mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
translated by Flowsnow
This commit is contained in:
parent
8b9acc78ce
commit
9f8371d5ba
@ -1,188 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by Flowsnow
|
||||
|
||||
A Front-end For Popular Package Managers
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Are you a distro-hopper who likes to try new Linux OSs every few days? If so, I have something for you. Say hello to **Sysget** , a front-end for popular package managers in Unix-like operating systems. You don’t need to learn about every package managers to do basic stuffs like installing, updating, upgrading and removing packages. You just need to remember one syntax for every package manager on every Unix-like operating systems. Sysget is a wrapper script for package managers and it is written in C++. The source code is freely available on GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
Using Sysget, you can do all sorts of basic package management operations including the following:
|
||||
|
||||
* Install packages,
|
||||
* Update packages,
|
||||
* Upgrade packages,
|
||||
* Search for packages,
|
||||
* Remove packages,
|
||||
* Remove orphan packages,
|
||||
* Update database,
|
||||
* Upgrade system,
|
||||
* Clear package manager cache.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**An Important note to Linux learners:**
|
||||
|
||||
Sysget is not going to replace the package managers and definitely not suitable for everyone. If you’re a newbie who frequently switch to new Linux OS, Sysget may help. It is just wrapper script that helps the distro hoppers (or the new Linux users) who become frustrated when they have to learn new commands to install, update, upgrade, search and remove packages when using different package managers in different Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re a Linux administrator or enthusiast who want to learn the internals of Linux, you should stick with your distribution’s package manager and learn to use it well.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Sysget
|
||||
|
||||
Installing sysget is trivial. Go to the [**releases page**][1] and download latest Sysget binary and install it as shown below. As of writing this guide, the latest version was 1.2.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo wget -O /usr/local/bin/sysget https://github.com/emilengler/sysget/releases/download/v1.2/sysget
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/share/sysget
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/sysget
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
Sysget commands are mostly same as APT package manager, so it should be easy to use for the newbies.
|
||||
|
||||
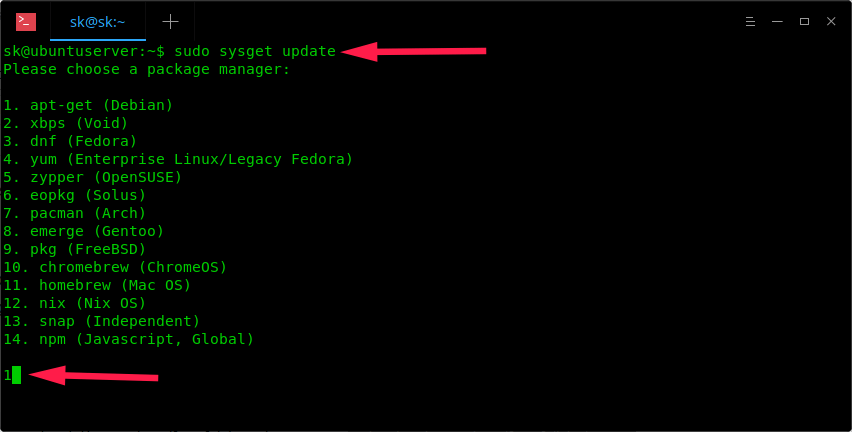
When you run Sysget for the first time, you will be asked to choose the package manager you want to use. Since I am on Ubuntu, I chose **apt-get**.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You must choose the right package manager depending upon the distribution you’re running. For instance, if you’re on Arch Linux, choose **pacman**. For CentOS, choose **yum**. For FreeBSD, choose **pkg**. The list of currently supported package managers are:
|
||||
|
||||
1. apt-get (Debian)
|
||||
2. xbps (Void)
|
||||
3. dnf (Fedora)
|
||||
4. yum (Enterprise Linux/Legacy Fedora)
|
||||
5. zypper (OpenSUSE)
|
||||
6. eopkg (Solus)
|
||||
7. pacman (Arch)
|
||||
8. emerge (Gentoo)
|
||||
9. pkg (FreeBSD)
|
||||
10. chromebrew (ChromeOS)
|
||||
11. homebrew (Mac OS)
|
||||
12. nix (Nix OS)
|
||||
13. snap (Independent)
|
||||
14. npm (Javascript, Global)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Just in case you assigned a wrong package manager, you can set a new package manager using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget set yum
|
||||
Package manager changed to yum
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Just make sure you have chosen your native package manager.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, you can perform the package management operations as the way you do using your native package manager.
|
||||
|
||||
To install a package, for example Emacs, simply run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget install emacs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will invoke the native package manager (In my case it is “apt-get”) and install the given package.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, to remove a package, simply run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget remove emacs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Update software repository (database):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget update
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Search for a specific package:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget search emacs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Upgrade a single package:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget upgrade emacs
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Upgrade all packages:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Remove all orphaned packages:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget autoremove
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Clear the package manager cache:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget clean
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, refer the help section:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sysget help
|
||||
Help of sysget
|
||||
sysget [OPTION] [ARGUMENT]
|
||||
|
||||
search [query] search for a package in the resporitories
|
||||
install [package] install a package from the repos
|
||||
remove [package] removes a package
|
||||
autoremove removes not needed packages (orphans)
|
||||
update update the database
|
||||
upgrade do a system upgrade
|
||||
upgrade [package] upgrade a specific package
|
||||
clean clean the download cache
|
||||
set [NEW MANAGER] set a new package manager
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Please remember that the sysget syntax is same for all package managers in different Linux distributions. You don’t need to memorize the commands for each package manager.
|
||||
|
||||
Again, I must tell you Sysget isn’t a replacement for a package manager. It is just wrapper for popular package managers in Unix-like systems and it performs the basic package management operations only.
|
||||
|
||||
Sysget might be somewhat useful for newbies and distro-hoppers who are lazy to learn new commands for different package manager. Give it a try if you’re interested and see if it helps.
|
||||
|
||||
And, that’s all for now. More good stuffs to come. Stay tuned!
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/sysget-a-front-end-for-popular-package-managers/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://github.com/emilengler/sysget/releases
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
|
||||
给受欢迎的包管理器加个前端
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你是一个喜欢每隔几天尝试Linux操作系统的新发行版的人吗? 如果是这样,我有一些东西对你有用。 尝试**Sysget**,这是类Unix操作系统中流行软件包管理器的前端。 你不需要了解每个包管理器来执行基本的操作,例如安装,更新,升级和删除包。 你只需要记住每个类Unix操作系统上每个包管理器的一种语法即可。 Sysget是包管理器的包装脚本,它是用C ++编写的。 源代码可在GitHub上免费获得。
|
||||
|
||||
使用Sysget,你可以执行各种基本的包管理操作,包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 安装包,
|
||||
- 更新包,
|
||||
- 升级包,
|
||||
- 搜索包,
|
||||
- 删除包,
|
||||
- 删除弃用包,
|
||||
- 更新数据库,
|
||||
- 升级系统,
|
||||
- 清除包管理器缓存。
|
||||
|
||||
**给Linux学习者的一个重要提示:**
|
||||
|
||||
Sysget不会取代软件包管理器,绝对不适合所有人。 如果你是经常切换到新Linux操作系统的新手,Sysget可能会有所帮助。 当在不同的Linux发行版中使用不同的软件包管理器时,就必须学习安装,更新,升级,搜索和删除软件包的新命令,这时Sysget就是帮助发行版收割机用户(或新Linux用户)的包装脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是Linux管理员或想要学习Linux深层的爱好者,你应该坚持使用你的发行版的软件包管理器并学习如何使用它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Sysget
|
||||
|
||||
安装sysget很简单。 转到[**发布页面**][1]并下载最新的Sysget二进制文件并按如下所示进行安装。 在编写本指南时,sysget最新版本为1.2。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo wget -O /usr/local/bin/sysget https://github.com/emilengler/sysget/releases/download/v1.2/sysget
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir -p /usr/local/share/sysget
|
||||
$ sudo chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/sysget
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 用法
|
||||
|
||||
Sysget命令与APT包管理器大致相同,因此它应该适合新手使用。
|
||||
|
||||
当你第一次运行Sysget时,系统会要求你选择要使用的包管理器。 由于我在Ubuntu,我选择了**apt-get**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你必须根据正在运行的发行版选择正确的包管理器。 例如,如果你使用的是Arch Linux,请选择**pacman**。 对于CentOS,请选择**yum**。 对于FreeBSD,请选择**pkg**。 当前支持的包管理器列表是:
|
||||
|
||||
1. apt-get (Debian)
|
||||
2. xbps (Void)
|
||||
3. dnf (Fedora)
|
||||
4. yum (Enterprise Linux/Legacy Fedora)
|
||||
5. zypper (OpenSUSE)
|
||||
6. eopkg (Solus)
|
||||
7. pacman (Arch)
|
||||
8. emerge (Gentoo)
|
||||
9. pkg (FreeBSD)
|
||||
10. chromebrew (ChromeOS)
|
||||
11. homebrew (Mac OS)
|
||||
12. nix (Nix OS)
|
||||
13. snap (Independent)
|
||||
14. npm (Javascript, Global)
|
||||
|
||||
如果你分配了错误的包管理器,则可以使用以下命令设置新的包管理器:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget set yum
|
||||
Package manager changed to yum
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
只需确保你选择了本地包管理器。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你可以像使用本机包管理器一样执行包管理操作。
|
||||
|
||||
要安装软件包,例如Emacs,只需运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget install emacs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令将调用本机包管理器(在我的例子中是“apt-get”)并安装给定的包。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
同样,要删除包,只需运行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget remove emacs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**更新软件仓库(数据库):**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget update
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**搜索特定包:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget search emacs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**升级单个包:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget upgrade emacs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**升级所有包:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget upgrade
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**移除废弃的包**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget autoremove
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**清理包管理器的缓存**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo sysget clean
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
有关更多详细信息,请参阅帮助部分:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sysget help
|
||||
Help of sysget
|
||||
sysget [OPTION] [ARGUMENT]
|
||||
|
||||
search [query] search for a package in the resporitories
|
||||
install [package] install a package from the repos
|
||||
remove [package] removes a package
|
||||
autoremove removes not needed packages (orphans)
|
||||
update update the database
|
||||
upgrade do a system upgrade
|
||||
upgrade [package] upgrade a specific package
|
||||
clean clean the download cache
|
||||
set [NEW MANAGER] set a new package manager
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
请记住,不同Linux发行版中的所有包管理器的sysget语法都是相同的。 你不需要记住每个包管理器的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
同样,我必须告诉你Sysget不是包管理器的替代品。 它只是类Unix系统中流行的包管理器的包装器,它只执行基本的包管理操作。
|
||||
|
||||
Sysget对于不想去学习不同包管理器的新命令的新手和发行版收割机用户可能有些用处。 如果你有兴趣,试一试,看看它是否有帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
而且,这就是本次所有的内容了。 更多干活即将到来。 敬请关注!
|
||||
|
||||
祝快乐!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/sysget-a-front-end-for-popular-package-managers/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[Flowsnow](https://github.com/Flowsnow)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://github.com/emilengler/sysget/releases
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user