mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-16 22:42:21 +08:00
commit
9dd34fd9d1
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
10个实用的关于linux中Squid代理服务器的面试问答
|
||||
10个关于linux中Squid代理服务器的实用面试问答
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
不仅是系统管理员和网络管理员时不时会听到“代理服务器”这个词,我们也经常听到。代理服务器已经是一种企业的文化,而且那是需要时间来积累的。它现在也在一些小型的学校或者大型跨国公司的自助餐厅里得到了实现。Squid(也可做代理服务)就是这样一个应用程序,它既可以被作为代理服务器,同时也是在其同类工具中比较被广泛使用的一种。
|
||||
不仅是系统管理员和网络管理员时不时会听到“代理服务器”这个词,我们也经常听到。代理服务器已经成为一种企业常态,而且经常会接触到它。它现在也出现在一些小型的学校或者大型跨国公司的自助餐厅里。Squid(常被视作代理服务的代名词)就是这样一个应用程序,它不但可以被作为代理服务器,其同时也是在该类工具中比较被广泛使用的一种。
|
||||
|
||||
本文旨在提高你在遇到关于代理服务器面试点时的一些基本应对能力。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10,12 +10,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 什么是代理服务器?代理服务器在计算机网络中有什么用途? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 代理服务器是指那些作为客户端和资源提供商或服务器之间的中间件的物理机或者应用程序。客户端从代理服务器中寻找文件、页面或者是数据而且代理服务器能处理客户端与服务器之间所有复杂事务从而满足客户端的生成的需求。
|
||||
代理服务器是WWW(万维网)的支柱,它们其中大部分都是Web代理。一台代理服务器能处理客户端与服务器之间的复杂通信事务。此外,它在网络上提供的是匿名信息那就意味着你的身份和浏览痕迹都是安全的。代理可以去配置允许哪些网站的客户能看到,哪些网站被屏蔽了。
|
||||
> **回答** : 代理服务器是指那些作为客户端和资源提供商或服务器之间的中间件的物理机或者应用程序。客户端从代理服务器中寻找文件、页面或者是数据,而且代理服务器能处理客户端与服务器之间所有复杂事务,从而满足客户端的生成的需求。
|
||||
|
||||
代理服务器是WWW(万维网)的支柱,它们其中大部分都是Web代理。一台代理服务器能处理客户端与服务器之间的复杂通信事务。此外,它在网络上提供的是匿名信息(LCTT 译注:指浏览者的 IP、浏览器信息等被隐藏),这就意味着你的身份和浏览痕迹都是安全的。代理可以去配置允许哪些网站的客户能看到,哪些网站被屏蔽了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Squid是什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : Squid是一个在GNU/GPL协议下发布的即可作为代理服务器同时也可作为Web缓存守护进程的应用软件。Squid主要是支持像HTTP和FTP那样的协议但是对其它的协议比如HTTPS,SSL,TLS等同样也能支持。其特点是Web缓存守护进程通过从经常上访问的网站里缓存Web和DNS从而让上网速度更快。Squid支持所有的主流平台,包括Linux,UNIX,微软公司的Windows和苹果公司的Mac。
|
||||
> **回答** : Squid是一个在GNU/GPL协议下发布的既可作为代理服务器,同时也可作为Web缓存守护进程的应用软件。Squid主要是支持像HTTP和FTP那样的协议,但是对其它的协议比如HTTPS,SSL,TLS等同样也能支持。其特点是Web缓存守护进程通过从经常上访问的网站里缓存Web和DNS数据,从而让上网速度更快。Squid支持所有的主流平台,包括Linux,UNIX,微软公司的Windows和苹果公司的Mac。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Squid的默认端口是什么?怎么去修改它的操作端口? ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,17 +67,17 @@ f. 保存配置文件并退出,重启Squid服务让其生效。
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 在Squid中什么是媒体范围限制和部分下载? ###
|
||||
### 5. 在Squid中什么是媒体范围限制(Media Range Limitation)和部分下载? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 媒体范围限制是Squid的一种特殊的功能,它只从服务器中获取所需要的数据而不是整个文件。这个功能很好的实现了用户在各种视频流媒体网站如YouTube和Metacafe看视频时,可以点击视频中的进度条来选择进度,因此整个视频不用全部都加载,除了一些需要的部分。
|
||||
|
||||
Squid部分下载功能的特点是很好地实现了在Windows更新时下载的文件能以一个个小数据包的形式暂停。正因为它的这个特点,正在下载文件的Windows机器能不用担心数据会丢失,从而进行恢复下载。Squid让媒体范围限制和部分下载功能只在存储一个完整文件的复件之后实现。此外,当用户指向另一个页面时,Squid要以某种方式进行特殊地配置,部分下载下来的文件才会不被删除且留有缓存。
|
||||
Squid部分下载功能的特点是很好地实现了类似在Windows更新时能以一个个小数据包的形式下载,并可以暂停,正因为它的这个特点,正在下载文件的Windows机器可以重新继续下载,而不用担心数据会丢失。Squid的媒体范围限制和部分下载功能只有在存储了一个完整文件的副本之后才行。此外,当用户访问另一个页面时,除非Squid进行了特定的配置,部分下载下来的文件会被删除且不留在缓存中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 什么是Squid的反向代理? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 反向代理是Squid的一个特点,这个功能被用来加快最终用户的上网速度。缩写为 ‘RS’ 的原服务器包含了所有资源,而代理服务器则叫 ‘PS’ 。客户端寻找RS所提供的数据,第一次指定的数据和它的复件会经过多次配置从RS上存储在PS上。这样的话每次从PS上请求的数据就等于就是从原服务器上获取的。这样就会减轻网络拥堵,减少CPU使用率,降低网络资源的利用率从而缓解原来实际服务器的负载压力。但是RS统计不了总流量的数据因为PS分担了部分原服务器的任务。‘X-Forwarded-For HTTP’ 就能记录下通过HTTP代理或负载均衡方式连接到RS的客户端最原始的IP地址。
|
||||
> **回答** : 反向代理是Squid的一个功能,这个功能被用来加快最终用户的上网速度。下面用缩写 ‘RS’ 的表示包含了资源的原服务器,而代理服务器则称作 ‘PS’ 。初次访问时,它会从RS得到其提供的数据,并将其副本按照配置好的时间存储在PS上。这样的话每次从PS上请求的数据就相当于就是从原服务器上获取的。这样就会减轻网络拥堵,减少CPU使用率,降低网络资源的利用率,从而缓解原来实际服务器的负载压力。但是RS统计不了总流量的数据,因为PS分担了部分原服务器的任务。‘X-Forwarded-For HTTP’ 信息能用于记录下通过HTTP代理或负载均衡方式连接到RS的客户端最原始的IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
严格意义上来说,用单个Squid服务器同时作为正向代理服务器和反向代理服务器是可行的。
|
||||
从技术上说,用单个Squid服务器同时作为正向代理服务器和反向代理服务器是可行的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 由于Squid能作为一个Web缓存守护进程,那缓存可以删除吗?怎么删除? ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -91,7 +92,7 @@ b. 创建交换分区目录。
|
||||
|
||||
# squid -z
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. 你身边有一台客户机,而你正在工作,如果想要限制儿童的访问时间段,你会怎么去设置那个场景? ###
|
||||
### 8. 你有一台工作中的机器可以访问代理服务器,如果想要限制你的孩子的访问时间,你会怎么去设置那个场景? ###
|
||||
|
||||
把允许访问的时间设置成晚上4点到7点三个小时,跨度为星期一到星期五。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -114,9 +115,9 @@ c. 重启Squid服务。
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Squid的缓存会存储到哪里? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : Squid存储的缓存是位于 ‘/var/spool/squid’ 的特殊目录下。
|
||||
> **回答** : Squid存储的缓存是位于 ‘/var/spool/squid’ 的特定目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
以上就是全部内容了,很快我还会带着其它有趣的内容回到这里,届时还请继续关注Tecmint。别忘了告诉我们你的反馈和评论。
|
||||
以上就是全部内容了,很快我还会带着其它有趣的内容回到这里。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -124,7 +125,7 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/squid-interview-questions/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
从命令行访问Linux命令小抄
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux命令行的强大在于其灵活及多样化,各个Linux命令都带有它自己那部分命令行选项和参数。混合并匹配它们,甚至还可以通过管道和重定向来联结不同的命令。理论上讲,你可以借助几个基本的命令来产生数以百计的使用案例。甚至对于浸淫多年的管理员而言,也难以完全使用它们。那正是命令行小抄成为我们救命稻草的一刻。
|
||||
Linux命令行的强大在于其灵活及多样化,各个Linux命令都带有它自己专属的命令行选项和参数。混合并匹配这些命令,甚至还可以通过管道和重定向来联结不同的命令。理论上讲,你可以借助几个基本的命令来产生数以百计的使用案例。甚至对于浸淫多年的管理员而言,也难以完全使用它们。那正是命令行小抄成为我们救命稻草的一刻。
|
||||
|
||||
[][1]
|
||||
|
||||
我知道联机手册页仍然是我们的良师益友,但我们想通过我们能自行支配的快速参考卡让这一切更为高效和有目的性。最终极的小抄可能被自豪地挂在你的办公室里,也可能作为PDF文件隐秘地存储在你的硬盘上,或者甚至设置成了你的桌面背景图。
|
||||
我知道联机手册页(man)仍然是我们的良师益友,但我们想通过我们能自行支配的快速参考卡让这一切更为高效和有目的性。最终极的小抄可能被自豪地挂在你的办公室里,也可能作为PDF文件隐秘地存储在你的硬盘上,或者甚至设置成了你的桌面背景图。
|
||||
|
||||
最为一个选择,也可以通过另外一个命令来访问你最爱的命令行小抄。那就是,使用[cheat][2]。这是一个命令行工具,它可以让你从命令行读取、创建或更新小抄。这个想法很简单,不过cheat经证明是十分有用的。本教程主要介绍Linux下cheat命令的使用方法。你不需要为cheat命令做个小抄了,它真的很简单。
|
||||
做为一个选择,也可以通过另外一个命令来访问你最爱的命令行小抄。那就是,使用[cheat][2]。这是一个命令行工具,它可以让你从命令行读取、创建或更新小抄。这个想法很简单,不过cheat经证明是十分有用的。本教程主要介绍Linux下cheat命令的使用方法。你不需要为cheat命令做个小抄了,它真的很简单。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Cheat到Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -59,9 +59,9 @@ cheat命令一个很酷的事是,它自带有超过90个的常用Linux命令
|
||||
|
||||
$ cheat -s <keyword>
|
||||
|
||||
在许多情况下,小抄适用于那些正派的人,而对其他某些人却没什么帮助。要想让内建的小抄更具个性化,cheat命令也允许你创建新的小抄,或者更新现存的那些。要这么做的话,cheat命令也会帮你在本地~/.cheat目录中保存一份小抄的副本。
|
||||
在许多情况下,小抄适用于某些人,而对另外一些人却没什么帮助。要想让内建的小抄更具个性化,cheat命令也允许你创建新的小抄,或者更新现存的那些。要这么做的话,cheat命令也会帮你在本地~/.cheat目录中保存一份小抄的副本。
|
||||
|
||||
要使用cheat的编辑功能,首先确保EDITOR环境变量设置为了你默认编辑器所在位置的完整路径。然后,复制(不可编辑)内建小抄到~/.cheat目录。你可以通过下面的命令找到内建小抄所在的位置。一旦你找到了它们的位置,只不过是将它们拷贝到~/.cheat目录。
|
||||
要使用cheat的编辑功能,首先确保EDITOR环境变量设置为你默认编辑器所在位置的完整路径。然后,复制(不可编辑)内建小抄到~/.cheat目录。你可以通过下面的命令找到内建小抄所在的位置。一旦你找到了它们的位置,只不过是将它们拷贝到~/.cheat目录。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cheat -d
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,7 +85,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/access-linux-command-cheat-sheets-command-line.h
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,12 +8,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加窗口按钮 ###
|
||||
|
||||
处于一些未知的原因,GNOME的开发者们决定对标准的窗口按钮(关闭,最小化,最大化)不屑一顾,而支持只有单个关闭按钮的窗口了。我缺少了最大化按钮(虽然你可以简单地拖动窗口到屏幕顶部来将它最大化),然而也可以通过在标题栏右击选择最小化或者最大化来进行最小化/最大化操作。这种变化仅仅增加了操作步骤,因此缺少最小化按钮实在搞得人云里雾里。所幸的是,有个简单的修复工具可以解决这个问题,下面说说怎样做吧:
|
||||
出于一些未知的原因,GNOME的开发者们决定对标准的窗口按钮(关闭,最小化,最大化)不屑一顾,而支持只有单个关闭按钮的窗口了。我缺少了最大化按钮(虽然你可以简单地拖动窗口到屏幕顶部来将它最大化),而且也可以通过在标题栏右击选择最小化或者最大化来进行最小化/最大化操作。这种变化仅仅增加了操作步骤,因此缺少最小化按钮实在搞得人云里雾里。所幸的是,有个简单的修复工具可以解决这个问题,下面说说怎样做吧:
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,你应该安装了GNOME优化工具。通过该工具,你可以打开最大化或最小化按钮(图1)。
|
||||
默认情况下,你应该安装了GNOME优化工具(GNOME Tweak Tool)。通过该工具,你可以打开最大化或最小化按钮(图1)。
|
||||
|
||||
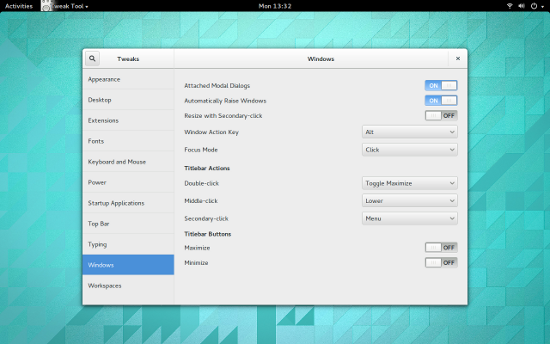
|
||||
Figure 1: 添加回最小化按钮到GNOME 3窗口
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
*图 1: 添加回最小化按钮到GNOME 3窗口*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
添加完后,你就可以看到最小化按钮了,它在关闭按钮的左边,等着为你服务呢。你的窗口现在管理起来更方便了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,36 +28,39 @@ Figure 1: 添加回最小化按钮到GNOME 3窗口
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加扩展 ###
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME 3的最佳特性之一,就是shell扩展,这些扩展为GNOME带来了全部种类的有用的特性。关于shell扩展,没必要从包管理器去安装。你可以访问[GNOME Shell扩展][2]站点,搜索你想要添加的扩展,点击扩展列表,点击打开按钮,然后扩展就安装完成了;或者你也可以从GNOME优化工具中添加它们(你在网站上会找到更多可用的扩展)。
|
||||
GNOME 3的最佳特性之一,就是shell扩展,这些扩展为GNOME带来了各种类别的有用特性。关于shell扩展,没必要从包管理器去安装。你可以访问[GNOME Shell扩展][2]站点,搜索你想要添加的扩展,点击扩展列表,点击打开按钮,然后扩展就安装完成了;或者你也可以从GNOME优化工具中添加它们(你在网站上会找到更多可用的扩展)。
|
||||
|
||||
注:你可能需要在浏览器中允许扩展安装。如果出现这样的情况,你会在第一次访问GNOME Shell扩展站点时见到警告信息。当出现提示时,只要点击允许即可。
|
||||
|
||||
令人印象更为深刻的(而又得心应手的扩展)之一,就是[Dash to Dock][3]。
|
||||
令人印象更为深刻的(而又得心应手的)扩展之一,就是[Dash to Dock][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
该扩展将Dash移出应用程序概览,并将它转变为相当标准的停靠栏(图2)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Figure 2: Dash to Dock添加一个停靠栏到GNOME 3.
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
*图 2: Dash to Dock添加一个停靠栏到GNOME 3*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
当你添加应用程序到Dash后,他们也将被添加到Dash to Dock。你也可以通过点击Dock底部的6点图标访问应用程序概览。
|
||||
|
||||
还有大量其它扩展聚焦于讲GNOME 3打造成一个更为高效的桌面,在这些更好的扩展中,包括以下这些:
|
||||
还有大量其它扩展致力于将GNOME 3打造成一个更为高效的桌面,在这些不错的扩展中,包括以下这些:
|
||||
|
||||
- [最近项目][4]: 添加一个最近使用项目的下拉菜单到面板。
|
||||
- [搜索Firefox书签提供者][5]: 从概览搜索(并启动)书签。
|
||||
- [Firefox书签搜索][5]: 从概览搜索(并启动)书签。
|
||||
- [跳转列表][6]: 添加一个跳转列表弹出菜单到Dash图标(该扩展可以让你快速打开和程序关联的新文档,甚至更多)
|
||||
- [待办列表][7]: 添加一个下拉列表到面板,它允许你添加项目到该列表。
|
||||
- [网页搜索对话框][8]: 允许你通过敲击Ctrl+空格来快速搜索网页并输入一个文本字符串(结果在新的浏览器标签页中显示)。
|
||||
- [网页搜索框][8]: 允许你通过敲击Ctrl+空格来快速搜索网页并输入一个文本字符串(结果在新的浏览器标签页中显示)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加一个完整停靠栏 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果Dash to dock对于而言功能还是太有限(你想要通知区域,甚至更多),那么向你推荐我最喜爱的停靠栏之一[Cairo Dock][9](图3)。
|
||||
如果Dash to dock对于你而言功能还是太有限(你想要“通知区域”,甚至更多),那么向你推荐我最喜爱的停靠栏之一[Cairo Dock][9](图3)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Figure 3: Cairo Dock待命
|
||||
<center>
|
||||
|
||||
在Cairo Dock添加到GNOME 3后,你的体验将成倍地增长。从你的发行版的包管理器中安装这个优秀的停靠栏吧。
|
||||
*图 3: Cairo Dock待命*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
不必将GNOME 3看作是一个效率不高的,用户不友好的桌面。只要稍作调整,GNOME 3可以成为和其它可用的桌面一样强大而用户友好的桌面。
|
||||
在将Cairo Dock添加到GNOME 3后,你的体验将成倍地增长。从你的发行版的包管理器中安装这个优秀的停靠栏吧。
|
||||
|
||||
不要将GNOME 3看作是一个效率不高的,用户不友好的桌面。只要稍作调整,GNOME 3可以成为和其它可用的桌面一样强大而用户友好的桌面。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,7 +68,7 @@ via: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/781916-easy-steps-to-make-gnome-3-more
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jack Wallen][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[ wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
什么时候Linux才能完美
|
||||
什么时候Linux才能完美?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
前几天我的同事兼损友,Ken Starks,在FOSS Force上发表了[一篇文章][1],关于他最喜欢发牢骚的内容:Linux系统中那些不能正常工作的事情。这次他抱怨的是在Mint里使用KDE时碰到的字体问题。这对于Ken来说也不是什么新鲜事了。过去他写了一些文章,关于各种Linux发行版中的缺陷从来都没有被认真修复过。他的观点是,这些在一次又一次的发布中从没有被修复过的“小问题”,对于Linux桌面系统在赢得大众方面的失败需要负主要责任。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,21 +14,21 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 也不全是这样子的 ###
|
||||
|
||||
早在2002年的时候,我第一次安装使用GNU/Linux,像大多数美国人那样,我搞不定拨号连接,在我呆的这个小地方当时宽带还没普及。我在当地Best Buy商店里花了差不多70美元买了用热缩膜包装的Mandrake 9.0的Powerpack版,当时那里同时在卖Mandrake和Red Hat,现在仍然还在经营桌面业务。
|
||||
早在2002年的时候,我第一次安装使用GNU/Linux,像大多数美国人那样,我搞不定拨号连接,在我呆的这个小地方当时宽带还没普及。我在当地Best Buy商店里花了差不多70美元买了用热缩膜包装的Mandrake 9.0的Powerpack版,当时那里同时在卖Mandrake和Red Hat,现在仍然还在经营桌面PC业务。
|
||||
|
||||
在那个恐龙时代,Mandrake被认为是易用的Linux发行版中做的最好的。它安装简单,还有人说比Windows还简单,它自带的分区工具更是让划分磁盘像切苹果馅饼一样简单。不过实际上,Linux老手们经常公开嘲笑Mandrake,暗示易用的Linux不是真的Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
但是我很喜欢它,感觉来到了一个全新的世界。再也不用担心Windows的蓝屏死机和几乎每天一死了。不幸的是,之前在Windows下“能用”的很多外围设备也随之而去。
|
||||
|
||||
安装完Mandrake之后我要做的第一件事就是,把我的小白盒拿给[Dragonware Computers][2]的Michelle,把便宜的winmodem换成硬件调制解调器。就算,一个硬件猫意味着计算机响应更快,但是计算机商店却在40英里外的地方,并不是很方便,而且费用我也有点压力。
|
||||
安装完Mandrake之后我要做的第一件事就是,把我的小白盒拿给[Dragonware Computers][2]的Michelle,把便宜的winmodem换成硬件调制解调器。就算是一个硬件猫意味着计算机响应更快,但是计算机商店却在40英里外的地方,并不是很方便,而且费用对我也有点压力。
|
||||
|
||||
但是我不介意。我对Microsoft并不感冒--而且使用一个“不同”的操作系统让我感觉自己就像一个计算机天才。
|
||||
|
||||
打印机也是个麻烦,但是这个问题对于Mandrake还好,不像其他大多数发行版还需要命令行里的操作才能解决。Mandrake提供了一个华丽的图形界面来设置打印机-如果你正好幸运的有一台能在Linux下工作的打印机的话。很多,不是大多数,都不行。
|
||||
打印机也是个麻烦,但是这个问题对于Mandrake还好,不像其他大多数发行版还需要命令行里的操作才能解决。Mandrake提供了一个华丽的图形界面来设置打印机-如果你正好幸运的有一台能在Linux下工作的打印机的话。很多打印机——就算不是大多数——都不行。
|
||||
|
||||
我的还在保修期的Lexmark,在Windows下比其他打印机多出很多华而不实的小功能,厂商并不支持Linux版本,但是我找到一个多少能用的开源逆向工程驱动。它能在Mozilla浏览器里正常打印网页,但是在Star Office软件里打印的话会是用很小的字体塞到页面的右上角里。打印机还会发出很大的机械响声,让我想起了汽车变速箱在报废时发出的噪音。
|
||||
|
||||
Star Office问题的变通方案是把所有文字都保存到文本文件,然后在文本编辑器里打印。而对于那个听上去像是打印机处于自解体模式的噪音?我的方法是尽量不要打印。
|
||||
Star Office问题的变通方案是把所有文字都保存到文本文件,然后在文本编辑器里打印。而对于那个听上去像是打印机处于天魔解体模式的噪音?我的方法是尽量不要打印。
|
||||
|
||||
### 更多的其他问题-对我来说太多了都快忘了 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,12 +36,13 @@ Star Office问题的变通方案是把所有文字都保存到文本文件,然
|
||||
|
||||
好吧,我还有个并口扫描仪,在我转移到Linux之前两个星期买的,之后它就基本是块砖了,因为没有Linux下的驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
我的观点是在那个年代里这些都不重要。我们大多数人都习惯了修改配置文件之类的事情,即便是运行微软产品的“IBM兼容”计算机。就像那个年代的大多数用户,我刚学开始接触使用命令行的DOS机器,在它上面打印机需要针对每个程序单独设置,而且写写简单的autoexec.bat是必须的技能。
|
||||
我的观点是在那个年代里这些都不重要。我们大多数人都习惯了修改配置文件之类的事情,即便是运行微软产品的“IBM兼容”计算机。就像那个年代的大多数用户,我刚学开始接触使用命令行的DOS机器,在它上面打印机需要针对每个程序单独设置,而且写写简单的autoexec.bat是必备的技能。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Linux就像1966年的“山羊”
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
能够摆弄操作系统内部的配置是能够拥有一台计算机的一个简单部分。我们大多数使用计算机的人要么是极客或是希望成为极客。我们为这种能够调整计算机按我们想要的方式运行的能力而感到骄傲。我们就是那个年代里高科技版本的好男孩,他们会在周六下午在树荫下改装他们肌肉车上的排气管,通风管,化油器之类的。
|
||||
<center>Linux就像1966年的“山羊”</center>
|
||||
|
||||
那时,能够摆弄操作系统内部的配置是能够拥有一台计算机的一个简单部分。我们大多数使用计算机的人要么是极客或是希望成为极客。我们为这种能够调整计算机按我们想要的方式运行的能力而感到骄傲。我们就是那个年代里高科技版本的好男孩,他们会在周六下午在树荫下改装他们肌肉车上的排气管,通风管,化油器之类的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 不过现在大家不是这样使用计算机的 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -59,7 +60,7 @@ via: http://fossforce.com/2014/08/when-linux-was-perfect-enough/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Christine Hall
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,20 +1,17 @@
|
||||
使用Clonezilla对硬盘进行镜像和克隆
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
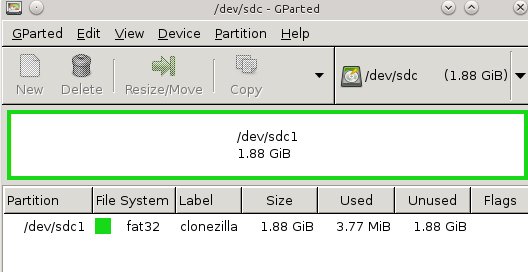
|
||||
|
||||
图1: 在USB存储棒上为Clonezilla创建分区
|
||||
Clonezilla是一个用于Linux,Free-Net-OpenBSD,Mac OS X,Windows以及Minix的分区和磁盘克隆程序。它支持所有主要的文件系统,包括EXT,NTFS,FAT,XFS,JFS和Btrfs,LVM2,以及VMWare的企业集群文件系统VMFS3和VMFS5。Clonezilla支持32位和64位系统,同时支持旧版BIOS和UEFI BIOS,并且同时支持MBR和GPT分区表。它是一个用于完整备份Windows系统和所有安装于上的应用软件的好工具,而我喜欢用它来为Linux测试系统做备份,以便我可以在其上做疯狂的实验搞坏后,可以快速恢复它们。
|
||||
|
||||
Clonezilla是一个用于Linux,Free-Net-,OpenBSD,Mac OS X,Windows以及Minix的分区和磁盘克隆程序。它支持所有主要的文件系统,包括EXT,NTFS,FAT,XFS,JFS和Btrfs,LVM2,以及VMWare的企业集群文件系统VMFS3和VMFS5。Clonezilla支持32位和64位系统,同时支持旧版BIOS和UEFI BIOS,并且同时支持MBR和GPT分区表。它是一个用于完整备份Windows系统和所有安装于上的应用软件的好工具,而我喜欢用它来为Linux测试系统做备份,以便我可以在其上做疯狂的实验搞坏后,可以快速恢复它们。
|
||||
Clonezilla也可以使用dd命令来备份不支持的文件系统,该命令可以复制块而非文件,因而不必在意文件系统。简单点说,就是Clonezilla可以复制任何东西。(关于块的快速说明:磁盘扇区是磁盘上最小的可编址存储单元,而块是由单个或者多个扇区组成的逻辑数据结构。)
|
||||
|
||||
Clonezilla也可以使用dd命令来备份不支持的文件系统,该命令可以复制块而非文件,因而不必弄明白文件系统。因此,简单点说,就是Clonezilla可以复制任何东西。(关于块的快速说明:磁盘扇区是磁盘上最小的可编址存储单元,而块是由单个或者多个扇区组成的逻辑数据结构。)
|
||||
|
||||
Clonezilla分为两个版本:Clonezilla Live和Clonezilla Server Edition(SE)。Clonezilla Live对于将单个计算机克隆岛本地存储设备或者网络共享来说是一流的。而Clonezilla SE则适合更大的部署,用于一次性快速多点克隆整个网络中的PC。Clonezilla SE是一个神奇的软件,我们将在今后讨论。今天,我们将创建一个Clonezilla Live USB存储棒,克隆某个系统,然后恢复它。
|
||||
Clonezilla分为两个版本:Clonezilla Live和Clonezilla Server Edition(SE)。Clonezilla Live对于将单个计算机克隆到本地存储设备或者网络共享来说是一流的。而Clonezilla SE则适合更大的部署,用于一次性快速多点克隆整个网络中的PC。Clonezilla SE是一个神奇的软件,我们将在今后讨论。今天,我们将创建一个Clonezilla Live USB存储棒,克隆某个系统,然后恢复它。
|
||||
|
||||
### Clonezilla和Tuxboot ###
|
||||
|
||||
当你访问下载页时,你会看到[稳定版和可选稳定发行版][1]。也有测试版本,如果你有兴趣帮助改善Clonezilla,那么我推荐你使用此版本。稳定版基于Debian,不含有非自由软件。可选稳定版基于Ubuntu,包含有一些非自由固件,并支持UEFI安全启动。
|
||||
|
||||
在你[下载Clonezilla][2]后,请安装[Tuxboot][3]来复制Clonezilla到USB存储棒。Tuxboot是一个Unetbootin的修改版,它支持Clonezilla;你不能使用Unetbootin,因为它无法工作。安装Tuxboot有点让人头痛,然而Ubuntu用户通过个人包归档压缩包(PPA)方便地安装:
|
||||
在你[下载Clonezilla][2]后,请安装[Tuxboot][3]来复制Clonezilla到USB存储棒。Tuxboot是一个Unetbootin的修改版,它支持Clonezilla;你不能使用Unetbootin,因为它无法配合工作。安装Tuxboot有点让人头痛,然而Ubuntu用户通过个人包归档包(PPA)方便地安装:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-add-repository ppa:thomas.tsai/ubuntu-tuxboot
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
@ -22,18 +19,24 @@ Clonezilla分为两个版本:Clonezilla Live和Clonezilla Server Edition(SE
|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有运行Ubuntu,并且你的发行版不包含打包好的Tuxboot版本,那么请[下载源代码tarball][4],并遵循README.txt文件中的说明来编译并安装。
|
||||
|
||||
安装完Tuxboot后,就可以使用它来创建你精巧的可直接启动的Clonezilla USB存储棒了。首先,创建一个最小200MB的FAT 32分区;图1(上面)展示了使用GParted来进行分区。我喜欢使用标签,比如“Clonezilla”,这会让我知道它是个什么东西。该例子中展示了将一个2GB的存储棒格式化成一个单个分区。
|
||||
Then fire up Tuxboot (figure 2). Check "Pre-downloaded" and click the button with the ellipsis to select your Clonezilla file. It should find your USB stick automatically, and you should check the partition number to make sure it found the right one. In my example that is /dev/sdd1. Click OK, and when it's finished click Exit. It asks you if you want to reboot now, but don't worry because it won't. Now you have a nice portable Clonezilla USB stick you can use almost anywhere.
|
||||
然后,启动Tuxboot(图2)。选中“预下载的(Pre-downloaded)”然后点击带省略号的按钮来选择Clonezilla文件。它会自动发现你的USB存储棒,而你需要选中分区号来确保它找到的是正确的那个,我的例子中是/dev/sdd1。点击确定,然后当它完成后点击退出。它会问你是否要重启动,请不要担心,因为它不会的。现在你有一个精巧的便携式Clonezilla USB存储棒了,你可以随时随地使用它了。
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
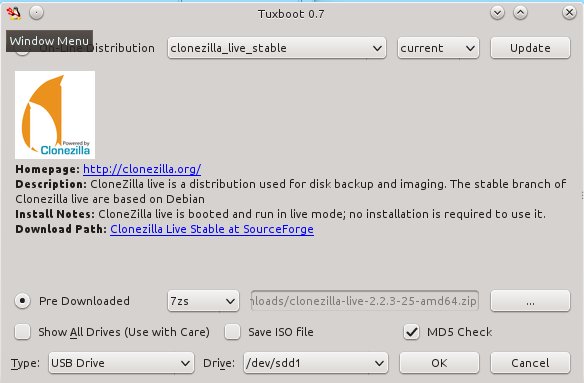
|
||||
图2: 启动Tuxboot
|
||||
<center>*图1: 在USB存储棒上为Clonezilla创建分区*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
安装完Tuxboot后,就可以使用它来创建你精巧的可直接启动的Clonezilla USB存储棒了。首先,创建一个最小200MB的FAT 32分区;图1(上图)展示了使用GParted来进行分区。我喜欢使用类似“Clonezilla”这样的标签,这会让我知道它是个什么东西。该例子中展示了将一个2GB的存储棒格式化成一个单个分区。
|
||||
|
||||
然后,启动Tuxboot(图2)。选中“预下载的(Pre-downloaded)”然后点击带省略号的按钮来选择Clonezilla文件。它会自动发现你的USB存储棒,而你需要选中分区号来确保它找到的是正确的那个,我的例子中是/dev/sdd1。点击确定,然后当它完成后点击退出。它会问你是否要重启动,不要担心,现在不用重启。现在你有一个精巧的便携式Clonezilla USB存储棒了,你可以随时随地使用它了。
|
||||
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>*图2: 启动Tuxboot*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建磁盘镜像 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在你想要备份的计算机上启动Clonezilla USB存储棒,第一个映入你眼帘的是常规的启动菜单。启动到默认条目。你会被问及使用何种语言和键盘,而当你到达启动Clonezilla菜单时,请选择启动Clonezilla。在下一级菜单中选择设备镜像,然后进入下一屏。
|
||||
|
||||
这一屏有点让人摸不着头脑,里头有什么local_dev,ssh_server,samba_server,以及nfs_server之类的选项。这里就是要你选择将备份的镜像拷贝到哪里,目标分区或者驱动器必须和你要拷贝的卷要一样大,甚至更大。如果你选择local_dev,那么你需要一个足够大的本地分区来存储你的镜像。附加USB硬盘驱动器是一个不错的,快速而又简单的选项。如果你选择任何服务器选项,你需要有线连接到服务器,并提供IP地址并登录上去。我将使用一个本地分区,这就是说要选择local_dev。
|
||||
这一屏有点让人摸不着头脑,里头有什么local_dev,ssh_server,samba_server,以及nfs_server之类的选项。这里就是要你选择将备份的镜像拷贝到哪里,目标分区或者驱动器必须和你要拷贝的卷要一样大,甚至更大。如果你选择local_dev,那么你需要一个足够大的本地分区来存储你的镜像。附加的USB硬盘驱动器是一个不错的,快速而又简单的选项。如果你选择任何服务器选项,你需要能连接到服务器,并提供IP地址并登录上去。我将使用一个本地分区,这就是说要选择local_dev。
|
||||
|
||||
当你选择local_dev时,Clonezilla会扫描所有连接到本地的存储折本,包括硬盘和USB存储设备。然后,它会列出所有分区。选择你想要存储镜像的分区,然后它会问你使用哪个目录并列出目录。选择你所需要的目录,然后进入下一屏,它会显示所有的挂载以及已使用/可用的空间。按回车进入下一屏,请选择初学者还是专家模式。我选择初学者模式。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,12 +44,13 @@ Then fire up Tuxboot (figure 2). Check "Pre-downloaded" and click the button wit
|
||||
|
||||
下一屏中,它会问你新建镜像的名称。在接受默认名称,或者输入你自己的名称后,进入下一屏。Clonezilla会扫描你所有的分区并创建一个检查列表,你可以从中选择你想要拷贝的。选择完后,在下一屏中会让你选择是否进行文件系统检查并修复。我才没这耐心,所以直接跳过了。
|
||||
|
||||
下一屏中,会问你是否想要Clonezilla检查你新创建的镜像,以确保它是可恢复的。选是吧,确保万无一失。接下来,它会给你一个命令行提示,如果你想用命令行而非GUI,那么你必须再次按回车。你需要再次确认,并输入y来确认制作拷贝。
|
||||
下一屏中,会问你是否想要Clonezilla检查你新创建的镜像,以确保它是可恢复的。选“是”吧,确保万无一失。接下来,它会给你一个命令行提示,如果你想用命令行而非GUI,那么你必须再次按回车。你需要再次确认,并输入y来确认制作拷贝。
|
||||
|
||||
在Clonezilla创建新镜像的时候,你可以好好欣赏一下这个友好的红、白、蓝三色的进度屏(图3)。
|
||||
|
||||
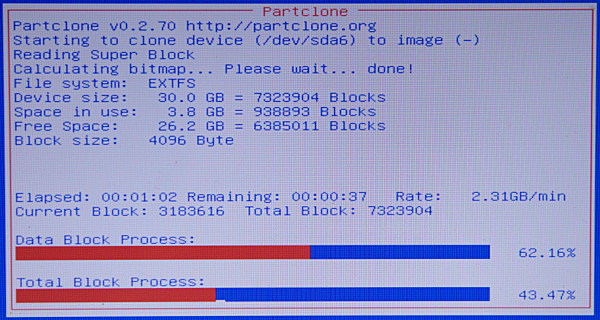
|
||||
图3: 守候创建新镜像
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>*图3: 守候创建新镜像*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
全部完成后,按回车然后选择重启,记得拔下你的Clonezilla USB存储棒。正常启动计算机,然后去看看你新创建的Clonezilla镜像吧。你应该看到像下面这样的东西:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -81,7 +85,7 @@ via: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/783416-how-to-image-and-clone-hard-dri
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Carla Schroder][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
|
||||
在哪儿以及怎么写代码:选择最好的免费代码编辑器
|
||||
何处写,如何写:选择最好的免费在线代码编辑器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
深入了解一下Cloud9,Koding和Nitrous.IO。
|
||||
> 深入了解一下Cloud9,Koding和Nitrous.IO。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**已经准备好开始你的第一个编程项目了吗?很好!只要配置一下**终端或命令行,学习如何使用并安装所有要用到的编程语言,插件库和API函数库。当最终准备好一切以后,再安装好[Visual Studio][1]就可以开始了,然后才可以预览自己的工作。
|
||||
已经准备好开始你的第一个编程项目了吗?很好!只要配置一下终端或命令行,学习如何使用它,然后安装所有要用到的编程语言,插件库和API函数库。当最终准备好一切以后,再安装好[Visual Studio][1]就可以开始了,然后才可以预览自己的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
至少这是大家过去已经熟悉的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
也难怪初学程序员们逐渐喜欢上在线集成开发环境(IDE)了。IDE是一个代码编辑器,不过已经准备好编程语言以及所有需要的依赖,可以让你避免把它们一一安装到电脑上的麻烦。
|
||||
也难怪初学程序员们逐渐喜欢上在线的集成开发环境(IDE)了。IDE是一个代码编辑器,不过已经准备好编程语言以及所有需要的依赖,可以让你避免把它们一一安装到电脑上的麻烦。
|
||||
|
||||
我想搞清楚到底是哪些因素能组成一个典型的IDE,所以我试用了一下免费级别的时下最受欢迎的三款集成开发环境:[Cloud9][2],[Koding][3]和[Nitrous.IO][4]。在这个过程中,我了解了许多程序员应该或不应该使用IDE的各种情形。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
假如有一个像Microsoft Word那样的文字编辑器,想想类似Google Drive那样的IDE吧。你可以拥有类似的功能,但是它还能支持从任意电脑上访问,还能随时共享。因为因特网在项目工作流中的影响已经越来越重要,IDE也让生活更轻松。
|
||||
|
||||
在我最近的一篇ReadWrite教程中我使用了Nitrous.IO,这是在文章[创建一个你自己的像Yo那样的极端简单的聊天应用][5]里的一个Python应用。当使用IDE的时候,你只要选择你要用的编程语言,然后通过IDE特别设计用来运行这种语言程序的虚拟机(VM),你就可以测试和预览你的应用了。
|
||||
在我最近的一篇ReadWrite教程中我使用了Nitrous.IO,这是在文章“[创建一个你自己的像Yo那样的极端简单的聊天应用][5]”里的一个Python应用。当使用IDE的时候,你只要选择你要用的编程语言,然后通过IDE特别为运行这种语言程序而设计的虚拟机(VM),你就可以测试和预览你的应用了。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你读过那篇教程,就会知道我的那个应用只用到了两个API库-信息服务Twilio和Python微框架Flask。在我的电脑上就算是使用文字编辑器和终端来做也是很简单的,不过我选择使用IDE还有一个方便的地方:如果大家都使用同样的开发环境,跟着教程一步步走下去就更简单了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,7 +28,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
但是不能用IDE来永久存储你的整个项目。把帖子保存在Google Drive文件中不会让你的博客丢失。类似Google Drive,IDE可以让你创建链接用于共享内容,但是任何一个都还不足以替代真正的托管服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
还有,IDE并不是设计成方便广泛共享。尽管各种IDE都在不断改善大多数文字编辑器的预览功能,还只能用来给你的朋友或同事展示一下应用预览,而不是,比如说,类似Hacker News的主页。那样的话,占用太多带宽的IDE也许会让你崩溃。
|
||||
还有,IDE并不是设计成方便广泛共享。尽管各种IDE都在不断改善大多数文字编辑器的预览功能,还只能用来给你的朋友或同事展示一下应用的预览,而不是像Hacker News一样的主页。那样的话,占用太多带宽的IDE也许会让你崩溃。
|
||||
|
||||
这样说吧:IDE只是构建和测试你的应用的地方,托管服务器才是它们生存的地方。所以一旦完成了你的应用,你会希望把它布置到能长期托管的云服务器上,最好是能免费托管的那种,例如[Heroku][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -44,7 +44,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
当我完成了Cloud9的注册后,它提示的第一件事情就是添加我的GitHub和BitBucket账号。马上,所有我的GitHub项目,个人的和协作的,都可以直接克隆到本地并使用Cloud9的开发工具开始工作。其他的IDE在和GitHub集成的方面都没有达到这种水准。
|
||||
|
||||
在我测试的这三款IDE中,Cloud9看起来更加侧重于一个可以让协同工作的人们无缝衔接工作的环境。在这里,它并不是角落里放个聊天窗口。实际上,按照CEO Ruben Daniels说的,试用Cloud9的协作者可以互相看到其他人实时的编码情况,就像Google Drive上的合作者那样。
|
||||
在我测试的这三款IDE中,Cloud9看起来更加侧重于一个可以让协同工作的人们无缝衔接工作的环境。在这里,它并不是角落里放个聊天窗口。实际上,按照其CEO Ruben Daniels说的,试用Cloud9的协作者可以互相看到其他人实时的编码情况,就像Google Drive上的合作者那样。
|
||||
|
||||
“大多数IDE服务的协同功能只能操作单一文件”,Daniels说,“而我们的产品可以支持整个项目中的不同文件。协同功能被完美集成到了我们的IDE中。”
|
||||
|
||||
@ -58,15 +58,15 @@ IDE可以提供你所需的工具来构建和测试所有开源编程语言的
|
||||
|
||||
### Nitrous.IO: An IDE Wherever You Want ###
|
||||
|
||||
相对于自己的桌面环境,使用IDE的最大优势是它是自包含的。你不需要安装任何其他的就可以使用。而另一方面,使用自己的桌面环境的最大优势就是你可以在本地工作,甚至在没有互联网的情况下。
|
||||
相对于自己的桌面环境,使用IDE的最大优势是它是自足的。你不需要安装任何其他的东西就可以使用。而另一方面,使用自己的桌面环境的最大优势就是你可以在本地工作,甚至在没有互联网的情况下。
|
||||
|
||||
Nitrous.IO结合了这两个优势。你可以在网站上在线使用这个IDE,你也可以把它下载到自己的饿电脑上,共同创始人AJ Solimine这样说。优点是你可以结合Nitrous的集成性和你最喜欢的文字编辑器的熟悉。
|
||||
Nitrous.IO结合了这两个优势。“你可以在网站上在线使用这个IDE,你也可以把它下载到自己的电脑上”,其共同创始人AJ Solimine这样说。优点是你可以结合Nitrous的集成性和你最喜欢的文字编辑器的熟悉。
|
||||
|
||||
他说:“你可以使用任意当代浏览器访问Nitrous.IO的在线IDE网站,但我们仍然提供了方便的Windows和Mac桌面应用,可以让你使用你最喜欢的编辑器来写代码。”
|
||||
他说:“你可以使用任意现代浏览器访问Nitrous.IO的在线IDE网站,但我们仍然提供了方便的Windows和Mac桌面应用,可以让你使用你最喜欢的编辑器来写代码。”
|
||||
|
||||
### 底线 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这一个星期的[使用][7]三个不同IDE的最让我意外的收获?它们是如此相似。[当用来做最基本的代码编辑的时候][8],它们都一样的好用。
|
||||
这一个星期[使用][7]三个不同IDE的最让我意外的收获是什么?它们是如此相似。[当用来做最基本的代码编辑的时候][8],它们都一样的好用。
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud9,Koding,[和Nitrous.IO都支持][9]所有主流的开源编程语言,从Ruby到Python到PHP到HTML5。你可以选择任何一种VM。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ Cloud9和Nitrous.IO都实现了GitHub的一键集成。Koding需要[多几个步
|
||||
|
||||
不好的一面,它们都有相同的缺陷,不过考虑到它们都是免费的也还合理。你每次只能同时运行一个VM来测试特定编程语言写出的程序。而当你一段时间没有使用VM之后,IDE会把VM切换成休眠模式以节省带宽,而下次要用的时候就得等它重新加载(Cloud9在这一点上更加费力)。它们中也没有任何一个为已完成的项目提供像样的永久托管服务。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,对咨询我是否有一个完美的免费IDE的人,答案是可能没有。但是这也要看你侧重的地方,对你的某个项目来说也许有一个完美的IDE。
|
||||
所以,对咨询我是否有一个完美的免费IDE的人来说,答案是可能没有。但是这也要看你侧重的地方,对你的某个项目来说也许有一个完美的IDE。
|
||||
|
||||
图片由[Shutterstock][11]友情提供
|
||||
|
||||
@ -86,7 +86,7 @@ via: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/14/cloud9-koding-nitrousio-integrated-developm
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Lauren Orsini][a]
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
|
||||
15个关于Linux的‘cd’命令的练习例子
|
||||
===========================
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux中,**‘cd‘(改变目录)**命令,是对新手和系统管理员来说,最重要最常用的命令。对管理无图形界面的服务器的管理员,‘**cd**‘是进入目录,检查日志,执行程序/应用软件/脚本和其余每个任务的唯一方法。对新手来说,是他们必须自己动手学习的最初始命令
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Linux中15个cd命令举例*
|
||||
|
||||
所以,请用心学习,我们在这会带给你**15**个基础的‘**cd**‘命令,它们富有技巧和捷径,学会使用这些了解到的技巧,会大大减少你在终端上花费的努力和时间
|
||||
|
||||
### 课程细节 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 命令名称:cd
|
||||
- 代表:切换目录
|
||||
- 使用平台:所有Linux发行版本
|
||||
- 执行方式:命令行
|
||||
- 权限:访问自己的目录或者其余指定目录
|
||||
- 级别:基础/初学者
|
||||
|
||||
1. 从当前目录切换到/usr/local
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd /usr/local
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$
|
||||
|
||||
2. 使用绝对路径,从当前目录切换到/usr/local/lib
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd /usr/local/lib
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib$
|
||||
|
||||
3. 使用相对路径,从当前路径切换到/usr/local/lib
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd lib
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib$
|
||||
|
||||
4. **(a)**切换当前目录到上级目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib$ cd -
|
||||
/usr/local
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$
|
||||
|
||||
**(b)**切换当前目录到上级目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib$ cd ..
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$
|
||||
|
||||
5. 显示我们最后一个离开的工作目录(使用‘-’选项)
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd --
|
||||
/home/avi
|
||||
|
||||
6. 从当前目录向上级返回两层
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd ../../
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/$
|
||||
|
||||
7. 从任何目录返回到用户home目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd ~
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$
|
||||
|
||||
或
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$
|
||||
|
||||
8. 切换工作目录到当前工作目录(LCTT:这有什么意义嘛?!)
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Downloads$ cd .
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Downloads$
|
||||
|
||||
或
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Downloads$ cd ./
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Downloads$
|
||||
|
||||
9. 你当前目录是“/usr/local/lib/python3.4/dist-packages”,现在要切换到“/home/avi/Desktop/”,要求:一行命令,通过向上一直切换直到‘/’,然后使用绝对路径
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib/python3.4/dist-packages$ cd ../../../../../home/avi/Desktop/
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Desktop$
|
||||
|
||||
10. 从当前工作目录切换到/var/www/html,要求:不要将命令打完整,使用TAB
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/var/www$ cd /v<TAB>/w<TAB>/h<TAB>
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/var/www/html$
|
||||
|
||||
11. 从当前目录切换到/etc/v__ _,啊呀,你竟然忘了目录的名字,但是你又不想用TAB
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd /etc/v*
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/etc/vbox$
|
||||
|
||||
**请注意:**如果只有一个目录以‘**v**‘开头,这将会移动到‘**vbox**‘。如果有很多目录以‘**v**‘开头,而且命令行中没有提供更多的标准,这将会移动到第一个以‘**v**‘开头的目录(按照他们在标准字典里字母存在的顺序)
|
||||
|
||||
12. 你想切换到用户‘**av**‘(不确定是avi还是avt)目录,不用**TAB**
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/etc$ cd /home/av?
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$
|
||||
|
||||
13. Linux下的pushed和poped
|
||||
|
||||
Pushed和poped是Linux bash命令,也是其他几个能够保存当前工作目录位置至内存,并且从内存读取目录作为当前目录的脚本,这些脚本也可以切换目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ pushd /var/www/html
|
||||
/var/www/html ~
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/var/www/html$
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令保存当前目录到内存,然后切换到要求的目录。一旦poped被执行,它会从内存取出保存的目录位置,作为当前目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/var/www/html$ popd
|
||||
~
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$
|
||||
|
||||
14. 切换到名字带有空格的目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd test\ tecmint/
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/test tecmint$
|
||||
|
||||
或
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd 'test tecmint'
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/test tecmint$
|
||||
|
||||
或
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd "test tecmint"/
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/test tecmint$
|
||||
|
||||
15. 从当前目录切换到下载目录,然后列出它所包含的内容(使用一行命令)
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr$ cd ~/Downloads && ls
|
||||
...
|
||||
.
|
||||
service_locator_in.xls
|
||||
sources.list
|
||||
teamviewer_linux_x64.deb
|
||||
tor-browser-linux64-3.6.3_en-US.tar.xz
|
||||
.
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
我们尝试使用最少的词句和一如既往的友好,来让你了解Linux的工作和执行
|
||||
|
||||
这就是所有内容。我很快会带着另一个有趣的主题回来的。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/cd-command-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[su-kaiyao](https://github.com/su-kaiyao)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQ -- 如何在CentOS或者RHEL上启用Nux Dextop仓库
|
||||
Linux有问必答:如何在CentOS或者RHEL上启用Nux Dextop仓库
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**: 我想要安装一个在Nux Dextop仓库的RPM包。我该如何在CentOS或者RHEL上设置Nux Dextop仓库?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ Linux FAQ -- 如何在CentOS或者RHEL上启用Nux Dextop仓库
|
||||
|
||||
要在CentOS或者RHEL上启用Nux Dextop,遵循下面的步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,要理解Nux Dextop被设计与EPEL仓库共存。因此,你需要使用Nux Dexyop仓库前先[启用 EPEL][2]。
|
||||
首先,要知道Nux Dextop被设计与EPEL仓库共存。因此,你需要在使用Nux Dexyop仓库前先[启用 EPEL][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
启用EPEL后,用下面的命令安装Nux Dextop仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,13 +26,13 @@ Linux FAQ -- 如何在CentOS或者RHEL上启用Nux Dextop仓库
|
||||
|
||||
### 对于 Repoforge/RPMforge 用户 ###
|
||||
|
||||
据作者所说,Nux Dextop目前所知会与其他第三方库比如Repoforge和ATrpms相冲突。因此,如果你启用了除了EPEL的其他第三方库,强烈建议你将Nux Dextop仓库设置成“default off”(默认关闭)状态。就是用文本编辑器打开/etc/yum.repos.d/nux-dextop.repo,并且在nux-desktop下面将"enabled=1" 改成 "enabled=0"。
|
||||
据作者所说,目前已知Nux Dextop会与其他第三方库比如Repoforge和ATrpms相冲突。因此,如果你启用了除了EPEL的其他第三方库,强烈建议你将Nux Dextop仓库设置成“default off”(默认关闭)状态。就是用文本编辑器打开/etc/yum.repos.d/nux-dextop.repo,并且在nux-desktop下面将"enabled=1" 改成 "enabled=0"。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/nux-dextop.repo
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/nux-dextop.repo
|
||||
|
||||
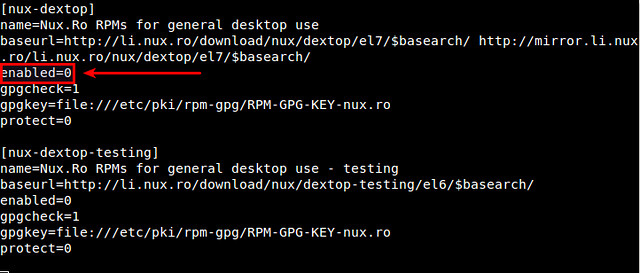
|
||||
|
||||
当你无论何时从Nux Dextop仓库安装包时,显式地用下面的命令启用仓库。
|
||||
无论何时当你从Nux Dextop仓库安装包时,显式地用下面的命令启用仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum --enablerepo=nux-dextop install <package-name>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ $ sudo vi /etc/yum.repos.d/nux-dextop.repo
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/enable-nux-dextop-repository-centos-rhel.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[ wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——如何修复“运行aclocal失败:没有该文件或目录”
|
||||
Linux有问必答:如何修复“运行aclocal失败:没有该文件或目录”
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:我试着在Linux上构建一个程序,该程序的开发版本是使用“autogen.sh”脚本进行的。当我运行它来创建配置脚本时,却发生了下面的错误:
|
||||
>
|
||||
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ Linux有问必答——如何修复“运行aclocal失败:没有该文件或
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/fix-failed-to-run-aclocal.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,7 @@
|
||||
Email生日快乐
|
||||
他发明了 Email ?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[编者按:本文所述的 Email 发明人的观点存在很大的争议,请读者留意,以我的观点来看,其更应该被称作为某个 Email 应用系统的发明人,其所发明的一些功能和特性,至今沿用。——wxy]
|
||||
|
||||
**一个印度裔美国人用他天才的头脑发明了电子邮件,而从此以后我们没有哪一天可以离开电子邮件。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
@ -18,6 +20,6 @@ via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=147170
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Sanchari Banerjee
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -6,13 +6,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote><em>通过入会声明,任何人都能轻易加入“匿名者”组织。某人类学家称,组织成员会“根据影响程度对重大事件保持着不同关注,特别是那些能挑起强烈争端的事件”。</em></blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<small>布景:Jeff Nishinaka / 摄影:Scott Dunbar</small>
|
||||
<small>纸雕作品:Jeff Nishinaka / 摄影:Scott Dunbar</small>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>1</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>上世纪七十年代中期,当 Christopher Doyon 还是一个生活在缅因州乡村的孩童时,就终日泡在 CB radio 上与各种陌生人聊天。他的昵称是“大红”,因为他有一头红色的头发。Christopher Doyon 把发射机挂在了卧室的墙壁上,并且说服了父亲在自家屋顶安装了两根天线。CB radio 主要用于卡车司机间的联络,但 Doyon 和一些人却将之用于不久后出现在 Internet 上的虚拟社交——自定义昵称、成员间才懂的笑话,以及施行变革的强烈愿望。</p>
|
||||
<p>上世纪七十年代中期,当 Christopher Doyon 还是一个生活在缅因州乡村的孩童时,就终日泡在 CB radio 上与各种陌生人聊天。他的昵称是“Big red”(大红),因为他有一头红色的头发。Christopher Doyon 把发射机挂在了卧室的墙壁上,并且说服了父亲在自家屋顶安装了两根天线。CB radio 主要用于卡车司机间的联络,但 Doyon 和一些人却将之用于不久后出现在 Internet 上的虚拟社交——自定义昵称、成员间才懂的笑话,以及施行变革的强烈愿望。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 很小的时候母亲就去世了,兄妹二人由父亲抚养长大,他俩都说受到过父亲的虐待。由此 Doyon 在 CB radio 社区中找到了慰藉和归属感。他和他的朋友们轮流监听当地紧急事件频道。其中一个朋友的父亲买了一个气泡灯并安装在了他的车顶上;每当这个孩子收听到来自孤立无援的乘车人的求助后,都会开车载着所有人到求助者所在的公路旁。除了拨打 911 外他们基本没有什么可做的,但这足以让他们感觉自己成为了英雄。</p>
|
||||
<p>Doyon 很小的时候母亲就去世了,兄妹二人由父亲抚养长大,他俩都说受到过父亲的虐待。由此 Doyon 在 CB radio 社区中找到了慰藉和目标感。他和他的朋友们轮流监听当地紧急事件频道。其中一个朋友的父亲买了一个气泡灯并安装在了他的车顶上;每当这个孩子收听到来自孤立无援的乘车人的求助后,都会开车载着所有人到求助者所在的公路旁。除了拨打 911 外他们基本没有什么可做的,但这足以让他们感觉自己成为了英雄。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>短小精悍的 Doyon 有着一口浓厚的新英格兰口音,并且非常喜欢《星际迷航》和阿西莫夫的小说。当他在《大众机械》上看到一则“组装你的专属个人计算机”构件广告时,就央求祖父给他买一套,接下来 Doyon 花了数月的时间把计算机组装起来并连接到 Internet 上去。与鲜为人知的 CB 电波相比,在线聊天室确实不可同日而语。“我只需要点一下按钮,再选中某个家伙的名字,然后我就可以和他聊天了,” Doyon 在最近回忆时说道,“这真的很惊人。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,11 +22,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 深深地沉溺于计算机中,虽然他并不是一位专业的程序员。在过去一年的几次谈话中,他告诉我他将自己视为激进主义分子,继承了 Abbie Hoffman 和 Eldridge Cleaver 的激进传统;技术不过是他抗议的工具。八十年代,哈佛大学和麻省理工学院的学生们举行集会,强烈抗议他们的学校从南非撤资。为了帮助抗议者通过安全渠道进行交流,PLF 制作了无线电套装:移动调频发射器、伸缩式天线,还有麦克风,所有部件都内置于背包内。Willard Johnson,麻省理工学院的一位激进分子和政治学家,表示黑客们出席集会并不意味着一次变革。“我们的大部分工作仍然是通过扩音器来完成的,”他解释道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>1992 年,在 Grateful Dead 的一场印第安纳的演唱会上,Doyon 秘密地向一位瘾君子出售了 300 粒药。由此他被判决在印第安纳州立监狱服役十二年,后来改为五年。服役期间,他对宗教和哲学产生了浓厚的兴趣,并于鲍尔州立大学学习了相应课程。</p>
|
||||
<p>1992 年,在印第安纳的一场 Grateful Dead 的演唱会上,Doyon 秘密地向一位瘾君子出售了 300 粒药。由此他被判决在印第安纳州立监狱服役十二年,后来改为五年。服役期间,他对宗教和哲学产生了浓厚的兴趣,并于鲍尔州立大学学习了相应课程。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>1994 年,第一款商业 Web 浏览器网景领航员正式发布,同一年 Doyon 被捕入狱。当他出狱并再次回到剑桥后,PLF 依然活跃着,并且他们的工具有了实质性的飞跃。Doyon 回忆起和他入狱之前的变化,“非常巨大——好比是‘烽火狼烟’跟‘电报传信’之间那么大的差距。”黑客们入侵了一个印度的军事网站,并修改其首页文字为“拯救克什米尔”。在塞尔维亚,黑客们攻陷了一个阿尔巴尼亚网站。Stefan Wray,一位早期网络激进主义分子,为一次纽约“反哥伦布日”集会上的黑客行径辩护。“我们视之为电子形式的公众抗议,”他告诉大家。</p>
|
||||
<p>1994 年,第一款商业 Web 浏览器 Netscape Navigator(网景领航员)正式发布,同一年 Doyon 被捕入狱。当他出狱并再次回到剑桥后,PLF 依然活跃着,并且他们的工具有了实质性的飞跃。Doyon 回忆起他和入狱之前对比的变化,“非常巨大——好比是‘烽火狼烟’跟‘电报传信’之间那么大的差距。”黑客们入侵了一个印度的军事网站,并修改其首页文字为“拯救克什米尔”。在塞尔维亚,黑客们攻陷了一个阿尔巴尼亚网站。Stefan Wray,一位早期网络激进主义分子,为一次纽约“反哥伦布日”集会上的黑客行径辩护。“我们视之为电子形式的公众抗议,”他告诉大家。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>1999 年,美国唱片业协会因为版权侵犯问题起诉了 Napster,一款文件共享软件。最终,Napster 于 2001 年关闭。Doyon 与其他黑客使用分布式拒绝服务(Distributed Denial of Service,DDoS,使大量数据涌入网站导致其响应速度减缓直至奔溃)的手段,攻击了美国唱片业协会的网站,使之停运时间长达一星期之久。Doyon为自己的行为进行了辩解,并高度赞扬了其他的“黑客主义者”。“我们很快意识到保卫 Napster 的战争象征着保卫 Internet 自由的战争,”他在后来写道。</p>
|
||||
<p>1999 年,美国唱片业协会因为版权侵犯问题起诉了 Napster,一款文件共享服务。最终,Napster 于 2001 年关闭。Doyon 与其他黑客使用分布式拒绝服务(Distributed Denial of Service,DDoS,使大量数据涌入网站导致其响应速度减缓直至奔溃)的手段,攻击了美国唱片业协会的网站,使之停运时间长达一星期之久。Doyon为自己的行为进行了辩解,并高度赞扬了其他的“黑客主义者”。“我们很快意识到保卫 Napster 的战争象征着保卫 Internet 自由的战争,”他在后来写道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2008 年的一天,Doyon 和 “Commander Adama” 在剑桥的 PLE 地下公寓相遇。Adama 当着 Doyon 的面点击了癫痫基金会的一个链接,与意料中将要打开的论坛不同,出现的是一连串闪烁的彩光。有些癫痫病患者对闪光灯非常敏感——这完全是出于恶意,有人想要在无辜群众中诱发癫痫病。已经出现了至少一名受害者。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,69 +42,69 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small>“我得谈谈我的感受。”</small></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Poole 希望匿名这一举措可以延续社区的尖锐性因素。“我们无意参与理智的涉外事件讨论,”他在网站上写道。4chan 社区里最具价值的事之一便是寻求“挑起强烈的争端”(lulz),这个词源自缩写 LOL。Lulz 经常是通过分享充满孩子气的笑话或图片来实现的,它们中的大部分不是色情的就是下流的。其中最令人震惊的部分被贴在了网站的“/b/”版块上,这里的用户们称呼自己为“/b/tards”。Doyon 知道 4chan 这个社区,但他认为那些用户是“一群愚昧无知的顽童”。2004 年前后,/b/ 上的部分用户开始把“匿名者”视为一个独立的实体。</p>
|
||||
<p>Poole 希望匿名这一举措可以延续社区的尖锐性因素。“我们无意参与理智的涉外事件讨论,”他在网站上写道。4chan 社区里最具价值的事之一便是寻求“挑起强烈的争端”(lulz),这个词源自缩写 LOL。Lulz 经常是通过分享幼稚的笑话或图片来实现的,其中大部分不是色情的就是下流的。其中最令人震惊的部分被贴在了网站的“/b/”版块上,这里的用户们称呼自己为“/b/tards”。Doyon 知道 4chan 这个社区,但他认为它的用户是“一群愚昧无知的顽童”。2004 年前后,/b/ 上的部分用户开始把“匿名者”视为一个独立的实体。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>这是一个全新的黑客团体。“这不是一个传统意义上的组织,”一位领导计算机安全工作的研究员 Mikko Hypponen 告诉我——倒不如,视之为一个非传统的亚文化群体。Barrett Brown,德克萨斯州的一名记者,同时也是众所周知的“匿名者”高层领导,把“匿名者”描述为“一连串前仆后继的伟大友谊”。无需任何会费或者入会仪式。任何想要加入“匿名者”组织,成为一名匿名者(Anon)的人,都可以通过简短的象征性的宣誓加入。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>尽管 4chan 的关注焦点是一些琐碎的话题,但许多匿名者认为自己就是“正义的十字军”。如果网上有不良迹象出现,他们就会发起具有针对性的治安维护行动。不止一次,他们以未成年少女的身份套取恋童癖的私人信息,然后把这些信息交给警察局。其他匿名者则是政治的厌恶者,为了挑起争端想方设法散布混乱的信息。他们中的一些人在 /b/ 上发布看着像是雷管炸弹的图片;另一些则叫嚣着要炸毁足球场并因此被联邦调查局逮捕。2007 年,一家洛杉矶当地的新闻联盟机构称呼“匿名者”组织为“互联网负能量制造机”。</p>
|
||||
<p>尽管 4chan 的关注焦点是一些琐碎的话题,但许多匿名者认为自己就是“正义的十字军”。如果网上有不良迹象出现,他们就会发起具有针对性的治安维护行动。不止一次,他们以未成年少女的身份使恋童癖陷入圈套,然后把他们的个人信息交给警察局。其他匿名者则是政治的厌恶者,为了挑起争端想方设法散布混乱的信息。他们中的一些人在 /b/ 上发布看着像是雷管炸弹的图片;另一些则叫嚣着要炸毁足球场并因此被联邦调查局逮捕。2007 年,一家洛杉矶当地的新闻联盟机构称呼“匿名者”组织为“互联网负能量制造机”。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2008 年 1 月,Gawker Media 上传了一段关于汤姆克鲁斯大力吹捧山达基优点的视频。这段视频是受版权保护的,山达基教会致信 Gawker,勒令其删除这段视频。“匿名者”组织认为教会企图控制网络信息。“是时候让 /b/ 来干票大的了,”有人在 4chan 上写道。“我说的是‘入侵’或者‘攻陷’山达基官方网站。”一位匿名者使用 YouTube 放出一段“新闻稿”,其中包括暴雨云视频和经过计算机处理的语音。“我们要立刻把你们从 Internet 上赶出去,并且在现有规模上逐渐瓦解山达基教会,”那个声音说,“你们无处可躲。”不到一个星期,这段 YouTube 视频的点击率就超过了两百万次。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“匿名者”组织已经不仅限于 4chan 社区。黑客们在专用的互联网中继聊天(Internet Relay Chat channels,IRC 聊天室)频道内进行交流,协商策略。通过 DDoS 攻击手段,他们使山达基的主网站间歇性崩溃了好几天。匿名者们制造了“谷歌炸弹”,由此导致 “dangerous cult” 的搜索结果中的第一条结果就是山达基主网站。其余的匿名者向山达基的欧洲总部寄送了数以百计的披萨,并用大量全黑的传真单耗干了洛杉矶教会总部的传真机墨盒。山达基教会,据报道拥有超过十亿美元资产的组织,当然能经得起墨盒耗尽的考验。但山达基教会的高层可不这么认为,他们还收到了严厉的恐吓,由此他们不得不向 FBI 申请逮捕“匿名者”组织的成员。</p>
|
||||
<p>“匿名者”组织已经不仅限于 4chan 社区。黑客们在专用的互联网中继聊天(Internet Relay Chat channels,IRC 聊天室)频道内进行交流,协商策略。通过 DDoS 攻击手段,他们使山达基的主网站间歇性崩溃了好几天。匿名者们制造了“谷歌炸弹”,由此导致 “dangerous cult” 的搜索结果中的第一条结果就是山达基主网站。其余的匿名者向山达基的欧洲总部寄送了数以百计的披萨,并用大量全黑的传真单耗干了洛杉矶教会总部的传真机墨盒。山达基教会,据报道是一个拥有超过十亿美元资产的组织,当然能经得起墨盒耗尽的考验。但山达基教会的高层可不这么认为,他们还收到了死亡恐吓,由此他们不得不向 FBI 申请调查“匿名者”组织的成员。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2008 年 3 月 15 日,在从伦敦到悉尼的一百多个城市里,数以千计匿名者们游行示威山达基教会。为了切合“匿名”这个主题,组织者下令所有的抗议者都应该佩戴相同的面具。深思熟虑过蝙蝠侠后,他们选定了 2005 年上映的反乌托邦电影《 V 字仇杀队》中 Guy Fawkes 的面具。“在每个大城市里都能以很便宜的价格大量购买,”广为人知的匿名者、游行组织者之一 Gregg Housh 告诉我说道。漫画式的面具上是一个的脸颊红润的男人,八字胡,有着灿烂的笑容。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>匿名者们并未“瓦解”山达基教会。并且汤姆克鲁斯的那段视频任然保留在网络上。匿名者们证明了自己的顽强。组织选择了一个相当浮夸的口号:“我们是一体。绝不宽恕。永不遗忘。相信我们。”(We are Legion. We do not forgive. We do not forget. Expect us.)</p>
|
||||
<p>匿名者们并未“瓦解”山达基教会。并且汤姆克鲁斯的那段视频任然保留在网络上。匿名者们证明了自己的顽强。组织选择了一个相当浮夸的口号:“我们是军团。绝不宽恕。永不遗忘。等待我们。”(We are Legion. We do not forgive. We do not forget. Expect us.)</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>3</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2010 年,Doyon 搬到了加利福尼亚州的圣克鲁斯,并加入了当地的“和平阵营”组织。利用从木材堆置场偷来的木头,他在山上盖起了一间简陋的小屋,“借用”附近住宅的 WiFi,使用太阳能电池板发电,并通过贩卖种植的大麻换取现金。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>与此同时,“和平阵营”维权者们每天晚上开始在公共场所休息,以此抗议圣克鲁斯政府此前颁布的“流浪者管理法案”,他们认为这项法案严重侵犯了流浪者的生存权。Doyon 出席了“和平阵营”的会议,并在网上发起了抗议活动。他留着蓬乱的红色山羊胡,戴一顶米黄色软呢帽,像军人那样不知疲倦。因此维权者们送给了他“罪恶制裁克里斯”的称呼。</p>
|
||||
<p>与此同时,“和平阵营”维权者们每天晚上开始在公共场所休息,以此抗议圣克鲁斯政府此前颁布的“流浪者管理法案”,他们认为这项法案严重侵犯了流浪者的生存权。Doyon 出席了“和平阵营”的会议,并在网上发起了抗议活动。他留着蓬乱的红色山羊胡,戴一顶米黄色软呢帽,类似军服的服装。因此维权者们送给了他“罪恶制裁克里斯”的称呼。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“和平阵营”的成员之一 Kelley Landaker 曾几次和 Doyong 讨论入侵事宜。Doyon 有时会吹嘘自己的技术是多么的厉害,但作为一名资深程序员的 Landaker 却不为所动。“他说得很棒,但却不是行动派的,”Landaker 告诉我。不过在那种场合下,的确更需要一位富有激情的领导者,而不是埋头苦干的技术员。“他非常热情并且坦率,”另一位成员 Robert Norse 如是对我说。“他创造出了大量的能够吸引媒体眼球的话题。我从事这行已经二十年了,在这一点上他比我见过的任何人都要厉害。”</p>
|
||||
<p>“和平阵营”的成员之一 Kelley Landaker 曾几次和 Doyong 讨论入侵事宜。Doyon 有时会吹嘘自己的技术是多么的厉害,但作为一名资深程序员的 Landaker 却不为所动。“他说得很棒,但却不是行动派,”Landaker 告诉我。不过在那种场合下,的确更需要一位富有激情的领导者,而不是埋头苦干的技术员。“他非常热情并且坦率,”另一位成员 Robert Norse 如是对我说。“他创造出了大量的能够吸引媒体眼球的话题。我从事这行已经二十年了,在这一点上他比我见过的任何人都要厉害。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 在 PLF 的上司,Commander Adama 仍然住在剑桥,并且通过电子邮件和 Doyon 保持着联络,他下令让 Doyon 潜入“匿名者”组织。以此获知其运作方式,并伺机为 PLF 招募新成员。因为癫痫基金会网站入侵事件的那段不愉快回忆,Doyon 拒绝了 Adama。Adama 给 Doyon 解释说,在“匿名者”组织里不怀好意的黑客只占极少数,与此相反,这个组织经常会有一些的轰动世界举动。Doyon 对这点表示怀疑。“4chan 怎么可能会轰动世界?”他质问道。但出于对 PLF 的忠诚,他还是答应了 Adama 的请求。</p>
|
||||
<p>Doyon 在 PLF 的上司,Commander Adama 仍然住在剑桥,并且通过电子邮件和 Doyon 保持着联络,他下令让 Doyon 监视“匿名者”组织,以此获知其运作方式,并伺机为 PLF 招募新成员。因为癫痫基金会网站入侵事件的那段不愉快回忆,Doyon 拒绝了 Adama。Adama 给 Doyon 解释说,在“匿名者”组织里不怀好意的黑客只占极少数,与此相反,这个组织经常会有一些的轰动世界举动。Doyon 对这点表示怀疑。“4chan 怎么可能会有轰动世界的大举动?”他质问道。但出于对 PLF 的忠诚,他还是答应了 Adama 的请求。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 经常带着一台宏基笔记本电脑出入于圣克鲁斯的一家名为 Coffee Roasting Company 的咖啡厅。“匿名者”组织的 IRC 聊天室主频道无需密码就能进入。Doyon 使用 PLF 的昵称进行登录并加入了聊天室。一段时间后,他发现了组织内大量的专用匿名者行动聊天频道,这些频道的规模更小,并相互重复。要想参与行动,你必须知道行动的专用聊天频道名称,并且聊天频道随时会因为陌生的闯入者而进行变更。这套交流系统并不具备较高的安全系数,但它的确很凑效。“这些专用行动聊天频道确保了行动机密的高度集中,”麦吉尔大学的人类学家 Gabriella Coleman 告诉我。</p>
|
||||
<p>Doyon 经常带着一台宏基笔记本电脑出入于圣克鲁斯的一家名为 Coffee Roasting Company 的咖啡厅。“匿名者”组织的 IRC 聊天室主频道无需密码就能进入。Doyon 使用 PLF 的昵称进行登录并加入了聊天室。一段时间后,他发现了组织内大量的专用匿名者行动聊天频道,这些频道的规模更小,更多专门的组内匿名者间对话相互重复。要想参与行动,你必须知道行动的专用聊天频道名称,并且聊天频道随时会因为陌生的闯入者而进行变更。这套交流系统并不具备较高的安全系数,但它的确很凑效。“这些专用行动聊天频道确保了行动机密的高度集中”麦吉尔大学的人类学家 Gabriella Coleman 告诉我。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>有些匿名者提议了一项行动,名为“反击行动”。如同新闻记者 Parmy Olson 于 2012 年在书中写道的,“我们是匿名者,”这项行动成为了又一次支援文件共享网站,如 Napster 的后继者海盗湾(Pirate Bay),的行动的前奏,但随后其目标却扩展到了政治领域。2010 年末,在美国国务院的要求下,包括万事达、Visa、PayPal 在内的几家公司终止了对维基解密,一家公布了成百上千份外交文件的民间组织,的捐助。在一段网络视频中,“匿名者”组织扬言要进行报复,发誓会对那些阻碍维基解密发展的公司进行惩罚。Doyon 被这种抗议企业的精神所吸引,决定参加这次行动。</p>
|
||||
<p>有些匿名者提议了一项行动,名为“反击行动”。如同新闻记者 Parmy Olson 于 2012 年在书中写道的,“我们是匿名者,” 这项行动是以又一次支持文件共享的网站而创立,如同 Napster 的后继者海盗湾(Pirate Bay),但随后其目标却扩展到了政治领域。2010 年末,在美国国务院的要求下,包括万事达、Visa、PayPal 在内的几家公司终止了对维基解密的捐助,维基解密是一家公布了成百上千份外交文件的自发性组织。在一段在线视频中,“匿名者”组织扬言要进行报复,发誓会对那些阻碍维基解密发展的公司进行惩罚。Doyon 被这种抗议企业的精神所吸引,决定参加这次行动。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="http://www.newyorker.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/140908_a18473-600.jpg" /></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small>潘多拉的魔盒</small></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在十二月初的“反击行动”中,“匿名者”组织指导那些新成员,或者说新兵,关于“如何他【哔~】加入组织”,教程中提到“首先配置你【哔~】的网络,这他【哔~】的很重要。”同时他们被要求下载“低轨道离子炮”,一款易于使用的开源软件。Doyon 下载了软件并在聊天室内等待着下一步指示。当开始的指令发出后,数千名匿名者将同时发动进攻。Doyon 收到了含有目标网址的指令——目标是,www.visa.com——同时,在软件的右上角有个按钮,上面写着“IMMA CHARGIN MAH LAZER.”(“反击行动”同时也发动了大量的复杂精密的入侵进攻。)几天后,“反击行动”攻陷了万事达、Visa、PayPal 公司的主页。在法院的控告单上,PayPal 称这次攻击给公司造成了 550 万美元的损失。</p>
|
||||
<p>在十二月初的“反击行动”中,“匿名者”组织指导那些新成员,或者说新兵,去看标题为“如何加入那个【哔~】的Hive”,参与者被要求“首先配置他们【哔~】的网络,这【哔~】的很重要。”同时他们被要求下载“低轨道离子炮”,一款易于使用的开源软件。Doyon 下载了软件并在聊天室内等待着下一步指示。当开始的指令发出后,数千名匿名者将同时发动进攻。Doyon 进入了目标网址——www.visa.com——同时,在软件的右上角有个按钮,上面写着“IMMA CHARGIN MAH LAZER.”(“反击行动”同时也发动了大量的复杂精密的入侵进攻。)几天后,“反击行动”攻陷了万事达、Visa、PayPal 公司的主页。在法院的控告单上,PayPal 称这次攻击给公司造成了 550 万美元的损失。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>但对 Doyon 来说,这是切实的激进主义体现。在剑桥反对种族隔离的行动中,他不能立即看到结果;而现在,只需指尖轻轻一点,就可以在攻陷大公司网站的行动中做出自己的贡献。隔天,赫芬顿邮报上出现了“万事达沦陷”的醒目标题。一位得意洋洋的匿名者发推特道:“有些事情维基解密是无能为力的。但这些事情却可以由‘反击行动’来完成。”</p>
|
||||
<p>但对 Doyon 来说,这是切实的激进主义体现。在剑桥反对种族隔离的行动中,他不能即可见效;而现在,只需指尖轻轻一点,就可以在攻陷大公司网站的行动中做出自己的贡献。隔天,赫芬顿邮报上出现了“万事达沦陷”的醒目标题。一位得意洋洋的匿名者发推特道:“有些事情维基解密是无能为力的。但这些事情却可以由‘反击行动’来完成。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>4</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2010 年的秋天,“和平阵营”的抗议活动终止,政府只做出了轻微的让步,“流浪者管理法案”仍然有效。Doyon 希望通过借助“匿名者”组织的方略扭转局势。他回忆当时自己的想法,“也许我可以发动‘匿名者’组织来教训这种看似不堪一击的市政府网站,这些人绝对会【哔~】地赞同我的提议。最终我们将使得市政府永久性的废除‘流浪者管理法案’。”</p>
|
||||
<p>2010 年的秋天,“和平阵营”的抗议活动终止,政府只做出了略微让步,“流浪者管理法案”仍然有效。Doyon 希望通过借助“匿名者”组织的方略扭转局势。他回忆当时自己的想法,“也许我可以发动‘匿名者’组织来教训这种看似不堪一击的市政府网站,它们绝对会【哔~】地沦陷。最终我们使得市政府永久性废除‘流浪者管理法案’。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Joshua Covelli 是一位 25 岁的匿名者,他的昵称是“Absolem”,他非常钦佩 Doyon 的果敢。“现在我们的组织完全是他【哔~】各种混乱的一盘散沙,”Covelli 告诉我道。在“Commander X”加入之后,“组织似乎开始变得有模有样了。”Covelli 的工作是俄亥俄州费尔伯恩的一所大学接待员,他从不了解任何有关圣克鲁斯的政治。但是当 Doyon 提及帮助“和平阵营”抗击活动的计划后,Covelli 立即回复了一封表示赞同的电子邮件:“我期待这样的行动很久了。”</p>
|
||||
<p>Joshua Covelli 是一位 25 岁的匿名者,他的昵称是“Absolem”,他非常钦佩 Doyon 的果敢。“过去我们的组织完全是各种混乱的一盘散沙,”Covelli 告诉我。在“Commander X”加入之后,“组织似乎开始变得有模有样了。”Covelli 的工作是俄亥俄州费尔伯恩的一所大学接待员,他从不了解任何有关圣克鲁斯的政治。但是当 Doyon 提及帮助“和平阵营”抗击活动的计划后,Covelli 立即回复了一封表示赞同的电子邮件:“我期待参加这样的行动已经很久了。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 使用 PLF 的昵称邀请 Covelli 在 IRC 聊天室进行了一次秘密谈话:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Absolem:抱歉,有个比较冒犯的问题...请问 PLF 也是组织的一员吗?</blockquote>
|
||||
<blockquote>Absolem:抱歉,有个比较冒犯的问题...请问 PLF 是组织的一部分还是分开的?</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Absolem:我会这么问,是因为我在频道里看过你的聊天记录,你像是一名训练有素的黑客,不太像是来自组织里的成员。</blockquote>
|
||||
<blockquote>Absolem:我会这么问,是因为看你们聊天,觉得你们都是非常有组织的。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>PLF:不不不,你的问题一点也不冒犯。很高兴遇到你。PLF 是一个来自波士顿的黑客组织,已经成立 22 年了。我在 1981 年就开始了我的黑客生涯,但那时我并没有使用计算机,而是使用的 PBX(Private Branch Exchange,电话交换机)。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>PLF:我们组织内所有成员的年龄都超过了 40 岁。我们当中有退伍士兵和学者。并且我们的成员“Commander Adama”,正在躲避一大帮警察还有间谍的追捕。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Absolem:听起来很棒!我对这次行动很感兴趣,不知道我是否可以提供一些帮助,我们的组织实在是太混乱了。我的电脑技术还不错,但我在入侵技术上还完全是一个新手。我有一些小工具,但不知道怎么去使用它们。</blockquote>
|
||||
<blockquote>Absolem:听起来很棒!我对这次行动很感兴趣,不过“匿名者”组织看起来太混乱无序,不知道我是否可以提供一些帮助。我的电脑技术还不错,但我在入侵技术上还完全是一个新手。我有一些小工具,但不知道怎么去使用它们。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>庄重的入会仪式后,Doyon 正式接纳 Covelli 加入 PLF:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>PLF:把所有可能对你不利的【哔~】敏感文件加密。</blockquote>
|
||||
<blockquote>PLF:把所有可能使你受牵连的敏感文件加密。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>PLF:还有,想要联系任何一位 PLF 成员的话,给我发消息就行。从现在起,请叫我... Commander X。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2012 年,美联社称“匿名者”组织为“一伙训练有素的黑客”;Quinn Norton 在《连线》杂志上发文称“‘匿名者’组织可以入侵任何坚不可摧的网站”,并在文末赞扬他们为“一群卓越的民间黑客”。事实上,有些匿名者的确是很有天赋的程序员,但绝大部分成员根本不懂任何技术。人类学家 Coleman 告诉我只有大约五分之一的匿名者是真正的黑客——其他匿名者则是“极客与抗议者”。</p>
|
||||
<p>2012 年,美联社称“匿名者”组织为“一帮专家级的黑客”;Quinn Norton 在《连线》杂志上发文称“‘匿名者’组织可以入侵任何坚不可摧的网站”,并在文末赞扬他们为“一群卓越的民间黑客”。事实上,有些匿名者的确是很有天赋的程序员,但绝大部分成员根本不懂任何技术。人类学家 Coleman 告诉我只有大约五分之一的匿名者是真正的黑客——其他匿名者则是“极客与抗议者”。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2010 年 12 月 16 日,Doyon 以 Commander X 的身份向几名记者发送了电子邮件。“明天当地时间 12:00 的时候,‘人民解放阵线’组织与‘匿名者’组织将大举进攻圣克鲁斯政府网站”,他在邮件中写道,“12:30 之后我们将恢复网站的正常运行。”</p>
|
||||
<p>2010 年 12 月 16 日,Doyon 以 Commander X 的身份向几名记者发送了电子邮件。“明天当地时间 12:00 的时候,‘人民解放阵线’组织与‘匿名者’组织将从互联网中删除圣克鲁斯政府网站”,他在邮件中写道,“12:30 之后我们将恢复网站的正常运行。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>圣克鲁斯数据中心的工作人员收到了警告,匆忙地准备应对攻击。他们在服务器上运行起安全扫描软件,并向当地的互联网供应商 AT & T 求助,后者建议他们向 FBI 报警。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -132,7 +132,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small>“Zach 很聪明... 并且... 是一个天才... 但.. 你们... 不在一个班。”</small></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 引用了一句电影台词。“拼命地跑,”他说。“我会躲起来,尽可能保持我的行动自由,用尽全力和这帮杂种们作斗争。”Frey 给了他两张 20 美元的钞票并祝他好运。</p>
|
||||
<p>Doyon 引用了一句电影台词。“拼命地跑,”他说。“我会躲起来,尽可能保持我的行动自由,用尽全力和这帮混蛋们作斗争。”Frey 给了他两张 20 美元的钞票并祝他好运。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>5</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -142,35 +142,35 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“突尼斯,” Brown 答道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“我知道,那是中东地区的一个国家,” Doyon 继续问,“然后呢?”</p>
|
||||
<p>“我知道,那是中东地区的一个国家,” Doyon 继续问,“具体任务是什么呢?”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“我们准备打倒那里的独裁者,” Brown 再次答道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“啊?!那里有一位独裁者吗?” Doyon 有点惊讶。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>几天后,“突尼斯行动”正式展开。Doyon 作为参与者向突尼斯政府域名下的电子邮箱发送了大量的垃圾邮件,以此阻塞其服务器。“我会提前写好关于那次行动邮件,接着一次又一次地把它们发送出去,” Doyon 说,“有时候实在没有时间,我就只简短的写上一句问候对方母亲的的话,然后发送出去。”短短一天时间里,匿名者们就攻陷了包括突尼斯证券交易所、工业部、总统办公室、总理办公室在内的多个网站。他们把总统办公室网站的首页替换成了一艘海盗船的图片,并配以文字“‘报复’是个贱人,不是吗?”</p>
|
||||
<p>几天后,“突尼斯行动”正式展开。Doyon 作为参与者向突尼斯政府域名下的电子邮箱发送了大量的垃圾邮件,以此阻塞其服务器。“我会提前写好关于那次行动邮件,接着一次又一次地把它们发送出去,” Doyon 说,“有时候实在没有时间,我就只简短的写上一句‘问候对方母亲’的话,然后发送出去。”短短一天时间里,匿名者们就攻陷了包括突尼斯证券交易所、工业部、总统办公室、总统办公室在内的多个网站。他们把总统办公室网站的首页替换成了一艘海盗船的图片,并配以文字“恶有恶报,不是吗?”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 不时会谈起他的网上“战斗”经历,似乎他刚从弹坑里爬出来一样。“伙计,自从干了这行我就变黑了,”他向我诉苦道。“你看我的脸,全是抽烟的时候熏的——而且可能已经粘在我的脸上了。我仔细地照过镜子,毫不夸张地说我简直就是一头棕熊。”很多个夜晚,Doyon 都是在 Golden Gate 公园里露营过夜的。“我就那样干了四天,我看了看镜子里的‘我’,感觉还可以——但其实我觉得‘我’也许应该去吃点东西、洗个澡了。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“匿名者”组织接着又在 YouTube 上声明了将要进行的一系列行动:“利比亚行动”、“巴林行动”、“摩洛哥行动”。作为解放广场事件的抗议者,Doyon 参与了“埃及行动”。在 Facebook 针对这次行动的宣传专页中,有一个为当地示威者准备的“行动套装”链接。“行动套装”通过文件共享网站 Megaupload 进行分发,其中含有一份加密软件以及应对瓦斯袭击的保护措施。并且在不久后,埃及政府关闭了埃及的所有互联网及子网络的时候,继续向当地抗议者们提供连接网络的方法。</p>
|
||||
<p>“匿名者”组织接着又在 YouTube 上声明了将要进行的一系列行动:“利比亚行动”、“巴林行动”、“摩洛哥行动”。作为解放广场事件的抗议者,Doyon 参与了“埃及行动”。在 Facebook 针对这次行动的宣传专页中,有一个为当地示威者准备的“行动套装”链接。“行动套装”通过文件共享网站 Megaupload 进行分发,其中含有一份加密软件以及应对瓦斯袭击的保护措施。在埃及政府关闭了埃及的所有互联网及子网络的时候不久后,“匿名者”组织继续向当地抗议者们提供连接网络的方法。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2011 年夏季,Doyon 接替 Adama 成为 PLF 的最高指挥官。Doyon 招募了六个新成员,并力图发展 PLF 成为“匿名者”组织的中坚力量。Covelli 成为了他的其中一技位术顾问。另一名黑客 Crypt0nymous 负责在 YouTube 上发布视频;其余的人负责研究以及组装电子设备。与松散的“匿名者”组织不同,PLF 内部有一套极其严格的管理体系。“Commander X 事必躬亲,”Covelli 说。“这是他的行事风格,也许不能称之为一种风格。”一位创立了 AnonInsiders 博客的黑客通过加密聊天告诉我,他认为 Doyon 总是一意孤行——这在“匿名者”组织中是很罕见的现象。“当我们策划发起一项行动时,他并不在乎其他人是否同意,”这位黑客补充道,“他会一个人列出行动方案,确定攻击目标,登录 IRC 聊天室,接着告诉所有人在哪里‘碰头’,然后发起 DDoS 攻击。”</p>
|
||||
<p>2011 年夏季,Doyon 接替 Adama 成为 PLF 的最高指挥官。Doyon 招募了六个新成员,并力图发展 PLF 成为“匿名者”组织的中坚力量。Covelli 成为了他的其中一位技术顾问。另一名黑客 Crypt0nymous 负责在 YouTube 上发布视频;其余的人负责研究以及组装电子设备。与松散的“匿名者”组织不同,PLF 内部有一套极其严格的管理体系。“Commander X 事必躬亲,”Covelli 说。“这是他的行事风格,要么不做,要么做好。”一位创立了 AnonInsiders 博客的黑客通过加密聊天告诉我,他认为 Doyon 总是一意孤行——这在“匿名者”组织中是很罕见的现象。“当我们策划发起一项行动时,他并不在乎其他人是否同意,”这位黑客补充道,“他会一个人列出行动方案,确定攻击目标,登录 IRC 聊天室,接着告诉所有人在哪里‘碰头’,然后发起 DDoS 攻击。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>一些匿名者把 PLF 视为可有可无的部分,认为 Doyon 的所作所为完全是个天大的笑柄。“他是因为吹牛出名的,”另一名昵称为 Tflow 的匿名者 Mustafa Al-Bassam 告诉我。不过,即使是那些极度反感 Doyon 的狂妄自大的人,也不得不承认他在“匿名者”组织发展过程中的重要性。“他所倡导的强硬路线有时很凑效,有时则完全不起作用,” Gregg Housh 说,并且补充道自己和其他优秀的匿名者都曾遇到过相同的问题。</p>
|
||||
<p>一些匿名者把 PLF 视为“面子项目”,认为 Doyon 的所作所为完全是个笑柄。“他是因为吹牛出名的,”另一名昵称为 Tflow 的匿名者 Mustafa Al-Bassam 告诉我。不过,即使是那些极度反感 Doyon 的狂妄自大的人,也不得不承认他在“匿名者”组织发展过程中的重要性。“他所倡导的强硬路线有时很凑效,有时则是碍事,” Gregg Housh 说,并且补充道自己和其他优秀的匿名者都曾遇到过相同的问题。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“匿名者”组织对外坚持声称自己是不分层次的平等组织。在由 Brian Knappenberger 制作的一部纪录片,《我们是一个团体》中,一名成员使用“一群鸟”来比喻组织,它们轮流领飞带动整个组织不断前行。Gabriella Coleman 告诉我,这个比喻不太切合实际,“匿名者”组织内实际上早就出现了一个非正式的领导阶层。“领导者非常重要,”她说。“有四五个人可以看做是我们的领头羊。”她把 Doyon 也算在了其中。但是匿名者们仍然倾向于反抗这种具有体系的组织结构。在一本即将出版的关于“匿名者”组织的书,《黑客、骗子、告密者、间谍》中,Coleman 这么写道,在匿名者中,“成员个体以及那些特立独行的人依然在一些重大事件上保持着服从的态度,优先考虑集体——特别是那些能引发强烈争端的事件。”</p>
|
||||
<p>“匿名者”组织对外坚持声称自己是不分层次的平等组织。在由 Brian Knappenberger 制作的一部纪录片,《我们是军团》中,一名成员使用“一群鸟”来比喻组织,它们轮流领飞带动整个组织不断前行。Gabriella Coleman 告诉我,这个比喻不太切合实际,“匿名者”组织内实际上早就出现了一个非正式的领导阶层。“领导者非常重要,”她说。“有四五个人可以看做是我们的领头羊。”她把 Doyon 也算在了其中。但是匿名者们仍然倾向于反抗这种体制结构。在一本即将出版的关于“匿名者”组织的书,《黑客、骗子、告密者、间谍》中,Coleman 这么写道,在匿名者中,“成员个体以及那些特立独行的人依然在一些重大事件上保持着服从的态度,优先考虑集体——特别是那些能引发强烈争端的事件。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>匿名者们谑称那些特立独行的成员为“自尊心超强的疯子”和“想让自己出名的疯子”。(不过许多匿名者已经不会再随便给他人取那种具有冒犯性的称号了。)“但还是有令人惊讶的极少数成员违反规则”打破传统上的看法,Coleman 说。“这么做的人,像 Commander X 这样的,都会在组织里受到排斥。”去年,在一家网络论坛上,有人写道,“当他开始把自己比作‘蝙蝠侠’的时候我就不想理他了。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Peter Fein,是一位以 n0pants 为昵称而出名的网络激进分子,也是众多反对 Doyon 的浮夸行为的众多匿名者之一。Fein 浏览了 PLF 的网站,其封面上有一个徽章,还有关于组织的宣言——“为了解放众多人类的灵魂而不断战斗”。Fein 沮丧的发现 Doyon 早就使用真名为这家网站注册过了,使他这种,以及其他想要找事的匿名者们无机可乘。“如果有人要对我的网站进行 DDoS 攻击,那完全可以,” Fein 回想起通过私密聊天告诉 Doyon 时的情景,“但如果你要这么做了的话,我会揍扁你的屁股。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2011 年 2 月 5 日,《金融时报》报道了在一家名为 HBGary Federal 的网络安全公司里,首席执行官 HBGary Federal 已经得到了“匿名者”组织骨干成员名单的消息。Barr 的调查结果表明,三位最高领导人其中之一就是‘ Commander X’,这位潜伏在加利福尼亚州的黑客有能力“策划一些大型网络攻击事件”。Barr 联系了 FBI 并提交了自己的调查结果。</p>
|
||||
<p>2011 年 2 月 5 日,《金融时报》报道了在一家名为 HBGary Federal 的网络安全公司,首席执行官 HBGary Federal 已经得到了“匿名者”组织骨干成员名单的消息。Barr 的调查结果表明,三位最高领导人其中之一就是‘ Commander X’,是一位潜伏在加利福尼亚州的黑客而且有能力“策划一些大型网络攻击事件”。Barr 联系了 FBI 并提交了自己的调查结果。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>和 Fein 一样,Barr 也发现了 PLF 网站的注册法人名为 Christopher Doyon,地址是 Haight 大街。基于 Facebook 和 IRC 聊天室的调查,Barr 断定‘ Commander X’的真实身份是一名家庭住址在 Haight 大街附近的网络激进分子 Benjamin Spock de Vries。Barr 通过 Facebook 和 de Vries 取得了联系。“请告诉组织里的普通阶层,我并不是来抓你们的,” Barr 留言道,“只是想让‘领导阶层’知晓我的意图。”</p>
|
||||
<p>和 Fein 一样,Barr 也发现了 PLF 网站的注册法人名为 Christopher Doyon,地址是 Haight 大街。基于 Facebook 和 IRC 聊天室的调查,Barr 断定‘ Commander X’的真实身份是一名家庭住址在 Haight 大街附近的网络激进分子 Benjamin Spock de Vries。Barr 通过 Facebook 和 de Vries 取得了联系。“请告诉我组织里的其他人,我并不是来抓你们的,” Barr 留言道,“只是想让‘领导阶层’知晓我的意图。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“‘领导阶层’? 2333,笑死我了,” de Vries 回复道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>《金融时报》发布报道的第二天,“匿名者”组织就进行了反击。HBGary Federal 的网站被进行了恶意篡改。Barr 的私人 Twitter 账户被盗取,他的上千封电子邮件被泄漏到了网上,同时匿名者们还公布了他的住址以及其他私人信息——这是一系列被称作“doxing”的惩罚。不到一个月后,Barr 就从 HBGary Federal 辞职了。</p>
|
||||
<p>《金融时报》发布报道的第二天,“匿名者”组织就进行了反击。HBGary Federal 的网站被进行了恶意篡改。Barr 的私人 Twitter 账户被盗取,他的上千封电子邮件被泄漏到了网上,同时匿名者们还公布了他的住址以及其他私人信息——这就是“冲动的惩罚”。不到一个月后,Barr 就从 HBGary Federal 辞职了。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>6</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -180,17 +180,17 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small>“这是我在 TED 夏令营里学到的东西。”</small></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>他时刻关注着“匿名者”组织的内部消息。那年春季,在 Barr 调查报告中提到的六位匿名者精锐成员,组建了“LulzSec 安全”组织(Lulz Security),简称 LulzSec。这个组织正如其名,这些成员认为“匿名者”组织已经变得太过严肃;他们的目标是重新引发起那些“能挑起强烈争端”的事件。当“匿名者”组织还在继续支持“阿拉伯之春”的抗议者的时候,LulzSec 入侵了公共电视网(Public Broadcasting Service,PBS)网站,并发布了一则虚假声明称已故说唱歌手 Tupac Shakur 仍然生活在新西兰。</p>
|
||||
<p>他时刻关注着“匿名者”组织的内部消息。那年春季,在 Barr 调查报告中提到的六位匿名者精锐成员,组建了“LulzSec 安全”组织(Lulz Security),简称 LulzSec。这个组织正如其名,这些成员认为“匿名者”组织已经变得太过严肃;他们的目标是重新引发起那些“能挑起强烈争端”的事件。当“匿名者”组织还在继续支持“阿拉伯之春”的抗议者时,LulzSec 入侵了公共电视网(Public Broadcasting Service,PBS)网站,并发布了一则虚假声明称已故说唱歌手 Tupac Shakur 仍然生活在新西兰。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>匿名者之间会通过 Pastebin.com 网站来共享文字。在这个网站上,LulzSec 发表了一则声明,称“很不幸,我们注意到北约和我们的好总统巴拉克,奥萨马·本·美洲驼(拉登同学)的好朋友,来自 24 世纪的奥巴马,最近明显提高了对我们这些黑客的关注程度。他们把黑客入侵行为视作一种战争的表现。”目标越高远,挑起的纷争就越大。6 月 15 日,LulzSec 表示对 CIA 网站受到的袭击行为负责,他们发表了一条推特,上面写道“目标击毙(Tango down,亦即target down)—— cia.gov ——这是起挑衅行为。”</p>
|
||||
<p>匿名者之间会通过 Pastebin.com 网站来共享文本。在这个网站上,LulzSec 发表了一则声明,称“很不幸,我们注意到北约和我们的好朋友巴拉克奥萨马——来自24世纪的奥巴马 已经提升了关于黑客的筹码,他们把黑客入侵行为视作一种战争的表现。”目标越高远,挑起的纷争就越大。6 月 15 日,LulzSec 表示对 CIA 网站受到的袭击行为负责,他们发表了一条推特,上面写道“目标击毙(Tango down,亦即target down)—— cia.gov ——这是起挑衅行为。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2011 年 6 月 20 日,LulzSec 的一名十九岁的成员 Ryan Cleary 因为对 CIA 的网站进行了 DDoS 攻击而被捕。7 月,FBI 探员逮捕了七个月前对 PayPal 进行 DDoS 攻击的其他十四名黑客。这十四名黑客,每人都面临着 15 年的牢狱之灾以及 500 万美元的罚款。他们因为图谋不轨以及故意破坏互联网,而被控违反了计算机欺诈与滥用处理条例。(该法案允许检察官进行酌情处置,并在去年网络激进分子 Aaron Swartz 因为被判处 35 年牢狱之灾而自杀身亡之后,受到了广泛的质疑和批评。)</p>
|
||||
<p>2011 年 6 月 20 日,LulzSec 的一名十九岁的成员 Ryan Cleary 因为对 CIA 的网站进行了 DDoS 攻击而被捕。7 月,FBI 探员逮捕了七个月前对 PayPal 进行 DDoS 攻击的其他十四名黑客。这十四名黑客,每人都面临着 15 年的牢狱之灾以及 50 万美元的罚款。他们因为图谋不轨以及故意破坏互联网而被控违反了计算机欺诈与滥用法案。(Computer Fraud and Abuse Act,该法案允许检察官拥有宽泛的起诉裁量权,并在去年网络激进分子 Aaron Swartz 因为被判处 35 年牢狱之灾而自杀身亡之后,受到了广泛的质疑和批评。)</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>LulzSec 的成员之一 Jake (Topiary) Davis 因为付不起法律诉讼费,给组织的成员们写了一封请求帮助的信件。Doyon 进入了 IRC 聊天室把 Davis 需要帮助的消息进行了扩散:</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX:那么请大家阅读信件并给予 Topiary 帮助...</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Toad:你真是和【哔~】一样消息灵通。</blockquote>
|
||||
<blockquote>Toad:你真是为了抓人眼球什么都做啊!</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Toad:这么说你得到 Topiary 的消息了?</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -198,15 +198,15 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>Katanon:唉...</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 越来越大胆。他在佛罗里达州当局逮捕了支持流浪者的激进分子后,就 DDoS 了奥兰多商务部商会网站。他使用个人笔记本电脑通过公用无线网络实施了攻击,并且没有花费太多精力来隐藏自己的网络行踪。“这种做法很勇敢,但也很愚蠢,”一位自称 Kalli 的 PLF 的资深成员告诉我。“他看起来并不在乎是否会被抓。他完全是一名自杀式黑客。”</p>
|
||||
<p>Doyon 越来越大胆。在佛罗里达州当局逮捕了支持流浪者的激进分子后,他就攻击 了奥兰多商务部商会网站。他使用个人笔记本电脑通过公用无线网络实施了攻击,并且没有花费太多精力来隐藏自己的网络行踪。“这种做法很勇敢,但也很愚蠢,”一位自称 Kalli 的 PLF 的资深成员告诉我。“他看起来并不在乎是否会被抓。他完全是一名自杀式黑客。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>两个月后,Doyon 参与了针对旧金山湾区快速交通系统(Bay Area Rapid Transit)的 DDoS 攻击,以此抗议一名 BART 的警官杀害一名叫做 Charles Hill 的流浪者的事件。随后 Doyon 现身“CBS 晚间新闻”为这次行动辩护,当然,他处理了自己的声音,把自己的脸用香蕉进行替代。他把 DDoS 攻击比作为公民的抗议行为。“与占用 Woolworth 午餐柜台的座位相比,这真的没什么不同,真的,”他说道。CBS 的主播 Bob Schieffer 笑称:“就我所见,它并不完全是一项民权运动。”</p>
|
||||
<p>两个月后,Doyon 参与了针对旧金山湾区快速交通系统(Bay Area Rapid Transit)的 DDoS 攻击,以此抗议一名 BART 的警官杀害一名叫做 Charles Hill 的流浪者的事件。随后 Doyon 现身“CBS 晚间新闻”为这次行动辩护,当然,他处理了自己的声音,用印花大手帕盖住了脸。他把 DDoS 攻击比作为公民的抗议行为。“与占用 Woolworth 午餐柜台的座位相比,这真的没什么不同,真的,”他说道。CBS 的主播 Bob Schieffer 笑称:“就我所见,它并不完全是一项民权运动。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2011 年 9 月 22 日,在加利福尼亚州的一家名为 Mountain View 的咖啡店里,Doyon 被捕,同时面临着“使用互联网非法破坏受保护的计算机”罪名指控。他被拘留了一个星期的时间,接着在签署协议之后获得假释。两天后,他不顾律师的反对,宣布将在圣克鲁斯郡法院召开新闻发布会。他梳起了马尾辫,戴着一副墨镜、一顶黑色海盗帽,同时还在脖子上围了一条五彩手帕。</p>
|
||||
<p>2011 年 9 月 22 日,在加利福尼亚州的一家名为 Mountain View 的咖啡店里,Doyon 被捕,同时面临着“使用互联网非法破坏受保护的计算机”的罪名指控。他被拘留了一个星期的时间,接着在签署协议之后获得假释。两天后,他不顾律师的反对,宣布将在圣克鲁斯郡法院召开会议。他梳起了马尾辫,戴着一副墨镜、一顶黑色海盗帽,同时还在脖子上围了一条五彩手帕。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 通过非常夸大的方式披露了自己的身份。“我就是 Commander X,”他告诉蜂拥的记者。他举起了拳头。“作为‘匿名者’组织的一员,作为一名核心成员,我感到非常的骄傲。”他在接受一名记者的采访时说,“想要成为一名顶尖黑客的话,你只需要准备一台电脑以及一副墨镜。任何一台电脑都行。”</p>
|
||||
<p>Doyon 通过非常夸大的方式揭露了自己的身份。“我就是 Commander X,”他告诉蜂拥的记者。他举起了拳头。“作为‘匿名者’组织的一员,作为一名核心成员,我感到非常的骄傲。”他在接受一名记者的采访时说,“想要成为一名顶尖黑客的话,你只需要准备一台电脑以及一副墨镜。任何一台电脑都行。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Kalli 非常担心 Doyon 会不小心泄露组织机密或者其他匿名者的信息。“这是所有环节中最薄弱的地方,如果这里出问题了,那么组织就完了,”他告诉我。曾在“和平阵营行动”中给予 Doyon 大力帮助的匿名者 Josh Covelli 告诉我,当他在网上看见 Doyon 的新闻发布会视频的时候,他感觉瞬间“下巴掉地下了”。“他的所作所为变得越来越不可捉摸,” Covelli 评价道。</p>
|
||||
<p>Kalli 非常担心 Doyon 会不小心泄露组织机密或者其他匿名者的信息。“这是所有环节中最薄弱的地方,如果这里出问题了,那么组织就完了,”他告诉我。曾在“和平阵营行动”中给予 Doyon 大力帮助的匿名者 Josh Covelli 告诉我,当他在网上看见 Doyon 的新闻发布会视频的时候,他感觉瞬间“下巴掉地上了”。“他的所作所为变得越来越不可捉摸,” Covelli 评价道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>三个月后,Doyon 的指定律师 Jay Leiderman 出席了圣荷西联邦法庭的辩护。Leiderman 已经好几个星期没有得到 Doyon 的消息了。“我需要得知被告无法出席的具体原因,”法官说。Leiderman 无法回答。Doyon 再次缺席了两星期后的另一场听证会。检控方表示:“很明显,看来被告已经逃跑了。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -214,7 +214,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“Xport 行动”是“匿名者”组织进行的所有同类行动中的第一个行动。这次行动的目标是协助如今已经背负两项罪名的通缉犯 Doyon 潜逃出国。负责调度的人是 Kalli 以及另一位曾在八十年代剑桥的迷幻药派对上和 Doyon 见过面的匿名者老兵。这位老兵是一位已经退休的软件主管,在组织内部威望很高。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 的终点站是这位软件主管的家,位于加拿大的偏远乡村。2011 年 12 月,他搭便车前往旧金山,并辗转来到了市区组织大本营。他找到了他的指定联系人,后者带领他到达了奥克兰的一家披萨店。凌晨 2 点,Doyon 通过披萨店的无线网络,接收了一条加密聊天消息。</p>
|
||||
<p>Doyon 的目的地是这位软件主管家,位于加拿大的偏远乡村。2011 年 12 月,他搭便车前往旧金山,并辗转来到了市区组织大本营。他找到了他的指定联系人,后者带领他到达了奥克兰的一家披萨店。凌晨 2 点,Doyon 通过披萨店的无线网络,接收了一条加密聊天消息。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“你现在靠近窗户吗?”那条消息问道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -222,13 +222,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“往大街对面看。看见一个绿色的邮箱了吗?十五分钟后,你去站到那个邮箱旁边,把你的背包取下来,然后把你的面具放在上面。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>一连几个星期的时间,Doyon 穿梭于海湾地区的安全屋之间,按照加密聊天那头的指示不断行动。最后,他搭上了前往西雅图的长途公交车,软件主管的一个朋友在那里接待了他。这个朋友是一名非常富有的退休人员,他花费了通过谷歌地球来帮助 Doyon 规划前往加拿大的路线。他们共同前往了一家野外用品供应商店,这位朋友为 Doyon 购置了价值 1500 美元的商品,包括登山鞋以及一个全新的背包。接着他又开车载着 Doyon 北上,两小时后到达距离国界只有几百英里的偏僻地区。随后 Doyon 见到了 Amber Lyon。</p>
|
||||
<p>一连几个星期的时间,Doyon 穿梭于海湾地区的安全屋之间,按照加密聊天那头的指示不断行动。最后,他搭上了前往西雅图的长途公交车,软件主管的一个朋友在那里接待了他。这个朋友是一名非常富有的退休人员,他花费了几小时的时间通过谷歌地球来帮助 Doyon 规划前往加拿大的路线。他们共同前往了一家野外用品供应商店,这位朋友为 Doyon 购置了价值 1500 美元的商品,包括登山鞋以及一个全新的背包。接着他又开车载着 Doyon 北上,两小时后到达距离国界只有几百英里的偏僻地区。随后 Doyon 见到了 Amber Lyon。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>几个月前,广播新闻记者 Lyon 曾在 CNN 的关于“匿名者”组织的节目里采访过 Doyon。Doyon 很欣赏她的报道,他们一直保持着联络。Lyon 要求加入 Doyon 的逃亡行程,为一部可能会发行的纪录片拍摄素材。软件主管认为这样太过冒险,但 Doyon 还是接受了她的请求。“我觉得他是想让自己出名,” Lyon 告诉我。四天的时间里,她用影像记录下了 Doyon 徒步北上,在林间露宿的行程。“那一切看起来不太像是仔细规划过的,” Lyon 回忆说。“他实在是无家可归了,所以他才会想要逃到国外去。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="http://www.newyorker.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/140908_a18506-600.jpg" /></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small>“这里是我们存放各种感觉的仓库。如果你发现了某种感觉,把它带到这里然后锁起来。”</small></center>
|
||||
<center><small>“这里是我们存放各种情感的仓库。如果你产生了某种情感,把它带到这里然后锁起来。”</small></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2012 年 2 月 11 日,Pastebin 上出现了一条消息。“PLF 很高兴的宣布‘ Commander X’,也就是 Christopher Mark Doyon,已经离开了美国的司法管辖区,抵达了加拿大一个比较安全的地方,”上面写着,“PLF 呼吁美国政府,希望政府能够醒悟过来并停止无谓的骚扰与监视行为——不要仅仅逮捕‘匿名者’组织的成员,对所有的激进组织应该一视同仁。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -236,13 +236,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Doyon 和软件主管在加拿大的小木屋里呆了几天。在一次同 Barrett Brown 的聊天中,Doyon 难掩内心的喜悦之情。
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>BarrettBrown:你现在应该足够安全了吧,其他的呢?...</blockquote>
|
||||
<blockquote>BarrettBrown:你现在足够多安全的藏身之处等等吧?</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX:是的,我现在很安全,现在加拿大既不缺钱也不缺藏身的地方。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX:Amber Lyon 想要你的一张照片。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX:去他【哔~】的怪人,Barrett,相信你会喜欢我告诉她应该怎样评价你的。</blockquote>
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX:去你【哔~】的怪人,Barrett,相信你会喜欢我的回复。我一直爱你,永远爱你。</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>CommanderX::-)</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -258,13 +258,13 @@ Doyon 和软件主管在加拿大的小木屋里呆了几天。在一次同 Barr
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>BarrettBrown:当然,估计我们不久后也得这样了</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在 Doyon 出逃十天后,《华尔街日报》上刊登了关于不久后升职为美国国家安全局及网络指挥部主任的 Keith Alexander 的报道,他在白宫举行的秘密会晤以及其他场合下,表达了对“匿名者”组织的高度关注。Alexander 发出警告,两年内,该组织必将会是国家电网改造的大患。参谋长联席会议的主席 General Martin Dempsey 告诉记者,这群人是国家的敌人。“他们有能力把这些使用恶意软件造成破坏的技术扩散到其他的边缘组织去,”随后又补充道,“我们必须防范这种情况发生。”</p>
|
||||
<p>在 Doyon 出逃十天后,《华尔街日报》上刊登了关于不久后升职为美国国家安全局及网络指挥部主任的 Keith Alexander 的报道,他在白宫以及其他场合举行的秘密会晤,表达了对“匿名者”组织的高度关注。Alexander 发出警告,两年内,该组织必将会是国家电网改造的大患。参谋长联席会议的主席 General Martin Dempsey 告诉记者,这群人是国家的敌人。“他们有能力把这些使用恶意软件造成破坏的技术扩散到其他的边缘组织去,”随后又补充道,“我们必须防范这种情况发生。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>3 月 8 日,国会议员们在国会大厦附近的一个敏感信息隔离设施附近举行了关于网络安全的会议。包括 Alexander、Dempsey、美国联邦调查局局长 Robert Mueller,以及美国国土安全部部长 Janet Napolitano 在内的多名美国安全方面的高级官员出席了这次会议。会议上,通过计算机向与会者模拟了东部沿海地区电力设施可能会遭受到的网络攻击时的情境。“匿名者”组织目前应该还不具备发动此种规模攻击的能力,但安全方面的官员担心他们会联合其他更加危险的组织来共同发动攻击。“在我们着手于不断增加的网络风险事故时,政府仍在就具体的处理细节进行不断协商讨论,” Napolitano 告诉我。当谈及潜在的网络安全隐患时,她补充道,“我们通常会把‘匿名者’组织的行动当做 A 级威胁来应对。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“匿名者”也许是当今世界上最强大的无政府主义黑客组织。即使如此,它却从未表现出过任何的会对公共基础设施造成破坏的迹象或意愿。一些网络安全专家称,那些关于“匿名者”组织的谣传太过危言耸听。“在奥兰多发布战前宣言和实际发动 Stuxnet 蠕虫病毒攻击之间是有很大的差距的,” Internet 研究与战略中心的一位职员 James Andrew Lewis 告诉我,这和 2007 年美国与以色列对伊朗原子能网站发动的黑客袭击有关。哈佛大学法学院的教授 Yochai Benkler 告诉我,“我们所看见的只是以主要防御为理由而进行的开销,否则,将很难自圆其说。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Keith Alexander 最近刚从政府部门退休,他拒绝就此事发表评论,因为他并不能代表国家安全局、联邦调查局、中央情报局以及国土安全部。尽管匿名者们从未真正盯上过政府部门的计算机网络,但他们对于那些激怒他们的人有着强烈的报复心理。前国土安全部国家网络安全部门负责人 Andy Purdy 告诉我他们“害怕被报复,”无论机构还是个人,都不同意政府公然反对“匿名者”组织。“每个人都非常脆弱,”他说。</p>
|
||||
<p>Keith Alexander 最近刚从政府部门退休,他拒绝就此事发表评论,因为他并不能代表国家安全局、联邦调查局、中央情报局以及国土安全部。尽管匿名者们从未真正盯上过政府部门的计算机网络,但他们对于那些激怒他们的人有着强烈的报复心理。前国土安全部国家网络安全部门负责人 Andy Purdy 告诉我他们“害怕被报复,”无论机构还是个人,都不同意政府公然反对“匿名者”组织。“每个人都容易成为被攻击对象,”他说。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>9</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -272,7 +272,7 @@ Doyon 和软件主管在加拿大的小木屋里呆了几天。在一次同 Barr
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 感到很烦躁,但他还是继续扮演着一名黑客——以此吸引关注。他在多伦多上映的纪录片上以戴着面具的匿名者形象出现。在接受《National Post》的采访时,他向记者大肆吹嘘未经证实的消息,“我们已经入侵了美国政府的所有机密数据库。现在的问题是我们该何时泄露这些机密数据,而不是我们是否会泄露。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2013 年 1 月,在另一名匿名者介入俄亥俄州<a href="https://gist.githubusercontent.com/SteveArcher/cdffc917a507f875b956/raw/c7b49cc11ae1e790d30c87f7b8de95482c18ec74/%E6%96%AF%E6%89%98%E6%9C%AC%E7%BB%B4%E5%B0%94%E8%BD%AE%E5%A5%B8%E6%A1%88%E5%86%8D%E8%B5%B7%E9%A3%8E%E6%B3%A2%20%E9%BB%91%E5%AE%A2%E7%BB%84%E7%BB%87%E4%BB%8B%E5%85%A5">斯托本维尔未成年少女轮奸案</a>,发起抗议行动之后,Doyon 重新启用了他两年前创办的网站 LocalLeaks,作为那起轮奸事件的信息汇总处理中心。如同许多其他“匿名者”组织的所作所为一样,LocalLeaks 网站非常具有影响力,但却也不承担任何责任。LocalLeaks 网站是第一家公布 12 分钟斯托本维尔高中毕业生猥亵视频的网站,这激起了众多当事人的愤怒。LocalLeaks 网站上同时披露了几份未被法庭收录的关于案件的材料,并且由此不小心透漏出了案件受害人的名字。Doyon向我承认他公开这些未经证实的信息的策略是存在争议的,但他同时回忆起自己当时的想法,“我们可以选择去除这些斯托本维尔案件的材料...也可以选择公开所有我们搜集的信息,基本上,给公众以提醒,不过,前提是你们得相信我们。”</p>
|
||||
<p>2013 年 1 月,在另一名匿名者介入俄亥俄州<a href="https://gist.githubusercontent.com/SteveArcher/cdffc917a507f875b956/raw/c7b49cc11ae1e790d30c87f7b8de95482c18ec74/%E6%96%AF%E6%89%98%E6%9C%AC%E7%BB%B4%E5%B0%94%E8%BD%AE%E5%A5%B8%E6%A1%88%E5%86%8D%E8%B5%B7%E9%A3%8E%E6%B3%A2%20%E9%BB%91%E5%AE%A2%E7%BB%84%E7%BB%87%E4%BB%8B%E5%85%A5">斯托本维尔未成年少女强奸案</a>,发起抗议行动之后,Doyon 重新启用了他两年前创办的网站 LocalLeaks,作为那起强奸事件的信息汇总处理中心。如同许多其他“匿名者”组织的所作所为一样,LocalLeaks 网站非常具有影响力,但却也不承担任何责任。LocalLeaks 网站是第一家公布 12 分钟斯托本维尔高中毕业生猥亵视频的网站,这激起了众多当事人的愤怒。LocalLeaks 网站上同时披露了几份未被法庭收录的关于案件的材料,并且由此不小心透漏出了案件受害人的名字。Doyon向我承认他公开这些未经证实的信息的策略是存在争议的,但他同时回忆起自己当时的想法,“我们可以选择销毁这些斯托本维尔案件的材料...也可以选择公开所有我们搜集的信息,基本上,给公众以提醒,不过,前提是你们得相信我们。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2013 年 3 月,一个名为 Rustle League 的组织入侵了 Doyon 的 Twitter 账户,该组织此前经常挑衅“匿名者”组织。Rustle League 的领导者之一 Shm00p 告诉我,“我们的本意并不是伤害那些家伙,只不过,哦,那些家伙说的话你就当是在放屁好了——我会这么做只是因为我感到很好笑。” Rustle League 组织使用 Doyon 的账户发布了含有如 www.jewsdid911.org 链接这样的,种族主义和反犹太主义的信息。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -290,37 +290,37 @@ Doyon 和软件主管在加拿大的小木屋里呆了几天。在一次同 Barr
|
||||
|
||||
<p>我们约定了一次面谈。Doyon 坚持让我通过加密聊天把面谈的详细情况提前告诉他。我坐了几个小时的飞机,租车来到了加拿大的一个偏远小镇,并且禁用了我的电话。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>最后,我在一个狭小安静的住宅区公寓里见到了 Doyon。他穿了一件绿色的军人夹克衫以及印有“匿名者”组织 logo 的 T 恤衫:一个脸被问号所替代的黑衣人形象。公寓里基本上没有什么家具,充满了一股烟味。他谈论起了美国政治(“我基本没怎么在众多的选举中投票——它们不过是暗箱操作的游戏罢了”),好战的伊斯兰教(“我相信,尼日利亚政府的人不过是相互勾结,以创建一个名为‘博科圣地’的基地组织的下属机构罢了”),以及他对“匿名者”组织的小小看法(“那些自称为怪人的人是真的是烂透了,意思是,邪恶的人”)。</p>
|
||||
<p>最后,我在一个狭小安静的住宅区公寓里见到了 Doyon。他穿了一件绿色的军人夹克衫以及印有“匿名者”组织 logo 的 T 恤衫:一个脸被问号所替代的黑衣人形象。公寓里基本上没有什么家具,充满了一股烟味。他谈论起了美国政治(“我基本没怎么在众多的选举中投票——它们不过是暗箱操作的游戏罢了”),好战的伊斯兰教(“我相信,尼日利亚政府的人不过是相互勾结,以创建一个名为‘博科圣地’的基地组织的下属机构罢了”),以及他对“匿名者”组织的小小看法(“那些自称为怪人的人是真的是烂透了,其实是邪恶的人”)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 剃去了他的胡须,但他却显得更加憔悴了。他说那是因为他病了的原因,他几乎很少出去。很小的写字台上有两台笔记本电脑、一摞关于佛教的书,还有一个堆满烟灰的烟灰缸。另一面裸露的泛黄墙壁上挂着盖伊·福克斯面具。他告诉我,“所谓‘Commander X’不过是一个处于极度痛苦中的小老头罢了。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在刚过去的圣诞节里,匿名者的新网站 AnonInsiders 的创建者拜访了 Doyon,并给他带来了馅饼和香烟。Doyon 询问来访的朋友是否可以继承自己的衣钵成为 PLF 的最高指挥官,同时希望能够递交出自己手里的“王国钥匙”——手里的所有密码,以及几份关于“匿名者”组织的机密文件。这位朋友委婉的拒绝了。“我有自己的生活,”他告诉了我拒绝的理由。</p>
|
||||
<p>在刚过去的圣诞节里,匿名者的新网站 AnonInsiders 的创建者拜访了 Doyon,并给他带来了馅饼和香烟。Doyon 询问来访的朋友是否可以接替自己成为 PLF 的最高指挥官,同时希望能够递交出自己手里的“王国钥匙”——手里的所有密码,以及几份关于“匿名者”组织的机密文件。这位朋友委婉的拒绝了。“我有自己的生活,”他告诉了我拒绝的理由。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<h2>11</h2>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>2014 年 8 月 9 日,当地时间下午 5 时 09 分,来自密苏里州圣路易斯郊区德尔伍德的一位说唱歌手同时也是激进分子的 Kareem (Tef Poe) Jackson,在 Twitter 上谈起了邻近城镇的一系列令人担忧的举措。“基本可以断定弗格森已经实施了戒严,任何人都无法出入,”他在 Twitter 上写道。“国内的朋友还有因特网上的朋友请帮助我们!!!”五个小时前,弗格森,一位十八岁的手无寸铁的非裔美国人 Michael Brown,被一位白人警察射杀。射杀警察声称自己这么做的原因是 Brown 意图伸手抢夺自己的枪支。而事发当时和 Brown 在一起的朋友 Dorian Johnson 却说,Brown 唯一做得不对的地方在于他当时拒绝离开街道中间。</p>
|
||||
<p>2014 年 8 月 9 日,当地时间下午 5 时 09 分,来自密苏里州圣路易斯郊区德尔伍德的一位说唱歌手同时也是激进分子的 Kareem (Tef Poe) Jackson,在 Twitter 上谈起了邻近城镇的一系列令人担忧的举措。“基本可以断定弗格森已经实施了戒严,任何人都无法出入,”他在 Twitter 上写道。“国内外的朋友们请帮助我们!!!”五个小时前,弗格森,一位十八岁的手无寸铁的非裔美国人 Michael Brown,被一位白人警察射杀。射杀警察声称自己这么做的原因是 Brown 意图伸手抢夺自己的枪支。而事发当时和 Brown 在一起的朋友 Dorian Johnson 却说,Brown 唯一做得不对的地方在于他当时拒绝离开街道中间。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>不到两小时,Jackson 就收到了一位名为 CommanderXanon 的 Twitter 用户的回复。“你完全可以相信我们,”回复信息里写道。“你是否可以给我们详细描述一下现场情况,那样会对我们很有帮助。”近几周的时间里,仍然呆在加拿大的 Doyon 复出了。六月,他在还有两个月满 50 岁的时候,成功戒烟(“#戒瘾成功 #电子香烟功不可没 #老了,”他在戒烟成功后在 Twitter 上写道)。七月,在加沙地带爆发武装对抗之后,Doyon 发表 Twiter 支持“匿名者”组织的“拯救加沙行动”,并发动了一系列针对以色列网站的 DDoS 攻击。Doyon 认为弗格森枪击事件更加令人关注。抛开他本人的个性,他有在事件发展到引人注目之前的早期,就迅速注意该事件的能力。</p>
|
||||
<p>不到两小时,Jackson 就收到了一位名为 CommanderXanon 的 Twitter 用户的回复。“你完全可以相信我们,”回复信息里写道。“你是否可以给我们详细描述一下现场情况,那样会对我们很有帮助。”近几周的时间里,仍然呆在加拿大的 Doyon 复出了。六月,他在还有两个月满 50 岁的时候,成功戒烟(“#戒瘾成功 #电子香烟功不可没 #老了,”他在戒烟成功后在 Twitter 上写道)。七月,在加沙地带爆发武装对抗之后,Doyon 发表 Twiter 支持“匿名者”组织的“拯救加沙行动”,并发动了一系列针对以色列网站的 DDoS 攻击。Doyon 认为弗格森枪击事件更加令人关注。抛开他本人的个性,他有能力在事件发展到引人注目之前,就迅速注意该事件。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“正在网上搜索关于那名警察以及当地政府的信息,” Doyon 发 Twitter 道。不到十分钟,他就为此专门在 IRC 聊天室里创建了一个频道。“‘匿名者’组织‘弗格森’行动正式启动,”他又发了一条 Twitter。但只有两个人转推了此消息。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>次日早晨,Doyon 发布了一条链接,链接指向的是一个初具雏形的网站,网站首页有一条致弗格森市民的信息——“你们并不孤单,我们将尽一切努力支持你们”——以及致当地警察的警告:“如果你们对对弗格森的抗议者们滥用职权、骚扰,或者伤害了他们,我们绝对会让你们所有政府部门的网站瘫痪。这不是威胁,这是承诺。”同时 Doyon 呼吁有 130 万粉丝的“匿名者”组织的 Twitter 账号 YourAnonNews 给与支持。“请支持‘弗格森’行动”,他发送了消息。一分钟后,YourAnonNews 回复表示同意。当天,包含话题 #OpFerguson 的 Twitter 发表/转推了超过六千次。</p>
|
||||
<p>次日早晨,Doyon 发布了一条链接,链接指向的是一个初具雏形的网站,网站首页有一条致弗格森市民的信息——“你们并不孤单,我们将尽一切努力支持你们”——以及致当地警察的警告:“如果你们对弗格森的抗议者们滥用职权、骚扰,或者伤害了他们,我们绝对会让你们所有政府部门的网站瘫痪。这不是威胁,这是承诺。”同时 Doyon 呼吁有 130 万粉丝的“匿名者”组织的 Twitter 账号 YourAnonNews 给与支持。“请支持‘弗格森’行动”,他发送了消息。一分钟后,YourAnonNews 回复表示同意。当天,包含话题 #OpFerguson 的 Twitter 被转发了超过六千次。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>这个事件迅速成为头条新闻,同时匿名者们在弗格森周围进行了大集会。与“阿拉伯之春行动”类似,“匿名者”组织向抗议者们发送了电子关怀包,包括抗暴指导(“把瓦斯弹捡起来回丢给警察”)与可打印的盖伊·福克斯面具。Jackson 和其他示威者在弗格森进行示威游行时,警察企图通过橡皮子弹和催泪瓦斯来驱散他们。“当时的情景真像是布鲁斯·威利斯的电影里的情节,” Jackson 后来告诉我。“不过巴拉克·奥巴马应该并不会支持‘匿名者’组织传授给我们的这些知识,”他笑称道。“让那些警察赶到束手无策真的是太爽了。”</p>
|
||||
<p>这个事件迅速成为头条新闻,同时匿名者们在弗格森周围进行了大集会。与“阿拉伯之春行动”类似,“匿名者”组织向抗议者们发送了电子关怀包,包括抗暴指导(“把瓦斯弹捡起来回丢给警察”)与可打印的盖伊·福克斯面具。Jackson 和其他示威者在弗格森进行示威游行时,警察企图通过橡皮子弹和催泪瓦斯来驱散他们。“当时的情景真像是布鲁斯·威利斯的电影里的情节,” Jackson 后来告诉我。“不过巴拉克·奥巴马应该并不会支持‘匿名者’组织传授给我们的这些知识,”他说道。“知道有人在你的背后支持你,真是感觉欣慰。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>有个域名是 www.opferguson.com 的网站,后来发现不过是一个骗局——一个用来收集访问者 ip 地址的陷阱,随后这些地址会被移交给执法机构。有些人怀疑 Commander X 是政府的线人。在 IRC 聊天室 #OpFerguson 频道,一个名叫 Sherlock 写道,“现在频道里每个人说的已经让我害怕去点击任何陌生的链接了。除非是一个我非常熟悉的网址,否则我绝对不会去点击。”</p>
|
||||
<p>有个网址是 www.opferguson.com 的网站,后来发现不过是一个骗局——一个用来收集访问者 ip 地址的陷阱,随后这些地址会被移交给执法机构。有些人怀疑 Commander X 是政府的线人。在 IRC 聊天室 #OpFerguson 频道,一个名叫 Sherlock 写道,“现在频道里每个人说的已经让我害怕去点击任何陌生的链接了。除非是一个我非常熟悉的网址,否则我绝对不会去点击。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>弗格森的抗议者要求当局公布射杀 Brown 的警察的名字。几天后,匿名者们附和了抗议者们的请求。有人在 Twitter 上写道,“弗格森警察局最好公布肇事警察的名字,否则‘匿名者’组织将会替他们公布。”8 月 12 的新闻发布会上,圣路易斯警察局的局长 Jon Belmar 拒绝了这个请求。“我们不会这样做,除非他们被某个罪名所指控,”他说道。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>作为报复,一名黑客使用名为 TheAnonMessage 的 Twitter 账户公布了一条链接,该链接指向一段来自警察的无线电设备所记录的音频文件,文件记录时间是 Brown 被枪杀的两小时左右。TheAnonMessage 同时也把矛头指向了 Belmar,在 Twitter 上公布了这位警察局长的家庭住址、电话号码以及他的家庭照片——一张是他的儿子在长椅上睡觉,另一张则是 Belmar 和他的妻子的合影。“不错的照片,Jon,” TheAnonMessage 在 Twitter 上写道。“你的妻子在她这个年龄算是一个美人了。你已经爱她爱得不耐烦了吗?”一个小时后,TheAnonMessage 又以 Belmar 的女儿为把柄进行了恐吓。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Richard Stallman,来自 MIT 的初代黑客,告诉我虽然他在很多地方赞同“匿名者”组织的行为,但他认为这些泄露私人信息的攻击行为是要受到谴责的。即使是在国内,TheAnonMessage 的行为也受到了谴责。“为何要泄露无辜的人的信息到网上?”一位匿名者通过 IRC 发问,并且表示威胁 Belmar 的家人实在是“相当愚蠢的行为”。但是 TheAnonMessage 和其他的一些匿名者仍然进行着不断搜寻,并企图在将来再次进行泄露信息的攻击。在互联网上可以得到所有弗格森警察局警员的名字,匿名者们不断地搜索着信息,企图找出具体是哪一个警察找出杀害了 Brown。</p>
|
||||
<p>Richard Stallman,来自 MIT 的初代黑客,告诉我虽然他在很多地方赞同“匿名者”组织的行为,但他认为这些泄露私人信息的攻击行为是要受到谴责的。即使是组织内部,TheAnonMessage 的行为也受到了谴责。“为何要泄露无辜的人的信息到网上?”一位匿名者通过 IRC 发问,并且表示威胁 Belmar 的家人实在是“相当愚蠢的行为”。但是 TheAnonMessage 和其他的一些匿名者仍然进行着不断搜寻,并企图在将来再次进行泄露信息的攻击。在互联网上可以得到所有弗格森警察局警员的名字,匿名者们不断地搜索着信息,企图找出具体是哪一个警察找出杀害了 Brown。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><img src="http://www.newyorker.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/09/140908_steig-1999-04-12-600.jpg" /></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center><small></small>1999 年 4 月 12 日 “我应该把镜头对向谁?”</center>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>8 月 14 日清晨,及位匿名者基于 Facebook 上的照片还有其他的证据,确定了射杀 Brown 的凶手是一位名叫 Bryan Willman 的 32 岁男子。根据一份 IRC 聊天记录,一位匿名者贴出了 Willman 的浮夸面孔的照片;另一位匿名者提醒道,“凶手声称自己的脸没有被任何人看到。”另一位昵称为 Anonymous|11057 的匿名者承认他对 Willman 的怀疑确实是“跳跃性的可能错误的逻辑过程推导出来的。”不过他还是写道,“我只是无法动摇自己的想法。虽然我没有任何证据,但我非常非常地确信就是他。”</p>
|
||||
<p>8 月 14 日清晨,几位匿名者基于 Facebook 上的照片还有其他的证据,确定了射杀 Brown 的凶手是一位名叫 Bryan Willman 的 32 岁男子。根据一份 IRC 聊天记录,一位匿名者贴出了 Willman 的肿胀面孔的照片;另一位匿名者提醒道,“凶手声称自己的脸没有被任何人看到。”另一位昵称为 Anonymous|11057 的匿名者承认他对 Willman 的怀疑确实是“跳跃性的可能错误的逻辑过程推导出来的。”不过他还是写道,“我只是无法动摇自己的想法。虽然我没有任何证据,但我非常非常地确信就是他。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>TheAnonMessage 看起来被这次对话逗乐了,写道,“#愿逝者安息,凶手是 BryanWillman。”另一位匿名者发出了强烈警告。“请务必确认,” Anonymous|2252 写道。“这不仅仅关乎到一个人的性命,我们可以不负责任地向公众公布我们的结果,但却很可能有无辜的人会因此受到不应受到的对待。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -356,15 +356,15 @@ Doyon 和软件主管在加拿大的小木屋里呆了几天。在一次同 Barr
|
||||
|
||||
<blockquote>anondepp:lol</blockquote>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>早晨 9 时 45 分,圣路易斯警察局对 TheAnonMessage 进行了答复。“Bryan Willman 从来没有在弗格森警察局或者圣路易斯警察局任过职,” 他们在 Twitter 上写道。“请不要再公布这位无辜市民的信息了。”(随后 FBI 对弗格森警察的电脑遭黑客入侵的事情展开了调查。)Twitter 管理员迅速封禁了 TheAnonMessage 的账户,但 Willman 的名字和家庭住址仍然被广泛传开。</p>
|
||||
<p>早晨 9 时 45 分,圣路易斯警察局对 TheAnonMessage 进行了答复。“Bryan Willman 从来没有在 警察局或者圣路易斯警察局任过职,” 他们在 Twitter 上写道。“请不要再公布这位无辜市民的信息了。”(随后 FBI 对弗格森警察的电脑遭黑客入侵的事情展开了调查。)Twitter 管理员迅速封禁了 TheAnonMessage 的账户,但 Willman 的名字和家庭住址仍然被广泛传开。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>实际上,Willman 是弗格森西郊圣安区的警察外勤负责人。当圣路易斯警察局的情报处打电话告诉 Willman,他已经被“确认”为凶手时,他告诉我,“我以为不过是个奇怪的笑话。”几小时后,他的社交账号上就收到了数百条要杀死他的威胁。他在警察的保护下,独自一人在家里呆了将近一个星期。“我只希望这一切都尽快过去,”他告诉我他的感受。他认为“匿名者”组织已经不可挽回地损害了他的名誉。“我不知道他们怎么会以为自己可以被再次信任的,”他说。</p>
|
||||
<p>实际上,Willman 是弗格森西郊圣安区的警察外勤负责人。当圣路易斯警察局的情报处打电话告诉 Willman,他已经被“确认”为凶手时,他告诉我,“我以为不过是个奇怪的笑话。”几小时后,他的社交账号上就收到了成百上千条死亡恐吓。他在警察的保护下,独自一人在家里呆了将近一个星期。“我只希望这一切都尽快过去,”他告诉我他的感受。他认为“匿名者”组织已经不可挽回地损害了他的名誉。“我不知道他们怎么会以为自己可以被再次信任的,”他说。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>“我们并不完美,” OpFerguson 在 Twitter 上说道。“‘匿名者’组织确实犯错了,过去的几天我们制造一些混乱。为此,我们道歉。”尽管 Doyon 并不应该为这次错误的信息泄露攻击负责,但其他的匿名者却因为他发起了一次无法控制的行动,而归咎他。YourAnonNews 在 Pastebin 上发表了一则消息,上面写道,“你们也许注意到了组织不同的 Twitter 账户发表的话题 #Ferguson 和 #OpFerguson,这两个话题下的 Twitter 与信息是相互矛盾的。为什么会在这些关键话题上出现分歧,部分原因是因为 CommanderX 是一个‘想让自己出名的疯子/想让公众认识自己的疯子’——这种人喜欢,或者至少不回避媒体的宣传——并且显而易见的,组织内大部分成员并不喜欢这样。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>在个人 Twitter 上,Doyon 否认了所有关于“弗格森行动”的职责,他写道,“我讨厌这样。我不希望这样的情况发生,我也不希望和我认为是朋友的人战斗。”沉寂了几天后,他又再度获吹响了战斗的号角。他最近在 Twitter 上写道,“你们称他们是暴民,我们却称他们是压迫下的反抗之声”以及“解放西藏”。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>Doyon 仍然处于藏匿状态。甚至连他的律师 Jay Leiderman 也不知道他在哪里。Leiderman 表示,除了在圣克鲁斯受到的指控,Doyon 很有可能因为攻击了 PayPal 和奥兰多而面临新的指控。一旦他被捕,所有的刑期加起来,他的余生就要在监狱里度过了。借鉴 Edward Snowden 的先例,他希望申请去俄罗斯避难。我们谈话时,他用一支点燃的香烟在他的公寓里比划着。“这里比他【哔~】的牢房强多了吧?我绝对不会出去,”他愤愤道。“我不会再联系我的家人了....这是相当高的代价,但我必须这么做,我会尽我的努力让所有人活得自由、明白。”</p>
|
||||
<p>Doyon 仍然处于藏匿状态。甚至连他的律师 Jay Leiderman 也不知道他在哪里。Leiderman 表示,除了在圣克鲁斯受到的指控,Doyon 很有可能因为攻击了 PayPal 和奥兰多而面临新的指控。一旦他被捕,所有的刑期加起来,他的余生就要在监狱里度过了。借鉴 Edward Snowden 的先例,他希望申请去俄罗斯避难。我们谈话时,他用一支点燃的香烟在他的公寓里比划着。“这里比【哔~】的牢房强多了吧?我绝对不会出去,”他愤愤道。“我不会再联系我的家人了....这是相当高的代价,但我必须这么做,我会尽我的努力让所有人活得自由、明白。”</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -372,6 +372,6 @@ Doyon 和软件主管在加拿大的小木屋里呆了几天。在一次同 Barr
|
||||
|
||||
<p>作者:<a href="http://www.newyorker.com/contributors/david-kushner">David Kushner</a></p>
|
||||
<p>译者:<a href="https://github.com/SteveArcher">SteveArcher</a></p>
|
||||
<p>校对:<a href="https://github.com/校对者ID">校对者ID</a></p>
|
||||
<p>校对:<a href="https://github.com/carolinewuyan">Caroline</a></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>本文由 <a href="https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject">LCTT</a> 原创翻译,<a href="http://linux.cn/">Linux中国</a>荣誉推出</p>
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
Jelly Conky为你的Linux桌面带来简约、时尚的状态信息
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**我把Conky当成壁纸一样使用:我会找出一个我喜欢的样式,下一周当我厌烦了想要一点小改变时我就更换另外一个样式。**
|
||||
|
||||
不断更换样式的部分原因是由于日益增多的样式目录。我最近最喜欢的样式是Jelly Conky。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Jelly Conky遵循了许多我们推荐的Conky风格采用的最小设计原则。它并不想成为一个大杂烩。它不会被那些喜欢一眼就能看到他们硬盘温度和IP地址的人所青睐。
|
||||
|
||||
它配备了三种不同的模式,它们都可以添加个性的或者静态背景图像:
|
||||
|
||||
- 时钟
|
||||
- 时钟加日期
|
||||
- 时钟加日期和天气
|
||||
|
||||
一些人不理解为什么要在桌面上拥有重复的时钟。这是很好理解的。对于我而言,这不仅仅是功能(虽然,个人而言,Conky的时钟比挤在上部面板上那渺小的数字要更容易看清)。
|
||||
|
||||
我想如果你的Android主屏幕有一个时间小部件的话,你不会介意在你的桌面上也有这么一个的,对吧?
|
||||
|
||||
你可以从下述链接下载Jelly Conky,zip 包里面有一个说明如何安装的 readme 文件。如果希望看到完整的教程,可以[参考我们的前一篇文章][3]。
|
||||
- [从Deviant Art上下载 Jelly Conky][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/jelly-conky-for-linux-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/conky-circle-theme-nod-lg-quick-cover
|
||||
[2]:http://zagortenay333.deviantart.com/art/Jelly-Conky-442559003
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/conky-circle-theme-nod-lg-quick-cover
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
在Ubuntu14.04上安装UberWriterMarkdown编辑器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
下面将展示如何通过官方的PPA源在Ubuntu14.04上安装UberWriter编辑器
|
||||
这是一篇快速教程指导我们如何通过官方的PPA源在Ubuntu14.04上安装UberWriter编辑器。
|
||||
|
||||
[UberWriter][1]是一款Ubuntu下的Markdown编辑器,它简洁的界面能让我们更致力于编辑文字。UberWriter利用了[pandoc][3](一个格式转换器)。但由于UberWriter的UI是基于GTK3的,因此不能完全兼容Unity桌面系统。以下是对UberWriter功能的列举:
|
||||
|
||||
- 简洁的界面
|
||||
@ -13,7 +14,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu14.04上安装UberWriter ###
|
||||
|
||||
UberWriter可以在[Ubuntu软件中心][4]中找到但是安装需要支付$5。如果你真的喜欢这款编辑器并想为开发者提供一些资金支持的话,我很建议你购买它。
|
||||
UberWriter可以在[Ubuntu软件中心][4]中找到但是安装需要支付5刀。如果你真的喜欢这款编辑器并想为开发者提供一些资金支持的话,我很建议你购买它。
|
||||
|
||||
除此之外,UberWriter也能通过官方的PPA源来免费安装。通过如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -29,16 +30,15 @@ UberWriter可以在[Ubuntu软件中心][4]中找到但是安装需要支付$5。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当想要导出到PDF的时候会提示先安装texlive。
|
||||
我尝试导出到PDF的时候被提示安装texlive。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
虽然导出到HTML和ODT格式是好的。
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux下还有一些其他的markdown编辑器。[Remarkable][5]是一款能够实时预览的编辑器,但UberWriter不能。如果你在寻找文本编辑器的话,你以可以试试[Texmaker LaTeX editor][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
系统这次展示能够帮你在Ubuntu14.04上成功安装UberWriter。我猜想UberWriter在Ubuntu12.04,Linux Mint 17,Elementary OS和其他在Ubuntu的基础上的Linux发行版上也能成功安装。
|
||||
在Linux下还有一些其他的markdown编辑器。[Remarkable][5]是一款能够实时预览的编辑器,UberWriter却不能,不过总的来说它是一款很不错的应用。如果你在寻找文本编辑器的话,你可以试试[Texmaker LaTeX editor][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
系统这个教程能够帮你在Ubuntu14.04上成功安装UberWriter。我猜想UberWriter在Ubuntu12.04,Linux Mint 17,Elementary OS和其他在Ubuntu的基础上的Linux发行版上也能成功安装。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/install-uberwriter-markdown-editor-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[John](https://github.com/johnhoow)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
QuiteRSS: Linux桌面的RSS阅读器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[QuiteRSS][1]是一个自由[开源][2]的RSS/Atome阅读器。它可以在Windows、Linux和Mac上运行。它用C++/QT编写,所以它有许多的特点。
|
||||
[QuiteRSS][1]是一个免费的[开源][2]RSS/Atome阅读器。它可以在Windows、Linux和Mac上运行。它用C++/QT编写。它有许多的特色功能。
|
||||
|
||||
QuiteRSS的界面让我想起Lotus Notes mail,会有很多RSS信息排列在大小合适的方块上,你可以通过标签分组。需要查找东西时,只需在下面板上打开RSS信息。
|
||||
QuiteRSS的界面让我想起Lotus Notes mail,会有很多RSS信息排列在右侧面板上,你可以通过标签分组。点击一个 RSS 条目时,会在下方的面板里面显示该信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
除了上述功能,它还有一个广告屏蔽器,一个报纸输出视图,通过URL特性导入RSS等众多功能。你可以在[这里][3]查找到完整的功能列表。
|
||||
除了上述功能,它还有一个广告屏蔽器,一个报纸视图,通过URL导入RSS源等众多功能。你可以在[这里][3]查找到完整的功能列表。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 上安装 QuiteRSS ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,19 +20,19 @@ QuiteRSS在Ubuntu 14.04 和 Linux Mint 17中可用。你可以通过以下命令
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install quiterss
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令在所有基于Ubuntu的发行版都支持,比如Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Linux Lite, Pinguy OS等等。对于其他Linux发行版和平台上,你可以从 [下载页][5]获得源码来安装。
|
||||
上面的命令支持所有基于Ubuntu的发行版,比如Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Linux Lite, Pinguy OS等等。对于其他Linux发行版和平台上,你可以从 [下载页][5]获得源码来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
### 卸载 QuiteRSS ###
|
||||
|
||||
用下方命令卸载 QuiteRSS:
|
||||
用下列命令卸载 QuiteRSS:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove quiterss
|
||||
|
||||
如果你使用了PPA,你还需要从源列表中把仓库删除:
|
||||
如果你使用了PPA,你还也应该从源列表中把仓库删除:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:quiterss/quiterss
|
||||
|
||||
QuiteRSS是一个不错的开源RSS阅读器,尽管我更喜欢[Feedly][6]。尽管现在 Feedly 还没有Linux桌面程序,但是你依然可以在网页浏览器中使用。希望你会觉得QuiteRSS值得在桌面Linux一试。
|
||||
QuiteRSS是一个不错的开源RSS阅读器,尽管我更喜欢[Feedly][6]。不过现在 Feedly 还没有Linux桌面程序,但是你依然可以在网页浏览器中使用。希望你会觉得QuiteRSS值得在桌面Linux一试。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——如何查找并移除Ubuntu上陈旧的PPA仓库
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:我试着通过运行apt-get update命令来再次同步包索引文件,但是却出现了“404 无法找到”的错误,看起来似乎是我不能从先前添加的第三方PPA仓库中获取最新的索引。我怎样才能清楚这些破损而且陈旧的PPA仓库呢?
|
||||
> **问题**:我试着通过运行apt-get update命令来再次同步包索引文件,但是却出现了“404 无法找到”的错误,看起来似乎是我不能从先前添加的第三方PPA仓库中获取最新的索引。我怎样才能清除这些破损而且陈旧的PPA仓库呢?
|
||||
|
||||
Err http://ppa.launchpad.net trusty/main amd64 Packages
|
||||
404 Not Found
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ Linux有问必答——如何查找并移除Ubuntu上陈旧的PPA仓库
|
||||
|
||||
E: Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead.
|
||||
|
||||
但你试着更新APT包索引时,“404 无法找到”错误总是会在版本更新之后发生。就是说,在你升级你的Ubuntu发行版后,你在旧的版本上添加的一些第三方PPA仓库就不再受新版本的支持。在此种情况下,你可以像下面这样来**鉴别并清除那些破损的PPA仓库**。
|
||||
当你试着更新APT包索引时,“404 无法找到”错误总是会在版本更新之后发生。就是说,在你升级你的Ubuntu发行版后,你在旧的版本上添加的一些第三方PPA仓库就不再受新版本的支持。在此种情况下,你可以像下面这样来**鉴别并清除那些破损的PPA仓库**。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,找出那些引起“404 无法找到”错误的PPA。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ Linux有问必答——如何查找并移除Ubuntu上陈旧的PPA仓库
|
||||
|
||||
在本例中,Ubuntu Trusty不再支持的PPA仓库是“ppa:finalterm/daily”。
|
||||
|
||||
去吧,去[移除PPA仓库][1]。
|
||||
去[移除PPA仓库][1]吧。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:finalterm/daily
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,14 +30,14 @@ Linux有问必答——如何查找并移除Ubuntu上陈旧的PPA仓库
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在移除所有过时PPA仓库后,重新运行“apt-get update”命令来检查它们是否都被移除。
|
||||
在移除所有过时的PPA仓库后,重新运行“apt-get update”命令来检查它们是否都被成功移除。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/find-remove-obsolete-ppa-repositories-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,27 +1,26 @@
|
||||
2q1w2007翻译中
|
||||
世界上最小的发行版之一Tiny Core有了新的更新
|
||||
世界上最小的发行版之一Tiny Core有了更新
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Tiny Core
|
||||
|
||||
**Robert Shingledecker 刚刚发布了最新可用的最终版本的Tiny Core 5.4,这也使它成为世界上最小的发行版之一**
|
||||
**Robert Shingledecker 宣布了最终版本的Tiny Core 5.4 Linux操作系统已经可以即刻下载,这也使它成为世界上最小的发行版之一。**
|
||||
|
||||
发行版的名字说明了一切,但是开发者依然集成了一些有意思的包和一个轻量的桌面。这次最新的迭代只有一个候选版本,而且它将会是有史以来最安静的版本。
|
||||
发行版的名字说明了一切,但是开发者依然集成了一些有意思的包和一个轻量的桌面来与它相匹配。这次最新的迭代只有一个候选版本,而且它也是迄今为止最安静的版本之一。
|
||||
|
||||
官网上的开发者说"Tiny Core是一个简单的例子来示范核心项目可以提供什么。,它提供了一个12MB的FLTK/FLWM桌面。用户对提供的程序和外加的硬件有完整的控制权。你可以把它用在桌面、笔记本或者服务器上,这可以由用户在从在线库中安装附加程序时选择,或者用提供的工具编译大多数你需要的。"
|
||||
官网上的开发者说"Tiny Core是一个简单的范例来说明核心项目可以提供什么。它提供了一个12MB的FLTK/FLWM桌面。用户对提供的程序和外加的硬件有完整的控制权。你可以把它用在桌面、笔记本或者服务器上,这可以由用户从在线库中安装附加程序时选择,或者用提供的工具编译大多数你需要的。"
|
||||
|
||||
根据更新日志,NFS的入口被添加,'Done'将在新的一行里显示,udev也升级到174来修复竞态条件问题。
|
||||
|
||||
关于修改和升级的完整内容可以在官方的[声明][1]里找到。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以下载Tiny Core Linux 5.4.
|
||||
你可以点击以下链接下载Tiny Core Linux 5.4.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Tiny Core Linux 5.4 (ISO)][2][iso] [14 MB]
|
||||
- [Tiny Core Plus 5.4 (ISO)][3][iso] [72 MB]
|
||||
- [Core 5.4 (ISO)][4][iso] [8.90 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
这些分发都有Live,你可以在安装之前试用。
|
||||
这些发行版都有Live,你可以在安装之前试用。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -29,7 +28,7 @@ via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/One-of-the-Smallest-Distros-in-the-World-Tin
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,4 +36,4 @@ via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/One-of-the-Smallest-Distros-in-the-World-Tin
|
||||
[1]:http://forum.tinycorelinux.net/index.php/topic,17487.0.html
|
||||
[2]:http://distro.ibiblio.org/pub/linux/distributions/tinycorelinux/5.x/x86/release/TinyCore-5.4.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://repo.tinycorelinux.net/5.x/x86/release/CorePlus-5.4.iso
|
||||
[4]:http://distro.ibiblio.org/tinycorelinux/5.x/x86/release/Core-current.iso
|
||||
[4]:http://distro.ibiblio.org/tinycorelinux/5.x/x86/release/Core-current.iso
|
||||
@ -1,26 +1,26 @@
|
||||
Red Hat公司8200万美元收购FeedHenry来推动手机开发
|
||||
Red Hat公司8200万美元收购FeedHenry来推动移动开发
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 这是Red Hat公司进入手机开发领域的一次关键收获。
|
||||
> 这是Red Hat公司进入移动开发领域的一次关键收获。
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat公司的JBoss开发者工具事业部一直注重于企业开发,而忽略了手机方面。而如今这一切将随着Red Hat公司宣布用8200万美元收购手机开发供应商 [FeedHenry][1] 开始发生改变。这笔交易将在Red Hat公司2015财年的第三季度结束。Red Hat公司已经在美国东部时间9月18号的4点公布它2015财年第二季度的收入。
|
||||
Red Hat公司的JBoss开发者工具事业部一直注重于企业开发,而忽略了移动方面。而如今这一切将随着Red Hat公司宣布用8200万美元收购移动开发供应商 [FeedHenry][1] 开始发生改变。这笔交易将在Red Hat公司2015财年的第三季度结束。
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat公司的中间件总经理Mike Piech说当交易结束后FeedHenry公司的员工将会变成Red Hat公司的员工。
|
||||
|
||||
FeedHenry公司的开发平台能让应用开发者快速地开发出Android、IOS、Windows Phone以及黑莓的手机应用。FeedHenry的平台Node.js的编程结构有着深远影响,而那不是过去JBoss所涉及的领域。
|
||||
FeedHenry公司的开发平台能让应用开发者快速地开发出Android、IOS、Windows Phone以及黑莓的移动应用。FeedHenry的平台Node.js的编程结构有着深远影响,而那不是过去JBoss所涉及的领域。
|
||||
|
||||
"FeedHenry公司的这次收购显著地提高了我们对于Node.js的支持与衔接。" Piech说。
|
||||
"这次对FeedHenry公司的收购显著地提高了我们对于Node.js的支持与衔接。" Piech说。
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat公司的平台即服务(PaaS)技术OpenShift已经有了一个Node.js的cartridge组件。此外,Red Hat公司的企业版Linux把Node.js的技术预览来作为Red Hat公司软件包的一部分。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管Node.js本身就是开源的,但不是所有FeedHenry公司的技术能在近期符合开源许可证的要求。作为Red Hat纵观历史的政策, 现在也是致力于让FeedHenry开源的时候了。
|
||||
尽管Node.js本身就是开源的,但不是所有FeedHenry公司的技术能在近期符合开源许可证的要求。作为Red Hat纵贯历史的政策, 现在也是致力于让FeedHenry开源的时候了。
|
||||
|
||||
"我们完成了收购,那么开源我们收购的技术就是公司的首要任务,并且我们没有理由去期待改变Feedhenry。"Piech说。
|
||||
"我们完成了收购,那么开源我们所收购的技术就是公司的首要任务,并且我们没有理由因Feedhenry而例外。"Piech说。
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat公司最后一次主要的非开源性公司的收购是在2012年用104万美元收购 [ManageIQ][2] 公司。在今年的5月份,Red Hat公司成立了ManageIQ公司的开源项目,开放之前闭源的云管理技术代码。
|
||||
|
||||
从整合的角度来看,Red Hat公司还尚未精确地提供FeedHenry公司适应它的完整细节。
|
||||
从整合的角度来看,Red Hat公司还尚未精确地提供FeedHenry公司如何融入它的完整信息。
|
||||
|
||||
"我们已经认出了一些FeedHenry公司和我们已经存在的技术和产品能很好地相互融合和集成," Piech说,"我们会在接下来的90天内分享更多我们发展蓝图的细节。"
|
||||
"我们已经确定了一些FeedHenry公司和我们已经存在的技术和产品能很好地相互融合和集成的范围," Piech说,"我们会在接下来的90天内分享更多我们发展蓝图的细节。"
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
103
published/20140922 Ten Blogs Every Ubuntu User Must Follow.md
Normal file
103
published/20140922 Ten Blogs Every Ubuntu User Must Follow.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
|
||||
10个 Ubuntu 用户一定要知道的博客
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**想要了解更多关于 ubuntu 的资讯,我们应该追哪些网站呢?**
|
||||
|
||||
这是初学者经常会问的一个问题,在这里,我会告诉你们10个我最喜欢的博客,这些博客可以帮助我们解决问题,能让我们及时了解所有 Ubuntu 版本的更新消息。不,我谈论的不是通常的 Linux 和 shell 脚本一类的东东。我是在说一个流畅的 Linux 桌面系统和一个普通的用户所要的关于 Ubuntu 的经验。
|
||||
|
||||
这些网站帮助你解决你正遇到的问题,提醒你关注各种应用和提供给你来自 Ubuntu 世界的最新消息。这个网站可以让你对 Ubuntu 更了解,所以,下面列出的是10个我最喜欢的博客,它们包括了 Ubuntu 的方方面面。
|
||||
|
||||
###10个Ubutun用户一定要知道的博客###
|
||||
|
||||
从我开始在 itsfoss 网站上写作开始,我特意把它排除在外,没有列入名单。我也并没有把[Planet Ubuntu][1]列入名单,因为它不适合初学者。废话不多说,让我们一起来看下**最好的乌邦图(ubuntu)博客**(排名不分先后):
|
||||
|
||||
### [OMG! Ubuntu!][2] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个只针对 ubuntu 爱好者的网站。无论多小,只要是和乌邦图有关系的,OMG!Ubuntu 都会收入站内!博客主要包括新闻和应用。你也可以再这里找到一些关于 Ubuntu 的教程,但不是很多。
|
||||
|
||||
这个博客会让你知道 Ubuntu 世界发生的各种事情。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Web Upd8][3] ###
|
||||
|
||||
Web Upd8 是我最喜欢的博客。除了涵盖新闻,它有很多容易理解的教程。Web Upd8 还维护了几个PPAs。博主[Andrei][4]有时会在评论里回答你的问题,这对你来说也会是很有帮助的。
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个你可以了解新闻资讯,学习教程的网站。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Noobs Lab][5] ###
|
||||
|
||||
和Web Upd8一样,Noobs Lab上也有很多教程,新闻,并且它可能是PPA里最大的主题和图标集。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是个新手,去Noobs Lab看看吧。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Linux Scoop][6] ###
|
||||
|
||||
大多数的博客都是“文字博客”。你通过看说明和截图来学习教程。而 Linux Scoop 上有很多录像来帮助初学者来学习,完全是一个视频博客。
|
||||
|
||||
比起阅读来,如果你更喜欢视频,Linux Scoop应该是最适合你的。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Ubuntu Geek][7] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个相对比较老的博客。覆盖面很广,并且有很多快速安装的教程和说明。虽然,有时我发现其中的一些教程文章缺乏深度,当然这也许只是我个人的观点。
|
||||
|
||||
想要快速小贴士,去Ubuntu Geek。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Tech Drive-in][8] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个网站的更新频率好像没有以前那么快了,可能是 Manuel 在忙于他的工作,但是仍然给我们提供了很多的东西。新闻,教程,应用评论是这个博客的亮点。
|
||||
|
||||
博客经常被收入到[Ubuntu的新闻邀请邮件中][9],Tech Drive-in肯定是一个很值得你去学习的网站。
|
||||
|
||||
### [UbuntuHandbook][10] ###
|
||||
|
||||
快速小贴士,新闻和教程是UbuntuHandbook的USP。[Ji m][11]最近也在参与维护一些PPAS。我必须很认真的说,这个博客的页面其实可以做得更好看点,纯属个人观点。
|
||||
|
||||
UbuntuHandbook 真的很方便。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Unixmen][12] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个网站是由很多人一起维护的,而且并不仅仅局限于Ubuntu,它也覆盖了很多的其他的Linux发行版。它有自己的论坛来帮助用户。
|
||||
|
||||
紧跟着 Unixmen 的步伐。。
|
||||
|
||||
### [The Mukt][13] ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Mukt是Muktware新的代表。Muktware是一个逐渐消亡的Linux组织,并以Mukt重生。Muktware是一个很严谨的Linux开源的博客,The Mukt涉及很多广泛的主题,包括,科技新闻,极客新闻,有时还有娱乐新闻(听起来是否有一种混搭风的感觉?)The Mukt也包括很多你感兴趣的Ubuntu新闻。
|
||||
|
||||
The Mukt 不仅仅是一个博客,它是一种文化潮流。
|
||||
|
||||
### [LinuxG][14] ###
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxG是一个你可以找到所有关于“怎样安装”类型文章的站点。几乎所有的文章都开始于一句话“你好,Linux geeksters,正如你所知道的……”,博客可以在不同的主题上做得更好。我经常发现有些是文章缺乏深度,并且是急急忙忙写出来的,但是它仍然是一个关注应用最新版本的好地方。
|
||||
|
||||
这是个快速浏览新的应用和它们最新的版本好地方。
|
||||
|
||||
### 你还有什么好的站点吗? ###
|
||||
|
||||
这些就是我平时经常浏览的 Ubuntu 博客。我知道还有很多我不知道的站点,可能会比我列出来的这些更好。所以,欢迎把你最喜爱的 Ubuntu 博客写在下面评论区。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/ten-blogs-every-ubuntu-user-must-follow/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://planet.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.webupd8.org/
|
||||
[4]:https://plus.google.com/+AlinAndrei
|
||||
[5]:http://www.noobslab.com/
|
||||
[6]:http://linuxscoop.com/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.techdrivein.com/
|
||||
[9]:https://lists.ubuntu.com/mailman/listinfo/ubuntu-news
|
||||
[10]:http://ubuntuhandbook.org/
|
||||
[11]:https://plus.google.com/u/0/+JimUbuntuHandbook
|
||||
[12]:http://www.unixmen.com/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.themukt.com/
|
||||
[14]:http://linuxg.net/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
Canonical解决了一个Ubuntu 14.04 LTS中的nginx漏洞
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 用户应该更新他们的系统来修复这个漏洞!
|
||||
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>*Ubuntu 14.04 LTS*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
**Canonical已经在安全公告中公布了这个影响到Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty Tahr)的nginx漏洞的细节。这个问题已经被确定并被修复了**
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu的开发者已经修复了nginx的一个小漏洞。他们解释nginx可能已经被利用来暴露网络上的敏感信息。
|
||||
|
||||
根据安全公告,“Antoine Delignat-Lavaud和Karthikeyan Bhargavan发现nginx错误地重复使用了缓存的SSL会话。攻击者可能利用此问题,在特定的配置下,可以从不同的虚拟主机获得信息“。
|
||||
|
||||
对于这些问题的更详细的描述,可以看到Canonical的安全[公告][1]。用户应该升级自己的Linux发行版以解决此问题。
|
||||
|
||||
这个问题可以通过在系统升级到最新nginx包(和依赖v包)进行修复。要应用该补丁,你可以直接运行升级管理程序。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不想使用软件更新器,您可以打开终端,输入以下命令(需要root权限):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
在一般情况下,一个标准的系统更新将会进行必要的更改。要应用此修补程序您不必重新启动计算机。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Canonical-Closes-Nginx-Exploit-in-Ubuntu-14-04-LTS-459677.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ubuntu.com/usn/usn-2351-1/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
Debian 8 "Jessie" 将把GNOME作为默认桌面环境
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Debian的GNOME团队已经取得了实质进展
|
||||
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>*GNOME 3.14桌面*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
**Debian项目开发者花了很长一段时间来决定将Xfce,GNOME或一些其他桌面环境中的哪个作为默认环境,不过目前看起来像是GNOME赢了。**
|
||||
|
||||
[我们两天前提到了][1],GNOME 3.14的软件包被上传到 Debian Testing(Debian 8 “Jessie”)的软件仓库中,这是一个令人惊喜的事情。通常情况下,GNOME的维护者对任何类型的软件包都不会这么快地决定添加,更别说桌面环境。
|
||||
|
||||
事实证明,关于即将到来的Debian 8的发行版中所用的默认桌面的争论已经尘埃落定,尽管这个词可能有点过于武断。无论什么情况下,总是有些开发者想要Xfce,另外一些则是喜欢 GNOME,看起来 MATE 也是不少人的备选。
|
||||
|
||||
### 最有可能的是,GNOME将Debian 8“Jessie” 的默认桌面环境###
|
||||
|
||||
我们之所以说“最有可能”是因为协议尚未达成一致,但它看起来GNOME已经遥遥领先了。Debian的维护者和开发者乔伊·赫斯解释了为什么会这样。
|
||||
|
||||
“根据从 https://wiki.debian.org/DebianDesktop/Requalification/Jessie 初步结果看,一些所需数据尚不可用,但在这一点上,我百分之八十地确定GNOME已经领先了。特别是,由于“辅助功能”和某些“systemd”整合的进度。在辅助功能方面:Gnome和Mate都领先了一大截。其他一些桌面的辅助功能改善了在Debian上的支持,部分原因是这一过程推动的,但仍需要上游大力支持。“
|
||||
|
||||
“Systemd /etc 整合方面:Xfce,Mate等尽力追赶在这一领域正在发生的变化,当技术团队停止了修改之后,希望有时间能在冻结期间解决这些问题。所以这并不是完全否决这些桌面,但要从目前的状态看,GNOME是未来的选择,“乔伊·赫斯[补充说][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
开发者在邮件中表示,在Debian的GNOME团队对他们所维护的项目[充满了激情][3],而Debian的Xfce的团队是决定默认桌面的实际阻碍。
|
||||
|
||||
无论如何,Debian 8“Jessie”没有一个具体发布时间,并没有迹象显示何时可能会被发布。在另一方面,GNOME 3.14已经发布了(也许你已经看到新闻了),它将很快应对好进行Debian的测试。
|
||||
|
||||
我们也应该感谢Jordi Mallach,在Debian中的GNOME包的维护者之一,他为我们指引了正确的讯息。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Debian-8-quot-Jessie-quot-to-Have-GNOME-as-the-Default-Desktop-459665.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[fbigun](https://github.com/fbigun)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Debian-8-quot-Jessie-quot-to-Get-GNOME-3-14-459470.shtml
|
||||
[2]:http://anonscm.debian.org/cgit/tasksel/tasksel.git/commit/?id=dce99f5f8d84e4c885e6beb4cc1bb5bb1d9ee6d7
|
||||
[3]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Debian-Maintainer-Says-that-Xfce-on-Debian-Will-Not-Meet-Quality-Standards-GNOME-Is-Needed-454962.shtml
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5产品线终结
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
2007年3月,红帽公司首次宣布它的[Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5][1](RHEL)平台。虽然如今看来很普通,RHEL 5特别显著的一点是它是红帽公司第一个强调虚拟化的主要发行版本,而这点是如今现代发行版所广泛接受的特性。
|
||||
|
||||
最初的计划是为RHEL 5提供七年的寿命,但在2012年该计划改变了,红帽为RHEL 5[扩展][2]至10年的标准支持。
|
||||
|
||||
刚刚过去的这个星期,Red Hat发布的RHEL 5.11是RHEL 5.X系列的最后的、次要里程碑版本。红帽现在进入了将持续三年的名为“production 3”的支持周期。在这阶段将没有新的功能被添加到平台中,并且红帽公司将只提供有重大影响的安全修复程序和紧急优先级的bug修复。
|
||||
|
||||
平台事业部副总裁兼总经理Jim Totton在红帽公司在一份声明中说:“红帽公司致力于建立一个长期,稳定的产品生命周期,这将给那些依赖Red Hat Enterprise Linux为他们的关键应用服务的企业客户提供关键的益处。虽然RHEL 5.11是RHEL 5平台的最终次要版本,但它提供了安全性和可靠性方面的增强功能,以保持该平台接下来几年的活力。”
|
||||
|
||||
新的增强功能包括安全性和稳定性更新,包括改进了红帽帮助用户调试系统的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
还有一些新的存储的驱动程序,以支持新的存储适配器和改进在VMware ESXi上运行RHEL的支持。
|
||||
|
||||
在安全方面的巨大改进是OpenSCAP更新到版本1.0.8。红帽在2011年五月的[RHEL5.7的里程碑更新][3]中第一次支持了OpenSCAP。 OpenSCAP是安全内容自动化协议(SCAP)框架的开源实现,用于创建一个标准化方法来维护安全系统。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxplanet.com/news/end-of-the-line-for-red-hat-enterprise-linux-5.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Sean Michael Kerner
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.internetnews.com/ent-news/article.php/3665641
|
||||
[2]:http://www.serverwatch.com/server-news/red-hat-extends-linux-support.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.internetnews.com/skerner/2011/05/red-hat-enterprise-linux-57-ad.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
KDE Plasma 5的第二个bug修复版本发布,带来了很多的改变
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 新的Plasma 5发布了,带来了新的外观
|
||||
|
||||
<center></center>
|
||||
|
||||
<center>*KDE Plasma 5*</center>
|
||||
|
||||
### Plasma 5的第二个bug修复版本发布,已可下载###
|
||||
|
||||
KDE Plasma 5的bug修复版本不断来到,它新的桌面体验将会是KDE的生态系统的一个组成部分。
|
||||
|
||||
[公告][1]称:“plasma-5.0.2这个版本,新增了一个月以来来自KDE的贡献者新的翻译和修订。Bug修复通常是很小但是很重要,如修正未翻译的文字,使用正确的图标和修正KDELibs 4软件的文件重复现象。它还增加了一个月以来辛勤的翻译成果,使其支持其他更多的语言”
|
||||
|
||||
这个桌面还没有在任何Linux发行版中默认安装,这将持续一段时间,直到我们测试完成。
|
||||
|
||||
开发者还解释说,更新的软件包可以在Kubuntu Plasma 5的开发版本中进行审查。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你个人需要它们,你也可以下载源码包。
|
||||
|
||||
- [KDE Plasma Packages][2]
|
||||
- [KDE Plasma Sources][3]
|
||||
|
||||
如果你决定去编译它,你必须需要知道 KDE Plasma 5.0.2是一组复杂的软件,可能你需要解决不少问题。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Second-Bugfix-Release-for-KDE-Plasma-5-Arrives-with-Lots-of-Changes-459688.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://kde.org/announcements/plasma-5.0.2.php
|
||||
[2]:https://community.kde.org/Plasma/Packages
|
||||
[3]:http://kde.org/info/plasma-5.0.2.php
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
文件管理器 Wal Commander Github 0.17版发布了
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> ### 描述 ###
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Wal Commander GitHub 版是一款多平台的开源文件管理器。适用于Windows、Linux、FreeBSD、和OSX。
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 这个从项目的目的是创建一个模仿Far管理器外观和感觉的便携式文件管理器。
|
||||
|
||||
Wal Commander 的下一个Github稳定版本0.17 已经出来了。主要功能包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用命令历史自动补全;
|
||||
- 文件关联绑定自定义命令对文件的各种操作;
|
||||
- 和用XQuartz实验性地支持OS X。
|
||||
|
||||
很多新的快捷键添加在此版本中。预编译二进制文件适用于Windows64、Linux,FreeBSD和OS X版本,这些可以直接从[GitHub中的源代码][1]编译。
|
||||
|
||||
### 主要特性 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 命令行自动补全 (使用Del键删除一条命令)
|
||||
- 文件关联 (主菜单 -> 命令 -> 文件关联)
|
||||
- XQuartz上实验性地支持OS X ([https://github.com/corporateshark/WalCommander/issues/5][2])
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下载:[http://wcm.linderdaum.com/downloads/][3]
|
||||
源代码: [https://github.com/corporateshark/WalCommander][4]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://wcm.linderdaum.com/release-0-17-0/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/corporateshark/WalCommander/releases
|
||||
[2]:https://github.com/corporateshark/WalCommander/issues/5
|
||||
[3]:http://wcm.linderdaum.com/downloads/
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/corporateshark/WalCommander
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Microsoft Lobby Denies the State of Chile Access to Free Software
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
Fuerza Chile
|
||||
|
||||
Fresh on the heels of the entire Munich and Linux debacle, another story involving Microsoft and free software has popped up across the world, in Chile. A prolific magazine from the South American country says that the powerful Microsoft lobby managed to turn around a law that would allow the authorities to use free software.
|
||||
|
||||
The story broke out from a magazine called El Sábado de El Mercurio, which explains in great detail how the Microsoft lobby works and how it can overturn a law that may harm its financial interests.
|
||||
|
||||
An independent member of the Chilean Parliament, Vlado Mirosevic, pushed a bill that would allow the state to consider free software when the authorities needed to purchase or renew licenses. The state of Chile pays $2.7 billion (€2 billion) on licenses from various companies, including Microsoft.
|
||||
|
||||
According to [ubuntizando.com][1], Microsoft representatives met with Vlado Mirosevic shortly after he announced his intentions, but the bill passed the vote, with 64 votes in favor, 12 abstentions, and one vote against it. That one vote was cast by Daniel Farcas, a member of a Chilean party.
|
||||
|
||||
A while later, the same member of the Parliament, Daniel Farcas, proposed another bill that actually nullified the effects of the previous one that had just been adopted. To make things even more interesting, some of the people who voted in favor of the first law also voted in favor of the second one.
|
||||
|
||||
The new bill is even more egregious, because it aggressively pushes for the adoption of proprietary software. Companies that choose to use proprietary software will receive certain tax breaks, which makes it very hard for free software to get adopted.
|
||||
|
||||
Microsoft has been in the news in the last few days because the [German city of Munich that adopted Linux][2] and dropped Windows system from its administration was considering, supposedly, returning to proprietary software.
|
||||
|
||||
This new situation in Chile give us a sample of the kind of pull a company like Microsoft has and it shows us just how fragile laws really are. This is not the first time a company tries to bend the laws in a country to maximize the profits, but the advent of free software and the clear financial advantages that it offers are really making a dent.
|
||||
|
||||
Five years ago, few people or governments would have considered adopting free software, but the quality of that software has risen dramatically and it has become a real competition [for the likes of Microsoft][3].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Microsoft-Lobby-Denies-the-State-of-Chile-Access-to-Free-Software-455598.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ubuntizando.com/2014/08/20/microsoft-chile-y-el-poder-del-lobby/
|
||||
[2]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Munich-Disappointed-with-Linux-Plans-to-Switch-Back-to-Windows-455405.shtml
|
||||
[3]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Munich-Switching-to-Windows-from-Linux-Is-Proof-that-Microsoft-Is-Still-an-Evil-Company-455510.shtml
|
||||
@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Transport Tycoon Deluxe Remake OpenTTD 1.4.2 Is an Almost Perfect Sim
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
Transport Tycoon
|
||||
|
||||
**OpenTTD 1.4.2, an open source simulation game based on the popular Microprose title Transport Tycoon written by Chris Sawyer, has been officially released.**
|
||||
|
||||
Transport Tycoon is a very old game that was originally launched back in 1995, but it made such a huge impact on the gaming community that, even almost 20 years later, it still has a powerful fan base.
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, Transport Tycoon Deluxe had such an impact on the gaming industry that it managed to spawn an entire generation of similar games and it has yet to be surpassed by any new title, even though many have tried.
|
||||
|
||||
Despite the aging graphics, the developers of OpenTTD have tried to provide new challenges for the fans of the original games. To put things into perspective, the original game is already two decades old. That means that someone who was 20 years old back then is now in his forties and he is the main audience for OpenTTD.
|
||||
|
||||
"OpenTTD is modelled after the original Transport Tycoon game by Chris Sawyer and enhances the game experience dramatically. Many features were inspired by TTDPatch while others are original," reads the official announcement.
|
||||
|
||||
OpenTTD features bigger maps (up to 64 times in size), stable multiplayer mode for up to 255 players in 15 companies, a dedicated server mode and an in-game console for administration, IPv6 and IPv4 support for all communication of the client and server, new pathfinding algorithms that makes vehicles go where you want them to, different configurable models for acceleration of vehicles, and much more.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the changelog, awk is now used instead of trying to convince cpp to preprocess nfo files, CMD_CLEAR_ORDER_BACKUP is no longer suppressed by pause modes, the Wrong breakdown sound is no longer played for ships, integer overflow in the acceleration code is no longer causing either too low acceleration or too high acceleration, incorrectly saved order backups are now discarded when clients join, and the game no longer crashes when trying to show an error about vehicle in a NewGRF and the NewGRF was not loaded at all.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the Slovak language no longer uses space as group separator in numbers, the parameter bound checks are now tighter on GSCargoMonitor functions, the days in dates are not represented by ordinal numbers in all languages, and the incorrect usage of string commands in the base language has been fixed.
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the [changelog][1] for a complete list of updates and fixes.
|
||||
|
||||
Download OpenTTD 1.4.2:
|
||||
|
||||
- [http://www.openttd.org/en/download-stable][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Transport-Tycoon-Deluxe-Remake-OpenTTD-1-4-2-Is-an-Almost-Perfect-Sim-455715.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://ftp.snt.utwente.nl/pub/games/openttd/binaries/releases/1.4.2/changelog.txt
|
||||
[2]:http://www.openttd.org/en/download-stable
|
||||
@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[sailing]
|
||||
Munich Council: LiMux Demise Has Been Greatly Exaggerated
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
LiMux – Munich City Council’s Official OS
|
||||
|
||||
A Munich city council spokesman has attempted to clarify the reasons behind its [plan to re-examine the role of open-source][1] software in local government IT systems.
|
||||
|
||||
The response comes after numerous German media outlets revealed that the city’s incoming mayor has asked for a report into the use of LiMux, the open-source Linux distribution used by more than 80% of municipalities.
|
||||
|
||||
Reports quoted an unnamed city official, who claimed employees were ‘suffering’ from having to use open-source software. Others called it an ‘expensive failure’, with the deputy mayor, Josef Schmid, saying the move was ‘driven by ideology’, not financial prudence.
|
||||
|
||||
With Munich often viewed as the poster child for large Linux migrations, news of the potential renege quickly went viral. Now council spokesman Stefan Hauf has attempted to bring clarity to the situation.
|
||||
|
||||
### ‘Plans for the future’ ###
|
||||
|
||||
Hauf confirms that the city’s new mayor has requested a review of the city’s IT systems, including its choice of operating systems. But the report is not, as implied in earlier reports, solely tasked with deciding whether to return to using Microsoft Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
**“It’s about the organisation, the costs, performance and the usability and satisfaction of the users,”** [Techrepublic][2] quote him as saying.
|
||||
|
||||
**“[It's about gathering the] facts so we can decide and make a proposal for the city council how to proceed in future.”**
|
||||
|
||||
Hauf also confirms that council staff have, and do, complain about LiMux, but that the majority of issues stem from compatibility issues in OpenOffice, something a potential switch to LibreOffice could solve.
|
||||
|
||||
So is Munich about to switch back to Windows? As we said in our original coverage: it’s just too early to say, but it’s not being ruled out.
|
||||
|
||||
No final date for the report’s recommendations is yet set, and any binding decision on Munich’s IT infrastructure will need to be made by its elected members, the majority of whom are said to ‘support’ the LiMux initiative.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/08/munich-council-say-talk-limux-demise-greatly-exaggerated
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/08/munich-city-linux-switching-back-windows
|
||||
[2]:http://www.techrepublic.com/article/no-munich-isnt-about-to-ditch-free-software-and-move-back-to-windows/
|
||||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Red Hat Shake-up, Desktop Users, and Outta Time
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Our top story tonight is the seemingly sudden resignation of Red Hat CTO Brian Stevens. In other news, John C. Dvorak says "Linux has run out of time" and Infoworld.com says there may be problems with Red Hat Enterprise 7. OpenSource.com has a couple of interesting interviews and Nick Heath has five big names that use Linux on the desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
**In a late afternoon** [press release][1], Red Hat announced the resignation of long-time CTO Brian Stevens. Paul Cormier will be handling CTO duties until Stevens' replacement is named. No reason for the sudden resignation was given although CEO Whitehurst said, "We want to thank Brian for his years of service and numerous contributions to Red Hat’s business. We wish him well in his future endeavors." However, Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols says some rumors are flying. One says friction between Stevens and Cormier caused the resignation and others say Stevens had higher ambitions than Red Hat could provide. He'd been with Red Hat since 2001 and had been CTO at Mission Critical Linux before that [according to Vaughan-Nichols][2] who also said Stevens' Red Hat page was gone within seconds of the announcement.
|
||||
|
||||
**Speaking of Red Hat**, InfoWorld.com has a review of RHEL 7 available to the general public today. Reviewer Paul Venezia runs down the new features, but soon mentions systemd as one of the many new features "certain to cause consternation." After offering his opinion on several other key features and even throwing in a tip or two, [Venezia concludes][3], "RHEL 7 is a fairly significant departure from the expected full-revision release from Red Hat. This is not merely a reskinning of the previous release with updated packages, a more modern kernel, and some new toolkits and widgets. This is a very different release than RHEL 6 in any form, mostly due to the move to Systemd."
|
||||
|
||||
**Our own Sam Dean** [today said][4] that Linux doesn't need to own the desktop because of its success in many other key areas. While that may be true, Nick Heath today listed "five big names that use Linux on the desktop." He said besides Munich, there's Google for one and they even have their own Ubuntu derivative. He lists a couple of US government agencies and then mentions CERN and others. See that [full story][5] for more.
|
||||
|
||||
Despite that feel-good report, John C. Dvorak said he's tired of waiting for someone to develop that one "killer app" that would bring in the masses or satisfy his needs. [He says][6] he has to make podcasts and "photographic art" and he just can't do that with Linux. Our native applications "do not cut it in the end."
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/red-hat-shake-up-desktop-users-and-outta-time
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Susan Linton][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ostatic.com/member/susan-linton
|
||||
[1]:http://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20140827006134/en/Brian-Stevens-Step-CTO-Red-Hat#.U_5AlvFdX0p
|
||||
[2]:http://www.zdnet.com/red-hat-chief-technology-officer-resigns-7000033058/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.infoworld.com/d/data-center/review-rhel-7-lands-jolt-249219
|
||||
[4]:http://ostatic.com/blog/linux-doesnt-need-to-own-the-desktop
|
||||
[5]:http://www.techrepublic.com/article/five-big-names-that-use-linux-on-the-desktop/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2465125,00.asp
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
LibreOffice 4.3.1 Has More than 100 Fixes and DOCX Embedded Objects Support
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
LibreOffice selection menu
|
||||
|
||||
**The Document Foundation announces that the stable version of LibreOffice 4.3.1 has been released and is now available for download.**
|
||||
|
||||
The developers from The Document Foundation have released a new update for the 4.3 branch of LibreOffice and they have implemented quite a few fixes and other various changes. The development cycle for this latest update has been rather short and the devs managed to repair most of the issues that have been found.
|
||||
|
||||
LibreOffice 4.3.1 is just maintenance release, which means that the focus has been about the bugs found so far. Don't expect to find anything extraordinary, but you should upgrade the software nonetheless.
|
||||
|
||||
"The Document Foundation announces LibreOffice 4.3.1, the first minor release of LibreOffice 4.3 'fresh' family, with over 100 fixes (including patches for two CVEs, backported to LibreOffice 4.2.6-secfix, which is also available for download now)."
|
||||
|
||||
"All LibreOffice users are invited to update their installation as soon as possible to avoid security issues. This includes users who are running LibreOffice 4.2.6 as originally released on August, 5th 2014. LibreOffice 4.3.1 and LibreOffice 4.2.6 will be shown on stage at the LibreOffice Conference in Bern, from September 3 to September 5, with a large number of sessions about development, community, marketing and migrations," reads the announcement made by The Linux Foundation.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the changelog, editing the text search with expanded fields is now working properly, the static value array for OOXML chart is now handled correctly, bullets now have the color as the following text by default, ww8import no longer creates a pagedesc if a continuous section changes margins, the 0 font height is now handled just like outdev, it's now possible to import OLE objects in the header with background wrapping, the XLSX export of revisions has been fixed in order to get it to work in Excel, and borders around data labels are now supported.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the table style for lastRow is now correctly applied, the rulers now have app-background by default, the graphics are now swapped in on DrawingML::WriteImage, the redundant 'Preferences' label has been removed in order to save some space, page breaks in tables are now ignored during the RTF import, some of the style hierarchy has been reworked, Data Statistics no longer crashes with any entry, DOCX embedded objects are now supported, and numerous other improvements have been made.
|
||||
|
||||
More details about this release can be found in the official [announcement][1].
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download LibreOffice 4.3.1 for Linux][2]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/LibreOffice-4-3-1-Has-More-Than-100-Fixes-and-DOCX-Embedded-Objects-Support-456916.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://blog.documentfoundation.org/2014/08/28/libreoffice-4-3-1-fresh-announced/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.libreoffice.org/download/libreoffice-fresh/
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Jelly Conky Adds Simple, Stylish Stats To Your Linux Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**I treat Conky setups a bit like wallpapers: I’ll find one I love, only to change it the next week because I’m bored of it and want a change.**
|
||||
|
||||
Part of the impatience is fuelled by the ever-growing catalog of designs available. One of my most recent favourites is Jelly Conky.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Jelly Conky sports the minimal design many of the Conky’s we’ve highlighted recently have followed. It’s not trying to be a kitchen sink. It won’t win favour with those who need constant at-a-glance data on their HDD temperatures and IP addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
It comes with three distinct modes that can all add personality to an otherwise static background image:
|
||||
|
||||
- Clock
|
||||
- Clock plus date
|
||||
- Clock plus date and weather
|
||||
|
||||
Some people don’t understand the point of having a duplicate clock on show on the desktop. That’s understandable. For me, it’s more about form than function (though, personally, I find Conky clocks easier to see than the minuscule digits nestled in my upper panel).
|
||||
|
||||
Chances are if you have a home screen widget on Android with the time, you won’t mind having one on your desktop, either!
|
||||
|
||||
You can download Jelly Conky from the link below. The .zip archive contains a readme with instructions on how to install. For a guided walkthrough, [revisit one of our previous articles][1].
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Jelly Conky on Deviant Art][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/jelly-conky-for-linux-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/conky-circle-theme-nod-lg-quick-cover
|
||||
[2]:http://zagortenay333.deviantart.com/art/Jelly-Conky-442559003
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
Oracle Linux 5.11 Features Updated Unbreakable Linux Kernel
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> A lot of packages have been updated in this release
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This is the last release for this branch
|
||||
|
||||
> **Oracle has announced that Oracle Linux Release 5.11 has been made available for download, but this is the enterprise version, so users will have to register in order to get the download.**
|
||||
|
||||
The new Oracle Linux update is probably the last one in the series. This operating system is based on Red Hat and the company has just pushed out the last update for the RHEL 5x branch, which means that this is the end of the line for the Oracle version as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Oracle Linux also comes with a series of features that make it very interesting, like zero-downtime kernel updates with the help of a tool called Ksplice that was originally developed for OpenSUSE, inclusion of the Oracle Database and Oracle Applications, and it's used in all x86-based Oracle Engineered Systems.
|
||||
|
||||
### What's so special about Oracle Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Despite the fact that Oracle Linux is based on Red Hat, its developers have actually made a list of reasons why you shouldn't use RHEL. There are quite a lot of them, but the main one is that anyone can download Oracle Linux (after registering) and RHEL is actually off limits for non-paying members.
|
||||
|
||||
"Providing advanced scalability and reliability for enterprise applications and systems, Oracle Linux delivers extreme performance and is used in all x86-based Oracle Engineered Systems. Oracle Linux is free to use, free to distribute, free to update, and easy to download. It is the only Linux distribution with production support for zero-downtime kernel updates with Oracle Ksplice, allowing customers the ability to apply patches for security and other updates without a reboot, as well as providing diagnostic features for debugging kernel issues on production systems," say the developers on their website.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most interesting features for Oracle Linux and unique for this distribution is its unbreakable kernel. This is the actual name used by the developers. It's based on an older Linux kernel from the 3.0.36 branch. Users also have access to a Red Hat-compatible Kernel (kernel-2.6.18-398.el5), which is provided by default in the distro.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel available in the Oracle Linux Release 5.11 features a ton of drivers for hardware and devices, but this latest update brought even better support.
|
||||
|
||||
You can check the comprehensive [release notes][1] for Oracle Linux 5.11, which will probably take you the rest of the day.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also download Oracle Linux 5.11:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Oracle Enterprise Linux 6.5 (ISO) 64-bit][2]
|
||||
- [Oracle Enterprise Linux 6.5 (ISO) 32-bit][3]
|
||||
- [Oracle Enterprise Linux 7.0 (ISO) 64-bit][4]
|
||||
- [Oracle Enterprise Linux 5.11 (ISO) 64-bit][5]
|
||||
- [Oracle Enterprise Linux 5.11 (ISO) 32-bit][6]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Oracle-Linux-5-11-Features-Updated-Unbreakable-Linux-Kernel-460129.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:https://oss.oracle.com/ol5/docs/RELEASE-NOTES-U11-en.html#Kernel_and_Driver_Updates
|
||||
[2]:http://mirrors.dotsrc.org/oracle-linux/OL6/U5/i386/OracleLinux-R6-U5-Server-i386-dvd.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://mirrors.dotsrc.org/oracle-linux/OL6/U5/x86_64/OracleLinux-R6-U5-Server-x86_64-dvd.iso
|
||||
[4]:https://edelivery.oracle.com/linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://ftp5.gwdg.de/pub/linux/oracle/EL5/U11/x86_64/Enterprise-R5-U11-Server-x86_64-dvd.iso
|
||||
[6]:http://ftp5.gwdg.de/pub/linux/oracle/EL5/U11/i386/Enterprise-R5-U11-Server-i386-dvd.iso
|
||||
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Red Hat's CEO Sees Open Source Cloud Domination
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Red Hat CEO Jim Whitehurst sees the business opportunity of a generation in what he calls a computing paradigm shift from client server to cloud architectures. “In those paradigm shifts, generally new winners emerge,” says Whitehurst and he intends to make sure Red Hat is one of those winners. His logic is sound and simple: disruptive technologies like the cloud that arise every couple decades level the playing field between large, established firms and smaller, innovative challengers since everyone, from corporate behemoth to a couple guys in a garage, starts from the same spot and must play by the same unfamiliar and changeable rules. With the cloud “there’s less of an installed based and an opportunity for new winners to be chosen,” Whitehurst adds. His mission is “to see that open source is the default choice for next generation architecture” and that Red Hat is the preferred choice, particularly for enterprise IT, of open source providers.
|
||||
|
||||
The case for open source dominating the cloud rests on the fact that it’s already the foundation for many popular cloud services and enterprise applications. Whitehurst aptly notes that outside of Microsoft Azure, the underlying infrastructure of all the major public cloud services is built upon open source software. Furthermore, software like Linux, Apache, MySQL, WordPress and many others are already widely used and trusted by most enterprises. “In many cases [open source] already is the default choice for next generation architectures, but it hasn’t fully driven itself through the traditional enterprise data center,” he says. Cloud software is the next and most important software category up for open source disruption.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Yet open source is still saddled with a reputation for widely variable software quality and support, something the recent OpenSSL Heartbleed bug only reinforced. However Whitehurst contends that strong enterprise adoption of Red Hat’s Linux distribution and it’s training and skills certification programs lends credibility to a similar plan for the cloud: [Red Hat’s Cloud Partner Program][1]. He believes such insurance policies alleviate enterprise IT’s fears of adopting open source software for both internal, private clouds and external public cloud services. Red Hat wants its imprimatur to be the Good Housekeeping seal of approval for open source in general and cloud software in specific, namely IT’s assurance that their applications will work and the service is trustworthy and reliable.
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat’s strategy to make open source clouds safe for the enterprise is mirrors that used to break into the market for enterprise server software. There, “Job one for Red Hat is making sure our operating system and layers above that work well on anyone’s infrastructure underneath,” says Whitehurst. Red Hat is applying this same model of polishing, integrating and supporting open source software to cloud stacks. “One of the most important parts about cloud, public, private or hybrid, is a sense that you can confidently run your applications,” says Whitehurst and he believes Red Hat’s track record on Linux and other open source products will carry over to make Red Hat “the enterprise choice” for cloud architectures.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cloud isn’t just virtualization 2.0 ###
|
||||
|
||||
One of the conundrums for OpenStack advocates like Whitehurst is the entrenchment of Microsoft and VMware in the enterprise market. Although virtual servers are a prerequisite for clouds, they’re sufficient. Countering the notion that enterprise clouds are just a natural extension of virtualized servers and storage, Whitehurst argues that by setting new rules for infrastructure and application design, cloud infrastructure is more than just the natural evolution of server virtualization.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Whitehurst draws an important distinction between traditional client-server and cloud-optimized applications. “One of the big questions will be how much of this [cloud adoption] is moving traditional Windows workloads, which frankly were written as stateful apps in the first place. [Instead] are we talking about a new generation of applications that are actually built with elasticity and scalability in mind.” Whitehurst clearly believes cloud infrastructure is much more appropriate for the latter and that in such Greenfield scenarios, OpenStack and other open source software have established themselves as the preferred platform. Contrasting OpenStack, based on the Linux KVM hypervisor and VMware or Microsoft using their proprietary virtual machine platforms, Whitehurst says, “Longer term, nobody really cares what the hypervisor is, you just expect it to work and bluntly, as long as Red Hat supports you on it, why do you have to care,” adding “more and more, you’ll see the hypervisor mattering less and less.” Of course, VMware and Microsoft probably agree, both having moved their energies to building more sophisticated management platforms and making the hypervisor a baseline feature.
|
||||
|
||||
But in Whitehurst’s view of the world, traditional virtualization platforms like VMware or Microsoft Hyper-V are legacy infrastructure designed for yesterday’s client-server software, not the sort of distributed, rapidly relocatable, elastically scalable applications that define the era of big data, SaaS and social software. “I’m not sure what good you get out of putting Exchange on a cloud,” he quips. Instead, he says this new generation of cloud-optimized applications are the sweet spot for OpenStack. According to Whitehurst, “If you look at where most new applications are getting built, and therefore where so much of the innovation around languages, frameworks and management paradigms are happening, it’s around an open infrastructure.” But there’s obviously some selection bias in Whitehurst’s account, as he lives in an open source world where it’s easy to be unaware, overlook or ignore the innovation happening on proprietary cloud platforms like Azure, AWS and vCloud.
|
||||
|
||||
In sum, Whitehurst hopes and expects OpenStack to do to VMware what Linux did to Windows: to become the first choice of cloud-savvy startups and if not the default choice, at least an accepted and respectable alternative within the enterprise. In my next column I’ll explain that even for an open source champion like Whitehurst, OpenStack versus VMware vCloud or Microsoft Azure isn’t an either/or choice and how he sees the fundamental notion of cloud computing as based on virtual machines as an design model likely to change.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.forbes.com/sites/kurtmarko/2014/06/08/red-hat-ceo-open-source-clouds/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.redhat.com/partners/become/cloud/
|
||||
@ -1,27 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux hiring frenzy: Why open source devs are being bombarded with offers to jump ship
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Summary: Figures from the Linux Foundation suggest skills shortages across disciplines and throughout Europe.
|
||||
|
||||
Nine out of ten (87 percent) of hiring managers in Europe have "hiring Linux talent" on their list of priorities and almost half (48 percent) say they are looking to hire people with Linux skills within the next six months.
|
||||
|
||||
But while they either need or want to hire more people with Linux skills, the data from the Linux Foundation suggests that this is easier said than done. Almost all — 93 percent — of the managers surveyed said they were having difficulty finding IT professionals with the Linux skills required and a quarter (25 percent) said they have "delayed projects as a result".
|
||||
|
||||
All of this makes it a good time to be a Linux expert.
|
||||
|
||||
Seven out of 10 Europe-based Linux professionals have received calls where they were pitched new positions in the past six months, and a third said they had received more calls than in the previous six months. One in three are looking to move anyway, and over half of them said it would be fairly or very easy. Salary is the biggest reason to move jobs, followed by work-life balance and the chance to gain additional skills.
|
||||
|
||||
Employers are trying harder to keep hold of staff too: In the past six months, 29 percent of Linux professionals say they have been offered a higher salary from their current employers, while a quarter said they’ve been offered a flexible work schedule and one in five have been extended additional training opportunities or certification.
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux Foundation, a non-profit organisation which supports the growth of Linux, and Dice Holdings, which provides career sites for technology professionals, produced the research which covers Europe and the US.
|
||||
|
||||
In terms of the specific skills organisations are looking for people with the developer (69 percent) and enterprise management (51 percent) skills. These are followed by 32 percent of respondents who are looking for people with a combination of development and operations skills (DevOps), and 19 percent who are in management/IT management.
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux Job Report has been produced for the last three years by the Linux Foundation and Dice but this is the first time that a specific report on European skills has been separated out of the worldwide report. Some 893 Linux professionals responded to the survey across Europe.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.zdnet.com/linux-hiring-frenzy-why-open-source-devs-are-being-bombarded-with-offers-to-jump-ship-7000030418/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
|
||||
The Companies That Support Linux: Rackspace
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[][1]
|
||||
|
||||
[Rackspace][1] has lately been in the news for its stock market gains and a [potential acquisition][2]. But over the past 16 years the company has become well known, first as a web hosting provider built on Linux and open source, and later as a [pioneer of the open source cloud][3] and founder of the OpenStack cloud platform.
|
||||
|
||||
In May, Rackspace became a [Xen Project][4] member and was one of [three companies to join the Linux Foundation][5] as a corporate member, along with CoreOS and Cumulus Networks.
|
||||
|
||||
“Many of the applications and infrastructure that we need to run for internal use or for customers run best on Linux,” said Paul Voccio, Senior Director of Software Development at Rackspace, via email. “This includes all the popular language frameworks and open virtualization platforms such as Xen, LXC, KVM, Docker, etc.”
|
||||
|
||||
In this Q&A, Voccio discusses the role of Rackspace in the cloud, how the company uses Linux, why they joined the Linux Foundation, as well as current trends and future technologies in the data center.
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux.com: What is Rackspace? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Paul Voccio: Rackspace is the managed cloud specialist and founder of OpenStack, the open-source operating system for the cloud. Hundreds of thousands of customers look to Rackspace to deliver the best-fit hybrid cloud solutions for their IT needs, leveraging a product and services portfolio that allows workloads to run where they perform best – whether on the public cloud, private cloud, dedicated servers, or a combination of platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
As a managed cloud pioneer, we give our customers 24x7 access to cloud engineers for everything from planning and architecting to building and operating clouds through our award-winning Fanatical Support®. We help customers successfully architect, deploy and run their most critical applications. Or, more plainly put, we’re cloud specialists so you don’t have to be. We are headquartered in San Antonio, Texas, and operate a global support and engineering organization with data centers on four continents.
|
||||
|
||||
### How and why do you use Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Rackspace uses Linux because it provides a stable and flexible platform for our customers' workloads. Our customers trust us to support their mission-critical applications and we need reliable infrastructure – including software and hardware – to meet their expectations. If you look under the hood in our dedicated environments or in our expansive cloud infrastructure, you'll find Linux running there.
|
||||
|
||||
Many of the applications and infrastructure that we need to run for internal use or for customers run best on Linux. This includes all the popular language frameworks and open virtualization platforms such as Xen, LXC, KVM, Docker, etc. Running combinations of these platforms give us the stability and performance we demand for the Rackspace Cloud. Our Cloud Servers product runs OpenStack services that manage tens of thousands of hypervisors – all running Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Using Linux also allows us to tap into a community of experts to solve problems. When we have an issue, we're comfortable asking questions. When we have a solution, we enjoy sharing it with the community. At Rackspace, we understand how to work and contribute in an open community and Linux has many opportunities to build relationships with other groups that have similar goals.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why did you join the Linux Foundation? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Joining the Linux Foundation allows us to show our support and engage the Linux community in new ways. We've learned plenty from running Linux in highly demanding environments at a large scale and we're eager to share those experiences. Other members of the community have probably run into different challenges than we have and this gives us a greater opportunity to learn from them as well.
|
||||
|
||||
### What interesting or innovative trends are you witnessing in the data center and what role does Linux play in them? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Virtualization and automation have changed how companies deploy hardware and software. Linux gives us several virtualization options and these allow us to automate more of our infrastructure deployments and maintenance tasks. Automation and configuration management frameworks allow us to reduce our costs, improve our testing capabilities, and bring products to market faster. The majority of these open source automation frameworks run best on Linux servers.
|
||||
|
||||
### How is Rackspace participating in that innovation? ###
|
||||
|
||||
We leverage several open-source Linux-based tools and projects to deliver great customer outcomes. One of our largest efforts in this area is with OpenStack. It's the software that runs our public and private clouds and we're actively engaged with the community to improve it. We're using Linux to find new ways to scale our large virtualization platform and deliver infrastructure to customers quickly.
|
||||
|
||||
The open-source nature of Linux inspires us to share the majority of these discoveries with the community. Our customers can improve OpenStack and those improvements will eventually make it into our product offering. We make contributions to a countless number of open source projects either as a company or as individual Rackers (our employees are called "Rackers") and many of these projects are designed to run on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### What other future technologies or industries do you think Linux and open source will increasingly become important in and why? ###
|
||||
|
||||
The move to software-defined infrastructure is a big shift. Customers already have access to virtualization platforms like Xen that allow them to define their infrastructure with software. Software-defined networking is quickly becoming more mature and scalable. However, customers want the ability to have a software defined datacenter at their fingertips. This may involve physical servers, virtual servers, and virtual networks that need high performance with flexible configurations. Many of the current technologies are designed to run on Linux due to technology already available in the kernel or userland frameworks provided by the community.
|
||||
|
||||
### Are you hiring? ###
|
||||
|
||||
From hacking on kernels to supporting thousands of virtual machines – we are always looking for talented admins, developers and engineers. You can find more information at Rackertalent.com.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/200-libby-clark/775890-the-companies-that-support-linux-rackspace/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.rackspace.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-05-15/rackspace-hires-morgan-stanley-to-evaluate-options.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.informationweek.com/cloud/infrastructure-as-a-service/9-more-cloud-computing-pioneers/d/d-id/1109120
|
||||
[4]:http://www.xenproject.org/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/news-media/announcements/2014/05/new-linux-foundation-members-advance-massively-scalable-secure
|
||||
@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Fire Phone Dynamic Perspective tracks eyes for 3D UI
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3D on phones is back, and it's Amazon giving it a try this time with Dynamic Perspective on the new [Fire Phone][1]. Eschewing a "true" 3D display as we've seen before, the Fire Phone's system instead uses four front-facing cameras to track the user's eyes, and adjusts the on-screen UI so that the various layers shift around to give the impression of 3D.
|
||||
|
||||
A combination of physically tilting the phone and moving your head as you hold it can be used to navigate through the interface and apps. So, tilting the Fire Phone can scroll through the browser, rather than having to swipe around with a fingertip.
|
||||
|
||||
youtube视频链接地址:[http://www.youtube.com/embed/iB75HJe8eiI][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, with a carousel of items in Amazon's store on the phone, tilting the handset left and right pans through the products.
|
||||
|
||||
youtube视频链接地址:[http://www.youtube.com/embed/lwj0hlE8CJc][3]
|
||||
|
||||
In ebooks, the Kindle app can scroll through according to how you're holding it. The settings can be switched between adjusting speed depending on how extreme the tilt angle is, or locking it to a fixed rate if you'd rather have things be predictable.
|
||||
|
||||
### This is the Amazon Fire Phone ###
|
||||
|
||||
Maps, too, get Dynamic Perspective support. Moving the Fire Phone around can show what's "hiding" behind 3D buildings or on different layers. Tilting can also be used to open up menus, in games for motion control, and even to navigate between the now-playing and lyrics UIs in the Prime Music app.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
All that 3D didn't come easy, though. Based on the fact that every face is different, with variations in hair color, shape, whether they wear glasses, and other factors, Amazon had to put Dynamic Perspective through some serious testing.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the companies labs, that involved a somewhat nightmarish rubber head on a stick, but then Amazon expanded that to use real-world data from thousands of photos of people. The use of four cameras means that, no matter what may be blocking the screen, the Fire Phone should be able to spot the user properly.
|
||||
|
||||
youtube视频链接地址:[http://www.youtube.com/embed/X-wPOq27iXk][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Whether it'll all work as Bezos says, or be something owners quickly turn off, remains to be seen. We'll know more when we spend some hands-on time with the Fire Phone soon.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.slashgear.com/fire-phone-dynamic-perspective-tracks-eyes-for-3d-ui-18334229/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.slashgear.com/tags/fire-phone
|
||||
[2]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/iB75HJe8eiI
|
||||
[3]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/lwj0hlE8CJc
|
||||
[4]:http://www.slashgear.com/this-is-the-amazon-fire-phone-18334195/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/X-wPOq27iXk
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
$2400 Valued Introduction To Linux Course Is Available For Free On edX
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Probably you have already heard it. [Linux Foundation][1] has tied up with [edX][2] (a major online learning platform founded by MIT and Harvard University) to provide its Introduction to Linux course, which usually costs $2400, for free.
|
||||
|
||||
edX has over 200 courses from over 50 elite universities, corporations and organizations worldwide. Over 2.5 million users attend these online courses across the globe.
|
||||
|
||||
**Introduction to Linux course is starting from 1st August**. There are three ways one can take this course (or most other edX courses):
|
||||
|
||||
- **Audit the course**: Simple register for **free** and get access to study material. Participate in course as per your own pace. There is no compulsion or penalty if you cannot complete the course.
|
||||
- **Honor code certificate**: It certifies that you have successfully completed the course, however, it doesn’t verify your identity. This too is for free.
|
||||
- **Verified certificate of achievement**: This certificates validates your identity and costs $250 for **Introduction to Linux** course.
|
||||
|
||||
Introduction to Linux requires a working knowledge of computers and common software. Program aims to provide experienced computer users, who may or may not have previous Linux experience, a good working knowledge of Linux, from both a graphical and command line perspective. It consists a course work of 40 to 60 hours and is designed by Dr. Jerry Cooperstein, who manages training content at Linux Foundation.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are planning to attend Introduction to Linux, it is advised to have Linux installed on your computer beforehand. Linux Foundation has [prepared a guide to set up the computer][3] to help users out.
|
||||
|
||||
What are you waiting for? If you ever wanted to learn Linux, this is the time and best of all, it’s FREE! Sign up to the course with the link below:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Introduction to Linux course at edX][4]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/introduction-linux-free-edx/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.edx.org/
|
||||
[3]:https://training.linuxfoundation.org/images/pdfs/Preparing_Your_Computer_for_LFS101x.pdf
|
||||
[4]:https://www.edx.org/course/linuxfoundationx/linuxfoundationx-lfs101x-introduction-1621#.U9gJ5nWSyb8
|
||||
@ -1,28 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Microsoft’s Raspberry Pi Will Cost $300
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I presume that you have heard of [Raspberry Pi][1]. A $35 microcomputer that has revolutionized the low cost computing and has cult following among hardware hobbyist and do-it-yourself enthusiasts. Several other followed in the footsteps of Raspberry Pi to provide low cost micro computers, [Arduino][2] is one of the successful examples.
|
||||
|
||||
Microsoft has decided to enter the world of “System on Chip” and to come up with its “own Raspberry Pi”. Teamed up with Intel and [CircuitCo][3], [Microsoft will be launching a micro computer named “Sharks Cove“][4].
|
||||
|
||||
Sharks Cove boasts of Intel Atom Z3735G, a quad-core chip with speeds up to 1.83GHz, 1GB of RAM, 16GB of flash storage and a MicroSD slot among many other things. You can read the full specifications [here][5]. The main aim of Shark Cove is to provide a platform to develop hardware and drivers for Windows and Android.
|
||||
|
||||
Everything sounds fine till it comes to price. Sharks Cove will cost $299 with a Windows 8.1 license. While Arduino costs around $55 and Raspberry Pi $35, I don’t think there will be many buyers for such a high price in a domain which is dominated by low cost Linux based devices. What do you think?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/microsofts-raspberry-pi/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.raspberrypi.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.arduino.cc/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.circuitco.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://blogs.msdn.com/b/windows_hardware_and_driver_developer_blog/archive/2014/07/26/the-sharks-cove-is-now-available-for-pre-order.aspx
|
||||
[5]:http://www.sharkscove.org/docs/
|
||||
@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Nostalgic Gaming On Linux With Good Old Games
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Thanks to the recent Linux support provided by DRM-free classic games provider, GOG.com, getting that nostalgic kick on Linux has never been easier. In this article I'll also detail a few of my favourite classic games that are now available to play in Linux.**
|
||||
|
||||
It's not all nostalgia, though. Some of the classic games you might think of are genuinely classic, amazing games no matter their age. Others, you might need to imagine you're back in, say, 1995 and look at the game from that point of view to appreciate how good it must have seemed at that time. Whatever the case though, there's no shortage of these old games out there to enjoy and thankfully it's recently gotten even easier with [GOG.com][1] recently announcing Linux support.
|
||||
|
||||
A lot of these old classic games actually run in [DOSBox][2], so a seasoned Linux gamer who has experience with such games may bring up the point that you could play a lot of these games provided by services such as GOG.com for years already, well before that recent announcement. Which is correct, I've done the same thing myself, but it does involve a bit of fiddling with files, so at the very least we now have a "turn-key" solution even with the DOSBox powered games - you download them, you launch them, they should just work. If you just want to purchase a game and play it right away, that's no bad thing.
|
||||
|
||||
Then there's the non-DOS games. A lot of old Windows 95/98 games do often work fine in WINE, but not always, or perhaps need workarounds to be manually applied or even a special version of WINE itself. Some old games just won't work at all no matter what you try, even on modern versions of Windows itself! So again, having an alternative available that is designed to work out-of-the-box (and DRM-free, no less) is a nice thing.
|
||||
|
||||
GOG.com initially provided 50 Linux compatible games on their penguin-friendly launch, but that number is and will keep growing. In coming months they say they hope to reach 100 games, and who knows how many thereafter, but it should grow to be a fairly considerable library.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few of my favourites so far, that are available right now:
|
||||
|
||||
### Rise Of The Triads Dark War (1994) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you crave some 90's style shoot-em-up action where you get to blow the hell out of, well, everything and everyone, Rise Of The Triads (ROTT) is one of the best choices and a favourite to many.
|
||||
|
||||
If you know these kinds of shooters, you probably know what to expect. There is a storyline, but really it's about blowing everything up and/or riddling enemies full of bullet holes. As a member of an elite group of operatives you are sent to a remote island to stop a mad cult leader, where typically everything goes pear-shaped and you have to kill everything and successfully navigate levels to save the day and get out alive in the process.
|
||||
|
||||
True to the arcade-style shooter of this vintage, weapons are all about being big, high-tech and fun. You might be in an elite operations group, but you ain't stuck with peashooters and standard rifles - no there's duel pistols all the way to heat seeking missiles and the Flamewall cannon and many more. It's all about genuine fun and doesn't take itself too seriously.
|
||||
|
||||
*Verdict: A blast (literally)*
|
||||
|
||||
### Realms Of The Haunting (1996) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This one is actually fairly new to me and isn't a game I remember from years back. Which is my loss really, as I can imagine this game must have seemed pretty incredible all the way back in 1996.
|
||||
|
||||
Realms Of The Haunting is something of a first-person shooter/point-and-click adventure combination. The controls at first seem a bit strange because of this (keyboard to control movement and attack etc. Mouse to move the context indicator/cursor around the screen and interact with objects) but you soon get used to it. The storyline, although I have not experienced all of it yet myself, is apparently very good and certainly my impressions of it have been good. This is also one of those classic games that uses good old FMV (Full Motion Video) for cutscenes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Basically you play as a young man who receives a suitably vague letter from your recently deceased father about a strange deserted mansion and it's curious happenings inside. Naturally, said young man decides to visit the mansion and discovers his father's spirit being held captive by the forces of evil and then sets out to try free him. That sounds like a pretty standard storyline at first but the difference lays in the execution and how it progresses.
|
||||
|
||||
From the moment the main character picks up a lantern and gazes around the dark, creepy surroundings of the mansion, it actually reminds me a bit of Amnesia: The Dark Descent. Sure, the gameplay and amount of actual combat means the comparison somewhat ends after that, but ROTH does also have it's fair share of exploration and puzzles. Despite a very dated looking graphics engine (it is based on the DOOM engine after all!) it strikes me how much attention to detail the game creators managed to pack into the environment, which further adds to the atmosphere and immersion despite the constant pixel party happening on screen.
|
||||
|
||||
All in all, Realms Of The Haunting is a creepy but very intriguing old game that is very much worth checking out. And if you love games that feature old-school FMV, there is heaps on offer here too.
|
||||
|
||||
*Verdict: Ahead of it's time?*
|
||||
|
||||
### Sid Meier's Colonization (1994) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Think Civilization, but with a colonial twist. Instead of building a nation from a mound of dirt in the middle of nowhere, Colonization tasks you with controlling either the forces of England, France, Spain or The Netherlands as you set about managing expansion across the Atlantic for your nation of choice. The aim of the game, as far as winning goes, is to achieve independence from your mother country and defeat the angry Royal Expeditionary Force that comes your way.
|
||||
|
||||
If big chunky pixels, even in text, is something that hurts your eyes you may want to avoid this one but the simple old graphics belie the actual gameplay and depth available here. If you have experience with the more modern Sid Meier turn-based strategy games like the Civilization series, you may be surprised just how much familiar elements and gameplay there is in this old game.
|
||||
|
||||
It may appear ancient and a little clunky, but like most of the classic Sid Meier games, you can sink hours upon hours into this game. Which considering it's price nowadays, no more than a piece of cake and a coffee, is fantastic value that is hard to beat. Do try it.
|
||||
|
||||
*Verdict: Superb turn-based strategy, all the way from 1994*
|
||||
|
||||
### Sword Of The Samurai (1989) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This one is a little more obscure and may surprise. For me, and this will sound a little cliché given the Japanese theme and setting, but there is something rather Zen about Sword Of The Samurai. A product in the year 1989, the graphics are obviously simple and have a very limited colour palette. Yet, I think even today the graphics work for this particular game and add to its charm and, again, the Zen.
|
||||
|
||||
Describing SOTS is difficult though. It's sort of... a strategy, war, dating, stealth, melee, dueling, diplomacy, choose-your-own adventure Samurai sim.
|
||||
|
||||
Seriously.
|
||||
|
||||
Somehow this old game, which weighs in less than 20 megabytes, fits in an incredible amount of different gameplay (and surprisingly smart artificial intelligence) and approaches you can take to achieve your goal. The core goal is get a very important thing called Honor. In the world of feudal Japan, Honor is a big, big thing and you must get more Honor any way you can in order to achieve the goal of unifying Japan under your rule, as Shogun.
|
||||
|
||||
While you can of course be the "good guy" and do everything you think is right to get Honor, the game is inherently deep and clever enough to allow you to achieve Honor even with, shall we say, more underhanded tactics.
|
||||
|
||||
It's difficult to truly describe all the ways you can play this game but my advice is to simply do so - play it, let it wash over you and soak in the Japanese culture and atmosphere that the game exudes in a really classy way, without being over-the-top. And yes, the game can also be educational! You can't beat that.
|
||||
|
||||
*Verdict: An under-appreciated masterpiece*
|
||||
|
||||
### Get your game on ###
|
||||
|
||||
So there we have it, there's some of my favourites that I've been (re)playing recently, on my Fedora 20 system no less. Some of these games may be older than Linux (the kernel) itself, but thanks to the likes of GOG.com and especially emulators like DOSBox, you can still enjoy the classic titles you remember from years gone by.
|
||||
|
||||
What are some of your favourite classic games? Are you also playing them now in your favourite Linux distro? Let us know in the comments!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thelinuxrain.com/articles/nostalgic-gaming-on-linux-with-good-old-games
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Andrew Powell
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://gog.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.dosbox.com/
|
||||
@ -1,132 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Five Awesome GOG.com Linux Games Everyone Should Play Once
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
GOG AKA ILU TUX NAO
|
||||
|
||||
**Ardent Linux gamers will have seen last week as a good one, as rising game distribution service [GOG.com brought a batch of more than 50 classic PC and indie titles to the platform][1], many for the very first time.**
|
||||
|
||||
Against the 775 DRM-free offerings offered to Windows users, not to mention the 600 strong Linux catalog on Steam, it might not sound like much. But the company says this is only the first wave and that another 50 games are set to land later in the year.
|
||||
|
||||
Last week [we asked][2] our Facebook fans which five games being sold by GOG they consider ‘must have’ titles.
|
||||
|
||||
After pruning the titles often found warming the shelves of the Humble Bundle (*e.g., Uplink: Hacker Elite, Darwinia, Don’t Starve and Anomaly Warzone Earth*), and throwing in a free title for good measure, we came up with the following list.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s not comprehensive, it’s not definitive and it’s certainly not going to be the five you’d pick. But for those either too young to have experienced some of these games for the first time, or old enough to level up nostalgia, it’s a great jumping in point.
|
||||
|
||||
Because we know it matters to some of you, we’ve listed the ‘port’ type for each entry, so you can avoid Wine or DOSBox where needed.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally (though it really should go without saying) if you’re looking for full HD immersive 3D worlds with GPU melting graphics requirements, this is not the list for you.
|
||||
|
||||
Now to hark back to rainy days spent cooped up inside, eyes firmly fixed on a CRT monitor…
|
||||
|
||||
### FlatOut ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 2005. **Genre**: Racing. **Port**: Wine. **Price**: $5.99 (inc. extras).
|
||||
|
||||
Unbuckle up and prepare for one bad-ass and throughly bumpy ride.
|
||||
|
||||
Trying to condense why FlatOut is a classic demolition rally game into just a few short sentences is traumatic. Almost as traumatic as being a driver in it must be.
|
||||
|
||||
Its premise — carnage, destruction, more carnage — reads fairly standard these days. Virtually every racing game (at least those worth their tread) implements an element of off-road mayhem. But FlatOut was one of the first, and even today remains one of the best.
|
||||
|
||||
With 36 course littered with more than 3000 items to crash and smash, plus 16 upgradeable vehicles, each made up of 40 “deformable pieces” for ultimate on-screen obliteration, FlatOut is flat out one of the best raucous racing games available on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
*Also check out Flat Out 2, released in 2011 and costing $9.99.*
|
||||
|
||||
- [Buy “FlatOut” on GOG][3]
|
||||
|
||||
### Duke Nukem 3D: Atomic Edition ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 1995. **Genre**: First-Person Shooter. **Port**: DOSBox. **Price**: $5.99 (inc. extras).
|
||||
|
||||
Politically incorrect, full of female objectification, and featuring more cheesy one-liners than the script of a straight-to-VHS Jean-Claude Van Damme action film. Yep, it’s Duke Nukem.
|
||||
|
||||
But c’mon; no list of retro PC classics would be complete without a least one Duke Nukem entry, right? They are bona fide classics. Along with Doom and Quake, it kickstarted the gory corridor crawling shooter genre.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of its strengths are in the pastiche; it is camp, cheesy and kaleidoscopically brash, and takes itself about as seriously as a Sega MegaCD video cutscene from Night Trap.
|
||||
|
||||
The environments are varied and rich. The gameplay mechanics easy to get to grips with. And while the less than subtle humour laced throughout may rile the easily offended, those of a certain age won’t be able to resist smirking at the pop-culture satire.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Buy “Duke Nukem: Atomic Edition” on GOG][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### The Last Federation ###
|
||||
|
||||
Youtobe 视频地址:
|
||||
https://www.youtube.com/embed/5RKXWpyf1i4?feature=oembed
|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 2014. **Genre**: Strategy. **Port**: Native. Price: $19.99.
|
||||
|
||||
The Last Federation is the most expensive title on this list and also the most modern, having debuted this year.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s a turn-based tactical combat set in space that burdens you with the task of ‘forging a lasting federation of planets and usher in an era of peace and prosperity to the solar system.’
|
||||
|
||||
But to forge a lasting truce you must indulge your inner machiavellian monsters.
|
||||
|
||||
*“Remember, when helping civilizations evolve, sometimes they evolve faster when a large multi-headed monster is glaring menacingly at them,” reads the game’s synopsis.*
|
||||
|
||||
Pricey, but one of the standout strategy games of 2014.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Buy “The Last Federation” on GOG][5]
|
||||
|
||||
### StarGunner ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 1996. **Genre**: Arcade. **Port**: DOSBox. Price: Free.
|
||||
|
||||
StarGunner is one of two Linux games available for free on GOG. It’s a space-based side scrolling shoot ‘em up, similar to thousands of mid-nineties arcade games now resting in a land fill somewhere.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s not to say it’s not any good; it’s great fun but just a little familiar.
|
||||
|
||||
Gameplay is fast, battlefields switch between space, ground and water often enough to maintain interest, and with more than 75 different enemy crafts (plus over 30 super adaptive bosses) things never get visually tired, either.
|
||||
|
||||
Look out for weapons and other power-ups littered through levels.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download “StarGunner” for free on GOG][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### Blocks That Matter ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 2011. **Price**: $2.99. **Genre**: Platformer. **Port**: Wine, 32-bit only.
|
||||
|
||||
Take some blocks, drop them into an isometrical world, add bit of jumping and a whole lot of puzzle solving. Finally, coat it all in a layer of cuteness. Aside from an needlessly drawn out introduction, you should end up with **Blocks That Matter**. And boy do these blocks matter.
|
||||
|
||||
Playing as a robot called Tetrobot, your sole aim is to waddle about each level drilling blocks of various materials (sand, ice, etc.) one by one. Blocks can be collected and inserted into the game to help you complete levels, but depending on the material this can often be a hindrance rather than a help.
|
||||
|
||||
An innovative 2D platform-puzzler, it offers up 40 levels in standard Adventure Mode with another 20 waiting to be unlocked. It’s cute, clever and cheap.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Buy “Blocks that Matter” on GOG][7]
|
||||
|
||||
### Honourable Mentions ###
|
||||
|
||||
####DarkLands####
|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 1992. **Genre**: RPG. **Port**: DOSBox. **Price**: $5.99 (inc. extras).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sid Meier’s Covert Action ####
|
||||
|
||||
**Year**: 1990. **Genre**: Action/Strategy. **Port**: DOSBox. **Price**: $5.99 (inc. extras).
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/08/five-best-linux-gog-com-games-available-now
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/50-classic-pc-games-now-available-linux-gog
|
||||
[2]:https://www.facebook.com/omgubuntu/posts/830930706919468
|
||||
[3]:http://www.gog.com/game/flatout
|
||||
[4]:http://www.gog.com/game/duke_nukem_3d_atomic_edition
|
||||
[5]:http://www.gog.com/game/last_federation_the
|
||||
[6]:http://www.gog.com/game/stargunner
|
||||
[7]:http://www.gog.com/game/blocks_that_matter
|
||||
@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by barney-ro
|
||||
|
||||
Interesting facts about Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Today, August, 25th, is the 23rd birthday of Linux. The modest [Usenet post][1] made by a 21 year old student at the University of Helsinki on August 25th, 1991, marks the birth of the venerable Linux as we know it today.
|
||||
|
||||
Fast forward 23 years, and now Linux is everywhere, not only installed on end user desktops, [smartphones][2] and embedded systems, but also fulfilling the needs of [leading enterprises][3] and powering mission-critical systems such as [US Navy's nuclear submarines][4] and [FAA's air traffic control][5]. Entering the era of ubiquitous cloud computing, Linux is continuing [its dominance][6] as by far the most popular platform for the cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
Celebrating the 23rd birthday of Linux today, let me show you **some interesting facts and history you may not know about Linux**. If there is anything to add, feel free to share it in the comments. In this article, I will use the terms "Linux", "kernel" or "Linux kernel" interchangeably to mean the same thing.
|
||||
|
||||
1. There is a never-ending debate on whether or not Linux is an operating system. Technically, the term "Linux" refers to the kernel, a core component of an operating system. Folks who argue that Linux is not an operating system are operating system purists who think that the kernel alone does not make the whole operating system, or free software ideologists who believe that the largest free operating system should be named "[GNU/Linux][7]" to give credit where credit is due (i.e., [GNU project][8]). On the other hand, some developers and programmers have a view that Linux qualifies as an operating system in a sense that it implements the [POSIX standard][9].
|
||||
|
||||
2. According to openhub.net, the majority (95%) of Linux is written in C language. The second popular language for Linux is assembly language (2.8%). The dominance of C lanaguage over C++ is no surprise given Linus's stance on C++. Here is the programming language breakdown for Linux.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3. Linux has been built by a total of [13,036 contributors][10] worldwide. The most prolific contributor is, of course, Linus Torvalds himself, who has committed code more than 20,000 times over the course of the lifetime of Linux. The following figures show the all-time top-10 contributors of Linux in terms of commit counts.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
4. The total source lines of code (SLOC) of Linux is over 17 million. The estimated cost for the entire code base is 5,526 person-years, or over 300M USD according to [basic COCOMO model][11].
|
||||
|
||||
5. Enterprises have not been simply consumers of Linux. Their employees have been [actively participated][12] in the development of Linux. The figure below shows the top-10 corporate sponsors of Linux kernel development, in terms of total commit counts from their employees, as of year 2013. They include commercial Linux distributors (Red Hat, SUSE), chip/embedded system makers (Intel, Texas Instruments, Wolfson), non-profits (Linaro), and other IT power houses (IBM, Samsung, Google).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
6. The official mascot of Linux is "Tux", a friendly penguin character. The idea of using a cuddly penguin as a mascot/logo was in fact [first conceived and asserted][13] by Linus himself. Why penguin? Personally Linus is fond of penguins, despite the fact that he once was bitten by a ferocious penguin, causing him infected with a disease.
|
||||
|
||||
7. A Linux "distribution" contains the Linux kernel, supporting GNU utilities/libraries, and other third-party applications. According to [distrowatch.com][14], there are a total of 286 actively maintained Linux distrutions. The oldest among them is [Slackware][15] whose very first release 1.0 became available in 1993.
|
||||
|
||||
8. Kernel.org, which is the main repository of Linux source code, was [compromised][16] by an unknown attacker in August, 2011, who managed to tamper with several kernel.org's servers. In an effort to tighten up access policies of the Linux kernel, Linux foundation recently [turned on][17] two-factor authentication at the official Git repositories hosting the Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
9. The dominance of Linux on top 500 supercomputers [continues to rise][18]. As of June 2014, 97% of the world-fastest computers are powered by Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
10. Spacewatch, a research group of Lunar and Planetary Laboratory at the University of Arizona, named several asteroids ([9793 Torvalds][19], [9882 Stallman][20], [9885 Linux][21] and [9965 GNU][22]) after GNU/Linux and their creators, in recognition of the free operating system which was instrumental in their asteroid survey activities.
|
||||
|
||||
11. In the modern history of Linux kernel development, there was a big jump in kernel version: from 2.6 to 3.0. The [renumbering to version 3][23] actually did not signify any major restructuring in kernel code, but was simply to celebrate the 20 year milestone of the Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
12. In 2000, Steve Jobs at Apple Inc. [tried to hire][24] Linus Torvalds to have him drop Linux development and instead work on "Unix for the biggest user base," which was OS X back then. Linus declined the offer.
|
||||
|
||||
13. The [reboot()][25] system call in the Linux kernel requires two magic numbers. The second magic number comes from the [birth dates][26] of Linus Torvalds and his three daughters.
|
||||
|
||||
14. With so many fans of Linux around the world, there are [criticisms][27] on current Linux distributions (mainly desktops), such as limited hardware support, lack of standardization, instability due to short upgrade/release cycles, etc. During the [Linux kernel panel][28] at LinuxCon 2014, Linus was quoted as saying "I still want the desktop" when asked where he thinks Linux should go next.
|
||||
|
||||
If you know any interesting facts about Linux, feel free to share them in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
Happy birthday, Linux!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/interesting-facts-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:https://groups.google.com/forum/message/raw?msg=comp.os.minix/dlNtH7RRrGA/SwRavCzVE7gJ
|
||||
[2]:http://developer.android.com/about/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://fortune.com/2013/05/06/how-linux-conquered-the-fortune-500/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/7789
|
||||
[5]:http://fcw.com/Articles/2006/05/01/FAA-manages-air-traffic-with-Linux.aspx
|
||||
[6]:http://thecloudmarket.com/stats
|
||||
[7]:http://www.gnu.org/gnu/why-gnu-linux.html
|
||||
[8]:http://www.gnu.org/gnu/gnu-history.html
|
||||
[9]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/POSIX
|
||||
[10]:https://www.openhub.net/p/linux/contributors/summary
|
||||
[11]:https://www.openhub.net/p/linux/estimated_cost
|
||||
[12]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/publications/linux-foundation/who-writes-linux-2013
|
||||
[13]:http://www.sjbaker.org/wiki/index.php?title=The_History_of_Tux_the_Linux_Penguin
|
||||
[14]:http://distrowatch.com/search.php?ostype=All&category=All&origin=All&basedon=All¬basedon=None&desktop=All&architecture=All&status=Active
|
||||
[15]:http://www.slackware.com/info/
|
||||
[16]:http://pastebin.com/BKcmMd47
|
||||
[17]:http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/203-konstantin-ryabitsev/784544-linux-kernel-git-repositories-add-2-factor-authentication
|
||||
[18]:http://www.top500.org/statistics/details/osfam/1
|
||||
[19]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9793
|
||||
[20]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9882
|
||||
[21]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9885
|
||||
[22]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9965
|
||||
[23]:https://lkml.org/lkml/2011/5/29/204
|
||||
[24]:http://www.wired.com/2012/03/mr-linux/2/
|
||||
[25]:http://lxr.free-electrons.com/source/kernel/reboot.c#L199
|
||||
[26]:http://www.nndb.com/people/444/000022378/
|
||||
[27]:http://linuxfonts.narod.ru/why.linux.is.not.ready.for.the.desktop.current.html
|
||||
[28]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8myENKt8bD0
|
||||
@ -1,92 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Making MySQL Better at GitHub
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> At GitHub we say, "it's not fully shipped until it's fast." We've talked before about some of the ways we keep our [frontend experience speedy][1], but that's only part of the story. Our MySQL database infrastructure dramatically affects the performance of GitHub.com. Here's a look at how our infrastructure team seamlessly conducted a major MySQL improvement last August and made GitHub even faster.
|
||||
|
||||
### The mission ###
|
||||
|
||||
Last year we moved the bulk of GitHub.com's infrastructure into a new datacenter with world-class hardware and networking. Since MySQL forms the foundation of our backend systems, we expected database performance to benefit tremendously from an improved setup. But creating a brand-new cluster with brand-new hardware in a new datacenter is no small task, so we had to plan and test carefully to ensure a smooth transition.
|
||||
|
||||
### Preparation ###
|
||||
|
||||
A major infrastructure change like this requires measurement and metrics gathering every step of the way. After installing base operating systems on our new machines, it was time to test out our new setup with various configurations. To get a realistic test workload, we used tcpdump to extract SELECT queries from the old cluster that was serving production and replayed them onto the new cluster.
|
||||
|
||||
MySQL tuning is very workload specific, and well-known configuration settings like innodb_buffer_pool_size often make the most difference in MySQL's performance. But on a major change like this, we wanted to make sure we covered everything, so we took a look at settings like innodb_thread_concurrency, innodb_io_capacity, and innodb_buffer_pool_instances, among others.
|
||||
|
||||
We were careful to only make one test configuration change at a time, and to run tests for at least 12 hours. We looked for query response time changes, stalls in queries per second, and signs of reduced concurrency. We observed the output of SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS, particularly the SEMAPHORES section, which provides information on work load contention.
|
||||
|
||||
Once we were relatively comfortable with configuration settings, we started migrating one of our largest tables onto an isolated cluster. This served as an early test of the process, gave us more space in the buffer pools of our core cluster and provided greater flexibility for failover and storage. This initial migration introduced an interesting application challenge, as we had to make sure we could maintain multiple connections and direct queries to the correct cluster.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to all our raw hardware improvements, we also made process and topology improvements: we added delayed replicas, faster and more frequent backups, and more read replica capacity. These were all built out and ready for go-live day.
|
||||
|
||||
### Making a list; checking it twice ###
|
||||
|
||||
With millions of people using GitHub.com on a daily basis, we did not want to take any chances with the actual switchover. We came up with a thorough [checklist][2] before the transition:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We also planned a maintenance window and [announced it on our blog][3] to give our users plenty of notice.
|
||||
|
||||
### Migration day ###
|
||||
|
||||
At 5am Pacific Time on a Saturday, the migration team assembled online in chat and the process began:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We put the site in maintenance mode, made an announcement on Twitter, and set out to work through the list above:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**13 minutes** later, we were able to confirm operations of the new cluster:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then we flipped GitHub.com out of maintenance mode, and let the world know that we were in the clear.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Lots of up front testing and preparation meant that we kept the work we needed on go-live day to a minimum.
|
||||
|
||||
### Measuring the final results ###
|
||||
|
||||
In the weeks following the migration, we closely monitored performance and response times on GitHub.com. We found that our cluster migration cut the average GitHub.com page load time by half and the 99th percentile by *two-thirds*:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### What we learned ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Functional partitioning ####
|
||||
|
||||
During this process we decided that moving larger tables that mostly store historic data to separate cluster was a good way to free up disk and buffer pool space. This allowed us to leave more resources for our "hot" data, splitting some connection logic to enable the application to query multiple clusters. This proved to be a big win for us and we are working to reuse this pattern.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Always be testing ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can never do too much acceptance and regression testing for your application. Replicating data from the old cluster to the new cluster while running acceptance tests and replaying queries were invaluable for tracing out issues and preventing surprises during the migration.
|
||||
|
||||
#### The power of collaboration ####
|
||||
|
||||
Large changes to infrastructure like this mean a lot of people need to be involved, so pull requests functioned as our primary point of coordination as a team. We had people all over the world jumping in to help.
|
||||
|
||||
Deploy day team map:
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe width="620" height="420" frameborder="0" src="https://render.githubusercontent.com/view/geojson?url=https://gist.githubusercontent.com/anonymous/5fa29a7ccbd0101630da/raw/map.geojson"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
This created a workflow where we could open a pull request to try out changes, get real-time feedback, and see commits that fixed regressions or errors -- all without phone calls or face-to-face meetings. When everything has a URL that can provide context, it's easy to involve a diverse range of people and make it simple for them give feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
### One year later.. ###
|
||||
|
||||
A full year later, we are happy to call this migration a success — MySQL performance and reliability continue to meet our expectations. And as an added bonus, the new cluster enabled us to make further improvements towards greater availability and query response times. I'll be writing more about those improvements here soon.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://github.com/blog/1880-making-mysql-better-at-github
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[samlambert][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://github.com/samlambert
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/blog/1756-optimizing-large-selector-sets
|
||||
[2]:https://help.github.com/articles/writing-on-github#task-lists
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/blog/1603-site-maintenance-august-31st-2013
|
||||
@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Drab Desktop? Try These 4 Beautiful Linux Icon Themes
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Ubuntu’s default icon theme [hasn’t changed much][1] in almost 5 years, save for the [odd new icon here and there][2]. If you’re tired of how it looks we’re going to show you a handful of gorgeous alternatives that will easily freshen things up.**
|
||||
|
||||
Do feel free to share links to your own favourite choices in the comments below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Captiva ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Captiva icons, elementary folders and Moka GTK
|
||||
|
||||
Captiva is a relatively new icon theme that even the least bling-prone user can appreicate.
|
||||
|
||||
Made by DeviantArt user ~[bokehlicia][3], Captiva shuns the 2D flat look of many current icon themes for a softer, rounded look. The icons themselves have an almost material or textured look, with subtle drop shadows and a rich colour palette adding to the charm.
|
||||
|
||||
It doesn’t yet include a set of its own folder icons, and will fallback to using elementary (if available) or stock Ubuntu icons.
|
||||
|
||||
To install Captiva icons in Ubuntu 14.04 you can add the official PPA by opening a new Terminal window and enter the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:captiva/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install captiva-icon-theme
|
||||
|
||||
Or, if you’re not into software source cruft, by downloading the icon pack direct from the DeviantArt page. To install, extract the archive and move the resulting folder to the ‘.icons‘ directory in Home.
|
||||
|
||||
However you choose to install it, you’ll need to apply this (and every other theme on this list) using a utility like [Unity Tweak Tool][4].
|
||||
|
||||
- [Captiva Icon Theme on DeviantArt][5]
|
||||
|
||||
### Square Beam ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Square Beam icon set with Orchis GTK
|
||||
|
||||
After something a bit angular? Check out Square Beam. It offers a more imposing visual statement than other sets on this list, with electric colours, harsh gradients and stark iconography. It claims to have more than 30,000 different icons (!) included (you’ll forgive me for not counting) so you should find very few gaps in its coverage.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Square Beam Icon Theme on GNOME-Look.org][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### Moka & Faba ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Moka/Faba Mono Icons with Orchis GTK
|
||||
|
||||
The Moka icon suite needs little introduction. In fact, I’d wager a good number of you are already using it
|
||||
|
||||
With pastel colours, soft edges and simple icon artwork, Moka is a truly standout and comprehensive set of application icons. It’s best used with its sibling, Faba, which Moka will inherit so as to fill in all the system icons, folders, panel icons, etc. The combined result is…well, you’ve got eyes!
|
||||
|
||||
For full details on how to install on Ubuntu head over to the official project website, link below.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Moka and Faba Icon Themes][7]
|
||||
|
||||
### Compass ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Compass Icon Theme with Numix Blue GTK
|
||||
|
||||
Last on our list, but by no means least, is Compass. This is a true adherent to the ’2D, two-tone’ UI design right now. It may not be as visually diverse as others on this list, but that’s the point. It’s consistent and uniform and all the better for it — just check out those folder icons!
|
||||
|
||||
It’s available to download and install manually through GNOME-Look (link below) or through the Nitrux Artwork PPA:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nitrux/nitrux-artwork
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install compass-icon-theme
|
||||
|
||||
- [Compass Icon Theme on GNOME-Look.org][8]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/4-gorgeous-linux-icon-themes-download
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2010/02/lucid-gets-new-icons-for-rhythmbox-ubuntuone-memenu-more
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2012/08/new-icon-theme-lands-in-lubuntu-12-10
|
||||
[3]:http://bokehlicia.deviantart.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/06/unity-tweak-tool-0-7-development-download
|
||||
[5]:http://bokehlicia.deviantart.com/art/Captiva-Icon-Theme-479302805
|
||||
[6]:http://gnome-look.org/content/show.php/Square-Beam?content=165094
|
||||
[7]:http://mokaproject.com/moka-icon-theme/download/ubuntu/
|
||||
[8]:http://gnome-look.org/content/show.php/Compass?content=160629
|
||||
@ -1,100 +0,0 @@
|
||||
5 Reasons Why I Hate GNU/Linux – Do You Hate (Love) Linux?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
This part of Linux, I don’t like to talk very often but sometimes I do really feel some of the aspects related to Linux is real pain. Here are the five points which I come across on a daily basis, almost.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
5 Reasons Why I Hate Linux
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Choose from Too Many Good Distros ###
|
||||
|
||||
While reading several on-line forum (a part of my hobby), I very often come across a question like – Hi, I am new to Linux, just [switched over from Windows to Linux][1]. Which Linux Distribution, I should get my hands dirty with? Oh! forgot to mention, I am an Engineering Student.
|
||||
|
||||
As soon as someone posted such question, there is a flood of comments. each distribution’s fan boy tries to make sense that the distro he is using leads all the rest, a few comments may look like:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Get your hands upon Linux Mint or Ubuntu, they are easy to use specially for newbies like you.
|
||||
1. Ubuntu is Sh** better go with Mint.
|
||||
1. If you want something like windows, better stay there.
|
||||
1. Nothing is better than Debian. It is easy to use and contains all the packages you may need.
|
||||
1. Slackware, for the point, if you learn slack you learn Linux.
|
||||
At this point, the student who asked question really gets confused and annoyed.
|
||||
1. CentOS – Nothing like this, when comes to stability.
|
||||
1. I will recommend Fedora, Bleeding edge technology implementation, you will get a lot to learn.
|
||||
1. Puppy Linux, SUSE, BSD, Manjaro, Megia, Kali, RedHat Beta, etc,……
|
||||
|
||||
At the end of discussion, the discussion forum may be used as a paper for research based upon the facts and figure provided in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
Now think the same in Windows or Mac – One may say are you Insane? Still using Windows XP or Vista but no one will try to prove that windows 8 is better than XP and XP is more on a User Friendly side. You won’t get a fan boy in Mac as well, who is trying to jump into the discussion just to make his point sounds louder.
|
||||
|
||||
You may frequently come across points like – Distros are like religion. These things makes the newbie puzzled. Anyone who have used Linux for a considerable time would be knowing that all the distros are same at the base. It is only the working interface and the way to perform task differs and that too rarely. You are using apt, yum, portage, emerge, spike or ABS who cares as far as the things are done and user is comfortable with it.
|
||||
|
||||
Well the above scenario is not only true in forums and groups on-line, it is sometimes taken to the corporate world.
|
||||
|
||||
I was recently being Interviewed by a company based in Mumbai (India). The person interviewing, asked me several questions and technologies, I have worked with. As per their requirements, I have worked with nearly half of the technologies they were looking for. A few of last conversation as mentioned below.
|
||||
|
||||
**Interviewer**: Do you know kernel editing? (Then he talked to himself for a couple of seconds – no, no not kernel editing, it is a very different thing.) Do you know how to compile a kernel on a monolithic side?
|
||||
|
||||
**Me**: Yes, we just need to make sure what we need to run in future. We need to select those options only that supports our need before compiling the kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
**Interviewer**: How do you compile a kernel?
|
||||
|
||||
**Me**: make menuconfig, fire it as………..(interrupted)
|
||||
|
||||
**Interviewer**: When have you compiled the kernel lastly without any help?
|
||||
|
||||
**Me**: Very recently on my Debian…..(Interrupted)
|
||||
|
||||
**Interviewer**: Debian? Do you know what we does? Debian-Febian is not of our use. We use CentOS. Ok, I will tell the management the result. They will call you.
|
||||
|
||||
**Not to Mention**: I didn’t get the call or job, but certainly the phrase **Debian-febian** forces me to think over and over again. He could have said we don’t use Debian, we use CentOS. The tone of him, was a bit racist, it is spread-ed all over.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Some of the very important software has no support in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
No! I am not talking about Photoshop. I understand Linux is not build to perform such task. But some backbone softwares required to connect your Android phone to PC for Updation – PC Suite certainly means a lot. I have been looking for a windows PC.
|
||||
|
||||
I know Linux is more like a server side OS. Really? Is not it trying to make a point that, it has been used as a Desktop as well? If Yes! It should have other developed desktop features. For a desktop user security, stability, RAID, Kernel does not mean much. They should get their work done with little or no effort.
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover the companies like Samsung, Sony, Micromax, etc are dealing with Android (Linux) Phones and they have no support to get their phone connected over a Linux PC.
|
||||
|
||||
Don’t drag me in PC suite discussion. For Linux to be a Desktop OS, it still lacks several things, Little or no gaming support – I mean high end gaming. No professional Video and Photo Editing Tools, I Said Professional. And yeah I remember Titanic and Avatar Movies were maid using some kind of FOSS video editor, I am coming to that point.
|
||||
|
||||
Agree or not, Linux still has to go a long way to be a distro for everyone.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Linuxer have a habit of living in virtual world ###
|
||||
|
||||
I am a Linux user, and I am superior than you. I can handle terminal much better than you. You know Linux is Everywhere in your wrist watch, mobile phones, remote control. You know what, Hacker’s use Linux. Are you aware as soon as you boot Linux you become hacker. You can do several things from Linux you can’t even think of using Windows and Mac.
|
||||
|
||||
Let me tell you, Linux is now being used in International Space Station. The world’s most successful movies Avatar and Titanic were build using Linux. Last but not the least, world’s 90% supercomputers are using Linux. World’s Top 5 fastest computer are using Linux. Facebook, Linkedin, Google, Yahoo all have their server based on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
I don’t mean they are wrong. I only mean they keeps on talking about the thing they very little know about.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. The long hours of compilation and dependency resolution ###
|
||||
|
||||
I am aware of automatic dependency resolution and the program getting smart day by day. Still think from corporate view, I was installing a program say ‘y‘, it had one dependency say ‘**x**‘ which was unable to be resolved automatically. While resolving ‘**x**‘ I came across 8 other dependency, a few of other were dependent on a few other libraries and program. Isn’t it painful?
|
||||
|
||||
The rule of corporate is to have the work done efficiently with less man power and as much less time as possible. Who cares if your piece of codes are coming from Windows or Mac or Linux as far as the work is done.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Too much manual work ###
|
||||
|
||||
No matter which distro you choose, you have to manually do a lot a things time-to-time. Lets say you are installing proprietary Nvidia Driver. Now you need to kill **X** manually, may need to edit **Xorg.conf** manually and still may have a broken **X**. Furthermore, you have to make sure that the next time kernel updates, it still be in working condition.
|
||||
|
||||
Think of same on Windows. You have nothing to do other than firing the executables and click** Next, Next, I Agree, Next, Forward, Finish, Reboot** and your system may very rarely have broken GUI. Though the demerit is a broken GUI is not possible to be repaired on Windows but easily on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Hey don’t tell me its because of security implementation. If you are installing something using ‘**root**‘, and still needs a lot of things done manually that not security. Some may have a point that it gives you power to configure your system to any extent. My friend at least give him a working interface from where he can configure it to next best level. Why Installer laves him to re-invent the wheel every-time in the name of security and configurability.
|
||||
|
||||
I myself is a Linux fan and have been working on this platform for nearly half a decades. I myself have used Distros of several kind and came to the above conclusion. You may have used a different distro’s and might you’ve came to a such conclusion, where you feel that Linux is not upto the mark.
|
||||
|
||||
Please do share with us, why do you hate (Love) Linux? via our comment section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/why-i-hate-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/useful-linux-commands-for-newbies/
|
||||
@ -1,86 +0,0 @@
|
||||
What’s wrong with IPv4 and Why we are moving to IPv6
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
For the past 10 years or so, this has been the year that IPv6 will become wide spread. It hasn’t happened yet. Consequently, there is little widespread knowledge of what IPv6 is, how to use it, or why it is inevitable.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
IPv4 and IPv6 Comparison
|
||||
|
||||
### What’s wrong with IPv4? ###
|
||||
|
||||
We’ve been using **IPv4** ever since RFC 791 was published in 1981. At the time, computers were big, expensive, and rare. IPv4 had provision for **4 billion IP** addresses, which seemed like an enormous number compared to the number of computers. Unfortunately, IP addresses are not use consequently. There are gaps in the addressing. For example, a company might have an address space of **254 (2^8-2)** addresses, and only use 25 of them. The remaining 229 are reserved for future expansion. Those addresses cannot be used by anybody else, because of the way networks route traffic. Consequently, what seemed like a large number in 1981 is actually a small number in 2014.
|
||||
|
||||
The Internet Engineering Task Force (**IETF**) recognized this problem in the early 1990s and came up with two solutions: Classless Internet Domain Router (**CIDR**) and private IP addresses. Prior to the invention of CIDR, you could get one of three network sizes: **24 bits** (16,777,214 addresses), **20 bits** (1,048,574 addresses) and **16 bits** (65,534 addresses). Once CIDR was invented, it was possible to split networks into subnetworks.
|
||||
|
||||
So, for example, if you needed **5 IP** addresses, your ISP would give you a network with a size of 3 bits which would give you **6 IP** addresses. So that would allow your ISP to use addresses more efficiently. Private IP addresses allow you to create a network where each machine on the network can easily connect to another machine on the internet, but where it is very difficult for a machine on the internet to connect back to your machine. Your network is private, hidden. Your network could be very large, 16,777,214 addresses, and you could subnet your private network into smaller networks, so that you could manage your own addresses easily.
|
||||
|
||||
You are probably using a private address right now. Check your own IP address: if it is in the range of **10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255** or **172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255** or **192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255**, then you are using a private IP address. These two solutions helped forestall disaster, but they were stopgap measures and now the time of reckoning is upon us.
|
||||
|
||||
Another problem with **IPv4** is that the IPv4 header was variable length. That was acceptable when routing was done by software. But now routers are built with hardware, and processing the variable length headers in hardware is hard. The large routers that allow packets to go all over the world are having problems coping with the load. Clearly, a new scheme was needed with fixed length headers.
|
||||
|
||||
Still another problem with **IPv4** is that, when the addresses were allocated, the internet was an American invention. IP addresses for the rest of the world are fragmented. A scheme was needed to allow addresses to be aggregated somewhat by geography so that the routing tables could be made smaller.
|
||||
|
||||
Yet another problem with IPv4, and this may sound surprising, is that it is hard to configure, and hard to change. This might not be apparent to you, because your router takes care of all of these details for you. But the problems for your ISP drives them nuts.
|
||||
|
||||
All of these problems went into the consideration of the next version of the Internet.
|
||||
|
||||
### About IPv6 and its Features ###
|
||||
|
||||
The **IETF** unveiled the next generation of IP in December 1995. The new version was called IPv6 because the number 5 had been allocated to something else by mistake. Some of the features of IPv6 included.
|
||||
|
||||
- 128 bit addresses (3.402823669×10³⁸ addresses)
|
||||
- A scheme for logically aggregating addresses
|
||||
- Fixed length headers
|
||||
- A protocol for automatically configuring and reconfiguring your network.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s look at these features one by one:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Addresses ####
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing everybody notices about **IPv6** is that the number of addresses is enormous. Why so many? The answer is that the designers were concerned about the inefficient organization of addresses, so there are so many available addresses that we could allocate inefficiently in order to achieve other goals. So, if you want to build your own IPv6 network, chances are that your ISP will give you a network of **64 bits** (1.844674407×10¹⁹ addresses) and let you subnet that space to your heart’s content.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Aggregation ####
|
||||
|
||||
With so many addresses to use, the address space can be allocated sparsely in order to route packets efficiently. So, your ISP gets a network space of **80 bits**. Of those 80 bits, 16 of them are for the ISPs subnetworks, and 64 bits are for the customer’s networks. So, the ISP can have 65,534 networks.
|
||||
|
||||
However, that address allocation isn’t cast in stone, and if the ISP wants more smaller networks, it can do that (although probably the ISP would probably simply ask for another space of 80 bits). The upper 48 bits is further divided, so that ISPs that are “**close**” to one another have similar network addresses ranges, to allow the networks to be aggregated in the routing tables.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fixed length Headers ####
|
||||
|
||||
An **IPv4** header has a variable length. An **IPv6** header always has a fixed length of 40 bytes. In IPv4, extra options caused the header to increase in size. In IPv6, if additional information is needed, that additional information is stored in extension headers, which follow the IPv6 header and are generally not processed by the routers, but rather by the software at the destination.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the fields in the IPv6 header is the flow. A flow is a **20 bit** number which is created pseudo-randomly, and it makes it easier for the routers to route packets. If a packet has a flow, then the router can use that flow number as an index into a table, which is fast, rather than a table lookup, which is slow. This feature makes **IPv6** very easy to route.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Automatic Configuration ####
|
||||
|
||||
In **IPv6**, when a machine first starts up, it checks the local network to see if any other machine is using its address. If the address is unused, then the machine next looks for an IPv6 router on the local network. If it finds the router, then it asks the router for an IPv6 address to use. Now, the machine is set and ready to communicate on the internet – it has an IP address for itself and it has a default router.
|
||||
|
||||
If the router should go down, then the machines on the network will detect the problem and repeat the process of looking for an IPv6 router, to find the backup router. That’s actually hard to do in IPv4. Similarly, if the router wants to change the addressing scheme on its network, it can. The machines will query the router from time to time and change their addresses automatically. The router will support both the old and new addresses until all of the machines have switched over to the new configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
IPv6 automatic configuration is not a complete solution. There are some other things that a machine needs in order to use the internet effectively: the name servers, a time server, perhaps a file server. So there is **dhcp6** which does the same thing as dhcp, only because the machine boots in a routable state, one dhcp daemon can service a large number of networks.
|
||||
|
||||
#### There’s one big problem ####
|
||||
|
||||
So if IPv6 is so much better than IPv4, why hasn’t adoption been more widespread (as of **May 2014**, Google estimates that its IPv6 traffic is about **4%** of its total traffic)? The basic problem is which comes first, the **chicken or the egg**? Somebody running a server wants the server to be as widely available as possible, which means it must have an **IPv4** address.
|
||||
|
||||
It could also have an IPv6 address, but few people would use it and you do have to change your software a little to accommodate IPv6. Furthermore, a lot of home networking routers do not support IPv6. A lot of ISPs do not support IPv6. I asked my ISP about it, and I was told that they will provide it when customers ask for it. So I asked how many customers had asked for it. One, including me.
|
||||
|
||||
By way of contrast, all of the major operating systems, Windows, OS X, and Linux support IPv6 “**out of the box**” and have for years. The operating systems even have software that will allow IPv6 packets to “**tunnel**” within IPv4 to a point where the IPv6 packets can be removed from the surrounding IPv4 packet and sent on their way.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Conclusion ####
|
||||
|
||||
IPv4 has served us well for a long time. IPv4 has some limitations which are going to present insurmountable problems in the near future. IPv6 will solve those problems by changing the strategy for allocating addresses, making improvements to ease the routing of packets, and making it easier to configure a machine when it first joins the network.
|
||||
|
||||
However, acceptance and usage of IPv6 has been slow, because change is hard and expensive. The good news is that all operating systems support IPv6, so when you are ready to make the change, your computer will need little effort to convert to the new scheme.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/ipv4-and-ipv6-comparison/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jeff Silverman][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/jeffsilverm/
|
||||
@ -1,190 +0,0 @@
|
||||
zpl1025
|
||||
Make Downloading Files Effortless
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A download manager is computer software that is dedicated to the task of downloading files, optimizing bandwidth usage, and operating in a more organized way. Some web browsers, such as Firefox, include a download manager as a feature, but their implementation lacks the sophistication of a dedicated download manager (or add-ons for the web browser), without using bandwidth optimally, and without good file management features.
|
||||
|
||||
Users that regularly download files benefit from using a good download manager. The ability to maximize download speeds (with download acceleration), resume and schedule downloads, make safer and more rewarding downloading. Download managers have lost some of their popularity, but the best of them offer real benefits including tight integration with browsers, support for popular sites such as YouTube and much more.
|
||||
|
||||
There are some sublime open source download managers for Linux, which makes selection somewhat problematic. I have compiled a roundup of my favorite download managers, and add-ons that turn a download manager into an excellent download manager for Firefox. Each application featured here is released under an open source license.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
uGet is a lightweight, easy-to-use and full-featured open source download manager. uGet allows the user to download in multiple parallel streams for download acceleration, put files in a download queue, pause & resume downloads, offers advanced category management, with browser integration, clipboard monitoring, batch downloads, localized into 26 languages, and many more features.
|
||||
|
||||
uGet is mature software; it has been in developed for more than 11 years. In that time, it has progressed into a highly versatile download manager, with an estimable set of features, yet maintaining ease of use.
|
||||
|
||||
uGet is written in the C language, uses cURL as a backend, and the applicable library, libcurl. uGet has excellent platform compatibility. uGet is primarily a project for Linux, but it also runs on Mac OS X, FreeBSD, Android, and Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Easy to use
|
||||
- Downloads queue place your downloads into a queue to download as many, or as few, downloads as you want simultaneously
|
||||
- Resume downloads
|
||||
- Categorized defaults
|
||||
- Clipboard monitor which is well implemented
|
||||
- Batch downloads
|
||||
- Import downloads import from HTML files
|
||||
- Support for downloading files through HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, BitTorrent & Metalink
|
||||
- Multi-connection (also known as Multi-Segment): up to 20 simultaneous connections per download with adaptive segment management which means that when one segment drops out then the other connections pick up the slack to ensure optimal download speeds at all times
|
||||
- Multi-mirror
|
||||
- FTP login & anonymous FTP
|
||||
- Powerful scheduler
|
||||
- FireFox integration via FlashGot
|
||||
- Aria2 plugin
|
||||
- Theme chameleoning
|
||||
- Quiet mode
|
||||
- Keyboard shortcuts
|
||||
- CLI / Terminal usage support
|
||||
- Folder auto-creation
|
||||
- Download history management
|
||||
- GnuTLS support
|
||||
- Supports 26 languages including: Arabic, Belarusian, Chinese (Simplified), Chinese (Traditional), Czech, Danish, English (default), French, Georgian, German, Hungarian, Indonesian, Italian, Polish, Portuguese (Brazil), Russian, Spanish, Turkish, Ukrainian, and Vietnamese
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [ugetdm.com][1]
|
||||
- Developer: C.H. Huang and contributors
|
||||
- License: GNU LGPL 2.1
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.10.5
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
DownThemAll! is a fast, reliable and easy-to-use, open source download manager/accelerator built inside Firefox. This add-on lets the user download all the links or images contained in a webpage and much more. The add-on gives the user full control over downloads, dedicated speed and number of parallel connections at any time. Use Metalinks or add mirrors manually to download a file from different servers at the same time.
|
||||
|
||||
DownThemAll reads the size of the files you want to download and splits them into multiple sections, which are downloaded in parallel.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Complete integration with Firefox
|
||||
- Multi-part download which allows the user to download the file in pieces, then combining the pieces after a completed download; thus increasing the download speed when connected to a slow server
|
||||
- Metalink support which allows multiple URLs for each file to be passed to DTA, along with checksums and other informatio
|
||||
- Spider a page with a single link
|
||||
- Filtering
|
||||
- Advanced auto-renaming options
|
||||
- Pause and restart downloads
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/downthemall][2]
|
||||
- Developer: Federico Parodi, Stefano Verna, Nils Maier
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 2.0.17
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
JDownloader is a free, open-source download management tool with a large community of developers that makes downloading easy and fast. Users can start, stop or pause downloads, set bandwith limitations, auto-extract archives and much more. It offers an easy-to-extend framework.
|
||||
|
||||
JDownloader simplifies downloading files from One-Click-Hosters. It also offers downloading in multiple parallel streams, captcha recognition, automatic file extraction and much more. Additionally, many "link encryption" sites are supported - so you just paste the "encrypted" links and JDownloader does the rest. JDownloader can import CCF, RSDF and DLC files.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Download several files at once
|
||||
- Download with multiple connections
|
||||
- JD has an own powerful OCR module
|
||||
- Automatic extractor (including password list search) (Rar archives)
|
||||
- Theme Support
|
||||
- Multilingual
|
||||
- About 110 hoster and over 300 decrypt plug-ins
|
||||
- Reconnect with JDLiveHeaderScripts: (1400 router supported)
|
||||
- Webupdate
|
||||
- Integrated package manager for additional modules (eg. Webinterface, Shutdown)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [jdownloader.org][3]
|
||||
- Developer: AppWork UG
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.9.581
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
FreeRapid Downloader is an easy to use open source downloader that supports downloading from Rapidshare, Youtube, Facebook, Picasa and other file-sharing services. Its engine is based on a list of plugins that make it possible to download from specific websites.
|
||||
|
||||
FreeRapid Downloader is an ideal choice for users needing a download manager specialized in sharing websites.
|
||||
|
||||
FreeRapid Downloader is written in Java. It needs at least Sun Java 7.0 to run.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Easy to use
|
||||
- Supports concurrent downloading from multiple services
|
||||
- Supports resuming downloads
|
||||
- Download using proxy list
|
||||
- Supports streamed videos or pictures
|
||||
- Download history
|
||||
- Smart clipboard monitoring
|
||||
- Automatic checking for file's existence on server
|
||||
- Auto shutdown options
|
||||
- Automatic plugins updates
|
||||
- Simple CAPTCHA recognition
|
||||
- Multi-platform support
|
||||
- Internationalization support: English, Bulgarian, Czech, Finnish, Portugal, Slovak, Hungarian, Simplified Chinese and many others
|
||||
- More than 700 supported sites
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [wordrider.net/freerapid/][4]
|
||||
- Developer: Vity and contributors
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.9u4
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
FlashGot is a free add-on for Firefox and Thunderbird, meant to handle single and massive ("all" and "selection") downloads with several external Download Managers.
|
||||
|
||||
FlashGot turns every supported download manager into a download manager for Firefox.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Supports in Linux: Aria, Axel Download Accelerator, cURL, Downloader 4 X, FatRat, GNOME Gwget, FatRat, JDownloader, KDE KGet, pyLoad, SteadyFlow, uGet, wxDFast, and wxDownload Fast)
|
||||
- Build Gallery functionality which helps to synthesize full media galleries in one page, from serial contents originally scattered on several pages, for easy and fast "download all"
|
||||
- FlashGot Link downloads through the default download manager the link under the mouse pointer
|
||||
- FlashGot Selection
|
||||
- FlashGot All
|
||||
- FlashGot Tabs
|
||||
- FlashGot Media
|
||||
- Capture all links from a page
|
||||
- Capture all links from all tabs
|
||||
- Filter the links using a mask (e.g. to download only certain types of files)
|
||||
- Make a selection on a web page and capture all links in that selection
|
||||
- Supports direct and batch download from the most popular link protection and file hosting services
|
||||
- Privacy options
|
||||
- Internationalization support
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [flashgot.net][5]
|
||||
- Developer: Giorgio Maone
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.5.6.5
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20140913062041384/DownloadManagers.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ugetdm.com/
|
||||
[2]:https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/downthemall/
|
||||
[3]:http://jdownloader.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://wordrider.net/freerapid/
|
||||
[5]:http://flashgot.net/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
barney-ro translating
|
||||
|
||||
ChromeOS vs Linux: The Good, the Bad and the Ugly
|
||||
ChromeOS 对战 Linux : 孰优孰劣 仁者见仁 智者见智
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> In the battle between ChromeOS and Linux, both desktop environments have strengths and weaknesses.
|
||||
|
||||
> 在 ChromeOS 和 Linux 的斗争过程中,不管是哪一家的操作系统都是有优有劣。
|
||||
|
||||
Anyone who believes Google isn't "making a play" for desktop users isn't paying attention. In recent years, I've seen [ChromeOS][1] making quite a splash on the [Google Chromebook][2]. Exploding with popularity on sites such as Amazon.com, it looks as if ChromeOS could be unstoppable.
|
||||
|
||||
任何不关注Google的人都不会相信Google在桌面用户当中扮演这一个很重要的角色。在近几年,我们见到的[ChromeOS][1]制造的[Google Chromebook][2]相当的轰动。和同期的人气火爆的Amazon一样,似乎ChromeOS势不可挡。
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, I'm going to look at ChromeOS as a concept to market, how it's affecting Linux adoption and whether or not it's a good/bad thing for the Linux community as a whole. Plus, I'll talk about the biggest issue of all and how no one is doing anything about it.
|
||||
|
||||
在本文中,我们要了解的是ChromeOS概念的市场,ChromeOS怎么影响着Linux的使用,和整个 ChromeOS 对于一个社区来说,是好事还是坏事。另外,我将会谈到一些重大的事情,和为什么没人去为他做点什么事情。
|
||||
|
||||
### ChromeOS isn't really Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
### ChromeOS 并不是真正的Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
When folks ask me if ChromeOS is a Linux distribution, I usually reply that ChromeOS is to Linux what OS X is to BSD. In other words, I consider ChromeOS to be a forked operating system that uses the Linux kernel under the hood. Much of the operating system is made up of Google's own proprietary blend of code and software.
|
||||
|
||||
每当有朋友问我说是否ChromeOS 是否是Linux 的一个分支时,我都会这样回答:ChromeOS 对于Linux 就好像是 OS X 对于BSD 。换句话说,我认为,ChromeOS 是一个派生的操作系统,运行于Linux 内核的引擎之下。很多操作系统就组成了Google 的专利代码和软件。
|
||||
|
||||
So while the ChromeOS is using the Linux kernel under its hood, it's still very different from what we might find with today's modern Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
尽管ChromeOS 是利用了Linux 内核引擎,但是它仍然有很大的不同和现在流行的Linux分支版本。
|
||||
|
||||
Where ChromeOS's difference becomes most apparent, however, is in the apps it offers the end user: Web applications. With everything being launched from a browser window, Linux users might find using ChromeOS to be a bit vanilla. But for non-Linux users, the experience is not all that different than what they may have used on their old PCs.
|
||||
|
||||
ChromeOS和它们最大的不同就在于它给终端用户提供的app,包括Web 应用。因为ChromeOS 每一个操作都是开始于浏览器窗口,对于Linux 用户来说,可能会有很多不一样的感受,但是,对于没有Linux 经验的用户来说,这与他们使用的旧电脑并没有什么不同。
|
||||
|
||||
For example: Anyone who is living a Google-centric lifestyle on Windows will feel right at home on ChromeOS. Odds are this individual is already relying on the Chrome browser, Google Drive and Gmail. By extension, moving over to ChromeOS feels fairly natural for these folks, as they're simply using the browser they're already used to.
|
||||
|
||||
就是说,每一个以Google-centric为生活方式的人来说,当他们回到家时在ChromeOS上的感觉将会非常良好。这样的优势就是这个人已经接受了Chrome 浏览器,Google 驱动器和Gmail 。久而久之,他们的亲朋好友也都对ChromeOs有了好感,就好像是他们很容易接受Chrome 流浪器,因为他们早已经用过。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux enthusiasts, however, tend to feel constrained almost immediately. Software choices feel limited and boxed in, plus games and VoIP are totally out of the question. Sorry, but [GooglePlus Hangouts][3] isn't a replacement for [VoIP][4] software. Not even by a long shot.
|
||||
|
||||
然而,对于Linux 爱好者来说,这样就立即带来了不适应。软件的选择是受限制的,盒装的,在加上游戏和VoIP 是完全不可能的。对不起,因为[GooglePlus Hangouts][3]是代替不了VoIP 软件的。甚至在很长的一段时间里。
|
||||
|
||||
### ChromeOS or Linux on the desktop ###
|
||||
|
||||
### ChromeOS 和Linux 的桌面化 ###
|
||||
Anyone making the claim that ChromeOS hurts Linux adoption on the desktop needs to come up for air and meet non-technical users sometime.
|
||||
|
||||
有人断言,ChromeOS 要是想在桌面系统中对Linux 产生影响,只有在Linux 停下来浮出水面换气的时候或者是满足某个非技术用户的时候。
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, desktop Linux is absolutely fine for most casual computer users. However it helps to have someone to install the OS and offer "maintenance" services like we see in the Windows and OS X camps. Sadly Linux lacks this here in the States, which is where I see ChromeOS coming into play.
|
||||
|
||||
是的,桌面Linux 对于大多数休闲型的用户来说绝对是一个好东西。它有助于有专人安装操作系统,并且提供“维修”服务,从windows 和 OS X 的阵营来看。但是,令人失望的是,在美国Linux 正好在这个方面很缺乏。所以,我们看到,ChromeOS 慢慢的走入我们的视线。
|
||||
|
||||
I've found the Linux desktop is best suited for environments where on-site tech support can manage things on the down-low. Examples include: Homes where advanced users can drop by and handle updates, governments and schools with IT departments. These are environments where Linux on the desktop is set up to be used by users of any skill level or background.
|
||||
|
||||
By contrast, ChromeOS is built to be completely maintenance free, thus not requiring any third part assistance short of turning it on and allowing updates to do the magic behind the scenes. This is partly made possible due to the ChromeOS being designed for specific hardware builds, in a similar spirit to how Apple develops their own computers. Because Google has a pulse on the hardware ChromeOS is bundled with, it allows for a generally error free experience. And for some individuals, this is fantastic!
|
||||
|
||||
Comically, the folks who exclaim that there's a problem here are not even remotely the target market for ChromeOS. In short, these are passionate Linux enthusiasts looking for something to gripe about. My advice? Stop inventing problems where none exist.
|
||||
|
||||
The point is: the market share for ChromeOS and Linux on the desktop are not even remotely the same. This could change in the future, but at this time, these two groups are largely separate.
|
||||
|
||||
### ChromeOS use is growing ###
|
||||
|
||||
No matter what your view of ChromeOS happens to be, the fact remains that its adoption is growing. New computers built for ChromeOS are being released all the time. One of the most recent ChromeOS computer releases is from Dell. Appropriately named the [Dell Chromebox][5], this desktop ChromeOS appliance is yet another shot at traditional computing. It has zero software DVDs, no anti-malware software, and offfers completely seamless updates behind the scenes. For casual users, Chromeboxes and Chromebooks are becoming a viable option for those who do most of their work from within a web browser.
|
||||
|
||||
Despite this growth, ChromeOS appliances face one huge downside – storage. Bound by limited hard drive size and a heavy reliance on cloud storage, ChromeOS isn't going to cut it for anyone who uses their computers outside of basic web browser functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
### ChromeOS and Linux crossing streams ###
|
||||
|
||||
Previously, I mentioned that ChromeOS and Linux on the desktop are in two completely separate markets. The reason why this is the case stems from the fact that the Linux community has done a horrid job at promoting Linux on the desktop offline.
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, there are occasional events where casual folks might discover this "Linux thing" for the first time. But there isn't a single entity to then follow up with these folks, making sure they’re getting their questions answered and that they're getting the most out of Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
In reality, the likely offline discovery breakdown goes something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
- Casual user finds out Linux from their local Linux event.
|
||||
- They bring the DVD/USB device home and attempt to install the OS.
|
||||
- While some folks very well may have success with the install process, I've been contacted by a number of folks with the opposite experience.
|
||||
- Frustrated, these folks are then expected to "search" online forums for help. Difficult to do on a primary computer experiencing network or video issues.
|
||||
- Completely fed up, some of the above frustrated bring their computers back into a Windows shop for "repair." In addition to Windows being re-installed, they also receive an earful about how "Linux isn't for them" and should be avoided.
|
||||
|
||||
Some of you might charge that the above example is exaggerated. I would respond with this: It's happened to people I know personally and it happens often. Wake up Linux community, our adoption model is broken and tired.
|
||||
|
||||
### Great platforms, horrible marketing and closing thoughts ###
|
||||
|
||||
If there is one thing that I feel ChromeOS and Linux on the desktop have in common...besides the Linux kernel, it's that they both happen to be great products with rotten marketing. The advantage however, goes to Google with this one, due to their ability to spend big money online and reserve shelf space at big box stores.
|
||||
|
||||
Google believes that because they have the "online advantage" that offline efforts aren't really that important. This is incredibly short-sighted and reflects one of Google's biggest missteps. The belief that if you're not exposed to their online efforts, you're not worth bothering with, is only countered by local shelf-space at select big box stores.
|
||||
|
||||
My suggestion is this – offer Linux on the desktop to the ChromeOS market through offline efforts. This means Linux User Groups need to start raising funds to be present at county fairs, mall kiosks during the holiday season and teaching free classes at community centers. This will immediately put Linux on the desktop in front of the same audience that might otherwise end up with a ChromeOS powered appliance.
|
||||
|
||||
If local offline efforts like this don't happen, not to worry. Linux on the desktop will continue to grow as will the ChromeOS market. Sadly though, it will absolutely keep the two markets separate as they are now.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/chromeos-vs-linux-the-good-the-bad-and-the-ugly-1.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matt Hartley][a]
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.datamation.com/author/Matt-Hartley-3080.html
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chrome_OS
|
||||
[2]:http://www.google.com/chrome/devices/features/
|
||||
[3]:https://plus.google.com/hangouts
|
||||
[4]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voice_over_IP
|
||||
[5]:http://www.pcworld.com/article/2602845/dell-brings-googles-chrome-os-to-desktops.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
What is a good subtitle editor on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you watch foreign movies regularly, chances are you prefer having subtitles rather than the dub. Grown up in France, I know that most Disney movies during my childhood sounded weird because of the French dub. If now I have the chance to be able to watch them in their original version, I know that for a lot of people subtitles are still required. And I surprise myself sometimes making subtitles for my family. Hopefully for me, Linux is not devoid of fancy and open source subtitle editors. In short, this is the non-exhaustive list of open source subtitle editors for Linux. Share your opinion on what you think of the best subtitle editor.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Gnome Subtitles ###
|
||||
|
||||
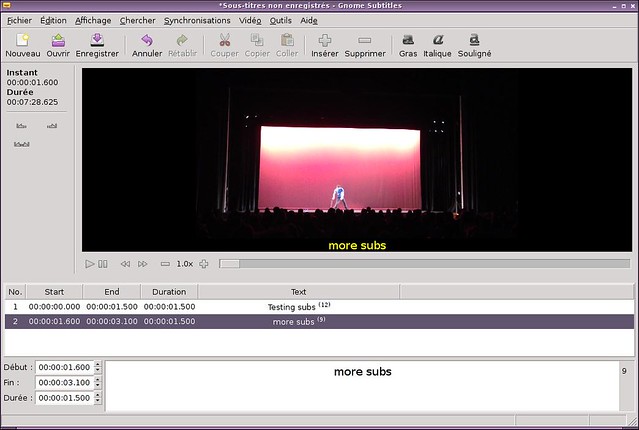
|
||||
|
||||
[Gnome Subtitles][2] is a bit my go to when it comes to quickly editing some existing subtitles. You can load the video, load the subtitle text files and instantly get going. I appreciate its balance between ease of use and advanced features. It comes with a synchronization tool as well as a spell check. Finally, last but not least, the shortcuts are what makes it good in the end: when you edit a lot of lines, you prefer to keep your hands on the keyboard, and use the built in shortcuts to move around.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Aegisub ###
|
||||
|
||||
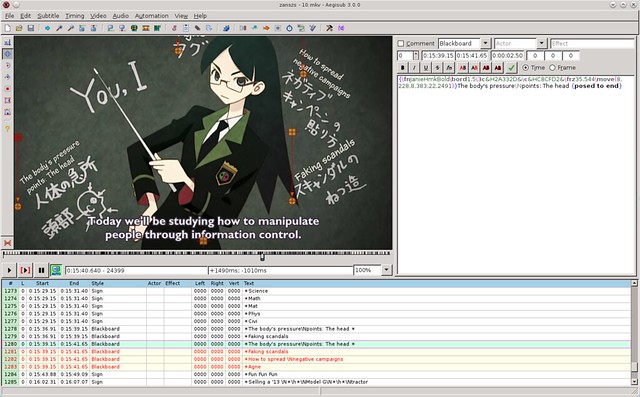
|
||||
|
||||
[Aegisub][2] is already one level of complexity higher. Just the interface reflects a learning curve. But besides its intimidating aspect, Aegisub is very complete software, providing tools beyond anything I could have imagined before. Like Gnome Subtitles, Aegisub has a WYSIWYG approach, but to a whole new level: it is possible to drag and drop the subtitles on the screen, see the audio spectrum on the side, and do everything with shortcuts. In addition to that, it comes with a Kanji tool, a karaoke mode, and the possibility to import lua script to automate some tasks. I really invite you to go read the [manual page][3] before starting using it.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Gaupol ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
At the other end of the complexity spectrum is [Gaupol][4]. Unlike Aegisub, Gaupol is quick to pick up and adopts an interface very close to Gnome Subtitles. But behind this relative simplicity, it comes with all the necessary tools: shortcuts, third party extension, spell checking, and even speech recognition (courtesy of [CMU Sphinx][5]). As a downside, however, I did notice some slow-downs while testing it, nothing too serious, but just enough to make me prefer Gnome Subtitles still.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Subtitle Editor ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Subtitle Editor][6] is very close to Gaupol. However, the interface is a little bit less intuitive, and the features are slightly more advanced. I appreciate the possibility to define "key frames" and all the given synchronization options. However, maybe more icons and less text would enhance the interface. As a goodie, Subtitle Editor can simulate a "type writer" effect, while I am not sure if it is extremely useful. And last but not least, the possibility to redefine the shortcuts is always handy.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Jubler ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Written in Java, [Jubler][7] is a multi-platform subtitle editor. I was actually very impressed by its interface. I definitely see the Java-ish aspect of it, but it remains well conceived and clear. Like Aegisub, you can drag and drop the subtitles on the image, making the experience far more pleasant than just typing. It is also possible to define a style for subtitles, play sound from another track, translate the subtitles, or use the spell checker. However, be careful as you will need MPlayer installed and correctly configured beforehand if you want to use Jubler fully. Oh and I give it a special credit for its easy installation process after downloading the script from the [official page][8].
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Subtitle Composer ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Defined as a "KDE subtitle composer," [Subtitle Composer][9] comes with most of the traditional features evoked previously, but with the KDE interface that we expect. This comes naturally with the option to redefine the shortcuts, which is very dear to me. But beyond all of this, what differentiates Subtitle Composer from all the previously mentioned programs is its ability to follow scripts written in JavaScript, Python, and even Ruby. A few examples are packaged with the software, and will definitely help you pick up the syntax and the usefulness of such feature.
|
||||
|
||||
To conclude, whether you, like me, just edit a few subtitles for your family, re-synchronize the entire track, or write everything from scratch, Linux has the tools for you. For me in the end, the shortcuts and the ease-of-use make all the difference, but for any higher usage, scripting or speech recognition can become super handy.
|
||||
|
||||
Which subtitle editor do you use and why? Or is there another one that you prefer not mentioned here? Let us know in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/good-subtitle-editor-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/adrien
|
||||
[1]:http://gnomesubtitles.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.aegisub.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://docs.aegisub.org/3.2/Main_Page/
|
||||
[4]:http://home.gna.org/gaupol/
|
||||
[5]:http://cmusphinx.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[6]:http://home.gna.org/subtitleeditor/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.jubler.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.jubler.org/download.html
|
||||
[9]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/subcomposer/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
|
||||
Shellshock: How to protect your Unix, Linux and Mac servers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Summary**: The Unix/Linux Bash security hole can be deadly to your servers. Here's what you need to worry about, how to see if you can be attacked, and what to do if your shields are down.
|
||||
|
||||
The only thing you have to fear with [Shellshock, the Unix/Linux Bash security hole][1], is fear itself. Yes, Shellshock can serve as a highway for worms and malware to hit your Unix, Linux, and Mac servers, but you can defend against it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you don't patch and defend yourself against Shellshock today, you may have lost control of your servers by tomorrow.
|
||||
|
||||
However, Shellshock is not as bad as [HeartBleed][2]. Not yet, anyway.
|
||||
|
||||
While it's true that the [Bash shell][3] is the default command interpreter on most Unix and Linux systems and all Macs — the majority of Web servers — for an attacker to get to your system, there has to be a way for him or her to actually get to the shell remotely. So, if you're running a PC without [ssh][4], [rlogin][5], or another remote desktop program, you're probably safe enough.
|
||||
|
||||
A more serious problem is faced by devices that use embedded Linux — such as routers, switches, and appliances. If you're running an older, no longer supported model, it may be close to impossible to patch it and will likely be vulnerable to attacks. If that's the case, you should replace as soon as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
The real and present danger is for servers. According to the National Institute of Standards (NIST), [Shellshock scores a perfect 10][6] for potential impact and exploitability. [Red Hat][7] reports that the most common attack vectors are:
|
||||
|
||||
- **httpd (Your Web server)**: CGI [Common-Gateway Interface] scripts are likely affected by this issue: when a CGI script is run by the web server, it uses environment variables to pass data to the script. These environment variables can be controlled by the attacker. If the CGI script calls Bash, the script could execute arbitrary code as the httpd user. mod_php, mod_perl, and mod_python do not use environment variables and we believe they are not affected.
|
||||
- **Secure Shell (SSH)**: It is not uncommon to restrict remote commands that a user can run via SSH, such as rsync or git. In these instances, this issue can be used to execute any command, not just the restricted command.
|
||||
- **dhclient**: The [Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol Client (dhclient)][8] is used to automatically obtain network configuration information via DHCP. This client uses various environment variables and runs Bash to configure the network interface. Connecting to a malicious DHCP server could allow an attacker to run arbitrary code on the client machine.
|
||||
- **[CUPS][9] (Linux, Unix and Mac OS X's print server)**: It is believed that CUPS is affected by this issue. Various user-supplied values are stored in environment variables when cups filters are executed.
|
||||
- **sudo**: Commands run via sudo are not affected by this issue. Sudo specifically looks for environment variables that are also functions. It could still be possible for the running command to set an environment variable that could cause a Bash child process to execute arbitrary code.
|
||||
- **Firefox**: We do not believe Firefox can be forced to set an environment variable in a manner that would allow Bash to run arbitrary commands. It is still advisable to upgrade Bash as it is common to install various plug-ins and extensions that could allow this behavior.
|
||||
- **Postfix**: The Postfix [mail] server will replace various characters with a ?. While the Postfix server does call Bash in a variety of ways, we do not believe an arbitrary environment variable can be set by the server. It is however possible that a filter could set environment variables.
|
||||
|
||||
So much for Red Hat's thoughts. Of these, the Web servers and SSH are the ones that worry me the most. The DHCP client is also troublesome, especially if, as it the case with small businesses, your external router doubles as your Internet gateway and DHCP server.
|
||||
|
||||
Of these, Web server attacks seem to be the most common by far. As Florian Weimer, a Red Hat security engineer, wrote: "[HTTP requests to CGI scripts][10] have been identified as the major attack vector." Attacks are being made against systems [running both Linux and Mac OS X][11].
|
||||
|
||||
Jaime Blasco, labs director at [AlienVault][12], a security management services company, ran a [honeypot][13] looking for attackers and found "[several machines trying to exploit the Bash vulnerability][14]. The majority of them are only probing to check if systems are vulnerable. On the other hand, we found two worms that are actively exploiting the vulnerability and installing a piece of malware on the system."
|
||||
|
||||
Other security researchers have found that the malware is the usual sort. They typically try to plant distributed denial of service (DDoS) IRC bots and attempt to guess system logins and passwords using a list of poor passwords such as 'root', 'admin', 'user', 'login', and '123456.'
|
||||
|
||||
So, how do you know if your servers can be attacked? First, you need to check to see if you're running a vulnerable version of Bash. To do that, run the following command from a Bash shell:
|
||||
|
||||
env x='() { :;}; echo vulnerable' bash -c "echo this is a test"
|
||||
|
||||
If you get the result:
|
||||
|
||||
*vulnerable this is a test*
|
||||
|
||||
Bad news, your version of Bash can be hacked. If you see:
|
||||
|
||||
*bash: warning: x: ignoring function definition attempt bash: error importing function definition for `x' this is a test*
|
||||
|
||||
You're good. Well, to be more exact, you're as protected as you can be at the moment.
|
||||
|
||||
While all major Linux distributors have released patches that stop most attacks — [Apple has not released a patch yet][15] — it has been discovered that "[patches shipped for this issue are incomplete][16]. An attacker can provide specially-crafted environment variables containing arbitrary commands that will be executed on vulnerable systems under certain conditions." While it's unclear if these attacks can be used to hack into a system, it is clear that they can be used to crash them, thanks to a null-pointer exception.
|
||||
|
||||
Patches to fill-in the [last of the Shellshock security hole][17] are being worked on now. In the meantime, you should update your servers as soon as possible with the available patches and keep an eye open for the next, fuller ones.
|
||||
|
||||
In the meantime, if, as is likely, you're running the Apache Web server, there are some [Mod_Security][18] rules that can stop attempts to exploit Shellshock. These rules, created by Red Hat, are:
|
||||
|
||||
Request Header values:
|
||||
SecRule REQUEST_HEADERS "^\(\) {" "phase:1,deny,id:1000000,t:urlDecode,status:400,log,msg:'CVE-2014-6271 - Bash Attack'"
|
||||
|
||||
SERVER_PROTOCOL values:
|
||||
SecRule REQUEST_LINE "\(\) {" "phase:1,deny,id:1000001,status:400,log,msg:'CVE-2014-6271 - Bash Attack'"
|
||||
|
||||
GET/POST names:
|
||||
SecRule ARGS_NAMES "^\(\) {" "phase:2,deny,id:1000002,t:urlDecode,t:urlDecodeUni,status:400,log,msg:'CVE-2014-6271 - Bash Attack'"
|
||||
|
||||
GET/POST values:
|
||||
SecRule ARGS "^\(\) {" "phase:2,deny,id:1000003,t:urlDecode,t:urlDecodeUni,status:400,log,msg:'CVE-2014-6271 - Bash Attack'"
|
||||
|
||||
File names for uploads:
|
||||
SecRule FILES_NAMES "^\(\) {" "phase:2,deny,id:1000004,t:urlDecode,t:urlDecodeUni,status:400,log,msg:'CVE-2014-6271 - Bash Attack'"
|
||||
|
||||
It is vital that you patch your servers as soon as possible, even with the current, incomplete ones, and to set up defenses around your Web servers. If you don't, you could come to work tomorrow to find your computers completely compromised. So get out there and start patching!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.zdnet.com/shellshock-how-to-protect-your-unix-linux-and-mac-servers-7000034072/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.zdnet.com/meet-the-team/us/steven-j-vaughan-nichols/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.zdnet.com/unixlinux-bash-critical-security-hole-uncovered-7000034021/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.zdnet.com/heartbleed-serious-openssl-zero-day-vulnerability-revealed-7000028166
|
||||
[3]:http://www.gnu.org/software/bash/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.openbsd.org/cgi-bin/man.cgi?query=ssh&sektion=1
|
||||
[5]:http://unixhelp.ed.ac.uk/CGI/man-cgi?rlogin
|
||||
[6]:http://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2014-7169
|
||||
[7]:http://www.redhat.com/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.isc.org/downloads/dhcp/
|
||||
[9]:https://www.cups.org/
|
||||
[10]:http://seclists.org/oss-sec/2014/q3/650
|
||||
[11]:http://www.zdnet.com/first-attacks-using-shellshock-bash-bug-discovered-7000034044/
|
||||
[12]:http://www.alienvault.com/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.sans.org/security-resources/idfaq/honeypot3.php
|
||||
[14]:http://www.alienvault.com/open-threat-exchange/blog/attackers-exploiting-shell-shock-cve-2014-6721-in-the-wild
|
||||
[15]:http://apple.stackexchange.com/questions/146849/how-do-i-recompile-bash-to-avoid-the-remote-exploit-cve-2014-6271-and-cve-2014-7
|
||||
[16]:https://bugzilla.redhat.com/show_bug.cgi?id=1141597#c27
|
||||
[17]:http://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2014-7169
|
||||
[18]:http://www.inmotionhosting.com/support/website/modsecurity/what-is-modsecurity-and-why-is-it-important
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
What Linux Users Should Know About Open Hardware
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> What Linux users don't know about manufacturing open hardware can lead them to disappointment.
|
||||
|
||||
Business and free software have been intertwined for years, but the two often misunderstand one another. That's not surprising -- what is just a business to one is way of life for the other. But the misunderstanding can be painful, which is why debunking it is a worth the effort.
|
||||
|
||||
An increasingly common case in point: the growing attempts at open hardware, whether from Canonical, Jolla, MakePlayLive, or any of half a dozen others. Whether pundit or end-user, the average free software user reacts with exaggerated enthusiasm when a new piece of hardware is announced, then retreats into disillusionment as delay follows delay, often ending in the cancellation of the entire product.
|
||||
|
||||
It's a cycle that does no one any good, and often breeds distrust – and all because the average Linux user has no idea what's happening behind the news.
|
||||
|
||||
My own experience with bringing products to market is long behind me. However, nothing I have heard suggests that anything has changed. Bringing open hardware or any other product to market remains not just a brutal business, but one heavily stacked against newcomers.
|
||||
|
||||
### Searching for Partners ###
|
||||
|
||||
Both the manufacturing and distribution of digital products is controlled by a relatively small number of companies, whose time can sometimes be booked months in advance. Profit margins can be tight, so like movie studios that buy the rights to an ancient sit-com, the manufacturers usually hope to clone the success of the latest hot product. As Aaron Seigo told me when talking about his efforts to develop the Vivaldi tablet, the manufacturers would much rather prefer someone else take the risk of doing anything new.
|
||||
|
||||
Not only that, but they would prefer to deal with someone with an existing sales record who is likely to bring repeat business.
|
||||
|
||||
Besides, the average newcomer is looking at a product run of a few thousand units. A chip manufacturer would much rather deal with Apple or Samsung, whose order is more likely in the hundreds of thousands.
|
||||
|
||||
Faced with this situation, the makers of open hardware are likely to find themselves cascading down into the list of manufacturers until they can find a second or third tier manufacturer that is willing to take a chance on a small run of something new.
|
||||
|
||||
They might be reduced to buying off-the-shelf components and assembling units themselves, as Seigo tried with Vivaldi. Alternatively, they might do as Canonical did, and find established partners that encourage the industry to take a gamble. Even if they succeed, they have usually taken months longer than they expected in their initial naivety.
|
||||
|
||||
### Staggering to Market ###
|
||||
|
||||
However, finding a manufacturer is only the first obstacle. As Raspberry Pi found out, even if the open hardware producers want only free software in their product, the manufacturers will probably insist that firmware or drivers stay proprietary in the name of protecting trade secrets.
|
||||
|
||||
This situation is guaranteed to set off criticism from potential users, but the open hardware producers have no choice except to compromise their vision. Looking for another manufacturer is not a solution, partly because to do so means more delays, but largely because completely free-licensed hardware does not exist. The industry giants like Samsung have no interest in free hardware, and, being new, the open hardware producers have no clout to demand any.
|
||||
|
||||
Besides, even if free hardware was available, manufacturers could probably not guarantee that it would be used in the next production run. The producers might easily find themselves re-fighting the same battle every time they needed more units.
|
||||
|
||||
As if all this is not enough, at this point the open hardware producer has probably spent 6-12 months haggling. The chances are, the industry standards have shifted, and they may have to start from the beginning again by upgrading specs.
|
||||
|
||||
### A Short and Brutal Shelf Life ###
|
||||
|
||||
Despite these obstacles, hardware with some degree of openness does sometimes get released. But remember the challenges of finding a manufacturer? They have to be repeated all over again with the distributors -- and not just once, but region by region.
|
||||
|
||||
Typically, the distributors are just as conservative as the manufacturers, and just as cautious about dealing with newcomers and new ideas. Even if they agree to add a product to their catalog, the distributors can easily decide not to encourage their representatives to promote it, which means that in a few months they have effectively removed it from the shelves.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, online sales are a possibility. But meanwhile, the hardware has to be stored somewhere, adding to the cost. Production runs on demand are expensive even in the unlikely event that they are available, and even unassembled units need storage.
|
||||
|
||||
### Weighing the Odds ###
|
||||
|
||||
I have been generalizing wildly here, but anyone who has ever been involved in producing anything will recognize what I am describing as the norm. And just to make matters worse, open hardware producers typically discover the situation as they are going through it. Inevitably, they make mistakes, which adds still more delays.
|
||||
|
||||
But the point is, if you have any sense of the process at all, your knowledge is going to change how you react to news of another attempt at hardware. The process means that, unless a company has been in serious stealth mode, an announcement that a product will be out in six months will rapidly prove to be an outdate guestimate. 12-18 months is more likely, and the obstacles I describe may mean that the product will never actually be released.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, as I write, people are waiting for the emergence of the first Steam Machines, the Linux-based gaming consoles. They are convinced that the Steam Machines will utterly transform both Linux and gaming.
|
||||
|
||||
As a market category, Steam Machines may do better than other new products, because those who are developing them at least have experience developing software products. However, none of the dozen or so Steam Machines in development have produced more than a prototype after almost a year, and none are likely to be available for buying until halfway through 2015. Given the realities of hardware manufacturing, we will be lucky if half of them see daylight. In fact, a release of 2-4 might be more realistic.
|
||||
|
||||
I make that prediction with next to no knowledge of any of the individual efforts. But, having some sense of how hardware manufacturing works, I suspect that it is likely to be closer to what happens next year than all the predictions of a new Golden Age for Linux and gaming. I would be entirely happy being wrong, but the fact remains: what is surprising is not that so many Linux-associated hardware products fail, but that any succeed even briefly.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/what-linux-users-should-know-about-open-hardware-1.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Bruce Byfield][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.datamation.com/author/Bruce-Byfield-6030.html
|
||||
@ -1,111 +0,0 @@
|
||||
alim0x translating
|
||||
|
||||
The history of Android
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Both screens of the Email app. The first two screenshots show the combined label/inbox view, and the last shows a message.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
The message view was—surprise!—white. Android's e-mail app has historically been a watered-down version of the Gmail app, and you can see that close connection here. The message and compose views were taken directly from Gmail with almost no modifications.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The “IM" applications. Screenshots show the short-lived provider selection screen, the friends list, and a chat.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
Before Google Hangouts and even before Google Talk, there was "IM"—the only instant messaging client that shipped on Android 1.0. Surprisingly, multiple IM services were supported: users could pick from AIM, Google Talk, Windows Live Messenger, and Yahoo. Remember when OS creators cared about interoperability?
|
||||
|
||||
The friends list was a black background with white speech bubbles for open chats. Presence was indicated with colored circles, and a little Android on the right hand side would indicate that a person was mobile. It's amazing how much more communicative the IM app was than Google Hangouts. Green means the person is using a device they are signed into, yellow means they are signed in but idle, red means they have manually set busy and don't want to be bothered, and gray is offline. Today, Hangouts only shows when a user has the app open or closed.
|
||||
|
||||
The chats interface was clearly based on the Messaging program, and the chat backgrounds were changed from white and blue to white and green. No one changed the color of the blue text entry box, though, so along with the orange highlight effect, this screen used white, green, blue, and orange.
|
||||
|
||||
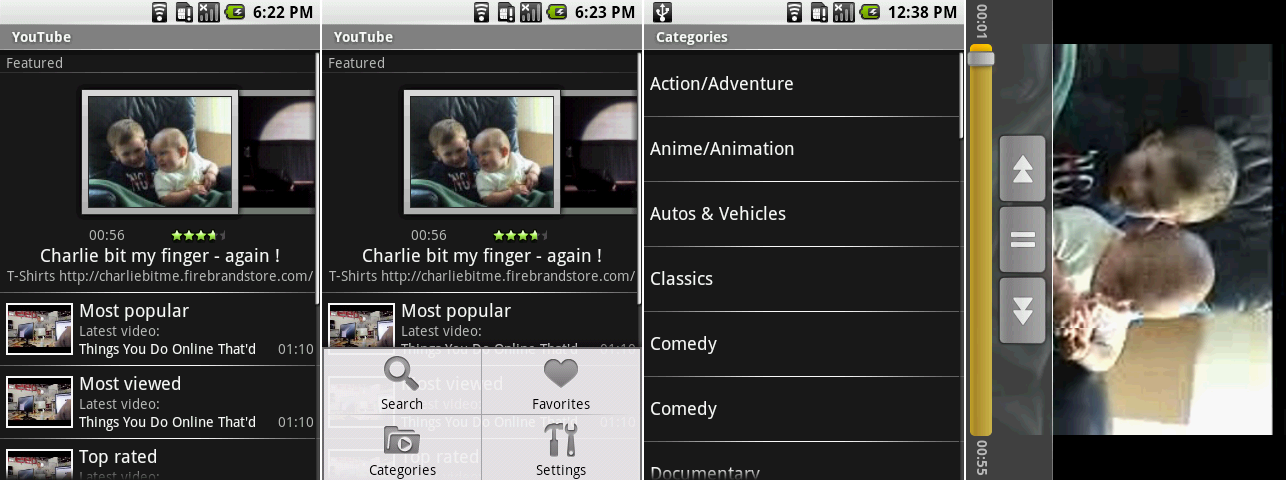
|
||||
YouTube on Android 1.0. The screens show the main page, the main page with the menu open, the categories screen, and the videos screen.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
YouTube might not have been the mobile sensation it is today with the 320p screen and 3G data speeds of the G1, but Google's video service was present and accounted for on Android 1.0. The main screen looked like a tweaked version of the Android Market, with a horizontally scrolling featured section along the top and vertically scrolling categories along the bottom. Some of Google's category choices were pretty strange: what would the difference be between "Most popular" and "Most viewed?"
|
||||
|
||||
In a sign that Google had no idea how big YouTube would eventually become, one of the video categories was "Most recent." Today, with [100 hours of video][1] uploaded to the site every minute, if this section actually worked it would be an unreadable blur of rapidly scrolling videos.
|
||||
|
||||
The menu housed search, favorites, categories, and settings. Settings (not pictured) was the lamest screen ever, housing one option to clear the search history. Categories was equally barren, showing only a black list of text.
|
||||
|
||||
The last screen shows a video, which only supported horizontal mode. The auto-hiding video controls weirdly had rewind and fast forward buttons, even though there was a seek bar.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
YouTube’s video menu, description page, and comments.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
Additional sections for each video could be brought up by hitting the menu button. Here you could favorite the video, access details, and read comments. All of these screens, like the videos, were locked to horizontal mode.
|
||||
|
||||
"Share" didn't bring up a share dialog yet; it just kicked the link out to a Gmail message. Texting or IMing someone a link wasn't possible. Comments could be read, but you couldn't rate them or post your own. You couldn't rate or like a video either.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The camera app’s picture taking interface, menu, and photo review mode.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
Real Android on real hardware meant a functional camera app, even if there wasn't much to look at. That black square on the left was the camera interface, which should be showing a viewfinder image, but the SDK screenshot utility can't capture it. The G1 had a hardware camera button (remember those?), so there wasn't a need for an on-screen shutter button. There were no settings for exposure, white balance, or HDR—you could take a picture and that was about it.
|
||||
|
||||
The menu button revealed a meager two options: a way to jump to the Pictures app and Settings screen with two options. The first settings option was whether or not to enable geotagging for pictures, and the second was for a dialog prompt after every capture, which you can see on the right. Also, you could only take pictures—there was no video support yet.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The Calendar’s month view, week view with the menu open, day view, and agenda.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
Like most apps of this era, the primary command interface for the calendar was the menu. It was used to switch views, add a new event, navigate to the current day, pick visible calendars, and go to the settings. The menu functioned as a catch-all for every single button.
|
||||
|
||||
The month view couldn't show appointment text. Every date had a bar next to it, and appointments were displayed as green sections in the bar denoting what time of day an appointment was. Week view couldn't show text either—the 320×480 display of the G1 just wasn't dense enough—so you got a white block with a strip of color indicating which calendar it was from. The only views that provided text were the agenda and day views. You could move through dates by swiping—week and day used left and right, and month and agenda used up and down.
|
||||
|
||||
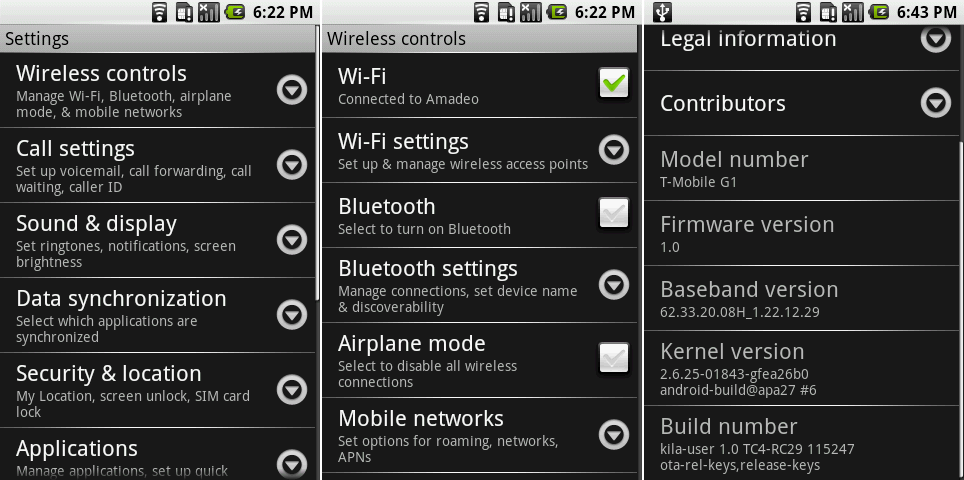
|
||||
The main settings page, the Wireless section, and the bottom of the about page.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
Android 1.0 finally brought a settings screen to the party. It was a black and white wall of text that was roughly broken down into sections. Down arrows next to each list item confusingly look like they would expand line-in to show more of something, but touching anywhere on the list item would just load the next screen. All the screens were pretty boring and samey looking, but hey, it's a settings screen.
|
||||
|
||||
Any option with an on/off state used a cartoony-looking checkbox. The original checkboxes in Android 1.0 were pretty strange—even when they were "unchecked," they still had a gray check mark in them. Android treated the check mark like a light bulb that would light up when on and be dim when off, but that's not how checkboxes work. We did finally get an "About" page, though. Android 1.0 ran Linux kernel 2.6.25.
|
||||
|
||||
A settings screen means we can finally open the security settings and change lock screens. Android 1.0 only had two styles, the gray square lock screen pictured in the Android 0.9 section, and pattern unlock, which required you to draw a pattern over a grid of 9 dots. A swipe pattern like this was easier to remember and input than a PIN even if it did not add any more security.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The Voice Dialer, pattern lock screen, low battery warning, and time picker.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
oice functions arrived in 1.0 with Voice Dialer. This feature hung around in various capacities in AOSP for a while, as it was a simple voice command app for calling numbers and contacts. Voice Dialer was completely unrelated to Google's future voice products, however, and it worked the same way a voice dialer on a dumbphone would work.
|
||||
|
||||
As for a final note, low battery popup would occur when the battery dropped below 15 percent. It was a funny graphic, depicting plugging the wrong end of the power cord into the phone. That wasn't (and still isn't) how phones work, Google.
|
||||
|
||||
Android 1.0 was a great first start, but there were still so many gaps in functionality. Physical keyboards and tons of hardware buttons were mandatory, as Android devices were still not allowed to be sold without a d-pad or trackball. Base smartphone functionality like auto-rotate wasn't here yet, either. Updates for built-in apps weren't possible through the Android Market the way they were today. All the Google Apps were interwoven with the operating system. If Google wanted to update a single app, an update for the entire operating system needed to be pushed out through the carriers. There was still a lot of work to do.
|
||||
|
||||
### Android 1.1—the first truly incremental update ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
All of Android 1.1’s new features: Search by voice, the Android Market showing paid app support, Google Latitude, and the new “system updates" option in the settings.
|
||||
Photo by Ron Amadeo
|
||||
|
||||
Four and a half months after Android 1.0, in February 2009, Android got its first public update in Android 1.1. Not much changed in the OS, and just about every new thing Google added with 1.1 has been shut down by now. Google Voice Search was Android's first foray into cloud-powered voice search, and it had its own icon in the app drawer. While the app can't communicate with Google's servers anymore, you can check out how it used to work [on the iPhone][2]. It wasn't yet Voice Actions, but you could speak and the results would go to a simple Google Search.
|
||||
|
||||
Support for paid apps was added to the Android Market, but just like the beta client, this version of the Android Market could no longer connect to the Google Play servers. The most that we could get to work was this sorting screen, which lets you pick between displaying free apps, paid apps, or a mix of both.
|
||||
|
||||
Maps added [Google Latitude][3], a way to share your location with friends. Latitude was shut down in favor of Google+ a few months ago and no longer works. There was an option for it in the Maps menu, but tapping on it just brings up a loading spinner forever.
|
||||
|
||||
Given that system updates come quickly in the Android world—or at least, that was the plan before carriers and OEMs got in the way—Google also added a button to the "About Phone" screen to check for system updates.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron is the Reviews Editor at Ars Technica, where he specializes in Android OS and Google products. He is always on the hunt for a new gadget and loves to rip things apart to see how they work.
|
||||
|
||||
[@RonAmadeo][t]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/7/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.youtube.com/yt/press/statistics.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y3z7Tw1K17A
|
||||
[3]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2009/02/google-tries-location-based-social-networking-with-latitude/
|
||||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
@ -1,107 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[bazz2 hehe]
|
||||
How to use systemd for system administration on Debian
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Soon enough, hardly any Linux user will be able to escape the ever growing grasp that systemd imposes on Linux, unless they manually opt out. systemd has created more technical, emotional, and social issues than any other piece of software as of late. This predominantly came to show in the [heated discussions][1] also dubbed as the 'Init Wars', that occupied parts of the Debian developer body for months. While the Debian Technical Comittee finally decided to include systemd in Debian 8 "Jessie", there were efforts to [supersede the decision][2] by a General Resolution, and even threats to the health of developers in favor of systemd.
|
||||
|
||||
This goes to show how deep systemd interferes with the way of handling Linux systems that has, in large parts, been passed down to us from the Unix days. Theorems like "one tool for the job" are overthrown by the new kid in town. Besides substituting sysvinit as init system, it digs deep into system administration. For right now a lot of the commands you are used to will keep on working due to the compatibility layer provided by the package systemd-sysv. That might change as soon as systemd 214 is uploaded to Debian, destined to be released in the stable branch with Debian 8 "Jessie". From thereon, users need to utilize the new commands that come with systemd for managing services, processes, switching run levels, and querying the logging system. A workaround is to set up aliases in .bashrc.
|
||||
|
||||
So let's have a look at how systemd will change your habits of administrating your computers and the pros and cons involved. Before making the switch to systemd, it is a good security measure to save the old sysvinit to be able to still boot, should systemd fail. This will only work as long as systemd-sysv is not yet installed, and can be easily obtained by running:
|
||||
|
||||
# cp -av /sbin/init /sbin/init.sysvinit
|
||||
|
||||
Thusly prepared, in case of emergency, just append:
|
||||
|
||||
init=/sbin/init.sysvinit
|
||||
|
||||
to the kernel boot-time parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Usage of systemctl ###
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl is the command that substitutes the old "/etc/init.d/foo start/stop", but also does a lot more, as you can learn from its man page.
|
||||
|
||||
Some basic use-cases are:
|
||||
|
||||
- systemctl - list all loaded units and their state (where unit is the term for a job/service)
|
||||
- systemctl list-units - list all units
|
||||
- systemctl start [NAME...] - start (activate) one or more units
|
||||
- systemctl stop [NAME...] - stop (deactivate) one or more units
|
||||
- systemctl disable [NAME...] - disable one or more unit files
|
||||
- systemctl list-unit-files - show all installed unit files and their state
|
||||
- systemctl --failed - show which units failed during boot
|
||||
- systemctl --type=mount - filter for types; types could be: service, mount, device, socket, target
|
||||
- systemctl enable debug-shell.service - start a root shell on TTY 9 for debugging
|
||||
|
||||
For more convinience in handling units, there is the package systemd-ui, which is started as user with the command systemadm.
|
||||
|
||||
Switching runlevels, reboot and shutdown are also handled by systemctl:
|
||||
|
||||
- systemctl isolate graphical.target - take you to what you know as init 5, where your X-server runs
|
||||
- systemctl isolate multi-user.target - take you to what you know as init 3, TTY, no X
|
||||
- systemctl reboot - shut down and reboot the system
|
||||
- systemctl poweroff - shut down the system
|
||||
|
||||
All these commands, other than the ones for switching runlevels, can be executed as normal user.
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Usage of journalctl ###
|
||||
|
||||
systemd does not only boot machines faster than the old init system, it also starts logging much earlier, including messages from the kernel initialization phase, the initial RAM disk, the early boot logic, and the main system runtime. So the days where you needed to use a camera to provide the output of a kernel panic or otherwise stalled system for debugging are mostly over.
|
||||
|
||||
With systemd, logs are aggregated in the journal which resides in /var/log/. To be able to make full use of the journal, we first need to set it up, as Debian does not do that for you yet:
|
||||
|
||||
# addgroup --system systemd-journal
|
||||
# mkdir -p /var/log/journal
|
||||
# chown root:systemd-journal /var/log/journal
|
||||
# gpasswd -a $user systemd-journal
|
||||
|
||||
That will set up the journal in a way where you can query it as normal user. Querying the journal with journalctl offers some advantages over the way syslog works:
|
||||
|
||||
- journalctl --all - show the full journal of the system and all its users
|
||||
- journalctl -f - show a live view of the journal (equivalent to "tail -f /var/log/messages")
|
||||
- journalctl -b - show the log since the last boot
|
||||
- journalctl -k -b -1 - show all kernel logs from the boot before last (-b -1)
|
||||
- journalctl -b -p err - shows the log of the last boot, limited to the priority "ERROR"
|
||||
- journalctl --since=yesterday - since Linux people normally do not often reboot, this limits the size more than -b would
|
||||
- journalctl -u cron.service --since='2014-07-06 07:00' --until='2014-07-06 08:23' - show the log for cron for a defined timeframe
|
||||
- journalctl -p 2 --since=today - show the log for priority 2, which covers emerg, alert and crit; resembles syslog priorities emerg (0), alert (1), crit (2), err (3), warning (4), notice (5), info (6), debug (7)
|
||||
- journalctl > yourlog.log - copy the binary journal as text into your current directory
|
||||
|
||||
Journal and syslog can work side-by-side. On the other hand, you can remove any syslog packages like rsyslog or syslog-ng once you are satisfied with the way the journal works.
|
||||
|
||||
For very detailed output, append "systemd.log_level=debug" to the kernel boot-time parameter list, and then run:
|
||||
|
||||
# journalctl -alb
|
||||
|
||||
Log levels can also be edited in /etc/systemd/system.conf.
|
||||
|
||||
### Analyzing the Boot Process with systemd ###
|
||||
|
||||
systemd allows you to effectively analyze and optimize your boot process:
|
||||
|
||||
- systemd-analyze - show how long the last boot took for kernel and userspace
|
||||
- systemd-analyze blame - show details of how long each service took to start
|
||||
- systemd-analyze critical-chain - print a tree of the time-critical chain of units
|
||||
- systemd-analyze dot | dot -Tsvg > systemd.svg - put a vector graphic of your boot process (requires graphviz package)
|
||||
- systemd-analyze plot > bootplot.svg - generate a graphical timechart of the boot process
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
systemd has pretty good documentation for such a young project under heavy developement. First of all, there is the [0pointer series by Lennart Poettering][3]. The series is highly technical and quite verbose, and holds a wealth of information. Another good source is the distro agnostic [Freedesktop info page][4] with the largest collection of links to systemd resources, distro specific pages, bugtrackers and documentation. A quick glance at:
|
||||
|
||||
# man systemd.index
|
||||
|
||||
will give you an overview of all systemd man pages. The command structure for systemd for various distributions is pretty much the same, differences are found mainly in the packaging.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/use-systemd-system-administration-debian.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://lists.debian.org/debian-devel/2013/10/msg00444.html
|
||||
[2]:https://lists.debian.org/debian-devel/2014/02/msg00316.html
|
||||
[3]:http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/systemd/
|
||||
@ -1,135 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Build a Raspberry Pi Arcade Machine
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Relive the golden majesty of the 80s with a little help from a marvel of the current decade.**
|
||||
|
||||
### WHAT YOU’LL NEED ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Raspberry Pi w/4GB SD-CARD.
|
||||
- HDMI LCD monitor.
|
||||
- Games controller or…
|
||||
- A JAMMA arcade cabinet.
|
||||
- J-Pac or I-Pac.
|
||||
|
||||
The 1980s were memorable for many things; the end of the cold war, a carbonated drink called Quatro, the Korg Polysix synthesiser and the Commodore 64. But to a certain teenager, none of these were as potent, or as perhaps familiarly illicit, as the games arcade. Enveloped by cigarette smoke and a barrage of 8-bit sound effects, they were caverns you visited only on borrowed time: 50 pence and a portion of chips to see you through lunchtime while you honed your skills at Galaga, Rampage, Centipede, Asteroids, Ms Pacman, Phoenix, R-Rype, Donkey Kong, Rolling Thunder, Gauntlet, Street Fighter, Outrun, Defender… The list is endless.
|
||||
|
||||
These games, and the arcade machine form factor that held them, are just as compelling today as they were 30 years ago. And unlike the teenage version of yourself, you can now play many of them without needing a pocket full of change, finally giving you an edge over the rich kids and their endless ‘Continues’. It’s time to build your own Linux-based arcade machine and beat that old high score.
|
||||
|
||||
We’re going to cover all the steps required to turn a cheap shell of an arcade machine into a Linux-powered multi-platform retro games system. But that doesn’t mean you’ve got to build the whole system at the same scale. You could, for example, forgo the large, heavy and potentially carcinogenic hulk of the cabinet itself and stuff the controlling innards into an old games console or an even smaller case. Or you could just as easily forgo the diminutive Raspberry Pi and replace the brains of your system with a much more capable Linux machine. This might make an ideal platform for SteamOS, for example, and for playing some of its excellent modern arcade games.
|
||||
|
||||
Over the next few pages we’ll construct a Raspberry Pi-based arcade machine, but you should be able to see plenty of ideas for your own projects, even if they don’t look just like ours. And because we’re building it on the staggeringly powerful MAME, you’ll be able to get it running on almost anything.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We did this project before the model B+ came out. It should all work exactly the same on the newer board, and you should be able to get by without a powered USB Hub (click for larger).
|
||||
|
||||
### Disclaimer ###
|
||||
|
||||
One again we’re messing with electrical components that could cause you a shock. Make sure you get any modifications you make checked by a qualified electrician. We don’t go into any details on how to obtain games, but there are legal sources such as old games releases and newer commercial titles based on the MAME emulator.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step1: The Cabinet ####
|
||||
|
||||
The cabinet itself is the biggest challenge. We bought an old two-player Bubble Bobble machine from the early 90s from eBay. It cost £220 delivered in the back of an old estate car. The prices for cabinets like these can vary. We’ve seen many for less than £100. At the other end of the scale, people pay thousands for machines with original decals on the side.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two major considerations when it comes to buying a cabinet. The first is the size: These things are big and heavy. They take up a lot of space and it takes at least two people to move them around. If you’ve got the money, you can buy DIY cabinets or new smaller form-factors, such as cabinets that fit on tables. And cocktail cabinets can be easier to fit, too.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cabinets can be cheap, but they’re heavy. Don’t lift them on your own. Older ones may need some TLC, such as are-spray and some repair work(click for larger).
|
||||
|
||||
One of the best reasons for buying an original cabinet, apart from getting a much more authentic gaming experience, is being able to use the original controls. Many machines you can buy on eBay will be for two concurrent players, with two joysticks and a variety of buttons for each player, plus the player one and player two controls. For compatibility with the widest number of games, we’d recommend finding a machine with six buttons for each player, which is a common configuration. You might also want to look into a panel with more than two players, or one with space for other input controllers, such as an arcade trackball (for games like Marble Madness), or a spinner (Arkanoid). These can be added without too much difficulty later, as modern USB devices exist.
|
||||
|
||||
Controls are the second, and we’d say most important consideration, because it’s these that transfer your twitches and tweaks into game movement. What you need to consider for when buying a cabinet is something called JAMMA, an acronym for Japan Amusement Machinery Manufacturers. JAMMA is a standard in arcade machines that defines how the circuit board containing the game chips connects to the game controllers and the coin mechanism. It’s an interface conduit for all the cables coming from the buttons and the joysticks, for two players, bringing them into a standard edge connector. The JAMMA part is the size and layout of this connector, as it means the buttons and controls will be connected to the same functions on whichever board you install so that the arcade owner would only have to change the cabinet artwork to bring in new players.
|
||||
|
||||
But first, a word of warning: the JAMMA connector also carries the 12V power supply, usually from a power unit installed in most arcade machines. We disconnecting the power supply completely to avoid damaging anything with a wayward short-circuit or dropped screwdriver. We don’t use any of the power connectors in any further stage of the tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 2: J-PAC ####
|
||||
|
||||
What’s brilliant is that you can buy a device that connects to the JAMMA connector inside your cabinet and a USB port on your computer, transforming all the buttons presses and keyboard movements into (configurable) keyboard commands that you can use from Linux to control any game you wish. This device is called the J-Pac ([www.ultimarc.com/jpac.html][1] – approximately £54).
|
||||
|
||||
Its best feature isn’t the connectivity; it’s the way it handles and converts the input signals, because it’s vastly superior to a standard USB joystick. Every input generates its own interrupt, and there’s no limit to the number of simultaneous buttons and directions you can press or hold down. This is vital for games like Street Fighter, because they rely on chords of buttons being pressed simultaneously and quickly, but it’s also essential when delivering the killing blow to cheating players who sulk and hold down all their own buttons. Many other controllers, especially those that create keyboard inputs, are restricted by their USB keyboard controllers to six inputs and a variety of Alt, Shift and Ctrl hacks. The J-Pac can also be connected to a tilt sensor and even some coin mechanisms, and it works in Linux without any pre-configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
Another option is a similar device called an I-Pac. It does the same thing as the J-Pac, only without the JAMMA connector. That means you can’t connect your JAMMA controls, but it does mean you can design your own controller layout and wire each control to the I-Pac yourself. This might be a little ambitious for a first project, but it’s a route that many arcade aficionados take, especially when they want to design a panel for four players, or one that incorporates many different kinds of controls. Our approach isn’t necessarily one we’d recommend, but we re-wired an old X-Arcade Tankstick control panel that suffered from input contention, replaced the joysticks and buttons with new units and connected it to a new JAMMA harness, which is an excellent way of buying all the cables you need plus the edge connector for a low price (£8).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Our J-Pac in situ. The blue and red wires on the right connect to the extra 1- and 2-player buttons on our cabinet (click for larger).
|
||||
|
||||
Whether you choose an I-Pac or a J-Pac, all the keys generated by both devices are the default values for MAME. That means you won’t have to make any manual input changes when you start to run the emulator. Player 1, for example, creates cursor up, down, left and right as well as left Ctrl, left ALT, Space and left Shift for fire buttons 1–4. But the really useful feature, for us, is the two-button shortcuts. While holding down the player 1 button, you can generate the P key to pause the game by pulling down on the player 1 joystick, adjust the volume by pressing up and enter MAME’s own configuration menu by pushing right. These escape codes are cleverly engineered to not get in the way of playing games, as they’re only activated when holding down the Player 1 button, and they enable you to do almost anything you need to from within a running game. You can completely reconfigure MAME, for example, using its own menus, and change input assignments and sensitivity while playing the game itself.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, holding down Player 1 and then pressing Player 2 will quit MAME, which is useful if you’re using a launch menu or MAME manager, as these manage launching games automatically, and let you get on with playing another game as quickly as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
We took a rather cowardly route with the screen, removing the original, bulky and broken CRT that came with the cabinet and replacing it with a low-cost LCD monitor. This approach has many advantages. First, the screen has HDMI, so it will interface with a Raspberry Pi or a modern graphics card without any difficulty. Second, you don’t have to configure the low-frequency update modes required to drive an arcade machine’s screen, nor do you need the specific graphics hardware that drives it. And third, this is the safest option because an arcade machine’s screen is often unprotected from the rear of a case, leaving very high voltages inches away from your hands. That’s not to say you shouldn’t use a CRT if that’s the experience you’re after – it’s the most authentic way to get the gaming experience you’re after, but we’ve fined-tuned the CRT emulation enough in software that we’re happy with the output, and we’re definitely happier not to be using an ageing CRT.
|
||||
|
||||
You might also want to look into using an older LCD with a 4:3 aspect ratio, rather than the widescreen modern options, because 4:3 is more practical for playing both vertical and horizontal games. A vertical shooter such as Raiden, for example, will have black bars on either side of the gaming area if you use a widescreen monitor. Those black bars can be used to display the game instructions, or you could rotate the screen 90 degrees so that every pixel is used, but this is impractical unless you’re only going to play vertical games or have easy access to a rotating mount.
|
||||
|
||||
Mounting a screen is also important. If you’ve removed a CRT, there’s nowhere for an LCD to go. Our solution was to buy some MDF cut to fit the space where the CRT was. This was then screwed into position and we fitted a cheap VESA mounting plate into the centre of the new MDF. VESA mounts can be used by the vast majority of screens, big and small. Finally, because our cabinet was fronted with smoked glass, we had to be sure both the brightness and contrast were set high enough.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Installation ###
|
||||
|
||||
With the large hardware choices now made, and presumably the cabinet close to where you finally want to install it, putting the physical pieces together isn’t that difficult. We safely split the power input from the rear of the cabinet and wired a multiple socket into the space at the back. We did this to the cable after it connects to the power switch.
|
||||
|
||||
Nearly all arcade cabinets have a power switch on the top-right surface, but there’s usually plenty of cable to splice into this at a lower point in the cabinet, and it meant we could use normal power connectors for our equipment. Our cabinet has a fluorescent tube, used to backlight the top marquee on the machine, connected directly to the power, and we were able to keep this connected by attaching a regular plug. When you turn the power on from the cabinet switch, power flows to the components inside the case – your Raspberry Pi and screen will come on, and all will be well with the world.
|
||||
|
||||
The J-Pac slides straight into the JAMMA interface, but you may also have to do a little manual wiring. The JAMMA standard only supports up to three buttons for each player (although many unofficially support four), while the J-Pac can handle up to six buttons. To get those extra buttons connected, you need to connect one side of the button’s switch to GND fed from the J-Pac with the other side of the switch going into one of the screw-mounted inputs in the side of the J-Pac. These are labelled 1SW4, 1SW5, 1SW6, 2SW4, 2SW5 and 2SW6. The J-Pac also includes passthrough connections for audio, but we’ve found this to be incredibly noisy. Instead, we wired the speaker in our cabinet to an old SoundBlaster amplifier and connected this to the audio outputs on the Raspberry Pi. You don’t want audio to be pristine, but you do want it to be loud enough.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Our Raspberry Pi is now connected to the J-Pac on the left and both the screen and the USB hub (click for larger).
|
||||
|
||||
The J-Pac or I-Pac then connects to your PC or Raspberry Pi using a PS2-to-USB cable, which should also be used to connect to a PS2 port on your PC directly. There is an additional option to use an old PS2 connector, if your PC is old enough to have one, but we found in testing that the USB performance is identical. This won’t apply to the PS2-less Raspberry Pi, of course, and don’t forget that the Pi will also need powering. We always recommend doing so from a compatible powered hub, as a lack of power is the most common source of Raspberry Pi errors. You’ll also need to get networking to your Raspberry Pi, either through the Ethernet port (perhaps using a powerline adaptor hidden in the cabinet), or by using a wireless USB device. Networking is essential because it enables you to reconfigure your PI while it’s tucked away within the cabinet, and it also enables you to change settings and perform administration tasks without having to connect a keyboard or mouse.
|
||||
|
||||
> ### Coin Mechanism ###
|
||||
|
||||
> In the emulation community, getting your coin mechanism to work with your emulator was often considered a step too close to commercial production. It meant you could potential charge people to use your machine. Not only would this be wrong, but considering the provenance of many of the games you run on your own arcade machine, it could also be illegal. And it’s definitely against the spirit of emulation. However, we and many other devotees thinking that a working coin mechanism is another step closer to the realism of an arcade machine, and is worth the effort in recreating the nostalgia of an old arcade. There’s nothing like dropping a 10p piece into the coin tray and to hear the sound of the credits being added to the machine.
|
||||
|
||||
> It’s not actually that difficult. It depends on the coin mechanism in your arcade machine and how it sends a signal to say how many credits had been inserted. Most coin mechanisms come in two parts. The large part is the coin acceptor/validator. This is the physical side of the process that detects whether a coin is authentic, and determines its value. It does this with the help of a credit/logic board, usually attached via a ribbon cable and featuring lots of DIP switches. These switches are used to change which coins are accepted and how many credits they generate. It’s then usually as simple as finding the output switch, which is triggered with a credit, and connecting this to the coin input on your JAMMA connector, or directly onto the J-Pac. Our coin mechanism is a Mars MS111, common in the UK in the early 90s, and there’s plenty of information online about what each of the DIP switches do, as well as how to programme the controller for newer coins. We were also able to wire the 12V connector from the mechanism to a small light for behind the coin entry slot.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step 4: Software ####
|
||||
|
||||
MAME is the only viable emulator for a project of this scale, and it now supports many thousands of different games running on countless different platforms, from the first arcade machines through to some more recent ones. It’s a project that has also spawned MESS, the multi-emulator super system, which targets platforms such as home computers and consoles from the 80s and 90s.
|
||||
|
||||
Configuring MAME could take a six-page article in itself. It’s a complex, sprawling, magnificent piece of software that emulates so many CPUs, so many sound devices, chips, controllers with so many options, that like MythTV, you never really stop configuring it.
|
||||
|
||||
But there’s an easier option, and one that’s purpose-built for the Raspberry Pi. It’s called PiMAME. This is both a distribution download and a script you can run on top of Raspbian, the Pi’s default distribution. Not only does it install MAME on your Raspberry Pi (which is useful because it’s not part of any of the default repositories), it also installs a selection of other emulators along with front-ends to manage them. MAME, for example, is a command-line utility with dozens of options. But PiMAME has another clever trick up its sleeve – it installs a simple web server that enables you to install new games through a browser connected to your network. This is a great advantage, because getting games into the correct folders is one of the trials of dealing with MAME, and it also enables you to make best use of whatever storage you’ve got connected to your Pi. Plus, PiMAME will update itself from the same script you use to install it, so keeping on top of updates couldn’t be easier. This could be especially useful at the moment, as at the time of writing the project was on the cusp of a major upgrade in the form of the 0.8 release. We found it slightly unstable in early March, but we’re sure everything will be sorted by the time you read this.
|
||||
|
||||
The best way to install PiMAME is to install Raspbian first. You can do this either through NOOBS, using a graphical tool from your desktop, or by using the dd command to copy the contents of the Raspbian image directly onto your SD card. As we mentioned in last month’s BrewPi tutorial, this process has been documented many times before, so we won’t waste the space here. Just install NOOBS if you want the easy option, following the instructions on the Raspberry Pi site. With Raspbian installed and running, make sure you use the configuration tool to free the space on your SD card, and that the system is up to date (sudo apt-get update; sudo apt-get upgrade). You then need to make sure you’ve got the git package already installed. Any recent version of Raspbian will have installed git already, but you can check by typing sudo apt-get install git just to check.
|
||||
|
||||
You then have to type the following command to clone the PiMAME installer from the project’s GitHub repository:
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ssilverm/pimame_installer
|
||||
|
||||
After that, you should get the following feedback if the command works:
|
||||
|
||||
Cloning into ‘pimame_installer’...
|
||||
remote: Reusing existing pack: 2306, done.
|
||||
remote: Total 2306 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
|
||||
Receiving objects: 100% (2306/2306), 4.61 MiB | 11 KiB/s, done.
|
||||
Resolving deltas: 100% (823/823), done.
|
||||
|
||||
This command will create a new folder called ‘pimame_installer’, and the next step is to switch into this and run the script it contains:
|
||||
|
||||
cd pimame_installer/
|
||||
sudo ./install.sh
|
||||
|
||||
This command installs and configures a lot of software. The length of time it takes will depend on your internet connection, as a lot of extra packages are downloaded. Our humble Pi with a 15Mb internet connection took around 45 minutes to complete the script, after which you’re invited to restart the machine. You can do this safely by typing sudo shutdown -r now, as this command will automatically handle any remaining write operations to the SD card.
|
||||
|
||||
And that’s all there is to the installation. After rebooting your Pi, you will be automatically logged in and the PiMAME launch menu will appear. It’s a great-looking interface in version 0.8, with photos of each of the platforms supported, plus small red icons to indicate how many games you’ve got installed.This should now be navigable through your controller. If you want to make sure the controller is correctly detected, use SSH to connect to your Pi and check for the existence of **/dev/input/by-id/usb-Ultimarc_I-PAC_Ultimarc_I-PAC-event-kbd**.
|
||||
|
||||
The default keyboard controls will enable you to select what kind of emulator you want to run on your arcade machine. The option we’re most interested in is the first, labelled ‘AdvMAME’, but you might also be surprised to see another MAME on offer, MAME4ALL. MAME4ALL is built specifically for the Raspberry Pi, and takes an old version of the MAME source code so that the performance of the ROMS that it does support is optimal. This makes a lot of sense, because there’s no way your Pi is going to be able to play anything too demanding, so there’s no reason to belabour the emulator with unneeded compatibility. All that’s left to do now is get some games onto your system (see the boxout below), and have fun!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/arcade-machine/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ben Everard][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/author/ben_everard/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ultimarc.com/jpac.html
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
Translating by SPccman
|
||||
How to configure SNMPv3 on ubuntu 14.04 server
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is an "Internet-standard protocol for managing devices on IP networks". Devices that typically support SNMP include routers, switches, servers, workstations, printers, modem racks and more.It is used mostly in network management systems to monitor network-attached devices for conditions that warrant administrative attention. SNMP is a component of the Internet Protocol Suite as defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). It consists of a set of standards for network management, including an application layer protocol, a database schema, and a set of data objects.[2]
|
||||
@ -96,4 +97,4 @@ via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/how-to-configure-snmpv3-on-ubuntu-14-04-server.ht
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,466 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux Tutorial: Install Ansible Configuration Management And IT Automation Tool
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Today I will be talking about ansible, a powerful configuration management solution written in python. There are many configuration management solutions available, all with pros and cons, ansible stands apart from many of them for its simplicity. What makes ansible different than many of the most popular configuration management systems is that its agent-less, no need to setup agents on every node you want to control. Plus, this has the benefit of being able to control you entire infrastructure from more than one place, if needed. That last point's validity, of being a benefit, may be debatable but I find it as a positive in most cases. Enough talk, lets get started with Ansible installation and configuration on a RHEL/CentOS, and Debian/Ubuntu based systems.
|
||||
|
||||
### Prerequisites ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. Distro: RHEL/CentOS/Debian/Ubuntu Linux
|
||||
1. Jinja2: A modern and designer friendly templating language for Python.
|
||||
1. PyYAML: A YAML parser and emitter for the Python programming language.
|
||||
1. parmiko: Native Python SSHv2 protocol library.
|
||||
1. httplib2: A comprehensive HTTP client library.
|
||||
1. Most of the actions listed in this post are written with the assumption that they will be executed by the root user running the bash or any other modern shell.
|
||||
|
||||
How Ansible works
|
||||
|
||||
Ansible tool uses no agents. It requires no additional custom security infrastructure, so it’s easy to deploy. All you need is ssh client and server:
|
||||
|
||||
+----------------------+ +---------------+
|
||||
|Linux/Unix workstation| SSH | file_server1 |
|
||||
|with Ansible |<------------------>| db_server2 | Unix/Linux servers
|
||||
+----------------------+ Modules | proxy_server3 | in local/remote
|
||||
192.168.1.100 +---------------+ data centers
|
||||
|
||||
Where,
|
||||
|
||||
1. 192.168.1.100 - Install Ansible on your local workstation/server.
|
||||
1. file_server1..proxy_server3 - Use 192.168.1.100 and Ansible to automates configuration management of all servers.
|
||||
1. SSH - Setup ssh keys between 192.168.1.100 and local/remote servers.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ansible Installation Tutorial ###
|
||||
|
||||
Installation of ansible is a breeze, many distributions have a package available in their 3rd party repos which can easily be installed, a quick alternative is to just pip install it or grab the latest copy from github. To install using your package manager, on [RHEL/CentOS Linux based systems you will most likely need the EPEL repo][1] then:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install ansible on a RHEL/CentOS Linux based system ####
|
||||
|
||||
Type the following [yum command][2]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install ansible
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install ansible on a Debian/Ubuntu Linux based system ####
|
||||
|
||||
Type the following [apt-get command][3]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
|
||||
$ sudo apt-add-repository ppa:ansible/ansible
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install ansible
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install ansible using pip ####
|
||||
|
||||
The [pip command is a tool for installing and managing Python packages][4], such as those found in the Python Package Index. The following method works on Linux and Unix-like systems:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pip install ansible
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install the latest version of ansible using source code ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can install the latest version from github as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd ~
|
||||
$ git clone git://github.com/ansible/ansible.git
|
||||
$ cd ./ansible
|
||||
$ source ./hacking/env-setup
|
||||
|
||||
When running ansible from a git checkout, one thing to remember is that you will need to setup your environment everytime you want to use it, or you can add it to your bash rc file:
|
||||
|
||||
# ADD TO BASH RC
|
||||
$ echo "export ANSIBLE_HOSTS=~/ansible_hosts" >> ~/.bashrc
|
||||
$ echo "source ~/ansible/hacking/env-setup" >> ~/.bashrc
|
||||
|
||||
The hosts file for ansible is basically a list of hosts that ansible is able to perform work on. By default ansible looks for the hosts file at /etc/ansible/hosts, but there are ways to override that which can be handy if you are working with multiple installs or have several different clients for whose datacenters you are responsible for. You can pass the hosts file on the command line using the -i option:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m shell -a "hostname" --ask-pass -i /etc/some/other/dir/ansible_hosts
|
||||
|
||||
My preference however is to use and environment variable, this can be useful if source a different file when starting work for a specific client. The environment variable is $ANSIBLE_HOSTS, and can be set as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
$ export ANSIBLE_HOSTS=~/ansible_hosts
|
||||
|
||||
Once all requirements are installed and you have you hosts file setup you can give it a test run. For a quick test I put 127.0.0.1 into the ansible hosts file as follow:
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo "127.0.0.1" > ~/ansible_hosts
|
||||
|
||||
Now lets test with a quick ping:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m ping
|
||||
|
||||
OR ask for the ssh password:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m ping --ask-pass
|
||||
|
||||
I have run across a problem a few times regarding initial setup, it is highly recommended you setup keys for ansible to use but in the previous test we used --ask-pass, on some machines you will need [to install sshpass][5] or add a -c paramiko like so:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m ping --ask-pass -c paramiko
|
||||
|
||||
Or you [can install sshpass][6], however sshpass is not always available in the standard repos so paramiko can be easier.
|
||||
|
||||
### Setup SSH Keys ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have gotten the configuration, and other simple stuff, out of the way lets move onto doing something productive. Alot of the power of ansible lies in playbooks, which are basically scripted ansible runs (for the most part), but we will start with some one liners before we build out a playbook. Lets start with creating and configuring keys so we can avoid the -c and --ask-pass options:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
|
||||
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa):
|
||||
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
|
||||
Enter same passphrase again:
|
||||
Your identification has been saved in /home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa.
|
||||
Your public key has been saved in /home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
|
||||
The key fingerprint is:
|
||||
94:a0:19:02:ba:25:23:7f:ee:6c:fb:e8:38:b4:f2:42 mike@ultrabook.linuxdork.com
|
||||
The key's randomart image is:
|
||||
+--[ RSA 2048]----+
|
||||
|... . . |
|
||||
|. . + . . |
|
||||
|= . o o |
|
||||
|.* . |
|
||||
|. . . S |
|
||||
| E.o |
|
||||
|.. .. |
|
||||
|o o+.. |
|
||||
| +o+*o. |
|
||||
+-----------------+
|
||||
|
||||
Now obviously there are plenty of ways to put this in place on the remote machine but since we are using ansible, lets use that:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m copy -a "src=/home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa.pub dest=/tmp/id_rsa.pub" --ask-pass -c paramiko
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
SSH password:
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | success >> {
|
||||
"changed": true,
|
||||
"dest": "/tmp/id_rsa.pub",
|
||||
"gid": 100,
|
||||
"group": "users",
|
||||
"md5sum": "bafd3fce6b8a33cf1de415af432774b4",
|
||||
"mode": "0644",
|
||||
"owner": "mike",
|
||||
"size": 410,
|
||||
"src": "/home/mike/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1407008170.46-208759459189201/source",
|
||||
"state": "file",
|
||||
"uid": 1000
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Next, add the public key in remote server, enter:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m shell -a "cat /tmp/id_rsa.pub >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys" --ask-pass -c paramiko
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
SSH password:
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
|
||||
/bin/sh: /root/.ssh/authorized_keys: Permission denied
|
||||
|
||||
Whoops, we want to be able to run things as root, so lets add a -u option:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m shell -a "cat /tmp/id_rsa.pub >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys" --ask-pass -c paramiko -u root
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
SSH password:
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | success | rc=0 >>
|
||||
|
||||
Please note, I wanted to demonstrate a file transfer using ansible, there is however a more built in way for managing keys using ansible:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m authorized_key -a "user=mike key='{{ lookup('file', '/home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa.pub') }}' path=/home/mike/.ssh/authorized_keys manage_dir=no" --ask-pass -c paramiko
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
SSH password:
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | success >> {
|
||||
"changed": true,
|
||||
"gid": 100,
|
||||
"group": "users",
|
||||
"key": "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQCq+Z8/usprXk0aCAPyP0TGylm2MKbmEsHePUOd7p5DO1QQTHak+9gwdoJJavy0yoUdi+C+autKjvuuS+vGb8+I+8mFNu5CvKiZzIpMjZvrZMhHRdNud7GuEanusTEJfi1pUd3NA2iXhl4a6S9a/4G2mKyf7QQSzI4Z5ddudUXd9yHmo9Yt48/ASOJLHIcYfSsswOm8ux1UnyeHqgpdIVONVFsKKuSNSvZBVl3bXzhkhjxz8RMiBGIubJDBuKwZqNSJkOlPWYN76btxMCDVm07O7vNChpf0cmWEfM3pXKPBq/UBxyG2MgoCGkIRGOtJ8UjC/daadBUuxg92/u01VNEB mike@ultrabook.linuxdork.com",
|
||||
"key_options": null,
|
||||
"keyfile": "/home/mike/.ssh/authorized_keys",
|
||||
"manage_dir": false,
|
||||
"mode": "0600",
|
||||
"owner": "mike",
|
||||
"path": "/home/mike/.ssh/authorized_keys",
|
||||
"size": 410,
|
||||
"state": "file",
|
||||
"uid": 1000,
|
||||
"unique": false,
|
||||
"user": "mike"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Now that the keys are in place lets try running an arbitrary command like hostname and hope we don't get prompted for a password
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m shell -a "hostname" -u root
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | success | rc=0 >>
|
||||
|
||||
Success!!! Now that we can run commands as root and not be bothered by using a password we are in a good place to easily configure any and all hosts in the ansible hosts file. Let's remove the key from /tmp:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m file -a "dest=/tmp/id_rsa.pub state=absent" -u root
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | success >> {
|
||||
"changed": true,
|
||||
"path": "/tmp/id_rsa.pub",
|
||||
"state": "absent"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Next, I'm going to make sure we have a few packages installed and on the latest version and we will move on to something a little more complicated:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m zypper -a "name=apache2 state=latest" -u root
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | success >> {
|
||||
"changed": false,
|
||||
"name": "apache2",
|
||||
"state": "latest"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Alright, the key we placed in /tmp is now absent and we have the latest version of apache installed. This brings me to the next point, something that makes ansible very flexible and gives more power to playbooks, many may have noticed the -m zypper in the previous commands. Now unless you use openSuse or Suse enterpise you may not be familiar with zypper, it is basically the equivalent of yum in the suse world. In all of the examples above I have only had one machine in my hosts file, and while everything but the last command should work on any standard *nix systems with standard ssh configs, this leads to a problem. What if we had multiple machine types that we wanted to manage? Well this is where playbooks, and the configurability of ansible really shines. First lets modify our hosts file a little, here goes:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat ~/ansible_hosts
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
[RHELBased]
|
||||
10.50.1.33
|
||||
10.50.1.47
|
||||
|
||||
[SUSEBased]
|
||||
127.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
First, we create some groups of servers, and give them some meaningful tags. Then we create a playbook that will do different things for the different kinds of servers. You might notice the similarity between the yaml data structures and the command line instructions we ran earlier. Basically the -m is a module, and -a is for module args. In the YAML representation you put the module then :, and finally the args.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
- hosts: SUSEBased
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- zypper: name=apache2 state=latest
|
||||
- hosts: RHELBased
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- yum: name=httpd state=latest
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we have a simple playbook, we can run it as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible-playbook testPlaybook.yaml -f 10
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY [SUSEBased] **************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
GATHERING FACTS ***************************************************************
|
||||
ok: [127.0.0.1]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [zypper name=apache2 state=latest] **************************************
|
||||
ok: [127.0.0.1]
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY [RHELBased] **************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
GATHERING FACTS ***************************************************************
|
||||
ok: [10.50.1.33]
|
||||
ok: [10.50.1.47]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [yum name=httpd state=latest] *******************************************
|
||||
changed: [10.50.1.33]
|
||||
changed: [10.50.1.47]
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************
|
||||
10.50.1.33 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
|
||||
10.50.1.47 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
|
||||
127.0.0.1 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
|
||||
|
||||
Now you will notice that you will see output from each machine that ansible contacted. The -f is what lets ansible run on multiple hosts in parallel. Instead of using all, or a name of a host group, on the command line you can put this passwords for the ask-pass prompt into the playbook. While we no longer need the --ask-pass since we have ssh keys setup, it comes in handy when setting up new machines, and even new machines can run from a playbook. To demonstrate this lets convert our earlier key example into a playbook:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
- hosts: SUSEBased
|
||||
remote_user: mike
|
||||
sudo: yes
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- authorized_key: user=root key="{{ lookup('file', '/home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa.pub') }}" path=/root/.ssh/authorized_keys manage_dir=no
|
||||
- hosts: RHELBased
|
||||
remote_user: mdonlon
|
||||
sudo: yes
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- authorized_key: user=root key="{{ lookup('file', '/home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa.pub') }}" path=/root/.ssh/authorized_keys manage_dir=no
|
||||
|
||||
Now there are plenty of other options here that could be done, for example having the keys dropped during a kickstart, or via some other kind of process involved with bringing up machines on the hosting of your choice, but this can be used in pretty much any situation assuming ssh is setup to accept a password. One thing to think about before writing out too many playbooks, version control can save you a lot of time. Machines need to change over time, you don't need to re-write a playbook every time a machine changes, just update the pertinent bits and commit the changes. Another benefit of this ties into what I said earlier about being able to manage the entire infrastructure from multiple places. You can easily git clone your playbook repo onto a new machine and be completely setup to manage everything in a repetitive manner.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Real world ansible example ####
|
||||
|
||||
I know a lot of people make great use of services like pastebin, and a lot of companies for obvious reasons setup their own internal instance of something similar. Recently, I came across a newish application called showterm and coincidentally I was asked to setup an internal instance of it for a client. I will spare you the details of this app, but you can google showterm if interested. So for a reasonable real world example I will attempt to setup a showterm server, and configure the needed app on the client to use it. In the process we will need a database server as well. So here goes, lets start with the client configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
- hosts: showtermClients
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- yum: name=rubygems state=latest
|
||||
- yum: name=ruby-devel state=latest
|
||||
- yum: name=gcc state=latest
|
||||
- gem: name=showterm state=latest user_install=no
|
||||
|
||||
That was easy, lets move on to the main server:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
- hosts: showtermServers
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- name: ensure packages are installed
|
||||
yum: name={{item}} state=latest
|
||||
with_items:
|
||||
- postgresql
|
||||
- postgresql-server
|
||||
- postgresql-devel
|
||||
- python-psycopg2
|
||||
- git
|
||||
- ruby21
|
||||
- ruby21-passenger
|
||||
- name: showterm server from github
|
||||
git: repo=https://github.com/ConradIrwin/showterm.io dest=/root/showterm
|
||||
- name: Initdb
|
||||
command: service postgresql initdb
|
||||
creates=/var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Start PostgreSQL and enable at boot
|
||||
service: name=postgresql
|
||||
enabled=yes
|
||||
state=started
|
||||
- gem: name=pg state=latest user_install=no
|
||||
handlers:
|
||||
- name: restart postgresql
|
||||
service: name=postgresql state=restarted
|
||||
|
||||
- hosts: showtermServers
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
sudo: yes
|
||||
sudo_user: postgres
|
||||
vars:
|
||||
dbname: showterm
|
||||
dbuser: showterm
|
||||
dbpassword: showtermpassword
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- name: create db
|
||||
postgresql_db: name={{dbname}}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: create user with ALL priv
|
||||
postgresql_user: db={{dbname}} name={{dbuser}} password={{dbpassword}} priv=ALL
|
||||
- hosts: showtermServers
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- name: database.yml
|
||||
template: src=database.yml dest=/root/showterm/config/database.yml
|
||||
- hosts: showtermServers
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- name: run bundle install
|
||||
shell: bundle install
|
||||
args:
|
||||
chdir: /root/showterm
|
||||
- hosts: showtermServers
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- name: run rake db tasks
|
||||
shell: 'bundle exec rake db:create db:migrate db:seed'
|
||||
args:
|
||||
chdir: /root/showterm
|
||||
- hosts: showtermServers
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- name: apache config
|
||||
template: src=showterm.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf.d/showterm.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Not so bad, now keeping in mind that this is a somewhat random and obscure app that we can now install in a consistent fashion on any number of machines, this is where the benefits of configuration management really come to light. Also, in most cases the declarative syntax almost speaks for itself and wiki pages need not go into as much detail, although a wiki page with too much detail is never a bad thing in my opinion.
|
||||
|
||||
### Expanding Configuration ###
|
||||
|
||||
We have not touched on everything here, Ansible has many options for configuring you setup. You can do things like embedding variables in your hosts file, so that Ansible will interpolate them on the remote nodes, eg.
|
||||
|
||||
[RHELBased]
|
||||
10.50.1.33 http_port=443
|
||||
10.50.1.47 http_port=80 ansible_ssh_user=mdonlon
|
||||
|
||||
[SUSEBased]
|
||||
127.0.0.1 http_port=443
|
||||
|
||||
While this is really handy for quick configurations, you can also layer variables across multiple files in yaml format. In you hosts file path you can make two sub directories named group_vars and host_vars. Any files in those paths that match the name of the group of hosts, or a host name in your hosts file will be interpolated at run time. So the previous example would look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # pwd
|
||||
/etc/ansible
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # tree
|
||||
.
|
||||
├── group_vars
|
||||
│ ├── RHELBased
|
||||
│ └── SUSEBased
|
||||
├── hosts
|
||||
└── host_vars
|
||||
├── 10.50.1.33
|
||||
└── 10.50.1.47
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
2 directories, 5 files
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # cat hosts
|
||||
[RHELBased]
|
||||
10.50.1.33
|
||||
10.50.1.47
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[SUSEBased]
|
||||
127.0.0.1
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # cat group_vars/RHELBased
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # cat group_vars/SUSEBased
|
||||
---
|
||||
http_port: 443
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # cat host_vars/10.50.1.33
|
||||
---
|
||||
http_port: 443
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # cat host_vars/10.50.1.47
|
||||
---
|
||||
http_port:80
|
||||
ansible_ssh_user: mdonlon
|
||||
|
||||
### Refining Playbooks ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are many ways to organize playbooks as well. In the previous examples we used a single file, and everything is really simplified. One way of organizing things that is commonly used is creating roles. Basically you load a main file as your playbook, and that then imports all the data from the extra files, the extra files are organized as roles. For example if you have a wordpress site, you need a web head, and a database. The web head will have a web server, the app code, and any needed modules. The database is sometimes ran on the same host and some times ran on remote hosts, and this is where roles really shine. You make a directory, and small playbook for each role. In this case we can have an apache role, mysql role, wordpress role, mod_php, and php roles. The big advantage to this is that not every role has to be applied on one server, in this case mysql could be applied to a separate machine. This also allows for code re-use, for example you apache role could be used with python apps and php apps alike. Demonstrating this is a little beyond the scope of this article, and there are many different ways of doing thing, I would recommend searching for ansible playbook examples. There are many people contributing code on github, and I am sure various other sites.
|
||||
|
||||
### Modules ###
|
||||
|
||||
All of the work being done behind the scenes in ansible is driven by modules. Ansible has an excellent library of built in modules that do things like package installation, transferring files, and everything we have done in this article. But for some people this will not be suitable for their setup, ansible has a means of adding your own modules. One great thing about the API provided by Ansible is that you are not restricted to the language it was written in, Python, you can use any language really. Ansible modules work by passing around JSON data structures, so as long as you can build a JSON data structure in your language of choice, which I am pretty sure any scripting language can do, you can begin coding something right away. There is much documentation on the Ansible site, about how the module interface works, and many examples of modules on github as well. Keep in mind that some obscure languages may not have great support, but that would only be because not enough people are contributing code in that language, try it out and publish your results somewhere!
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In conclusion, there are many systems around for configuration management, I hope this article shows the ease of setup for ansible which I believe is one of its strongest points. Please keep in mind that I was trying to show a lot of different ways to do things, and not everything above may be considered best practice in your private infrastructure, or the coding world abroad. Here are some more links to take you knowledge of ansible to the next level:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ansible project][7] home page.
|
||||
- [Ansible project documentation][8].
|
||||
- [Multistage environments with Ansible][9].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/python-tutorials/linux-tutorial-install-ansible-configuration-management-and-it-automation-tool/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Nix Craft][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/about-us
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/fedora-sl-centos-redhat6-enable-epel-repo/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/rhel-centos-fedora-linux-yum-command-howto/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-debian-package-management-cheat-sheet.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/debian-ubuntu-centos-rhel-linux-install-pipclient/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/noninteractive-shell-script-ssh-password-provider/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/noninteractive-shell-script-ssh-password-provider/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.ansible.com/
|
||||
[8]:http://docs.ansible.com/
|
||||
[9]:http://rosstuck.com/multistage-environments-with-ansible/
|
||||
@ -1,219 +0,0 @@
|
||||
DoubleC is translating
|
||||
How to create a site-to-site IPsec VPN tunnel using Openswan in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A virtual private network (VPN) tunnel is used to securely interconnect two physically separate networks through a tunnel over the Internet. Tunneling is needed when the separate networks are private LAN subnets with globally non-routable private IP addresses, which are not reachable to each other via traditional routing over the Internet. For example, VPN tunnels are often deployed to connect different NATed branch office networks belonging to the same institution.
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes VPN tunneling may be used simply for its security benefit as well. Service providers or private companies may design their networks in such a way that vital servers (e.g., database, VoIP, banking servers) are placed in a subnet that is accessible to trusted personnel through a VPN tunnel only. When a secure VPN tunnel is required, [IPsec][1] is often a preferred choice because an IPsec VPN tunnel is secured with multiple layers of security.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will show how we can easily create a site-to-site VPN tunnel using [Openswan][2] in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### Topology ###
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will focus on the following topologies for creating an IPsec tunnel.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Packages and Preparing VPN Servers ###
|
||||
|
||||
Usually, you will be managing site-A only, but based on the requirements, you could be managing both site-A and site-B. We start the process by installing Openswan.
|
||||
|
||||
On Red Hat based Systems (CentOS, Fedora or RHEL):
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install openswan lsof
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian based Systems (Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint):
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install openswan
|
||||
|
||||
Now we disable VPN redirects, if any, in the server using these commands:
|
||||
|
||||
# for vpn in /proc/sys/net/ipv4/conf/*;
|
||||
# do echo 0 > $vpn/accept_redirects;
|
||||
# echo 0 > $vpn/send_redirects;
|
||||
# done
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we modify the kernel parameters to allow IP forwarding and disable redirects permanently.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
|
||||
net.ipv4.conf.all.accept_redirects = 0
|
||||
net.ipv4.conf.all.send_redirects = 0
|
||||
|
||||
Reload /etc/sysctl.conf:
|
||||
|
||||
# sysctl -p
|
||||
|
||||
We allow necessary ports in the firewall. Please make sure that the rules are not conflicting with existing firewall rules.
|
||||
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 500 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 4500 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 4500 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we create firewall rules for NAT.
|
||||
|
||||
# iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s site-A-private-subnet -d site-B-private-subnet -j SNAT --to site-A-Public-IP
|
||||
|
||||
Please make sure that the firewall rules are persistent.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Note: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- You could use MASQUERADE instead of SNAT. Logically it should work, but it caused me to have issues with virtual private servers (VPS) in the past. So I would use SNAT if I were you.
|
||||
- If you are managing site-B as well, create similar rules in site-B server.
|
||||
- Direct routing does not need SNAT.
|
||||
|
||||
### Preparing Configuration Files ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first configuration file that we will work with is ipsec.conf. Regardless of which server you are configuring, always consider your site as 'left' and remote site as 'right'. The following configuration is done in siteA's VPN server.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/ipsec.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## general configuration parameters ##
|
||||
|
||||
config setup
|
||||
plutodebug=all
|
||||
plutostderrlog=/var/log/pluto.log
|
||||
protostack=netkey
|
||||
nat_traversal=yes
|
||||
virtual_private=%v4:10.0.0.0/8,%v4:192.168.0.0/16,%v4:172.16.0.0/16
|
||||
## disable opportunistic encryption in Red Hat ##
|
||||
oe=off
|
||||
|
||||
## disable opportunistic encryption in Debian ##
|
||||
## Note: this is a separate declaration statement ##
|
||||
include /etc/ipsec.d/examples/no_oe.conf
|
||||
|
||||
## connection definition in Red Hat ##
|
||||
conn demo-connection-redhat
|
||||
authby=secret
|
||||
auto=start
|
||||
ike=3des-md5
|
||||
## phase 1 ##
|
||||
keyexchange=ike
|
||||
## phase 2 ##
|
||||
phase2=esp
|
||||
phase2alg=3des-md5
|
||||
compress=no
|
||||
pfs=yes
|
||||
type=tunnel
|
||||
left=<siteA-public-IP>
|
||||
leftsourceip=<siteA-public-IP>
|
||||
leftsubnet=<siteA-private-subnet>/netmask
|
||||
## for direct routing ##
|
||||
leftsubnet=<siteA-public-IP>/32
|
||||
leftnexthop=%defaultroute
|
||||
right=<siteB-public-IP>
|
||||
rightsubnet=<siteB-private-subnet>/netmask
|
||||
|
||||
## connection definition in Debian ##
|
||||
conn demo-connection-debian
|
||||
authby=secret
|
||||
auto=start
|
||||
## phase 1 ##
|
||||
keyexchange=ike
|
||||
## phase 2 ##
|
||||
esp=3des-md5
|
||||
pfs=yes
|
||||
type=tunnel
|
||||
left=<siteA-public-IP>
|
||||
leftsourceip=<siteA-public-IP>
|
||||
leftsubnet=<siteA-private-subnet>/netmask
|
||||
## for direct routing ##
|
||||
leftsubnet=<siteA-public-IP>/32
|
||||
leftnexthop=%defaultroute
|
||||
right=<siteB-public-IP>
|
||||
rightsubnet=<siteB-private-subnet>/netmask
|
||||
|
||||
Authentication can be done in several different ways. This tutorial will cover the use of pre-shared key, which is added to the file /etc/ipsec.secrets.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/ipsec.secrets
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
siteA-public-IP siteB-public-IP: PSK "pre-shared-key"
|
||||
## in case of multiple sites ##
|
||||
siteA-public-IP siteC-public-IP: PSK "corresponding-pre-shared-key"
|
||||
|
||||
### Starting the Service and Troubleshooting ###
|
||||
|
||||
The server should now be ready to create a site-to-site VPN tunnel. If you are managing siteB as well, please make sure that you have configured the siteB server with necessary parameters. For Red Hat based systems, please make sure that you add the service into startup using chkconfig command.
|
||||
|
||||
# /etc/init.d/ipsec restart
|
||||
|
||||
If there are no errors in both end servers, the tunnel should be up now. Taking the following into consideration, you can test the tunnel with ping command.
|
||||
|
||||
1. The siteB-private subnet should not be reachable from site A, i.e., ping should not work if the tunnel is not up.
|
||||
1. After the tunnel is up, try ping to siteB-private-subnet from siteA. This should work.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the routes to the destination's private subnet should appear in the server's routing table.
|
||||
|
||||
# ip route
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[siteB-private-subnet] via [siteA-gateway] dev eth0 src [siteA-public-IP]
|
||||
default via [siteA-gateway] dev eth0
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, we can check the status of the tunnel using the following useful commands.
|
||||
|
||||
# service ipsec status
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
IPsec running - pluto pid: 20754
|
||||
pluto pid 20754
|
||||
1 tunnels up
|
||||
some eroutes exist
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# ipsec auto --status
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## output truncated ##
|
||||
000 "demo-connection-debian": myip=<siteA-public-IP>; hisip=unset;
|
||||
000 "demo-connection-debian": ike_life: 3600s; ipsec_life: 28800s; rekey_margin: 540s; rekey_fuzz: 100%; keyingtries: 0; nat_keepalive: yes
|
||||
000 "demo-connection-debian": policy: PSK+ENCRYPT+TUNNEL+PFS+UP+IKEv2ALLOW+SAREFTRACK+lKOD+rKOD; prio: 32,28; interface: eth0;
|
||||
|
||||
## output truncated ##
|
||||
000 #184: "demo-connection-debian":500 STATE_QUICK_R2 (IPsec SA established); EVENT_SA_REPLACE in 1653s; newest IPSEC; eroute owner; isakmp#183; idle; import:not set
|
||||
|
||||
## output truncated ##
|
||||
000 #183: "demo-connection-debian":500 STATE_MAIN_I4 (ISAKMP SA established); EVENT_SA_REPLACE in 1093s; newest ISAKMP; lastdpd=-1s(seq in:0 out:0); idle; import:not set
|
||||
|
||||
The log file /var/log/pluto.log should also contain useful information regarding authentication, key exchanges and information on different phases of the tunnel. If your tunnel doesn't come up, you could check there as well.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are sure that all the configuration is correct, and if your tunnel is still not coming up, you should check the following things.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Many ISPs filter IPsec ports. Make sure that UDP 500, TCP/UDP 4500 ports are allowed by your ISP. You could try connecting to your server IPsec ports from a remote location by telnet.
|
||||
1. Make sure that necessary ports are allowed in the firewall of the server/s.
|
||||
1. Make sure that the pre-shared keys are identical in both end servers.
|
||||
1. The left and right parameters should be properly configured on both end servers.
|
||||
1. If you are facing problems with NAT, try using SNAT instead of MASQUERADING.
|
||||
|
||||
To sum up, this tutorial focused on the procedure of creating a site-to-site IPSec VPN tunnel in Linux using Openswan. VPN tunnels are very useful in enhancing security as they allow admins to make critical resources available only through the tunnels. Also VPN tunnels ensure that the data in transit is secured from eavesdropping or interception.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps. Let me know what you think.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/create-site-to-site-ipsec-vpn-tunnel-openswan-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPsec
|
||||
[2]:https://www.openswan.org/
|
||||
@ -1,213 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Setup Thin Provisioning Volumes in Logical Volume Management (LVM) – Part IV
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Logical Volume management has great features such as snapshots and Thin Provisioning. Previously in (Part – III) we have seen how to snapshot the logical volume. Here in this article, we will going to see how to setup thin Provisioning volumes in LVM.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Setup Thin Provisioning in LVM
|
||||
|
||||
### What is Thin Provisioning? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Thin Provisioning is used in lvm for creating virtual disks inside a thin pool. Let us assume that I have a **15GB** storage capacity in my server. I already have 2 clients who has 5GB storage each. You are the third client, you asked for 5GB storage. Back then we use to provide the whole 5GB (Thick Volume) but you may use 2GB from that 5GB storage and 3GB will be free which you can fill it up later.
|
||||
|
||||
But what we do in thin Provisioning is, we use to define a thin pool inside one of the large volume group and define the thin volumes inside that thin pool. So, that whatever files you write will be stored and your storage will be shown as 5GB. But the full 5GB will not allocate the entire disk. The same process will be done for other clients as well. Like I said there are 2 clients and you are my 3rd client.
|
||||
|
||||
So, let us assume how much total GB I have assigned for clients? Totally 15GB was already completed, If someone comes to me and ask for 5GB can I give? The answer is “**Yes**“, here in thin Provisioning I can give 5GB for 4th Client even though I have assigned 15GB.
|
||||
|
||||
**Warning**: From 15GB, if we are Provisioning more than 15GB it is called Over Provisioning.
|
||||
|
||||
### How it Works? and How we provide storage to new Clients? ###
|
||||
|
||||
I have provided you 5GB but you may used only 2GB and other 3GB will be free. In Thick Provisioning we can’t do this, because it will allocate the whole space at first itself.
|
||||
|
||||
In thin Provisioning if I’m defining 5GB for you it won’t allocate the whole disk space while defining a volume, it will grow till 5GB according to your data write, Hope you got it! same like you, other clients too won’t use the full volumes so there will be a chance to add 5GB to a new client, This is called over Provisioning.
|
||||
|
||||
But it’s compulsory to monitored each and every volume growth, if not it will end-up in a disaster. While over Provisioning is done if the all 4 clients write the data’s badly to disk you may face an issue because it will fill up your 15GB and overflow to get drop the volumes.
|
||||
|
||||
### Requirements ###
|
||||
|
||||
注:此三篇文章如果发布后可换成发布后链接,原文在前几天更新中
|
||||
|
||||
- [Create Disk Storage with LVM in Linux – PART 1][1]
|
||||
- [How to Extend/Reduce LVM’s in Linux – Part II][2]
|
||||
- [How to Create/Restore Snapshot of Logical Volume in LVM – Part III][3]
|
||||
|
||||
#### My Server Setup ####
|
||||
|
||||
Operating System – CentOS 6.5 with LVM Installation
|
||||
Server IP – 192.168.0.200
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Setup Thin Pool and Volumes ###
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s do it practically how to setup the thin pool and thin volumes. First we need a large size of Volume group. Here I’m creating Volume group with **15GB** for demonstration purpose. Now, list the volume group using the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
# vgcreate -s 32M vg_thin /dev/sdb1
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Listing Volume Group
|
||||
|
||||
Next, check for the size of Logical volume availability, before creating the thin pool and volumes.
|
||||
|
||||
# vgs
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check Logical Volume
|
||||
|
||||
We can see there is only default logical volumes for file-system and swap is present in the above lvs output.
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating a Thin Pool ###
|
||||
|
||||
To create a Thin pool for 15GB in volume group (vg_thin) use the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvcreate -L 15G --thinpool tp_tecmint_pool vg_thin
|
||||
|
||||
- **-L** – Size of volume group
|
||||
- **–thinpool** – To o create a thinpool
|
||||
- **tp_tecmint_poolThin** - pool name
|
||||
- **vg_thin** – Volume group name were we need to create the pool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Create Thin Pool
|
||||
|
||||
To get more detail we can use the command ‘lvdisplay’.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvdisplay vg_thin/tp_tecmint_pool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Logical Volume Information
|
||||
|
||||
Here we haven’t created Virtual thin volumes in this thin-pool. In the image we can see Allocated pool data showing **0.00%**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating Thin Volumes ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can define thin volumes inside the thin pool with the help of ‘lvcreate’ command with option -V (Virtual).
|
||||
|
||||
# lvcreate -V 5G --thin -n thin_vol_client1 vg_thin/tp_tecmint_pool
|
||||
|
||||
I have created a Thin virtual volume with the name of **thin_vol_client1** inside the **tp_tecmint_pool** in my **vg_thin** volume group. Now, list the logical volumes using below command.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
List Logical Volumes
|
||||
|
||||
Just now, we have created the thin volume above, that’s why there is no data showing i.e. **0.00%M**.
|
||||
|
||||
Fine, let me create 2 more Thin volumes for other 2 clients. Here you can see now there are 3 thin volumes created under the pool (**tp_tecmint_pool**). So, from this point, we came to know that I have used all 15GB pool.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Creating File System ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, create mount points and mount these three thin volumes and copy some files in it using below commands.
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir -p /mnt/client1 /mnt/client2 /mnt/client3
|
||||
|
||||
List the created directories.
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l /mnt/
|
||||
|
||||
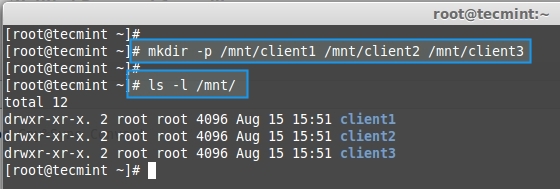
|
||||
Creating Mount Points
|
||||
|
||||
Create the file system for these created thin volumes using ‘mkfs’ command.
|
||||
|
||||
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/vg_thin/thin_vol_client1 && mkfs.ext4 /dev/vg_thin/thin_vol_client2 && mkfs.ext4 /dev/vg_thin/thin_vol_client3
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Create File System
|
||||
|
||||
Mount all three client volumes to the created mount point using ‘mount’ command.
|
||||
|
||||
# mount /dev/vg_thin/thin_vol_client1 /mnt/client1/ && mount /dev/vg_thin/thin_vol_client2 /mnt/client2/ && mount /dev/vg_thin/thin_vol_client3 /mnt/client3/
|
||||
|
||||
List the mount points using ‘df’ command.
|
||||
|
||||
# df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Print Mount Points
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we can see all the 3 clients volumes are mounted and therefore only 3% of data are used in every clients volumes. So, let’s add some more files to all 3 mount points from my desktop to fill up some space.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Add Files To Volumes
|
||||
|
||||
Now list the mount point and see the space used in every thin volumes & list the thin pool to see the size used in pool.
|
||||
|
||||
# df -h
|
||||
# lvdisplay vg_thin/tp_tecmint_pool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check Mount Point Size
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check Thin Pool Size
|
||||
|
||||
The above command shows, the three mount pints along with their sizes in percentage.
|
||||
|
||||
13% of datas used out of 5GB for client1
|
||||
29% of datas used out of 5GB for client2
|
||||
49% of datas used out of 5GB for client3
|
||||
|
||||
While looking into the thin-pool we can see only **30%** of data is written totally. This is the total of above three clients virtual volumes.
|
||||
|
||||
### Over Provisioning ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now the **4th** client came to me and asked for 5GB storage space. Can I give? Because I had already given 15GB Pool to 3 clients. Is it possible to give 5GB more to another client? Yes it is possible to give. This is when we use **Over Provisioning**, which means giving the space more than what I have.
|
||||
|
||||
Let me create 5GB for the 4th Client and verify the size.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvcreate -V 5G --thin -n thin_vol_client4 vg_thin/tp_tecmint_pool
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Create thin Storage
|
||||
|
||||
I have only 15GB size in pool, but I have created 4 volumes inside thin-pool up-to 20GB. If all four clients start to write data to their volumes to fill up the pace, at that time, we will face critical situation, if not there will no issue.
|
||||
|
||||
Now I have created file system in **thin_vol_client4**, then mounted under **/mnt/client4** and copy some files in it.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Verify Thin Storage
|
||||
|
||||
We can see in the above picture, that the total used size in newly created client 4 up-to **89.34%** and size of thin pool as **59.19%** used. If all these users are not writing badly to volume it will be free from overflow, drop. To avoid the overflow we need to extend the thin-pool size.
|
||||
|
||||
**Important**: Thin-pools are just a logical volume, so if we need to extend the size of thin-pool we can use the same command like, we’ve used for logical volumes extend, but we can’t reduce the size of thin-pool.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvextend
|
||||
|
||||
Here we can see how to extend the logical thin-pool (**tp_tecmint_pool**).
|
||||
|
||||
# lvextend -L +15G /dev/vg_thin/tp_tecmint_pool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Extend Thin Storage
|
||||
|
||||
Next, list the thin-pool size.
|
||||
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Verify Thin Storage
|
||||
|
||||
Earlier our **tp_tecmint_pool** size was 15GB and 4 thin volumes which was over Provision by 20GB. Now it has extended to 30GB so our over Provisioning has been normalized and thin volumes are free from overflow, drop. This way you can add ever more thin volumes to the pool.
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we have seen how to create a thin-pool using a large size of volume group and create thin-volumes inside a thin-pool using Over-Provisioning and extending the pool. In the next article we will see how to setup a lvm Striping.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/setup-thin-provisioning-volumes-in-lvm/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Babin Lonston][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/babinlonston/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/create-lvm-storage-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/extend-and-reduce-lvms-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/take-snapshot-of-logical-volume-and-restore-in-lvm/
|
||||
@ -1,107 +0,0 @@
|
||||
wangjiezhe translating
|
||||
6 Interesting Funny Commands of Linux (Fun in Terminal) – Part II
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In our past following articles, we’ve shown some useful articles on some funny commands of Linux, which shows that Linux is not as complex as it seems and can be fun if we know how to use it. Linux command line can perform any complex task very easily and with perfection and can be interesting and joyful.
|
||||
|
||||
- [20 Funny Commands of Linux – Part I][1]注,此篇的原文应该翻译过,文件名应该是:20 Funny Commands of Linux or Linux is Fun in Terminal
|
||||
- [Fun in Linux Terminal – Play with Word and Character Counts][2]注:这篇文章刚刚补充上
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Funny Linux Commands
|
||||
|
||||
The former Post comprises of 20 funny Linux Commands/Script (and subcommands) which was highly appreciated by our readers. The other post, though not that much popular as former comprises of Commands/ Scripts and Tweaks which lets you play with text files, words and strings.
|
||||
|
||||
This post aims at bringing some new fun commands and one-liner scripts which is going to rejoice you.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. pv Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
You might have seen simulating text in movies. It appears as, it is being typed in real time. Won’t it be nice, if you can have such an effect in terminal?
|
||||
|
||||
This can be achieved, by installing ‘**pv**‘ command in your Linux system by using ‘**apt**‘ or ‘**yum**‘ tool. Let’s install ‘**pv**‘ command as shown.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install pv [On RedHat based Systems]
|
||||
|
||||
# sudo apt-get install pv [On Debian based Systems]
|
||||
|
||||
Once, ‘**pv**‘ command installed successfully on your system, let’s try to run the following one liner command to see the real time text effect on the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo "Tecmint[dot]com is a community of Linux Nerds and Geeks" | pv -qL 10
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
pv command in action
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: The ‘**q**‘ option means ‘quite’, no output information and option ‘**L**‘ means the Limit of Transfer of bytes per second. The number value can be adjusted in either direction (must be integer) to get desired simulation of text.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. toilet Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
How about printing text with border in terminal, using an one-liner script command ‘**toilet**‘. Again, you must have ‘**toilet**‘ command installed on your system, if not use apt or yum to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ while true; do echo “$(date | toilet -f term -F border –Tecmint)”; sleep 1; done
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
toilet command in action
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: The above script needs to be suspended using **ctrl+z** key.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. rig Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
This command generates a random identity and address, every time. To run, this command you need to install ‘**rig**‘ using apt or yum.
|
||||
|
||||
# rig
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
rig command in action
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. aview Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
How about viewing an image in ASCII format on the terminal? We must have a package ‘**aview**‘ installed, just apt or yum it. I’ve an image named ‘**elephant.jpg**‘ in my current working directory and I want view it on terminal as ASCII format.
|
||||
|
||||
$ asciiview elephant.jpg -driver curses
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
aview command in action
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. xeyes Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
In last article we introduced a command ‘**oneko**‘ which attaches jerry with mouse pointer and keeps on chasing it. A similar program ‘**xeyes**‘ which is a graphical programs and as soon as you fire the command you will see two monster eyes chasing your movement.
|
||||
|
||||
$ xeyes
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
xeyes command in action
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. cowsay Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
Do you remember last time we introduced command, which is useful in output of desired text with animated character cow. What if you want other animal in place of cow? Check a list of available animals.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cowsay -l
|
||||
|
||||
How about Elephant inside ASCII Snake?
|
||||
|
||||
$ cowsay -f elephant-in-snake Tecmint is Best
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
cowsay command in action
|
||||
|
||||
How about Elephant inside ASCII goat?
|
||||
|
||||
$ cowsay -f gnu Tecmint is Best
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
cowsay goat in action
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I’ll be here again with another interesting article. Till then stay update and connected to Tecmint. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-funny-commands/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[wangjiezhe](https://github.com/wangjiezhe)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-funny-commands-of-linux-or-linux-is-fun-in-terminal/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/play-with-word-and-character-counts-in-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
johnhoow translating...
|
||||
Use LaTeX In Ubuntu 14.04 and Linux Mint 17 With Texmaker
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[LaTeX][1] is a document markup language and document preparation system. It is widely used as a standard in universities and academics to write professional scientific papers, thesis and other such documents. In this quick post, we shall see **how to use LaTeX in Ubuntu 14.04**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Texmaker to use LaTeX in Ubuntu 14.04 & Linux Mint 17 ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Texmaker][2] is a free and open source LaTeX editor which is available for all major desktop OS i.e. Windows, Linux and OS X. Followings are the salient features of the Texmaker:
|
||||
|
||||
- Unicode editor
|
||||
- Spell checker
|
||||
- Code folding
|
||||
- Code completion
|
||||
- Fast navigation
|
||||
- Integrated Pdf viewer
|
||||
- Easy compilation
|
||||
- 370 Mathematical symbols
|
||||
- LaTeX documentation
|
||||
- Export to html and odt via TeX4ht
|
||||
- Regex support
|
||||
|
||||
You can install Texmaker in Ubuntu 14.04 by downloading the binaries from the given link:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Texmaker LaTeX editor][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Since it is .deb packaging, same installation files can be used n any other Debian based distribution such as Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Pinguy OS etc.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want a Github type markdown editor, you should check [Remarkable editor][4]. I hope Texmaker helps you with **LaTeX in Ubuntu** and Linux Mint.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-latex-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.latex-project.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.xm1math.net/texmaker/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.xm1math.net/texmaker/download.html#linux
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/remarkable-markdown-editor-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,236 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to set up Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE) in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
As far as network management is concerned, Nagios is one of the most powerful tools. Nagios can monitor the reachability of remote hosts, as well as the state of services running on them. However, what if we want to monitor something other than network services for a remote host? For example, we may want to monitor the disk utilization or [CPU processor load][1] of a remote host. Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE) is a tool that can help with doing that. NRPE allows one to execute Nagios plugins installed on remote hosts, and integrate them with an [existing Nagios server][2].
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will cover how to set up NRPE on an existing Nagios deployment. The tutorial is primarily divided into two parts:
|
||||
|
||||
- Configure remote hosts.
|
||||
- Configure a Nagios monitoring server.
|
||||
|
||||
We will then finish off by defining some custom commands that can be used with NRPE.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure Remote Hosts for NRPE ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step One: Installing NRPE Service ####
|
||||
|
||||
You need to install NRPE service on every remote host that you want to monitor using NRPE. NRPE service daemon on each remote host will then communicate with a Nagios monitoring server.
|
||||
|
||||
Necessary packages for NRPE service can easily be installed using apt-get or yum, subject to the platform. In case of CentOS, we will need to [add Repoforge repository][3] as NRPE is not available in CentOS repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
**On Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install nagios-nrpe-server
|
||||
|
||||
**On CentOS, Fedora or RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install nagios-nrpe
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Two: Preparing Configuration File ####
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration file /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg is similar for Debian-based and RedHat-based systems. The configuration file is backed up, and then updated as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## NRPE service port can be customized ##
|
||||
server_port=5666
|
||||
|
||||
## the nagios monitoring server is permitted ##
|
||||
## NOTE: There is no space after the comma ##
|
||||
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,X.X.X.X-IP_v4_of_Nagios_server
|
||||
|
||||
## The following examples use hard-coded command arguments.
|
||||
## These parameters can be modified as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
## NOTE: For CentOS 64 bit, use /usr/lib64 instead of /usr/lib ##
|
||||
|
||||
command[check_users]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_users -w 5 -c 10
|
||||
command[check_load]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_load -w 15,10,5 -c 30,25,20
|
||||
command[check_hda1]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /dev/hda1
|
||||
command[check_zombie_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 5 -c 10 -s Z
|
||||
command[check_total_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 150 -c 200
|
||||
|
||||
Now that the configuration file is ready, NRPE service is ready to be fired up.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Three: Initiating NRPE Service ####
|
||||
|
||||
For RedHat-based systems, the NRPE service needs to be added as a startup service.
|
||||
|
||||
**On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# service nagios-nrpe-server restart
|
||||
|
||||
**On CentOS, Fedora or RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# service nrpe restart
|
||||
# chkconfig nrpe on
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Four: Verifying NRPE Service Status ####
|
||||
|
||||
Information about NRPE daemon status can be found in the system log. For a Debian-based system, the log file will be /var/log/syslog. The log file for a RedHat-based system will be /var/log/messages. A sample log is provided below for reference.
|
||||
|
||||
nrpe[19723]: Starting up daemon
|
||||
nrpe[19723]: Listening for connections on port 5666
|
||||
nrpe[19723]: Allowing connections from: 127.0.0.1,X.X.X.X
|
||||
|
||||
In case firewall is running, TCP port 5666 should be open, which is used by NRPE daemon.
|
||||
|
||||
# netstat -tpln | grep 5666
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5666 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 19885/nrpe
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure Nagios Monitoring Server for NRPE ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first step in configuring an existing Nagios monitoring server for NRPE is to install NRPE plugin on the server.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step One: Installing NRPE Plugin ####
|
||||
|
||||
In case the Nagios server is running on a Debian-based system (Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint), a necessary package can be installed using apt-get.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install nagios-nrpe-plugin
|
||||
|
||||
After the plugin is installed, the check_nrpe command, which comes with the plugin, is modified a bit.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios-plugins/config/check_nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## the default command is overwritten ##
|
||||
define command{
|
||||
command_name check_nrpe
|
||||
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -c '$ARG1$'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
In case the Nagios server is running on a RedHat-based system (CentOS, Fedora or RHEL), you can install NRPE plugin using yum. On CentOS, [adding Repoforge repository][4] is necessary.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install nagios-plugins-nrpe
|
||||
|
||||
Now that the NRPE plugin is installed, proceed to configure a Nagios server following the rest of the steps.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Two: Defining Nagios Command for NRPE Plugin ####
|
||||
|
||||
First, we need to define a command in Nagios for using NRPE.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios/objects/commands.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## NOTE: For CentOS 64 bit, use /usr/lib64 instead of /usr/lib ##
|
||||
define command{
|
||||
command_name check_nrpe
|
||||
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -c '$ARG1$'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Three: Adding Host and Command Definition ####
|
||||
|
||||
Next, define remote host(s) and commands to execute remotely on them.
|
||||
|
||||
The following shows sample definitions of a remote host a command to execute on the host. Naturally, your configuration will be adjusted based on your requirements. The path to the file is slightly different for Debian-based and RedHat-based systems. But the content of the files are identical.
|
||||
|
||||
**On Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios3/conf.d/nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
**On CentOS, Fedora or RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios/objects/nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
define host{
|
||||
use linux-server
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
alias server-1
|
||||
address X.X.X.X-IPv4_address_of_remote_host
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
define service {
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
service_description Check Load
|
||||
check_command check_nrpe!check_load
|
||||
check_interval 1
|
||||
use generic-service
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Four: Restarting Nagios Service ####
|
||||
|
||||
Before restarting Nagios, updated configuration is verified with a dry run.
|
||||
|
||||
**On Ubuntu, Debian, or Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# nagios3 -v /etc/nagios3/nagios.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
**On CentOS, Fedora or RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# nagios -v /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
If everything goes well, Nagios service can be restarted.
|
||||
|
||||
# service nagios restart
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring Custom Commands with NRPE ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Setup on Remote Servers ####
|
||||
|
||||
The following is a list of custom commands that can be used with NRPE. These commands are defined in the file /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg located at the remote servers.
|
||||
|
||||
## Warning status when load average exceeds 1, 2 and 1 for 1, 5, 15 minute interval, respectively.
|
||||
## Critical status when load average exceeds 3, 5 and 3 for 1, 5, 15 minute interval, respectively.
|
||||
command[check_load]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_load -w 1,2,1 -c 3,5,3
|
||||
|
||||
## Warning level 25% and critical level 10% for free space of /home.
|
||||
## Could be customized to monitor any partition (e.g. /dev/sdb1, /, /var, /home)
|
||||
command[check_disk]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w 25% -c 10% -p /home
|
||||
|
||||
## Warn if number of instances for process_ABC exceeds 10. Critical for 20 ##
|
||||
command[check_process_ABC]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 1:10 -c 1:20 -C process_ABC
|
||||
|
||||
## Critical if the number of instances for process_XYZ drops below 1 ##
|
||||
command[check_process_XYZ]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 1: -c 1: -C process_XYZ
|
||||
|
||||
#### Setup on Nagios Monitoring Server ####
|
||||
|
||||
To apply the custom commands defined above, we modify the service definition at Nagios monitoring server as follows. The service definition could go to the file where all the services are defined (e.g., /etc/nagios/objects/nrpe.cfg or /etc/nagios3/conf.d/nrpe.cfg)
|
||||
|
||||
## example 1: check process XYZ ##
|
||||
define service {
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
service_description Check Process XYZ
|
||||
check_command check_nrpe!check_process_XYZ
|
||||
check_interval 1
|
||||
use generic-service
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
## example 2: check disk state ##
|
||||
define service {
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
service_description Check Process XYZ
|
||||
check_command check_nrpe!check_disk
|
||||
check_interval 1
|
||||
use generic-service
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
To sum up, NRPE is a powerful add-on to Nagios as it provides provision for monitoring a remote server in a highly configurable fashion. Using NRPE, we can monitor server load, running processes, logged in users, disk states and other parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/03/nagios-remote-plugin-executor-nrpe-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2012/08/how-to-measure-average-cpu-utilization.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/install-configure-nagios-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
translating by cvsher
|
||||
Sysstat – All-in-One System Performance and Usage Activity Monitoring Tool For Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Sysstat** is really a handy tool which comes with number of utilities to monitor system resources, their performance and usage activities. Number of utilities that we all use in our daily bases comes with sysstat package. It also provide the tool which can be scheduled using cron to collect all performance and activity data.
|
||||
@ -121,4 +122,4 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-sysstat-in-linux/
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/kuldeepsharma47/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-with-vmstat-and-iostat-commands/
|
||||
[2]:http://sebastien.godard.pagesperso-orange.fr/download.html
|
||||
[3]:http://sebastien.godard.pagesperso-orange.fr/documentation.html
|
||||
[3]:http://sebastien.godard.pagesperso-orange.fr/documentation.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,73 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to install Arch Linux the easy way with Evo/Lution
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The one who ventures into an install of Arch Linux and has only experienced installing Linux with Ubuntu or Mint is in for a steep learning curve. The number of people giving up halfway is probably higher than the ones that pull it through. Arch Linux is somewhat cult in the way that you may call yourself a weathered Linux user if you succeed in setting it up and configuring it in a useful way.
|
||||
|
||||
Even though there is a [helpful wiki][1] to guide newcomers, the requirements are still too high for some who set out to conquer Arch. You need to be at least familiar with commands like fdisk or mkfs in a terminal and have heard of mc, nano or chroot to make it through this endeavour. It reminds me of a Debian install 10 years ago.
|
||||
|
||||
For those ambitious souls that still lack some knowledge, there is an installer in the form of an ISO image called [Evo/Lution Live ISO][2] to the rescue. Even though it is booted like a distribution of its own, it does nothing but assist with installing a barebone Arch Linux. Evo/Lution is a project that aims to diversify the user base of Arch by providing a simple way of installing Arch as well as a community that provides comprehensive help and documentation to that group of users. In this mix, Evo is the (non-installable) live CD and Lution is the installer itself. The project's founders see a widening gap between Arch developers and users of Arch and its derivative distributions, and want to build a community with equal roles between all participants.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The software part of the project is the CLI installer Lution-AIS which explains every step of what happens during the installation of a pure vanilla Arch. The resulting installation will have all the latest software that Arch has to offer without adding anything from AUR or any other custom packages.
|
||||
|
||||
After booting up the ISO image, which weighs in at 422 MB, we are presented with a workspace consisting of a Conky display on the right with shortcuts to the options and a LX-Terminal on the left waiting to run the installer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After setting off the actual installer by either right-clicking on the desktop or using ALT-i, you are presented with a list of 16 jobs to be run. It makes sense to run them all unless you know better. You can either run them one by one or make a selection like 1 3 6 or 1-4 or do them all at once by entering 1-16. Most steps need to be confirmed with a 'y' for yes, and the next task waits for you to hit Enter. This will allow time to read the installation guide which is hidden behind ALT-g or even walking away from it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The 16 steps are divided in "Base Install" and "Desktop Install". The first group takes care of localization, partitioning, and installing a bootloader.
|
||||
|
||||
The installer leads you through partitioning with gparted, gdisk, and cfdisk as options.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After you have created partitions (e.g., /dev/sda1 for root and /dev/sda2 for swap using gparted as shown in the screenshot), you can choose 1 out of 10 file systems. In the next step, you can choose your kernel (latest or LTS) and base system.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After installing the bootloader of your choice, the first part of the install is done, which takes approximately 12 minutes. This is the point where in plain Arch Linux you reboot into your system for the first time.
|
||||
|
||||
With Lution you just move on to the second part which installs Xorg, sound and graphics drivers, and then moves on to desktop environments.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The installer detects if an install is done in VirtualBox, and will automatically install and load the right generic drivers for the VM and sets up **systemd** accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
In the next step, you can choose between the desktop environments KDE, Gnome, Cinnamon, LXDE, Enlightenment, Mate or XFCE. Should you not be friends with the big ships, you can also go with a Window manager like Awesome, Fluxbox, i3, IceWM, Openbox or PekWM.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Part two of the installer will take under 10 minutes with Cinnamon as the desktop environment; however, KDE will take longer due to a much larger download.
|
||||
|
||||
Lution-AIS worked like a charm on two tries with Cinnamon and Awesome. After the installer was done and prompted me to reboot, it took me to the desired environments.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I have only two points to criticize: when the installer offered me to choose a mirror list and when it created the fstab file. In both cases it opened a second terminal, prompting me with an informational text. It took me a while to figure out I had to close the terminals before the installer would move on. When it prompts you after creating fstab, you need to close the terminal, and answer 'yes' when asked if you want to save the file.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The second of my issues probably has to do with VirtualBox. When starting up, you may see a message that no network has been detected. Clicking on the top icon on the left will open wicd, the network manager that is used here. Clicking on "Disconnect" and then "Connect" and restarting the installer will get it automatically detected.
|
||||
|
||||
Evo/Lution seems a worthwhile project, where Lution works fine. Not much can be said on the community part yet. They started a brand new website, forum, and wiki that need to be filled with content first. So if you like the idea, join [their forum][3] and let them know. The ISO image can be downloaded from [the website][4].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/install-arch-linux-easy-way-evolution.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ferdinand Thommes][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/ferdinand
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.archlinux.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.evolutionlinux.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.evolutionlinux.com/forums/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.evolutionlinux.com/downloads.html
|
||||
@ -1,182 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Network Installation of “Debian 7 (Whezzy) on Client Machines using DNSMASQ Network Boot Server
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
This tutorial will guide you on how you can install **Debian 7 (Whezzy)** directly from a network location using **DNSMASQ** as a **PXE Server (Preboot eXecution Environment)**, in case your server doesn’t provide any method to boot from a CD/DVD/USB media drive or it just can operate with an attached monitor, keyboard and mouse.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Debian 7 Network Installation on Client Machines
|
||||
|
||||
**DNSMASQ** is a lightweight network infrastructure server which can provide crucial network services such as DNS, DHCP and Network Boot, using a build-in DNS, DHCP and TFTP server.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the PXE server is up and running you can instruct all your clients machines to directly boot from network, with the specifications that your clients must own a network card that supports network booting, which can be enabled from BIOS under Network Boot or Boot Services option.
|
||||
|
||||
### Requirements ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [Debian 7 (Wheezy) Installation Guide][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Install and Configure DNSMASQ Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
**1.** On first hand, after you install Debian Server assure that your system uses a **Static IP Address**, because, besides network booting, will also provide DHCP service for your entire network segment. Once the Static IP Address has been configured run the following command from root account or using a user with root powers to install DNSMASQ server.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install dnsmasq
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Install Dnsmasq Package
|
||||
|
||||
**2.** Once DNSMASQ package installed, you can start editing its configuration file. First create a backup of the main configuration and then start editing **dnsmasq.conf** file by issuing the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
# mv /etc/dnsmasq.conf /etc/dnsmasq.conf.backup
|
||||
# nano /etc/dnsmasq.conf
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Backup Dnsmasq Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
**3.** The above backup process consisted on renaming the main configuration file, so the new file should be an empty one. Use the following excerpt for **DNSMASQ** configuration file as described below.
|
||||
|
||||
interface=eth0
|
||||
domain=debian.lan
|
||||
dhcp-range=192.168.1.3,192.168.1.253,255.255.255.0,1h
|
||||
dhcp-boot=pxelinux.0,pxeserver,192.168.1.100
|
||||
pxe-prompt="Press F8 for menu.", 60
|
||||
#pxe-service types: x86PC, PC98, IA64_EFI, Alpha, Arc_x86, Intel_Lean_Client, IA32_EFI, BC_EFI, Xscale_EFI and X86-64_EFI
|
||||
pxe-service=x86PC, "Install Debian 7 Linux from network server 192.168.1.100", pxelinux
|
||||
enable-tftp
|
||||
tftp-root=/srv/tftp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Configuration of Dnsmasq
|
||||
|
||||
- **interface** – The network interface that the server should listen.
|
||||
- **domain** – Replace it with your domain name.
|
||||
- **dhcp-range** – Replace it with your network IP range defined by your network mask.
|
||||
- **dhcp-boot** – Leave it as default but replace the IP statement with your server IP Address.
|
||||
- **pxe-prompt** – Leave it as default – requires **F8 key strike** to enter menu 60 with seconds wait time.
|
||||
- **pxe=service** – Use **x86PC** for 32-bit/64-bit architectures and enter a menu description prompt under string quotes. Other values types can be: PC98, IA64_EFI, Alpha, Arc_x86, Intel_Lean_Client, IA32_EFI, BC_EFI, Xscale_EFI and X86-64_EFI.
|
||||
- **enable-tftp** – Enables the build-in TFTP server.
|
||||
- **tftp-root** – Use /srv/tftp is the location for Debian netboot files.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Download Debian Netboot Files and Open Firewall Connection ###
|
||||
|
||||
**4.** Now it’s time to download Debian Network Boot files. First, change your current working directory path to **TFTP Root** location defined by the last configuration statement (**/srv/tftp** system path ).
|
||||
|
||||
Go to a offical page mirror of [Debian Netinstall][2] – [Network boot section][3] and grab the following files depending on your system architecture that you want to install it on your clients.
|
||||
|
||||
Once, you download **netboot.tar.gz** file, extract archive at the same time (this procedure describes only for 64-bit but the same procedure applies for other system architectures).
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /srv/tftp/
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-amd64/current/images/netboot/netboot.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar xfz netboot.tar.gz
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-amd64/current/images/SHA256SUMS
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/Release
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/Release.gpg
|
||||
|
||||
Also it may be necessary to make all files in **TFTP** directory readable for TFTP server.
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod -R 755 /srv/tftp/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Download Debian NetBoot Files
|
||||
|
||||
Use the following variables for **Debian Netinstall** mirrors and architectures.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-"$ARCH"/current/images/netboot/netboot.tar.gz
|
||||
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-"$ARCH"/current/images/SHA256SUMS
|
||||
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/Release
|
||||
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/Release.gpg
|
||||
|
||||
**5.** On the next step start or restart DNSMASQ daemon and run netstat command to get a list of ports that the server is listening.
|
||||
|
||||
# service dnsmasq restart
|
||||
# netstat -tulpn | grep dnsmasq
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Start Dnsmasq Service
|
||||
|
||||
**6.** Debian based distribution usually ships with **UFW Firewall** package. Use the following commands to open the required **DNSMASQ** port numbers: **67** (Bootps), **69** (TFTP) **53** (DNS), **4011** (proxyDHCP) udp and **53** tcp (DNS).
|
||||
|
||||
# ufw allow 69/udp
|
||||
# ufw allow 4011/udp ## Only if you have a ProxyDHCP on the network
|
||||
# ufw allow 67/udp
|
||||
# ufw allow 53/tcp
|
||||
# ufw allow 53/udp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Open Dnsmasq Ports
|
||||
|
||||
Now, the PXE loader located on your client network interface will load **pxelinux** configuration files from **/srv/tftp/pxelinux.cfg** directory using this order.
|
||||
|
||||
- GUID files
|
||||
- MAC files
|
||||
- Default file
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Configure Clients to Boot from Network ###
|
||||
|
||||
**7.** To enable network boot for a client computer enter your system **BIOS configuration** (please consult the hardware motherboard vendor documentation for entering BIOS settings).
|
||||
|
||||
Go to **Boot menu** and select **Network boot** as the **primary boot device** (on some systems you can select the boot device without entering BIOS configuration just by pressing a key during **BIOS POST**).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Select BIOS Settings
|
||||
|
||||
**8.** After editing the boot order sequence, usually, press **F10** to save BIOS settings. After reboot, your client computer should boot directly from network and the first **PXE** prompt should appear demanding you to press **F8** key to enter menu.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, hit **F8** key to move forward and a new prompt should appear. Hit **Enter** key again and the main **Debian Installer** prompt should appear on your screen as in the screenshots below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Boot Menu Selection
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Select Debian Installer Boot
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Select Debian Install
|
||||
|
||||
From here on you can start install Debian on your machine using the Debian 7 Wheezy procedure (installation link given above), but you can also need to make sure that your machine has an active Internet connection in order to be able to finish installation process.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Debug DNSMASQ Server and Enable it System-Wide ###
|
||||
|
||||
**9.** To diagnosticate the server for eventual occurred problems or other information offered to clients run the following command to open log file.
|
||||
|
||||
# tailf /var/log/daemon.log
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Debug DNSMASQ Server
|
||||
|
||||
**10.** If everything is in place during server tests you can now enable **DNSMASQ** daemon to automatically start after system reboot with the help of **sysv-rc-conf** package.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install sysv-rc-conf
|
||||
# sysv-rc-conf dnsmaq on
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enable DNSMASQ Daemon
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all! Now your **PXE** server is ready to allocate IP addresses (**DHCP**) and to offer the required boot information for all your network segment clients which will be configured to boot and install Debian Wheezy from network.
|
||||
|
||||
Using PXE network boot installation has some advantages on networks with an increased number of server hosts because you can set up the entire network infrastructure in a short period of time or the same time, facilitates the distribution upgrading process, and, can also automate the entire installation process using kickstart files.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/network-installation-of-debian-7-on-client-machines/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/debian-gnulinux-7-0-code-name-wheezy-server-installation-guide/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.debian.org/distrib/netinst#netboot
|
||||
[3]:http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/main/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,151 @@
|
||||
How to manage configurations in Linux with Puppet and Augeas
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Although [Puppet][1](注:此文原文原文中曾今做过,文件名:“20140808 How to install Puppet server and client on CentOS and RHEL.md”,如果翻译发布过,可修改此链接为发布地址) is a really unique and useful tool, there are situations where you could use a bit of a different approach. Situations like modification of configuration files which are already present on several of your servers and are unique on each one of them at the same time. Folks from Puppet labs realized this as well, and integrated a great tool called [Augeas][2] that is designed exactly for this usage.
|
||||
|
||||
Augeas can be best thought of as filling for the gaps in Puppet's capabilities where an objectspecific resource type (such as the host resource to manipulate /etc/hosts entries) is not yet available. In this howto, you will learn how to use Augeas to ease your configuration file management.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is Augeas? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Augeas is basically a configuration editing tool. It parses configuration files in their native formats and transforms them into a tree. Configuration changes are made by manipulating this tree and saving it back into native config files.
|
||||
|
||||
### What are we going to achieve in this tutorial? ###
|
||||
|
||||
We will install and configure the Augeas tool for use with our previously built Puppet server. We will create and test several different configurations with this tool, and learn how to properly use it to manage our system configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
### Prerequisites ###
|
||||
|
||||
We will need a working Puppet server and client setup. If you don't have it, please follow my previous tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
Augeas package can be found in our standard CentOS/RHEL repositories. Unfortunately, Puppet uses Augeas ruby wrapper which is only available in the puppetlabs repository (or [EPEL][4]). If you don't have this repository in your system already, add it using following command:
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS/RHEL 6.5:
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -ivh https://yum.puppetlabs.com/el/6.5/products/x86_64/puppetlabsrelease610.noarch.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS/RHEL 7:
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -ivh https://yum.puppetlabs.com/el/7/products/x86_64/puppetlabsrelease710.noarch.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
After you have successfully added this repository, install RubyAugeas in your system:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install rubyaugeas
|
||||
|
||||
Or if you are continuing from my last tutorial, install this package using the Puppet way. Modify your custom_utils class inside of your /etc/puppet/manifests/site.pp to contain "rubyaugeas" inside of the packages array:
|
||||
|
||||
class custom_utils {
|
||||
package { ["nmap","telnet","vimenhanced","traceroute","rubyaugeas"]:
|
||||
ensure => latest,
|
||||
allow_virtual => false,
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
### Augeas without Puppet ###
|
||||
|
||||
As it was said in the beginning, Augeas is not originally from Puppet Labs, which means we can still use it even without Puppet itself. This approach can be useful for verifying your modifications and ideas before applying them in your Puppet environment. To make this possible, you need to install one additional package in your system. To do so, please execute following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install augeas
|
||||
|
||||
### Puppet Augeas Examples ###
|
||||
|
||||
For demonstration, here are a few example Augeas use cases.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Management of /etc/sudoers file ####
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add sudo rights to wheel group
|
||||
|
||||
This example will show you how to add simple sudo rights for group %wheel in your GNU/Linux system.
|
||||
|
||||
# Install sudo package
|
||||
package { 'sudo':
|
||||
ensure => installed, # ensure sudo package installed
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Allow users belonging to wheel group to use sudo
|
||||
augeas { 'sudo_wheel':
|
||||
context => '/files/etc/sudoers', # The target file is /etc/sudoers
|
||||
changes => [
|
||||
# allow wheel users to use sudo
|
||||
'set spec[user = "%wheel"]/user %wheel',
|
||||
'set spec[user = "%wheel"]/host_group/host ALL',
|
||||
'set spec[user = "%wheel"]/host_group/command ALL',
|
||||
'set spec[user = "%wheel"]/host_group/command/runas_user ALL',
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's explain what the code does: **spec** defines the user section in /etc/sudoers, **[user]** defines given user from the array, and all definitions behind slash ( / ) are subparts of this user. So in typical configuration this would be represented as:
|
||||
|
||||
user host_group/host host_group/command host_group/command/runas_user
|
||||
|
||||
Which is translated into this line of /etc/sudoers:
|
||||
|
||||
%wheel ALL = (ALL) ALL
|
||||
|
||||
2. Add command alias
|
||||
|
||||
The following part will show you how to define command alias which you can use inside your sudoers file.
|
||||
|
||||
# Create new alias SERVICES which contains some basic privileged commands
|
||||
augeas { 'sudo_cmdalias':
|
||||
context => '/files/etc/sudoers', # The target file is /etc/sudoers
|
||||
changes => [
|
||||
"set Cmnd_Alias[alias/name = 'SERVICES']/alias/name SERVICES",
|
||||
"set Cmnd_Alias[alias/name = 'SERVICES']/alias/command[1] /sbin/service",
|
||||
"set Cmnd_Alias[alias/name = 'SERVICES']/alias/command[2] /sbin/chkconfig",
|
||||
"set Cmnd_Alias[alias/name = 'SERVICES']/alias/command[3] /bin/hostname",
|
||||
"set Cmnd_Alias[alias/name = 'SERVICES']/alias/command[4] /sbin/shutdown",
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Syntax of sudo command aliases is pretty simple: **Cmnd_Alias** defines the section of command aliases, **[alias/name]** binds all to given alias name, /alias/name **SERVICES** defines the actual alias name and alias/command is the array of all the commands that should be part of this alias. The output of this command will be following:
|
||||
|
||||
Cmnd_Alias SERVICES = /sbin/service , /sbin/chkconfig , /bin/hostname , /sbin/shutdown
|
||||
|
||||
For more information about /etc/sudoers, visit the [official documentation][5].
|
||||
|
||||
#### Adding users to a group ####
|
||||
|
||||
To add users to groups using Augeas, you might want to add the new user either after the gid field or after the last user. We'll use group SVN for the sake of this example. This can be achieved by using the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
In Puppet:
|
||||
|
||||
augeas { 'augeas_mod_group:
|
||||
context => '/files/etc/group', # The target file is /etc/group
|
||||
changes => [
|
||||
"ins user after svn/*[self::gid or self::user][last()]",
|
||||
"set svn/user[last()] john",
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Using augtool:
|
||||
|
||||
augtool> ins user after /files/etc/group/svn/*[self::gid or self::user][last()] augtool> set /files/etc/group/svn/user[last()] john
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
By now, you should have a good idea on how to use Augeas in your Puppet projects. Feel free to experiment with it and definitely go through the official Augeas documentation. It will help you get the idea how to use Augeas properly in your own projects, and it will show you how much time you can actually save by using it.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any questions feel free to post them in the comments and I will do my best to answer them and advise you.
|
||||
|
||||
### Useful Links ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [http://www.watzmann.net/categories/augeas.html][6]: contains a lot of tutorials focused on Augeas usage.
|
||||
- [http://projects.puppetlabs.com/projects/1/wiki/puppet_augeas][7]: Puppet wiki with a lot of practical examples.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/manage-configurations-linux-puppet-augeas.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jaroslav Štěpánek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/jaroslav
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/install-puppet-server-client-centos-rhel.html
|
||||
[2]:http://augeas.net/
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/manage-configurations-linux-puppet-augeas.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[5]:http://augeas.net/docs/references/lenses/files/sudoers-aug.html
|
||||
[6]:http://www.watzmann.net/categories/augeas.html
|
||||
[7]:http://projects.puppetlabs.com/projects/1/wiki/puppet_augeas
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
|
||||
Translating by GOLinux!
|
||||
How to monitor user login history on CentOS with utmpdump
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Keeping, maintaining and analyzing logs (i.e., accounts of events that have happened during a certain period of time or are currently happening) are among the most basic and essential tasks of a Linux system administrator. In case of user management, examining user logon and logout logs (both failed and successful) can alert us about any potential security breaches or unauthorized use of our system. For example, remote logins from unknown IP addresses or accounts being used outside working hours or during vacation leave should raise a red flag.
|
||||
|
||||
On a CentOS system, user login history is stored in the following binary files:
|
||||
|
||||
- /var/run/utmp (which logs currently open sessions) is used by who and w tools to show who is currently logged on and what they are doing, and also by uptime to display system up time.
|
||||
- /var/log/wtmp (which stores the history of connections to the system) is used by last tool to show the listing of last logged-in users.
|
||||
- /var/log/btmp (which logs failed login attempts) is used by lastb utility to show the listing of last failed login attempts. `
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In this post I'll show you how to use utmpdump, a simple program from the sysvinit-tools package that can be used to dump these binary log files in text format for inspection. This tool is available by default on stock CentOS 6 and 7. The information gleaned from utmpdump is more comprehensive than the output of the tools mentioned earlier, and that's what makes it a nice utility for the job. Besides, utmpdump can be used to modify utmp or wtmp, which can be useful if you want to fix any corrupted entries in the binary logs.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Use Utmpdump and Interpret its Output ###
|
||||
|
||||
As we mentioned earlier, these log files, as opposed to other logs most of us are familiar with (e.g., /var/log/messages, /var/log/cron, /var/log/maillog), are saved in binary file format, and thus we cannot use pagers such as less or more to view their contents. That is where utmpdump saves the day.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to display the contents of /var/run/utmp, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# utmpdump /var/run/utmp
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To do the same with /var/log/wtmp:
|
||||
|
||||
# utmpdump /var/log/wtmp
|
||||
|
||||
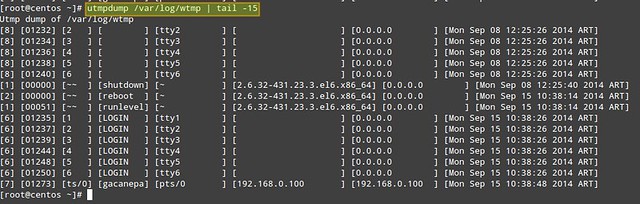
|
||||
|
||||
and finally with /var/log/btmp:
|
||||
|
||||
# utmpdump /var/log/btmp
|
||||
|
||||
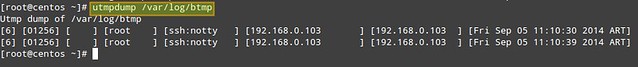
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, the output formats of three cases are identical, except for the fact that the records in the utmp and btmp are arranged chronologically, while in the wtmp, the order is reversed.
|
||||
|
||||
Each log line is formatted in multiple columns described as follows. The first field shows a session identifier, while the second holds PID. The third field can hold one of the following values: ~~ (indicating a runlevel change or a system reboot), bw (meaning a bootwait process), a digit (indicates a TTY number), or a character and a digit (meaning a pseudo-terminal). The fourth field can be either empty or hold the user name, reboot, or runlevel. The fifth field holds the main TTY or PTY (pseudo-terminal), if that information is available. The sixth field holds the name of the remote host (if the login is performed from the local host, this field is blank, except for run-level messages, which will return the kernel version). The seventh field holds the IP address of the remote system (if the login is performed from the local host, this field will show 0.0.0.0). If DNS resolution is not provided, the sixth and seventh fields will show identical information (the IP address of the remote system). The last (eighth) field indicates the date and time when the record was created.
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage Examples of Utmpdump ###
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few simple use cases of utmpdump.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Check how many times (and at what times) a particular user (e.g., gacanepa) logged on to the system between August 18 and September 17.
|
||||
|
||||
# utmpdump /var/log/wtmp | grep gacanepa
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you need to review login information from prior dates, you can check the wtmp-YYYYMMDD (or wtmp.[1...N]) and btmp-YYYYMMDD (or btmp.[1...N]) files in /var/log, which are the old archives of wtmp and btmp files, generated by [logrotate][1].
|
||||
|
||||
2. Count the number of logins from IP address 192.168.0.101.
|
||||
|
||||
# utmpdump /var/log/wtmp | grep 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3. Display failed login attempts.
|
||||
|
||||
# utmpdump /var/log/btmp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the output of /var/log/btmp, every log line corresponds to a failed login attempt (e.g., using incorrect password or a non-existing user ID). Logon using non-existing user IDs are highlighted in the above impage, which can alert you that someone is attempting to break into your system by guessing commonly-used account names. This is particularly serious in the cases when the tty1 was used, since it means that someone had access to a terminal on your machine (time to check who has keys to your datacenter, maybe?).
|
||||
|
||||
4. Display login and logout information per user session.
|
||||
|
||||
# utmpdump /var/log/wtmp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In /var/log/wtmp, a new login event is characterized by '7' in the first field, a terminal number (or pseudo-terminal id) in the third field, and username in the fourth. The corresponding logout event will be represented by '8' in the first field, the same PID as the login in the second field, and a blank terminal number field. For example, take a close look at PID 1463 in the above image.
|
||||
|
||||
- On [Fri Sep 19 11:57:40 2014 ART] the login prompt appeared in tty1.
|
||||
- On [Fri Sep 19 12:04:21 2014 ART], user root logged on.
|
||||
- On [Fri Sep 19 12:07:24 2014 ART], root logged out.
|
||||
|
||||
On a side note, the word LOGIN in the fourth field means that a login prompt is present in the terminal specified in the fifth field.
|
||||
|
||||
So far I covered somewhat trivial examples. You can combine utmpdump with other text sculpting tools such as awk, sed, grep or cut to produce filtered and enhanced output.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can use the following command to list all login events of a particular user (e.g., gacanepa) and send the output to a .csv file that can be viewed with a pager or a workbook application, such as LibreOffice's Calc or Microsoft Excel. Let's display PID, username, IP address and timestamp only:
|
||||
|
||||
# utmpdump /var/log/wtmp | grep -E "\[7].*gacanepa" | awk -v OFS="," 'BEGIN {FS="] "}; {print $2,$4,$7,$8}' | sed -e 's/\[//g' -e 's/\]//g'
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As represented with three blocks in the image, the filtering logic is composed of three pipelined steps. The first step is used to look for login events ([7]) triggered by user gacanepa. The second and third steps are used to select desired fields, remove square brackets in the output of utmpdump, and set the output field separator to a comma.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, you need to redirect the output of the above command to a file if you want to open it later (append "> [name_of_file].csv" to the command).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In more complex examples, if you want to know what users (as listed in /etc/passwd) have not logged on during the period of time, you could extract user names from /etc/passwd, and then run grep the utmpdump output of /var/log/wtmp against user list. As you see, possibility is limitless.
|
||||
|
||||
Before concluding, let's briefly show yet another use case of utmpdump: modify utmp or wtmp. As these are binary log files, you cannot edit them as is. Instead, you can export their content to text format, modify the text output, and then import the modified content back to the binary logs. That is:
|
||||
|
||||
# utmpdump /var/log/utmp > tmp_output
|
||||
<modify tmp_output using a text editor>
|
||||
# utmpdump -r tmp_output > /var/log/utmp
|
||||
|
||||
This can be useful when you want to remove or fix any bogus entry in the binary logs.
|
||||
|
||||
To sum up, utmpdump complements standard utilities such as who, w, uptime, last, lastb by dumping detailed login events stored in utmp, wtmp and btmp log files, as well as in their rotated old archives, and that certainly makes it a great utility.
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to enhance this post with your comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/monitor-user-login-history-centos-utmpdump.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/gabriel
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/logrotate-manage-log-files-linux.html
|
||||
112
sources/tech/20140928 How to Use Systemd Timers.md
Normal file
112
sources/tech/20140928 How to Use Systemd Timers.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
|
||||
Translating by johnhoow...
|
||||
How to Use Systemd Timers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I was setting up some scripts to run backups recently, and decided I would try to set them up to use [systemd timers][1] rather than the more familiar to me [cron jobs][2].
|
||||
|
||||
As I went about trying to set them up, I had the hardest time, since it seems like the required information is spread around in various places. I wanted to record what I did so firstly, I can remember, but also so that others don’t have to go searching as far and wide as I did.
|
||||
|
||||
There are additional options associated with the each step I mention below, but this is the bare minimum to get started. Look at the man pages for **systemd.service**, **systemd.timer**, and **systemd.target** for all that you can do with them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Running a Single Script ###
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s say you have a script **/usr/local/bin/myscript** that you want to run every hour.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Service File ####
|
||||
|
||||
First, create a service file, and put it wherever it goes on your Linux distribution (on Arch, it is either **/etc/systemd/system/** or **/usr/lib/systemd/system**).
|
||||
|
||||
myscript.service
|
||||
|
||||
[Unit]
|
||||
Description=MyScript
|
||||
|
||||
[Service]
|
||||
Type=simple
|
||||
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/myscript
|
||||
|
||||
Note that it is important to set the **Type** variable to be “simple”, not “oneshot”. Using “oneshot” makes it so that the script will be run the first time, and then systemd thinks that you don’t want to run it again, and will turn off the timer we make next.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Timer File ####
|
||||
|
||||
Next, create a timer file, and put it also in the same directory as the service file above.
|
||||
|
||||
myscript.timer
|
||||
|
||||
[Unit]
|
||||
Description=Runs myscript every hour
|
||||
|
||||
[Timer]
|
||||
# Time to wait after booting before we run first time
|
||||
OnBootSec=10min
|
||||
# Time between running each consecutive time
|
||||
OnUnitActiveSec=1h
|
||||
Unit=myscript.service
|
||||
|
||||
[Install]
|
||||
WantedBy=multi-user.target
|
||||
|
||||
#### Enable / Start ####
|
||||
|
||||
Rather than starting / enabling the service file, you use the timer.
|
||||
|
||||
# Start timer, as root
|
||||
systemctl start myscript.timer
|
||||
# Enable timer to start at boot
|
||||
systemctl enable myscript.timer
|
||||
|
||||
### Running Multiple Scripts on the Same Timer ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now let’s say there a bunch of scripts you want to run all at the same time. In this case, you will want make a couple changes on the above formula.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Service Files ####
|
||||
|
||||
Create the service files to run your scripts as I [showed previously][3], but include the following section at the end of each service file.
|
||||
|
||||
[Install]
|
||||
WantedBy=mytimer.target
|
||||
|
||||
If there is any ordering dependency in your service files, be sure you specify it with the **After=something.service** and/or **Before=whatever.service** parameters within the **Description** section.
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively (and perhaps more simply), create a wrapper script that runs the appropriate commands in the correct order, and use the wrapper in your service file.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Timer File ####
|
||||
|
||||
You only need a single timer file. Create **mytimer.timer**, as I [outlined above][4].
|
||||
|
||||
#### Target File ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can create the target that all these scripts depend upon.
|
||||
|
||||
mytimer.target
|
||||
|
||||
[Unit]
|
||||
Description=Mytimer
|
||||
# Lots more stuff could go here, but it's situational.
|
||||
# Look at systemd.unit man page.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Enable / Start ####
|
||||
|
||||
You need to enable each of the service files, as well as the timer.
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl enable script1.service
|
||||
systemctl enable script2.service
|
||||
...
|
||||
systemctl enable mytimer.timer
|
||||
systemctl start mytimer.service
|
||||
|
||||
Good luck.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://jason.the-graham.com/2013/03/06/how-to-use-systemd-timers/#enable--start-1
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Jason Graham
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/User:Johannbg/QA/Systemd/Systemd.timer
|
||||
[2]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cron
|
||||
[3]:http://jason.the-graham.com/2013/03/06/how-to-use-systemd-timers/#service-file
|
||||
[4]:http://jason.the-graham.com/2013/03/06/how-to-use-systemd-timers/#timer-file-1
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,223 @@
|
||||
How to turn your CentOS box into an OSPF router using Quagga
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Quagga][1] is an open source routing software suite that can be used to turn your Linux box into a fully-fledged router that supports major routing protocols like RIP, OSPF, BGP or ISIS router. It has full provisions for IPv4 and IPv6, and supports route/prefix filtering. Quagga can be a life saver in case your production router is down, and you don't have a spare one at your disposal, so are waiting for a replacement. With proper configurations, Quagga can even be provisioned as a production router.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, we will connect two hypothetical branch office networks (e.g., 192.168.1.0/24 and 172.17.1.0/24) that have a dedicated link between them.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Our CentOS boxes are located at both ends of the dedicated link. The hostnames of the two boxes are set as 'site-A-RTR' and 'site-B-RTR' respectively. IP address details are provided below.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Site-A**: 192.168.1.0/24
|
||||
- **Site-B**: 172.16.1.0/24
|
||||
- **Peering between 2 Linux boxes**: 10.10.10.0/30
|
||||
|
||||
The Quagga package consists of several daemons that work together. In this tutorial, we will focus on setting up the following daemons.
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Zebra**: a core daemon, responsible for kernel interfaces and static routes.
|
||||
1. **Ospfd**: an IPv4 OSPF daemon.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Quagga on CentOS ###
|
||||
|
||||
We start the process by installing Quagga using yum.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install quagga
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS 7, SELinux prevents /usr/sbin/zebra from writing to its configuration directory by default. This SELinux policy interferes with the setup procedure we are going to describe, so we want to disable this policy. For that, either [turn off SELinux][2] (which is not recommended), or enable the 'zebra_write_config' boolean as follows. Skip this step if you are using CentOS 6.
|
||||
|
||||
# setsebool -P zebra_write_config 1
|
||||
|
||||
Without this change, we will see the following error when attempting to save Zebra configuration from inside Quagga's command shell.
|
||||
|
||||
Can't open configuration file /etc/quagga/zebra.conf.OS1Uu5.
|
||||
|
||||
After Quagga is installed, we configure necessary peering IP addresses, and update OSPF settings. Quagga comes with a command line shell called vtysh. The Quagga commands used inside vtysh are similar to those of major router vendors such as Cisco or Juniper.
|
||||
|
||||
### Phase 1: Configuring Zebra ###
|
||||
|
||||
We start by creating a Zebra configuration file, and launching Zebra daemon.
|
||||
|
||||
# cp /usr/share/doc/quagga-XXXXX/zebra.conf.sample /etc/quagga/zebra.conf
|
||||
# service zebra start
|
||||
# chkconfig zebra on
|
||||
|
||||
Launch vtysh command shell:
|
||||
|
||||
# vtysh
|
||||
|
||||
First, we configure the log file for Zebra. For that, enter the global configuration mode in vtysh by typing:
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR# configure terminal
|
||||
|
||||
and specify log file location, then exit the mode:
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config)# log file /var/log/quagga/quagga.log
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config)# exit
|
||||
|
||||
Save configuration permanently:
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR# write
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we identify available interfaces and configure their IP addresses as necessary.
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR# show interface
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Interface eth0 is up, line protocol detection is disabled
|
||||
. . . . .
|
||||
Interface eth1 is up, line protocol detection is disabled
|
||||
. . . . .
|
||||
|
||||
Configure eth0 parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR# configure terminal
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config)# interface eth0
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-if)# ip address 10.10.10.1/30
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-if)# description to-site-B
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-if)# no shutdown
|
||||
|
||||
Go ahead and configure eth1 parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config)# interface eth1
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-if)# ip address 192.168.1.1/24
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-if)# description to-site-A-LAN
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-if)# no shutdown
|
||||
|
||||
Now verify configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-if)# do show interface
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Interface eth0 is up, line protocol detection is disabled
|
||||
. . . . .
|
||||
inet 10.10.10.1/30 broadcast 10.10.10.3
|
||||
. . . . .
|
||||
Interface eth1 is up, line protocol detection is disabled
|
||||
. . . . .
|
||||
inet 192.168.1.1/24 broadcast 192.168.1.255
|
||||
. . . . .
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-if)# do show interface description
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Interface Status Protocol Description
|
||||
eth0 up unknown to-site-B
|
||||
eth1 up unknown to-site-A-LAN
|
||||
|
||||
Save configuration permanently:
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-if)# do write
|
||||
|
||||
Repeat the IP address configuration step on site-B server as well.
|
||||
|
||||
If all goes well, you should be able to ping site-B's peering IP 10.10.10.2 from site-A server.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that once Zebra daemon has started, any change made with vtysh's command line interface takes effect immediately. There is no need to restart Zebra daemon after configuration change.
|
||||
|
||||
### Phase 2: Configuring OSPF ###
|
||||
|
||||
We start by creating an OSPF configuration file, and starting the OSPF daemon:
|
||||
|
||||
# cp /usr/share/doc/quagga-XXXXX/ospfd.conf.sample /etc/quagga/ospfd.conf
|
||||
# service ospfd start
|
||||
# chkconfig ospfd on
|
||||
|
||||
Now launch vtysh shell to continue with OSPF configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
# vtysh
|
||||
|
||||
Enter router configuration mode:
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR# configure terminal
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config)# router ospf
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally, set the router-id manually:
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-router)# router-id 10.10.10.1
|
||||
|
||||
Add the networks that will participate in OSPF:
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-router)# network 10.10.10.0/30 area 0
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-router)# network 192.168.1.0/24 area 0
|
||||
|
||||
Save configuration permanently:
|
||||
|
||||
site-A-RTR(config-router)# do write
|
||||
|
||||
Repeat the similar OSPF configuration on site-B as well:
|
||||
|
||||
site-B-RTR(config-router)# network 10.10.10.0/30 area 0
|
||||
site-B-RTR(config-router)# network 172.16.1.0/24 area 0
|
||||
site-B-RTR(config-router)# do write
|
||||
|
||||
The OSPF neighbors should come up now. As long as ospfd is running, any OSPF related configuration change made via vtysh shell takes effect immediately without having to restart ospfd.
|
||||
|
||||
In the next section, we are going to verify our Quagga setup.
|
||||
|
||||
### Verification ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Test with ping ####
|
||||
|
||||
To begin with, you should be able to ping the LAN subnet of site-B from site-A. Make sure that your firewall does not block ping traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@site-A-RTR ~]# ping 172.16.1.1 -c 2
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Check routing tables ####
|
||||
|
||||
Necessary routes should be present in both kernel and Quagga routing tables.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@site-A-RTR ~]# ip route
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
10.10.10.0/30 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 10.10.10.1
|
||||
172.16.1.0/30 via 10.10.10.2 dev eth0 proto zebra metric 20
|
||||
192.168.1.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.1.1
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[root@site-A-RTR ~]# vtysh
|
||||
site-A-RTR# show ip route
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Codes: K - kernel route, C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, O - OSPF,
|
||||
I - ISIS, B - BGP, > - selected route, * - FIB route
|
||||
|
||||
O 10.10.10.0/30 [110/10] is directly connected, eth0, 00:14:29
|
||||
C>* 10.10.10.0/30 is directly connected, eth0
|
||||
C>* 127.0.0.0/8 is directly connected, lo
|
||||
O>* 172.16.1.0/30 [110/20] via 10.10.10.2, eth0, 00:14:14
|
||||
C>* 192.168.1.0/24 is directly connected, eth1
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Verifying OSPF neighbors and routes ####
|
||||
|
||||
Inside vtysh shell, you can check if necessary neighbors are up, and proper routes are being learnt.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@site-A-RTR ~]# vtysh
|
||||
site-A-RTR# show ip ospf neighbor
|
||||
|
||||
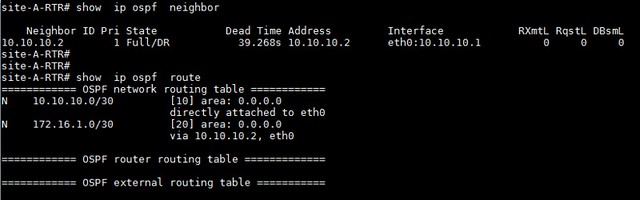
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, we focused on configuring basic OSPF using Quagga. In general, Quagga allows us to easily configure a regular Linux box to speak dynamic routing protocols such as OSPF, RIP or BGP. Quagga-enabled boxes will be able to communicate and exchange routes with any other router that you may have in your network. Since it supports major open standard routing protocols, it may be a preferred choice in many scenarios. Better yet, Quagga's command line interface is almost identical to that of major router vendors like Cisco or Juniper, which makes deploying and maintaining Quagga boxes very easy.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/turn-centos-box-into-ospf-router-quagga.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
[1]:http://www.nongnu.org/quagga/
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-disable-selinux.html
|
||||
117
sources/tech/20140928 How to use xargs command in Linux.md
Normal file
117
sources/tech/20140928 How to use xargs command in Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,117 @@
|
||||
zpl1025
|
||||
How to use xargs command in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Have you ever been in the situation where you are running the same command over and over again for multiple files? If so, you know how tedious and inefficient this can feel. The good news is that there is an easier way, made possible through the xargs command in Unix-based operating systems. With this command you can process multiple files efficiently, saving you time and energy. In this tutorial, you will learn how to execute a command or script for multiple files at once, avoiding the daunting task of processing numerous log files or data files individually.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two ingredients for the xargs command. First, you must specify the files of interest. Second, you must indicate which command or script will be executed for each of the files you specified.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will cover three scenarios in which the xargs command can be used to process files located within several different directories:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Count the number of lines in all files
|
||||
1. Print the first line of specific files
|
||||
1. Process each file using a custom script
|
||||
|
||||
Consider the following directory named xargstest (the directory tree can be displayed using the tree command with the combined -i and -f options, which print the results without indentation and with the full path prefix for each file):
|
||||
|
||||
$ tree -if xargstest/
|
||||
|
||||
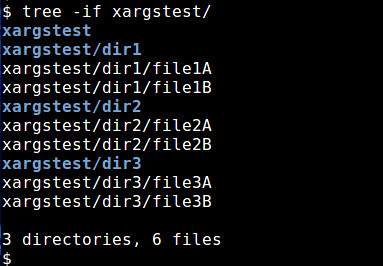
|
||||
|
||||
The contents of each of the six files are as follows:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The **xargstest** directory, its subdirectories and files will be used in the following examples.
|
||||
|
||||
### Scenario 1: Count the number of lines in all files ###
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned earlier, the first ingredient for the xargs command is a list of files for which the command or script will be run. We can use the find command to identify and list the files that we are interested in. The **-name 'file??'** option specifies that only files with names beginning with "file" followed by any two characters will be matched within the xargstest directory. This search is recursive by default, which means that the find command will search for matching files within xargstest and all of its sub-directories.
|
||||
|
||||
$ find xargstest/ -name 'file??'
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
xargstest/dir3/file3B
|
||||
xargstest/dir3/file3A
|
||||
xargstest/dir1/file1A
|
||||
xargstest/dir1/file1B
|
||||
xargstest/dir2/file2B
|
||||
xargstest/dir2/file2A
|
||||
|
||||
We can pipe the results to the sort command to order the filenames sequentially:
|
||||
|
||||
$ find xargstest/ -name 'file??' | sort
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
xargstest/dir1/file1A
|
||||
xargstest/dir1/file1B
|
||||
xargstest/dir2/file2A
|
||||
xargstest/dir2/file2B
|
||||
xargstest/dir3/file3A
|
||||
xargstest/dir3/file3B
|
||||
|
||||
We now need the second ingredient, which is the command to execute. We use the wc command with the -l option to count the number of newlines in each file (printed at the beginning of each output line):
|
||||
|
||||
$ find xargstest/ -name 'file??' | sort | xargs wc -l
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
1 xargstest/dir1/file1A
|
||||
2 xargstest/dir1/file1B
|
||||
3 xargstest/dir2/file2A
|
||||
4 xargstest/dir2/file2B
|
||||
5 xargstest/dir3/file3A
|
||||
6 xargstest/dir3/file3B
|
||||
21 total
|
||||
|
||||
You'll see that instead of manually running the wc -l command for each of these files, the xargs command allows you to complete this operation in a single step. Tasks that may have previously seemed unmanageable, such as processing hundreds of files individually, can now be performed quite easily.
|
||||
|
||||
### Scenario 2: Print the first line of specific files ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you know the basics of how to use the xargs command, you have the freedom to choose which command you want to execute. Sometimes, you may want to run commands for only a subset of files and ignore others. In this case, you can use the find command with the -name option and the ? globbing character (matches any single character) to select specific files to pipe into the xargs command. For example, if you want to print the first line of all files that end with a "B" character and ignore the files that end with an "A" character, use the following combination of the find, xargs, and head commands (head -n1 will print the first line in a file):
|
||||
|
||||
$ find xargstest/ -name 'file?B' | sort | xargs head -n1
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
==> xargstest/dir1/file1B <==
|
||||
one
|
||||
|
||||
==> xargstest/dir2/file2B <==
|
||||
one
|
||||
|
||||
==> xargstest/dir3/file3B <==
|
||||
one
|
||||
|
||||
You'll see that only the files with names that end with a "B" character were processed, and all files that end with an "A" character were ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
### Scenario 3: Process each file using a custom script ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, you may want to run a custom script (in Bash, Python, or Perl for example) for the files. To do this, simply substitute the name of your custom script in place of the wc and head commands shown previously:
|
||||
|
||||
$ find xargstest/ -name 'file??' | xargs myscript.sh
|
||||
|
||||
The custom script **myscript.sh** needs to be written to take a file name as an argument and process the file. The above command will then invoke the script for every file found by find command.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the above examples include file names that do not contain spaces. Generally speaking, life in a Linux environment is much more pleasant when using file names without spaces. If you do need to handle file names with spaces, the above commands will not work, and should be tweaked to accommodate them. This is accomplished with the -print0 option for find command (which prints the full file name to stdout, followed by a null character), and -0 option for xargs command (which interprets a null character as the end of a string), as shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
$ find xargstest/ -name 'file*' -print0 | xargs -0 myscript.sh
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the argument for the -name option has been changed to 'file*', which means any files with names beginning with "file" and trailed by any number of characters will be matched.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
After reading this tutorial you will understand the capabilities of the xargs command and how you can implement this into your workflow. Soon you'll be spending more time enjoying the efficiency offered by this command, and less time doing repetitive tasks. For more details and additional options you can read the xargs documentation by entering the 'man xargs' command in your terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/xargs-command-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joshua Reed][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/joshua
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
Git Rebase Tutorial: Going Back in Time with Git Rebase
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A programmer since the tender age of 10, Christoph Burgdorf is the the founder of the HannoverJS meetup, and he has been an active member in the AngularJS community since its very beginning. He is also very knowledgeable about the ins and outs of git, where he hosts workshops at [thoughtram][1] to help beginners master the technology.
|
||||
|
||||
The following tutorial was originally posted on his [blog][2].
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Tutorial: Git Rebase ###
|
||||
|
||||
Imagine you are working on that radical new feature. It’s going to be brilliant but it takes a while. You’ve been working on that for a couple of days now, maybe weeks.
|
||||
|
||||
Your feature branch is already six commits ahead of master. You’ve been a good developer and have crafted meaningful semantical commits. But there’s the thing: you are slowly realizing that this beast will still take some more time before it’s really ready to be merged back into master.
|
||||
|
||||
m1-m2-m3-m4 (master)
|
||||
\
|
||||
f1-f2-f3-f4-f5-f6(feature)
|
||||
|
||||
What you also realize is that some parts are actually less coupled to the new feature. They could land in master earlier. Unfortunately, the part that you want to port back into master earlier is in a commit somewhere in the middle of your six commits. Even worse, it also contains a change that relies on a previous commits of your feature branch. One could argue that you should have made that two commits in the first place, but then nobody is perfect.
|
||||
|
||||
m1-m2-m3-m4 (master)
|
||||
\
|
||||
f1-f2-f3-f4-f5-f6(feature)
|
||||
^
|
||||
|
|
||||
mixed commit
|
||||
|
||||
At the time that you crafted the commit, you didn’t foresee that you might come into a situation where you want to gradually bring the feature into master. Heck! You wouldn’t have guessed that this whole thing could take us so long.
|
||||
|
||||
What you need is a way to go back in history, open up the commit and split it into two commits so that you can separate out all the things that are safe to be ported back into master by now.
|
||||
|
||||
Speaking in terms of a graph, we want to have it like this.
|
||||
|
||||
m1-m2-m3-m4 (master)
|
||||
\
|
||||
f1-f2-f3a-f3b-f4-f5-f6(feature)
|
||||
|
||||
With the work split into two commits, we could just cherry-pick the precious bits into master.
|
||||
|
||||
Turns out, git comes with a powerful command git rebase -i which lets us do exactly that. It lets us change the history. Changing the history can be problematic and as a rule of thumb should be avoided as soon as the history is shared with others. In our case though, we are just changing history of our local feature branch. Nobody will get hurt. Promised!
|
||||
|
||||
Ok, let’s take a closer look at what exactly happened in commit f3. Turns out we modified two files: userService.js and wishlistService.js. Let’s say that the changes to userService.js could go straight back into master whereas the changes to wishlistService.js could not. Because wishlistService.js does not even exist in master. It was introduced in commit f1.
|
||||
|
||||
> Pro Tip: even if the changes would have been in one file, git could handle that. We keep things simple for this blog post though.
|
||||
|
||||
We’ve set up a [public demo repository][3] that we will use for this exercise. To make it easier to follow, each commit message is prefixed with the pseudo SHAs used in the graphs above. What follows is the branch graph as printed by git before we start to split the commit f3.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now the first thing we want to do is to checkout our feature branch with git checkout feature. To get started with the rebase we run git rebase -i master.
|
||||
|
||||
Now what follows is that git opens a temporary file in the configured editor (defaults to Vim).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This file is meant to provide you some options for the rebase and it comes with a little cheat sheet (the blue text). For each commit we could choose between the actions pick, reword, edit, squash, fixup and exec. Each action can also be referred to by its short form p, r, e, s, f and e. It’s out of the scope of this article to describe each and every option so let’s focus on our specific task.
|
||||
|
||||
We want to choose the edit option for our f3 commit hence we change the contents to look like that.
|
||||
|
||||
Now we save the file (in Vim <ESC> followed by :wq, followed by <RETURN>). The next thing we notice is that git stops the rebase at the commit for which we choose the edit option.
|
||||
|
||||
What this means is that git started to apply f1, f2 and f3 as if it was a regular rebase but then stopped **after** applying f3. In fact, we can prove that if we just look at the log at the point where we stopped.
|
||||
|
||||
To split our commit f3 into two commits, all we have to do at this point is to reset gits pointer to the previous commit (f2) while keeping the working directory the same as it is right now. This is exactly what the mixed mode of git reset does. Since mixed is the default mode of git reset we can just write git reset head~1. Let’s do that and also run git status right after it to see what happened.
|
||||
|
||||
The git status tells us that both our userService.js and our wishlistService.js are modified. If we run git diff we can see that those are exactly the changes of our f3 commit.
|
||||
|
||||
If we look at the log again at this point we see that the f3 is gone though.
|
||||
|
||||
We are now at the point that we have the changes of our previous f3 commit ready to be committed whereas the original f3 commit itself is gone. Keep in mind though that we are still in the middle of a rebase. Our f4, f5 and f6 commits are not lost, they’ll be back in a moment.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s make two new commits: Let’s start with the commit for the changes made to the userService.js which are fine to get picked into master. Run git add userService.js followed by git commit -m "f3a: add updateUser method".
|
||||
|
||||
Great! Let’s create another commit for the changes made to wishlistService.js. Run git add wishlistService.js followed by git commit -m "f3b: add addItems method".
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s take a look at the log again.
|
||||
|
||||
This is exactly what we wanted except our commits f4, f5 and f6 are still missing. This is because we are still in the middle of the interactive rebase and we need to tell git to continue with the rebase. This is done with the command git rebase --continue.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s check out the log again.
|
||||
|
||||
And that’s it. We now have the history we wanted. The previous f3 commit is now split into two commits f3a and f3b. The only thing left to do is to cherry-pick the f3a commit over to the master branch.
|
||||
|
||||
To finish the last step we first switch to the master branch. We do this with git checkout master. Now we can pick the f3a commit with the cherry-pick command. We can refer to the commit by its SHA key which is bd47ee1 in this case.
|
||||
|
||||
We now have the f3a commit sitting on top of latest master. Exactly what we wanted!
|
||||
|
||||
Given the length of the post this may seem like a lot of effort but it’s really only a matter of seconds for an advanced git user.
|
||||
|
||||
> Note: Christoph is currently writing a book on [rebasing with Git][4] together with Pascal Precht, and you can subscribe to it at leanpub to get notified when it’s ready.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.codementor.io/git-tutorial/git-rebase-split-old-commit-master
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[cburgdorf][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.codementor.io/cburgdorf
|
||||
[1]:http://thoughtram.io/
|
||||
[2]:http://blog.thoughtram.io/posts/going-back-in-time-to-split-older-commits/
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/thoughtram/interactive-rebase-demo
|
||||
[4]:https://leanpub.com/rebase-the-complete-guide-on-rebasing-in-git
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
||||
Learning Vim in 2014: Working with Files
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
As a software developer, you shouldn't have to spend time thinking about how to get to the code you want to edit. One of the messiest parts of my transition to using Vim full time was its way of dealing with files. Coming to Vim after primarily using Eclipse and Sublime Text, it frustrated me that Vim doesn't bundle a persistent file system viewer, and the built-in ways of opening and switching files always felt extremely painful.
|
||||
|
||||
At this point I appreciate the depth of Vim's file management features. I've put together a system that works for me even better than more visual editors once did. Because it's purely keyboard based, it allows me to move through my code much faster. That took some time though, and involves several plugins. But the first step was me understanding Vim's built in options for dealing with files. This post will be looking at the most important structures Vim provides you for file management, with a quick peek at some of the more advanced features you can get through plugins.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Basics: Opening a new file ###
|
||||
|
||||
One of the biggest obstacles to learning Vim is its lack of visual affordances. Unlike modern GUI based editors, there is no obvious way to do anything when you open a new instance of Vim in the terminal. Everything is done through keyboard commands, and while that ends up being more efficient for experienced users, new Vim users will find themselves looking up even basic commands routinely. So lets start with the basics.
|
||||
|
||||
The command to open a new file in Vim is **:e <filename>. :e** opens up a new buffer with the contents of the file inside. If the file doesn't exist yet it opens up an empty buffer and will write to the file location you specify once you make changes and save. Buffers are Vim's term for a "block of text stored in memory". That text can be associated with an existing file or not, but there will be one buffer for each file you have open.
|
||||
|
||||
After you open a file and make changes, you can save the contents of the buffer back to the file with the write command **:w**. If the buffer is not yet associated with a file or you want to save to a different location, you can save to a specific file with **:w <filename>**. You may need to add a ! and use **:w! <filename>** if you're overwriting an existing file.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the survival level knowledge for dealing with Vim files. Plenty of developers get by with just these commands, and its technically all you need. But Vim offers a lot more for those who dig a bit deeper.
|
||||
|
||||
### Buffer Management ###
|
||||
|
||||
Moving beyond the basics, let's talk some more about buffers. Vim handles open files a bit differently than other editors. Rather than leaving all open files visible as tabs, or only allowing you to have one file open at a time, Vim allows you to have multiple buffers open. Some of these may be visible while others are not. You can view a list of all open buffers at any time with **:ls**. This shows each open buffer, along with their buffer number. You can then switch to a specific buffer with the **:b <buffer-number>** command, or move in order along the list with the **:bnext** and **:bprevious** commands. (these can be shortened to **:bn** and **:bp** respectively).
|
||||
|
||||
While these commands are the fundamental Vim solutions for managing buffers, I've found that they don't map well to my own way of thinking about files. I don't want to care about the order of buffers, I just want to go to the file I'm thinking about, or maybe to the file I was just in before the current one. So while its important to understand Vim's underlying buffer model, I wouldn't necessarily recommend its builtin commands as your main file management strategy. There are more powerful options available.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Splits ###
|
||||
|
||||
One of the best parts of managing files in Vim is its splits. With Vim, you can split your current window into 2 windows at any time, and then resize and arrange them into any configuration you like. Its not unusual for me to have 6 files open at a given time, each with its own small split of the window.
|
||||
|
||||
You can open a new split with **:sp <filename>** or **:vs <filename>**, for horizontal and vertical splits respectively. There are keyword commands you can use to then resize the windows the way you want them, but to be honest this is the one Vim task I prefer to do with my mouse. A mouse gives me more precision without having to guess the number of columns I want or fiddle back and forth between 2 widths.
|
||||
|
||||
After you create some splits, you can switch back and forth between them with **ctrl-w [h|j|k|l]**. This is a bit clunky though, and it's important for common operations to be efficient and easy. If you use splits heavily, I would personally recommend aliasing these commands to **ctrl-h** **ctrl-j** etc in your .vimrc using this snippet.
|
||||
|
||||
nnoremap <C-J> <C-W><C-J> "Ctrl-j to move down a split
|
||||
nnoremap <C-K> <C-W><C-K> "Ctrl-k to move up a split
|
||||
nnoremap <C-L> <C-W><C-L> "Ctrl-l to move right a split
|
||||
nnoremap <C-H> <C-W><C-H> "Ctrl-h to move left a split
|
||||
|
||||
### The jumplist ###
|
||||
|
||||
Splits solve the problem of viewing multiple related files at a time, but we still haven't seen a satisfactory solution for moving quickly between open and hidden files. The jumplist is one tool you can use for that.
|
||||
|
||||
The jumplist is one of those Vim features that can appear weird or even useless at first. Vim keeps track of every motion command and file switch you make as you're editing files. Every time you "jump" from one place to another in a split, Vim adds an entry to the jumplist. While this may initially seem like a small thing, it becomes powerful when you're switching files a lot, or moving around in a large file. Instead of having to remember your place, or worry about what file you were in, you can instead retrace your footsteps quickly using some quick key commands. **Ctrl-o** allows you to jump back to your last jump location. Repeating it multiple times allows you to quickly jump back to the last file or code chunk you were working on, without having to keep the details of where that code is in your head. You can then move back up the chain with **ctrl-i**. This turns out to be immensely powerful when you're moving around in code quickly, debugging a problem in multiple files or flipping back and forth between 2 files. Instead of typing file names or remembering buffer numbers, you can just move up and down the existing path. It's not the answer to everything, but like other Vim concepts, it's a small focused tool that adds to the overall power of the editor without trying to do everything.
|
||||
|
||||
### Plugins ###
|
||||
|
||||
So let's be real, if you're coming to Vim from something like Sublime Text or Atom, there's a good chance all of this looks a bit arcane, scary, and inefficient. "Why would I want to type the full path to open a file when Sublime has fuzzy finding?" "How can I get a view of a project's structure without a sidebar to show the directory tree?" Legitimate questions. The good news is that Vim has solutions. They're just not baked into the Vim core. I'll touch more on Vim configuration and plugins in later posts, but for now here's a pointer to 3 helpful plugins that you can use to get Sublime-like file management.
|
||||
|
||||
- [CtrlP][1] is a fuzzy finding file search similar to Sublime's "Go to Anything" bar. It's lightning fast and pretty configurable. I use it as my main way of opening new files. With it I only need to know part of the file name and don't need to memorize my project's directory structure.
|
||||
- [The NERDTree][2] is a "file navigation drawer" plugin that replicates the side file navigation that many editors have. I actually rarely use it, as fuzzy search always seems faster to me. But it can be useful coming into a project, when you're trying to learn the project structure and see what's available. NERDTree is immensely configurable, and also replaces Vim's built in directory tools when installed.
|
||||
- [Ack.vim][3] is a code search plugin for Vim that allows you to search across your project for text expressions. It acts as a light wrapper around Ack or Ag, [2 great code search tools][4], and allows you to quickly jump to any occurrence of a search term in your project.
|
||||
|
||||
Between it's core and its plugin ecosystem, Vim offers enough tools to allow you to craft your workflow anyway you want. File management is a key part of a good software development system, and it's worth experimenting to get it right.
|
||||
|
||||
Start with the basics for long enough to understand them, and then start adding tools on top until you find a comfortable workflow. It will all be worth it when you're able to seamlessly move to the code you want to work on without the mental overhead of figuring out how to get there.
|
||||
|
||||
### More Resources ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [Seamlessly Navigate Vim & Tmux Splits][5] This is a must read for anyone who wants to use vim with [tmux][6]. It presents an easy system for treating Vim and Tmux splits as equals, and moving between them easily.
|
||||
- [Using Tab Pages][7] One file management feature I didn't cover, since it's poorly named and a bit confusing to use, is Vim's "tab" feature. This post on the Vim wiki gives a good overview of how you can use "tab pages" to have multiple views of your current workspace
|
||||
- [Vimcasts: The edit command][8] Vimcasts in general is a great resource for anyone learning Vim, but this screenshot does a good job of covering the file opening basics mentioned above, with some suggestions on improving the builtin workflow
|
||||
|
||||
### Subscribe ###
|
||||
|
||||
This was the third in a series of posts on learning Vim in a modern way. If you enjoyed the post consider subscribing to the [feed][8] or joining my [mailing list][10]. I'll be continuing with [a post on Vim configuration next week][11] after a brief JavaScript interlude later this week. You should also checkout the first 2 posts in this series, on [the basics of using Vim][12], and [the language of Vim and Vi][13].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://benmccormick.org/2014/07/07/learning-vim-in-2014-working-with-files/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ben McCormick][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://benmccormick.org/2014/07/07/learning-vim-in-2014-working-with-files/
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/kien/ctrlp.vim
|
||||
[2]:https://github.com/scrooloose/nerdtree
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/mileszs/ack.vim
|
||||
[4]:http://benmccormick.org/2013/11/25/a-look-at-ack/
|
||||
[5]:http://robots.thoughtbot.com/seamlessly-navigate-vim-and-tmux-splits
|
||||
[6]:http://tmux.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[7]:http://vim.wikia.com/wiki/Using_tab_pages
|
||||
[8]:http://vimcasts.org/episodes/the-edit-command/
|
||||
[9]:http://feedpress.me/benmccormick
|
||||
[10]:http://eepurl.com/WFYon
|
||||
[11]:http://benmccormick.org/2014/07/14/learning-vim-in-2014-configuring-vim/
|
||||
[12]:http://benmccormick.org/2014/06/30/learning-vim-in-2014-the-basics/
|
||||
[13]:http://benmccormick.org/2014/07/02/learning-vim-in-2014-vim-as-language/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
|
||||
wangjiezhe translating
|
||||
|
||||
Using GIT to backup your website files on linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Well not exactly Git but a software based on Git known as BUP. I generally use rsync to backup my files and that has worked fine so far. The only problem or drawback is that you cannot restore your files to a particular point in time. Hence, I started looking for an alternative and found BUP a git based software which stores your data in repositories and gives you the option to restore data to a particular point in time.
|
||||
|
||||
With BUP you will first need to initialize an empty repository, then take a backup of all your files. When BUP takes a backup it creates a restore point which you can later restore to. It also creates an index of all your files, this index contains file attributes and checksum. When another backup is scheduled BUP compares the files with this attribute and only saves data if anything has changed. This saves you a lot of space.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing BUP (Tested on Centos 6 & 7) ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ensure you have RPMFORGE and EPEL repos installed.
|
||||
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$sudo yum groupinstall "Development Tools"
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$ sudo yum install python python-devel
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$ sudo yum install fuse-python pyxattr pylibacl
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$ sudo yum install perl-Time-HiRes
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$ git clone git://github.com/bup/bup
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$cd bup
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$ make
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$ make test
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
For debian/ubuntu users you can do “apt-get build-dep bup” on recent versions for more information check out https://github.com/bup/bup
|
||||
You may get errors on CentOS 7 at “make test”, but you can continue to run make install.
|
||||
|
||||
The first step like git is to initialize an empty repository.
|
||||
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$bup init
|
||||
|
||||
By default, bup will store it’s repository under “~/.bup” but you can change that by setting the “export BUP_DIR=/mnt/user/bup” environment variable
|
||||
|
||||
Next you create an index of all files. The index, as I mentioned earlier stores a listing of files, their attributes, and their git object ids (sha1 hashes). ( Attributes include soft links, permissions as well as the immutable bit
|
||||
|
||||
bup index /path/to/file
|
||||
bup save -n nameofbackup /path/to/file
|
||||
|
||||
#Example
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$ bup index /var/www/html
|
||||
Indexing: 7973, done (4398 paths/s).
|
||||
bup: merging indexes (7980/7980), done.
|
||||
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$ bup save -n techarena51 /var/www/html
|
||||
|
||||
Reading index: 28, done.
|
||||
Saving: 100.00% (4/4k, 28/28 files), done.
|
||||
bloom: adding 1 file (7 objects).
|
||||
Receiving index from server: 1268/1268, done.
|
||||
bloom: adding 1 file (7 objects).
|
||||
|
||||
“BUP save” will split all the contents of the file into chunks and store them as objects. The “-n” option takes the name of backup.
|
||||
|
||||
You can check a list of backups as well as a list of backed up files.
|
||||
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$ bup ls
|
||||
local-etc techarena51 test
|
||||
#Check for a list of backups available for my site
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$ bup ls techarena51
|
||||
2014-09-24-064416 2014-09-24-071814 latest
|
||||
#Check for the files available in these backups
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$ bup ls techarena51/2014-09-24-064416/var/www/html
|
||||
apc.php techarena51.com wp-config-sample.php wp-load.php
|
||||
|
||||
Backing up files on the same server is never a good option. BUP allows you to remotely backup your website files, you however need to ensure that your SSH keys and BUP are installed on the remote server.
|
||||
|
||||
bup index path/to/dir
|
||||
bup save-r remote-vps.com -n backupname path/to/dir
|
||||
|
||||
### Example: Backing up the “/var/www/html” directory ###
|
||||
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$bup index /var/www/html
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$ bup save -r user@remotelinuxvps.com: -n techarena51 /var/www/html
|
||||
Reading index: 28, done.
|
||||
Saving: 100.00% (4/4k, 28/28 files), done.
|
||||
bloom: adding 1 file (7 objects).
|
||||
Receiving index from server: 1268/1268, done.
|
||||
bloom: adding 1 file (7 objects).
|
||||
|
||||
### Restoring your Backup ###
|
||||
|
||||
Log into the remote server and type the following
|
||||
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$bup restore -C ./backup techarena51/latest
|
||||
|
||||
#Restore an older version of the entire working dir elsewhere
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$bup restore -C /tmp/bup-out /testrepo/2013-09-29-195827
|
||||
#Restore one individual file from an old backup
|
||||
[techarena51@vps ~]$bup restore -C /tmp/bup-out /testrepo/2013-09-29-201328/root/testbup/binfile1.bin
|
||||
|
||||
The only drawback is you cannot restore files to another server, you have to manually copy the files via SCP or even rsync.
|
||||
|
||||
View your backups via an integrated web server
|
||||
|
||||
bup web
|
||||
#specific port
|
||||
bup web :8181
|
||||
|
||||
You can run bup along with a shell script and a cron job once everyday.
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
bup index /var/www/html
|
||||
bup save -r user@remote-vps.com: -n techarena51 /var/www/html
|
||||
|
||||
BUP may not be perfect, but it get’s the job done pretty well. I would definitely like to see more development on this project and hopefully a remote restore as well.
|
||||
|
||||
You may also like to read using [inotify-tools][1] for real time file syncing.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://techarena51.com/index.php/using-git-backup-website-files-on-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Leo G][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://techarena51.com/
|
||||
[1]:http://techarena51.com/index.php/inotify-tools-example/
|
||||
85
translated/talk/20140828 Interesting facts about Linux.md
Normal file
85
translated/talk/20140828 Interesting facts about Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
Linux趣事
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
今天,8月25号,是Linux的第23个生日。1991年,8月25日,21岁的赫尔辛基大学的学生发布了举世闻名的[新闻组][1](Usenet post),标志着现在世界著名的Linux正式诞生。
|
||||
|
||||
23年以后的今天,linux已经无处不在,不仅仅被安装于桌面系统,[智能手机][2]和嵌入式系统,甚至也被[龙头企业][3]用于他们的关键系统,比如说像[美国海军的核潜艇][4](US Navy's nuclear submarines)和[联邦航空局的空中管制系统][5](FAA's air traffic control)。进入无处不在的云计算时代,linux在云计算平台方面仍然保持着它的优势。
|
||||
|
||||
今天,我们一起庆祝linux 23岁生日,就让我们告诉你**一些你可能不知道的linux趣事和linux历史**。如果有什么要补充的,请在评论中分享出来。在这篇文章里,我可能用会用“linux”,“kernel”和“Linux kernel”来表示同一个意思。
|
||||
|
||||
1.关于linux是否是一个开源的操作系统这种争论一直是无休无止的。事实上,“Linux”操作系统的核心组件参照的是Linux kernel(内核)。而反派认为Linux不是一个纯粹的操作系统,因为他们认为仅仅一个内核(kernel),并不是一个操作系统,自由软件的推崇者认为最大的操作系统应叫做“[GNU/Linux][7]”把功劳归于应得的人。(比如:[GNU project][8])。另一方面,一些linux的开发者认为,linux拥有成为一个操作系统的资格,因为它实现了[POSIX标准][9]。
|
||||
|
||||
2.从openhub网站的统计来看,绝大部分(95%)的Linux是用C语言写的。第二(2.8%)受欢迎的是汇编语言。毫无疑问,C语言比C++ 的更受欢迎,也表明了linus对C++的立场。下面是Linus编程语言的分类。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3.在世界上,Linux已经被[13,036个贡献者][10]创建和修改。当然,贡献最多的还是Linus Torvalds自己。直到目前,他提交了20,000次以上的代码。下图显示了所有提交次数最多的前十位Linux贡献者。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
4.Linux的代码行(SLOC)有超过1700万行。估计整个代码库的花费大概是5,526人年,或者是超过300M(1M=10*1000万亿)美元,[基于模型的基本估算法][11](basic COCOMO model)。
|
||||
|
||||
5.企业并不是单纯的Linux消费者。他们的员工也在[积极参与][12]Linux的开发。下图显示了前十的Linux内核开发参与的企业员工2013年提交次数的总和。他们包括linux的商业版发行者(Red Hat,SUSE),芯片/嵌入式系统制造商(Intel,Texas Instrument,wolfson),非盈利性组织(Linaro)和其他的IT公司(IBM,Samsung,Google)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
6.Linux的官方吉祥物是“小企鹅”,一个非常可爱的企鹅标志。[第一次提出][13]并决定小企鹅作为Linux吉祥物/标志这个想法的是Linus自己。为什么是小企鹅呢?因为Linus本人很喜欢企鹅,尽管他曾经被一只凶猛的企鹅咬伤过,还导致他得了一场病。
|
||||
|
||||
7.一个Linux系统“包括”Linux内核、支持GUN的组件和库、和一些第三方的应用。[distrowatch网站][14]显示,现在总共有286个活跃的Linux发行版。其中最老的一个版本叫[Slackware][15],它是从1993年正式发布出来的一个可用的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
8.Kernel.org是一个Linux源码的主要仓库,曾经在2011年8月被一个匿名的攻击者[攻陷][16],攻击者打算篡改kernel.org的服务器。为了加强linux内核的访问策略的安全性,Linux基金会最近在Linux内核的Git官方托管的仓库上[开启了][17]双重认证。
|
||||
|
||||
9.Linux在500强超级计算机中的优势还在[增加][18]。截至2014年6月,运算速度最快的计算机97%都是运行在Linux上面的。
|
||||
|
||||
10.太空监视(spacewatch),是亚利桑那大学月球与行星实验室的一个研究项目,在GNU/Linux和它的创造者们出现之后,用他们名字命名了几颗小行星([小行星9793 Torvalds][19],[小行星9882 Stallman][20],[小行星9885 Linux][21],[小行星9965 GUN][22]),以表彰他们把开源操作系统用于他们的小行星调查活动。
|
||||
|
||||
11.纵观Linux内核发展得近代史,版本从2.6到3.0有一个很大的跳跃。这个[重编的版本号3][23]实际上并不是意味着Linux内核有什么重大的构建,但却标志着Linux 20周年的一个里程碑。
|
||||
|
||||
12.在2000年的时候,乔帮主还在苹果。他当时就[尝试雇佣][24]Linus Torvalds,让他放弃Linux的开发,转而为“Unix最大的用户群工作”,这个项目后面发展成了MAC OS X。当时,linus拒绝了乔帮主的邀请。
|
||||
|
||||
13.Linux 内核的重启函数[reboot()][25]要求两个神奇的数字,而这第二个数字来自Linus Torvalds和他的3个女儿的出生日期。
|
||||
|
||||
14.虽然全世界都有Linux的很多粉丝,但是也仍然存在很多对Linux的批评(主要是桌面系统),如缺乏硬件支持,缺乏标准化,由于很短的升级和发布周期导致系统的不稳定,等。2014年Linux内核小组在linuxCon大会上,当Linus被问及Linux的未来将何去何从,他表示“I still want the desktop”(我仍然希望桌面化)。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你还知道些关于Linux的趣事,请写在评论里。
|
||||
|
||||
生日快乐,Linux!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/interesting-facts-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:https://groups.google.com/forum/message/raw?msg=comp.os.minix/dlNtH7RRrGA/SwRavCzVE7gJ
|
||||
[2]:http://developer.android.com/about/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://fortune.com/2013/05/06/how-linux-conquered-the-fortune-500/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/article/7789
|
||||
[5]:http://fcw.com/Articles/2006/05/01/FAA-manages-air-traffic-with-Linux.aspx
|
||||
[6]:http://thecloudmarket.com/stats
|
||||
[7]:http://www.gnu.org/gnu/why-gnu-linux.html
|
||||
[8]:http://www.gnu.org/gnu/gnu-history.html
|
||||
[9]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/POSIX
|
||||
[10]:https://www.openhub.net/p/linux/contributors/summary
|
||||
[11]:https://www.openhub.net/p/linux/estimated_cost
|
||||
[12]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/publications/linux-foundation/who-writes-linux-2013
|
||||
[13]:http://www.sjbaker.org/wiki/index.php?title=The_History_of_Tux_the_Linux_Penguin
|
||||
[14]:http://distrowatch.com/search.php?ostype=All&category=All&origin=All&basedon=All¬basedon=None&desktop=All&architecture=All&status=Active
|
||||
[15]:http://www.slackware.com/info/
|
||||
[16]:http://pastebin.com/BKcmMd47
|
||||
[17]:http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/203-konstantin-ryabitsev/784544-linux-kernel-git-repositories-add-2-factor-authentication
|
||||
[18]:http://www.top500.org/statistics/details/osfam/1
|
||||
[19]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9793
|
||||
[20]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9882
|
||||
[21]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9885
|
||||
[22]:http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=9965
|
||||
[23]:https://lkml.org/lkml/2011/5/29/204
|
||||
[24]:http://www.wired.com/2012/03/mr-linux/2/
|
||||
[25]:http://lxr.free-electrons.com/source/kernel/reboot.c#L199
|
||||
[26]:http://www.nndb.com/people/444/000022378/
|
||||
[27]:http://linuxfonts.narod.ru/why.linux.is.not.ready.for.the.desktop.current.html
|
||||
[28]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8myENKt8bD0
|
||||
92
translated/talk/20140904 Making MySQL Better at GitHub.md
Normal file
92
translated/talk/20140904 Making MySQL Better at GitHub.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
||||
优化 GitHub 服务器上的 MySQL 数据库性能
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 在 GitHub 我们总是说“如果网站响应速度不够快,我们就不应该让它上线运营”。我们之前在[前端的体验速度][1]这篇文章中介绍了一些提高网站响应速率的方法,但这只是故事的一部分。真正影响到 GitHub.com 性能的因素是 MySQL 数据库架构。让我们来瞧瞧我们的基础架构团队是如何无缝升级了 MySQL 架构吧,这事儿发生在去年8月份,成果就是大大提高了 GitHub 网站的速度。
|
||||
|
||||
### 任务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
去年我们把 GitHub 上的大部分数据移到了新的数据中心,这个中心有世界顶级的硬件资源和网络平台。自从使用了 MySQL 作为我们的后端基本存储系统,我们一直期望着一些改进来大大提高数据库性能,但是在数据中心使用全新的硬件来部署一套全新的集群环境并不是一件简单的工作,所以我们制定了一套计划和测试工作,以便数据能平滑过渡到新环境。
|
||||
|
||||
### 准备工作 ###
|
||||
|
||||
像我们这种关于架构上的巨大改变,在执行的每一步都需要收集数据指标。新机器上安装好了基础操作系统,接下来就是测试新配置下的各种性能。为了模拟真实的工作负载环境,我们使用 tcpdump 工具从老集群那里复制正在发生的 SELECT 请求,并在新集群上重新响应一遍。
|
||||
|
||||
MySQL 微调是个繁琐的细致活,像众所周知的 innodb_buffer_pool_size 这个参数往往能对 MySQL 性能产生巨大的影响。对于这类参数,我们必须考虑在内,所以我们列了一份参数清单,包括 innodb_thread_concurrency,innodb_io_capacity,和 innodb_buffer_pool_instances,还有其它的。
|
||||
|
||||
在每次测试中,我们都很小心地只改变一个参数,并且让一次测试至少运行12小时。我们会观察响应时间的变化曲线,每秒的响应次数,以及有可能会导致并发性降低的参数。我们使用 “SHOW ENGINE INNODB STATUS” 命令打印 InnoDB 性能信息,特别观察了 “SEMAPHORES” 一节的内容,它为我们提供了工作负载的状态信息。
|
||||
|
||||
当我们在设置参数后对运行结果感到满意,然后就开始将我们最大的一个数据表格迁移到一套独立的集群上,这个步骤作为整个迁移过程的早期测试,保证我们的核心集群空出更多的缓存池空间,并且为故障切换和存储功能提供更强的灵活性。这步初始迁移方案也引入了一个有趣的挑战:我们必须维持多条客户连接,并且要将这些连接重定向到正确的集群上。
|
||||
|
||||
除了硬件性能的提升,还需要补充一点,我们同时也对处理进程和拓扑结构进行了改进:我们添加了延时拷贝技术,更快、更高频地备份数据,以及更多的读拷贝空间。这些功能已经准备上线。
|
||||
|
||||
### 列出任务清单,三思后行 ###
|
||||
|
||||
每天有上百万用户的使用 GitHub.com,我们不可能有机会进行实际意义上的数据切换。我们有一个详细的[任务清单][2]来执行迁移:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我们还规划了一个维护期,并且[在我们的博客中通知了大家][3],让用户注意到这件事情。
|
||||
|
||||
### 迁移时间到 ###
|
||||
|
||||
太平洋时间星期六上午5点,我们的迁移团队上线集合聊天,同时数据迁移正式开始:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我们将 GitHub 网站设置为维护模式,并在 Twitter 上发表声明,然后开始按上述任务清单的步骤开始工作:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**13 分钟**后,我们确保新的集群能正常工作:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
然后我们让 GitHub.com 脱离维护期,并且让全世界的用户都知道我们的最新状态:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
大量前期的测试工作与准备工作,让我们将维护期缩到最短。
|
||||
|
||||
### 检验最终的成果 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在接下来的几周时间里,我们密切监视着 GitHub.com 的性能和响应时间。我们发现迁移后网站的平均加载时间减少一半,并且在99%的时间里,能减少*三分之二*:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 我们学到了什么 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能划分 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在迁移过程中,我们采用了一个比较好的方法是:将大的数据表(主要记录了一些历史数据)先迁移过去,空出旧集群的磁盘空间和缓存池空间。这一步给我们留下了更过的资源用户维护“热”数据,将一些连接请求分离到多套集群里面。这步为我们之后的胜利奠定了基础,我们以后还会使用这种模式来进行迁移工作。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 测试测试测试 ####
|
||||
|
||||
为你的应用做验收测试和回归测试,越多越好,多多益善,不要嫌多。从老集群复制数据到新集群的过程中,如果进行验收测试和响应状态测试,得到的数据是不准的,如果数据不理想,这是正常的,不要惊讶,不要试图拿这些数据去分析原因。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 合作的力量 ####
|
||||
|
||||
对基础架构进行大的改变,通常需要涉及到很多人,我们要像一个团队一样为共同的目标而合作。我们的团队成员来自全球各地。
|
||||
|
||||
团队成员地图:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
本次合作新创了一种工作流程:我们提交更改(pull request),获取实时反馈,查看修改了错误的 commit —— 全程没有电话交流或面对面的会议。当所有东西都可以通过 URL 提供信息,不同区域的人群之间的交流和反馈会变得非常简单。
|
||||
|
||||
### 一年后。。。 ###
|
||||
|
||||
整整一年时间过去了,我们很高兴地宣布这次数据迁移是很成功的 —— MySQL 性能和可靠性一直处于我们期望的状态。另外,新的集群还能让我们进一步去升级,提供更好的可靠性和响应时间。我将继续记录这些优化过程。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://github.com/blog/1880-making-mysql-better-at-github
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[samlambert][a]
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://github.com/samlambert
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/blog/1756-optimizing-large-selector-sets
|
||||
[2]:https://help.github.com/articles/writing-on-github#task-lists
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/blog/1603-site-maintenance-august-31st-2013
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
||||
桌面看腻了?试试这 4 款漂亮的 Linux 图标主题吧
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Ubuntu 的默认图标主题在 5 年内[并未发生太大的变化][1],那些说“[图标早就彻底更新过了][2]”的你过来,我保证不打你。如果你确实想尝试一些新鲜的东西,我们将向你展示一些惊艳的替代品,它们会让你感到眼前一亮。**
|
||||
|
||||
如果还是感到不太满意,你可以在文末的评论里留下你比较中意的图标主题的链接地址。
|
||||
|
||||
### Captiva ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Captiva 图标 + elementary 文件夹图标 + Moka GTK
|
||||
|
||||
Captiva 是一款相对较新的图标主题,即使那些有华丽图标倾向的用户也会接受它。
|
||||
|
||||
Captiva 由 DeviantArt 的用户 ~[bokehlicia][3] 制作,它并未使用现在非常流行的平面扁平风格,而是采用了一种圆润、柔和的外观。图标本身呈现出一种很有质感的材质外观,同时通过微调的阴影和亮丽的颜色提高了自身的格调。
|
||||
|
||||
不过 Captiva 图标主题并未包含文件夹图标在内,因此它将使用 elementary(如果可以的话)或者普通的 Ubuntu 文件夹图标。
|
||||
|
||||
要想在 Ubuntu 14.04 中安装 Captiva 图标,你可以新开一个终端,按如下方式添加官方 PPA 并进行安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:captiva/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install captiva-icon-theme
|
||||
|
||||
或者,如果你不擅长通过软件源安装的话,你也可以直接从 DeviantArt 的主页上下载图标压缩包。把解压过的文件夹挪到家目录的‘.icons’目录下,即可完成安装。
|
||||
|
||||
不过在你完成安装后,你必须得通过像 [Unity Tweak Tool][4] 这样的工具来把你安装的图标主题(本文列出的其他图标主题也要这样)应用到系统上。
|
||||
|
||||
- [DeviantArt 上的 Captiva 图标主题][5]
|
||||
|
||||
### Square Beam ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Square Beam 图标在 Orchis GTK 主题下
|
||||
|
||||
厌倦有棱角的图标了?尝试下 Square Beam 吧。Square Beam 因为其艳丽的色泽、尖锐的坡度变化和鲜明的图标形象,比本文列出的其他图标具有更加宏大的视觉效果。Square Beam 声称自己有超过 30,000 个(抱歉,我没有仔细数过...)的不同图标(!),因此你很难找到它没有考虑到的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
- [GNOME-Look.org 上的 Square Beam 图标主题][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### Moka & Faba ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Moka/Faba Mono 图标在 Orchis GTK 主题下
|
||||
|
||||
这里得稍微介绍下 Moka 图标集。事实上,我敢打赌阅读此文的绝大部分用户正在使用这款图标。
|
||||
|
||||
柔和的颜色、平滑的边缘以及简洁的图标艺术设计,Moka 是一款真正出色的覆盖全面的应用图标。它的兄弟 Faba 将这些特点展现得淋漓尽致,而 Moka 也将延续这些 —— 涵盖所有的系统图标、文件夹图标、面板图标,等等。
|
||||
|
||||
欲知 Ubuntu 上的安装详情、访问项目官方网站?请点击下面的链接。
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载 Moka & Faba 图标主题][7]
|
||||
|
||||
### Compass ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Compass 图标在 Numix Blue GTK 主题下
|
||||
|
||||
在本文最后推荐的是 Compass,最后推荐当然不是最差的意思。这款图标现在仍然保持着‘2D,双色’的 UI 设计风格。它也许是不像本文推荐的其他图标那样鲜明,但这正是它的特色。Compass 秉持这点并与之不断的完善 —— 看看文件夹的图标就知道了!
|
||||
|
||||
可以通过 GNOME-Look(下面有链接)进行下载和安装,或者通过添加 Nitrux Artwork 的 PPA 安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nitrux/nitrux-artwork
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install compass-icon-theme
|
||||
|
||||
- [GNOME-Look.org 上的 Compass 图标主题][8]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/4-gorgeous-linux-icon-themes-download
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[SteveArcher](https://github.com/SteveArcher)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2010/02/lucid-gets-new-icons-for-rhythmbox-ubuntuone-memenu-more
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2012/08/new-icon-theme-lands-in-lubuntu-12-10
|
||||
[3]:http://bokehlicia.deviantart.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/06/unity-tweak-tool-0-7-development-download
|
||||
[5]:http://bokehlicia.deviantart.com/art/Captiva-Icon-Theme-479302805
|
||||
[6]:http://gnome-look.org/content/show.php/Square-Beam?content=165094
|
||||
[7]:http://mokaproject.com/moka-icon-theme/download/ubuntu/
|
||||
[8]:http://gnome-look.org/content/show.php/Compass?content=160629
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
|
||||
IPv6:IPv4犯的罪,为什么要我来弥补
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
(LCTT:标题党了一把,哈哈哈好过瘾,求不拍砖)
|
||||
|
||||
在过去的十年间,IPv6 本来应该得到很大的发展,但事实上这种好事并没有降临。由此导致了一个结果,那就是大部分人都不了解 IPv6 的一些知识:它是什么,怎么使用,以及,为什么它会存在?(LCTT:这是要回答蒙田的“我是谁”哲学思考题吗?)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
IPv4 和 IPv6 的区别
|
||||
|
||||
### IPv4 做错了什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
自从1981年发布了 RFC 791 标准以来我们就一直在使用 **IPv4**。在那个时候,电脑又大又贵还不多见,而 IPv4 号称能提供**40亿条 IP 地址**,在当时看来,这个数字好大好大。不幸的是,这么多的 IP 地址并没有被充分利用起来,地址与地址之间存在间隙。举个例子,一家公司可能有**254(2^8-2)**条地址,但只使用其中的25条,剩下的229条被空占着,以备将来之需。于是这些空闲着的地址不能服务于真正需要它们的用户,原因就是网络路由规则的限制。最终的结果是在1981年看起来那个好大好大的数字,在2014年看起来变得好小好小。
|
||||
|
||||
互联网工程任务组(**IETF**)在90年代指出了这个问题,并提供了两套解决方案:无类型域间选路(**CIDR**)以及私有地址。在 CIDR 出现之前,你只能选择三种网络地址长度:**24 位** (共可用16,777,214个地址), **20位** (共可用1,048,574个地址)以及**16位** (共可用65,534个地址)。CIDR 出现之后,你可以将一个网络再划分成多个子网。
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子,如果你需要**5个 IP 地址**,你的 ISP 会为你提供一个子网,里面的主机地址长度为3位,也就是说你最多能得到**6个地址**(LCTT:抛开子网的网络号,3位主机地址长度可以表示0~7共8个地址,但第0个和第7个有特殊用途,不能被用户使用,所以你最多能得到6个地址)。这种方法让 ISP 能尽最大效率分配 IP 地址。“私有地址”这套解决方案的效果是,你可以自己创建一个网络,里面的主机可以访问外网的主机,但外网的主机很难访问到你创建的那个网络上的主机,因为你的网络是私有的、别人不可见的。你可以创建一个非常大的网络,因为你可以使用16,777,214个主机地址,并且你可以将这个网络分割成更小的子网,方便自己管理。
|
||||
|
||||
也许你现在正在使用私有地址。看看你自己的 IP 地址,如果这个地址在这些范围内:**10.0.0.0 – 10.255.255.255**、**172.16.0.0 – 172.31.255.255**或**192.168.0.0 – 192.168.255.255**,就说明你在使用私有地址。这两套方案有效地将“IP 地址用尽”这个灾难延迟了好长时间,但这毕竟只是权宜之计,现在我们正面临最终的审判。
|
||||
|
||||
**IPv4** 还有另外一个问题,那就是这个协议的消息头长度可变。如果数据通过软件来路由,这个问题还好说。但现在路由器功能都是由硬件提供的,处理变长消息头对硬件来说是一件困难的事情。一个大的路由器需要处理来自世界各地的大量数据包,这个时候路由器的负载是非常大的。所以很明显,我们需要固定消息头的长度。
|
||||
|
||||
还有一个问题,在分配 IP 地址的时候,美国人发了因特网(LCTT:这个万恶的资本主义国家占用了大量 IP 地址)。其他国家只得到了 IP 地址的碎片。我们需要重新定制一个架构,让连续的 IP 地址能在地理位置上集中分布,这样一来路由表可以做的更小(LCTT:想想吧,网速肯定更快)。
|
||||
|
||||
还有一个问题,这个问题你听起来可能还不大相信,就是 IPv4 配置起来比较困难,而且还不好改变。你可能不会碰到这个问题,因为你的路由器为你做了这些事情,不用你去操心。但是你的 ISP 对此一直是很头疼的。
|
||||
|
||||
下一代因特网需要考虑上述的所有问题。
|
||||
|
||||
### IPv6 和它的优点 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**IETF** 在1995年12月公布了下一代 IP 地址标准,名字叫 IPv6,为什么不是 IPv5?因为某个错误原因,“版本5”这个编号被其他项目用去了。IPv6 的优点如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 128位地址长度(共有3.402823669×10³⁸个地址)
|
||||
- 这个架构下的地址在逻辑上聚合
|
||||
- 消息头长度固定
|
||||
- 支持自动配置和修改你的网络。
|
||||
|
||||
我们一项一项地分析这些特点:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 地址 ####
|
||||
|
||||
人们谈到 **IPv6** 时,第一件注意到的事情就是它的地址好多好多。为什么要这么多?因为设计者考虑到地址不能被充分利用起来,我们必须提供足够多的地址,让用户去挥霍,从而达到一些特殊目的。所以如果你想架设自己的 IPv6 网络,你的 ISP 可以给你分配拥有**64位**主机地址长度的网络(可以分配1.844674407×10¹⁹台主机),你想怎么玩就怎么玩。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 聚合 ####
|
||||
|
||||
有这么多的地址,这个地址可以被稀稀拉拉地分配给主机,从而更高效地路由数据包。算一笔帐啊,你的 ISP 拿到一个**80位**地址长度的网络空间,其中16位是 ISP 的子网地址,剩下64位分给你作为主机地址。这样一来,你的 ISP 可以分配65,534个子网。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,这些地址分配不是一成不变地,如果 ISP 想拥有更多的小子网,完全可以做到(当然,土豪 ISP 可能会要求再来一个80位网络空间)。最高的48位地址是相互独立地,也就是说 ISP 与 ISP 之间虽然可能分到相同地80位网络空间,但是这两个空间是相互隔离的,好处就是一个网络空间里面的地址会聚合在一起。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 固定的消息头长度 ####
|
||||
|
||||
**IPv4** 消息头长度可变,但 **IPv6** 消息头长度被固定为40字节。IPv4 会由于额外的参数导致消息头变长,IPv6 中,如果有额外参数,这些信息会被放到一个紧挨着消息头的地方,不会被路由器处理,当消息到达目的地时,这些额外参数会被软件提取出来。
|
||||
|
||||
IPv6 消息头有一个部分叫“flow”,是一个20位伪随机数,用于简化路由器对数据包地路由过程。如果一个数据包存在“flow”,路由器就可以根据这个值作为索引查找路由表,不必慢吞吞地遍历整张路由表来查询路由路径。这个优点使 **IPv6** 更容易被路由。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 自动配置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
**IPv6** 中,当主机开机时,会检查本地网络,看看有没有其他主机使用了自己的 IP 地址。如果地址没有被使用,就接着查询本地的 IPv6 路由器,找到后就向它请求一个 IPv6 地址。然后这台主机就可以连上互联网了 —— 它有自己的 IP 地址,和自己的默认路由器。
|
||||
|
||||
如果这台默认路由器当机,主机就会接着找其他路由器,作为备用路由器。这个功能在 IPv4 协议里实现起来非常困难。同样地,假如路由器想改变自己的地址,自己改掉就好了。主机会自动搜索路由器,并自动更新路由器地址。路由器会同时保存新老地址,直到所有主机都把自己地路由器地址更新成新地址。
|
||||
|
||||
IPv6 自动配置还不是一个完整地解决方案。想要有效地使用互联网,一台主机还需要另外的东西:域名服务器、时间同步服务器、或者还需要一台文件服务器。于是 **dhcp6** 出现了,提供与 dhcp 一样的服务,唯一的区别是 dhcp6 的机器可以在可路由的状态下启动,一个 dhcp 进程可以为大量网络提供服务。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 唯一的大问题 ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果 IPv6 真的比 IPv4 好那么多,为什么它还没有被广泛使用起来(Google 在**2014年5月份**估计 IPv6 的市场占有率为**4%**)?一个最基本的原因是“先有鸡还是先有蛋”问题,用户需要让自己的服务器能为尽可能多的客户提供服务,这就意味着他们必须部署一个 **IPv4** 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,他们可以同时使用 IPv4 和 IPv6 两套地址,但很少有客户会用到 IPv6,并且你还需要对你的软件做一些小修改来适应 IPv6。另外比较头疼的一点是,很多家庭的路由器压根不支持 IPv6。还有就是 ISP 也不愿意支持 IPv6,我问过我的 ISP 这个问题,得到的回答是:只有客户明确指出要部署这个时,他们才会用 IPv6。然后我问了现在有多少人有这个需求,答案是:包括我在内,共有1个。
|
||||
|
||||
与这种现实状况呈明显对比的是,所有主流操作系统:Windows、OS X、Linux 都默认支持 IPv6 好多年了。这些操作系统甚至提供软件让 IPv6 的数据包披上 IPv4 的皮来骗过那些会丢弃 IPv6 数据包的主机,从而达到传输数据的目的(LCTT:呃,这是高科技偷渡?)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 总结 ####
|
||||
|
||||
IPv4 已经为我们服务了好长时间。但是它的缺陷会在不远的将来遭遇不可克服的困难。IPv6 通过改变地址分配规则、简化数据包路由过程、简化首次加入网络时的配置过程等策略,可以完美解决这个问题。
|
||||
|
||||
问题是,大众在接受和使用 IPv6 的过程中进展缓慢,因为改变代价太大了。好消息是所有操作系统都支持 IPv6,所以当你有一天想做出改变,你的电脑只需要改变一点点东西,就能转到全新的架构体系中去。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/ipv4-and-ipv6-comparison/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jeff Silverman][a]
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/jeffsilverm/
|
||||
189
translated/talk/20140915 Make Downloading Files Effortless.md
Normal file
189
translated/talk/20140915 Make Downloading Files Effortless.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,189 @@
|
||||
让下载更方便
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
下载管理器是一个电脑程序,专门处理下载文件,优化带宽占用,以及让下载更有条理等任务。有些网页浏览器,例如Firefox,也集成了一个下载管理器作为功能,但是它们的方式还是没有专门的下载管理器(或者浏览器插件)那么专业,没有最佳地使用带宽,也没有好用的文件管理功能。
|
||||
|
||||
对于那些经常下载的人,使用一个好的下载管理器会更有帮助。它能够最大化下载速度(加速下载),断点续传以及制定下载计划,让下载更安全也更有价值。下载管理器已经没有之前流行了,但是最好的下载管理器还是很实用,包括和浏览器的紧密结合,支持类似YouTube的主流网站,以及更多。
|
||||
|
||||
有好几个能在Linux下工作都非常优秀的开源下载管理器,以至于让人无从选择。我整理了一个摘要,是我喜欢的下载管理器,以及Firefox里的一个非常好用的下载插件。这里列出的每一个程序都是开源许可发布的。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
uGet是一个轻量级,容易使用,功能完备的开源下载管理器。uGet允许用户从不同的源并行下载来加快速度,添加文件到下载序列,暂停或继续下载,提供高级分类管理,和浏览器集成,监控剪贴板,批量下载,支持26种语言,以及其他许多功能。
|
||||
|
||||
uGet是一个成熟的软件;保持开发超过11年。在这个时间里,它发展成一个非常多功能的下载管理器,拥有一套很高价值的功能集,还保持了易用性。
|
||||
|
||||
uGet是用C语言开发的,使用了cURL作为底层支持,以及应用库libcurl。uGet有非常好的平台兼容性。它一开始是Linux系统下的项目,但是被移植到在Mac OS X,FreeBSD,Android和Windows平台运行。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能点: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 容易使用
|
||||
- 下载队列可以让下载任务按任意多或少或你希望的数量同时进行。
|
||||
- 断点续传
|
||||
- 默认分类
|
||||
- 完美实现的剪贴板监控功能
|
||||
- 批量下载
|
||||
- 支持从HTML文件导入下载任务
|
||||
- 支持通过HTTP,HTTPS,FTP,BitTorrent和Metalink下载
|
||||
- 多线程下载(也被称为分块下载):每个下载任务支持最多20个线程同时连接,支持自适应的分块管理,意味着如果某个下载块中断了,那么会其他连接会把它捡起来,以时刻保证最佳的下载速度。
|
||||
- 多镜像下载
|
||||
- FTP登录和匿名FTP
|
||||
- 强大的计划任务
|
||||
- 通过FlashGot和FireFox集成
|
||||
- Aria2插件
|
||||
- 多变的主题
|
||||
- 安静模式
|
||||
- 键盘快捷键
|
||||
- 支持命令行/终端控制
|
||||
- 自动创建目录
|
||||
- 下载历史管理
|
||||
- 支持GnuTLS
|
||||
- 支持26种语言,包括:阿拉伯语,白俄罗斯语,简体中文,繁体中文,捷克语,丹麦语,英语(默认),法语,格鲁吉亚语,德语,匈牙利语,印尼语,意大利语,波兰语,葡萄牙语(巴西),俄语,西班牙语,土耳其语,乌克兰语,以及越南语。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[ugetdm.com][1]
|
||||
- 开发人员:C.H. Huang and contributors
|
||||
- 许可:GNU LGPL 2.1
|
||||
- 版本:1.10.5
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
DownThemAll!是一个小巧的,可靠的以及易用的,开源下载管理器/加速器,是Firefox的一个组件。它可以让用户下载一个页面上所有链接和图片以及更多功能。它可以让用户完全控制下载任务,随时分配下载速度以及同时下载的任务数量。通过使用Metalinks或者手动添加镜像的方式,可以同时从不同的服务器下载同一个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
DownThemAll会根据你要下载的文件大小,切割成不同的部分,然后并行下载。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能点: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 和Firefox的完全集成
|
||||
- 分块下载,允许用户下载不同的文件块,完成之后再拼接成完整的文件;这样的话当连接到一个缓慢的服务器的时候可以加快下载速度。
|
||||
- 支持Metalink,允许发送下载文件的多个URL以及它的校验值和其他信息到DTA
|
||||
- 支持爬虫方式通过一个单独的链接遍历整个网页
|
||||
- 下载过滤
|
||||
- 高级重命名选项
|
||||
- 暂停和继续下载任务
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/downthemall][2]
|
||||
- 开发人员:Federico Parodi, Stefano Verna, Nils Maier
|
||||
- 许可:GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本:2.0.17
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
JDownloader是一个免费,开源的下载管理工具,拥有一个大型社区的开发者支持,让下载更简单和快捷。用户可以开始,停止或暂停下载,设置带宽限制,自动解压缩包,以及更多功能。它提供了一个容易扩展的框架。
|
||||
|
||||
JDownloader简化了从一键下载网站下载文件。它还支持从不同并行资源下载,手势识别,自动文件解压缩以及更多功能。另外,还支持许多“加密链接”网站-所以你只需要复制粘贴“加密的”链接,然后JDownloader会处理剩下的事情。JDownloader还能导入CCF,RSDF和DLC文件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能点: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 一次下载多个文件
|
||||
- 从多个连接同时下载
|
||||
- JD有一个自己实现的强大的OCR模块
|
||||
- 自动解压(包括密码搜索)(RAR压缩包)
|
||||
- 支持主题
|
||||
- 支持多国语言
|
||||
- 大约110个站点以及超过300个解密插件
|
||||
- 通过JDLiveHeaderScripts重连:(支持1400路由)
|
||||
- 网页更新
|
||||
- 集成包管理器支持额外模块(例如,Webinterface,Shutdown)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[jdownloader.org][3]
|
||||
- 开发人员:AppWork UG
|
||||
- 许可:GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- 版本:0.9.581
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
FreeRapid Downloader是一个易用的开源下载程序,支持从Rapidshare,Youtube,Facebook,Picasa和其他文件分享网站下载。他的下载引擎基于一些插件,所以可以从特殊站点下载。
|
||||
|
||||
对于需要针对特定文件分享网站的下载管理器用户来说,FreeRapid Downloader是理想的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
FreeRapid Downloader使用Java语言编写。需要至少Sun Java 7.0版本才可以运行。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能点: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 容易使用
|
||||
- 支持从不同服务站点并行下载
|
||||
- 支持断点续传
|
||||
- 支持通过代理列表下载
|
||||
- 支持流视频或图片
|
||||
- 下载历史
|
||||
- 聪明的剪贴板监控
|
||||
- 自动检查服务器文件后缀
|
||||
- 自动关机选项
|
||||
- 插件自动更新
|
||||
- 简单验证码识别
|
||||
- 支持跨平台
|
||||
- 支持多国语言:英语,保加利亚语,捷克语,芬兰语,葡萄牙语,斯洛伐克语,匈牙利语,简体中文,以及其他
|
||||
- 支持超过700个站点
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[wordrider.net/freerapid/][4]
|
||||
- 开发人员:Vity and contributors
|
||||
- 许可:GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本:0.9u4
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
FlashGot是一个Firefox和Thunderbird的免费组件,旨在通过外置下载管理器来处理单个和大规模(“所有”和“已选”)下载。
|
||||
|
||||
FlashGot把所支持的所有下载管理器统一成Firefox中的一个下载管理器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能点: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Linux下支持:Aria, Axel Download Accelerator, cURL, Downloader 4 X, FatRat, GNOME Gwget, FatRat, JDownloader, KDE KGet, pyLoad, SteadyFlow, uGet, wxDFast, 和wxDownload Fast
|
||||
- 支持图库功能,可以帮助把原来分散在不同页面的系列资源,整合到一个所有媒体库页面中,然后可以轻松迅速地“下载所有”
|
||||
- FlashGot Link会使用默认下载管理器下载当前鼠标选中的链接
|
||||
- FlashGot Selection
|
||||
- FlashGot All
|
||||
- FlashGot Tabs
|
||||
- FlashGot Media
|
||||
- 抓取页面里所有链接
|
||||
- 抓取所有标签栏的所有链接
|
||||
- 链接过滤(例如,只下载指定类型文件)
|
||||
- 在网页上抓取点击所产生的所有链接
|
||||
- 支持从大多数链接保护和文件托管服务器直接和批量下载
|
||||
- 隐私选项
|
||||
- 支持国际化
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[flashgot.net][5]
|
||||
- 开发人员:Giorgio Maone
|
||||
- 许可:GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本:1.5.6.5
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20140913062041384/DownloadManagers.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ugetdm.com/
|
||||
[2]:https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/downthemall/
|
||||
[3]:http://jdownloader.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://wordrider.net/freerapid/
|
||||
[5]:http://flashgot.net/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
7个杀手级的开源监测工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
想要更清晰的了解你的网络吗?没有比这几个免费的工具更好用的了。
|
||||
|
||||
网络和系统监控是一个很宽的范畴。有监控服务器正常工作,网络设备,应用的方案。也有跟踪这些系统和设备性能,提供趋势性能分析的解决方案。有些工具像个闹钟一样,当发现问题的时候就会报警,而另外的一些工具甚至可以在警报响起的时候触发一些动作。这里,收集了一些开源的工具,旨在解决上述的一些甚至大部分问题。
|
||||
|
||||
### Cacti ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cacti是一个性能广泛的图表和趋势分析工具,可以用来跟踪,并且几乎可以绘制出任何可监测指标,并描绘出图表。从硬盘的利用率到风扇的转速,在一个电脑管理系统中,只要是可以被监测的指标,Cacti都可以监测,并快速的转换成可视化的图表。
|
||||
|
||||
### Nagios ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Nagios是一个经典的老牌系统和网络监测工具。运行速度快,可靠,需要针对应用定制。Nagios对于初学者是一个挑战。但是它的极其复杂的配置正好也反应出它的强大,因为它几乎可以适用于任何监控任务。要说缺点的话就是不怎么耐看,但是其强劲的动力和可靠性弥补了这个缺点。
|
||||
|
||||
### Icinga ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Icinga 是一个正在重建的Nagios的分支,它提供了一个全面的监控和警报的框架,致力于设计一个像Nagios一样的开放的和可扩展性的平台。但是和Nagios拥有不一样的Web界面。Icinga 1 是Nagios非常的相近,不过Icinga 2就重写了。两个版本都能很好的兼容,而且,Nagios用户可以很轻松的转到Icinga 1平台。
|
||||
|
||||
### NeDi ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
NeDi可能不如其他的工具一样文明全世界,但它确是一个跟踪网络接入的一个强大的解决方案。它可以很流畅的运行网络基础设施和设备目录,保持对任何事件的跟踪。并且可以提供任意设备的当前位置,也包括历史位置。
|
||||
|
||||
NeDi可以被用于定位被偷的,或者是丢失掉的设备,只要设备出现在网络上。它甚至可以在地图上显示所有已发现的节点。并且很清晰的告诉人们网络是怎么互联的到物理设备端口的。
|
||||
|
||||
### Observium ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Observium 综合系统网路在性能趋势监测上有很好的表现,它支持静态和动态发现来确认服务器和网络设备,利用多种监测方法,可以监测任何可用的指标。Web界面非常的整洁,易用。
|
||||
|
||||
就如我们看到的,Observium也可以在地图上显示任何被监测节点的实际位置。需要注意的是面板上关于活跃设备和警报的计数。
|
||||
|
||||
### Zabbix ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Zabbix 利用广泛的矩阵工具监测服务器和网络。代理商的Zabbix针对大多数的操作系统,你可以被动的或者是使用外部检查,包括SNMP来监控主机和网络设备。你也会发现很多提醒和通知设施,和一个非常人性化的Web界面,适用于不同的面板,此外,Zabbix还拥有一些特殊的管理工具来监测Web应用和虚拟化的管理程序。
|
||||
|
||||
Zabbix 还可以提供详细的互联图,以便于我们了解某些对象是怎么连接的。这些图是可以定制的,并且,图也可以以被监测的服务器和主机的分组形式被创建。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ntop ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ntop是一个数据包嗅探工具。有一个整洁的Web界面,用来显示被监测网络的实时数据。即时的网络数据通过一个高级的绘图工具可以可视化。主机信息流和主机通信信息对也可以被实时的进行可视化显示。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.networkworld.com/article/2686794/asset-management/164219-7-killer-open-source-monitoring-tools.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Paul Venezia][a]
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.networkworld.com/author/Paul-Venezia/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
||||
安卓编年史
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
电子邮件应用的所有界面。前两张截图展示了标签/收件箱结合的视图,最后一张截图展示了一封邮件。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
邮件视图是——令人惊讶的!——白色。安卓的电子邮件应用从历史角度来说算是个打了折扣的Gmail应用,你可以在这里看到紧密的联系。读邮件以及写邮件视图几乎没有任何修改地就从Gmail那里直接取过来使用。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
即时通讯应用。截图展示了服务提供商选择界面,朋友列表,以及一个对话。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
在Google Hangouts之前,甚至是Google Talk之前,就有“IM”——安卓1.0带来的唯一一个即时通讯客户端。令人惊奇的是,它支持多种IM服务:用户可以从AIM,Google Talk,Windows Live Messenger以及Yahoo中挑选。还记得操作系统开发者什么时候关心过互通性吗?
|
||||
|
||||
朋友列表是聊天中带有白色聊天气泡的黑色背景界面。状态用一个带颜色的圆形来指示,右侧的小安卓机器人指示出某人正在使用移动设备。IM应用相比Google Hangouts远比它有沟通性,这真是十分神奇的。绿色代表着某人正在使用设备并且已经登录,黄色代表着他们登录了但处于空闲状态,红色代表他们手动设置状态为忙,不想被打扰,灰色表示离线。现在Hangouts只显示用户是否打开了应用。
|
||||
|
||||
聊天对话界面明显基于信息应用,聊天的背景从白色和蓝色被换成了白色和绿色。但是没人更改信息输入框的颜色,所以加上橙色的高亮效果,界面共使用了白色,绿色,蓝色和橙色。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安卓1.0上的YouTube。截图展示了主界面,打开菜单的主界面,分类界面,视频播放界面。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
YouTube仅仅以G1的320p屏幕和3G网络速度可能不会有今天这样的移动意识,但谷歌的视频服务在安卓1.0上就被置入发布了。主界面看起来就像是安卓市场调整过的版本,顶部带有一个横向滚动选择部分,下面有垂直滚动分类列表。谷歌的一些分类选择还真是奇怪:“最热门”和“最多观看”有什么区别?
|
||||
|
||||
一个谷歌没有意识到YouTube最终能达到多庞大的标志——有一个视频分类是“最近更新”。在今天,每分钟有[100小时时长的视频][1]上传到Youtube上,如果这个分类能正常工作的话,它会是一个快速滚动的视频列表,快到以至于变为一片无法阅读的模糊。
|
||||
|
||||
菜单含有搜索,喜爱,分类,设置。设置(没有图片)是有史以来最简陋的,只有个清除搜索历史的选项。分类都是一样的平淡,仅仅是个黑色的文本列表。
|
||||
|
||||
最后一张截图展示了视频播放界面,只支持横屏模式。尽管自动隐藏的播放控制有个进度条,但它还是很奇怪地包含了后退和前进按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
YouTube的视频菜单,描述页面,评论。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
每个视频的更多选项可以通过点击菜单按钮来打开。在这里你可以把视频标记为喜爱,查看详细信息,以及阅读评论。所有的这些界面,和视频播放一样,是锁定横屏模式的。
|
||||
|
||||
然而“共享”不会打开一个对话框,它只是向Gmail邮件中加入了视频的链接。想要把链接通过短信或即时消息发送给别人是不可能的。你可以阅读评论,但是没办法评价他们或发表自己的评论。你同样无法给视频评分或赞。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
相机应用的拍照界面,菜单,照片浏览模式。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
在实体机上跑上真正的安卓意味着相机功能可以正常运作,即便那里没什么太多可关注的。左边的黑色方块是相机的界面,原本应该显示取景器图像,但SDK的截图工具没办法捕捉下来。G1有个硬件实体的拍照键(还记得吗?),所以相机没必要有个屏幕上的快门键。相机没有曝光,白平衡,或HDR设置——你可以拍摄照片,仅此而已。
|
||||
|
||||
菜单按钮显示两个选项:跳转到相册应用和带有两个选项的设置界面。第一个设置选项是是否给照片加上地理标记,第二个是在每次拍摄后显示提示菜单,你可以在上面右边看到截图。同样的,你目前还只能拍照——还不支持视频拍摄。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
日历的月视图,打开菜单的周视图,日视图,以及日程。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
就像这个时期的大多数应用一样,日历的主命令界面是菜单。菜单用来切换视图,添加新事件,导航至当天,选择要显示的日程,以及打开设置。菜单扮演着每个单独按钮的入口的作用。
|
||||
|
||||
月视图不能显示约会事件的文字。每个日期旁边有个侧边,约会会显示为侧边上的绿色部分,通过位置来表示约会是在一天中的什么时候。周视图同样不能显示预约文字——G1的320×480的显示屏像素还不够密——所以你会在日历中看到一个带有颜色指示条的白块。唯一一个显示文字的是日程和日视图。你可以用滑动来切换日期——左右滑动切换周和日,上下滑动切换月份和日程。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
设置主界面,无线设置,关于页面的底部。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
安卓1.0最终带来了设置界面。这个界面是个带有文字的黑白界面,粗略地分为各个部分。每个列表项边的下箭头让人误以为点击它会展开折叠的更多东西,但是触摸列表项的任何位置只会加载下一屏幕。所有的界面看起来确实无趣,都差不多一样,但是嘿,这可是设置啊。
|
||||
|
||||
任何带有开/关状态的选项都使用了卡通风的复选框。安卓1.0最初的复选框真是奇怪——就算是在“未选中”状态时,它们还是有个灰色的勾选标记在里面。安卓把勾选标记当作了灯泡,打开时亮起来,关闭的时候变得黯淡,但这不是复选框的工作方式。然而我们最终还是见到了“关于”页面。安卓1.0运行Linux内核2.6.25版本。
|
||||
|
||||
设置界面意味着我们终于可以打开安全设置并更改锁屏。安卓1.0只有两种风格,安卓0.9那样的灰色方形锁屏,以及需要你在9个点组成的网格中画出图案的图形解锁。像这样的滑动图案相比PIN码更加容易记忆和输入,尽管它没有增加多少安全性。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
语音拨号,图形锁屏,电池低电量警告,时间设置。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
语音功能和语音拨号一同来到了1.0。这个特性以各种功能实现在AOSP徘徊了一段时间,然而它是一个简单的拨打号码和联系人的语音命令应用。语音拨号是个和谷歌未来的语音产品完全无关的应用,但是,它的工作方式和非智能机上的语音拨号一样。
|
||||
|
||||
关于最后一个值得注意的,当电池电量低于百分之十五的时候会触发低电量弹窗。这是个有趣的图案,它把电源线错误的一端插入手机。谷歌,那可不是(现在依然不是)手机应该有的充电方式。
|
||||
|
||||
安卓1.0是个伟大的开头,但是功能上仍然有许多缺失。实体键盘和大量硬件按钮被强制要求配备,因为不带有十字方向键或轨迹球的安卓设备依然不被允许销售。另外,基本的智能手机功能比如自动旋转依然缺失。内置应用不可能像今天这样通过安卓市场来更新。所有的谷歌系应用和系统交织在一起。如果谷歌想要升级一个单独的应用,需要通过运营商推送整个系统的更新。安卓依然还有许多工作要做。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安卓1.1——第一个真正的增量更新 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安卓1.1的所有新特性:语音搜索,安卓市场付费应用支持,谷歌纵横,设置中的新“系统更新”选项。
|
||||
Ron Amadeo供图
|
||||
|
||||
安卓1.0发布四个半月后,2009年2月,安卓在安卓1.1中得到了它的第一个公开更新。系统方面没有太多变化,谷歌向1.1中添加新东西现如今也都已被关闭。谷歌语音搜索是安卓向云端语音搜索的第一个突击,它在应用抽屉里有自己的图标。尽管这个应用已经不能与谷歌服务器通讯,你可以[在iPhone上][2]看到它以前是怎么工作的。它还没有语音操作,但你可以说出想要搜索的,结果会显示在一个简单的谷歌搜索中。
|
||||
|
||||
安卓市场添加了对付费应用的支持,但是就像beta客户端中一样,这个版本的安卓市场不再能够连接Google Play服务器。我们最多能够看到分类界面,你可以在免费应用,付费应用和全部应用中选择。
|
||||
|
||||
地图添加了[谷歌纵横][3],一个向朋友分享自己位置的方法。纵横在几个月前为了支持Google+而被关闭并且不再能够工作。地图菜单里有个纵横的选项,但点击它现在只会打开一个带载入中圆圈的画面,并永远停留在这里。
|
||||
|
||||
安卓世界的系统更新来得更加迅速——或者至少是一条在运营商和OEM推送之前获得更新的途径——谷歌向“关于手机”界面添加了检查系统更新按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Ron Amadeo][a] / Ron是Ars Technica的评论编缉,专注于安卓系统和谷歌产品。他总是在追寻新鲜事物,还喜欢拆解事物看看它们到底是怎么运作的。
|
||||
|
||||
[@RonAmadeo][t]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-history-of-googles-mobile-os/7/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.youtube.com/yt/press/statistics.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y3z7Tw1K17A
|
||||
[3]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2009/02/google-tries-location-based-social-networking-with-latitude/
|
||||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
||||
在 Debian 上使用 systemd 管理系统
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
人类已经无法阻止 systemd 占领全世界的 Linux 系统了,唯一阻止它的方法是在你自己的机器上手动卸载它。到目前为止,systemd 已经创建了比任何软件都多的技术问题、感情问题和社会问题。这一点从[热议][1](也称 Linux 初始化软件之战)上就能看出,这场争论在 Debian 开发者之间持续了好几个月。当 Debian 技术委员会最终决定将 systemd 放到 Debian 8(代号 Jessie)的发行版里面时,其反对者试图通过多种努力来[取代这项决议][2],甚至有人扬言要威胁那些支持 systemd 的开发者的生命安全。
|
||||
|
||||
这也说明了 systemd 对 Unix 传承下来的系统处理方式有很大的干扰。“一个软件只做一件事情”的哲学思想已经被这个新来者彻底颠覆。除了取代了 sysvinit 成为新的系统初始化工具外,systemd 还是一个系统管理工具。目前为止,由于 systemd-sysv 这个软件包提供的兼容性,那些我们使用惯了的工具还能继续工作。但是当 Debian 将 systemd 升级到214版本后,这种兼容性就不复存在了。升级措施预计会在 Debian 8 "Jessie" 的稳定分支上进行。从此以后用户必须使用新的命令来管理系统、执行任务、变换运行级别、查询系统日志等等。不过这里有一个应对方案,那就是在 .bashrc 文件里面添加一些别名。
|
||||
|
||||
现在就让我们来看看 systemd 是怎么改变你管理系统的习惯的。在使用 systemd 之前,你得先把 sysvinit 保存起来,以防 systemd 出错的时候还能用 sysvinit 启动系统。这种方法只有在没安装 systemd-sysv 的情况下才能生效,具体操作方法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# cp -av /sbin/init /sbin/init.sysvinit
|
||||
|
||||
在紧急情况下,可以把下面的文本:
|
||||
|
||||
init=/sbin/init.sysvinit
|
||||
|
||||
添加到内核启动参数项那里。
|
||||
|
||||
### systemctl 的基本用法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl 的功能是替代“/etc/init.d/foo start/stop”这类命令,另外,其实它还能做其他的事情,这点你可以参考 man 文档。
|
||||
|
||||
一些基本用法:
|
||||
|
||||
- systemctl - 列出所有单元(UNIT)以及它们的状态(这里的 UNIT 指的就是系统上的 job 和 service)
|
||||
- systemctl list-units - 列出所有 UNIT
|
||||
- systemctl start [NAME...] - 启动一项或多项 UNIT
|
||||
- systemctl stop [NAME...] - 停止一项或多项 UNIT
|
||||
- systemctl disable [NAME...] - 将 UNIT 设置为开机不启动
|
||||
- systemctl list-unit-files - 列出所有已安装的 UNIT,以及它们的状态
|
||||
- systemctl --failed - 列出开机启动失败的 UNIT
|
||||
- systemctl --type=mount - 列出某种类型的 UNIT,类型包含:service, mount, device, socket, target
|
||||
- systemctl enable debug-shell.service - 将一个 shell 脚本设置为开机启动,用于调试
|
||||
|
||||
为了更方便处理这些 UNIT,你可以使用 systemd-ui 软件包,你只要输入 systemadm 命令就可以使用这个软件。
|
||||
|
||||
你同样可以使用 systemctl 实现转换运行级别、重启系统和关闭系统的功能:
|
||||
|
||||
- systemctl isolate graphical.target - 切换到运行级别5,就是有桌面的级别
|
||||
- systemctl isolate multi-user.target - 切换到运行级别3,没有桌面的级别
|
||||
- systemctl reboot - 重启系统
|
||||
- systemctl poweroff - 关机
|
||||
|
||||
所有命令,包括切换到其他运行级别的命令,都可以在普通用户的权限下执行。
|
||||
|
||||
### journalctl 的基本用法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
systemd 不仅提供了比 sysvinit 更快的启动速度,还让日志系统在更早的时候启动起来,可以记录内核初始化阶段、内存初始化阶段、前期启动步骤以及主要的系统执行过程的日志。所以以前那种需要通过对显示屏拍照或者暂停系统来调试程序的日子已经一去不复返啦。
|
||||
|
||||
systemd 的日志文件都被放在 /var/log 目录。如果你想使用它的日志功能,需要执行一些命令,因为 Debian 没有打开日志功能。命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# addgroup --system systemd-journal
|
||||
# mkdir -p /var/log/journal
|
||||
# chown root:systemd-journal /var/log/journal
|
||||
# gpasswd -a $user systemd-journal
|
||||
|
||||
通过上面的设置,你就可以以普通用户权限使用 journal 软件查看日志。使用 journalctl 查询日志可以获得一些比 syslog 软件更方便的玩法:
|
||||
|
||||
- journalctl --all - 显示系统上所有日志,以及它的用户
|
||||
- journalctl -f - 监视系统日志的变化(类似 tail -f /var/log/messages 的效果)
|
||||
- journalctl -b - 显示系统启动以后的日志
|
||||
- journalctl -k -b -1 - 显示上一次(-b -1)系统启动前产生的内核日志
|
||||
- journalctl -b -p err - 显示系统启动后产生的“ERROR”日志
|
||||
- journalctl --since=yesterday - 当系统不会经常重启的时候,这条命令能提供比 -b 更短的日志记录
|
||||
- journalctl -u cron.service --since='2014-07-06 07:00' --until='2014-07-06 08:23' - 显示 cron 服务在某个时间段内打印出来的日志
|
||||
- journalctl -p 2 --since=today - 显示优先级别为2以内的日志,包含 emerg、alert、crit三个级别。所有日志级别有: emerg (0), alert (1), crit (2), err (3), warning (4), notice (5), info (6), debug (7)
|
||||
- journalctl > yourlog.log - 将二进制日志文件复制成文本文件并保存到当前目录
|
||||
|
||||
Journal 和 syslog 可以很好的共存。而另一方面,一旦你习惯了操作 journal,你也可以卸载掉所有 syslog 的软件,比如 rsyslog 或 syslog-ng。
|
||||
|
||||
如果想要得到更详细的日志信息,你可以在内核启动参数上添加“systemd.log_level=debug”,然后运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# journalctl -alb
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以编辑 /etc/systemd/system.conf 文件来修改日志级别。
|
||||
|
||||
### 利用 systemd 分析系统启动过程 ###
|
||||
|
||||
systemd 可以让你能更有效地分析和优化你的系统启动过程:
|
||||
|
||||
- systemd-analyze - 显示本次启动系统过程中用户态和内核态所花的时间
|
||||
- systemd-analyze blame - 显示每个启动项所花费的时间明细
|
||||
- systemd-analyze critical-chain - 按时间顺序打印 UNIT 树
|
||||
- systemd-analyze dot | dot -Tsvg > systemd.svg - 为开机启动过程生成向量图(需要安装 graphviz 软件包)
|
||||
- systemd-analyze plot > bootplot.svg - 产生开机启动过程的时间图表
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
systemd 虽然是个年轻的项目,但存在大量文档。首先要介绍的是[Lennart Poettering 的 0pointer 系列][3]。这个系列非常详细,非常有技术含量。另外一个是[免费桌面信息文档][4],它包含了最详细的关于 systemd 的链接:发行版特性文件、bug 跟踪系统和说明文档。你可以使用下面的命令来查询 systemd 都提供了哪些文档:
|
||||
|
||||
# man systemd.index
|
||||
|
||||
不同发行版之间的 systemd 提供的命令基本一样,最大的不同之处就是打包方式。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/07/use-systemd-system-administration-debian.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://lists.debian.org/debian-devel/2013/10/msg00444.html
|
||||
[2]:https://lists.debian.org/debian-devel/2014/02/msg00316.html
|
||||
[3]:http://0pointer.de/blog/projects/systemd.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.freedesktop.org/wiki/Software/systemd/
|
||||
135
translated/tech/20140819 Build a Raspberry Pi Arcade Machine.md
Normal file
135
translated/tech/20140819 Build a Raspberry Pi Arcade Machine.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
自制一台树莓派街机
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**利用当代神奇设备来重温80年代的黄金威严。**
|
||||
|
||||
### 你需要以下硬件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 一台树莓派以及一张4GBSD卡
|
||||
- 一台支持HDMI的LCD显示屏
|
||||
- 游戏手柄或者...
|
||||
- 一个JAMMA街机游戏机外壳机箱
|
||||
- J-Pac或者I-Pac
|
||||
|
||||
80年代有太多难忘的记忆;冷战结束,Quatro碳酸饮料,Korg Polysix合成器,以及Commodore 64家用电脑。但对于某些年轻人来说,这些都没有街机游戏机那样有说服力,或那种甜蜜的叛逆。笼罩着烟味和此起彼伏的8比特音效,它们就是在挤出来的时间里去探索的洞穴:50分钱和一份代币能让你消耗整个午餐时间,在这些游戏上磨练着你的技能:小蜜蜂,城市大金刚,蜈蚣,行星射击,吃豆小姐,火凤凰,R-Rype,大金刚,雷霆计划,铁手套,街头霸王,超越赛车,防卫者争战...这个列表太长了。
|
||||
|
||||
这些游戏,以及玩这些游戏的街机机器,仍然像30年前那样有吸引力。不像年轻时候那样,现在可以不用装一兜零钱就能玩了,最终让你超越那些有钱的孩子以及他们无休止的‘继续游戏’。所以是时候打造一个你自己的基于Linux的街机游戏机了,然后挑战一下过去的最高分。
|
||||
|
||||
我们将会覆盖所有的步骤,来将一个便宜的街机游戏机器外壳变成一台Linux驱动的多平台复古游戏系统。但是这并不意味着你就一定要搭建一个同样的系统。比如说,你可以放弃那个又大又重还有潜在致癌性外壳的箱子本身,而是将内部控制核心装进一个旧游戏主机或同等大小的盒子里。或者说,你也可以简单地放弃小巧的树莓派,而将系统的大脑换成一台更强劲的Linux主机。举个例子,它可以作为运行SteamOS的一个理想平台,用来玩那些更优秀的现代街机游戏。
|
||||
|
||||
在之后的几个页面里,我们将搭建一台基于树莓派的街机游戏机,你应该也能从其中发现很多点子应用到你自己的项目上,即使它们和我们这个项目不太一样。然后因为我们是用无比强大的MAME来做这件事情,你几乎可以让它在任意平台上运行。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我们在B+型号出来以前完成的这个项目。它应该也可以同样工作在更新的主板上,你应该不用一个带电源的USB Hub也可以(点击看大图)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 声明 ###
|
||||
|
||||
强调一下,我们捣腾的电子器件可能会让你受到电击。请确保你做的任何改动都是有资质的电子工程师帮你检查过的。我们也不会深入讨论如何获取游戏,但是有很多合法的资源,例如基于MAME模拟器的老游戏,以及较新的商业游戏。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第一步:街机机柜 ####
|
||||
|
||||
街机机柜本身就是最大的挑战。我们在eBay上淘了个二手的90年代初的双人泡泡龙游戏机。然后花了£220装在一台旅行车后面送过来。类似这种机柜的价格并不确定。我们看到过很多在£100以内的。而另一方面,还有很多人愿意花数千块钱去买原版侧面贴纸完整的机器。
|
||||
|
||||
决定买一个街机机柜,主要有两个考虑。第一个是它的体积:这东西又大又重。又占地方,而且需要至少两个人才能搬动。如果你不缺钱的话,还可以买DIY机柜或者全新的小一点的,例如适合摆在桌子上的那种。然后,酒柜也能很合适。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这种机柜可能很便宜,但是他们都很重。不要一个人去搬。一些更古老的机器可能还会需要一点小关怀,例如重新喷个漆以及一些修理工作(点击看大图)。
|
||||
|
||||
除了获得更加真实的游戏体验以外,购买原版的街机机柜的一个绝佳理由是可以使用原版的控制器。从eBay上买到的大多数机器都支持两个人同时玩,有两个摇杆以及每个玩家各自的一些按钮,再加上玩家一和玩家二的选择按钮。为了兼容更多游戏,我们建议您找一台每个玩家都有6个按键,这个是通用配置。也许你还想看看支持超过两位玩家的控制台,或者有空间放其他游戏控制器的,比如说街机轨迹球(类似疯狂弹珠这种游戏需要的),或者一个旋钮(打砖块)。这些待会都可以轻松装上去,因为有现成的现代USB设备。
|
||||
|
||||
控制器是第二考虑的,而且我们认为是最重要的,因为要通过它把你的摇动和拍打转变成游戏里的动作。当你准备买一个机柜时需要考虑一种叫JAMMA的东西,它是日本娱乐机械制造商协会(Japan Amusement Machinery Manufacturers Association)的缩写。JAMMA是街机游戏机里的行业标准,定义了包含游戏芯片的电路板和游戏控制器的连接方式,以及投币机制。它是一个连接两个玩家的摇杆和按钮的所有线缆的接口电路,把它们统一到一个标准的连接头。JAMMA就是这个连接头的大小以及引脚定义,这就意味着不管你安装的主板是什么,按钮和控制器都将会连接到相同功能接口,所以街机的主人只需要再更换下机柜上的外观图片,就可以招揽新玩家了。
|
||||
|
||||
但是首先,提醒一下:JAMMA连接头上带有12V电压供电,通常由大多数街机里都有的电源模块供给。为了避免意外短路或是不小心掉个螺丝刀什么的造成损坏,我们完全切断了这个供电。在本教程后面的任何阶段,我们也不会用到这个连接头上的任何电源脚。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 第二步:J-PAC ####
|
||||
|
||||
有一点非常方便,你可以买到这样一种设备,连接街机机柜里的JAMMA接头和电脑的USB端口,将机柜上的摇杆和按键动作都转换成(可配置的)键盘命令,它们可以在Linux里用来控制任何想玩的游戏。这个设备就叫J-Pac([www.ultimarc.com/jpac.html][1] – 大概£54)。
|
||||
|
||||
它最大的特点不是它的连接性;而是它处理和转换输入信号的方式,因为它比标准的USB手柄强太多太多了。每一个输入都有自己独立的中断,而且没有限制同时按下或按住的按钮或摇杆方向的数量。这对于类似街头霸王的游戏来说非常关键,因为他们依赖于同时迅速按下的组合键,而且用来对那些发飙后按下自己所有按键的不良对手发出致命一击时也必不可少。许多其他控制器,特别是那些生成键盘输入的,受到他们所采用的USB控制器的同时六个输入的限制,以及一堆的Alt,Shift和Ctrl键的特殊处理的限制。J-Pac还可以接入倾角传感器,甚至某些投币装置,不用预先配置就可以在Linux下工作了。
|
||||
|
||||
另外的选择是一个类似的叫I-Pac的设备。它做了和J-Pac相同的事情,只不过不支持JAMMA接头。这意味着你不能把JAMMA控制器接上去,但同时也就是说你可以设计你自己的控制器布局,再把每个控制接到I-Pac上去。这对第一个项目来说也许有点小难,但是这却是许多街机迷们选择的方式,特别是他们想设计一个支持四个玩家的控制板的时候,或者是一个整合许多不同类型控制的面板的时候。我们采用的方式并不是我们推荐必须要做的,我们改造了一个输入有问题的二手X-Arcade Tankstick控制面板,换上了新的摇杆和按钮,再接到新的JAMMA接口,这样有一个非常好的地方就是可以用便宜的价格(£8)买到所有用到的线材包括电路板边缘插头。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我们的已经装到机柜上的J-Pac。右边的蓝色和红色导线接到我们的机柜上额外的1号和2号玩家按钮(点击看大图)。
|
||||
|
||||
不管你选择的是I-Pac或是J-Pac,它们产生的按键都是MAME的默认值。也就是说运行模拟器之后不需要手动调整输入。例如玩家1,会默认将键盘方向键映射成上下左右,以及将左边的Ctrl,左边的ALT,空格和左边的Shift键映射到按钮1-4。但是真正实用的功能是,对于我们来说,是双键快捷方式。当按下并按住玩家1按钮后,就可以通过把玩家1的摇杆拉到下的位置发出用来暂停游戏的P按键,推到上的位置调整音量,以及推到右的位置来进入MAME自己的设置界面。这些特殊组合键设计的很巧妙,不会对正常玩游戏带来任何干扰,因为他们只有在按住玩家1按钮后才会生效,然后可以让你正在运行游戏的时候也能做任何需要的事情。例如,你可以完全地重新配置MAME,使用它自己的菜单,在玩游戏的时候改变输入绑定和灵敏度。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,按住玩家1按钮然后按下玩家2按钮就可以退出MAME,如果你使用了启动菜单或MAME管理器的话就很有用了,因为他们会自动启动游戏,然后你就可以用最快的速度开始玩另一个游戏了。
|
||||
|
||||
对于显示屏我们采取了比较保守的方式,拿掉了街机原装的笨重的而且已经坏掉的CRT,换成一个低成本的LCD显示器。这样做有很多好处。首先,这个显示器有HDMI接口,这样他就可以轻易地直接连接到树莓派或是现代的显卡上。第二,你也不用去设定驱动街机屏幕所需要的低频率刷新模式,也不需要驱动它的专用图形硬件。第三,这也是最安全的方式,因为街机屏幕往往在机身背后没有保护措施,让很高的电压离你的手只有几英寸的距离。也不是说你完全不能用CRT,如果那就是你追求的体验的话 – 这也是获得所追求的游戏体验的最真实的方式,但是我们在软件里充分细调了CRT模拟部分,我们对输出已经很满意了,而且不需要用那个古老的CRT更是让我们高兴。
|
||||
|
||||
你也许还需要考虑用一个老式的4:3长宽比的LCD,而不是那种宽屏的现代产品,因为4:3模式用来玩竖屏或横屏的游戏更实用。比如说玩竖屏的射击游戏,例如雷电,如果使用宽屏显示器的话,会在屏幕两边都有一个黑条。这些黑条一般会用来显示一些游戏指引,或者你也可以把屏幕翻转90度,这样就可以用上每个像素了,但这却不实用,除非你只玩竖屏游戏或者有一个容易操作的旋转支座。
|
||||
|
||||
装载显示屏也很重要。如果你拿掉了CRT的话,没有现成的地方安装LCD。我们的方式是买了一些中密度纤维板(MDF)并切割成适合原来摆放CRT的地方。固定以好,我们把一个便宜的VESA支座放在中间。VESA底座可以用来挂载大多数屏幕,大的或小的。最后,因为我们的机柜前面有烟玻璃,我们必须保证亮度和对比度都设置的足够高。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第三步:装配 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在几个硬件大件都选好了,而且也基本上确定了最终街机机柜要摆放的地方,把这几个配件装到一起并没有太大难度。我们安全地把机柜后面的电源输入部分拆开,然后在背后的空间接了一个符合插座。接在了电源开关之后的电线上。
|
||||
|
||||
几乎所有的街机机柜右上角都有个电源开关,但通常在机柜靠下一点的地方有大量的导线铰接在它上面,也就是说我们的设备可以使用普通的电源连接头。我们的机柜上还有一个荧光管,用做机器上边灯罩的背光,之前是直接连接到电源上的,我们可以用一个普通插头让它保持和电源连接。当你打开机柜上的电源开关的时候,电流会流入机柜里的各个部件 - 你的树莓派和显示屏都会开机,所有一切就都准备好了。
|
||||
|
||||
J-Pac模块直接插到JAMMA接口上,但你可能还需要一点手动调整。标准的JAMMA只支持每个玩家最多三个按键(尽管许多非正式的支持四个),而J-Pac可以支持六个。为了连接额外的按钮,你需要把按钮开关的一端接到J-Pac的GND上,另一端接到J-Pac板边有螺丝固定的输入上。它们被标记成1SW4,1SW5,1SW6,2SW4,2SW5和2SW6。J-Pac也有声音的直通连接,但是我们发现杂音太多没法用。改成把机柜上的喇叭连接到一个二手的SoundBlaster功放上,再接到树莓派的音频输出端口。声音不一定要纯正,但音量一定要足够大。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我们的树莓派已经接到J-Pac左边,也已经连接了显示屏和USB hub(点击看大图)。
|
||||
|
||||
然后把J-Pac或I-Pac模块通过PS2转USB连接线接到你的PC或树莓派,也可以直接接到PC的PS2接口。要用旧的PS2接头的话额外还有个要求,你的电脑得足够古老还有这个,但是我们测试发现用USB性能是一样的。当然,这个不能用于不带PS2的树莓派,而且别忘了树莓派也需要供电。我们一般建议使用一个带电源的USB hub,因为没有供电是树莓派不工作最常见的错误。你还需要保证树莓派的网络正常,要么通过以太网(也许使用一个藏到机柜里的电力线适配器),或者通过无线USB设备。网络很关键是因为在树莓派被藏到机柜里后你还可以重新配置它,不用接键盘或鼠标就可以让你调整设置以及执行管理任务。
|
||||
|
||||
> ### 投币装置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> 在街机模拟社区里,让投币装置工作在模拟器上工作就会和商业产品太接近了。这就意味着你有潜在的可能对使用你机器的人收取费用。这不仅仅只是不正当,考虑到运行在你自己街机上的那些游戏的来源,这将会是非法的。这很显然违背了模拟的精神。不过,我们和其他热爱者觉得一个能工作的投币装置更进一步地靠近了街机的真实,而且值得付出努力来营造对那个过去街机的怀念。丢个10便士硬币到投币口然后再听到机器发出增加点数的声音,没有什么比得上。
|
||||
|
||||
> 实际上难度也不大。取决于你街机上的投币装置,以及它如何发信号通知投了几个币。大多数投币装置分为两个部分。较大的一部分是硬币接收和验证装置。这是投币过程的物理部分,用于检测硬币是否真实以及确定它的价值。这是通过一个游戏点数逻辑电路板来实现的,通常用一个排线连接,上边还带有很多DIP开关。这些开关用来决定接受哪种硬币,以及一个硬币能产生多少点数。然后就是简单地找到输出开关,每个点数都会触发它一次,然后把它接到JAMMA连接头的投币输入上,或者直接接到J-Pac。我们的投币装置型号是Mars MS111,在90年代早期的英国很常见,网上有大量关于每个DIP开关作用的信息,也有如何重新编程控制器来接受新硬币的方法。我们还能在这个装置的12V上接个小灯用来照亮投币孔。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第四步:软件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
MAME是这种规模项目唯一可行的模拟器,它如今支持运行在数不清的不同平台上的各种各样的游戏,从第一代街机到一些最近的机器。从这个项目中还孕育出了MESS,一个多模拟器的超级系统,针对的平台是80到90年代的家庭电脑以及电视游戏机。
|
||||
|
||||
如何配置MAME本身都可以写上六页的文章了。它是一个复杂的,无序的,伟大的软件程序,模拟了如此之多的CPU,声卡,芯片,控制器以及那么多的选项,就像MythTV,你都永远不能真正停止配置它。
|
||||
|
||||
但是也有个相对省事的方式,一个特别为树莓派构建的版本。它叫PiMAME。它是一个可下载的发布版和脚本,基于Raspbian,这是树莓派的默认发布版。它不仅仅会把MAME装到树莓派上(这很有用因为没有哪个默认仓库里有这个),还会安装其他一些精选出来的模拟器,并通过一个前端来管理他们。MAME,举个例子,是一个有数十个参数的命令行应用。但是PiMAME还有一个妙招 - 它安装了一个简单的网页服务器,可以在连接上网络后让你通过浏览器来安装新游戏。这是一个很好的优点,因为把游戏文件放到正确的目录下是使用MAME的困难之一,这还能让你连接到树莓派的存储设备得到最优使用。还有,PiMAME会通过用来安装它的脚本更新自己,所以保持最新版本就太简单了。目前来说这个非常有用,因为在编写这个项目的时候,正好在0.8版这样一个重大更新发布的时间点上。我们在三月份早期时发现有一些轻微的不稳定,但是我们确定在你读到这篇文章的时候一切都会解决。
|
||||
|
||||
安装PiMAME最好的方式就是先装Raspbian。你可以通过NOOBS安装,使用电脑上的图形工具,或者通过dd命令把Raspbian的内容直接写入到你的SD卡中。就像我们上个月的BrewPi教程里曾提到的,这个过程在之前已经被记录过很多次,所以就不再浪费口水了。想简单点就装一下NOOBS,参照树莓派网站上的指引。在装好Raspbian并跑起来以后,请确保使用配置工具来释放SD卡上的空间,以及确保系统已经更新到最新(`sudo apt-get update; sudo apt-get upgrade`)。然后再确保已经安装好了git工具包。当前任意Raspbian版本都会自带git,不过你仍然可以通过命令`sudo apt-get install git`检查一下。
|
||||
|
||||
然后再在终端里输入下面的命令把PiMAME安装器从项目的GitHub仓库克隆到本地:
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/ssilverm/pimame_installer
|
||||
|
||||
之后,如果命令工作正常的话你应该能看到如下的反馈输出:
|
||||
|
||||
Cloning into ‘pimame_installer’...
|
||||
remote: Reusing existing pack: 2306, done.
|
||||
remote: Total 2306 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0)
|
||||
Receiving objects: 100% (2306/2306), 4.61 MiB | 11 KiB/s, done.
|
||||
Resolving deltas: 100% (823/823), done.
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令会创建一个叫‘pimame_installer’的新目录,然后下一步就是进入这个目录再执行它里面的脚本:
|
||||
|
||||
cd pimame_installer/
|
||||
sudo ./install.sh
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令会安装和配置很多软件。所需的时间长短也取决于你的因特网速度,因为需要下载大量的包。我们那个简陋的树莓派加15Mb因特网连接用了差不多45分钟来执行完这个脚本,在这之后你会收到重启机器的提示。你现在可以安全的通过输入`sudo shutdown -r`来重启了,因为这个命令会自动处理剩下的SD卡写入操作。
|
||||
|
||||
这就是安装的全部事情了。在重启树莓派后,就会自动登录,然后会出现PiMAME启动菜单。在0.8版本里这是个非常漂亮的界面,有每个支持平台的图片,还有红色图标提示已经安装了多少个游戏。现在应该可以用控制器来操作了。如果需要检查控制器是否正确连接,可以用SSH连接到树莓派然后检查一下文件**/dev/input/by-id/usb-Ultimarc_I-PAC_Ultimarc_I-PAC-event-kbd**是否存在。
|
||||
|
||||
默认的按键配置就可以让你选择要在你的街机上运行哪个模拟器。我们最感兴趣的就是第一个,名字叫‘AdvMAME’,不过你也许会很惊讶看到还有一个MAME可选的,MAME4ALL。MAME4ALL是特别为树莓派构建的,使用了旧版的MAME源代码,所以它所支持的ROMS的性能也是最佳的。这是很合理的,因为你的树莓派不可能玩那些要求很高的游戏,所以没有理由苛求模拟器的没必要的兼容性。现在剩下的事情就是找些游戏装到你的系统里(参考下面的方法),然后尽情享受吧!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/arcade-machine/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ben Everard][a]
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/author/ben_everard/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ultimarc.com/jpac.html
|
||||
@ -1,173 +0,0 @@
|
||||
15个关于Linux‘cd’命令的练习例子
|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux中,**‘cd‘(改变目录)**命令,是对新手和系统管理员来说,最重要最常用的命令。对管理无屏幕服务器的管理员,‘**cd**‘是引导进入目录,检查日志,执行程序/应用软件/脚本和其余每个任务的唯一方法。对新手来说,是他们必须自己动手学习的最初始命令
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Linux中15个cd命令举例
|
||||
|
||||
所以,请用心,我们在这会带给你**15**个基础的‘**cd**‘命令,它们富有技巧和捷径,学会使用这些了解到的技巧,会大大减少你在终端上花费的努力和时间
|
||||
|
||||
### 课程细节 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 命令名称:cd
|
||||
- 代表:切换目录
|
||||
- 使用平台:所有Linux发行版本
|
||||
- 执行方式:命令行
|
||||
- 权限:访问自己的目录或者其余指定目录
|
||||
- 级别:基础/初学者
|
||||
|
||||
1. 从当前目录切换到/usr/local
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd /usr/local
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$
|
||||
|
||||
2. 使用绝对路径,从当前目录切换到/usr/local/lib
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd /usr/local/lib
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib$
|
||||
|
||||
3. 使用相对路径,从当前路径切换到/usr/local/lib
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd lib
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib$
|
||||
|
||||
4. **(a)**切换当前目录到上级目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib$ cd -
|
||||
|
||||
/usr/local
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$
|
||||
|
||||
4. **(b)**切换当前目录到上级目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib$ cd ..
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$
|
||||
|
||||
5. 显示我们最后一个离开的工作目录(使用‘-’选项)
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd --
|
||||
|
||||
/home/avi
|
||||
|
||||
6. 从当前目录向上级返回两层
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd ../ ../
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr$
|
||||
|
||||
7. 从任何目录返回到用户home目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd ~
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local$ cd
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$
|
||||
|
||||
8. 切换工作目录到当前工作目录(通常情况下看上去没啥用)
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Downloads$ cd .
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Downloads$
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Downloads$ cd ./
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Downloads$
|
||||
|
||||
9. 你当前目录是“/usr/local/lib/python3.4/dist-packages”,现在要切换到“home/avi/Desktop/”,要求:一行命令,通过向上一直切换直到‘/’,然后使用绝对路径
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr/local/lib/python3.4/dist-packages$ cd ../../../../../home/avi/Desktop/
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/Desktop$
|
||||
|
||||
10. 从当前工作目录切换到/var/www/html,要求:不要将命令打完整,使用TAB
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/var/www$ cd /v<TAB>/w<TAB>/h<TAB>
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/var/www/html$
|
||||
|
||||
11. 从当前目录切换到/etc/v__ _,啊呀,你竟然忘了目录的名字,但是你又不想用TAB
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd /etc/v*
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/etc/vbox$
|
||||
|
||||
**请注意:**如果只有一个目录以‘**v**‘开头,这将会移动到‘**vbox**‘。如果有很多目录以‘**v**‘开头,而且命令行中没有提供更多的标准,这将会移动到第一个以‘**v**‘开头的目录(按照他们在标准字典里字母存在的顺序)
|
||||
|
||||
12. 你想切换到用户‘**av**‘(不确定是avi还是avt)目录,不用**TAB**
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/etc$ cd /home/av?
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$
|
||||
|
||||
13. Linux下的pushed和poped
|
||||
|
||||
Pushed和poped是Linux bash命令,也是其他几个能够保存当前工作目录位置至内存,并且从内存读取目录作为当前目录的脚本,这些脚本也可以切换目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ pushd /var/www/html
|
||||
|
||||
/var/www/html ~
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/var/www/html$
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令保存当前目录到内存,然后切换到要求的目录。一旦poped被执行,它会从内存取出保存的目录位置,作为当前目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/var/www/html$ popd
|
||||
~
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$
|
||||
|
||||
14. 切换到带有空格的目录
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd test\ tecmint/
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/test tecmint$
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd 'test tecmint'
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/test tecmint$
|
||||
|
||||
or
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~$ cd "test tecmint"/
|
||||
avi@tecmint:~/test tecmint$
|
||||
|
||||
15. 从当前目录切换到下载目录,然后列出它所包含的内容(使用一行命令)
|
||||
|
||||
avi@tecmint:/usr$ cd ~/Downloads && ls
|
||||
|
||||
…
|
||||
.
|
||||
service_locator_in.xls
|
||||
sources.list
|
||||
teamviewer_linux_x64.deb
|
||||
tor-browser-linux64-3.6.3_en-US.tar.xz
|
||||
.
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
我们尝试使用最少的词句和一如既往的友好,来让你了解Linux的工作和执行
|
||||
|
||||
这就是所有内容。我很快会带着另一个有趣的主题回来的。在此之前,保持和Tecmint的联系,别忘了在下面给我们提供你宝贵的反馈和评论
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/cd-command-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[su-kaiyao](https://github.com/su-kaiyao)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,466 @@
|
||||
Linux 教程:安装 Ansible 配置管理和 IT 自动化工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
今天我来谈谈 ansible,一个由 Python 编写的强大的配置管理解决方案。尽管市面上已经有很多可供选择的配置管理解决方案,但他们各有优劣,而 ansible 的特点就在于它的简洁。让 ansible 在主流的配置管理系统中与众不同的一点便是,它并不需要你在想要配置的每个节点上安装自己的组件。同时提供的一个优点在于,如果需要的话,你可以在不止一个地方控制你的整个基础结构。最后一点是它的正确性,或许这里有些争议,但是我认为在大多数时候这仍然可以作为它的一个优点。说得足够多了,让我们来着手在 RHEL/CentOS 和基于 Debian/Ubuntu 的系统中安装和配置 Ansible.
|
||||
|
||||
### 准备工作 ####
|
||||
|
||||
1. 发行版:RHEL/CentOS/Debian/Ubuntu Linux
|
||||
1. Jinja2:Python 的一个对设计师友好的现代模板语言
|
||||
1. PyYAML:Python 的一个 YAML 编码/反编码函数库
|
||||
1. paramiko:纯 Python 编写的 SSHv2 协议函数库 (译者注:原文对函数库名有拼写错误,校对时请去掉此条注解)
|
||||
1. httplib2:一个功能全面的 HTTP 客户端函数库
|
||||
1. 本文中列出的绝大部分操作已经假设你将在 bash 或者其他任何现代的 shell 中以 root 用户执行。
|
||||
|
||||
Ansible 如何工作
|
||||
|
||||
Ansible 工具并不使用守护进程,它也不需要任何额外的自定义安全架构,因此它的部署可以说是十分容易。你需要的全部东西便是 SSH 客户端和服务器了。
|
||||
|
||||
+-----------------+ +---------------+
|
||||
|安装了 Ansible 的| SSH | 文件服务器1 |
|
||||
|Linux/Unix 工作站|<------------------>| 数据库服务器2 | 在本地或远程
|
||||
+-----------------+ 模块 | 代理服务器3 | 数据中心的
|
||||
192.168.1.100 +---------------+ Unix/Linux 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
其中:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 192.168.1.100 - 在你本地的工作站或服务器上安装 Ansible。
|
||||
1. 文件服务器1到代理服务器3 - 使用 192.168.1.100 和 Ansible 来自动管理所有的服务器。
|
||||
1. SSH - 在 192.168.1.100 和本地/远程的服务器之间设置 SSH 密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ansible 安装教程 ###
|
||||
|
||||
ansible 的安装轻而易举,许多发行版的第三方软件仓库中都有现成的软件包,可以直接安装。其他简单的安装方法包括使用 pip 安装它,或者从 github 里获取最新的版本。若想使用你的软件包管理器安装,在[基于 RHEL/CentOS Linux 的系统里你很可能需要 EPEL 仓库][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在基于 RHEL/CentOS Linux 的系统中安装 ansible ####
|
||||
|
||||
输入如下 [yum 命令][2]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install ansible
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在基于 Debian/Ubuntu Linux 的系统中安装 ansible ####
|
||||
|
||||
输入如下 [apt-get 命令][3]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install software-properties-common
|
||||
$ sudo apt-add-repository ppa:ansible/ansible
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install ansible
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 pip 安装 ansible ####
|
||||
|
||||
[pip 命令是一个安装和管理 Python 软件包的工具][4],比如它能管理 Python Package Index 中的那些软件包。如下方式在 Linux 和类 Unix 系统中通用:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pip install ansible
|
||||
|
||||
#### 从源代码安装最新版本的 ansible ####
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过如下命令从 github 中安装最新版本:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd ~
|
||||
$ git clone git://github.com/ansible/ansible.git
|
||||
$ cd ./ansible
|
||||
$ source ./hacking/env-setup
|
||||
|
||||
当你从一个 git checkout 中运行 ansible 的时候,请记住你每次用它之前都需要设置你的环境,或者你可以把这个设置过程加入你的 bash rc 文件中:
|
||||
|
||||
# 加入 BASH RC
|
||||
$ echo "export ANSIBLE_HOSTS=~/ansible_hosts" >> ~/.bashrc
|
||||
$ echo "source ~/ansible/hacking/env-setup" >> ~/.bashrc
|
||||
|
||||
ansible 的 hosts 文件包括了一系列它能操作的主机。默认情况下 ansible 通过路径 /etc/ansible/hosts 查找 hosts 文件,不过这个行为也是可以更改的,这样当你想操作不止一个 ansible 或者针对不同的数据中心的不同客户操作的时候也是很方便的。你可以通过命令行参数 -i 指定 hosts 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m shell -a "hostname" --ask-pass -i /etc/some/other/dir/ansible_hosts
|
||||
|
||||
不过我更倾向于使用一个环境变量,这可以在你想要通过 source 一个不同的文件来切换工作目标的时候起到作用。这里的环境变量是 $ANSIBLE_HOSTS,可以这样设置:
|
||||
|
||||
$ export ANSIBLE_HOSTS=~/ansible_hosts
|
||||
|
||||
一旦所有需要的组件都已经安装完毕,而且你也准备好了你的 hosts 文件,你就可以来试一试它了。为了快速测试,这里我把 127.0.0.1 写到了 ansible 的 hosts 文件里:
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo "127.0.0.1" > ~/ansible_hosts
|
||||
|
||||
现在来测试一个简单的 ping:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m ping
|
||||
|
||||
或者提示 ssh 密码:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m ping --ask-pass
|
||||
|
||||
我在刚开始的设置中遇到过几次问题,因此这里强烈推荐为 ansible 设置 SSH 公钥认证。不过在刚刚的测试中我们使用了 --ask-pass,在一些机器上你会需要[安装 sshpass][5] 或者像这样指定 -c paramiko:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m ping --ask-pass -c paramiko
|
||||
|
||||
当然你也可以[安装 sshpass][6],然而 sshpass 并不总是在标准的仓库中提供,因此 paramiko 可能更为简单。
|
||||
|
||||
### 设置 SSH 公钥认证 ###
|
||||
|
||||
于是我们有了一份配置,以及一些基础的其他东西。现在让我们来做一些实用的事情。ansible 的强大很大程度上体现在 playbooks 上,后者基本上就是一些写好的 ansible 脚本(大部分来说),不过在制作一个 playbook 之前,我们将先从一些一句话脚本开始。现在让我们创建和配置 SSH 公钥认证,以便省去 -c 和 --ask-pass 选项:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
|
||||
|
||||
样例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
|
||||
Enter file in which to save the key (/home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa):
|
||||
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
|
||||
Enter same passphrase again:
|
||||
Your identification has been saved in /home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa.
|
||||
Your public key has been saved in /home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
|
||||
The key fingerprint is:
|
||||
94:a0:19:02:ba:25:23:7f:ee:6c:fb:e8:38:b4:f2:42 mike@ultrabook.linuxdork.com
|
||||
The key's randomart image is:
|
||||
+--[ RSA 2048]----+
|
||||
|... . . |
|
||||
|. . + . . |
|
||||
|= . o o |
|
||||
|.* . |
|
||||
|. . . S |
|
||||
| E.o |
|
||||
|.. .. |
|
||||
|o o+.. |
|
||||
| +o+*o. |
|
||||
+-----------------+
|
||||
|
||||
现在显然有很多种方式来把它放到远程主机上应该的位置。不过既然我们正在使用 ansible,就用它来完成这个操作吧:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m copy -a "src=/home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa.pub dest=/tmp/id_rsa.pub" --ask-pass -c paramiko
|
||||
|
||||
样例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
SSH password:
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | success >> {
|
||||
"changed": true,
|
||||
"dest": "/tmp/id_rsa.pub",
|
||||
"gid": 100,
|
||||
"group": "users",
|
||||
"md5sum": "bafd3fce6b8a33cf1de415af432774b4",
|
||||
"mode": "0644",
|
||||
"owner": "mike",
|
||||
"size": 410,
|
||||
"src": "/home/mike/.ansible/tmp/ansible-tmp-1407008170.46-208759459189201/source",
|
||||
"state": "file",
|
||||
"uid": 1000
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
下一步,把公钥文件添加到远程服务器里。输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m shell -a "cat /tmp/id_rsa.pub >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys" --ask-pass -c paramiko
|
||||
|
||||
样例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
SSH password:
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | FAILED | rc=1 >>
|
||||
/bin/sh: /root/.ssh/authorized_keys: Permission denied
|
||||
|
||||
矮油,我们需要用 root 来执行这个命令,所以还是加上一个 -u 参数吧:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m shell -a "cat /tmp/id_rsa.pub >> /root/.ssh/authorized_keys" --ask-pass -c paramiko -u root
|
||||
|
||||
样例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
SSH password:
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | success | rc=0 >>
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,我刚才这是想要演示通过 ansible 来传输文件的操作。事实上 ansible 有一个更加方便的内置 SSH 密钥管理支持:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m authorized_key -a "user=mike key='{{ lookup('file', '/home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa.pub') }}' path=/home/mike/.ssh/authorized_keys manage_dir=no" --ask-pass -c paramiko
|
||||
|
||||
样例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
SSH password:
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | success >> {
|
||||
"changed": true,
|
||||
"gid": 100,
|
||||
"group": "users",
|
||||
"key": "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQCq+Z8/usprXk0aCAPyP0TGylm2MKbmEsHePUOd7p5DO1QQTHak+9gwdoJJavy0yoUdi+C+autKjvuuS+vGb8+I+8mFNu5CvKiZzIpMjZvrZMhHRdNud7GuEanusTEJfi1pUd3NA2iXhl4a6S9a/4G2mKyf7QQSzI4Z5ddudUXd9yHmo9Yt48/ASOJLHIcYfSsswOm8ux1UnyeHqgpdIVONVFsKKuSNSvZBVl3bXzhkhjxz8RMiBGIubJDBuKwZqNSJkOlPWYN76btxMCDVm07O7vNChpf0cmWEfM3pXKPBq/UBxyG2MgoCGkIRGOtJ8UjC/daadBUuxg92/u01VNEB mike@ultrabook.linuxdork.com",
|
||||
"key_options": null,
|
||||
"keyfile": "/home/mike/.ssh/authorized_keys",
|
||||
"manage_dir": false,
|
||||
"mode": "0600",
|
||||
"owner": "mike",
|
||||
"path": "/home/mike/.ssh/authorized_keys",
|
||||
"size": 410,
|
||||
"state": "file",
|
||||
"uid": 1000,
|
||||
"unique": false,
|
||||
"user": "mike"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
现在这些密钥已经设置好了。我们来试着随便跑一个命令,比如 hostname,希望我们不会被提示要输入密码
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m shell -a "hostname" -u root
|
||||
|
||||
样例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | success | rc=0 >>
|
||||
|
||||
成功!!!现在我们可以用 root 来执行命令,并且不会被输入密码的提示干扰了。我们现在可以轻易地配置任何在 ansible hosts 文件中的主机了。让我们把 /tmp 中的公钥文件删除:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m file -a "dest=/tmp/id_rsa.pub state=absent" -u root
|
||||
|
||||
样例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | success >> {
|
||||
"changed": true,
|
||||
"path": "/tmp/id_rsa.pub",
|
||||
"state": "absent"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
下面我们来做一些更复杂的事情,我要确定一些软件包已经安装了,并且已经是最新的版本:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible all -m zypper -a "name=apache2 state=latest" -u root
|
||||
|
||||
样例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
127.0.0.1 | success >> {
|
||||
"changed": false,
|
||||
"name": "apache2",
|
||||
"state": "latest"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
很好,我们刚才放在 /tmp 中的公钥文件已经消失了,而且我们已经安装好了最新版的 apache。下面我们来看看前面命令中的 -m zypper,一个让 ansible 非常灵活,并且给了 playbooks 更多能力的功能。如果你不使用 openSuse 或者 Suse enterprise 你可能还不熟悉 zypper, 它基本上就是 suse 世界中相当于 yum 的存在。在上面所有的例子中,我的 hosts 文件中都只有一台机器。除了最后一个命令外,其他所有命令都应该在任何标准的 *nix 系统和标准的 ssh 配置中使用,这造成了一个问题。如果我们想要同时管理多种不同的机器呢?这便是 playbooks 和 ansible 的可配置性闪闪发光的地方了。首先我们来少许修改一下我们的 hosts 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat ~/ansible_hosts
|
||||
|
||||
样例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
[RHELBased]
|
||||
10.50.1.33
|
||||
10.50.1.47
|
||||
|
||||
[SUSEBased]
|
||||
127.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们创建了一些分组的服务器,并且给了他们一些有意义的标签。然后我们来创建一个为不同类型的服务器执行不同操作的 playbook。你可能已经发现这个 yaml 的数据结构和我们之前运行的命令行语句中的相似性了。简单来说,-m 是一个模块,而 -a 用来提供模块参数。在 YAML 表示中你可以先指定模块,然后插入一个冒号 :,最后指定参数。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
- hosts: SUSEBased
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- zypper: name=apache2 state=latest
|
||||
- hosts: RHELBased
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- yum: name=httpd state=latest
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们有一个简单的 playbook 了,我们可以这样运行它:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ansible-playbook testPlaybook.yaml -f 10
|
||||
|
||||
样例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY [SUSEBased] **************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
GATHERING FACTS ***************************************************************
|
||||
ok: [127.0.0.1]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [zypper name=apache2 state=latest] **************************************
|
||||
ok: [127.0.0.1]
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY [RHELBased] **************************************************************
|
||||
|
||||
GATHERING FACTS ***************************************************************
|
||||
ok: [10.50.1.33]
|
||||
ok: [10.50.1.47]
|
||||
|
||||
TASK: [yum name=httpd state=latest] *******************************************
|
||||
changed: [10.50.1.33]
|
||||
changed: [10.50.1.47]
|
||||
|
||||
PLAY RECAP ********************************************************************
|
||||
10.50.1.33 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
|
||||
10.50.1.47 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0
|
||||
127.0.0.1 : ok=2 changed=0 unreachable=0 failed=0
|
||||
|
||||
注意,你会看到 ansible 联系到的每一台机器的输出。-f 参数让 ansible 在多台主机上同时运行指令。除了指定全部主机,或者一个主机分组的名字以外,你还可以把导入 ssh 公钥的操作从命令行里转移到 playbook 中,这将在设置新主机的时候提供很大的方便,甚至让新主机直接可以运行一个 playbook。为了演示,我们把我们之前的公钥例子放进一个 playbook 里:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
- hosts: SUSEBased
|
||||
remote_user: mike
|
||||
sudo: yes
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- authorized_key: user=root key="{{ lookup('file', '/home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa.pub') }}" path=/root/.ssh/authorized_keys manage_dir=no
|
||||
- hosts: RHELBased
|
||||
remote_user: mdonlon
|
||||
sudo: yes
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- authorized_key: user=root key="{{ lookup('file', '/home/mike/.ssh/id_rsa.pub') }}" path=/root/.ssh/authorized_keys manage_dir=no
|
||||
|
||||
除此之外还有很多可以做的事情,比如在启动的时候把公钥配置好,或者引入其他的流程来让你按需配置一些机器。不过只要 SSH 被配置成接受密码登陆,这些几乎可以用在所有的流程中。在你准备开始写太多 playbook 之前,另一个值得考虑的事情是,代码管理可以有效节省你的时间。机器需要不断变化,然而你并不需要在每次机器发生变化时都重新写一个 playbook,只需要更新相关的部分并提交这些修改。与此相关的另一个好处是,如同我之前所述,你可以从不同的地方管理你的整个基础结构。你只需要将你的 playbook 仓库 git clone 到新的机器上,就完成了管理所有东西的全部设置流程。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 现实中的 ansible 例子 ####
|
||||
|
||||
我知道很多用户经常使用 pastebin 这样的服务,以及很多公司基于显而易见的理由配置了他们内部使用的类似东西。最近,我遇到了一个叫做 showterm 的程序,巧合之下我被一个客户要求配置它用于内部使用。这里我不打算赘述这个应用程序的细节,不过如果你感兴趣的话,你可以使用 Google 搜索 showterm。作为一个合理的现实中的例子,我将会试图配置一个 showterm 服务器,并且配置使用它所需要的客户端应用程序。在这个过程中我们还需要一个数据库服务器。现在我们从配置客户端开始:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
- hosts: showtermClients
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- yum: name=rubygems state=latest
|
||||
- yum: name=ruby-devel state=latest
|
||||
- yum: name=gcc state=latest
|
||||
- gem: name=showterm state=latest user_install=no
|
||||
|
||||
这部分很简单。下面是主服务器:
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
- hosts: showtermServers
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- name: ensure packages are installed
|
||||
yum: name={{item}} state=latest
|
||||
with_items:
|
||||
- postgresql
|
||||
- postgresql-server
|
||||
- postgresql-devel
|
||||
- python-psycopg2
|
||||
- git
|
||||
- ruby21
|
||||
- ruby21-passenger
|
||||
- name: showterm server from github
|
||||
git: repo=https://github.com/ConradIrwin/showterm.io dest=/root/showterm
|
||||
- name: Initdb
|
||||
command: service postgresql initdb
|
||||
creates=/var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Start PostgreSQL and enable at boot
|
||||
service: name=postgresql
|
||||
enabled=yes
|
||||
state=started
|
||||
- gem: name=pg state=latest user_install=no
|
||||
handlers:
|
||||
- name: restart postgresql
|
||||
service: name=postgresql state=restarted
|
||||
|
||||
- hosts: showtermServers
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
sudo: yes
|
||||
sudo_user: postgres
|
||||
vars:
|
||||
dbname: showterm
|
||||
dbuser: showterm
|
||||
dbpassword: showtermpassword
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- name: create db
|
||||
postgresql_db: name={{dbname}}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: create user with ALL priv
|
||||
postgresql_user: db={{dbname}} name={{dbuser}} password={{dbpassword}} priv=ALL
|
||||
- hosts: showtermServers
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- name: database.yml
|
||||
template: src=database.yml dest=/root/showterm/config/database.yml
|
||||
- hosts: showtermServers
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- name: run bundle install
|
||||
shell: bundle install
|
||||
args:
|
||||
chdir: /root/showterm
|
||||
- hosts: showtermServers
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- name: run rake db tasks
|
||||
shell: 'bundle exec rake db:create db:migrate db:seed'
|
||||
args:
|
||||
chdir: /root/showterm
|
||||
- hosts: showtermServers
|
||||
remote_user: root
|
||||
tasks:
|
||||
- name: apache config
|
||||
template: src=showterm.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf.d/showterm.conf
|
||||
|
||||
还凑合。请注意,从某种意义上来说这是一个任意选择的程序,然而我们现在已经可以持续地在任意数量的机器上部署它了,这便是配置管理的好处。此外,在大多数情况下这里的定义语法几乎是不言而喻的,wiki 页面也就不需要加入太多细节了。当然在我的观点里,一个有太多细节的 wiki 页面绝不会是一件坏事。
|
||||
|
||||
### 扩展配置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们并没有涉及到这里所有的细节。Ansible 有许多选项可以用来配置你的系统。你可以在你的 hosts 文件中内嵌变量,而 ansible 将会把它们应用到远程节点。如:
|
||||
|
||||
[RHELBased]
|
||||
10.50.1.33 http_port=443
|
||||
10.50.1.47 http_port=80 ansible_ssh_user=mdonlon
|
||||
|
||||
[SUSEBased]
|
||||
127.0.0.1 http_port=443
|
||||
|
||||
尽管这对于快速配置来说已经非常方便,你还可以将变量分成存放在 yaml 格式的多个文件中。在你的 hosts 文件路径里,你可以创建两个子目录 group_vars 和 host_vars。在这些路径里放置的任何文件,只要能对得上一个主机分组的名字,或者你的 hosts 文件中的一个主机名,它们都会在运行时被插入进来。所以前面的一个例子将会变成这样:
|
||||
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # pwd
|
||||
/etc/ansible
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # tree
|
||||
.
|
||||
├── group_vars
|
||||
│ ├── RHELBased
|
||||
│ └── SUSEBased
|
||||
├── hosts
|
||||
└── host_vars
|
||||
├── 10.50.1.33
|
||||
└── 10.50.1.47
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
2 directories, 5 files
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # cat hosts
|
||||
[RHELBased]
|
||||
10.50.1.33
|
||||
10.50.1.47
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[SUSEBased]
|
||||
127.0.0.1
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # cat group_vars/RHELBased
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # cat group_vars/SUSEBased
|
||||
---
|
||||
http_port: 443
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # cat host_vars/10.50.1.33
|
||||
---
|
||||
http_port: 443
|
||||
ultrabook:/etc/ansible # cat host_vars/10.50.1.47
|
||||
---
|
||||
http_port:80
|
||||
ansible_ssh_user: mdonlon
|
||||
|
||||
### 改善 Playbooks ###
|
||||
|
||||
组织 playbooks 也已经有很多种现成的方式。在前面的例子中我们用了一个单独的文件,因此这方面被大幅地简化了。组织这些文件的一个常用方式是创建角色。简单来说,你将一个主文件加载为你的 playbook,而它将会从其它文件中导入所有的数据,这些其他的文件便是角色。举例来说,如果你有了一个 wordpress 网站,你需要一个 web 前端,和一个数据库。web 前端将包括一个 web 服务器,应用程序代码,以及任何需要的模块。数据库有时候运行在同一台主机上,有时候运行在远程的主机上,这时候角色就可以派上用场了。你创建一个目录,并对每个角色创建对应的小 playbook。在这个例子中我们需要一个 apache 角色,mysql 角色,wordpress 角色,mod_php,以及 php 角色。最大的好处是,并不是每个角色都必须被应用到同一台机器上。在这个例子中,mysql 可以被应用到一台单独的机器。这同样为代码重用提供了可能,比如你的 apache 角色还可以被用在 python 和其他相似的 php 应用程序中。展示这些已经有些超出了本文的范畴,而且做一件事总是有很多不同的方式,我建议搜索一些 ansible 的 playbook 例子。有很多人在 github 上贡献代码,当然还有其他一些网站。
|
||||
|
||||
### 模块 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在 ansible 中,对于所有完成的工作,幕后的工作都是由模块主导的。Ansible 有一个非常丰富的内置模块仓库,其中包括软件包安装,文件传输,以及我们在本文中做的所有事情。但是对一部分人来说,这些并不能满足他们的配置需求,ansible 也提供了方法让你添加自己的模块。Ansible 的 API 有一个非常棒的事情是,它并没有限制模块也必须用编写它的语言 Python 来编写,也就是说,你可以用任何语言来编写模块。Ansible 模块通过传递 JSON 数据来工作,因此你只需要用想用的语言生成一段 JSON 数据。我很确定任何脚本语言都可以做到这一点,因此你现在就可以开始写点什么了。在 Ansible 的网站上有很多的文档,包括模块的接口是如何工作的,以及 Github 上也有很多模块的例子。注意一些小众的语言可能没有很好的支持,不过那只可能是因为没有多少人在用这种语言贡献代码。试着写点什么,然后把你的结果发布出来吧!
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
总的来说,虽然在配置管理方面已经有很多解决方案,我希望本文能显示出 ansible 简单的设置过程,在我看来这是它最重要的一个要点。请注意,因为我试图展示做一件事的不同方式,所以并不是前文中所有的例子都是适用于你的个别环境或者对于普遍情况的最佳实践。这里有一些链接能让你对 ansible 的了解进入下一个层次:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ansible 项目][7]主页.
|
||||
- [Ansible 项目文档][8].
|
||||
- [多级环境与 Ansible][9].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/python-tutorials/linux-tutorial-install-ansible-configuration-management-and-it-automation-tool/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Nix Craft][a]
|
||||
译者:[felixonmars](https://github.com/felixonmars)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/about-us
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/fedora-sl-centos-redhat6-enable-epel-repo/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/rhel-centos-fedora-linux-yum-command-howto/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-debian-package-management-cheat-sheet.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/debian-ubuntu-centos-rhel-linux-install-pipclient/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/noninteractive-shell-script-ssh-password-provider/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/noninteractive-shell-script-ssh-password-provider/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.ansible.com/
|
||||
[8]:http://docs.ansible.com/
|
||||
[9]:http://rosstuck.com/multistage-environments-with-ansible/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,212 @@
|
||||
在逻辑卷管理中设置精简资源调配卷——第四部分
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
逻辑卷管理有许多特性,比如像快照和精简资源调配。在先前(第三部分中),我们已经介绍了如何为逻辑卷创建快照。在本文中,我们将了解如何在LVM中设置精简资源调配。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
在LVM中设置精简资源调配
|
||||
|
||||
### 精简资源调配是什么? ###
|
||||
精简资源调配用于lvm以在精简池中创建虚拟磁盘。我们假定我服务器上有**15GB**的存储容量,而我已经有2个客户各自占去了5GB存储空间。你是第三个客户,你也请求5GB的存储空间。在以前,我们会提供整个5GB的空间(富卷)。然而,你可能只使用5GB中的2GB,其它3GB以后再去填满它。
|
||||
|
||||
而在精简资源调配中我们所做的是,在其中一个大卷组中定义一个精简池,再在精简池中定义一个精简卷。这样,不管你写入什么文件,它都会保存进去,而你的存储空间看上去就是5GB。然而,这所有5GB空间不会全部铺满整个硬盘。对其它客户也进行同样的操作,就像我说的,那儿已经有两个客户,你是第三个客户。
|
||||
|
||||
那么,让我们想想,我到底为客户分配了总计多少GB的空间呢?所有15GB的空间已经全部分配完了,如果现在有某个人来问我是否能提供5GB空间,我还可以分配给他么?答案是“可以”。在精简资源调配中,我可以为第四位客户分配5GB空间,即使我已经把那15GB的空间分配完了。
|
||||
|
||||
**警告**:从那15GB空间中,如果我们对资源调配超过15GB了,那就是过度资源调配了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 它是怎么工作的?我们又是怎样为客户提供存储空间的? ###
|
||||
|
||||
我已经提供给你5GB空间,但是你可能只用了2GB,而其它3GB还空闲着。在富资源调配中,我们不能这么做,因为它一开始就分配了整个空间。
|
||||
|
||||
在精简资源调配中,如果我为你定义了5GB空间,它就不会在定义卷时就将整个磁盘空间全部分配,它会根据你的数据写入而增长,希望你看懂了!跟你一样,其它客户也不会使用全部卷,所以还是有机会为一个新客户分配5GB空间的,这称之为过度资源调配。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,必须对各个卷的增长情况进行监控,否则结局会是个灾难。在过度资源调配完成后,如果所有4个客户都极度地写入数据到磁盘,你将碰到问题了。因为这个动作会填满15GB的存储空间,甚至溢出,从而导致这些卷下线。
|
||||
|
||||
### 需求 ###
|
||||
|
||||
注:此三篇文章如果发布后可换成发布后链接,原文在前几天更新中
|
||||
|
||||
- [使用LVM在Linux中创建逻辑卷——第一部分][1]
|
||||
- [在Linux中扩展/缩减LVM——第二部分][2]
|
||||
- [在LVM中创建/恢复逻辑卷快照——第三部分][3]
|
||||
|
||||
#### 我的服务器设置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
操作系统 — 安装有LVM的CentOS 6.5
|
||||
服务器IP — 192.168.0.200
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤1: 设置精简池和卷 ###
|
||||
|
||||
理论讲太多了,让我们还是来点实际的吧,我们一起来设置精简池和精简卷。首先,我们需要一个大尺寸的卷组。这里,我创建了一个**15GB**的卷组用于演示。现在,用下面的命令来列出卷组。
|
||||
|
||||
# vgcreate -s 32M vg_thin /dev/sdb1
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
列出卷组
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,在创建精简池和精简卷之前,检查逻辑卷有多少空间可用。
|
||||
|
||||
# vgs
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
检查逻辑卷
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以在上面的lvs命令输出中看到,只显示了一些默认逻辑用于文件系统和交换分区。
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建精简池 ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令在卷组(vg_thin)中创建一个15GB的精简池。
|
||||
|
||||
# lvcreate -L 15G --thinpool tp_tecmint_pool vg_thin
|
||||
|
||||
- **-L** – 卷组大小
|
||||
- **–thinpool** – 创建精简池
|
||||
- **tp_tecmint_poolThin** - 精简池名称
|
||||
- **vg_thin** – 我们需要创建精简池的卷组名称
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
创建精简池
|
||||
|
||||
使用‘lvdisplay’命令来查看详细信息。
|
||||
|
||||
# lvdisplay vg_thin/tp_tecmint_pool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
逻辑卷信息
|
||||
|
||||
这里,我们还没有在该精简池中创建虚拟精简卷。在图片中,我们可以看到分配的精简池数据为**0.00%**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建精简卷 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们可以在带有-V(Virtual)选项的‘lvcreate’命令的帮助下,在精简池中定义精简卷了。
|
||||
|
||||
# lvcreate -V 5G --thin -n thin_vol_client1 vg_thin/tp_tecmint_pool
|
||||
|
||||
我已经在我的**vg_thin**卷组中的**tp_tecmint_pool**内创建了一个精简虚拟卷,取名为**thin_vol_client1**。现在,使用下面的命令来列出逻辑卷。
|
||||
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
列出逻辑卷
|
||||
|
||||
刚才,我们已经在上面创建了精简卷,这就是为什么没有数据,显示为**0.00%M**。
|
||||
|
||||
好吧,让我为其它2个客户再创建2个精简卷。这里,你可以看到在精简池(**tp_tecmint_pool**)下有3个精简卷了。所以,从这一点上看,我们开始明白,我已经使用所有15GB的精简池。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 创建文件系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,使用下面的命令为这3个精简卷创建挂载点并挂载,然后拷贝一些文件进去。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir -p /mnt/client1 /mnt/client2 /mnt/client3
|
||||
|
||||
列出创建的目录。
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l /mnt/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
创建挂载点
|
||||
|
||||
使用‘mkfs’命令为这些创建的精简卷创建文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/vg_thin/thin_vol_client1 && mkfs.ext4 /dev/vg_thin/thin_vol_client2 && mkfs.ext4 /dev/vg_thin/thin_vol_client3
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
创建文件系统
|
||||
|
||||
使用‘mount’命令来挂载所有3个客户卷到创建的挂载点。
|
||||
|
||||
# mount /dev/vg_thin/thin_vol_client1 /mnt/client1/ && mount /dev/vg_thin/thin_vol_client2 /mnt/client2/ && mount /dev/vg_thin/thin_vol_client3 /mnt/client3/
|
||||
|
||||
使用‘df’命令来列出挂载点。
|
||||
|
||||
# df -h
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
打印挂载点
|
||||
|
||||
这里,我们可以看到所有3个客户卷已经挂载了,而每个客户卷只使用了3%的数据空间。那么,让我们从桌面添加一些文件到这3个挂载点,以填充一些空间。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
添加文件到卷
|
||||
|
||||
现在列出挂载点,并查看每个精简卷使用的空间,然后列出精简池来查看池中已使用的大小。
|
||||
|
||||
# df -h
|
||||
# lvdisplay vg_thin/tp_tecmint_pool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
检查挂载点大小
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
检查精简池大小
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令显示了3个挂载点及其使用大小百分比。
|
||||
|
||||
13% of datas used out of 5GB for client1
|
||||
29% of datas used out of 5GB for client2
|
||||
49% of datas used out of 5GB for client3
|
||||
|
||||
在查看精简池时,我们看到总共只有**30%**的数据被写入,这是上面3个客户虚拟卷的总使用量。
|
||||
|
||||
### 过度资源调配 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,**第四个**客户来申请5GB的存储空间。我能给他吗?因为我已经把15GB的池分配给了3个客户。能不能再给另外一个客户分配5GB的空间呢?可以,这完全可能。在我们使用**过度资源调配**时,就可以实现。过度资源调配可以给我们比我们所拥有的更大的空间。
|
||||
|
||||
让我来为第四位客户创建5GB的空间,然后再验证一下大小吧。
|
||||
|
||||
# lvcreate -V 5G --thin -n thin_vol_client4 vg_thin/tp_tecmint_pool
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
创建精简存储
|
||||
|
||||
在精简池中,我只有15GB大小的空间,但是我已经在精简池中创建了4个卷,其总量达到了20GB。如果4个客户都开始写入数据到他们的卷,并将空间填满,到那时我们将面对严峻的形势。如果不填满空间,那不会有问题。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我已经创建在**thin_vol_client4**中创建了文件系统,然后挂载到了**/mnt/client4**下,并且拷贝了一些文件到里头。
|
||||
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
验证精简存储
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以在上面的图片中看到,新创建的client 4总计使用空间达到了**89.34%**,而精简池的已用空间达到了**59.19**。如果所有这些用户不在过度对卷写入,那么它就不会溢出,下线。要避免溢出,我们需要扩展精简池大小。
|
||||
|
||||
**重要**:精简池只是一个逻辑卷,因此,如果我们需要对其进行扩展,我们可以使用和扩展逻辑卷一样的命令,但我们不能缩减精简池大小。
|
||||
|
||||
# lvextend
|
||||
|
||||
这里,我们可以看到怎样来扩展逻辑精简池(**tp_tecmint_pool**)。
|
||||
|
||||
# lvextend -L +15G /dev/vg_thin/tp_tecmint_pool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
扩展精简存储
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,列出精简池大小。
|
||||
|
||||
# lvs
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
验证精简存储
|
||||
|
||||
前面,我们的**tp_tecmint_pool**大小为15GB,而在对第四个精简卷进行过度资源配置后达到了20GB。现在,它扩展到了30GB,所以我们的过度资源配置又回归常态,而精简卷也不会溢出,下线了。通过这种方式,我们可以添加更多的精简卷到精简池中。
|
||||
|
||||
在本文中,我们已经了解了怎样来使用一个大尺寸的卷组创建一个精简池,以及怎样通过过度资源配置在精简池中创建精简卷和扩着精简池。在下一篇文章中,我们将介绍怎样来移除逻辑卷。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/setup-thin-provisioning-volumes-in-lvm/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Babin Lonston][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/babinlonston/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/create-lvm-storage-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/extend-and-reduce-lvms-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/take-snapshot-of-logical-volume-and-restore-in-lvm/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
6个有趣的命令行工具(终端中的乐趣) - 第二部分
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在之前, 我们给出类一些有关有趣的 Linux 命令行命令的文章, 这些文章告诉我们, Linux 并不像看起来那样复杂, 如果我们知道如何使用的话, 反而会非常有趣. Linux 命令行可以简洁而完美地执行一些复杂的任务, 并且十分有趣.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Linux命令及Linux终端的20个趣事][3]
|
||||
- [Fun in Linux Terminal – Play with Word and Character Counts][2]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
有趣的 Linux 命令
|
||||
|
||||
之前的一篇文章包含了 20 个有趣的 Linux 命令/脚本(和子命令), 得到了读者的高度赞扬. 而另一篇文章则包含了一些处理文字文件, 单词和字符串的命令/脚本和改进, 虽然没有之前那篇文章那么受欢迎.
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章介绍了一些新的有趣的命令和单行脚本.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. pv 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你也许曾经看见电影里的模仿文字, 它们好像是被实时打出来的. 如果我么能在终端里实现这样的效果, 那不是很好?
|
||||
|
||||
这是可以做到的. 我们可以安装通过 '**apt**' 或者 '**yum**' 工具在 Linux 系统上安装 '**pv**' 命令. 安装命令如下?
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install pv [在基于 RedHat 的系统上]
|
||||
|
||||
# sudo apt-get install pv [在基于 Debian 的系统上]
|
||||
|
||||
'**pv**' 命令安装成功之后, 我们尝试输入下面的命令来在终端查看实时文字输出的效果.
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo "Tecmint[dot]com is a community of Linux Nerds and Geeks" | pv -qL 10
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
正在运行的 pv 命令
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: '**q**' 选项表示'安静'(没有其他输出信息), '**L**' 选项表示每秒转化的字节数上限. 数字变量(必须是整数)用来调整预设的文本模拟.(To be fixed: 这里翻译有问题)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. toilet 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
用单行命令 '**toilet**' 在终端里显示有边框的文字值一个不错的主意. 同样, 你必须保证 '**toilet**' 已经安装在你的电脑上. 如果没有的话, 请使用 apt 或 yum 安装. (译者注: 'toilet' 并不在 Fedora 的官方仓库里, 你可以从 github 上下载源代码来安装)
|
||||
|
||||
$ while true; do echo “$(date | toilet -f term -F border –Tecmint)”; sleep 1; done
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
正在运行的 toilet 命令
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 上面的脚本需要使用 **ctrl+z** 键来暂停.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. rig 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令每次生成一个随机的身份信息和地址. 要运行这个命令, 你需要用 apt 或 yum 安装 '**rig**'. (译者注: 'rig' 不在 Fedora 的官方仓库中, 我只在 rpmseek 上找到了 Ubuntu 的 deb 包, 可以使用它来安装.)
|
||||
|
||||
# rig
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
正在运行的 rig 命令
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. aview 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你认为在终端用 ASCII 格式显示图片怎么样? 我们必须用 apt 或 yum 安装软件包 '**aview**'. (译者注: 'avieww' 不在 Fedora 的官方仓库中, 可以从 aview 的[项目主页][4]上下载源代码来安装. ) 在当前文件夹下有一个名为 '**elephant.jpg**' 的图片, 我想用 ASCII 模式在终端查看.
|
||||
|
||||
$ asciiview elephant.jpg -driver curses
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
正在运行的 aview 命令
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. xeyes 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在上一篇文章中, 我们介绍了 '**oneko**' 命令, 它可以显示一个追随鼠标指针运动的小老鼠. '**xeyes**' 是一个类似的程序, 当你运行程序时, 你可以看见两个怪物的眼球追随鼠标的运动.
|
||||
|
||||
$ xeyes
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
正在运行的 xeyes 命令
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. cowsay 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你是否还记得上一次我们介绍的这个命令? 它可以显示一段预先确定的文本和一个字符构成的奶牛. 如果你想使用其它动物来代替奶牛怎么办? 查看可用的动物列表:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cowsay -l
|
||||
|
||||
蟒蛇吃大象怎么样?
|
||||
|
||||
$ cowsay -f elephant-in-snake Tecmint is Best
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
正在运行的 cowsay 命令
|
||||
|
||||
山羊怎么样?
|
||||
|
||||
$ cowsay -f gnu Tecmint is Best
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
正在运行的 山羊cowsay 命令
|
||||
|
||||
今天就到这里吧. 我将带着另一篇有趣的文章回来. 跟踪 Tecmint 来获得最新消息. 不要忘记在下面的评论里留下你的有价值的回复.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-funny-commands/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[wangjiezhe](https://github.com/wangjiezhe)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-funny-commands-of-linux-or-linux-is-fun-in-terminal/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/play-with-word-and-character-counts-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://linux.cn/article-2831-1.html
|
||||
[4]:http://aa-project.sourceforge.net/aview/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
在Ubuntu 14.04和拥有Texmaker的Linux Mint 17(基于ubuntu和debian的Linux发行版)中使用LaTeX
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[LaTeX][1]是一种文本标记语言,也可以说是一种文档制作系统。经常在很多大学或者机构中作为一种标准来书写专业的科学文献,毕业论文或其他类似的文档。在这篇文章中,我们会看到如何在Ubuntu 14.04中使用LaTeX。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu 14.04或Linux Mint 17中安装Texmaker
|
||||
|
||||
[Texmaker][2]是一款免费开源的LaTeX编辑器,它支持一些主流的桌面操作系统,比如Window,Linux和OS X。下面是Texmaker的主要特点:
|
||||
|
||||
- 支持Unicode编码的编辑器
|
||||
- 拼写检查
|
||||
- 代码折叠
|
||||
- 自动补全
|
||||
- 快速导航
|
||||
- PDF查看器
|
||||
- 编译简单
|
||||
- 支持370个数学符号
|
||||
- LaTeX格式文本
|
||||
- 通过TeX4ht导出到html和odt文件
|
||||
- 支持正则表达式
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu 14.04下,你可以通过下面的链接下载Texmaker的二进制包
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载Texmaker编辑器][3]
|
||||
|
||||
你通过链接下载到的是一个.deb包,因此你在一些像Linux Mint,Elementary OS,Pinguy OS等等类Debain的发行版中可以使用相同的安装方式。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想使用像Github类型的markdown编辑器,你可以试试[Remarkable编辑器][4]。
|
||||
|
||||
希望Texmaker能够在Ubuntu和Linux Mint中帮到你
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-latex-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[john](https://github.com/johnhoow)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.latex-project.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.xm1math.net/texmaker/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.xm1math.net/texmaker/download.html#linux
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/remarkable-markdown-editor-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,236 @@
|
||||
如何在 Linux 环境下配置 Nagios Remote Plugin Executor (NRPE)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
就网络管理而言,Nagios 是最强大的工具之一。Nagios 可以监控远程主机的可访问性,以及其中正在运行的服务的状态。不过,如果我们想要监控远程主机中网络服务以外的东西呢?比方说,我们可能想要监控远程主机上的磁盘利用率或者 [CPU 处理器负载][1]。Nagios Remote Plugin Executor(NRPE)便是一个可以帮助你完成这些操作的工具。NRPE 允许你执行在远程主机上安装的 Nagios 插件,并且将它们集成到一个[已经存在的 Nagios 服务器][2]里。
|
||||
|
||||
本教程将会介绍如何在一个已经部署好的 Nagios 中配置 NRPE。本教程主要分为两部分:
|
||||
|
||||
- 配置远程主机。
|
||||
- 配置 Nagios 监控服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
之后我们会以定义一些可以被 NRPE 使用的自定义命令来结束本教程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 为 NRPE 配置远程主机 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第一步:安装 NRPE 服务 ####
|
||||
|
||||
你需要在你想要使用 NRPE 监控的每一台远程主机上安装 NRPE 服务。每一台远程主机上的 NRPE 服务守护进程将会与一台 Nagios 监控服务器进行通信。
|
||||
|
||||
取决于所在的平台, NRPE 服务所需要的软件包可以很容易地用 apt-get 或者 yum 来安装。对于 CentOS 来说,由于 NRPE 并不在 CentOS 的仓库中,我们需要[添加 Repoforge 仓库][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 Debian、Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install nagios-nrpe-server
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 CentOS、Fedora 或者 RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install nagios-nrpe
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第二步:准备配置文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
配置文件 /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg 在基于 Debian 或者 RedHat 的系统中比较相近。让我们备份并修改配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## NRPE 服务端口是可以自定义的 ##
|
||||
server_port=5666
|
||||
|
||||
## 允许 Nagios 监控服务器访问 ##
|
||||
## 注意:逗号后面没有空格 ##
|
||||
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,X.X.X.X-IP_v4_of_Nagios_server
|
||||
|
||||
## 下面的例子中我们硬编码了参数。
|
||||
## 这些参数可以按需修改。
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意:对于 CentOS 64 位用户,请使用 /usr/lib64 替代 /usr/lib ##
|
||||
|
||||
command[check_users]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_users -w 5 -c 10
|
||||
command[check_load]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_load -w 15,10,5 -c 30,25,20
|
||||
command[check_hda1]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /dev/hda1
|
||||
command[check_zombie_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 5 -c 10 -s Z
|
||||
command[check_total_procs]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 150 -c 200
|
||||
|
||||
现在配置文件已经准备好了,NRPE 服务已经可以启动了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第三步:初始化 NRPE 服务 ####
|
||||
|
||||
对于基于 RedHat 的系统,NRPE 服务需要被添加为启动服务。
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 Debian、Ubuntu、Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# service nagios-nrpe-server restart
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 CentOS、Fedora 或者 RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# service nrpe restart
|
||||
# chkconfig nrpe on
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第四步:验证 NRPE 服务状态 ####
|
||||
|
||||
NRPE 守护进程的状态信息可以在系统日志中找到。对于基于 Debian 的系统,日志文件在 /var/log/syslog,而基于 RedHat 的系统的日志文件则是 /var/log/messages。下面提供一段样例日志以供参考:
|
||||
|
||||
nrpe[19723]: Starting up daemon
|
||||
nrpe[19723]: Listening for connections on port 5666
|
||||
nrpe[19723]: Allowing connections from: 127.0.0.1,X.X.X.X
|
||||
|
||||
如果使用了防火墙,被 NRPE 守护进程使用的 TCP 端口 5666 应该被开启。
|
||||
|
||||
# netstat -tpln | grep 5666
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5666 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 19885/nrpe
|
||||
|
||||
### 为 NRPE 配置 Nagios 监控服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为 NRPE 配置已有的 Nagios 监控服务器的第一步是在服务器上安装 NRPE 插件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第一步:安装 NRPE 插件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
当 Nagios 服务器运行在基于 Debian 的系统(Debian、Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint)上时,需要的软件宝可以通过 apt-get 安装。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install nagios-nrpe-plugin
|
||||
|
||||
插件安装完成后,对随插件安装的 check_nrpe 命令稍作修改。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios-plugins/config/check_nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## 默认命令会被覆盖 ##
|
||||
define command{
|
||||
command_name check_nrpe
|
||||
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -c '$ARG1$'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
如果 Nagios 服务器运行在基于 RedHat 的系统(CentOS、Fedora 或者 RHEL)上,你可以通过 yum 安装 NRPE 插件。对于 CentOS,[添加 Repoforge 仓库][4] 是必要的。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install nagios-plugins-nrpe
|
||||
|
||||
现在 NRPE 插件已经安装完成,继续下面的步骤以配置一台 Nagios 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第二步:为 NRPE 插件定义 Nagios 命令 ####
|
||||
|
||||
我们需要首先在 Nagios 中定义一个命令来使用 NRPE。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios/objects/commands.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
## 注意:对于 CentOS 64 位用户,请使用 /usr/lib64 替代 /usr/lib ##
|
||||
define command{
|
||||
command_name check_nrpe
|
||||
command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_nrpe -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -c '$ARG1$'
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第三步:添加主机与命令定义 ####
|
||||
|
||||
接下来定义远程主机以及我们将要在它们上面运行的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的例子为一台远程主机定义了一个可以在上面执行的命令。一般来说,你的配置需要按照你的需求来改变。配置文件的路径在基于 Debian 和基于 RedHat 的系统上略有不同,不过文件的内容是完全一样的。
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 Debian、Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios3/conf.d/nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 CentOS、Fedora 或者 RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/nagios/objects/nrpe.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
define host{
|
||||
use linux-server
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
alias server-1
|
||||
address X.X.X.X-IPv4_address_of_remote_host
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
define service {
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
service_description Check Load
|
||||
check_command check_nrpe!check_load
|
||||
check_interval 1
|
||||
use generic-service
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#### 第四步:重启 Nagios 服务 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在重启 Nagios 之前,可以通过测试来验证配置。
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 Ubuntu、Debian 或者 Linux Mint:**
|
||||
|
||||
# nagios3 -v /etc/nagios3/nagios.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 CentOS、Fedora 或者 RHEL:**
|
||||
|
||||
# nagios -v /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
如果一切正常,我们就可以重启 Nagios 服务了。
|
||||
|
||||
# service nagios restart
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 为 NRPE 配置自定义命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 远程服务器上的配置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
下面列出了一些可以用于 NRPE 的自定义命令。这些命令在远程服务器的 /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg 文件中定义。
|
||||
|
||||
## 当 1、5、15 分钟的平均负载分别超过 1、2、1 时进入警告状态
|
||||
## 当 1、5、15 分钟的平均负载分别超过 3、5、3 时进入严重警告状态
|
||||
command[check_load]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_load -w 1,2,1 -c 3,5,3
|
||||
|
||||
## 对于 /home 目录的可用空间设置了警告级别为 25%,以及严重警告级别为 10%。
|
||||
## 可以定制为监控任何分区(比如 /dev/sdb1、/、/var、/home)
|
||||
command[check_disk]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_disk -w 25% -c 10% -p /home
|
||||
|
||||
## 当 process_ABC 的实例数量超过 10 时警告,超过 20 时严重警告 ##
|
||||
command[check_process_ABC]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 1:10 -c 1:20 -C process_ABC
|
||||
|
||||
## 当 process_ABC 的实例数量跌到 1 以下时严重警告 ##
|
||||
command[check_process_XYZ]=/usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_procs -w 1: -c 1: -C process_XYZ
|
||||
|
||||
#### Nagios 监控服务器上的配置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
我们通过修改 Nagios 监控服务器里的服务定义来应用上面定义的自定义命令。服务定义可以写在所有服务被定义的地方(比如 /etc/nagios/objects/nrpe.cfg 或 /etc/nagios3/conf.d/nrpe.cfg)
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例 1:检查进程 XYZ ##
|
||||
define service {
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
service_description Check Process XYZ
|
||||
check_command check_nrpe!check_process_XYZ
|
||||
check_interval 1
|
||||
use generic-service
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例 2:检查磁盘状态 ##
|
||||
define service {
|
||||
host_name server-1
|
||||
service_description Check Process XYZ
|
||||
check_command check_nrpe!check_disk
|
||||
check_interval 1
|
||||
use generic-service
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
总而言之,NRPE 是 Nagios 的一个强大的扩展,它提供了高度可定制的远程服务器监控方案。使用 NRPE,我们可以监控系统的负载、运行的进程、已登录的用户、磁盘状态,以及其它的指标。
|
||||
|
||||
希望这些可以帮到你。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/03/nagios-remote-plugin-executor-nrpe-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||||
译者:[felixonmars](https://github.com/felixonmars)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2012/08/how-to-measure-average-cpu-utilization.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/install-configure-nagios-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@ Linux有问必答——如何在CentOS或RHEL 7上修改主机名
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 问题:在CentOS/RHEL 7上修改主机名的正确方法是什么(永久或临时)?
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS或RHEL中,有三种定义的主机名:(1)静态的,(2)瞬态的,以及(3)优雅的。“静态”主机名也成为内核主机名,是系统在启动时从/etc/hostname自动初始化的主机名。“瞬态”主机名是在系统运行时临时分配的主机名,例如,通过DHCP或mDNS服务器分配。静态主机名和瞬态主机名都遵从作为互联网域名同样的字符限制规则。而另一方面,“优雅”主机名则被允许使用自由形式(包括特殊/空白字符)的主机名,以展示给终端用户(如Dan's Computer)。
|
||||
在CentOS或RHEL中,有三种定义的主机名:(1)静态的(2)瞬态的,以及(3)灵活的。“静态”主机名也称为内核主机名,是系统在启动时从/etc/hostname自动初始化的主机名。“瞬态”主机名是在系统运行时临时分配的主机名,例如,通过DHCP或mDNS服务器分配。静态主机名和瞬态主机名都遵从作为互联网域名同样的字符限制规则。而另一方面,“灵活”主机名则允许使用自由形式(包括特殊/空白字符)的主机名,以展示给终端用户(如Dan's Computer)。
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS/RHEL 7中,有个叫hostnamectl的命令行工具,它允许你查看或修改与主机名相关的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,31 +12,31 @@ Linux有问必答——如何在CentOS或RHEL 7上修改主机名
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
只查看静态、瞬态或优雅主机名,分别使用“--static”,“--transient”或“--pretty”选项。
|
||||
只查看静态、瞬态或灵活主机名,分别使用“--static”,“--transient”或“--pretty”选项。
|
||||
|
||||
$ hostnamectl status [--static|--transient|--pretty]
|
||||
|
||||
要同时修改所有三个主机名:静态、瞬态和优雅主机名:
|
||||
要同时修改所有三个主机名:静态、瞬态和灵活主机名:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname <host-name>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
就像上面展示的那样,在修改静态/瞬态主机名时,任何特殊字符或空白字符会被移除,而提供的参数中的任何大写字母会自动转化为小写。一旦修改了静态主机名,/etc/hostname将被自动更新。然而,/etc/hosts不会更新以对修改作出回应,所以你需要手动更新/etc/hosts。
|
||||
就像上面展示的那样,在修改静态/瞬态主机名时,任何特殊字符或空白字符会被移除,而提供的参数中的任何大写字母会自动转化为小写。一旦修改了静态主机名,/etc/hostname将被自动更新。然而,/etc/hosts不会更新来回应所做的修改,所以你需要手动更新/etc/hosts。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你只想修改特定的主机名(静态,瞬态或优雅),你可以使用“--static”,“--transient”或“--pretty”选项。
|
||||
如果你只想修改特定的主机名(静态,瞬态或灵活),你可以使用“--static”,“--transient”或“--pretty”选项。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,要永久修改主机名,你可以修改静态主机名:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo hostnamectl --static set-hostname <host-name>
|
||||
|
||||
注意,你不必重启机器以激活永久主机名修改。上面的命令会立即修改内核主机名。注销并重新登入后在命令行提示观察新的静态主机名。
|
||||
注意,你不必重启机器以激活永久主机名修改。上面的命令会立即修改内核主机名。注销并重新登入后在命令行提示来观察新的静态主机名。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/change-hostname-centos-rhel-7.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
Arch Linux安装捷径:Evo/Lution
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
有些人只体验过Ubuntu或Mint的安装,却鼓起勇气想要安装Arch Linux,他们的学习道路是那样的陡峭和严峻,安装过程中半途而废的人数可能要比顺利过关的人多。如果你成功以有用的方式跑起并配置了Arch Linux,那么它已经把你培养成了一个饱经风霜的Linux用户。
|
||||
|
||||
即使有[有帮助的维基][1]可以为新手提供指南,对于那些想要征服Arch的人而言要求仍然太高。你需要至少熟悉诸如fdisk或mkfs之类的终端命令,并且听过mc、nano或chroot这些,并努力掌握它们。这让我回想起了10年前的Debian安装。
|
||||
|
||||
对于那些满怀抱负而又缺乏知识的生灵,有一个叫[Evo/Lution Live ISO][2]的ISO镜像格式安装器可以拯救他们。即便它貌似和自有发行版一样启动,但它也什么都没干,除了辅助安装Arch Linux准系统。Evo/Lution是一个项目,它旨在通过提供Arch的简单安装方式让Arch的用户基础多样化,就像为那些用户提供全面帮助和文档的社区一样。在这样一个组合中,Evo是Live CD(不可安装),而Lution是个安装器。项目创立者看到了Arch开发者和用户之间的巨大鸿沟及其衍生发行版,而想要在所有参与者之间构筑一个平等身份的社区。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
项目的软件部分是命令行安装器Lution-AIS,它解释了一个普通的纯净的Arch安装过程中的每一步。安装完毕后,你将获得Arch提供的没有从AUR添加任何东西的最新软件或其它任何自定义的包。
|
||||
|
||||
启动这个422MB大小的ISO镜像后,一个由显示在右边的带有选项快捷方式的Conky和一个左边等待运行安装器的LX-Terminal组成的工作区便呈现在我们眼前。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在通过右击桌面或使用ALT-i启动实际的安装器后,一个写满了16个等待运行的任务的列表就出现在你面前了。除非你有一个更好的了解,否则将这些命令全部运行一遍。你可以一次运行,也可以进行选择,如1 3 6,或者1-4,也可以一次将它们全部运行,输入1-16。大多数步骤需要‘y’,即yes,来确认,而下一个任务则等着你敲击回车来执行。在此期间,你有足够的时间来阅读安装指南,它可以通过ALT-g来打开。当然,你也可以出去溜达一圈再回来。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这16个步骤分成“基础安装”和“桌面安装”两组。第一个组安装主要关注本地化、分区,以及安装启动器。
|
||||
|
||||
安装器带领你穿越分区世界,你可以选择使用gparted、gdisk,以及cfdisk。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建完分区后(如,像截图中所示,用gparted划分/dev/sda1用于root,/dev/sda2用于swap),你可以在10个文件系统中选择其中之一。在下一步中,你可以选择内核(最新或长期支持LTS)和基础系统。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装完你喜爱的启动加载器后,第一部分安装就完成了,这大约需要花费12分钟。这是在普通的Arch Linux中你第一次重启进入系统所处之处。
|
||||
|
||||
在Lution的帮助下,继续进入第二部分,在这一部分中将安装Xorg、声音和图形驱动,然后进入桌面环境。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装器会检测是否在VirtualBox中安装,并且会自动为VM安装并加载正确的通用驱动,然后相应地设置**systemd**。
|
||||
|
||||
在下一步中,你可以选择KDE、Gnome、Cinnamon、LXDE、Englightenment、Mate或XFCE作为你的桌面环境。如果你不喜欢臃肿的桌面,你也可以试试这些窗口管理器:Awesome、Fluxbox、i3、IceWM、Openbox或PekWM。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在使用Cinnamon作为桌面环境的情况下,第二部分安装将花费不到10分钟的时间;而选择KDE的话,因为要下载的东西多得多,所以花费的时间也会更长。
|
||||
|
||||
Lution-AIS在Cinnamon和Awesome上像个妩媚的小妖精。在安装完成并提示重启后,它就带我进入了我所渴望的环境。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我要提出两点非议:一是在安装器要我选择一个镜像列表时,另外一个是在创建fstab文件时。在这两种情况下,它都另外开了一个终端,给出了一些文本信息提示。这让我花了点时间才搞清楚,原来我得把它关了,安装器才会继续。在创建fstab后,它又会提示你,而你需要关闭终端,并在问你是否想要保存文件时回答‘是’。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我碰到的第二个问题,可能与VirtualBox有关了。在启动的时候,你可以看到没有网络被检测到的提示信息。点击顶部左边的图标,将会打开wicd,这里所使用的网络管理器。点击“断开”,然后再点击“连接”并重启安装器,就可以让它自动检测到了。
|
||||
|
||||
Evo/Lution我以为是个有价值的项目,在这里Lution工作一切顺利,目前还没有什么可告诉社区的。他们开启了一个全新的网站、论坛和维基,需要填充内容进去啊。所以,如果你喜欢这主意,加入[他们的论坛][3]并告诉他们吧。本文中的ISO镜像可以从[此网站][4]下载。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/install-arch-linux-easy-way-evolution.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ferdinand Thommes][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/ferdinand
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.archlinux.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.evolutionlinux.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.evolutionlinux.com/forums/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.evolutionlinux.com/downloads.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
|
||||
客户机通过DNSMASQ网络启动服务器网络安装“Debian 7(Wheezy)”
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
本教程将指引你直接通过使用**DNSMASQ**作为**PXE服务器(预启动执行环境)**的网络位置安装**Debian 7(Wheezy)**,此种情况是假定你的服务器不提供任何CD/DVD/USB介质驱动器,或者它只能通过相连的监视器、键盘和鼠标操作。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
客户机上的Debian 7网络安装
|
||||
|
||||
**DNSMASQ**是一个轻量级网络基础架构服务器,它可以通过内建的DNS、DHCP和TFTP服务器提供如DNS、DHCP和网络启动等关键服务。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦PXE服务器启动并运行,你可以指示你所有的客户机直接从网络启动,前提是你的客户机必须拥有一张支持网络启动的网卡,网络启动可以从BIOS的网络启动或启动服务选项中启用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 需求 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [Debian 7 (Wheezy)安装指南][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤1: 安装及配置DNSMASQ服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**1.** 首先,在安装Debian服务器后,要确保你的系统使用的是**静态IP地址**。因为除了网络启动之外,也要为你的整个网段提供DHCP服务。设置好静态IP地址后,以root帐号或具有root权力的用户来运行以下命令,进行DNSMASQ服务器的安装。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install dnsmasq
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装Dnsmasq包
|
||||
|
||||
**2.** 安装好DNSMASQ包后,你可以开始编辑配置文件。首先创建一个主配置文件的备份,然后使用下面的命令对**dnsmasq.conf**文件进行编辑。
|
||||
|
||||
# mv /etc/dnsmasq.conf /etc/dnsmasq.conf.backup
|
||||
# nano /etc/dnsmasq.conf
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
备份Dnsmasq配置
|
||||
|
||||
**3.** 上面的备份过程适合重命名配置文件,所以新的文件应该是空,你可以使用以下下面描述的**DNSMASQ**配置文件节录。
|
||||
|
||||
interface=eth0
|
||||
domain=debian.lan
|
||||
dhcp-range=192.168.1.3,192.168.1.253,255.255.255.0,1h
|
||||
dhcp-boot=pxelinux.0,pxeserver,192.168.1.100
|
||||
pxe-prompt="Press F8 for menu.", 60
|
||||
#pxe-service types: x86PC, PC98, IA64_EFI, Alpha, Arc_x86, Intel_Lean_Client, IA32_EFI, BC_EFI, Xscale_EFI and X86-64_EFI
|
||||
pxe-service=x86PC, "Install Debian 7 Linux from network server 192.168.1.100", pxelinux
|
||||
enable-tftp
|
||||
tftp-root=/srv/tftp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Dnsmasq配置
|
||||
|
||||
- **interface** – 服务器监听的网络接口。
|
||||
- **domain** – 用你自己的域名替换。
|
||||
- **dhcp-range** – 用你自己的网络掩码定义的网络IP地址范围。
|
||||
- **dhcp-boot** – 保持默认,但使用你自己的服务器IP地址替换IP声明。
|
||||
- **pxe-prompt** – 保持默认 – 要求在**敲击F8键** 进入菜单时等待60秒。
|
||||
- **pxe=service** – 使用**x86PC**作为32位/64位架构,并进入引号字符串的菜单描述提示。其它值类型可能是:PC98,IA64_EFI,Alpha,Arc_x86,Intel_Lean_Client,IA32_EFI, BC_EFI,Xscale_EFI和 X86-64_EFI。
|
||||
- **enable-tftp** – 启用内建TFTP服务器。
|
||||
- **tftp-root** – 使用/srv/tftp作为Debian网络启动文件的存放位置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤2: 下载Debian网络启动文件并打开防火墙连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**4.** 现在,该下载Debian网络启动文件了。首先,修改你当前工作目录路径到**TFTP根目录**位置,此位置由最后的配置语句定义(**/srv/tftp**系统路径)。
|
||||
|
||||
转到[Debian网络安装][2] – [网络启动部分][3]的官方页面镜像,抓取以下文件,要抓取的文件取决于你想要安装到客户端的系统架构。
|
||||
|
||||
下载好**netboot.tar.gz**文件后,同时提取归档(该过程描述只适用于64位,但对于其它系统架构也基本相同)。
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /srv/tftp/
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-amd64/current/images/netboot/netboot.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar xfz netboot.tar.gz
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-amd64/current/images/SHA256SUMS
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/Release
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/Release.gpg
|
||||
|
||||
同时,必须确保**TFTP**目录中的所有文件都可让TFTP服务器读取。
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod -R 755 /srv/tftp/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下载Debian网络启动文件
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下变量用于**Debian网络安装**镜像和架构。
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-"$ARCH"/current/images/netboot/netboot.tar.gz
|
||||
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-"$ARCH"/current/images/SHA256SUMS
|
||||
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/Release
|
||||
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/Release.gpg
|
||||
|
||||
**5.** 下一步,启动或重启DNSMASQ守护进程,并运行netstat命令来获取服务器监听的端口列表。
|
||||
|
||||
# service dnsmasq restart
|
||||
# netstat -tulpn | grep dnsmasq
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
启动Dnsmasq服务
|
||||
|
||||
**6.** 基于Debian的发行版通常附带了**UFW防火墙**包。使用以下命令来打开需要的**DNSMASQ**端口号:**67**(Bootps),**69**(TFTP),**53**(DNS)**4011**(代理DHCP)udp和**53** tcp(DNS)。
|
||||
# ufw allow 69/udp
|
||||
# ufw allow 4011/udp ## Only if you have a ProxyDHCP on the network
|
||||
# ufw allow 67/udp
|
||||
# ufw allow 53/tcp
|
||||
# ufw allow 53/udp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
开启Dnsmasq端口
|
||||
|
||||
Now, the PXE loader located on your client network interface will load **pxelinux** configuration files from **/srv/tftp/pxelinux.cfg** directory using this order.
|
||||
现在,位于你的客户机网络接口上的PXE加载器将使用按以下顺序从**/srv/tftp/pxelinux.cfg**目录加载**pxelinux**配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
- GUID文件
|
||||
- MAC文件
|
||||
- 默认文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤3: 配置客户端从网络启动 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**7.** 要为你的客户端计算机启用网络启动,请进入系统**BIOS配置**(如何进入BIOS设置,请查阅硬件主板提供商的文档)。
|
||||
|
||||
转到**启动菜单**,然后选择**网络启动**作为**首要启动设备**(在某些系统上,你可以不用进入BIOS配置就能选择启动设备,只要在**BIOS自检**时按一个键就可以进行选择了)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
选择BIOS设置
|
||||
|
||||
**8。** 在编辑启动顺序后,通常按**F10**来保存BIOS设置。重启后,你的客户端计算机应该可以直接从网络启动了,应该会出第一个**PXE**提示,要求你按**F8**键进入菜单。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,敲击**F8**键来进入,会出现一个新的提示。敲击**回车**键,屏幕上会出现**Debian安装器**主界面提示,如下图所示。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
启动菜单选择
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
选择Debian安装器启动
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
选择Debian安装
|
||||
|
||||
从这里开始,你可以使用Debian 7 Wheezy安装进程将Debian安装到你的机器上了(安装链接见上面)。然而,为了能够完成安装进程,你也需要确保你的机器上互联网连接已经激活。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤4: DNSMASQ服务器排障并在系统范围内启用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**9.** 要诊断服务器以查询最终是否发生问题或要查询其它提供给客户端的信息,运行以下命令来打开日志文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# tailf /var/log/daemon.log
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
DNSMASQ服务器排障
|
||||
|
||||
**10.** 如果服务器测试中已一切就绪,你现在可以在**sysv-rc-conf**包的帮助下,启用**DNSMASQ**守护进程自启动,以使该进程在系统重启后自动启动。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install sysv-rc-conf
|
||||
# sysv-rc-conf dnsmaq on
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
启用DNSMASQ守护进程
|
||||
|
||||
到此为止吧!现在你的**PXE**服务器已经整装待发,随时准备好分配IP地址了(**DHCP**),并为你所有网段中的客户端提供需要的启动信息,这些信息配置用来从网络启动并安装Debian Wheezy。
|
||||
|
||||
使用PXE网络启动安装在服务器主机数量增长时很有优势,因为你可以在短时间内火同时设置整个网络基础架构,为版本升级提供了方便,也可以通过kickstart文件使整个安装的全自动化。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/network-installation-of-debian-7-on-client-machines/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/debian-gnulinux-7-0-code-name-wheezy-server-installation-guide/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.debian.org/distrib/netinst#netboot
|
||||
[3]:http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/main/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
安卓应用乾坤大挪移,Ubuntu上的搬运工:ARChon
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Android, Chrome, Ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
**Google最近发布了首批[能在Chrome OS本地运行的安卓应用集][1],通过‘安卓运行时’扩展完成了该壮举。**
|
||||
|
||||
现在,一位开发者已经[指明了将安卓应用带入桌面版Chrome的路][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
[弗拉德·菲利波夫][3]的[chromeos-apk脚本][4]和[ARChon安卓运行时扩展][5]手拉手一起开展工作,将安卓应用带进了Windows,Mac和Linux桌面上的Chrome中。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
运行在Ubuntu 14.04 LTS上的安卓应用:IMDB,Flipboard和Twitter
|
||||
|
||||
通过运行时运行的应用的性能不是很令人惊异,任何想要运行Dead Trigger 2或者其它图形密集型游戏的雄心壮志可以放到一边了。
|
||||
|
||||
同样地,作为官方运行时的非官方重构包并在Chrome OS之外运行,系统整合(如网络摄像头,扬声器等)可能不完整或者根本不可能。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的指南只是提供原样,并不保证一定成功。它只能作为高度实验性进行,里面遍布漏洞,很不稳定——甚至平出恶魔。只能出于好奇而尝试,不去高度寄予厚望,那么你就不会深受其困扰。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安卓应用转战Linux大法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要通过Chrome在Linux上运行安卓应用,很明显,你需要安装Chrome,要求的版本是37,或者更高。坦率地讲,如果你打算玩玩潜在不稳定的版本,那么你也可以下载并[为Linux安装不稳定的Google Chrome版本][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
已经安装了Chrome的某个版本?你可以通过命令行来安装开发版,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install google-chrome-unstable
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,你需要下载官方定制版,而不是Google或Chronium捐赠的版本——由弗拉德·菲利波夫创建的安卓运行时。这个版本和官方的有着诸多的不同,最突出的就是它可以运行在桌面版的浏览器上。
|
||||
|
||||
- [从BitBucket下载ARChon v1.0][7]
|
||||
|
||||
下载好运行时后,你需要从.zip解压内容,并移动解压后的文件夹到你的Home文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
要安装,打开Google Chrome,点击汉堡式菜单按钮,然后导航到扩展页。检查‘启用开发者模式’并点击‘加载解包的扩展’按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
运行时本身不会做太多事情,所以你需要从安卓应用创建兼容包。要完成这项工作,你需要‘[chromeos-apk][8]’[命令行Javascript工具][9],它可以从节点封装模块管理器安装。
|
||||
|
||||
首先运行:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install npm nodejs nodejs-legacy
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 64位用户?你也需要攫取以下库:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install lib32stdc++6
|
||||
|
||||
现在,运行命令来暗转脚本吧:
|
||||
|
||||
npm install -g chromeos-apk
|
||||
|
||||
根据你的配置,你可能需要过会儿使用sudo来运行。如果你不喜欢[通过sudo安装npm模块,你可以][10]玩玩鬼把戏。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你直接回家了。去Google找找你想要试试的应用的APK吧,请牢记**不是所有的安卓应用都会工作**,而**那些可以工作的也未必工作得很好**,或者缺少功能。
|
||||
|
||||
把你想要的安卓APK放到~/Home,然后回到终端中使用以下命令来转换,你可以将APK命名成任何你想要的名字:
|
||||
|
||||
chromeos-apk replaceme.apk --archon
|
||||
|
||||
该命令将花一点时间来完成这项工作,也许也就是一眨眼的时间。[实际上,不需要眨眼的时间][11]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
现在,在你的Home文件夹内有个ARChon生成的Chrome APK extension-y folder-y这样的东西。所有剩下来要做的事,就是安装并查看它是否正常工作!
|
||||
|
||||
回到chrome://extensions页面,再次轻敲‘加载解封装扩展’按钮,但这次选择上面脚本创建的文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
应用应该会继续安装,不会有任何问题,但是它确实会没有问题吗?打开Chrome应用启动器或应用页面并启动它来看看是否有问题。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 深度探索 ####
|
||||
|
||||
由于ARChon运行时支持不限数量的chrome化的APK,你可以反复进行该操作,你想做多少次都行。Chrome APK [subreddit][12]用于跟踪成功/失败情况,所以如果你感到很有用,一定要贴出你的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/install-android-apps-ubuntu-archon
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgchrome.com/first-4-chrome-android-apps-released/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgchrome.com/run-android-apps-on-windows-mac-linux-archon/
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/vladikoff/
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/blob/master/archon.md
|
||||
[6]:http://www.chromium.org/getting-involved/dev-channel
|
||||
[7]:https://bitbucket.org/vladikoff/archon/get/v1.0.zip
|
||||
[8]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/blob/master/README.md
|
||||
[9]:https://github.com/vladikoff/chromeos-apk/blob/master/README.md
|
||||
[10]:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/19352976/npm-modules-wont-install-globally-without-sudo/21712034#21712034
|
||||
[11]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jKXLkWrBo7o
|
||||
[12]:http://www.reddit.com/r/chromeapks
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,199 @@
|
||||
Linux日志文件总管——logrotate
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
日志文件包含了关于系统中发生的事件的有用信息,在排障过程中或者系统性能分析时经常被用到。对于忙碌的服务器,日志文件大小会快速增长,服务器会很快消耗磁盘空间,这成了个问题。除此之外,处理一个单个的庞大日志文件也常常是件十分棘手的事。
|
||||
|
||||
logrotate是个十分有用的工具,它可以自动对日志进行分解(或轮循)、压缩以及删除旧日志文件。例如,你可以设置logrotate,让/var/log/foo日志文件每30天轮循,并删除超过6个月的日志。配置完后,logrotate的运作完全自动化,不必进行任何进一步的认为干预。另外,旧日志也可以通过电子邮件发送,不过该选项超出了本教程的讨论范围。
|
||||
|
||||
主流Linux发行版上都默认安装有logrotate包,如果出于某种原因,logrotate没有出现在里头,你可以使用apt-get或yum命令来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
在Debian或Ubuntu上:
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install logrotate cron
|
||||
|
||||
在Fedora,CentOS或RHEL上:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install logrotate crontabs
|
||||
|
||||
logrotate的配置文件是/etc/logrotate.conf,通常不需要对它进行修改。日志文件的轮循设置在独立的配置文件中,它(们)放在/etc/logrotate.d/目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
### 样例一 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在第一个样例中,我们将创建一个10MB的日志文件/var/log/log-file。我们将展示怎样使用logrotate来管理该日志文件。
|
||||
|
||||
我们从创建一个日志文件开始吧,然后在其中填入一个10MB的随机比特流数据。
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /var/log/log-file
|
||||
# head -c 10M < /dev/urandom > /var/log/log-file
|
||||
|
||||
由于现在日志文件已经准备好,我们将配置logrotate来轮循该日志文件。让我们为该文件创建一个配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
/var/log/log-file {
|
||||
monthly
|
||||
rotate 5
|
||||
compress
|
||||
delaycompress
|
||||
missingok
|
||||
notifempty
|
||||
create 644 root root
|
||||
postrotate
|
||||
/usr/bin/killall -HUP rsyslogd
|
||||
endscript
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
这里:
|
||||
|
||||
- **monthly**: 日志文件将按月轮循。其它可用值为‘daily’,‘weekly’或者‘yearly’。
|
||||
- **rotate 5**: 一次将存储5个归档日志。对于第六个归档,时间最久的归档将被删除。
|
||||
- **compress**: 在轮循任务完成后,已轮循的归档将使用gzip进行压缩。
|
||||
- **delaycompress**: 总是与compress选项一起用,delaycompress选项指示logrotate不要将最近的归档压缩,压缩将在下一次轮循周期进行。这在你或任何软件仍然需要读取最新归档时很有用。
|
||||
- **missingok**: 在日志轮循其间,任何错误将被忽略,例如“文件无法找到”之类的错误。
|
||||
- **notifempty**: 如果日志文件为空,轮循不会进行。
|
||||
- **create 644 root root**: 以指定的权限创建全新的日志文件,同时logrotate也会重命名原始日志文件。
|
||||
- **postrotate/endscript**: 在所有其它指令完成后,postrotate和endscript之间指定的命令将被执行。在这种情况下,rsyslogd 进程将立即再次读取其配置并继续运行。
|
||||
|
||||
上面的模板是通用的,而配置参数则根据你的需求进行调整,不是所有的参数都是必要的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 样例二 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在本例中,我们只想要轮循一个日志文件,然而日志文件大小会增长到50MB。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
/var/log/log-file {
|
||||
size=50M
|
||||
rotate 5
|
||||
create 644 root root
|
||||
postrotate
|
||||
/usr/bin/killall -HUP rsyslogd
|
||||
endscript
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
### 样例三 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们想要让旧日志文件以创建日期命名,这可以通过添加dateext常熟实现。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
/var/log/log-file {
|
||||
monthly
|
||||
rotate 5
|
||||
dateext
|
||||
create 644 root root
|
||||
postrotate
|
||||
/usr/bin/killall -HUP rsyslogd
|
||||
endscript
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
这将导致归档文件在它们的文件名中包含日期信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 排障 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里提供了一些logrotate设置的排障提示。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 手动运行logrotate ####
|
||||
|
||||
**logrotate**可以在任何时候从命令行手动调用。
|
||||
|
||||
要调用为/etc/lograte.d/下配置的所有日志调用**logrotate**:
|
||||
|
||||
# logrotate /etc/logrotate.conf
|
||||
|
||||
要为某个特定的配置调用logrotate:
|
||||
|
||||
# logrotate /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 演练 ####
|
||||
|
||||
排障过程中的最佳选择是使用‘-d’选项以预演方式运行logrotate。要进行验证,不用实际轮循任何日志文件,可以模拟演练日志轮循并显示其输出。
|
||||
|
||||
# logrotate -d /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
正如我们从上面的输出结果可以看到的,logrotate判断该轮循是不必要的。如果文件的时间小于一天,这就会发生了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. 强制运行 ####
|
||||
|
||||
即使轮循条件没有满足,我们也可以通过使用‘-f’选项来强制logrotate轮循日志文件,‘-v’参数提供了详细的输出。
|
||||
|
||||
# logrotate -vf /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
reading config file /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||||
reading config info for /var/log/log-file
|
||||
|
||||
Handling 1 logs
|
||||
|
||||
rotating pattern: /var/log/log-file forced from command line (5 rotations)
|
||||
empty log files are rotated, old logs are removed
|
||||
considering log /var/log/log-file
|
||||
log needs rotating
|
||||
rotating log /var/log/log-file, log->rotateCount is 5
|
||||
dateext suffix '-20140916'
|
||||
glob pattern '-[0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9][0-9]'
|
||||
renaming /var/log/log-file.5.gz to /var/log/log-file.6.gz (rotatecount 5, logstart 1, i 5),
|
||||
old log /var/log/log-file.5.gz does not exist
|
||||
renaming /var/log/log-file.4.gz to /var/log/log-file.5.gz (rotatecount 5, logstart 1, i 4),
|
||||
old log /var/log/log-file.4.gz does not exist
|
||||
. . .
|
||||
renaming /var/log/log-file.0.gz to /var/log/log-file.1.gz (rotatecount 5, logstart 1, i 0),
|
||||
old log /var/log/log-file.0.gz does not exist
|
||||
log /var/log/log-file.6.gz doesn't exist -- won't try to dispose of it
|
||||
renaming /var/log/log-file to /var/log/log-file.1
|
||||
creating new /var/log/log-file mode = 0644 uid = 0 gid = 0
|
||||
running postrotate script
|
||||
compressing log with: /bin/gzip
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. Logrotate记录日志 ####
|
||||
|
||||
logrotate自身的日志通常存放于/var/lib/logrotate/status目录。如果处于排障目的,我们想要logrotate记录到任何指定的文件,我们可以指定像下面这样从命令行指定。
|
||||
|
||||
# logrotate -vf –s /var/log/logrotate-status /etc/logrotate.d/log-file
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. Logrotate定时任务 ####
|
||||
|
||||
logrotate需要的**cron**任务应该在安装时就自动创建了,我把cron文件的内容贴出来,以供大家参考。
|
||||
|
||||
# cat /etc/cron.daily/logrotate
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/sh
|
||||
|
||||
# Clean non existent log file entries from status file
|
||||
cd /var/lib/logrotate
|
||||
test -e status || touch status
|
||||
head -1 status > status.clean
|
||||
sed 's/"//g' status | while read logfile date
|
||||
do
|
||||
[ -e "$logfile" ] && echo "\"$logfile\" $date"
|
||||
done >> status.clean
|
||||
mv status.clean status
|
||||
|
||||
test -x /usr/sbin/logrotate || exit 0
|
||||
/usr/sbin/logrotate /etc/logrotate.conf
|
||||
|
||||
小结一下,logrotate工具对于防止因庞大的日志文件而耗尽存储空间是十分有用的。配置完毕后,进程是全自动的,可以长时间在不需要人为干预下运行。本教程重点关注几个使用logrotate的几个基本样例,你也可以定制它以满足你的需求。
|
||||
|
||||
希望本文对你有所帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/logrotate-manage-log-files-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
在Ubuntu 14.04中重置Unity和Compiz设置【小贴士】
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如果你一直在试验你的Ubuntu系统,你可能最终以Unity和Compiz的一片混乱收场。在此贴士中,我们将看看怎样来重置Ubuntu 14.04中的Unity和Compiz。事实上,全部要做的事,仅仅是运行几个命令而已。
|
||||
|
||||
### 重置Ubuntu 14.04中的Unity和Compiz ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端(Ctrl+Alt+T),并使用以下命令来重置compiz:
|
||||
|
||||
dconf reset -f /org/compiz/
|
||||
|
||||
重置compiz后,重启Unity:
|
||||
|
||||
setsid unity
|
||||
|
||||
此外,如果你想将Unity图标也进行重置,试试以下的命令吧:
|
||||
|
||||
unity --reset-icons
|
||||
|
||||
### 可能的疑难解决方案: ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在重置compiz时遇到如下错误:
|
||||
|
||||
> error: GDBus.Error:org.gtk.GDBus.UnmappedGError.Quark._g_2dfile_2derror_2dquark.Code17: Cannot open dconf database: invalid gvdb header
|
||||
|
||||
可能的原因是用户文件被搞乱了。备份dconf配置,并移除配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
mv ~/.config/dconf/ ~/.config/dconf.bak
|
||||
|
||||
希望本贴士对你重置Ubuntu 14.04中Unity和compiz有所帮助,欢迎您随时提出问题和建议。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/reset-unity-compiz-settings-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
在CentOS 7上安装Vmware 10
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在CentOS 7上安装Vmware 10.0.3,我将给你们我的经验。通常,这个版本上不能在CentOS 7工作的,因为它只能运行在比较低的内核版本3.10上。
|
||||
|
||||
1 - 以正常方式下载并安装(没有问题)。唯一的问题是在后来体验vmware程序的时候。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何修复? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**1 – 进入/usr/lib/vmware/modules/source。**
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/lib/vmware/modules/source
|
||||
|
||||
**2 – 解压vmnet.tar.**
|
||||
|
||||
tar -xvf vmnet.tar
|
||||
|
||||
**3 – 进入vmnet-only目录。**
|
||||
|
||||
cd vmnet-only
|
||||
|
||||
**4 – 编辑filter.c文件。**
|
||||
|
||||
vi filter.c
|
||||
|
||||
在206和259行,替换以下字符串:
|
||||
|
||||
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE < KERNEL_VERSION(3, 13, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
为:
|
||||
|
||||
#if LINUX_VERSION_CODE < KERNEL_VERSION(3, 0, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
**5 – 回到先前文件夹。**
|
||||
|
||||
cd ../
|
||||
|
||||
**6 – 再次压缩文件夹。**
|
||||
|
||||
tar -uvf vmnet.tar vmnet-only
|
||||
|
||||
**7 – 移除旧目录。**
|
||||
|
||||
rm -fr vmnet-only
|
||||
|
||||
**8 – 启动vmware并体验。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-vmware-10-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者: M.el Khamlichi
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 14.04历史文件清理
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
这个简明教程对Ubuntu 14.04历史文件清理进行了说明,它用于初学者。
|
||||
|
||||
要从dash搜索删除历史记录,请遵循以下程序。
|
||||
|
||||
转到系统设置(System Settings)并打开安全与隐私(Security & Privacy)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在文件与应用(Files and Applications)标签下,点击清除用户数据(Clear Usage Data)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你也可以关闭“记录文件与应用使用(Record file and Application usage)以阻止系统记录你当前使用的文件和应用。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/how-to-delete-recently-opened-files-history-in-ubuntu-14-04.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu下使用CloudFlare作为ddclient提供商
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
DDclient是一个Perl客户端,用于更新动态DNS网络服务提供商帐号下的动态DNS条目。它最初是由保罗·巴利编写的,现在大多数是由维姆潘科在做。它能做的不仅仅是动态DNS,也可以通过几种不同的方式获取你的WAN口IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
CloudFlare有一点已知的功能,它允许你通过API或叫做ddclient的命令行脚本更新你的DNS记录。不管哪一个,结果都一样,而且它是个免费软件。
|
||||
|
||||
不幸的是,ddclient并不能在CloudFlare中即开即用。它需要打补丁,这里就是要介绍怎样在Debian或Ubuntu上破解它,它也能在带有Raspberry Pi的Raspbian上工作。
|
||||
|
||||
### 需求 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先保证你有一个自有域名,然后登录到CloudFlare,添加你的域名。遵循指令操作,使用它给出的默认值就行了。你将让CloudFlare来托管你的域,所以你需要调整你的注册机构的设置。如果你想要使用子域名,请为它添加一条‘A’记录。目前,任何IP地址都可以。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu上安装ddclient ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端,并运行以下命令
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ddclient
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你需要使用以下命令来安装补丁
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install curl sendmail libjson-any-perl libio-socket-ssl-perl
|
||||
|
||||
curl -O http://blog.peter-r.co.uk/uploads/ddclient-3.8.0-cloudflare-22-6-2014.patch
|
||||
|
||||
sudo patch /usr/sbin/ddclient < ddclient-3.8.0-cloudflare-22-6-2014.patch
|
||||
|
||||
以上命令用来完成ddclient的安装和打补丁
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置ddclient ###
|
||||
|
||||
你需要使用以下命令来编辑ddclient.conf文件
|
||||
|
||||
sudo vi /etc/ddclient.conf
|
||||
|
||||
添加以下信息
|
||||
|
||||
##
|
||||
### CloudFlare (cloudflare.com)
|
||||
###
|
||||
ssl=yes
|
||||
use=web, web=dyndns
|
||||
protocol=cloudflare, \
|
||||
server=www.cloudflare.com, \
|
||||
zone=domain.com, \
|
||||
login=you@email.com, \
|
||||
password=api-key \
|
||||
host.domain.com
|
||||
|
||||
Comment out:
|
||||
|
||||
#daemon=300
|
||||
|
||||
来自CloudFlare帐号页面的api密钥
|
||||
|
||||
ssl=yes might already be in that file
|
||||
|
||||
use=web, web=dyndns will use dyndns to check IP (useful for NAT)
|
||||
|
||||
你已经搞定了。登录到https://www.cloudflare.com并检查列出的与你域名对应的IP地址是否匹配到了http://checkip.dyndns.com。
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令来验证你的设置
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ddclient -daemon=0 -debug -verbose -noquiet
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/how-to-use-cloudflare-as-a-ddclient-provider-under-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
130
translated/tech/20140924 Unix----stat -- more than ls.md
Normal file
130
translated/tech/20140924 Unix----stat -- more than ls.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
|
||||
Unix: stat -- 获取比 ls 更多的信息
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 厌倦了 ls 命令, 并且想查看更多有关你的文件的有趣的信息? 试一试 stat!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ls 命令可能是每一个 Unix 使用者第一个学习的命令之一, 但它仅仅显示了 stat 命令能给出的信息的一小部分.
|
||||
|
||||
stat 命令从文件的索引节点获取信息. 正如你可能已经了解的那样, 每一个系统里的文件都存有三组日期和时间, 它们包括最近修改时间(即使用 ls -l 命令时显示的日期和时间), 最近状态改变时间(包括重命名文件)和最近访问时间.
|
||||
|
||||
使用长列表模式查看文件信息, 你会看到类似下面的内容:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls -l trythis
|
||||
-rwx------ 1 shs unixdweebs 109 Nov 11 2013 trythis
|
||||
|
||||
使用 stat 命令, 你会看到下面这些:
|
||||
|
||||
$ stat trythis
|
||||
File: `trythis'
|
||||
Size: 109 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 262144 regular file
|
||||
Device: 18h/24d Inode: 12731691 Links: 1
|
||||
Access: (0700/-rwx------) Uid: ( 263/ shs) Gid: ( 100/ unixdweebs)
|
||||
Access: 2014-09-09 19:27:58.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Modify: 2013-11-11 08:40:10.000000000 -0500
|
||||
Change: 2013-11-11 08:40:10.000000000 -0500
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的情形中, 文件的状态改变和文件修改的日期/时间是相同的, 而访问时间则是相当近的时间. 我们还可以看到文件使用了 8 个块, 以及两种格式显示的文件权限 -- 八进制(0700)格式和 rwx 格式. 在第三行显示的索引节点是 12731681. 文件没有其它的硬链接(Links: 1). 而且, 这个文件是一个常规文件.
|
||||
|
||||
重命名文件, 你会看到状态改变时间发生变化.
|
||||
|
||||
这里的 ctime 信息, 最早设计用来存储文件的创建日期和时间, 但之前的某个时间变为用来存储状态修改时间.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mv trythis trythat
|
||||
$ stat trythat
|
||||
File: `trythat'
|
||||
Size: 109 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 262144 regular file
|
||||
Device: 18h/24d Inode: 12731691 Links: 1
|
||||
Access: (0700/-rwx------) Uid: ( 263/ shs) Gid: ( 100/ unixdweebs)
|
||||
Access: 2014-09-09 19:27:58.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Modify: 2013-11-11 08:40:10.000000000 -0500
|
||||
Change: 2014-09-21 12:46:22.000000000 -0400
|
||||
|
||||
改变文件的权限也会改变 ctime 域.
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以配合通配符来使用 stat 命令以列出一组文件的状态:
|
||||
|
||||
$ stat myfile*
|
||||
File: `myfile'
|
||||
Size: 20 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 262144 regular file
|
||||
Device: 18h/24d Inode: 12731803 Links: 1
|
||||
Access: (0640/-rw-r-----) Uid: ( 263/ shs) Gid: ( 100/ unixdweebs)
|
||||
Access: 2014-08-23 03:00:36.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Modify: 2014-08-22 12:02:12.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Change: 2014-08-22 12:02:12.000000000 -0400
|
||||
File: `myfile2'
|
||||
Size: 20 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 262144 regular file
|
||||
Device: 18h/24d Inode: 12731806 Links: 1
|
||||
Access: (0640/-rw-r-----) Uid: ( 263/ shs) Gid: ( 100/ unixdweebs)
|
||||
Access: 2014-08-23 03:00:36.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Modify: 2014-08-22 12:03:30.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Change: 2014-08-22 12:03:30.000000000 -0400
|
||||
File: `myfile3'
|
||||
Size: 40 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 262144 regular file
|
||||
Device: 18h/24d Inode: 12730533 Links: 1
|
||||
Access: (0640/-rw-r-----) Uid: ( 263/ shs) Gid: ( 100/ unixdweebs)
|
||||
Access: 2014-08-23 03:00:36.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Modify: 2014-08-22 12:03:59.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Change: 2014-08-22 12:03:59.000000000 -0400
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们喜欢的话, 我们也可以通过其他命令来获取这些信息.
|
||||
|
||||
向 ls -l 命令添加 "u" 选项, 你会获得下面的结果. 注意这个选项会显示最后访问时间, 而添加 "c" 选项则会显示状态改变时间(在本例中, 是我们重命名文件的时间).
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls -lu trythat
|
||||
-rwx------ 1 shs unixdweebs 109 Sep 9 19:27 trythat
|
||||
$ ls -lc trythat
|
||||
-rwx------ 1 shs unixdweebs 109 Sep 21 12:46 trythat
|
||||
|
||||
stat 命令也可应用与文件夹.
|
||||
|
||||
在这个例子中, 我们可以看到有许多的链接.
|
||||
|
||||
$ stat bin
|
||||
File: `bin'
|
||||
Size: 12288 Blocks: 24 IO Block: 262144 directory
|
||||
Device: 18h/24d Inode: 15089714 Links: 9
|
||||
Access: (0700/drwx------) Uid: ( 263/ shs) Gid: ( 100/ unixdweebs)
|
||||
Access: 2014-09-21 03:00:45.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Modify: 2014-09-15 17:54:41.000000000 -0400
|
||||
Change: 2014-09-15 17:54:41.000000000 -0400
|
||||
|
||||
在这里, 我们查看一个文件系统.
|
||||
|
||||
$ stat -f /dev/cciss/c0d0p2
|
||||
File: "/dev/cciss/c0d0p2"
|
||||
ID: 0 Namelen: 255 Type: tmpfs
|
||||
Block size: 4096Fundamental block size: 4096
|
||||
Blocks: Total: 259366 Free: 259337 Available: 259337
|
||||
Inodes: Total: 223834 Free: 223531
|
||||
|
||||
注意 Namelen (文件名长度)域, 如果文件名长于 255 个字符的话, 你会很幸运地在文件名处看到心形符号!
|
||||
|
||||
stat 命令还可以一次显示所有我们想要的信息. 下面的例子中, 我们只想查看文件类型, 然后是硬连接数.
|
||||
|
||||
$ stat --format=%F trythat
|
||||
regular file
|
||||
$ stat --format=%h trythat
|
||||
1
|
||||
|
||||
在下面的例子中, 我们查看了文件权限 -- 分别以两种可用的格式 -- 然后是文件的 SELinux 安全环境.
|
||||
|
||||
译者注: 原文到这里就结束了, 但很明显缺少结尾. 最后一段的例子可以分别用
|
||||
|
||||
$ stat --format=%a trythat
|
||||
$ stat --format=%A trythat
|
||||
$ stat --format=%C trythat
|
||||
|
||||
来实现.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.itworld.com/operating-systems/437351/unix-stat-more-ls
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sandra Henry-Stocker][a]
|
||||
译者:[wangjiezhe](https://github.com/wangjiezhe)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.itworld.com/sandra-henry-stocker
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
Linux 有问必答-- 如何在Perl中捕捉并处理信号
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**: 我需要通过使用Perl的自定义信号处理程序来处理一个中断信号。在一般情况下,我怎么在Perl程序中捕获并处理各种信号(如INT,TERM)?
|
||||
|
||||
作为POSIX标准的异步通知机制,信号由操作系统发送给进程某个事件来通知它。当产生信号时,目标程序的执行是通过操作系统中断,并且该信号被发送到处理该信号的处理程序。任何人可以定义和注册自定义信号处理程序或依赖于默认的信号处理程序。
|
||||
|
||||
在Perl中,信号可以被捕获并被一个全局的%SIG哈希变量处理。这个%SIG哈希变量被信号号锁定并包含对相应的信号处理程序。因此,如果你想为特定的信号定义自定义信号处理程序,你可以直接更新%SIG的信号的哈希值。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个代码段来处理使用自定义信号处理程序中断(INT)和终止(TERM)的信号。
|
||||
|
||||
$SIG{INT} = \&signal_handler;
|
||||
$SIG{TERM} = \&signal_handler;
|
||||
|
||||
sub signal_handler {
|
||||
print "This is a custom signal handler\n";
|
||||
die "Caught a signal $!";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
%SIG其他有效的哈希值有'IGNORE'和'DEFAULT'。当所分配的哈希值是'IGNORE'(例如,$SIG{CHLD}='IGNORE')时,相应的信号将被忽略。分配'DEFAULT'的哈希值(例如,$SIG{HUP}='DEFAULT'),意味着我们将使用一个默认的信号处理程序。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/catch-handle-interrupt-signal-perl.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答 -- 如何在CentOS7上改变网络接口名
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**: 在CentOS7,我想将分配的网络接口名更改为别的名字。有什么合适的方法来来重命名CentOS或RHEL7的网络接口?
|
||||
|
||||
传统上,Linux的网络接口被枚举为eth[0123...],但这些名称并不一定符合实际的硬件插槽,PCI位置,USB接口数量等,这引入了一个不可预知的命名问题(例如,由于不确定的设备探测行为),这可能会导致不同的网络配置错误(例如,由无意的接口改名引起的禁止接口或者防火墙旁路)。基于MAC地址的udev规则在虚拟化的环境中并不有用,这里的MAC地址如端口数量一样无常。
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS/RHEL6还推出了[一致和可预测的网络设备命名][1]网络接口的方法。这些特性可以唯一地确定网络接口的名称以使定位和区分设备更容易,并且在这样一种方式下,它随着启动,时间和硬件改变的情况下是持久的。然而,这种命名规则并不是默认在CentOS/RHEL6上开启。
|
||||
|
||||
从CentOS/RHEL7起,可预见的命名规则变成了默认。根据这一规则,接口名称被自动基于固件,拓扑结构和位置信息来确定。现在,即使添加或移除网络设备,接口名称仍然保持固定,而无需重新枚举,和坏掉的硬件可以无缝替换。
|
||||
|
||||
* 基于接口类型的两个字母前缀:
|
||||
* en -- 以太网
|
||||
* sl -- 串行线路IP (slip)
|
||||
* wl -- wlan
|
||||
* ww -- wwan
|
||||
*
|
||||
* Type of names:
|
||||
* b<number> -- BCMA总线和新书
|
||||
* ccw<name> -- CCW总线组名
|
||||
* o<index> -- 车载设备的索引号
|
||||
* s<slot>[f<function>][d<dev_port>] -- 热插拔插槽索引号
|
||||
* x<MAC> -- MAC 地址
|
||||
* [P<domain>]p<bus>s<slot>[f<function>][d<dev_port>]
|
||||
* -- PCI 位置
|
||||
* [P<domain>]p<bus>s<slot>[f<function>][u<port>][..]1[i<interface>]
|
||||
* -- USB端口号链
|
||||
|
||||
新的命名方案的一个小的缺点是接口名称相比传统名称有点难以阅读。例如,你可能会发现像enp0s3名字。再者,你再也无法来控制接口名了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果由于某种原因,你喜欢旧的方式,并希望能够选择任意名称分配给CentOS/ RHEL7的设备,你需要重写默认的可预测的命名规则,定义基于MAC地址udev规则。
|
||||
|
||||
**下面是如何在CentOS或RHEL7命名网络接口。**
|
||||
|
||||
首先,让我们来禁用该可预测命名规则。对于这一点,你可以在启动时传递“net.ifnames=0”的内核参数。这是通过编辑/etc/default/grub并加入“net.ifnames=0”到GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX变量来实现的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
然后运行这条命令来重新生成GRUB配置并更新内核参数。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
接下来,编辑(或创建)一个udev的网络命名规则文件(/etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules),并添加下面一行。更换成你自己的MAC地址和接口。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/udev/rules.d/70-persistent-net.rules
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
SUBSYSTEM=="net", ACTION=="add", DRIVERS=="?*", ATTR{address}=="08:00:27:a9:7a:e1", ATTR{type}=="1", KERNEL=="eth*", NAME="sushi"
|
||||
|
||||
最后,重启电脑并验证新的接口名。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
请注意,配置重命名后的接口仍然是你的责任。如果网络配置(例如,IPv4设置,防火墙规则)是基于旧名称(变更前)的,则需要更新的网络配置以反映更改的名称。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/change-network-interface-name-centos7.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/6/html/Deployment_Guide/appe-Consistent_Network_Device_Naming.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——如何为CentOS 7配置静态IP地址
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:在CentOS 7上,我想要将我其中一个网络接口从DHCP改为静态IP地址配置,如何才能永久为CentOS或RHEL 7上的网络接口分配静态IP地址?
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要为CentOS 7中的某个网络接口设置静态IP地址,有几种不同的方法,这取决于你是否想要使用网络管理器。
|
||||
|
||||
网络管理器是一个动态的网络控制与配置系统,它用于在网络设备可用时保持设备和连接开启并激活。默认情况下,CentOS/RHEL 7安装有网络管理器,并处于启用状态。
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令来验证网络管理器服务的状态:
|
||||
|
||||
$ systemctl status NetworkManager.service
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令来检查受网络管理器管理的网络接口:
|
||||
|
||||
$ nmcli dev status
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果某个接口的nmcli的输出结果是“已连接”(如本例中的enp0s3),这就是说该接口受网络管理器管理。你可以轻易地为某个特定接口禁用网络管理器,以便你可以自己为它配置一个静态IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
下面将介绍**在CentOS 7上为网络接口配置静态IP地址的两种方式**,在例子中我们将对名为enp0s3的网络接口进行配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 不使用网络管理配置静态IP地址 ###
|
||||
|
||||
进入/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts目录,找到该接口的配置文件(ifcfg-enp0s3)。如果没有,请创建一个。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
打开配置文件并编辑以下变量:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在上图中,“NM_CONTROLLED=no”表示该接口将通过该配置进行设置,而不是通过网络管理器进行管理。“ONBOOT=yes”告诉我们,系统将在启动时开启该接口。
|
||||
|
||||
保存修改并使用以下命令来重启网络服务:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart network.service
|
||||
|
||||
现在验证接口是否配置正确:
|
||||
|
||||
# ip add
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用网络管理器配置静态IP地址 ###
|
||||
如果你想要使用网络管理器来管理该接口,你可以使用nmtui(网络管理器文本用户界面),它提供了在终端环境中配置配置网络管理器的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
在使用nmtui之前,首先要在/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3中设置“NM_CONTROLLED=yes”。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,请按以下方式安装nmtui。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install NetworkManager-tui
|
||||
|
||||
然后继续去编辑enp0s3接口的网络管理器配置:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmtui edit enp0s3
|
||||
|
||||
在下面的屏幕中,我们可以手动输入与/etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3中所包含的内容相同的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
使用箭头键在屏幕中导航,按回车选择值列表中的内容(或填入想要的内容),最后点击屏幕底部右侧的确定按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后,重启网络服务。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart network.service
|
||||
|
||||
好了,现在一切就绪。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/configure-static-ip-address-centos7.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答-- 如何用Perl检测Linux的发行版本
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**:我需要写一个Perl程序,它会包含Linux发行版相关的代码。为此,Perl程序需要能够自动检测运行中的Linux的发行版(如Ubuntu、CentOS、Debian、Fedora等等),以及它是什么版本号。如何用Perl检测Linux的发行版本?
|
||||
|
||||
如果要用Perl脚本检测Linux的发行版,你可以使用一个名为[Linux::Distribution][1]的Perl模块。该模块通过检查/etc/lsb-release以及其他特定的/etc下的发行版特定的目录来猜测底层Linux操作系统。它支持检测所有主要的Linux发行版,包括Fedora、CentOS、Arch Linux、Debian、Ubuntu、SUSE、Red Hat、Gentoo、Slackware、Knoppix和Mandrake。
|
||||
|
||||
要在Perl中使用这个模块,你首先需要安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Debian或者Ubuntu上安装 Linux::Distribution ###
|
||||
|
||||
基于Debian的系统直接用apt-get安装
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install liblinux-distribution-packages-perl
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Fedora、CentOS 或者RHEL上安装 Linux::Distribution ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的Linux没有Linux::Distribution模块的安装包(如基于红帽的系统),你可以使用CPAN来构建。
|
||||
|
||||
首先确保你的Linux系统安装了CPAN
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum -y install perl-CPAN
|
||||
|
||||
使用这条命令来构建并安装模块:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo perl -MCPAN -e 'install Linux::Distribution'
|
||||
|
||||
### 用Perl确定Linux发行版 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux::Distribution模块安装完成之后,你可以使用下面的代码片段来确定你运行的Linux发行版本。
|
||||
|
||||
use Linux::Distribution qw(distribution_name distribution_version);
|
||||
|
||||
my $linux = Linux::Distribution->new;
|
||||
|
||||
if ($linux) {
|
||||
my $distro = $linux->distribution_name();
|
||||
my $version = $linux->distribution_version();
|
||||
print "Distro: $distro $version\n";
|
||||
}
|
||||
else {
|
||||
print "Distro: unknown\n";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/detect-linux-distribution-in-perl.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://metacpan.org/pod/Linux::Distribution
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答-- 如何在PDF中嵌入LaTex中的所有字体
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**: 我通过编译LaTex源文件生成了一份PDF文档。然而,我注意到,并不是所有字体都嵌入到了PDF文档中。我怎样才能确保所有的字体嵌入在由LaTex生成的PDF文档中?
|
||||
|
||||
当你创建一个PDF文件时,在PDF文件中嵌入字体是一个好主意。如果你不嵌入字体,PDF浏览器可以在计算机上没有字体的情况下使用其他东西代替。这将导致文件被在不同的PDF浏览器或操作系统平台上呈现不同的样式。当你打印出来的文档时,缺少的字体是一个问题。
|
||||
|
||||
当你从LaTex中生成PDF文档时(例如用pdflatex或dvipdfm),可能并不是所有的字体都嵌入在PDF文档中。例如,[pdffonts][1]下面的输出中提示PDF文档中有缺少的字体(如Helvetica)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
为了避免这样的问题,下面是如何在LaTex编译时嵌入所有的字体。
|
||||
|
||||
$ latex document.tex
|
||||
$ dvips -Ppdf -G0 -t letter -o document.ps document.dvi
|
||||
$ ps2pdf -dPDFSETTINGS=/prepress \
|
||||
-dCompatibilityLevel=1.4 \
|
||||
-dAutoFilterColorImages=false \
|
||||
-dAutoFilterGrayImages=false \
|
||||
-dColorImageFilter=/FlateEncode \
|
||||
-dGrayImageFilter=/FlateEncode \
|
||||
-dMonoImageFilter=/FlateEncode \
|
||||
-dDownsampleColorImages=false \
|
||||
-dDownsampleGrayImages=false \
|
||||
document.ps document.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以看到所有的字体都被嵌入到PDF中了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/embed-all-fonts-pdf-document-latex.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/check-which-fonts-are-used-pdf-document.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
如何重置CentOS 7的Root密码
|
||||
===
|
||||
|
||||
重置Centos 7 Root密码的方式和Centos 6完全不同。让我来展示一下到底如何操作。
|
||||
|
||||
1 - 在启动grub菜单,选择编辑选项启动
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2 - 按键盘e键,来进入编辑界面
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3 - 找到Linux 16的那一行,将ro改为rw init=/sysroot/bin/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
4 - 现在按下 Control+x ,使用单用户模式启动
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
5 - 现在,可以使用下面的命令访问系统
|
||||
|
||||
chroot /sysroot
|
||||
|
||||
6 - 重置密码
|
||||
|
||||
passwd root
|
||||
|
||||
7 - 更新系统信息
|
||||
|
||||
touch /.autorelabel
|
||||
|
||||
8 - 退出chroot
|
||||
|
||||
exit
|
||||
|
||||
9 - 重启你的系统
|
||||
|
||||
reboot
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样!
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/reset-root-password-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:M.el Khamlichi
|
||||
译者:[su-kaiyao](https://github.com/su-kaiyao)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user