mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2024-12-26 21:30:55 +08:00
Merge remote-tracking branch 'LCTT/master'
This commit is contained in:
commit
9e722540fd
@ -5,7 +5,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
起初,这个想法可能看起来荒谬可笑或者不怀好意。因为你仍能看到Ubuntu的狂热支持者们在为其每一个发行版的改进鼓掌叫好呐喊助威;记者们也还在谄媚地报道Ubuntu创始人Mark Shuttleworth所说的每一句话。
|
||||
|
||||
社区负责人Jono Bacon正在为Ubuntu Touch移动操作系统开发一个新的应用开发者社区;最近,Ubuntu的商业部门Canonical还公布了一些重大项目,例如与中国政府合作,为其开发[国家级的中文操作系统][1],以及被Linux基金会选中负责实现[Steam][2]游戏平台等等。
|
||||
> 社区负责人Jono Bacon正在为Ubuntu Touch移动操作系统开发一个新的应用开发者社区;最近,Ubuntu的商业部门Canonical还公布了一些重大项目,例如与中国政府合作,为其开发[国家级的中文操作系统][1],以及被Linux基金会选中负责实现[Steam][2]游戏平台等等。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,[Ubuntu在Google上搜索量][3]的锐减趋势也许能说明一些问题。除了Android和Mageia,其他Linux[主流发行版][4]情况类似,都有所下降,但事实是,即便这样,却没有哪个发行版像Ubuntu一样下降得如此厉害 —— 搜索量还不到2007年10月的一半,为2006年六月以来的最低值。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
和去年形成鲜明对比的是Ubuntu的早几年。2005年到2007年,三年间,Ubuntu成为了Linux桌面世界最新最伟大的希望之星,批评言论主要限于那些认为没有给Debian足够荣誉或是质疑某个古怪暴发户投资动机的人。
|
||||
|
||||
在那些风光的年月里,Ubuntu确实做出了很多努力,大大推进了Linux桌面系统的易用性与普遍性。也许最值得铭记的就是它对多语言环境和键盘区域切换的支持,现在这已成为各大主流发行版的标准。
|
||||
在那些风光的年月里,Ubuntu确实做出了很多努力,大大推进了Linux桌面系统的易用性与普遍性。也许最值得铭记的就是它对多语言环境和本地化键盘切换的支持,现在这已成为各大主流发行版的标准。
|
||||
|
||||
但好景不长,渐渐地,Ubuntu和Canonical开始将自己孤立于主流自由软件社区之外。Shuttleworth的那些美好初衷,诸如项目协作、强调易用性等等,都被严重忽略了。由于对GNOME开发速度不满 —— 也或者是被GNOME社区视为爆发户 —— Shuttleworth开始了Unity 接口开发,他对此如此着迷,以致甘愿放弃Canonical CEO的职位。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,11 +35,11 @@ Ubuntu为什么要这么做?Upstart和Mir虽然都保留着自由软件许可
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical将自己孤立得越发遥远,它却越想控制整个Ubuntu社区。
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical之所以这样,也许可以解释为这是越来越坚定想努力盈利的结果。尽管Canonical一直在忙于宣布获得了新的合作与支持,但是[这些声明][10]中却总是缺少任何提及合作资金数额的词句。要说这是遗漏了?经过长达九年的商业化运行,很难想象他们会漏掉任何可以报道的好消息。但是,无论原因是什么,Canonical已经越来越多地不经任何商讨,就将它的决定强加给志愿者社区。
|
||||
Canonical之所以这样,也许可以解释为这是越来越坚定想努力盈利的结果。尽管Canonical一直在忙于宣布获得了新的合作与支持,但是[这些声明][10]中却总是缺少任何提及合作资金数额的词句。要说这是遗漏了?经过长达九年的商业化运行,很难想象他们会漏掉任何可以报道的好消息。但是,无论原因是什么,Canonical已经越来越多地不经任何商讨,就将它的决定强加给Ubuntu志愿者社区。
|
||||
|
||||
其中的许多决定都是很琐碎的。范围从决定不再支持完全自由许可的Ubuntu版本或者一个基于KDE的版本到标题栏图标的重新定位,以及替换[HUD][11]菜单的介绍。
|
||||
其中的许多决定都是很琐碎的。范围从决定不再支持完全自由许可的Ubuntu版本或者一个基于KDE的版本,到标题栏图标的重新定位,以及替换[HUD][11]菜单的介绍。
|
||||
|
||||
其实,在争论中,解决问题并不是最重要的,重要的是解决问题时人们之间的关系。与Canonical不同,Ubuntu每天的运行看起来就像是任何预期中规范的自由软件项目一样,有讨论有商议。而Canonical呢?据说,Canonical公司中的高级雇员经常滥用否决权,即便是礼貌的否定,都可能会导致摩擦 —— 更何况,这种否定还常常是粗鲁的。Canonical已经不再欢迎开诚布公的讨论,而是借着“为了让Ubuntu成功”的名义越来越倾向于扼杀人们的不同意见。
|
||||
其实,在争论中,解决问题并不是最重要的,重要的是解决问题时人们之间的关系。与Canonical不同,Ubuntu社区每天的运行看起来就像是任何预期中规范的自由软件项目一样,有讨论有商议。而Canonical呢?据说,Canonical公司中的高级雇员经常滥用否决权,即便是礼貌的否定,都可能会导致摩擦 —— 更何况,这种否定还常常是粗鲁的。Canonical已经不再欢迎开诚布公的讨论,而是借着“为了让Ubuntu成功”的名义越来越倾向于扼杀人们的不同意见。
|
||||
|
||||
矛盾积蓄久了终会爆发。经过长时间的公开质问,Ubuntu社区贡献者们的地位仍得不到肯定,2013年2月,许多人开始考虑退出社区(事实上,貌似只有一个人付诸行动)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ Bacon再一次平息了事态,在局外人看来,这几个月社区似乎重
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical是否曾经相信Ubuntu发行版能够盈利,这我们不得而知。当然,之前无数的教训已经警告了Canonical,为赚钱而生的发行版成功的几率有多渺茫。但是多年来在Ubuntu上付出的努力似乎表明Canonical希望——或者曾经希望——能将不可能变为可能。又或者,也许Canonical只是简单地将一个优秀发行版看作是其宏伟目标的踏脚石。
|
||||
|
||||
一方面,如今看来,在Unity上付出如此多的努力已经是一步错棋。直到今天,Canonical似乎仍然缺乏一个商业计划为其带来任何可以盈利的合理机会。
|
||||
不管怎样,如今看来,在Unity上付出如此多的努力已经是一步错棋。直到今天,Canonical似乎仍然缺乏一个商业计划为其带来任何可以盈利的合理机会。
|
||||
|
||||
至于那些周边产品,诸如在线存储、音乐商店、或者Dash中的合作广告,这些努力可能有助于弥补开发Ubuntu所需的花销,但要说这些东西就能帮助Ubuntu盈利,没人会张这个嘴。而用在线会议代替实际会议,这只能说明一家公司正在寻找削减开支的手段,而不是盈利的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ Canonical用了一年时间来[解决个人隐私问题][13],但即使这样
|
||||
|
||||
其他方面,像[Ubuntu TV][14],仍然没有成形。当然,Ubuntu的主战略看起来正向多样化多元素靠拢,但是尝试闯入一个饱和市场,其合理性仍然值得怀疑。Ubuntu Touch计划于10月份同13.10一起发布,但是如果有手机制造商要搭载预装产品,Canonical还将推迟发布日期。
|
||||
|
||||
更糟的是[Ubuntu Edge][15]投资人计划,该计划打算通过众筹基金打造一款时尚前卫的经典手机,如果能够成功,Canonical就可以在市场中为其建立一个小生态圈。
|
||||
更糟的是[Ubuntu Edge][15]资金筹集计划,该计划打算通过众筹基金打造一款时尚前卫的经典手机,如果能够成功,Canonical就可以在市场中为其建立一个小生态圈。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,最终3200万美元的筹资目标只达到了四成,Canonical对此只能“强颜欢笑”,因为参与众筹的投资者们也确实为产品卖力的宣传了。但是这个结果意味着Canonical在潜在的商业伙伴眼中背上了失败者的名声,现实就是如此残酷。Ubuntu Edge的失败给Canonical的商业计划留下的是更多的不确定性,希望愈加渺茫。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -71,20 +71,18 @@ Canonical用了一年时间来[解决个人隐私问题][13],但即使这样
|
||||
|
||||
如果问题依旧,即使再过一个9年,Canonical和Ubuntu也不会成功。Linux桌面那些早年的主要贡献者,他们甚至都没有对自己的代码有所创新,更不要提一般的自由软件了。长此以往,要么困惑要么绝望,都将会加速Ubuntu的没落。
|
||||
|
||||
如果不加以改革,Ubuntu和Canonical也许能改变之前失败者的印象,尽管Ubuntu Edge项目表明这种可能性并不大。但是,渐渐地,Canonical和Ubuntu已经开始失去他们多年来拥有的领袖地位。
|
||||
即使不加以改革,Ubuntu和Canonical也有可能恢复之前的威望,虽然Ubuntu Edge项目表明这种可能性并不大。但是,渐渐地,Canonical和Ubuntu已经开始失去他们多年来拥有的领袖地位。
|
||||
|
||||
到底是扭转颓势,还是依靠不疼不痒的措施加速没落,这些都是未知数。接下来的这几年会很有趣,充满变数,让我们拭目以待!
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/are-we-witnessing-the-decline-of-ubuntu-1.html
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT][] 原创翻译,[Linux中国][] 荣誉推出
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿][] 校对:[jasminepeng][ ]
|
||||
译者:[tinyeyeser](https://github.com/tinyeyeser) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
|
||||
|
||||
[LCTT]:https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject
|
||||
[Linux中国]:http://linux.cn/portal.php
|
||||
[Mr小眼儿]:http://github/tinyeyeser
|
||||
[jasminepeng]:http://linux.cn/space/jasminepeng
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.canonical.com/content/canonical-and-chinese-standards-body-announce-ubuntu-collaboration
|
||||
[2]:http://games.slashdot.org/story/13/02/14/2318247/valve-officially-launches-steam-for-linux
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu联系人应用已支持增强的头像功能
|
||||
==============================
|
||||
|
||||
为下一代Ubuntu设计的新一代软件们正在通过多方面的支持逐步的建立起来,包括了一套由第三方的程序员和Ubuntu程序员及设计者们一起开发出来的核心应用,以及他们开发出来的越来越多的官方应用。
|
||||
|
||||
在官方的开发出来的软件们中有一个联系人应用程序,它非常的容易上手,在漂亮的界面里面集成了联系人管理功能。有许多可以编辑的字段、 快速滚动条,此外列出来的项目还会提供一个有趣的相关联系的应用(正在研发中。)
|
||||
|
||||
[联系人应用][1]升级了另外一个附加的功能,就是我们[最近][2]介绍的新功能里,那个叫做联系人头像的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
在它的上一个版本中,用户可以通过联系人中心支持头像的选择,现在在主界面中也开始支持头像的显示了。
|
||||
|
||||
这个意思是,点击一个联系人,按下下方的`编辑`按钮来为这个联系人添加一个图片作为头像,来替代之前的单色图标,添加图片后,点击保存。之后回到主界面就能够看到之前添加的头像了,之前的单色图标就被我们替换成刚刚添加的图片。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
此外,头像的四角修饰成了圆角,以美化联系人的显示。甚至在用户选择一个非正方形的图片时候会生成带圆角的缩略图。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,点击那些已经开启avatar的联系人。点开联系人,在看到用户的图片的地方,可以用新的图片替换掉旧 图片。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
联系人应用已经[可以][3]在Ubuntu13.10的 Ubuntu软件中心中找到了,已经可以安装使用或测试了。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/contacts-app-updated-enhanced-avatar-support
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[FineFan](https://github.com/FineFan) 校对:[wxy](https://linux.cn/space/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/address-book-app
|
||||
[2]:http://iloveubuntu.net/contacts-app-updated-avatar-editing-support
|
||||
[3]:apt://address-book-app
|
||||
@ -1,30 +1,30 @@
|
||||
E-Mail应用Geary得到改观,增添新功能
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
E-Mail应用Geary的新外观和新功能
|
||||
==============================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*新面貌: Geary 0.4 现在可以下载*
|
||||
|
||||
随着[一款照片实用工具Shotwell的更新][1]一起到来的是新版本的Geary - 流行的开源桌面e-mail应用.
|
||||
随着[一款照片实用工具Shotwell的更新][1]一起到来的是新版本的Geary - 流行的开源桌面e-mail应用。
|
||||
|
||||
这是客户端背后的团队Yorba自从在4月[众筹$100,000的目标失败][2]之后的第一次发布.
|
||||
这是客户端背后的团队Yorba自从在4月[众筹$100,000的目标失败][2]之后的第一次发布。
|
||||
|
||||
这个轻量级app,很久以来是我酷爱的东西,今天的更新版本增加了一些长久需求的新功能.
|
||||
这个轻量级app,很久以来一直是我酷爱的东西,今天的更新版本增加了一些一直被要求增加的新功能。
|
||||
|
||||
Geary现在有 **每个账户搜索** **自动保存e-mails草稿** 和 **一个内置安全工具** 用来检查外展连接的恶意内容.
|
||||
Geary现在有 **每个账户搜索** **自动保存草稿** 和一个用来检查包含恶意内容的外部连接的 **内置安全工具** 。
|
||||
|
||||
应用的界面也更新了,总是把焦点集中在信件和chrome上.
|
||||
应用的界面也更新了,可以让你总是把注意力集中在信件和chrome上。
|
||||
|
||||
侧边栏显示 **每个文件夹的未读数目** ,账户和文件夹使用了一个套新的 **单色图标** ;工具栏已被一个新的'菜单按钮'刷新.
|
||||
显示了 **每个文件夹的未读数目** 的侧边栏里面的账户及文件夹使用了一个套新的 **单色图标** ;工具栏也换了一套新的'菜单按钮'.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Geary的新菜单按钮和侧边栏图标*
|
||||
|
||||
e-mail列表默认隐藏取消星号和读取状态图标,鼠标悬停显示选择.当检查时,它们保持可见.
|
||||
e-mail列表默认隐藏取消星号和读取状态图标,鼠标悬停时显示选择。当选中后,它们才保持可见。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*顶部 - 底部:未读&加星; 读和取消加星;未读*
|
||||
*从上到下:未读且加星、已读且没有加星、未读*
|
||||
|
||||
**在Ubuntu安装Geary0.4**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,10 +13,10 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
新的系统状态区
|
||||
旧的系统状态区
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
旧的系统状态区
|
||||
新的系统状态区
|
||||
|
||||
新系统状态区不仅仅是统一了所有的面板菜单,而且它也将仅显示你所关注的主要信息。用鼠标点击,你可以看到你的笔记本电脑的电量还能剩多少时间使用(也显示百分比)、连接无线宽带或者是WI-Fi、及调整音量和亮度。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,23 +1,25 @@
|
||||
正在开发中基于GTK3的Twitter应用“Corebird”
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
正在开发中基于GTK3的新Twitter应用“Corebird”
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
Corebird是一个Twitter应用,它的界面让人想到了Twitter在OS X上的[官方应用](https://itunes.apple.com/gb/app/twitter/id409789998?mt=12%27)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Corebird是由一个Archlinux用户开发的,它具有GNOME 3.10的外观和功能集。
|
||||
|
||||
Corebird的界面使用GTK3开发,因此当你把它放在其他的GTK应用旁边时,Corebird会感觉在家一样。Corebird充分利用了最新版GNOME 3.10 release的新标题栏,这正是GNOME 3.10 release所强调的顶级功能。Corebird的标题栏展示了你的Twitter,头像,以及一个快速编写微博文章的按钮。这把本该是单独的工具栏整合为了一个紧凑,简洁的标题。
|
||||
Corebird的界面使用GTK3开发,因此当你把它放在其他的GTK应用旁边时,Corebird和它们看起来非常协调。Corebird充分利用了最新版GNOME 3.10 release的新标题栏,这正是GNOME 3.10 release所强调的顶级功能。Corebird的标题栏展示了你的Twitter,头像,以及一个快速编写微博文章的按钮。这把本该是单独的工具栏整合为了一个紧凑,简洁的标题栏。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然Corebird的界面可能是为了GNOME 3.10而设计,但Corebird具备的功能是要让所有的Twitter用户之间交友,无论你是使用GNOME或是其他桌面环境。
|
||||
虽然Corebird的界面可能是为了GNOME 3.10而设计,但Corebird具备的功能是要让所有的Twitter用户之间的联系,无论你是使用GNOME或是其他桌面环境。
|
||||
|
||||
## 功能 ##
|
||||
Corebird在某些方面与Mac的官方Twitter应用相似(这当然是好事!),而且它有一套功能集来充分展现Twitter。转发,喜爱,收听,搜索,个人资料查看,会话,音视频上传,以及其他的一系列功能都可以正常使用。
|
||||
###功能
|
||||
|
||||
Corebird在某些方面与Mac的官方Twitter应用相似(这当然是好事!),而且它有一套功能集来充分展现Twitter。转发,喜爱,收听,搜索,查看个人资料,会话,音视频上传,以及其他的一系列功能都可以正常使用。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你管理着几个帐号,多帐号设置也是支持的,但是要注意,在最新的版本中,重新打开Corebird后,你之前配置的账户都会被移除。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*GNOME锁屏时的Corebird提醒*
|
||||
*GNOME锁屏的Corebird提醒*
|
||||
|
||||
在GNOME锁屏时,Corebird也会有提醒,当你回到电脑前,它会提示你有多少个Twitter提醒。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,14 +27,15 @@ Corebird在某些方面与Mac的官方Twitter应用相似(这当然是好事
|
||||
|
||||
Corebird有浅色的主题,也有深色的主题,这当然是为了让你晚上玩Twitter时眼睛更舒服。Corebird还有一些其他的设置选项,包括显示哪些提醒,是否显示微博内的音视频等,你可以在设定对话框中进行设置。
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何获取Corebird ##
|
||||
###如何获取Corebird
|
||||
|
||||
如果你还在使用Ubuntu 13.04,非常不走运,Corebird使用了GNOME 3.10的新功能,因此Ubuntu 13.04并不支持。如果你把系统升级为13.10(下周将发布release版本),你就可以在Saucy(13.10的代号简称)的GNOME 3 PPA中体验GNOME 3.10了。
|
||||
|
||||
Corebird仍在开发当中,而且PPA也还没有(Corebird已经在[AUR][3]里建了仓库,Archlinux用户进去逛过就会知道),因此,你要使用Corebird就必须手动编译了。
|
||||
|
||||
这个项目给了那些开发逐渐慢下来的Linux Twitter应用一个希望的信号,例如,Birdie在今年的夏天没有达成它的[crowdfunding][4]目标。
|
||||
这个项目给了那些开发逐渐慢下来的Linux Twitter应用一个希望的信号,例如,Birdie在今年的夏天就没有达成它的[crowdfunding目标][4]。
|
||||
|
||||
如果Corebird不是你的菜,去看看[gFeedline][5],另一个基于GTK3的Twitter应用。
|
||||
如果Corebird不是你的菜,也可以去看看[gFeedline][5],另一个基于GTK3的Twitter应用。
|
||||
|
||||
Corebird的更多内容:http://corebird.baedert.org/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,7 +45,7 @@ via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/corebird-twitter-app-gtk3-gnome
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[will.qian](https://github.com/willqian) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[will.qian](https://github.com/willqian) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://itunes.apple.com/gb/app/twitter/id409789998?mt=12%27
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/09/10-best-features-gnome-3-10
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu 13.04和13.10上安装iOS 7的图标
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
==================================
|
||||
|
||||
**这个简单的教程将指导你如何在你的Ubuntu 12.04、13.04和13.10上安装苹果iOS 7操作系统的所有图标。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
上面是效果图,安装完的图标虽然看起来改变不大,但是对于审美观来讲却是重大提高,如果Canonical没有在每一个发行版中使用种类图标,那你将不会那么容易识别出Ubuntu,差异甚微。
|
||||
上面是效果图,安装的图标虽然并不多,但是对于外观的改进来讲却是重大提高。如果Canonical没有在每一个发行版中使用差异甚小的同类图标,那你就不太容易分辨出Ubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
以前在Ubuntu安装主题、图标甚至是鼠标光标,那叫一个麻烦,但是近几年这事变得容易多了。想要安装新的图标,只需要输入几条命令就行。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnome-tweak-tool
|
||||
|
||||
你会发现这个软件在Ubuntu下是以Tweak Tool命名的。
|
||||
你会发现这个软件在Ubuntu下叫做Tweak Tool。
|
||||
|
||||
安装PPA,然后更新一下:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,6 +50,8 @@ Ubuntu 13.04、Ubuntu 13.10安iOS装图标:
|
||||
|
||||
享受你的新图标吧!
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Install-the-iOS-7-Icons-in-Ubuntu-13-04-and-Ubuntu-13-10-387709.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
Mark Shuttleworth认为苹果5S使用了Ubuntu Edge终端融合的创意
|
||||
=====================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical公司的创始人Mark Shuttleworth通过这一有趣的说法将Ubuntu Egde智能手机与iPhone 5S联系了起来。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
几个月前,Canonical和Mark Shuttleworth尝试筹资来推出一款手机,该手机被认为是手机中的“F1赛车”。虽然筹资失败了,但是他认为苹果已经从这款手机(Ubuntu Edge)的概念中获得了灵感。
|
||||
|
||||
“我认为Ubuntu Edge可能加速了终端融合的概念,你看苹果描述他们的新的CPU为‘桌面级’的,我认为这并不是偶然。”他在接受[ZDnet][1]采访时这么说。
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical公司的创始人可能有一些我们不能获得的内部消息,不过这也许只是一个有趣的猜测。
|
||||
|
||||
苹果是否会按照Canonical的Ubuntu Edge手机描绘的终端聚合方向发展还有待观察。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Mark-Shuttleworth-Thinks-Apple-Used-the-Ubuntu-Edge-Convergence-Idea-for-iPhone-5S-390507.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[SCUSJS](https://github.com/SCUSJS) 校对:[wxy](https://linux.cn/space/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.zdnet.com/mark-shuttleworth-on-how-the-ubuntu-edge-dream-lives-on-in-the-iphone-7000021857/
|
||||
89
published/Mastering the “Kill” Command in Linux.md
Normal file
89
published/Mastering the “Kill” Command in Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
||||
精通Linux的“kill”命令
|
||||
=================
|
||||
|
||||
无论你使用哪种操作系统,你一定会遇到某个行为失常的应用,它把自己锁死并拒绝关闭。在Linux(还有Mac),你可以用一个"kill"命令强制终结它。在这个教程中,我们将展示给你多种方式使用"kill"命令终结应用。
|
||||
|
||||
###Kill命令和信号
|
||||
|
||||
当你执行一个"kill"命令,你实际上发送了一个信号给系统,让它去终结不正常的应用。总共有60个你可以使用的信号,但是基本上你只需要知道SIGTERM(15)和SIGKILL(9)。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以用这个命令看到所有信号的列表:
|
||||
|
||||
kill -l
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- SIGTERM - 此信号请求一个进程停止运行。此信号是可以被忽略的。进程可以用一段时间来正常关闭,一个程序的正常关闭一般需要一段时间来保存进度并释放资源。换句话说,它不是强制停止。
|
||||
- SIGKILL - 此信号强制进程立刻停止运行。程序不能忽略此信号,而未保存的进度将会丢失。
|
||||
|
||||
使用"kill"的语法是:
|
||||
|
||||
kill [信号或选项] PID(s)
|
||||
|
||||
默认信号(当没有指定的时候)是SIGTERM。当它不起作用时,你可以使用下面的命令来强制kill掉一个进程:
|
||||
|
||||
kill SIGKILL PID
|
||||
|
||||
或者
|
||||
|
||||
kill -9 PID
|
||||
|
||||
这里"-9"代表着SIGKILL信号。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不知道应用的PID,仅需要运行这个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
ps ux
|
||||
|
||||
它会显示所有正在运行的应用还有应用的PID。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
例如,要kill掉Chrome,我会运行命令:
|
||||
|
||||
kill -9 3629
|
||||
|
||||
也可以在同一时间kill多个进程。
|
||||
|
||||
kill -9 PID1 PID2 PID3
|
||||
|
||||
###PKill
|
||||
|
||||
"pkill"命令允许使用扩展的正则表达式和其它匹配方式。你现在可以使用应用的进程名kill掉它们,而不是使用PID。例如,要kill掉Firefox浏览器,只需要运行命令:
|
||||
|
||||
pkill firefox
|
||||
|
||||
使用正则表达式匹配的话,你可以输入进程名的部分字符,比如:
|
||||
|
||||
pkill fire
|
||||
|
||||
为了避免kill掉错误的进程,你应该用一下"pgrep -l [进程名]"列表来匹配进程名称。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
###Killall
|
||||
|
||||
killall同样使用进程名替代PID,并且它会kill掉所有的同名进程。例如,如果你正在运行多个Firefox浏览器的实例,可以用命令把它们全部kill掉:
|
||||
|
||||
killall firefox
|
||||
|
||||
在Gnome中,你可以使用这个命令重启Nautilus:
|
||||
|
||||
killall nautilus
|
||||
|
||||
###xkill
|
||||
|
||||
xkill 是图形方式kill一个应用。当你在终端键入"xkill",你的光标将立刻变成一个"十字"。你只需要做的是在不正常的应用上点击一下,它就会立刻kill掉这个应用。如果你经常用的话,你也可以添加一个[键盘快捷键来激活xkill][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
###结论
|
||||
|
||||
当应用不正常而导致系统挂起的时候,人们往往重启计算机并且再一次开启所有的任务。而有了这些"kill"命令,你将能够更好的处理不正常的应用,从而避免导致系统崩溃。当你不想因一个不正常的进程而导致服务器宕机时,它尤其的有用。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.maketecheasier.com/kill-command-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[flsf](https://github.com/flsf) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.maketecheasier.com/quick-tips/kill-unresponsive-application-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
@ -1,42 +1,42 @@
|
||||
开源是冷酷无情的:谷歌Chris DiBona访谈
|
||||
==============================================================
|
||||
===============================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Chris DiBona是谷歌开源执行总监。他也是开源界杰出的领军人物之一,这还要追溯到他的大学时期,那时他对Linux可谓一见钟情。
|
||||
Chris DiBona是谷歌开源总监。他也是开源界杰出的领军人物之一,这还要追溯到他的大学时期,那时他对Linux可谓一见钟情。
|
||||
|
||||
在今年的 ”一切皆开源“ 大会上,Christ将会提供谷歌目前的开源软件活动的最新消息以及回顾过去,还有Android的起源和现况。
|
||||
在今年的 “一切皆开源” 大会上,Christ将会提供谷歌目前的开源软件活动的最新消息以及对过去的回顾,还有Android的起源和现况。
|
||||
|
||||
我遇到了Christ,我们讨论了他最喜爱的Linux发行版、开源的无情法则以及他对谷歌作为业界领袖应有的责任的看法。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是访谈详情。
|
||||
|
||||
问:对于你加入谷歌并且在开源部门展开工作,有那些方面是我们所不知道的?
|
||||
###问:对于你加入谷歌并且在开源部门展开工作,有那些方面是我们所不知道的?
|
||||
|
||||
答:
|
||||
第一次使用Linux是在上学的时候,由于当时选修了操作系统课程,因此,我需要写一些有关客户端/服务器的东西。出乎意料的是,那时候Sun工作站实验室很热闹,因为公开探讨问题的风气使然,编码味十足,使用的终端跑得相当慢。我在想,瓶颈在哪,不妨就用一直都摆放在家里的一台486-16上试试这个linux到底怎么样。这是有史以来最棒的一次决定!从此我喜欢上了linux系统。linux太棒了,运行很快,与其他unix系统相比,功能齐全。OS这门课程,我也得了A。
|
||||
第一次使用Linux是在上学的时候,由于当时选修了操作系统课程,因此,我需要写一些有关客户端/服务器的东西。出乎意料的是,那时候Sun工作站实验室很热闹,因为公开探讨问题的风气使然,编码味十足,使用的终端跑得相当慢。我在想,瓶颈在哪,不妨就用一直都摆放在家里的一台486-16上试试这个linux到底怎么样。这是我有史以来最棒的一次决定!从此我喜欢上了linux系统。linux太棒了,运行很快,与其他unix系统相比,功能齐全。OS这门课程,我也得了A。
|
||||
|
||||
问:下面这个问题的危险程度跟询问你最喜欢的球队一样,你最喜欢哪个linux发行版?
|
||||
###问:下面这个问题的危险程度跟询问你最喜欢的球队一样,你最喜欢哪个linux发行版?
|
||||
|
||||
答:
|
||||
哈!如果轻率地回答,那么是Android,因为Android是基于linux内核的,而我对linux内核的使用频度远远超过其他一些东西。尽管通常情况下讨论Android时,多数人都不把它当做一个发行版。我在Ubuntu/Debian衍生版本上运行的Chrome浏览器中输入了这个问题的回答,我在谷歌计算引擎上运行的是Debian,在家里则经常用Fedora。出席公共场合的时候,大多数情况下我携带Chomebook,感觉用它最安全。那么最喜欢的就是Android。
|
||||
哈!如果轻率地回答,那么是Android,因为Android是基于linux内核的,而我对它的使用频度远远超过其他一些东西。尽管通常情况下讨论Android时,多数人都不把它当做一个发行版。我现在正在一个Ubuntu/Debian衍生版本上运行的Chrome浏览器中回复你这个问题的回答,我在谷歌计算引擎上运行的是Debian,在家里则经常用Fedora。出席公共场合的时候,大多数情况下我携带Chromebook,感觉用它最安全。那么最喜欢的就是Android。
|
||||
|
||||
问:2004年加入谷歌之前,你在开源和linux领域投入了许多时间,是什么原因促使你加入谷歌?
|
||||
###问:2004年加入谷歌之前,你在开源和linux领域投入了许多精力,是什么原因促使你加入谷歌?
|
||||
|
||||
答:
|
||||
从事了一小段时间咨询方面的工作以后,当我决定开始全职工作,谷歌的offer对我来说最富有吸引力。 成为谷歌开源人、白手起家开始创业的想法深深地吸引着我。我感觉无论过去还是现在,谷歌始终在计算机科学领域做着有趣的事情,而且以它独有的方式吸引着我,这些是其他offer所不具备的。
|
||||
|
||||
问:你不但指导各种项目的开发,而且也参与了Google Ventures,为该项目的启动注资,那么你在一个项目中想要寻求什么,是什么让你说出“是的,我就是想帮你”这样的话 ?
|
||||
###问:你不但指导各种项目的开发,而且也参与了Google Ventures,为该项目的启动注资,那么你在一个项目中想要寻求什么,是什么让你说出“是的,我就是想帮你”这样的话 ?
|
||||
|
||||
答:
|
||||
呃,坦白说,我希望它能够做的有趣。对于Google Ventures,我并不需要过多的深入其中,而开源问题就不同了,有趣而且参与者众多。
|
||||
|
||||
问:多年前的一次采访中你曾经说过:”谷歌与开源社区同行。赞助意味着责任,这是相当严肃的一件事情。“谷歌是否打算避免在自己参与的社区中担责,二者之间存在必然联系吗?
|
||||
###问:多年前的一次采访中你曾经说过:“谷歌与开源社区同行。赞助意味着责任,这是相当严肃的一件事情。”谷歌是否打算避免在自己参与的社区中担责,二者之间存在必然联系吗?
|
||||
|
||||
答:
|
||||
我想是这样的。我希望谷歌工程师和非谷歌开源界的工程师都能把对方看做计算机科学领域的同侪。我们得意识到,对开源项目的广泛资助预示着责任,比如项目控制,大家都知道,事情就应该这么做,即使真的没什么联系。
|
||||
|
||||
问:你曾经称开源是“无情”的,具体是什么意思?
|
||||
###问:你曾经称开源是“无情”的,具体是什么意思?
|
||||
|
||||
答:
|
||||
呃,我还以为你会问为什么开源可以行得通,什么时候会考虑开源软件工程管理在业内是如何运作,但是你没有。分散的、不同特性的团队在公司里相当难运作,但是在开源领域,可以创作出世界级非常优秀的软件。为什么会这样?
|
||||
@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ Chris DiBona是谷歌开源执行总监。他也是开源界杰出的领军人
|
||||
|
||||
所以,我想说,开源世界是一个适者生存、优胜劣汰的残酷机制,但是这样却能生产出高质量的软件产品。诚然,对新手来说比较难上手……
|
||||
|
||||
问:14年前,你编辑过一本有关开源的书-O'Reilly。这些年开源领域是否了发生大的变化?你认为将来开源模式会取代专有模式吗?
|
||||
###问:14年前,你在O'Reilly出版过一本有关开源的书。这些年开源领域是否了发生大的变化?你认为将来开源模式会取代专有模式吗?
|
||||
|
||||
答:
|
||||
开源界确实发生了一些变化,非常显著的一点就是公司里从事开源工作的人数的增长。而且我还觉察到学术界参与开源的人数有所下降,我把它归咎于技术转让专利申请,对代码许可权确实是个障碍。类似的,一些来自大学和公司的开源代码不足以称之为开源,因为围绕着专利要应付相当多的问题。我很想说要不是有专利授权许可,我们应该都持怀疑态度,但是在这个时候说这样的话就有一点走极端了。
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
Shotwell 0.15发布了!添加了更多新功能及修复!
|
||||
======================================
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 默认安装了Shotwell,它能轻松的管理图片,提供基本的图库管理和图片编辑功能,以后将提供更多有用的功能.
|
||||
|
||||
Shotwell 已经更新到0.15版本,带来了新的特征,修复了大量已知的bug,并进行了更多的优化。
|
||||
|
||||
`右击图片-->打开方式-->Shotwell图片编辑`,用Shotwell打开图片后,在下边有几个选项,其中包括Adjust(调整)选项。
|
||||
|
||||
点击`Adjust`按钮,用户能清楚的发现最新的Highlights(高亮)条目,这对于微调高亮很有帮助;举例来说,将'Highlights'设置调到很低,这样就能降低正在编辑的图片的明暗程度。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
点击按钮条中的`Crop`按钮,弹出可更改大小的会话框,允许用户根据要求自定义大小裁剪图片,0.15版本的对话框增加了 **尺寸显示** 的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
改变会话框的大小,会实时的显示目前的尺寸大小,用户能自由随意观察修剪框中的尺寸;举个例子,为了得到一张640*480的图片,用户可以将裁剪框调整到640*480,在图片编辑器中便利地增添图片清晰度。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
除此以外,Shotwell 0.15 还增添了:
|
||||
|
||||
- 支持Youtube插件 OAuth/OpenID 认证
|
||||
|
||||
- 增强视频文件的再次导入
|
||||
|
||||
- 优化了视频的缩略图生成
|
||||
|
||||
- 修复了很多漏洞
|
||||
|
||||
我们怎么**安装** Shotwell 0.15呢?
|
||||
|
||||
添加以下 **官方** PPA(Ubuntu 12.10, Ubuntu 13.04)
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yorba/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install shotwell
|
||||
|
||||
Shotwell 0.15已经被放入了Ubuntu 13.10,你只需要定期的更新软件,便会帮你自动安装,享受它带给你的乐趣吧!
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/shotwell-015-released-new-features-and-fixes
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.yorba.org/projects/shotwell/
|
||||
[2]:http://blog.yorba.org/eric/2013/10/shotwell-0-15-has-arrived.html
|
||||
@ -1,31 +1,30 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10评论:日趋完善,一个伟大的Linux桌面系统。
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10评论:日趋完善,一个伟大的Linux桌面系统
|
||||
=============================================
|
||||
|
||||
***摘要**:Ubuntu 13.10也许并不是最激动人心的桌面Linux,但它却非常可靠,拥有许多有用的新特性。*
|
||||
**摘要:Ubuntu 13.10也许并不是最激动人心的桌面Linux,但它却非常可靠,拥有许多有用的新特性。**
|
||||
|
||||
许多桌面发烧友至今仍然对Ubuntu转用Unity耿耿于怀,另外有些人不喜欢[Ubuntu][2]的母公司[Canonical][1]一意孤行,用Mir代替更主流的Wayland,还有些人不喜欢Ubuntu将本地搜索与Web搜索合并在一起。我想说,那又怎样!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Ubuntu 13.10下周发布,本文只是预热。*
|
||||
*Ubuntu 13.10即将发布,本文只是预热。*
|
||||
|
||||
让我来告诉你们,什么是事实!回首2011年4月,Ubuntu的创始人Mark Shuttleworth曾经说过,Ubuntu新的发展方向是,“为普通消费者带来[快乐、自由、创新、性能和安全,而这些正是Linux平台中一直所缺少的东西][3]”。如今,他做到了!
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10,代号“俏皮的蝾螈(Saucy Salamander)”,已经进入发布前的最后阶段。的确,Ubuntu也许不是那些每天热衷于编译内核代码的Linux专家们所喜爱的桌面Linux,因为它本就不是为那些人准备的。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu是一个所有人,甚至包括我那81岁的老岳母,都能使用的Linux桌面操作系统。基于这个角度,Ubuntu已经成功了,而下周最终发布的新版本,对于那些仅仅只是想学习使用一台电脑的新人来说,其意义绝不亚于一场胜利。
|
||||
Ubuntu是一个所有人,甚至[包括我那81岁的老岳母][3-1],都能使用的Linux桌面操作系统。基于这个角度,Ubuntu已经成功了,而下周最终发布的新版本,对于那些仅仅只是想学习使用一台电脑的新人来说,其意义绝不亚于一场胜利。
|
||||
|
||||
为了目睹新版的Ubuntu是如何做到这一点的,我在两套系统上分别安装运行了beta版和发布版。第一套测试环境是我2007年产的Dell Inspiron 530S,搭载2.2GHz Intel奔腾 E2200双核处理器、4G内存、500GSATA串口硬盘,集成Intel 3100GMA显示芯片组。第二套测试环境是2008年入手的Gateway DX4710,搭载2.5GHz Intel酷睿2四核处理器,6G内存,1T串口硬盘,同样集成了Intel GMA 3100显卡。
|
||||
为了目睹新版的Ubuntu是如何做到这一点的,我在两套系统上分别安装运行了beta版和RC版。第一套测试环境是我2007年产的Dell Inspiron 530S,搭载2.2GHz Intel奔腾 E2200双核处理器、4G内存、500GSATA串口硬盘,集成Intel 3100GMA显示芯片组。第二套测试环境是2008年入手的Gateway DX4710,搭载2.5GHz Intel酷睿2四核处理器,6G内存,1T串口硬盘,同样集成了Intel GMA 3100显卡。
|
||||
|
||||
安装过程小菜一碟。首先说明一下,我并没有尝试在有Windows 8 Secure Boot锁定的系统上安装Ubuntu,如果你想尝试的话,这里有[如何安装Ubuntu与Win8双系统的教程][4],如果是其他使用统一可扩展固件接口(Unified Extensible Firmware Interface - UEFI)的系统,也可以看下这个教程。
|
||||
|
||||
安装过程中有个出色的新特性,就是安装的同时你可以登录并打开[Ubuntu One][5]的云端服务账户。Ubuntu One是一款类似Dropbox的存储服务,提供5G免费空间,[商业版费用为39.95美刀][6],提供20G空间和音乐流媒体支持。该服务除了完美集成在Ubuntu系统中,你也可以在Windows、Mac OS、Android和IOS系统中使用它。
|
||||
安装过程中有个不错的新功能,就是安装的同时你可以登录或创建一个免费[Ubuntu One][5]的云端服务账户。Ubuntu One是一款类似Dropbox的存储服务,提供5G免费空间,[商业版费用为39.95美刀][6],提供20G空间和音乐流媒体支持。该服务除了完美集成在Ubuntu系统中,你也可以在Windows、Mac OS、Android和IOS系统中使用它。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,安装完成后,我注意到的第一件事是,在我这两台老电脑上,Ubuntu 13.10运行非常流畅,就像在顶级配置的电脑上运行一样。(译者表示,这样的配置竟然还叫老电脑,让译者的1G内存情何以堪,你们有考虑过老闪龙的感受吗!)如果你的机子比我的还老,跑Windows 7以上的系统都嫌慢,并且比较在意即将结束的XP官方支持,可以考虑一下Ubuntu,或者其他易于上手的Linux发行版,比如Mint。
|
||||
|
||||
再来看看核心部分。首先,“俏皮的蝾螈”运行[Linux 3.11 内核][7]。
|
||||
|
||||
在此基础上,再看看图形架构,本来大家预测的是Mir,但是PC上的Mir暂时还没有准备好迎来它的黄金时期。内有Ubuntu家族中诸如[Kubuntu][8]的反对,[外有Intel的抵制][9],Mir需要同时面对“内忧外患”。
|
||||
在此基础上,再看看显示引擎,本来大家预测的是Mir,但是PC上的Mir暂时还没有准备好迎来它的黄金时期。内有Ubuntu家族中诸如[Kubuntu][8]的反对,[外有Intel的抵制][9],Mir需要同时面对“内忧外患”。
|
||||
|
||||
最后的结果就是13.10将仍然默认使用老旧的Xorg-server 1.4.3。如果你富有冒险精神,可以选择尝试一下Mir。如果你想要在智能手机上运行Ubuntu,也就是传说中的[Ubuntu Touch,恰好,你就可以用到Mir][10]。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,12 +34,16 @@ Ubuntu是一个所有人,甚至包括我那81岁的老岳母,都能使用的
|
||||
|
||||
如果确实不习惯Unity,你也可以方便地在安装时去掉它。或者,你也可以使用其他[Ubuntu家族的Linux发行版][12],例如面向KDE用户的Kubuntu,Cinnamon粉丝喜欢的Mint,又或者专门针对LXDE爱好者的[Lubuntu][13]。搭载Unity的Ubuntu主要为新手用户提供,你完全可以挑选你喜欢的任一款Ubuntu桌面系统。
|
||||
|
||||
在新版Ubuntu的软件包最终敲定之前,人们都以为它会选用Google浏览器Chrome的开源版本Chromium。但是最终,它还是选择了Firefox 24作为默认浏览器。
|
||||
在新版Ubuntu的软件包最终敲定之前,人们都以为它会选用Google的Chrome浏览器的开源版本Chromium。但是最终,它还是选择了Firefox 24作为默认浏览器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
其他应用程序都将是Ubuntu或Linux桌面用户熟悉的面孔。办公套件为LibreOffice 4.12;邮件客户端为Thunderbird 24;照片编辑有Gimp 2.8.6,默认的音乐播放器为Rhythmbox 2.99.1。
|
||||
|
||||
对新用户来说,最值得一提的新特性将是[Smart Scopes][14](之前叫做Lens)。Lens最初被提出来的时候,其功能只是根据本地Unity Dash的搜索结果对Amazon的搜索结果进行整合。原本是作为默认功能的,但最终该特性被改为了可选。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu 13.10中,当你使用Unity Dash搜索时,不但可以使用Amazon,还可以选择Facebook、Google、Yelp以及其他多个在线Web页面。
|
||||
|
||||
它是如何工作的呢?当你在Unity Dash中输入一个搜索条目时,Ubuntu会尝试猜测最佳匹配项。例如,如果我搜索“最炫民族风”,它除了在我的电脑中搜索,还会在Web的音乐分类下进行搜索。
|
||||
@ -78,11 +81,12 @@ via: http://www.zdnet.com/ubuntu-13-10-review-a-great-linux-desktop-gets-better-
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[小眼儿](https://github.com/tinyeyeser) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[小眼儿](https://github.com/tinyeyeser) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.canonical.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.markshuttleworth.com/archives/671
|
||||
[3-1]:http://www.zdnet.com/blog/open-source/if-my-mother-in-law-can-use-ubuntu-linux-anyone-can/10802
|
||||
[4]:https://help.ubuntu.com/community/UEFI
|
||||
[5]:https://one.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[6]:https://one.ubuntu.com/services
|
||||
@ -97,4 +101,4 @@ via: http://www.zdnet.com/ubuntu-13-10-review-a-great-linux-desktop-gets-better-
|
||||
[15]:http://www.wikipedia.org/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.wordnik.com/
|
||||
[17]:http://www.zotero.org/
|
||||
[18]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy
|
||||
[18]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy
|
||||
@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
|
||||
A Pentesting Release for the Raspberry Pi
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The Raspberry Pi** is a credit-card-sized single-board computer developed in the UK by the Raspberry Pi Foundation with the intention of promoting the teaching of basic computer science in schools. The Raspberry Pi is manufactured through licensed manufacturing deals with **Newark element14 (Premier Farnell), RS Components** and **Egoman**. All of these companies sell the Raspberry Pi online. Egoman produces a version for distribution solely in China and Taiwan, which can be distinguished from other Pis by their red coloring and lack of FCC/CE marks. The hardware is the same across all manufacturers. (wikipedia)
|
||||
|
||||
Pwnie Express team has announced the initial release of Raspberry Pwn which can be used to turn your raspberry pi into a full-featured security penetration testing and auditing platform. This release of Raspberry Pwn and includes all the tool needed to perform a penetration testing. So, doing penetration testing from your raspberry pi, how does that make you feel? Sqlmap, nmap, wireshark, scapy, nikto, xprobe, socat, do you want more tools for pentesting your network?
|
||||
|
||||
Raspberry Pwn comes with the following tools:
|
||||
|
||||
- nmap
|
||||
- dsniff
|
||||
- netcat
|
||||
- nikto
|
||||
- xprobe
|
||||
- scapy
|
||||
- wireshark
|
||||
- tcpdump
|
||||
- ettercap
|
||||
- hping3
|
||||
- medusa
|
||||
- macchanger
|
||||
- nbtscan
|
||||
- john
|
||||
- ptunnel
|
||||
- p0f
|
||||
- ngrep
|
||||
- tcpflow
|
||||
- openvpn
|
||||
- iodine
|
||||
- httptunnel
|
||||
- cryptcat
|
||||
- sipsak
|
||||
- yersinia
|
||||
- smbclient
|
||||
- sslsniff
|
||||
- tcptraceroute
|
||||
- pbnj
|
||||
- netdiscover
|
||||
- netmask
|
||||
- udptunnel
|
||||
- dnstracer
|
||||
- sslscan
|
||||
- medusa
|
||||
- ipcalc
|
||||
- dnswalk
|
||||
- socat
|
||||
- onesixtyone
|
||||
- tinyproxy
|
||||
- dmitry
|
||||
- fcrackzip
|
||||
- ssldump
|
||||
- fping
|
||||
- ike-scan
|
||||
- gpsd
|
||||
- darkstat
|
||||
- swaks
|
||||
- arping
|
||||
- tcpreplay
|
||||
- sipcrack
|
||||
- proxychains
|
||||
- proxytunnel
|
||||
- siege
|
||||
- sqlmap
|
||||
- wapiti
|
||||
- skipfish
|
||||
- w3af
|
||||
|
||||
Let us me give you a short description of the above tools. I am not gonna explain everything. Just want to explain a two or three tools. A simple Google search will help you to find the details of the remaining tools.
|
||||
|
||||
**Nmap**
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap is a free and open-source tool for network discovery, helping us to map the network. Network administrators find it very useful in their daily job, so if you are planning to be a network administrator you should learn how to use Nmap. Nmap can help us to discover how many hosts are in a network, what operating systems are they running, what open ports do they have and services running in these open ports. It is a command line tool but for those that do not like to remember many commands there is a graphical version of Nmap that is called Zenmap. Both Nmap and Zenmap are multi-platform (Linux, Windows, Mac OS, BSD, etc.), so you do not have to worry about the operating system you need in order to use these tools. Nmap has the ability to save scan results to files and we can use these files for later analyzes. The great thing that I like about Nmap is its scripting engine (NSE). We can write our own scripts and use them with Nmap. See more at: [http://www.unixmen.com/scan-your-home-network-with-nmap/][1]
|
||||
|
||||
**Netcat**
|
||||
|
||||
Netcat is a command-line networking tool which is able to read and write data across Transmission Control Protocol TCP and User Datagram Protocol. Originally coded for Unix, it was released in 1996 and has been ported to a number of operating systems and facts tell that it still stays strong in the game. It has been 17 years and netcat belongs in every network admin/security professional’s toolbox. People say “old is gold” and in my opinion this is true when it comes to netcat. Virtually, you can use netcat for everything and your imagination is the limit. Depending on what your intentions are you can use it for good or you can use it for bad. Netcat operates as a client and as a server. Even if there are few exceptions, netcat’s command options are the same for both Windows and Linux and this makes netcat a more powerful tool. In the next article you will be introduced to netcat command options and will learn how perform some basic operations with netcat. – See more at: [http://www.unixmen.com/short-introduction-to-netcat][2]
|
||||
|
||||
**Sqlmap**
|
||||
|
||||
If you need a tool to exploit sql injection flaws in your web application or taking over database servers, sqlmap is the right one. Sqlmap is a tool used by penetration testers all over the world and it is full of feaures. Some of its features are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Full support for MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Access, IBM DB2, SQLite, Firebird, Sybase and SAP MaxDB database management systems.
|
||||
- Full support for six SQL injection techniques: boolean-based blind, time-based blind, error-based, UNION query, stacked queries and out-of-band.
|
||||
- Support to directly connect to the database without passing via a SQL injection, by providing DBMS credentials, IP address, port and database name.
|
||||
- Support to enumerate users, password hashes, privileges, roles, databases, tables and columns.
|
||||
- Automatic recognition of password hash formats and support for cracking them using a dictionary-based attack.
|
||||
- Support to dump database tables entirely, a range of entries or specific columns as per user’s choice. The user can also choose to dump only a range of characters from each column’s entry.
|
||||
- Support to search for specific database names, specific tables across all databases or specific columns across all databases’ tables.
|
||||
|
||||
**Medusa**
|
||||
|
||||
Do you need a login brute-forcer? Medusa was developed on Gentoo Linux and FreeBSD for bruteforcing network services. Medusa works with FTP, HTTP, IMAP, MS-SQL, MySQL, NCP (NetWare), NNTP, PcAnywhere, POP3, PostgreSQL,rexec, rlogin, rsh, SMB, SMTP (AUTH/VRFY), SNMP, SSHv2, SVN and many other services. You can read more about Medusa here.
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see there are all tools you need for penetration testing in this release of Raspberry Pwn. Do you have a pi? Then go and turn it into a pentester machine.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/pentesting-release-raspberry-pi/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/scan-your-home-network-with-nmap/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unixmen.com/short-introduction-to-netcat/
|
||||
69
sources/BetaPizza Hackaton Results.md
Normal file
69
sources/BetaPizza Hackaton Results.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
BetaPizza Hackaton Results
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Friday a week ago a [Beta Pizza Hackaton][1] took place at the SUSE offices and online. 121 people went over more than 580 bugs, screening 440 and fixing 140 of them. The contest was won by Stephan ‘coolo’ Kulow and Dominique ‘DimStar‘ Leuenberger, with top gold fixers Josef Reidinger and Michael Chang and a honorable mention for Antoine Saroufim.
|
||||
|
||||
## The BetaPizza Party Concept Turned Hackaton ##
|
||||
|
||||
Usually, the BetaPizza is as much about testing as about party. This time we added in the fixing of bugs as well! The SUSE engineers joined on Friday the 27th to catch and kill as many of these pesky little creatures as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
We set up some facilities:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- a [bug list prepared][2] in bugzilla, labeled as [GOLD][3], [SILVER][4] and [BRONZE][5] as part of a contest)
|
||||
- [a Google hangout][6]
|
||||
- a [#openSUSE-pizza-hackaton IRC channel on Freenode][7]
|
||||
|
||||
In the various offices, a local BetaPizzaMaster made sure a common room was reserved and pizza was available at the appropriate time.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Results and winners of the bug fixing contest ##
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s start our results section with some great statistics:
|
||||
|
||||
- **140** fixed (19 GOLD, 4 SILVER, 0 BRONZE, 117 OTHER)
|
||||
- **440** screened (46 GOLD, 19 SILVER, 0 BRONZE, 375 OTHER)
|
||||
- **121** participants (76 employees, 45 volunteer)
|
||||
|
||||
As we said in the initial article announcing the event, we have some SUSE provided prizes for top contributors. An evaluation committee was established with Richard Brown (openSUSE Board member), Frederic Crozat (SLE department, openSUSE contributor) and Michal Hrusecky (openSUSE Team) as members.
|
||||
|
||||
It was a tough decision, but in the end, the committee selected two hackers, well known to Factory contributors, as overall winners: Stephan ‘coolo’ Kulow and Dominique ‘DimStar’ Leuenberger. The committee furthermore awarded the top contributors working on the preselected golden bugs: Josef Reidinger and Michael Chang. The committee finally decided on a Honorable mention. This one goes to Antoine Saroufim, who was helping the GNOME team a lot with testing and providing feedback regarding various bugs and crashes over IRC.
|
||||
|
||||
So in the end, we have three awards with following winners:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Winners**: Stephan ‘coolo’ Kulow and Dominique ‘DimStar’ Leuenberger
|
||||
- **Top gold fixers**: Josef Reidinger and Michael Chang
|
||||
- **Honorable mention**: Antoine Saroufim
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Local experiences at the SUSE Offices
|
||||
|
||||
Taipei kicked off the long day, opening the hangout and working from a single room. Beijing had the biggest showing with 40 participants and 18 pizza’s eliminated though part of the Pizza eaters were kicking off [hackweek][8] and didn’t participate in the hackaton. The Pizza Master David Liang reports that the team enjoyed the IRC bot which reported the results of their work and other teams echo-ed this.
|
||||
|
||||
The Provo team noted that being in the last timezone meant being pretty lonely. Pizza Master Scott suggested we need to set up a teleportation unit and get everybody physically in one place next time. The openSUSE team is evaluating this option and suggestions for reasonably priced teleportation devices are welcome.
|
||||
|
||||
More testing?
|
||||
|
||||
All in all, we fixed lots of bugs, rid the world of some pizza (don’t worry, the world isn’t running out, and it’s [easy to make][9]) and had fun. But there’s more work to do – [openSUSE 13.1 RC1 is out][10] and we’re looking forward to more bug reports and fixes!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://news.opensuse.org/2013/10/15/betapizza-hackaton-results/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://news.opensuse.org/2013/09/25/beta-pizza-hackaton-starting-friday/
|
||||
[2]:https://bugzilla.novell.com/buglist.cgi?query_format=advanced&bug_status=UNCONFIRMED&bug_status=NEW&bug_status=ASSIGNED&bug_status=NEEDINFO&bug_status=REOPENED&bug_status=VERIFIED&resolution=---&product=openSUSE%2012.3&product=openSUSE%20Factory
|
||||
[3]:https://bugzilla.novell.com/buglist.cgi?field0-0-0=status_whiteboard&type0-0-0=substring&value0-0-0=GOLD
|
||||
[4]:https://bugzilla.novell.com/buglist.cgi?field0-0-0=status_whiteboard&type0-0-0=substring&value0-0-0=SILVER
|
||||
[5]:https://bugzilla.novell.com/buglist.cgi?field0-0-0=status_whiteboard&type0-0-0=substring&value0-0-0=BRONZE
|
||||
[6]:https://plus.google.com/events/csnu5vk431s6b2292dbi911vumc
|
||||
[7]:irc://freenode.net/#openSUSE-pizza-hackaton
|
||||
[8]:http://hackweek.suse.com/
|
||||
[9]:https://news.opensuse.org/2011/09/30/opensuse-pizza-parties-the-geeko-way/
|
||||
[10]:https://news.opensuse.org/2013/10/11/opensuse-13-1-rc-1-available-time-to-test/
|
||||
@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Luox翻译中.........
|
||||
Calibre 1.6 released with handy mark-book feature
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Calibre][1] is a free open-source ebook library management tool, designed in mind with satisfying a diverse and complex range of ebook-related requirements and necessities, offering powerful conversion process, dedicated ebook reader, hassle-free library creation and management, online service integration, etc, basically, a modern ebook experience.
|
||||
|
||||
Calibre has been updated to version **1.6**, introducing an exciting **book-marking** feature, as well as numerous new fixes and enhancements.
|
||||
|
||||
The book-marking feature presents itself as a handy manner of **temporarily** (restarting Calibre, loses the marking) selecting books, functionality allowing the user to mark books and to act on the marked books 1-click away, feature proving itself handy in multiple situations.
|
||||
|
||||
The newly-implemented book-marking feature is disabled by default, yet, enabling it is as simple as navigating to `Preferences-->Toolbar-->The main toolbar-->`click on `Mark Books-->hit the left-pointed arrow-->Apply`, action that adds the `Mark Books` button on its toolbar.
|
||||
|
||||
**Marking**, for example, three books is to be achieved by manually selecting the books (holding the Ctrl key and clicking on the three preferred to-be-marked books) and directly clicking on the toolbar's Mark Books button, action that marks the books.
|
||||
|
||||
The **result**: the newly-marked three books gain a marking-specific icon, thus the user is able to clearly observe marked books.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After the books have been marked, the user can act on the marked books by `right-clicking on the toolbar's Mark Books-->Show marked books`, action that displays on Calibre's main view only the marked books, while hiding the non-marked regular books.
|
||||
|
||||
The book-marking functionality allows users to hassle-free isolate preferred books in a matter of seconds by simply clicking on the mentioned button, isolation process fully exposing to the user only certain books, while clearing the view from at-the-moment unwanted books.
|
||||
|
||||
Reselecting the marked books and clicking again on the `Mark Books` button, unmarks the books, button acting as a mark/unmark toggle.
|
||||
|
||||
Calibre comes by default with a handy ebook viewer, ebook viewer enriched in the 1.6 release with extra configurable keyboard shortcuts, meaning, the user is now able to select a different **keyboard shortcut** (for example) for zoom in/out when reading ebooks.
|
||||
|
||||
Adjusting a keyboard shortcut is to be preformed by opening E-book Viewer, clicking on the sidebar's Preferences and navigating to `Keyboard shortcuts`, where double-clicking on an entry, makes the entry fully editable.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The mentioned features, along with numerous bug fixes, new news sources (various Uruguyan news) and improved news sources (National Geographic Magazine, New York Review of Books, Focus, Carta Capital, Ming Pao, Neu Osnabrucker Zeitung), come to deliver a more strengthened solid Calibre.
|
||||
|
||||
How do we **install** Calibre 1.6?
|
||||
|
||||
Paste the following command into a terminal
|
||||
|
||||
sudo python -c "import sys; py3 = sys.version_info[0] > 2; u = __import__('urllib.request' if py3 else 'urllib', fromlist=1); exec(u.urlopen('http://status.calibre-ebook.com/linux_installer').read()); main()"
|
||||
|
||||
and hit the `Enter` key on the `Enter the installation directory for calibre [/opt]` (command that will appear in the terminal after pasting the above-presented command)
|
||||
|
||||
**For users** having Calibre installed via PPA, type in a terminal (**before** pasting the above command)
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove calibre calibre-bin
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/calibre-16-released-handy-mark-book-feature
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://calibre-ebook.com/
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
[scusjs占坑]Daily Ubuntu Tips – Adding User Accounts In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu is a multi-user operating system. Multi-user OS means that more than one users are access the computer with separate and individual profile with home folder, documents, and settings. User A can login and make changes to his/her profile without affecting user **B’s** profile.
|
||||
|
||||
So, instead of creating a single shared account for everyone in your household, you can create an individual account for each user who will be using your home computer. This brief tutorial is going to show you how to do that when using Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
To get started, click on the far fight of the menu bar and select the gear icon, then click System Settings.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When that opens, click ‘**User Accounts**’ from the bottom of your screen as shown below
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You need administrative privileges to add user accounts to Ubuntu. If you do, click Unlock before adding accounts.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, click the plus ( + ) button to create a user account.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There are two primary account types when creating new users. **Standard User** and **Administrator**. User with administrative rights can delete users, install software and drivers, change the date and time and can make changes that may render the computer unstable.
|
||||
|
||||
Standard won’t be able to make these changes. He/she can only change stuff in his/her profile.
|
||||
|
||||
When you enter the full name of the user, the username will automatically be selected for you based on his full name. It’s ok to keep it but you can change it if you like. When you’re done, click Create to create the account.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the account is disabled and will remain so until you change/add a password. To enable the account, click the Account disabled button, then type a new password.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you want to user to automatically logon without typing password, you can choose the drop-down option while setting his/her password to logon automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/daily-ubuntu-tips-adding-user-accounts-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
伸个懒腰-----------------------
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Adding Users To Existing Groups
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
For new users and newbies who are just starting out with Ubuntu, managing users and groups can be challenging especially since the old users and group management tool doesn’t come with Ubuntu anymore. In prior versions of Ubuntu, one could easily manage users and group with the users-admin tool which is part of Gnome system tools.
|
||||
|
||||
That tool no longer come with Ubuntu. Now the only tool that’s available is simplified and only allows you to create, manage and delete user accounts. So, if you need to add or delete users from groups in Ubuntu, you’re going to use the commands terminal or console.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you want to give certain users access to files or increase their access level, the best way to do it is with group permissions. You create a group, then give the group the correct permissions and add users to the group to assume those permissions.
|
||||
|
||||
Since there’s no easy way to manage group permissions in Ubuntu currently, this brief tutorial is going to show you how to do it from the command console. It’s just a one-line command and not too complicated once you understand it.
|
||||
|
||||
To get started, press **Ctrl – Alt – T** on your keyboard to open the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
To view all current groups on Ubuntu, type the command groupmod and (**hit the tab key 3 times**).
|
||||
|
||||
groupmod <HIT TAB 3 TIMES>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
That will list all the current groups on your system. Now to add user to existing groups in Ubuntu, run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo adduser USERNAME GROUPNAME
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you wish to add Richard the sudo group, run the commands below
|
||||
|
||||
sudo adduser richard sudo
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. To verify a user group membership, run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
id richard
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/daily-ubuntu-tips-adding-users-existing-groups/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
[scusjs占坑]Daily Ubuntu Tips – Easiest Way To Access Your Files From Windows
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Whether you’re a new user or someone with deep knowledge working with Ubuntu and Windows, one thing that’s true is using Samba is the best way to share / access Ubuntu files from Windows. It’s also easy to setup and manage using many other third-party tools.
|
||||
|
||||
For new users or newbies who want to learn how to quickly access Ubuntu files from Windows, this brief post is going to show you how. Our goal here is to help new users. We manage to write our tutorials so newbies can read and understand them without too much trouble.
|
||||
|
||||
We’re not going to go into too much details here about what Samba is or how to configure Samba to join a domain and all of that. What we’re going to do is just show you how to install and setup Samba in Ubuntu to access your files from Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to learn all about Samba, I suggest you search Google or Wikipedia. To get started, open your terminal / console in Ubuntu and run the commands below to install Samba and other Samba related tools.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install samba cifs-utils
|
||||
|
||||
The above commands will install Samba and other related tools. In previous versions of Ubuntu, you may have to replace cifs-utils with **smbfs**. But if the top commands work for you, then you’re good.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, using gedit, open the main Samba configuration file and make the following changes. To do that, run the commands below to open Samba config file.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo gedit /etc/samba/smb.conf
|
||||
|
||||
When the file opens, look for the line shown below and uncomment (remove the ; before the text) it. It should be like this:
|
||||
|
||||
security = user
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, scroll down in the file and also uncomment the lines as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
[homes]
|
||||
|
||||
Doing this will allow users to access content in their home directories or folders. For instance, if your uncomment the [homes], user should be able to access their home content by typing the server name followed by their account name.
|
||||
|
||||
\\192.168.0.2\username
|
||||
|
||||
Next, run the commands below to add your account to Samba Database. Doing this allows you to use Samba to access shares.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo smbpasswd -a usernmame
|
||||
|
||||
Replace username with your account name.
|
||||
|
||||
When prompted to create a password, create and confirm it. Finally, restart Samba or restart your computer.
|
||||
|
||||
To access your files from Windows, go **Start –> Run** and type the line below. Or open Explorer and type it as in the image below.
|
||||
|
||||
\\ubuntu_machine_IP\username
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tips-easiest-way-access-files-windows/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
[scusjs占坑]Daily Ubuntu Tips – How To Install Google Chrome Browser
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
For new users who are just starting out with Ubuntu and want to install Google Chrome browser, here’s the quickest way to do it. There are many ways to install Google Chrome in Ubuntu. Some prefer going directly to [Google Chrome download page][1] and getting the **deb** installer.
|
||||
|
||||
Others prefer to install it via PPA from the Chromium build. I prefer downloading it via the command line using **wget** command and installing it. The command line method is the quickest and this is what this post is about to show you.
|
||||
|
||||
As you may already know, Google Chrome has gone from nothing to one of the most popular web browsers. In fact, it’s my favorite web browser. I started with Internet Explorer, then moved to Firefox and I’ve finally switched to Google Chrome.
|
||||
|
||||
I am not telling you to switch, but if you want Chrome in Ubuntu, then go and get it.
|
||||
|
||||
To get started with Chrome, you have few options. First you can use Firefox and go to [Chrome download page][1] and download a copy there. If you’re not comfortable with using the command line, you may want to use this method.
|
||||
|
||||
For users who are comfortable using the command line console, use the commands below to download Google Chrome.
|
||||
|
||||
cd /tmp
|
||||
|
||||
For the **32-bit** version of Google Chrome, use the link below.
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_i386.deb
|
||||
|
||||
The 64-bit version can be downloaded using this link.
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://dl.google.com/linux/direct/google-chrome-stable_current_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
After downloading it, run the commands below to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i google-chrome*; sudo apt-get -f install
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it! After installing, go to Unity Dash and search for Chrome and launch it.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tips-install-google-chrome-browser/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://www.google.com/intl/en/chrome/browser/#eula
|
||||
53
sources/Daily Ubuntu Tips – Protect Your Home Folders.md
Normal file
53
sources/Daily Ubuntu Tips – Protect Your Home Folders.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Protect Your Home Folders
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Few days ago we [showed][1] you how to change your home folder in Ubuntu so that only authorized users may see your content. We said that the adduser utility creates user’s directories in such a way that make them world readable. This means that any all users who have accounts on the machine will be able to browse and view content in your home directory by default,
|
||||
|
||||
To read our previous post on this, [please click here][2]. In that post, we also showed you which permission settings to apply to your home folder to that it isn’t browseable by anyone.
|
||||
|
||||
In this blog post, you can accomplish the same by encrypting your home folder. When encrypt your home folder, unauthorized users will also not be able to browse or access your home directories.
|
||||
|
||||
Encrypting your home folder may not be suitable for everyone in every environment so make sure you’re absolutely certain that you want to use this feature in Ubuntu before actually using it.
|
||||
|
||||
To get started encrypting your home directory, logon to Ubuntu and run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ecryptfs-utils
|
||||
|
||||
Since your can’t be logged-in while encrypting your exiting home folder, you must create a temporary account and login with it. Then run the commands below to encrypt your home folder. Replace USERNAME with your account name.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ecryptfs-migrate-home -u USERNAME
|
||||
|
||||
When you login as the temporary user, run the **su** command plus your username to run commands as you, since your account has root / admin rights. You’ll be prompted for your password.
|
||||
|
||||
su USERNAME
|
||||
|
||||
Replace USERNAME with the username of the account that has root / admin rights.
|
||||
|
||||
After that, encrypt your home folder by running the **ecryptfs-migrate-home –u USERNAME** command.
|
||||
|
||||
To create a user in Ubuntu, run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo adduser USERNAME
|
||||
|
||||
To delete user in Ubuntu, run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo deluser USERNAME
|
||||
|
||||
When you login, you’ll see the screen shot below giving you more information about your encrypted home folder.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To create future users with encrypted home directory, run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
adduser –encrypt-home USERNAME
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/daily-ubuntu-tips-protect-home-folders/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/daily-ubuntu-tipsprevent-users-browsing-folders/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/daily-ubuntu-tipsprevent-users-browsing-folders/
|
||||
37
sources/Daily Ubuntu Tips – Resize Ubuntu Unity Launcher.md
Normal file
37
sources/Daily Ubuntu Tips – Resize Ubuntu Unity Launcher.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Resize Ubuntu Unity Launcher
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Here’s another tip for users who are new to Ubuntu. This series aims to help new users to Ubuntu configure and manage their computer easily. It’s not geared towards Ubuntu power users or pros, rather users who are just starting with Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu launcher is a key part of Ubuntu Unity Desktop. The launcher is the vertical bar with icons that sits on the left hand side of your screen when you logon. It allows you to easily open or launch programs from your desktop. It also provides quick access to applications, workspaces, removable devices and the trash bin.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the launch size is set to 48 even for smaller screens. If you want to increase or decrease the size of the launcher, then continue below to learn how.
|
||||
|
||||
There are many reasons why you’d want to adjust Unity launcher. One good reason is to resize it to fit on smaller screens. If your screen is small and the default size isn’t suitable, then you may want to change it.
|
||||
|
||||
If the default size of the icons are too small and want to increase it, then adjust the launcher to increase the icons so they’re easy to click.
|
||||
|
||||
To get started, click the gear button at the top right of the menu bar as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next, select Appearance
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Finally, use the slider to adjust (increase / decrease) the launcher icon size.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The changes should apply automatically. Remember, if you want to stick with the default, move it back to 48.
|
||||
|
||||
This is another Ubuntu tip for new users. Keep coming back for more tips on Ubuntu. If you’re power users and wish to contribute, please leave a comment below
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/daily-ubuntu-tips-resize-ubuntu-unity-launcher/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Restore Your Machine To A Previous State
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
When you compare Windows and Ubuntu, you’ll see that Windows has many advantages over Ubuntu and maybe Ubuntu has few over Windows as well. But one feature that stands out is the ability to restore your machine to a previous state. Windows has had this feature going back to Windows XP and worked great at times and can save your a lot of time when you need to fix issues.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu on the other hand don’t have it. You can’t just restore your machine to a previous state in Ubuntu. You may be able to restore individual files and folders but not the entire machine like what Windows does.
|
||||
|
||||
Well, thanks to [TimeShift][1], you may just be able to restore your entire Ubuntu machine to a previous state like Windows. TimeShift may not give you all the benefits that you get in Windows, but it’s a step closer.
|
||||
|
||||
TimeShift is a open source application that provides the same function as Windows Restore in Windows or Time Machine in Mac OS X. It takes snapshots of you system at scheduled time that can be restore in the event you need to undo changes that were made after a snapshot.
|
||||
|
||||
To install TimeShift in Ubuntu, run the command below to add its PPA archive.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-add-repository -y ppa:teejee2008/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
Next, run the commands below to update your system as well as install TimeShift.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install timeshift
|
||||
|
||||
After installing it, go to Unity Dash and search for TimeShift. Next launch it and set your preferred settings. When it first launch it may take few minutes scanning your machine for available space and files to backup.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you like the default settings, you can keep. To perform immediate backup, click the Backup button at on the menu. You’ll use the same apps to restore your machine in the event you need to.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tips-restore-machine-previous-state/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Timeszoro](https://github.com/Timeszoro) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://teejeetech.blogspot.com/2013/10/introducing-timeshift.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Understanding The App Menus And Buttons
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu is a decent operating system. It can do almost anything a modern OS can do and sometimes, even better. If you’re new to Ubuntu, there are some things you won’t know right away. Things that are common to power users may not be so common to you and this series called ‘Daily Ubuntu Tips’ is here to help you, the new users learn how to configure and manage Ubuntu easily.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu comes with a menu bar. The main menu bar is the dark strip at the top of your screen which contains the status menu or indicator with (Date/Time, volume button), the App menus and Windows management buttons.
|
||||
|
||||
Windows management buttons are at the top left corner of the main menu (dark strip). When you open an application, the buttons on the main menu at the top left corner with close, minimize, maximize and restore is called Windows management buttons.
|
||||
|
||||
The App menus is located at the right of the Windows management button. It shows application menus when they are opened.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Ubuntu hides the app menus and windows management buttons unless you move your mouse to the left corner, you wouldn’t be able to see them. If you open an application and can’t find the menu, just move your mouse to the left corner of your screen to show it.
|
||||
|
||||
If this is confusing and you want to disable the app menus so that each application can have its own menu, then continue below.
|
||||
|
||||
To uninstall or remove the app menus, run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get autoremove indicator-appmenu
|
||||
|
||||
Running the command above will remove the app menu also known as global-menu. Now for the change to take effect, log out and log back in.
|
||||
|
||||
Now when you open applications in Ubuntu, each application will show its own menus instead of hiding it on the global menu or main menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
That’s it! To go back to what it was, run the commands below
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install indicator-appmenu
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/daily-ubuntu-tips-understanding-app-menus-buttons/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Upgrade To Ubuntu 13.10 Saucy Salamander
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In a few weeks, Ubuntu 13.10 will be released and many folks will want to upgrade to the latest version. For new users who want to upgrade, this brief post will show you how to easily do it from Ubuntu 13.04 if you haven’t already done so.
|
||||
|
||||
There are many ways to upgrade to the latest version of Ubuntu. Some prefer upgrading via a DVD disc while others with stable Internet connections prefer to upgrade directly from the Internet. The Internet option is the easiest and fastest because you don’t have to wait for the DVD disc to arrive before upgrading.
|
||||
|
||||
If you don’t have good Internet bandwidth, please upgrade from a DVD disc. This post is going to show you how to upgrade via the Internet only.
|
||||
|
||||
For those with good Internet connections, please update your current version by running the commands below. The commands below install all pending updates as well as remove packages and kernel headers that are no longer needed. Leaving these may cause issues with upgrading.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade && sudo apt-get autoremove
|
||||
|
||||
After running the above commands and finish updating all pending packages, restart your computer. When you log back on, press the **Alt + F2** keys on your keyboard. When the run commands box opens, type the below command and press Enter.
|
||||
|
||||
update-manager -d
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Software Updater windows show open. From there, hit the upgrade button to begin upgrading.
|
||||
|
||||
Before upgrading, please make sure to disable or remove all external PPA repositories from your machine. Also backup your computer before upgrading.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once you’re done upgrading restart your computer and verify if everything is running ok.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tips-upgrade-ubuntu-13-10-saucy-salamander/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Webcam Support In Ubuntu Via Cheese
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
For new users who are just starting with Ubuntu, here’s some information that may help you if you want to use webcam in Ubuntu. You see, Ubuntu aims to support the vast majority of webcam right out of the box. Most webcam manufacturers don’t provide drivers for for Linux systems, including Ubuntu. So Linux developers must do the hard work by enabling support for most webcam devices in the Linux Kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
Webcam support for Linux is provided by the Linux UVC Project’s [UVC][1] driver. The aim of this project is to provide a universal USB support for webcam in the same way a general USB driver handles USB devices like thumb drives, external USB devices and others.
|
||||
|
||||
The vast majority of USB webcam out there should work with Linux systems, including Ubuntu with the support of the Linux UVC project driver. If you want to purchase a webcam for your Ubuntu computer, but want to make sure it’s supported, [check out the UVC supported webcam list][2].
|
||||
|
||||
Webcam on the list above support Linux machines easily. So, before purchasing webcam for your machine check out the list and find the model you like and purchase it.
|
||||
|
||||
After purchasing a model that supports Linux systems, you’ll need an application in to display or view your videos. Currently the most popular webcam application for Ubuntu is Cheese. Cheese allows you to access your webcam and display the video easily.
|
||||
|
||||
To install Cheese, run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install cheese
|
||||
|
||||
After installing it, open it via Unity Dash and launch it. If the webcam device is already attached, Cheese should begin showing the video from the webcam.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a laptop equipped with webcam, chances are it should work because support for generic USB webcam is common with Ubuntu. All you have to do is install Cheese and enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
If you can’t get your current webcam to work in Ubuntu, you may have to purchase a model that works.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/daily-ubuntu-tips-webcam-support-ubuntu-via-cheese/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://help.ubuntu.com/community/UVC
|
||||
[2]:http://www.ideasonboard.org/uvc/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips–Change The Logon Screen Background
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Here’s a simple tip that shows you how to change Ubuntu logon screen background with custom images. Ubuntu logon screen is ok and maybe better than most Linux distributions, but if you want to show custom images like ones that remind you of special places and things, you may be able to change it using the steps below.
|
||||
|
||||
There are many ways to do this and this post is just one of many. The method below uses dconf-editor and lightdm user to accomplish to get the same results. To do it, change to the root user and give lightdm user access to the x-server. Next using lightdm user credentials, run dconf-editor and make the change.
|
||||
|
||||
After setting the custom logon image and restarting, you should see the picture everytime you start your machine. If image is one you love and brings back a log of memories, you should be delighted everytime you startup Ubuntu to logon.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial assumes you already have dconf-editor installed on your machine. If not, run the commands below to install dconf-editor.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install dconf-editor
|
||||
|
||||
Next, choose the image you wish to use as your logon image. Then take notes of the location, including the image name. Next, run the commands below to change to the root user.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo –i
|
||||
|
||||
Next, run the commands below to give lightdm user access to the X-Server. Lightdm is the service that manages the logon background so if you need to make changes to the logon screen, it should be done as lightdm user.
|
||||
|
||||
xhost +SI:localuser:lightdm
|
||||
|
||||
Next, change to lightdm user by running the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
su lightdm -s /bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
Then run the commands below to start dconf-editor.
|
||||
|
||||
dconf-editor
|
||||
|
||||
When the tool opens, browse to **com –> canonical –> unity-greeter**. Then change the background value to the custom image. You may also want to disable draw-grid.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Restart your computer and enjoy your~
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/daily-ubuntu-tipschange-logon-screen-background/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
47
sources/Daily Ubuntu Tips–Knowing About The Root Account.md
Normal file
47
sources/Daily Ubuntu Tips–Knowing About The Root Account.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips–Knowing About The Root Account
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
For new users who just starting with Ubuntu and wanting to know about the root account, here’s a brief post that gives you a little insight about the root account and how / why to use it. You see, every Ubuntu edition comes with a root account.
|
||||
|
||||
The root account is also known as the administrator account. Think of the root account as an account with god-like rights. It can delete any file, any folder and make any change to the system. The power of the root account is limitless.
|
||||
|
||||
Because the root account is so powerful, it is automatically created with a password value with no possible encrypted match on the system, which makes it unusable to sign on with. So instead of directly logging on with the root account, users are encouraged to use the sudo command.
|
||||
|
||||
The sudo command allows authorized users to temporary elevate their privileges using their own password without knowing the root password or using the root account.
|
||||
|
||||
If you still want to enable and logon with the root account for other unknown reasons, simply give it a password. This will enable the root account.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo passwd
|
||||
|
||||
The commands above will enable the root account but to sign on as the root user, you must enable manual logon since it’s now been disabled in Ubuntu. The manual logon option allows for users to type their logon name as well as the password for the account instead of just selecting an account from the logon screen.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable manual logon with **Ubuntu 13.10**, open the config file by running the commands below
|
||||
|
||||
sudo gedit /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf.d/50-unity-greeter.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Then add the line below as shown in the image.
|
||||
|
||||
greeter-show-manual-login=true
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and restart your computer.
|
||||
|
||||
For earlier versions of Ubuntu, you may find this config file in a different location under **/etc/lightdm**. It may be called **lightdm.conf**.
|
||||
|
||||
On the logon screen, you can then type the root username with password to sign on.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you want to lock / disable the root account, run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo passwd -l root
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/daily-ubuntu-tipsknowing-root-account/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linchenguang翻译中
|
||||
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips–Things To Do After Installing Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Many users from Windows find themselves stuck when starting out with Ubuntu. It’s a completely different from Windows and getting confortable with it may not be the easiest thing at first. Ubuntu is way different from Windows. The commands, the layout of the file system and application names are all foreign to many. But heck, we’re here to help.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re coming from Windows or Mac OS X and want to learn Ubuntu, you’re in the right place. We try to help new users get started with Ubuntu. Our slogan here is “**Tutorials for newbies**”, which is rightly so.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of our tutorials are not for pros. They are for people who are just starting out with Windows and Ubuntu. So, for all your Ubuntu needs, keep coming back.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, back to the topic. One of our readers asked us this question few days ago.
|
||||
|
||||
> What should you do first after installing Ubuntu?
|
||||
|
||||
Simple. When you first install Ubuntu, there are many things you may want to get started with. But the most important thing is to get it right. Don’t worry about the difficult things, those you’ll learn later.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the first few things you’ll want do after installing Ubuntu. There might be more, but these are important.
|
||||
|
||||
- Update your system – The very first thing is to update your system. Updating allows you to install newer packages and install fixes for other programs. The commands below will show you how to properly update your system when using Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade && sudo apt-get autoremove
|
||||
|
||||
- Another thing to do right after installing Ubuntu is to run the below command. This command helps you install codecs or packages that were left out of Ubuntu for legal reasons. Ubuntu comes without these important programs and they are very useful. Without them you may not be able to listen to music, watch movies and do other things. So, if you installed Ubuntu and can’t play some DVDs or listen to music CDs, then run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras
|
||||
|
||||
The commands above are not the only commands you’ll run in Ubuntu, but they are few of the first you should run after installing Ubuntu. I hope this helps.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tipsthings-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
|
||||
【SCUSJS翻译中】Debian 7.2 "Wheezy" Officially Released
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The Debian project announced the immediate availability for download of the second maintenance release of the Debian 7 Linux operating system.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Debian 7.2 is just a maintenance update, but it does feature a wide array of updates and fixes for the current stable branch and a lot of packages have been upgraded.
|
||||
|
||||
“Please note that this update does not constitute a new version of Debian 7 but only updates some of the packages included. There is no need to throw away older wheezy CDs or DVDs but only to update via an up-to-date Debian mirror after an installation, to cause any out of date packages to be updated,” reads the official announcement.
|
||||
|
||||
This means that users who already have a Debian 7.0 or 7.1 installation won't have to reinstall the system all over again. They just need to perform a regular update, as only a small number of packages will be downloaded from security.debian.org.
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the complete changelog in the official [announcement][1].
|
||||
|
||||
**Debian GNU/Linux 7.1.0: Free Download**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Debian GNU/Linux 7.1.0 (ISO) 32-bit[iso]][2] [3.70 GB]
|
||||
- [Debian GNU/Linux 7.1.0 (ISO) 64-bit[iso]][3] [3.80 GB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Debian-7-2-quot-Wheezy-quot-Officially-Released-390694.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.debian.org/News/2013/20131012
|
||||
[2]:http://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/7.1.0/i386/iso-dvd/debian-7.1.0-i386-DVD-1.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/7.1.0/amd64/iso-dvd/debian-7.1.0-amd64-DVD-1.iso
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
crowner翻译
|
||||
FreeBSD 10.0 Beta 1 Available for Download and Testing
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**FreeBSD 10.0 Beta 1, an operating system for x86, ARM, IA-64, PowerPC, PC-98, and UltraSPARC architectures, has been released and it's now available for download and testing.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The FreeBSD developers are moving with an incredible speed and are releasing one version after another. The new Beta has arrived after no less than five Alpha versions, but not without any problems.
|
||||
|
||||
“Due to a last minute problem found in the 10.0-BETA1 freebsd-update(8) builds, freebsd-update(8) is NOT supported for 10.0-BETA1 upgrades. Please do not use freebsd-update(8) to upgrade to 10.0-BETA1. Please be aware that cvsup and CVS are not supported methods of updating the src/ tree,” reads the official [announcement][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Also, according to the developers, the ports.txz distribution hasn't been included in the 10.0 Beta 1 release, however, it is expected to be included with disc1.iso for subsequent builds during the release cycle.
|
||||
|
||||
Highlights of FreeBSD 10.0 Beta 1:
|
||||
|
||||
- freebsd-version, which is intended to be used as an auditing tool, has been implemented. This is a very important tool if you want to determine the userland patch level when it differs from what 'uname -r' reports;
|
||||
- The ZFS lzjb decompress performance has been improved;
|
||||
- Two new MIPS CPU families, mips24k and mips74k, have been added;
|
||||
- The "jail_<jname>_*" rc.conf(5) variables for per-jail configuration are automatically converted to /var/run/jail.<jname>.conf before the jail(8) utility is invoked, so the new jail.conf(5) syntax is used;
|
||||
- Most of the ATF tools and the _atf user have been removed;
|
||||
|
||||
Users have been encouraged to test the distribution and report any problems they find. The official [changelog][1] comes with a complete list of fixes and modifications. Download FreeBSD 10.0 Beta 1 right now from Softpedia.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember that this is a development release and it should NOT be installed on production machines. It is intended to be used for testing purposes only.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/FreeBSD-10-0-Beta-1-Available-for-Download-and-Testing-391246.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lists.freebsd.org/pipermail/freebsd-current/2013-October/045524.html
|
||||
20
sources/GCC 4.8.2 Compiler Brings 70+ Bug Fixes.md
Normal file
20
sources/GCC 4.8.2 Compiler Brings 70+ Bug Fixes.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
crowner翻译
|
||||
GCC 4.8.2 Compiler Brings 70+ Bug Fixes
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Jakub Jelinek of Red Hat released GNU Compiler Collection 4.8.2 this morning.
|
||||
|
||||
GCC 4.8.2 is the latest point release in the stable [GCC 4.8][1] series while all major new developments are centered around [GCC 4.9][2] that should be out in H1'2014.
|
||||
|
||||
GCC 4.8.2 corrects over 70 bugs compared to the 4.8.1 release from late May. More details on the GCC 4.8.2 compiler release can be found from the [mailing list announcement][3].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTQ4NzA
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=GCC+4.8
|
||||
[2]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=GCC+4.9
|
||||
[3]:http://gcc.gnu.org/ml/gcc/2013-10/msg00168.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
GNOME Control Center 3.10.1 Released with Multiple Improvements
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**GNOME Control Center, GNOME's main interface for configuration of various aspects of your desktop, is now at version 3.10.1.**
|
||||
|
||||
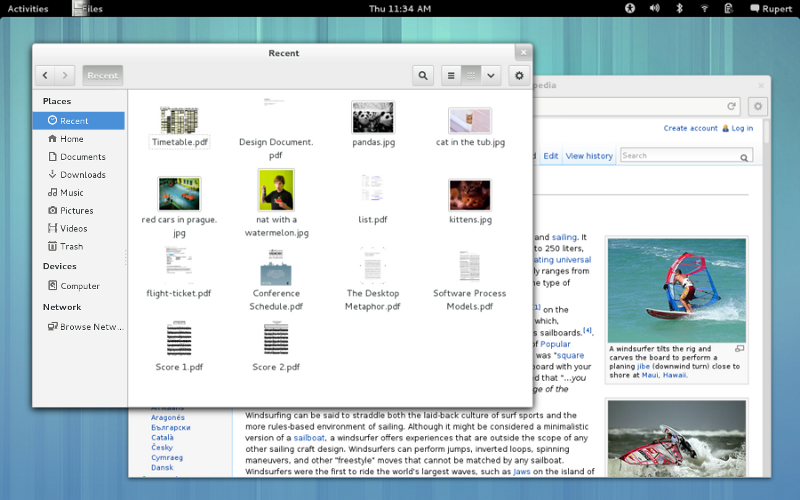
|
||||
|
||||
The Gnome Control Center allows users to configure different parts of their system using a vast collection of tools.
|
||||
|
||||
**Highlights of GNOME Control Center 3.10.1:**
|
||||
|
||||
- Several memory leaks have been corrected;
|
||||
- A consistent set of permissions are now used when creating directories;
|
||||
- The mouse speed is no longer reset;
|
||||
- Screen sharing is now approved without the remote control enabled;
|
||||
- Duplicate folders are no longer being selected for media sharing;
|
||||
- When enabling DLNA, also make sure to enable the MediaExport plugin;
|
||||
- The buttons in the “headerbar” have been aligned.
|
||||
|
||||
A complete list of changes, updates, and bug fixes can be found in the official [changelog][1].
|
||||
|
||||
- Download [GNOME Control Center 3.10.1 tar.xz][2][sources] [6.50 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/GNOME-Control-Center-3-10-1-Released-with-Multiple-Improvements-391831.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-control-center/3.10/gnome-control-center-3.10.1.news
|
||||
[2]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-control-center/3.10/gnome-control-center-3.10.1.tar.xz
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
GNOME Software 3.10.1 Fixes Bugs and Adds New Features
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The GNOME Project has announced last evening, October 14, that the first maintenance release for the recently introduced GNOME Software application for the GNOME 3.10 desktop environment is available for download/upgrade.**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME Software 3.10.1 is a maintenance release that mostly fixes bugs reported by users who had the chance to test this new application, which was originally introduced with the release of the GNOME 3.10 desktop environment.
|
||||
|
||||
However, the new release of GNOME Software also introduces some new features, among which we can mention a loading icon for empty tiles, support for the new 16:9 screenshots format, support for per-repo icon directories, support the 'X-AppInstall-Package' extension in desktop files, and the IBus frameworks installed by default are marked as system apps.
|
||||
|
||||
The hardcoded ratings and screenshot plugins were removed from this version of GNOME Software, with the mention that they will not be available until the release of the GNOME 3.12 desktop environment, next year.
|
||||
|
||||
Among the bugs fixed in GNOME Software 3.10.1, we can mention re-implementation of the hover state to feature tile, strings in the AppData file are now translatable, memory corruption is now prevented when doing dedupe() more than once, notify::state is no longer transmitted from a thread, and the "Remove" option is now displayed for installed apps that are updatable.
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover, a critical error has been fixed in gs_string_replace(), some small memory leaks were fixed, a refcounting error, which could cause a crash, has been fixed, the application widget will no longer be removed twice when it changes state, and local applications have names, icons and comments.
|
||||
|
||||
Last but not least, the following translations have been updated in this release: Indonesian, Latvian, Brazilian Portuguese, Czech, Hungarian, Italian, Polish, Slovenian, Spanish, and Traditional Chinese. More details can be found in the official raw [changelog][1].
|
||||
|
||||
- [GNOME 3.10.1 tar.xz][2][sources] [1.40 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/GNOME-Software-3-10-1-Fixes-Bugs-and-Adds-New-Features-391284.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-software/3.10/gnome-software-3.10.1.news
|
||||
[2]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-software/3.10/gnome-software-3.10.1.tar.xz
|
||||
19
sources/GNOME To Work On Wayland Accessibility Support.md
Normal file
19
sources/GNOME To Work On Wayland Accessibility Support.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
GNOME To Work On Wayland Accessibility Support
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Now that GNOME 3.10 has shipped and with it comes initial native Wayland support, GNOME developers are beginning to focus on the GNOME 3.12 release cycle and working on some of the open work items in Wayland enablement.
|
||||
|
||||
Matthias Clasen of Red Hat has written to the Wayland developers about improving the accessibility support. In the GNOME Wayland porting, among the accessibility items that will likely need to be implemented within the GNOME Shell Mutter Wayland compositor are input tweaks (slow keys / bounce keys), zoom and color adjustments, text protocol support for on-screen keyboards and the like, and other improvements for properly handling the on-screen keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
In terms of why Clasen is bringing this GNOME work up with Wayland developers, "All of these features violate the careful separation between clients that Wayland maintains, so that probably calls for some privileged interface for ATs. I would appreciate feedback and discussion on this. Has anybody else thought about these problems already?"
|
||||
|
||||
The new mailing list thread can be found on [Wayland-devel][1].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTQ4NzI
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lists.freedesktop.org/archives/wayland-devel/2013-October/011487.html
|
||||
32
sources/Install Or Upgrade VMware Tools In Ubuntu.md
Normal file
32
sources/Install Or Upgrade VMware Tools In Ubuntu.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
Install Or Upgrade VMware Tools In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Few days ago, VMware Workstation 10 was released. VMware Workstation is a virtualization software that lets you run multiple operating systems using a single host machine. With this software, you can run guest machines such as Windows XP, Vista 7 and 8 though 8.1. You can also run Linux operating systems, including Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Because we use VMware Workstation to run some guest machines, we had to upgrade VMware tools on all of them. It is very important that you install VMware Tools in the guest operating system. That’s because the tool provides required support for shared folders, drag and drop operations, better graphic and improved performance.
|
||||
|
||||
This brief tutorial is going to show you what we did to install and upgrade all our guest machines that run under VMware Workstation. Other benefits that the tool provides is synchronization of time between the guest machine and the host, grabbing and releasing of the mouse, coping and pasting between the guest and hose machines and more.
|
||||
|
||||
To get started, open VMware Workstation and select the Ubuntu guest machine and start it or turn it on. Next, click **VM –> Install VMware Tools…** from the host menu.
|
||||
|
||||
For you information, I am running Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) but this method may work with previous versions.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A virtual CD/DVD Rom should be mounted with VMware Tools archive. Next, run the commands below to extract the package to the temp directory.
|
||||
|
||||
tar -xvf /media/$USER/"VMware Tools"/VMwareTools*.gz -C /tmp
|
||||
|
||||
Next, run the below commands to begin the installation.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo /tmp/vmware-tools-distrib/vmware-install.pl
|
||||
|
||||
During the installation, just press the Enter key to accept the defaults when prompted. The tool will install itself along with any required packages.
|
||||
|
||||
When it’s done, restart your computer and begin enjoying your machine.
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/install-upgrade-vmware-tools-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
|
||||
【SCUSJS翻译中】Install Rhythmbox 3.0 In Ubuntu 13.10 Or 13.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Rhythmbox 3.0 was released more than a month ago, bringing an improved user interface, Python 3 support for the plugins and more. Unfortunately, the new version didn't make it into Ubuntu 13.10, but there's a PPA you can use to install it (also available for Ubuntu 13.04).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Changes in Rhythmox 3.0:
|
||||
|
||||
- the plugins now use Python 3;
|
||||
- new task progress display below the track list (used for various things including track transfers and import jobs);
|
||||
- support for composer tags;
|
||||
- restyled playback controls;
|
||||
- restyled source list using symbolic icons;
|
||||
- better introspection of everything;
|
||||
- separate CBR and VBR encoding styles with different sets of exposed properties;
|
||||
- playlist settings (browser visibility etc.) saved in playlists.xml;
|
||||
- better use of RTL icons where appropriate;
|
||||
- fixed IM status and ReplayGain plugins;
|
||||
- many other bug fixes.
|
||||
|
||||
A complete Rhythmbox 3.0 changelog can be found [HERE][1].
|
||||
|
||||
## Install Rhythmbox 3.0 in Ubuntu 13.10 or 13.04 ##
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Rhythmbox 3.0 in Ubuntu 13.10 (Unity)*
|
||||
|
||||
Because Rhythmbox 3.0 uses Python3 for plugins instead of Python 2, **none of the plugins available in the Rhythmbox [third-party plugins PPA][2] will work**. You can get some of them to work by installing them manually (including the Equalizer plugin and the cool **[CoverArt browser][3]**) - for more info, see **[THIS][4]** article.
|
||||
|
||||
Rhythmbox 3.0 is available in an unofficial PPA maintained by Jacob Zimmermann, for Ubuntu 13.10 and 13.04 (and derivatives). **Add the PPA and install/upgrade Rhythmbox 3.0 using the following commands**:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:jacob/media
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install rhythmbox
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.webupd8.org/2013/10/install-rhythmbox-30-in-ubuntu-1310-or.html
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/rhythmbox/3.0/rhythmbox-3.0.news
|
||||
[2]:http://www.webupd8.org/2012/08/rhythmbox-third-party-plugins-ubuntu-ppa.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.webupd8.org/2013/08/rhythmbox-coverart-browser-plugin-gets.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xpressubuntu.wordpress.com/2013/10/06/how-to-install-rhythmbox-3-0-in-saucy/
|
||||
93
sources/Interview with Ding Zhou of Ubuntu Tweak.md
Normal file
93
sources/Interview with Ding Zhou of Ubuntu Tweak.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
Interview with Ding Zhou of Ubuntu Tweak
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Ubuntu tweak][1] is a well known application which allows Ubuntu users to tweak various aspects of their system. The founder of the project, Ding Zhou aka Tualatrix Chou, is talking to us about the nature and the usability of Ubuntu Tweak, the relation with Canonical and the future plans of the project. Enjoy
|
||||
|
||||
**When did you start using linux and at what point did you decide to develop Ubuntu tweak?**
|
||||
|
||||
I started using Linux when I just started my college life at late 2006. I was learning C programming then, a friend recommended that Linux is a great platform to learn programming. So I started my Linux life from the Fedora Core 6. But after just one week I switched to Ubuntu 6.10, because Ubuntu had a better community in China , and also had very good and fast repositories/mirrors. I fall in love with Ubuntu immediately, and switched from Windows in just one week.
|
||||
|
||||
After half years’ both happy and hard time with Ubuntu, I realized that Ubuntu was not so friendly for Chinese people, because after a fresh installation, people had to config the font, input method and many others. So I decided to develop an application to help the newbies to easily config Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
So at July 2007, I started to develop Ubuntu Tweak. At that point, only for Chinese people, but soon I made Ubuntu Tweak be an international application and released its first version at Sep 2007
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu tweak is already a very successful project. Many Ubuntu users use it to tweak various aspects of their system. Tell us a few words about what Ubuntu Tweak can do.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Tweak can be used to toggle the desktop icon display, set the fonts, enable/disable the user switch, logo.
|
||||
|
||||
In the latest version of Ubuntu Tweak (0.6), you can also use it to tweak your Unity desktop.ut and shutdown functions.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use Ubuntu Tweak to cleanup system cruft to free space and make system clean.
|
||||
|
||||
**Canonical decides not to include Ubuntu Tweak in their distro by default. What does that mean? Is there some kind of risk for inexperienced users who want to tweak their system using your application?**
|
||||
|
||||
That’s right. Because in the previous version of Ubuntu Tweak, it provided a feature to enable the popular PPA, I wasn’t able to ensure all the PPA were safe, so Ubuntu Tweak had some security risks.
|
||||
|
||||
As you see, Source Center has been removed since 0.6. But please don’t mix the “include default by Ubuntu” and “put into the repository”, Ubuntu Tweak first should be put into the universal repository, then can be included by default in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
From the bug reports and user feedback, Ubuntu Tweak has became a lot more stable and easy to use than the old versions.
|
||||
|
||||
**What kind of support or collaboration (if any) you have from/with Canonical and the Ubuntu developers?**
|
||||
|
||||
Of course I received some help from the company, they helped me try to put Ubuntu Tweak into repository. It is still a work in progress.
|
||||
|
||||
I also received a lot of help from community, people help to translate, design, test and report bugs, and some of them even submitted patch for it.
|
||||
|
||||
**How many people are involved in the development of Ubuntu Tweak?**
|
||||
|
||||
If you say “programmer”, I’m the only one. But we have designers: the logo was designed by M.Sharp, Kevin Chou helped to design the mockup UI of Ubuntu Tweak, it became the 0.6. And currently Jeonkwan Chan are helping me polish the UI, it will become 0.7. Anyone can be involved in the development of Ubuntu Tweak, if they like :)
|
||||
|
||||
**When Unity came out on 11.04, a lot of Ubuntu users complained about the lack of configurability. What is your opinion on that, and what are the adaptability-configurability that this particular desktop environment can have?**
|
||||
|
||||
I’d like a desktop to have adaptability-configurability, that’s the advantage of Linux, isn’t it?
|
||||
|
||||
For example, I don’t like the auto-hide feature of Unity Launcher, so I set it to never hide.
|
||||
|
||||
Actually, Unity is configurable, the only thing that Unity is missing (through the ccsm) is that you can’t place Launcher to bottom or right – that’s maybe unfriendly for the left-handedness. Hah, just a joke.
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, Ubuntu 12.04 has already added the hide/show toggle, Launcher size setting in system settings, I think Unity will be more configurable in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
**In general, do you think that the development of the Unity desktop environment was the right decision for Canonical? Was it something inevitable because of the problematic collaboration they had with the Gnome developers?**
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, I think it’s the right decision for Canonical. If you look back three years, when Ubuntu first introduced the Indicator for GNOME Panel, it was a better design than the original GNOME Panel applet. But there’s some problematic collaboration between Canonical and GNOME Developers, so it has never landed in GNOME, until in GNOME 3, the GNOME Shell itself removed the GNOME Panel, and the design of GNOME Shell panel is almost the same as that of the Indicator. If they could share the same API, the desktop Linux world would be better.
|
||||
|
||||
So, between the company, community and GNOME, the different opinions for user interface finally made the Unity desktop out.
|
||||
|
||||
I think it’s a good thing, at least I like Unity more than GNOME Shell right now.
|
||||
|
||||
**Although you are developing an Ubuntu specialized application, I suppose you are using another distro for more advanced users. What is your distro of choice and why?**
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, I had played with Fedora, Arch, OpenSUSE, especially with Gentoo, I had been using it for one year long. It’s my second favourite Linux distribution, because it has one of the most advanced package management systems.
|
||||
|
||||
But now I only use Ubuntu for desktop and server, I also use Mac OS X. I got many design inspiration from it :)
|
||||
|
||||
**Can Ubuntu Tweak, be tweaked or forked or changed a little bit, in order to become useful in other linux distributions like Fedora, or OpenSuse, or Debian? Is the idea of a “Linux Tweak” application that people would choose distro and desktop environment plausible or not?**
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, Ubuntu Tweak can be easily adapted to be used under other distributions. Ubuntu Tweak is modular and very easy to hack.
|
||||
|
||||
In 2008, I released an “Ubuntu Tweak for Fedora”, but finally I gave up the maintenance of this version cause I should keep focus on Ubuntu, and I also don’t have that much energy.
|
||||
|
||||
**So what is the future of Ubuntu Tweak? Maybe Canonical will embrace it making it a default part of their distro, or they could use it to base their own tweaking tool. What do you think and what will be your next steps?**
|
||||
|
||||
Of course the future of Ubuntu Tweak will be bright. Hah.
|
||||
|
||||
I have already started the process of putting Ubuntu Tweak to the Software Center, it would be easier if users can install Ubuntu Tweak from the Software Center.
|
||||
|
||||
Now I’m focusing on developing the 0.7 version, It will be a better polished and well integrated version for Unity desktop than ever before, and it will also introduce some useful new features. I’d like to adapt Ubuntu Tweak to work better under Unity desktop as much as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
I plan to release the new version along with Ubuntu 12.04, hope everyone will like it :)
|
||||
|
||||
And one more thing to tell, I’ve already joined Canonical, in Beijing, and response for OEM things. Although Ubuntu Tweak is still a personal project and I’m not involved in the development of Ubuntu, I will try to move to the development team when possible :)
|
||||
|
||||
**That was great! Thanks Tualatrix.**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/interview-with-ding-zhou-of-ubuntu-tweak/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ubuntu-tweak.com/
|
||||
113
sources/KDE vs GNOME- Settings, Apps, Widgets.md
Normal file
113
sources/KDE vs GNOME- Settings, Apps, Widgets.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
KDE vs GNOME: Settings, Apps, Widgets
|
||||
=====================================
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes to desktop environments, choosing the one that's right for you can be a deeply personal matter. In this article, I'll look into the differences between two of the most popular Linux desktop environments – Gnome and KDE. I’ll explore what each desktop environment offers, comparing their strengths and weaknesses.
|
||||
|
||||
###Initial impressions
|
||||
|
||||
Upon first encountering the desktop, one can argue that KDE looks more polished than Gnome, and offers a more tech-friendly appearance. Additionally, if you are used to a Windows environment, KDE will feel much more familiar, thanks to the menu and button layout at the bottom of your screen. You can easily locate the K menu, launch programs and find documents with just a few clicks of your mouse.
|
||||
|
||||
Another important and familiar benefit with KDE is the easy to use minimize and close buttons with each open document, picture or application. To someone coming from another platform, features this basic might be taken for granted. But considering desktops like Gnome don't offer a true minimize option any longer, it's worth giving KDE props here.
|
||||
|
||||
Loading up Gnome 3 for the first time, the desktop might be perceived as a very alien experience if you're coming from another platform. Like classic Gnome, your access to docs and tools are not located at the bottom of your screen. Even stranger for some newbies, the method for closing open windows is – to be kind – "different." In defense of Gnome 3, however, I've found it to be quite a pleasant experience once you get used to this new way of doing things. And the new users I know who have tested Gnome 3 generally felt the same way.
|
||||
|
||||
###Widgets and extensions
|
||||
|
||||
The divide between the two desktop environments continues to broaden as we dive into the extensions and widgets provided for Gnome and KDE. While both desktops provide additions you can run to further enhance your desktop experience, the lines between them become different in how the desktops handle extended functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
KDE takes an interesting approach in that you can group widgets into what are called "Activities." The idea is you can have one Activity with a set number of desktop widgets, that help with specific work-flows.
|
||||
|
||||
By contrast, Gnome defines activities with a different approach. Instead of being widget-centric, Gnome makes its Activities more task- and application-based. For example, if I was using multiple apps, switching to the Gnome Activities overview allows you to gain a visualization and immediate access to each task.
|
||||
|
||||
###Settings for your desktop
|
||||
|
||||
While Gnome has gotten better about providing adequate settings controls from a GUI, KDE remains the reigning king in this space.
|
||||
|
||||
With KDE, you can find settings to control nearly every aspect of your desktop experience. Some Linux distributions, such as [OpenSUSE][1], go ever further by tightly integrating their own tools ([YaST][2]) into the KDE settings experience.
|
||||
|
||||
With the updates to the Gnome desktop since Gnome 3, I've found the biggest areas where I see KDE offering greater functionality is with ease of access to settings. Gnome tends to put application specific settings into an easy to find area of each application.
|
||||
|
||||
But KDE tends to offer greater granular control with their applications. One of my favorite examples is [Kontact][3] vs [Evolution][4]. Both are powerful PIMs for Gnome and KDE. But the difference is that Kontact is a suite of applications bundled with a suite of controls for each app, while Evolution is a single application with limited control. The same can be said of [AmaroK][5] vs [Rhythmbox][6], among other desktop-specific titles.
|
||||
|
||||
###File management
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes to finding the right file manager for your desktop, both Gnome and KDE do the work for you by providing their own defaults. [Nautilus][7] is the default file manager for Gnome where KDE, offers up [Dolphin][8] as its main offering.
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes to desktop environments, choosing the one that's right for you can be a deeply personal matter. In this article, I'll look into the differences between two of the most popular Linux desktop environments – Gnome and KDE. I’ll explore what each desktop environment offers, comparing their strengths and weaknesses.
|
||||
|
||||
###Initial impressions
|
||||
|
||||
Upon first encountering the desktop, one can argue that KDE looks more polished than Gnome, and offers a more tech-friendly appearance. Additionally, if you are used to a Windows environment, KDE will feel much more familiar, thanks to the menu and button layout at the bottom of your screen. You can easily locate the K menu, launch programs and find documents with just a few clicks of your mouse.
|
||||
|
||||
Another important and familiar benefit with KDE is the easy to use minimize and close buttons with each open document, picture or application. To someone coming from another platform, features this basic might be taken for granted. But considering desktops like Gnome don't offer a true minimize option any longer, it's worth giving KDE props here.
|
||||
|
||||
Loading up Gnome 3 for the first time, the desktop might be perceived as a very alien experience if you're coming from another platform. Like classic Gnome, your access to docs and tools are not located at the bottom of your screen. Even stranger for some newbies, the method for closing open windows is – to be kind – "different." In defense of Gnome 3, however, I've found it to be quite a pleasant experience once you get used to this new way of doing things. And the new users I know who have tested Gnome 3 generally felt the same way.
|
||||
|
||||
Widgets and extensions
|
||||
|
||||
The divide between the two desktop environments continues to broaden as we dive into the extensions and widgets provided for Gnome and KDE. While both desktops provide additions you can run to further enhance your desktop experience, the lines between them become different in how the desktops handle extended functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
KDE takes an interesting approach in that you can group widgets into what are called "Activities." The idea is you can have one Activity with a set number of desktop widgets, that help with specific work-flows.
|
||||
|
||||
By contrast, Gnome defines activities with a different approach. Instead of being widget-centric, Gnome makes its Activities more task- and application-based. For example, if I was using multiple apps, switching to the Gnome Activities overview allows you to gain a visualization and immediate access to each task.
|
||||
|
||||
Settings for your desktop
|
||||
|
||||
While Gnome has gotten better about providing adequate settings controls from a GUI, KDE remains the reigning king in this space.
|
||||
|
||||
With KDE, you can find settings to control nearly every aspect of your desktop experience. Some Linux distributions, such as OpenSUSE, go ever further by tightly integrating their own tools (YaST) into the KDE settings experience.
|
||||
|
||||
With the updates to the Gnome desktop since Gnome 3, I've found the biggest areas where I see KDE offering greater functionality is with ease of access to settings. Gnome tends to put application specific settings into an easy to find area of each application.
|
||||
|
||||
But KDE tends to offer greater granular control with their applications. One of my favorite examples is Kontact vs Evolution. Both are powerful PIMs for Gnome and KDE. But the difference is that Kontact is a suite of applications bundled with a suite of controls for each app, while Evolution is a single application with limited control. The same can be said of AmaroK vs Rhythmbox, among other desktop-specific titles.
|
||||
|
||||
File management
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes to finding the right file manager for your desktop, both Gnome and KDE do the work for you by providing their own defaults. Nautilus is the default file manager for Gnome where KDE, offers up Dolphin as its main offering.
|
||||
|
||||
Out of the box, I've found Nautilus offers Gnome users a polished, easy to use file management tool that won't overwhelm new Linux users. Flashing over to KDE, however, Dolphin is a highly configurable and not newbie friendly file management solution for those who want tons of control.
|
||||
|
||||
Simply looking at the sidebar for each file manager, you'll notice that Nautilus offers up the most straight forward approach to navigation. KDE's Dolphin, however, goes further with features like dates for files last used, and other related options.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're an advanced Linux user, you'll likely find yourself gravitating to Dolphin as it offers the most options and control. For those of us who simply want to navigate files without tons of "stuff", Nautilus wins in terms of simplicity.
|
||||
|
||||
###Desktop applications
|
||||
|
||||
One area that causes some disagreement among Linux enthusiasts is the claim that one desktop offers better default applications than the other. That said, this is certainly the case with Gnome vs KDE.
|
||||
|
||||
My findings in this area are that in many areas, Gnome wins without even trying that hard. For example: GIMP, Evince, and Pidgin are all applications that are simply less of a headache to rely on than their KDE counterparts. Kmail is another app that, in my opinion, gives new KDE users a bad taste in their mouths. Apps like this are overly complex and in general, abysmal to use.
|
||||
|
||||
On the flip side, there are some worthwhile exceptions in favor of KDE. [Calligra][9] vs [AbiWord][10] is an easy win for KDE, since [LibreOffice][11] isn't "truly" a Gnome specific option. Just because it's often the default suite for many Linux distributions doesn't make it the desktop environment default.
|
||||
|
||||
In the end, one of the wonders of Linux is that you can install GTK or Qt libraries and enjoy the benefits of the apps that best meet with your needs. For myself, I've found the Gnome application defaults to be the clear winner in most instances.
|
||||
|
||||
Final thoughts
|
||||
|
||||
If I ever found myself trapped on an island with only one desktop environment made available to me, it'd have to be Gnome. Even though I enjoy some aspects of KDE more than Gnome, overall I find Gnome is less work to keep up. Too often I’ve found KDE experiencing a messed up configuration or, worse: weird alerts claiming my sound card has disappeared. Under Gnome, I experience none of these problems.
|
||||
|
||||
Because I value my time and my sanity, I'll continue to recommend Gnome over KDE; while suggesting some KDE apps when appropriate. To anyone who claims that KDE is easier to use – I'd like to point out that for me, simply learning Gnome's approach to doing things has offered me greater stability in the long run.
|
||||
|
||||
Photo courtesy of [Shutterstock][12].
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/kde-vs-gnome-settings-apps-widgets-2.html
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.opensuse.org/en/
|
||||
[2]:http://en.opensuse.org/YaST_Software_Management
|
||||
[3]:http://userbase.kde.org/Kontact
|
||||
[4]:https://projects.gnome.org/evolution/
|
||||
[5]:http://amarok.kde.org/
|
||||
[6]:https://projects.gnome.org/rhythmbox/
|
||||
[7]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nautilus_%28file_manager%29
|
||||
[8]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dolphin_%28file_manager%29
|
||||
[9]:http://www.calligra-suite.org/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.abisource.com/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.libreoffice.org/
|
||||
[12]:http://www.shutterstock.com/pic-137314787/stock-photo-information-concept-golden-gears-on-digital-background-d-render.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
Kubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) Officially Released
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Following the release of Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander), we are proud to announce the immediate availability for download of Kubuntu 13.10.**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Kubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) is an operating system based on several different technologies, such as KDE Software, Plasma, Linux kernel, Debian, and Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Kubuntu is based on KDE SC 4.11, which comes with a lot of interesting and exciting new features. This distribution could prove to be a good replacement for people who are avoiding Unity.
|
||||
|
||||
**Highlights of Kubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander):**
|
||||
|
||||
- KDE SC has been updated to version 4.11;
|
||||
- Faster Nepomuk indexing has been added, Kontact improvements such as a new theme editor for e-mails have been implemented.
|
||||
- The distribution prepares the ground for future developments using Wayland and Qt 5;
|
||||
- A friendly way to discover and install applications is now available with Muon Discover;
|
||||
- The User Manager is now providing a simpler way to manage the system users. For advanced management of groups or LDAP, users can install kuser;
|
||||
- Wireless Setup is now available right from the installer. Users can now setup WiFi networking from the installer, making it easier to install updates and extra packages during the actual procedure;
|
||||
- Chat application KDE Telepathy has been updated to version 0.6.2 and adds several improved features;
|
||||
- The new Network Manager applet now provides a simpler UI for connecting to a range of network types;
|
||||
- A new About System page has been added in System Settings.
|
||||
|
||||
A complete list of changes and updates can be found in the official [announcement][1].
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Kubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander):**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Kubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit][2][iso] [1 GB]
|
||||
- [Kubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit][3][iso] [1 GB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Kubuntu-13-10-Saucy-Salamander-Officially-Released-392042.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.kubuntu.org/news/kubuntu-13.10
|
||||
[2]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/kubuntu/releases/13.10/release/kubuntu-13.10-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/kubuntu/releases/13.10/release/kubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
47
sources/Kubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) Screenshot Tour.md
Normal file
47
sources/Kubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) Screenshot Tour.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
Kubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) Screenshot Tour
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The new Kubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) is now available for download, so it's time to see how much it has changed from the previous release with the help of a small screenshot tour.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The most important change in Kubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) is the introduction of the new KDE 4.11.2, which comes with a lot of interesting features.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are just a few of the features promised by the developers: faster Nepomuk indexing, Kontact improvements such as a new theme editor for e-mails, and preparations for future developments using Wayland and Qt.
|
||||
|
||||
Keep in mind that this is not an LTS release, which means that the support period for this operating system is just nine months.
|
||||
|
||||
Check out our initial report on the launch for more details about the distribution.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Download Kubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander):**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Kubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit][1][iso] [1 GB]
|
||||
- [Kubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit][2][iso] [1 GB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Kubuntu-13-10-Saucy-Salamander-Screenshot-Tour-392170.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/kubuntu/releases/13.10/release/kubuntu-13.10-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[2]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/kubuntu/releases/13.10/release/kubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
Linux Top 3: RHEL 6.5, Debian 7.2 and EOL for Linux 3.0.x
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Linux 3.0.100 Released**
|
||||
|
||||
Though it might seem like Linux 3.0 was released just yesterday, the truth is that it was [released back in July of 2011][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Since then some 100 milestone update have been released fixing bugs and providing some security updates. The Linux 3.0.x kernel had been selected as a Long Term Support kernel, meaning that it is maintained for up to two years.
|
||||
|
||||
In August of this year, Linux kernel developer, Greg Kroah-Hartman [declared][2] that the 3.10 Linux kernel would be a longterm support release. That release now supersedes the longterm 3.0.x kernel
|
||||
|
||||
"Linux stable kernel 3.0.100 is now released, please move to 3.4.x or 3.10.x as this might be the last release of 3.0.x," Kroah-Hartman wrote on October 13th.
|
||||
|
||||
**Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6.5 Beta**
|
||||
|
||||
Barely a week after Red Hat released Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.10, the Linux vendor is now out with a beta release for its next generation platform.
|
||||
|
||||
RHEL 6.5 beta provides support for the precision timing protocol, as an improvement of the traditional network timing protocol (NTP). Precision Time Protocol (PTP) is important to users who require sub-microsecond time stamping of transactions.
|
||||
|
||||
**Debian 7.2**
|
||||
|
||||
Debian is also out with an update. The Debian 7.2 update is the second since Debian 7.x aka Wheezy was released earlier this year.
|
||||
|
||||
"This update mainly adds corrections for security problems to the stable release, along with a few adjustments for serious problems," The Debian project [stated][3]. "Security advisories were already published separately and are referenced where available. Please note that this update does not constitute a new version of Debian 7 but only updates some of the packages included."
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxplanet.com/news/linux-top-3-rhel-6-5-debian-7-2-and-eol-for-linux-3.html
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.datamation.com/open-source/linux-3.0-debuts-with-xen-integration.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.eweek.com/developer/linux-3.10-goes-long-term-why-it-matters-for-the-enterprise-consumers/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.debian.org/News/2013/20131012
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
Linux Won't Get Aura UI Stack Until Google Chrome 33
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
While Google's Chrome 32 web-browser will feature the Aura UI stack from Chrome OS, the Chrome desktop web-browser on Linux won't get the GPU-accelerated interface until one version later.
|
||||
|
||||
Aura is the UI stack used by Google Chrome OS that can fully take advantage of graphics processors where supported. The only native element/widget is the top-level window while everything else is handled by Chrome and composited by the program itself. Google's goal is to use the same UI stack across Windows, Linux, and Chrome OS (albeit not on OS X or other platforms). While Aura is designed to take advantage of modern GPUs, there is a pure software fallback mode too.
|
||||
|
||||
With Chrome 32, Aura will now be used as the UI stack. Windows 7 and Windows 8 systems will support the GPU acceleration code-path while Windows XP and Vista users will be limited to software-accelerated support. The Aura code-path also determines whether WebGL and Pepper-based Flash is using GPU support too.
|
||||
|
||||
As shared via the [Chromium Google Group][1] last week, the Linux version of Chromium now won't see Aura with GPU acceleration until version 33. In other words, the UI stack should arrive on Linux right around the end of the calendar year.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTQ4NzE
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://groups.google.com/a/chromium.org/forum/#!topic/chromium-dev/UMwGGgP0P9c
|
||||
@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
|
||||
小眼儿占坑!
|
||||
Linux only needs one 'killer' game to explode, says Battlefield director
|
||||
========================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It would only take one "killer" game for the Linux platform to explode its way into mainstream gaming, DICE creative director Lars Gustavsson told Polygon, revealing that the development studio would "strongly" like to get into Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
"We strongly want to get into Linux for a reason," Gustavsson said. "It took Halo for the first Xbox to kick off and go crazy — usually, it takes one killer app or game and then people are more than willing [to adopt it] — it is not hard to get your hands on Linux, for example, it only takes one game that motivates you to go there."
|
||||
|
||||
"I think, even then, customers are getting more and more convenient, so you really need to convince them how can they marry it into their daily lives and make an integral part of their lives," he explained, sharing that the studio has used Linux servers because it was a "superior operating system to do so."
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Valve's recently announced Steam OS and Steam Machines are healthy for the console market, Gustavsson said when asked for his opinion on Valve's recent announcements. He believes the products will open up the market to explore new, and perhaps better, ways of consuming games.
|
||||
|
||||
"Basically for different ways of accessing customers and giving them possibilities of play, I think it is super exciting," he said. "The only thing I know is that from five or ten years from now gaming and especially how you consume it won't look like it does today. I do think with streaming services and new input devices and so on, it wouldn't surprise me if there is less need of hardware and more on demand gaming experience."
|
||||
|
||||
> WELL, WILL AAA TITLES SURVIVE? ARE THEY MAMMOTHS THAT DON'T KNOW THAT THEY ARE DEAD YET?
|
||||
|
||||
"I think, hopefully, competition usually means a better experience for the customer. Sometimes. You know, was the VHS tape better than BetaMax? VHS won," he continued. "So it does not always go in the right direction but overall I think it is healthy with competition. It is truly welcomed, so that we can have better games in the future."
|
||||
|
||||
The director believes that with its recent rise and success, indie game development is in a better position to cater for the Linux video game market despite its limited audience.
|
||||
|
||||
"With indie, for a long time, it seemed that it was only AAA title that will survive and then the explosion came with mobile and indie games," he said. "So I'm really happy to see that has swung back to where people say 'Well, will AAA titles survive? Are they mammoths that don't know that they are dead yet?'
|
||||
|
||||
"So, to me, I think that the possibilities are many and I think indies can build for Linux even though we don't have enormous audience," he said.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
With the impending launch of [Battlefield 4][1], DICE has spoken a lot about how it intends to smooth out the difficult learning curve and high point of entry seen in [Battlefield 3][2], Gustavsson said it hasn't forgotten about the hardcore gamers, rather the opposite: DICE has to continually rein itself in from going "too hardcore" when developing a Battlefield title.
|
||||
|
||||
"To be honest, our problem isn't to not think about the hardcore, rather, there are so many people like me doing Battlefield since '99 or at least 2000 that everyday we need to stop ourselves from going too hardcore, we really have to hold ourselves back," he explained when asked how DICE doesn't lose sight developing for experienced players when chiselling out the new features. "That is the natural gear that we have: the hardcore side. Then we need to remind ourselves that we need to make it for everyone."
|
||||
|
||||
While they have set out to make Battlefield 4 [more accessible][3] for newcomers, DICE also made it better for the veterans, hinting that perhaps some aspects the shooter is even too nuanced for the diehards. For example, Gustavsson mentioned the [new battle test range][4] that players of all skill levels can take advantage of.
|
||||
|
||||
> EVERYDAY WE NEED TO STOP OURSELVES FROM GOING TOO HARDCORE, WE REALLY HAVE TO HOLD OURSELVES BACK.
|
||||
|
||||
"Even though people have been playing Battlefield from the start, they choose not to fly because they don't feel safe," he said. "So it is not about losing sight of the hardcore. If you look at hardcore forums, there are so many times that you see 'I don't how this weapon works or this gadget' and then everyone tells each other. It is beautiful. It is just beautiful. But sometimes you feel that a game should be self explaining, it doesn't have to be more stupid."
|
||||
|
||||
A comparison tool for weapons and attachments has been introduced to help with the above example. "As, even I, who has made the game, had a hard time knowing which attachment did what for what weapon," Gustavsson said.
|
||||
|
||||
To cater for experienced Battlefield fans the game features an overhauled control system, reworked network code to remove latency and upped the number of players, to name a few. Battlefield 4 also introduces the hardcore [perma-death mode Diffuse][5] and a [Field Upgrade system][6] to [encourage][7] players to play together, along with the long-time community-demanded Spectator mode.
|
||||
|
||||
"Which, to be honest, I have been ashamed to going to shows and admitting once again that we don't have spectator mode," he said. "That's why I'm a bit taller and prouder this time around now that we do have it. With the next-generation of consoles, like sharing and broadcasting features, I'm really looking forward to seeing what the community comes up with."
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.polygon.com/2013/10/12/4826190/linux-only-needs-one-killer-game-to-explode-says-battlefield-director
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.polygon.com/game/battlefield-4/10364
|
||||
[2]:http://www.polygon.com/game/battlefield-3/1762
|
||||
[3]:http://www.polygon.com/2013/10/3/4798128/we-should-be-slapped-for-battlefield-3s-unlocks-says-dice-creative
|
||||
[4]:http://www.polygon.com/2013/9/4/4694158/battlefield-4-vehicle-test-range-server-options
|
||||
[5]:http://www.polygon.com/2013/9/26/4775632/battlefield-4s-multiplayer-modes-player-counts-detailed-by-dice
|
||||
[6]:http://www.polygon.com/2013/8/16/4627536/battlefield-4-kit-customization-field-upgrade-system-detailed
|
||||
[7]:http://www.polygon.com/2013/8/9/4607030/battlefield-4-will-encourage-but-never-force-team-play
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
Lubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) Officially Released – Screenshot Tour
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Lubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) has been officially released and it's now available for download.**
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical has announced the release of the final version for its upcoming Ubuntu Linux operating system, including Lubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander).
|
||||
|
||||
There aren't too many differences from the previous update, but the distribution comes with a new version of pcmanfm / libfm (1.1.0) including a built-in search utility, artwork improvements, featuring new wallpapers, community wallpapers, new icons, and quite a few other things.
|
||||
|
||||
The system requirements have remained the same: “A Pentium II or Celeron system with 128 MB of RAM is probably a bottom-line configuration that may yield slow yet usable system with a standard Lubuntu desktop.”
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
More details about this release can be found in the official [announcement][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Download the Lubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander):
|
||||
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit Alternate CD][2][iso] [663 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit Alternate CD][3][iso] [674 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit + Mac Alternate CD][4][iso] [677 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) PowerPC Alternate CD][5][iso] [703 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit Desktop CD][6][iso] [696 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit Desktop CD][7][iso] [702 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) PowerPC Desktop CD][8][iso] [710 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit + Mac Desktop CD][9][iso] [700 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (tar.gz) Armhf + AC100][10][binary] [469 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Lubuntu-13-10-Saucy-Salamander-Officially-Released-Screenshot-Tour-392208.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/SaucySalamander/ReleaseNotes/Lubuntu
|
||||
[2]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-alternate-i386.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-alternate-amd64.iso
|
||||
[4]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-alternate-amd64+mac.iso
|
||||
[5]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-alternate-powerpc.iso
|
||||
[6]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[7]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
[8]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-desktop-powerpc.iso
|
||||
[9]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64+mac.iso
|
||||
[10]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-preinstalled-desktop-armhf+ac100.tar.gz
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,6 @@
|
||||
|
||||
翻译认领Vic020
|
||||
|
||||
Mark Shuttleworth to attend and conduct keynote at OpenStack Summit in Hong Kong, November 5th - 8th 2013
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
By analyzing [Canonical][1], the inquirer is to observe several attributes, among which vision, bold goals and according-to actions, attributes that have gradually positioned Canonical at the top of the computing world, where it is leading a significant portion of innovation spanning across all relevant form factors and computing environments.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
Metal Backup and Recovery Is Now Possible with Debian-Based Clonezilla Live 2.2.0-13
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Clonezilla Live 2.2.0-13, a Linux distribution based on DRBL, Partclone, and udpcast that allows users to do bare metal backup and recovery, is now available for testing.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Clonezilla Live 2.2.0-13][1] is a new development version for this distribution and the developers have chosen to move a little faster with the numbering systems. There are no major differences, but some packages have been updated.
|
||||
|
||||
“The underlying GNU/Linux operating system was upgraded. This release is based on the Debian Sid repository (as of 2013/Oct/14). Package drbl has been updated to 2.5.12-drbl1, and clonezilla has been updated to 3.7.15-drbl1,” reads the announcement.
|
||||
|
||||
The developers also integrated Samba 4.0.10, which isn't exactly the last stable one released, but it's still recently new.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember that this is a development version and it should NOT be installed on production machines. It is intended for testing purposes only.
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Clonezilla Live 2.2.0-13**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Clonezilla LiveCD 2.1.2-53 (ISO) i486 Stable][2][iso] [120 MB]
|
||||
- [Clonezilla LiveCD 2.1.2-53 (ISO) i686 PAE Stable][3][iso] [121 MB]
|
||||
- [Clonezilla LiveCD 2.1.2-53 (ISO) amd64 Stable][4][iso] [123 MB]
|
||||
- [Clonezilla LiveCD 2.2.0-13 (ISO) i486 Testing][5][iso] [134 MB]
|
||||
- [Clonezilla LiveCD 2.2.0-13 (ISO) i686 PAE Testing][6][iso] [135 MB]
|
||||
- [Clonezilla LiveCD 2.2.0-13 (ISO) amd64 Testing][7][iso] [138 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Metal-Backup-and-Recovery-Is-Now-Possible-with-Debian-Based-Clonezilla-Live-2-2-0-13-391374.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://free.nchc.org.tw/clonezilla-live/testing/ChangeLog-Clonezilla-live.txt
|
||||
[2]:http://downloads.sourceforge.net/clonezilla/clonezilla-live-2.1.2-53-i486.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://downloads.sourceforge.net/clonezilla/clonezilla-live-2.1.2-53-i686-pae.iso
|
||||
[4]:http://downloads.sourceforge.net/clonezilla/clonezilla-live-2.1.2-53-amd64.iso
|
||||
[5]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/clonezilla/files/clonezilla_live_testing/2.2.0-8/clonezilla-live-2.2.0-13-i486.iso/download
|
||||
[6]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/clonezilla/files/clonezilla_live_testing/2.2.0-8/clonezilla-live-2.2.0-13-i686-pae.iso/download
|
||||
[7]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/clonezilla/files/clonezilla_live_testing/2.2.0-8/clonezilla-live-2.2.0-13-amd64.iso/download
|
||||
48
sources/New GNOME IRC App ‘Polari’.md
Normal file
48
sources/New GNOME IRC App ‘Polari’.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
New GNOME IRC App ‘Polari’
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
You have to hand it to the GNOME designers and developers: their work in creating a coherent, integrated set of apps for the desktop is showing true promise.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*The latest build of Polari in action.*
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, they’ve barely sat still over the last couple of years, creating app after app.
|
||||
|
||||
There are now dedicated apps for Music, Video and Photos; a virtual machine manager in the shape of Boxes; the Maps, Weather & Notes tools are all looking fantastic. And the new GNOME Software Store? Design wise it knocks Ubuntu’s aged offering out of the park!
|
||||
|
||||
But it seems that the GNOME app gurus aren’t done yet. Work has recently begun on a new GNOME 3 IRC app called ‘Polari’.
|
||||
|
||||
*(As an aside, it’s a testament to the focus within the GNOME development community on putting users first that the one tool they likely use most often to communicate is one of the last to get the GNOME app treatment.)*
|
||||
|
||||
## Polari – Planned Features ##
|
||||
|
||||
It’s not fixed in a dusty coding tome that all IRC clients have to resemble something from an 80s sci-fi movie, or be intimidating to the general user. Even in today’s world of instant communications via social networks, IRC remains a great way for people to chat.
|
||||
|
||||
To this end, if [Polari][1] (expect a name change further down the line) had a slogan it would be “*An IRC client for dummies.*”
|
||||
|
||||
- Connect to IRC servers & rooms
|
||||
- Clearly see mentions & notifications
|
||||
- Support GNOME 3 notifications
|
||||
- Integration with Contacts, the GNOME contacts app
|
||||
- History & transcript features
|
||||
- Link previews
|
||||
- File transfers
|
||||
|
||||
Developer-orientated features have also been mooted, including integrated support for Pastebin & Bugzilla.
|
||||
|
||||
So when can you try it? Not quite yet. Development of Polari is still in its early stages, but, if you’re willing to build it from Git (requires GNOME 3.10) you’ll find that it’s already capable of handling the basics, including delivering notifications for mentions.
|
||||
|
||||
For code-compiling-phobes Polari is expected to feature (most likely as an app preview) in GNOME 3.12, due next year.
|
||||
|
||||
- [More about Polari][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/gnome-irc-app-polari-in-development
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://git.gnome.org/browse/polari
|
||||
[2]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Polari
|
||||
@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Powerful chess application PyChess 0.12 BETA 4 released with new improvements
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[PyChess][1] is a lovely enjoyable chess application presenting itself as an advanced manner of digesting chess activities, stressing one's brain and chess skills with intelligent computer opponents, while exposing its activities with user-friendly intuitive visuals and details.
|
||||
|
||||
PyChess displays on its main view relevant chess components, translating professional chess activities into a computing experience, where animated table, specific sounds, written-in-real-time movements, hints, annotations, offer draw/abort, chronometer are to fully immerse the user in solid chess actions.
|
||||
|
||||
**PyChess 0.12 Anderssen BETA 4** has been released, unstable version marking the fourth iteration of the interesting BETA journey, 0.12 series bringing a significant amount of changes and improvements spanning across multiple levels, [including][2] new themes, new menu options, as well as computer-resources optimizations (removing the high CPU usage).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The BETA 4 comes with extended support for extra [FICS][3] variants (Free Internet Chess Server), as well as various fixes and improvements, version further strengthening the powerful chess application.
|
||||
|
||||
PyChess 0.12 BETA 4 is available for download on [http://pychess.googlecode.com/files/pychess_0.12beta4-1_all.deb][4]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/powerful-chess-application-pychess-012-beta-4-released-new-improvements
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://pychess.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://iloveubuntu.net/powerful-chess-game-pychess-012-beta-3-released-numerous-new-features-and-improvements
|
||||
[3]:http://www.freechess.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://pychess.googlecode.com/files/pychess_0.12beta4-1_all.deb
|
||||
291
sources/Raspberry Pi--the Perfect Home Server.md
Normal file
291
sources/Raspberry Pi--the Perfect Home Server.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,291 @@
|
||||
Raspberry Pi: the Perfect Home Server
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ever since the announcement of the Raspberry Pi, sites all across the Internet have offered lots of interesting and challenging uses for this exciting device. Although all of those ideas are great, the most obvious and perhaps least glamorous use for the Raspberry Pi (**RPi**) is creating your perfect home server.
|
||||
|
||||
If you've got several different computers in need of a consistent and automated backup strategy, the RPi can do that. If you have music and video you'd like to be able to access from almost any screen in the house, the RPi can make that happen too. Maybe you have a printer or two you'd like to share with everyone easily? The Raspberry Pi can fill all those needs with a minimal investment in hardware and time.
|
||||
|
||||
**Raspberry Pi Benefits**
|
||||
|
||||
Low cost: for $35, the RPi model B is nearly a complete computer with 512MB of RAM, 100Mb Ethernet, an SD card slot, two USB ports, audio out and HDMI or RCA video out. I've seen HDMI cables that cost more than that.
|
||||
|
||||
Energy efficient: hardware costs are only one component of a server's expense, because you also need to consider the energy cost to keep the device running constantly. The services needed for home use aren't going to tax the CPU much, and most of the time it will just be idling, waiting for something to do. The RPi's ultra-low power components are a perfect fit for this workload, which helps keep your power bill down. My model B unit plus external hard drive consume only 8 watts total, while the old Athlon-based box it replaced drew 54 watts at idle. Assuming 10 cents per kilowatt hour, that puts the yearly power bill for an RPi at $7 vs. $47 for an Athlon-based machine. The RPi basically pays for itself in less than a year!
|
||||
|
||||
Low noise: because the RPi doesn't have fans or moving parts, the only component in your final configuration that generates noise or any appreciable heat will be the hard disk. If you're concerned about noise, enthusiast sites like [Silent PC Review][1] often include noise benchmarks in their storage reviews. My experience is that any modern drive is quiet enough to avoid detection anywhere there's something else already running (such as a media center, gaming console or other computer). If your home doesn't provide a lot of flexibility for wiring options, the RPi's small size, minimal thermal output and low-noise footprint may make it possible to sneak in a server where it was difficult to justify one in the past.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Figure 1. A Compact, but Highly Capable Home Server
|
||||
|
||||
New opportunities: a less tangible benefit is the simple joy of trying something new! For me, this was my first time really working on a Debian-based distribution, and it's probably the first time many Linux enthusiasts will have a chance to try an ARM-based architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
**Arranging the Hardware**
|
||||
|
||||
For a home server, you'll need a medium-size SD Flash card for local storage. It's possible to use a USB thumbdrive for booting, but that would use up one of the two precious USB slots. The Flash storage card doesn't need to be large, but the faster the better. I chose a name-brand SD card with an 8GB capacity and class 10 speed rating. For backups and multimedia files, a large hard drive with a USB dock is a must. I chose a 1.5TB hard drive and a Calvary EN-CAHDD-D 2-bay USB 2.0 hard drive dock. This dock has a feature to run two drives in RAID-0 mode, which could be useful someday. Finally, the RPi doesn't come with a power supply, but most smartphone chargers supply the required 5v-over-micro USB. To see if the RPi was fussy about the power source, I swapped through three different micro-USB cell-phone chargers for power supplies. I tried each one for about a week, with no issues on any of the units.
|
||||
|
||||
**Installing the Operating System**
|
||||
|
||||
Installing the RPi operating system is covered in extensive detail elsewhere, but here are a few home-server-specific tips, roughly in the order needed.
|
||||
|
||||
1) Get the Raspbian "Wheezy" install image directly from [http://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads][2], and copy it onto the SD card, using the steps listed on the site.
|
||||
|
||||
2) When booting the RPi for the first time, attach a keyboard, mouse and monitor. Don't forget to turn on the monitor before booting the RPi, so that it can detect the correct HDMI or composite output port.
|
||||
|
||||
3) The RPi has a nice "raspi-config" screen that you'll see on first boot. For a home server, the following selections will be useful:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- expand_rootfs: resizes the default 2GB OS image to fill the rest of the Flash card.
|
||||
- change_pass: the default password is "raspberry", but something more secure than that would be better.
|
||||
- Set your locale and timezone.
|
||||
- memory_split: assign the minimum amount possible (16) to the GPU to leave as much room as possible for services.
|
||||
- SSH: don't forget to enable the SSH server.
|
||||
- boot_behaviour: turn off boot to desktop (again, to save memory for your services).
|
||||
|
||||
When finished, you'll be at the `pi@raspberrypi` prompt. The setup script can be re-run at any time via `sudo raspi-config`.
|
||||
|
||||
There are just a few more configuration items, and then the operating system is ready to go.
|
||||
|
||||
1) A static IP makes everything easier, so switch the network settings for eth0:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo nano -w /etc/network/interfaces
|
||||
|
||||
change the eth0 line `iface eth0 inet dhcp` to the following (modify to meet your home network setup):
|
||||
|
||||
======/etc/network/interfaces======
|
||||
...
|
||||
iface eth0 inet static
|
||||
address 192.168.1.10
|
||||
netmask 255.255.255.0
|
||||
gateway 192.168.1.1
|
||||
...
|
||||
======/etc/network/interfaces======
|
||||
|
||||
2) Create a local user, and put it in the users and sudo group:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo adduser YOURUSERIDHERE
|
||||
>> sudo usermod -a -G users YOURUSERIDHERE
|
||||
>> sudo usermod -a -G sudo YOURUSERIDHERE
|
||||
|
||||
3) Update the system to ensure that it has the latest and greatest copies of all the libraries:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo apt-get update; sudo apt-get upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
4) At this point, you're ready to go headless! Shut down the PI:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo /sbin/shutdown -h now
|
||||
|
||||
Once it's down (monitor the green status LEDs on the RPi circuit board to know when it has finished shutting down), unplug the monitor, keyboard, mouse and power cord. Attach the USB storage, then restart the RPi by plugging the power back in.
|
||||
|
||||
5) Once the RPi starts up (again, those green LEDs are the clue to its state), you can ssh in to the RPi from any other machine on the network and finish all the configuration remotely from here on out (modify the following for your static IP):
|
||||
|
||||
`>> ssh YOURUSERIDHERE@192.168.1.10`
|
||||
|
||||
Congratulations, you have a working Raspberry Pi!
|
||||
|
||||
**Peripherals**
|
||||
|
||||
The first order of business is to get the external storage device mounted. Use dmesg to look for where the storage device was found—it almost certainly will be /dev/sda. I like using automounter to handle mounting removable storage devices, as it is more flexible about handing devices that may not be present or ready at boot time:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo apt-get install autofs
|
||||
>> sudo nano -w /etc/auto.master
|
||||
======/etc/auto.master======
|
||||
...
|
||||
/misc /etc/auto.misc
|
||||
...
|
||||
======/etc/auto.master======
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo nano -w /etc/auto.misc
|
||||
|
||||
Note, my external storage device is formatted with ext4—modify this for your needs if required:
|
||||
|
||||
======/etc/auto.misc======
|
||||
...
|
||||
storage -fstype=ext4:/dev/sda1
|
||||
...
|
||||
======/etc/auto.misc======
|
||||
>> sudo /etc/init.d/autofs restart
|
||||
>> ls -lat /misc/storage
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally, create a symlink to shorten the path a smidgen:
|
||||
|
||||
>> ln -s /misc/storage /storage
|
||||
|
||||
**Backup Repository**
|
||||
|
||||
At the top of any home server feature list is providing rock-solid backups. With the RPi, this is pretty simple, due to the wide range of network-sharing options in Linux: Samba/CIFS for Windows machines, NFS for UNIX-based devices and even SFTP for more advanced backup clients like deja-dup. Because the RPi has only 100Mb Ethernet, and the storage device is on USB, it's not going to have super-fast transfer speeds. On the other hand, good backup clients run automatically and in the background, so it's unlikely that you'll notice the slightly slower transfer speeds.
|
||||
|
||||
My home network includes one Windows 7 machine. For it, I exported a backup directory on the RPi's external USB storage device via Samba. Because the backup utility in the basic version of Windows 7 doesn't support network drives as a backup destination, I used [SyncBack Free][3] to set up automated, daily backups.
|
||||
|
||||
Configuring Samba is simple.
|
||||
|
||||
1) Install the samba and common-bin library (which has the smbpasswd utility):
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo apt-get install samba samba-common-bin
|
||||
|
||||
2) Use `smbpasswd` to let your local ID have access:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo smbpasswd -a YOURUSERIDHERE
|
||||
|
||||
3) Edit the samba configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo nano -w /etc/samba/smb.conf
|
||||
|
||||
4) Change the `workgroup = WORKGROUP` line to match your Windows workgroup name.
|
||||
|
||||
5) Comment out or delete the [homes] and [printers] share. (Printer sharing will be done later via direct CUPS access.)
|
||||
|
||||
6) Add an entry for the Windows backup paths. Here's my example, which I placed at the bottom of the file:
|
||||
|
||||
======/etc/samba/smb.conf======
|
||||
...
|
||||
[win7pc]
|
||||
comment=Backup for windows PC
|
||||
path=/storage/win7pc
|
||||
writeable=Yes
|
||||
create mask=0777
|
||||
directory mask=0777
|
||||
browsable=Yes
|
||||
public=Yes
|
||||
valid users=YOURUSERIDHERE
|
||||
...
|
||||
======/etc/samba/smb.conf======
|
||||
|
||||
7) Restart Samba to implement your edits:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo /etc/init.d/samba restart
|
||||
|
||||
8) Test connectivity from the Windows machine by mapping a network drive from the file explorer.
|
||||
|
||||
For Linux devices, deja-dup is brilliantly simple to set up and use. It's been installed by default on both my Fedora 18 and Ubuntu 12.10 installs. While the package name is "deja-dup", the front end is simply called "Backup". Although the RPi easily could support NFS export, I've found that using deja-dup's SSH option is easier and more portable, and it eliminates the need for an additional service on the RPi. Specifying a deja-dup encryption password is probably a good idea, unless you like the idea of all your files walking off if someone pockets the storage drive:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo mkdir /storage/linuxlaptop
|
||||
>> sudo chown -R YOURUSERIDHERE:YOURUSERIDHERE /storage/linuxlaptop
|
||||
|
||||
From the client Linux machine, launch the backup utility, choose "SSH" as the backup location, and enter the RPi's IP address and the storage location you just created. The first backup will be slow, but future runs will be sending only incremental changes, which is significantly faster.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Figure 2. Deja-dup Client Setup
|
||||
|
||||
**Multimedia Server: DLNA**
|
||||
|
||||
Now that everyone's files are backed up safely, let's move on to some fun! A DLNA server will give you a central place to store your movies, music and pictures. From this central repository, DLNA clients from every screen in the house can play back this content with ease.
|
||||
|
||||
At least, that's the promise. The reality is that the DNLA specs don't quite nail down many important things like which formats or encodings are supported. Each client typically has a slightly different idea of what formats and server features it would like to support. A much higher-power server might be able to transcode local content to device-supported formats on the fly, but that's not possible on the RPi, and the on-the-fly transcoding often messes up other features like pause, fast-forward and rewind. In general, higher-powered devices like the PS3, Xbox and WD TV devices can handle most formats without any transcoding. Lower-end devices like smart TVs or Blu-ray players support a much more limited list of codecs.
|
||||
|
||||
For the RPi, your best bet is simply to encode to the standards your primary DLNA device supports and then test your other DLNA clients. If they won't play nicely, the tips in the next section may help. In my case, my PlayStation 3 acts as the DLNA client, which plays nicely with the compact .m4v files generated by Handbrake.
|
||||
|
||||
Minidlna is a great choice for the RPi DLNA server. It's already in the Raspbian distribution, is quite simple to set up and uses minimal server resources while running:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo apt-get install minidlna
|
||||
>> sudo nano -w /etc/minidlna.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the relevant sections of my /etc/minidlna.conf:
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
# I found keeping video + audio in different paths helpful
|
||||
media_dir=V,/storage/dlna/video
|
||||
media_dir=A,/storage/dlna/music
|
||||
...
|
||||
presentation_url=http://192.168.1.10:8200/
|
||||
...
|
||||
friendly_name=MyRPi
|
||||
...
|
||||
# Since I add new media infrequently, turning off
|
||||
# inotify keeps minidlna for polling for
|
||||
# content changes. It's simple enough to run
|
||||
# sudo /etc/init.d/minidlna force-reload
|
||||
# when new content is added.
|
||||
inotify=no
|
||||
|
||||
Once done editing, tell minidlna to restart and rescan for content:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo /etc/init.d/minidlna force-reload
|
||||
|
||||
Minidlna has the ability to provide movie-poster thumbnails for your movies for devices that support it (like the PS3). It makes finding a specific movie when scrolling through dozens of movie files much more convenient. I've found that the most compatible file layout is to have one directory per movie, containing just the movie file plus the thumbnail image named "Cover.jpg". Using a format like "MovieName.m4v" and "MovieName.jpg" works fine for the PS3, but it breaks VLC (if you can convince the VLC uPNP plugin to find the server in the first place).
|
||||
|
||||
From the PS3, you can test connectivity by going to "Video" on the XMB bar. The "friendly_name" you set previously should be visible when scrolling down in the Video section. If you cant find it, test to ensure that Minidlna is up by going to http://192.168.1.10:8200/ with a Web browser.
|
||||
|
||||
**Multimedia for Non-DLNA Devices**
|
||||
|
||||
Once you get DNLA working with some of your devices, you may find devices it doesn't want to work with, so a multimedia plan B is a good idea. The nginx Web server has an MP4 plugin that tries to improve streaming over plain-old HTTP, but browser playback performance varied widely, and fast-forwarding within a movie didn't work consistently either. It seems like the lowest common denominator for multimedia sharing across fussy or non-DLNA devices is a good-old-fashioned Samba share with guest read-only access.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an sample section from /etc/samba/smb.conf:
|
||||
|
||||
[dlna]
|
||||
path=/storage/dlna
|
||||
read only=yes
|
||||
browsable=yes
|
||||
public=yes
|
||||
|
||||
After defining the share and restarting Samba (`sudo /etc/init.d/samba restart`), you can start to test out your clients.
|
||||
|
||||
I tested the following clients with a mix of videos encoded with Handbrake as m4v files:
|
||||
|
||||
- Android 4.0.4 phone: "ES File Explorer" with "ES Media Player" (player comes with install).
|
||||
- Android 4.1.2 tablet: "ES File Explorer" with "ES Media Player" (player comes with install).
|
||||
- Linux devices: automount ://192.168.1.10/dlna, then use VLC or MPlayer.
|
||||
- Windows: mount //192.168.1.10:/dlna, then use VLC.
|
||||
|
||||
All devices were able to start playing almost instantly and fast-forward with no delays.
|
||||
|
||||
**Print Server**
|
||||
|
||||
The RPi runs CUPS quite well, so it's easy to share an older printer that doesn't have native networking features.
|
||||
|
||||
Install CUPS and any packages needed by your printer. I needed hplip-cups since I have an HP inkjet printer:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo apt-get install cups hplip-cups
|
||||
|
||||
Update the "Listen" line and add the `Allow @LOCAL` block to the Location directives as shown below (so you can use other machines on your LAN to administer CUPS):
|
||||
|
||||
======/etc/cups/cupsd.conf======
|
||||
#Listen localhost:631 #Comment this out
|
||||
Listen 192.168.1.10:631 #Add this line
|
||||
...
|
||||
<Location />
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow @LOCAL
|
||||
</Location>
|
||||
|
||||
# Restrict access to the admin pages...
|
||||
<Location /admin>
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow @LOCAL
|
||||
</Location>
|
||||
|
||||
# Restrict access to configuration files...
|
||||
<Location /admin/conf>
|
||||
AuthType Default
|
||||
Require user @SYSTEM
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow @LOCAL
|
||||
</Location>
|
||||
======/etc/cups/cupsd.conf======
|
||||
|
||||
Add your local ID to the lpadmin group so you can administer CUPS:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo usermod -a -G lpadmin YOURUSERIDHERE
|
||||
|
||||
Restart CUPS:
|
||||
|
||||
>> sudo /etc/init.d/cups restart
|
||||
|
||||
Then, go to http://192.168.1.10:631/ and click "Adding Printers and Classes" to set up your printer. My printer was auto-discovered on the USB, so all I had do to was click "share". Also access https://192.168.1.10:631/admin, and make sure to check "Share printers connected to this system".
|
||||
|
||||
Once you're done, you can set up your clients the usual way. My Linux clients auto-discovered the printer and picked the right printer drivers once I entered the hostname. On my Windows 7 machine, once I selected "Network Printer", I had to click "The printer that I want isn't listed", select "Select a shared printer by name" and then enter the URL from the CUPS Web interface: http://192.168.1.10:631/printers/HP_J4500.
|
||||
|
||||
**Conclusion**
|
||||
|
||||
With a minimal amount of additional hardware and configuration, the Raspberry Pi can be a highly capable, compact home server. It can bring the wide range of enterprise services offered by Linux into a home environment with minimal hardware expense.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/raspberry-pi-perfect-home-server
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.silentpcreview.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads
|
||||
[3]:http://www.2brightsparks.com/freeware/freeware-hub.html
|
||||
@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
|
||||
翻译认领:Vic020
|
||||
Salvation Prophecy Military Space Epic Arrives on Steam for Linux
|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Salvation Prophecy, a title developed and published on Steam by Firedance Games, has been launched on the Linux platform.**
|
||||
|
||||
According to the developers, Salvation Prophecy is a military space epic in which the players will be able to play as fighter pilots in space, but also on the surface of planets, in FPS mode.
|
||||
|
||||
“Battles rage as space fleets collide. Invaders clash against fortified enemy colonies. Yet the greatest danger is the impending annihilation foretold by an apocalyptic prophecy. You must seek out the mysteries of distant alien worlds, and master ancient powers to withstand the coming storm,” reads the official [synopsis][1].
|
||||
|
||||
The minimum Linux system requirements are pretty low, considering the complexity of the game: Ubuntu 12.04 or Ubuntu 12.10, a Dual-core processor, 2 GB RAM, NVIDIA GeForce 8600 GT, ATI Radeon HD 2600, or better, and 1 GB of available space.
|
||||
|
||||
More details about this release can be found on the official Steam [website][2].
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Salvation-Prophecy-Military-Space-Epic-Arrives-on-Steam-for-Linux-390849.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://store.steampowered.com/news/11613/
|
||||
[2]:http://store.steampowered.com/app/248450/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
Sound Recording and Editing Professional Tool Audacity 2.0.5 RC1 Now Ready for Testing
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Audacity, a tool that can be used to record live audio through a microphone or mixer, or digitize recordings from cassette tapes, records, or mini-discs, is now at version 2.0.5 RC1**
|
||||
|
||||
Audacity 2.0.5 RC1 comes with a ton of features and can record from microphone, line input, USB/Firewire devices, and more. It can also manage multiple input and output devices, dub over existing tracks to create multi-track recordings, record at sample rates up to 192,000 Hz (subject to appropriate hardware), and record multiple channels at once.
|
||||
|
||||
**Highlights of Audacity 2.0.5 RC1:**
|
||||
|
||||
- The separate commands that aligned track start or end with the cursor or with selection start are now combined into "Cursor/Selection Start" commands;
|
||||
- "Align and Move Cursor" has been renamed to "Move Selection when Aligning";
|
||||
- Labels Editor now allows empty labels to be saved on closing the editor;
|
||||
- PortAudio has been updated to version r1910 to fix memory leaks and other bugs under ALSA.
|
||||
|
||||
A complete list of changes, updates, and new features can be found in the [changelog][1].
|
||||
|
||||
**Download:**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Audacity 2.0.5 RC1 tar.xz (2.0.4 Stable)][2][sources] [4.90 MB]
|
||||
- [Audacity 2.0.5 RC1 tar.xz (2.0.5 RC1 Development)][3][sources] [5.10 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Sound-Recording-and-Editing-Professional-Tool-Audacity-2-0-5-Now-Ready-for-Testing-391718.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.softpedia.com/progChangelog/Audacity-Changelog-350.html
|
||||
[2]:http://audacity.googlecode.com/files/audacity-minsrc-2.0.4.tar.xz
|
||||
[3]:https://audacity.googlecode.com/files/audacity-minsrc-2.0.5rc1.tar.xz
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
System 76 Ubuntu Touchscreen Laptop Now Available to Pre-Order
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu PC makers System 76 have unveiled a new touchscreen notebook running Ubuntu 13.10. **
|
||||
|
||||
The Darter Ultra Thin features a 14.1-inch HD **multitouch display that works out of the box with Ubuntu**. It’s housed in a slender 0.9″ thick chassis weighing in at 4.60 lbs (around 2 kg). Battery life is estimated at around 5 hours – which, for Linux and its power management issues, is actually quite impressive!
|
||||
|
||||
Alongside the touchscreen the laptop also offers more traditional methods of input, namely a multi-touch trackpad and chiclet-style keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Pricing starts at $899** for the base model specification. This gets you:
|
||||
|
||||
- Intel i5-4200U @ 1.5Ghz (Dual core)
|
||||
- 4GB DDR3 RAM
|
||||
- Intel HD 4400 Graphics
|
||||
- 500 GB 5400 RPM HDD
|
||||
- Integrated WiFi & Bluetooth
|
||||
- 1MP Webcam
|
||||
|
||||
As with all System 76 computers you can craft your dream machine by bumping up specifications and adding optional extras. Options on offer for the Darter include:
|
||||
-
|
||||
- Intel Core i5 & i7 CPUs
|
||||
- Up to 16GB DDR3 RAM
|
||||
- Dual-storage, including SSD + HDD combo
|
||||
|
||||
All essential ports are provided:
|
||||
|
||||
- HDMI out
|
||||
- Ethernet
|
||||
- 2 x USB 3.0
|
||||
- Separate Headphone & Mic Jacks
|
||||
- SD Card Reader
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on the Darter Thin head over to the System 76 website where, until October 28th, you can pre-order the Darter Thin and pay just $5 for ground shipping in the US.
|
||||
|
||||
- [System76 Darter UltraThin Laptop][1]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/system76-touchscreen-ubuntu-laptop-available-pre-order
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://www.system76.com/laptops/model/daru4
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,449 @@
|
||||
(runningwater翻译中)Top Things To Do After Installing Ubuntu 13.10 ‘Saucy Salamander’
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Ubuntu 13.10 Saucy Salamander** will be released on coming **October 17th** with many new salient features, updates and significant performance improvements. In this brief how-to let us discuss how we can enhance Ubuntu 13.10 further for day to day activities. This post we will share some interesting insight and ideas about what you can and should do after a successful installation.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have already a previous release of Ubuntu, and want to upgrade to the latest 13.10 version, then please follow our step by step guide [upgrade to Ubuntu 13.10 Saucy Salamander][1].
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, after fresh installation of Ubuntu 13.10 Saucy, check the following few things first.
|
||||
|
||||
**A. If sound is working, if not, [check our previous post to resolve the issue][2].
|
||||
|
||||
B. If wifi connection speed is normal or if it is too slow, [check our previous post to resolve the issue][3].**
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. Update System ##
|
||||
|
||||
After install the Ubuntu 13.10 Saucy, the first and important thing to do is update/upgrade software repositories and make sure your systems contains latest versions of all softwares.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. Ubuntu Tweak ##
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu Tweak** is a must have application for Ubuntu and it’s derivatives. It is an application to config Ubuntu easier for everyone. It provides many useful desktop and system options that the default desktop environment doesn’t provide. Using Ubuntu Tweak you can install all needed applications with a simple click, you can change the window buttons from Left to right…etc.
|
||||
|
||||
**Read our [Interview with Ding Zhou of Ubuntu Tweak][4].**
|
||||
|
||||
**Install Ubuntu Tweak via PPA**
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: Ubuntu-Tweak Stable PPA is not ready yet. But there is an another PPA is available to install Ubutun-Tweak from the team.
|
||||
|
||||
Open terminal and enter the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:tualatrix/next
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install ubuntu-tweak
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the applications listed in this post, can be installed from Ubuntu Tweak Center with one click.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to learn how to use [Ubuntu Tweak, read our previous post][5].
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. Desktop Environments ##
|
||||
|
||||
**Don’t like Unity in Ubuntu 13.10, why don’t you give a try to Cinnamon or Gnome?**
|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon is a GNOME 3 fork that allow you to have a panel at the bottom with a classic Menu, this is useful for people that want to use Ubuntu with a classic Bottom Menu. Cinnamon is available in the default repositories of Ubuntu 13.10, therefore you can install it with the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to install the most recent version of cinnamon, then add the follow the steps below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gwendal-lebihan-dev/cinnamon-nightly
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install cinnamon
|
||||
|
||||
Logout from the current session and select Cinnamon as your desktop session at the user login prompt. Now you’ll able to get the Cinnamon Desktop Environment.
|
||||
|
||||
**Warning**: Latest version of Cinnamon corrupts Unity both on Ubuntu 13.04 and 13.10. Hope this bug will be fixed soon before the Ubuntu 13.10 stable release. For more information please refer this [link][7].
|
||||
|
||||
**Install GNOME 3 in Ubuntu 13.10**
|
||||
|
||||
To install GNOME 3 in Ubuntu 13.10, enter the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnome-shell ubuntu-gnome-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
During installation, the installer will ask you to select the login manager of your choice (LightDM is the default Unity manager and GDM is the GNOME default — Both will work).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 4. Accounts Configuration ##
|
||||
|
||||
**Configure UbuntuOne Account**
|
||||
|
||||
**UbuntuOne** enables users to store files online and sync them between computers and mobile devices, as well as stream audio and music from cloud to mobile devices. If you have already an account, you will need top sing in, setup a folder in your computer and start synchronizing your data, contacts, photos …etc.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Also you can run **UbuntuOne** from the left side unity launcher:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Configure Online Accounts**
|
||||
|
||||
One of the top things you need to do is to setup your online accounts (Facebook, twitter…). To do that click on the **gear** button on the top right corner and select **System Settings**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then select Online Accounts (see below).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now setup your online accounts and get notifications in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## 5. System Monitoring & Eye Candy Tools ##
|
||||
|
||||
**Install Conky for Ubuntu 13.10**
|
||||
|
||||
**[Conky][8]** is a free, light-weight system monitor for X, that displays any information on your desktop. There are many nice themes available for conky that can display clock, CPU usage, RAM usage, swap, disk, net and more. Check [our previous post for installation and configuration][9] of conky in Ubuntu 12.04, 12.10, 13.04 and Ubuntu 13.10.
|
||||
|
||||
**Don’t like the default icons, Wanna try some cool icons? **
|
||||
|
||||
Try the following cool Icon collections.
|
||||
|
||||
Want to change the default icons to something that match your taste? [Check this nice collection of icons for Ubuntu][10] (PPA included).
|
||||
|
||||
## 6. Multimedia ##
|
||||
|
||||
**- Players
|
||||
|
||||
1-VLC Media Player:**
|
||||
|
||||
[VLC][11] is the best media player for Linux it play almost everything, it has many features that you can not find in any other media player, read this post if you want to know what VLC can do: [25 things you can do with VLC Media player][12]!
|
||||
|
||||
You can install VLC from Ubuntu Software Center or via terminal by using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install vlc
|
||||
|
||||
Or install the most recent version 2.1.1 using the following PPA.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:videolan/stable-daily
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install vlc
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**2- XMBC:**
|
||||
|
||||
**[XBMC][13]** is an award-winning free and open source (GPL) software media player and entertainment hub for digital media. XBMC is available for Linux, OS X, Windows, and the original Xbox. While XBMC functions very well as a standard media player application for your computer, it has been designed to be the perfect companion for your HTPC. Supporting an almost endless range of remote controls, and combined with its beautiful interface and powerful skinning engine, XBMC feels very natural to use from the couch and is the ideal solution for your home theater.
|
||||
|
||||
Open terminal and copy the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install xbmc
|
||||
|
||||
**- Video Editors
|
||||
|
||||
Openshot video editor:**
|
||||
|
||||
My favorite Video editor is [Openshot][14], the best existing actually for Linux. You can install Openshot from Ubuntu Software Center, but if you want to install the latest release, you can do that by adding the following repositories:
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: PPA is not yet working in 13.10 at the time of writing this article. Hope it will be updated soon.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:openshot.developers/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install openshot openshot-doc
|
||||
|
||||
Read also our [interview with Jonathan Thomas][15] the main developer of Openshot.
|
||||
|
||||
**- Video Encoders
|
||||
|
||||
Handbrake:**
|
||||
|
||||
Check our previous article to know about the powerful video encoder called “Handbrake”.
|
||||
|
||||
[Encode Movies And Videos Using Handbrake][16]
|
||||
|
||||
## 7. Install Common Codecs And Enable DVD playback ##
|
||||
|
||||
Perhaps installing a few common codecs might give you better sensibility of your system:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gstreamer0.10-plugins-ugly gstreamer0.10-ffmpeg libxine1-ffmpeg gxine mencoder libdvdread4 totem-mozilla icedax tagtool easytag id3tool lame nautilus-script-audio-convert libmad0 mpg321 gstreamer1.0-libav
|
||||
|
||||
To play encrypted DVDs, the libdvdcss2 package is essential. libdvdcss is a simple library designed for accessing DVDs like a block device without having to bother about the decryption.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo /usr/share/doc/libdvdread4/./install-css.sh
|
||||
|
||||
## 8. Enable Flash Support On Browsers ##
|
||||
|
||||
**For Ubuntu 32 bit & 64 bit**: To be able to watch some videos and see flash website in your browser (Firefox/Chrome), you need to install flash plugin, go to **Ubuntu Software Center** and search word “**flash**” and install it.
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively enter the following command to install flash plugins.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install flashplugin-installer
|
||||
|
||||
## 9. Torrent Softwares ##
|
||||
|
||||
**uTorrent:**
|
||||
|
||||
**uTorrent** is a lightweight and efficient BitTorrent client for Linux, Windows OS and Mac OS. The installation of uTorrent in Linux is different from Windows and Mac OS. In Linux, uTorrent runs as a web server. You will access uTorrent from your browser. You should start the uTorrent server in order to access it from your browser.
|
||||
|
||||
Check our previous article to know more about uTorrent.
|
||||
|
||||
[How To Install uTorrent Client in Ubuntu/Debian/Linux Mint][17]
|
||||
|
||||
**Deluge:**
|
||||
|
||||
The Deluge application was designed to be a full-featured torrent client. Deluge uses libtorrent in its back-end and PyGTK for its user interface and is currently usable on POSIX-compliant operating systems. It is intended to bring a native, full-featured client to GTK desktop environments such as GNOME and Xfce. An official Windows port is also available.
|
||||
|
||||
Open terminal and type the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install deluge
|
||||
|
||||
## 10. Messengers ##
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the list of recommended Messengers for your system. Don’t install everything. Install one by one and pick up the right one for your requirement and delete the rest.
|
||||
|
||||
[Pidgin][18],The best messenger client and 30 plugins, you can do voice and video chat with friends.
|
||||
|
||||
To install Pidgin, enter the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install pidgin
|
||||
|
||||
[aMSN][19] is a free windows Live Messenger clone. aMSN attempts to emulate the look and feel of Windows Live Messenger, and supports many of its features.
|
||||
|
||||
aMSN has features not present in Windows Live Messenger. Users can set alarms, are able to see others who have removed them from their contact list, and are able to open many profiles at once. It is also very customizable, with extensions and themes available at the main site.
|
||||
|
||||
To install aMsn, enter the following command in your terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install amsn
|
||||
|
||||
**Skype:**
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re want to install Skype, check our previous post: [How to install Skype in Ubuntu 13.04 ‘Raring Ringtail][20]’
|
||||
|
||||
**Jitsi:**
|
||||
|
||||
Jitsi is an open source and multi platform audio/video Internet phone and instant messenger written in Java. It supports some of the most popular instant messaging and telephony protocols such as SIP, Jabber/XMPP (and hence Facebook and Google Talk), AIM, ICQ, MSN, Yahoo! Messenger.
|
||||
|
||||
For details about Jitsi please check our previous article in the following link.
|
||||
|
||||
[Install Jitsi Instant Messenger in Ubuntu][21]
|
||||
|
||||
## 11. Gaming & Emulators ##
|
||||
|
||||
**Gaming made easy with Playdeb:**
|
||||
|
||||
If you are a grate fan of gaming so is important to add PlayDeb repositories to your Lucid Lynx. PlayDeb is a gaming repository for Ubuntu aimed to provide titles already available on getdeb.net in an easier to install and update format. You can install many games by a simple click.
|
||||
|
||||
[Click to install PlayDeb repositories][22]
|
||||
|
||||
**Wine**
|
||||
|
||||
Wine enables Linux, Mac, FreeBSD, and Solaris users to run Windows applications without a copy of Microsoft Windows. Wine is free software under constant development. Other platforms may benefit as well.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install wine
|
||||
|
||||
Or
|
||||
|
||||
Please follow instructions in our previous post : [How to install and configure games on WINE][23]
|
||||
|
||||
## 12. Sharing Files/Folders ##
|
||||
|
||||
**Samba:**
|
||||
|
||||
In order to share folders in **Raring Ringtail** with other Linux and windows machines in your network, you will need to install and configure Samba share, for instructions how to configure Samba in Ubuntu check our previous post : [Install and Configure Samba share in Ubuntu 13.04 ‘Raring Ringtail][24]’
|
||||
|
||||
**Gigola:**
|
||||
|
||||
Gigola is an another option to share files between Linux and Windows systems. Unlike Samba, we can use Gigola to send files between Linux-to-Linux and Linux-to-Windows systems.
|
||||
|
||||
Learn more about Gigola from the below link.
|
||||
|
||||
[How to Access Remote Linux and Windows Shares with Gigolo][25]
|
||||
|
||||
## 13. Extras & Miscellaneous ##
|
||||
|
||||
**- Install Archive Management Apps:**
|
||||
|
||||
Install the following packages will allow you to deal with almost all and any zip formated files.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install unace unrar zip unzip p7zip-full p7zip-rar sharutils rar uudeview mpack arj cabextract file-roller
|
||||
|
||||
**- Y PPA Manager:**
|
||||
|
||||
Y PPA Manager is a GUI tool to easily add PPAs, search a package in all [Launchpad PPAs][26], remove duplicate PPAs (only works with separate .list files), backup PPAs and other PPA-related tasks. Check out the Launchpad page for a complete features list.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/y-ppa-manager
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install y-ppa-manager
|
||||
|
||||
Y-PPA-Manager can be launched either from Dash or Menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Install Java 7**
|
||||
|
||||
Java is fast, secure, and reliable programming and computing platform. There are lots of applications and websites that will not work unless you have Java installed, and more are created every day. To install java simply run the following command from your terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install openjdk-7-jdk
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to try oracle-java 7, try the following steps.
|
||||
|
||||
First you need to remove OpenJDK for this run the following command from your terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get purge openjdk*
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can install Java 7 by adding the following repository:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install oracle-java7-installer
|
||||
|
||||
To remove Java 7, run this in terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove oracle-java7-installer
|
||||
|
||||
**FileZilla:**
|
||||
|
||||
[Filezilla][27] is one of the best ftp client for Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Install it via command line:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install filezilla
|
||||
|
||||
**Dropbox:**
|
||||
|
||||
Dropbox is a free service that lets you bring all your photos, docs, and videos anywhere. This means that any file you save to your Dropbox will automatically save to all your computers, phones and even the [Dropbox website][28]. Dropbox also makes it super easy to share with others, whether you’re a student or professional, parent or grandparent.
|
||||
|
||||
[Download the Dropbox package][29]
|
||||
|
||||
**Oracle VirtualBox:**
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to run another OS in a virtual machine, install Virtualbox.
|
||||
|
||||
For installation, [follow the instructions in our previous post][30].
|
||||
|
||||
**Cheese: Web Cam Software**
|
||||
|
||||
Cheese uses your webcam to take photos and videos, applies fancy special effects and lets you share the fun with others. To install cheese on your Ubuntu desktop, enter the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
**sudo apt-get install cheese**
|
||||
|
||||
**digikam**
|
||||
|
||||
digiKam is an advanced digital photo management application for Linux, Windows, and Mac-OSX. It can be used by Photographers to view, manage, edit, enhance, organize, tag, and share photographs under Linux systems.
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily install it using command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install digikam
|
||||
|
||||
**Gimp:**
|
||||
|
||||
Regardless of whether you need to edit images daily on a professional level or just a hobbyist, GIMP is an essential tool for all.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gimp gimp-data gimp-plugin-registry gimp-data-extras
|
||||
|
||||
**Install Compiz**
|
||||
|
||||
To install Compiz use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install compiz compizconfig-settings-manager compiz-plugins
|
||||
|
||||
## 14. Desktop Effects ##
|
||||
|
||||
Want to spice-up your desktop with awesome wallpapers, well you can use the following two programs to change your desktop wallpapers in a particular interval.
|
||||
|
||||
**a- Variety:**
|
||||
|
||||
Variety is a wallpaper changer for Ubuntu which is feature-full, yet slim and very easy to use. It can automatically download wallpapers from various online sources such as Flickr, Wallbase.cc, World sunlight map (a live wallpaper that changes as the day progresses), Wallpapers.net, NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day, Desktoppr.co etc. It allows rotating them on a regular interval or on demand, and provides easy to use ways to separate the great images from the junk.
|
||||
|
||||
To install it under Ubuntu follow our previous post instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
[Automatically Change the Desktop Wallpaper Using Variety on Ubuntu/Linux Mint][31]
|
||||
|
||||
**b- Wallch:**
|
||||
|
||||
Wallch is an application that can be used to change your Ubuntu (Ubuntu derivatives) desktop wallpapers automatically at a particular period of time. It supports Gnome and Unity. It also let you to stop/start wallch, change to next/previous wallpaper. You can adjust/change the wallpaper changing interval. Wallch supports live Earth wallpapers which updates automatically every half an hour, therefore you can set the live Earth wallpapers as your desktop background.
|
||||
|
||||
To install it under Ubuntu follow our previous post instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
[Change Ubuntu Systems Wallpaper Automatically With Wallch][32]
|
||||
|
||||
## 15. Other worth trying applications ##
|
||||
|
||||
**a- App Grid:**
|
||||
|
||||
App Grid is a light weight alternative for Ubuntu Software Center. It allows you to filter applications by installed, pending, categories, name and rating. It is released under proprietary license and is available for Ubuntu 12.04, 12.10, 13.04 and 13.10.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about App Grid, check our previous article in the following link.
|
||||
|
||||
[App Grid: A New Alternative For Ubuntu Software Center][33]
|
||||
|
||||
**b- Boot UP Manager(BUM):**
|
||||
|
||||
Boot-Up Manager is a Perl-Gtk2 application to manage runlevels configuration of any Ubuntu/Debian derivative systems. Using this program we can easily start and stop boot-up scripts, without the necessity to handle through complex symbolic links and permissions.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about BUM, check our previous article in the following link.
|
||||
|
||||
[Manage Startup Services With BUM (Boot-Up Manager) On Ubuntu/Debian][34]
|
||||
|
||||
**c- TLP: Improve Battery performance**
|
||||
|
||||
TLP is an advanced power management tool for Linux that gives the settings and tweaks to enhance your existing power management automatically without the need to know every technical details. It is purely a command-line tool and doesn’t have a GUI. It should work on almost all laptops.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about TLP, check our previous article in the following link.
|
||||
|
||||
[How to Improve Laptop Battery Life and Usage in Linux Using TLP][35]
|
||||
|
||||
**d- BleachBit: Clean up your system**
|
||||
|
||||
BleachBit deletes the unnecessary files, free up cache, delete cookies, clear internet history, shred temporary files, delete logs, and discard junk you didn’t know was there. This tool can be used in both Windows OS and Linux systems. And it will support the following applications such as Firefox, Internet Explorer, Adobe Flash, Google Chrome, Opera, Safari and more. It not only deletes the files, but it includes some advanced features such as shredding files to prevent recovery, wiping free disk space to hide traces of files deleted by other applications, and vacuuming Firefox to make it faster.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about BleachBit, check our previous article in the following link.
|
||||
|
||||
[Clean up your systems using BleachBit][36]
|
||||
|
||||
Also install the following useful software’s if you like. This is gonna help you some time.
|
||||
|
||||
[Opera][37] – The fastest browser on Earth is even faster. But that is not all. Use Opera Turbo to double your page-download speed on slow connections.
|
||||
|
||||
[Google Chrome][38] – Web browser from Google
|
||||
|
||||
[Google Earth][39] – Travel to cities across the globe, dive into the depths of the ocean, explore remote islands or even fly to faraway galaxies.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you’ve reached the end of the article. At this stage, you’ll have a perfect and full fledged Ubuntu 13.10 Desktop. Cheers!!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/top-things-installing-ubuntu-13-10/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/upgrade-ubuntu-13-04-raring-ubuntu-13-10-saucy-salamander/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unixmen.com/2012003-howto-resolve-nosound-problem-on-ubuntu/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.unixmen.com/resolve-slow-connexion-when-using-wifi-in-ubuntu-1104-natty-narwhal
|
||||
[4]:http://www.unixmen.com/interview-with-ding-zhou-of-ubuntu-tweak/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.unixmen.com/after-a-fresh-install-of-ubuntu-1010-maverick-meerkat-configuration-made-easy-with-ubuntu-tweak/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.unixmen.com/lefebvre-clem-gives-new-cinnamon-de-for-the-good-old-gnome-2x-experience/
|
||||
[7]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Cinnamon-2-0-Corrupts-Unity-on-Ubuntu-13-10-390736.shtml
|
||||
[8]:http://conky.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.unixmen.com/configure-conky-lua-in-ubuntu-11-10-12-04-fedora-debian-and-linuxmint-howto-conky/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.unixmen.com/nice-collection-of-iconsets-themes-for-your-linux-desktop-with-installation-instructions-ubuntu-ppa/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.unixmen.com/042013-top-things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-13-04-raring-ringtail/www.videolan.org
|
||||
[12]:http://www.unixmen.com/22-things-you-can-do-with-vlc/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.unixmen.com/xbmc-11-0-eden-has-been-released-ppa-ubuntu/
|
||||
[14]:http://www.openshotvideo.com/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.unixmen.com/interview-with-jonathan-thomas-of-openshot/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.unixmen.com/how-to-encode-moviesvideos-using-handbrake/
|
||||
[17]:http://www.unixmen.com/how-to-install-utorrent-on-ubuntu-debian/
|
||||
[18]:http://www.pidgin.im/
|
||||
[19]:http://www.unixmen.com/042013-top-things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-13-04-raring-ringtail/www.amsn-project.net/
|
||||
[20]:http://www.unixmen.com/howto-install-skype-in-ubuntu-12-04-precise-pangolin/
|
||||
[21]:http://www.unixmen.com/top-things-installing-ubuntu-13-10/www.unixmen.com/install-jitsi-instant-messenger-ubuntu/
|
||||
[22]:http://archive.getdeb.net/install_deb/playdeb_0.3-1%7Egetdeb1_all.deb
|
||||
[23]:http://www.unixmen.com/install-and-configure-wine-to-play-latest-windows-games-in-linux-ubuntu-linuxmint-fedora/
|
||||
[24]:http://www.unixmen.com/howto-install-and-configure-samba-share-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
[25]:http://www.unixmen.com/how-to-access-remote-linux-and-windows-shares-with-gigolo/
|
||||
[26]:https://launchpad.net/y-ppa-manager
|
||||
[27]:http://www.filezilla-project.org/
|
||||
[28]:http://www.dropbox.com/
|
||||
[29]:https://www.dropbox.com/install?os=lnx
|
||||
[30]:http://www.unixmen.com/virtualbox-4-1-12-has-been-released-ppa-ubuntu12-04-lts/
|
||||
[31]:http://www.unixmen.com/automatically-change-the-desktop-wallpaper-using-variety-on-ubuntulinux-mint/
|
||||
[32]:http://www.unixmen.com/change-ubuntu-systems-wallpaper-automatically-wallch/
|
||||
[33]:http://www.unixmen.com/app-grid-a-new-alternative-for-ubuntu-software-center/
|
||||
[34]:http://www.unixmen.com/manage-startup-services-with-bumboot-up-manager-on-ubuntudebian/
|
||||
[35]:http://www.unixmen.com/how-to-improve-laptop-battery-life-and-usage-in-linux-using-tlp/
|
||||
[36]:http://www.unixmen.com/clean-up-your-linux-systems-using-bleachbit/
|
||||
[37]:http://www.opera.com/browser/
|
||||
[38]:http://www.google.com/chrome/index.html?hl=en-GB&brand=CHMB&utm_campaign=nl&utm_source=nl-ha-emea-nl-bk&utm_medium=ha
|
||||
[39]:http://www.unixmen.com/how-to-install-google-earth-in-linux/
|
||||
127
sources/Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) Officially Released.md
Normal file
127
sources/Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) Officially Released.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) Officially Released
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Canonical has announced that the next installment of their operating system, Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) has been officially released and it's now available for download.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) may not seem like much when compared with the previous Ubuntu 13.04 (Raring Ringtail) released, but it's an obvious evolution, at least in terms of stability.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the biggest changes in Ubuntu is the implementation of a new Linux kernel, which right now is actually the latest stable version available. This is great news for the owners of new hardware who will be able to enjoy the new operating system without much fuss.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the developers, Ubuntu 13.10 includes the 3.11.0-12.19 Ubuntu Linux kernel which was based on the v3.11.3 upstream Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
Other important changes include a number of improvements for AppArmor, which has received some extra attention during this development cycle.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, support has been added for fine-grained DBus mediation for bus, binding name, object path, interface and member/method, AppArmor has been integrated with several services as part of the ApplicationConfinement work in support of click packages and the Ubuntu appstore, and the support for policy generation via the aa-easyprof tool and apparmor-easyprof-ubuntu policy has been improved.
|
||||
|
||||
[Ubuntu 13.10][1] (Saucy Salamander) also comes with Unity 7, which is a shame because everyone was expecting Unity 8, which will be integrated on the phones.
|
||||
|
||||
In any case, users will enjoy the “101 Scopes” upgrade. Formerly known under the name of Lenses, the Scopes have been integrated much better with Unity, providing much more relevant responses to the user's queries in the Dash.
|
||||
|
||||
Users will be able to upgrade to the new version of Ubuntu in no time. Just open Software Sources and Press Alt+F2 and type in "update-manager -d" (without the quotes) into the command box.
|
||||
|
||||
This should trigger the updates and the rest is a piece of cake. Just follow the instructions and you will have Ubuntu 13.10 installed in no time.
|
||||
|
||||
## If you want a fresh install, just download Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander): ##
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander).**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit][2][iso] [895 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit][3][iso] [883 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit + Mac][4][iso] [881 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Ubuntu Server 13.10 (Saucy Salamander).**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Server 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit][5][iso] [658 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Server 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit][6][iso] [672 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Server 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit Mac][7][iso] [673 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Server 13.10 (img) Armhf + OMAP4][8][binary] [694 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Ubuntu Core 13.10 (Saucy Salamander).**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Core 13.10 tar.gz (32-bit)][9][sources] [37 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Core 13.10 tar.gz (64-bit)][10][sources] [38 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Core 13.10 tar.gz (PowerPC)][11][sources] [37 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Ubuntu Studio 13.10 (Saucy Salamander).**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Studio 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit][12][iso] [2.40 GB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Studio 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit][13][iso] [2.40 GB]
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Kubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander).**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Kubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit][14][iso] [1 GB]
|
||||
- [Kubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit][15][iso] [1 GB]
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Xubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander).**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Xubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit][16][iso] [834 MB]
|
||||
- [Xubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit][17][iso] [842 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Edubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander).**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Edubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit][18][iso] [2.80 GB]
|
||||
- [Edubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit][19][iso] [2.80 GB]
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Lubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander).**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit Alternate CD][20][iso] [663 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit Alternate CD][21][iso] [674 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit + Mac Alternate CD][22][iso] [677 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) PowerPC Alternate CD][23][iso] [703 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit Desktop CD][24][iso] [696 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit Desktop CD][25][iso] [702 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) PowerPC Desktop CD][16][iso] [710 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit + Mac Desktop CD][17][iso] [700 MB]
|
||||
- [Lubuntu 13.10 (tar.gz) Armhf + AC100][28][binary] [469 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Ubuntu-GNOME 13.10 (Saucy Salamander).**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ubuntu GNOME 3.10 (ISO) 32-bit][29][iso] [876 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu GNOME 3.10 (ISO) 64-bit][30][iso] [865 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Ubuntu Kylin 13.10 (Saucy Salamander).**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Kylin 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit][31][iso] [934 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Kylin 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit][32][iso] [941 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Ubuntu-13-10-Saucy-Salamander-Officially-Released-391964.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.canonical.com/content/latest-ubuntu-1310-includes-first-step-mobile-pc-convergence
|
||||
[2]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy/ubuntu-13.10-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy/ubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
[4]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy/ubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64+mac.iso
|
||||
[5]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy/ubuntu-13.10-server-i386.iso
|
||||
[6]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy/ubuntu-13.10-server-amd64.iso
|
||||
[7]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy/ubuntu-13.10-server-amd64+mac.iso
|
||||
[8]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy/ubuntu-13.10-server-armhf+omap4.img
|
||||
[9]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-core/releases/13.10/release/ubuntu-core-13.10-core-i386.tar.gz
|
||||
[10]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-core/releases/13.10/release/ubuntu-core-13.10-core-arm64.tar.gz
|
||||
[11]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-core/releases/13.10/release/ubuntu-core-13.10-core-powerpc.tar.gz
|
||||
[12]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntustudio/releases/13.10/release/ubuntustudio-13.10-dvd-i386.iso
|
||||
[13]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntustudio/releases/13.10/release/ubuntustudio-13.10-dvd-amd64.iso
|
||||
[14]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/kubuntu/releases/13.10/release/kubuntu-13.10-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[15]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/kubuntu/releases/13.10/release/kubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
[16]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/xubuntu/releases/13.10/release/xubuntu-13.10-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[17]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/xubuntu/releases/13.10/release/xubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
[18]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/edubuntu/releases/13.10/release/edubuntu-13.10-dvd-i386.iso
|
||||
[19]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/edubuntu/releases/13.10/release/edubuntu-13.10-dvd-amd64.iso
|
||||
[20]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-alternate-i386.iso
|
||||
[21]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-alternate-amd64.iso
|
||||
[22]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-alternate-amd64+mac.iso
|
||||
[23]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-alternate-powerpc.iso
|
||||
[24]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[25]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
[26]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-desktop-powerpc.iso
|
||||
[27]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64+mac.iso
|
||||
[28]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/lubuntu/releases/13.10/release/lubuntu-13.10-preinstalled-desktop-armhf+ac100.tar.gz
|
||||
[29]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-gnome/releases/13.10/release/ubuntu-gnome-13.10-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[30]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-gnome/releases/13.10/release/ubuntu-gnome-13.10-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
[31]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntukylin/releases/13.10/release/ubuntukylin-13.10-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[32]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntukylin/releases/13.10/release/ubuntukylin-13.10-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
54
sources/Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) Screenshot Tour.md
Normal file
54
sources/Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) Screenshot Tour.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) Screenshot Tour
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) is now officially available for download, so we’re taking a closer look at the latest operating system from Canonical.**
|
||||
|
||||
This latest version of Ubuntu, 13.10, was supposed to integrate Mir, the new display server from Canonical, but last minute problems forced the developers to drop it for now.
|
||||
|
||||
Even without Mir, Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) still features quite a few improvements, such as a new Linux kernel, Unity 7, improves Dash search, Ubuntu One integration, and a lot more changes under the hood.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the developers, [Ubuntu][4] 13.10 includes the 3.11.0-12.19 Ubuntu Linux kernel which is based on the v3.11.3 upstream Linux kernel. Also, the distribution will only be supported for 9 months. Non-LTS releases prior to Ubuntu 13.04 were supported for 18 months.
|
||||
|
||||
You can download Ubuntu 13.10 right now from Softpedia, and don't forget to check out the screenshot tour below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Download Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander):**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit][1][iso] [895 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit][2][iso] [883 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit + Mac][3][iso] [881 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Ubuntu-13-10-Saucy-Salamander-Screenshot-Tour-392149.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy/ubuntu-13.10-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[2]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy/ubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy/ubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64+mac.iso
|
||||
[5]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/SaucySalamander/ReleaseNotes
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 Released – But Is It An Essential Upgrade?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**It’s release day for Ubuntu 13.10. After 6 long months in development the ‘Saucy Salamander’ is finally available to download.**
|
||||
|
||||
With a growing user base of some 20 million plus, every update to Ubuntu, no matter how trivial it turns out to be, commands attention. This release is no exception.
|
||||
|
||||
But is it an essential upgrade?
|
||||
|
||||
Read on for our verdict, or hit the button below to grab a copy and find out for yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Ubuntu 13.10**:[http://releases.ubuntu.com/13.10/][1]
|
||||
|
||||
## “Ubuntu 13.10 Is Boring” - The Internet ##
|
||||
|
||||
I’ve seen many people – tech journalists, bloggers and arm-chair critics alike – describe Ubuntu 13.10 as a ‘boring’ release.
|
||||
|
||||
While it’s true that the Saucy Salamander brings fewer new features to the desktop than previous releases have, there are definite improvements and changes to be found – it’s just that most of them are relatively minor.
|
||||
|
||||
Emphasis on ‘most‘.
|
||||
|
||||
**A Dash Full of Things**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*How much of this is actually useful?*
|
||||
|
||||
Unity’s new Smart Scopes feature is the big draw of this release. It super-charges the Dash with semantic intelligence, drawing together information from a wide range of online sources for every search you make.
|
||||
|
||||
*Amazon, eBay, Etsy, Wikipedia, Weather Channel, SoundCloud* - over 50 web services are queried.
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘…unintelligible, irrelevant mess.’
|
||||
|
||||
On paper the feature sounds helpful: with the tap of a key you can bypass your browser and find whatever it is you’re looking for, wherever it may be, right from the desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
In practice it’s less of a help and more of a hindrance. With so many web services offering results for a search term – however innocuous it might be – the Dash ends up resembling a wall painted in unintelligible, irrelevant mess.
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘In its current form the feature fails to trump the browser experience.’
|
||||
|
||||
There is an attempt at bring order to this chaos. Results are ‘grouped’ by theme, e.g. Shopping, Music, Video. The Results Filter also helps give some control over the flood of info.
|
||||
|
||||
But, quite honestly, in its current form the feature fails to trump the browser experience. Google is smarter at knowing what it is I’m trying to find, and presents results in a format that is, visually, easier to browse and filter.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu developers say that **results will become more relevant** as the service ‘learns’ from users, so there is hope.
|
||||
|
||||
Turn Scopes Off
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Each Scope can be turned off individually*
|
||||
|
||||
Switching the ‘Smart Scopes’ feature off entirely is simple enough, though my tip would be to individually disable the Scopes returning results of no relevance to you. That way you can continue using the feature, but filter out the noise.
|
||||
|
||||
## The Ubuntu 13.10 Desktop ##
|
||||
|
||||
**Indicator Keyboard**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Whether you need it or not, a new ‘Keyboard Indicator’ has been added to Ubuntu to make switching between multiple input languages easier.
|
||||
|
||||
To turn off the applet head to Text Entry Settings and uncheck the box next to ‘Show Current Input Source in Menu Bar’.
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu One Login**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A login/sign-up page for Ubuntu One has been added to the Ubuntu installer, saving the need to configure accounts after installation.
|
||||
|
||||
**Performance**
|
||||
|
||||
With Unity 7 now sticking around for a lot longer than originally planned (it’ll be default in 14.04 LTS, due in April) some much needed maintenance has gone on.
|
||||
|
||||
While I haven’t run any benchmarks myself, those who have done so note there are notable performance gains arriving with this release.
|
||||
|
||||
The Unity Dash is especially responsive, while Compiz leaves less weight on system resources.
|
||||
|
||||
**Applications**
|
||||
|
||||
Although the Ubuntu Software Center is on hand for all your application needs, the latest versions of Firefox, Thunderbird, LibreOffice and Shotwell come pre-installed out of the box.
|
||||
|
||||
The Ubuntu repositories are also stocked with newer versions of other popular apps, like the [Geary mail client][2] and popular image editor GIMP.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, [GTK3 apps now look better under Ubuntu’s default theme][3].
|
||||
|
||||
## Summary ##
|
||||
|
||||
> A solid, reliable release – more of a footnote than the start of a new chapter
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 is a solid, reliable release that cements its position as the ‘go to’ Linux distro for new users and seasoned pros alike.
|
||||
|
||||
At face value this release does seem like more of a footnote in Ubuntu’s history than the start of a whole new chapter. A handful of small, iterative changes, including a more performant Unity desktop, certainly make it a worthwhile upgrade – but far from an essential one.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/ubuntu-13-10-review-available-for-download
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/13.10/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/geary-0-4-released-with-new-look-new-features
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/08/ubuntu-themes-fix-coming-to-saucy
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
97
sources/Ubuntu 13.10 released and available for download.md
Normal file
97
sources/Ubuntu 13.10 released and available for download.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 released and available for download
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Six months have passed since the previous Ubuntu release, six months full of development incarnated now in the public space as Ubuntu 13.10.
|
||||
|
||||
The Saucy Salamander development cycle has been characterized by numerous optimizations and improvements, as well as by new features and an overall increase in stability, reliability and speed.
|
||||
|
||||
What is **new** in Ubuntu 13.10?
|
||||
|
||||
**Unity 7** presents itself now as a significantly enriched place for searches, allowing the user to search through a massive amount of data sources ranging from local folders, locally-stored music tracks to Wikipedia and deviantART due to the newly-implemented Smart Scopes Project.
|
||||
|
||||
Essentially, via the Smart Scopes project, the Dash has been extended to embrace the web and its sources, gathering under a single view a wide, diverse and useful range of sources, typing a term in the search area, pushes the typed word through relevant online sources of the Internet, returning explanatory images, weather forecasts, historic references, places to look further, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
In Ubuntu 13.10, the Dash has been imprinted with the capacity of mixing one of the most important and useful data sources, permitting search actions in a matter of seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
Unity 7 exposes by default numerous scopes (data sources) in the Applications scope, in order to satisfy the user; clicking on a scope, allows the user to 1-click away enable/disable the scope, disabling a scope, temporarily removes the scope from the searched-through data sources.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 uses the handy **Alt+Tab Switcher**, manner of switching between opened applications receiving mouse pointer support, hitting now the keyboard's `Alt+Tab` keys, summons the `Alt+Tab` Switcher, while retaining the functionality-enabled mouse pointer on the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
As a consequence, the user is able to act with the mouse pointer on the switcher.
|
||||
|
||||
nstalling Ubuntu 13.10, the user is to notice the default addition of Indicator Keyboard, appindicator housing language-specific functionalities on the easiness of the Unity panel, while featuring 1-click away functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
Shifting from one language to another is now doable by simply clicking on the Indicator Keyboard's preferred language.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 increases its **chameleonic** nature on the desktop, transforming the desktop's selection area into a background's average color handler; selecting files and folders on the desktop, the user is to be delighted by the newly-acquired chameleonic color used by the selection block, chameleonic area generating more consistency on the desktop.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu Software Center** has been updated with a more refined behavior when installing applications, featuring now more accurate trajectories of apps and subtly-refreshed animations, feature paired with handy offline DEB-installation support.
|
||||
|
||||
Having no Internet connection, the user is still able to install DEB packages via Ubuntu Software Center.
|
||||
|
||||
In Ubuntu 13.10, clearing all logged events is easier and more hassle-free via the new **Activity Log Manager**, featuring now a new look, feel and more deep coverage of logged event.
|
||||
|
||||
Activity Log Manager allows now the (on demand) removal of all Zeitgeist's logged events, removal affecting recent files and open with-like dialogs, too.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ambiance** and **Radiance**, Ubuntu's default light themes, come with significant long-awaited refinements, beautifying the desktop with consistent toolbars (fully dark, fully light), consistent menus, properly-rendered buttons, removal of unpleasant anesthetic white lines on dark backgrounds, etc, basically, being finely-tuned and affecting numerous applications and corners of the desktop.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Evince**, the handy document reader, gained a modern toolbar, where the eye is to be pleased by the new toolbar containing monochrome icons, more button-ized feel and relocated search area, transforming one's reading experience into a more enjoyable activity.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Shotwell** is now able to display the size of the about-to-be-cropped portion from edited images, thus the user can clearly observe the size of cropped areas, as well as being able to more accurately crop specific intended sizes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Playing music tracks has a superior approach in Ubuntu 13.10 due to Rhythmbox's visually enriched look, subtle changes adding elegance into the simplistic-yet-handy music player; newly-added buttons and the text-less toolbar align Rhythmbox to the latest version of Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As usual, Ubuntu 13.10 has received the fruits of the **wallpaper**-submission contests and the default wallpaper, enriching the desktop with interesting shapes, colorful patterns and an evolved version of the default wallpaper, resulting more vivid full-of-vitality visuals decorating Ubuntu 13.10.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The 2.8 series of **Transmission** increases the amount of details exposed in torrent-specific actions, pushing a useful bundle of new features into Ubuntu 13.10's torrent-downloading experience, as in the case of several fixes and extra informations (like for example, allowing the user to observe the size of the free space when adding torrents).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Devices (USB sticks, disk partitions) are now fully exposed on the GNOME Disks' main view, permitting an intuitive manner of selecting devices and acting on them; erasing a USB stick is as simple as selecting it and hitting the bottom-bar's button, without the need of navigating through GNOME Disks' internals.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Typing assistance, popups and sound support are features implemented in Ubuntu 13.10's Onboard, default virtual keyboard offering modernism and significantly-enriched capabilities to users seeking to utilize the user-friendly virtual keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 comes with **updated** versions for its default software, among which Firefox, Linux kernel, LibreOffice, etc, each and each application offering new features, optimizations and an overall up-to-date nature.
|
||||
|
||||
Installing and running Ubuntu 13.10, the user is to notice the level of **strength**, **speed** and **smoothness**, **fluid** Ubuntu experience fully penetrating all corners of the desktop; faster Unity, more responsive applications, less used resources and an overall agile feel are part of Ubuntu 13.10.
|
||||
|
||||
Along with new features, Unity 7 has received several bug-fixes-only releases, versions solidifying and strengthening Unity, in order to deliver a Unity version almost reaching perfection, Unity presenting itself as no-compromise and suitable for every and every situation, ranging from maneuvering tens of opened windows to not-interfering with fullscreen games.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 is recommended for immediate installation, being a clear win in terms of performance, speed and agility, as compared to the previous Ubuntu 13.04.
|
||||
|
||||
Across the latest six months, the Ubuntu **quality** team has continued to extend the automated tests in more and more layers and areas of Ubuntu, generating even more solid and robust Ubuntu pieces, automated tests having the goal of stressing the 13.10 desktop, in order to detect more and more issues, issues then fixed and implemented in the powerful operating system.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 is available for download on [http://www.ubuntu.com/download][1]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/ubuntu-1310-released-and-available-download
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ubuntu.com/download
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 ‘Saucy Salamander’ Final has been released! | Installation Instructions With Screenshots
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Finally, the most expected distribution in Linux World, **Ubuntu 13.10 ‘Saucy Salamander’** final has been released, there is **no official release announcement yet**, but the [download page of Saucy has been updated][1] with the final packages. Just like most of you, We also expected it very long. This awesome distribution has come with plenty of new features and improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
**Download**
|
||||
|
||||
- **[Download Ubuntu 13.10 ‘Saucy Salamander’][1]**
|
||||
|
||||
If you have already a previous release of Ubuntu, and want to upgrade to the latest 13.10 version, then please follow our [step by step guide upgrade to Ubuntu 13.10 Saucy Salamander][2].
|
||||
|
||||
You can also Download the Getting Started Manual from the following link.
|
||||
|
||||
- **[Getting Started With Ubuntu 13.10][3]**
|
||||
|
||||
**What’s New in Ubuntu 13.10?**
|
||||
|
||||
- Kernel 3.11
|
||||
- Unity 7
|
||||
- Search hundreds of different online sources directly from the Dash.
|
||||
- Filter Dash results in several different ways.
|
||||
- [Smart Scopes][5]
|
||||
- Add or remove scopes from the Dash to customize your experience.
|
||||
- Browse messages from your social networks with the new Friends scope.
|
||||
- Comes with the latest OpenStack cloud platform (Code name: Havana).
|
||||
- Enhanced support for Linux Containers ([LXC][6]).
|
||||
- Get work done in style with LibreOffice 4.0, now with new, modern presentation templates and built-in support for Ubuntu’s integrated menu bar.
|
||||
|
||||
**Install steps of Ubuntu 13.10 for Newbies**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Press Continue:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Choose the first option and continue:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Here we have 3 options:
|
||||
|
||||
1- Install Ubuntu alongside them, this mean if you have windows installed on your hard drive, ubuntu will be installed alongside windows.
|
||||
|
||||
2- Erase Disk and install Ubuntu : **Be careful** because choosing this option will erase all the data on your hard disk. Only use it if you are testing in an old computer or if you have an empty hard drive
|
||||
|
||||
3- Something else: You can use this option if you have many partitions on your hard drive, use the empty one then to install Ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you choosed “something else” in the previous screen, You will got this screen, as you see in my case i chooses the free space on my hard disk :
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Choose your language:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enter your name, username, password …etc.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you don`t have an Ubuntu One account, choose “Login Later”.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Installation will start now.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now installation is done. Press reboot and enjoy the new release of Ubuntu 13.10 Saucy Salamander.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ok, you have successfully installed Ubuntu 13.10, What’s now? Well, We have made a comprehensive guide about [Top things to do after installing Ubuntu 13.10 Saucy Salamander][6]. This guide will help you to enhance Ubuntu 13.10 further for day to day activities and it contains lot of interesting insight and ideas about what you can and should do after a successful installation.
|
||||
|
||||
Still having some issues? well, don’t hesitate to contact us via [our brand new forum][7] or [IRC chat channel][8].
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/ubuntu-13-10-saucy-salamander-released-screenshots/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://releases.ubuntu.com/saucy/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unixmen.com/upgrade-ubuntu-13-04-raring-ubuntu-13-10-saucy-salamander/
|
||||
[3]:http://ubuntu-manual.org/
|
||||
[4]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/SmartScopes1304Spec
|
||||
[5]:http://lxc.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.unixmen.com/top-things-installing-ubuntu-13-10/
|
||||
[7]:http://ask.unixmen.com/BB/
|
||||
[8]:http://ask.unixmen.com/BB/chat.php
|
||||
65
sources/Ubuntu 13.10--It just works.md
Normal file
65
sources/Ubuntu 13.10--It just works.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10: It just works
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Find out why Jack Wallen thinks that Ubuntu 13.10 is a solid, reliable platform that just works. Do you agree? **
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I've been using Ubuntu for a very long time. I was one of the few in the media who adopted Unity as my primary desktop interface. In fact, I've grown so used to Unity that I have trouble finding any form of efficiency in other desktops. So, naturally, when a new Ubuntu release is about to be unleashed upon the world, I grab a beta and install it.
|
||||
|
||||
The hype surrounding the upcoming 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) was fairly significant. Leading this charge was the much-anticipated switch to Xmir. Well, thanks to a few show-stopping issues (such as dual-monitor support), Xmir has been pushed back to 14.04. Is this a big deal? Yes and no. Yes, because Xmir will be a major change to the sub-systems of Ubuntu. No, because Xmir must be faultless when released -- otherwise, the backlash will knock Canonical back so far in the past that they'll have a hard time recovering in the eyes of the Linux community.
|
||||
|
||||
Beyond Xmir, the biggest change from .04 to .10 is the much-maligned inclusion of Smart Scopes. What are Smart Scopes? Let me explain it in the simplest terms as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
When you open your browser and begin typing a string of characters, you know how that browser will make suggestions for you based on search terms, location, and history? Smart Scopes brings that same functionality to the desktop. I've run some tests on it, and it's pretty incredible. Search for nearly anything, and it will return results based on a number of criteria. Want to know the location of a restaurant in your area? I conducted a search for my favorite Mexican restaurant, Bazos, and an entry appeared in Smart Scopes (**Figure A**). Click the entry to get the address or open that entry in a web browser to get more information (and even reviews).
|
||||
|
||||
**Figure A**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**My favorite place to eat listed in Smart Scopes.**
|
||||
|
||||
I get it, there are people out there suffering from apoplectic fits of terror because Smart Scopes is an invasion of privacy. This is no different than what your web browser is doing. So, unless you constantly run your web browser in Incognito mode, all those search strings are saved and compared anyway. And the truth is, why wouldn't you want your search results based on your preferences and behavior instead of some generic algorithm? Personally, I don't mind my search results being quantified and qualified, so long as it constantly refines the search results based on my needs.
|
||||
|
||||
Smart Scopes isn't limited to seeking out search results from the network. You'll be happily searching for anything and everything on your local (or locally attached) drives as well. With this inclusion, Smart Scopes becomes one of the single most powerful search tools available.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, if you don't like Smart Scopes, you can turn them off. Here's how:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Click the Settings launcher
|
||||
1. Select Security & Privacy
|
||||
1. In the Search tab, turn Include online search results to Off (**Figure B**)
|
||||
|
||||
**Figure B**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**It's easy to turn off the Smart Scopes feature.**
|
||||
|
||||
With all of that said, let's step away from the arguments for or against search privacy and let me explain exactly why Ubuntu 13.10 is the perfect desktop for nearly any user.
|
||||
|
||||
The install was fresh from the latest daily build. During the installation, I included third-party software, updates, and was even able to authenticated to my UbuntuOne account. The install was incredibly simple (as most modern Linux distributions are), and at first login, everything was smooth.
|
||||
|
||||
What initially struck me about Ubuntu 13.10 is how everything worked out of the box. There was no need to install codecs to listen or view various multi-media files, flash worked, and everything was ready for average, daily computer use. You could work on office documents, set up your email account... you name it. But that has become the standard operating procedure for Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
So, what's different? Honestly, not much. However, what little difference there is should go a long way with the average user. Probably the single most important thing I've found is that a lot of the little quirks and oddities are gone. There are no longer any strange errors that randomly pop up to cause confusion and disdain among new users. Windows don't artifact or stall, the Dash is very responsive (as is Smart Scopes), and the compositing is smooth and effortless against your CPU. Also, the bug is resolved that plagued the Dash when trying to use the arrow keys to navigate through search results.
|
||||
|
||||
## Ubuntu 13.10 just works ##
|
||||
|
||||
I would go as far to say that Ubuntu has done to the desktop what Apple did with hardware/software -- it developed a clean, solid convergence of pieces to create a cohesive whole. Although that whole has ruffled some feathers, Ubuntu 13.10 should go a long way to smooth them out. How is that possible, considering how many users have turned their back (thanks to [the Wayland kerfuffle][1])?
|
||||
|
||||
Outside of Smart Scopes, there are no major changes. There's little excitement on the desktop -- it's still the same old look and feel. Oh sure, there are tiny tweaks here and there, but overall, 13.10 and 13.04 look the same at first blush. Under the hood? Same thing. You'll find a new kernel (3.11) and a few other tweaks, but nothing to cause the cheerleaders of the world to frustratingly toss their pompoms in the air.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, Ubuntu 13.10 is a refinement of something that was already there and polished. There are no show stopping or curtain call worthy new features -- just countless tweaks here and there that make the whole system run smooth and fast.
|
||||
|
||||
The final release of Saucy Salamander is set for October 17, 2013. You can get a copy of the [daily build][2] or wait for the release date. Either way, you're going to get a solid, reliable platform that just works.
|
||||
What are your thoughts about Saucy Salamander? Share your opinion in the discussion thread below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.techrepublic.com/blog/linux-and-open-source/ubuntu-1310-it-just-works/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.techrepublic.com/blog/linux-and-open-source/the-canonical-conundrum-why-the-ubuntu-hate/
|
||||
[2]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/daily-live/current/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu Countdown, third-party Ubuntu 13.10-related interesting widget
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Two days left for the exciting arrival of Ubuntu 13.10, stable Ubuntu release marking a fresh new Ubuntu experience with new features, optimizations and under-the-hood enhancements.
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu Countdown** is a **third-party** widget that displays in real time the amount of time left until Ubuntu 13.10's release, offering an interesting clock rendered on top of an Ubuntu-wise wallpaper.
|
||||
|
||||
The Ubuntu Countdown widget comes with minimalism and readability, allowing the viewer to easily observe the interval of time between the now and the October 17th's long-awaited release.
|
||||
|
||||
A definitely interesting aspect of the mentioned countdown is its double-sided nature: on one hand, there is the countdown, on the other hand, there is the encapsulated [ubuntu.com][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Meaning, clicking on the widget, changes the countdown with the official ubuntu.com website, permitting further actions on ubuntu.com, actions happening inside the same widget.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Countdown can be easily embedded into a webpage by simply copying & pasting the embed code available on [http://www.corbindavenport.com/ubuntu/][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/ubuntu-countdown-third-party-ubuntu-1310-related-interesting-widget
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.corbindavenport.com/ubuntu/
|
||||
23
sources/Ubuntu Mobile icon theme sees new icons.md
Normal file
23
sources/Ubuntu Mobile icon theme sees new icons.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu Mobile icon theme sees new icons
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Unity 8, Web Browser App, Friends App, Ubuntu SDK are pieces of the upcoming Ubuntu converged, pieces that are gradually forming the whole,--the convergence-enabled Ubuntu--, with a constantly-maintained vigorous development covering all the pieces via a consistent uniform development energy.
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu Mobile** is a fancy icon theme used by Ubuntu Touch, icon theme presently containing relevant icons for used actions and applications, progressively being expanded to cover the Ubuntu Touch's needs.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Mobile has been updated to another release, adding new icons, among which icons located under the actions category.
|
||||
|
||||
`Add-to-call`, `browser-timeline`, `calendar`, `calendar-today`, `dropdown-menu`, `external-link`, `media-playlist-repeat`, `media-playlist-shuffle`, `navigation-menu`, `new-event`, `remove-from-call` are among the newly-introduced icons`, new icons increasing the available actions and buttons of the growing and growing Ubuntu Mobile theme.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Mobile (while being used in Ubuntu Touch by default) is [available][1] for installation via Ubuntu 13.10's Ubuntu Software Center.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/ubuntu-mobile-icon-theme-sees-new-icons
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:apt://ubuntu-mobile-icons
|
||||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
will.qian is translating this article
|
||||
Unity 8 updated with interesting refinements
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Unity 8][1] is the next-generation Unity aimed at and being developed in mind with Ubuntu converged, Unity 8 that is to deliver beauty, power and professional designs for phones, tablets and desktops.
|
||||
|
||||
Unity 8 has been updated to yet-another meaningful release, optimizing its elements with more clarity and natural behaviors.
|
||||
|
||||
Weeks ago, Unity 8 received support for the carousel effect in the Videos scope, carousel item-listing shortly after adopted by the Music scope, basically, Unity 8 featuring coverflow manners of rendering and organizing content in its Videos and Music scopes.
|
||||
|
||||
The latest Unity 8 version brings refinements for the **coverflow** effect used by the Music scope, rendering their covers (the big-sized thumbnails generated by music tracks) with a subtly-refined shape.
|
||||
|
||||
Opening the Music scope, the user is to notice the new shape used by the cycled-through covers featuring a more square look, increasing their width and decreasing their height; the result: the covers have now more elegance, emanating style and class, moreover, being now visually aligned with the other thumbnails from (for example) the `Albums` category (featuring the same look & feel).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unity 8 comes with several search areas, search areas enriched with support for activity indicators; typing now a term in the search area, displays a vivid extremely-energetic spinning circle, transmitting to the user its in-progress state.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unity 8 is [available][2] for testing via Ubuntu 13.10's Ubuntu Software Center.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/unity-8-updated-interesting-refinements
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/unity8
|
||||
[2]:apt://unity8
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
VirtualBox 4.3 comes with New Multi-Touch Support, virtual cam and more
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Oracle announced [the release of VirtualBox 4.3][1], this is a major release that comes with important new features, devices support and improvements. According to the announcement, “*Oracle VM VirtualBox 4.3 adds a unique virtual multi-touch interface to support touch-based operating systems, and other new virtual devices and utilities, including webcam devices and a session recording facility. This release also builds on previous releases with support for the latest Microsoft, Apple, Linux and Oracle Solaris operating systems, new virtual devices, and improved networking functionality.* “
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
What`s new in VirtualBox 4.3:
|
||||
|
||||
- **New operating system platform support**: Oracle VM VirtualBox 4.3 supports the input device features, of the latest platforms such as Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2 and Mac OS X 10.9 in a virtual environment. For Windows 8.1, the new release can also simulate a 10 point multi-touch device. Additionally, improved 3D acceleration accommodates the translucent effects in the latest Linux distributions from Ubuntu and Fedora, and enhanced multi-monitor support allows users with multiple screens to use them from within the virtual environment.
|
||||
- **New devices and management utilities**: A new virtual USB webcam device enables video conferencing applications such as Skype or Google Hangouts to run in virtual machines. New recording session capabilities allow users to record part, or all, of a virtual machine session using a new video-capture facility. For easy playback, movies are created in WebM format by a range of movie-players.
|
||||
- **Networking improvements**: A new Network Address Translation (NAT) option allows virtual machines to talk to each other on the same host, and communicate with the outside world. IPv6 is now offered across Bridged, Host-only, Internal and the new NAT networking modes. In addition, the remote display server built-in to Oracle VM VirtualBox can accommodate RDP connections over IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation: ##
|
||||
|
||||
For Ubuntu, Fedora, LinuxMint, Debian, Open Suse and Mandriva, You can download the new release and the Guest additions pack from [this Link][2] . (You need to download the package related to your distro version)
|
||||
|
||||
For Ubuntu via repository:
|
||||
|
||||
To start the installation, first open a terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
Copy and paste the following in to your command-line. Press Enter to download and install key from Oracle. Type user password and press Enter to continue:
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget -q http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/debian/oracle_vbox.asc -O- | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
|
||||
After Oracle’s Public Key has been downloaded and installed successfully you will see an OK message in the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
Now run this command to add VirtualBox to your repository:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://download.virtualbox.org/virtualbox/debian raring contrib" >> /etc/apt/sources.list.d/virtualbox.list'
|
||||
|
||||
When prompted, input password and press Enter.
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, run the combined command below to update your system and install VirtualBox.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install virtualbox-4.3
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/virtualbox-4-3-released/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.oracle.com/us/corporate/press/2033376?rssid=rss_ocom_pr
|
||||
[2]:http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/server-storage/virtualbox/downloads/index.html?ssSourceSiteId=ocomen#vboxhttp://
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
||||
l3b2w1 translating When open source invests in diversity, everyone wins
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Jessica McKellar is an entrepreneur, software engineer, and open source developer. She helps organize the Boston Python user group and plays a big role in diversity outreach by introducing and welcoming more beginners and women. Participation has increased from 0-2% to 15% and the user group has sustained this over the past two years.
|
||||
|
||||
It's results like this that convince Jessica that when open source communities invest in diversity outreach, everyone benefits. Since implementing a beginner series, intermediate workshops, and open source sprints, the Boston Python user group has over quintupled in size, from 700 members to 4000+. They are now the largest Python user group in the world. That type of growth is something all open source communities should aspire to.
|
||||
|
||||
Read more about [Jessica McKellar][1] in this interview.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
**How long have you been in the open source community? Did you have a mentor when you started?**
|
||||
|
||||
My first ever contribution to an open source project was some documentation for the [Twisted project][2] in 2009 (Twisted is an event-driven networking engine written in Python). I've been involved with the project ever since, am now a core contributor, and have even had the pleasure of writing a book about Twisted.
|
||||
|
||||
I had a great first experience contributing to Twisted: the community had detailed new contributor documentation and was supportive and patient as I stumbled through using the process and tools for the first time. I wouldn't say that I had a specific mentor, but I benefited from the collective support of the Twisted community and the patient feedback from the reviewers on my first tickets.
|
||||
|
||||
**How have you seen open source software evolve since you join the community?**
|
||||
|
||||
There has been a clear and wonderful progression towards embracing diversity and diversity outreach, and in particular supporting beginners of all backgrounds. The increasing adoption of Codes of Conduct by technical conferences, the [GNOME Outreach Program for Women][3], the [Python Software Foundation's][4] Outreach and Education program, and PyCon's [Young Coders][5] events are just a few examples of great work the open source community is doing to make itself a welcoming and supportive environment.
|
||||
|
||||
**You're heavily involved with the Python community. Why Python? What was your initial experience with the language?**
|
||||
|
||||
I first used Python in school (I was at MIT right on the cusp of the core CS curriculum switching from Scheme to Python) and have used it at every job I've had. It's also my go-to language for most side projects. Besides being a language I think is a joy to develop in, I invest in the Python community because of its commitment to fostering a supportive and welcoming environment for people of all backgrounds.
|
||||
|
||||
**You and Asheesh Laroia had [a great presentation][6] during PyCon 2012 about the Boston Python user group increasing its diversity. Can you describe what you folks did?**
|
||||
|
||||
For the past 2 years, Boston Python has been running a recurring pipeline of events focusing on bringing more women into the local Python community. The first step in this pipeline is a hands-on weekend workshop for first-time programmers, which we've run eight times for over 400 women.
|
||||
|
||||
Our goals with this initiative are to:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Bring more women into the local programming community, with a specific goal of reaching 15% women at all Boston Python user group events.
|
||||
1. Show the local programming community examples of great women programmers.
|
||||
1. Develop resources for other programming user groups to run their own diversity outreach events.
|
||||
|
||||
Prior to running these workshops, a typical Boston Python user group event had 0-2% women. Since running these workshops, general user group events have met or exceeded 15% women. These are large events bringing in 80-120 people, so this represents a huge leap both as a percentage and in absolute terms for the number of women attending. Even more remarkable is that these results have been sustained for 2 years!
|
||||
|
||||
The great secret of all of this outreach is that even though you are focusing on a specific under-represented group, everyone benefits. Running these intro workshops forced us to learn how to truly support beginners. We started running a monthly "Project Night" as a follow-up to the intro workshops, to give beginning and intermediate learners more opportunities to learn and practice the language with in-person mentoring. We've developed curricula and practice projects that have been used all over the world. We've run intermediate workshops and open source sprints. Through all of this, the user group has over quintupled in size, from 700 members to 4000+, making us the largest Python user group in the world.
|
||||
|
||||
In a nutshell, when you invest in diversity outreach, everyone wins.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://opensource.com/life/13/10/interview-jessica-mckellar
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://web.mit.edu/jesstess/www/
|
||||
[2]:https://twistedmatrix.com/trac/
|
||||
[3]:https://wiki.gnome.org/OutreachProgramForWomen
|
||||
[4]:http://www.python.org/psf/
|
||||
[5]:https://us.pycon.org/2013/events/letslearnpython/
|
||||
[6]:http://pyvideo.org/video/719/diversity-in-practice-how-the-boston-python-user
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
Xubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) Officially Released
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Canonical has announced that Xubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) operating system is now officially available for download.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Xubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander) has been released along with all the other distribution, but it's not a major improvement over the previous version. Still, users should upgrade as soon as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the changelog, a new version of xfce4-settings has been uploaded bringing amongst other things a new dialog to set up your displays, and a tool for changing your theme colors easily, gtk-theme-config, has been added to the default installation, just to mention a couple of changes.
|
||||
|
||||
Starting from 13.04, the Xubuntu images will not fit on standard CDs anymore. To install Xubuntu, you will need other media such as a USB device or a DVD.
|
||||
|
||||
More details about this release can be found in the official [announcement][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Download Xubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander):
|
||||
|
||||
- [Xubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 32-bit][2][iso] [834 MB]
|
||||
- [Xubuntu 13.10 (ISO) 64-bit][3][iso] [842 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Xubuntu-13-10-Saucy-Salamander-Officially-Released-392132.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/SaucySalamander/ReleaseNotes/Xubuntu
|
||||
[2]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/xubuntu/releases/13.10/release/xubuntu-13.10-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/xubuntu/releases/13.10/release/xubuntu-13.10-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Vito
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast: Improve apt-get Download Speed
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**[apt-fast][1]** is a “**shell script wrapper**” for **apt-get** and **aptitude** that can drastically improve APT download times by downloading packages with multiple connections per package. apt-fast uses **aria2c** or **axel** download managers to speed up the APT download time. Just like the traditional apt-get package manager, apt-fast supports almost all apt-get functions such as **install, remove, update, upgrade, dist-upgrade** etc. And one more notable feature is it supports proxy too.
|
||||
|
||||
**Install apt-fast On Ubuntu**
|
||||
|
||||
Use the following PPA to install apt-fast. apt-fast developer says “**Some distros, such as PCLinuxOS include apt-fast in their default repos**”. I expect the same in Ubuntu/Debian default repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
To Add apt-fast PPA, enter the following command in Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apt-fast/stable
|
||||
|
||||
Update the sources list with command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
Now install it using command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install apt-fast
|
||||
|
||||
During installation it will ask you to select the maximum number connections to download packages.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Select No and continue installation. If you select Yes, apt-get won’t ask you the confirmation during any package installation.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I found **aria2** download manager has been installed along with apt-fast installation automatically. So you don’t have to install it separately.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want re-configure apt-fast options, you can do it using command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg-reconfigure apt-fast
|
||||
|
||||
**Usage**
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to apt-get functions, we can use:
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast install package
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast remove package
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast update
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast dist-upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
and more.
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast package manager in action:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Create alias (Optional)**
|
||||
|
||||
Edit **~/.bashrc** file and add the following line at the end.
|
||||
|
||||
alias apt-get='apt-fast'
|
||||
|
||||
Or simply run the following command to add it in your **~/.bashrc** file.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo echo "alias apt-get='apt-fast'" >> ~/.bashrc
|
||||
|
||||
From now whenever you run apt-get command to install, remove, update and upgrade packages, it will use apt-fast automatically in the background. Sounds cool? Yes it should.
|
||||
|
||||
During testing i found it very fast compared to apt-get when downloading packages. Give it a try, you will agree with me. Cheers!!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/improve-apt-get-download-speed-apt-fast/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/ilikenwf/apt-fast
|
||||
50
sources/‘Polari’ – An Awesome New IRC App for GNOME.md
Normal file
50
sources/‘Polari’ – An Awesome New IRC App for GNOME.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
‘Polari’ – An Awesome New IRC App for GNOME
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
You have to hand it to the GNOME designers and developers: their work in creating a coherent, integrated set of apps for the desktop is showing true promise.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*The latest build of Polari in action.*
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, they’ve barely sat still over the last couple of years, creating app after app.
|
||||
|
||||
There are now dedicated apps for Music, Video and Photos; a virtual machine manager in the shape of Boxes; the Maps, Weather & Notes tools are all looking fantastic. And the new GNOME Software Store? Design wise it knocks Ubuntu’s aged offering out of the park!
|
||||
|
||||
But it seems that the GNOME app gurus aren’t done yet. Work has recently begun on a new GNOME 3 IRC app called ‘Polari’.
|
||||
|
||||
(As an aside, it’s a testament to the focus within the GNOME development community on putting users first that the one tool they likely use most often to communicate is one of the last to get the GNOME app treatment.)
|
||||
|
||||
## Polari – Planned Features ##
|
||||
|
||||
It’s not fixed in a dusty coding tome that all IRC clients have to resemble something from an 80s sci-fi movie, or be intimidating to the general user. Even in today’s world of instant communications via social networks, IRC remains a great way for people to chat.
|
||||
|
||||
To this end, if [Polari][1] (expect a name change further down the line) had a slogan it would be “*An IRC client for dummies*.”
|
||||
|
||||
On the features n’ functionality front Polari aims to offer:
|
||||
|
||||
- Easy connection to IRC servers & rooms
|
||||
- Clearly see mentions & notifications
|
||||
- Support GNOME 3 notifications
|
||||
- Integration with Contacts, the GNOME contacts app
|
||||
- History & transcript features
|
||||
- Link previews
|
||||
- File transfers
|
||||
|
||||
Developer-orientated features have also been mooted, including integrated support for Pastebin & Bugzilla.
|
||||
|
||||
So when can you try it? Not quite yet. Development of Polari is still in its early stages, but, if you’re willing to build it from Git (requires GNOME 3.10) you’ll find that it’s already capable of handling the basics, including delivering notifications for mentions.
|
||||
|
||||
For code-compiling-phobes Polari is expected to feature (most likely as an app preview) in GNOME 3.12, due next year.
|
||||
|
||||
- [More about Polari][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/gnome-irc-app-polari-in-development
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://git.gnome.org/browse/polari
|
||||
[2]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Polari
|
||||
@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Manage Passwords Securely in Ubuntu with KeePassX
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**With security issues becoming more and more important, the emphasis on secure passwords (as well as other methods like multiple step authentication) has never been greater.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
With that in mind I recently tried out several secure password managers to try and find something secure, but also easy to use and cross-platform.
|
||||
|
||||
First, I went to [LastPass][1]. It’s probably the most known tool for managing your passwords, and since it’s based on the web, it’s the most **cross platform** of them all. However, I found the interface lacking, and the number of tools and options on offer was overwhelming.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, I tried [KeePass 2][2]. While this is a perfectly capable app, very similar to the tool I’m going to talk about in a minute, it doesn’t provide official Linux packages, and the community ports, while serviceable, aren’t the nicest looking apps out there. So I tried other apps.
|
||||
|
||||
My favourite of all those I tested was **KeePassX**. It started out as a Linux port of KeePass, but eventually evolved as its own app. It bests KeePass 2 with a nicer, more native looking interface.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using KeePassX in Ubuntu ##
|
||||
|
||||
Conveniently, KeePassX already has packages in Ubuntu available for installation.
|
||||
|
||||
Install keepassx from the command line or **install it from the Software Centre**:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Install KeePassX from the Ubuntu Software Centre][3]
|
||||
|
||||
When you open it, you’ll see a blank window. Use the first button on the toolbar to create a new database. You can either protect it by using key files, or a password. You probably want a password which is quite easy to remember and type — you’ll be typing it in a lot, but on the other hand you don’t want anyone else accessing your database.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you need to save it somewhere. I saved mine in my Dropbox, so I can access it from multiple locations. Dropbox uses two factor authentication, so if anyone wants to get into my Dropbox to access this database, they’ll also need to have my phone, which makes the process secure enough.
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can use other services like Google Drive and Skydrive which both use standard [Authenticator][4] apps, or Box which uses SMS for two factor authentication.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, if you’re **really** worried about your passwords, you probably won’t want to save it where other parties can theoretically access it.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*The main screen of KeePassX in Ubuntu*
|
||||
|
||||
Using the app is actually pretty straightforward. You can add groups, and into those groups you can add keys. KeePassX includes a handy password generator whenever you need to input a password. I tend to generate my passwords with all the basic characters and special characters selected as well, at 20 characters long, but that of course depends on what the website accepts.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s important to note that some websites don’t always tell you how long a password they’ll accept, and opt to just put a limit on the input box. If your pasted in password doesn’t quite look long enough, it probably isn’t. It’s happened to me a few times.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*KeePassX password generator*
|
||||
|
||||
n my everyday usage of KeePassX, I’ve noticed a few things that should make using it a bit easier:
|
||||
|
||||
**Copy & Paste Paranoia**
|
||||
|
||||
You might be worried about the notion of copying and pasting passwords. It sure is more efficient than typing them out manually. By default, KeePassX clears the clipboard about a minute, but you can shrink this in the settings. You don’t need to be worried about someone else pasting the password and viewing it on your computer. You can also use a feature called AutoType, which types your password automatically, but this is a bit useless since for some reason it puts the password together with the username in the same field.
|
||||
|
||||
**Database Dilemma**
|
||||
|
||||
If you save the database in the cloud, don’t set the password to the cloud service to something completely random. It’s no good having the password to it saved inside the cloud if you can’t access the cloud. It might seem obvious, but it’s not something I originally realised.
|
||||
|
||||
**SECURE ALL THE PASSWORDS**
|
||||
|
||||
Whipping out your phone constantly while at work or school to access your most commonly used accounts can be a pain, so keep that in mind when settings passwords.
|
||||
|
||||
## The future ##
|
||||
|
||||
If you’ve looked into KeePass 2 and KeePassX previously, you might’ve noticed that they use different database formats.
|
||||
|
||||
KeePass 2 uses a newer version of the format, which offers things like custom fields. Even though KeePassX is not yet ready for the newer .kdbx format, a new version of it is in development which supports this format.
|
||||
|
||||
You can view the new version of KeePassX, with a vastly improved interface below. You can also download it to compile it yourself on [GitHub][6].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Main screen of KeePassX 2.0 *
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Details of a single password*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Additional attributes of a single password *
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Entry history, most likely replacing the ‘Backup’ folder from the previous version*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Settings in KeePassX 2.0 *
|
||||
|
||||
## Other devices ##
|
||||
|
||||
As I said in the beggining of my post, **I was looking for something cross platform**. This is a great advantage of the .kdb format — there are quite a few apps currently supporting it. KeePassX is also much easier to get running on Mac OS X than KeePass 2, and runs fine on Windows too.
|
||||
|
||||
On Android I use [KeePassDroid][6], which works solidly both on my phone and tablet.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/manage-passwords-securely-keepassx
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://lastpass.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://keepass.info/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://apt.ubuntu.com/p/keepassx
|
||||
[4]:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.google.android.apps.authenticator2&hl=en
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/keepassx/keepassx
|
||||
[6]:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.android.keepass&hl=en_GB
|
||||
105
translated/A Pentesting Release for the Raspberry Pi.md
Normal file
105
translated/A Pentesting Release for the Raspberry Pi.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
一个树莓派的渗透测试套件发布
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**树莓派(Raspbeery Pi)** 是一款只有一张信用卡大小的单板机计算机.它由英国的树莓派基金会所开发,目的是以低价硬件及自由软件刺激在学校的基本的计算机教育. 树莓派的生产是通过有生产许可的**Newark element14 (Premier Farnell), RS Components** and **Egoman**公司.这些公司都在网上出售树莓派.Egoman生产的版本分布在中国和台湾(译者注:原文如此,我可没说台湾不是中国,台湾当然是中华民国了),可以从它们的颜色是红色和没有FCC/CE标志上区别其它的树莓派.所有生产商产品硬件都是一样的.(维基百科)
|
||||
|
||||
Pwnie Express 团队已经宣布首次发行Paspbeery Pwn,它可以用于将你的树莓派变成一个全功能的安全渗透测试和审计平台.此版本的Raspbberry Pwn 包含所有渗透测试平台所需的工具.在你的树莓派上做渗透测试,让你有什么感觉?Sqlmap, nmap, wireshark, scapy, nikto, xprobe, socat,你想要更多的工具来渗透测试你的网络?
|
||||
|
||||
Raspbeery Pwn 自带下面的工具:
|
||||
- nmap
|
||||
- dsniff
|
||||
- netcat
|
||||
- nikto
|
||||
- xprobe
|
||||
- scapy
|
||||
- wireshark
|
||||
- tcpdump
|
||||
- ettercap
|
||||
- hping3
|
||||
- medusa
|
||||
- macchanger
|
||||
- nbtscan
|
||||
- john
|
||||
- ptunnel
|
||||
- p0f
|
||||
- ngrep
|
||||
- tcpflow
|
||||
- openvpn
|
||||
- iodine
|
||||
- httptunnel
|
||||
- cryptcat
|
||||
- sipsak
|
||||
- yersinia
|
||||
- smbclient
|
||||
- sslsniff
|
||||
- tcptraceroute
|
||||
- pbnj
|
||||
- netdiscover
|
||||
- netmask
|
||||
- udptunnel
|
||||
- dnstracer
|
||||
- sslscan
|
||||
- medusa
|
||||
- ipcalc
|
||||
- dnswalk
|
||||
- socat
|
||||
- onesixtyone
|
||||
- tinyproxy
|
||||
- dmitry
|
||||
- fcrackzip
|
||||
- ssldump
|
||||
- fping
|
||||
- ike-scan
|
||||
- gpsd
|
||||
- darkstat
|
||||
- swaks
|
||||
- arping
|
||||
- tcpreplay
|
||||
- sipcrack
|
||||
- proxychains
|
||||
- proxytunnel
|
||||
- siege
|
||||
- sqlmap
|
||||
- wapiti
|
||||
- skipfish
|
||||
- w3af
|
||||
|
||||
我来为你们对上面的工具做一个简短的说明.我不会说明所有的工具.仅想说说上面的两三个工具.简单的Google搜索将会帮你找到所有工具的详细说明.
|
||||
|
||||
**Nmap**
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap是一个免费开源的网络探索工具,帮助我们map网络.网络管理者们发现它在每天的工作中非常有用,如果你有计划做一名网管的话,你应该学习如何使用Nmap.Nmap能够帮助我们探索一个网络中有多少主机(host),它们正在用什么操作系统,还有它们开放的端口并且这些端口上正在运行什么服务.它是一个命令行工具要是你不喜欢记这么多命令,这有一个叫做Zenmap的Nmap图形化版本.Namp和Zenmap都是多平台的(Linux,Windows,Mac OS,BSD,等),因此你不必担心操作系统.Nmap有将扫描(scan)结果保存为文件的功能并且我们能够在以后的分析中使用这些文件.更好的是我喜欢Nmap的是它的脚本引擎(NSE).我们可以自己写脚本在Nmap中使用.浏览更多:[http://www.unixmen.com/scan-your-home-network-with-nmap/][1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Netcat**
|
||||
|
||||
Netcat 是一个命令行网络工具,它能够通过传输控制协议TCP和用户数据报协议UDP读写数据.最初为Unix而写,在1996年发布,已经被一直到多个操作系统,事实说明它在游戏中依然保持强劲.17年来netcat是属于每一个网络管理/安全专家的工具箱.人们说"姜还是老的辣",在我看来对netcat来说是真的.事实是,只有你想不到的没有netcat做不到的,根据你的意图,你可以用它做好事或者不好的事.Netcat作为一个客户端和作为一个服务器运行.即使有少数例外,newcat的命令选项在Windows和Linux是一样的,这使得netcat成为一个更强大的工具.在下一篇文章中将为你介绍netcat的命令选项还有你将学习到如何执行一些基本的netcat操作. - 浏览更多:[http://www.unixmen.com/short-introduction-to-netcat][2]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Sqlmap**
|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要一个工具在你的web应用中利用(译者注:exploit在计算机安全术语中,这个词通常表示利用程序中的某些漏洞,来得到计算机的控制权这个词同时也表示为了利用这个漏洞而编写的攻击程序)sql注入漏洞或者接管数据库服务器,sqlmap是适合的.Sqlmap是一个被全世界所有渗透测试者使用的工具,它具备全部的功能.它的一些功能:
|
||||
|
||||
- 完全支持MySQL, Oracle, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, Microsoft Access, IBM DB2, SQLite, Firebird, Sybase and SAP MaxDB数据库管理系统.
|
||||
- 完全支持6个SQL注入技术:boolean-based blind, time-based blind, error-based, UNION query, stacked queries and out-of-band.
|
||||
- 支持不用通过SQL注入直接连接到数据库,通过提供DBMS凭证,IP地址,端口和数据库名称.
|
||||
- 支持枚举用户,密码哈希,权限,角色,数据库,表和列.
|
||||
- 自动识别密码散列格式,支持使用基于字典的攻击cracking它们.
|
||||
- 支持完全转储数据库表,更具每个用户的选择的范围内的条目或特别的列.用户可以从每个列条目选择只转储一定范围内的字符.
|
||||
- 支持搜索具体的数据库名称,所有数据库具体的表或所有数据库表中具体的列.
|
||||
|
||||
**Medusa**
|
||||
|
||||
你需要一个暴力破解(brute-forcer)登陆器? Mesusa为破解网络服务发开于Gentoo Linux 和 FreeBSD.Mesusa和FTP, HTTP, IMAP, MS-SQL, MySQL, NCP (NetWare), NNTP, PcAnywhere, POP3, PostgreSQL,rexec, rlogin, rsh, SMB, SMTP (AUTH/VRFY), SNMP, SSHv2, SVN还有其它服务一起工作.你可以在这里浏览更多关于Medusa的信息.
|
||||
|
||||
在Raspbeery Pwn这次发布中你能看到所有渗透测试所需要的工具.你有一个树莓派吗?把它变成一个渗透机器吧.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/pentesting-release-raspberry-pi/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[flsf](https://github.com/flsf) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/scan-your-home-network-with-nmap/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unixmen.com/short-introduction-to-netcat/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
携带便利的图书标记特性,Calibre 1.6 正式发布!!!
|
||||
====
|
||||
|
||||
[Calibre][1]是一个免费的开源电子丛书管理工具,令人心动的设计思想,综合电子书相关的多领域的要求和需求,提供强大的转换处理,专注电子书的阅读,书库轻而易举的创建和管理,在线集成服务等,总而言之,给你真真正正的现代化电子书阅读.
|
||||
|
||||
Calibre 已经更新到**1.6**版本,介绍了一个已存在的**图书标记**(book-mark)特性,也有大量的修补和功能增强.
|
||||
|
||||
**图书标记**作为一种**暂定**选书的简便方式(重启Calibre,就会失去标记),允许用户标记图书,再点击已标记的图书便取消标记,该特性能在多场景提供便利.
|
||||
|
||||
最新应用的图书标记功能并没有默认开启,当然,开启它也是很容易的`首选项(Prefences)-->工具栏(Toolbar)-->主工具栏(The main toolbar)-->点击标记图书(Mark Books)-->点击左端的箭头-->应用(Apply)`,之后在工具栏上就有图书标记按钮
|
||||
|
||||
**标记**,举个例子,手动的标记三本书(按住Ctrl键,并点击首选的三本图书),也可以通过工具栏上的按钮,标记图书.
|
||||
|
||||
最新标记的三本书将显示一个特殊标记的图标,这样用户可以清楚的观察到标记的书本.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在标记图书后,用户可以通过'右击标记按钮-->显示标记书本'来只显示已标记的图书,同时隐藏未标记的图书.
|
||||
|
||||
在有些时候想清楚观察重点图书,图书标记功能允许用户轻而易举的隔离出偏爱的图书,想通过几秒钟点击标记按钮,隔离处理能完全的展示某一书本
|
||||
|
||||
再次选择标记图书或再点击标记图书按钮,将取消标记,按钮就像是一个标记/不标记的按钮
|
||||
|
||||
Calibre默认携带了好用的电子书阅读器,在1.6版本增加了额外的快捷键配置,意味着现在用户能通过自己的喜好制定不同的**快捷键**例如放大缩小
|
||||
|
||||
打开电子书阅读器之前先调整快捷键,点击工具条的首选项来操纵快捷键,双击一个条目进行编辑.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
以上提及的特性,连同大量的漏洞的修补,增加最新的新闻源(大量的乌拉圭新闻)和改良了一些新闻源(国家地理杂志,纽约书评,聚焦,Carta Capital,明报,Neu Osnabrucker Zeitung),去感受更强大的Calibre吧!!!!!
|
||||
|
||||
我们怎么**安装**Calibre 1.6呢?
|
||||
|
||||
复制制以下命令到终端
|
||||
|
||||
sudo python -c "'import sys; py3 = sys.version_info[0] > 2; u = __import__('urllib.request' if py3 else 'urllib', fromlist=1); exec(u.urlopen('http://status.calibre-ebook.com/linux_installer').read()); main()
|
||||
|
||||
按回车键,出现`Enter the installation directory for calibre [/opt]`再按回车键
|
||||
|
||||
如果用户通过PPA安装了Calibre,那么请先执行下列命令(在执行以上命令之前).
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove calibre calibre-bin
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/calibre-16-released-handy-mark-book-feature
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://calibre-ebook.com/
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
联系人应用已经支持高级avatar功能
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
为下一代Ubuntu设计的新一代软件们正在通过多方面的支持逐步的建立起来,包括了一组由第三方的程序员和Ubntu程序员还有Ubuntu的设计者们一起开发出来的核心软件,同样还有由Ubuntu的开发者和设计者们创建出来的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在官方的开发出来的软件们中有一个联系人应用程序,它非常的容易上手,并且是一个拥有友好界面的联系人信息收集管理程序。拥有许多可以编辑的字段。 快速滚动条 还有被列出来的项目还会提供一个有趣的相关联系的应用(正在研发中。)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[联系人应用][1]被更新了另外的一个附加的功能,正在展现出来的[最近几个新的][2]功能。也就是所说的 avatar的联系人支持
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在它的上一个版本中,用户可以通过联系人中心选择avatars的支持。现在在主界面中也开始支持图片显示了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
意思是,点击一个联系人,按下下方的`编辑`按钮来为这个联系人添加一个虚拟的头像在之前单色图标的位置,在点击保存之后那个那个头像就会被保存下来了。之后回到主界面就能够看到之前添加的头像了,之前的单色调的方块图片被我们替换成刚刚添加的图片。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
此外,avatar可以将四角变成圆角,用于美化联系人的显示。如果用户选择的话甚至可以同时将缩略图也美化成圆角的,其实对于avatar来说,一般情况都是采用没有棱角的图片。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
还有更多的功能呦~点击那些已经开启avatar的联系人。点开联系人,在用户查看之前保存图片的地方,可以新的图片替换掉就 图片。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
联系人应用已经[可以][3]在Ubuntu13.10的 Ubuntu软件中心中找到了,并且可用用来安装使用或者用来做测试。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/contacts-app-updated-enhanced-avatar-support
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[FineFan](https://github.com/FineFan) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/address-book-app
|
||||
[2]:http://iloveubuntu.net/contacts-app-updated-avatar-editing-support
|
||||
[3]:apt://address-book-app
|
||||
31
translated/Daily Ubuntu Tips – Disable Ubuntu Lock Screen.md
Normal file
31
translated/Daily Ubuntu Tips – Disable Ubuntu Lock Screen.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
每日Ubuntu技巧 - 禁用Ubuntu的屏幕锁定
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
当您刚成为一名Ubuntu新用户时,有一些事情您还无法马上知道。例如,修改您的密码、禁用某些功能和创建新用户帐号。当新用户测试了Ubuntu之后,一个经常被他们问到的问题是如何关闭屏幕锁定或阻止Ubuntu屏幕逐渐变暗。
|
||||
|
||||
这里为Ubuntu新手准备了一些简单技巧。这些技巧对于Ubuntu老手而言毫无新意,当然,它们也不是为Ubuntu老手而准备的,它们仅供Ubuntu新手学习使用。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu被设计成自动经过几分钟后就自行进行锁定,您必须输入您的密码来解锁才能再次使用它。如果这给您带来了太多的麻烦,那么您也许想要关闭这个自动锁屏功能,而这正是下面马上将要向您介绍的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
您计算机的自我锁定是出于安全的原因,如果您禁用或关闭了它,您的计算机将不再被锁定,任何可以物理接触到您计算机的人都可以登录并且使用它。如果对您而言,这不是什么大问题,那么继续下面学习具体如何来做。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,登录Ubuntu,点击控制选项(位于菜单栏的最右边的图标)图标并选择**系统设置**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
接着,点击系统设置面板里的“亮度和锁屏”图标
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后,关闭“锁定屏幕选项”。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
禁用Ubuntu屏幕锁定的所有操作就是这些!如果您要重新开启它,那么再次点击“锁定屏幕选项”切换回去即可。屏幕锁定是一个很好的特性,可以保护您的计算机,但如果您知道您的隐私或信息不会有风险,那么您可以禁用它。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/09/daily-ubuntu-tips-disable-ubuntu-lock-screen/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
日常Ubuntu使用小技巧——安装Ubuntu后做什么
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
许多Windows用户开始使用Ubuntu时都感到束手无策。Ubuntu与Windows截然不同,想要轻松驾驭Ubuntu可不是一件简单的事情。Ubuntu的使用方式不同于Windows。许多用户对命令行、文件系统的布局和应用程序的名称都感到陌生。但是不用管那些,我们会提供帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你以前是Windows或者Mac OS X用户现在想学Ubuntu,那你来对地方了。我们正努力帮助新用户开始Ubuntu之旅。我们的口号理所当然就是“**菜鸟教程**”。
|
||||
|
||||
我们的教程大多不是针对专业人士的,而是面向刚开始学习Windows和Ubuntu的新手。所以,为了你所有的Ubuntu需求,经常回来转转。.
|
||||
|
||||
好了,言归正传。几天前一个读者问了我们一个问题,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
> 安装好Ubuntu后首先要做什么?
|
||||
|
||||
很简单,第一次安装Ubuntu时,你可能有很多事情想做。但是最重要的是让它正常工作。不要担心遇到难题,这些你很快就会明白。
|
||||
|
||||
这里有一些安装好Ubuntu之后你最初想要做的事。可能你想做的比这还多,但这些是比较重要的。
|
||||
|
||||
- 更新系统 -首先更新你的系统。系统更新可以让你安装比较新的软件包和一些其它程序的修正。使用Ubuntu时你可以使用下面的命令正确地进行系统更新。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade && sudo apt-get autoremove
|
||||
|
||||
- 安装好Ubuntu后要做的另外一件事就是运行下面的命令。这条命令能帮助你安装编解码器和因法律原因而排除在Ubuntu外的软件包。Ubuntu并未预装这些比较重要的程序。而没有这些程序你可能无法听音乐、看电影或者做其它的事情。所以,如果你安装了Ubuntu但是不能播放DVD或者听音乐CD,那就运行下面的命令吧。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
以上这些命令并非你将在Ubuntu运行的全部的命令,但它们是安装好Ubuntu后你首先要运行的。希望这些能帮助到你。
|
||||
|
||||
使用愉快!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tipsthings-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Linchenguang](https://github.com/Linchenguang) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
30
translated/Debian 7.2 Wheez Officially Released.md
Normal file
30
translated/Debian 7.2 Wheez Officially Released.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
Debian 7.2 "Wheezy"正式发布
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Debian项目宣布即将推出可供下载的第二个维护版本的Debian 7 Linux操作系统。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Debian 7.2仅仅是一个维护更新版本,但是它确实进行了一系列的升级并且为当前稳定版本进行了一些修正,也为其更新了许多包。
|
||||
|
||||
“请注意这次更新并不是使用了一个新的Debian 7,而仅仅是更新了其中的一些包。因此没有必要将以前废旧的Wheezy CD或DVD丢掉,只需要在安装系统完成后,通过最新的Debian镜像更新一些过期的包即可。”官方公告这么说。
|
||||
|
||||
这意味着已经安装有Debian 7.0或7.1的用户不用再重新安装系统。他们只需完成定期的升级即可,这样只需要从security.debian.org下载很少部分包。
|
||||
|
||||
在官方[声明][1]中可以查看完整的更新日志。
|
||||
|
||||
**Debian GNU/Linux 7.1.0: 免费下载地址**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Debian GNU/Linux 7.1.0 (ISO) 32-bit[iso]][2] [3.70 GB]
|
||||
- [Debian GNU/Linux 7.1.0 (ISO) 64-bit[iso]][3] [3.80 GB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
来自: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Debian-7-2-quot-Wheezy-quot-Officially-Released-390694.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[SCUSJS](https://github.com/scusjs) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.debian.org/News/2013/20131012
|
||||
[2]:http://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/7.1.0/i386/iso-dvd/debian-7.1.0-i386-DVD-1.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/7.1.0/amd64/iso-dvd/debian-7.1.0-amd64-DVD-1.iso
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
各大平台,发布优秀的Clementine音乐播放器 1.2版
|
||||
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**Clementine 1.2, 是受到了Amarok 1.4的启发制作的多平台音乐播放器,关注一个对于搜索和播放音乐的快速而又易于使用的界面,并已经发布,同时带有漂亮而又有趣的新特性.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Clmentine 是一个卓越的媒体播放器,并被一些新的放行版所采用,它是极其稳定的,也不会那些习惯现在的播放的人产生不习惯.
|
||||
|
||||
这个版本也兼容安卓的Climentine远程控制程序,它能让你用你的安卓设备远程控制Clementine
|
||||
|
||||
'Clemntine 也添加了对Subsonic的支持.现在你能听存储在Box,Dropbox,Skydrive和Ubuntu One中的音乐.最后一个主要的特性是能星标你的播放列表,我们能在左侧工具条上添加的新的播放列表条目中安全的关闭和恢复他们',从[公告][2]中读取
|
||||
|
||||
能在官方[公告][2]了解关于新版本的变化和新特性的完整列表.
|
||||
|
||||
**下载Clementine 1.2**
|
||||
|
||||
- [tar.gz][3][sources] [9.30 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 13.04 DEB i386][4][ubuntu_deb] [7.10 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 13.04 DEB amd64][5][ubuntu_deb] [7.30 MB]
|
||||
- [Fedora 19 RPM i686][6][fedora_rpm] [5.30 MB]
|
||||
- [Fedora 19 RPM x86_64][7][fedora_rpm] [5.30 MB]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 11.04/Ubuntu 10.10/Ubuntu 10.04 DEB ALL][8][ubuntu_deb] [0 KB]
|
||||
- [Fedora 16 RPM noarch][9][fedora_rpm] [0 KB]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Excellent-Music-Player-Clementine-1-2-Released-on-Multiple-Platforms-391342.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://code.google.com/p/clementine-player/source/browse/Changelog?name=release-1.2
|
||||
[2]:http://www.clementine-player.org/
|
||||
[3]:https://clementine-player.googlecode.com/files/clementine-1.2.0.tar.gz
|
||||
[4]:https://clementine-player.googlecode.com/files/clementine_1.2.0%7Eraring_i386.deb
|
||||
[5]:https://clementine-player.googlecode.com/files/clementine_1.2.0%7Eraring_amd64.deb
|
||||
[6]:https://clementine-player.googlecode.com/files/clementine-1.2.0-1.fc19.i686.rpm
|
||||
[7]:https://clementine-player.googlecode.com/files/clementine-1.2.0-1.fc19.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
[8]:http://code.google.com/p/clementine-player/downloads/list
|
||||
[9]:http://code.google.com/p/clementine-player/downloads/list
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
crowner翻译
|
||||
FreeBSD 10.0 Beta 1已经可以下载测试
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**FreeBSD 10.0 Beta 1, 一个可以运行在x86, ARM, IA-64, PowerPC, PC-98, and UltraSPARC 等架构上的操作系统, 已经发布并且可供下载测试。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
FreeBSD的开发者在以不可思议的速度前进,并且不断地发布一个有一个的版本. 新的测试版在有五个内测版的情况下完成,但是没有任何问题。
|
||||
|
||||
官方[公告][1]称,“因为在最终发现的存在于10.0-BETA1 freebsd-update(8) 套件中的问题,freebsd-update(8) 将 不被支持用于升级10.0-BETA1。请不要用freebsd-update(8) 来升级 10.0-BETA1。请注意 cvsup和CVS不被支持用于的升级src/ tree。” 。
|
||||
|
||||
而且, 据开发者说, ports.txz发行版没有被包含在 10.0 Beta 1 发布版中,但是它有望在发行周期中被纳入后续版本的disc1.iso中。
|
||||
|
||||
FreeBSD 10.0 Beta 1的亮点:
|
||||
|
||||
- freebsd-version,用于审核的工具,已经实现。如果你想确定客户端补丁级别,当它与'uname -r'的报告不同时这是一个很重要的工具;
|
||||
- ZFS lzjb的解压表现有所改进;
|
||||
- 两种新的MIPS CPU, mips24k和mips74k获得支持;
|
||||
- 在jail(8)组件调用前,for 每一个jail的"jail_<jname>_*" rc.conf(5) 变量的配置是自动转换为/var/run/jail.<jname>.conf的, 因此新的jail.conf(5)语法已被使用;
|
||||
- 绝大多数的ATF工具和_atf用户被移除;
|
||||
|
||||
发行方鼓励用户们测试发行版并报告任何发现的问题. 官方[变更目录][1] 有完整的修正和修改列表. 现在可以在Softpedia立刻下载FreeBSD 10.0 Beta 1。
|
||||
|
||||
请注意这是一个开发者版本请不要再任何产品端上安装。它仅被希望用于测试目的.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/FreeBSD-10-0-Beta-1-Available-for-Download-and-Testing-391246.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
鏈枃鐢?[LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 鍘熷垱缈昏瘧锛孾Linux涓浗](http://linux.cn/) 鑽h獕鎺ㄥ嚭
|
||||
|
||||
璇戣€咃細[crowner](https://github.com/璇戣€匢D) 鏍″锛歔鏍″鑰匢D](https://github.com/鏍″鑰匢D)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lists.freebsd.org/pipermail/freebsd-current/2013-October/045524.html
|
||||
50
translated/Install Rhythmbox 3.0 In Ubuntu 13.10 Or 13.04.md
Normal file
50
translated/Install Rhythmbox 3.0 In Ubuntu 13.10 Or 13.04.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
在Ubuntu 13.10或者13.04上安装Rhythmbox 3.0
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Rhythmbox 3.0已经发布了超过一个月了,这个版本有一些用户界面的改进,使用Python 3来支持插件。不幸的是,新版本并没有集成到13.10里面,但是你可以使用PPA来安装它(Ubuntu 13.04也支持)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Rhythmox 3.0更新日志:
|
||||
|
||||
- 插件现在使用Python 3;
|
||||
- 新的任务进度显示在曲目列表的下方(可以供很多东西使用包括包括轨道更换和导入作业等);
|
||||
- 支持作曲家标签;
|
||||
- 重新制作播放控制栏;
|
||||
- 使用象征性的图片重新设计源列表;
|
||||
- 所有东西都更好的优化过;
|
||||
- 通过不同的公开属性将CBR和VBR编码方式区分开;
|
||||
- 播放列表设置内容(浏览方式等)保存到playlists.xml文件;
|
||||
- 在适当情况下更好的使用了RTL图标;
|
||||
- 修复了IM状态和ReplayGain插件;
|
||||
- 修复了其他很多漏洞。
|
||||
|
||||
能在[这里][1]找到完整的Rhythmbox 3.0更新日志。
|
||||
|
||||
## 在Ubuntu 13.10或者13.04下安装Rhythmbox 3.0##
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Ubuntu 13.10 (Unity)下的Rhythmbox 3.0*
|
||||
|
||||
因为Rhythmbox 3.0的插件使用Python3而不是Python 2,
|
||||
**[第三方插件 PPA][2]里面的插件都不能在Rhythmbox里面使用了** 。你可以通过手动安装的方式来使用它们中的一些(包括Equalizer的超酷的**[CoverArt browser][3]**)
|
||||
- 更多信息请看**[这篇][4]**文章。
|
||||
|
||||
Rhythmbox 3.0现在可以在一个由Jacob Zimmermann维护的一个为Ubuntu 13.10和13.04(及衍生系统)准备的非官方PPA里面找到。**通过以下命令添加这个PPA然后安装/升级Rhythmbox 3.0**:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:jacob/media
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install rhythmbox
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
来自: http://www.webupd8.org/2013/10/install-rhythmbox-30-in-ubuntu-1310-or.html
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[SCUSJS](https://github.com/scusjs) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/rhythmbox/3.0/rhythmbox-3.0.news
|
||||
[2]:http://www.webupd8.org/2012/08/rhythmbox-third-party-plugins-ubuntu-ppa.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.webupd8.org/2013/08/rhythmbox-coverart-browser-plugin-gets.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xpressubuntu.wordpress.com/2013/10/06/how-to-install-rhythmbox-3-0-in-saucy/
|
||||
17
translated/Linux RNG May Be Insecure After All.md
Executable file
17
translated/Linux RNG May Be Insecure After All.md
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,17 @@
|
||||
Linux 随机数生成器可能还是不安全的
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 在 Linus 向那些质疑 Linux 随机数生成器安全性的人们发表了自己的观点之后,现在,一篇新的学术论文[分析了 Linux 中的 /dev/urandom 和 /dev/random 的健壮性][2]。论文中写道:“从实际的角度来说,我们也对 Linux 的两种伪随机数生成器 /dev/random 和 /dev/urandom 的安全性做了精确的评估。特别是,我们展示了几种攻击手段来证明 Linux 中的这两种伪随机数生成器并不符合我们对健壮性的定义,而且熵没有适当地累积起来。这些攻击能起效是由于熵估计器及 Linux 伪随机数生成器的内部混合函数存在弱点。由于这些攻击的存在,Linux 的伪随机数生成器并不满足安全学中‘健壮性’这一概念,但是,在实际情况中,我们并不清楚这些攻击手段是否存在真正可利用的漏洞。”
|
||||
|
||||
当然,你[甚至可能连硬件随机数生成器都不相信][3]。论文作者们并非只是简单地证明 Linux 伪随机数生成器是不健壮的(通过使用 Linux 的运行时熵估计器),他们提出了一个新的性质用于检验伪随机数生成器的熵累计阶段是否健壮,并且,他们还提供了另一个伪随机数生成器的模型,他们证明,这个模型不仅是健壮的,而且比现有的 Linux 伪随机数生成器更加高效。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://it.slashdot.org/story/13/10/14/2318211/linux-rng-may-be-insecure-after-all
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[will.qian](https://github.com/willqian) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.slashdot.org/story/13/09/10/1311247/linus-responds-to-rdrand-petition-with-scorn
|
||||
[2]:http://eprint.iacr.org/2013/338.pdf
|
||||
[3]:http://slashdot.org/story/13/09/13/1228216/stealthy-dopant-level-hardware-trojans
|
||||
@ -1,15 +1,12 @@
|
||||
(runningwater认领)
|
||||
Linux Terminal: Seeing the unseen characters with cat!
|
||||
Linux终端:用cat命令查看隐藏的字符
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Sometimes a program or software don’t start for a syntax error, and if you check the files there is nothing wrong..apparently.
|
||||
There are a lot of characters that usually are not printed if you use a normal text editor, but you can easily check if they are present with your terminal and the command cat.
|
||||
时常,某个程序或软件并没有语法错误,并且你检查它的相关内容也确实没有发现问题。这是因为你用普通文本编辑器软件来查看的时候,有许多字符没有显示出来,但在终端使用cat命令可以很容易地检测出是否存在这些字符。
|
||||
|
||||
As first thing let’s create a simple text file with these special characters, open a terminal and run the command:
|
||||
首先,我们创建一个简单的文本文件,写入一些特殊字符。打开终端,运行命令:
|
||||
|
||||
printf 'testing\012\011\011testing\014\010\012more testing\012\011\000\013\000even more testing\012\011\011\011\012' > /tmp/testing.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Now if you open the file with an editor you’ll have different results.
|
||||
A simple cat will show:
|
||||
现在用不同的编辑器软件打开,显示的结果会不同。用简单的cat打开将显示:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat /tmp/testing.txt
|
||||
testing
|
||||
@ -19,7 +16,7 @@ A simple cat will show:
|
||||
|
||||
even more testing
|
||||
|
||||
While if you open it with nano or vim you’ll see :
|
||||
如果用nano或者vim打开,将会看到:
|
||||
|
||||
testing
|
||||
testing^L^H
|
||||
@ -27,9 +24,9 @@ While if you open it with nano or vim you’ll see :
|
||||
more testing
|
||||
^@^K^@even more testing
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can see some options of cat to print special characters.
|
||||
现在我们给cat加上一些选项参数,以便能显示出特殊字符来。
|
||||
|
||||
1) Use cat -T to display TAB characters as ^I
|
||||
1) 用cat -T命令来显示TAB键的字符^I
|
||||
|
||||
cat -T /tmp/testing.txt
|
||||
testing
|
||||
@ -40,7 +37,7 @@ Now we can see some options of cat to print special characters.
|
||||
even more testing
|
||||
^I^I^I
|
||||
|
||||
2) Use cat -E to display $ at end of each line
|
||||
2) 用cat -E命令来显示行尾的结束字符$
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat -E /tmp/testing.txt
|
||||
testing$
|
||||
@ -51,7 +48,7 @@ Now we can see some options of cat to print special characters.
|
||||
even more testing$
|
||||
$
|
||||
|
||||
3) Use a simple cat -A to show up all the invisible characters:
|
||||
3) 用简单的cat -A命令就可以显示所有不可见的字符:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat -A /tmp/testing.txt
|
||||
testing$
|
||||
@ -66,7 +63,7 @@ via: http://linuxaria.com/pills/linux-terminal-seeing-the-unseen-characters-with
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
||||
|
||||
“Linux想要屌丝逆袭?只需要一款杀手级游戏。”
|
||||
========================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux平台只需要一款杀手级游戏就能杀入主流游戏市场,DICE创意总监Lars Gustavsson如是告诉记者,他还透露,开发工作室其实“非常愿意”入驻Linux平台。
|
||||
|
||||
“我们之所以如此强烈想要入驻Linux,原因只有一个”,Gustavsson说,“就如同Xbox凭借着光晕(Halo)一举成功逆袭并使粉丝们为之疯狂 —— 通常,只需要一款杀手级应用或游戏,人们就更愿意去[适应新平台] —— 对于Linux来说,这并不难,例如,它只需要一款能吸引人们主动去玩的游戏而已。”
|
||||
|
||||
“我认为,即使这样,消费者正变得越来越挑剔,所以,我们必须说服他们如何才愿意玩某一款游戏,并将其作为日常生活的一部分,”他解释道,工作室目前已经开始使用Linux服务器,因为Linux在这方面本就是最佳选择。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当被问道对Valve公司最近关于Steam操作系统和Steam主机的声明有何看法时,Gustavsson认为,这对游戏机市场来说非常有益,他相信相关产品会打开新的市场,拓展出消费游戏新的发展道路,也许比这更好。
|
||||
“基本上,通过各种方法获取消费者的青睐并给予他们娱乐的各种可能性,我认为这才是最令人激动的,”他说,“我只知道一件事,往前推5到10年,谁能想象游戏市场会是今天这个样子。也许我们能预料到更低的硬件需求和更丰富的游戏体验,但流媒体服务和新的输入设备等等这些东西才真的让人惊讶。”
|
||||
|
||||
>现在哪还有三A级经典游戏?就像活着的猛犸象一样少见!
|
||||
|
||||
“我认为,有时竞争往往意味着消费者拥有更好的体验。VHS难道比BetaMax更强吗?但VHS最终获胜了。(译者注:他指的是当年索尼和JVC的录像带之争,索尼的BetaMax在专业领域优势很大,但JVC的VHS由于更适合当时普通消费者的家庭使用,因此,他在这里举了这个例子)”,他继续说道,“因此,尽管竞争的最终结果不一定就是完全正确的方向,但总体来看,竞争还是利大于弊的。何况消费者也欢迎,因此,我相信未来我们一定能做出更好的游戏。”
|
||||
|
||||
总监相信,尽管用户数量有限,但独立游戏开发正不断上升并开始取得成功,现在正处在一个更有利的位置,能够迎合Linux视频游戏市场。
|
||||
|
||||
“长久以来,独立制作一般就意味着三A级经典,直到伴随着移动终端产业的爆发,独立游戏开始扎堆泛滥,”他说,“因此,我非常高兴能看到独立制作又回到了它曾经的现状,就好像人们在说,’现在哪还有三A级经典游戏?就跟活着的猛犸象一样少见‘“。
|
||||
|
||||
“所以,对我来说,我认为尽管Linux平台上的用户数量并不特别多,但独立制作游戏成功的可能性很大。”
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
对于即将启动的[战地4][1],DICE已经讲述了许多如何降低上手难度和准入门槛等在[战地3][2]中出现的问题,Gustavsson说,他们并没有忘记骨灰级玩家,恰恰相反,DICE在开发战地4的过程中,不断需要克制自己不要“太过于骨灰”。
|
||||
|
||||
当被问道DICE如何在开发新特性的过程中避免忽视老玩家时,他解释道:“说老实话,我们的问题并不在于忽视骨灰级玩家,而是有太多人向我一样从99年或至少2000年就开始每天玩战地,我们需要的是控制自己,避免自己太沉溺于其中。沉迷游戏,是每个玩家的天性。所以,我们需要提醒自己,同时提醒每一个人”
|
||||
|
||||
战地4对于新玩家[更好上手][3],但同时,它也将充分照顾到老玩家,DICE透露,也许老玩家会发现游戏中有些方面射手与恐怖分子几乎没有区别。例如,Gustavsson提到,[新的战斗测试][4]涵盖了各个技术水平的玩家都可以发挥的范围。
|
||||
|
||||
> 我们需要的是控制自己,避免自己太沉溺于其中。
|
||||
|
||||
“有些人即使从最开始到现在一直在玩战地,游戏里他依然不会选择坐飞机,因为他觉得不安全,所以这并不是是否忽略老玩家的问题。如果你去玩家论坛转转,你会无数次看到诸如‘我不知道这件武器或这个装备怎么用‘这样的问题,然后每个人都会来回答他。这是件很和谐、很美妙的事。但有时你又会觉得,一个游戏不能太傻了,应该智能一些。”
|
||||
|
||||
针对上面例子中的问题,他们已经提供了一个武器装备比较工具。Gustavsson说,“即使是我,做游戏的人,有时也会蒙圈到底哪件装备配哪件武器。”
|
||||
|
||||
为了迎合战地的资深老玩家们,游戏还特地推出了一款检修控制系统,重写了网络代码,移除了一些隐患,增加了角色数量,并相应地给予命名。除了社区呼声已久的旁观者模式,战地4还介绍了[无重生模式][5]和[战场升级系统][6],[鼓励][7]玩家们一起游戏。
|
||||
|
||||
“说实话,一直以来,我都不好意思参加访谈活动,因为总是要一次次承认我们确实没有旁观者模式。但这次活动我腰板硬多了,因为我们终于有旁观者模式啦!伴随着新一代游戏机中的分享和广播等新特性,我十分期待社区会带来哪些意想不到的惊喜。”
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.polygon.com/2013/10/12/4826190/linux-only-needs-one-killer-game-to-explode-says-battlefield-director
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[小眼儿](https://github.com/tinyeyeser) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.polygon.com/game/battlefield-4/10364
|
||||
[2]:http://www.polygon.com/game/battlefield-3/1762
|
||||
[3]:http://www.polygon.com/2013/10/3/4798128/we-should-be-slapped-for-battlefield-3s-unlocks-says-dice-creative
|
||||
[4]:http://www.polygon.com/2013/9/4/4694158/battlefield-4-vehicle-test-range-server-options
|
||||
[5]:http://www.polygon.com/2013/9/26/4775632/battlefield-4s-multiplayer-modes-player-counts-detailed-by-dice
|
||||
[6]:http://www.polygon.com/2013/8/16/4627536/battlefield-4-kit-customization-field-upgrade-system-detailed
|
||||
[7]:http://www.polygon.com/2013/8/9/4607030/battlefield-4-will-encourage-but-never-force-team-play
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
保护密码的利器:Ubuntu 之 KeePassX
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**随着安全性问题变得越来越重要,密码当然是越安全越理想(比如多步认证),这一点再强调也不为过。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
既然这样想了,于是我最近就试用了几个安全密码管理器,试图找到一款比较可靠,易于使用并且跨平台的应用软件。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我尝试了LastPass[1]。LastPass大概最为人们所熟知,基于网络管理密码,是所有软件中平台无关性最强的。但是我发现它的界面简陋,而且提供太多的工具和选项,比较繁琐。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,我又试了试KeePass 2[2]。尽管是一款功能相当完善的应用软件,非常类似于下面我将要描述的,但是官方又不提供Linux上的安装包和公共接口,虽然可用,还算不上最好的。所以我又尝试了其他应用。
|
||||
|
||||
在所有的试用过的软件中,我最喜欢的是**KeePassX**. KeePassX起初是作为linux的一个分支,但是后来逐渐演变为属于自己的应用程序。凭借更漂亮、更为本地化的接口,KeePassX 打败了KeePass 2。
|
||||
## 在ubuntu中使用KeePassX ##
|
||||
|
||||
方便的是,KeePassX已经提供在ubuntu上安装的软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
从命令行安装KeePassX或者**从软件管理中心安装**:
|
||||
- [Install KeePassX from the Ubuntu Software Centre][3]
|
||||
|
||||
打开它,你会看到一个空白窗口。点击工具条上的按钮创建一个数据库。可以使用密钥文件或者密码保护刚刚创建的数据库。你很可能使用密码,因为只需要记住它并输入就行了 - 你可能会键入许多字符,但是另一方面,你不会让其他人进入你的数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,你得把它存到某个位置。我保存在我的Dropbox里面,这样就可以从多个地方获取。Dropbox使用双重认证,所以如果有人想进到我的Dropbox里面,他就得用到我的手机,这样的方式是还是相当安全的。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,你可以使用其他的服务,比如Google Drive和Skydrive,它们都使用标准认证器[4];再比如Box,使用SMS进行双重认证。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,如果**的的确确**担心自己的密码,你很可能不打算把密码存到其他的一些组织团体,因为理论上密码是可以被他们获取到的。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Ubuntu中KeePassX的主界面*
|
||||
|
||||
使用该应用还是相当直接的。你可以添加分组,然后在分组里添加密码。KeePassX带有一个很方便的密码生成器,当你需要输入一个密码的时候可以使用该生成器,而不用自己构思一个。我倾向于使用所有基本的字符以及挑选的特殊的字符来生成密码,
|
||||
20个字符的长度,当然这得看网站接不接受了。
|
||||
|
||||
需要注意一点,有些网站并不告诉你他们接受多长字符的密码,倾向于只在输入框限制输入长度。如果你粘贴进去的密码看起来没那么长,事实上可能不是那么一回事,也有可能是被截断了。这种情况我碰到过几次。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*KeePassX 密码生成器*
|
||||
|
||||
根据日常的使用经验,我积累了一些小的技巧,使得操作KeePassX更简单一些:
|
||||
|
||||
**疯狂地复制粘贴**
|
||||
|
||||
像这样复制粘贴密码,你可能会比较担心。可以肯定的是这比手动输入高效多了。默认情况下,KeePassX会在一分钟之内清空粘贴板,也可以设置更短的时间,所以不必担心有人会在你电脑上把密码粘贴下来查看。你也可以开启一个AutoType的特性,该特性会自动输入密码,不过出于某种原因,它会把密码紧跟着用户名输入到同一个地方,这样一来该特性似乎用处不大。
|
||||
|
||||
**数据库的困境**
|
||||
|
||||
如果你把数据库存放到云端,就不要为云端服务设置完全随机的密码。如果你不能进入到云,但是又把云密码存储到云里边,这是完全没有益处的。这看起来似乎很明显,但是刚开始我却没有意识到这一点。
|
||||
|
||||
**确保所有的密码都是安全的**
|
||||
|
||||
为了查看常用的账号,工作或者学习的时候要频繁地掏手机,这也是一件挺痛苦的事儿,所以设置密码的时候不妨想象一下这种情形,哈。
|
||||
|
||||
## 未来 ##
|
||||
|
||||
如果你以前也深入了解过KeePass 2和KeePassX,或许会注意到二者使用不同的数据库格式。
|
||||
|
||||
KeePass 2使用一种新的版本格式,比如允许自定义字段。尽管KeePassX目前还不支持新的.kdbx格式,正在开发中的新的版本会加上这一点。
|
||||
|
||||
可以预览一下新版本的KeePassX,界面大为改善。你也可以从GitHub上[6]下载后自己安装。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*KeePassX 2.0 主界面*
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*密码项的一些细节*
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*密码项的附加属性*
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*历史登陆信息,比如从先前的版本替换掉"Backup"文件夹之类的*
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*KeePassX 2.0 中的配置*
|
||||
|
||||
## 其他建议 ##
|
||||
|
||||
正如本文开头所说,**我在寻找能够跨平台的东西**。这正是.kdb格式的优点 - 很多应用都支持这种格式。KeePassX 在 Mac OS X上运行起来要比KeePass 2容易得多,在windows上也可以。
|
||||
|
||||
Android系统上,我使用KeePassDroid[6],在我的手机和平板上运行都很稳定。
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/manage-passwords-securely-keepassx
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[l3b2w1](https://github.com/l3b2w1) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://lastpass.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://keepass.info/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://apt.ubuntu.com/p/keepassx
|
||||
[4]:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.google.android.apps.authenticator2&hl=en
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/keepassx/keepassx
|
||||
[6]:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.android.keepass&hl=en_GB
|
||||
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Mark Shuttleworth认为苹果5S使用了Ubuntu Edge收敛的创意
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Canonical公司的创始人Mark Shuttleworth通过这一有趣的说法将Ubuntu Egde智能手机与iPhone 5S联系了起来。
|
||||
|
||||
几个月前,Canonical和Mark Shuttleworth尝试筹资来推出一款手机,该手机被认为是手机中的“F1赛车”。虽然失败了,但是他认为苹果已经从这款手机(Ubuntu Edge)的概念中获得了灵感。
|
||||
|
||||
“我认为[Ubuntu Edge]可能加速了收敛的概念,你看苹果描述他们的新的CPU为‘桌面级’的,我认为这并不是偶然。”他在接受[ZDnet][1]采访时这么说。
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical公司的创始人可能有一些我们不能获得的内部消息,但是这是一个对无缘无故将事情相提并论完全不感兴趣的人的有趣的推断。
|
||||
|
||||
苹果是否会按照Canonical的Ubuntu Edge手机描绘的收敛性发展还有待观察。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Mark-Shuttleworth-Thinks-Apple-Used-the-Ubuntu-Edge-Convergence-Idea-for-iPhone-5S-390507.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[SCUSJS](https://github.com/SCUSJS) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.zdnet.com/mark-shuttleworth-on-how-the-ubuntu-edge-dream-lives-on-in-the-iphone-7000021857/
|
||||
@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
|
||||
精通Linux "kill"命令
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
你使用哪种操作系统没有关系,你一定会遇到某个行为失常的应用,它把自己锁起来拒绝关闭.在Linux(还有Mac), 你可以用一个"kill"命令强制终结它.在这个教程中,我们将展示给你多种方式使用"kill"命令终结应用.
|
||||
|
||||
**Kill命令和信号**
|
||||
|
||||
当你执行一个"kill"命令,你实际上发送了一个信号给从左系统指示它终结不正常的应用.总共有60个你可一使用的信号,但是基本上你只需要知道SIGTERM(15)和SIGKILL(9).
|
||||
|
||||
你可以用这个命令看到所有的信号:
|
||||
|
||||
kill -l
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- SIGTERM - 此信号请求一个进程停止运行.此信号是可以被忽略.进程被给一段时间正常关闭.一个程序正常关闭意味着给一段时间来保存进度并释放资源.换句话说,它不是强制停止
|
||||
- SIGKILL - 此个信号强制进程立刻停止运行.程序不能忽略此信号.未保存进度将丢失.
|
||||
|
||||
使用"kill"的语法是:
|
||||
|
||||
kill [信号或选项] PID(s)
|
||||
|
||||
默认信号(当没有指定的时候)是SIGTERM.当它不起作用时,你可以使用下面的命令来强制kill掉一个进程:
|
||||
|
||||
kill SIGKILL PID
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
kill -9 PID
|
||||
|
||||
这里"-9"引用SIGKILL信号.
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不知道应用的PID,仅需要运行这个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
ps ux
|
||||
|
||||
它会显示所有正在运行的应用还有应用的PID.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
例如,要kill掉Chrome,我会运行命令:
|
||||
|
||||
kill -9 3629
|
||||
|
||||
也可以在同一时间kill多个进程.
|
||||
|
||||
kill -9 PID1 PID2 PID 3
|
||||
|
||||
**PKill**
|
||||
|
||||
"pkill"命令允许使用扩展的正则表达式和其它匹配标准.你现在可以使用应用的进程名kill掉它们,取代了使用PID.例如,kill Firefox浏览器,只需要运行命令:
|
||||
|
||||
pkill firefox
|
||||
|
||||
匹配正则表达式,你可以输入部分进程名,比如:
|
||||
|
||||
pkill fire
|
||||
|
||||
为了避免kill掉错误的进程,你应该用一下"pgrep -l [进程名]"列表来匹配进程.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Killall**
|
||||
|
||||
killall同样使用进程名替代PID,并且它会kill掉所有的同名进程.例如,如果你正在运行多个Firefox浏览器的instances(实例),可以用命令把它们全部kill掉:
|
||||
|
||||
killall firefox
|
||||
|
||||
在Gnome,你可以重启Nautilus,使用这个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
killall nautilus
|
||||
|
||||
**xkill**
|
||||
|
||||
xkill 是图形方式kill一个应用.当你在终端键入"xkill",你的光标将立刻变成一个"十字".你必须在失常的应用上点击一下,它就会立刻kill掉这个应用.如果你喜欢精简,你也可以添加一个[键盘快捷键来激活xkill][1].
|
||||
|
||||
**结论**
|
||||
|
||||
当app失常导致系统挂起的时候,它非常有诱惑力相比于重启计算机并且再一次开启所有的会话.有了这些"kill"命令,你将能够更好的管理失常的应用避免导致系统崩溃.当你不想一个失常的进程带来服务器荡机时,它尤其的有用.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.maketecheasier.com/kill-command-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[flsf](https://github.com/flsf) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.maketecheasier.com/quick-tips/kill-unresponsive-application-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
强大的国际象棋应用PyChess 0.12 BETA 4发布
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[PyChess][1] 是一个可爱的愉快的国际象棋应用程序,介绍它自己是作为一个先进的领悟国际象棋活动的方式.强调一个人的头脑和棋力对抗一个智能计算机对手,同时用直观的视觉效果和细节揭示它的用户友好界面
|
||||
|
||||
PyChess在主视图显示国际象棋相关组件.专业国际象棋活动转换成一个计算经历,位置移动的动画,声音特效,实时写入移动,提示,注释,提供拖拽/停止,精密的计时器让用户完全沉浸于象棋操作.
|
||||
|
||||
**PyChess 0.12 Anderssen BETA 4** 已经发布, 不稳定版本标志着第四次重复有趣的BETA旅程,一连串0.12版本带来了显著的很跨多层次的改变和改善,[including][2]新主题,新菜单选项,以及计算机资源优化(消除过高CPU占用)(译者注:译者使用archlinux试用,发现还是很高,结论是原文作者在扯淡).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
BETA 4带有对额外[FICS][3]变体(免费网络国际象棋服务器)的扩展支持,以及多种修复和改善,进一步加强了这个强大的国际象棋应用.
|
||||
|
||||
PyChess 0.12 BETA 4 可供下载 [http://pychess.googlecode.com/files/pychess_0.12beta4-1_all.deb][4].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/powerful-chess-application-pychess-012-beta-4-released-new-improvements
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[flsf](https://github.com/flsf) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://pychess.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://iloveubuntu.net/powerful-chess-game-pychess-012-beta-3-released-numerous-new-features-and-improvements
|
||||
[3]:http://www.freechess.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://pychess.googlecode.com/files/pychess_0.12beta4-1_all.deb
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
太空军事题材巨作《救赎预言》登陆Linux Steam游戏平台
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**由Firedance Games公司在Steam平台开发并发布的游戏《救赎预言》,现已在Linux平台推出。**
|
||||
|
||||
根据开发人员介绍,《救赎预言》是一款太空军事题材游戏,玩家不仅可以扮演战斗机驾驶员在太空中战斗,还可以在行星表面以FPS模式对抗。
|
||||
|
||||
官方的[产品介绍][1]为“太空舰队碰撞冲突引发激烈的战斗,入侵者与强化的敌方殖民地交战。然而,最大的危险是世界即将毁灭的世界末日预言。你必须寻找出来自遥远外星世界的奥秘, 并掌握远古的力量来抵抗即将到来的风暴。”
|
||||
|
||||
Linux系统最低配置要求:
|
||||
|
||||
系统:Ubuntu 12.04 或者 12.10 版本
|
||||
处理器:双核处理器
|
||||
内存:2GB内存
|
||||
显卡:NVIDIA GeForce 8600 GT、 ATI Radeon HD 2600 或者更好
|
||||
硬盘:至少1GB可用空间
|
||||
|
||||
更多详情请关注Steam[官方网站][2]。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Salvation-Prophecy-Military-Space-Epic-Arrives-on-Steam-for-Linux-390849.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic___](https://github.com/Vic020) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://store.steampowered.com/news/11613/
|
||||
[2]:http://store.steampowered.com/app/248450/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Shotwell 0.15发布了!添加了更多新功能及修复!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 默认安装了Shotwell,它能轻松的管理图片,提供基本的图片展示功能和图片编辑.以后将提供更多更多有用的功能.
|
||||
|
||||
Shotwell 已经更新到0.15版本,介绍了最新的特征和修复了大量已知的bug,并进行了更多的优化.
|
||||
|
||||
`右击图片-->打开方式-->Shotwell图片编辑`,用Shotwell打开图片后,在下边有几个选项,其中包括Adjust(调整)选项
|
||||
|
||||
点击'Adjust'按钮,用户能清楚的发现最新的Highlights(高亮)条目,这对于微调'Highlig'很有帮助;举例来说,尽可能调低'Highlights'设置,这样就能删除正在编辑的图片的光亮度.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
点击按钮条中的'Crop'按钮,弹出可更改大小的会话框,允许用户根据要求自定义裁剪图片,0.15版本的对话框增加了 **尺寸显示** 的功能.
|
||||
|
||||
改变会话框的大小,会实时的显示目前的尺寸大小,用户能自由随意观察修剪框中的尺寸;举个例子,为了得到一张640*480的图片,用户可以将裁剪框调整到640*480,在图片编辑器中便利地增添图片清晰度.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
除此以外,Shotwell 0.15 还增添了:
|
||||
|
||||
--Youtube 插件 OAuth / OpenID 的使用
|
||||
|
||||
--加强视频文件的导入
|
||||
|
||||
--优化了视频的缩略图
|
||||
|
||||
--修复了很多漏洞
|
||||
|
||||
我们怎么**安装** Shotwell 0.15呢?
|
||||
|
||||
添加以下 **官方** PPA(Ubuntu 12.10, Ubuntu 13.04)
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yorba/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install shotwell
|
||||
|
||||
Shotwell 0.15 已经登入Ubuntu 13.10,你只需要定期的更新软件,便会帮你自动安装,享受它带给你的乐趣吧!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/shotwell-015-released-new-features-and-fixes
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.yorba.org/projects/shotwell/
|
||||
[2]:http://blog.yorba.org/eric/2013/10/shotwell-0-15-has-arrived.html
|
||||
@ -1,49 +1,43 @@
|
||||
Debian OpenSSL Bug - 后门还是安全事故?
|
||||
======================================================
|
||||
|
||||
周一,Ed 写了篇文章《软件透明度》[1],主旨是如果软件开发的过程是透明的,那么软件本身对恶意的后门(无心的安全漏洞)更具抵抗性。
|
||||
软件透明的因素包括公开源代码,可以获取一个项目的追踪议题,以及允许参与内部开发者会议。他提到一种情况,在这儿我想详细讨论一下:
|
||||
2008年,Debian项目(一个流行的用于web服务器的linux发行版),宣称[2]Debian中OpenSSL[3]的伪随机数生成器遭到破解,已经不安全了。
|
||||
周一,Ed 写了篇文章《软件透明度》[1],主旨是如果软件开发的过程是透明的,那么软件对恶意的后门(以及无心的安全漏洞)就更具抵抗性。
|
||||
软件透明的因素包括公开源代码,可以读取或为一个项目的追踪议题做出贡献,以及参与内部开发讨论。他提到一种情况,在这儿我想详细讨论一下:
|
||||
2008年,Debian项目(一个用于web服务器的很流行的linux发行版),宣称[2]Debian中OpenSSL[3]的伪随机数生成器遭到破解,已经不安全了。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,了解一些背景信息:伪随机数生成器(PRNG)就是一个程序,假定代号为F。给定一个随机种子s,通过F(s)进行处理后,
|
||||
会得到一个长的比特流。如果我和你都使用同样的种子s,两个人会得到同样的比特流。但是如果我随机选择一个s,也不告诉你s是什么,
|
||||
首先,了解一些背景信息:伪随机数生成器(PRNG)就是一个程序,假定代号为F。给定一个随机种子s,则会得到一个长的比特流F(s),看起来像个随机数。如果我和你都使用同样的种子s,两个人会得到同样的比特流。但是如果我随机选择一个s,也不告诉你s是什么,
|
||||
你根本不能够推测F(s)的结果,如你所知,F(s)也是随机的。OpenSSL中的PRNG试图从系统中抓取不可预测的信息("熵"),比如当前进程ID,
|
||||
或者很有可能是不同的内存数据(比如,未初始化的内存,该内存,可能或者就是,由其它一些进程控制)等等。把这些东西转换成种子s,
|
||||
经F(s)处理,就会得到随机比特流。
|
||||
或者很有可能是不同的内存内容(比如,由其它一些进程控制或可能控制的未初始化的内存)等等。把这些东西转换成种子s,就会得到随机比特流F(s)。
|
||||
|
||||
2006年,为了解决一条从一个查找软件内存存取bug的工具[5]生成的警告[4],一名Debian维护者决定注释掉[6]OpenSSL PRNG里的两行代码[7]。
|
||||
结果这两行代码非常重要,代码负责抓取几乎所有的不可预测的熵,抓取的熵会作为OpenSSL PRNG的种子。没有这些代码,
|
||||
PRNG只有总共32,767个选择可作为种子,因而也就是说只有这么多的选择可用于F(s)进行处理。
|
||||
2006年,为了解决一个用于查找软件内存存取bug的工具[5]的警告问题[4],一名Debian维护者决定注释掉[6]OpenSSL PRNG里的两行代码[7]。
|
||||
但是这两行代码非常重要,它们负责抓取几乎所有的不可预测的熵,以作为OpenSSL PRNG的种子。没有这些代码,PRNG只有总共32,767个选择可作为种子s,因而也只有这么多的F(s)供选择。
|
||||
|
||||
很多依赖于OpenSSL随机数生成器的程序,其实并不拥有那么多的随机选择,但是他们原以为会有那么多的。
|
||||
一个这样的程序要为SSL(安全网络浏览)和SSH(安全远程登录)生成秘钥。问题的关键在于,这些秘钥必须是随机的:如果你可以猜到我的秘钥,
|
||||
这样一来,很多依赖于OpenSSL随机数生成器的程序,其实并没有它们以为的那么多的随机选择。比如,一个这样的程序要为SSL(安全网络浏览)和SSH(安全远程登录)生成秘钥。严格来说,这些秘钥必须是随机的:如果你可以猜到我的秘钥,
|
||||
你就可以破解我使用该秘钥保护的任何东西。这意味着你有能力读取加密的通讯信息,登录到远程服务器[8],或者伪造看起来似乎是真实的信息[9]。
|
||||
这个漏洞是2006年第一次引入,而且进入到Ubuntu中[10](另一个流行的linux发行版,广泛应用于网络服务器)。漏洞影响到数以千计的服务器而且
|
||||
存在了很长一段时间[11],因为只是给受影响的服务器打补丁还不足以解决问题,必须替换掉任何在漏洞存在情况下生成的秘钥。
|
||||
|
||||
顺便说一句,为伪随机数生成器寻找熵是个著名[12]的难题[13]。事实上,在今天来看要解决这个问题依然是个巨大的挑战。随机错误难以检测,
|
||||
因为当你盯着输出看,每次运行程序结果都不一样,就像随机的一样。弱随机性很难定位,但是它可以使(貌似)安全的加密系统失效。
|
||||
依然如此,Debian中的那个漏洞一经发现在安全界[15]就常常被当做笑柄[16]。
|
||||
因为当你盯着输出看时,每次运行程序结果都不一样,就像随机的一样。弱随机性很难发现,但是它可以使(貌似)安全的加密系统失效。
|
||||
不过,Debian中的那个漏洞很醒目,被发现后在安全社区[15]引起了很多嘲笑[16]。
|
||||
|
||||
这是个后门,故意设置的吗?似乎不大可能。[Kurt Roeckx][17],代码维护者,后来成为Debian项目的主管。显然他是个可靠的家伙,
|
||||
不是为了故意设置漏洞而由NSA伪造出来的身份。想进入Debian项目组的核心,需要做出巨大的努力,那真是出了名的难进。
|
||||
这样看来,错误根本不是自己冒出来,而是一系列失误导致的,而且后果严重。
|
||||
于是有人问,这是个后门,故意设置的吗?似乎不大可能。做出这个更改的代码维护者 [Kurt Roeckx][17],后来成为Debian项目的主管。这意味着他是个可靠的家伙,
|
||||
不是为了插入漏洞而由NSA伪造出来的身份。想进入Debian项目组的核心,需要做出巨大的努力,那真是出了名的难进。
|
||||
这样看来,错误根本不是有意为之,而是一系列失误导致的,而且后果严重。
|
||||
|
||||
漏洞确实是在一个透明的环境下引入的。所做的任何一件事都是公开的。但是漏洞就在那儿,而且呆了相当长一段时间。
|
||||
部分原因在于,正因为所有的事情都是透明的,才导致极大的混乱,人们对那个显而易见的漏洞也都没太在意。
|
||||
另外,也因为漏洞本身太过微妙。让修改带来的影响随便给谁看都能那么明显,这也不是设计该系统的目的。
|
||||
漏洞确实是在一个透明的环境下发生的。所做的任何一件事都是公开的。但是漏洞还是引入了,而且长时间未被注意到。部分原因在于,透明引起了很多混乱,导致本应发现这个显而易见的漏洞的人们也都没太在意。
|
||||
另外,也因为漏洞本身太过微妙,一个随意的观察者很难发现修改带来的影响。
|
||||
|
||||
这是否意味着软件透明没什么益处? 我可不这么认为。许多人都赞同透明软件要比不透明软件更安全。
|
||||
但是这也并不表示漏洞不会产生,或者认为有其他人都看着呢而我们自己就可以掉以轻心。
|
||||
这是否意味着软件透明没什么帮助? 我可不这么认为。许多人都赞同透明软件要比不透明软件更安全。但是这也并不表示漏洞不会产生,或者认为有其他人都看着呢而我们自己就可以掉以轻心。
|
||||
|
||||
至少,多年以后,透明可以让我们回想起,究竟是什么导致的那个漏洞,原来是工程上的纰漏而非人为破坏。
|
||||
至少,多年以后,透明可以让我们回顾,究竟是什么导致了某个漏洞--本文例子中,就是工程上的纰漏,而非人为破坏。
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://freedom-to-tinker.com/blog/kroll/software-transparency-debian-openssl-bug/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[l3b2w1](https://github.com/l3b2w1) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[l3b2w1](https://github.com/l3b2w1) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://freedom-to-tinker.com/blog/felten/software-transparency/
|
||||
@ -64,4 +58,4 @@ via: https://freedom-to-tinker.com/blog/kroll/software-transparency-debian-opens
|
||||
[16]:http://www.xkcd.com/424/
|
||||
[17]:http://www.roeckx.be/journal/
|
||||
[18]:http://lists.debian.org/debian-devel-announce/2009/02/msg00009.html
|
||||
[19]:http://research.swtch.com/openssl
|
||||
[19]:http://research.swtch.com/openssl
|
||||
|
||||
30
translated/Unity 8 updated with interesting refinements.md
Executable file
30
translated/Unity 8 updated with interesting refinements.md
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
更新了有趣细节的 Unity 8
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
作为下一代 Unity 的 [Unity 8][1],其目标是在发展理念上与 Ubuntu 设备桌面系统趋于一致。Unity 8 旨在手机、平板,及电脑设备上展现其独到的审美、强大的功能和专业的设计。
|
||||
|
||||
Unity 8 已经更新了又一个重要的 release 版本,在这一新版本中,Unity的基本元素经过优化处理后,显得更加清新和自然了。
|
||||
|
||||
几周前,Unity 8 在 Video 域中支持了旋转效果,随后,旋转效果又加入到了 Music 域中。简单来说,在 Videos 域和 Music 域中,Unity 8 使用精心设计的 coverflow 效果来呈现和组织内容。
|
||||
|
||||
最新版本的 Unity 8 在 Music 域中为 **coverflow** 效果增加了不少细节,使用巧妙精致的形状渲染音乐的封面(音乐曲目的大号缩略图)。
|
||||
|
||||
打开 Music 域,映入眼帘的是循环铺展着的封面,通过使用新的外观(增加了宽度并且减少了高度),使得封面看起来更接近于方形。这样修改的效果是,封面显得更加精致典雅,散发出了一种风格和品质。此外,封面与 `Albums` 的缩略图(例如)看起来更加一致(具有一样的外观和感觉)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unity 8 自带了多个搜索框,搜索框支持显示 **动态提示符** 。当您在搜索框中输入一个单词时,您可以看到一个色泽鲜艳的圆圈在不停旋转,这代表正在搜索中。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 13.10 的软件中心,您可以[下载][2] Unity 8 的测试版。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/unity-8-updated-interesting-refinements
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[will.qian](https://github.com/willqian) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/unity8
|
||||
[2]:apt://unity8
|
||||
79
translated/apt-fast--Improve apt-get Download Speed.md
Normal file
79
translated/apt-fast--Improve apt-get Download Speed.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
||||
apt-fast:改善apt-get下载速度
|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast是一个为 **apt-get** 和 **aptitude** 的“ **shell脚本封装** ”,通过用每个包的多种连接的方式下载包可以大大改善APT下载时间。apt-fast使用aria2c或axel下载管理器去加快APT下载时间。就像传统的apt-get包管理器,apt-fast支持几乎所有的apt-get功能,如, **install** , **remove** , **update** , **upgrade** , **dist-upgrade** 等等。并且一个显著的特征是它也支持proxy。
|
||||
|
||||
**在Ubuntu上安装apt-fast**
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下PPA去安装apt-fast。apt-fast开发者说:“ **一些发行版,如PCLinux在他们默认的仓库中包括apt-fast** 。”我期待同样包含在Ubuntu/Debian默认仓库中。
|
||||
|
||||
添加apt-fast的PPA。在终端中输入以下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:apt-fast/stable
|
||||
|
||||
用命令更新源:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
使用命令安装apt-fast:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install apt-fast
|
||||
|
||||
在安装期间,它将问你下载包的最大链接数。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
选择No并继续安装。如果你选择Yes,apt-get在任何包安装期间不会问你确认与否。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我发现 **aria2** 下载管理器已经随着apt-fast的安装而自动安装。所以,你不必单独安装aria2。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想重新配置apt-fast选项,你可以使用命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg-reconfigure apt-fast
|
||||
|
||||
**用法**
|
||||
|
||||
与apt-get相同的功能,我们可以使用:
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast install package
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast remove package
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast update
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
apt-fast dist-upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
更多。
|
||||
|
||||
工作中的apt-fast包管理器:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**创建别名(可选)**
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 **~/.bashrc** 文件在末尾添加下面这行。
|
||||
|
||||
alias apt-get='apt-fast'
|
||||
|
||||
或者简单运行以下命令在你的 **~/.bashrc** 中添加它。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo echo "alias apt-get='apt-fast'" >> ~/.bashrc
|
||||
|
||||
从现在每当你运行apt-get命令去,移除,更新和升级包时,它将在后台自动使用apt-fast。听起来很酷?是的,这是必须的。
|
||||
|
||||
在测试期间,当下载包时我发现它与apt-get相比非常快。试一试,你将赞同我。感谢阅读!!
|
||||
|
||||
-------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/improve-apt-get-download-speed-apt-fast/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vito](https://github.com/Vito) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/ilikenwf/apt-fast
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user