||
|
||||
在第 4 集剧情中,我们恶搞了一下电影 “阿凡达(Avatar)”。不管你喜欢还是讨厌,现实中的 “阿凡达(Avatar)” 在荧屏上的效果还是让人记忆深刻的。在没有 Linux 的世界中,电影的效果就变得非常丑陋,但是我们并不知道它有多难看,因为那已经是最好的了。但实际上,“阿凡达(Avatar)” 是使用 Linux 来进行效果制作的。Weta 数码使用了当时世界上最大的 Linux 集群来给电影做效果渲染和 3D 建模。据报道,指环王(Lord of the Rings)、神奇四侠(Fantastic Four)和金刚(King Kong)等电影都用到了 Linux。我希望该短片能引起人们关注,因为它所做的这方面的工作还并不广为人知。
|
||||
|
||||
### 很多人对短片的原始剧情进行了批判,其中就包括“没有 Linux 将没有因特网”的剧情的指责。你对此持什么样的看法? ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们很喜欢人们在短片刚上映就进行激烈的辩论。该短片上映当天就超过了 100,000 的观众,这引起了人们对 Linux 在社会中扮演的角色以及对全世界的社区贡献者和维护者的关注。当然了,没有 Linux 的话,因特网也是会出现的,只是不会像当前我们所熟知的互联网那么成熟而已。每一个短片都对 Linux 在我们每天生活中扮演的角色进行了大胆且有趣的描述。我们希望,这些短片能够把关于 Linux 的故事推广到全世界的人的心里去。
|
||||
|
||||
### 为什么 Sam 和 Annie 的那只猫叫做 String? ###
|
||||
|
||||
该短片系列中没有一处剧情是随意的。仔细的观看的话,你就会发现其中关于 Linux 和极客们的各种玩笑。小猫 String 是我们的 Linux.com 主编 Libby Clark 以弦理论(string theory)亲自来命名的。在物理学里,弦理论(string theory)是一个理论框架,它用一个叫做弦(String)的一维对象替换了粒子物理学中粒子状的粒子。弦理论(string theory)描述了这些弦(String)如何在空间传播以及相互影响。就像 Sam、Annie 和 String 在那个没有 Linux 的世界里的关系那样。
|
||||
|
||||
### 我们期待已久的下两集是什么样的,特别是,最后那集什么时候上映? ###
|
||||
|
||||
在第 5 集短片中,我们将到太空并体验一下没有 Linux 的世界对太空探索的影响。这就像是一场疯狂的骑行。在短片的最后,我们最终还是会见到没有 Linux 的世界里的 Linus。贯穿整个短片系列,里边已经给出关于结局的线索,我在这就不能给太多提示了,因为还有好多人在找线索比赛中继续寻找着。并且我也不能给你们说出关于结局短片的上映日期。你们要自己跟进 #WorldWithoutLinux 主题帖来获取更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 你可给一些关于第 4 集短片相关线索的提示吗? ###
|
||||
|
||||
在该短片中有另外一个关于免费汉堡餐厅(Free Burger Restaurant)的线索。在那个没有 Linux 的世界里,Linux 最后还是以一种很隐秘的方式出现了,可以说,就像是以另一种语言来解读 Linux。当然,这只是为了好玩,String 也以另外一个模样出现。
|
||||
|
||||
### 那么,该系列短片达到你所想要的效果了吗? ###
|
||||
|
||||
是的,达到了。我们很高兴看到人们分享并参与到这些故事中去。我们希望向那些可能不知道 Linux 的人传达更多关于 Linux 的故事并了解到 Linux 在当今世界中是无处不在的。全部的短片就是为了把这些关于 Linux 的真相推广给大家,并感谢那些全球性社区的开发者和公司对 Linux 的支持,Linux 使得一切成为可能。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/linux-foundation-explains-world-without-linux-and-open-so
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Christopher Tozzi][a]
|
||||
译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://thevarguy.com/author/christopher-tozzi
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/world-without-linux
|
||||
[3]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/new-linux-foundation-video-highlights-role-open-source-3d
|
||||
[4]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/100715/would-internet-exist-without-linux-yes-without-open-sourc
|
||||
87
published/20151201 Cinnamon 2.8 Review.md
Normal file
87
published/20151201 Cinnamon 2.8 Review.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8 新变化一览
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
除了Gnome和KDE外,Cinnamon是另一个很多人使用的桌面环境。它是由创作Linux Mint的团队制作的,并且可以被安装在许多其他发行版上。该桌面环境的最新版本 - Cinnamon 2.8 - 于去年底发布,此版本修复了许多的Bug、做了许多改进并添加了一些新功能。
|
||||
|
||||
我将仔细介绍该发行版本的主要改进,以及如何更新到Cinnamon 2.8或者第一次安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 对Applets的改进 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在此版本中,对面板中已有的Applets做了若干的改进。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 声音 Applet ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
声音Applet经过修正,目前可以显示音轨信息并且可以在音频文件的艺术家封面上面进行媒体控制。对于支持拖动的音乐播放器来说(例如Banshee),会有一个进度条显示同样的播放进度,您可以用它来改变音轨位置。在applet的面板上右击将显示对输入和输出设备静音的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 电源 Applet ####
|
||||
|
||||
电源applet则会使用电池制造商的数据而不是通用名称来显示每一个连接的电池和设备。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 窗口缩略图 ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Cinnamon 2.8中,可以在鼠标悬停于面板里窗口列表时展示窗口缩略图。如果您不喜欢该功能,您还可以关闭该选项。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 工作区切换 Applet ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
添加工作区切换applet到您的面板将为您显示一个代表该工作区的可视化图像,一些矩形嵌套显示在其中,代表您的窗口的位置。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 系统托盘 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8支持在系统托盘中显示应用程序指示器。您可以很容易地在设置中禁用它,这将强制应用程序到以前使用状态图标的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 视觉改进 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8还做了很多视觉上的改进。经典的切换器和Alt + Tab预览切换器都被精细打磨,有了显著的改进,同时修复了Alt + F2对话框的bug,并赋予了它更好的命令自动补全功能。
|
||||
|
||||
而且,传统的最小化窗口时动画效果的问题现已被解决,并可用于多个面板。
|
||||
|
||||
### Nemo 的改进 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon默认的文件管理器也修复了一些bug,并有了新的“快速重命名”的功能,用于重命名文件和文件夹。可以通过两次点击文件或文件夹并在两次点击之间进行简短的停顿以重命名文件。
|
||||
|
||||
Nemo也会自动地检测缩略图存在的问题,并提示您快速地修复它们。
|
||||
|
||||
### 其他值得注意的改进 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Applets如今会在它们被更新的时候自动地重新加载一次。
|
||||
- 对于多个监视器的支持有了显著的提高。
|
||||
- 对话框窗口有了改进,并且会附加到它的父窗口上。
|
||||
- HiDPI检测有了改进。
|
||||
- QT5应用程序现在看起来更加原生并使用了默认的GTK主题。
|
||||
- 窗口管理和渲染性能有了提升。
|
||||
- 修复了许多bug。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何获得 Cinnamon 2.8 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果您在运行Linux Mint,您会在更新Linux Mint 17.3 “Rosa”Cinnamon版本的时候获得Cinnamon 2.8的更新。BETA版本现在已经放出,因此,如果您想立刻尝试新的软件,您可以试试。
|
||||
|
||||
对于Arch的用户来说,Cinnamon 2.8已经在Arch的官方仓库了,您可以通过更新软件包和系统级的更新获得Cinnamon的最新版本。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,对于Ubuntu用户来说,您可以通过下面的命令安装或更新Cinnamon 2.8:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:moorkai/cinnamon
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install cinnamon
|
||||
|
||||
您已经尝试了Cinnamon 2.8了么?感觉如何呢?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/cinnamon-2-8-review/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ayo Isaiah][a]
|
||||
译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/ayoisaiah/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
如何 Mutt 邮件客户端中使用密文密码
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Mutt 是一个 Linux/UNIX 终端环境下的开源的邮件客户端。Mutt 以及 [Alpine][1] 在 Linux 命令行爱好者中有着最忠诚的追随者,这不是没有原因的。想一下你所期待邮件客户端应有的功能,Mutt 拥有:多协议支持(例如,POP3、IMAP 和 SMTP),S/MIME 和 PGP/GPG 集成,会话线索,颜色标记,可定制宏/快捷键,等等。另外,基于命令行的 Mutt 相比粗重的基于浏览器的邮件客户端(如:Gmail,Ymail)或图形用户界面的邮件客户端(如:Thunderbird,MS Outlook)而言,是一个使用电子邮件的轻量级替代品。
|
||||
|
||||
当你想使用 Mutt 通过公司的 SMTP/IMAP 服务器访问或发送邮件,或取代网页邮件服务,可能所关心的一个问题是如何保护您的邮件凭据(如:SMTP/IMAP 密码),它们存储在一个纯文本 Mutt 配置文件(~/.muttrc)中。
|
||||
|
||||
对于这些人对安全的担忧,确实有一个容易的方法来**加密 Mutt 配置文件***,以防止这种风险。在这个教程中,我描述了如何加密 Mutt 敏感配置,比如使用 GnuPG(GPG)加密 SMTP/IMAP 密码,GPG 是一个开源的 OpenPGP 实现。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一步 (可选):创建 GPG 密钥 ###
|
||||
|
||||
因为我们将要使用 GPG 加密 Mutt 配置文件,如果你没有 GPG 密钥,第一步就是创建一个(公钥/私钥对)。如果有,请忽略这步。
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个新 GPG 密钥,输入下面命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ gpg --gen-key
|
||||
|
||||
选择密钥类型(RSA),密钥长度(2048 bits),和过期时间(0 代表不过期)。当出现用户 ID 提示时,输入关联到该公钥/私钥对的名字(Dan Nanni) 和邮箱地址(myemail@email.com)。最后,输入一个密码来保护你的私钥。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
生成一个 GPG 密钥需要大量的随机字节来构成熵,所以在生成密钥期间确保在你的系统上执行一些随机行为(如:敲打键盘,移动鼠标或者读写磁盘)。根据密钥长度,生成 GPG 密钥要花几分钟或更多时间。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 第二步:加密 Mutt 敏感配置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下一步,在 ~/.mutt 目录创建一个新的文本文件,然后把一些你想隐藏的 Mutt 敏感配置放进去。这个例子里,我指定了 SMTP/IMAP 密码。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mkdir ~/.mutt
|
||||
$ vi ~/.mutt/password
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
set smtp_pass="XXXXXXX"
|
||||
set imap_pass="XXXXXXX"
|
||||
|
||||
现在通过 GPG 使用你的公钥加密这个文件如下:
|
||||
|
||||
$ gpg -r myemail@email.com -e ~/.mutt/password
|
||||
|
||||
这将创建 ~/.mutt/password.gpg,这是一个原始文件的 GPG 加密版本。
|
||||
|
||||
然后删除 ~/.mutt/password,只保留 GPG 加密版本。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第三步:创建完整 Mutt 配置文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在你已经在一个单独的文件放置了加密的 Mutt 敏感配置,你可以在 ~/.muttrc 指定其余的 Mutt 配置。然后增加下面这行在 ~/.muttrc 末尾。
|
||||
|
||||
source "gpg -d ~/.mutt/password.gpg |"
|
||||
|
||||
当你启动 Mutt 时,这行将解密 ~/.mutt/password.gpg ,然后将解密内容应用到你的 Mutt 配置中。
|
||||
|
||||
下面展示一个完整 Mutt 配置例子,这可以让你通过 Mutt 访问 Gmail,而没有暴露你的 SMTP/IMAP 密码。用你的 Gmail ID 替代下面的 `yourgmailaccount`,此外你也需要在[你的 Goolgle 账户设置][3]中启用“支持不太安全的应用访问”。
|
||||
|
||||
set from = "yourgmailaccount@gmail.com"
|
||||
set realname = "Your Name"
|
||||
set smtp_url = "smtp://yourgmailaccount@smtp.gmail.com:587/"
|
||||
set imap_user = "yourgmailaccount@gmail.com"
|
||||
set folder = "imaps://imap.gmail.com:993"
|
||||
set spoolfile = "+INBOX"
|
||||
set postponed = "+[Google Mail]/Drafts"
|
||||
set trash = "+[Google Mail]/Trash"
|
||||
set header_cache =~/.mutt/cache/headers
|
||||
set message_cachedir =~/.mutt/cache/bodies
|
||||
set certificate_file =~/.mutt/certificates
|
||||
set move = no
|
||||
set imap_keepalive = 900
|
||||
|
||||
# encrypted IMAP/SMTP passwords
|
||||
source "gpg -d ~/.mutt/password.gpg |"
|
||||
|
||||
### 第四步(可选):配置 GPG 代理 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这时候,你将可以使用加密了IMAP/SMTP 密码的 Mutt。然而,每次你运行 Mutt,你都要先被提示输入一个 GPG 密码来使用你的私钥解密 IMAP/SMTP 密码。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你想避免这样的 GPG 密码提示,你可以部署一个 gpg-agent。它以后台守护进程方式运行,gpg-agent 可以安全地缓存你的 GPG 密码,无需手工干预,gpg 可以自动从 gpg-agent 获得你的 GPG 密码。如果你正在使用 Linux 桌面,你可以配置使用一些等同于 gpg-agent 的特定的桌面软件,例如,GNOME 桌面的 gnome-keyring-daemon。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在基于 Debian 系统安装 gpg-agent:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install gpg-agent
|
||||
|
||||
gpg-agent 在基于 Red Hat 的系统上是预装好的。
|
||||
|
||||
现在增加下面这些到你的 .bashrc 文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
envfile="$HOME/.gnupg/gpg-agent.env"
|
||||
if [[ -e "$envfile" ]] && kill -0 $(grep GPG_AGENT_INFO "$envfile" | cut -d: -f 2) 2>/dev/null; then
|
||||
eval "$(cat "$envfile")"
|
||||
else
|
||||
eval "$(gpg-agent --daemon --allow-preset-passphrase --write-env-file "$envfile")"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
export GPG_AGENT_INFO
|
||||
|
||||
重载 .bashrc,或简单的登出然后重新登录。
|
||||
|
||||
$ source ~/.bashrc
|
||||
|
||||
现在确认 GPG_AGENT_INFO 环境变量已经设置妥当。
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo $GPG_AGENT_INFO
|
||||
|
||||
/tmp/gpg-0SKJw8/S.gpg-agent:942:1
|
||||
|
||||
并且,当你输入 gpg-agent 命令时,你应该看到下面的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
$ gpg-agent
|
||||
|
||||
gpg-agent: gpg-agent running and available
|
||||
|
||||
一旦 gpg-agent 启动运行,它将会在第一次提示你输入密码时缓存你的 GPG 密码。随后你多次运行 Mutt ,都不会被提示要 GPG 密码(gpg-agent 一直开着,缓存就不会过期)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这个指导里,我提供一个使用 GnuPG 加密如 SMTP/IMAP 密码这样的 Mutt 敏感配置的方法。注意,如果你想在 Mutt 上使用 GnuPG 来加密或签名你的邮件,你可以参考[官方指南][2]关于 GPG 与 Mutt 结合的部分。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你知道任何使用 Mutt 的安全技巧,欢迎分享它。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/mutt-email-client-encrypted-passwords.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[wyangsun](https://github.com/wyangsun)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/gmail-command-line-linux-alpine.html
|
||||
[2]:http://dev.mutt.org/trac/wiki/MuttGuide/UseGPG
|
||||
[3]:https://www.google.com/settings/u/1/security
|
||||
51
published/20151206 Supporting secure DNS in glibc.md
Normal file
51
published/20151206 Supporting secure DNS in glibc.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
通过修改 glibc 支持 DNS 加密
|
||||
========================
|
||||
|
||||
域名解析系统(DNS)是互联网安全的许多薄弱环节之一;可以将应用程序所访问的主机对应的 IP 地址误导到其它地方。也就是说,会连接到错误的位置,从而引发中间人(man-in-the-middle )攻击等等。而 [DNSSEC][1] 扩展协议则通过为 DNS 信息建立一条加密的可信通道来解决这个漏洞。在正确地配置好 DNSSEC 后,应用程序将可以得到可靠的主机查询信息。通过关于[尝试将 DNSSEC 更好地集成到 GNU C 库里][2]的讨论,我们知道,确保 DNS 查询信息安全这件事并不是那么简单。
|
||||
|
||||
从某种意义上来说,这个问题多年以前就解决了,我们可以配置一个本地域名服务实现完整的 DNSSEC 校验(verification)并允许应用程序通过 glibc 函数来使用该服务。DNSSEC 甚至还可以用于提高其他领域的安全性,比如,它可以携带 SSH 或 TLS 密钥指纹,让应用程序可以确认其在与正确的服务器对话。不过,当我们希望确认这条自称带有 DNSSEC 校验的 DNS 结果是不是真的已通过认证的时候 - 也就是说,当我们想依赖 DNSSEC 所承诺的安全的时候,事情变得有点复杂。
|
||||
|
||||
### /etc/resolv.conf 问题
|
||||
|
||||
从 glibc 的角度来看,这个问题一部分是因为 glibc 本身并没有做 DNSSEC 校验,而是引用 /etc/resolv.conf 文件,从该文件里读出的服务器来做解析以及校验,再将结果返回给应用程序。如果应用程序使用底层 res_query() 接口,那结果中将会包含“已认证数据(authenticated data)”(AD)标识(如果域名服务器设定了的话)以表示 DNSSEC 校验已经成功。但是 glibc 却完全不知道提供这些结果的域名服务器的信用,所以它其实并不能告诉应用程序结果是否真的可靠。
|
||||
|
||||
由 glibc 的维护者 Carlos O'Donell 提出的建议是在 resolv.conf 文件里增加一个选项(dns-strip-dnssec-ad-bit)告诉 glibc 无条件移除 AD 标识。这个选项可以由各发行版设定,表示 DNSSEC 级别的 DNS 查询结果并不可靠。而一旦建立好合适的环境可以获得可靠的查询结果后,再移除这个选项。这样一来,虽然问题还没有完全解决,至少应用程序有依据来评价从 glibc 获取的 DNS 查询结果的可靠性。
|
||||
|
||||
一个可靠的环境配置应该是什么样?标准情况应该和这个差不太多:有一个本地域名服务器,通过环路(loopback)接口访问,作为访问 /etc/resolv.conf 文件的唯一条目。这个域名服务器应该配置来做校验,而在校验失败后就只是简单地不返回任何结果。绝大多数情况下,应用程序就不再需要关心 AD 标识,如果结果不可靠,应用程序就根本看不到。一些发行版已经倾向于这种模型,不过情况仍然不像一些人所设想的那么简单。
|
||||
|
||||
其中一个问题是,这种方式将 /etc/resolv.conf 文件放到整个系统可信任度的中心。但是,在一个典型的 Linux 系统里,有无数的 DHCP 客户端、网络脚本以及其他更多的程序可以修改这个文件。就像 Paul Wouters 所[指出][3]的,在短时间内锁定这个文件是不可能的。有时候这种修改是必须的:在一个无盘系统启动的时候,在自身的域名服务器启动之前也是需要域名服务的;一个系统的整个 DNS 环境也会根据所连接的网络不同而有所改变;运行在容器里的系统也最好是配置成使用宿主机的域名服务器;等等。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,现在一般认为,现有系统里的 /etc/resolv.conf 文件并不可信。于是有人提出增加另一个配置文件(/etc/secure-resolv.conf 或其他什么),但这并没有从根本上解决问题。除此之外,有些参与者觉得就算有一个运行在环路接口上的域名服务器也不是真正可靠,比如 Zack Weinberg 甚至[建议][4]系统管理员可以有意禁用 DNSSEC 确认(validation)。
|
||||
|
||||
既然当前系统里的配置不足以信任,那可以这样推断,在情况有改善能够取得可信的结果后,glibc 需要有一种方式来通知应用程序。可以是上面讨论的屏蔽 AD 标识的方式(或者与之相反,增加一个显示的“此域名服务器可以信任”选项);当然,这都需要一定程度上锁定系统以免 /etc/resolv.conf 受到任何不可预计的修改。按 Petr Spacek 的[建议][5],还有一种引申方式,就是提供一种途径允许应用程序查询 glibc 当前通讯的是不是本地域名服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 glibc 里来处理?
|
||||
|
||||
另一种方式是不管域名服务器,而是让 glibc 本身来做 DNSSEC 确认。不过,把这么大一坨加密相关代码放进 glibc 也是有很大阻力。这样将增加库本身的大小,从而感觉会增加使用它的应用程序的受攻击可能性。这个方向再引申一下,由 Zack 提出的[建议][6],可以把确认相关代码放到域名服务缓冲守护进程(nscd)里。因为 nscd 也是 glibc 的一部分,由 glibc 开发人员维护,因此在一定程度上可以相信能正确执行 DNSSEC 确认。而且 nscd 的通讯 socket 所在位置也是公开的,所以可以不考虑 /etc/resolv.conf 问题。不过,Carlos [担心][7]这种方式不能让那些不想使用 nscd 缓存功能的用户所接受;在他看来,基本可以排除 nscd 的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,至少近期内,glibc 不太可能全部执行 DNSSEC 确认了的整个查询过程。这意味着,如果一个有安全考虑的应用要使用 glibc 库来查询域名,该库将需要提供一个标识来评价从独立域名服务器返回的结果有多大程度的可靠性。这几乎肯定需要发行版或系统管理员做出一些明确的改动。就像 Simo Sorce [说的][8]那样:
|
||||
|
||||
> 如果 glibc 不使用明确的配置选项来通知应用程序它所用的域名解析是可信的,不会有什么用……不改一下还有很大弊端,因为应用程序开发者将马上认识到他们不能信任从 glibc 获取的任何信息,从而在处理 DNSSEC 相关信息时就简单地不用它。
|
||||
|
||||
要配置一个系统能正常使用 DNSSEC 需要改动该系统的很多组件 - 这是一个发行版范围的问题,需要时间来完全解决。在这个转变过程中 glibc 所扮演的角色很可能会比较小,但是很重要的一部分:如果应用程序不实现一套自己的域名解析代码,glibc 很可能是保证 DNS 结果可信的唯一方式。在一个系统中运行多个 DNSSEC 实现方式看起来不像是一种安全的方式,所以最好还是把事情做对了。
|
||||
|
||||
glibc 项目目前并没有确定用哪种方式来做这个事情,虽然从 /etc/resolv.conf 文件里的某些标记看上去快好了。这种改动应该需要发布新版本;考虑到 glibc 开发的保守天性,很可能来不及加入预计二月份发布的 2.23 版本了。所以 glibc 中暂时还不会有更高安全性的 DNSSEC ,不过在这个方向上也有一些进展了。
|
||||
|
||||
---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://lwn.net/Articles/664776/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Jonathan Corbet
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domain_Name_System_Security_Extensions
|
||||
[2]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664790/
|
||||
[3]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664794/
|
||||
[4]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664782/
|
||||
[5]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664784/
|
||||
[6]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664796/
|
||||
[7]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664786/
|
||||
[8]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664787/
|
||||
@ -1,53 +1,54 @@
|
||||
GHLandy Translated
|
||||
|
||||
LibreOffice 中的六大实用扩展组件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
图片来源:Opensource.com
|
||||
|
||||
LibreOffice 是最好的免费办公套件,并在所有的主要 Linux 发行版中得到应用。尽管 LibreOffice 已经拥有了大多数特性,它仍然可以添加特定的附加组件,即扩展。
|
||||
LibreOffice 是最好的自由办公套件,并在所有的主要 Linux 发行版中得到应用。尽管 LibreOffice 已经拥有了大多数特性,它仍然可以通过添加一种叫做扩展(extension)的特定的附加组件来增加功能。
|
||||
|
||||
LibreOffice 的扩展组件的网站是 [extensions.libreoffice.org][1]。扩展组件只是一些工具,可以在安装主体上进行独立添加或者移除,以便增加新功能或者让已有功能更容易使用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 多格式保存组件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
多格式保存组件可以根据用户的设置,同时将文档保存为开源文档、微软 Office 文档或者 PDF 文档。在你将微软 Office 文档格式转为标准的[开源文档格式][2]的时候,这个组件就很实用了,因为该组件同时提供了两种选择:互操作性较强的 ODF 文档格式以及为所有用户让在实用的微软 Office 文档格式保持兼容性。这样使管理员的文档迁移过程变得更具弹性、更易于管理。
|
||||
多格式保存组件可以根据用户的设置,同时将文档保存为开源文档(OpenDocument)、微软 Office 文档或者 PDF 文档。在你需要将微软 Office 文档格式转为标准的[开源文档格式][2]的时候,这个组件就很实用了,因为该组件同时提供了两种选择:互操作性较强的 ODF 文档格式,以及微软 Office 文档格式,以便同所有需要使用老旧的文档格式的用户保持兼容性。这样使管理员的文档迁移过程变得更具弹性、更易于管理。
|
||||
|
||||
**[下载 多格式保存组件][3]**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Writer 中可交替使用的查找与替换组件(交替搜索) ###
|
||||
### 2. Writer 中可备选使用的查找与替换组件(备选搜索 (AltSearch)) ###
|
||||
|
||||
该组件向 Writer 中的查找与替换功能添加了许多新特性:可以查找和替换一段或多段文本;一次执行在多个查找和替换;搜索:书签、笔记、文本字段、交叉引用和参考标志内容、名称或标志及其插入;搜索和插入脚注和尾注;通过名称来搜索表格对象、图像和文本框;搜索帮助手册页的分栏符以及创建和失活时间;根据光标位置搜索相同格式的文本。还可以保存/加载查找和替换参数,并在多个同时打开的文件中执行批处理。
|
||||
该组件向 Writer 中的查找与替换功能添加了许多新特性:可以查找和替换一段或多段文本;一次执行多个查找和替换;搜索:书签、笔记、文本字段、交叉引用和参考标志内容、名称或标志及其插入;搜索和插入脚注和尾注;通过名称来搜索表格对象、图像和文本框;搜索帮助手册页和分栏符以及创建和失活时间;根据光标位置搜索相同格式的文本。还可以保存/加载查找和替换参数,并在多个同时打开的文件中执行批处理。
|
||||
|
||||
**[下载 Writer 中可交替使用的查找与替换组件(交替搜索)][4]**
|
||||
**[下载 Writer 中可交替使用的查找与替换组件(交替搜索 (AltSearch))][4]**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Pepito 清除组件 ###
|
||||
中 LibreOffice 中, Pepito 清除组件主要用来快速清除并修复旧扫描件、导入的 PDF 以及每个电子文本文档的格式错误。通过点击 LibreOffice 工具栏中的 Pepito 图标,用户可以打开一个用于分析文档并呈现文档错误类型。当你将 PDF 文档转换为 ODF 文档时,这个工具就非常有用了,它会自动清除转换过程中出现的错误。
|
||||
|
||||
Pepito 清除组件是一个 LibreOffice 扩展,主要用来快速清除并修复旧式扫描件、导入的 PDF 以及每个电子文本文档的格式错误。通过点击 LibreOffice 工具栏中的 Pepito 图标,用户可以打开一个用于分析文档并按类型呈现文档错误。当你将 PDF 文档转换为 ODF 文档时,这个工具就非常有用了,它会自动清除转换过程中出现的错误。
|
||||
|
||||
**[下载 Pepito 清除组件][5]**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. ImpressRunner 组件###
|
||||
Impress Runner 是将 [Impress][6] 文档转换成自动播放文件的扩展组件。该组件会添加两个图标,用以设置或移除自动开始播放的功能,我们还可以通过编辑 文件 | 属性 | 自定义属性 菜单来手动添加这两个图标,并将自动运行按钮添加到四个文本域之前。在会议与活动组织而且幻灯片无人主持的时候,这个扩展组件就变得非常有用。
|
||||
|
||||
Impress Runner 是将 [Impress][6] 文档转换成自动播放文件的扩展组件。该组件会添加两个图标,用以设置或移除自动开始播放的功能,我们还可以通过编辑 文件 | 属性 | 自定义属性 菜单来手动添加这两个图标,并将自动运行按钮添加到前四个文本域之一前面。在会议与组织活动时,如果幻灯片无人主持,这个扩展组件就变得非常有用。
|
||||
|
||||
**[下载 ImpressRunner 组件][7]**
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 导出为图像组件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
导出为图像组件是 Impress 和 [Draw][8] 中文件菜单里边的一个入口——导出为图像...,,主要用于将所有的幻灯片和页面导出成 JPG、PNG、GIF、BMP 和 TIFF 等图像格式,并且允许用户自定义导出图像的名称、大小以及其他参数。
|
||||
导出为图像组件为 Impress 和 [Draw][8] 中文件菜单里增加了一个入口——“导出为图像...”,主要用于将所有的幻灯片和页面导出成 JPG、PNG、GIF、BMP 和 TIFF 等图像格式,并且允许用户自定义导出图像的名称、大小以及其他参数。
|
||||
|
||||
**[下载 导出为图像组件][9]**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Anaphraseus 组件###
|
||||
Anaphraseus 是一个 CAT(Computer-Aided Translation,计算机辅助翻译)工具组件,用来创建、管理双语翻译。Anaphraseus 是一个设置成扩展组件或者独立文档的 LibreOffice 宏。最开始,开发者设计 Anaphraseus 为快速翻译(Wordfast)格式,但现在它可以将文件导入或者到出成 TMX 格式。其主要特性:分本分割、在翻译记录中模糊搜索、术语识别以及导入导出 TMX(OmegaT translation memory format,OmegaT 翻译存储格式)。
|
||||
|
||||
Anaphraseus 是一个 CAT(Computer-Aided Translation,计算机辅助翻译)工具组件,用来创建、管理双语翻译。Anaphraseus 是一个 LibreOffice 宏集合,可以作为扩展组件或者用在单独的文档中。最开始,Anaphraseus 支持快速翻译(Wordfast)格式,但现在它可以导入或者导出成 TMX 格式。其主要特性:分本分割、在翻译记录(Translation Memory)中模糊搜索、术语识别以及导入导出 TMX(OmegaT translation memory format,OmegaT 翻译存储格式)。
|
||||
|
||||
**[下载 Anaphraseus 组件][10]**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,8 +61,8 @@ Anaphraseus 是一个 CAT(Computer-Aided Translation,计算机辅助翻译
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/business/15/12/6-useful-libreoffice-extensions
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Italo Vignoli][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,36 +1,37 @@
|
||||
如何在FreeBSD 10.2上配置Apache和SSL并安装Bugzilla
|
||||
在 FreeBSD 10.2 上如何通过配置 Apache 和 SSL 安装 Bugzilla
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Bugzilla是一款bug跟踪系统和测试工具,它基于web且开源,由mozilla计划开发并由Mozilla公共许可证授权。它经常被一些高科技公司如mozilla、红帽公司和gnome使用。Bugzilla起初由Terry Weissman在1998年创立,它用perl语言编写,用MySQL作为后端数据库。它是一款旨在帮助管理软件开发的服务器软件,它功能丰富、高优化度的数据库、卓越的安全性、高级的搜索工具、整合邮件功能等等。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我们将给web服务器安装bugzilla 5.0的apache并为它启用SSL,然后在freebsd 10.2上安装mysql 5.1来作为数据库系统。
|
||||
Bugzilla 是一款开源的 Web 应用,用于 bug 跟踪系统和测试工具,由 mozilla 开发,并采用 Mozilla 公共许可证授权(MPL)。它经常被一些高科技公司如 mozilla、红帽公司和 gnome 使用。Bugzilla 起初由 Terry Weissman开发于1998年,它用 perl 语言编写,用 MySQL 作为后端数据库。它是一款旨在帮助管理软件开发的服务器软件,它有丰富的功能、高度优化的数据库、卓越的安全性、高级的搜索工具、集成了邮件功能等等。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我们将安装 bugzilla 5.0 ,采用 apache 作为 Web 服务器,并为它启用 SSL,然后在 freebsd 10.2 上安装 mysql 5.1 来作为数据库系统。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 准备 ####
|
||||
|
||||
FreeBSD 10.2 - 64位
|
||||
Root权限
|
||||
- FreeBSD 10.2 - 64位
|
||||
- Root 权限
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一步 - 更新系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
用ssl登录freebsd服务器,并更新库:
|
||||
用 ssh 登录 freebsd 服务器,并更新软件库:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo su
|
||||
freebsd-update fetch
|
||||
freebsd-update install
|
||||
|
||||
### 第二步 - 安装并配置Apache ###
|
||||
### 第二步 - 安装并配置 Apache ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这一步我们将从freebsd库中用pkg命令安装apache,然后在apache24目录下编辑"httpd.conf"文件,启用SSL和CGI支持。
|
||||
在这一步我们将使用 pkg 命令从 freebsd 软件库中安装 apache,然后在 apache24 目录下编辑 "httpd.conf" 文件,来配置 apache 以启用 SSL 和 CGI 支持。
|
||||
|
||||
用pkg命令安装apache:
|
||||
用 pkg 命令安装 apache:
|
||||
|
||||
pkg install apache24
|
||||
|
||||
进入apache目录并用nano编辑器编辑"httpd.conf"文件:
|
||||
进入 apache 目录并用 nano 编辑器编辑"httpd.conf"文件:
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/local/etc/apache24
|
||||
nano -c httpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
反注释掉下面列出的行:
|
||||
取消下面列出行的注释:
|
||||
|
||||
#第70行
|
||||
LoadModule authn_socache_module libexec/apache24/mod_authn_socache.so
|
||||
@ -55,11 +56,11 @@ Bugzilla是一款bug跟踪系统和测试工具,它基于web且开源,由moz
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
接着,我们需要从freebsd库中安装mod perl,并启用它:
|
||||
接着,我们需要从 freebsd 库中安装 mod perl,并启用它:
|
||||
|
||||
pkg install ap24-mod_perl2
|
||||
|
||||
启用mod_perl,编辑"httpd.conf"文件并添加"Loadmodule"行:
|
||||
启用 mod_perl,编辑"httpd.conf"文件并添加"Loadmodule"行:
|
||||
|
||||
nano -c httpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
@ -70,20 +71,20 @@ Bugzilla是一款bug跟踪系统和测试工具,它基于web且开源,由moz
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
在启用apache之前,用sysrc命令添加以下行来在引导的时候启动:
|
||||
在启用 apache 之前,用 sysrc 命令添加以下行作为开机启动项:
|
||||
|
||||
sysrc apache24_enable=yes
|
||||
service apache24 start
|
||||
|
||||
### 第三步 - 安装并配置MySQL数据库 ###
|
||||
### 第三步 - 安装并配置 MySQL 数据库 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们要用mysql 5.1来作为后端数据库并且支持perl模块。用pkg命令安装mysql 5.1:
|
||||
我们要用 mysql 5.1 来作为后端数据库并且支持 perl 模块。用 pkg 命令安装 mysql 5.1:
|
||||
|
||||
pkg install p5-DBD-mysql51 mysql51-server mysql51-client
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们要在启动时添加mysql服务并启动,然后为mysql配置root密码。
|
||||
现在我们要将 mysql 服务设置为开机启动,然后为 mysql 配置 root 密码。
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令来完成所有操作:
|
||||
运行以下命令来完成上述所有操作:
|
||||
|
||||
sysrc mysql_enable=yes
|
||||
service mysql-server start
|
||||
@ -91,13 +92,13 @@ Bugzilla是一款bug跟踪系统和测试工具,它基于web且开源,由moz
|
||||
|
||||
注意:
|
||||
|
||||
这里mysql密码为:aqwe123
|
||||
这里 mysql 密码为:aqwe123
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
以上步骤都完成之后,我们用root登录mysql shell,然后为bugzilla安装创建一个新的数据库和用户。
|
||||
以上步骤都完成之后,我们用 root 登录 mysql shell,然后为 bugzilla 安装创建一个新的数据库和用户。
|
||||
|
||||
用以下命令登录mysql shell:
|
||||
用以下命令登录 mysql shell:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql -u root -p
|
||||
password: aqwe123
|
||||
@ -112,32 +113,32 @@ Bugzilla是一款bug跟踪系统和测试工具,它基于web且开源,由moz
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
bugzilla的数据库创建好了,名字为"bugzilladb",用户名和密码分别为"bugzillauser"和"bugzillauser@"。
|
||||
bugzilla 的数据库创建好了,名字为"bugzilladb",用户名和密码分别为"bugzillauser"和"bugzillauser@"。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第四步 - 生成新的SSL证书 ###
|
||||
### 第四步 - 生成新的 SSL 证书 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在bugzilla站点的"ssl"目录里生成新的自签名SSL证书。
|
||||
在 bugzilla 站点的 "ssl" 目录里生成新的自签名 SSL 证书。
|
||||
|
||||
前往apache24目录并在此创建新目录"ssl":
|
||||
前往 apache24 目录并在此创建新目录 "ssl":
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/local/etc/apache24/
|
||||
mkdir ssl; cd ssl
|
||||
|
||||
接着,用openssl命令生成证书文件,然后更改其权限:
|
||||
接着,用 openssl 命令生成证书文件,然后更改其权限:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /usr/local/etc/apache24/ssl/bugzilla.key -out /usr/local/etc/apache24/ssl/bugzilla.crt
|
||||
chmod 600 *
|
||||
|
||||
### 第五步 - 配置虚拟主机 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们将在"/usr/local/www/bugzilla"目录里安装bugzilla,所以我们必须为它创建新的虚拟主机配置。
|
||||
我们将在 "/usr/local/www/bugzilla" 目录里安装 bugzilla,所以我们必须为它创建新的虚拟主机配置。
|
||||
|
||||
前往apache目录并为虚拟主机文件创建名为"vhost"的新目录:
|
||||
前往 apache 目录并为虚拟主机文件创建名为 "vhost" 的新目录:
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/local/etc/apache24/
|
||||
mkdir vhost; cd vhost
|
||||
|
||||
现在为虚拟主机文件创建新文件"bugzilla.conf":
|
||||
现在为虚拟主机文件创建新文件 "bugzilla.conf":
|
||||
|
||||
nano -c bugzilla.conf
|
||||
|
||||
@ -173,9 +174,9 @@ bugzilla的数据库创建好了,名字为"bugzilladb",用户名和密码分
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
上述都完成之后,为bugzilla安装创建新目录并通过添加虚拟主机配置至httpd.conf文件来启用bugzilla虚拟主机。
|
||||
上述都完成之后,为 bugzilla 安装创建新目录,并在 httpd.conf 文件添加虚拟主机配置来启用 bugzilla虚拟主机。
|
||||
|
||||
在"apache24"目录下运行以下命令:
|
||||
在 "apache24" 目录下运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p /usr/local/www/bugzilla
|
||||
cd /usr/local/etc/apache24/
|
||||
@ -187,72 +188,72 @@ bugzilla的数据库创建好了,名字为"bugzilladb",用户名和密码分
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
现在用"apachectl"命令测试一下apache的配置并重启它:
|
||||
现在用 "apachectl" 命令测试一下 apache 的配置并重启它:
|
||||
|
||||
apachectl configtest
|
||||
service apache24 restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 第六步 - 安装Bugzilla ###
|
||||
### 第六步 - 安装 Bugzilla ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以通过下载源来手动安装bugzilla了,或从freebsd库中安装也可以。在这一步中我们将用pkg命令从freebsd库中安装bugzilla:
|
||||
我们可以通过下载源来手动安装 bugzilla 了,或从 freebsd 库中安装也可以。在这一步中我们将用 pkg 命令从 freebsd 库中安装 bugzilla:
|
||||
|
||||
pkg install bugzilla50
|
||||
|
||||
以上步骤都完成之后,前往bugzilla安装目录并安装所有bugzilla需要的perl模块。
|
||||
以上步骤都完成之后,前往 bugzilla 安装目录并安装所有 bugzilla 需要的 perl 模块。
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/local/www/bugzilla
|
||||
./install-module --all
|
||||
|
||||
要等到所有都完成,这需要点时间。
|
||||
|
||||
下一步,在bugzilla的安装目录中执行"checksetup.pl"文件来生成配置文件"localconfig"。
|
||||
下一步,在 bugzilla 的安装目录中执行 "checksetup.pl" 文件来生成配置文件 "localconfig"。
|
||||
|
||||
./checksetup.pl
|
||||
|
||||
你会看到一条关于数据库配置错误,你得用nano编辑器编辑一下"localconfig"文件:
|
||||
你会看到一条关于数据库配置错误的消息,你得用 nano 编辑器编辑一下 "localconfig" 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
nano -c localconfig
|
||||
|
||||
现在添加第三步创建的数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
#第五十七行
|
||||
#第57行
|
||||
$db_name = 'bugzilladb';
|
||||
|
||||
#第六十行
|
||||
#第60行
|
||||
$db_user = 'bugzillauser';
|
||||
|
||||
#第六十七行
|
||||
#第67行
|
||||
$db_pass = 'bugzillauser@';
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
然后再次运行"checksetup.pl":
|
||||
然后再次运行 "checksetup.pl":
|
||||
|
||||
./checksetup.pl
|
||||
|
||||
你会收到输入邮箱名和管理员账号的提示,你只要输入你得邮箱、用户名和密码就行了。
|
||||
你会收到输入邮箱名和管理员账号的提示,你只要输入你的邮箱、用户名和密码就行了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后,我们需要把安装目录的属主改成"www",然后用服务命令重启apache:
|
||||
最后,我们需要把安装目录的属主改成 "www",然后用服务命令重启 apache:
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/local/www/
|
||||
chown -R www:www bugzilla
|
||||
service apache24 restart
|
||||
|
||||
现在Bugzilla已经安装好了,你可以通过访问mybugzilla.me来查看,并且将会重定向到https连接。
|
||||
现在 Bugzilla 已经安装好了,你可以通过访问 mybugzilla.me 来查看,并且将会重定向到 https 连接。
|
||||
|
||||
Bugzilla首页:
|
||||
Bugzilla 首页:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Bugzilla admin面板:
|
||||
Bugzilla admin 面板:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Bugzilla是一个基于web并能帮助你管理软件开发的应用,它用perl开发并使用MySQL作为数据库系统。Bugzilla被mozilla,redhat,gnome等等公司用来帮助它们的软件开发工作。Bugzilla有很多功能并易于配置和安装。
|
||||
Bugzilla 是一个基于 web 的应用,并能帮助你管理软件开发,它用 perl 开发并以 MySQL 作为数据库系统。Bugzilla 帮助 mozilla、redhat、gnome 等公司完成软件开发工作。Bugzilla 有很多功能并易于配置和安装。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -260,7 +261,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/tools/install-bugzilla-apache-ssl-freebsd-10-2/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arul][a]
|
||||
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
|
||||
Linux / Unix桌面之趣:终端上的圣诞树
|
||||
Linux/Unix 桌面趣事:终端上的圣诞树
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
给你的Linux或Unix控制台创造一棵圣诞树玩玩吧。在此之前,需要先安装一个Perl模块,命名为Acme::POE::Tree。这是一棵很喜庆的圣诞树,我已经在Linux、OSX和类Unix系统上验证过了。
|
||||
|
||||
给你的Linux或Unix控制台创造一棵圣诞树玩玩吧。在此之前,需要先安装一个Perl模块,命名为Acme::POE::Tree。这是一棵很喜庆的圣诞树,我已经在Linux、OSX和类Unix系统上验证过了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 Acme::POE::Tree ###
|
||||
|
||||
安装perl模块最简单的办法就是使用cpan(Perl综合典藏网)。打开终端,把下面的指令敲进去便可安装Acme::POE::Tree。
|
||||
安装perl模块最简单的办法就是使用CPAN(Perl综合典藏网(Comprehensive Perl Archive Network))。打开终端,把下面的指令敲进去便可安装Acme::POE::Tree。
|
||||
|
||||
## 以root身份运行 ##
|
||||
perl -MCPAN -e 'install Acme::POE::Tree'
|
||||
|
||||
**案例输出:**
|
||||
**示例输出:**
|
||||
|
||||
Installing /home/vivek/perl5/man/man3/POE::NFA.3pm
|
||||
Installing /home/vivek/perl5/man/man3/POE::Kernel.3pm
|
||||
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ Linux / Unix桌面之趣:终端上的圣诞树
|
||||
|
||||
perl -MAcme::POE::Tree -e 'Acme::POE::Tree->new()->run()'
|
||||
|
||||
**案例输出**
|
||||
**示例输出**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ Gif 01: 一棵用Perl写的喜庆圣诞树
|
||||
);
|
||||
$tree->run();
|
||||
|
||||
这样就可以通过修改star_delay、run_for和light_delay参数的值来自定义你的树了。一棵提供消遣的终端圣诞树就此诞生。
|
||||
这样就可以通过修改star_delay、run_for和light_delay参数的值来自定义你的树了。一棵好玩的终端圣诞树就此诞生。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -79,6 +79,6 @@ via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/open-source/command-line-hacks/linux-unix-desktop-
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[soooogreen](https://github.com/soooogreen)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,232 @@
|
||||
KDE 的19年进化历程
|
||||
================
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
<iframe width="660" height="371" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/1UG4lQOMBC4?feature=oembed" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
## 概述
|
||||
|
||||
KDE – 史上功能最强大的桌面环境之一;开源且可自由使用。19年前,1996年10月14日,德国程序员 Matthias Ettrich 开始了这个美观的桌面环境的开发。KDE 提供了用户界面以及其他很多日常使用的程序。今日,KDE 被成千上万人在 Unix 和 Windows 上使用。19年,一个对软件项目而言极为漫长的年岁。现在是时候让我们回到最初,看看这一切肇始于何处。
|
||||
|
||||
K Desktop Environment(KDE)有很多创新之处:新设计,美观,一致的体验,易于使用,对普通用户和专业用户都足够强大的应用库。“KDE”这个名字是对单词“通用桌面环境”(Common Desktop Environment)玩的一个简单谐音游戏,“K”即“Cool”。 第一代 KDE 在双许可证授权下使用了 Trolltech 公司专利的 Qt framework(现 Qt 的前身),这两个许可证分别是开源的 QPL(Q public license)和商业专利许可证(proprietary commercial license)。在2000年 Trolltech 公司让一部分 Qt 软件库开始发布在 GPL 证书下; Qt 4.5 发布在了 LGPL 2.1 许可证下。自2009起 KDE 桌面环境由三部分构成:Plasma Workspaces(用做交互界面),KDE Applications,作为 KDE Software 编译的 KDE Platform。
|
||||
|
||||
## 各发布版本
|
||||
|
||||
### 预发布版本 – 1996年10月14日
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当时名称为 Kool Desktop Environment;“Kool”这个单词在很快就被弃用了。最初,所有 KDE 的组件都是被单独发布在开发社区里的,它们并没有被一个大的项目所贯穿起来。开发组邮件列表中的首选通信是发往kde@fiwi02.wiwi.uni-Tubingen.de 邮件列表。
|
||||
|
||||
### KDE 1.0 – 1998年7月12日
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个版本受到了颇有争议的反馈。很多人反对使用 Qt 框架,因为当时的 FreeQt 许可证和自由软件许可证并不兼容,他们建议开发组使用 Motif 或者 LessTif 替代。尽管有着这些反对声,KDE 仍然被很多用户所青睐,并且成功作为第一个 Linux 发行版的环境被集成了进去。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*1999年1月28日*
|
||||
|
||||
有一次升级,**K Desktop Environment 1.1**,更快,更稳定的同时加入了很多小的改进。这个版本同时也加入了很多新的图标,背景和材质纹理。和这些全面翻新同时出现的还有 Torsten Rahn 绘制的全新 KDE 图标----一个放在齿轮前的字母 K ;这个图标的修改版也一直沿用至今。
|
||||
|
||||
### KDE 2.0 – 2000年10月23日
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
重大更新:
|
||||
|
||||
- DCOP (Desktop COmmunication Protocol),一个端到端的通信协议
|
||||
- KIO,一个应用程序 I/O 库
|
||||
- KParts,组件对象模型
|
||||
- KHTML,一个符合 HTML 4.0 标准的渲染绘制引擎。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2001年2月26日*
|
||||
|
||||
**K Desktop Environment 2.1** 首次发布了媒体播放器 noatun,它使用了模组化、插件设计。为了便利开发者,K Desktop Environment 2.1 打包了 KDevelop。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2001年8月15日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE 2.2**版本在 GNU/Linux 上加快了50%的应用启动速度,同时提高了 HTML 渲染、JavaScript 稳定性和性能,同时还增加了一些 KMail 的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
### KDE 3.0 – 2002年4月3日
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
K Desktop Environment 3.0 加入了更好的限制使用功能,这个功能在电话亭、网咖,企业公用电脑上被广泛需求,它可以禁止用户完全使用软件的某些能力。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2003年1月28日*
|
||||
|
||||
**K Desktop Environment 3.1** 加入了新的默认窗口(Keramik)和图标样式(Crystal)和其他一些改进。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2004年2月3日*
|
||||
|
||||
**K Desktop Environment 3.2** 加入了诸如在网页表格、书写邮件中拼写检查的新功能;增强了邮件和日历功能。完善了 Konqueror 中的标签机制和对 Microsoft Windows 桌面共享协议(RDP)的支持。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2004年8月19日*
|
||||
|
||||
**K Desktop Environment 3.3** 侧重于组合不同的桌面组件。Kontact 被放进了群件应用 Kolab 并与 Kpilot 结合。Konqueror 的加入让 KDE 有了更好的 IM 交流功能,比如支持发送文件,以及其他 IM 协议(如IRC)的支持。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2005年3月16日*
|
||||
|
||||
**K Desktop Environment 3.4** 侧重于提高易用性。这次更新为 Konqueror、Kate、KPDF 加入了文字-语音转换功能;也在桌面系统中加入了独立的 KSayIt 文字-语音转换软件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2005年11月29日*
|
||||
|
||||
**The K Desktop Environment 3.5** 发布加入了 SuperKaramba,为桌面环境提供了易于安装的插件(widgets)机制。 Konqueror 加入了广告屏蔽功能并成为了有史以来第二个通过 Acid2 CSS 测试的浏览器。
|
||||
|
||||
### KDE SC 4.0 – 2008年1月11日
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
大部分的开发投身于把最新的技术和开发框架整合进 KDE 4 当中。Plasma 和 Oxygen 是两次最大的用户界面风格变更。同时,Dolphin 替代 Konqueror 成为默认文件管理器,Okular 成为了默认文档浏览器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2008年7月29日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE 4.1** 引入了一个在 PIM 和 Kopete 中共享使用的表情主题系统;引入了可以让用户便利地从互联网上一键下载数据的 DXS。同时引入了 GStreamer、QuickTime 和 DirectShow 9 Phonon 后端。加入了新应用如:
|
||||
|
||||
- Dragon Player
|
||||
- Kontact
|
||||
- Skanlite — 扫描仪软件
|
||||
- Step —— 物理模拟软件
|
||||
- 新游戏: Kdiamond、Kollision、KBreakout 和更多......
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2009年1月27日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE 4.2** 被认为是在已经极佳的 KDE 4.1 基础上的又一次全面超越,同时也成为了大多数用户替换旧 3.5 版本的完美选择。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2009年8月4日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE 4.3** 修复了超过10000个 bug,同时加入了让近2000个用户要求的功能。整合一些新的技术例如:PolicyKit、NetworkManage & Geolocation services 等也是这个版本的一大重点。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2010年2月9日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE SC 4.4** 基于 Qt 4 toolkit 的 4.6 版本,加入新的应用 KAddressBook。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2010年8月10日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE SC 4.5** 增加了一些新特性:整合了开源的浏览器引擎 WebKit 库,其现在也在 Apple Safari 和 Google Chrome 中广泛使用。KPackageKit 替换了 Kpackage。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2011年1月26日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE SC 4.6** 加强了 OpenGl 的性能,同时照常更新了无数bug和小改进。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2011年7月27日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE SC 4.7** 升级 KWin 以兼容 OpenGL ES 2.0 ,更新了 Qt Quick,Plasma Desktop 带来许多增强和在应用里的大量新特性, 修复了1.2万个 bug。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2012年1月25日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE SC 4.8**: 更好的 KWin 性能与 Wayland 支持,更崭新的 Doplhin 的外观设计。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2012年8月1日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE SC 4.9**: 向 Dolphin 文件管理器增加了一些更新,比如重新加入了实时文件重命名,鼠标辅助按钮支持,更好的位置面板和更多文件分类管理功能。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2013年2月6日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE SC 4.10**: 很多 Plasma 插件使用 QML 重写; Nepomuk、Kontact 和 Okular 得到了很大程度的性能和功能提升。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2013年8月14日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE SC 4.11**: Kontact 和 Nepomuk 有了很多优化。 第一代 Plasma Workspaces 进入了单纯维护阶段。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2013年12月18日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE SC 4.12**: Kontact 得到了极大的提升,包括许多小的改进。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2014年4月16日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE SC 4.13**: Nepomuk 语义搜索功能替代了桌面上的原有的 Baloo 搜索。 KDE SC 4.13 以53个语言版本发布。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2014年8月20日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE SC 4.14**: 这个发布版本侧重于稳定性提升:大量的 bug 修复和增加了一些小的功能。这是最后一个 KDE SC 4 发布版本。
|
||||
|
||||
### KDE Plasma 5.0 – 2014年7月15日
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
KDE Plasma 5 – 第五代 KDE。大幅改进了设计和系统,新的默认主题 Breeze 完全迁移到了 QML,更好的 OpenGL 性能,更完美的 HiDPI (高分辨率)显示支持。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2014年11月11日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE Plasma 5.1**:迁移了从 Plasma 4 里丢失的功能。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2015年1月27日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE Plasma 5.2**:新组件:BlueDevil、KSSHAskPass、Muon、SDDM 主题设置、KScreen、GTK+ 样式设置和 KDecoration。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2015年4月28日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE Plasma 5.3**:Plasma Media Center 技术预览。新的蓝牙和触摸板小程序;改良了电源管理。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2015年8月25日*
|
||||
|
||||
**KDE Plasma 5.4**:Wayland 登场,新的基于 QML 的音频管理程序,一个全屏的程序启动器替代品。
|
||||
|
||||
万分感谢 [KDE][1] 开发者及社区,并感谢 Wikipedia 为书写 [概述][2] 带来的帮助,同时,感谢所有读者。让我们保持自由精神(be free)并继续支持如同 KDE 一样的开源的自由软件发展。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: [https://tlhp.cf/kde-history/](https://tlhp.cf/kde-history/)
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pavlo Rudyi][a]
|
||||
译者:[jerryling315](https://github.com/jerryling315)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]: https://www.kde.org/
|
||||
[2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/KDE_Plasma_5
|
||||
[a]: https://tlhp.cf/author/paul/
|
||||
@ -1,42 +1,43 @@
|
||||
|
||||
开源代码开发的十四点教学技巧
|
||||
在大学培养学生们参与开源代码开发的十四个技巧
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
对于培养和塑造开源代码开发者,Academia就是一个很好的平台。研究中发现,我们偶尔会开源自己编写的软件。这样做有两个理由,一是为了提升自己编写的工具使用率,二是为了了解人们使用这些工具时会遇到哪些问题。在这样一个编写研究软件的背景下,我的任务就是为 Bradford 大学重新设计二年级的软件工程课程。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这是一个巨大的挑战,因为我所面对的 80 个学生是来自不同专业的,包括 IT、商务计算和软件工程,这些学生将要在一起上课。最有难度的是,需要和这些编程经验差距很大的学生一起编写代码。按照传统,该课程允许学生选择自己的小组,然后给他们布置构建一个存储数据库系统构的任务,最后提交报告作为评估的一部分。
|
||||
学术界是培养和塑造未来的开源开发者的最佳平台。研究中发现,我们偶尔会开源自己编写的软件。这样做有两个理由,一是为了推广自己编写的工具的使用,二是为了了解人们使用这些工具时会遇到哪些问题。在这样一个编写研究软件的背景下,我的任务就是为 Bradford 大学重新设计二年级的本科软件工程课程。
|
||||
|
||||
而我决定重新设计课程,让学生了解现实中的软件团队是如何协作的过程。根据学生的专业和编程技能,我将他们分为五六个人一组。这是为了确保每个小组的整体水平相当,避免小组之间的不公平。
|
||||
这是一个挑战,因为我所面对的 80 个学生是来自不同专业的,包括 IT、商务计算和软件工程,这些学生将要在一起上课。最有难度的是,需要和这些编程经验差距很大的学生一起编写代码。按照传统,该课程允许学生选择自己的小组,然后给他们布置构建一个加油站数据库系统的任务,最后提交报告作为评估的一部分。
|
||||
|
||||
而我决定重新设计课程,让学生了解现实中的软件团队是如何协作的过程。根据学生的专业和编程技能,我将他们分为五、六个人一组。这是为了确保每个小组的整体水平相当,避免小组之间的不等。
|
||||
|
||||
### 核心课程 ###
|
||||
|
||||
课程的形式升级为文化课和实践课两项结合在一起。然而实践部分只是充当辅助,主要是老师监督各个小组的实践进度以及他们如何处理客户和产品之间的关系。传统的教学方式由项目管理、软件测试、工程需求分析以及类似主题的讲座组成,再辅以实践和导师会议。这些会议可以很好的考核学生的水平以及检测出他们是否可以跟得上我们在讲座部分中的软件工程方法。本年的教学主题包括以下内容:
|
||||
课程的形式改为讲座和实践课两项结合在一起。然而实践课作为指导过程,主要是老师监督各个小组的实践进度以及他们如何处理客户和产品之间的关系。而传统的教学方式由项目管理、软件测试、工程需求分析以及类似主题的讲座组成,再辅以实践和导师会议。这些会议可以很好的考核学生的水平以及检测出他们是否可以跟得上我们在讲座部分中的软件工程方法。本年的教学主题包括以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
- 工程需求分析
|
||||
- 如何与客户及其他团队成员互动
|
||||
- 程序设计方法,如敏捷和极限编程方法
|
||||
- 如何通过学习不同的软件工程方法进行短期的水平提高
|
||||
- 小组会议及文档编写
|
||||
- 项目管理及项目进展图表
|
||||
- 项目管理及项目进展图表(甘特图)
|
||||
- UML 图表及系统描述
|
||||
- 使用 Git 来进行代码的版本控制
|
||||
- 软件测试及 BUG 跟踪
|
||||
- 使用开源库
|
||||
- 开源代码许可及其选择
|
||||
- 软件分发
|
||||
- 软件交付
|
||||
|
||||
在这些讲座之后,会有一些来自世界各地的嘉宾为我们说说他们在软件分发过程中的经验。我们也设法请来大学里知识产权律师谈关于软件在英国的知识产权问题,以及如何处理软件的知识产权问题。
|
||||
在这些讲座之后,会有一些来自世界各地的嘉宾为我们说说他们在软件交付过程中的经验。我们也设法请来大学里知识产权律师谈关于软件在英国的知识产权问题,以及如何处理软件的知识产权问题。
|
||||
|
||||
### 协作工具 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了让上述教学内容的顺利进行,我们将会介绍一些工具,并训练学生在他们的项目中使用这些工具。如下:
|
||||
为了让上述教学内容的顺利进行,我们将会引入一些工具,并训练学生在他们的项目中使用这些工具。如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- Google Drive:团队与导师之间进行共享的工具,暂时存储用于描述项目的文档和图表、需求收集、会议纪要以及项目时间跟踪等信息。采取这样一个方式来监控并提供直接反馈到每个团队,是非常有效的。
|
||||
- [Basecamp][1]:同样是用于分享文档,在随后的课程中,我们可能会考虑用它取代 Google Drive。
|
||||
- BUG 报告工具,如 [Mantis][2]:只能让有限的用户自由提交 BUG。稍后我们提到的 Git 可以让小组内的所有人员用做 BUG 提交。
|
||||
- BUG 报告工具,如 [Mantis][2]:只能让有限的用户免费提交 BUG。稍后我们提到的 Git 可以让小组内的所有人员用做 BUG 提交。
|
||||
- 远程视频会议工具:在人员不在校内,甚至去了其他城市的情况下使用。学生们可以定期通过 Skype 来交流并记录会议内容或则进行录音作为今后其他用处。
|
||||
- 同时,学生们的项目中还会用到大量的开源工具包。他们可以根据自己小组的项目需求来选择自己使用的工具包和编程语言。唯一的条件是,这些项目必须开源,最后成果可以安装到大学里的实验室,并且大多的研究人员都支持这个条件。
|
||||
- 最后,所有团队必须向客户交付他们的项目,包括完整的工作版本的软件、文档和他们自己选择的开放源码许可。大多数的团队选择了 GPLv3 许可证。
|
||||
- 同时,学生们的项目中还会用到大量的开源工具包。他们可以根据自己小组的项目需求来选择自己使用的工具包和编程语言。唯一的条件是,这些项目必须开源,最后成果可以安装到大学里的实验室,并且大多的研究人员都非常支持这个条件。
|
||||
- 最后,所有团队必须向客户交付他们的项目,包括完整的可以工作的软件版本、文档和他们自己选择的开放源码许可。大多数的团队选择了 GPLv3 许可证。
|
||||
|
||||
### 技巧和经验教训 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -48,29 +49,29 @@
|
||||
|
||||
3. 学生更加愿意与校外的客户一起协作。他们期待着与外部公司代表或校外人员协作,不过是为了获得新体验而已。与导师进行交流时,他们都能够表现得很专业,这样使得老师非常放心。
|
||||
|
||||
4. 很多团队版开发单元测试的部分放到项目结束之后,从极限编程方法的角度来说,这是一个严重的禁忌。也许测试应包括在不同阶段的评估中,来提醒他们需要与并行开展软件开发和单元测试。
|
||||
4. 很多团队版将开发单元测试的部分放到项目结束之后,从极限编程方法的角度来说,这是一个严重的禁忌。也许测试应包括在不同阶段的评估中,来提醒他们需要并行开展软件开发和单元测试。
|
||||
|
||||
5. 在这个班的 80 个人里边,仅有 4 个女生,每个女都分在不同的小组里边。我观察到,男生们总是充分准备好来承担起领队角色,并将最有趣的代码分配给他们自己来编写,女生则多大遵循安排或者是编写文档。出于某种原因,女生选择不显示权威,即使在女性辅导员鼓励下,她们也不愿编写代码。这仍然是一个需要解决的主要问题。
|
||||
5. 在这个班的 80 个人里边,仅有 4 个女生,每个女生都分在不同的小组里边。我观察到,男生们总是充分准备好来承担起领队角色,并将最有趣的代码部分留给他们自己来编写,女生则多大遵循安排或者是编写文档。出于某种原因,女生选择不出头,即使在女性辅导员鼓励下,她们也不愿编写代码。这仍然是一个需要解决的主要问题。
|
||||
|
||||
6. 允许不同风格项目文档,比方说,UML 图表、状态图或其他形式的。让学生学习这些并与其他课程融汇贯通来提高他们的学习经验。
|
||||
|
||||
7. 学生里边,有些是很好的开发人员,有些做商务计算的则没有多少编程经验。我们要鼓励团队共同努力,避免开发人员做得比那些只做会议记录或文档的其他成员更好的错误认知。我们常在辅导课程中鼓励角色转换,让每个人都有机会学习如何编程。
|
||||
|
||||
8. 小组进行与导师每周见面沟通是非常重要的,可以有效监督各个小组进展情况,还可以了解是谁做了大部分工作。通常,没来参加会议的小组成员基本就是没有参与到他们的团队工作中去的,并且通过其他成员提交的工作报告也可以确定哪些人不活跃。
|
||||
8. 小组与导师每周见面沟通是非常重要的,可以有效监督各个小组进展情况,还可以了解是谁做了大部分工作。通常,没来参加会议的小组成员基本就是没有参与到他们的团队工作中去的,并且通过其他成员所提交的工作报告也可以确定哪些人不活跃。
|
||||
|
||||
9. 我们鼓励学生们把许可证附加到项目中去,使用外部库以及和客户协作的时候要表明确切知识产权问题。 这样可让打破陈规,开拓思维,并了解真实的软件交付问题。
|
||||
|
||||
10. 给学生们自己选择技术空间。
|
||||
10. 给学生们自己选择所用技术的空间。
|
||||
|
||||
11. 助教是关键。同时管理 80 个学生显然很有难度,特别是需要对他们进行评估的那几周。明年我一定会找个助教来帮我一起管理各个小组。
|
||||
|
||||
12. 实验室的技术支持是非常重要的。大学里的技术支持对于本课程是非常赞同的。他们正在考虑明年将虚拟机分配给每个团队,这样没个团队可以根据需要自行在虚拟机中安装任何软件。
|
||||
12. 实验室的技术支持是非常重要的。大学里的技术支持人员对于本课程是非常赞同的。他们正在考虑明年将虚拟机分配给每个团队,这样没个团队可以根据需要自行在虚拟机中安装任何软件。
|
||||
|
||||
13. 团队合作,相互帮助。大多数团队自然而然的支持其他团队成员,同时指导员在中间也帮助了不少。
|
||||
|
||||
14. 来自其他技术人员的帮助会锦上添花。作为一名新的大学导师,我需要从经验中学习,如果我想了解如何管理某些学生和团队,或者对如何让学生适应课程感到困惑时,我会通过多个方面来寻求建议。来自高级技术人员的支持对我来说是一种极大的鼓励。
|
||||
14. 来自其他同事的帮助会锦上添花。作为一名新的大学导师,我需要从经验中学习,如果我想了解如何管理某些学生和团队,或者对如何让学生适应课程感到困惑时,我会通过多个方面来寻求建议。来自资深同事的支持对我来说是一种极大的鼓励。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,对于作为导师的我以及所有的学生来说,这都是个有趣的课程。在学习目标和传统的分级方案上还有有一些问题需解决,以减少教师的工作量。明年,我计划会保留这种教学模式,并希望能够提出更好的分级方案以及介绍更多的软件来帮助监督项目和控制代码版本。
|
||||
最后,对于作为导师的我以及所有的学生来说,这都是个有趣的课程。在学习目标和传统评分方案上还有有一些问题需解决,以减少教师的工作量。明年,我计划会保留这种教学模式,并希望能够提出更好的评分方案以及引入更多的软件来帮助监督项目和控制代码版本。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
sed 和 awk,所有的 Linux 管理员都应该会的技能!
|
||||
==========================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*图片来源: Shutterstock*
|
||||
|
||||
**我们不要让下一代 Linux 和 Unix 的管理员忘记初始化脚本和基本工具的好处**
|
||||
|
||||
我曾经有一次在 Reddit 看到一个帖子,“[请问如何操作文本文件][1]”。这是一个很简单的需求,就像我们常用 Unix 的人每天遇到的一样。他的问题是,如何删除文件中的重复行,只保留不重复的。 这听起来似乎很简单,但是当文件足够大时,就会有些复杂。
|
||||
|
||||
这个问题有很多种不同的答案。你可以使用几乎任何一种语言来写这样的一个脚本,只是时间的投入和代码的复杂性不同罢了。根据你的个人水平,它大概会花费20-60分钟。但是如果你使用了 Perl、Python、Ruby 中的一种,你可能很快实现它。
|
||||
|
||||
或者你可以使用下面的一个方法,让你无比暖心的: 只用 awk。
|
||||
|
||||
这个答案是迄今为止最简明、最简单的解决问题的方法。它只要一行!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
awk '!seen[$0]++' <filename>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
让我们来看看发生了什么:
|
||||
|
||||
在这个命令中,其实隐藏了很多代码。awk 是一种文本处理语言,并且它内部有很多预设。首先,你看到的实际上是一个 for 循环的结果。awk 假定你想通过循环处理输入文件的每一行,所以你不需要明确的去指定它。awk 还假定了你需要打印输出处理后的数据,所以你也不需要去指定它。最后,awk 假定循环在最后一句指令执行完结束,这一块也不再需要你去指定它。
|
||||
|
||||
这个例子中的字符串 seen 是一个关联数组的名字。$0 是一个变量,表示整个当前行。所以,这个命令翻译成人类语言就是“对这个文件的每一行进行检查,如果你之前没有见过它,就打印出来。” 如果该关联数组的键名还不存在就添加到数组,并增加其取值,这样 awk 下次遇到同样的行时就会不匹配(条件判断为“假”),从而不打印出来。
|
||||
|
||||
一些人认为这样是优雅的,另外的人认为这可能会造成混淆。任何在日常工作上使用 awk 的都是第一类人。awk 就是设计用来做这个的。在 awk 中,你可以写多行代码。你甚至可以[用 awk 写一些让人不安的复杂功能][2]。但终究来说,awk 还是一个进行文本处理的程序,一般是通过管道。去掉(没必要的)循环定义是很常见的快捷用法,不过如果你乐意,你也可以用下面的代码做同样的事情:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
awk '{ if (!seen[$0]) print $0; seen[$0]++ }’
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这会产生相同的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
awk 是完成这项工作的完美工具。不过,我相信很多管理员--特别是新管理员会转而使用 [Bash][3] 或 Python 来完成这一任务,因为对 awk 的知识和对它的能力的了解看起来随着时间而慢慢被人淡忘。我认为这是标志着一个问题,由于对之前的解决方案缺乏了解,那些已经解决了几十年的问题又突然出现了。
|
||||
|
||||
shell、grep、sed 和 awk 是 Unix 的基础。如果你不能非常轻松的使用它们,你将会被自己束缚住,因为它们构成了通过命令行和脚本与 Unix 系统交互的基础。学习这些工具如何工作最好的方法之一就是观察真实的例子和实验,你可以在各种 Unix 衍生系统的初始化系统中找到很多,但在 Linux 发行版中它们已经被 [systemd][4] 取代了。
|
||||
|
||||
数以百万计的 Unix 管理员了解 Shell 脚本和 Unix 工具如何读、写、修改和用在初始化脚本上。不同系统的初始化脚本有很大不同,甚至是不同的 Linux 发行版也不同。但是它们都源自 sh,而且它们都用像 sed、awk 还有 grep 这样的核心的命令行工具。
|
||||
|
||||
我每天都会听到很多人抱怨初始化脚本太“古老”而且很“难”。但是实际上,初始化脚本和 Unix 管理员每天使用的工具一样,还提供了一个非常好的方式来更加熟悉和习惯这些工具。说初始化脚本难于阅读和难于使用实际上是承认你缺乏对 Unix 基础工具的熟悉。
|
||||
|
||||
说起在 Reddit 上看到的内容,我也碰到过这个问题,来自一个新入行的 Linux 系统管理员, “[问他是否应该还要去学老式的初始化系统 sysvinit][5]”。 这个帖子的大多数的答案都是正面的——是的,应该学习 sysvinit 和 systemd 两个。一位评论者甚至指出,初始化脚本是学习 Bash 的好方法。而另一个消息是,Fortune 50 强的公司还没有计划迁移到以 systemd 为基础的发行版上。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,这提醒了我这确实是一个问题。如果我们继续沿着消除脚本和脱离操作系统核心组件的方式发展下去,由于疏于接触,我们将会不经意间使新管理员难于学习基本的 Unix 工具。
|
||||
|
||||
我不知道为什么有些人想在一层又一层的抽象化来掩盖 Unix 内部,但是这样发展下去可能会让新一代的系统管理员们变成只会按下按钮的工人。我觉得这不是一件好事情。
|
||||
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2985804/linux/remember-sed-awk-linux-admins-should.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Paul Venezia][a]
|
||||
译者:[Bestony](https://github.com/Bestony)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.infoworld.com/author/Paul-Venezia/
|
||||
[1]: https://www.reddit.com/r/linuxadmin/comments/3lwyko/how_do_i_remove_every_occurence_of_duplicate_line/
|
||||
[2]: http://intro-to-awk.blogspot.com/2008/08/awk-more-complex-examples.html
|
||||
[3]: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2613338/linux/linux-how-to-script-a-bash-crash-course.html
|
||||
[4]: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2608798/data-center/systemd--harbinger-of-the-linux-apocalypse.html
|
||||
[5]: https://www.reddit.com/r/linuxadmin/comments/3ltq2y/when_i_start_learning_about_linux_administration/
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu / Fedora / Debian 中安装 GitLab
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu/Fedora/Debian 中安装 GitLab
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在 Git 问世之前,分布式版本控制从来都不是一件简单的事。Git 是一个免费、开源的软件,旨在轻松且快速地对从小规模到非常巨大的项目进行管理。Git 最开始由 Linus Torvalds 开发,他同时也是著名的 Linux 内核的创建者。在 git 和分布式版本控制系统领域中,[GitLab][1] 是一个极棒的新产品。它是一个基于 web 的 Git 仓库管理应用,包含代码审查、wiki、问题跟踪等诸多功能。使用 GitLab 可以很方便、快速地创建、审查、部署及托管代码。与 Github 类似,尽管它也提供在其官方的服务器托管免费的代码仓库,但它也可以运行在我们自己的服务器上。GitLab 有两个不同的版本:社区版(Community Edition)和企业版(Enterprise Edition)。社区本完全免费且开源,遵循 MIT 协议;而企业版则遵循一个专有的协议,包含一些社区版中没有的功能。下面介绍的是有关如何在我们自己的运行着 Ubuntu、Fedora 或 Debian 操作系统的机子上安装 GitLab 社区版的简单步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Git 问世之前,分布式版本控制从来都不是一件简单的事。Git 是一个自由开源的软件,旨在轻松且快速地对从小规模到非常巨大的项目进行管理。Git 最开始由 Linus Torvalds 开发,他同时也是著名的 Linux 内核的创建者。在 git 和分布式版本控制系统领域中,[GitLab][1] 是一个极棒的新产品。它是一个基于 web 的 Git 仓库管理应用,包含代码审查、wiki、问题跟踪等诸多功能。使用 GitLab 可以很方便、快速地创建、审查、部署及托管代码。尽管它在其官方的服务器提供了与 Github 类似的免费托管的代码仓库,但它也可以运行在我们自己的服务器上。GitLab 有两个不同的版本:社区版(Community Edition)和企业版(Enterprise Edition)。社区版本完全免费且开源,遵循 MIT 协议;而企业版则遵循一个专有的协议,包含一些社区版中没有的功能。下面介绍的是有关如何在我们自己的运行着 Ubuntu、Fedora 或 Debian 操作系统的机器上安装 GitLab 社区版的简单步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 安装先决条件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们需要安装 GitLab 所依赖的软件包。我们将安装 `curl`,用以下载我们所需的文件;安装`openssh-server` ,以此来通过 ssh 协议登陆到我们的机子上;安装`ca-certificates`,用它来添加 CA 认证;以及 `postfix`,把它作为一个 MTA(Mail Transfer Agent,邮件传输代理)。
|
||||
首先,我们需要安装 GitLab 所依赖的软件包。我们将安装 `curl`,用以下载我们所需的文件;安装`openssh-server` ,以此来通过 ssh 协议登录到我们的机器上;安装`ca-certificates`,用它来添加 CA 认证;以及 `postfix`,把它作为一个 MTA(Mail Transfer Agent,邮件传输代理)。
|
||||
|
||||
注: 若要安装 GitLab 社区版,我们需要一个至少包含 2 GB 内存和 2 核 CPU 的 linux 机子。
|
||||
注: 若要安装 GitLab 社区版,我们需要一个至少包含 2 GB 内存和 2 核 CPU 的 linux 机器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Ubuntu 14 .04/Debian 8.x 中 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,7 +19,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Fedora 22 中 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在 Fedora 22 中,由于 `yum` 已经被弃用了,所以默认的包管理器是 `dnf`。为了安装上面那些需要的软件包,我们只需运行下面的 dnf 命令:
|
||||
在 Fedora 22 中,由于 `yum` 已经被弃用了,默认的包管理器是 `dnf`。为了安装上面那些需要的软件包,我们只需运行下面的 dnf 命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# dnf install curl openssh-server postfix
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,11 +27,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 打开并开启服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们将使用我们默认的 init 系统来打开 sshd 和 postfix 服务。并且我们将使得它们在每次系统启动时被自动开启。
|
||||
现在,我们将使用我们默认的初始化系统来打开 sshd 和 postfix 服务。并且我们将使得它们在每次系统启动时被自动开启。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Ubuntu 14.04 中 ####
|
||||
|
||||
由于 SysVinit 在 Ubuntu 14.04 中作为 init 系统被安装,我们将使用 service 命令来开启 sshd 和 postfix 守护进程:
|
||||
由于在 Ubuntu 14.04 中安装的是 SysVinit 初始化系统,我们将使用 service 命令来开启 sshd 和 postfix 守护进程:
|
||||
|
||||
# service sshd start
|
||||
# service postfix start
|
||||
@ -42,24 +43,24 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Fedora 22/Debian 8.x 中 ####
|
||||
|
||||
鉴于 Fedora 22 和 Debi 8.x 已经用 Systemd 代替了 SysVinit 来作为默认的 init 系统,我们只需运行下面的命令来开启 sshd 和 postfix 服务:
|
||||
鉴于 Fedora 22 和 Debian 8.x 已经用 Systemd 代替了 SysVinit 来作为默认的初始化系统,我们只需运行下面的命令来开启 sshd 和 postfix 服务:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start sshd postfix
|
||||
|
||||
现在,为了使得它们在每次开机启动时被自动地开启,我们需要运行下面的 systemctl 命令:
|
||||
现在,为了使得它们在每次开机启动时可以自动运行,我们需要运行下面的 systemctl 命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable sshd postfix
|
||||
|
||||
从 /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/sshd.service 建立软链接到 /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service.
|
||||
从 /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/postfix.service 建立软链接到 /usr/lib/systemd/system/postfix.service.
|
||||
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/sshd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service.
|
||||
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/postfix.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/postfix.service.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 下载 GitLab ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们将使用 curl 从官方的 GitLab 社区版仓库下载二进制安装文件。首先,为了得到所需文件的下载链接,我们需要浏览到该软件仓库的页面。为此,我们需要在运行着相应操作系统的 linux 机子上运行下面的命令。
|
||||
现在,我们将使用 curl 从官方的 GitLab 社区版仓库下载二进制安装文件。首先,为了得到所需文件的下载链接,我们需要浏览到该软件仓库的页面。为此,我们需要在运行着相应操作系统的 linux 机器上运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Ubuntu 14.04 中 ####
|
||||
|
||||
由于 Ubuntu 和 Debian 使用相同格式的 debian 文件,我们需要在 [https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce?filter=debs][2] 下搜索所需版本的 GitLab,然后点击有着 ubuntu/trusty 标签的链接,这是因为我们运作着 Ubuntu 14.04。接着一个新的页面将会出现,我们将看到一个下载按钮,然后我们在它的上面右击,得到文件的链接,然后像下面这样使用 curl 来下载它。
|
||||
由于 Ubuntu 和 Debian 使用相同的 debian 格式的安装包,我们需要在 [https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce?filter=debs][2] 下搜索所需版本的 GitLab,然后点击有着 ubuntu/trusty 标签的链接,即我们运行着的 Ubuntu 14.04。接着一个新的页面将会出现,我们将看到一个下载按钮,然后我们在它的上面右击,得到文件的链接,然后像下面这样使用 curl 来下载它。
|
||||
|
||||
# curl https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce/packages/ubuntu/trusty/gitlab-ce_8.1.2-ce.0_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
@ -67,7 +68,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Debian 8.x 中 ####
|
||||
|
||||
与 Ubuntu 类似,我们需要在 [https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce?filter=debs][3] 页面中搜索所需版本的 GitLab,然后点击带有 debian/jessie 标签的链接,这是因为我们运行的是 Debian 8.x。接着,一个新的页面将会出现,然后我们在下载按钮上右击,得到文件的下载链接。最后我们像下面这样使用 curl 来下载该文件。
|
||||
与 Ubuntu 类似,我们需要在 [https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce?filter=debs][3] 页面中搜索所需版本的 GitLab,然后点击带有 debian/jessie 标签的链接,即我们运行着的 Debian 8.x。接着,一个新的页面将会出现,然后我们在下载按钮上右击,得到文件的下载链接。最后我们像下面这样使用 curl 来下载该文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# curl https://packages.gitlab.com/gitlab/gitlab-ce/packages/debian/jessie/gitlab-ce_8.1.2-ce.0_amd64.deb/download
|
||||
|
||||
@ -83,11 +84,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 安装 GitLab ###
|
||||
|
||||
在相应的软件源被添加到我们的 linux 机子上之后,现在我们将使用相应 linux 发行版本中的默认包管理器来安装 GitLab 社区版。
|
||||
在相应的软件源被添加到我们的 linux 机器上之后,现在我们将使用相应 linux 发行版本中的默认包管理器来安装 GitLab 社区版。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Ubuntu 14.04/Debian 8.x 中 ####
|
||||
|
||||
要在运行着 Ubuntu 14.04 或 Debian 8.x linux 发行版本的机子上安装 GitLab 社区版,我们只需运行如下的命令:
|
||||
要在运行着 Ubuntu 14.04 或 Debian 8.x linux 发行版本的机器上安装 GitLab 社区版,我们只需运行如下的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -i gitlab-ce_8.1.2-ce.0_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
@ -95,7 +96,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Fedora 22 中 ####
|
||||
|
||||
我们只需执行下面的 dnf 命令来在我们的 Fedora 22 机子上安装 GitLab。
|
||||
我们只需执行下面的 dnf 命令来在我们的 Fedora 22 机器上安装 GitLab。
|
||||
|
||||
# dnf install gitlab-ce-8.1.2-ce.0.el7.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
@ -103,7 +104,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 配置和开启 GitLab ###
|
||||
|
||||
由于 GitLab 社区版已经成功地安装在我们的 linux 系统中了,接下来我们将要配置和开启它了。为此,我们需要运行下面的命令,这在 Ubuntu、Debian 和 Fedora 发行版本上都一样:
|
||||
GitLab 社区版已经成功地安装在我们的 linux 系统中了,接下来我们将要配置和开启它了。为此,我们需要运行下面的命令,这在 Ubuntu、Debian 和 Fedora 发行版本上都一样:
|
||||
|
||||
# gitlab-ctl reconfigure
|
||||
|
||||
@ -111,19 +112,19 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 允许通过防火墙 ###
|
||||
|
||||
假如在我们的 linux 机子中已经启用了防火墙程序,为了使得 GitLab 社区版的 web 界面可以通过网络进行访问,我们需要允许 80 端口通过防火墙,这个端口是 GitLab 社区版的默认端口。为此,我们需要运行下面的命令。
|
||||
假如在我们的 linux 机器中已经启用了防火墙程序,为了使得 GitLab 社区版的 web 界面可以通过网络进行访问,我们需要允许 80 端口通过防火墙,这个端口是 GitLab 社区版的默认端口。为此,我们需要运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Iptables 中 ####
|
||||
#### 在 iptables 中 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 14.04 默认安装和使用 Iptables。所以,我们将运行下面的 iptables 命令来打开 80 端口:
|
||||
Ubuntu 14.04 默认安装和使用的是 iptables。所以,我们将运行下面的 iptables 命令来打开 80 端口:
|
||||
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
|
||||
# /etc/init.d/iptables save
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Firewalld 中 ####
|
||||
#### 在 firewalld 中 ####
|
||||
|
||||
由于 Fedora 22 和 Debian 8.x 默认安装了 systemd,它包含了作为防火墙程序的 firewalld。为了使得 80 端口(http 服务) 能够通过 firewalld,我们需要执行下面的命令。
|
||||
由于 Fedora 22 和 Debian 8.x 默认安装了 systemd,它包含了作为防火墙程序的 firewalld。为了使得 80 端口(http 服务) 能够通过 firewalld,我们需要执行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
|
||||
|
||||
@ -139,13 +140,13 @@ Ubuntu 14.04 默认安装和使用 Iptables。所以,我们将运行下面的
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在,为了登陆进面板,我们需要点击登陆按钮,它将询问我们的用户名和密码。然后我们将输入默认的用户名和密码,即 **root** 和 **5iveL!fe** 。在登陆进控制面板后,我们将被强制要求为我们的 GitLab root 用户输入新的密码。
|
||||
现在,为了登录进面板,我们需要点击登录按钮,它将询问我们的用户名和密码。然后我们将输入默认的用户名和密码,即 **root** 和 **5iveL!fe** 。在登录进控制面板后,我们将被强制要求为我们的 GitLab root 用户输入新的密码。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 8. 创建仓库 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在我们成功地更改密码并登陆到我们的控制面板之后,现在,我们将为我们的新项目创建一个新的仓库。为此,我们需要来到项目栏,然后点击 **新项目** 绿色按钮。
|
||||
在我们成功地更改密码并登录到我们的控制面板之后,现在,我们将为我们的新项目创建一个新的仓库。为此,我们需要来到项目栏,然后点击 **新项目** 绿色按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -153,13 +154,15 @@ Ubuntu 14.04 默认安装和使用 Iptables。所以,我们将运行下面的
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
做完这些后,我们将能够使用任何包含基本 git 命令行的 Git 客户端来访问我们的 Git 仓库。我们可以看到在仓库中进行的任何活动,例如创建一个里程碑,管理 issue,合并请求,管理成员,便签,Wiki 等。
|
||||
做完这些后,我们将能够使用任何包含基本 git 命令行的 Git 客户端来访问我们的 Git 仓库。我们可以看到在仓库中进行的任何活动,例如创建一个里程碑,管理问题,合并请求,管理成员,便签,Wiki 等。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
GitLab 是一个用来管理 git 仓库的很棒的开源 web 应用。它有着漂亮,响应式的带有诸多酷炫功能的界面。它还打包有许多酷炫功能,例如管理群组,分发密钥,连续集成,查看日志,广播消息,钩子,系统 OAuth 应用,模板等。(注:OAuth 是一个开放标准,允许用户让第三方应用访问该用户在某一网站上存储的私密的资源(如照片,视频,联系人列表),而无需将用户名和密码提供给第三方应用。--- 摘取自 [维基百科上的 OAuth 词条](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/OAuth)) 它还可以和大量的工具进行交互如 Slack,Hipchat,LDAP,JIRA,Jenkins,很多类型的钩子和一个完整的 API。它至少需要 2 GB 的内存和 2 核 CPU 来流畅运行,支持多达 500 个用户,但它也可以被扩展到多个活动的服务器上。假如你有任何的问题,建议,回馈,请将它们写在下面的评论框中,以便我们可以提升或更新我们的内容。谢谢!
|
||||
GitLab 是一个用来管理 git 仓库的很棒的开源 web 应用。它有着漂亮的带有诸多酷炫功能的响应式界面。它还打包有许多酷炫功能,例如管理群组,分发密钥,持续集成,查看日志,广播消息,钩子,系统 OAuth 应用,模板等。(注:OAuth 是一个开放标准,允许用户让第三方应用访问该用户在某一网站上存储的私密的资源(如照片,视频,联系人列表),而无需将用户名和密码提供给第三方应用。--- 摘取自 [维基百科上的 OAuth 词条](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/OAuth)) 它还可以和大量的工具进行交互如 Slack,Hipchat,LDAP,JIRA,Jenkins,有很多类型的钩子和完整的 API。它至少需要 2 GB 的内存和 2 核 CPU 来流畅运行,支持多达 500 个用户,但它也可以被扩展到多个工作服务器上。
|
||||
|
||||
假如你有任何的问题,建议,回馈,请将它们写在下面的评论框中,以便我们可以提升或更新我们的内容。谢谢!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -167,7 +170,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-gitlab-on-ubuntu-fedora-debian/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,171 @@
|
||||
Linux 101:最有效地使用 Systemd
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
干嘛要这么做?
|
||||
|
||||
- 理解现代 Linux 发行版中的显著变化;
|
||||
- 看看 Systemd 是如何取代 SysVinit 的;
|
||||
- 搞定单元(unit)和新的 journal 日志。
|
||||
|
||||
吐槽邮件、人身攻击、死亡威胁——Lennart Poettering,Systemd 的作者,对收到这些东西早就习以为常了。这位 Red Hat 公司的员工之前在 Google+ 上怒斥 FOSS 社区([http://tinyurl.com/poorlennart][1])的本质,悲痛且失望地表示:“那真是个令人恶心的地方”。他着重指出 Linus Torvalds 在邮件列表上言辞极其刻薄的帖子,并谴责这位内核的领导者为在线讨论定下基调,并使得人身攻击及贬抑之辞成为常态。
|
||||
|
||||
但为何 Poettering 会遭受如此多的憎恨?为何就这么个搞搞开源软件的人要忍受这等愤怒?答案就在于他的软件的重要性。如今大多数发行版中,Systemd 是 Linux 内核发起的第一个程序,并且它还扮演多种角色。它会启动系统服务、处理用户登录,每隔特定的时间执行一些任务,还有很多很多。它在不断地成长,并逐渐成为 Linux 的某种“基础系统”——提供系统启动和发行版维护所需的所有工具。
|
||||
|
||||
如今,在以下几点上 Systemd 颇具争议:它逃避了一些已经确立的 Unix 传统,例如纯文本的日志文件;它被看成是个“大一统”的项目,试图接管一切;它还是我们这个操作系统的支柱的重要革新。然而大多数主流发行版已经接受了(或即将接受)它,因此它就活了下来。而且它确实是有好处的:更快地启动,更简单地管理那些有依赖的服务程序,提供强大且安全的日志系统等。
|
||||
|
||||
因此在这篇教程中,我们将探索 Systemd 的特性,并向您展示如何最有效地利用这些特性。即便您此刻并不是这款软件的粉丝,读完本文后您至少可以更加了解和适应它。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*这部没正经的动画片来自[http://tinyurl.com/m2e7mv8][2],它把 Systemd 塑造成一只狂暴的动物,吞噬它路过的一切。大多数批评者的言辞可不像这只公仔一样柔软。*
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动及服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
大多数主流发行版要么已经采用 Systemd,要么即将在下个发布中采用(如 Debian 和 Ubuntu)。在本教程中,我们使用 Fedora 21(该发行版已经是 Systemd 的优秀实验场地)的一个预览版进行演示,但不论您用哪个发行版,要用到的命令和注意事项都应该是一样的。这是 Systemd 的一个加分点:它消除了不同发行版之间许多细微且琐碎的区别。
|
||||
|
||||
在终端中输入 `ps ax | grep systemd`,看到第一行,其中的数字 **1** 表示它的进程号是1,也就是说它是 Linux 内核发起的第一个程序。因此,内核一旦检测完硬件并组织好了内存,就会运行 `/usr/lib/systemd/systemd` 可执行程序,这个程序会按顺序依次发起其他程序。(在还没有 Systemd 的日子里,内核会去运行 `/sbin/init`,随后这个程序会在名为 SysVinit 的系统中运行其余的各种启动脚本。)
|
||||
|
||||
Systemd 的核心是一个叫*单元* (unit)的概念,它是一些存有关于服务(service)(在运行在后台的程序)、设备、挂载点、和操作系统其他方面信息的配置文件。Systemd 的其中一个目标就是简化这些事物之间的相互作用,因此如果你有程序需要在某个挂载点被创建或某个设备被接入后开始运行,Systemd 可以让这一切正常运作起来变得相当容易。(在没有 Systemd 的日子里,要使用脚本来把这些事情调配好,那可是相当丑陋的。)要列出您 Linux 系统上的所有单元,输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl list-unit-files
|
||||
|
||||
现在,`systemctl` 是与 Systemd 交互的主要工具,它有不少选项。在单元列表中,您会注意到这儿有一些格式化:被使能(enabled)的单元显示为绿色,被禁用(disabled)的显示为红色。标记为“static”的单元不能直接启用,它们是其他单元所依赖的对象。若要限制输出列表只包含服务,使用以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl list-unit-files --type=service
|
||||
|
||||
注意,一个单元显示为“enabled”,并不等于对应的服务正在运行,而只能说明它可以被开启。要获得某个特定服务的信息,以 GDM (Gnome Display Manager) 为例,输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl status gdm.service
|
||||
|
||||
这条命令提供了许多有用的信息:一段给人看的服务描述、单元配置文件的位置、启动的时间、进程号,以及它所从属的 CGroups(用以限制各组进程的资源开销)。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您去查看位于 `/usr/lib/systemd/system/gdm.service` 的单元配置文件,您可以看到各种选项,包括要被运行的二进制文件(“ExecStart”那一行),相冲突的其他单元(即不能同时进入运行的单元),以及需要在本单元执行前进入运行的单元(“After”那一行)。一些单元有附加的依赖选项,例如“Requires”(必要的依赖)和“Wants”(可选的依赖)。
|
||||
|
||||
此处另一个有趣的选项是:
|
||||
|
||||
Alias=display-manager.service
|
||||
|
||||
当您启动 **gdm.service** 后,您将可以通过 `systemctl status display-manager.service` 来查看它的状态。当您知道有*显示管理程序* (display manager)在运行并想对它做点什么,但您不关心那究竟是 GDM,KDM,XDM 还是什么别的显示管理程序时,这个选项会非常有用。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*使用 systemctl status 命令后面跟一个单元名,来查看对应的服务有什么情况。*
|
||||
|
||||
### “目标(target)”锁定 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果您在 `/usr/lib/systemd/system` 目录中输入 `ls` 命令,您将看到各种以 `.target` 结尾的文件。*启动目标* (target)是一种将多个单元聚合在一起以致于将它们同时启动的方式。例如,对大多数类 Unix 操作系统而言有一种“多用户(multi-user)”状态,意思是系统已被成功启动,后台服务正在运行,并且已准备好让一个或多个用户登录并工作——至少在文本模式下。(其他状态包括用于进行管理工作的单用户(single-user)状态,以及用于机器关机的重启(reboot)状态。)
|
||||
|
||||
如果您打开 **multi-user.target** 文件一探究竟,您可能期待看到的是一个要被启动的单元列表。但您会发现这个文件内部几乎空空如也——其实,一个服务会通过 **WantedBy** 选项让自己成为启动目标的依赖。因此如果您去打开 **avahi-daemon.service**, **NetworkManager.service** 及其他 **.service** 文件看看,您将在 Install 段看到这一行:
|
||||
|
||||
WantedBy=multi-user.target
|
||||
|
||||
因此,切换到多用户启动目标会使能(enable)那些包含上述语句的单元。还有其他一些启动目标可用(例如 **emergency.target** 提供一个紧急情况使用的 shell,以及 **halt.target** 用于机器关机),您可以用以下方式轻松地在它们之间切换:
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl isolate emergency.target
|
||||
|
||||
在许多方面,这些都很像 SysVinit 中的*运行级* (runlevel),如文本模式的 **multi-user.target** 类似于第3运行级,**graphical.target** 类似于第5运行级,**reboot.target** 类似于第6运行级,诸如此类。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**与传统的脚本相比,单元配置文件也许看起来很陌生,但并不难以理解。**
|
||||
|
||||
### 开启与停止 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在您也许陷入了沉思:我们已经看了这么多,但仍没看到如何停止和开启服务!这其实是有原因的。从外部看,Systemd 也许很复杂,像野兽一般难以驾驭。因此在您开始摆弄它之前,有必要从宏观的角度看看它是如何工作的。实际用来管理服务的命令非常简单:
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl stop cups.service
|
||||
systemctl start cups.service
|
||||
|
||||
(若某个单元被禁用了,您可以先通过 `systemctl enable` 加上该单元名的方式将其使能。这种做法会为该单元创建一个符号链接,并将其放置在当前启动目标的 `.wants` 目录下,这些 `.wants` 目录在`/etc/systemd/system` 文件夹中。)
|
||||
|
||||
还有两个有用的命令是 `systemctl restart` 和 `systemctl reload`,后面接单元名。后者用于让单元重新加载它的配置文件。Systemd 的绝大部分都有良好的文档,因此您可以查看手册 (`man systemctl`) 了解每条命令的细节。
|
||||
|
||||
### 定时器单元:取代 Cron ###
|
||||
|
||||
除了系统初始化和服务管理,Systemd 还染指了其他方面。在很大程度上,它能够完成 **cron** 的工作,而且可以说是以更灵活的方式(并带有更易读的语法)。**cron** 是一个以规定时间间隔执行任务的程序——例如清除临时文件,刷新缓存等。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您再次进入 `/usr/lib/systemd/system` 目录,您会看到那儿有多个 `.timer` 文件。用 `less` 来查看这些文件,您会发现它们与 `.service` 和 `.target` 文件有着相似的结构,而区别在于 `[Timer]` 段。举个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
[Timer]
|
||||
OnBootSec=1h
|
||||
OnUnitActiveSec=1w
|
||||
|
||||
**OnBootSec** 选项告诉 Systemd 在系统启动一小时后启动这个单元。第二个选项的意思是:自那以后每周启动这个单元一次。关于定时器有大量选项您可以设置,输入 `man systemd.time` 查看完整列表。
|
||||
|
||||
Systemd 的时间精度默认为一分钟。也就是说,它会在设定时刻的一分钟内运行单元,但不一定精确到那一秒。这么做是基于电源管理方面的原因,但如果您需要一个没有任何延时且精确到毫秒的定时器,您可以添加以下一行:
|
||||
|
||||
AccuracySec=1us
|
||||
|
||||
另外, **WakeSystem** 选项(可以被设置为 true 或 false)决定了定时器是否可以唤醒处于休眠状态的机器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*有一个 Systemd 的图形界面程序,即便它已有多年未被积极维护。*
|
||||
|
||||
### 日志文件:向 journald 问声好 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Systemd 的第二个主要部分是 journal 。这是个日志系统,类似于 syslog 但也有些显著区别。如果您是个 Unix 日志管理模式的粉丝,准备好出离愤怒吧:这是个二进制日志,因此您不能使用常规的命令行文本处理工具来解析它。这个设计决定不出意料地在网上引起了激烈的争论,但它的确有些优点。例如,日志可以被更系统地组织,带有更多的元数据,因此可以更容易地根据可执行文件名和进程号等过滤出信息。
|
||||
|
||||
要查看整个 journal,输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
journalctl
|
||||
|
||||
像许多其他的 Systemd 命令一样,该命令将输出通过管道的方式引向 `less` 程序,因此您可以使用空格键向下滚动,键入`/`(斜杠)查找,以及其他熟悉的快捷键。您也能在此看到少许颜色,像红色的警告及错误信息。
|
||||
|
||||
以上命令会输出很多信息。为了限制其只输出本次启动的消息,使用如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
journalctl -b
|
||||
|
||||
这就是 Systemd 大放异彩的地方!您想查看自上次启动以来的全部消息吗?试试 **journalctl -b -1** 吧。再上一次的?用 **-2** 替换 **-1** 吧。那自某个具体时间,例如2014年10月24日16:38以来的呢?
|
||||
|
||||
journalctl -b --since=”2014-10-24 16:38”
|
||||
|
||||
即便您对二进制日志感到遗憾,那依然是个有用的特性,并且对许多系统管理员来说,构建类似的过滤器比起写正则表达式而言容易多了。
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经可以根据特定的时间来准确查找日志了,那可以根据特定程序吗?对单元而言,试试这个:
|
||||
|
||||
journalctl -u gdm.service
|
||||
|
||||
(注意:这是个查看 X server 产生的日志的好办法。)那根据特定的进程号?
|
||||
|
||||
journalctl _PID=890
|
||||
|
||||
您甚至可以请求只看某个可执行文件产生的消息:
|
||||
|
||||
journalctl /usr/bin/pulseaudio
|
||||
|
||||
若您想将输出的消息限制在某个优先级,可以使用 **-p** 选项。该选项参数为 0 的话只会显示紧急消息(也就是说,是时候向 **$DEITY** 祈求保佑了)(LCTT 译注: $DEITY 是一个计算机方面的幽默,DEITY 是指广义上的“神”,$前缀表示这是一个变量),为 7 的话会显示所有消息,包括调试消息。请查看手册 (`man journalctl`) 获取更多关于优先级的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
值得指出的是,您也可以将多个选项结合在一起,若想查看在当前启动中由 GDM 服务输出的优先级数小于等于 3 的消息,请使用下述命令:
|
||||
|
||||
journalctl -u gdm.service -p 3 -b
|
||||
|
||||
最后,如果您仅仅想打开一个随 journal 持续更新的终端窗口,就像在没有 Systemd 时使用 `tail` 命令实现的那样,输入 `journalctl -f` 就好了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*二进制日志并不流行,但 journal 的确有它的优点,如非常方便的信息查找及过滤。*
|
||||
|
||||
### 没有 Systemd 的生活?###
|
||||
|
||||
如果您就是完全不能接受 Systemd,您仍然有一些主流发行版中的选择。尤其是 Slackware,作为历史最为悠久的发行版,目前还没有做出改变,但它的主要开发者并没有将其从未来规划中移除。一些不出名的发行版也在坚持使用 SysVinit 。
|
||||
|
||||
但这又将持续多久呢?Gnome 正越来越依赖于 Systemd,其他的主流桌面环境也会步其后尘。这也是引起 BSD 社区一阵恐慌的原因:Systemd 与 Linux 内核紧密相连,导致在某种程度上,桌面环境正变得越来越不可移植。一种折衷的解决方案也许会以 Uselessd ([http://uselessd.darknedgy.net][3]) 的形式到来:一种裁剪版的 Systemd,纯粹专注于启动和监控进程,而不消耗整个基础系统。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
若您不喜欢 Systemd,可以尝试一下 Gentoo 发行版,它将 Systemd 作为初始化工具的一种选择,但并不强制用户使用 Systemd。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/linux-101-get-the-most-out-of-systemd/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Mike Saunders][a]
|
||||
译者:[Ricky-Gong](https://github.com/Ricky-Gong)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/author/mike/
|
||||
[1]:http://tinyurl.com/poorlennart
|
||||
[2]:http://tinyurl.com/m2e7mv8
|
||||
[3]:http://uselessd.darknedgy.net/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
为什么主线内核不能运行在我的手机上?
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
对于自由软件来说,其最大的自由之一就是能够用一个更新或修改的版本来替换原始版本的程序。尽管如此,数千万使用那些手机里面装着所谓 Linux 的用户却很少能够在他们的手机上运行主线内核(mainline kernel),即使他们拥有替换内核代码的专业技能。可悲的是,我们必须承认目前仍然没有可以运行主线内核的主流手机。在由 Rob Herring 主持的2015届内核峰会(Kernel Summit)上,与会人员共同探讨了这个问题,并进一步谈论了他们应该怎么做才能解决这个问题。
|
||||
|
||||
当主持人提问的时候,在座的大多数开发人员都表示他们更乐意在他们的手机上面运行主线内核,然而也有少数人持相反的看法。在 Project Ara 的支持下,Rob 在这个问题上已经研究了近一年半的时间(参见:https://lwn.net/Articles/648400/ )。但是最新的研究成果并不理想。
|
||||
|
||||
Rob 表示,通常手机上运行了太多的过期(out-of-tree)代码;主线内核只是缺少能使手机正常运行所必须的驱动。每台常规的手机都在运行着100万行到300万行的过期(out-of-tree)代码。几乎所有的这些手机的内核版本都不超过3.10,有一些甚至更加古老。造成这种情况的原因有很多,但是有一点是很清楚的,在手机的世界里,一切都变化的太快以至于无法跟上内核社区的步伐。如果真是那样,他问到,我们还担心什么呢?
|
||||
|
||||
Tim Bird 指出,第一台 Android 手机 Nexus 1 从来没有运行过任何一个主线内核,并且以后也不会。它打破了开源的承诺,也使得用户不可能做到将一个新的内核放到手机中。从这一点上来说,没有任何一款手机支持这种能力。Peter Zijlstra 想知道从一台手机到另一台手机到底复制了多少能够工作的过期代码;Rob表示,迄今为止,他已经见到了三个独立开发的热插拔 [Governors][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
Dirk Hohndel 提出了很少有人注意到的建议。他说,对于世界上的数以亿计的手机,大约只有他们27个人关心他们的手机是否运行着主线内核。剩下的用户仅仅只是想让他们的手机正常工作。或许那些关注手机是否在运行主线内核的开发者正在努力去解决这个令人不解的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
Chris Mason 说,那些手机厂商当前正面临着相同类型的问题,而这些问题也是那些 Linux 发行版过去所面临过的问题。他们疲于应付大量的无效且重复和能被复用的工作。一旦这些发行版决定将他们的工作配合主线内核而不是使用自己维护的内核,那么问题将会变得好解决的多。解决问题的关键就是去帮助手机制造商们认识到他们可以通过同样的方式获得便利,形成这种认识的关键并不是通过来自用户的压力。这样一来,问题就可以解决了。
|
||||
|
||||
Grant Likely 提出了对于安全问题的担忧,这种担忧来自于那些不能升级他们的手机系统的 android 设备。他说,我们需要的是一个真正专为手机设立的发行版。但是,只要手机厂商仍然掌控着手机中的应用软件,那么手机的同步更新将无法实现。我们接下来将面临一个很大的安全难题。Peter 补充说,随着 [Stagefright 漏洞][2]的出现,难题已经出现在我们面前了。
|
||||
|
||||
Ted Ts'o 说,运行主线内核并不是他的主要关注点。他很乐于见到这个假期中所售卖的手机能够运行3.18或者4.1的内核,而不是继续停留在3.10。他认为这是一个更可能被解决的问题。Steve Rostedt 认为,按照 Ted Ts'o 所说的那样去做并不能解决手机的安全问题,但是,Ted 认为使用一个更新一些的内核至少可以让漏洞修复变得更加容易。Grant 对此回应说,接下来的一年里,这一切都将再次发生。过渡到更新的内核也是一个渐进式的对系统的完善。Kees Cook 补充说,我们无法从修复旧版本的内核漏洞的过程中得到太多的益处,真正的问题是我们没有对 bug 的应对措施(他会在今天的另外一个对话中讲到这个话题)。
|
||||
|
||||
Rob 说,任何一种解决方案都需要得到当前市场上的手机供应商的支持。否则,由于厂商对安装到他们生产的手机上的操作系统的封锁,运行主线内核的策略将会陷入麻烦。Paolo Bonzini 提问说是否可以因为那些没有修复的安全漏洞而控告手机厂商,尤其当手机仍然处于保修期内。Grant 认为对于手机的可更新能力(upgradeability)的保证必须来源于市场需求,否则是无法实现的。而促使它实现的原因可能会是一个严重的安全问题,然后用户开始对手机的可更新能力提出要求。同时,内核开发人员必须不断朝着这个方向努力。Rob 表示,除了到目前为止指出的所有优点之外,运行主线内核也能帮助开发者对安卓设备上的新特性进行测试和验证。
|
||||
|
||||
Josh Triplett 提问说,如果手机厂商提出对主线内核提供支持的想法,那么内核社区又将采取什么措施呢?那样将会针对手机各方面的特性要求对内核进行大量的测试和验证;[Android 的兼容性测试套件][3]中出现的失败将不得不被再次回归到内核。Rob 提议这个问题可以在明年讨论,即先将最基本的功能做好。但是,Josh 强调说,如果这个需求出现了,我们就应该能够给出一个好的答案。
|
||||
|
||||
Tim 认为,当前,我们和厂商之间存在很大的脱节。厂商根本不会主动报告或者贡献任何反馈给社区。他们之间完全脱节了,这样的话永远不会有进步。Josh 表示,当厂商们开始报告他们正在使用的旧内核的相关 bug 时,双方之间的接受度将变得更加友好。Arnd Bergmann 认为,我们需要的是得到一个大芯片厂商对使用主线内核的认可,并且将该厂商的硬件提升到能够支持主线内核的运行的这样一个水平,而这样将会在其他方面增加负担。但是,他补充说,实现这个目标要求存在一个跟随硬件一起分发的自由 GPU 驱动程序——然而这种程序当前并不存在。
|
||||
|
||||
Rob 给存在问题的领域列了一个清单,但是现在已经没有太多的时间去讨论其中的细节了。WiFi 驱动仍然是一个问题,尤其是当这个新特性被添加到 Android 设备上的时候。Johannes Berg 对新特性仍然存在问题表示赞同;Android 的开发人员甚至在这些新特性被应用到 Android 设备上之前都不会去谈论它们是否存在问题。然而,对这些特性中的大多数的技术支持最终都会落实在主线内核中。
|
||||
|
||||
随着会议逐渐接近尾声,Ben Herrenschmidt 再次重申:实现在 Android 手机上运行主线内核的关键还是在于让厂商认识到使用主线内核是它们获得最大利润的最好选择。从长远看,使用主线内核能节省大量的工作。Mark Brown 认为,以前,当搭载在 Android 设备上的内核版本以更稳定的方式向前推进的时候,上游工作的好处对运营商来说更加明显。以现在的情况来看,手机上的内核版本似乎停留在了3.10,那种压力是不一样的。
|
||||
|
||||
这次谈话以开发者决定进一步改善当前的状况而结束,但是却并没有对如何改善提出一个明确的计划。
|
||||
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://lwn.net/Articles/662147/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jonathan Corbet][a]
|
||||
译者:[kylepeng93](https://github.com/kylepeng93)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://lwn.net/Articles/KernelSummit2015/
|
||||
[1]:http://androidmodguide.blogspot.com/p/blog-page.html
|
||||
[2]:https://lwn.net/Articles/652728/
|
||||
[3]:https://source.android.com/compatibility/cts/index.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,153 @@
|
||||
grep 命令系列:如何在 Linux/UNIX 中使用 grep 命令
|
||||
==========================================
|
||||
|
||||
我该怎样在 Linux、Apple OS X 及其他类 UNIX 系统中使用 grep 命令,你能给我展示一些简单的例子吗?
|
||||
|
||||
grep 命令用来搜索文本,或从给定的文件中搜索行内包含了给定字符串或单词的文件。通常来说,grep 显示匹配到的行。使用 grep 来搜索包括一个或多个正则表达式匹配到的文本行,然后只显示匹配到的行。grep 被视作在 Linux/ Unix 系统中最有用的命令之一。
|
||||
|
||||
### 你知道吗 ###
|
||||
|
||||
grep 这个名字,来源于一个 Unix/Linux 中的古老的文本编辑器 ed 中执行相似操作的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
g/re/p
|
||||
|
||||
### grep 命令的语法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
语法如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
grep 'word' 文件名
|
||||
grep 'word' 文件1 文件2 文件3
|
||||
grep '字符串1 字符串2' 文件名
|
||||
cat 某个文件 | grep '某个东西'
|
||||
command | grep '某个东西'
|
||||
command 选项1 | grep '数据'
|
||||
grep --color '数据' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
###怎么样使用 grep 来搜索一个文件###
|
||||
|
||||
搜索 /etc/passwd 文件下的 boo 用户,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep boo /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
输出内容:
|
||||
|
||||
foo:x:1000:1000:foo,,,:/home/foo:/bin/ksh
|
||||
|
||||
可以使用 grep 去强制忽略大小写。例如,使用 -i 选项可以匹配 boo, Boo, BOO 和其他组合:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -i "boo" /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
### 递归使用 grep ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以递归地使用 grep 进行搜索。例如,在文件目录下面搜索所有包含字符串“192.168.1.5”的文件
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -r "192.168.1.5" /etc/
|
||||
|
||||
或者是:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -R "192.168.1.5" /etc/
|
||||
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
/etc/ppp/options:# ms-wins 192.168.1.50
|
||||
/etc/ppp/options:# ms-wins 192.168.1.51
|
||||
/etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/Wired connection 1:addresses1=192.168.1.5;24;192.168.1.2;
|
||||
|
||||
你会看到搜索到 192.168.1.5 的结果每一行都前缀以找到匹配的文件名(例如:/etc/ppp/options)。输出之中包含的文件名可以加 -h 选项来禁止输出:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -h -R "192.168.1.5" /etc/
|
||||
|
||||
或者
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -hR "192.168.1.5" /etc/
|
||||
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
# ms-wins 192.168.1.50
|
||||
# ms-wins 192.168.1.51
|
||||
addresses1=192.168.1.5;24;192.168.1.2;
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 grep 去搜索文本 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当你搜索 boo 时,grep 命令将会匹配 fooboo,boo123, barfoo35 和其他所有包含 boo 的字符串,你可以使用 -w 选项去强制只输出那些仅仅包含那个整个单词的行(LCTT译注:即该字符串两侧是英文单词分隔符,如空格,标点符号,和末端等,因此对中文这种没有断字符号的语言并不适用。)。
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -w "boo" file
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 grep 命令去搜索两个不同的单词 ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用 egrep 命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
$ egrep -w 'word1|word2' /path/to/file
|
||||
|
||||
(LCTT 译注:这里使用到了正则表达式,因此使用的是 egrep 命令,即扩展的 grep 命令。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 统计文本匹配到的行数 ###
|
||||
|
||||
grep 命令可以通过加 -c 参数显示每个文件中匹配到的次数:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -c 'word' /path/to/file
|
||||
|
||||
传递 -n 选项可以输出的行前加入匹配到的行的行号:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -n 'root' /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
1:root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
|
||||
1042:rootdoor:x:0:0:rootdoor:/home/rootdoor:/bin/csh
|
||||
3319:initrootapp:x:0:0:initrootapp:/home/initroot:/bin/ksh
|
||||
|
||||
### 反转匹配(不匹配) ###
|
||||
|
||||
可以使用 -v 选项来输出不包含匹配项的内容,输出内容仅仅包含那些不含给定单词的行,例如输出所有不包含 bar 单词的行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -v bar /path/to/file
|
||||
|
||||
### UNIX/Linux 管道与 grep 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
grep 常常与管道一起使用,在这个例子中,显示硬盘设备的名字:
|
||||
|
||||
# dmesg | egrep '(s|h)d[a-z]'
|
||||
|
||||
显示 CPU 型号:
|
||||
|
||||
# cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep -i 'Model'
|
||||
|
||||
然而,以上命令也可以按照以下方法使用,不使用管道:
|
||||
|
||||
# grep -i 'Model' /proc/cpuinfo
|
||||
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
model : 30
|
||||
model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i7 CPU Q 820 @ 1.73GHz
|
||||
model : 30
|
||||
model name : Intel(R) Core(TM) i7 CPU Q 820 @ 1.73GHz
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何仅仅显示匹配到内容的文件名字? ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用 -l 选项去显示那些文件内容中包含 main() 的文件名:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -l 'main' *.c
|
||||
|
||||
最后,你可以强制 grep 以彩色输出:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep --color vivek /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-use-grep-command-in-linux-unix/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[zky001](https://github.com/zky001)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
校对者ID:
|
||||
[1]:http://bash.cyberciti.biz/guide/Pipes
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,240 @@
|
||||
grep 命令系列:grep 中的正则表达式
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 、类 Unix 系统中我该如何使用 Grep 命令的正则表达式呢?
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 附带有 GNU grep 命令工具,它支持扩展正则表达式(extended regular expressions),而且 GNU grep 在所有的 Linux 系统中都是默认有的。Grep 命令被用于搜索定位存储在您服务器或工作站上的任何信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 正则表达式 ###
|
||||
|
||||
正则表达式就是用于匹配每行输入的一种模式,模式是指一串字符序列。下面是范例:
|
||||
|
||||
^w1
|
||||
w1|w2
|
||||
[^ ]
|
||||
|
||||
#### grep 正则表达式示例 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在 /etc/passswd 目录中搜索 'vivek'
|
||||
|
||||
grep vivek /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
输出例子:
|
||||
|
||||
vivek:x:1000:1000:Vivek Gite,,,:/home/vivek:/bin/bash
|
||||
vivekgite:x:1001:1001::/home/vivekgite:/bin/sh
|
||||
gitevivek:x:1002:1002::/home/gitevivek:/bin/sh
|
||||
|
||||
搜索大小写任意的 vivek(即不区分大小写的搜索)
|
||||
|
||||
grep -i -w vivek /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
搜索大小写任意的 vivek 或 raj
|
||||
|
||||
grep -E -i -w 'vivek|raj' /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
上面最后的例子显示的,就是一个扩展的正则表达式的模式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 锚点 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以分别使用 ^ 和 $ 符号来正则匹配输入行的开始或结尾。下面的例子搜索显示仅仅以 vivek 开始的输入行:
|
||||
|
||||
grep ^vivek /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
输出例子:
|
||||
|
||||
vivek:x:1000:1000:Vivek Gite,,,:/home/vivek:/bin/bash
|
||||
vivekgite:x:1001:1001::/home/vivekgite:/bin/sh
|
||||
|
||||
你可以仅仅只搜索出以单词 vivek 开始的行,即不显示 vivekgit、vivekg 等(LCTT 译注:即该单词后面是空格、符号等英文的单词分隔符。)
|
||||
|
||||
grep -w ^vivek /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
找出以单词 word 结尾的行:
|
||||
|
||||
grep 'foo$' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
匹配仅仅只包含 foo 的行:
|
||||
|
||||
grep '^foo$' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
如下所示的例子可以搜索空行:
|
||||
|
||||
grep '^$' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
### 字符类 ###
|
||||
|
||||
匹配 Vivek 或 vivek:
|
||||
|
||||
grep '[vV]ivek' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
或者
|
||||
|
||||
grep '[vV][iI][Vv][Ee][kK]' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
也可以匹配数字 (即匹配 vivek1 或 Vivek2 等等):
|
||||
|
||||
grep -w '[vV]ivek[0-9]' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
可以匹配两个数字字符(即 foo11、foo12 等):
|
||||
|
||||
grep 'foo[0-9][0-9]' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
不仅仅局限于数字,也能匹配至少一个字母的:
|
||||
|
||||
grep '[A-Za-z]' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
显示含有 "w" 或 "n" 字符的所有行:
|
||||
|
||||
grep [wn] 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
放在括号内的表达式,即包在 "[:" 和 ":]" 之间的字符类的名字,它表示的是属于此类的所有字符列表。标准的字符类名称如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- [:alnum:] - 字母数字字符
|
||||
- [:alpha:] - 字母字符
|
||||
- [:blank:] - 空字符: 空格键符 和 制表符
|
||||
- [:digit:] - 数字: '0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9'
|
||||
- [:lower:] - 小写字母: 'a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z'
|
||||
- [:space:] - 空格字符: 制表符、换行符、垂直制表符、换页符、回车符和空格键符
|
||||
- [:upper:] - 大写字母: 'A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z'
|
||||
|
||||
在这个例子所示的是匹配所有大写字母:
|
||||
|
||||
grep '[:upper:]' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
### 通配符 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用 "." 来匹配单个字符。例子中匹配以 "b" 开头以 "t" 结尾的3个字符的单词:
|
||||
|
||||
grep '\<b.t\>' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
在这儿,
|
||||
|
||||
- `\<` 匹配单词前面的空字符串
|
||||
- `\>` 匹配单词后面的空字符串
|
||||
|
||||
打印出只有两个字符的所有行:
|
||||
|
||||
grep '^..$' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
显示以一个点和一个数字开头的行:
|
||||
|
||||
grep '^\.[0-9]' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
#### 点字符转义 ####
|
||||
|
||||
下面要匹配到 IP 地址为 192.168.1.254 的正则式是不正确的:(LCTT 译注:可以匹配到该 IP 地址,但是也有可能匹配到间隔符号不是点的类似格式)
|
||||
|
||||
grep '192.168.1.254' /etc/hosts
|
||||
|
||||
三个点字符都需要转义:
|
||||
|
||||
grep '192\.168\.1\.254' /etc/hosts
|
||||
|
||||
下面的例子只能匹配出 IP 地址:(LCTT 译注:实际上由于 IP 地址中数字的取值范围,该正则表达式并不精确)
|
||||
|
||||
egrep '[[:digit:]]{1,3}\.[[:digit:]]{1,3}\.[[:digit:]]{1,3}\.[[:digit:]]{1,3}' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
### 怎么样搜索以 - 符号开头的匹配模式? ###
|
||||
|
||||
要使用 -e 选项来搜索匹配 '--test--' 字符串,如果不使用 -e 选项,grep 命令会试图把 '--test--' 当作自己的选项参数来解析:
|
||||
|
||||
grep -e '--test--' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
### 怎么使用 grep 的“或”匹配? ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下的语法:
|
||||
|
||||
grep -E 'word1|word2' 文件名
|
||||
或
|
||||
egrep 'word1|word2' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
或者是
|
||||
|
||||
grep 'word1\|word2' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
### 怎么使用 grep 的“和”匹配? ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的语法来显示既包含 'word1' 又包含 'word2' 的所有行
|
||||
|
||||
grep 'word1' 文件名 | grep 'word2'
|
||||
|
||||
### 怎么样使用序列检测? ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下的语法,您可以检测一个字符在序列中重复出现次数:
|
||||
|
||||
{N}
|
||||
{N,}
|
||||
{min,max}
|
||||
|
||||
要匹配字符 “v" 出现两次:
|
||||
|
||||
egrep "v{2}" 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令能匹配到 "col" 和 "cool" :
|
||||
|
||||
egrep 'co{1,2}l' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令将会匹配出至少有三个 'c' 字符的所有行。
|
||||
|
||||
egrep 'c{3,}' 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
下面的例子会匹配 91-1234567890(即二个数字-十个数字) 这种格式的手机号。
|
||||
|
||||
grep "[[:digit:]]\{2\}[ -]\?[[:digit:]]\{10\}" 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
### 怎么样使 grep 命令高亮显示?###
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下的语法:
|
||||
|
||||
grep --color 正则表达式 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
### 怎么样仅仅只显示匹配出的字符,而不是匹配出的行? ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下语法:
|
||||
|
||||
grep -o 正则表达式 文件名
|
||||
|
||||
### 正则表达式限定符###
|
||||
|
||||
| 限定符 | 描述|
|
||||
|------|----|
|
||||
|`.`|匹配任意的一个字符。|
|
||||
|`?`|匹配前面的子表达式,最多一次。|
|
||||
|`*`|匹配前面的子表达式零次或多次。|
|
||||
|`+`|匹配前面的子表达式一次或多次。|
|
||||
|`{N}`|匹配前面的子表达式 N 次。|
|
||||
|`{N,}`|匹配前面的子表达式 N 次到多次。|
|
||||
|`{N,M}`|匹配前面的子表达式 N 到 M 次,至少 N 次至多 M 次。|
|
||||
|`-`|只要不是在序列开始、结尾或者序列的结束点上,表示序列范围。|
|
||||
|`^`|匹配一行开始的空字符串;也表示字符不在要匹配的列表中。|
|
||||
|`$`|匹配一行末尾的空字符串。|
|
||||
|`\b`|匹配一个单词前后的空字符串。|
|
||||
|`\B`|匹配一个单词中间的空字符串。|
|
||||
|`\<`|匹配单词前面的空字符串。|
|
||||
|`\>`|匹配单词后面的空字符串。|
|
||||
|
||||
#### grep 和 egrep ####
|
||||
|
||||
egrep 等同于 **grep -E** 。它会以扩展的正则表达式的模式来解释模式。下面来自 grep 的帮助页:
|
||||
|
||||
基本的正则表达式元字符 ?、+、 {、 |、 ( 和 ) 已经失去了它们原来的意义,要使用的话用反斜线的版本 \?、\+、\{、\|、\( 和 \) 来代替。
|
||||
传统的 egrep 并不支持 { 元字符,一些 egrep 的实现是以 \{ 替代的,所以一个可移植的脚本应该避免在 grep -E 使用 { 符号,要匹配字面的 { 应该使用 [}]。
|
||||
GNU grep -E 试图支持传统的用法,如果 { 出在在无效的间隔规范字符串这前,它就会假定 { 不是特殊字符。
|
||||
例如,grep -E '{1' 命令搜索包含 {1 两个字符的串,而不会报出正则表达式语法错误。
|
||||
POSIX.2 标准允许这种操作的扩展,但在可移植脚本文件里应该避免这样使用。
|
||||
|
||||
参考:
|
||||
|
||||
- grep 和 regex 帮助手册页(7)
|
||||
- grep 的 info 页
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/grep-regular-expressions/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,6 @@
|
||||
使用 grep 命令来搜索多个单词/字符串模式
|
||||
grep 命令系列:使用 grep 命令来搜索多个单词
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
要使用 grep 命令来搜索多个字符串或单词,我们该怎么做?例如我想要查找 /path/to/file 文件中的 word1、word2、word3 等单词,我怎么样命令 grep 查找这些单词呢?
|
||||
|
||||
[grep 命令支持正则表达式][1]匹配模式。要使用多单词搜索,请使用如下语法:
|
||||
@ -10,7 +11,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep 'warning\|error\|critical' /var/log/messages
|
||||
|
||||
仅仅只是要匹配单词的话,可以加上 -w 选项参数:
|
||||
仅仅只是要匹配单词(即该词两侧是单词分界符,针对西方以空格分隔的语言而言)的话,可以加上 -w 选项参数:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -w 'warning\|error\|critical' /var/log/messages
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,7 +27,7 @@ egrep 命令可以跳过上面的语法格式,其使用的语法格式如下
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Fig.01: Linux / Unix egrep 命令查找多个单词输出例子
|
||||
图一: Linux / Unix egrep 命令查找多个单词输出例子
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -34,8 +35,8 @@ via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/searching-multiple-words-string-using-grep/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/grep-regular-expressions/
|
||||
[1]:https://linux.cn/article-6941-1.html
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
||||
Grep 命令统计匹配的字符串/单词行数
|
||||
grep 命令系列:用 grep 命令统计匹配字符串的行数
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 或 UNIX 操作系统下,对于给定的单词或字符串,我们应该怎么统计它们在每个输入文件中存在的行数呢?
|
||||
|
||||
您需要通过添加 -c 或者 --count 选项参数来抑制正常的输出。它将会显示对输入文件单词匹配的行数,如下示:
|
||||
您需要通过添加 -c 或者 --count 选项参数来抑制正常的输出。它将会显示对输入文件单词匹配的行数,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -c vivek /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,6 +29,6 @@ via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/grep-count-lines-if-a-string-word-matches/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
|
||||
(translating by runningwater)
|
||||
Grep From Files and Display the File Name
|
||||
grep 命令系列:从文件中搜索并显示文件名
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
How do I grep from a number of files and display the file name only?
|
||||
|
||||
When there is more than one file to search it will display file name by default:
|
||||
我怎样从几个文件中搜索(grep),并只显示匹配到的文件的文件名?
|
||||
|
||||
grep "word" filename
|
||||
当你从不止一个的文件中搜索时,默认它将显示文件名:
|
||||
|
||||
grep "word" 文件名
|
||||
grep root /etc/*
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
/etc/bash.bashrc: See "man sudo_root" for details.
|
||||
/etc/crontab:17 * * * * root cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.hourly
|
||||
@ -20,12 +20,12 @@ Sample outputs:
|
||||
/etc/logrotate.conf: create 0664 root utmp
|
||||
/etc/logrotate.conf: create 0660 root utmp
|
||||
|
||||
The first name is file name (e.g., /etc/crontab, /etc/group). The -l option will only print filename if th
|
||||
每行开始的第一个部分是文件名(如:/etc/crontab、/etc/group)。使用 -l 选项可以只显示文件名:
|
||||
|
||||
grep -l "string" filename
|
||||
grep -l root /etc/*
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
/etc/aliases
|
||||
/etc/arpwatch.conf
|
||||
@ -36,12 +36,12 @@ Sample outputs:
|
||||
/etc/crontab
|
||||
/etc/group
|
||||
|
||||
You can suppress normal output; instead print the name of each input file from **which no output would normally have been** printed:
|
||||
你也可以逆转输出;使用 -L 选项来输出**那些不匹配的文件的文件名**:
|
||||
|
||||
grep -L "word" filename
|
||||
grep -L root /etc/*
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
/etc/apm
|
||||
/etc/apparmor
|
||||
@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ Sample outputs:
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/grep-from-files-and-display-the-file-name/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,21 +1,17 @@
|
||||
如何在 UNIX 中根据文件内容查找文件
|
||||
How To Find Files by Content Under UNIX
|
||||
grep 命令系列:如何在 UNIX 中根据文件内容查找文件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
为了完成课程作业,我写了很多 C 语言代码并把它们保存为 /home/user/c/*.c and *.h。那么在 UNIX shell 窗口中我如何能通过字符串或者单词(例如函数名 main())文件内容来查找文件呢?
|
||||
I had written lots of code in C for my school work and saved it as source code under /home/user/c/*.c and *.h. How do I find files by content such as string or words (function name such as main() under UNIX shell prompt?
|
||||
|
||||
为了完成课程作业,我写了很多 C 语言代码并把它们保存为 /home/user/c/*.c 和 *.h。那么在 UNIX shell 窗口中我如何能通过字符串或者单词(例如函数名 main())文件内容来查找文件呢?
|
||||
|
||||
你需要用到以下工具:
|
||||
You need to use the following tools:
|
||||
|
||||
[a] **grep 命令** : 输出匹配模式的行。
|
||||
|
||||
[b] **find 命令**: 在目录层次中查找文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### [使用 grep 命令根据内容查找文件][1]
|
||||
### [grep Command To Find Files By][1] Content ###
|
||||
|
||||
输入以下命令:
|
||||
Type the command as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
grep 'string' *.txt
|
||||
grep 'main(' *.c
|
||||
@ -25,48 +21,37 @@ Type the command as follows:
|
||||
grep -iR 'ultra' *.conf
|
||||
|
||||
其中
|
||||
Where
|
||||
|
||||
- **-i** : 忽视模式(匹配字符串 valid、 VALID、 ValID )和输入文件(匹配 file.c FILE.c FILE.C)的大小写。
|
||||
- **-i** : 忽略模式(匹配字符串 valid、 VALID、 ValID )和输入文件(匹配 file.c FILE.c FILE.C)的大小写。
|
||||
- **-R** : 递归读取每个目录下的所有文件。
|
||||
- **-i** : Ignore case distinctions in both the PATTERN (match valid, VALID, ValID string) and the input files (math file.c FILE.c FILE.C filename).
|
||||
- **-R** : Read all files under each directory, recursively
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 高亮匹配到的模式 ###
|
||||
### Highlighting searched patterns ###
|
||||
|
||||
在搜索大量文件的时候你可以轻松地高亮模式:
|
||||
You can highlight patterns easily while searching large number of files:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep --color=auto -iR 'getChar();' *.c
|
||||
|
||||
### 为查找到的模式显示文件名和行号 ###
|
||||
### Displaying file names and line number for searched patterns ###
|
||||
|
||||
你也许需要显示文件名和行号:
|
||||
You may also need to display filenames and numbers:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep --color=auto -iRnH 'getChar();' *.c
|
||||
|
||||
其中,
|
||||
Where,
|
||||
|
||||
- **-n** : 在输出的每行前面添加文件中以 1 开始的行号。
|
||||
- **-n** : 在输出的每行前面添加以 1 开始的行号。
|
||||
- **-H** : 为每个匹配打印文件名。要搜索多个文件时这是默认选项。
|
||||
- **-n** : Prefix each line of output with the 1-based line number within its input file.
|
||||
- **-H** Print the file name for each match. This is the default when there is more than one file to search.
|
||||
|
||||
$grep --color=auto -nH 'DIR' *
|
||||
|
||||
输出样例:
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Fig.01: grep 命令显示搜索到的模式
|
||||
*Fig.01: grep 命令显示搜索到的模式*
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以使用 find 命令:
|
||||
You can also use find command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ find . -name "*.c" -print | xargs grep "main("
|
||||
|
||||
@ -76,7 +61,7 @@ via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/unix-linux-finding-files-by-content/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](http://mutouxiaogui.cn/blog/)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,9 @@
|
||||
Linux / UNIX 下只查看配置文件的有效配置行(配置文件中未被注释的命令行)
|
||||
grep 命令系列:如何只查看配置文件中未被注释的有效配置行
|
||||
=========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
大多数的Linux和类Unix系统的配置文件中都有许多的注释行,但是有时候我只想看其中的有效配置行。那我怎么才能只看到quid.conf或httpd.conf这样的配置文件中的非注释命令行呢?怎么去掉这些注释或者空行呢?
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以使用UNIX / BSD / OS X / Linux 这些操作系统自身提供的grep,sed,awk,perl或者其他文本处理工具来查看配置文件中的有效配置命令行。
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以使用 UNIX/BSD/OS X/Linux 这些操作系统自身提供的 grep,sed,awk,perl或者其他文本处理工具来查看配置文件中的有效配置命令行。
|
||||
|
||||
### grep 命令示例——去掉注释 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -100,7 +99,7 @@ Linux / UNIX 下只查看配置文件的有效配置行(配置文件中未被
|
||||
|
||||
Include /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/
|
||||
|
||||
想要跳过空行,可以使用 [egrep 命令][1], 示例:
|
||||
想要跳过其中的空行,可以使用 [egrep 命令][1], 示例:
|
||||
|
||||
egrep -v "^#|^$" /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
|
||||
## or pass it to the page such as more or less ##
|
||||
@ -119,23 +118,24 @@ Linux / UNIX 下只查看配置文件的有效配置行(配置文件中未被
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Fig.01: Unix/Linux Egrep 除去注释行和空行
|
||||
*图 01: Unix/Linux Egrep 除去注释行和空行*
|
||||
|
||||
### 理解 grep/egrep 命令行选项 ###
|
||||
|
||||
-v 选项,选择出不匹配的命令行。该选项适用于所有基于posix的系统。正则表达式 ^$ 匹配出所有的非空行, ^#匹配出所有的不以“#”开头的非注释行。
|
||||
-v 选项,选择出不匹配的命令行。该选项适用于所有基于posix的系统。正则表达式 `^$` 匹配出所有的非空行, `^#` 匹配出所有的不以“#”开头的非注释行。
|
||||
|
||||
### sed 命令示例 ###
|
||||
|
||||
可以按照如下示例使用 GNU / sed 命令:
|
||||
可以按照如下示例使用 GNU 上的 sed 命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sed '/ *#/d; /^ *$/d' /path/to/file
|
||||
$ sed '/ *#/d; /^ *$/d' /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
|
||||
GNU or BSD sed 也可以修改配置文件。下面的语法是编辑文件,修改扩展名(比如 .bak)进行文件备份:
|
||||
|
||||
GNU 或 BSD 上的 sed 也可以修改配置文件。下面的命令的作用是原地编辑文件,并以特定(比如 .bak)备份文件:
|
||||
|
||||
sed -i'.bak.2015.12.27' '/ *#/d; /^ *$/d' /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
|
||||
|
||||
更多信息见参考手册 - [grep(1)][2], [sed(1)][3]
|
||||
更多信息见参考手册 - [grep(1)][2], [sed(1)][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -143,7 +143,7 @@ via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/shell-display-uncommented-lines-only/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[sonofelice](https://github.com/sonofelice)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,162 @@
|
||||
在 Linux 上安装和配置 Munin 监控服务器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Munin 是一款类似 [RRD tool][1] 的非常棒的系统监控工具,它能提供给你多方面的系统性能信息,例如 **磁盘、网络、进程、系统和用户**。这些是 Munin 默认监控的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
### Munin 如何工作? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Munin 以客户端-服务器模式运行。主服务器上运行的 Munin 服务器进程会从本地运行的客户端守护进程(Munin 可以监控它自己的资源)或者远程客户端(Munin 可以监控上百台机器)收集数据,然后在它的 web 界面上以图形的方式显示出来。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 nutshell 中配置 Munin ###
|
||||
|
||||
要配置服务器端和客户端,我们需要完成以下两步。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装 Munin 服务器软件包并配置,使得它能从客户端收集数据。
|
||||
2. 安装 Munin 客户端,使得服务器能连接到客户端守护进程进行数据收集。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 上安装 munin 服务器端 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在基于 Ubuntu/Debian 的机器上安装 Munin 服务器:
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install munin apache2
|
||||
|
||||
在基于 Redhat/CentOS 的机器上安装 Munin 服务器:
|
||||
|
||||
在基于 Redhat 的机器上安装 Munin 之前,你需要确保 [启用 EPEL 软件仓库][2],因为基于 Redhat 的机器的软件仓库默认没有 Munin。
|
||||
|
||||
yum install munin httpd
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 上配置 Munin 服务器端 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下面是我们要在服务器上启动 Munini 所进行的步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在 /etc/munin/munin.conf 中添加需要监控的主机详情。
|
||||
2. 配置 apache web 服务器使其包括 munin 配置。
|
||||
3. 为 web 界面创建用户名和密码
|
||||
4. 重启 apache 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
####步骤 1####
|
||||
|
||||
在 **/etc/munin/munin.conf** 文件中添加主机条目。调到文件末尾添加要监控的客户端。在这个例子中,我添加了要监控的数据库服务器和它的 IP 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
|
||||
[db.linuxnix.com]
|
||||
address 192.168.1.25
|
||||
use_node_name yes
|
||||
|
||||
保存文件并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
####步骤 2####
|
||||
|
||||
在 /etc/apache2/conf.d 目录中编辑或创建文件 munin.conf 用于包括 Munin 和 Apache 相关的配置。另外注意一点,默认其它和 web 相关的 Munin 配置保存在 /var/www/munin 目录。
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/apache2/conf.d/munin.conf
|
||||
|
||||
内容:
|
||||
|
||||
Alias /munin /var/www/munin
|
||||
<Directory /var/www/munin>
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow from localhost 127.0.0.0/8 ::1
|
||||
AllowOverride None
|
||||
Options ExecCGI FollowSymlinks
|
||||
AddHandler cgi-script .cgi
|
||||
DirectoryIndex index.cgi
|
||||
AuthUserFile /etc/munin/munin.passwd
|
||||
AuthType basic
|
||||
AuthName "Munin stats"
|
||||
require valid-user
|
||||
<IfModule mod_expires.c>
|
||||
ExpiresActive On
|
||||
ExpiresDefault M310
|
||||
</IfModule>
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
|
||||
保存文件并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
####步骤 3####
|
||||
|
||||
现在为查看 munin 的图示而创建用户名和密码:
|
||||
|
||||
htpasswd -c /etc/munin/munin-htpasswd munin
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:对于 Redhat/Centos 机器,要访问你的配置文件,需要在每个路径中用 “**httpd**” 替换 “**apache2**”。
|
||||
|
||||
####步骤 4####
|
||||
|
||||
重启 Apache 服务器,使得 Munin 配置生效。
|
||||
|
||||
基于 Ubuntu/Debian :
|
||||
|
||||
service apache2 restart
|
||||
|
||||
基于 Centos/Redhat :
|
||||
|
||||
service httpd restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 上安装和配置 Munin 客户端 ###
|
||||
|
||||
####步骤 1####
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 上安装 Munin 客户端
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install munin-node
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:如果你想监控你的 Munin 服务器端,你也需要在服务器端安装 munin-node。
|
||||
|
||||
####步骤 2####
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 munin-node.conf 文件配置客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/munin/munin-node.conf
|
||||
|
||||
示例:
|
||||
|
||||
allow ^127\.0\.0\.1$
|
||||
allow ^10\.10\.20\.20$
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# 监听到哪个地址上
|
||||
host *
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# 以及哪个端口
|
||||
port 4949
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 10.10.20.20 是我的 Munin 服务器,它连接到客户端的 4949 端口获取数据。
|
||||
|
||||
####步骤 3####
|
||||
|
||||
在客户端机器中重启 munin-node:
|
||||
|
||||
service munin-node restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
检查你是否能从服务器的连接到客户端的 4949 端口,如果不行,你需要在客户端机器中的防火墙打开该端口。
|
||||
|
||||
telnet db.linuxnix.com 4949
|
||||
|
||||
访问 Munin web 页面
|
||||
|
||||
http://munin.linuxnix.com/munin/index.html
|
||||
|
||||
希望这些能对你配置基本的 Munin 服务器有所帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxnix.com/install-and-configure-munin-monitoring-server-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Surendra Anne][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](http://mutouxiaogui.cn/blog/)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxnix.com/author/surendra/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxnix.com/network-monitoringinfo-gathering-tools-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://linux.cn/article-2324-1.html
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Linux / Unix: jobs 命令示例
|
||||
jobs 命令示例
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
我是个新的 Linux 或 Unix 用户。如何在 Linux 或类 Unix 系统中使用 BASH/KSH/TCSH 或者基于 POSIX 的 shell 来查看当前正在进行的作业?在 Unix/Linux 上怎样显示当前作业的状态?
|
||||
我是个新的 Linux/Unix 用户。我该如何在 Linux 或类 Unix 系统中使用 BASH/KSH/TCSH 或者基于 POSIX 的 shell 来查看当前正在进行的作业(job)?在 Unix/Linux 上怎样显示当前作业的状态?(LCTT 译注:job,也常称为“任务”)
|
||||
|
||||
作业控制的是什么,停止/暂停进程(命令)的执行并按你的要求继续/恢复它们的执行。这是根据你的操作系统和 shell 如,bash/ksh 或 POSIX shell 来执行的。
|
||||
作业控制是一种能力,可以停止/暂停进程(命令)的执行并按你的要求继续/恢复它们的执行。这是通过你的操作系统和诸如 bash/ksh 或 POSIX shell 等 shell 来执行的。
|
||||
|
||||
shell 会将当前所执行的作业保存在一个表中,可以用 jobs 命令来显示。
|
||||
|
||||
### 目的 ###
|
||||
### 用途 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> 在当前 shell 会话中显示作业的状态。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,7 +29,7 @@ shell 会将当前所执行的作业保存在一个表中,可以用 jobs 命
|
||||
|
||||
在开始使用 jobs 命令前,你需要在系统上先启动多个作业。执行以下命令来启动作业:
|
||||
|
||||
## 启动 xeyes, calculator, 和 gedit 文本编辑器 ###
|
||||
### 启动 xeyes, calculator, 和 gedit 文本编辑器 ###
|
||||
xeyes &
|
||||
gnome-calculator &
|
||||
gedit fetch-stock-prices.py &
|
||||
@ -39,7 +38,7 @@ shell 会将当前所执行的作业保存在一个表中,可以用 jobs 命
|
||||
|
||||
ping www.cyberciti.biz
|
||||
|
||||
按 **Ctrl-Z** 键来暂停 ping 命令的作业。
|
||||
按 **Ctrl-Z** 键来挂起(suspend) ping 命令的作业。
|
||||
|
||||
### jobs 命令示例 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,7 +53,7 @@ shell 会将当前所执行的作业保存在一个表中,可以用 jobs 命
|
||||
[3]- 7910 Running gedit fetch-stock-prices.py &
|
||||
[4]+ 7946 Stopped ping cyberciti.biz
|
||||
|
||||
要显示进程 ID 或作业名称请使用 “P” 选项,输入:
|
||||
要显示名字以“p”开头的进程 ID 或作业名称,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ jobs -p %p
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,7 +65,7 @@ shell 会将当前所执行的作业保存在一个表中,可以用 jobs 命
|
||||
|
||||
[4]- Stopped ping cyberciti.biz
|
||||
|
||||
字符 % 后加一个作业。在这个例子中,你需要使用作业的名称来暂停它,如 %ping。
|
||||
字符 % 是一个指定任务的方法。在这个例子中,你可以使用作业名称开头字符串来来暂停它,如 %ping。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何显示进程 ID 不包含其他正常的信息? ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -77,7 +76,8 @@ shell 会将当前所执行的作业保存在一个表中,可以用 jobs 命
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Fig.01: 在 shell 中显示 jobs 的状态
|
||||
|
||||
*Fig.01: 在 shell 中显示 jobs 的状态*
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何只列出最近一次状态改变的进程? ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ Fig.01: 在 shell 中显示 jobs 的状态
|
||||
|
||||
$ sleep 100 &
|
||||
|
||||
现在,只显示作业最近一次的状态(停止或退出),输入:
|
||||
现在,只显示自从上次提示过停止或退出之后的作业,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ jobs -n
|
||||
|
||||
@ -137,43 +137,18 @@ Fig.01: 在 shell 中显示 jobs 的状态
|
||||
|
||||
摘自 [bash(1)][1] 命令 man 手册页:
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table border="1">
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>Option</td>
|
||||
<td>Description</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><kbd><strong>-l</strong></kbd></td>
|
||||
<td>Show process id's in addition to the normal information.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><kbd><strong>-p</strong></kbd></td>
|
||||
<td>Show process id's only.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><kbd><strong>-n</strong></kbd></td>
|
||||
<td>Show only processes that have changed status since the last notification are printed.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><kbd><strong>-r</strong></kbd></td>
|
||||
<td>Restrict output to running jobs only.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><kbd><strong>-s</strong></kbd></td>
|
||||
<td>Restrict output to stopped jobs only.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><kbd><strong>-x</strong></kbd></td>
|
||||
<td>COMMAND is run after all job specifications that appear in ARGS have been replaced with the process ID of that job's process group leader./td></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|选项|描述|
|
||||
|---|------------------|
|
||||
|`-l`| 列出进程 ID 及其它信息。|
|
||||
|`-p`| 仅列出进程 ID。|
|
||||
|`-n`| 仅列出自从上次输出了状态变化提示(比如显示有进程退出)后的发生了状态变化的进程。|
|
||||
|`-r`| 仅显示运行中的作业。|
|
||||
|`-s`| 仅显示停止的作业。|
|
||||
|`-x`| 运行命令及其参数,并用新的命令的进程 ID 替代所匹配的原有作业的进程组 ID。|
|
||||
|
||||
### 关于 /usr/bin/jobs 和 shell 内建的说明 ###
|
||||
|
||||
输入以下 type 命令找出是否 jobs 命令是 shell 的内建命令或是外部命令:
|
||||
输入以下 type 命令找出是否 jobs 命令是 shell 的内建命令或是外部命令还是都是:
|
||||
|
||||
$ type -a jobs
|
||||
|
||||
@ -182,15 +157,15 @@ Fig.01: 在 shell 中显示 jobs 的状态
|
||||
jobs is a shell builtin
|
||||
jobs is /usr/bin/jobs
|
||||
|
||||
在几乎所有情况下,jobs 命令都是作为 BASH/KSH/POSIX shell 内建命令被实现的。/usr/bin/jobs 命令不能被用在当前 shell 中。/usr/bin/jobs 命令工作在不同的环境中不共享父 bash/ksh 的 shells 来执行作业。
|
||||
在几乎所有情况下,你都需要使用 BASH/KSH/POSIX shell 内建的jobs 命令。/usr/bin/jobs 命令不能被用在当前 shell 中。/usr/bin/jobs 命令工作在不同的环境中,并不共享其父 bash/ksh 的 shell 作业。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/unix-linux-jobs-command-examples-usage-syntax/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/strugglingyouth)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
IPv6 互联网中的隐私保护和网络管理器
|
||||
==============================
|
||||
|
||||
IPv6 的使用量正在不断增加,让我们始料未及的是,伴随这个协议不断增加的使用量,大量的隐私问题涌现出来。互联网社区在积极发布相关解决方案。当前状况是怎样的呢?网络管理器(NetworkManager)又是如何跟上的呢?让我们来瞧瞧吧!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 通过 IPv6 方式连接的主机的特性
|
||||
|
||||
启用了 IPv6 的节点(LCTT 译注:节点在网络中指一个联网的设备)并不需要类似 IPv4 网络中 [DHCP](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc2132) 服务器的中央机构来配置他们的地址。它们发现(discover)自己所在的网络,然后通过生成主机部分来[自主生成地址](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4862)。这种方式使得网络配置更加简单,并且能够更好的扩展到更大规模的网络。然而,这种方式也有一些缺点。首先,这个节点需要确保它的地址不会和网络上其他节点冲突。其次,如果这个节点在进入的每一个网络中使用相同的主机部分,它的运动就可以被追踪,如此一来,隐私便处于危险之中。
|
||||
|
||||
负责制定因特网标准的组织 Internet 工程任务组(Internet Engineering Task Force,IETF)[意识到了这个问题](https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-iesg-serno-privacy-00),这个组织建议取消使用硬件序列号来识别网络上的节点。
|
||||
|
||||
但实际的实施情况是怎样的呢?
|
||||
|
||||
地址唯一性问题可以通过[重复地址检测(Duplicate Address Detection, DAD)](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4862#section-5.4)机制来解决。当节点为自身创建地址的时候,它首先通过[邻居发现协议(Neighbor Discovery Protocol)](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4861)(一种不同于 IPv4 [ARP](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc826)协议的机制)来检查另一个节点是否使用了相同的地址。当它发现地址已经被使用,它必须抛弃掉这个地址。
|
||||
|
||||
解决另一个问题——隐私问题,有一点困难。一个 IP 地址(无论 IPv4 或 IPv6)由网络部分和主机部分组成(LCTT 译注:网络部分用来划分子网,主机部分用来从相应子网中找到具体的主机)。主机查找出相关的地址的网络部分,并且生成地址的主机部分。传统上它只使用了源自网络硬件(MAC)地址的接口识别器(Interface Identifier)。MAC 地址在硬件制造的时候就被设置好了,它可以唯一的识别机器。这样就确保了地址的稳定性和唯一性。这对避免地址冲突来说是件好事,但是对隐私来说一点也不好。主机部分在不同网络下保持恒定意味着机器在进入不同网络时可以被唯一的识别。这在协议制定的时候看起来无可非议,但是随着 IPv6 的流行,人们对于隐私问题的担忧也愈演愈烈。幸运的是,解决办法还是有的。
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用隐私扩展(privacy extensions)
|
||||
|
||||
IPv4 的最大问题——地址枯竭,已经不是什么秘密。对 IPv6 来说,这一点不再成立,事实上,使用 IPv6 的主机能够相当大方的利用地址。多个 IPv6 地址对应一块网卡绝对没有任何不合适,正好相反,这是一种标准情形。最起码每个节点都有一个“本地连接(link-local)地址”,它被用来与同一物理链路的节点联络。当网络包含了一个连接其他网络的路由器,这个网络中的每个节点都有一个与每个直接连接的网络相联络的地址。如果主机在同一个网络有更多的地址,该节点(LCTT 译注:指路由器)将接受它们全部的传入流量。对于外发连接,它会把地址显示给远程主机,内核会挑选最适合的地址。但到底是哪一个呢?
|
||||
|
||||
启用了隐私扩展,就像 [RFC4941](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4941) 定义的那样,时常会生成带有随机主机部分的新地址。最新的那个被用于最新的外发连接,与此同时,那些不被使用了的旧地址将被丢弃。这是一个极好的策略——主机不会对外暴露其固定地址,因为它不用于外发连接,但它仍然会接受知道其固定地址的主机连接。
|
||||
|
||||
但这也存在美中不足之处——某些应用会把地址与用户识别绑定在一起。让我们来考虑一下这种情形,一个 web 应用在用户认证的时候生成一个 HTTP Cookie,但它只接受实施认证的地址的连接。当内核生成了一个新的临时地址,服务器会拒绝使用这个地址的请求,实际上相当于用户登出了。地址是不是建立用户认证的合适机制值得商榷,但这确实是现实中应用程序正在做的。
|
||||
|
||||
## 解救之道——隐私固定寻址(Privacy stable addressing)
|
||||
|
||||
解决这个问题可能需要另辟蹊径。唯一的(当然咯)地址确实有必要,对于特定网络来说是稳定的,但当用户进入了另一个网络后仍然会变,这样的话追踪就变得几乎不可能。RFC7217 介绍了一种如上所述的机制。
|
||||
|
||||
创建隐私固定地址依赖于伪随机值,这个随机值只被主机本身知晓,它不会暴露给网络上的其他主机。这个随机值随后被一个密码安全算法加密,一起被加密的还有一些与网络连接的特定值。这些值包含:用以标识网卡的名称;网络地址;对于这个网络来说有可能的其他特殊值,例如无线网络的 SSID。使用这个安全密钥使其他主机很难预测结果地址,与此同时,当进入不同的网络时,网络的特殊数据会让地址变得不同。
|
||||
|
||||
这也巧妙的解决了地址重复问题。因为有随机值的存在,冲突也不太可能发生。万一发生了冲突,结果地址会得到重复地址检测失败的记录,这时会生成一个不同的地址而不会断开网络连接。看,这种方式很聪明吧。
|
||||
|
||||
使用隐私固定地址一点儿也不会妨碍隐私扩展。你可以在使用 RFC4941 所描述的临时地址的同时使用 [RFC7217](https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7217)中的固定地址。
|
||||
|
||||
## 网络管理器(NetworkManager)处于什么样的状况?
|
||||
|
||||
我们已经在网络管理器1.0.4版本中实现了隐私扩展(privacy extensions)。在这个版本中,隐私扩展默认开启。你可以用 ipv6.ip6-privacy 参数来控制它。
|
||||
|
||||
在网络管理器1.2版本中,我们将会加入固定隐私寻址(stable privacy addressing)。应该指出的是,目前的隐私扩展还不符合这种需求。我们可以使用 ipv6.addr-gen-mode 参数来控制这个特性。如果它被设置成固定隐私,那么将会使用固定隐私寻址。设置成“eui64”或者干脆不设置它将会保持传统的默认寻址方式。
|
||||
|
||||
敬请期待2016年年初网络管理器1.2版本的发布吧!如果你想尝试一下最新的版本,不妨试试 Fedora Rawhide,它最终会变成 Fedora 24。
|
||||
|
||||
*我想感谢 Hannes Frederic Sowa,他给了我很有价值的反馈。如果没有他的帮助,这篇文章的作用将会逊色很多。另外,Hannes 也是 RFC7217 所描述机制的内核实现者,当网络管理器不起作用的时候,它将发挥作用。*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://blogs.gnome.org/lkundrak/2015/12/03/networkmanager-and-privacy-in-the-ipv6-internet/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Lubomir Rintel
|
||||
译者:[itsang](https://github.com/itsang)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,20 +1,20 @@
|
||||
如何更新ISPConfig 3 SSL证书
|
||||
如何更新 ISPConfig 3 SSL 证书
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
本教程描述了如何再ISPConfig 3控制面板中更新SSL证书。有两个可选的方法:
|
||||
本教程描述了如何在 ISPConfig 3控制面板中更新 SSL 证书。有两个可选的方法:
|
||||
|
||||
- 用OpenSSL创建一个新的OpenSSL证书和CSR。
|
||||
- 用ISPConfig updater更新SSL证书
|
||||
- 用 OpenSSL 创建一个新的 OpenSSL 证书和 CSR。
|
||||
- 用 ISPConfig updater 更新 SSL 证书
|
||||
|
||||
我将会用手工的方法更新ssl证书。
|
||||
我将从用手工的方法更新 SSL 证书开始。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1)用OpenSSL创建一个新的ISPConfig 3 SSL 证书 ###
|
||||
### 1)用 OpenSSL 创建一个新的 ISPConfig 3 SSL 证书 ###
|
||||
|
||||
用root用户登录你的服务器。在创建一个新的SSL证书之前,备份现有的。SSL证书是安全敏感的,因此我将它存储在/root/目录下。
|
||||
用 root 用户登录你的服务器。在创建一个新的 SSL 证书之前,先备份现有的。SSL 证书是安全敏感的,因此我将它存储在 /root/ 目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
tar pcfz /root/ispconfig_ssl_backup.tar.gz /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/ssl
|
||||
chmod 600 /root/ispconfig_ssl_backup.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
> 现在创建一个新的SSL证书密钥,证书请求(csr)和自签发证书。
|
||||
> 现在创建一个新的 SSL 证书密钥,证书请求(CSR)和自签发证书。
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/local/ispconfig/interface/ssl
|
||||
openssl genrsa -des3 -out ispserver.key 4096
|
||||
@ -25,13 +25,13 @@
|
||||
mv ispserver.key ispserver.key.secure
|
||||
mv ispserver.key.insecure ispserver.key
|
||||
|
||||
重启apache来加载新的SSL证书
|
||||
重启 apache 来加载新的 SSL 证书
|
||||
|
||||
service apache2 restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 2)用ISPConfig安装器来更新SSL证书 ###
|
||||
### 2)用 ISPConfig 安装器来更新 SSL 证书 ###
|
||||
|
||||
另一个获取新的SSL证书的替代方案是使用ISPConfig更新脚本。下载ISPConfig到/tmp目录下,解压包并运行脚本。
|
||||
另一个获取新的 SSL 证书的替代方案是使用 ISPConfig 更新脚本。下载 ISPConfig 到 /tmp 目录下,解压包并运行脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
cd /tmp
|
||||
wget http://www.ispconfig.org/downloads/ISPConfig-3-stable.tar.gz
|
||||
@ -39,11 +39,11 @@
|
||||
cd ispconfig3_install/install
|
||||
php -q update.php
|
||||
|
||||
更新脚本会在更新时询问下面的额问题:
|
||||
更新脚本会在更新时询问下面的问题:
|
||||
|
||||
Create new ISPConfig SSL certificate (yes,no) [no]:
|
||||
|
||||
这里回答“yes”,SSL证书创建对话框就会启动。
|
||||
这里回答“yes”,SSL 证书创建对话框就会启动。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ via: http://www.faqforge.com/linux/how-to-renew-the-ispconfig-3-ssl-certificate/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Till][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,62 +1,61 @@
|
||||
五大开源社区指标追踪
|
||||
衡量开源社区的五大指标
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你决定使用指标来追踪你的免费开源的软件社区。那么问题来了:我应该去追踪哪些指标呢?
|
||||
如果你想要使用指标来追踪你的自由开源软件(FOSS)的社区。现在就面临着一个问题:我应该去追踪哪些指标呢?
|
||||
|
||||
要回答这个问题,你必须知道你需要什么信息。比如,你可能想要知道一个项目社区的可持续性。一个社区对问题的应对速度有多快。一个社区怎么吸引、维护或者流失贡献者。一旦你知道需要哪类信息,你就可以找出哪些社区活动可以提供你想要知道的内容。幸运的是,免费开源软件社区(FOSS)一些遵从开放式开发模型的项目在其软件开发仓库里留下了大量的公共数据,我们可以对这些数据进行分析,并从中收集到一些有用的数据。
|
||||
要回答这个问题,你必须知道你需要什么信息。比如,你可能想要知道一个项目社区的可持续性。一个社区对问题的应对速度有多快。一个社区怎么吸引、维护或者流失贡献者。一旦你知道需要哪类信息,你就可以找出哪些社区活动可以提供你想要知道的内容。幸运的是,自由开源软件(FOSS)遵从开放式开发模型,在其软件开发仓库里留下了大量的公共数据,我们可以对这些数据进行分析,并从中收集到一些有用的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我会介绍一些指标,从而为你的项目社区提供一个多方位的视角分析。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 社区活动 ###
|
||||
### 1. 社区活动(Activity) ###
|
||||
|
||||
一个社区的总体活动和这个社区怎样随着时间演变,是度量所有社区好坏的非常有用的指标。社区活动是评价一个社区工作量的第一印象,也可以用来追踪不同种类的活动。比如,提交次数,给人的第一印象就是跟开发工作量挂钩。通过开放的投票数我们可以大概知道提交了多少bug或者又提出了多少新特性。邮件列表的数量或者论坛帖子的数量可以让我们了解到有过多少次公开的讨论。
|
||||
一个社区的总体活动和这个社区怎样随着时间演变,是度量所有社区好坏的非常有用的指标。社区活动是评价一个社区工作量的第一印象,也可以用来追踪不同种类的活动。比如,提交次数,给人的第一印象就是跟开发工作量挂钩。通过提出的问题(tickets opened)我们可以大概知道提交了多少 bug 或者又提出了多少新特性。邮件列表中的邮件数量或者论坛帖子的数量可以让我们了解到有过多少次公开讨论。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[OpenStack活动看板][1]上面显示的项目代码提交次数和代码评审之后代码合并次数随时间变化的趋势图(周数据)
|
||||
[OpenStack 活动看板][1]上面显示的项目代码提交次数和代码评审之后代码合并次数随时间变化的趋势图(周数据)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 社区规模 ###
|
||||
### 2. 社区规模(Size) ###
|
||||
|
||||
社区的规模指的是参与到这个社区的人数,但是,基于不同形式的参与人数也有很大的差别。好消息是,通常你只对积极活跃的贡献者比较感兴趣。活跃的贡献者会在项目的仓库留下一些线索。这意味着你可以通过查看git仓库存放的代码中**author**字段来统计积极贡献代码的人数,或者通过看积极参与问题解决的人的得票数来统计活跃人数。
|
||||
社区的规模指的是参与到这个社区的人数,但是,基于不同形式的参与人数也有很大的差别。好消息是,通常你只对积极活跃的贡献者比较感兴趣。活跃的贡献者会在项目的仓库留下一些线索。这意味着你可以通过查看git仓库存放的代码中**author**字段来统计积极贡献代码的人数,或者通过看积极参与问题解决的人数来统计活跃人数。
|
||||
|
||||
所谓活跃(某些人做了某些事)可以扩展到很多方面。一种常见的跟踪活动的方式是看有多少人做了工作量相当可观的任务。比如,通常一个项目代码的贡献者是来自这个项目社区的一小部分人。了解了这一小部分人,就对核心的工作组(比如,领导这个社区的人)有一个基本的认识了。
|
||||
所谓活动(某些人做了某些事)可以扩展到很多方面。一种常见的跟踪活动的方式是看有多少人做了工作量相当可观的任务。比如,通常一个项目代码的贡献者是来自这个项目社区的一小部分人。了解了这一小部分人,就对核心的工作组(比如,领导这个社区的人)有一个基本的认识了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[Xen项目开发看板][2]上展示的该项目邮件列表上作者人数和提交人数随时间的变化趋势(每月数据)
|
||||
[Xen 项目开发看板][2]上展示的该项目邮件列表上作者人数和提交人数随时间的变化趋势(每月数据)
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 社区表现 ###
|
||||
### 3. 社区表现(Performance) ###
|
||||
|
||||
到目前为止,关注点主要集中在活动数量和贡献者数量的统计上了。你也可以分析流程还有用户的表现如何。比如,你可以测量某流程需要多久才能执行完成。解决或者关闭问题的时间可以表明一个需要及时响应的项目对新信息的应对如何,比如修复一个报告过来的 bug 或者实现一个新需求。代码评审花费的时间,即从代码修改提交到被通过的时间,可以看出更新一个提出的改变要达到社区期望的标准需要多久。
|
||||
|
||||
到目前为止,关注点主要集中在活动数量和贡献者数量的统计上了。你也可以分析流程还有用户的表现如何。比如,你可以测量某流程需要多久才能执行完成。解决或者关闭投票的时间可以表明一个需要及时响应的项目对新信息的应对如何,比如修复一个已经提出的bug或者实现一个新需求。代码评审花费的时间,即从代码修改提交到被通过的时间,可以看出更新一个提出的改变要达到社区期望的标准需要多久。
|
||||
|
||||
其他的一些指标主要与项目处理挂起的工作表现如何有关,比如新的和被关闭投票的比例,或者仍然没有关闭的代码评审的后台日志。这些参数能告诉我们像投入到解决这些问题的资源是否充足这样的一些信息。
|
||||
其他的一些指标主要与项目处理挂起的工作表现如何有关,比如新的和被关闭问题的比例,或者仍然没有完成的代码评审的队列。这些参数能告诉我们像投入到解决这些问题的资源是否充足这样的一些信息。
|
||||
|
||||
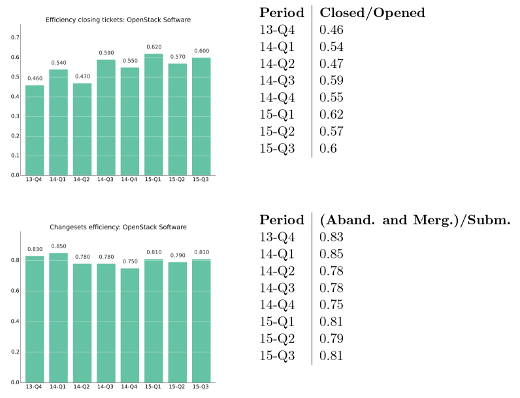
|
||||
|
||||
在[2015第三季度OpenStack开发报告][3]上显示的,每季度关闭与打开状态的投票数之比,接受与放弃的改变提案与最新的改变提案之比。
|
||||
在[2015第三季度 OpenStack 开发报告][3]上显示的,每季度关闭与打开状态的问题数之比,接受与放弃的改变提案与最新的改变提案之比。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 社区人口统计 ###
|
||||
### 4. 社区人口特征(Demographics) ###
|
||||
|
||||
随着贡献者的参与或者退出,社区也在不断改变。社区的年龄(从社区成员加入时算起)取决于随着时间变化,人们怎么加入和退出社区。[社区年龄统计图表][4]很直观的展现了这些改变随时间的变化。图标是由一系列的水平条组成,每两条水平条代表加入到社区的一代人。对于每一代,Attracted水平条表示在相应的时间里有多少人加入到了社区。Retained水平条表示有多少人目前仍然活跃在社区。
|
||||
随着贡献者的参与或者退出,社区也在不断改变。随着人们加入和退出社区,社区成员的会龄(从社区成员加入时算起)也各异。[社区会龄统计图表][4]很直观的展现了这些改变随时间的变化。图表是由一系列的水平条组成,每两条水平条代表加入到社区的一代人。对于每一代,吸引力(Attracted)水平条表示在相应的时间里有多少人加入到了社区。活跃度(Retained)水平条表示有多少人目前仍然活跃在社区。
|
||||
|
||||
代表一代人的两个水平条的关系就是滞留比例:依然在这个项目中的那一代人的一部分。Attracted水平条的完整集合表示这个项目在过去有多么受欢迎。Retained水平条的完整集合则表示社区目前的年龄结构。
|
||||
代表一代人的两个水平条的关系就是滞留比例:依然在这个项目中的那一代人的一部分。吸引力(Attracted)水平条的完整集合表示这个项目在过去有多么受欢迎。活跃度(Retained)水平条的完整集合则表示社区目前的会龄结构。
|
||||
|
||||
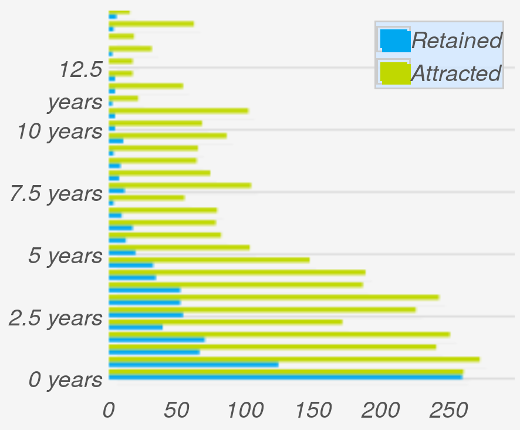
|
||||
|
||||
[Eclipse开发看板][5]上显示的Eclipse社区的社区年龄表。每六个月定义一次。
|
||||
[Eclipse 开发看板][5]上显示的 Eclipse 社区的社区年龄表。每六个月定义一次。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 社区多样性 ###
|
||||
### 5. 社区多样性(Diversity) ###
|
||||
|
||||
多样性是一个社区保持弹性的很关键的因素。通常来说,一个社区越具有多样性(人或者组织参与的多元化),那么这个社区的弹性也就越大。比如,如果一个公司要决定离开一个免费开源社区,那么这个公司的员工贡献5%要远比贡献85%所可能引起的潜在问题要小很多。
|
||||
多样性是一个社区保持弹性的很关键的因素。通常来说,一个社区越具有多样性(人或者组织参与的多元化),那么这个社区的弹性也就越大。比如,如果一个公司要决定离开一个自由开源社区,那么这个公司的员工贡献5%要远比贡献85%所可能引起的潜在问题要小很多。
|
||||
|
||||
[小马因素][6],是[Daniel Gruno][7] 为“最少的开发者贡献了50%的代码提交量”这一现象定义的术语。基于这一小马因素,大象因素则是指最少量的公司其员工贡献了50%的代码提交量。这两个数据提供了一种指示,即这个社区依赖多少人或者公司。
|
||||
[小马因素(Pony Factor)][6],是 [Daniel Gruno][7] 为“最少的开发者贡献了50%的代码提交量”这一现象定义的术语。基于小马因素,大象因素(Elephant Factor)则是指最少量的公司其员工贡献了50%的代码提交量。这两个数据提供了一种指示,即这个社区依赖多少人或者公司。
|
||||
|
||||
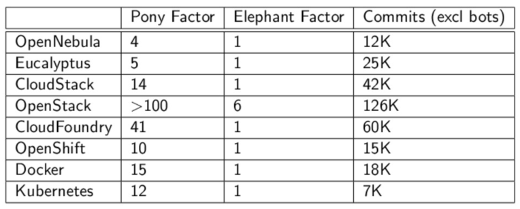
|
||||
|
||||
[2015开发云数量状态统计][8]显示的在云计算领域的几个免费开源社区项目的小马和大象因素。
|
||||
[2015开发云数量状态统计][8]显示的在云计算领域的几个自由开源社区项目的小马和大象因素。
|
||||
|
||||
还有许多其他的指标来衡量一个社区。在决定收集哪些指标时,可以考虑一下社区的目标,还有哪些指标能帮到你。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,7 +65,7 @@ via: https://opensource.com/business/15/12/top-5-open-source-community-metrics-t
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jesus M. Gonzalez-Barahona][a]
|
||||
译者:[sonofelice](https://github.com/sonofelice)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
||||
修复:无法与SFTP服务器建立FTP连接
|
||||
错误:无法与 SFTP 服务器建立 FTP 连接
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
### 问题 ###
|
||||
|
||||
有一天我要连接到我的web服务器。我使用[FileZilla][1]连接到FTP服务器。当我输入主机名和密码后来连接服务器后,我得到了下面的错误。
|
||||
有一天我要连接到我的 web 服务器。我使用 [FileZilla][1] 连接到 FTP 服务器。当我输入主机名和密码连接服务器后,我得到了下面的错误。
|
||||
|
||||
> Error: Cannot establish FTP connection to an SFTP server. Please select proper protocol.
|
||||
>
|
||||
@ -12,25 +13,25 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 原因 ###
|
||||
|
||||
看见错误信息后我意识到了我的错误。我尝试与一台SFTP服务器建立一个[FTP][2]连接。很明显我没有使用一个正确的协议(应该是SFTP而不是FTP)。
|
||||
看见错误信息后我意识到了我的错误是什么。我尝试与一台 **SFTP** 服务器建立一个 **[FTP][2]** 连接。很明显我没有使用一个正确的协议(应该是SFTP而不是FTP)。
|
||||
|
||||
如你在上图所见,FileZilla默认使用的是FTP协议。
|
||||
如你在上图所见,FileZilla 默认使用的是FTP协议。
|
||||
|
||||
### 解决“Cannot establish FTP connection to an SFTP server”的方案 ###
|
||||
### 解决 “Cannot establish FTP connection to an SFTP server” 的方案 ###
|
||||
|
||||
解决方案很简单。使用SFTP协议而不是FTP。一个你或许要面对的问题是把协议修改成SFTP。这就是我要帮助你的。
|
||||
解决方案很简单。使用 SFTP 协议而不是 FTP。你要做的就是把协议修改成 SFTP。这就是我要告诉你的。
|
||||
|
||||
再FileZilla菜单中,进入 **文件->站点管理**.
|
||||
在 FileZilla 菜单中,进入 **文件->站点管理**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在站点管理中,进入通用选项并选择SFTP协议。同样填上主机、端口号、用户密码等。
|
||||
在站点管理中,进入通用选项并选择 SFTP 协议。同样填上主机、端口号、用户密码等。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我希望你从这里可以开始处理。
|
||||
我希望你从这里可以开始工作了。
|
||||
|
||||
我希望本篇教程可以帮助你修复“Cannot establish FTP connection to an SFTP server. Please select proper protocol.”这个问题。在相关的文章中,你可以读[了解在Linux中如何设置FTP][4]。
|
||||
我希望本篇教程可以帮助你修复 “Cannot establish FTP connection to an SFTP server. Please select proper protocol.”这个问题。在相关的文章中,你可以读[了解在 Linux 中如何设置 FTP][4]。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,7 +39,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/fix-establish-ftp-connection-sftp-server/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
如何在 Linux 中根据国家位置来阻断网络流量
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
作为一名维护 Linux 生产服务器的系统管理员,你可能会遇到这样一些情形:你需要**根据地理位置,选择性地阻断或允许网络流量通过。** 例如你正经历一次由注册在某个特定国家的 IP 发起的 DoS 攻击;或者基于安全考虑,你想阻止来自未知国家的 SSH 登录请求;又或者你的公司对某些在线视频有分销权,它要求只能在特定的国家内合法发行;抑或是由于公司的政策,你需要阻止某个本地主机将文件上传至任意一个非美国的远程云端存储。
|
||||
|
||||
所有的上述情形都需要设置防火墙,使之具有**基于国家位置过滤流量**的功能。有几个方法可以做到这一点,其中之一是你可以使用 TCP wrappers 来为某个应用(例如 SSH,NFS, httpd)设置条件阻塞。但其缺点是你想要保护的那个应用必须以支持 TCP wrappers 的方式构建。另外,TCP wrappers 并不总是能够在各个平台中获取到(例如,Arch Linux [放弃了][2]对它的支持)。另一种方式是结合基于国家的 GeoIP 信息,设置 [ipset][3],并将它应用到 iptables 的规则中。后一种方式看起来更有希望一些,因为基于 iptables 的过滤器是与应用无关的,且容易设置。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我将展示 **另一个基于 iptables 的 GeoIP 过滤器,它由 xtables-addons 来实现**。对于那些不熟悉它的人来说, xtables-addons 是用于 netfilter/iptables 的一系列扩展。一个包含在 xtables-addons 中的名为 xt\_geoip 的模块扩展了 netfilter/iptables 的功能,使得它可以根据流量来自或流向的国家来进行过滤,IP 掩蔽(NAT)或丢包。若你想使用 xt\_geoip,你不必重新编译内核或 iptables,你只需要使用当前的内核构建环境(/lib/modules/\`uname -r`/build)以模块的形式构建 xtables-addons。同时也不需要进行重启。只要你构建并安装了 xtables-addons , xt\_geoip 便能够配合 iptables 使用。
|
||||
|
||||
至于 xt\_geoip 和 ipset 之间的比较,[xtables-addons 的官方网站][3] 上是这么说的: 相比于 ipset,xt\_geoip 在内存占用上更胜一筹,但对于匹配速度,基于哈希的 ipset 可能更有优势。
|
||||
|
||||
在教程的余下部分,我将展示**如何使用 iptables/xt\_geoip 来根据流量的来源地或流入的国家阻断网络流量**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 中安装 xtables-addons ###
|
||||
|
||||
下面介绍如何在各种 Linux 平台中编译和安装 xtables-addons。
|
||||
|
||||
为了编译 xtables-addons,首先你需要安装一些依赖软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Debian,Ubuntu 或 Linux Mint 中安装依赖 ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install iptables-dev xtables-addons-common libtext-csv-xs-perl pkg-config
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 CentOS,RHEL 或 Fedora 中安装依赖 ####
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS/RHEL 6 需要事先设置好 EPEL 仓库(为 perl-Text-CSV\_XS 所需要)。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install gcc-c++ make automake kernel-devel-`uname -r` wget unzip iptables-devel perl-Text-CSV_XS
|
||||
|
||||
#### 编译并安装 xtables-addons ####
|
||||
|
||||
从 `xtables-addons` 的[官方网站][4] 下载源码包,然后按照下面的指令编译安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/xtables-addons/Xtables-addons/xtables-addons-2.10.tar.xz
|
||||
$ tar xf xtables-addons-2.10.tar.xz
|
||||
$ cd xtables-addons-2.10
|
||||
$ ./configure
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
需要注意的是,对于基于红帽的系统(CentOS、RHEL、Fedora),它们默认开启了 SELinux,所以有必要像下面这样调整 SELinux 的策略。否则,SELinux 将阻止 iptables 加载 xt\_geoip 模块。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chcon -vR --user=system_u /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/extra/*.ko
|
||||
$ sudo chcon -vR --type=lib_t /lib64/xtables/*.so
|
||||
|
||||
### 为 xtables-addons 安装 GeoIP 数据库 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下一步是安装 GeoIP 数据库,它将被 xt\_geoip 用来查询 IP 地址与国家地区之间的对应关系。方便的是,`xtables-addons` 的源码包中带有两个帮助脚本,它们被用来从 MaxMind 下载 GeoIP 数据库并将它转化为 xt\_geoip 可识别的二进制形式文件;它们可以在源码包中的 geoip 目录下找到。请遵循下面的指导来在你的系统中构建和安装 GeoIP 数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd geoip
|
||||
$ ./xt_geoip_dl
|
||||
$ ./xt_geoip_build GeoIPCountryWhois.csv
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/share/xt_geoip
|
||||
$ sudo cp -r {BE,LE} /usr/share/xt_geoip
|
||||
|
||||
根据 [MaxMind][5] 的说明,他们的 GeoIP 数据库能够以 99.8% 的准确率识别出 ip 所对应的国家,并且每月这个数据库将进行更新。为了使得本地安装的 GeoIP 数据是最新的,或许你需要设置一个按月执行的 [cron job][6] 来时常更新你本地的 GeoIP 数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
### 阻断来自或流向某个国家的网络流量 ###
|
||||
|
||||
一旦 xt\_geoip 模块和 GeoIP 数据库安装好后,你就可以在 iptabels 命令中使用 geoip 的匹配选项。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -m geoip --src-cc country[,country...] --dst-cc country[,country...]
|
||||
|
||||
你想要阻断流量的那些国家是使用[2个字母的 ISO3166 代码][7] 来特别指定的(例如 US(美国)、CN(中国)、IN(印度)、FR(法国))。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,假如你想阻断来自也门(YE) 和 赞比亚(ZM)的流量,下面的 iptabels 命令便可以达到此目的。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -I INPUT -m geoip --src-cc YE,ZM -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
假如你想阻断流向中国(CN) 的流量,可以运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -A OUTPUT -m geoip --dst-cc CN -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
匹配条件也可以通过在 `--src-cc` 或 `--dst-cc` 选项前加 `!` 来达到相反的目的:
|
||||
|
||||
假如你想在你的服务器上阻断来自所有非美国的流量,可以运行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -I INPUT -m geoip ! --src-cc US -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
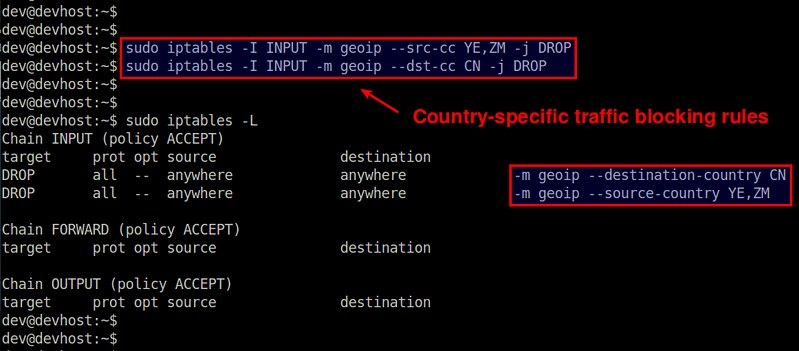
|
||||
|
||||
#### 对于使用 Firewall-cmd 的用户 ####
|
||||
|
||||
某些发行版本例如 CentOS/RHEL7 或 Fedora 已经用 firewalld 替代了 iptables 来作为默认的防火墙服务。在这些系统中,你可以类似使用 xt\_geoip 那样,使用 firewall-cmd 来阻断流量。利用 firewall-cmd 命令,上面的三个例子可被重新写为:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter INPUT 0 -m geoip --src-cc YE,ZM -j DROP
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter OUTPUT 0 -m geoip --dst-cc CN -j DROP
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --direct --add-rule ipv4 filter INPUT 0 -m geoip ! --src-cc US -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我展示了使用 iptables/xt\_geoip 来根据流量的来源地或流入的国家轻松地阻断网络流量。假如你有这方面的需求,把它部署到你的防火墙系统中可以使之成为一个实用的办法。作为最后的警告,我应该提醒你的是:在你的服务器上通过基于 GeoIP 的流量过滤来禁止特定国家的流量并不总是万无一失的。GeoIP 数据库本身就不是很准确或齐全,且流量的来源或目的地可以轻易地通过使用 VPN、Tor 或其他任意易受攻击的中继主机来达到欺骗的目的。基于地理位置的过滤器甚至可能会阻止本不该阻止的合法网络流量。在你决定把它部署到你的生产环境之前请仔细考虑这个限制。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/block-network-traffic-by-country-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:https://www.archlinux.org/news/dropping-tcp_wrappers-support/
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/block-unwanted-ip-addresses-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xtables-addons.sourceforge.net/geoip.php
|
||||
[4]:http://xtables-addons.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[5]:https://support.maxmind.com/geoip-faq/geoip2-and-geoip-legacy-databases/how-accurate-are-your-geoip2-and-geoip-legacy-databases/
|
||||
[6]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/add-cron-job-linux.html
|
||||
[7]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISO_3166-1
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
如何在 CentOS / RHEL 上设置 SSH 免密码登录
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
作为系统管理员,你计划在 Linux 上使用 OpenSSH,完成日常工作的自动化,比如文件传输、备份数据库转储文件到另一台服务器等。为实现该目标,你需要从主机 A 能自动登录到主机 B。自动登录也就是说,要在 shell 脚本中使用ssh,而无需要输入任何密码。
|
||||
|
||||
本文会告诉你怎样在 CentOS/RHEL 上设置 SSH 免密码登录。自动登录配置好以后,你可以通过它使用 SSH (Secure Shell)和安全复制 (SCP)来移动文件。
|
||||
|
||||
SSH 是开源的,是用于远程登录的最为可靠的网络协议。系统管理员用它来执行命令,以及通过 SCP 协议在网络上向另一台电脑传输文件。
|
||||
|
||||
通过配置 SSH 免密码登录,你可以享受到如下的便利:
|
||||
|
||||
- 用脚本实现日常工作的自动化。
|
||||
- 增强 Linux 服务器的安全性。这是防范虚拟专用服务器(VPS)遭受暴力破解攻击的一个推荐的方法,SSH 密钥单凭暴力破解是几乎不可攻破的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 ssh-keygen ###
|
||||
|
||||
ssh-keygen 是一个用来生成、创建和管理 SSH 认证用的公私钥的工具。通过 ssh-keygen 命令,用户可以创建支持SSH1 和 SSH2 两个协议的密钥。ssh-keygen 为 SSH1 协议创建 RSA 密钥,SSH2 则可以是 RSA 或 DSA。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 ssh-copy-id ###
|
||||
|
||||
ssh-copy-id 是用来将本地公钥拷贝到远程的 authorized_keys 文件的脚本命令,它还会将身份标识文件追加到远程机器的 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys 文件中,并给远程主机的用户主目录适当的的权限。
|
||||
|
||||
### SSH 密钥 ###
|
||||
|
||||
SSH 密钥为登录 Linux 服务器提供了更好且安全的机制。运行 ssh-keygen 后,将会生成公私密钥对。你可以将公钥放置到任意服务器,从持有私钥的客户端连接到服务器的时,会用它来解锁。两者匹配时,系统无需密码就能解除锁定。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 CentOS 和 RHEL 上设置免密码登录 SSH ###
|
||||
|
||||
以下步骤在 CentOS 5/6/7、RHEL 5/6/7 和 Oracle Linux 6/7 上测试通过。
|
||||
|
||||
节点1 : 192.168.0.9
|
||||
节点2 : 192.168.l.10
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤1 : ####
|
||||
|
||||
测试节点1到节点2的连接和访问:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@node1 ~]# ssh root@192.168.0.10
|
||||
The authenticity of host '192.168.0.10 (192.168.0.10)' can't be established.
|
||||
RSA key fingerprint is 6d:8f:63:9b:3b:63:e1:72:b3:06:a4:e4:f4:37:21:42.
|
||||
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
|
||||
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.0.10' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
|
||||
root@192.168.0.10's password:
|
||||
Last login: Thu Dec 10 22:04:55 2015 from 192.168.0.1
|
||||
[root@node2 ~]#
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤二: ####
|
||||
|
||||
使用 ssh-key-gen 命令生成公钥和私钥,这里要注意的是可以对私钥进行加密保护以增强安全性。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@node1 ~]# ssh-keygen
|
||||
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
|
||||
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
|
||||
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
|
||||
Enter same passphrase again:
|
||||
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
|
||||
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
|
||||
The key fingerprint is:
|
||||
b4:51:7e:1e:52:61:cd:fb:b2:98:4b:ad:a1:8b:31:6d root@node1.ehowstuff.local
|
||||
The key's randomart image is:
|
||||
+--[ RSA 2048]----+
|
||||
| . ++ |
|
||||
| o o o |
|
||||
| o o o . |
|
||||
| . o + .. |
|
||||
| S . . |
|
||||
| . .. .|
|
||||
| o E oo.o |
|
||||
| = ooo. |
|
||||
| . o.o. |
|
||||
+-----------------+
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤三: ####
|
||||
|
||||
用 ssh-copy-id 命令将公钥复制或上传到远程主机,并将身份标识文件追加到节点2的 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys 中:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@node1 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub 192.168.0.10
|
||||
root@192.168.0.10's password:
|
||||
Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '192.168.0.10'", and check in:
|
||||
|
||||
.ssh/authorized_keys
|
||||
|
||||
to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤四: ####
|
||||
|
||||
验证免密码 SSH 登录节点2:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@node1 ~]# ssh root@192.168.0.10
|
||||
Last login: Sun Dec 13 14:03:20 2015 from www.ehowstuff.local
|
||||
|
||||
我希望这篇文章能帮助到你,为你提供 SSH 免密码登录 CentOS / RHEL 的基本认知和快速指南。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ehowstuff.com/ssh-login-without-password-centos/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[skytech][a]
|
||||
译者:[fw8899](https://github.com/fw8899)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ehowstuff.com/author/skytech/
|
||||
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Glances 是一个跨平台、基于命令行、文本模式的系统监控工具。它是用 Python 编写的,使用 `psutil` 库从系统获取信息。你可以用它来监控 CPU、平均负载、内存、网络接口、磁盘 I/O,文件系统空间利用率、挂载的设备、所有活动进程以及消耗资源最多的进程。Glances 有很多有趣的选项。它的主要特性之一是可以在配置文件中设置阀值(careful[小心]、warning[警告]、critical[致命]),然后它会用不同颜色显示信息以表明系统的瓶颈。
|
||||
Glances 是一个用于监控系统的跨平台、基于文本模式的命令行工具。它是用 Python 编写的,使用 `psutil` 库从系统获取信息。你可以用它来监控 CPU、平均负载、内存、网络接口、磁盘 I/O,文件系统空间利用率、挂载的设备、所有活动进程以及消耗资源最多的进程。Glances 有很多有趣的选项。它的主要特性之一是可以在配置文件中设置阀值(careful[小心]、warning[警告]、critical[致命]),然后它会用不同颜色显示信息以表明系统的瓶颈。
|
||||
|
||||
### Glances 的功能
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,11 +18,11 @@ Glances 是一个跨平台、基于命令行、文本模式的系统监控工具
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 Glances
|
||||
|
||||
Glances 在 Ubuntu 的软件源中,所以安装很简单。执行下面的命令安装 Glances:
|
||||
Glances 在 Ubuntu 的软件仓库中,所以安装很简单。执行下面的命令安装 Glances:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install glances
|
||||
|
||||
(LCTT 译注:若安装后无法正常使用,可考虑使用 pip 安装/升级glances:`sudo pip install --upgrade glances`)
|
||||
(LCTT 译注:若安装后无法正常使用,可考虑使用 pip 安装/升级 glances:`sudo pip install --upgrade glances`)
|
||||
|
||||
### Glances 使用方法
|
||||
|
||||
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ Glances 在 Ubuntu 的软件源中,所以安装很简单。执行下面的命
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要退出 Glances 终端,按 ESC 键或 “Ctrl + C”。
|
||||
要退出 Glances 终端,按 ESC 键或 `Ctrl + C`。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,时间间隔(LCTT 译注:显示数据刷新的时间间隔)是 1s,不过你可以在从终端启动 Glances 时自定义时间间隔。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,10 +46,10 @@ Glances 在 Ubuntu 的软件源中,所以安装很简单。执行下面的命
|
||||
|
||||
Glances 中不同颜色的含义:
|
||||
|
||||
- `绿色`:正常
|
||||
- `蓝色`:需要注意
|
||||
- `紫色`:警告
|
||||
- `红色`:严重
|
||||
- `绿色`:正常(OK)
|
||||
- `蓝色`:小心(careful)
|
||||
- `紫色`:警告(warning)
|
||||
- `红色`:致命(critical)
|
||||
|
||||
默认设置下,Glances 的阀值设置是:careful=50,warning=70,critical=90。你可以通过 “/etc/glances/” 目录下的默认配置文件 glances.conf 来自定义这些阀值。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/glances-monitor-system-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Hitesh Jethva][a]
|
||||
译者:[bianjp](https://github.com/bianjp)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,15 +1,16 @@
|
||||
使用Nmon监控Linux的系统性能
|
||||
使用 Nmon 监控 Linux 的系统性能
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Nmon(得名于Nigel's的监控器)是IBM的员工Nigel Griffiths为AIX和Linux系统开发的一款计算机性能系统监控工具。Nmon可以把操作系统的统计数据展示在屏幕上或者存储到一份数据文件里,来帮助理解计算机资源的使用情况、调整选项和系统瓶颈。这个系统基准测试工具只需要使用一条命令就能得到大量重要的性能数据。使用Nmon可以很轻松的监控系统的CPU、内存、网络、硬盘、文件系统、NFS、高耗进程、资源和微分区功率的信息。
|
||||
Nmon(得名于 Nigel 的监控器)是IBM的员工 Nigel Griffiths 为 AIX 和 Linux 系统开发的一款计算机性能系统监控工具。Nmon 可以把操作系统的统计数据展示在屏幕上或者存储到一份数据文件里,来帮助了解计算机资源的使用情况、调整方向和系统瓶颈。这个系统基准测试工具只需要使用一条命令就能得到大量重要的性能数据。使用 Nmon 可以很轻松的监控系统的 CPU、内存、网络、硬盘、文件系统、NFS、高耗进程、资源和 IBM Power 系统的微分区的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### Nmon 安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Nmon默认是存在于Ubuntu的仓库中的。你可以通过下面的命令安装Nmon:
|
||||
Nmon 默认是存在于 Ubuntu 的仓库中的。你可以通过下面的命令安装 Nmon:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install nmon
|
||||
|
||||
怎么使用Nmon来监控Linux的性能
|
||||
安装完成后,通过在终端输入`nmon` 命令来启动Nmon
|
||||
### 怎么使用Nmon来监控Linux的性能 ###
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,通过在终端输入`nmon` 命令来启动 Nmon
|
||||
|
||||
nmon
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,25 +18,24 @@ Nmon默认是存在于Ubuntu的仓库中的。你可以通过下面的命令安
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
从上面的截图可以看到nmon命令行工具完全是交互式运行的,你可以使用快捷键来轻松查看对应的统计数据。
|
||||
你可以使用下面的nmon快捷键来显示不同的系统统计数据:
|
||||
从上面的截图可以看到 nmon 命令行工具完全是交互式运行的,你可以使用快捷键来轻松查看对应的统计数据。你可以使用下面的 nmon 快捷键来显示不同的系统统计数据:
|
||||
|
||||
- `q` : 停止或编辑Nmon
|
||||
- `q` : 停止并退出 Nmon
|
||||
- `h` : 查看帮助
|
||||
- `c` : 查看CPU统计数据
|
||||
- `c` : 查看 CPU 统计数据
|
||||
- `m` : 查看内存统计数据
|
||||
- `d` : 查看硬盘统计数据
|
||||
- `k` : 查看内核统计数据
|
||||
- `n` : 查看网络统计数据
|
||||
- `N` : 查看NFS统计数据
|
||||
- `N` : 查看 NFS 统计数据
|
||||
- `j` : 查看文件系统统计数据
|
||||
- `t` : 查看高耗进程
|
||||
- `V` : 查看虚拟内存统计数据
|
||||
- `v` : 详细模式
|
||||
|
||||
### 核查CPU处理器 ###
|
||||
### 核查 CPU 处理器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想收集关于CPU性能相关的统计数据,你应该按下键盘上的`c`键,之后你将会看到下面的输出:
|
||||
如果你想收集关于 CPU 性能相关的统计数据,你应该按下键盘上的`c`键,之后你将会看到下面的输出:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ Nmon默认是存在于Ubuntu的仓库中的。你可以通过下面的命令安
|
||||
|
||||
### 核查网络统计数据 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果想收集Linux系统网络统计数据,按下`n`键,你将会看到下面输出:
|
||||
如果想收集 Linux 系统的网络统计数据,按下`n`键,你将会看到下面输出:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -59,19 +59,19 @@ Nmon默认是存在于Ubuntu的仓库中的。你可以通过下面的命令安
|
||||
|
||||
### 核查内核信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Nmon一个非常重要的快捷键是`k`键,用来显示系统内核相关的概要信息。按下`k`键之后,会看到下面输出:
|
||||
Nmon 一个非常重要的快捷键是`k`键,用来显示系统内核相关的概要信息。按下`k`键之后,会看到下面输出:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 获取系统信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
对每个系统管理员来说一个非常有用的快捷键是`r`键,可以用来显示计算机系统结构、操作系统版本号和CPU等不同资源的信息。按下`r`键之后会看到下面输出:
|
||||
对每个系统管理员来说一个非常有用的快捷键是`r`键,可以用来显示计算机的系统结构、操作系统版本号和 CPU 等不同资源的信息。按下`r`键之后会看到下面输出:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
还有许多其他的工具实现的功能和Nmon一样,不过Nmon对一个Linux新手来说还是很友好的。如果你有什么问题,尽管评论。
|
||||
还有许多其他的工具做的和 Nmon 同样的工作,不过 Nmon 对一个 Linux 新手来说还是很友好的。如果你有什么问题,尽管评论。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/monitor-linux-system-performance/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Hitesh Jethva][a]
|
||||
译者:[sonofelice](https://github.com/sonofelice)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
||||
2015年 Linux 世界的十个大事件
|
||||
======================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2015年已经过去,我在这里(It's FOSS)发表《2015年的大事件》系列。这个系列的第一篇文章为《2015年 Linux 世界的十个大事件》。这些事件在 Linux 世界中产生了极大的影响,无论它们是积极的还是消极的。
|
||||
|
||||
我总结了2015发生的十件产生了最大影响的事件。让我们来看看:
|
||||
|
||||
### 2015年度十大 Linux /开源相关事件
|
||||
|
||||
补充一句,以下这些事件没有按照时间顺序排列。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 微软与 Linux 的结盟
|
||||
|
||||
在9月下旬,所有人听到[微软构建了自己的 Linux 发行版][1]这个消息时都大吃一惊。其在后来被揭露,这其实是一个微软开发的用于它的 Azure cloud switches 的[软件][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
但故事还没结束。微软真的与 Canonical(Ubuntu Linux 的母公司)达成合作来开发 [HDInsight][3],这是微软在 Azure 上构建的 Hadoop 大数据服务。 Ubuntu 是[微软在其上部署应用][4]的第一个 Linux 系统。
|
||||
|
||||
微软会继续保持它与 Linux 的关系吗? 还是在使用 Linux 达到其目的(Azure)就会收手?只有时间能告诉我们一切。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 微软发布适用于 Linux 的 Visual Studio Code
|
||||
|
||||
在微软发布 Linux 发行版引起喧嚣之前,微软扔下了另一枚炸弹——发布 [Linux 版 Visual Studio Code][27], 与其一并发布的还有 Windows 版以及 OS X 版。尽管 Visual Studio Code 并不是开源的,从某种意义上讲,发布 Linux 版本仍然是 Linux 用户的胜利。(LCTT 译注:此处原文消息有误,[Visual Studio Code 已开源][28]。)无论如何,Linus Torvalds 曾说过一句很著名的话:“如果微软给 Linux 开发过一款应用的话,这就意味着我已经赢了”。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以看这个教程来学习[如何在 Ubuntu 中安装 Visual Studio Code][5]。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 苹果公司开源编程语言 Swift
|
||||
|
||||
在向 Linux 及开源“示爱”方面,苹果公司也不甘示弱。苹果用来制作 iOS 应用的首选编程语言 Swift,[现已开源][6]并移植到 Linux 中。虽然其还在测试中,但你已经可以轻易地[在 Ubuntu 中安装 Swift][7]。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,苹果就是苹果,它[开始吹嘘][8]其为“第一个视开源开发为公司关键的软件开发策略的计算机公司巨头(原文如此)”。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu 手机终于发布
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 手机终于在今年年初发布。因其早期使用者及开发者,Ubuntu 深受 Ubuntu 社区喜爱。主流智能机用户仍然回避它,主要是[因为该系统还在重度开发中][9]。对于 Ubuntu 手机的问世,2016年将成为决定性的一年。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Jolla 遭受经济危机
|
||||
|
||||
Jolla 是 Sailfish OS 这个基于 Linux 的智能手机系统的幕后公司,它遭受了严重的财政困难。这导致了[一半的Jolla 员工被裁][10]。
|
||||
|
||||
Jolla 在2014年针对它的平板电脑完成了一次非常[成功的众筹][11],显然,他们将大部分预算都花在了 Sailfish OS 的开发上,而在主要投资者退出后,公司正在挣扎以求生存。
|
||||
|
||||
不过有一个好消息,Jolla 成功拿到了一些雄厚的资金,而且他们[已经继续运营了][12]。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Firefox OS 已死
|
||||
|
||||
作为安卓的开源替代品,Mozila 的移动操作系统 Firefox OS 在去年底慢性死亡。本打算在发展中国家售卖低至25美金的智能手机,可基于 Firefox OS 的手机却一直没有流行起来。我认为主要原因是它的硬件配置不高,以及它缺少流行应用。
|
||||
|
||||
在十二月,[Mozilla 宣布][13]其将停止开发 Firefox OS,并停止出售 Firefox 智能手机。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然没有正式宣布过,我认为 [Tizen][14],这个 Linux 基金会旗下的基于 Linux 的移动操作系统,也已经消失了。我没有看到任何关于 Tizen 开发的消息,而且 Linux 基金会从未推动过它的开发。Tizen 何时死亡只是一个时间问题。(LCTT 译注:此处原文消息有误,[Tizen 在2015年发布了 3.0 版本][29]。)
|
||||
|
||||
#### “Ubuntu 家族”内讧
|
||||
|
||||
五月份时,Kubuntu 项目的领导者 Jonathan Riddell [被 Ubuntu 社区委员会强制要求下台][15],这引起了很多激烈的讨论。Jonathan 曾质问 Ubuntu 所收捐款的使用情况,他抱怨 Kubuntu 从未见到过这些钱。
|
||||
|
||||
这导致了两方的互相谴责。最终。Ubuntu 的大老板,[Mark Shuttleworth 要求 Jonathan 下台][16]。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 女性 Linux 内核开发者因“野蛮的沟通方式”而退出
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 之父 Linus Torvalds 以其粗俗的语言而著称。Linux 内核开发者 [Sarah Sharp][17] 也因为嘴快心直而闻名。
|
||||
|
||||
Sarah Sharp 曾在2013年与 Linus Torvalds 公开争执,[建议 Linus 将“语言暴力”赶出邮件列表][18]。但 Linus 也没有[委婉地][19]回复她。
|
||||
|
||||
那是在2013年。2015年,Sarah 宣布她正在[逐步停止她在内核社区的工作][20],因为他们的交流方式缺乏基本礼仪,并且野蛮而充满亵渎。
|
||||
|
||||
这一举动让人们开始讨论 Linux 内核社区是否真的应该改变他们的行为方式,还是 Sarah 做的太过分了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Unity 游戏编辑器移植到 Linux平台
|
||||
|
||||
尽管[在 Linux 上玩游戏][21]仍是 Linux 用户们的阿克琉斯之踵,而在游戏引擎 Unity 宣布其正在测试[Linux 下的游戏编辑器][22]时整个社区都沸腾了。因为在渲染图像时,Linux 是一个最流行的选择,所以我们推测这将使游戏开发者向 Linux 靠拢。不过,Unity 是否真的会推出一个最终版本的游戏编辑器,这个问题还未被证实。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 政府机构采用开源软件
|
||||
|
||||
欧洲数个城市的管理机构决定[抛弃先前的软件][23],并使用其开源的替代品。大多数城市管理机构将 Microsoft Office 替换为 LibreOffice 或 OpenOffice. 一些城市管理机构和[公立学校][24]也在跟进,将 Microsoft Windows 换成 Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
对于这一行为,削减成本是一个重要的因素,因为城市管理机构通过采用开源软件省下了无数欧元。
|
||||
|
||||
大学也并没有在采用开源软件的道路上落后。这一年,我们听到了[大学如何抛弃 Photoshop 改用 Krita][25] 以及[大学使用开源 Office 软件][26]的消息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
与其他年一样,2015年同样有许多令 Linux 爱好者感到积极或消极的时刻。我们看到 Linux 的竞争者,如微软和苹果,向 Linux 靠拢,政府机构采用开源软件。同时,我们还见证了 Firefox 智能手机系统的失败。我想说,这真是喜忧参半的一年。
|
||||
|
||||
你认为呢?我希望你们分享你所认为对于 Linuxer 们来说最重要的新闻,和你们对这一年的整体感受。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/biggest-linux-stories-2015/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[StdioA](https://github.com/StdioA)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]: https://linux.cn/article-6269-1.html
|
||||
[2]: http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2015/09/microsoft-has-built-software-but-not-a-linux-distribution-for-its-software-switches/
|
||||
[3]: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/hdinsight/
|
||||
[4]: http://www.zdnet.com/article/microsoft-deploys-first-major-server-application-on-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
[5]: https://linux.cn/article-5423-1.html
|
||||
[6]: https://linux.cn/article-6689-1.html
|
||||
[7]: https://linux.cn/article-6781-1.html
|
||||
[8]: https://business.facebook.com/itsfoss/photos/pb.115098615297581.-2207520000.1450817108./634288916711879/?type=3&theater
|
||||
[9]: http://www.engadget.com/2015/07/24/ubuntu-phone-review/
|
||||
[10]: https://linux.cn/article-6621-1.html
|
||||
[11]: https://www.indiegogo.com/projects/jolla-tablet-world-s-first-crowdsourced-tablet#/
|
||||
[12]: https://linux.cn/article-6757-1.html
|
||||
[13]: https://linux.cn/article-6800-1.html
|
||||
[14]: https://www.tizen.org/
|
||||
[15]: https://linux.cn/article-5529-1.html
|
||||
[16]: http://www.cio.com/article/2926838/linux/mark-shuttleworth-ubuntu-community-council-ask-kubuntu-developer-to-step-down-as-leader.html
|
||||
[17]: http://sarah.thesharps.us/
|
||||
[18]: http://www.techeye.net/chips/linus-torvalds-and-intel-woman-in-sweary-spat
|
||||
[19]: http://marc.info/?l=linux-kernel&m=137392506516022&w=2
|
||||
[20]: https://linux.cn/article-6361-1.html
|
||||
[21]: https://linux.cn/article-6258-1.html
|
||||
[22]: http://itsfoss.com/unity-gaming-engine-linux/
|
||||
[23]: https://linux.cn/article-6459-1.html
|
||||
[24]: http://itsfoss.com/spanish-school-ditches-windows-ubuntu/
|
||||
[25]: http://itsfoss.com/french-university-dumps-adobe-photoshop-open-source-app-krita/
|
||||
[26]: http://itsfoss.com/hungarian-universities-switch-eurooffice/
|
||||
[27]: https://linux.cn/article-5376-1.html
|
||||
[28]: https://linux.cn/article-6604-1.html
|
||||
[29]: https://linux.cn/article-6261-1.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
|
||||
哪个文件系统最适合你的 Linux 系统?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
文件系统: 它们不是世界上最激动人心的技术,但是仍然很重要。本文我们将细数那些流行的 Linux 文件系统 - 它们是什么,它们能够做什么,以及它们的目标用户。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ext4 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你曾经安装过 Linux,你可能在安装过程中看到过“Ext4”字样。用它有一个不错的理由: 它是当前每个可用的 Linux 发行版所选择的文件系统。当然,还有其他的一些选择,但是不可否认的是,Ext4(Extended 4)几乎是所有 Linux 用户都会选择的文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 它能做什么? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Ext4 拥有之前的文件系统(Ext2/Ext3)中你所期待的所有优点, 同时还带来了一些改进。还有很多内容可以发掘,这里列举出了 Ext4 为你带来的最好的部分:
|
||||
|
||||
- 日志型文件系统
|
||||
- 日志校验
|
||||
- 多重块文件分配
|
||||
- 向后兼容 Ext2 && Ext3
|
||||
- 持续的空闲空间预分配
|
||||
- 改进的文件系统校验(相比于之前的版本)
|
||||
- 当然,同时支持更大的文件
|
||||
|
||||
#### 目标用户 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Ext4 针对那些寻找超级可靠的基础环境或者那些只需要能工作就行的用户。这个文件系统不会对你的系统做快照;它甚至没有最好的 SSD 支持,但是如果你不是太挑剔的话,你会觉得它也还不错。
|
||||
|
||||
### BtrFS ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
B 树(B-tree)文件系统 (也被当做是 butterFS,黄油文件系统) 是 Oracle 为 Linux 研发的一款文件系统。它是一个全新的文件系统,而且正处于主要开发阶段。Linux 社区认为其有时候使用上还有些不稳定。BtrFS 的核心原则是围绕着写时复制(copy-on-write)原则展开的。**写时复制**基本上意味着在写入数据完成前,这份数据的每一比特都有单独的一份副本。当数据写入完毕后,相当于它做了一份副本。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 它能做什么 ####
|
||||
|
||||
除了支持写时复制之外,BtrFS 也能够胜任许多其他的事务 - 事实上,它可以一直列出各种特性。这里列举最值得一提的特性:支持只读快照、文件克隆、子卷、透明压缩、离线文件系统校验、从 ext3 & 4 原地转换到 BtrFS、在线碎片整理,还支持 RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 和 RAID 10。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 目标用户 ####
|
||||
|
||||
BtrFS 的开发者们许诺过,该文件系统是当前其他文件系统的新一代替代者。非常正确,虽然目前其处于开发中。它有很多面向高级用户的杀手级特性,对于基本用户也是这样(包括 SSD 上面的更佳性能)。这个文件系统针对那些想要从文件系统中获取更多(特性),以及那些想尝试用写时复制机制做一些事情的用户。
|
||||
|
||||
### XFS ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
由 Silicon Graphics 公司创造开发,XFS 是一个高端文件系统,定位于速度和性能方面。处于对性能方面的专注,使得在并行 IO 方面,XFS 表现的尤其出色。XFS 文件系统能够处理数量庞大的数据,事实上某些 XFS 用户的数据接近300TB 以上。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 它能做什么 ####
|
||||
|
||||
XFS 是一个经历良好测试的数据存储文件系统,它是为了高性能操作而诞生的。其特性包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- RAID 阵列的条带化分配
|
||||
- 日志型文件系统
|
||||
- 块大小可变
|
||||
- 直接 I/O
|
||||
- 指定速率(guaranteed-rate) I/O
|
||||
- 快照
|
||||
- 在线碎片整理
|
||||
- 在线调整文件系统大小
|
||||
|
||||
#### 目标用户 ####
|
||||
|
||||
XFS 针对那些想要一个坚如磐石的文件系统方案的用户。它始于1993年,并且随着时间的变迁它变得越来越好。如果你有一台家庭服务器,而且你苦恼于如何部署存储环境,那么可以考虑下 XFS。它拥有的众多特性(比如快照)能够有助于你的文件存储系统。尽管如此,它不局限于服务器端。如果你是一个相对高级一点的用户或者你对 BtrFS 所承诺的很多特性感兴趣的话,尝试一下 XFS。它实现了很多与 BtrFS 相似的特性,并且没有稳定性方面的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
### Reiser4 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Reiser4 是 ReiserFS 的继任者,由 Namesys 公司创造研发。它的诞生可以追溯到 Linspire 项目和 DARPA。它与众不同的地方在于众多的事务模式。并不止于单一的一种写入数据的方式;取而代之的是,有很多方式(来写入)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 它能做什么 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Reiser4 拥有着使用多种不同事务模式的独特能力。它能够使用写时复制模式 (像 BtrFS),任意位置写入(write-anywhere),日志,以及混合事务模式。它在 ReiserFS 的基础上做了许多的改进,包括更好的基于漫游日志的文件系统日志,对较小文件的支持更好,以及更快速的目录处理。Reiser4 提供了许多功能特性。还有更多的特性可以探讨,不过简单来讲,相比于 ReiserFS 它不但做了非常大的改进,而且增加了众多特性。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 目标用户 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Resier4 适合那些想要将一个文件系统应用到多种场景下的用户。可能你想在一台机器上使用写时复制机制,在另一台机器上使用任意位置写入机制,还会在另一台机器上使用混合事务,而你又不希望使用多种不同类型的文件系统来完成这项任务。Reiser4 是适合这种情况的完美方案。
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 上有许多可用的文件系统。每个文件系统都有其特定的用途,以便于特定用户解决不同的问题。本文的焦点集中在 Linux 平台上文件系统的主流选择。毫无疑问,其它的场景下还有一些别的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
你在 Linux 上最喜欢的文件系统是什么?在下面的评论区告诉我们吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/best-file-system-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Derrik Diener][a]
|
||||
译者:[icecoobe](https://github.com/icecoobe)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/derrikdiener/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
||||
提升 emacs 生产力的十大最佳插件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
一年前的这个时候,我想要寻找[将 Vim 打造成一个成熟的全功能的 IDE][1] 的最好插件。有趣的是,那篇文章的很多评论提到了 Emacs 已经大部分有了这些内置插件,已经是一个很棒的 IDE 了。尽管我对 Emacs 的难以置信的多样化表示赞同,它依旧不是一个可以开箱即用的高级编辑器。还好,其庞大的插件库可以解决这个问题。但在过多的选择中,有时很难弄清该如何入手。因此,现在让我试着收集一个不可或缺的插件的简短列表,来提升你使用 Emacs 时的工作效率。 虽然我主要侧重于与编程相关的生产力提升,但是这些插件对所有人或不同用途都是有用的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Ido-mode ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ido 或许是对新手最有用的一个插件,Ido 的意思是交互式工作(interactively do)。它取代了大部分的用花哨字符匹配菜单的枯燥提示。好比说,它用列出了当前目录所有文件的列表来取代了常规的打开文件提示符。输入一些字符,Ido 将尝试匹配最合适的文件。它通过可视化让你的操作变得更容易,这也是一个快速遍历所有文件都有相同前缀的文件夹的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Smex ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
它不算最著名的一个、但却是一个替代 Ido-mode 的好选择:Smex 可以优雅的替代普通的`M-x`提示符,灵感大部分来自于 Ido-mode。它也给调用`M-x`后输入的命令带来了同样的交互搜索能力。它简单而有效,是一个为常用操作提升效率的最好方法。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Auto Complete ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
知道这个插件的存在之前,我在 Emacs 里面有一半的时间花在敲击 `M-/` 来补完单词上。现在,我有一个漂亮的弹出菜单可以为我做自动补全。无须多说,我们都需要它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. YASnippet ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这是真正的程序员必备利器。总有一些代码片段会让我们觉得我们一辈子都在写它。对我来说,就是调试 PHP 时不断输入的 `var_dump(...);exit;`。经过一段时间一遍又一遍的输入`var_dump(...);exit;`,我觉得我可以预先把其做成录制好的、方便用到的代码片段。使用 YASnippets,可以很容易导入代码片段文件或者自己做个。之后,只要按下一个 tab 键,就可以将一个小的关键词扩展成一大段预先写好的代码,然后可以很方便地在里面修改。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Org-mode ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
免责声明,我最近才开始使用 Org-mode,但它已经深深的吸引了我。从我看过数以百计的文章来说,Org-mode 可以改变你的生活。它背后的想法很简单:它是一种用普通文本做简单备注的模式,可以很容易地在任务列表和各种数据中转来转去,并进行一些比如按优先级或到期日期的过滤,或设置一个重复日期。然而,虽然思路简单,但你可以做到很多,用各种方法用于各种用途。与其去看一个长长的介绍,我觉得你可以去读读[现有教程][2],有很多视频可以看,自己去体验一下 Org-mode 是多么强大。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Helm ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
一些使用者喜欢它,但是其他人没有这么大的使用热情。我是后者的一部分。但在拥有这样一个庞大的追随者的情况下,是不能不提到它的。Helm 旨在完全变换你的 Emacs 使用体验。简单来说,Helm 是一个在 Emacs 中帮助你快速找到一个文件或命令的框架。根据你的输入,它将尝试使用词语自动完成来引导你将大脑的念头变为行动。起初感觉有点奇怪,但对一些人来说,Helm 本身就是一个信仰。虽然我不是 Helm 的粉丝,我欣赏 helm-occur 这一个伟大的工具可以在一个大文档搜索字符串并且在一个单独的缓冲区显示所有匹配结果,以便很容易在它们之间跳转。如果你正在寻找一个快速演示来了解 Helm 能做什么,我推荐[这篇文章][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. ace-jump-mode ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这是另一个有一大群追随者的插件,我正在试图成为 ace-jump-mode 的粉丝。掌握这个插件,你会体验到超越鼠标感受。简单描述一下,通过你选择的快捷方式触发 ace-jump-mode 后,你会被提示输入字符。输入一个字符,所有以该字符开头的单词中的那个字符就会替换成一个唯一字符并被高亮。输入一个屏幕上的高亮字符,你的光标会直接跳转到高亮显示的那个词。我不得不承认,这让我使用它时有点反应不过来,但是,一旦你掌握它,它将显著提升你在一个文档里的移动速度。(LCTT 译注:用文字描述比较困难,如截图中,你输入的是一个“i”,然后屏幕中所有以“i”开头的单词中的那个“i”都被替换成了从 a 到 z 的字符,并高亮;你可以输入这些高亮的字符直接跳转到那个位置。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. find-file-in-project ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你喜欢 Sublime text 以及它可以用非常方便的`Ctrl-p`模糊搜索来打开一个项目中的任何文件的功能,你将会喜欢上 find-file-in-project (简称 ffip)的。使用设置指定了您的版本控制的根文件夹后,您可以轻松地调出一个很酷的文本条,通过快速扫描和搜索你的代码,来根据你输入的名称找到匹配的文件。我喜欢把它绑定到键盘上的 F6 键。如果你不知道整个目录从上到下的复杂结构,这很简单,而且非常易用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Flymake ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
对 IDE 的爱好者来说,我认为语法检查器是 IDE 最强大的特性之一,它非常适合初学者和方便了那些疲惫的程序员。感谢 Flymake,Emacs 用户也可以享受到了语法检查器。因为我工作中用 PHP 很多,Flymake 就不需要任何额外的配置。当我写代码的时候,它会自动检查我的代码和高亮任何一个包含问题的行。对于编译语言,Flymake 将寻找一个用于检查你的代码的 Makefile。真神奇。
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. electric-pair ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,但并非最不重要,在我看来,electric-pair 是最简单但最强大的插件之一。它会自动关闭你输入的括号。它起初看起来并不是很有用,但相信我,在被寻找配对括号折磨几百次之后,你会很高兴有这么一个插件,可以确保你所有的表达式的括号都是一一对应的。
|
||||
|
||||
总结一下,Emacs 是一个奇妙的工具。这可不是一个令人惊讶的说法。试试这些插件,看着你的效率直线飙升吧。这个列表当然不是详尽的列表。如果你想贡献你的建议,请在评论中这样做。我自己一直在寻找新的插件来试着发现 Emacs 的新体验。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/best-plugins-to-increase-productivity-on-emacs.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[zky001](https://github.com/zky001)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/adrien
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/turn-vim-full-fledged-ide.html
|
||||
[2]:http://orgmode.org/worg/org-tutorials/
|
||||
[3]:http://tuhdo.github.io/helm-intro.html
|
||||
236
published/201601/20151229 Grub 2--Heal your bootloader.md
Normal file
236
published/201601/20151229 Grub 2--Heal your bootloader.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
|
||||
Grub 2:拯救你的 bootloader
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**没有什么事情比 bootloader 坏掉更让气人的了。充分发挥 Grub 2 的作用,让 bootloader 安分工作吧。**
|
||||
|
||||
为什么这么说?
|
||||
|
||||
- Grub 2 是最受欢迎的 bootloader ,几乎用在所有 Linux 发行版上。
|
||||
- bootloader 是一个至关重要的软件,但是非常容易损坏。
|
||||
- Grub 2 是兼具扩展性和灵活性的一款引导加载程序,提供了大量可定制选项。
|
||||
|
||||
Grub 2 是一款精彩的功能强大的软件。它不是 bootloader 界的一枝独秀,但却最受欢迎,几乎所有主要的桌面发行版都在使用它。 Grub 的工作有两个。首先,它用一个菜单展示计算机上所有已经安装的操作系统供你选择。其次,当你从启动菜单中选择了一个 Linux 操作系统, Grub 便加载这个 Linux 的内核。
|
||||
|
||||
你知道,如果使用 Linux ,你就离不开 bootloader 。然而它却是 Linux 发行版内部最鲜为人知的部分。在这篇文章里,我们将带你熟悉 Grub 2 一些著名的特性,强化你相关技能,使你在 bootloader 跑飞的时候能够自行处理。
|
||||
|
||||
Grub 2 最重要的部分是一堆文本文件和两个脚本文件。首先需要了解的是 `/etc/default/grub` 。这是一个文本文件,你可以在里面设置通用配置变量和 Grub 2 菜单(见下方 “常见用户设置” )的其它特性。
|
||||
|
||||
Grub 2 另一个重要的部分是 `/etc/grub.d` 文件夹。定义每个菜单项的所有脚本都放置在这里。这些脚本的名称必须有两位的数字前缀。其目的是,在构建 Grub 2 菜单时定义脚本的执行顺序以及相应菜单项的顺序。文件 `00_header` 首先被读取,负责解析 `/etc/default/grub` 配置文件。然后是 Linux 内核的菜单项,位于 `10_linux` 文件中。这个脚本在默认的 `/boot` 分区为每个内核创建一个正规菜单项和一个恢复菜单项。
|
||||
|
||||
紧接着的是为第三方应用所用的脚本,如 `30_os-prober` 和 `40_custom` 。 **os-prober** 脚本为内核和其它分区里的操作系统创建菜单项。它能识别安装的 Linux、 Windows、 BSD 以及 Mac OS X 。 如果你的硬盘布局比较独特,使得 **os-prober** 无法找到已经安装的发行版,你可以在 `40_custom` 文件(见下方 “添加自定义菜单项”)中添加菜单项。
|
||||
|
||||
**Grub** 2 不需要你手动维护你的启动选项的配置文件:取而代之的是使用 `grub2-mkconfig` 命令产生 `/boot/grub/grub.cfg` 文件。这个功能会解析 `/etc/grub.d` 目录中的脚本以及 `/etc/default/grub` 设置文件来定义你的设置情况。
|
||||
|
||||
###图形化的引导修复###
|
||||
|
||||
多亏了 Boot Repair 应用,只需要点击按钮,Grub 2 许许多多的问题都能轻易解决。这个漂亮小巧的应用有一个直观的用户界面,可以扫描并识别多种硬盘布局和分区方案,还能发现并正确识别安装在其中的操作系统。这个应用可以处理传统计算机里的主引导记录(Master Boot Record) (MBR),也可以处理新型 UEFI 计算机中的 GUID 分区表(GUID Partition Table)(GPT)。
|
||||
|
||||
Boot Repair 最简单的使用方式是安装到 Live Ubuntu 会话中。在一个 bootloader 损坏的机器上启动 Ubuntu Live 发行版,先通过添加它的 PPA 版本库来安装 Boot Repair ,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yannubuntu/Boot Repair
|
||||
|
||||
然后刷新版本库列表:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
安装应用,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install -y Boot Repair
|
||||
|
||||
安装完毕后就启动应用。在显示它的界面(由一对按键组成)之前将会扫描你的硬盘。根据工具的指示,只需按下 Recommended Repair(推荐的修复)按钮,即可修复大部分坏掉的 bootloader 。修复 bootloader 之后,这个工具会输出一个短小的 URL ,你应该把它记录下来。这个 URL 包含了硬盘详尽的信息:分区信息以及重要的 Grub 2 文件(如 `/etc/default/grub` 和 `/boot/grub/grub.cfg` )的内容。如果工具不能解决 bootloader 的问题,可以把你这个 URL 共享在你的发行版的论坛上,让其他人可以分析你的硬盘布局以便给你建议。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Boot Repair 也可以让你定制 Grub 2 的选项。*
|
||||
|
||||
### Bootloader 急救 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Grub 2 引导问题会让系统处于几种不同状态。屏幕(如你所想,本该显示 bootloader 菜单的地方)所展示的文本会指示出系统的当前状态。如果系统中止于 **grub>** 提示符,表明 Grub 2 模块已经被加载,但是找不到 **grub.cfg** 文件。当前是完全版的 Grub 2 命令行 shell,你可以通过多种方式解决此问题。如果你看到的是 **grub rescue>** 提示符,表明 bootloader 不能找到 Grub 2 模块或者找不到任何引导文件( boot files )。然而,如果你的屏幕只显示 ‘GRUB’ 一词,表明 bootloader 找不到通常位于主引导记录( Master Boot Record )里的最基本的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过使用 live CD 或者在 Grub 2 shell 中修正此类错误。如果你够幸运, bootloader 出现了 **grub>** 提示符,你就能获得 Grub 2 shell 的支配权,来帮助你排错。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来几个命令工作在 **grub>** 和 **grub rescue>** 提示符下。 **set pager=1** 命令设置显示分页( pager ),防止文本在屏幕上一滚而过。你还可以使用 **ls** 命令列出 Grub 识别出的所有分区,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
grub> ls
|
||||
(hd0) (hd0,msdos5) (hd0,msdos6) (hd1,msdos1)
|
||||
|
||||
如你所见,这个命令列出分区的同时一并列出了分区表方案(即 msdos)。
|
||||
|
||||
你还可以在每个分区上面使用 **ls** 来查找你的根文件系统:
|
||||
|
||||
grub> ls (hd0,5)/
|
||||
lost+found/ var/ etc/ media/ bin/ initrd.gz
|
||||
boot/ dev/ home/ selinux/ srv/ tmp/ vmlinuz
|
||||
|
||||
你可以不写上分区名的 **msdos** 部分。同样,如果你忘记了尾部的斜杠( trailing slash )只输入 `ls (hd0,5)` ,那你将获得分区的信息,比如文件系统类型、总体大小和最后修改时间。如果你有多个分区,可以使用 `cat` 读取 `/etc/issue` 文件中的内容,来确定发行版,格式如 `cat (hd0,5)/etc/issue` 。
|
||||
|
||||
假设你在 **(hd0,5)** 中找到根文件系统,请确保它包含 `/boot/grub` 目录,以及你想引导进入的内核镜像,如 **vmlinuz-3.13.0-24-generic** 。此时输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
grub> set root=(hd0,5)
|
||||
grub> linux /boot/vmlinuz-3.13.0-24-generic root=/dev/sda5
|
||||
grub> initrd /boot/initrd.img-3.13.0-24-generic
|
||||
|
||||
第一个命令把 Grub 指向我们想引导进入的发行版所在的分区。接着第二个命令告知 Grub 内核镜像在分区中的位置,以及根文件系统的位置。最后一行设置虚拟文件系统( initial ramdisk )文件的位置。你可以使用 tab 补全功能补全内核名字和虚拟文件系统( initrd: initial ramdisk )的名字,节省时间和精力。
|
||||
|
||||
输入完毕,在下一个 **grub>** 提示符后输入 `boot` , Grub 将会引导进入指定的操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在 **grub rescue>** 提示符下,情况会有些许不同。因为 bootloader 未能够找到并加载任何必需的模块,你需要手动添加这些模块:
|
||||
|
||||
grub rescue> set root=(hd0,5)
|
||||
grub rescue> insmod (hd0,5)/boot/grub/normal.mod
|
||||
grub rescue> normal
|
||||
grub> insmod linux
|
||||
|
||||
如上所示,跟之前一样,使用 `ls` 命令列出所有分区之后,使用 `set` 命令标记起来。然后添加 **normal** 模块,此模块激活时将会恢复到标准 **grub>** 模式。如果 linux 模块没加载,接下来的命令会进行添加。如果这个模块已经加载,你可以跟之前一样,把引导加载程序指向内核镜像和虚拟文件系统( initrd )文件,然后使用 `boot` 启动发行版,完美收官。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦成功启动发行版,别忘了为 Grub 重新产生新的配置文件,使用
|
||||
|
||||
grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
命令。你还需要往 MBR 里安装一份 bootloader 的拷贝,使用
|
||||
|
||||
sudo grub2-install /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
命令。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*想要禁用 `/etc/grub.d` 目录下的脚本,你只需移除其可执行位,比如使用 `chmod -x /etc/grub.d/20_memtest86+` 就能将 ‘Memory Test’ 选项从菜单中移除。*
|
||||
|
||||
### Grub 2 和 UEFI ###
|
||||
|
||||
在支持 UEFI 的机器(最近几年上市的机器大部分都是)调试坏掉的 Grub 2 增加了另一复杂的层次。恢复安装在 UEFI 机器上的 **Grub 2** 的和安装在非 UEFI 机器上的并没多大区别,只是新的固件处理方式不一样,从而导致了很多种恢复结果。
|
||||
|
||||
对于基于 UEFI 的系统,不要在 MBR 上安装任何东西。相反,你要在 EFI 系统分区(EFI System Partition)( ESP )里安装 Linux EFI bootloader,并且借助工具把它设置为 EFI 的默认启动程序,这个工具对于 Linux 用户是 `efibootmgr` ,对于 window 用户则是 `bcdedit` 。
|
||||
|
||||
照目前情况看,在安装任何与 Windows 8 兼容的主流桌面 Linux 发行版前,应该正确安装好 Grub 2。然而,如果 bootloader 损坏,你可以使用 live 发行版修复机器。在启动 live 介质之时,请确保是以 UEFI 模式启动。计算机每个可移动驱动器的启动菜单将会有两个: 一个普通的和一个以 EFI 标记的。使用后者会用到 **/sys/firmware/efi/** 文件中的 EFI 变量。
|
||||
|
||||
在 live 环境中,挂载教程前面所提的安装挂掉系统的根文件系统。除此之外,还需要挂载 ESP 分区。假设分区是 **/dev/sda1** ,你可以如下所示挂载:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/boot/efi
|
||||
|
||||
接着在 chroot 到安装完毕的发行版前之前,使用 `modprobe efivars` 加载 **efivars** 模块。
|
||||
|
||||
在这里, Fedora 用户可以使用如下命令重新安装 bootloader
|
||||
|
||||
yum reinstall grub2-efi shim
|
||||
|
||||
但在此之前,需要使用
|
||||
|
||||
grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
来产生新的配置文件。 Ubuntu 用户则改用以下命令
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install --reinstall grub-efi-amd64
|
||||
|
||||
一旦 bootloader 正确就位,退出 chroot ,卸载所有分区,重启到 Grub 2 菜单。
|
||||
|
||||
### 伙计,我的 Grub 哪去了? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Grub 2 最好的特性是可以随时重新安装。因此,当其它像 Windows 之类的系统用它们自己的 bootloader 替换后,导致 Grub 2 丢失,你可以使用 live 发行版,寥寥数步即可重装 Grub 。假设你在 `/dev/sda5` 安装了一个发行版,若要重装 Grub ,你只需首先使用以下命令为发行版创建一个挂载目录:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo mkdir -p /mnt/distro
|
||||
|
||||
然后挂载分区,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
mount /dev/sda5 /mnt/distro
|
||||
|
||||
接着就能重装 Grub 了,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
grub2-install --root-directory=/mnt/distro /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令会改写 `/dev/sda` 设备上的 MBR 信息,指向当前 Linux 系统,并重写一些 Grub 2 文件,如 **grubenv** 和 **device.map** 。
|
||||
|
||||
另一个问题常见于装有多个发行版的计算机上。当你安装了新的 Linux 发行版,它的 bootloader 应当要能找到所有已经安装的发行版。一旦不行,只要引导进入新安装的发行版,并运行
|
||||
|
||||
grub2-mkconfig
|
||||
|
||||
在运行这个命令之前,请确保启动菜单中缺失的发行版的 root 分区已经挂载。如果你想添加的发行版有单独的 `/root` 和 `/home` 分区,在运行 `grub2-mkconfig` 之前,只需挂载包含 `/root` 的分区。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然 Grub 2 能够找到大部分发行版,但是在 Ubuntu 中尝试添加安装的 Fedora 系统需要额外的一个步骤。如果你以默认设置安装了 Fedora ,则发行版的安装器已经创建了 LVM 分区。此时你需要使用发行版的包管理系统安装 **lvm2** 驱动,如下
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install lvm2
|
||||
|
||||
才能使得 Grub 2 的 `os-prober` 脚本能够找到并将 Fedora 添加进启动菜单。
|
||||
|
||||
### 常见用户设置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Grub 2 有很多可配置变量。 这里有一些 `/etc/default/grub` 文件中你最可能会修改到的常见变量。 **GRUB_DEFAULT** 变量指定默认的启动项,可以设置为数字值,比如 0 ,表示第一个菜单项,或者设置为 “saved” ,将指向上一次启动时选中的菜单项。 **GRUB\_TIMEOUT** 变量指定启动默认菜单项之前的停留时间。 **GRUB\_CMDLINE\_LINUX** 列出了要传递给所有 Linux 菜单项的内核命令行参数。
|
||||
|
||||
如果 **GRUB\_DISABLE\_RECOVERY** 变量设置为 **true** ,那么将不生成恢复模式菜单项。这些菜单项会以单用户模式启动发行版,这种模式下允许你利用命令行工具修复系统。 **GRUB_GFXMODE** 变量同样有用,它指定了菜单上文本显示的分辨率,它可以设置为你的显卡所支持的任何数值。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Grub 2 有个命令行模式,通过在 bootloader 菜单上按 C 进入。*
|
||||
|
||||
### 彻底的修复 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果 `grub2-install` 命令不能正常运作,使得你无法引导进入 Linux ,你需要完整地重装以及重新配置 bootloader 。为此目的,需要用到强大的 **chroot** 功能将运行环境从 live CD 环境切换至我们想修复的 Linux 的安装位置。任何拥有 **chroot** 工具的 Linux live CD 都可以实现这个目的。不过需要确保 live 介质的系统架构和硬盘上系统的架构一致。因此当你希望 **chroot** 到 64 位系统,你必须使用 amd64 live 发行版。
|
||||
|
||||
启动进入 live 发行版之后,首先需要检查机器上的分区。使用 `fdisk -l` 列出磁盘上所有分区,记录你想修复的 Grub 2 系统所在的分区。
|
||||
|
||||
假设我们希望从安装在 `/dev/sda5` 中的发行版中恢复 bootloader 。启动终端使用如下命令挂载分区:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo mount /dev/sda5 /mnt
|
||||
|
||||
此时需要绑定(bind)Grub 2 bootloader 需要进入的目录,以便检测其它操作系统:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mount --bind /dev /mnt/dev
|
||||
$ sudo mount --bind /dev/pts /mnt/dev/pts
|
||||
$ sudo mount --bind /proc /mnt/proc
|
||||
$ sudo mount --bind /sys /mnt/sys
|
||||
|
||||
此时可以离开 live 环境进入安装在 **/dev/sda5** 分区中的发行版了,通过 **chroot** :
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chroot /mnt /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
现在可以安装、检测、以及升级 Grub 了,跟之前一样,使用
|
||||
|
||||
sudo grub2-install /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
命令来重装 bootloader 。因为 **grub2-install** 命令不能创建**grub.cfg** 文件,需要手动创建,如下
|
||||
|
||||
sudo grub-mkconfig -o /boot/grub/grub.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
这样应该就可以了。现在你就有了 Grub 2 的一份全新拷贝,罗列了机器上所有的操作系统和发行版。在重启电脑之前,你需要依次退出 chroot 系统,卸载所有分区,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
$ exit
|
||||
$ sudo umount /mnt/sys
|
||||
$ sudo umount /mnt/proc
|
||||
$ sudo umount /mnt/dev/pts
|
||||
$ sudo umount /mnt/dev
|
||||
$ sudo umount /mnt
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以安全地重启电脑了,而它应该会回退到 Grub 2 的控制之中,你已经修好了这个 bootloader。
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加自定义菜单项 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果希望往 bootloader 菜单里添加菜单项,你需要在 **40_custom** 文件里添加一个启动段( boot stanza )。例如,你可以使用它展示一个菜单项来启动安装在可移动 USB 驱动里的 Linux 发行版。假设你的 USB 驱动器是 **sdb1** ,并且 vmlinuz 内核镜像和虚拟文件系统( initrd )都位于根 (/)目录下,在 **40_custom** 文件中添加以下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
menuentry “Linux on USB” {
|
||||
set root=(hd1,1)
|
||||
linux /vmlinuz root=/dev/sdb1 ro quiet splash
|
||||
initrd /initrd.img
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
相比使用设备和分区名,使用它们的 UUID 可以获得更精确结果,比如
|
||||
|
||||
set root=UUID=54f22dd7-eabe
|
||||
|
||||
使用
|
||||
|
||||
sudo blkid
|
||||
|
||||
来获得所有已连接的驱动器和分区的 UUID 。你还可以为你磁盘上没被 os-prober 脚本找到的发行版添加菜单项,只要你知道该发行版的安装位置以及其内核和虚拟文件系统( initrd )的位置即可。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.linuxvoice.com/grub-2-heal-your-bootloader/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Mayank Sharma][a]
|
||||
译者:[soooogreen](https://github.com/soooogreen)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.linuxvoice.com/author/mayank/
|
||||
@ -1,13 +1,15 @@
|
||||
Linux系统下使用命令行来查看硬件信息
|
||||
Linux 系统下查看硬件信息命令大全
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
有许多可用的命令可以用来查看Linux系统上的硬件信息。有些命令只能够打印出像CPU和内存这一特定的硬件组件信息,其余的命令可以查看其余硬件单元的信息。
|
||||
有许多命令可以用来查看 Linux 系统上的硬件信息。有些命令只能够打印出像 CPU 和内存这一特定的硬件组件信息,另外一些命令可以查看多种硬件组件的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
这个教程可以带大家快速了解一下查看各种硬件设备的信息和配置详情的最常用的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
这个教程可以带大家快速学习一下查看各种硬件设备的信息和配置详情的最常用的命令。
|
||||
### lscpu ###
|
||||
|
||||
`lscpu`命令能够查看CPU和处理单元的信息。该命令没有任何其他选项或者别的功能。
|
||||
`lscpu`命令能够查看 CPU 和处理单元的信息。该命令没有任何其他选项或者别的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
lscpu
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,7 +19,7 @@ Linux系统下使用命令行来查看硬件信息
|
||||
|
||||
### lspci ###
|
||||
|
||||
`lspci`是另一个命令行工具,可以用来列出所有的PCI总线,还有与PCI总线相连的设备的详细信息,比如VGA适配器、显卡、网络适配器、usb端口、SATA控制器等。
|
||||
`lspci`是另一个命令行工具,可以用来列出所有的 PCI 总线,还有与 PCI 总线相连的设备的详细信息,比如 VGA 适配器、显卡、网络适配器、usb 端口、SATA 控制器等。
|
||||
|
||||
lspci
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,7 +37,7 @@ Linux系统下使用命令行来查看硬件信息
|
||||
|
||||
### lshw ###
|
||||
|
||||
`lshw`是一个通用的工具,可以列出多种硬件单元的详细或者概要的信息,比如CPU、内存、usb控制器、硬盘等。`lshw`能够从不同的“/proc”文件中提取出相关的信息。
|
||||
`lshw`是一个通用的工具,可以列出多种硬件单元的详细或者概要的信息,比如 CPU、内存、usb 控制器、硬盘等。`lshw`能够从各个“/proc”文件中提取出相关的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
lshw -short
|
||||
|
||||
@ -45,7 +47,7 @@ Linux系统下使用命令行来查看硬件信息
|
||||
|
||||
### lsscsi ###
|
||||
|
||||
通过运行下面的命令可以列出像硬盘和光驱等scsi/sata设备的信息:
|
||||
通过运行下面的命令可以列出像硬盘和光驱等 scsi/sata 设备的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
lsscsi
|
||||
|
||||
@ -55,7 +57,7 @@ Linux系统下使用命令行来查看硬件信息
|
||||
|
||||
### lsusb ###
|
||||
|
||||
`lsusb`命令能够列出USB控制器和与USB控制相连的设备的详细信息。默认情况下,`lsusb`命令只打印出概要信息。可以通过使用-v参数打印每一个usb端口的详细信息。
|
||||
`lsusb`命令能够列出 USB 控制器和与 USB 控制器相连的设备的详细信息。默认情况下,`lsusb`命令只打印出概要信息。可以通过使用-v参数打印每一个usb端口的详细信息。
|
||||
|
||||
lsusb
|
||||
|
||||
@ -65,9 +67,9 @@ Linux系统下使用命令行来查看硬件信息
|
||||
|
||||
### Inxi ###
|
||||
|
||||
`Inxi`是一个bash脚本,能够从系统的多个源文件和命令行抓取硬件信息,并打印出一个非技术人员也能看懂的友好的报告。
|
||||
`Inxi`是一个 bash 脚本,能够从系统的多个来源和命令获取硬件信息,并打印出一个非技术人员也能看懂的友好的报告。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,Ubuntu上没有安装`inxi`。可以通过运行下面命令来安装`Inxi`:
|
||||
默认情况下,Ubuntu 上没有安装`inxi`。可以通过运行下面命令来安装`Inxi`:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install inxi
|
||||
|
||||
@ -81,7 +83,8 @@ Linux系统下使用命令行来查看硬件信息
|
||||
|
||||
### df ###
|
||||
|
||||
`df`命令能够列出不同分区的概要信息,挂载点,已用的和可用的空间。
|
||||
`df`命令能够列出不同分区的概要信息、挂载点、已用的和可用的空间。
|
||||
|
||||
可以在使用`df`命令的时候加上`-H`参数。
|
||||
|
||||
df -H
|
||||
@ -92,7 +95,7 @@ Linux系统下使用命令行来查看硬件信息
|
||||
|
||||
### Free ###
|
||||
|
||||
通过使用`free`命令可以查看系统中使用的、闲置的和总体的RAM数量。
|
||||
通过使用`free`命令可以查看系统中使用的、闲置的和 RAM 的总体数量。
|
||||
|
||||
free -m
|
||||
|
||||
@ -102,7 +105,7 @@ Linux系统下使用命令行来查看硬件信息
|
||||
|
||||
### Dmidecode ###
|
||||
|
||||
`dmidecode`命令与其他命令不同。该命令是从DMI表中读取硬件信息的。
|
||||
`dmidecode`命令与其他命令不同。该命令是从硬件中的 DMI 表中读取信息的。
|
||||
|
||||
要查看处理器的信息,运行下面命令:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -116,7 +119,7 @@ Linux系统下使用命令行来查看硬件信息
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要查看bios的信息,运行下面命令:
|
||||
要查看 bios 的信息,运行下面命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dmidecode -t bios
|
||||
|
||||
@ -124,7 +127,7 @@ Linux系统下使用命令行来查看硬件信息
|
||||
|
||||
### Hdparm ###
|
||||
|
||||
`hdparm`命令可以用来显示想硬盘这样的sata设备的信息。
|
||||
`hdparm`命令可以用来显示像硬盘这样的 sata 设备的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo hdparm
|
||||
|
||||
@ -134,7 +137,7 @@ Linux系统下使用命令行来查看硬件信息
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
每个命令都有不同的方式来获取硬件的信息。在查看特定的硬件信息的时候,可以尝试使用不同的方式。上面所有的命令行工具在大部分的Linux发型版本中都是可以使用的,可以很容易的从仓库中获取安装。
|
||||
每个命令都有不同的方式来获取硬件的信息。在查看特定的硬件信息的时候,可以尝试使用不同的方式。上面所有的命令行工具在大部分的 Linux 发行版本中都是可以使用的,可以很容易的从仓库中获取安装。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -142,7 +145,7 @@ via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/check-hardware-information-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Hitesh Jethva][a]
|
||||
译者:[sonofelice](https://github.com/sonofelice)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
||||
开源 DJ 软件 Mixxx 2.0 版发布
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
时隔三年,开源 DJ 混音软件 [Mixxx][1] 再度发布一个大的版本更新----Mixxx 2.0。
|
||||
|
||||
Mixxx 是一个跨平台的自由、开源的 DJ 混音软件,它几乎提供了当你想自己混音时需要的一切功能。Mixxx 近几年在专业人士以及业余爱好者中都很火。
|
||||
|
||||
甚至在 Mixxx 中你能使用你的 iTunes 音乐库。它的强有力的引擎使它支持多种文件格式。Mixxx 默认即支持超过85种MIDI DJ 调节器以及少部分 HID 调节器。它也包含一个自动选项,可以让你在混音时休息一下。
|
||||
|
||||
Mixxx 的完整功能列表可以在[这里][2]找到。在查看完整列表之前,让我们看看最新版有何更新。
|
||||
|
||||
### Mixxx 2.0更新 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 可动态调整大小的外观
|
||||
- 4 轨道混音并且和主轨道同步
|
||||
- 内置特效
|
||||
- 谐波混频(Harmonic Mixing)与音乐按键检测
|
||||
- RGB 音频波形
|
||||
- 4 个麦克风输入和 4 个音频输入,麦克风音量可调
|
||||
- 黑胶音源输入、输出
|
||||
- 支持自定义封面
|
||||
- 核心混音引擎改进
|
||||
- 更新的音乐库
|
||||
- 改进增强了 DJ 调节器
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在[这里][3]中看到所有的新功能。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在基于 Ubuntu 的发行版中安装 Mixxx 2.0 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Mixxx 提供了他们自己的ppa源,这使得在基于 Ubuntu 的发行版,如 Linux Mint、elementary OS、 Zorin OS 上安装Mixxx 2.0 变得十分简单.
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端,并输入如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:mixxx/mixxx
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install mixxx
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令卸载 Mixxx:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove mixxx
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:mixxx/mixxx
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经在使用旧版本的 Mixxx。它将很快升级到2.0版。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在其他发行版中安装 Mixxx 2.0 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Archliunx
|
||||
|
||||
sudo pacman -S mixxx
|
||||
|
||||
对于其他发行版,你还可以从源码编译安装 Mixxx。从下列地址下载源代码:
|
||||
|
||||
- [源码地址][4]
|
||||
|
||||
由于 Mixxx 是个跨平台的应用,你也可以下载它的 Windows 版或者 Mac OS 版,请访问 Mixxx 下载页面找到对应的下载链接:
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载地址][5]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/dj-mixxx-2/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[name1e5s](https://github.com/name1e5s)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://mixxx.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://mixxx.org/features/
|
||||
[3]:http://mixxx.org/whats-new-in-mixxx-2-0/
|
||||
[4]:http://downloads.mixxx.org/mixxx-2.0.0/mixxx-2.0.0-src.tar.gz
|
||||
[5]:http://mixxx.org/download/
|
||||
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ Ubuntu 里的“间谍软件”将在 Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 中被禁用
|
||||
|
||||
[电子前哨基金会 (EFF)][2]也在一系列博文中表达出对此的关注,并且建议 Canonical 将这个功能做成用户自由选择是否开启的功能。Privacy International 比其他的组织走的更远,对于 Ubuntu 的工作,他们给 Ubuntu 的缔造者发了一个“[老大哥奖][3]”。
|
||||
|
||||
[Canonical][4] 坚称] Unity 的在线搜索功能所收集的数据是匿名的以及“不可识别是来自哪个用户的”。
|
||||
[Canonical][4] 坚称 Unity 的在线搜索功能所收集的数据是匿名的以及“不可识别是来自哪个用户的”。
|
||||
|
||||
在[2013年 Canoical 发布的博文中][5]他们解释道:“**(我们)会使用户了解我们收集哪些信息以及哪些第三方服务商将会在他们搜索时从 Dash 栏中给出结果。我们只会收集能够提升用户体验的信息。**”
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,22 +1,22 @@
|
||||
Linux 教学之教你玩音乐
|
||||
与 Linux 一起学习:玩音乐
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Linux 学习系列][1]的所有文章:
|
||||
[与 Linux 一起学习:][1]的所有文章:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之教你练打字][2]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之物理模拟][3]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之教你玩音乐][4]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之两款地理软件][5]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之掌握数学][6]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:学习打字][2]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:物理模拟][3]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:玩音乐][4]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:两款地理软件][5]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:掌握数学][6]
|
||||
|
||||
引言:Linux 提供大量的教学软件和工具,面向各个年级段以及年龄段,提供大量学科的练习实践,其中大多数是可以与用户进行交互的。本“Linux 教学”系列就来介绍一些教学软件。
|
||||
引言:Linux 提供大量的教学软件和工具,面向各个年级段以及不同年龄段,提供大量学科的练习实践,其中大多数是可以与用户进行交互的。本“与 Linux 一起学习:”系列就来介绍一些教学软件。
|
||||
|
||||
学习音乐是一个很好的消遣方式。训练你的耳朵能识别音阶与和弦、掌握一门乐器、控制自己的嗓音,这些都需要大量的练习,以及会遇到很多困难。音乐理论非常博大精深,有太多东西需要记忆,你需要非常勤奋才能讲这些东西变成你的“技术”。在你的音乐之路上,Linux 提供了杰出的软件来帮助你前行。它们不能让你立刻成为一个音乐家,但可以作为一个降低学习难度的好助手。
|
||||
学习音乐是一个很好的消遣方式。训练你的耳朵能识别音阶与和弦、掌握一门乐器、控制自己的嗓音,这些都需要大量的练习,以及会遇到很多困难。音乐理论非常博大精深,有太多东西需要记忆,你需要非常勤奋才能将这些东西变成你的“技术”。在你的音乐之路上,Linux 提供了杰出的软件来帮助你前行。它们不能让你立刻成为一个音乐家,但可以作为一个降低学习难度的好助手。
|
||||
|
||||
### Gnu Solfège ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Solfège][7] 是一个世界流行的音乐教学工具,适用于各个级别的音乐教育。很多流行的教学方法(比如著名的柯达伊教学法)就使用 Solfège 作为它们的基础。相比于学到音乐知识,Solfège 更关注于让用户不断练习音乐。它假想的用户是那些已经有一些音乐基础,并且想不断练习音乐技巧的学生。
|
||||
[Solfège][7] 是一个世界流行的音乐教学工具,适用于各个级别的音乐教育。很多流行的教学方法(比如著名的柯达伊教学法)就使用 Solfège 作为它们的基础。相比于学到音乐知识,Solfège 更关注于让用户不断练习音乐。它预期的用户是那些已经有一些音乐基础,并且想不断练习音乐技巧的学生。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是 GNU 网站的开发者声明:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ Linux 教学之教你玩音乐
|
||||
|
||||
这款软件兑现了它的承诺,你可以在试听帮手的帮助下练习几乎所有音乐技巧。
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 和 Ubuntu 的远端库上有这款软件,在终端运行下面命令安装软件:
|
||||
Debian 和 Ubuntu 的仓库上有这款软件,在终端运行下面命令安装软件:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install solfege
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,9 +78,9 @@ Tete 只有一个简单的界面,所有内容都在这里了。
|
||||
|
||||
### JalMus ###
|
||||
|
||||
Jalmus 是用 JAVA 写的键盘音符阅读训练器。可以外接 MIDI 键盘,也可以使用虚拟键盘。它提供很多简单的课程练习来训练你的音符阅读能力。这个软件在2013年之后就不再更新了,但还是比较实用的。
|
||||
Jalmus 是用 JAVA 写的键盘音符阅读训练器。可以外接 MIDI 键盘,也可以使用虚拟键盘。它提供很多简单的课程练习来训练你的音符阅读能力。虽然这个软件在2013年之后就不再更新了,但还是比较实用的。
|
||||
|
||||
进入[sourceforge 页面][11]下载最后版本(v2.3)的 JAVA 安装器,或者在终端输入下面的命令下载:
|
||||
进入 [sourceforge 页面][11]下载最后版本(v2.3)的 JAVA 安装器,或者在终端输入下面的命令下载:
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://garr.dl.sourceforge.net/project/jalmus/Jalmus-2.3/installjalmus23.jar
|
||||
|
||||
@ -102,11 +102,11 @@ Jalmus 的主界面非常朴素。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Jalmus 也包含一些训练,内容和课程相似,只是没有那些视觉上的提示了。当完成训练后,屏幕上会显示你的乐谱。它还提供不同难度的节拍训练,你能听到看到这些训练里面播放的旋律。在多行乐谱同时播放时,一个节拍器(能听见能看见)可以帮你理解
|
||||
Jalmus 也包含一些阅读单个音符的训练,内容和课程相似,只是没有那些视觉上的提示了。当完成训练后,屏幕上会显示你的乐谱。它还提供不同难度的节拍训练,你能听到并看到这些训练里面播放的节拍。在多行乐谱同时播放时,一个节拍器(能听见能看见)可以帮你理解
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
和阅读乐谱。(LCTT 写给王老板的话:我特么实在编不下去了,这段你得帮我改改。)
|
||||
和阅读乐谱。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -121,11 +121,12 @@ Jalmus 也包含一些训练,内容和课程相似,只是没有那些视觉
|
||||
对于吉他练习者,[TuxGuitar][12] 看起来很像 Windows 下面的 Guitar Pro 软件(它也可以读 Guitar Pro 格式的文件)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### PianoBooster ####
|
||||
|
||||
[Piano Booster][13] 可以练习钢琴技巧,它能播放 MIDI 文件,你可以使用外接键盘来弹钢琴,同时还能查看屏幕上滑过的乐谱。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 提供很多优秀的工具供你学习,如果你对音乐感兴趣,你完全不用担心没有软件能帮你练习音乐技术。实际上,可供学习音乐的学生选择的优秀软件数量远比上面介绍的要多。如果你还知道其他的音乐训练软件,请在写下你的评论,让我们能够知道。
|
||||
Linux 提供很多优秀的工具供你学习,如果你对音乐感兴趣,你完全不用担心没有帮你练习音乐技术的软件。实际上,可供学习音乐的学生选择的优秀软件数量远比上面介绍的要多。如果你还知道其他的音乐训练软件,请在写下你的评论,让我们能够知道。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -133,7 +134,7 @@ via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,36 +1,36 @@
|
||||
Linux 教学之教你练打字
|
||||
与 Linux 一起学习:学习打字
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Linux 学习系列][1]的所有文章:
|
||||
[与 Linux 一起学习][1]的所有文章:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之教你练打字][2]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之物理模拟][3]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之教你玩音乐][4]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之两款地理软件][5]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之掌握数学][6]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:学习打字][2]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:物理模拟][3]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:玩音乐][4]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:两款地理软件][5]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习: 使用这些 Linux 应用来征服你的数学学习][6]
|
||||
|
||||
引言:Linux 提供大量的教学软件和工具,面向各个年级段以及年龄段,提供大量学科的练习实践,其中大多数是可以与用户进行交互的。本“Linux 教学”系列就来介绍一些教学软件。
|
||||
Linux 提供大量的教学软件和工具,面向各个年级以及不同年龄段,提供大量学科的练习实践,其中大多数是可以与用户进行交互的。本“与 Linux 一起学习”系列就来介绍一些教学软件。
|
||||
|
||||
很多人都要打字,操作键盘已经成为他们的第二天性。 但是这些人中有多少是依然使用两个手指头来快速地按键盘的?即使学校有教我们使用键盘的方法(LCTT 译注:呃。。。),我们也会慢慢地抛弃正确的打字姿势,养成只用两个大拇指玩键盘的习惯。
|
||||
很多人都要打字,操作键盘已经成为他们的第二天性。但是这些人中有多少是依然使用两个手指头来快速地按键盘的?即使学校有教我们使用键盘的方法,我们也会慢慢地抛弃正确的打字姿势,养成只用两个大拇指玩键盘的习惯。(LCTT 译注:呃,你确认是拇指而不是食指?)
|
||||
|
||||
下面要介绍的两款软件可以帮你掌控你的键盘,然后你就可以让你的手指跟上你的思维,然后你的思维就不会被打断了。当然,还有很多更炫更酷的软件可供选择,但本文所选的这两款是最简单、最容易上手的。
|
||||
下面要介绍的两款软件可以帮你掌控你的键盘,然后你就可以让你的手指跟上你的思维,这样你的思维就不会被打断了。当然,还有很多更炫更酷的软件可供选择,但本文所选的这两款是最简单、最容易上手的。
|
||||
|
||||
### TuxType (或者叫 TuxTyping) ###
|
||||
|
||||
TuxType 是给小孩子玩的。在一些有趣的游戏中,小学生们可以通过完成一些简单的练习来 get “10个手指打字”的新技能。
|
||||
TuxType 是给小孩子玩的。在一些有趣的游戏中,小学生们可以通过完成一些简单的练习来 Get “双手打字以示清白”的新技能。
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 及其衍生版本(包含所有 Ubuntu 衍生版本)的标准软件仓库都有 TuxType,使用下面的命令安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install tuxtype
|
||||
|
||||
软件开始时有一个简单的 Tux 界面和一段难听的 midi 音乐,幸运的是你可以通过右下角的喇叭按钮把声音调低了。(LCTT译注:Tux 就是那只 Linux 吉祥物,Linus 说它的表情被设计成刚喝完啤酒后的满足感,见《Just For Fun》。)
|
||||
软件开始时有一个简单的 Tux 界面和一段难听的 midi 音乐,幸运的是你可以通过右下角的喇叭按钮把声音调低了。(LCTT 译注:Tux 就是那只 Linux 吉祥物,Linus 说它的表情被设计成刚喝完啤酒后的满足感,见《Just For Fun》。)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最开始处的两个选项“Fish Cascade”和“Comet Zap”是打字游戏,当你开始游戏时,你需要很投入到这个课程。
|
||||
最开始处的两个选项“Fish Cascade”和“Comet Zap”是打字游戏,当你开始游戏时,你就投入到了这个课程。
|
||||
|
||||
第3个选项为“Lession”,提供40多个简单的课程,每个课程会增加一个字母让你来练习,练习过程中会给出一些提示,比如应该用哪个手指按键盘上的字母。
|
||||
第3个选项为“Lessions”,提供40多个简单的课程,每个课程会增加一个字母让你来练习,练习过程中会给出一些提示,比如应该用哪个手指按键盘上的字母。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -68,7 +68,7 @@ GNU Typist 也在大多数 Debian 衍生版本的软件库中,运行下面的
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在交互练习的过程中,如果你输入错误,会将错误点高亮显示。不会像其他漂亮界面分散你的注意力,你可以专注于练习。每个课程的右下角都有一组统计数据来展示你的表现,如果你犯了很多错误,就可能无法通过关卡了。
|
||||
在交互练习的过程中,如果你输入错误,会将错误位置高亮显示。不会像其他漂亮界面分散你的注意力,你可以专注于练习。每个课程的右下角都有一组统计数据来展示你的表现,如果你犯了很多错误,就可能无法通过关卡了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -106,7 +106,7 @@ via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-to-type-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -116,4 +116,4 @@ via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-to-type-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-physics-simulation/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-geography-apps/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-linux-maths/
|
||||
[6]:https://linux.cn/article-6546-1.html
|
||||
@ -1,22 +1,22 @@
|
||||
Linux 教学之物理模拟
|
||||
与 Linux 一起学习:物理模拟
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Linux 学习系列][1]的所有文章:
|
||||
[与 Linux 一起学习][1]的所有文章:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之教你练打字][2]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之物理模拟][3]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之教你玩音乐][4]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之两款地理软件][5]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之掌握数学][6]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:学习打字][2]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:物理模拟][3]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:玩音乐][4]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:两款地理软件][5]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:掌握数学][6]
|
||||
|
||||
引言:Linux 提供大量的教学软件和工具,面向各个年级段以及年龄段,提供大量学科的练习实践,其中大多数是可以与用户进行交互的。本“Linux 教学”系列就来介绍一些教学软件。
|
||||
Linux 提供大量的教学软件和工具,面向各个年级段以及不同年龄段,提供大量学科的练习实践,其中大多数是可以与用户进行交互的。本“与 Linux 一起学习”系列就来介绍一些教学软件。
|
||||
|
||||
物理是一个有趣的课题,证据就是任何物理课程都可以用具体的图片演示给你看。能看到物理变化过程是一个很妙的体验,特别是你不需要到教室就能体验到。Linux 上有很多很好的科学软件来为你提供这种美妙感觉,本篇文章只着重介绍其中几种。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Step ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Step][7] 是一个交互型物理模拟器,KDEEdu[8](KDE 教育)项目的一部分。没人会比它的作者更了解它的作用。在项目官网主页上写着“[Step] 是这样玩的:你放点东西进来,添加一些力(地心引力或者弹簧),然后点击‘模拟’按钮,这款软件就会为你模拟这个物体在真实世界的物理定律影响下的运动状态。你可以改变物体或力的属性(允许在模拟过程中进行修改),然后观察不同属性下产生的现象。Step 可以让你从体验中学习物理!”
|
||||
[Step][7] 是一个交互型物理模拟器,属于 [KDEEdu][8](KDE 教育)项目的一部分。没人会比它的作者更了解它的作用。在项目官网主页上写着“[Step] 是这样玩的:你放点东西进来,添加一些力(地心引力或者弹簧),然后点击‘模拟(Simulate)’按钮,这款软件就会为你模拟这个物体在真实世界的物理定律影响下的运动状态。你可以改变物体或力的属性(允许在模拟过程中进行修改),然后观察不同属性下产生的现象。Step 可以让你从体验中学习物理!”
|
||||
|
||||
Step 依赖 Qt 以及其他一些 KDE 所依赖的软件,正是由于像 KDEEdu 之类的项目存在,才使得 KDE 变得如此强大,当然,你可能需要忍受由此带来的庞大的桌面系统。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ Step 有个简单的交互界面,你进去后直接可以进行模拟操作。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你会发现所有物品在屏幕左边,包括不同的质点,空气,不同形状的物体,弹簧,以及不同的力(见1区域) 。如果你选中一个物体,屏幕右边会出现简短的描述信息(见2区域),以及你创造的世界的介绍(主要介绍这个世界中包含的物体)(见3区域),以及你当前选中的物体的属性(见4区域),以及你的操作历史(见5区域)。
|
||||
你会发现所有物品在屏幕左边,包括不同的质点,空气,不同形状的物体,弹簧,以及不同的力(见区域1) 。如果你选中一个物体,屏幕右边会出现简短的描述信息(见区域2),以及你创造的世界的介绍(主要介绍这个世界中包含的物体)(见区域3),以及你当前选中的物体的属性(见区域4),以及你的操作历史(见区域5)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ Step 有个简单的交互界面,你进去后直接可以进行模拟操作。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
想要更多了解 Step,按 F1 键,KDE 帮助中心会打印详细的软件操作手册。
|
||||
想要更多了解 Step,按 F1 键,KDE 帮助中心会显示出详细的软件操作手册。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Lightspeed ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,10 +50,10 @@ Lightspeed 是一个简单的基于 GTK+ 和 OpenGL 的模拟器,可以模拟
|
||||
|
||||
受到相对速度影响的现象如下(LCTT 译注:都可以从“光速不变”理论推导出来):
|
||||
|
||||
- **洛伦兹收缩** —— 物体看起来变短了
|
||||
- **多普乐红移/蓝移** —— 物体的颜色变了
|
||||
- **前灯效应** —— 物体的明暗变化(LCTT 译注:当物体接近光速移动时,会在它前进的方向强烈地辐射光子,从这个角度看,物体会变得很亮,相反,从物体背后观察,会发现它很暗)
|
||||
- **光行差效应** —— 物体扭曲变形了
|
||||
- **洛伦兹收缩(The Lorentz contraction)** —— 物体看起来变短了
|
||||
- **多普勒红移/蓝移(The Doppler red/blue shift)** —— 物体的颜色变了
|
||||
- **前灯效应(The headlight effect)** —— 物体的明暗变化(LCTT 译注:当物体接近光速移动时,会在它前进的方向强烈地辐射光子,从这个角度看,物体会变得很亮,相反,从物体背后观察,会发现它很暗)
|
||||
- **光行差效应(Optical aberration)** —— 物体扭曲变形了
|
||||
|
||||
Lightspeed 有 Debian 的源,执行下面的命令来安装:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,9 +75,13 @@ Lightspeed 有 Debian 的源,执行下面的命令来安装:
|
||||
|
||||
### 特别推荐: Physion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Physion 是个非常有趣并且美观的物理模拟软件,比上面介绍的两款软件都好玩好看。可惜在写本文章的时候它的[官网][10]出现问题了,下载页面无法使用。
|
||||
Physion 是个非常有趣并且美观的物理模拟软件,比上面介绍的两款软件都好玩好看。
|
||||
|
||||
从他们放在 Youtube 上的视频来看,Physion 还是值得我们下载下来玩玩的。在官网恢复之前,我们只能看看演示视频了。
|
||||
可以从它的[官网][10]下载:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Linux][11]
|
||||
|
||||
从他们放在 Youtube 上的视频来看,Physion 还是值得我们下载下来玩玩的。\
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
<iframe frameborder="0" src="//www.youtube.com/embed/P32UHa-3BfU?autoplay=1&autohide=2&border=0&wmode=opaque&enablejsapi=1&controls=0&showinfo=0" id="youtube-iframe"></iframe>
|
||||
@ -90,18 +94,19 @@ via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-physics-simulation/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/series/learn-with-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-to-type-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://linux.cn/article-6902-1.html
|
||||
[3]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-physics-simulation/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-geography-apps/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-linux-maths/
|
||||
[6]:https://linux.cn/article-6546-1.html
|
||||
[7]:https://edu.kde.org/applications/all/step
|
||||
[8]:https://edu.kde.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://lightspeed.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.physion.net/
|
||||
[11]:http://physion.net/en/downloads/linux/13-physion-linux-x8664/download
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
|
||||
Linux 教学之两款地理软件
|
||||
与 Linux 一起学习:学习地理
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Linux 学习系列][1]的所有文章:
|
||||
[与 Linux 一起学习][1]的所有文章:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之教你练打字][2]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之物理模拟][3]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之教你玩音乐][4]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之两款地理软件][5]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之掌握数学][6]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:学习打字][2]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:物理模拟][3]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:玩音乐][4]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:学习地理][5]
|
||||
- [与 Linux 一起学习:掌握数学][6]
|
||||
|
||||
引言:Linux 提供大量的教学软件和工具,面向各个年级段以及年龄段,提供大量学科的练习实践,其中大多数是可以与用户进行交互的。本“Linux 教学”系列就来介绍一些教学软件。
|
||||
引言:Linux 提供大量的教学软件和工具,面向各个年级段以及各个年龄段,提供大量学科的练习实践,其中大多数是可以与用户进行交互的。本“与 Linux 一起学习”系列就来介绍一些教学软件。
|
||||
|
||||
地理是一门有趣的学科,我们每天都能接触到,虽然可能没有意识到,但当你打开 GPS、SatNav 或谷歌地图时,你就已经在使用这些软件提供的地理数据了;当你在新闻中看到一个国家的消息或听到一些金融数据时,这些信息都可以归于地理学范畴。Linux 提供了很多学习地理学的软件,可用于教学,也可用于自学。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -62,11 +62,11 @@ Marble 专注于地图绘制,它的主界面就是一张地图。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
除了有包含不同界面和大量数据的离线地图,Marble 还提供其他信息。你可以在菜单中打开或关闭不同的离线 info-boxes
|
||||
除了有包含不同界面和大量数据的离线地图,Marble 还提供其他信息。你可以在菜单中打开或关闭不同的离线信息框
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
和在线的 online services。
|
||||
和在线服务。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -86,7 +86,7 @@ via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-geography-apps/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,371 @@
|
||||
怎样在 ubuntu 和 debian 中通过命令行管理 KVM
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
有很多不同的方式去管理运行在 KVM 管理程序上的虚拟机。例如,virt-manager 就是一个流行的基于图形界面的前端虚拟机管理工具。然而,如果你想要在没有图形窗口的服务器环境下使用 KVM ,那么基于图形界面的解决方案显然是行不通的。事实上,你可以单纯使用包装了 kvm 命令行脚本的命令行来管理 KVM 虚拟机。作为替代方案,你可以使用 virsh 这个容易使用的命令行程序来管理客户虚拟机。在 virsh 中,它通过和 libvirtd 服务通信来达到控制虚拟机的目的,而 libvirtd 可以控制多个不同的虚拟机管理器,包括 KVM,Xen,QEMU,LXC 和 OpenVZ。
|
||||
|
||||
当你想要对虚拟机的前期准备和后期管理实现自动化操作时,像 virsh 这样的命令行管理工具是非常有用的。同样,virsh 支持多个管理器也就意味着你可以通过相同的 virsh 接口去管理不同的虚拟机管理器。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我会示范**怎样在 ubuntu 和 debian 上通过使用 virsh 命令行去运行 KVM**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一步:确认你的硬件平台支持虚拟化 ###
|
||||
|
||||
第一步,首先要确认你的 CPU 支持硬件虚拟化扩展(e.g.,Intel VT 或者 AMD-V),这是 KVM 对硬件的要求。下面的命令可以检查硬件是否支持虚拟化。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ egrep '(vmx|svm)' --color /proc/cpuinfo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
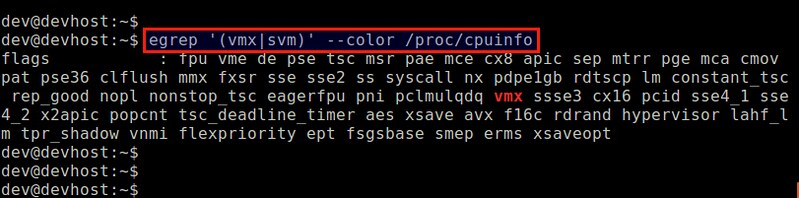
|
||||
|
||||
如果在输出中不包含 vmx 或者 svm 标识,那么就意味着你的 cpu 不支持硬件虚拟化。因此你不能在你的机器上使用 KVM 。确认了 cpu 支持 vmx 或者 svm 之后,接下来开始安装 KVM。
|
||||
|
||||
对于 KVM 来说,它不要求运行在拥有 64 位内核系统的主机上,但是通常我们会推荐在 64 位系统的主机上面运行 KVM。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第二步:安装KVM ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `apt-get` 安装 KVM 和相关的用户空间工具。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install qemu-kvm libvirt-bin
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装期间,libvirtd 用户组(在 debian 上是 libvirtd-qemu 用户组)将会被创建,并且你的用户 id 将会被自动添加到该组中。这样做的目的是让你可以以一个普通用户而不是 root 用户的身份去管理虚拟机。你可以使用 `id` 命令来确认这一点,下面将会告诉你怎么去显示你的组 id:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ id <your-userID>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果因为某些原因,libvirt(在 debian 中是 libvirt-qemu)没有在你的组 id 中被找到,你也可以手动将你自己添加到对应的组中,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
在 ubuntu 上:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo adduser [youruserID] libvirtd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 debian 上:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo adduser [youruserID] libvirt-qemu
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
按照如下命令重新载入更新后的组成员关系。如果要求输入密码,那么输入你的登陆密码即可。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ exec su -l $USER
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这时,你应该可以以普通用户的身份去执行 virsh 了。做一个如下所示的测试,这个命令将会以列表的形式列出可用的虚拟机(当前的列表是空的)。如果你没有遇到权限问题,那意味着到目前为止一切都是正常的。
|
||||
|
||||
$ virsh list
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Id Name State
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
### 第三步:配置桥接网络 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了使 KVM 虚拟机能够访问外部网络,一种方法是通过在 KVM 宿主机上创建 Linux 桥来实现。创建之后的桥能够将虚拟机的虚拟网卡和宿主机的物理网卡连接起来,因此,虚拟机能够发送和接收由物理网卡传输的数据包。这种方式叫做网络桥接。
|
||||
|
||||
下面将告诉你如何创建并且配置网桥,我们创建一个网桥称它为 br0。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,安装一个必需的包,然后用命令行创建一个网桥。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install bridge-utils
|
||||
$ sudo brctl addbr br0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下一步就是配置已经创建好的网桥,即修改位于 `/etc/network/interfaces` 的配置文件。我们需要将该桥接网卡设置成开机启动。为了修改该配置文件,你需要关闭你的操作系统上的网络管理器(如果你在使用它的话)。跟随[操作指南][1]的说明去关闭网络管理器。
|
||||
|
||||
关闭网络管理器之后,接下来就是通过修改配置文件来配置网桥了。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#auto eth0
|
||||
#iface eth0 inet dhcp
|
||||
|
||||
auto br0
|
||||
iface br0 inet dhcp
|
||||
bridge_ports eth0
|
||||
bridge_stp off
|
||||
bridge_fd 0
|
||||
bridge_maxwait 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的配置中,我假设 eth0 是主要网卡,它也是连接到外网的网卡,同样,我假设 eth0 将会通过 DHCP 协议自动获取 ip 地址。注意,之前在 `/etc/network/interfaces` 中还没有对 eth0 进行任何配置。桥接网卡 br0 引用了 eth0 的配置,而 eth0 也会受到 br0 的制约。
|
||||
|
||||
重启网络服务,并确认网桥已经被成功的配置好。如果成功的话,br0 的 ip 地址将会是 eth0 自动分配的 ip 地址,而且 eth0 不会被分配任何 ip 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/networking restart
|
||||
$ ifconfig
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果因为某些原因,eth0 仍然保留了之前分配给了 br0 的 ip 地址,那么你可能必须手动删除 eth0 的 ip 地址。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 第四步:用命令行创建一个虚拟机 ###
|
||||
|
||||
对于虚拟机来说,它的配置信息被存储在它对应的xml文件中。因此,创建一个虚拟机的第一步就是准备一个与虚拟机对应的 xml 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个示例 xml 文件,你可以根据需要手动修改它。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<domain type='kvm'>
|
||||
<name>alice</name>
|
||||
<uuid>f5b8c05b-9c7a-3211-49b9-2bd635f7e2aa</uuid>
|
||||
<memory>1048576</memory>
|
||||
<currentMemory>1048576</currentMemory>
|
||||
<vcpu>1</vcpu>
|
||||
<os>
|
||||
<type>hvm</type>
|
||||
<boot dev='cdrom'/>
|
||||
</os>
|
||||
<features>
|
||||
<acpi/>
|
||||
</features>
|
||||
<clock offset='utc'/>
|
||||
<on_poweroff>destroy</on_poweroff>
|
||||
<on_reboot>restart</on_reboot>
|
||||
<on_crash>destroy</on_crash>
|
||||
<devices>
|
||||
<emulator>/usr/bin/kvm</emulator>
|
||||
<disk type="file" device="disk">
|
||||
<driver name="qemu" type="raw"/>
|
||||
<source file="/home/dev/images/alice.img"/>
|
||||
<target dev="vda" bus="virtio"/>
|
||||
<address type="pci" domain="0x0000" bus="0x00" slot="0x04" function="0x0"/>
|
||||
</disk>
|
||||
<disk type="file" device="cdrom">
|
||||
<driver name="qemu" type="raw"/>
|
||||
<source file="/home/dev/iso/CentOS-6.5-x86_64-minimal.iso"/>
|
||||
<target dev="hdc" bus="ide"/>
|
||||
<readonly/>
|
||||
<address type="drive" controller="0" bus="1" target="0" unit="0"/>
|
||||
</disk>
|
||||
<interface type='bridge'>
|
||||
<source bridge='br0'/>
|
||||
<mac address="00:00:A3:B0:56:10"/>
|
||||
</interface>
|
||||
<controller type="ide" index="0">
|
||||
<address type="pci" domain="0x0000" bus="0x00" slot="0x01" function="0x1"/>
|
||||
</controller>
|
||||
<input type='mouse' bus='ps2'/>
|
||||
<graphics type='vnc' port='-1' autoport="yes" listen='0.0.0.0'/>
|
||||
<console type='pty'>
|
||||
<target port='0'/>
|
||||
</console>
|
||||
</devices>
|
||||
</domain>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面的主机xml配置文件定义了如下的虚拟机内容。
|
||||
|
||||
- 1GB内存,一个虚拟cpu和一个硬件驱动
|
||||
|
||||
- 磁盘镜像:`/home/dev/images/alice.img`
|
||||
|
||||
- 从 CD-ROM 引导(`/home/dev/iso/CentOS-6.5-x86_64-minomal.iso`)
|
||||
|
||||
- 网络:一个桥接到 br0 的虚拟网卡
|
||||
|
||||
- 通过 VNC 远程访问
|
||||
|
||||
`<uuid></uuid>` 中的 UUID 字符串可以随机生成。为了得到一个随机的 uuid 字符串,你可能需要使用 uuid 命令行工具。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install uuid
|
||||
$ uuid
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成一个主机 xml 配置文件的方式就是通过一个已经存在的虚拟机来导出它的 xml 配置文件。如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh dumpxml alice > bob.xml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 第五步:使用命令行启动虚拟机 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在启动虚拟机之前,我们需要创建它的初始磁盘镜像。为此,你需要使用 qemu-img 命令来生成一个 qemu-kvm 镜像。下面的命令将会创建 10 GB 大小的空磁盘,并且它是 qcow2 格式的。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ qemu-img create -f qcow2 /home/dev/images/alice.img 10G
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用 qcow2 格式的磁盘镜像的好处就是它在创建之初并不会给它分配全部大小磁盘容量(这里是 10 GB),而是随着虚拟机中文件的增加而逐渐增大。因此,它对空间的使用更加有效。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你可以通过使用之前创建的 xml 配置文件启动你的虚拟机了。下面的命令将会创建一个虚拟机,然后自动启动它。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh create alice.xml
|
||||
Domain alice created from alice.xml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 如果你对一个已经存在的虚拟机执行了了上面的命令,那么这个操作将会在没有任何警告的情况下抹去那个已经存在的虚拟机的全部信息。如果你已经创建了一个虚拟机,你可能会使用下面的命令来启动虚拟机。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh start alice.xml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令确认一个新的虚拟机已经被创建并成功的被启动。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Id Name State
|
||||
----------------------------------------------------
|
||||
3 alice running
|
||||
|
||||
同样,使用如下命令确认你的虚拟机的虚拟网卡已经被成功的添加到了你先前创建的 br0 网桥中。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo brctl show
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 远程连接虚拟机 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了远程访问一个正在运行的虚拟机的控制台,你可以使用VNC客户端。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,你需要使用如下命令找出用于虚拟机的VNC端口号。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo netstat -nap | egrep '(kvm|qemu)'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在这个例子中,用于 alice 虚拟机的 VNC 端口号是 5900。 然后启动一个VNC客户端,连接到一个端口号为5900的VNC服务器。在我们的例子中,虚拟机支持由CentOS光盘文件启动。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 virsh 管理虚拟机 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下面列出了 virsh 命令的常规用法:
|
||||
|
||||
创建客户机并且启动虚拟机:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh create alice.xml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
停止虚拟机并且删除客户机:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh destroy alice
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
关闭虚拟机(不用删除它):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh shutdown alice
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
暂停虚拟机:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh suspend alice
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
恢复虚拟机:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh resume alice
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
访问正在运行的虚拟机的控制台:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh console alice
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
设置虚拟机开机启动:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh autostart alice
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
查看虚拟机的详细信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh dominfo alice
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
编辑虚拟机的配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh edit alice
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面的这个命令将会使用一个默认的编辑器来调用主机配置文件。该配置文件中的任何改变都将自动被libvirt验证其正确性。
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以在一个virsh会话中管理虚拟机。下面的命令会创建并进入到一个virsh会话中:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 virsh 提示中,你可以使用任何 virsh 命令。
|
||||
|
||||
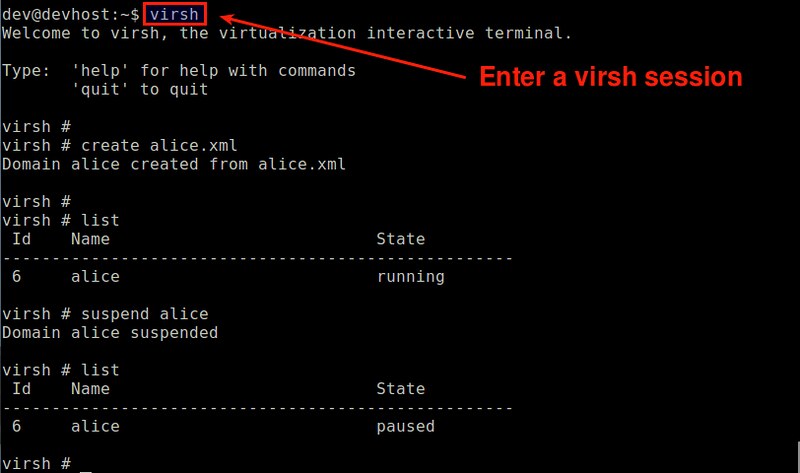
|
||||
|
||||
### 问题处理 ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. 我在创建虚拟机的时候遇到了一个错误:
|
||||
|
||||
error: internal error: no supported architecture for os type 'hvm'
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的硬件不支持虚拟化的话你可能就会遇到这个错误。(例如,Intel VT或者AMD-V),这是运行KVM所必需的。如果你遇到了这个错误,而你的cpu支持虚拟化,那么这里可以给你一些可用的解决方案:
|
||||
|
||||
首先,检查你的内核模块是否丢失。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ lsmod | grep kvm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果内核模块没有加载,你必须按照如下方式加载它。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo modprobe kvm_intel (for Intel processor)
|
||||
$ sudo modprobe kvm_amd (for AMD processor)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
第二个解决方案就是添加 `--connect qemu:///system` 参数到 `virsh` 命令中,如下所示。当你正在你的硬件平台上使用超过一个虚拟机管理器的时候就需要添加这个参数(例如,VirtualBox,VMware)。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh --connect qemu:///system create alice.xml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 当我试着访问我的虚拟机的登陆控制台的时候遇到了错误:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ virsh console alice
|
||||
error: internal error: cannot find character device <null>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这个错误发生的原因是你没有在你的虚拟机配置文件中定义控制台设备。在 xml 文件中加上下面的内部设备部分即可。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<console type='pty'>
|
||||
<target port='0'/>
|
||||
</console>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/use-kvm-command-line-debian-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[kylepeng93](https://github.com/kylepeng93 )
|
||||
校对:[Ezio](https://github.com/oska874)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/disable-network-manager-linux.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
|
||||
如何将 Debian Linux 中的默认的 Python 版本切换为替代版本
|
||||
====================================================
|
||||
|
||||
当你安装 Debian Linux 时,安装过程有可能同时为你提供多个可用的 Python 版本,因此系统中会存在多个 Python 的可执行二进制文件。你可以按照以下方法使用 `ls` 命令来查看你的系统中都有那些 Python 的二进制文件可供使用。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls /usr/bin/python*
|
||||
/usr/bin/python /usr/bin/python2 /usr/bin/python2.7 /usr/bin/python3 /usr/bin/python3.4 /usr/bin/python3.4m /usr/bin/python3m
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
执行如下命令查看默认的 Python 版本信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ python --version
|
||||
Python 2.7.8
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
###1、基于用户修改 Python 版本:
|
||||
|
||||
想要为某个特定用户修改 Python 版本,只需要在其 home 目录下创建一个 `alias`(别名) 即可。打开该用户的 `~/.bashrc` 文件,添加新的别名信息来修改默认使用的 Python 版本。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
alias python='/usr/bin/python3.4'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
一旦完成以上操作,重新登录或者重新加载 `.bashrc` 文件,使操作生效。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ . ~/.bashrc
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
检查当前的 Python 版本。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ python --version
|
||||
Python 3.4.2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
###2、 在系统级修改 Python 版本
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以使用 `update-alternatives` 来为整个系统更改 Python 版本。以 root 身份登录,首先罗列出所有可用的 python 替代版本信息:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# update-alternatives --list python
|
||||
update-alternatives: error: no alternatives for python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果出现以上所示的错误信息,则表示 Python 的替代版本尚未被 `update-alternatives` 命令识别。想解决这个问题,我们需要更新一下替代列表,将 `python2.7` 和 `python3.4` 放入其中。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python2.7 1
|
||||
update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/python2.7 to provide /usr/bin/python (python) in auto mode
|
||||
# update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/python python /usr/bin/python3.4 2
|
||||
update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/python3.4 to provide /usr/bin/python (python) in auto mode
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`--install` 选项使用了多个参数用于创建符号链接。最后一个参数指定了此选项的优先级,如果我们没有手动来设置替代选项,那么具有最高优先级的选项就会被选中。这个例子中,我们为 `/usr/bin/python3.4` 设置的优先级为2,所以 `update-alternatives` 命令会自动将它设置为默认 Python 版本。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# python --version
|
||||
Python 3.4.2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,我们再次列出可用的 Python 替代版本。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# update-alternatives --list python
|
||||
/usr/bin/python2.7
|
||||
/usr/bin/python3.4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
现在开始,我们就可以使用下方的命令随时在列出的 Python 替代版本中任意切换了。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# update-alternatives --config python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# python --version
|
||||
Python 2.7.8
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
###3、移除替代版本
|
||||
|
||||
一旦我们的系统中不再存在某个 Python 的替代版本时,我们可以将其从 `update-alternatives` 列表中删除掉。例如,我们可以将列表中的 python2.7 版本移除掉。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# update-alternatives --remove python /usr/bin/python2.7
|
||||
update-alternatives: removing manually selected alternative - switching python to auto mode
|
||||
update-alternatives: using /usr/bin/python3.4 to provide /usr/bin/python (python) in auto mode
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linuxconfig.org/how-to-change-from-default-to-alternative-python-version-on-debian-linux
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[mr-ping](https://github.com/mr-ping)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
魅族 Pro 5 Ubuntu 版即将发布
|
||||
========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**Canonical 和魅族刚刚透露魅族 Pro 5 Ubuntu 版将在 2016 世界移动大会召开期间开始预售**
|
||||
|
||||
自从上次听到魅族的消息到现在已经很久了,但是看起来 Canonical 和这个中国的硬件厂商之间的合作关系仍然存在。从表面来看,之前魅族的 MX4 Ubuntu 版只是进行了小范围的发布,所以只有很少的设备卖出去了。
|
||||
|
||||
我们仅仅希望魅族 Pro 5 Ubuntu 版可以提高供货量,尤其是因为它是魅族的一款相当新且还提供支持的手机。
|
||||
|
||||
最新的魅族 Pro 5 是第 5 个支持 Ubuntu Touch 的官方设备,2016 年我们可能会看到更多的手机甚至是平板都会预装这个操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
## 魅族 Pro 5 Ubuntu 版将会非常震撼
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical 宣称 Pro 5 是目前已发布了的 Ubuntu 智能手机中最强大的一个,他们说的是对的,但还有一点没有被提及,即如果不考虑平板,它也是最大的 Ubuntu Touch 设备。魅族 Pro 5 采用了一颗 Exynos 7420 8 核处理器和 5.7 英寸分辨率为 1920x1080 的 AMOLED 屏,配备第三代康宁大猩猩玻璃以及 LPDDR4 内存技术。
|
||||
|
||||
很多人也许会问这个新手机的系统是否可以和桌面版系统一样,现在看起来真是如此。
|
||||
|
||||
该公司解释说,“Canonical 一直致力于通过向各种个人设备提供一个统一的自适应平台来重塑个人计算的视觉表现。因此尽管魅族 Pro 5 缺少 MHL 输出,但它运行的是最新的代码,这些代码与新近发布的平板和其它设备一样,可提供一种接近传统桌面的体验。”
|
||||
|
||||
魅族 Pro 5 最初于 2015 年 9 月发布,拥有一个 2100 万像素的后置摄像头,可以拍摄 30fps 的 2160p 视频。同时它还带有一个指纹传感器和支持快速充电的 3050 mAh 的锂电池。
|
||||
|
||||
目前这款手机只在中国和欧洲有售,预定将从 2016 年 2 月 22 日至 25 日的世界移动大会期间开始。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/meizu-pro-5-ubuntu-edition-announced-and-it-s-a-beast-photos-500526.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[osk874](https://github.com/osk874)
|
||||
校对:[Yuking](https://github.com/Yuking-net)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
35
published/20160218 Russia Announces Switch to Linux.md
Normal file
35
published/20160218 Russia Announces Switch to Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
本周 Linux 新闻: 俄罗斯宣布政府电脑系统迁移到 Linux
|
||||
=========================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
本周 Linux 新闻包括:俄罗斯宣布可能会将系统迁移到 Linux 上、Jack Wallen 思考 2016 年对 Linux 桌面系统的重要性,等等。下面就让我们看看本周 Linux 界都有那些重要新闻。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 俄罗斯宣布有可能切换到 Linux , 以此来反击西方因克里米亚问题而实施的商业禁运。
|
||||
|
||||
[俄罗斯可能将成千上万台政府的电脑系统从 Windows 切换成 Linux](http://www.techradar.com/news/world-of-tech/russia-might-switch-thousands-of-government-computers-to-linux-to-spite-microsoft-1314762) - TechRadar
|
||||
|
||||
2. Jack Wallen 写到:“对于 Linux 来说,占有桌面系统市场 1% 或者 99% 并不重要”
|
||||
|
||||
[为了 Linux 桌面系统奋斗是否真的很重要?](http://www.techrepublic.com/article/should-the-fight-for-the-linux-desktop-really-matter/) - TechRepublic
|
||||
|
||||
3. 自从去年 12 月以来,参与 Linux 基金会的 HYPERLEDGER 计划的合作伙伴有了显著的增加
|
||||
|
||||
[Linux 基金会的 HYPERLEDGER 计划已经有了 30 个合作伙伴](http://www.coindesk.com/linux-foundation-led-hyperledger-project-swells-to-30-members/) - CoinDesk
|
||||
|
||||
4. Docker 的创始人和 CTO , Solomon Hykes 建议将 Alpine Linux 作为公司新的默认操作系统
|
||||
|
||||
[Docker 将会抛弃 Ubuntu 吗?](http://www.infoworld.com/article/3031847/open-source-tools/is-docker-ditching-ubuntu-linux-confusion-reigns.html) - InfoWorld
|
||||
|
||||
5. Linux 基金会的合作项目 Node.js 基金会计划引入流行的第三方软件包“Express”
|
||||
|
||||
[Node.js 基金会计划引入社区里最流行的框架软件 Express 进行孵化](http://thenextweb.com/dd/2016/02/10/the-node-js-foundation-plans-to-incubate-one-of-the-communitys-most-popular-packages/)- The Next Web
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/software/applications/885174-this-week-in-linux-news-russia-announces-switch-to-linux-outdated-fight-for-the-linux-desktop-a-more
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[linux.com][linux.com]
|
||||
译者:[oska874](https://github.com/oska874)
|
||||
校对:[Yuking_net](https://github.com/Yuking-net)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
118
published/20160218 The Best Linux Distros of 2016.md
Normal file
118
published/20160218 The Best Linux Distros of 2016.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
|
||||
2016:如何选择 Linux 发行版
|
||||
================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[不管是在企业级应用还是在消费者领域](http://www.cio.com/article/3017983/linux/2015s-most-exciting-linux-devices.html),2015 对于 Linux 来说都是极其重要的一年。作为一个从 2005 年就开始使用 Linux 的老用户,我有幸见证了 Linux 过去这 10 年里的重大发展,[并且,我相信它在 2016 年里会更加令人激动](http://www.cio.com/article/3017177/linux/11-predictions-for-linux-in-2016.html)。在这篇文章里,我会挑选几个将在 2016 年里大放光彩的最佳发行版给大家介绍一下。
|
||||
|
||||
## 强势归来的发行版:openSUSE
|
||||
|
||||
SUSE 是 openSUSE 发行版背后的公司,同时也是起步最早的 Linux 公司;[它在 Linus Torvalds 发布 Linux 的第二年就成立了](http://www.linux.com/news/software/applications/866964-exclusive-interview-with-suse-president-nils-brauckmann)。该公司的成立实际上早于现在的 Linux 公司之王 —— Red Hat。同时 SUSE 也是 [openSUSE](https://www.opensuse.org/) 社区发行版的发起者和赞助商。
|
||||
|
||||
2015 年,openSUSE 的开发团队决定向 SUSE Linux 企业版 (SLE) 靠拢,以便让用户可以获得企业服务器特性的发行版——类似于 CentOS 和 Ubuntu 那样。因此,openSUSE 变成了 [openSUSE Leap](https://en.opensuse.org/Portal:Leap),一个直接基于 SLE SP1 的发行版。
|
||||
|
||||
两个发行版共用相同的基础代码,相互受益 —— SUSE 会选用 openSUSE 中好的代码,反之亦然。如此,openSUSE 也放弃了原本常规的发布周期,新版本与 SLE 同步发行。这意味着每个版本将会有更长的生命周期。
|
||||
|
||||
这样做的结果是,openSUSE 就成了一个非常重要的发行版,因为潜在的 SLE 用户现在可以使用 openSUSE Leap 了。不过,这还不是全部,openSUSE 同样也有发行版 [Tumbleweed](http://www.cio.com/article/3008856/open-source-tools/is-opensuse-tumbleweed-good-enough-for-a-seasoned-arch-user.html) —— 一个纯净的滚动式版本。所以,用户们可以选择使用很稳定的 openSUSE Leap 或者经常更新的 openSUSE Tumbleweed。
|
||||
|
||||
在我的记忆中,还没有其他的发行版做了这样一个令人印象深刻的强势归来。
|
||||
|
||||
## 最高可定制性的发行版:Arch Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Arch Linux 是目前最好的滚动式更新的发行版。好吧,我可能有些偏见,因为我是一名 Arch Linux 用户 ( LCTT 译注:译者也是 Arch Linux 用户,它的定制性真的很好)。然而,我认为它好的真正原因是 Arch 在很多其他领域也都表现的非常优越,并且这才是我为什么用它作为主系统的原因。
|
||||
|
||||
- 对于那些想要学习 Linux 方方面面的用户来说,[Arch Linux](https://www.archlinux.org/) 无疑是一个绝佳的选择。因为你需要手动安装所有自己需要的东西,这样你会慢慢学到 Linux 系统的所有细节。
|
||||
|
||||
- Arch 是一个可高度定制发行版。任何桌面环境 (DE) 都没有了 “Arch” 的原味。你能够得到的只是一个基础系统,然后你可以在上边构建你所想要的发行版。无论好坏,也不像 openSUSE 或者 Ubuntu 那样,Arch 没有额外的补丁或者集成环境。你得到的基本就是上游开发者所创建的原始软件。
|
||||
|
||||
- Arch Linux 同时也是最好的滚动式更新的发行版之一。它需要经常保持着更新。用户所运行的基本上是最新的软件,当然,也可以通过非稳定仓库运行预发行版的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
- Arch 闻名于拥有为数众多的优秀文档。Arch Wiki 是我用以了解所有 Linux 相关事情的完整资源。
|
||||
|
||||
- Arch 中,我最喜欢的是,它提供了“任何”其他发行版中可用的的包和软件,同时还要感谢 AUR (Arch User Repository,Arch 用户仓库)。
|
||||
|
||||
## 最美观的发行版:elementary OS
|
||||
|
||||
不同的发行版会有不同的关注点——多数情况下表现为技术的不同。在大多数的 Linux 发行版中,外观和用户感觉并非他们优先考虑的事情 —— 这通常是桌面环境需要考虑的事情。
|
||||
|
||||
[elementary OS](https://elementary.io/) 正在尝试改变这一事实。在这个发行版中,设计是占据重要位置,并且原因明显——这个发行版是由那些以在 Linux 世界创建漂亮图标而闻名的设计人员所开发的。
|
||||
|
||||
elementary OS 相当注重整体外观和用户感觉。开发者创建了他们自己的组件,包括桌面环境。此外,他们只会选择那些符合设计规范的应用来加入到软件仓库。你可以发现 elementary OS 有很浓重的 Mac OS X 气息。
|
||||
|
||||
## 最好的新晋发行版:Solus
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[Solus](https://solus-project.com/) 最近获得非常大的关注程度。它是一个看起来中规中矩、从零开始构建的操作系统,它并非 Debian 或者 Ubuntu 的衍生版本。它使用的 Budgie 桌面环境同样是从零开始构建的,但它的目标是兼容 Gnome。Solus 和 Google 的 Chrome OS 一样——一切从简。
|
||||
|
||||
我个人没怎么玩过 Solus,但它看起来很有前途。Solus 实际上并不是一个 “新” 系统。它曾以不同的形式和名称存在了很长时间,但直到 2015 年整个项目才以现在这个新名称重归大众视野。
|
||||
|
||||
## 最好的云操作系统:Chrome OS
|
||||
|
||||
[Chrome OS](https://www.chromium.org/chromium-os) 可能不会成为你的典型 Linux 发行版,毕竟它是基于浏览器的操作系统,主要用以在线使用。但由于它基于 Linux ,任何人都可以获取其源码进行编译,它同样是一个吸引人的系统。我每天都使用 Chrome OS,它是一个优秀、不用自己维护并且总是保持最新状态的系统,每个人都可以单纯地用它来进行 web 相关的用途。Chrome OS 和 Android 对于推动 Linux 在 PC 市场和移动市场的占有率有着不可或缺的功劳。
|
||||
|
||||
## 最好的笔记本计算机操作系统:Ubuntu MATE
|
||||
|
||||
大多数的笔记本计算机都没有高端的硬件,假如你运行了一个很耗费资源的桌面环境,那么你可能没有足够的系统资源或电量来维持你的使用 —— 因为基本上被操作系统自身消耗了。于是我找到了 [Ubuntu MATE](http://www.cio.com/article/2848475/ubuntu-mate-enterprise-customers.html) 这个优秀的系统。它是轻量级的环境,但提供了能让你拥有不错体验的所有软件。也幸好它的轻量级设计,大部分的系统资源都留来给你的软件使用,让你依旧可以完成一些繁重的任务。我认为它对于低端硬件来说是最好的发行版。
|
||||
|
||||
## 为老旧硬件支持而生的发行版:Lubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
假如你身边拥有一些过时的笔记本或 PC,给它安装 [Lubuntu](http://lubuntu.net/) 来获得重生吧。Lubuntu 使用的是 LXDE 桌面环境,但该项目与 Razor Qt 合并之后,变成了 LXQt。尽管最新的版本 15.04 依旧使用 LXDE,但之后的版本将会使用 LXQt。Lubuntu 对于老旧硬件来说是最合适不过的系统了。
|
||||
|
||||
## 为物联网 (IoT) 而生的发行版:Snappy Ubuntu Core
|
||||
|
||||
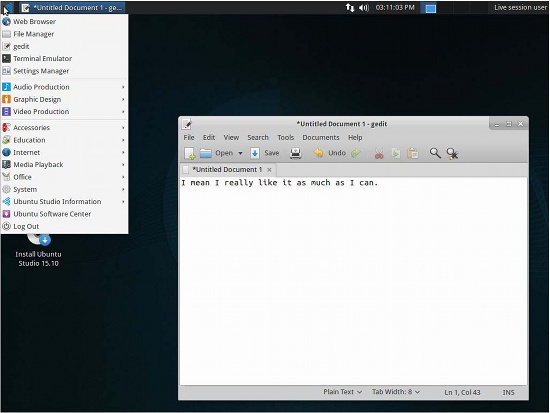
|
||||
|
||||
Snappy Ubuntu Core 是为物联网 (IoT) 及此类设备而生的 Linux 操作系统。该系统拥有巨大潜力,它可以将我们身边绝大多数的东西 —— 如路由器、咖啡机和无人机等——变成智能设备。让它更有趣的是,软件管理更新的方式以及为增加安全而提供的容器化支持。
|
||||
|
||||
## 为桌面系统而生的发行版:Linux Mint Cinnamon
|
||||
|
||||
[Linux Mint Cinnamon](http://www.linux.com/news/software/applications/838569-review-linux-mint-172-release/) 对于台式机和一些有强大硬件的笔记本来说是最好的操作系统。我一般把它叫做 Linux 世界里的 Mac OS X。老实说,由于 Cinnamon 的不稳定,我在很长一段时间内并不是 Linux Mint 的忠实粉丝。但是,在开发者使用Ubuntu LTS (Long Term Support,长期支持)作为基础版本之后,该发行版就变得难以想象的稳定。因为开发者不必花费精力来跟上 Ubuntu 的开发进度,他们现在可以将所有精力放到提升 Cinnamon 上。
|
||||
|
||||
## 为游戏而生的发行版:Steam OS
|
||||
|
||||
对于桌面版 Linux 来说,玩游戏同样是短板。很多用户为了能够玩游戏,安装了 Linux 和 Windows 双系统。而 Valve 则尝试改变这个局面。Valve 是一个游戏发行商,它提供一个可以在不同平台上运行游戏的客户端。并且,Valve 也同样创建了它自己的开源操作系统——[Steam OS](http://store.steampowered.com/steamos/)——为了创建一个基于 Linux 的游戏平台。截至 2015 年底,它的合作伙伴开始把搭载了 Steam OS 的机器推向市场。
|
||||
|
||||
## 为隐私而生的发行版:Tails
|
||||
|
||||
在充斥着大量监控和营销者的跟踪 (对目标内容进行的匿名跟踪通常是可接受的)的岁月,隐私保护就变成了一个重要问题。如果你想脱离政府或者市场机构的监控和跟踪,那么你需要一款始终考虑到隐私问题的操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
在出于保护隐私的考虑上,没有任何一款系统可以超越 [Tails](https://tails.boum.org/)。它是一款基于 Debian 的发行版,并且在设计之初就考虑了隐私和匿名的支持。Tails 非常优秀,而且据报道说,NSA 认为这是对他们的监控的主要威胁之一。
|
||||
|
||||
## 为多媒体制作而生的发行版:Ubuntu Studio
|
||||
|
||||
基于 Linux 的操作系统有一个明显的弱点,那就是对多媒体制作的支持并不友好。所有专业级应用基本只能运行在 Windows 或者 Mac OS X 上。Linux 系统从来都不缺乏像样的音频/视频制作软件,但这样还是远远不够的。应该要有一款轻量级的桌面环境,使得那些宝贵的系统资源——如 CPU 和 RAM——尽量少占用,以便用于多媒体制作。目前,[Ubuntu Studio](https://ubuntustudio.org/tour/) 对多媒体制作的支持最好。它使用了 Xfce 桌面环境,并且有各种各样的音频、视频以及图像编辑应用。
|
||||
|
||||
## 最好的企业发行版:SLE/RHEL
|
||||
|
||||
企业级用户并不会通过浏览像这样的文章来了解他们的服务器该运行什么发行版。他们通常非常明确地知道该到哪里获取信息:即 [Red Hat Enterprise Linux](https://www.redhat.com/en/technologies/linux-platforms/enterprise-linux) 或 [SUSE Linux Enterprise](https://www.suse.com/)。这两个名字已经成了企业服务器的代名词了。同时,这些公司也都通过创新来推动将一切都容器化和变成软件定义的。
|
||||
|
||||
## 最好的服务器操作系统:Debian/CentOS
|
||||
|
||||
假如你在考虑自己运行一台服务器,但有不希望支付 RHEL 或者 SLE 授权的费用,那么 [Debian](https://www.debian.org/) 或者 [CentOS](https://www.centos.org/) 将是你最好的选择。这两个发行版是社区主导的服务器操作系统,具有不可动摇的地位。并且它们有着长期支持,你不必担忧需要经常去升级系统。
|
||||
|
||||
## 最好的移动操作系统:Plasma Mobile
|
||||
|
||||
尽管,基于 Linux 的 Android 系统称雄于移动操作系统市场,但是大多数的开源社区——也包括我在内——也仍然强烈希望能有一个发行版可以为移动设备提供传统 Linux 的桌面应用。同时,这样的一个发行版由开源社区来维护会比由商业公司来维护好的多,只有这样,用户才能成为这个发行版的关注点,而不是由公司的商业目标来决定这个发行版的发展趋势。KDE 的 [Plasma Mobile](https://community.kde.org/Plasma/Mobile) 刚好实现了我们的愿望。
|
||||
|
||||
这个基于 Kubuntu 的发行版始于 2015 年。因为 KDE 社区以坚守标准和为公众开发应用而闻名,我非常期待 Plasma Mobile 能够一直坚持下去。
|
||||
|
||||
## 为 ARM 设备而生的发行版:Arch Linux ARM
|
||||
|
||||
随着 Android 系统的成功,我们的生活也围绕者越来越多的 ARM 设备——从树莓派 (Raspberry Pi) 到 Chromebook 以及 Nvidia Shield。为 Intel/AMD 架构的 CPU 而编写的传统发行版并不能够在这些 ARM 架构的设备上运行。而一些为 ARM 而编写的发行版却仅仅只能在特定的硬件上运行,比如只能运行在树莓派 (Raspberry Pi) 上的 Raspbian 系统。这就是为什么 [Arch Linux ARM](http://archlinuxarm.org/) (ALARM) 让人眼前一亮的原因。它是一个基于 Arch Linux 的纯粹由社区主导的发行版,可以在树梅派 (Raspberry Pi)、Chromebook、Android 设备以及 Nvidia Shield 等设备上运行。同时,更好的是,也由于 AUR,你可以安装很多在其他发行版可能无法获取的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
## 结论
|
||||
|
||||
在我写完本文的时候,连我自己都震惊了。能够在 Linux 的世界里为大家写点东西真的是很令人激动。不必去管 Linux 统治桌面电脑的时代是否会到来,我们都要一样享受自己使用 Linux 的每一刻快乐时光。
|
||||
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/software/applications/878620-the-best-linux-distros-of-2016
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Swapnil Bhartiya][a]
|
||||
译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
|
||||
校对:[mudongliang](https://github.com/mudongliang),[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/61003
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
||||
Linux Mint 18 将拥有自己的应用集
|
||||
=============================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
对于发行版开发者来说,创建和发布一系列专为他们发行版设计的应用是再平常不过的事情。一个最典型的例子就是 [elementary OS](https://elementary.io/) 。而在经过九年的努力后,Linux Mint 终于孤注一掷做了相同的事情。
|
||||
|
||||
[Linux Mint](http://www.linuxmint.com/) 是现今最著名的 Linux 发行版之一。其基于 Ubuntu 和 Debian,Linux Mint 努力去创建一个现代的、优雅的、舒适的操作系统,不但强大而且易用。(LCTT 译注:Linux Mint 基于 Ubuntu,而 Linux Mint Debian Edition 基于 Debian。)Linux Mint 背后的团队同时也积极参与 [MATE](http://itsfoss.com/install-mate-desktop-ubuntu-14-04/) 和 [Cinnamon](http://itsfoss.com/install-cinnamon-ubuntu-14-04/) 桌面环境开发。
|
||||
|
||||
## 前有 X 战警(X-men),后有 X 应用(X-Apps)
|
||||
|
||||
周四, Linux Mint 项目领导者 Clement Lefebvre [宣布](http://blog.linuxmint.com/?p=2985) X-Apps 的创建。X-Apps 被设计为不依赖特定桌面环境,以便开发者可以直接更新它们而不必针对每一种桌面环境做调整。Lefebvre 声明这些 X-Apps 将会被作为 Cinnamon、MATE 和 Xfce 桌面环境的默认应用。
|
||||
|
||||
## Linux 是否需要更多的应用?
|
||||
|
||||
据 Lefebvre 所述,X-Apps 的创建是因 GNOME 3.18 发布所需。对于 GNOME 3.18 的发布,他这样说:
|
||||
|
||||
> “GTK 本身和一些 GNOME 应用都在 GNOME SHELL 上集成地很好,而且看起来风格很一致。坏消息就是它们在任何别的地方看起来很不相称。使事情变得更糟的是,Ubuntu 的旗舰产品 Unity 重度依赖 GTK、GNOME 应用及 GNOME 环境本身,所以我们这里不能在上游的 3.18 版本中处理,而这一系列的补丁会带来它们自己的问题(举一个例子,Ubuntu 在应用中重新引入菜单条和标题栏,但是不重写它们的头部栏..所以你有时会看到它们三者一起出现)。”
|
||||
|
||||
在过去,Linux Mint 团队通过“应用降级(例如 Linux Mint 17 使用 gedit 2.30),给 GNOME 打补丁以及使用替代品(大部分在 MATE 和 Xfce)”来处理这个问题。
|
||||
|
||||
Lefebvre 也说为 Cinnamon 和 MATE 构建特定应用没有意义。这就是为什么他们选择开发那些通用的,可以完美地适应运行在 Cinnamon,MATE 和 Xfce(以及其他可能的桌面环境)的应用。
|
||||
|
||||
他进一步补充道:
|
||||
|
||||
>“X-Apps 将会是一个通用的,使用传统的接口 GTK3 应用的集合。它能被用作 Cinnamon,MATE 和 Xfce 默认的桌面组件。在 Mint 18 中,“X apps” 将允许我们去维护一个本地风格及更高层面的集成。因为它们将会被用于替代看起来很不一致的 GNOME 桌面应用。长期来讲,X-App 项目将会允许我们去开发新的功能和改进应用本身(这是一些我们无法通过打补丁,临时分支或者特定桌面的分支做到的事情,比如说 MATE 桌面应用,因为它代价太高)。”
|
||||
|
||||
## 将会有什么类型的应用?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Lefebvre 只透露其中一个即将来临的 X-Apps:一个名为 xedit 的文本编辑器。下面是这个软件提供的一些特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 基于 Pluma,很容易学会使用
|
||||
- 使用 GTK3
|
||||
- 不依赖 GNOME 或 MATE
|
||||
|
||||
## 何时呢?
|
||||
|
||||
X-Apps 将会和 [Linux Mint 18](http://itsfoss.com/linux-mint-18-codenamed-sarah/) 一同到来。而 Linux Mint 18 将会在 Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 发布之后数月后发布。[Ubuntu 16.04 LTS 计划于四月发布。](http://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-1604-release-schedule/)
|
||||
|
||||
## 总结
|
||||
|
||||
就我而言,无论何时当我听见某人发布一个新发行版特定的应用,我都会局促不安。Linux 世界本身已经难以想象的碎片化了。我们真的需要花费时间和精力去创建更多的重复的项目吗?但不要误解我,我喜欢桌面无关软件的想法。它将修复大量的一个桌面一个应用样子的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
使我发愁的问题是“它们是否会成功?”。正如我之前所说,Linux Mint 团队成员也在两种桌面环境工作。目前增加了应用开发就让这些混在一起了。我自己没有写过一个软件(除了 Hello World),但是我知道当你尝试且使一个项目复杂化,就会发生不好的事情。许多项目已经变成了不断膨胀的恶龙。我希望这样的事不要发生在这里。
|
||||
|
||||
你有不同的想法吗?在下方评论以便让我知道。
|
||||
|
||||
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/linux-mint-own-apps/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[JOHN PAUL][a]
|
||||
译者:[mudongliang](https://github.com/mudongliang)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/john/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
我们能通过快速、开放的研究来战胜寨卡病毒吗?
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
关于寨卡病毒,最主要的问题就是我们对于它了解的太少了。这意味着我们需要尽快对它作出很多研究。
|
||||
|
||||
寨卡病毒现已严重威胁到世界人民的健康。在 2015 年爆发之后,它就成为了全球性的突发公共卫生事件,并且这个病毒也可能与儿童的出生缺陷有关。根据[维基百科][4],在这个病毒在 40 年代末期被发现以后,早在 1952 年就被观测到了对于人类的影响。
|
||||
|
||||
在 2 月 10 日,开放杂志 PLoS [发布了一个声明][1],这个是声明是关于有关公众紧急状况的信息共享。在此之后,刊登在研究期刊 F1000 的一篇文章 [对于能治疗寨卡病毒的开源药物(Open drug)的研究][2],它讨论了寨卡病毒及其开放研究的状况。那篇来自 PLoS 的声明列出了超过 30 个开放了对于寨卡病毒的研究进度的数据的重要组织。并且世界卫生组织实施了一个特别规定,以[创作共用许可证][3]公布提交到他们那里的资料。
|
||||
|
||||
快速公布,无限制的重复利用,以及强调研究结果的传播是推动开放科研社区的战略性一步。看到我们所关注的突发公共卫生事件能够以这样的方式开始是很令人受鼓舞的。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/life/16/2/how-rapid-open-science-could-change-game-zika-virus
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Marcus D. Hanwell][a]
|
||||
译者:[name1e5s](https://github.com/name1e5s)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/mhanwell
|
||||
[1]: http://blogs.plos.org/plos/2016/02/statement-on-data-sharing-in-public-health-emergencies/
|
||||
[2]: http://f1000research.com/articles/5-150/v1
|
||||
[3]: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/igo/
|
||||
[4]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zika_virus
|
||||
0
published/20160226 Development Release
Normal file
0
published/20160226 Development Release
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
Xubuntu 16.04 Beta 1 开发发布
|
||||
============================================
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 发布组宣布为选定的社区版本而准备的最新的 beta 测试镜像已经可以使用了。新的发布版名称是 16.04 beta 1 ,这个版本只推荐给测试人员测试用,并不适合普通人进行日常使用。
|
||||
|
||||
“这个 beta 特性的镜像主要是为 [Lubuntu][1], Ubuntu Cloud, [Ubuntu GNOME][2], [Ubuntu MATE][3], [Ubuntu Kylin][4], [Ubuntu Studio][5] 和 [Xubuntu][6] 这几个发布版准备的。Xenial Xerus (LCTT 注: ubuntu 16.04 的开发代号) 的这个预发布版本并不推荐那些需要稳定版本的人员使用,同时那些不希望在系统运行中偶尔或频繁的出现 bug 的人也不建议使用这个版本。这个版本主要还是推荐给那些喜欢 ubuntu 的开发人员,以及那些想协助我们测试、报告 bug 和修改 bug 的人使用,和我们一起努力让这个发布版本早日准备就绪。” 更多的信息可以从 [发布日志][7] 获取。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.linux.com/news/software/applications/888731-development-release-xubuntu-1604-beta-1
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[DistroWatch][a]
|
||||
译者:[Ezio](https://github.com/oska874)
|
||||
校对:[Ezio](https://github.com/oska874)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/284
|
||||
[1]: http://distrowatch.com/lubuntu
|
||||
[2]: http://distrowatch.com/ubuntugnome
|
||||
[3]: http://distrowatch.com/ubuntumate
|
||||
[4]: http://distrowatch.com/ubuntukylin
|
||||
[5]: http://distrowatch.com/ubuntustudio
|
||||
[6]: http://distrowatch.com/xubuntu
|
||||
[7]: https://lists.ubuntu.com/archives/ubuntu-devel-announce/2016-February/001173.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
逾千万使用 https 的站点受到新型解密攻击的威胁
|
||||
===========================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
低成本的 DROWN 攻击能在数小时内完成数据解密,对采用了 TLS 的邮件服务器也同样奏效。
|
||||
|
||||
一国际研究小组于周二发出警告,据称逾 1100 万家网站和邮件服务采用的用以保证服务安全的[传输层安全协议][1],对于一种新发现的、成本低廉的攻击而言异常脆弱,这种攻击会在几个小时内解密敏感的通信,在某些情况下解密甚至能瞬间完成。 1 百万家最为流行的网站中有超过 81,000 家正处于这些脆弱的 HTTPS 协议的保护之下。
|
||||
|
||||
这种攻击主要针对受 TLS 保护、依赖于 [RSA 加密系统][2]的通信。如果密钥泄露了,即使是间接的由 SSLv2,一种在 20 年前就因为自身缺陷而退休了的 LTS 前辈。该漏洞允许攻击者,可以通过反复使用 SSLv2 创建与服务器连接的方式,解密截获的 TLS 连接。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.linux.com/news/software/applications/889455--more-than-11-million-https-websites-imperiled-by-new-decryption-attack
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ArsTechnica][a]
|
||||
译者:[Ezio](https://github.com/oska874)
|
||||
校对:[martin2011qi](https://github.com/martin2011qi)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/112
|
||||
[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security
|
||||
[2]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RSA_(cryptosystem)
|
||||
53
sources/news/20160129 Recognizing correct code.md
Normal file
53
sources/news/20160129 Recognizing correct code.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
# Recognizing correct code
|
||||
|
||||
Automatic bug-repair system fixes 10 times as many errors as its predecessors.
|
||||
------
|
||||
DongShuaike is translating.
|
||||
|
||||
MIT researchers have developed a machine-learning system that can comb through repairs to open-source computer programs and learn their general properties, in order to produce new repairs for a different set of programs.
|
||||
|
||||
The researchers tested their system on a set of programming errors, culled from real open-source applications, that had been compiled to evaluate automatic bug-repair systems. Where those earlier systems were able to repair one or two of the bugs, the MIT system repaired between 15 and 18, depending on whether it settled on the first solution it found or was allowed to run longer.
|
||||
|
||||
While an automatic bug-repair tool would be useful in its own right, professor of electrical engineering and computer science Martin Rinard, whose group developed the new system, believes that the work could have broader ramifications.
|
||||
|
||||
“One of the most intriguing aspects of this research is that we’ve found that there are indeed universal properties of correct code that you can learn from one set of applications and apply to another set of applications,” Rinard says. “If you can recognize correct code, that has enormous implications across all software engineering. This is just the first application of what we hope will be a brand-new, fabulous technique.”
|
||||
|
||||
Fan Long, a graduate student in electrical engineering and computer science at MIT, presented a paper describing the new system at the Symposium on Principles of Programming Languages last week. He and Rinard, his advisor, are co-authors.
|
||||
|
||||
Users of open-source programs catalogue bugs they encounter on project websites, and contributors to the projects post code corrections, or “patches,” to the same sites. So Long was able to write a computer script that automatically extracted both the uncorrected code and patches for 777 errors in eight common open-source applications stored in the online repository GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
**Feature performance**
|
||||
|
||||
As with [all][1] machine-learning systems, the crucial aspect of Long and Rinard’s design was the selection of a “[feature set][2]” that the system would analyze. The researchers concentrated on values stored in memory — either variables, which can be modified during a program’s execution, or constants, which can’t. They identified 30 prime characteristics of a given value: It might be involved in an operation, such as addition or multiplication, or a comparison, such as greater than or equal to; it might be local, meaning it occurs only within a single block of code, or global, meaning that it’s accessible to the program as a whole; it might be the variable that represents the final result of a calculation; and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
Long and Rinard wrote a computer program that evaluated all the possible relationships between these characteristics in successive lines of code. More than 3,500 such relationships constitute their feature set. Their machine-learning algorithm then tried to determine what combination of features most consistently predicted the success of a patch.
|
||||
|
||||
“All the features we’re trying to look at are relationships between the patch you insert and the code you are trying to patch,” Long says. “Typically, there will be good connections in the correct patches, corresponding to useful or productive program logic. And there will be bad patterns that mean disconnections in program logic or redundant program logic that are less likely to be successful.”
|
||||
|
||||
**Ranking candidates**
|
||||
|
||||
In earlier work, Long had developed an algorithm that attempts to repair program bugs by systematically modifying program code. The modified code is then subjected to a suite of tests designed to elicit the buggy behavior. This approach may find a modification that passes the tests, but it could take a prohibitively long time. Moreover, the modified code may still contain errors that the tests don’t trigger.
|
||||
|
||||
Long and Rinard’s machine-learning system works in conjunction with this earlier algorithm, ranking proposed modifications according to the probability that they are correct before subjecting them to time-consuming tests.
|
||||
|
||||
The researchers tested their system, which they call Prophet, on a set of 69 program errors that had cropped up in eight popular open-source programs. Of those, 19 are amenable to the type of modifications that Long’s algorithm uses; the other 50 have more complicated problems that involve logical inconsistencies across larger swaths of code.
|
||||
|
||||
When Long and Rinard configured their system to settle for the first solution that passed the bug-eliciting tests, it was able to correctly repair 15 of the 19 errors; when they allowed it to run for 12 hours per problem, it repaired 18.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, that still leaves the other 50 errors in the test set untouched. In ongoing work, Long is working on a machine-learning system that will look at more coarse-grained manipulation of program values across larger stretches of code, in the hope of producing a bug-repair system that can handle more complex errors.
|
||||
|
||||
“A revolutionary aspect of Prophet is how it leverages past successful patches to learn new ones,” says Eran Yahav, an associate professor of computer science at the Technion in Israel. “It relies on the insight that despite differences between software projects, fixes — patches — applied to projects often have commonalities that can be learned from. Using machine learning to learn from ‘big code’ holds the promise to revolutionize many programming tasks — code completion, reverse-engineering, et cetera.”
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.mit.edu/2016/faster-automatic-bug-repair-code-errors-0129
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Larry Hardesty
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/翻译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://news.mit.edu/2013/teaching-computers-to-see-by-learning-to-see-like-computers-0919
|
||||
[2]:http://news.mit.edu/2015/automating-big-data-analysis-1016
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
Zephyr Project for Internet of Things, releases from Facebook, IBM, Yahoo, and more news
|
||||
===========================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In this week's edition of our open source news roundup, we take a look at the new IoT project from the Linux Foundation, three big corporations releasing open source, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
**News roundup for February 21 - 26, 2016**
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux Foundation unveils the Zephyr Project
|
||||
|
||||
The Internet of Things (IoT) is shaping up to be the next big thing in consumer technology. At the moment, most IoT solutions are proprietary and closed source. Open source is making numerous in-roads into the IoT world, and that's undoubtedly going to accelerate now that the Linux Foundation has [announced the Zephyr Project][1].
|
||||
|
||||
The Zephyr Project, according to ZDNet, "hopes to bring vendors and developers together under a single operating system which could make the development of connected devices an easier, less expensive and more stable process." The Project "aims to incorporate input from the open source and embedded developer communities and to encourage collaboration on the RTOS (real-time operating system)," according to the [Linux Foundation's press release][2].
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, Intel Corporation, NXP Semiconductors N.V., Synopsys, Inc., and UbiquiOS Technology Limited are the main supporters of the project. The Linux Foundation intends to attract other IoT vendors to this effort as well.
|
||||
|
||||
### Releases from Facebook, IBM, Yahoo
|
||||
|
||||
As we all know, open source isn't just about individuals or small groups hacking on code and hardware. Quite a few large corporations have significant investments in open source. This past week, three of them affirmed their commitment to open source.
|
||||
|
||||
Yahoo again waded into open source waters this week with the [release of CaffeOnSpark][3] artificial intelligence software under an Apache 2.0 license. CaffeOnSpark performs "a popular type of AI called 'deep learning' on the vast swaths of data kept in its Hadoop open-source file system for storing big data," according to VentureBeat. If you're curious, you can [find the source code on GitHub][4].
|
||||
|
||||
Earlier this week, Facebook "[unveiled a new project that seeks not only to accelerate the evolution of technologies that drive our mobile networks, but to freely share this work with the world’s telecoms][5]," according to Wired. The company plans to build "everything from new wireless radios to nee optical fiber equipment." The designs, according to Facebook, will be open source so any telecom firm can use them.
|
||||
|
||||
As part of the [Open Mainframe Project][6], IBM has open sourced the code for its Anomaly Detection Engine (ADE) for Linux logs. [According to IBM][7], "ADE detects anomalous time slices and messages in Linux logs using statistical learning" to detect suspicious behaviour. You can grab the [source code for ADE][8] from GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
### European Union to fund research
|
||||
|
||||
The European Research Council, the European Union's science and technology funding body, is [funding four open source research projects][9] to the tune of about €2 million. According to joinup.ec.europa.eu, the projects being funded are:
|
||||
|
||||
- A code audit of Mozilla's open source Rust programming language
|
||||
|
||||
- An initiative at INRIA (France's national computer science research center) studying secure programming
|
||||
|
||||
- A project at Austria's Technische Universitat Graz testing "ways to secure code against attacks that exploit certain properties of the computer hardware"
|
||||
|
||||
- The "development of techniques to prove popular cryptographic protocols and schemes" at IST Austria
|
||||
|
||||
### In other news
|
||||
|
||||
- [Infosys' newest weapon: open source][10]
|
||||
|
||||
- [Intel demonstrates Android smartphone running a Linux desktop][11]
|
||||
|
||||
- [BeeGFS file system goes open source][12]
|
||||
|
||||
A big thanks, as always, to the Opensource.com moderators and staff for their help this week.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/life/16/2/weekly-news-feb-26
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Scott Nesbitt][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/scottnesbitt
|
||||
[1]: http://www.zdnet.com/article/the-linux-foundations-zephyr-project-building-an-operating-system-for-iot-devices/
|
||||
[2]: http://www.linuxfoundation.org/news-media/announcements/2016/02/linux-foundation-announces-project-build-real-time-operating-system
|
||||
[3]: http://venturebeat.com/2016/02/24/yahoo-open-sources-caffeonspark-deep-learning-framework-for-hadoop/
|
||||
[4]: https://github.com/yahoo/CaffeOnSpark
|
||||
[5]: http://www.wired.com/2016/02/facebook-open-source-wireless-gear-forge-5g-world/
|
||||
[6]: https://www.openmainframeproject.org/
|
||||
[7]: http://openmainframeproject.github.io/ade/
|
||||
[8]: https://github.com/openmainframeproject/ade
|
||||
[9]: https://joinup.ec.europa.eu/node/149541
|
||||
[10]: http://www.businessinsider.in/Exclusive-Infosys-is-using-Open-Source-as-its-mostlethal-weapon-yet/articleshow/51109129.cms
|
||||
[11]: http://www.theregister.co.uk/2016/02/23/move_over_continuum_intel_shows_android_smartphone_powering_bigscreen_linux/
|
||||
[12]: http://insidehpc.com/2016/02/beegfs-parallel-file-system-now-open-source/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
Node.js 5.7 released ahead of impending OpenSSL updates
|
||||
=============================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
>Once again, OpenSSL fixes must be evaluated by keepers of the popular server-side JavaScript platform
|
||||
|
||||
The Node.js Foundation is gearing up this week for fixes to OpenSSL that could mean updates to Node.js itself.
|
||||
|
||||
Releases to OpenSSL due on Tuesday will fix defects deemed to be of "high" severity, Rod Vagg, foundation technical steering committee director, said [in a blog post][1] on Monday. Within a day of the OpenSSL releases, the Node.js crypto team will assess their impacts, saying, "Please be prepared for the possibility of important updates to Node.js v0.10, v0.12, v4 and v5 soon after Tuesday, the 1st of March."
|
||||
|
||||
[ Deep Dive: [How to rethink security for the new world of IT][2]. | Discover how to secure your systems with InfoWorld's [Security newsletter][3]. ]
|
||||
|
||||
The high severity status actually means the issues are of lower risks than critical, perhaps affecting less-common configurations or less likely to be exploitable. Due to an embargo, the exact nature of these fixes and their impact on Node.js remain uncertain, said Vagg. "Node.js v0.10 and v0.12 both use OpenSSL v1.0.1, and Node.js v4 and v5 both use OpenSSL v1.0.2, and releases from nodejs.org and some other popular distribution sources are statically compiled. Therefore, all active release lines are impacted by this update." OpenSSL also impacted Node.js in December, [when two critical vulnerabilities were fixed][4].
|
||||
|
||||
The latest OpenSSL developments follow [the release of Node.js 5.7.0][5], which is clearing a path for the upcoming Node.js 6. Version 5 is the main focus for active development, said foundation representative Mikeal Rogers, "However, v5 won't be supported long-term, and most users will want to wait for v6, which will be released by the end of April, for the new features that are landing in v5."
|
||||
|
||||
Release 5.7 has more predictability for C++ add-ons' interactions with JavaScript. Node.js can invoke JavaScript code from C++ code, and in version 5.7, the C++ node::MakeCallback() API is now re-entrant; calling it from inside another MakeCallback() call no longer causes the nextTick queue or Promises microtask queue to be processed out of order, [according to release notes][6].
|
||||
|
||||
Also fixed is an HTTP bug where handling headers mistakenly trigger an "upgrade" event where the server just advertises protocols. The bug can prevent HTTP clients from communicating with HTTP2-enabled servers. Version 5.7 performance improvements are featured in the path, querystring, streams, and process.nextTick modules.
|
||||
|
||||
This story, "Node.js 5.7 released ahead of impending OpenSSL updates" was originally published by [InfoWorld][7].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.itworld.com/article/3039005/security/nodejs-57-released-ahead-of-impending-openssl-updates.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Paul Krill][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.itworld.com/author/Paul-Krill/
|
||||
[1]: https://nodejs.org/en/blog/vulnerability/openssl-march-2016/
|
||||
[2]: http://www.infoworld.com/resources/17273/security-management/how-to-rethink-security-for-the-new-world-of-it#tk.ifw-infsb
|
||||
[3]: http://www.infoworld.com/newsletters/signup.html#tk.ifw-infsb
|
||||
[4]: http://www.infoworld.com/article/3012157/security/why-nodejs-waited-for-openssl-security-update-before-patching.html
|
||||
[5]: https://nodejs.org/en/blog/release/v5.7.0/
|
||||
[6]: https://nodejs.org/en/blog/release/v5.7.0/
|
||||
[7]: http://www.infoworld.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
OpenSSH 7.2 Out Now with Support for RSA Signatures Using SHA-256/512 Algorithms
|
||||
========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**Today, February 29, 2016, the OpenBSD project had the great pleasure of announcing the release and immediate availability for download of OpenSSH 7.2 for all supported platforms.**
|
||||
|
||||
According to the internal [release notes][1], also attached at the end of the article for reference, OpenSSH 7.2 is primarily a bugfix release, fixing most of the issues reported by users or discovered by the development team since the release of OpenSSH 7.1p2, but we can see several new features as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Among these, we can mention support for RSA signatures using SHA-256 or SHA-256 512 hash algorithms, the addition of an AddKeysToAgent client option to add private keys used for authentication to the ssh-agent, and the implementation of the "restrict" authorized_keys option for storing key restrictions.
|
||||
|
||||
Furthermore, there's now an ssh_config CertificateFile option for explicitly listing certificates, the ssh-keygen is now capable of changing the key comment for all supported formats, fingerprinting is now allowed from standard input and for multiple public keys in a file.
|
||||
|
||||
### ssh-keygen now supports multiple certificates
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the changes mentioned above, OpenSSH 7.2 adds support for multiple certificates to ssh-keygen, one per line, implements the "none" argument for sshd_config ChrootDirectory and Foreground, and the "-c" flag allows ssh-keyscan to fetch certificates instead of plain keys.
|
||||
|
||||
Last but not least, OpenSSH 7.2 no longer enables by default all flavors of the rijndael-cbc aliases for AES, blowfish-cbc, and cast128-cbc legacy ciphers, as well as MD5-based and truncated HMAC algorithms. The getrandom() syscall is now supported under Linux. [Download OpenSSH 7.2][2] and check the changelog below for some additional details about exactly what has been fixed in this major release.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/openssh-7-2-out-now-with-support-for-rsa-signatures-using-sha-256-512-algorithms-501111.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Marius Nestor][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/marius-nestor
|
||||
[1]: http://www.openssh.com/txt/release-7.2
|
||||
[2]: http://linux.softpedia.com/get/Security/OpenSSH-4474.shtml
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
translating by tastynoodle
|
||||
5 best open source board games to play online
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I have always had a fascination with board games, in part because they are a device of social interaction, they challenge the mind and, most importantly, they are great fun to play. In my misspent youth, myself and a group of friends gathered together to escape the horrors of the classroom, and indulge in a little escapism. The time provided an outlet for tension and rivalry. Board games help teach diplomacy, how to make and break alliances, bring families and friends together, and learn valuable lessons.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -333,4 +333,4 @@ via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2982920/open-source-tools/bossie-awards-20
|
||||
[43]:http://www.infoworld.com/article/2982429/bossie-awards-2015-the-best-open-source-big-data-tools.html
|
||||
[44]:http://www.infoworld.com/article/2982923/bossie-awards-2015-the-best-open-source-data-center-and-cloud-software.html
|
||||
[45]:http://www.infoworld.com/article/2982630/bossie-awards-2015-the-best-open-source-desktop-and-mobile-software.html
|
||||
[46]:http://www.infoworld.com/article/2982962/bossie-awards-2015-the-best-open-source-networking-and-security-software.html
|
||||
[46]:http://www.infoworld.com/article/2982962/bossie-awards-2015-the-best-open-source-networking-and-security-software.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,6 @@
|
||||
robot527 translating
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Bossie Awards 2015: The best open source networking and security software
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
InfoWorld's top picks of the year among open source tools for building, operating, and securing networks
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
|
||||
bazz2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
|
||||
Review EXT4 vs. Btrfs vs. XFS
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To be honest, one of the things that comes last in people’s thinking is to look at which file system on their PC is being used. Windows users as well as Mac OS X users even have less reason for looking as they have really only 1 choice for their operating system which are NTFS and HFS+. Linux operating system, on the other side, has plenty of various file system options, with the current default is being widely used ext4. However, there is another push for changing the file system to something other which is called btrfs. But what makes btrfs better, what are other file systems, and when can we see the distributions making the change?
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s first have a general look at file systems and what they really do, then we will make a small comparison between famous file systems.
|
||||
|
||||
### So, What Do File Systems Do? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Just in case if you are unfamiliar about what file systems really do, it is actually simple when it is summarized. The file systems are mainly used in order for controlling how the data is stored after any program is no longer using it, how access to the data is controlled, what other information (metadata) is attached to the data itself, etc. I know that it does not sound like an easy thing to be programmed, and it is definitely not. The file systems are continually still being revised for including more functionality while becoming more efficient in what it simply needs to do. Therefore, however, it is a basic need for all computers, it is not quite as basic as it sounds like.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Partitioning? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Many people have a vague knowledge of what the partitions are since each operating system has an ability for creating or removing them. It can seem strange that Linux operating system uses more than 1 partition on the same disk, even while using the standard installation procedure, so few explanations are called for them. One of the main goals of having different partitions is achieving higher data security in the disaster case.
|
||||
|
||||
By dividing your hard disk into partitions, the data may be grouped and also separated. When the accidents occur, only the data stored in the partition which got the hit will only be damaged, while data on the other partitions will survive most likely. These principles date from the days when the Linux operating system didn’t have a journaled file system and any power failure might have led to a disaster.
|
||||
|
||||
The using of partitions will remain for security and the robustness reasons, then the breach on 1 part of the operating system does not automatically mean that whole computer is under risk or danger. This is currently most important factor for the partitioning process. For example, the users create scripts, the programs or web applications which start filling up the disk. If that disk contains only 1 big partition, then entire system may stop functioning if that disk is full. If the users store data on separate partitions, then only that data partition can be affected, while system partitions and the possible other data partitions will keep functioning.
|
||||
|
||||
Mind that to have a journaled file system will only provide data security in case if there is a power failure as well as sudden disconnection of the storage devices. Such will not protect the data against the bad blocks and the logical errors in the file system. In such cases, the user should use a Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks (RAID) solution.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Switch File Systems? ###
|
||||
|
||||
The ext4 file system has been an improvement for the ext3 file system that was also an improvement over the ext2 file system. While the ext4 is a very solid file system which has been the default choice for almost all distributions for the past few years, it is made from an aging code base. Additionally, Linux operating system users are seeking many new different features in file systems which ext4 does not handle on its own. There is software which takes care of some of such needs, but in the performance aspect, being able to do such things on the file system level could be faster.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ext4 File System ###
|
||||
|
||||
The ext4 has some limits which are still a bit impressive. The maximum file size is 16 tebibytes (which is roughly 17.6 terabytes) and is much bigger than any hard drive a regular consumer can currently buy. While, the largest volume/partition you can make with ext4 is 1 exbibyte (which is roughly 1,152,921.5 terabytes). The ext4 is known to bring the speed improvements over ext3 by using multiple various techniques. Like in the most modern file systems, it is a journaling file system that means that it will keep a journal of where the files are mainly located on the disk and of any other changes that happen to the disk. Regardless all of its features, it doesn’t support the transparent compression, the data deduplication, or the transparent encryption. The snapshots are supported technically, but such feature is experimental at best.
|
||||
|
||||
### Btrfs File System ###
|
||||
|
||||
The btrfs, many of us pronounce it different ways, as an example, Better FS, Butter FS, or B-Tree FS. It is a file system which is completely made from scratch. The btrfs exists because its developers firstly wanted to expand the file system functionality in order to include snapshots, pooling, as well as checksums among the other things. While it is independent from the ext4, it also wants to build off the ideas present in the ext4 that are great for the consumers and the businesses alike as well as incorporate those additional features that will benefit everybody, but specifically the enterprises. For the enterprises who are using very large programs with very large databases, they are having a seemingly continuous file system across the multiple hard drives could be very beneficial as it will make a consolidation of the data much easier. The data deduplication could reduce the amount of the actual space data could occupy, and the data mirroring could become easier with the btrfs as well when there is a single and broad file system which needs to be mirrored.
|
||||
|
||||
The user certainly can still choose to create multiple partitions so that he does not need to mirror everything. Considering that the btrfs will be able for spanning over the multiple hard drives, it is a very good thing that it can support 16 times more drive space than the ext4. A maximum partition size of the btrfs file system is 16 exbibytes, as well as maximum file size is 16 exbibytes too.
|
||||
|
||||
### XFS File System ###
|
||||
|
||||
The XFS file system is an extension of the extent file system. The XFS is a high-performance 64-bit journaling file system. The support of the XFS was merged into Linux kernel in around 2002 and In 2009 Red Hat Enterprise Linux version 5.4 usage of the XFS file system. XFS supports maximum file system size of 8 exbibytes for the 64-bit file system. There is some comparison of XFS file system is XFS file system can’t be shrunk and poor performance with deletions of the large numbers of files. Now, the RHEL 7.0 uses XFS as the default filesystem.
|
||||
|
||||
### Final Thoughts ###
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, the arrival date for the btrfs is not quite known. But officially, the next-generation file system is still classified as “unstable”, but if the user downloads the latest version of Ubuntu, he will be able to choose to install on a btrfs partition. When the btrfs will be classified actually as “stable” is still a mystery, but users shouldn’t expect the Ubuntu to use the btrfs by default until it’s indeed considered “stable”. It has been reported that Fedora 18 will use the btrfs as its default file system as by the time of its release a file system checker for the btrfs should exist. There is a good amount of work still left for the btrfs, as not all the features are yet implemented and the performance is a little sluggish if we compare it to the ext4.
|
||||
|
||||
So, which is better to use? Till now, the ext4 will be the winner despite the identical performance. But why? The answer will be the convenience as well as the ubiquity. The ext4 is still excellent file system for the desktop or workstation use. It is provided by default, so the user can install the operating system on it. Also, the ext4 supports volumes up to 1 Exabyte and files up to 16 Terabyte in size, so there’s still a plenty of room for the growth where space is concerned.
|
||||
|
||||
The btrfs might offer greater volumes up to 16 Exabyte and improved fault tolerance, but, till now, it feels more as an add-on file system rather than one integrated into the Linux operating system. For example, the btrfs-tools have to be present before a drive will be formatted with the btrfs, which means that the btrfs is not an option during the Linux operating system installation though that could vary with the distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
Even though the transfer rates are so important, there’s more to a just file system than speed of the file transfers. The btrfs has many useful features such as Copy-on-Write (CoW), extensive checksums, snapshots, scrubbing, self-healing data, deduplication, as well as many more good improvements that ensure the data integrity. The btrfs lacks the RAID-Z features of ZFS, so the RAID is still in an experimental state with the btrfs. For pure data storage, however, the btrfs is the winner over the ext4, but time still will tell.
|
||||
|
||||
Till the moment, the ext4 seems to be a better choice on the desktop system since it is presented as a default file system, as well as it is faster than the btrfs when transferring files. The btrfs is definitely worth to look into, but to completely switch to replace the ext4 on desktop Linux might be few years later. The data farms and the large storage pools could reveal different stories and show the right differences between ext4, XCF, and btrfs.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a different or additional opinion, kindly let us know by commenting on this article.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/review-ext4-vs-btrfs-vs-xfs/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[M.el Khamlichi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/pirat9/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[translating by ray]
|
||||
|
||||
Interviews: Linus Torvalds Answers Your Question
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Last Thursday you had a chance to [ask Linus Torvalds][1] about programming, hardware, and all things Linux. You can read his answers to those questions below. If you'd like to see what he had to say the last time we sat down with him, [you can do so here][2].
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,205 +0,0 @@
|
||||
213edu Translating
|
||||
|
||||
Gaming On Linux: All You Need To Know
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Can I play games on Linux?**
|
||||
|
||||
This is one of the most frequently asked questions by people who are thinking about [switching to Linux][1]. After all, gaming on Linux often termed as a distant possibility. In fact, some people even wonder if they can listen to music or watch movies on Linux. Considering that, question about native Linux games seem genuine.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, I am going to answer most of the Linux gaming questions a Linux beginner may have. For example, if it is possible to play games on Linux, if yes, what are the Linux games available, where can you **download Linux games** from or how do you get more information of gaming on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
But before I do that, let me make a confession. I am not a PC gamer or rather I should say, I am not desktop Linux gamer. I prefer to play games on my PS4 and I don’t care about PC games or even mobile games (no candy crush request sent to anyone in my friend list). This is the reason you see only a few articles in [Linux games][2] section of It’s FOSS.
|
||||
|
||||
So why am I covering this topic then?
|
||||
|
||||
Because I have been asked questions about playing games on Linux several times and I wanted to come up with a Linux gaming guide that could answer all those question. And remember, it’s not just gaming on Ubuntu I am talking about here. I am talking about Linux in general.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can you play games on Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Yes and no!
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you can play games on Linux and no, you cannot play ‘all the games’ in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Confused? Don’t be. What I meant here is that you can get plenty of popular games on Linux such as [Counter Strike, Metro Last Night][3] etc. But you might not get all the latest and popular Windows games on Linux, for e.g., [PES 2015][4].
|
||||
|
||||
The reason, in my opinion, is that Linux has less than 2% of desktop market share and these numbers are demotivating enough for most game developers to avoid working on the Linux version of their games.
|
||||
|
||||
Which means that there is huge possibility that the most talked about games of the year may not be playable in Linux. Don’t despair, there are ‘other means’ to get these games on Linux and we shall see it in coming sections, but before that let’s talk about what kind of games are available for Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
If I have to categorize, I’ll divide them in four categories:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Native Linux Games
|
||||
1. Windows games in Linux
|
||||
1. Browser Games
|
||||
1. Terminal Games
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s start with the most important one, native Linux games, first.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Where to find native Linux games? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Native Linux games mean those games which are officially supported in Linux. These games have native Linux client and can be installed like most other applications in Linux without requiring any additional effort (we’ll see about these in next section).
|
||||
|
||||
So, as you see, there are games developed for Linux. Next question that arises is where can you find these Linux games and how can you play them. I am going to list some of the resources where you can get Linux games.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Steam ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
“[Steam][5] is a digital distribution platform for video games. As Amazon Kindle is digital distribution platform for e-Books, iTunes for music, similarly Steam is for games. It provides you the option to buy and install games, play multiplayer and stay in touch with other games via social networking on its platform. The games are protected with [DRM][6].”
|
||||
|
||||
A couple of years ago, when gaming platform Steam announced support for Linux, it was a big news. It was an indication that gaming on Linux is being taken seriously. Though Steam’s decision was more influenced with its own Linux-based gaming console and a separate [Linux distribution called Steam OS][7], it still was a reassuring move that has brought a number of games on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
I have written a detailed article about installing and using Steam. If you are getting started with Steam, do read it.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Install and use Steam for gaming on Linux][8]
|
||||
|
||||
#### GOG.com ####
|
||||
|
||||
[GOG.com][9] is another platform similar to Steam. Like Steam, you can browse and find hundreds of native Linux games on GOG.com, purchase the games and install them. If the games support several platforms, you can download and use them across various operating systems. Your purchased games are available for you all the time in your account. You can download them anytime you wish.
|
||||
|
||||
One main difference between the two is that GOG.com offers only DRM free games and movies. Also, GOG.com is entirely web based. So you don’t need to install a client like Steam. You can simply download the games from browser and install them in your system.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Portable Linux Games ####
|
||||
|
||||
[Portable Linux Games][10] is a website that has a collection of a number of Linux games. The unique and best thing about Portable Linux Games is that you can download and store the games for offline installation.
|
||||
|
||||
The downloaded files have all the dependencies (at times Wine and Perl installation) and these are also platform independent. All you need to do is to download the files and double click to install them. Store the downloadable file on external hard disk and use them in future. Highly recommend if you don’t have continuous access to high speed internet.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Game Drift Game Store ####
|
||||
|
||||
[Game Drift][11] is actually a Linux distribution based on Ubuntu with sole focus on gaming. While you might not want to start using this Linux distribution for the sole purpose of gaming, you can always visit its game store online and see what games are available for Linux and install them.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Linux Game Database ####
|
||||
|
||||
As the name suggests, [Linux Game Database][12] is a website with a huge collection of Linux games. You can browse through various category of games and download/install them from the game developer’s website. As a member of Linux Game Database, you can even rate the games. LGDB, kind of, aims to be the IGN or IMDB for Linux games.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Penguspy ####
|
||||
|
||||
Created by a gamer who refused to use Windows for playing games, [Penguspy][13] showcases a collection of some of the best Linux games. You can browse games based on category and if you like the game, you’ll have to go to the respective game developer’s website.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Software Repositories ####
|
||||
|
||||
Look into the software repositories of your own Linux distribution. There always will be some games in it. If you are using Ubuntu, Ubuntu Software Center itself has an entire section for games. Same is true for other Linux distributions such as Linux Mint etc.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. How to play Windows games in Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
So far we talked about native Linux games. But there are not many Linux games, or to be more precise, most popular Linux games are not available for Linux but they are available for Windows PC. So the questions arises, how to play Windows games in Linux?
|
||||
|
||||
Good thing is that with the help of tools like Wine, PlayOnLinux and CrossOver, you can play a number of popular Windows games in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Wine ####
|
||||
|
||||
Wine is a compatibility layer which is capable of running Windows applications in systems like Linux, BSD and OS X. With the help of Wine, you can install and use a number of Windows applications in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
[Installing Wine in Ubuntu][14] or any other Linux is easy as it is available in most Linux distributions’ repository. There is a huge [database of applications and games supported by Wine][15] that you can browse.
|
||||
|
||||
#### CrossOver ####
|
||||
|
||||
[CrossOver][16] is an improved version of Wine that brings professional and technical support to Wine. But unlike Wine, CrossOver is not free. You’ll have to purchase the yearly license for it. Good thing about CrossOver is that every purchase contributes to Wine developers and that in fact boosts the development of Wine to support more Windows games and applications. If you can afford $48 a year, you should buy CrossOver for the support they provide.
|
||||
|
||||
### PlayOnLinux ###
|
||||
|
||||
PlayOnLinux too is based on Wine but implemented differently. It has different interface and slightly easier to use than Wine. Like Wine, PlayOnLinux too is free to use. You can browse the [applications and games supported by PlayOnLinux on its database][17].
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Browser Games ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Needless to say that there are tons of browser based games that are available to play in any operating system, be it Windows or Linux or Mac OS X. Most of the addictive mobile games, such as [GoodGame Empire][18], also have their web browser counterparts.
|
||||
|
||||
Apart from that, thanks to [Google Chrome Web Store][19], you can play some more games in Linux. These Chrome games are installed like a standalone app and they can be accessed from the application menu of your Linux OS. Some of these Chrome games are playable offline as well.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Terminal Games ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Added advantage of using Linux is that you can use the command line terminal to play games. I know that it’s not the best way to play games but at times, it’s fun to play games like [Snake][20] or [2048][21] in terminal. There is a good collection of Linux terminal games at [this blog][22]. You can browse through it and play the ones you want.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### How to stay updated about Linux games? ###
|
||||
|
||||
When you have learned a lot about what kind of games are available on Linux and how could you use them, next question is how to stay updated about new games on Linux? And for that, I advise you to follow these blogs that provide you with the latest happenings of the Linux gaming world:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Gaming on Linux][23]: I won’t be wrong if I call it the nest Linux gaming news portal. You get all the latest rumblings and news about Linux games. Frequently updated, Gaming on Linux has dedicated fan following which makes it a nice community of Linux game lovers.
|
||||
- [Free Gamer][24]: A blog focusing on free and open source games.
|
||||
- [Linux Game News][25]: A Tumbler blog that updates on various Linux games.
|
||||
|
||||
#### What else? ####
|
||||
|
||||
I think that’s pretty much what you need to know to get started with gaming on Linux. If you are still not convinced, I would advise you to [dual boot Linux with Windows][26]. Use Linux as your main desktop and if you want to play games, boot into Windows. This could be a compromised solution.
|
||||
|
||||
I think that’s pretty much what you need to know to get started with gaming on Linux. If you are still not convinced, I would advise you to [dual boot Linux with Windows][27]. Use Linux as your main desktop and if you want to play games, boot into Windows. This could be a compromised solution.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s time for you to add your inputs. Do you play games on your Linux desktop? What are your favorites? What blogs you follow to stay updated on latest Linux games?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
投票项目:
|
||||
How do you play games on Linux?
|
||||
|
||||
- I use Wine and PlayOnLinux along with native Linux Games
|
||||
- I am happy with Browser Games
|
||||
- I prefer the Terminal Games
|
||||
- I use native Linux games only
|
||||
- I play it on Steam
|
||||
- I dual boot and go in to Windows to play games
|
||||
- I don't play games at all
|
||||
|
||||
注:投票代码
|
||||
<div class="PDS_Poll" id="PDI_container9132962" style="display:inline-block;"></div>
|
||||
<div id="PD_superContainer"></div>
|
||||
<script type="text/javascript" charset="UTF-8" src="http://static.polldaddy.com/p/9132962.js"></script>
|
||||
<noscript><a href="http://polldaddy.com/poll/9132962">Take Our Poll</a></noscript>
|
||||
|
||||
注,发布时根据情况看怎么处理
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/linux-gaming-guide/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/reasons-switch-linux-windows-xp/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/category/games/
|
||||
[3]:http://blog.counter-strike.net/
|
||||
[4]:https://pes.konami.com/tag/pes-2015/
|
||||
[5]:http://store.steampowered.com/
|
||||
[6]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_rights_management
|
||||
[7]:http://itsfoss.com/valve-annouces-linux-based-gaming-operating-system-steamos/
|
||||
[8]:http://itsfoss.com/install-steam-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.gog.com/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.portablelinuxgames.org/
|
||||
[11]:http://gamedrift.org/GameStore.html
|
||||
[12]:http://www.lgdb.org/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.penguspy.com/
|
||||
[14]:http://itsfoss.com/wine-1-5-11-released-ppa-available-to-download/
|
||||
[15]:https://appdb.winehq.org/
|
||||
[16]:https://www.codeweavers.com/products/
|
||||
[17]:https://www.playonlinux.com/en/supported_apps.html
|
||||
[18]:http://empire.goodgamestudios.com/
|
||||
[19]:https://chrome.google.com/webstore/category/apps
|
||||
[20]:http://itsfoss.com/nsnake-play-classic-snake-game-linux-terminal/
|
||||
[21]:http://itsfoss.com/play-2048-linux-terminal/
|
||||
[22]:https://ttygames.wordpress.com/
|
||||
[23]:https://www.gamingonlinux.com/
|
||||
[24]:http://freegamer.blogspot.fr/
|
||||
[25]:http://linuxgamenews.com/
|
||||
[26]:http://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu-1404-dual-boot-mode-windows-8-81-uefi/
|
||||
[27]:http://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu-1404-dual-boot-mode-windows-8-81-uefi/
|
||||
@ -1,172 +0,0 @@
|
||||
For my dear RMS
|
||||
|
||||
30 Years of Free Software Foundation: Best Quotes of Richard Stallman
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
<iframe width="660" height="495" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/aIL594DTzH4?feature=oembed" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
**Richard Matthew Stallman** (rms) – one of biggest figure in Information Technology. He is a computer programmer and architect (GNU Compiler Collection (GCC)), GNU Debugger, Emacs), software freedom evangelist, [GNU Project][1] and [FSF][2] founder.
|
||||
|
||||
**GNU** is a recursive acronym “GNU’s Not Unix!”. GNU – collection of free computer software for Unix-based operation system. Can be used with GNU/Hurd and Linux kernels. Announced on September 27, 1983. General components:
|
||||
|
||||
- GNU Compiler Collection (GCC)
|
||||
- GNU C library (glibc)
|
||||
- GNU Core Utilities (coreutils)
|
||||
- GNU Debugger (GDB)
|
||||
- GNU Binary Utilities (binutils)
|
||||
- GNU Bash shell
|
||||
- NOME desktop environment
|
||||
|
||||
注:视频
|
||||
<video src="//static.fsf.org/nosvn/FSF30-video/FSF_30_720p.webm" controls="controls" width="640" height="390"></video>
|
||||
|
||||
**Free Software Foundation** (FSF) – non-profit organization for free software and computer user freedom promotion and defend their rights. Read more information here. Founded on 4 October 1985.
|
||||
|
||||
- The freedom to run the program as you wish, for any purpose (freedom 0).
|
||||
- The freedom to study how the program works, and change it so it does your computing as you wish (freedom 1). Access to the source code is a precondition for this.
|
||||
- The freedom to redistribute copies so you can help your neighbor (freedom 2).
|
||||
- The freedom to distribute copies of your modified versions to others (freedom 3). By doing this you can give the whole community a chance to benefit from your changes. Access to the source code is a precondition for this.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the Four Freedoms of free software.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is quotes of Richard Stallman about freedom, software, social, philosophy and others things.
|
||||
|
||||
**About Facebook:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Facebook is not your friend, it is a surveillance engine.
|
||||
|
||||
**About Android:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Android is very different from the GNU/Linux operating system because it contains very little of GNU. Indeed, just about the only component in common between Android and GNU/Linux is Linux, the kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
**About computer industry:**
|
||||
|
||||
> The computer industry is the only industry that is more fashion-driven than women's fashion.
|
||||
|
||||
**About cloud computing:**
|
||||
|
||||
> The interesting thing about cloud computing is that we've redefined cloud computing to include everything that we already do.
|
||||
|
||||
**About ethics:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Whether gods exist or not, there is no way to get absolute certainty about ethics. Without absolute certainty, what do we do? We do the best we can.
|
||||
|
||||
**About freedom:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Free software is software that respects your freedom and the social solidarity of your community. So it's free as in freedom.
|
||||
|
||||
**About goal and idealism:**
|
||||
|
||||
> If you want to accomplish something in the world, idealism is not enough - you need to choose a method that works to achieve the goal.
|
||||
|
||||
**About sharing:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Sharing is good, and with digital technology, sharing is easy.
|
||||
|
||||
**About facebook (extended version):**
|
||||
|
||||
> Facebook mistreats its users. Facebook is not your friend; it is a surveillance engine. For instance, if you browse the Web and you see a 'like' button in some page or some other site that has been displayed from Facebook. Therefore, Facebook knows that your machine visited that page.
|
||||
|
||||
**About web application:**
|
||||
|
||||
> One reason you should not use web applications to do your computing is that you lose control.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> If you use a proprietary program or somebody else's web server, you're defenceless. You're putty in the hands of whoever developed that software.
|
||||
|
||||
**About books:**
|
||||
|
||||
> With paper printed books, you have certain freedoms. You can acquire the book anonymously by paying cash, which is the way I always buy books. I never use a credit card. I don't identify to any database when I buy books. Amazon takes away that freedom.
|
||||
|
||||
**About MPAA:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Officially, MPAA stands for Motion Picture Association of America, but I suggest that MPAA stands for Malicious Power Attacking All.
|
||||
|
||||
**About money and career:**
|
||||
|
||||
> I could have made money this way, and perhaps amused myself writing code. But I knew that at the end of my career, I would look back on years of building walls to divide people, and feel I had spent my life making the world a worse place.
|
||||
|
||||
**About proprietary software:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Proprietary software keeps users divided and helpless. Divided because each user is forbidden to redistribute it to others, and helpless because the users can't change it since they don't have the source code. They can't study what it really does. So the proprietary program is a system of unjust power.
|
||||
|
||||
**About smartphone:**
|
||||
|
||||
> A smartphone is a computer - it's not built using a computer - the job it does is the job of being a computer. So, everything we say about computers, that the software you run should be free - you should insist on that - applies to smart phones just the same. And likewise to those tablets.
|
||||
|
||||
**About CD and digital content:**
|
||||
|
||||
> CD stores have the disadvantage of an expensive inventory, but digital bookshops would need no such thing: they could write copies at the time of sale on to memory sticks, and sell you one if you forgot your own.
|
||||
|
||||
**About paradigm of competition:**
|
||||
|
||||
> The paradigm of competition is a race: by rewarding the winner, we encourage everyone to run faster. When capitalism really works this way, it does a good job; but its defenders are wrong in assuming it always works this way.
|
||||
|
||||
**About vi and emacs:**
|
||||
|
||||
> People sometimes ask me if it is a sin in the Church of Emacs to use vi. Using a free version of vi is not a sin; it is a penance. So happy hacking.
|
||||
|
||||
**About freedom and history:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Value your freedom or you will lose it, teaches history. 'Don't bother us with politics', respond those who don't want to learn.
|
||||
|
||||
**About patents:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Fighting patents one by one will never eliminate the danger of software patents, any more than swatting mosquitoes will eliminate malaria.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Software patents are dangerous to software developers because they impose monopolies on software ideas.
|
||||
|
||||
**About copyrights:**
|
||||
|
||||
> In practice, the copyright system does a bad job of supporting authors, aside from the most popular ones. Other authors' principal interest is to be better known, so sharing their work benefits them as well as readers.
|
||||
|
||||
**About pay for work:**
|
||||
|
||||
> There is nothing wrong with wanting pay for work, or seeking to maximize one's income, as long as one does not use means that are destructive.
|
||||
|
||||
**About Chrome OS:**
|
||||
|
||||
> In essence, Chrome OS is the GNU/Linux operating system. However, it is delivered without the usual applications, and rigged up to impede and discourage installing applications.
|
||||
|
||||
**About Linux users:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Many users of the GNU/Linux system will not have heard the ideas of free software. They will not be aware that we have ideas, that a system exists because of ethical ideals, which were omitted from ideas associated with the term 'open source.'
|
||||
|
||||
**About privacy in facebook:**
|
||||
|
||||
> If there is a Like button in a page, Facebook knows who visited that page. And it can get IP address of the computer visiting the page even if the person is not a Facebook user.
|
||||
|
||||
**About programming:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Programming is not a science. Programming is a craft.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> My favorite programming languages are Lisp and C. However, since around 1992 I have worked mainly on free software activism, which means I am too busy to do much programming. Around 2008 I stopped doing programming projects.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> C++ is a badly designed and ugly language. It would be a shame to use it in Emacs.
|
||||
|
||||
**About hacking and learn programming:**
|
||||
|
||||
> People could no longer learn hacking the way I did, by starting to work on a real operating system, making real improvements. In fact, in the 1980s I often came across newly graduated computer science majors who had never seen a real program in their lives. They had only seen toy exercises, school exercises, because every real program was a trade secret. They never had the experience of writing features for users to really use, and fixing the bugs that real users came across. The things you need to know to do real work.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> It is hard to write a simple definition of something as varied as hacking, but I think what these activities have in common is playfulness, cleverness, and exploration. Thus, hacking means exploring the limits of what is possible, in a spirit of playful cleverness. Activities that display playful cleverness have "hack value".
|
||||
|
||||
**About web browsing:**
|
||||
|
||||
> For personal reasons, I do not browse the web from my computer. (I also have no net connection much of the time.) To look at page I send mail to a daemon which runs wget and mails the page back to me. It is very efficient use of my time, but it is slow in real time.
|
||||
|
||||
**About music sharing:**
|
||||
|
||||
> Friends share music with each other, they don't allow themselves to be divided by a system that says that nobody is supposed to have copies.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://tlhp.cf/fsf-richard-stallman/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pavlo Rudyi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://tlhp.cf/author/paul/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.gnu.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.fsf.org/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
sonofelice translating
|
||||
How bad a boss is Linus Torvalds?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,51 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux Foundation Explains a "World without Linux" and Open Source
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> The Linux Foundation responds to questions about its "World without Linux" movies, including what the Internet would be like without Linux and other open source software.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Would the world really be tremendously different if Linux, the open source operating system kernel, did not exist? Would there be no Internet or movies? Those are the questions some viewers of the [Linux Foundation's][1] ongoing "[World without Linux][2]" video series are asking. Here are some answers.
|
||||
|
||||
In case you've missed it, the "World without Linux" series is a collection of quirky short films that depict, well, a world without Linux (and open source software more generally). They have emphasized themes like [Linux's role in movie-making][3] and in [serving the Internet][4].
|
||||
|
||||
To offer perspective on the series's claims, direction and hidden symbols, Jennifer Cloer, vice president of communications at The Linux Foundation, recently sent The VAR Guy responses to some common queries about the movies. Below are the answers, in her own words.
|
||||
|
||||
### The latest episode takes Sam and Annie to the movies. Would today's graphics really be that much different without Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
In episode #4, we do a bit of a parody on "Avatar." Love it or hate it, the graphics in the real "Avatar" are pretty impressive. In a world without Linux, the graphics would be horrible but we wouldn't even know it because we wouldn't know any better. But in fact, "Avatar" was created using Linux. Weta Digital used one of the world's largest Linux clusters to render the film and do 3D modeling. It's also been reported that "Lord of the Rings," "Fantastic Four" and "King Kong," among others, have used Linux. We hope this episode can bring attention to that work, which hasn't been widely reported.
|
||||
|
||||
### Some people criticized the original episode for concluding there would be no Internet without Linux. What's your reaction? ###
|
||||
|
||||
We enjoyed the debate that resulted from the debut episode. With more than 100,000 views to date of that episode alone, it brought awareness to the role that Linux plays in society and to the worldwide community of contributors and supporters. Of course the Internet would exist without Linux but it wouldn't be the Internet we know today and it wouldn't have matured at the pace it has. Each episode makes a bold and fun statement about Linux's role in our every day lives. We hope this can help extend the story of Linux to more people around the world.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why is Sam and Annie's cat named String? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Nothing in the series is a coincidence. Look closely and you'll find all kinds of inside Linux and geek jokes. String is named after String theory and was named by our Linux.com Editor Libby Clark. In physics, string theory is a theoretical framework in which the point-like particles of particle physics are replaced by one-dimensional objects called strings. String theory describes how these strings propagate through space and interact with each other. Kind of like Sam, Annie and String in a World Without Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### What can we expect from the next two episodes and, in particular, the finale? When will it air? ###
|
||||
|
||||
In episode #5, we'll go to space and experience what a world without Linux would mean to exploration. It's a wild ride. In the finale, we finally get to see Linus in a world without Linux. There have been clues throughout the series as to what this finale will include but I can't give more than that away since there are ongoing contests to find the clues. And I can't give away the air date for the finale! You'll have to follow #WorldWithoutLinux to learn more.
|
||||
|
||||
### Can you give us a hint on the clues in episode #4? ###
|
||||
|
||||
There is another reference to the Free Burger Restaurant in this episode. Linux also actually does appear in this world without Linux but in a very covert way; you could say it's like reading Linux in another language. And, of course, just for fun, String makes another appearance.
|
||||
|
||||
### Is the series achieving what you hoped? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Yes. We're really happy to see people share and engage with these stories. We hope that it's reaching people who might not otherwise know the story of Linux or understand its pervasiveness in the world today. It's really about surfacing this to a broader audience and giving thanks to the worldwide community of developers and companies that support Linux and all the things it makes possible.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/linux-foundation-explains-world-without-linux-and-open-so
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Christopher Tozzi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://thevarguy.com/author/christopher-tozzi
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/world-without-linux
|
||||
[3]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/new-linux-foundation-video-highlights-role-open-source-3d
|
||||
[4]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/100715/would-internet-exist-without-linux-yes-without-open-sourc
|
||||
@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Microsoft and Linux: True Romance or Toxic Love?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Every now and then, you come across a news story that makes you choke on your coffee or splutter hot latte all over your monitor. Microsoft's recent proclamations of love for Linux is an outstanding example of such a story.
|
||||
|
||||
Common sense says that Microsoft and the FOSS movement should be perpetual enemies. In the eyes of many, Microsoft embodies most of the greedy excesses that the Free Software movement rejects. In addition, Microsoft previously has labeled Linux as a cancer and the FOSS community as a "pack of thieves".
|
||||
|
||||
We can understand why Microsoft has been afraid of a free operating system. When combined with open-source applications that challenge Microsoft's core line, it threatens Microsoft's grip on the desktop/laptop market.
|
||||
|
||||
In spite of Microsoft's fears over its desktop dominance, the Web server marketplace is one arena where Linux has had the greatest impact. Today, the majority of Web servers are Linux boxes. This includes most of the world's busiest sites. The sight of so much unclaimed licensing revenue must be painful indeed for Microsoft.
|
||||
|
||||
Handheld devices are another realm where Microsoft has lost ground to free software. At one point, its Windows CE and Pocket PC operating systems were at the forefront of mobile computing. Windows-powered PDA devices were the shiniest and flashiest gadgets around. But, that all ended when Apple released its iPhone. Since then, Android has stepped into the limelight, with Windows Mobile largely ignored and forgotten. The Android platform is built on free and open-source components.
|
||||
|
||||
The rapid expansion in Android's market share is due to the open nature of the platform. Unlike with iOS, any phone manufacturer can release an Android handset. And, unlike with Windows Mobile, there are no licensing fees. This has been really good news for consumers. It has led to lots of powerful and cheap handsets appearing from manufacturers all over the world. It's a very definite vindication of the value of FOSS software.
|
||||
|
||||
Losing the battle for the Web and mobile computing is a brutal loss for Microsoft. When you consider the size of those two markets combined, the desktop market seems like a stagnant backwater. Nobody likes to lose, especially when money is on the line. And, Microsoft does have a lot to lose. You would expect Microsoft to be bitter about it. And in the past, it has been.
|
||||
|
||||
Microsoft has fought back against Linux and FOSS using every weapon at its disposal, from propaganda to patent threats, and although these attacks have slowed the adoption of Linux, they haven't stopped it.
|
||||
|
||||
So, you can forgive us for being shocked when Microsoft starts handing out t-shirts and badges that say "Microsoft Loves Linux" at open-source conferences and events. Could it be true? Does Microsoft really love Linux?
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, PR slogans and free t-shirts do not equal truth. Actions speak louder than words. And when you consider Microsoft's actions, Microsoft's stance becomes a little more ambiguous.
|
||||
|
||||
On the one hand, Microsoft is recruiting hundreds of Linux developers and sysadmins. It's releasing its .NET Core framework as an open-source project with cross-platform support (so that .NET apps can run on OS X and Linux). And, it is partnering with Linux companies to bring popular distros to its Azure platform. In fact, Microsoft even has gone so far as to create its own Linux distro for its Azure data center.
|
||||
|
||||
On the other hand, Microsoft continues to launch legal attacks on open-source projects directly and through puppet corporations. It's clear that Microsoft hasn't had some big moral change of heart over proprietary vs. free software, so why the public declarations of adoration?
|
||||
|
||||
To state the obvious, Microsoft is a profit-making entity. It's an investment vehicle for its shareholders and a source of income for its employees. Everything it does has a single ultimate goal: revenue. Microsoft doesn't act out of love or even hate (although that's a common accusation).
|
||||
|
||||
So the question shouldn't be "does Microsoft really love Linux?" Instead, we should ask how Microsoft is going to profit from all this.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take the open-source release of .NET Core. This move makes it easy to port the .NET runtime to any platform. That extends the reach of Microsoft's .NET framework far beyond the Windows platform.
|
||||
|
||||
Opening .NET Core ultimately will make it possible for .NET developers to produce cross-platform apps for OS X, Linux, iOS and even Android--all from a single codebase.
|
||||
|
||||
From a developer's perspective, this makes the .NET framework much more attractive than before. Being able to reach many platforms from a single codebase dramatically increases the potential target market for any app developed using the .NET framework.
|
||||
|
||||
What's more, a strong Open Source community would provide developers with lots of code to reuse in their own projects. So, the availability of open-source projects would make the .NET framework.
|
||||
|
||||
On the plus side, opening .NET Core reduces fragmentation across different platforms and means a wider choice of apps for consumers. That means more choice, both in terms of open-source software and proprietary apps.
|
||||
|
||||
From Microsoft's point of view, it would gain a huge army of developers. Microsoft profits by selling training, certification, technical support, development tools (including Visual Studio) and proprietary extensions.
|
||||
|
||||
The question we should ask ourselves is does this benefit or hurt the Free Software community?
|
||||
|
||||
Widespread adoption of the .NET framework could mean the eventual death of competing open-source projects, forcing us all to dance to Microsoft's tune.
|
||||
|
||||
Moving beyond .NET, Microsoft is drawing a lot of attention to its Linux support on its Azure cloud computing platform. Remember, Azure originally was Windows Azure. That's because Windows Server was the only supported operating system. Today, Azure offers support for a number of Linux distros too.
|
||||
|
||||
There's one reason for this: paying customers who need and want Linux services. If Microsoft didn't offer Linux virtual machines, those customers would do business with someone else.
|
||||
|
||||
It looks like Microsoft is waking up to the fact that Linux is here to stay. Microsoft cannot feasibly wipe it out, so it has to embrace it.
|
||||
|
||||
This brings us back to the question of why there is so much buzz about Microsoft and Linux. We're all talking about it, because Microsoft wants us to think about it. After all, all these stories trace back to Microsoft, whether it's through press releases, blog posts or public announcements at conferences. The company is working hard to draw attention to its Linux expertise.
|
||||
|
||||
What other possible purpose could be behind Chief Architect Kamala Subramaniam's blog post announcing Azure Cloud Switch? ACS is a custom Linux distro that Microsoft uses to automate the configuration of its switch hardware in the Azure data centers.
|
||||
|
||||
ACS is not publicly available. It's intended for internal use in the Azure data center, and it's unlikely that anyone else would be able to find a use for it. In fact, Subramaniam states the same thing herself in her post.
|
||||
|
||||
So, Microsoft won't be making any money from selling ACS, and it won't attract a user base by giving it away. Instead, Microsoft gets to draw attention to Linux and Azure, strengthening its position as a Linux cloud computing platform.
|
||||
|
||||
Is Microsoft's new-found love for Linux good news for the community?
|
||||
|
||||
We shouldn't be slow to forget Microsoft's mantra of Embrace, Extend and Exterminate. Right now, Microsoft is very much in the early stages of embracing Linux. Will Microsoft seek to splinter the community through custom extensions and proprietary "standards"?
|
||||
|
||||
Let us know what you think in the comments below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/microsoft-and-linux-true-romance-or-toxic-love-0
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[James Darvell][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/users/james-darvell
|
||||
@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8 Review
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Other than Gnome and KDE, Cinnamon is another desktop environment that is used by many people. It is made by the same team that produces Linux Mint (and ships with Linux Mint) and can also be installed on several other distributions. The latest version of this DE – Cinnamon 2.8 – was released earlier this month, and it brings a host of bug fixes and improvements as well as some new features.
|
||||
|
||||
I’m going to go over the major improvements made in this release as well as how to update to Cinnamon 2.8 or install it for the first time.
|
||||
|
||||
### Improvements to Applets ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are several improvements to already existing applets for the panel.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sound Applet ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The Sound applet was revamped and now displays track information as well as the media controls on top of the cover art of the audio file. For music players with seeking support (such as Banshee), a progress bar will be displayed in the same region which you can use to change the position of the audio track. Right-clicking on the applet in the panel will display the options to mute input and output devices.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Power Applet ####
|
||||
|
||||
The Power applet now displays the status of each of the connected batteries and devices using the manufacturer’s data instead of generic names.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Window Thumbnails ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8 brings the option to show window thumbnails when hovering over the window list in the panel. You can turn it off if you don’t like it, though.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Workspace Switcher Applet ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Adding the Workspace switcher applet to your panel will show you a visual representation of your workspaces with little rectangles embedded inside to show the position of your windows.
|
||||
|
||||
#### System Tray ####
|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8 brings support for app indicators in the system tray. You can easily disable this in the settings which will force affected apps to fall back to using status icons instead.
|
||||
|
||||
### Visual Improvements ###
|
||||
|
||||
A host of visual improvements were made in Cinnamon 2.8. The classic and preview Alt + Tab switchers were polished with noticeable improvements, while the Alt + F2 dialog received bug fixes and better auto completion for commands.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the issue with the traditional animation effect for minimizing windows is now sorted and works with multiple panels.
|
||||
|
||||
### Nemo Improvements ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The default file manager for Cinnamon also received several bug fixes and has a new “Quick-rename” feature for renaming files and directories. This works by clicking the file or directory twice with a short pause in between to rename the files.
|
||||
|
||||
Nemo also detects issues with thumbnails automatically and prompts you to quickly fix them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Other Notable improvements ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Applets now reload themselves automatically once they are updated.
|
||||
- Support for multiple monitors was improved significantly.
|
||||
- Dialog windows have been improved and now attach themselves to their parent windows.
|
||||
- HiDPI dectection has been improved.
|
||||
- QT5 applications now look more native and use the default GTK theme.
|
||||
- Window management and rendering performance has been improved.
|
||||
- There are various bugfixes.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Get Cinnamon 2.8 ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re running Linux Mint you will get Cinnamon 2.8 as part of the upgrade to Linux Mint 17.3 “Rosa” Cinnamon Edition. The BETA release is already out, so you can grab that if you’d like to get your hands on the new software immediately.
|
||||
|
||||
For Arch users, Cinnamon 2.8 is already in the official Arch repositories, so you can just update your packages and do a system-wide upgrade to get the latest version.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, for Ubuntu users, you can install or upgrade to Cinnamon 2.8 by running in turn the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:moorkai/cinnamon
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install cinnamon
|
||||
|
||||
Have you tried Cinnamon 2.8? What do you think of it?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/cinnamon-2-8-review/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ayo Isaiah][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/ayoisaiah/
|
||||
@ -1,98 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by icecoobe.
|
||||
|
||||
What’s the Best File System for My Linux Install?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
File systems: they’re not the most exciting things in the world, but important nonetheless. In this article we’ll go over the popular choices for file systems on Linux – what they’re about, what they can do, and who they’re for.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ext4 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you’ve ever installed Linux before, chances are you’ve seen the “Ext4” during installation. There’s a good reason for that: it’s the file system of choice for just about every Linux distribution available right now. Sure, there are some that choose other options, but there’s no denying that Extended 4 is the file system of choice for almost all Linux users.
|
||||
|
||||
#### What can it do? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Extended 4 has all of the goodness that you’ve come to expect from past file system iterations (Ext2/Ext3) but with enhancements. There’s a lot to dig into, but here are the best parts of what Ext4 can do for you:
|
||||
|
||||
- file system journaling
|
||||
- journal checksums
|
||||
- multi-block file allocation
|
||||
- backwards compatibility support for Extended 2 and 3
|
||||
- persistent pre-allocation of free space
|
||||
- improved file system checking (over previous versions)
|
||||
- and of course, support for larger files
|
||||
|
||||
#### Who is it for? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Extended 4 is for those looking for a super-stable foundation to build upon, or for those looking for something that just works. This file system won’t snapshot your system; it doesn’t even have the greatest SSD support, but If your needs aren’t too extravagant, you’ll get along with it just fine.
|
||||
|
||||
### BtrFS ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The B-tree file system (also known as butterFS) is a file system for Linux developed by Oracle. It’s a new file system and is in heavy development stages. The Linux community considers it unstable to use for some. The core principle of BtrFS is based around the principle of copy-on-write. **Copy on write** basically means that the system has one single copy of a bit of data before the data has been written. When the data has been written, a copy of it is made.
|
||||
|
||||
#### What can it do? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Besides supporting copy-on-write, BtrFS can do many other things – so many things, in fact, that it’d take forever to list everything. Here are the most notable features: The file system supports read-only snapshots, file cloning, subvolumes, transparent compression, offline file system check, in-place conversion from ext3 and 4 to Btrfs, online defragmentation, anew has support for RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 and RAID 10.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Who is it for? ####
|
||||
|
||||
The developers of BtrFS have promised that this file system is the next-gen replacement for other file systems out there. That much is true, though it certainly is a work in progress. There are many killer features for advanced users and basic users alike (including great performance on SSDs). This file system is for those looking to get a little bit more out of their file system and who want to try the copy-on-write way of doing things.
|
||||
|
||||
### XFS ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Developed and created by Silicon Graphics, XFS is a high-end file system that specializes in speed and performance. XFS does extremely well when it comes to parallel input and output because of its focus on performance. The XFS file system can handle massive amounts of data, so much in fact that some users of XFS have close to 300+ terabytes of data.
|
||||
|
||||
#### What can it do? ####
|
||||
|
||||
XFS is a well-tested data storage file system created for high performance operations. Its features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- striped allocation of RAID arrays
|
||||
- file system journaling
|
||||
- variable block sizes
|
||||
- direct I/O
|
||||
- guaranteed-rate I/O
|
||||
- snapshots
|
||||
- online defragmentation
|
||||
- online resizing
|
||||
|
||||
#### Who is it for? ####
|
||||
|
||||
XFS is for those looking for a rock-solid file solution. The file system has been around since 1993 and has only gotten better and better with time. If you have a home server and you’re perplexed on where you should go with storage, consider XFS. A lot of the features the file system comes with (like snapshots) could aid in your file storage system. It’s not just for servers, though. If you’re a more advanced user and you’re interested in a lot of what was promised in BtrFS, check out XFS. It does a lot of the same stuff and doesn’t have stability issues.
|
||||
|
||||
### Reiser4 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Reiser4, the successor to ReiserFS, is a file system created and developed by Namesys. The creation of Reiser4 was backed by the Linspire project as well as DARPA. What makes Reiser4 special is its multitude of transaction models. There isn’t one single way data can be written; instead, there are many.
|
||||
|
||||
#### What can it do? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Reiser4 has the unique ability to use different transaction models. It can use the copy-on-write model (like BtrFS), write-anywhere, journaling, and the hybrid transaction model. It has a lot of improvements upon ReiserFS, including better file system journaling via wandering logs, better support for smaller files, and faster handling of directories. Reiser4 has a lot to offer. There are a lot more features to talk about, but suffice it to say it’s a huge improvement over ReiserFS with tons of added features.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Who is it for? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Resier4 is for those looking to stretch one file system across multiple use-cases. Maybe you want to set up one machine with copy-on-write, another with write-anywhere, and another with hybrid transaction, and you don’t want to use different types of file systems to accomplish this task. Reiser4 is perfect for this type of use-case.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are many file systems available on Linux. Each serves a unique purpose for unique users looking to solve different problems.This post focuses on the most popular choices for the platform. There is no doubt there are other choices out there for other use-cases.
|
||||
|
||||
What’s your favorite file system to use on Linux? Tell us why below!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/best-file-system-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Derrik Diener][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/derrikdiener/
|
||||
@ -1,86 +0,0 @@
|
||||
alim0x translating
|
||||
|
||||
The history of Android
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Android 4.2, Jelly Bean—new Nexus devices, new tablet interface ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Android Platform was rapidly maturing, and with Google hosting more and more apps in the Play Store, there was less and less that needed to go out in the OS update. Still, the relentless march of updates must continue, and in November 2012 Android 4.2 was released. 4.2 was still called "Jelly Bean," a nod to the relatively small amount of changes that were present in this release.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
The LG-made Nexus 4 and Samsung-made Nexus 10.
|
||||
Photo by Google/Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
Along with Android 4.2 came two flagship devices, the Nexus 4 and the Nexus 10, both of which were sold direct by Google on the Play Store. The Nexus 4 applied the Nexus 7 strategy of a quality device at a shockingly low price and sold for $300 unlocked. The Nexus 4 had a quad-core 1.5 GHz Snapdragon S4 Pro, 2GB of RAM and a 4.7-inch 1280×768 LCD. Google's new flagship phone was manufactured by LG, and with the manufacturer switch came a focus on materials and build quality. The Nexus 4 had a glass front and back, and while you couldn't drop it, it was one of the nicest-feeling Android phones to date. The biggest downside to the Nexus 4 was the lack of LTE at a time when most phones, including the Verizon Galaxy Nexus, came with the faster modem. Still, demand for the Nexus 4 greatly exceeded Google's expectations—the launch rush crashed the Play Store Web site on launch day. The device sold out in under an hour.
|
||||
|
||||
The Nexus 10 was Google's first 10-inch Nexus tablet. The highlight of the device was the 2560×1600 display, which was the highest resolution in its class. All those pixels were powered by a dual core, 1.7GHz Cortex A15 processor and 2GB of RAM. With each passing month, it's looking more and more like the Nexus 10 is the first and last 10-inch Nexus tablet. Usually these devices are upgraded every year, but the Nexus 10 is now 16 months old, and there's no sign of the new model on the horizon. Google is doing well with smaller-sized 7-inch tablets, and it seems content to let partners [like Samsung][1] explore the larger end of the tablet spectrum.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The new lock screen, wallpaper, and clock widget design.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
4.2 brought lots of changes to the lock screen. The font was centered and used an extremely thick weight for the hour and a thin font for the minutes. The lock screen was now paginated and could be customized with widgets. Rather than a simple clock on the lock screen, users could replace it with another widget or add extra pages to the lock screen for more widgets.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The lock screen's add widget page, the list of widgets, the Gmail widget on the lock screen, and swiping over to the camera.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
The lock screen now worked like a stripped-down version of the home screen. Page outlines would pop up on the left and right sides of the lock screen to hint to users that they could swipe to other pages with other widgets. Swiping to the left would show a simple blank page with a plus sign in the center, and tapping on it would bring up a list of widgets that were compatible with the lock screen. Lock screens were limited to one widget per page and could be expanded or collapsed by dragging up or down on the widget. The right-most page was reserved for the camera—a simple over would open the camera interface, but you weren't able to swipe back.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
The new Quick Settings panel and a composite image of the app lineup.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
One of the biggest additions to 4.2 was the new "Quick Settings" panel. Android 3.0 brought a way to quickly change power settings to tablets, and 4.2 finally brought that ability to phones. A new icon was added to the top right corner of the notification panel that would switch between the normal list of notifications and the new quick settings screen. Quick Settings offered faster access to screen brightness, network connections, and battery and data usage without having to dig through the full settings screen. The top level settings button in Android 4.1 was removed, and a square was added to the Quick Settings screen for it.
|
||||
|
||||
There were lots of changes to the app drawer and 4.2's lineup of apps and icons. Thanks to the wider aspect ratio of the Nexus 4 (5:3 vs 16:9 on the Galaxy Nexus), the app drawer on that device could now show a five-wide grid of icons. 4.2 replaced the stock browser with Google Chrome and the stock calendar with Google Calendar, both of which brought new icon designs. The Clock and Camera apps were revamped in 4.2, and new icons were part of the deal. "Google Settings" was a new app that offered shortcuts to all the existing Google Account settings around the OS, and it had a unified look with Google Search and the new Google+ icon. Google Maps got a new icon, and Google Latitude, which was part of Google Maps, was retired in favor of Google+ location.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The browser was replaced with Chrome, and the new camera interface with a full screen viewfinder.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
The stock browser did its best Chrome imitation for a while—it took many cues from Chrome’s interface, many Chrome features, and was even using Chrome’s javascript engine—but by the time Android 4.2 rolled around, Google deemed the Android version of Chrome ready to replace the imitator. On the surface, it didn't seem like much of a difference; the interface looked different, and early versions of Chrome for Android didn't scroll as smoothly as the stock browser. Under the hood, though, everything was different. Development of Android's main browser was now handled by the Google Chrome team instead of being a side project of the Android team. Android's default browser moved from being a stagnant app tied to Android releases to a Play Store app that was continually updated. Today there is even a beta channel that receives several updates per month.
|
||||
|
||||
The camera interface was redesigned. It was now a completely full-screen app, showing a live view of the camera and places controls on top of it. The layout aesthetic had a lot in common with the [camera design][2] of Android 1.5: minimal controls with a focus on the viewfinder output. The circle of controls in the center appeared when you either held your finger on the screen or pressed the circle icon in the bottom right corner. When holding your finger down, you could slide around to pick the options around the circle, often expanding out into a sub-menu. Releasing over a highlighted item would select it. This was clearly inspired by the Quick Controls in the Android 4.0 browser, but arranging the options in a circle meant your finger was almost always blocking part of the interface.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The clock app, which went from a two-screen app to a feature-packed, useful application.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
The clock application was completely revamped, going from a simple two-screen alarm clock to a world clock, alarm, timer, and stopwatch. The clock app design was like nothing Google introduced before, with an ultra-minimal aesthetic and red highlights. It seemed to be an experiment for Google. Even several versions later, this design language seemed to be confined only to this app.
|
||||
|
||||
The clock's time picker was particularly well-designed. It showed a simple number pad, and it would intelligently disable numbers that would result in an invalid time. It was also impossible to set an alarm time without implicitly selecting AM or PM, forever solving the problem of accidentally setting an alarm for 9pm instead of 9am.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The new system UI for tablets used a stretched-out phone interface.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
The most controversial change in Android 4.2 was made to the tablet UI, which switched from a unified single bottom system bar to a two-bar interface with a top status bar and bottom system bar. The new design unified the phone and tablet interfaces, but critics said it was a waste of space to stretch the phone interface to a 10-inch landscape tablet. Since the navigation buttons had the whole bottom bar to themselves now, they were centered, just like the phone interface.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Multiple users on a tablet, and the new gesture-driven keyboard.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
On tablets, Android 4.2 brought support for multiple users. In the settings, a "Users" section was added, where you could manage users on a device. Setup was done from within each user account, where Android would keep separate settings, home screens, apps, and app data for each user.
|
||||
|
||||
4.2 also added a new keyboard with swiping abilities. Rather than just tapping each individual letter, users could now keep a finger on the screen the whole time and just slide from letter to letter to type.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
|
||||
|
||||
[@RonAmadeo][t]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/22/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/01/hands-on-with-samsungs-notepro-and-tabpro-new-screen-sizes-and-magazine-ui/
|
||||
[2]:http://cdn.arstechnica.net/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/device-2013-12-26-11016071.png
|
||||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,10 @@
|
||||
taichirain 翻译中
|
||||
FSSlc translating
|
||||
|
||||
5 great Raspberry Pi projects for the classroom
|
||||
5 伟大的树莓派项目教室
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Image by : opensource.com
|
||||
图片来源 : opensource.com
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Minecraft Pi ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
translated by iov-wang
|
||||
translated by bestony
|
||||
How to Install OsTicket Ticketing System in Fedora 22 / Centos 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In this article, we'll learn how to setup help desk ticketing system with osTicket in our machine or server running Fedora 22 or CentOS 7 as operating system. osTicket is a free and open source popular customer support ticketing system developed and maintained by [Enhancesoft][1] and its contributors. osTicket is the best solution for help and support ticketing system and management for better communication and support assistance with clients and customers. It has the ability to easily integrate with inquiries created via email, phone and web based forms into a beautiful multi-user web interface. osTicket makes us easy to manage, organize and log all our support requests and responses in one single place. It is a simple, lightweight, reliable, open source, web-based and easy to setup and use help desk ticketing system.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
translated by ivo-wang
|
||||
How to Configure OpenNMS on CentOS 7.x
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Systems management and monitoring services are very important that provides information to view important systems management information that allow us to to make decisions based on this information. To make sure the network is running at its best and to minimize the network downtime we need to improve application performance. So, in this article we will make you understand the step by step procedure to setup OpenNMS in your IT infrastructure. OpenNMS is a free open source enterprise level network monitoring and management platform that provides information to allow us to make decisions in regards to future network and capacity planning.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,198 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translated by ivo-wang
|
||||
How to install Suricata intrusion detection system on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
With incessant security threats, intrusion detection system (IDS) has become one of the most critical requirements in today's data center environments. However, as more and more servers upgrade their NICs to 10GB/40GB Ethernet, it is increasingly difficult to implement compute-intensive intrusion detection on commodity hardware at line rates. One approach to scaling IDS performance is **multi-threaded IDS**, where CPU-intensive deep packet inspection workload is parallelized into multiple concurrent tasks. Such parallelized inspection can exploit multi-core hardware to scale up IDS throughput easily. Two well-known open-source efforts in this area are [Suricata][1] and [Bro][2].
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I am going to demonstrate **how to install and configure Suricata IDS on Linux server**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Suricata IDS on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
Let's build Suricata from the source. You first need to install several required dependencies as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install Dependencies on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install wget build-essential libpcre3-dev libpcre3-dbg automake autoconf libtool libpcap-dev libnet1-dev libyaml-dev zlib1g-dev libcap-ng-dev libjansson-dev
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install Dependencies on CentOS, Fedora or RHEL ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install wget libpcap-devel libnet-devel pcre-devel gcc-c++ automake autoconf libtool make libyaml-devel zlib-devel file-devel jansson-devel nss-devel
|
||||
|
||||
Once you install all required packages, go ahead and install Suricata as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
First, download the latest Suricata source code from [http://suricata-ids.org/download/][3], and build it. As of this writing, the latest version is 2.0.8.
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://www.openinfosecfoundation.org/download/suricata-2.0.8.tar.gz
|
||||
$ tar -xvf suricata-2.0.8.tar.gz
|
||||
$ cd suricata-2.0.8
|
||||
$ ./configure --sysconfdir=/etc --localstatedir=/var
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the example output of configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
Suricata Configuration:
|
||||
AF_PACKET support: yes
|
||||
PF_RING support: no
|
||||
NFQueue support: no
|
||||
NFLOG support: no
|
||||
IPFW support: no
|
||||
DAG enabled: no
|
||||
Napatech enabled: no
|
||||
Unix socket enabled: yes
|
||||
Detection enabled: yes
|
||||
|
||||
libnss support: yes
|
||||
libnspr support: yes
|
||||
libjansson support: yes
|
||||
Prelude support: no
|
||||
PCRE jit: yes
|
||||
LUA support: no
|
||||
libluajit: no
|
||||
libgeoip: no
|
||||
Non-bundled htp: no
|
||||
Old barnyard2 support: no
|
||||
CUDA enabled: no
|
||||
|
||||
Now compile and install it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
Suricata source code comes with default configuration files. Let's install these default configuration files as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make install-conf
|
||||
|
||||
As you know, Suricata is useless without IDS rule sets. Conveniently, the Makefile comes with IDS rule installation option. To install IDS rules, run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make install-rules
|
||||
|
||||
The above rule installation command will download the current snapshot of community rulesets available from [EmergingThreats.net][4], and store them under /etc/suricata/rules.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Configure Suricata IDS the First Time ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now it's time to configure Suricata. The configuration file is located at **/etc/suricata/suricata.yaml**. Open the file with a text editor for editing.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some basic setup for you to get started.
|
||||
|
||||
The "default-log-dir" keyword should point to the location of Suricata log files.
|
||||
|
||||
default-log-dir: /var/log/suricata/
|
||||
|
||||
Under "vars" section, you will find several important variables used by Suricata. "HOME_NET" should point to the local network to be inspected by Suricata. "!$HOME_NET" (assigned to EXTERNAL_NET) refers to any other networks than the local network. "XXX_PORTS" indicates the port number(s) use by different services. Note that Suricata can automatically detect HTTP traffic regardless of the port it uses. So it is not critical to specify the HTTP_PORTS variable correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
vars:
|
||||
HOME_NET: "[192.168.122.0/24]"
|
||||
EXTERNAL_NET: "!$HOME_NET"
|
||||
HTTP_PORTS: "80"
|
||||
SHELLCODE_PORTS: "!80"
|
||||
SSH_PORTS: 22
|
||||
|
||||
The "host-os-policy" section is used to defend against some well-known attacks which exploit the behavior of an operating system's network stack (e.g., TCP reassembly) to evade detection. As a counter measure, modern IDS came up with so-called "target-based" inspection, where inspection engine fine-tunes its detection algorithm based on a target operating system of the traffic. Thus, if you know what OS individual local hosts are running, you can feed that information to Suricata to potentially enhance its detection rate. This is when "host-os-policy" section is used. In this example, the default IDS policy is Linux; if no OS information is known for a particular IP address, Suricata will apply Linux-based inspection. When traffic for 192.168.122.0/28 and 192.168.122.155 is captured, Suricata will apply Windows-based inspection policy.
|
||||
|
||||
host-os-policy:
|
||||
# These are Windows machines.
|
||||
windows: [192.168.122.0/28, 192.168.122.155]
|
||||
bsd: []
|
||||
bsd-right: []
|
||||
old-linux: []
|
||||
# Make the default policy Linux.
|
||||
linux: [0.0.0.0/0]
|
||||
old-solaris: []
|
||||
solaris: ["::1"]
|
||||
hpux10: []
|
||||
hpux11: []
|
||||
irix: []
|
||||
macos: []
|
||||
vista: []
|
||||
windows2k3: []
|
||||
|
||||
Under "threading" section, you can specify CPU affinity for different Suricata threads. By default, [CPU affinity][5] is disabled ("set-cpu-affinity: no"), meaning that Suricata threads will be scheduled on any available CPU cores. By default, Suricata will create one "detect" thread for each CPU core. You can adjust this behavior by specifying "detect-thread-ratio: N". This will create N*M detect threads, where M is the total number of CPU cores on the host.
|
||||
|
||||
threading:
|
||||
set-cpu-affinity: no
|
||||
detect-thread-ratio: 1.5
|
||||
|
||||
With the above threading settings, Suricata will create 1.5*M detection threads, where M is the total number of CPU cores on the system.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about Suricata configuration, you can read the default configuration file itself, which is heavily commented for clarity.
|
||||
|
||||
### Perform Intrusion Detection with Suricata ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now it's time to test-run Suricata. Before launching it, there's one more step to do.
|
||||
|
||||
When you are using pcap capture mode, it is highly recommended to turn off any packet offloead features (e.g., LRO/GRO) on the NIC which Suricata is listening on, as those features may interfere with live packet capture.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how to turn off LRO/GRO on the network interface eth0:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ethtool -K eth0 gro off lro off
|
||||
|
||||
Note that depending on your NIC, you may see the following warning, which you can ignore. It simply means that your NIC does not support LRO.
|
||||
|
||||
Cannot change large-receive-offload
|
||||
|
||||
Suricata supports a number of running modes. A runmode determines how different threads are used for IDS. The following command lists all [available runmodes][6].
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /usr/local/bin/suricata --list-runmodes
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The default runmode used by Suricata is autofp (which stands for "auto flow pinned load balancing"). In this mode, packets from each distinct flow are assigned to a single detect thread. Flows are assigned to threads with the lowest number of unprocessed packets.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, let's start Suricata, and see it in action.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /usr/local/bin/suricata -c /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml -i eth0 --init-errors-fatal
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In this example, we are monitoring a network interface eth0 on a 8-core system. As shown above, Suricata creates 13 packet processing threads and 3 management threads. The packet processing threads consist of one PCAP packet capture thread, and 12 detect threads (equal to 8*1.5). This means that the packets captured by one capture thread are load-balanced to 12 detect threads for IDS. The management threads are one flow manager and two counter/stats related threads.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a thread-view of Suricata process (plotted by [htop][7]).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Suricata detection logs are stored in /var/log/suricata directory.
|
||||
|
||||
$ tail -f /var/log/suricata/fast.log
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
04/01/2015-15:47:12.559075 [**] [1:2200074:1] SURICATA TCPv4 invalid checksum [**] [Classification: (null)] [Priority: 3] {TCP} 172.16.253.158:22 -> 172.16.253.1:46997
|
||||
04/01/2015-15:49:06.565901 [**] [1:2200074:1] SURICATA TCPv4 invalid checksum [**] [Classification: (null)] [Priority: 3] {TCP} 172.16.253.158:22 -> 172.16.253.1:46317
|
||||
04/01/2015-15:49:06.566759 [**] [1:2200074:1] SURICATA TCPv4 invalid checksum [**] [Classification: (null)] [Priority: 3] {TCP} 172.16.253.158:22 -> 172.16.253.1:46317
|
||||
|
||||
For ease of import, the log is also available in JSON format:
|
||||
|
||||
$ tail -f /var/log/suricata/eve.json
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
{"timestamp":"2015-04-01T15:49:06.565901","event_type":"alert","src_ip":"172.16.253.158","src_port":22,"dest_ip":"172.16.253.1","dest_port":46317,"proto":"TCP","alert":{"action":"allowed","gid":1,"signature_id":2200074,"rev":1,"signature":"SURICATA TCPv4 invalid checksum","category":"","severity":3}}
|
||||
{"timestamp":"2015-04-01T15:49:06.566759","event_type":"alert","src_ip":"172.16.253.158","src_port":22,"dest_ip":"172.16.253.1","dest_port":46317,"proto":"TCP","alert":{"action":"allowed","gid":1,"signature_id":2200074,"rev":1,"signature":"SURICATA TCPv4 invalid checksum","category":"","severity":3}}
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I demonstrated how you can set up Suricata IDS on a multi-core Linux server. Unlike single-threaded [Snort IDS][8], Suricata can easily benefit from multi-core/many-core hardware with multi-threading. There is great deal of customization in Suricata to maximize its performance and detection coverage. Suricata folks maintain [online Wiki][9] quite well, so I strongly recommend you check it out if you want to deploy Suricata in your environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Are you currently using Suricata? If so, feel free to share your experience.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/install-suricata-intrusion-detection-system-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://suricata-ids.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.bro.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://suricata-ids.org/download/
|
||||
[4]:http://rules.emergingthreats.net/
|
||||
[5]:http://xmodulo.com/run-program-process-specific-cpu-cores-linux.html
|
||||
[6]:https://redmine.openinfosecfoundation.org/projects/suricata/wiki/Runmodes
|
||||
[7]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/view-threads-process-linux.html
|
||||
[8]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-compile-and-install-snort-from-source-code-on-ubuntu.html
|
||||
[9]:https://redmine.openinfosecfoundation.org/projects/suricata/wiki
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
chisper 翻译中
|
||||
How to Install Pure-FTPd with TLS on FreeBSD 10.2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
FTP or File Transfer Protocol is application layer standard network protocol used to transfer file from the client to the server, after user logged in to the FTP server over the TCP-Network, such as internet. FTP has been round long time ago, much longer then P2P Program, or World Wide Web, and until this day it was a primary method for sharing file with other over the internet and it it remain very popular even today. FTP provide an secure transmission, that protect username, password and encrypt the content with SSL/TLS.
|
||||
@ -151,4 +152,4 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-pure-ftpd-tls-freebsd-10-2/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arulm/
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arulm/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translation by strugglingyouth
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install Ubuntu desktop behind a proxy
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: My computer is connected to a corporate network sitting behind an HTTP proxy. When I try to install Ubuntu desktop on the computer from a CD-ROM drive, the installation hangs and never finishes while trying to retrieve files, which is presumably due to the proxy. However, the problem is that Ubuntu installer never asks me to configure proxy during installation procedure. Then how can I install Ubuntu desktop behind a proxy?
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike Ubuntu server, installation of Ubuntu desktop is pretty much auto-pilot, not leaving much room for customization, such as custom disk partitioning, manual network settings, package selection, etc. While such simple, one-shot installation is considered user-friendly, it leaves much to be desired for those users looking for "advanced installation mode" to customize their Ubuntu desktop installation.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, one big problem of the default Ubuntu desktop installer is the absense of proxy settings. If your computer is connected behind a proxy, you will notice that Ubuntu installation gets stuck while preparing to download files.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This post describes how to get around the limitation of Ubuntu **installer and install Ubuntu desktop when you are behind a proxy**.
|
||||
|
||||
The basic idea is as follows. Instead of starting with Ubuntu installer directly, boot into live Ubuntu desktop first, configure proxy settings, and finally launch Ubuntu installer manually from live desktop. The following is the step by step procedure.
|
||||
|
||||
After booting from Ubuntu desktop CD/DVD or USB, click on "Try Ubuntu" on the first welcome screen.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once you boot into live Ubuntu desktop, click on Settings icon in the left.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Go to Network menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Configure proxy settings manually.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, open a terminal.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enter a root session by typing the following:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo su
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, type the following command as the root.
|
||||
|
||||
# ubiquity gtk_ui
|
||||
|
||||
This will launch GUI-based Ubuntu installer as follows.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Proceed with the rest of installation.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-ubuntu-desktop-behind-proxy.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
@ -1,157 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by KnightJoker
|
||||
How to send email notifications using Gmail SMTP server on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Suppose you want to configure a Linux app to send out email messages from your server or desktop. The email messages can be part of email newsletters, status updates (e.g., [Cachet][1]), monitoring alerts (e.g., [Monit][2]), disk events (e.g., [RAID mdadm][3]), and so on. While you can set up your [own outgoing mail server][4] to deliver messages, you can alternatively rely on a freely available public SMTP server as a maintenance-free option.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most reliable **free SMTP servers** is from Google's Gmail service. All you have to do to send email notifications within your app is to add Gmail's SMTP server address and your credentials to the app, and you are good to go.
|
||||
|
||||
One catch with using Gmail's SMTP server is that there are various restrictions in place, mainly to combat spammers and email marketers who often abuse the server. For example, you can send messages to no more than 100 addresses at once, and no more than 500 recipients per day. Also, if you don't want to be flagged as a spammer, you cannot send a large number of undeliverable messages. When any of these limitations is reached, your Gmail account will temporarily be locked out for a day. In short, Gmail's SMTP server is perfectly fine for your personal use, but not meant for commercial bulk emails.
|
||||
|
||||
With that being said, let me demonstrate **how to use Gmail's SMTP server in Linux environment**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Google Gmail SMTP Server Setting ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to send emails from your app using Gmail's SMTP server, remember the following details.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Outgoing mail server (SMTP server)**: smtp.gmail.com
|
||||
- **Use authentication**: yes
|
||||
- **Use secure connection**: yes
|
||||
- **Username**: your Gmail account ID (e.g., "alice" if your email is alice@gmail.com)
|
||||
- **Password**: your Gmail password
|
||||
- **Port**: 587
|
||||
|
||||
Exact configuration syntax may vary depending on apps. In the rest of this tutorial, I will show you several useful examples of using Gmail SMTP server in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### Send Emails from the Command Line ###
|
||||
|
||||
As the first example, let's try the most basic email functionality: send an email from the command line using Gmail SMTP server. For this, I am going to use a command-line email client called mutt.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install mutt:
|
||||
|
||||
For Debian-based system:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install mutt
|
||||
|
||||
For Red Hat based system:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install mutt
|
||||
|
||||
Create a mutt configuration file (~/.muttrc) and specify in the file Gmail SMTP server information as follows. Replace <gmail-id> with your own Gmail ID. Note that this configuration is for sending emails only (not receiving emails).
|
||||
|
||||
$ vi ~/.muttrc
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
set from = "<gmail-id>@gmail.com"
|
||||
set realname = "Dan Nanni"
|
||||
set smtp_url = "smtp://<gmail-id>@smtp.gmail.com:587/"
|
||||
set smtp_pass = "<gmail-password>"
|
||||
|
||||
Now you are ready to send out an email using mutt:
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo "This is an email body." | mutt -s "This is an email subject" alice@yahoo.com
|
||||
|
||||
To attach a file in an email, use "-a" option:
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo "This is an email body." | mutt -s "This is an email subject" alice@yahoo.com -a ~/test_attachment.jpg
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Using Gmail SMTP server means that the emails appear as sent from your Gmail account. In other words, a recepient will see your Gmail address as the sender's address. If you want to use your domain as the email sender, you need to use Gmail SMTP relay service instead.
|
||||
|
||||
### Send Email Notification When a Server is Rebooted ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you are running a [virtual private server (VPS)][5] for some critical website, one recommendation is to monitor VPS reboot activities. As a more practical example, let's consider how to set up email notifications for every reboot event on your VPS. Here I assume you are using systemd on your VPS, and show you how to create a custom systemd boot-time service for automatic email notifications.
|
||||
|
||||
First create the following script reboot_notify.sh which takes care of email notifications.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /usr/local/bin/reboot_notify.sh
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/sh
|
||||
|
||||
echo "`hostname` was rebooted on `date`" | mutt -F /etc/muttrc -s "Notification on `hostname`" alice@yahoo.com
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chmod +x /usr/local/bin/reboot_notify.sh
|
||||
|
||||
In the script, I use "-F" option to specify the location of system-wide mutt configuration file. So don't forget to create /etc/muttrc file and populate Gmail SMTP information as described earlier.
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's create a custom systemd service as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/lib/systemd/system
|
||||
$ sudo vi /usr/local/lib/systemd/system/reboot-task.service
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[Unit]
|
||||
Description=Send a notification email when the server gets rebooted
|
||||
DefaultDependencies=no
|
||||
Before=reboot.target
|
||||
|
||||
[Service]
|
||||
Type=oneshot
|
||||
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/reboot_notify.sh
|
||||
|
||||
[Install]
|
||||
WantedBy=reboot.target
|
||||
|
||||
Once the service file is created, enable and start the service.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl enable reboot-task
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl start reboot-task
|
||||
|
||||
From now on, you will be receiving a notification email every time the VPS gets rebooted.
|
||||
|
||||
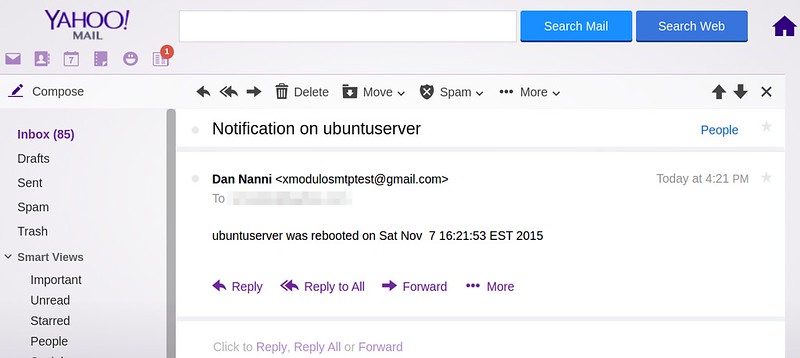
|
||||
|
||||
### Send Email Notification from Server Usage Monitoring ###
|
||||
|
||||
As a final example, let me present a real-world application called [Monit][6], which is a pretty useful server monitoring application. It comes with comprehensive [VPS][7] monitoring capabilities (e.g., CPU, memory, processes, file system), as well as email notification functions.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to receive email notifications for any event on your VPS (e.g., server overload) generated by Monit, you can add the following SMTP information to Monit configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
set mailserver smtp.gmail.com port 587
|
||||
username "<your-gmail-ID>" password "<gmail-password>"
|
||||
using tlsv12
|
||||
|
||||
set mail-format {
|
||||
from: <your-gmail-ID>@gmail.com
|
||||
subject: $SERVICE $EVENT at $DATE on $HOST
|
||||
message: Monit $ACTION $SERVICE $EVENT at $DATE on $HOST : $DESCRIPTION.
|
||||
|
||||
Yours sincerely,
|
||||
Monit
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# the person who will receive notification emails
|
||||
set alert alice@yahoo.com
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the example email notification sent by Monit for excessive CPU load.
|
||||
|
||||
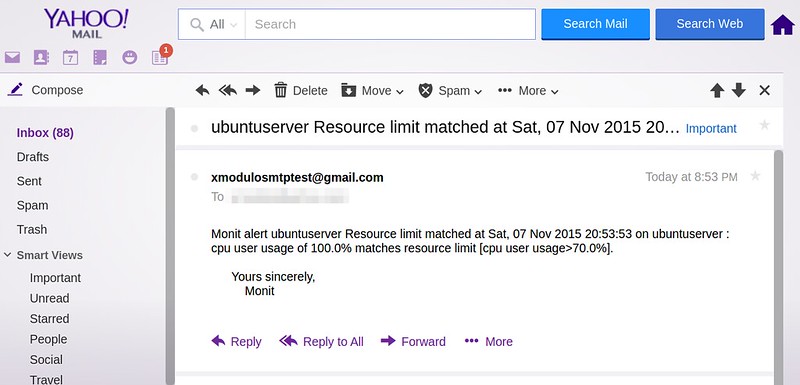
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
As you can imagine, there will be so many different ways to take advantage of free SMTP servers like Gmail. But once again, remember that the free SMTP server is not meant for commercial usage, but only for your own personal project. If you are using Gmail SMTP server inside any app, feel free to share your use case.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/send-email-notifications-gmail-smtp-server-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/setup-system-status-page.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/server-monitoring-system-monit.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/create-software-raid1-array-mdadm-linux.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/mail-server-ubuntu-debian.html
|
||||
[5]:http://xmodulo.com/go/digitalocean
|
||||
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/server-monitoring-system-monit.html
|
||||
[7]:http://xmodulo.com/go/digitalocean
|
||||
@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
|
||||
zpl1025
|
||||
Install Android On BQ Aquaris Ubuntu Phone In Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you happen to own the first Ubuntu phone and want to **replace Ubuntu with Android on the bq Aquaris e4.5**, this post is going to help you.
|
||||
|
||||
There can be plenty of reasons why you might want to remove Ubuntu and use the mainstream Android OS. One of the foremost reason is that the OS itself is at an early stage and intend to target developers and enthusiasts. Whatever may be your reason, installing Android on bq Aquaris is a piece of cake, thanks to the tools provided by bq.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s see what to do we need to install Android on bq Aquaris.
|
||||
|
||||
### Prerequisite ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Working Internet connection to download Android factory image and install tools for flashing Android
|
||||
- USB data cable
|
||||
- A system running Linux
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial is performed using Ubuntu 15.10. But the steps should be applicable to most other Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
### Replace Ubuntu with Android in bq Aquaris e4.5 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1: Download Android firmware ####
|
||||
|
||||
First step is to download the Android image for bq Aquaris e4.5. Good thing is that it is available from the bq’s support website. You can download the firmware, around 650 MB in size, from the link below:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Android for bq Aquaris e4.5][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you would get OTA updates with it. At present the firmware version is 2.0.1 which is based on Android Lolipop. Over time, there could be a new firmware based on Marshmallow and then the above link could be outdated.
|
||||
|
||||
I suggest to check the [bq support page and download][2] the latest firmware from there.
|
||||
|
||||
Once downloaded, extract it. In the extracted directory, look for **MT6582_Android_scatter.txt** file. We shall be using it later.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: Download flash tool ####
|
||||
|
||||
bq has provided its own flash tool, Herramienta MTK Flash Tool, for easier installation of Android or Ubuntu on the device. You can download the tool from the link below:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download MTK Flash Tool][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Since the flash tool might be upgraded in future, you can always get the latest version of flash tool from the [bq support page][4].
|
||||
|
||||
Once downloaded extract the downloaded file. You should see an executable file named **flash_tool** in it. We shall be using it later.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 3: Remove conflicting packages (optional) ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using recent version of Ubuntu or Ubuntu based Linux distributions, you may encounter “BROM ERROR : S_UNDEFINED_ERROR (1001)” later in this tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
To avoid this error, you’ll have to uninstall conflicting package. Use the commands below:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove modemmanager
|
||||
|
||||
Restart udev service with the command below:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo service udev restart
|
||||
|
||||
Just to check for any possible side effects on kernel module cdc_acm, run the command below:
|
||||
|
||||
lsmod | grep cdc_acm
|
||||
|
||||
If the output of the above command is an empty list, you’ll have to reinstall this kernel module:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo modprobe cdc_acm
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 4: Prepare to flash Android ####
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the downloaded and extracted flash tool directory (in step 2). Use command line for this purpose because you’ll have to use the root privileges here.
|
||||
|
||||
Presuming that you saved it in the Downloads directory, use the command below to go to this directory (in case you do not know how to navigate between directories in command line).
|
||||
|
||||
cd ~/Downloads/SP_Flash*
|
||||
|
||||
After that use the command below to run the flash tool as root:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ./flash_tool
|
||||
|
||||
You’ll see a window popped as the one below. Don’t bother about Download Agent field, it will be automatically filled. Just focus on Scatter-loading field.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Remember we talked about **MT6582_Android_scatter.txt** in step 1? This text file is in the extracted directory of the Andriod firmware you downloaded in step 1. Click on Scatter-loading (in the above picture) and point to MT6582_Android_scatter.txt file.
|
||||
|
||||
When you do that, you’ll see several green lines like the one below:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 5: Flashing Android ####
|
||||
|
||||
We are almost ready. Switch off your phone and connect it to your computer via a USB cable.
|
||||
|
||||
Select Firmware Upgrade from the dropdown and after that click on the big download button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If everything is correct, you should see a flash status in the bottom of the tool:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When the procedure is successfully completed, you’ll see a notification like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unplug your phone and power it on. You should see a white screen with AQUARIS written in the middle and at bottom, “powered by Android” would be displayed. It might take upto 10 minutes before you could configure and start using Android.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: If something goes wrong in the process, Press power, volume up, volume down button together and boot in to fast boot mode. Turn off again and connect the cable again. Repeat the process of firmware upgrade. It should work.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks to the tools provided, it becomes easier to **flash Android on bq Ubuntu Phone**. Of course, you can use the same steps to replace Android with Ubuntu. All you need is to download Ubuntu firmware instead of Android.
|
||||
|
||||
I hope this tutorial helped you to replace Ubuntu with Android on your bq phone. If you have questions or suggestions, feel free to ask in the comment section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-android-ubuntu-phone/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:https://storage.googleapis.com/otas/2014/Smartphones/Aquaris_E4.5_L/2.0.1_20150623-1900_bq-FW.zip
|
||||
[2]:http://www.bq.com/gb/support/aquaris-e4-5
|
||||
[3]:https://storage.googleapis.com/otas/2014/Smartphones/Aquaris_E4.5/Ubuntu/Web%20version/Web%20version/SP_Flash_Tool_exe_linux_v5.1424.00.zip
|
||||
[4]:http://www.bq.com/gb/support/aquaris-e4-5-ubuntu-edition
|
||||
@ -1,125 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Install Android On BQ Aquaris Ubuntu Phone In Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you happen to own the first Ubuntu phone and want to **replace Ubuntu with Android on the bq Aquaris e4.5**, this post is going to help you.
|
||||
|
||||
There can be plenty of reasons why you might want to remove Ubuntu and use the mainstream Android OS. One of the foremost reason is that the OS itself is at an early stage and intend to target developers and enthusiasts. Whatever may be your reason, installing Android on bq Aquaris is a piece of cake, thanks to the tools provided by bq.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s see what to do we need to install Android on bq Aquaris.
|
||||
|
||||
### Prerequisite ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Working Internet connection to download Android factory image and install tools for flashing Android
|
||||
- USB data cable
|
||||
- A system running Linux
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial is performed using Ubuntu 15.10. But the steps should be applicable to most other Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
### Replace Ubuntu with Android in bq Aquaris e4.5 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 1: Download Android firmware ####
|
||||
|
||||
First step is to download the Android image for bq Aquaris e4.5. Good thing is that it is available from the bq’s support website. You can download the firmware, around 650 MB in size, from the link below:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Android for bq Aquaris e4.5][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, you would get OTA updates with it. At present the firmware version is 2.0.1 which is based on Android Lolipop. Over time, there could be a new firmware based on Marshmallow and then the above link could be outdated.
|
||||
|
||||
I suggest to check the [bq support page][2] and download the latest firmware from there.
|
||||
|
||||
Once downloaded, extract it. In the extracted directory, look for **MT6582_Android_scatter.txt** file. We shall be using it later.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: Download flash tool ####
|
||||
|
||||
bq has provided its own flash tool, Herramienta MTK Flash Tool, for easier installation of Android or Ubuntu on the device. You can download the tool from the link below:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download MTK Flash Tool][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Since the flash tool might be upgraded in future, you can always get the latest version of flash tool from the [bq support page][4].
|
||||
|
||||
Once downloaded extract the downloaded file. You should see an executable file named **flash_tool** in it. We shall be using it later.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 3: Remove conflicting packages (optional) ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using recent version of Ubuntu or Ubuntu based Linux distributions, you may encounter “BROM ERROR : S_UNDEFINED_ERROR (1001)” later in this tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
To avoid this error, you’ll have to uninstall conflicting package. Use the commands below:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove modemmanager
|
||||
|
||||
Restart udev service with the command below:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo service udev restart
|
||||
|
||||
Just to check for any possible side effects on kernel module cdc_acm, run the command below:
|
||||
|
||||
lsmod | grep cdc_acm
|
||||
|
||||
If the output of the above command is an empty list, you’ll have to reinstall this kernel module:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo modprobe cdc_acm
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 4: Prepare to flash Android ####
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the downloaded and extracted flash tool directory (in step 2). Use command line for this purpose because you’ll have to use the root privileges here.
|
||||
|
||||
Presuming that you saved it in the Downloads directory, use the command below to go to this directory (in case you do not know how to navigate between directories in command line).
|
||||
|
||||
cd ~/Downloads/SP_Flash*
|
||||
|
||||
After that use the command below to run the flash tool as root:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ./flash_tool
|
||||
|
||||
You’ll see a window popped as the one below. Don’t bother about Download Agent field, it will be automatically filled. Just focus on Scatter-loading field.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Remember we talked about **MT6582_Android_scatter.txt** in step 1? This text file is in the extracted directory of the Andriod firmware you downloaded in step 1. Click on Scatter-loading (in the above picture) and point to MT6582_Android_scatter.txt file.
|
||||
|
||||
When you do that, you’ll see several green lines like the one below:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 5: Flashing Android ####
|
||||
|
||||
We are almost ready. Switch off your phone and connect it to your computer via a USB cable.
|
||||
|
||||
Select Firmware Upgrade from the dropdown and after that click on the big download button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If everything is correct, you should see a flash status in the bottom of the tool:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When the procedure is successfully completed, you’ll see a notification like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unplug your phone and power it on. You should see a white screen with AQUARIS written in the middle and at bottom, “powered by Android” would be displayed. It might take upto 10 minutes before you could configure and start using Android.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: If something goes wrong in the process, Press power, volume up, volume down button together and boot in to fast boot mode. Turn off again and connect the cable again. Repeat the process of firmware upgrade. It should work.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Thanks to the tools provided, it becomes easier to **flash Android on bq Ubuntu Phone**. Of course, you can use the same steps to replace Android with Ubuntu. All you need is to download Ubuntu firmware instead of Android.
|
||||
|
||||
I hope this tutorial helped you to replace Ubuntu with Android on your bq phone. If you have questions or suggestions, feel free to ask in the comment section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-android-ubuntu-phone/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:https://storage.googleapis.com/otas/2014/Smartphones/Aquaris_E4.5_L/2.0.1_20150623-1900_bq-FW.zip
|
||||
[2]:http://www.bq.com/gb/support/aquaris-e4-5
|
||||
[3]:https://storage.googleapis.com/otas/2014/Smartphones/Aquaris_E4.5/Ubuntu/Web%20version/Web%20version/SP_Flash_Tool_exe_linux_v5.1424.00.zip
|
||||
[4]:http://www.bq.com/gb/support/aquaris-e4-5-ubuntu-edition
|
||||
@ -1,242 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Install Revive Adserver on Ubuntu 15.04 / CentOS 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Revive AdserverHow to Install Revive Adserver on Ubuntu 15.04 / CentOS 7 is a free and open source advertisement management system that enables publishers, ad networks and advertisers to serve ads on websites, apps, videos and manage campaigns for multiple advertiser with many features. Revive Adserver is licensed under GNU Public License which is also known as OpenX Source. It features an integrated banner management interface, URL targeting, geo-targeting and tracking system for gathering statistics. This application enables website owners to manage banners from both in-house advertisement campaigns as well as from paid or third-party sources, such as Google's AdSense. Here, in this tutorial, we'll gonna install Revive Adserver in our machine running Ubuntu 15.04 or CentOS 7.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Installing LAMP Stack ###
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, as Revive Adserver requires a complete LAMP Stack to work, we'll gonna install it. LAMP Stack is the combination of Apache Web Server, MySQL/MariaDB Database Server and PHP modules. To run Revive properly, we'll need to install some PHP modules like apc, zlib, xml, pcre, mysql and mbstring. To setup LAMP Stack, we'll need to run the following command with respect to the distribution of linux we are currently running.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 15.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install apache2 mariadb-server php5 php5-gd php5-mysql php5-curl php-apc zlibc zlib1g zlib1g-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev libapache2-mod-php5 zip
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install httpd mariadb php php-gd php-mysql php-curl php-mbstring php-xml php-apc zlibc zlib1g zlib1g-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev zip
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Starting Apache and MariaDB server ###
|
||||
|
||||
We’ll now start our newly installed Apache web server and MariaDB database server in our linux machine. To do so, we'll need to execute the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 15.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04 is shipped with Systemd as its default init system, so we'll need to execute the following commands to start apache and mariadb daemons.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start apache2 mysql
|
||||
|
||||
After its started, we'll now make it able to start automatically in every system boot by running the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable apache2 mysql
|
||||
|
||||
Synchronizing state for apache2.service with sysvinit using update-rc.d...
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d apache2 defaults
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d apache2 enable
|
||||
Synchronizing state for mysql.service with sysvinit using update-rc.d...
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d mysql defaults
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d mysql enable
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Also in CentOS 7, systemd is the default init system so, we'll run the following command to start them.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start httpd mariadb
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we'll enable them to start automatically in every startup of init system using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable httpd mariadb
|
||||
|
||||
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service'
|
||||
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service'
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Configuring MariaDB ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7/Ubuntu 15.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Now, as we are starting MariaDB for the first time and no password has been assigned for MariaDB so, we’ll first need to configure a root password for it. Then, we’ll gonna create a new database so that it can store data for our Revive Adserver installation.
|
||||
|
||||
To configure MariaDB and assign a root password, we’ll need to run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
|
||||
This will ask us to enter the password for root but as we haven’t set any password before and its our first time we’ve installed mariadb, we’ll simply press enter and go further. Then, we’ll be asked to set root password, here we’ll hit Y and enter our password for root of MariaDB. Then, we’ll simply hit enter to set the default values for the further configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
….
|
||||
so you should just press enter here.
|
||||
|
||||
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
|
||||
OK, successfully used password, moving on…
|
||||
|
||||
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
|
||||
root user without the proper authorisation.
|
||||
|
||||
Set root password? [Y/n] y
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Re-enter new password:
|
||||
Password updated successfully!
|
||||
Reloading privilege tables..
|
||||
… Success!
|
||||
…
|
||||
installation should now be secure.
|
||||
Thanks for using MariaDB!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Creating new Database ###
|
||||
|
||||
After we have assigned the password to our root user of mariadb server, we'll now create a new database for Revive Adserver application so that it can store its data into the database server. To do so, first we'll need to login to our MariaDB console by running the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# mysql -u root -p
|
||||
|
||||
Then, it will ask us to enter the password of root user which we had just set in the above step. Then, we'll be welcomed into the MariaDB console in which we'll create our new database, database user and assign its password and grant all privileges to create, remove and edit the tables and data stored in it.
|
||||
|
||||
> CREATE DATABASE revivedb;
|
||||
> CREATE USER 'reviveuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Pa$$worD123';
|
||||
> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON revivedb.* TO 'reviveuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
|
||||
> EXIT;
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Downloading Revive Adserver Package ###
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we'll download the latest release of Revive Adserver ie version 3.2.2 in the time of writing this article. So, we'll first get the download link from the official Download Page of Revive Adserver ie [http://www.revive-adserver.com/download/][1] then we'll download the compressed zip file using wget command under /tmp/ directory as shown bellow.
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /tmp/
|
||||
# wget http://download.revive-adserver.com/revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip
|
||||
|
||||
--2015-11-09 17:03:48-- http://download.revive-adserver.com/revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip
|
||||
Resolving download.revive-adserver.com (download.revive-adserver.com)... 54.230.119.219, 54.239.132.177, 54.230.116.214, ...
|
||||
Connecting to download.revive-adserver.com (download.revive-adserver.com)|54.230.119.219|:80... connected.
|
||||
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
|
||||
Length: 11663620 (11M) [application/zip]
|
||||
Saving to: 'revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip'
|
||||
revive-adserver-3.2 100%[=====================>] 11.12M 1.80MB/s in 13s
|
||||
2015-11-09 17:04:02 (906 KB/s) - 'revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip' saved [11663620/11663620]
|
||||
|
||||
After the file is downloaded, we'll simply extract its files and directories using unzip command.
|
||||
|
||||
# unzip revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll gonna move the entire Revive directories including every files from /tmp to the default webroot of Apache Web Server ie /var/www/html/ directory.
|
||||
|
||||
# mv revive-adserver-3.2.2 /var/www/html/reviveads
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Configuring Apache Web Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
We'll now configure our Apache Server so that revive will run with proper configuration. To do so, we'll create a new virtualhost by creating a new configuration file named reviveads.conf . The directory here may differ from one distribution to another, here is how we create in the following distributions of linux.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 15.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /etc/apache2/sites-available/reviveads.conf
|
||||
# ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/reviveads.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/reviveads.conf
|
||||
# nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/reviveads.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll gonna add the following lines of configuration into this file using our favorite text editor.
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerAdmin info@reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/reviveads/
|
||||
ServerName reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
ServerAlias www.reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
<Directory /var/www/html/reviveads/>
|
||||
Options FollowSymLinks
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/reviveads.linoxide.com-error_log
|
||||
CustomLog /var/log/apache2/reviveads.linoxide.com-access_log common
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After done, we'll gonna save the file and exit our text editor. Then, we'll restart our Apache Web server.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart apache2
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
In CentOS, we'll directly create the file reviveads.conf under /etc/httpd/conf.d/ directory using our favorite text editor.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/reviveads.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll gonna add the following lines of configuration into the file.
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerAdmin info@reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/reviveads/
|
||||
ServerName reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
ServerAlias www.reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
<Directory /var/www/html/reviveads/>
|
||||
Options FollowSymLinks
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/reviveads.linoxide.com-error_log
|
||||
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/reviveads.linoxide.com-access_log common
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once done, we'll simply save the file and exit the editor. And then, we'll gonna restart our apache web server.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart httpd
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Fixing Permissions and Ownership ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll gonna fix some file permissions and ownership of the installation path. First, we'll gonna set the ownership of the installation directory to Apache process owner so that apache web server will have full access of the files and directories to edit, create and delete.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 15.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# chown www-data: -R /var/www/html/reviveads
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# chown apache: -R /var/www/html/reviveads
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Allowing Firewall ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll gonna configure our firewall programs to allow port 80 (http) so that our apache web server running Revive Adserver will be accessible from other machines in the network across the default http port ie 80.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 15.04/CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
As CentOS 7 and Ubuntu 15.04 both has systemd installed by default, it contains firewalld running as firewall program. In order to open the port 80 (http service) on firewalld, we'll need to execute the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Web Installation ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, after everything is done as expected, we'll now be able to access the web interface of the application using a web browser. We can go further towards the web installation, by pointing the web browser to the web server we are running in our linux machine. To do so, we'll need to point our web browser to http://ip-address/ or http://domain.com assigned to our linux machine. Here, in this tutorial, we'll point our browser to http://reviveads.linoxide.com/ .
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we'll see the Welcome page of the installation of Revive Adserver with the GNU General Public License V2 as Revive Adserver is released under this license. Then, we'll simply click on I agree button in order to continue the installation.
|
||||
|
||||
In the next page, we'll need to enter the required database information in order to connect Revive Adserver with the MariaDB database server. Here, we'll need to enter the database name, user and password that we had set in the above step. In this tutorial, we entered database name, user and password as revivedb, reviveuser and Pa$$worD123 respectively then, we set the hostname as localhost and continue further.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We'll now enter the required information like administration username, password and email address so that we can use these information to login to the dashboard of our Adserver. After done, we'll head towards the Finish page in which we'll see that we have successfully installed Revive Adserver in our server.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we'll be redirected to the Adverstiser page where we'll add new Advertisers and manage them. Then, we'll be able to navigate to our Dashboard, add new users to the adserver, add new campaign for our advertisers, banners, websites, video ads and everything that its built with.
|
||||
|
||||
For enabling more configurations and access towards the administrative settings, we can switch our Dashboard user to the Administrator account. This will add new administrative menus in the dashboard like Plugins, Configuration through which we can add and manage plugins and configure many features and elements of Revive Adserver.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we learned some information on what is Revive Adserver and how we can setup on linux machine running Ubuntu 15.04 and CentOS 7 distributions. Though Revive Adserver's initial source code was bought from OpenX, currently the code base for OpenX Enterprise and Revive Adserver are completely separate. To extend more features, we can install more plugins which we can also find from [http://www.adserverplugins.com/][2] . Really, this piece of software has changed the way of managing the ads for websites, apps, videos and made it very easy and efficient. If you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below so that we can improve or update our contents. Thank you !
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-revive-adserver-ubuntu-15-04-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.revive-adserver.com/download/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.adserverplugins.com/
|
||||
@ -1,203 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by DongShuaike
|
||||
|
||||
Data Structures in the Linux Kernel
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Radix tree
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
As you already know linux kernel provides many different libraries and functions which implement different data structures and algorithms. In this part we will consider one of these data structures - [Radix tree](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radix_tree). There are two files which are related to `radix tree` implementation and API in the linux kernel:
|
||||
|
||||
* [include/linux/radix-tree.h](https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/include/linux/radix-tree.h)
|
||||
* [lib/radix-tree.c](https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/lib/radix-tree.c)
|
||||
|
||||
Lets talk about what a `radix tree` is. Radix tree is a `compressed trie` where a [trie](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie) is a data structure which implements an interface of an associative array and allows to store values as `key-value`. The keys are usually strings, but any data type can be used. A trie is different from an `n-tree` because of its nodes. Nodes of a trie do not store keys; instead, a node of a trie stores single character labels. The key which is related to a given node is derived by traversing from the root of the tree to this node. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
+-----------+
|
||||
| |
|
||||
| " " |
|
||||
| |
|
||||
+------+-----------+------+
|
||||
| |
|
||||
| |
|
||||
+----v------+ +-----v-----+
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
| g | | c |
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
+-----------+ +-----------+
|
||||
| |
|
||||
| |
|
||||
+----v------+ +-----v-----+
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
| o | | a |
|
||||
| | | |
|
||||
+-----------+ +-----------+
|
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
+-----v-----+
|
||||
| |
|
||||
| t |
|
||||
| |
|
||||
+-----------+
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
So in this example, we can see the `trie` with keys, `go` and `cat`. The compressed trie or `radix tree` differs from `trie` in that all intermediates nodes which have only one child are removed.
|
||||
|
||||
Radix tree in linux kernel is the datastructure which maps values to integer keys. It is represented by the following structures from the file [include/linux/radix-tree.h](https://github.com/torvalds/linux/blob/master/include/linux/radix-tree.h):
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
struct radix_tree_root {
|
||||
unsigned int height;
|
||||
gfp_t gfp_mask;
|
||||
struct radix_tree_node __rcu *rnode;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This structure presents the root of a radix tree and contains three fields:
|
||||
|
||||
* `height` - height of the tree;
|
||||
* `gfp_mask` - tells how memory allocations will be performed;
|
||||
* `rnode` - pointer to the child node.
|
||||
|
||||
The first field we will discuss is `gfp_mask`:
|
||||
|
||||
Low-level kernel memory allocation functions take a set of flags as - `gfp_mask`, which describes how that allocation is to be performed. These `GFP_` flags which control the allocation process can have following values: (`GF_NOIO` flag) means sleep and wait for memory, (`__GFP_HIGHMEM` flag) means high memory can be used, (`GFP_ATOMIC` flag) means the allocation process has high-priority and can't sleep etc.
|
||||
|
||||
* `GFP_NOIO` - can sleep and wait for memory;
|
||||
* `__GFP_HIGHMEM` - high memory can be used;
|
||||
* `GFP_ATOMIC` - allocation process is high-priority and can't sleep;
|
||||
|
||||
etc.
|
||||
|
||||
The next field is `rnode`:
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
struct radix_tree_node {
|
||||
unsigned int path;
|
||||
unsigned int count;
|
||||
union {
|
||||
struct {
|
||||
struct radix_tree_node *parent;
|
||||
void *private_data;
|
||||
};
|
||||
struct rcu_head rcu_head;
|
||||
};
|
||||
/* For tree user */
|
||||
struct list_head private_list;
|
||||
void __rcu *slots[RADIX_TREE_MAP_SIZE];
|
||||
unsigned long tags[RADIX_TREE_MAX_TAGS][RADIX_TREE_TAG_LONGS];
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This structure contains information about the offset in a parent and height from the bottom, count of the child nodes and fields for accessing and freeing a node. This fields are described below:
|
||||
|
||||
* `path` - offset in parent & height from the bottom;
|
||||
* `count` - count of the child nodes;
|
||||
* `parent` - pointer to the parent node;
|
||||
* `private_data` - used by the user of a tree;
|
||||
* `rcu_head` - used for freeing a node;
|
||||
* `private_list` - used by the user of a tree;
|
||||
|
||||
The two last fields of the `radix_tree_node` - `tags` and `slots` are important and interesting. Every node can contains a set of slots which are store pointers to the data. Empty slots in the linux kernel radix tree implementation store `NULL`. Radix trees in the linux kernel also supports tags which are associated with the `tags` fields in the `radix_tree_node` structure. Tags allow individual bits to be set on records which are stored in the radix tree.
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we know about radix tree structure, it is time to look on its API.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux kernel radix tree API
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
We start from the datastructure initialization. There are two ways to initialize a new radix tree. The first is to use `RADIX_TREE` macro:
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
RADIX_TREE(name, gfp_mask);
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see we pass the `name` parameter, so with the `RADIX_TREE` macro we can define and initialize radix tree with the given name. Implementation of the `RADIX_TREE` is easy:
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
#define RADIX_TREE(name, mask) \
|
||||
struct radix_tree_root name = RADIX_TREE_INIT(mask)
|
||||
|
||||
#define RADIX_TREE_INIT(mask) { \
|
||||
.height = 0, \
|
||||
.gfp_mask = (mask), \
|
||||
.rnode = NULL, \
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
At the beginning of the `RADIX_TREE` macro we define instance of the `radix_tree_root` structure with the given name and call `RADIX_TREE_INIT` macro with the given mask. The `RADIX_TREE_INIT` macro just initializes `radix_tree_root` structure with the default values and the given mask.
|
||||
|
||||
The second way is to define `radix_tree_root` structure by hand and pass it with mask to the `INIT_RADIX_TREE` macro:
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
struct radix_tree_root my_radix_tree;
|
||||
INIT_RADIX_TREE(my_tree, gfp_mask_for_my_radix_tree);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
where:
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
#define INIT_RADIX_TREE(root, mask) \
|
||||
do { \
|
||||
(root)->height = 0; \
|
||||
(root)->gfp_mask = (mask); \
|
||||
(root)->rnode = NULL; \
|
||||
} while (0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
makes the same initialziation with default values as it does `RADIX_TREE_INIT` macro.
|
||||
|
||||
The next are two functions for inserting and deleting records to/from a radix tree:
|
||||
|
||||
* `radix_tree_insert`;
|
||||
* `radix_tree_delete`;
|
||||
|
||||
The first `radix_tree_insert` function takes three parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
* root of a radix tree;
|
||||
* index key;
|
||||
* data to insert;
|
||||
|
||||
The `radix_tree_delete` function takes the same set of parameters as the `radix_tree_insert`, but without data.
|
||||
|
||||
The search in a radix tree implemented in two ways:
|
||||
|
||||
* `radix_tree_lookup`;
|
||||
* `radix_tree_gang_lookup`;
|
||||
* `radix_tree_lookup_slot`.
|
||||
|
||||
The first `radix_tree_lookup` function takes two parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
* root of a radix tree;
|
||||
* index key;
|
||||
|
||||
This function tries to find the given key in the tree and return the record associated with this key. The second `radix_tree_gang_lookup` function have the following signature
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
unsigned int radix_tree_gang_lookup(struct radix_tree_root *root,
|
||||
void **results,
|
||||
unsigned long first_index,
|
||||
unsigned int max_items);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and returns number of records, sorted by the keys, starting from the first index. Number of the returned records will not be greater than `max_items` value.
|
||||
|
||||
And the last `radix_tree_lookup_slot` function will return the slot which will contain the data.
|
||||
|
||||
Links
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
* [Radix tree](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Radix_tree)
|
||||
* [Trie](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trie)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://github.com/0xAX/linux-insides/edit/master/DataStructures/radix-tree.md
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[0xAX]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -105,4 +105,4 @@ via: http://www.itworld.com/article/3003865/open-source-tools/8-things-to-do-aft
|
||||
[3]:https://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/857788-how-to-convert-videos-in-linux-using-the-command-line
|
||||
[4]:https://www.google.com/intl/en/chrome/browser/desktop/index.html#brand=CHMB&utm_campaign=en&utm_source=en-ha-na-us-sk&utm_medium=ha
|
||||
[5]:http://opensuse-community.org/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.itworld.com/article/2875981/the-5-best-open-source-email-clients-for-linux.html
|
||||
[6]:http://www.itworld.com/article/2875981/the-5-best-open-source-email-clients-for-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,145 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Install and Configure Munin monitoring server in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Munin is an excellent system monitoring tool similar to [RRD tool][1] which will give you ample information about system performance in multiple fronts like **disk, network, process, system and users**. These are some of the default properties Munin monitors.
|
||||
|
||||
### How Munin works? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Munin works in a client-server model. Munin server process on main server try to collect data from client daemon which is running locally(Munin can monitor it’ss own resources) or from remote client(Munin can monitor hundreds of machines) and displays them in graphs on its web interface.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring Munin in nutshell ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is of two steps as we have to configure both server and client.
|
||||
1)Install Munin server package and configure it so that it get data from clients.
|
||||
2)Configure Munin client so that server will connect to client daemon for data collocation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install munin server in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
Munin server installation on Ubuntu/Debian based machines
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install munin apache2
|
||||
|
||||
Munin server installation on Redhat/Centos based machines. Make sure that you [enable EPEL repo][2] before installing Munin on Redhat based machines as by default Redhat based machines do not have Munin in their repos.
|
||||
|
||||
yum install munin httpd
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring Munin server in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
Below are the steps we have to do in order to bring server up.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add host details which need monitoring in /etc/munin/munin.conf
|
||||
1. Configure apache web server to include munin details.
|
||||
1. Create User name and password for web interface
|
||||
1. Restart apache server
|
||||
|
||||
**Step 1**: Add hosts entry in this file in **/etc/munin/munin.conf**. Go to end of the file and a client to monitor. Here in this example, I added my DB server and its IP address to monitor
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
[db.linuxnix.com]
|
||||
address 192.168.1.25
|
||||
use_node_name yes
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
**Step 2**: Edit/create munin.conf file in /etc/apache2/conf.d folder to include Munin Apache related configs. In another note, by default other Munin web related configs are kept in /var/www/munin folder.
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/apache2/conf.d/munin.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Content:
|
||||
|
||||
Alias /munin /var/www/munin
|
||||
<Directory /var/www/munin>
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow from localhost 127.0.0.0/8 ::1
|
||||
AllowOverride None
|
||||
Options ExecCGI FollowSymlinks
|
||||
AddHandler cgi-script .cgi
|
||||
DirectoryIndex index.cgi
|
||||
AuthUserFile /etc/munin/munin.passwd
|
||||
AuthType basic
|
||||
AuthName "Munin stats"
|
||||
require valid-user
|
||||
<IfModule mod_expires.c>
|
||||
ExpiresActive On
|
||||
ExpiresDefault M310
|
||||
</IfModule>
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and exit
|
||||
|
||||
**Step 3**: Now create a username and password for viewing muning graphs:
|
||||
|
||||
htpasswd -c /etc/munin/munin-htpasswd munin
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: For Redhat/Centos machines replace “**apache2**” with “**httpd**” in each path to access your config files.
|
||||
|
||||
**Step 3**: Restart Apache server so that Munin configurations are picked-up by Apache.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu/Debian based: ####
|
||||
|
||||
service apache2 restart
|
||||
|
||||
#### Centos/Redhat based: ####
|
||||
|
||||
service httpd restart
|
||||
|
||||
### Install and configure Munin client in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Step 1**: Install Munin client in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install munin-node
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: If you want to monitor your Munin server, then you have to install munin-node on that as well.
|
||||
|
||||
**Step 2**: Configure client by editing munin-node.conf file.
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/munin/munin-node.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
allow ^127\.0\.0\.1$
|
||||
allow ^10\.10\.20\.20$
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# Which address to bind to;
|
||||
host *
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# And which port
|
||||
port 4949
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: 10.10.20.20 is my Munin server and it connections to 4949 port on client to get its data.
|
||||
|
||||
**Step 3**: Restart munin-node on client server
|
||||
|
||||
service munin-node restart
|
||||
|
||||
### Testing connection ###
|
||||
|
||||
check if you are able to connect client from server on 4949 port, other wise you have to open that port on client machine.
|
||||
|
||||
telnet db.linuxnix.com 4949
|
||||
|
||||
Accessing Munin web interface
|
||||
|
||||
http://munin.linuxnix.com/munin/index.html
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps to configure basic Munin server.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxnix.com/install-and-configure-munin-monitoring-server-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Surendra Anne][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxnix.com/author/surendra/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxnix.com/network-monitoringinfo-gathering-tools-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxnix.com/how-to-install-and-enable-epel-repo-in-rhel-centos-oracle-scentific-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Supporting secure DNS in glibc
|
||||
========================
|
||||
|
||||
Credit: Jonathan Corbet
|
||||
|
||||
One of the many weak links in Internet security is the domain name system (DNS); it is subject to attacks that, among other things, can mislead applications regarding the IP address of a system they wish to connect to. That, in turn, can cause connections to go to the wrong place, facilitating man-in-the-middle attacks and more. The DNSSEC protocol extensions are meant to address this threat by setting up a cryptographically secure chain of trust for DNS information. When DNSSEC is set up properly, applications should be able to trust the results of domain lookups. As the discussion over an attempt to better integrate DNSSEC into the GNU C Library shows, though, ensuring that DNS lookups are safe is still not a straightforward problem.
|
||||
|
||||
In a sense, the problem was solved years ago; one can configure a local nameserver to perform full DNSSEC verification and use that server via glibc calls in applications. DNSSEC can even be used to increase security in other areas; it can, for example, carry SSH or TLS key fingerprints, allowing applications to verify that they are talking to the right server. Things get tricky, though, when one wants to be sure that DNS results claiming to have DNSSEC verification are actually what they claim to be — when one wants the security that DNSSEC is meant to provide, in other words.
|
||||
|
||||
The /etc/resolv.conf problem
|
||||
|
||||
Part of the problem, from the glibc perspective, is that glibc itself does not do DNSSEC verification. Instead, it consults /etc/resolv.conf and asks the servers found therein to do the lookup and verification; the results are then returned to the application. If the application is using the low-level res_query() interface, those results may include the "authenticated data" (AD) flag (if the nameserver has set it) indicating that DNSSEC verification has been successfully performed. But glibc knows nothing about the trustworthiness of the nameserver that has provided those results, so it cannot tell the application anything about whether they should really be trusted.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the first steps suggested by glibc maintainer Carlos O'Donell is to add an option (dns-strip-dnssec-ad-bit) to the resolv.conf file telling glibc to unconditionally remove the AD bit. This option could be set by distributions to indicate that the DNS lookup results cannot be trusted at a DNSSEC level. Once things have been set up so that the results can be trusted, that option can be removed. In the meantime, though, applications would have a way to judge the DNS lookup results they get from glibc, something that does not exist now.
|
||||
|
||||
What would a trustworthy setup look like? The standard picture looks something like this: there is a local nameserver, accessed via the loopback interface, as the only entry in /etc/resolv.conf. That nameserver would be configured to do verification and, in the case that verification fails, simply return no results at all. There would, in almost all cases, be no need to worry about whether applications see the AD bit or not; if the results are not trustworthy, applications will simply not see them at all. A number of distributions are moving toward this model, but the situation is still not as simple as some might think.
|
||||
|
||||
One problem is that this scheme makes /etc/resolv.conf into a central point of trust for the system. But, in a typical Linux system, there are no end of DHCP clients, networking scripts, and more that will make changes to that file. As Paul Wouters pointed out, locking down this file in the short term is not really an option. Sometimes those changes are necessary: when a diskless system is booting, it may need name-resolution service before it is at a point where it can start up its own nameserver. A system's entire DNS environment may change depending on which network it is attached to. Systems in containers may be best configured to talk to a nameserver on the host. And so on.
|
||||
|
||||
So there seems to be a general belief that /etc/resolv.conf cannot really be trusted on current systems. Ideas to add secondary configuration files (/etc/secure-resolv.conf or whatever) have been floated, but they don't much change the basic nature of the situation. Beyond that, some participants felt that even a local nameserver running on the loopback interface is not really trustworthy; Zack Weinberg suggested that administrators might intentionally short out DNSSEC validation, for example.
|
||||
|
||||
Since the configuration cannot be trusted on current systems, the reasoning goes, glibc needs to have a way to indicate to applications when the situation has improved and things can be trusted. That could include the AD-stripping option described above (or, conversely, an explicit "this nameserver is trusted" option); that, of course, would require that the system be locked down to a level where surprising changes to /etc/resolv.conf no longer happen. A variant, as suggested by Petr Spacek, is to have a way for an application to ask glibc whether it is talking to a local nameserver or not.
|
||||
|
||||
Do it in glibc?
|
||||
|
||||
An alternative would be to dispense with the nameserver and have glibc do DNSSEC validation itself. There is, however, resistance to putting a big pile of cryptographic code into glibc itself. That would increase the size of the library and, it is felt, increase the attack surface of any application using it. A variant of this idea, suggested by Zack, would be to put the validation code into the name-service caching daemon (nscd) instead. Since nscd is part of glibc, it is under the control of the glibc developers and there could be a certain amount of confidence that DNSSEC validation is being performed properly. The location of the nscd socket is well known, so the /etc/resolv.confissues don't come into play. Carlos worried, though, that this approach might deter adoption by users who do not want the caching features of nscd; in his mind, that seems to rule out the nscd option.
|
||||
|
||||
So, in the short term, at least, it seems unlikely that glibc will take on the full task of performing validated DNSSEC lookups. That means that, if security-conscious applications are going to use glibc for their name lookups, the library will have to provide an indication of how trustworthy the results received from a separate nameserver are. And that will almost certainly require explicit action on the part of the distributor and/or system administrator. As Simo Sorce put it:
|
||||
|
||||
A situation in which glibc does not use an explicit configuration option to signal applications that it is using a trusted resolver is not useful ... no scratch that, it is actively harmful, because applications developers will quickly realize they cannot trust any information coming from glibc and will simply not use it for DNSSEC related information.
|
||||
|
||||
Configuring a system to properly use DNSSEC involves change to many of the components of that system — it is a distribution-wide problem that will take time to solve fully. The role that glibc plays in this transition is likely to be relatively small, but it is an important one: glibc is probably the only place where applications can receive some assurance that their DNS results are trustworthy without implementing their own resolver code. Running multiple DNSSEC implementations on a system seems like an unlikely path to greater security, so it would be good to get this right.
|
||||
|
||||
The glibc project has not yet chosen a path by which it intends to get things right, though some sort of annotation in /etc/resolv.conf looks like a likely outcome. Any such change would then have to get into a release; given the conservative nature of glibc development, it may already be late for the 2.23 release, which is likely to happen in February. So higher DNSSEC awareness in glibc may not happen right away, but there is at least some movement in that direction.
|
||||
|
||||
---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://lwn.net/Articles/663474/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Jonathan Corbet
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,7 +1,3 @@
|
||||
translating by ezio
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Securi-Pi: Using the Raspberry Pi as a Secure Landing Point
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
【Translating by cposture 2016-03-01】
|
||||
* * *
|
||||
|
||||
# GCC-Inline-Assembly-HOWTO
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
translating by fw8899
|
||||
What is good stock portfolio management software on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you are investing in the stock market, you probably understand the importance of a sound portfolio management plan. The goal of portfolio management is to come up with the best investment plan tailored for you, considering your risk tolerance, time horizon and financial goals. Given its importance, no wonder there are no shortage of commercial portfolio management apps and stock market monitoring software, each touting various sophisticated portfolio performance tracking and reporting capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
136
sources/tech/20160204 An Introduction to SELinux.md
Normal file
136
sources/tech/20160204 An Introduction to SELinux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
||||
An Introduction to SELinux
|
||||
===============================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
>Figure 1: The getenforce command reporting SELinux is set to Enforcing.
|
||||
|
||||
Way back in kernel 2.6, a new security system was introduced to provide a mechanism for supporting access control security policies. This system was [Security Enhanced Linux (SELinux)][1] and was introduced by the [National Security Administration (NSA)][2] to incorporate a strong Mandatory Access Control architecture into the subsystems of the Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’ve spent your entire Linux career either disabling or ignoring SELinux, this article is dedicated to you — an introduction to the system that lives “under the hood” of your Linux desktop or server to limit privilege or even eliminate the possibility of damage should programs or daemons become compromised.
|
||||
|
||||
Before I begin, you should know that SELinux is primarily a tool for Red Hat Linux and its derivatives. The likes of Ubuntu and SUSE (and their derivatives) make use of AppArmor. SELinux and AppArmor are significantly different. You can install SELinux on SUSE, openSUSE, Ubuntu, etc., but it’s an incredibly challenging task unless you’re very well versed in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
With that said, let me introduce you to SELinux.
|
||||
|
||||
### DAC vs. MAC
|
||||
|
||||
The old-guard standard form of access control on Linux was Discretionary Access Control (DAC). With this form, an application or daemon runs under either User ID (UID) or Set owner User ID (SUID) and holds object permissions (for files, sockets, and other processes) of that user. This made it easier for malicious code to be run with a permission set that would grant it access to crucial subsystems.
|
||||
|
||||
Mandatory Access Control (MAC), on the other hand, enforces the separation of information based on both confidentiality and integrity to enable the confinement of damage. The confinement unit operates independently of the traditional Linux security mechanisms and has no concept of a superuser.
|
||||
|
||||
### How SELinux Works
|
||||
|
||||
Consider these pieces of the SELinux puzzle:
|
||||
|
||||
- Subjects
|
||||
|
||||
- Objects
|
||||
|
||||
- Policy
|
||||
|
||||
- Mode
|
||||
|
||||
When a subject (such as an application) attempts to access an object (such as a file), the SELinux Security Server (inside the kernel) runs a check against the Policy Database. Depending on the current mode, if the SELinux Security Server grants permission, the subject is given access to the object. If the SELinux Security Server denies permission, a denied message is logged in /var/log/messages.
|
||||
|
||||
Sounds relatively simple, right? There’s actually more to it than that, but for the sake of introduction, those are the important steps.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Modes
|
||||
|
||||
SELinux has three modes (which can be set by the user). These modes will dictate how SELinux acts upon subject request. The modes are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Enforcing — SELinux policy is enforced and subjects will be denied or granted access to objects based on the SELinux policy rules
|
||||
|
||||
- Permissive — SELinux policy is not enforced and does not deny access, although denials are logged
|
||||
|
||||
- Disabled — SELinux is completely disabled
|
||||
|
||||
Out of the box, most systems have SELinux set to Enforcing. How do you know what mode your system is currently running? You can use a simple command to report the mode; that command is getenforce. This command is incredibly simple to use (as it has the singular purpose of reporting the SELinux mode). To use this tool, open up a terminal window and issue the command getenforce. The report will come back with either, Enforcing, Permissive, or Disabled (see Figure 1 above).
|
||||
|
||||
Setting the SELinux mode is actually quite simple — depending upon the mode you want to set. Understand this: It is never recommended to set SELinux to Disable. Why? When you do this, you open up the possibility that files on your disk will be mislabeled and require a re-label to fix. It is also not possible to change the mode of a system when it has been booted in Disabled mode. Your best modes are either Enabled or Permissive.
|
||||
|
||||
You can change the SELinux mode from the command line or in the /etc/selinux/config file. To set the mod via command line, you use the setenforce tool. To set the mode to Enforcing, do the following:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Open up a terminal window
|
||||
|
||||
2. Issue the command su and then enter your administrator password
|
||||
|
||||
3. Issue the command setenforce 1
|
||||
|
||||
4. Issue the command getenforce to ensure the mode has been set (Figure 2)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
>Figure 2: Setting the SELinux mode to Enforcing.
|
||||
|
||||
To set the mode to Permissive, do this:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Open up a terminal window
|
||||
|
||||
2. Issue the command su and then enter your administrator password
|
||||
|
||||
3. Issue the command setenforce 0
|
||||
|
||||
4. Issue the command getenforce to ensure the mode has been set (Figure 3)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
>Figure 3: Setting the SELinux mode to Permissive.
|
||||
|
||||
NOTE: Setting the mode via command line overrides the setting in the SELinux config file.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’d prefer to set the mode in the SELinux command file, open up that particular file in your favorite text editor and look for the line:
|
||||
|
||||
>SELINUX=permissive
|
||||
|
||||
You can change the mode to suit your preference and then save the file.
|
||||
|
||||
There is also a third method of changing the SELinux mode (via the bootloader), but I don’t recommend it for a beginning user.
|
||||
|
||||
### Policy Type
|
||||
|
||||
There are two types of SELinux policies:
|
||||
|
||||
- Targeted — only targeted network daemons (dhcpd, httpd, named, nscd, ntpd, portmap, snmpd, squid, and syslogd) are protected
|
||||
|
||||
- Strict — full SELinux protection for all daemons
|
||||
|
||||
You can change the policy type within the /etc/selinux/config file. Open the file in your favorite text editor and look for the line:
|
||||
|
||||
>SELINUXTYPE=targeted
|
||||
|
||||
Change the option in that line to either targeted or strict to match your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Checking the Full SELinux Status
|
||||
|
||||
There is a handy SELinux tool you might want to know about that will display a detailed status report of your SELinux-enabled system. The command is run from a terminal window like this:
|
||||
|
||||
>sestatus -v
|
||||
|
||||
You should see output similar to that shown in Figure 4.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
>Figure 4: The output of the sestatus -v command.
|
||||
|
||||
### Just Scratching the Surface
|
||||
|
||||
As you might expect, I have only scratched the surface of SELinux. It is quite a complex system and will require diving much deeper to obtain a solid understanding of how it works for you and how you can make it better work for your desktops and servers. I still have yet to cover troubleshooting and creating custom SELinux policies.
|
||||
|
||||
SELinux is a powerful tool that any Linux administrator should know. Now that you’ve been introduced, I highly recommend you return to Linux.com (when more tutorials on the subject are posted) or take a look at the [NSA SELinux documentation][3] for very in-depth tutorials.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.linux.com/learn/docs/ldp/883671-an-introduction-to-selinux
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jack Wallen][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/93
|
||||
[1]: http://selinuxproject.org/page/Main_Page
|
||||
[2]: https://www.nsa.gov/research/selinux/
|
||||
[3]: https://www.nsa.gov/research/selinux/docs.shtml
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user