mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
tranlated SteamOS installation
This commit is contained in:
parent
4cd81744c2
commit
a2d45c00e5
@ -1,84 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by pandachow
|
||||
How to Install SteamOS in VirtualBox
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The following tutorial will teach all Linux users how to install Valve's brand new SteamOS GNU/Linux operating system in a virtual machine, using the powerful and popular VirtualBox software.**
|
||||
|
||||
As you already know, the [SteamOS Linux has been officially released on December 13][1] and is based on Debian GNU/Linux operating system, using GNOME as its (optional) desktop environment.
|
||||
|
||||
SteamOS is very easy to install if you have the right hardware components, which involves a UEFI-capable computer with a powerful video card for playing games. However, as Valve did not publish an ISO image of SteamOS, many have encountered difficulties in installing the system.
|
||||
|
||||
The following tutorial is comprised of two important sections, one that helps you create an ISO image from the SteamOSInstaller.zip file provided by Valve, and a second one where you learn how to install SteamOS in VirtualBox if you don't want to install it on a real computer.
|
||||
|
||||
To get started, you need to have a working installation of the latest VirtualBox software. Also, you need to install a software called [GNU xorriso][2], which you'll use to generate the ISO image from the SteamOSInstaller folder.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1 – Generate SteamOS ISO image ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Download the SteamOSInstaller.zip from Softpedia][3], save it on your home folder, and extract the files. A folder named “SteamOSInstaller” will be output. Now, open a terminal in the home folder and execute the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
xorriso -as mkisofs -r -checksum_algorithm_iso md5,sha1 -V 'Steam OS' -o ~/SteamOSInstaller.iso -J -joliet-long -cache-inodes -no-emul-boot -boot-load-size 4 -boot-info-table -eltorito-alt-boot --efi-boot boot/grub/efi.img -append_partition 2 0x01 ~/SteamOSInstaller/boot/grub/efi.img -partition_offset 16 ~/SteamOSInstaller
|
||||
|
||||
The SteamOS.iso file will be generated in a few seconds on your home folder and will have approximately 1GB in size. That's all, you can now proceed to the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2 – Install SteamOS in VirtualBox ###
|
||||
|
||||
Considering the fact that you already have a working VirtualBox installation and that you already know how to use the software, you must create a new virtual machine with UEFI support. On VirtualBox's main window, press the New button to start the process of creating a new virtual machine.
|
||||
|
||||
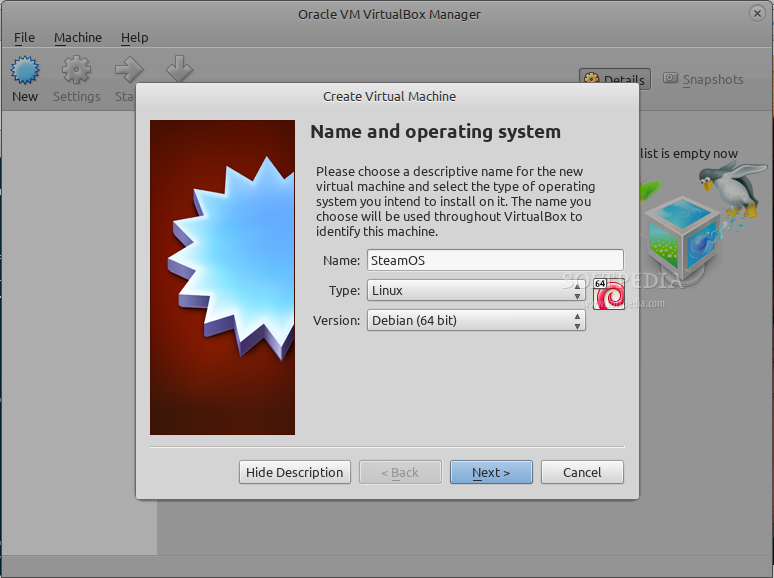
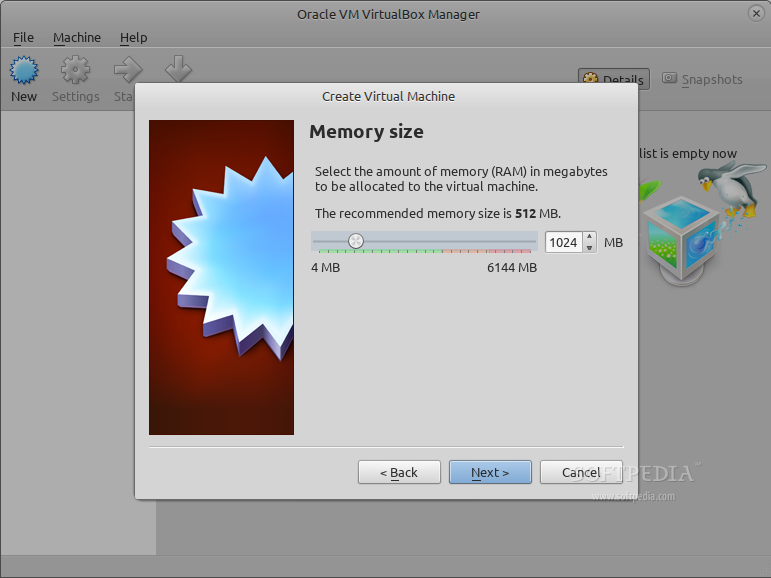
In the name field type SteamOS, choose Linux as the operating system type, select Debian 64-bit from the Linux version drop-down box, and click Next to continue. Set 1024 or 2048 for the memory size (this depends on how much physical RAM your computer has), create a virtual hard drive of VDI file type and fixed size with 15GB. Click the Continue button and wait for the hard drive creation process to finish.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Create a new virtual machine*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Set the memory size*
|
||||
|
||||
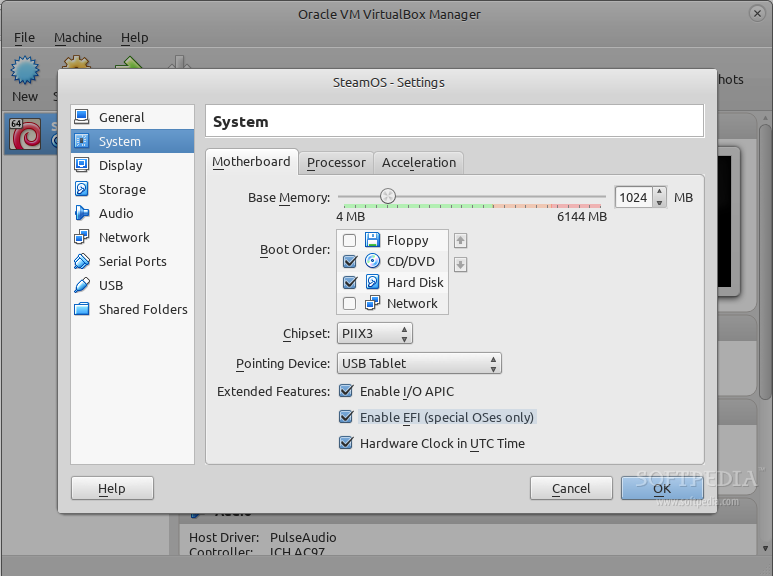
Now that the virtual machine has been created, let’s make a few adjustments for the SteamOS operating system. Go to Settings, click the System section in the sidebar, and uncheck the “Floppy” entry from the Boot Order box, and make sure you check the “Enable EFI (special OSes only)” option.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Enable EFI and remove Floppy*
|
||||
|
||||
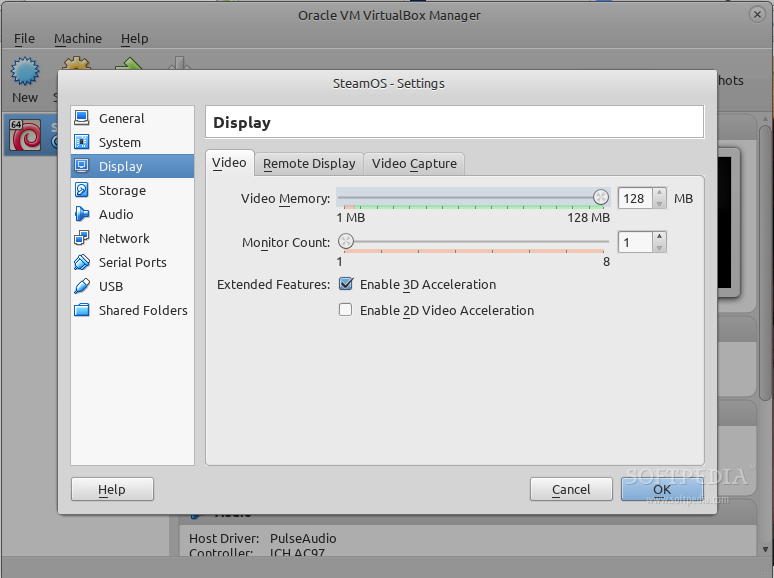
Next, click the Display section in the sidebar, set the Video Memory to 128MB, and check the “Enable 3D Acceleration” option. Then, go to the Storage section in the sidebar, click the “Empty” line under “Controller: IDE” and add the SteamOSInstaller.iso image generated in the first step by clicking on the small CD icon next to the CD/DVD Drive drop-down box. Click OK when done.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Set Video Memory size and 3D acceleration*
|
||||
|
||||
And now, let’s start the virtual machine by pressing the big “Start” button on the main window. You will immediately see the SteamOS boot screen. Just press Enter with the “Automated install (WILL ERASE DISK!) option highlighted, sit back, and relax until the system is installed, which will take some time, depending on your computer’s specs.
|
||||
|
||||
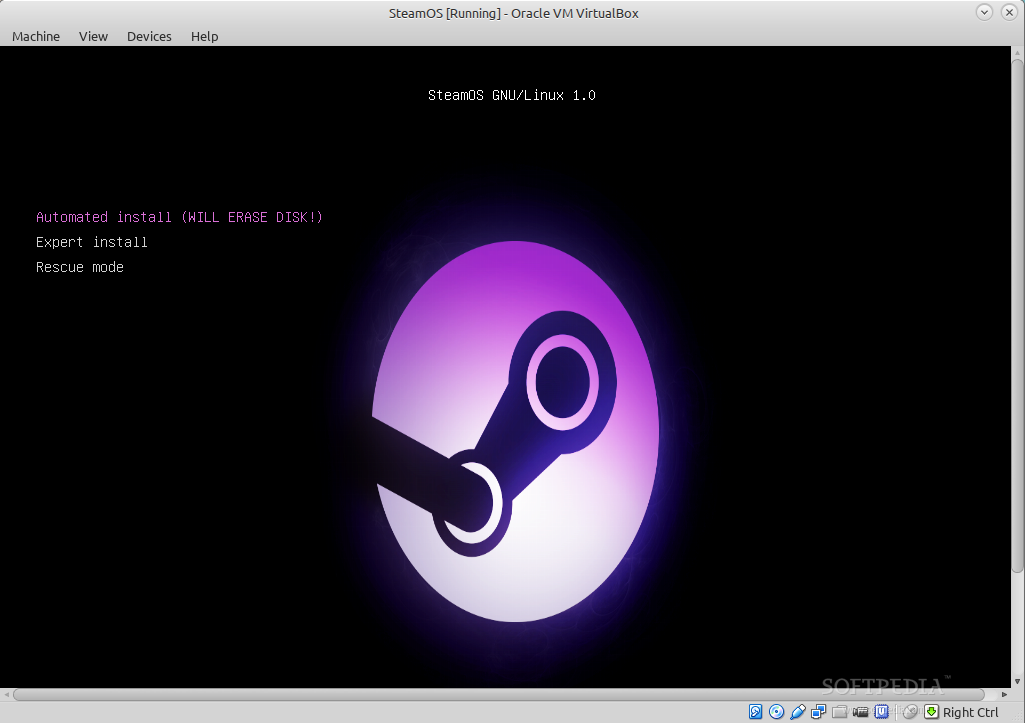
|
||||
*Prepare to install SteamOS*
|
||||
|
||||
Once the installation process is finished, you can close the virtual machine, remove the ISO image from the Storage section, and boot into your new SteamOS. But, before you start exploring SteamOS, you will need to install the VirtualBox Guest Additions. To do that, start the SteamOS virtual machine, select the second entry on the GRUB boot loader screen (Recovery), and type the following commands when you hit the SteamOS command-line prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
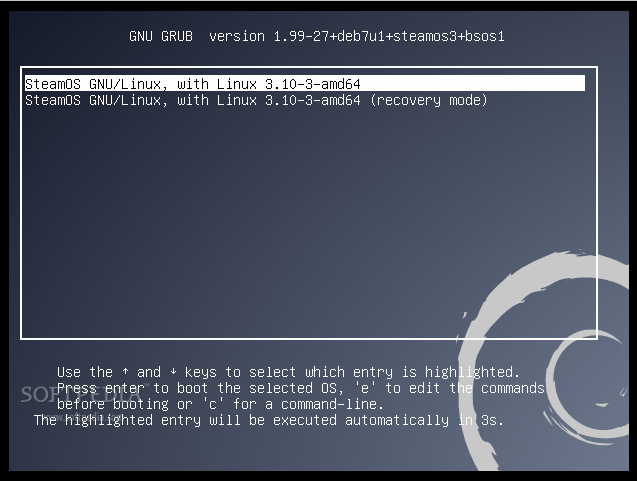
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg --get-selections | grep nvidia
|
||||
apt-get purge <name of the packages outputted by the above command>
|
||||
rm /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/55-nvidia.conf
|
||||
dpkg-reconfigure xserver-xorg
|
||||
|
||||
Go to Devices and click on Insert Guest Additions CD image. Download the Guest Additions image when prompted, mount it and run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sh /media/cdrom/VBoxLinuxAdditions.run
|
||||
|
||||
Wait for the Guest Additions to install its drivers and reboot the virtual machine with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
shutdown now -r
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*SteamOS command-line shell prompt*
|
||||
|
||||
The virtual machine will reboot, let it boot into the SteamOS and, when you arrive at the login prompt, use desktop/desktop or steam/steam as the username and password to login. Do not hesitate to comment below if you encounter problems during the installation.
|
||||
|
||||
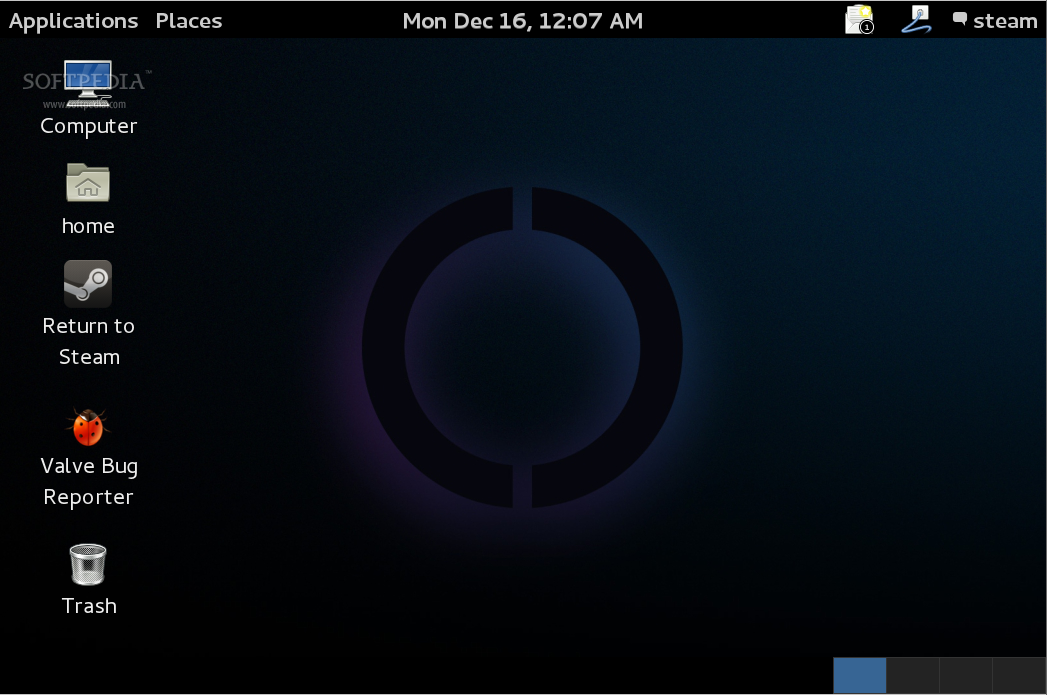
|
||||
*SteamOS with GNOME 3*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Install-SteamOS-in-VirtualBox-409363.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Download-SteamOS-1-0-Based-on-Debian-Linux-409214.shtml
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.softpedia.com/get/Programming/Libraries/GNU-xorriso-36759.shtml
|
||||
[3]:http://linux.softpedia.com/get/System/Operating-Systems/Linux-Distributions/SteamOS-103040.shtml
|
||||
80
translated/How to Install SteamOS in VirtualBox.md
Normal file
80
translated/How to Install SteamOS in VirtualBox.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
如何在 VirtualBox 中安装 SteamOS
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**下面的教程将指导 Linuxer 在 VirtualBox 中全新安装 SteamOS GNU/Linux。**
|
||||
|
||||
如你已经了解的那样,SteamOS Linux 已经在12月13日正式发布了。作为一款基于 Debian GNU/Linux 的操作系统,它默认使用了 GNOME 作为桌面环境,当然这是可选的。
|
||||
|
||||
如果硬件上没有问题的话,比如你的电脑拥有强大游戏显卡,且支持UEFI的,那么安装 SteamOS 将是一件非常容易的事情,然而,因为 Valve 并没有发布 SteamOS 的 ISO 镜像,在安装过程中可能并不是那么顺利。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的教程由两个重要的部分组成,第一部分将会帮助你用 Valve 官方的 SteamOSInstaller.zip 来创建一个 ISO 镜像;如果你不希望在自己的电脑上真正安装,那么第二部分将会告诉你如何在 VirtualBox 中来体验 SteamOS。
|
||||
|
||||
在一开始你需要一个已经正确安装的最新的 VirtualBox。当然,你还需要一款叫做[GNUxorriso][2]的软件用来制作 ISO 镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一步,制作 SteamISO 镜像
|
||||
[从 Softpedia 下载 SteamOSInstaller.zip][3],将它保存到你的 home 目录下并解压缩。完毕之后你将会看到 SteamOSInstaller 文件夹。现在,从终端里打开它并执行下面的命令:
|
||||
xorriso -as mkisofs -r -checksum_algorithm_iso md5,sha1 -V 'Steam OS' -o ~/SteamOSInstaller.iso -J -joliet-long -cache-inodes -no-emul-boot -boot-load-size 4 -boot-info-table -eltorito-alt-boot --efi-boot boot/grub/efi.img -append_partition 2 0x01 ~/SteamOSInstaller/boot/grub/efi.img -partition_offset 16 ~/SteamOSInstaller
|
||||
|
||||
稍等几秒钟之后,SteamOS.iso 文件将会在你的 home 目录下出现,大约有 1GB。好了,这一步就完成了,下面进入第二步。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第二步,在 VirtualBox 中安装 SteamOS
|
||||
|
||||
考虑到你已经正确安装了 VirtualBox 并且了解它的正确用法,那么我们下面需要来建立一个拥有 UEFI 支持的全新虚拟机。在 VirtualBox 的主窗口,点击 New 按钮来开始安装吧。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Name 框输入 SteamOS,在操作系统类型种选择 Linux,并在下拉框的版本列表中选择 Debain 64-bit,点击 Next 继续。Memory Size 中设置1024或者2048MB(当然,这取决于你的计算机实际内存大小),我们创建一个 VDI 格式的虚拟硬盘驱动器,将大小固定为15GB。点击 Continue 来继续,并等待创建过程结束。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*创建一个新的虚拟机*
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*设置内存大小*
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们的虚拟机已经创建完毕了,接下来让我们来为 SteamOS 做一些小小的调整。来到 Settings 选项,点击边栏的 System,然后在 Boot Order 中取消选择 "Floppy",并检查确认已经选择 "Enable EFI (special OSes only)" 选项。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*允许 EFI 并移除 Floppy*
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,点击边栏中的 Display 按钮,将 Video Memory 设置为128MB,并勾上 "Enable 3D Acceleration" 选项。然后,进入边栏的 Storage 部分,点击 "Controller: IDE" 下面的 "Empty",并点击 CD/DVD 驱动下拉栏旁边小 CD 图标来添加上一步制作的 SteamOSInstall.iso 镜像文件。当一切完成之后,点击 OK。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*设置 Video Memory 大小 和 3D 加速*
|
||||
|
||||
那么现在,让我们按下主窗口中的 "Start" 按钮来启动虚拟机。你将会立即看到 SteamOS 启动画面。只需要高亮 "Automated install (WILL ERASE DISK)" 后按下 Enter 键即可。接下来可以稍微放松一下,直到我们的安装结束。整个安装过程可能需要一段时间,当然这取决于你的电脑。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*准备安装 SteamOS*
|
||||
|
||||
"只要我们的安装过程结束,你就可以关闭虚拟机,然后从 Storage 中移除 ISO 镜像,然后启动进入全新的 SteamOS。但是,在我们正式进入 SteamOS 的世界之前,还需要安装 VirtualBox Guest Additions。先点击开始 SteamOS 虚拟机,选择 GRUB 启动器中的第二个选项,然后在 SteamOS 的命令行提示后输入下面的命令:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
dpkg --get-selections | grep nvidia
|
||||
apt-get purge <name of the packages outputted by the above command>
|
||||
rm /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/55-nvidia.conf
|
||||
dpkg-reconfigure xserver-xorg
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
进入到 Devices 中然后点击 Insert Guest Additions CD 镜像。根据提示来下载 Guest Additions 镜像,挂载它并执行下面的命令:
|
||||
sh /media/cdrom/VBoxLinuxAdditions.run
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
等待 Guest Additions 安装完驱动,用下面的命令来重启我们的虚拟机:
|
||||
shutdown now -r
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*SteamOS 命令行提示*
|
||||
|
||||
接下来我们的虚拟机会重启,让它启动进入 SteamOS。当我们抵达登录提示界面之后,使用 desktop/desktop 或者 steam/steam 作为用户名和密码来登录。如果您在安装过程中遇到了一些问题,请别犹豫,在下面评论中告诉我们。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*SteamOS 和 GNOME 3*
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Install-SteamOS-in-VirtualBox-409363.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/pandachow) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Download-SteamOS-1-0-Based-on-Debian-Linux-409214.shtml
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.softpedia.com/get/Programming/Libraries/GNU-xorriso-36759.shtml
|
||||
[3]:http://linux.softpedia.com/get/System/Operating-Systems/Linux-Distributions/SteamOS-103040.shtml
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
||||
Linux vmstat 命令 - 报告虚拟内存统计的工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
众所周知,计算机必须有称之为RAM(随机访问内存)的存储器使得计算机工作。RAM指的是插在计算机主板上的物理存储。这里的RAM被用于加载像浏览器、文字处理器这类的程序、实际上,你使用的程序都运行在内存上。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们假设你有2GB的内存。当你在运行操作系统时,你的可用内存可能只有1.5GB。接着你使用了大量的程序。当内存使用满之后,你可能再也无法加载更多的程序。浅显地说,计算机可能会说:"抱歉,你不能在运行更多的程序了,如果你还要运行其他的程序请先关闭一些程序。"
|
||||
|
||||
为了解决这个问题,操作系统包括Linux使用了一个方法称之为虚拟内存。这个方法会搜索最近不在使用的程序的内存区域,接着将它们拷贝到计算机硬盘上。这会腾出一些剩余内存空间给你有机会运行更多的程序。
|
||||
|
||||
为了监视虚拟内存的活动,我们使用**vmstat**工具。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么事 vmstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
vmstat是一个提供报告虚拟内存统计的工具。他/她覆盖了系统内存、交换和实时处理器利用率。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何运行 vmstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
和[mpstat][1]一样,vmstat包含在sysstat包中。如果你还没有,请安装sysstat包。
|
||||
|
||||
为了运行vmstat,只需在控制台输入vmstat。不带参数运行vmstat会显示vmstat的默认结果。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
让我们看下如何读取vmstat提供的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
### Procs ###
|
||||
|
||||
procs有 **r**列和**b**列。**r**列代表等待访问CPU进程的数量。而b列意味着睡眠进程的数量。在这些列的下面,是它们的值。从上面的截图中,我门有2个进程正在等待访问CPU,0个睡眠进程。
|
||||
|
||||
### Memory ###
|
||||
|
||||
memory有**swpd、 free、 buff** 和 **cache** 这些列.这些信息和命令**free -m**相同。**swpd列**显示了有多少内存已经被交换到了交换文件或者磁盘。**free列**显示了未分配的可用内存。**buff列**显示了使用中的内存。**cache列**显示了有多少内存可以被交换到交换文件或者磁盘上如果一些应用需要他们。
|
||||
|
||||
### Swap ###
|
||||
|
||||
swap显示了从交换系统上发送或取回了多少内存。**si**列告诉我们每秒有多少内存被**从swap移到真实内存**中。**so**列告诉我们每秒有多少内存被**从真实内存移到swap**中。
|
||||
|
||||
### I/O ###
|
||||
|
||||
**io**依据块的读写显示了每秒输入输出的活动。**bi**列告诉我们块收到的数量,**bo**列告诉我们块发送的数量。
|
||||
|
||||
### System ###
|
||||
|
||||
system显示了每秒的系统操作数量。**in**列显示了系统每秒被中断的数量。**cs**列显示了系统为了处理所以任务而上下文切换的数量。
|
||||
|
||||
### CPU ###
|
||||
|
||||
CPU告诉了我们CPU资源的使用情况。**us列**显示了处理器在非内核程序消耗的时间。**sy列**显示了处理器在内核相关任务上消耗的时间。**id列**显示了处理器的空闲时间。**wa列**显示了处理器在等待IO操作完成以继续处理任务上的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
### 代延迟使用vmstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个统计工具,使用vmstat最好的方法是使用**延迟**。你可以间断地捕捉活动。让我假设以5秒的延迟使用vmstat。只需要在你的控制台中输入**vmstat 5**就行。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
命令将会每5秒运行一次**直到**你按下Ctrl-C来终止它。你可以使用**count**来显示vmstat运行的次数。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令会**以5秒的间隔运行7次vmstat**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 显示活跃和非活跃内存 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要这么做,你可以在vmstat后加入**-a**选项。这是个示例。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 显示磁盘统计数据总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想,vmstat可以打印系统磁盘统计。使用**-D**选项就行。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 显示单位 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以选择你想打印的显示单位字符。在**-S后跟上k (1000)、 K (1024)、 m (1000000)、 M (1048576)** 字节. 如果你不想选择单位,默认使用的是K (1024)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 为特定分区打印详细统计数据 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要这么做,你可以使用**-p选项跟上设备名**。这里有个例子。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
vmstat使用这些文件工作。
|
||||
|
||||
/proc/meminfo
|
||||
/proc/stat
|
||||
/proc/*/stat
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
vmstat** on your console. It will bring you to vmstat manual page.
|
||||
如果你感觉系统运行超出内存了,在你增加物理内存前,这个工具可以帮助你确定问题的根本原因。通常上,你可以在控制台中输入**man vmstat**获取更多的关于vmstat的详细信息。这会带你进入vmstat的手册页。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-vmstat-command-tool-report-virtual-memory-statistics/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-mpstat-command/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user