mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-13 22:30:37 +08:00
commit
9c94437129
@ -1,13 +1,13 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu上转换图片音频和视频格式
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu上转换图像、音频和视频格式
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的工作中需要接触到各种不同编码格式的图片、音频和视频,那么你或许正在使用多个工具来转换这些不同的媒介格式。如果存在一个能够处理所有文件/音频/视频格式的多和一的转换工具,那就太好了。
|
||||
如果你的工作中需要接触到各种不同编码格式的图像、音频和视频,那么你很有可能正在使用多个工具来转换这些多种多样的媒体格式。如果存在一个能够处理所有图像/音频/视频格式的多合一转换工具,那就太好了。
|
||||
|
||||
[Format Junkie][1] 就是这样一个有着极其友好的用户界面的多和一的媒介转换工具。更棒的是它是一个免费软件。你可以使用 Format Junkie 来转换几乎所有的流行格式的图像、音频、视频和归档文件(或称压缩文件),所有这些只需要简单地点击几下鼠标而已。
|
||||
[Format Junkie][1] 就是这样一个多合一的媒体转换工具,它有着极其友好的用户界面。更棒的是它是一个免费软件。你可以使用 Format Junkie 来转换几乎所有的流行格式的图像、音频、视频和归档文件(或称压缩文件),所有这些只需要简单地点击几下鼠标而已。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu 12.04, 12.10 和 13.04 上安装 Format Junkie ###
|
||||
|
||||
Format Junkie 可以通过 Ubuntu PPA format-junkie-team 进行安装。这个PPA支持Ubuntu 12.04, 12.10 和 13.04。在以上任意一种Ubuntu版本中安装Format Junkie的话,简单的执行一下命令即可:
|
||||
Format Junkie 可以通过 Ubuntu PPA format-junkie-team 进行安装。这个PPA支持Ubuntu 12.04, 12.10 和 13.04。在以上任意一种Ubuntu版本中安装Format Junkie的话,简单的执行以下命令即可:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:format-junkie-team/release
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ Format Junkie 可以通过 Ubuntu PPA format-junkie-team 进行安装。这个PP
|
||||
|
||||
### 将 Format Junkie 安装到 Ubuntu 13.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你正在运行Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander),你可以按照以下步骤下载 .deb 安装包来进行安装。由于Format Junkie 的 .deb 安装包只有很少的依赖包,所以使用 [gdebi deb installer][2] 来按安装它。
|
||||
如果你正在运行Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander),你可以按照以下步骤下载 .deb 安装包来进行安装。由于Format Junkie 的 .deb 安装包只有很少的依赖包,所以使用 [gdebi deb installer][2] 来安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
在32位版Ubuntu 13.10上:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,9 +30,9 @@ Format Junkie 可以通过 Ubuntu PPA format-junkie-team 进行安装。这个PP
|
||||
$ sudo gdebi formatjunkie_1.07-1~raring0.2_amd64.deb
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /opt/extras.ubuntu.com/formatjunkie/formatjunkie /usr/bin/formatjunkie
|
||||
|
||||
### 将 Format Junkie 安装到 Ubuntu 14.04 或 之后版本 ###
|
||||
### 将 Format Junkie 安装到 Ubuntu 14.04 或之后版本 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现有的可供使用的官方 Format Junkie .deb 文件 需要 libavcodec-extra-53,这个东西从Ubuntu 14.04开始就已经过时了。所以如果你想在Ubuntu 14.04或之后版本上安装Format Junkie的话,可以使用以下的第三方PPA来代替。
|
||||
现有可供使用的官方 Format Junkie .deb 文件需要 libavcodec-extra-53,不过它从Ubuntu 14.04开始就已经过时了。所以如果你想在Ubuntu 14.04或之后版本上安装Format Junkie,可以使用以下的第三方PPA来代替。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:jon-severinsson/ffmpeg
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
|
||||
@ -47,11 +47,11 @@ Format Junkie 可以通过 Ubuntu PPA format-junkie-team 进行安装。这个PP
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 Format Junkie 来转换音频、视频、图像和归档格式 ####
|
||||
|
||||
就像下方展示的一样,Format Junkie 的用户界面简单而且直观。在音频、视频、图像和iso媒介之间进行选择,在顶部四个标签当中点击你需要的那个。你可以根据需要添加无限量的文件用于批量转换。添加文件后,选择输出格式,直接点击 "Start Converting" 按钮进行转换。
|
||||
就像下方展示的一样,Format Junkie 的用户界面简单而且直观。在顶部的音频、视频、图像和iso媒体四个标签当中点击你需要的那个。你可以根据需要添加任意数量的文件用于批量转换。添加文件后,选择输出格式,直接点击 "Start Converting" 按钮进行转换。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Format Junkie支持以下媒介媒介媒介格式间的转换:
|
||||
Format Junkie支持以下媒体格式间的转换:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Audio**: mp3, wav, ogg, wma, flac, m4r, aac, m4a, mp2.
|
||||
- **Video**: avi, ogv, vob, mp4, 3gp, wmv, mkv, mpg, mov, flv, webm.
|
||||
@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ Format Junkie支持以下媒介媒介媒介格式间的转换:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 用 Format Junkie 进行字幕编码 ####
|
||||
|
||||
除了媒介转换,Format Junkie 可提供了字幕编码的图形界面。实际的字幕编码是由MEncoder来完成的。为了使用Format Junkie的字幕编码接口,首先你需要安装MEencoder。
|
||||
除了媒体转换,Format Junkie 可提供了字幕编码的图形界面。实际的字幕编码是由MEncoder来完成的。为了使用Format Junkie的字幕编码接口,首先你需要安装MEencoder。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install mencoder
|
||||
|
||||
@ -68,9 +68,9 @@ Format Junkie支持以下媒介媒介媒介格式间的转换:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
总而言之,Format Junkie 是一个非常易于使用和多才多艺的媒介转换工具。但也有一个缺陷,它不允许对转换进行任何定制化(例如:比特率,帧率,采样频率,图像质量,尺寸)。所以这个工具推荐正在寻找一个简单易用的媒介转换工具的新手使用。
|
||||
总而言之,Format Junkie 是一个非常易于使用和多才多艺的媒体转换工具。但也有一个缺陷,它不允许对转换进行任何定制化(例如:比特率,帧率,采样频率,图像质量,尺寸)。所以这个工具推荐给正在寻找一个简单易用的媒体转换工具的新手使用。
|
||||
|
||||
喜欢这篇文章吗?在facebook、twitter和google+上给我点赞吧。多谢!
|
||||
喜欢这篇文章吗?请在下面发表评论吧。多谢!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,7 +78,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/how-to-convert-image-audio-and-video-formats-on-ubuntu.h
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[Ping](https://github.com/mr-ping)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,17 +2,17 @@
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我上网时最担心的一件事情是,我该如何确保我的数据安全和隐私。在搜索答案的过程中,我找到了很多保持匿名的方法,比如使用代理网站。但是使用第三方的服务不能完全保证。我需要的是有一款软件可以我自己安装并运行,那样我就能确保只有我才能访问数据。
|
||||
我上网时最担心的一件事情是,我该如何确保我的数据安全和隐私。在搜索答案的过程中,我找到了很多保持匿名的方法,比如使用代理网站。但是使用第三方的服务不能完全保证。我需要的是有一款软件可以让我自己安装并运行,那样我就能确保只有我才能访问数据。
|
||||
|
||||
这款软件叫什么呢?
|
||||
|
||||
它叫VPN服务,就是虚拟隐私网络的简称。它允许访问时通过SSL加密你的数据。因为是加密的连接,所以你的ISP不能看到你的浏览信息。
|
||||
|
||||
在本篇Linux教程中,我会在CentOS 7上安装一个OpenVPN服务。OpenVPN很容易使用,开源且拥有基于社区的支持。它的客户端有Windows、Android和Mac。
|
||||
在本篇Linux教程中,我会在CentOS 7上安装一个OpenVPN服务。OpenVPN很容易使用,开源且拥有社区的支持。它的客户端支持Windows、[Android][1]和Mac。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一步: 在你的Linux机器或者 [VPS][1]上安装OpenVPN服务 ###
|
||||
### 第一步: 在你的Linux机器或者 VPS 上安装OpenVPN服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
从https://openvpn.net/index.php/access-server/download-openvpn-as-sw.html下载安装包,Ubuntu用户也可以找到合适的安装包并安装。
|
||||
从 https://openvpn.net/index.php/access-server/download-openvpn-as-sw.html 下载安装包,Ubuntu用户也可以找到合适的安装包并安装。
|
||||
|
||||
[leo@vps ]$ cd /tmp
|
||||
[leo@vps tmp]$ wget http://swupdate.openvpn.org/as/openvpn-as-2.0.10-CentOS7.x86_64.rpm
|
||||
@ -61,11 +61,10 @@ via: http://techarena51.com/index.php/how-to-install-an-opensource-vpn-server-on
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Leo G][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://techarena51.com/
|
||||
[1]:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=net.openvpn.openvpn&hl=en
|
||||
[2]:http://supportinc.net/vps-hosting.php
|
||||
[3]:https://openvpn.net/index.php/access-server/docs/admin-guides-sp-859543150/howto-connect-client-configuration.html
|
||||
@ -2,39 +2,27 @@
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
今天我们将会向你展示如何使用 **lsblk** 和 **blkid** 工具来查找关于块设备的信息,我们使用的是一台安装了 CentOS 7.0 的机器。
|
||||
|
||||
## lsblk ##
|
||||
|
||||
**lsblk** 是一个 Linux 工具,它会显示有关你系统里所有可用块设备的信息。它从 [sysfs 文件系统][1] 中获取信息。默认情况下,这个工具将会以树状格式显示(除了内存虚拟磁盘外的)所有块设备。
|
||||
|
||||
### lsblk 默认输出 ###
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下 lsblk 会将块设备输出为树状格式:
|
||||
|
||||
**NAME**
|
||||
- **NAME** —— 设备的名称
|
||||
|
||||
—— 设备的名称
|
||||
- **MAJ:MIN** —— Linux 操作系统中的每个设备都以一个文件表示,对块(磁盘)设备来说,这里用主次设备编号来描述设备。
|
||||
|
||||
**MAJ:MIN**
|
||||
- **RM** —— 可移动设备。如果这是一个可移动设备将显示 1,否则显示 0。
|
||||
|
||||
—— Linux 操作系统中的每个设备都以一个文件表示,对块(磁盘)设备来说,这里用主次设备编号来描述设备。
|
||||
- **TYPE** —— 设备的类型
|
||||
|
||||
**RM**
|
||||
- **MOUNTPOINT** —— 设备挂载的位置
|
||||
|
||||
—— 可移动设备。如果这是一个可移动设备将显示 1,否则显示 0。
|
||||
- **RO** —— 对于只读文件系统,这里会显示 1,否则显示 0。
|
||||
|
||||
**TYPE**
|
||||
|
||||
—— 设备的类型
|
||||
|
||||
**MOUNTPOINT**
|
||||
|
||||
—— 设备挂载的位置
|
||||
|
||||
**RO**
|
||||
|
||||
—— 对于只读文件系统,这里会显示 1,否则显示 0。
|
||||
|
||||
**SIZE**
|
||||
|
||||
—— 设备的容量
|
||||
- **SIZE** —— 设备的容量
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,12 +42,14 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 在脚本中使用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
高级技巧:如果你想要在脚本中使用而不希望表头被显示出来,你可以这样使用 -n 选项:
|
||||
高级技巧:如果你想要在脚本中使用而希望剔除表头,你可以这样使用 -n 选项:
|
||||
|
||||
lsblk -ln
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## blkid ##
|
||||
|
||||
**blkid** 命令是一个命令行工具,它可以显示关于可用块设备的信息。它可以识别一个块设备内容的类型(如文件系统、交换区)以及从内容的元数据(如卷标或 UUID 字段)中获取属性(如 tokens 和键值对)。它主要有两类作用:用指定的键值对搜索一个设备,或是显示一个或多个设备的键值对。
|
||||
|
||||
### blkid 使用方法 ###
|
||||
@ -84,7 +74,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 详细信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要获取更多详细信息,你可以使用 -p 和 -o udev 选项来将它们用漂亮的格式显示出来,像这样:
|
||||
如果你想要获取更多详细信息,你可以使用 -p 和 -o udev 选项来将它们用整齐的格式显示出来,像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
# blkid -po udev /dev/sda1
|
||||
|
||||
@ -102,7 +92,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-command-lsblk-blkid/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
|
||||
译者:[felixonmars](https://github.com/felixonmars)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,20 +2,19 @@
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu默认自带了很多字体。但你或许对这些字体还不满意。因此,你可以做的是在**Ubuntu 14.04、 14.10或者像Linux Mint其他的系统中安装额外的字体**。
|
||||
Ubuntu默认自带了很多字体。但有时候你或许对这些字体还不满意。因此,你可以做的是在**Ubuntu 14.04、 14.10或者像Linux Mint之类的其它Linux系统中安装额外的字体**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一步: 获取字体 ###
|
||||
|
||||
第一步也是最重要的,下载你选择的字体。现在你或许在考虑从哪里下载字体。不要担心,Google搜索可以给你提供几个免费的字体网站。你可以先去看看[ Lost Type 的字体][1]。[Squirrel的字体][2]同样也是一个下载字体的好地方。
|
||||
第一步也是最重要的一步,下载你选择的字体。现在你或许在考虑从哪里下载字体。不要担心,Google搜索可以给你提供几个免费的字体网站。你可以先去看看[ Lost Type 的字体][1]。[Squirrel][2]同样也是一个下载字体的好地方。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第二步:在Ubuntu中安装新字体 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Font Viewer. In here, you can see the option to install the font in top right corner:
|
||||
下载的字体文件可能是一个压缩包。先解压它。大多数字体文件的格式是[TTF][3] (TrueType Fonts) 或者[OTF][4] (OpenType Fonts)。无论是哪种,只要双击字体文件。它会自动用字体查看器打开。这里你可以在右上角看到安装安装选项。
|
||||
下载的字体文件可能是一个压缩包,先解压它。大多数字体文件的格式是[TTF][3] (TrueType字体) 或者[OTF][4] (OpenType字体)。无论是哪种,只要双击字体文件。它会自动用字体查看器打开。这里你可以在右上角看到安装选项。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在安装字体时不会看到其他信息。几秒钟后,你会看到状态变成已安装。不用猜,这就是已安装的字体。
|
||||
在安装字体时不会看到其他信息。几秒钟后,你会看到状态变成已安装。不用猜,字体已经安装完毕。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,20 +22,20 @@ Font Viewer. In here, you can see the option to install the font in top right co
|
||||
|
||||
### 第二步:在Linux上一次安装几个字体 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我没有打错。这仍旧是第二步但是只是是一个备选方案。我上面看到的在Ubuntu中安装字体的方法是不错的。但是这有一个小问题。当你有20个新字体要安装时。一个个单独双击即繁琐又麻烦。你不这么认为么?
|
||||
我没有打错。这仍旧是第二步但是只是一个备选方案。我们上面看到的在Ubuntu中安装字体的方法是不错的。但是这有一个小问题。当你有20个新字体要安装时。一个个单独双击即繁琐又麻烦。你不这么认为么?
|
||||
|
||||
要在Ubuntu中一次安装几个字体,你要做的是创建一个.fonts文件夹,如果在你的家目录下还不存在这个目录的话。并把解压后的TTF和OTF文件复制到这个文件夹内。
|
||||
要在Ubuntu中一次安装几个字体,你唯一要做的是在你的家目录下创建一个.fonts文件夹,如果它不存在的话。并把解压后的TTF和OTF文件复制到这个文件夹内。
|
||||
|
||||
在文件管理器中进入家目录。按下Ctrl+H [显示Ubuntu中的隐藏文件][5]。 右键创建一个文件夹并命名为.fonts。 这里的点很重要。在Linux中,在文件的前面加上点意味在普通的视图中都会隐藏。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 备选方案: ####
|
||||
|
||||
另外你可以安装字体管理程序来以GUI的形式管理字体。要在Ubuntu中安装字体管理程序,打开终端并输入下面的命令:
|
||||
另外你可以安装字体管理程序,在图形用户界面管理字体。要在Ubuntu中安装字体管理程序,打开终端并输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install font-manager
|
||||
|
||||
Open the Font Manager from Unity Dash. You can see installed fonts and option to install new fonts, remove existing fonts etc here.
|
||||
从Unity Dash中打开字体管理器。你可以看到已安装的字体和安装新字体、删除字体等选项。
|
||||
|
||||
从Unity Dash中打开字体管理器。在这里你可以看到已安装的字体和安装新字体、删除字体等选项。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -44,7 +43,7 @@ Open the Font Manager from Unity Dash. You can see installed fonts and option to
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove font-manager
|
||||
|
||||
我希望这篇文章可以帮助你在Ubuntu或其他Linux系统上安装字体。如果你有任何问题或建议请让我知道。
|
||||
我希望这篇文章可以帮助你在Ubuntu或其它Linux系统上安装字体。如果你有任何问题或建议请在下方评论中告诉我。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,7 +51,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/install-fonts-ubuntu-1404-1410/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -61,4 +60,4 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/install-fonts-ubuntu-1404-1410/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.fontsquirrel.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/TrueType
|
||||
[4]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/OpenType
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/hide-folders-and-show-hidden-files-in-ubuntu-beginner-trick/
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/hide-folders-and-show-hidden-files-in-ubuntu-beginner-trick/
|
||||
@ -1,47 +1,49 @@
|
||||
在CentOS7.0 VPS上搭建 Bind Chroot DNS 服务器
|
||||
在 CentOS7.0 上搭建 Chroot 的 Bind DNS 服务器
|
||||
====================
|
||||
|
||||
BIND(Berkeley internet Name Daemon)也叫做NAMED是现今互联网上使用最为广泛的DNS 服务器程序。这篇文章将要讲述如何在 chroot jail (chroot “监牢”,所谓“监牢”就是指通过chroot机制来更改某个进程所能看到的根目录,即将某进程限制在指定目录中,保证该进程只能对该目录及其子目录的文件有所动作,从而保证整个服务器的安全)中运行 BIND,这样它就无法访问文件系统中除“jail”以外的其它部分。例如,在这篇文章中,我会将BIND的运行根目录改为/var/named/chroot/。当然,对于BIND来说,这个目录就是/(根目录)。 “jail”(监牢,下同)是一个软件机制,其功能是使得某个程序无法访问规定区域之外的资源,同样也为了增强安全性。Bind Chroot DNS 服务器的默认“jail”为/var/named/chroot。你可以按照下列步骤,在CentOS 7.0 虚拟专用服务器(VPS)上部署 Bind Chroot DNS 服务器。
|
||||
BIND(Berkeley internet Name Daemon)也叫做NAMED,是现今互联网上使用最为广泛的DNS 服务器程序。这篇文章将要讲述如何在 chroot 监牢中运行 BIND,这样它就无法访问文件系统中除“监牢”以外的其它部分。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 安装Bind Chroot DNS 服务器:
|
||||
例如,在这篇文章中,我会将BIND的运行根目录改为 /var/named/chroot/。当然,对于BIND来说,这个目录就是 /(根目录)。 “jail”(监牢,下同)是一个软件机制,其功能是使得某个程序无法访问规定区域之外的资源,同样也为了增强安全性(LCTT 译注:chroot “监牢”,所谓“监牢”就是指通过chroot机制来更改某个进程所能看到的根目录,即将某进程限制在指定目录中,保证该进程只能对该目录及其子目录的文件进行操作,从而保证整个服务器的安全)。Bind Chroot DNS 服务器的默认“监牢”为 /var/named/chroot。你可以按照下列步骤,在CentOS 7.0 上部署 Bind Chroot DNS 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# yum install bind-chroot bind -y
|
||||
### 1、安装Bind Chroot DNS 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
2. 拷贝bind相关文件,准备bind chroot 环境
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# yum install bind-chroot bind -y
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# cp -R /usr/share/doc/bind-*/sample/var/named/* /var/named/chroot/var/named/
|
||||
### 2、拷贝bind相关文件,准备bind chroot 环境
|
||||
|
||||
3. 在bind chroot 的目录中创建相关文件
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# cp -R /usr/share/doc/bind-*/sample/var/named/* /var/named/chroot/var/named/
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# touch /var/named/chroot/var/named/data/cache_dump.db
|
||||
### 3、在bind chroot 的目录中创建相关文件
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# touch /var/named/chroot/var/named/data/named_stats.txt
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# touch /var/named/chroot/var/named/data/cache_dump.db
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# touch /var/named/chroot/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# touch /var/named/chroot/var/named/data/named_stats.txt
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# touch /var/named/chroot/var/named/data/named.run
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# touch /var/named/chroot/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# mkdir /var/named/chroot/var/named/dynamic
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# touch /var/named/chroot/var/named/data/named.run
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# touch /var/named/chroot/var/named/dynamic/managed-keys.bind
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# mkdir /var/named/chroot/var/named/dynamic
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# touch /var/named/chroot/var/named/dynamic/managed-keys.bind
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
4. 将 Bind 锁定文件设置为可写:
|
||||
### 4、 将 Bind 锁定文件设置为可写
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# chmod -R 777 /var/named/chroot/var/named/data
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# chmod -R 777 /var/named/chroot/var/named/dynamic
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# chmod -R 777 /var/named/chroot/var/named/data
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# chmod -R 777 /var/named/chroot/var/named/dynamic
|
||||
|
||||
5. 将 /etc/named.conf 拷贝到 bind chroot目录
|
||||
### 5、 将 /etc/named.conf 拷贝到 bind chroot目录
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# cp -p /etc/named.conf /var/named/chroot/etc/named.conf
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# cp -p /etc/named.conf /var/named/chroot/etc/named.conf
|
||||
|
||||
6. 在/etc/named.conf中对 bind 进行配置。在文件尾添加 example.local 域信息:
|
||||
### 6、 在/etc/named.conf中对 bind 进行配置。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# vi /var/named/chroot/etc/named.conf
|
||||
|
||||
在 named.conf 中创建转发域(Forward Zone)与反向域(Reverse Zone):
|
||||
在 named.conf 文件尾添加 **example.local** 域信息, 创建转发域(Forward Zone)与反向域(Reverse Zone)(LCTT 译注:这里example.local 并非一个真实有效的互联网域名,而是通常用于本地测试的一个域名;如果你需要做权威 DNS 解析,你可以将你拥有的域名如这里所示配置解析。):
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# vi /var/named/chroot/etc/named.conf
|
||||
|
||||
--
|
||||
..
|
||||
..
|
||||
zone "example.local" {
|
||||
@ -56,7 +58,7 @@ BIND(Berkeley internet Name Daemon)也叫做NAMED是现今互联网上使用
|
||||
..
|
||||
..
|
||||
|
||||
named.conf 完全配置
|
||||
named.conf 完全配置如下:
|
||||
|
||||
//
|
||||
// named.conf
|
||||
@ -123,9 +125,9 @@ named.conf 完全配置
|
||||
include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones";
|
||||
include "/etc/named.root.key";
|
||||
|
||||
7. 为 example.local 域名创建转发域与反向域文件
|
||||
### 7、 为 example.local 域名创建转发域与反向域文件
|
||||
|
||||
a)创建转发域
|
||||
#### a)创建转发域
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# vi /var/named/chroot/var/named/example.local.zone
|
||||
|
||||
@ -154,11 +156,11 @@ a)创建转发域
|
||||
ns1 IN A 192.168.0.70
|
||||
ns2 IN A 192.168.0.80
|
||||
|
||||
b)创建反向域
|
||||
#### b)创建反向域
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# vi /var/named/chroot/var/named/192.168.0.zone
|
||||
|
||||
----
|
||||
--
|
||||
|
||||
;
|
||||
; Addresses and other host information.
|
||||
@ -175,7 +177,9 @@ b)创建反向域
|
||||
|
||||
70.0.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN PTR mx.example.local.
|
||||
70.0.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN PTR ns1.example.local.
|
||||
80.0.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN PTR ns2.example.local.。开机自启动 bind-chroot 服务:
|
||||
80.0.168.192.in-addr.arpa. IN PTR ns2.example.local.。
|
||||
|
||||
### 8、开机自启动 bind-chroot 服务:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# /usr/libexec/setup-named-chroot.sh /var/named/chroot on
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# systemctl stop named
|
||||
@ -184,15 +188,13 @@ b)创建反向域
|
||||
[root@centos7 ~]# systemctl enable named-chroot
|
||||
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/named-chroot.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/named-chroot.service'
|
||||
|
||||
[跳转到档案页,阅读更多文章][1]
|
||||
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ehowstuff.com/how-to-setup-bind-chroot-dns-server-on-centos-7-0-vps/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[skytech][a]
|
||||
译者:[SPccman](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[SPccman](https://github.com/SPccman)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
(translating by runningwater)
|
||||
Compact Text Editors Great for Remote Editing and Much More
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A text editor is software used for editing plain text files. This type of software has many different uses including modifying configuration files, writing programming language source code, jotting down thoughts, or even making a grocery list. Given that editors can be used for such a diverse range of activities, it is worth spending the time finding an editor that best suites your preferences.
|
||||
@ -207,7 +208,7 @@ nano, like Pico, is keyboard-oriented, controlled with control keys.
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20141011073917230/TextEditors.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,157 +0,0 @@
|
||||
A Step By Step Guide To Installing Xubuntu Linux
|
||||
================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
### Introduction To Installing Xubuntu Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This guide shows how to install Xubuntu Linux using step by step instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
Why would you want to install Xubuntu? Here are three reasons:
|
||||
|
||||
1. You have a computer running Windows XP that is out of support
|
||||
2. You have [a computer that is running really slowly][1] and you want a lightweight but modern operating system
|
||||
3. You want to be able to customise your computing experience
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing you need to do is download Xubuntu and create a bootable USB drive.
|
||||
|
||||
After you have done this boot into a live version of Xubuntu and click on the install Xubuntu icon.
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose Your Installation Language ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The first step is to choose your language.
|
||||
|
||||
Click on the language in the left pane and then click "Continue"
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose Wireless Connection ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The second step requires you to choose your internet connection. This is not a required step and there are reasons why you might choose not to set up your internet connection at this stage.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a [poor internet connection][3] it is a good idea not to choose a wireless network because the installer will attempt to download updates as part of the installation. Your installation will therefore take a long time to complete.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a really [good internet connection][4] choose your wireless network and enter the security key.
|
||||
|
||||
### Be Prepared ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You will now see a checklist which shows how well prepared you are for installing Xubuntu:
|
||||
|
||||
- Do you have at least 6.2 gigabytes of disk space
|
||||
- Are you connected to the internet
|
||||
- Are you connected to a power source
|
||||
|
||||
The only one that is a necessity is the disk space.
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned in the previous step you can install Xubuntu without being connected to the internet. You can install updates once the installation is complete.
|
||||
|
||||
You only need to be connected to a power source if you are likely to run out of battery power during the installation.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that if you are connected to the internet there is a checkbox to turn off the option to download updates while installing.
|
||||
|
||||
There is also a checkbox that lets you install third party software to enable you to [play MP3s][5] and watch [Flash videos][6]. This is a step that can be completed post installation as well.
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose Your Installation Type ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The next step is to choose the installation type. The options available will depend on what is already installed on the computer.
|
||||
|
||||
In my case I was installing Xubuntu on a netbook over the top of [Ubuntu MATE][7] and so I had options to reinstall Ubuntu, erase and reinstall, install Xubuntu alongside Ubuntu or something else.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have Windows on your computer you will have options to install alongside, replace Windows with Xubuntu or something else.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide shows how to install Xubuntu on a computer and not how to dual boot. That is a completely different guide altogether.
|
||||
|
||||
Choose the option to replace your operating system with Xubuntu and click "Continue"
|
||||
|
||||
Note: This will cause your disk to be wiped and you should backup all of your data before continuing
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose The Disk To Install To ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Select the drive you wish to install Xubuntu to.
|
||||
|
||||
Click "Install Now".
|
||||
|
||||
A warning will appear telling you that the drive will be wiped and you will be shown a list of partitions that will be created.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: This is the very last chance to change your mind. If you click continue the disk will be wiped and Xubuntu will be installed
|
||||
|
||||
Click "Continue" to install Xubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose Your Location ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You are now required to choose your location by clicking on the map. This sets your timezone so that your clock is set to the right time.
|
||||
|
||||
After you have selected the correct location click "Continue".
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose Your Keyboard Layout ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Choose your keyboard layout.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this select the language of your keyboard in the left hand pane and then choose the exact layout in the right pane such as dialect, number of keys etc.
|
||||
|
||||
You can click the "Detect Keyboard Layout" button to automatically select the best keyboard layout.
|
||||
|
||||
To make sure the keyboard layout is set correctly enter text into the "Type here to test your keyboard". Pay close attention to function keys and symbols such as pound and dollar symbols.
|
||||
|
||||
Don't worry if you don't get this right during installation. You can set the keyboard layout again within Xubuntu's system settings post installation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Add A User ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
n order to use Xubuntu you will need to have at least one user set up and so the installer requires you to create a default user.
|
||||
|
||||
Enter your name and a name to distinguish the computer into the first two boxes.
|
||||
|
||||
Choose a username and [set up a password][8] for the user. You will need to type the password in twice to make sure you have set the password correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want Xubuntu to automatically login without having to enter a password check the box marked "Log in automatically". Personally I would never recommend doing this though.
|
||||
|
||||
The better option is to check the "Require my password to log in" radio button and if you want to be completely secure check the "Encrypt my home folder" option.
|
||||
|
||||
Click "Continue" to move on.
|
||||
|
||||
### Wait For Installation To Complete ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The files will now be copied to your computer and Xubuntu will be installed.
|
||||
|
||||
During this process you will see a short slide show. You can go and [make some coffee][9] at this point and relax.
|
||||
|
||||
A message will appear stating that you can continue to try Xubuntu or reboot to start using the newly installed Xubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
When you are ready, reboot and remove the USB drive.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: To install Xubuntu on a UEFI based machine requires some extra steps not included here. These instructions will be added as a separate guide
|
||||
|
||||
via : http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/A-Step-By-Step-Guide-To-Installing-Xubuntu-Linux.htm#step-heading
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gary Newell][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linux.about.com/bio/Gary-Newell-132058.htm
|
||||
[1]:http://windows.about.com/od/maintainandfix/a/8ways2speedup.htm
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-Persistent-Bootable-Xubuntu-Linux-USB-Drive.htm
|
||||
[3]:http://netforbeginners.about.com/od/basicinternethardware/f/Why-Internet-Connections-Can-Be-Slow.htm
|
||||
[4]:http://netforbeginners.about.com/b/2011/09/07/test-your-internet-connection-speed-here.htm
|
||||
[5]:http://mp3.about.com/od/freebies/tp/freemusictp.htm
|
||||
[6]:http://animation.about.com/od/2danimationtutorials/ss/2d_fla_lesson1.htm
|
||||
[7]:http://www.everydaylinuxuser.com/2014/11/ubuntu-mate-vs-lubuntu-on-old-netbook.html
|
||||
[8]:http://netsecurity.about.com/cs/generalsecurity/a/aa112103b.htm
|
||||
[9]:http://coffeetea.about.com/od/preparationandrecipes/
|
||||
@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
|
||||
(translating by runningwater)
|
||||
2015: Open Source Has Won, But It Isn't Finished
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> After the wins of 2014, what's next?
|
||||
|
||||
At the beginning of a new year, it's traditional to look back over the last 12 months. But as far as this column is concerned, it's easy to summarise what happened then: open source has won. Let's take it from the top:
|
||||
|
||||
**Supercomputers**. Linux is so dominant on the Top 500 Supercomputers lists it is almost embarrassing. The [November 2014 figures][1] show that 485 of the top 500 systems were running some form of Linux; Windows runs on just one. Things are even more impressive if you look at the numbers of cores involved. Here, Linux is to be found on 22,851,693 of them, while Windows is on just 30,720; what that means is that not only does Linux dominate, it is particularly strong on the bigger systems.
|
||||
|
||||
**Cloud computing**. The Linux Foundation produced an interesting [report][2] last year, which looked at the use of Linux in the cloud by large companies. It found that 75% of them use Linux as their primary platform there, against just 23% that use Windows. It's hard to translate that into market share, since the mix between cloud and non-cloud needs to be factored in; however, given the current popularity of cloud computing, it's safe to say that the use of Linux is high and increasing. Indeed, the same survey found Linux deployments in the cloud have increased from 65% to 79%, while those for Windows have fallen from 45% to 36%. Of course, some may not regard the Linux Foundation as totaly disinterested here, but even allowing for that, and for statistical uncertainties, it's pretty clear which direction things are moving in.
|
||||
|
||||
**Web servers**. Open source has dominated this sector for nearly 20 years - an astonishing record. However, more recently there's been some interesting movement in market share: at one point, Microsoft's IIS managed to overtake Apache in terms of the total number of Web servers. But as Netcraft explains in its most recent [analysis][3], there's more than meets the eye here:
|
||||
|
||||
> This is the second month in a row where there has been a large drop in the total number of websites, giving this month the lowest count since January. As was the case in November, the loss has been concentrated at just a small number of hosting companies, with the ten largest drops accounting for over 52 million hostnames. The active sites and web facing computers metrics were not affected by the loss, with the sites involved being mostly advertising linkfarms, having very little unique content. The majority of these sites were running on Microsoft IIS, causing it to overtake Apache in the July 2014 survey. However the recent losses have resulted in its market share dropping to 29.8%, leaving it now over 10 percentage points behind Apache.
|
||||
|
||||
As that indicates, Microsoft's "surge" was more apparent than real, and largely based on linkfarms with little useful content. Indeed, Netcraft's figures for active sites paints a very different picture: Apache has 50.57% market share, with nginx second on 14.73%; Microsoft IIS limps in with a rather feeble 11.72%. This means that open source has around 65% of the active Web server market - not quite at the supercomputer level, but pretty good.
|
||||
|
||||
**Mobile systems**. Here, the march of open source as the foundation of Android continues. Latest figures show that Android accounted for [83.6%][4] of smartphone shipments in the third quarter of 2014, up from 81.4% in the same quarter the previous year. Apple achieved 12.3%, down from 13.4%. As far as tablets are concerned, Android is following a similar trajectory: for the second quarter of 2014, Android notched up around [75% of global tablet sales][5], while Apple was on 25%.
|
||||
|
||||
**Embedded systems**. Although it's much harder to quantify the market share of Linux in the important embedded system market, but figures from one 2013 study indicated that around [half of planned embedded systems][6] would use it.
|
||||
|
||||
**Internet of Things**. In many ways this is simply another incarnation of embedded systems, with the difference that they are designed to be online, all the time. It's too early to talk of market share, but as I've [discussed][7] recently, AllSeen's open source framework is coming on apace. What's striking by their absence are any credible closed-source rivals; it therefore seems highly likely that the Internet of Things will see supercomputer-like levels of open source adoption.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, this level of success always begs the question: where do we go from here? Given that open source is approaching saturation levels of success in many sectors, surely the only way is down? In answer to that question, I recommend a thought-provoking essay from 2013 written by Christopher Kelty for the Journal of Peer Production, with the intriguing title of "[There is no free software.][8]" Here's how it begins:
|
||||
|
||||
> Free software does not exist. This is sad for me, since I wrote a whole book about it. But it was also a point I tried to make in my book. Free software—and its doppelganger open source—is constantly becoming. Its existence is not one of stability, permanence, or persistence through time, and this is part of its power.
|
||||
|
||||
In other words, whatever amazing free software 2014 has already brought us, we can be sure that 2015 will be full of yet more of it, as it continues its never-ending evolution.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.computerworlduk.com/blogs/open-enterprise/open-source-has-won-3592314/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[lyn Moody][a]
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.computerworlduk.com/author/glyn-moody/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.top500.org/statistics/list/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/publications/linux-foundation/linux-end-user-trends-report-2014
|
||||
[3]:http://news.netcraft.com/archives/2014/12/18/december-2014-web-server-survey.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.cnet.com/news/android-stays-unbeatable-in-smartphone-market-for-now/
|
||||
[5]:http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/tech/tech-news/Android-tablet-market-share-hits-70-in-Q2-iPads-slip-to-25-Survey/articleshow/38966512.cms
|
||||
[6]:http://linuxgizmos.com/embedded-developers-prefer-linux-love-android/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.computerworlduk.com/blogs/open-enterprise/allseen-3591023/
|
||||
[8]:http://peerproduction.net/issues/issue-3-free-software-epistemics/debate/there-is-no-free-software/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[Translating by Stevearzh]
|
||||
Why Mac users don’t switch to Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux and Mac users share at least one common thing: they prefer not to use Windows. But after that the two groups part company and tend to go their separate ways. But why don’t more Mac users switch to Linux? Is there something that prevents Mac users from making the jump?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
Linus Torvalds responds to Ars about diversity, niceness in open source
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Acknowledges diversity factors, says "we're different in so many other ways."
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
See, sometimes Linus isn't flicking people off.
|
||||
|
||||
Athanasios Kasampalis
|
||||
|
||||
On Thursday, Linux legend Linus Torvalds sent a lengthy statement to Ars Technica responding to [statements he made in Auckland, New Zealand earlier that day about diversity and "niceness"][2] in the open source sector.
|
||||
|
||||
"What I wanted to say [at the keynote]—and clearly must have done very badly—is that one of the great things about open source is exactly the fact that different people are so different," Torvalds wrote via e-mail. "I think people sometimes look at it as being just 'programmers,' which is not true. It's about all the people who are more oriented toward commercial things, too. It's about all those people who are interested in legal issues—and the social ones, too!"
|
||||
|
||||
Torvalds spoke to what he thought was a larger concept of "diversity" than what has been mentioned a lot in recent stories on the topic, including economic disparity, language, and culture (even between neighboring European countries). "There's a lot of talk about gender and sexual preferences and race, but we're different in so many other ways, too," he wrote.
|
||||
|
||||
"'Open source' as a term and as a movement hasn't been about 'you have to be a believer,'" Torvalds added. "It's not a religion. It's not an 'us vs them' thing. We've been able to work with all those 'evil commercial interests' and companies who also do proprietary software. And I think that was one of the things that the Linux community (and others—don't get me wrong, it's not unique to us) did and does well."
|
||||
|
||||
Torvalds also talked about progress since the GPL vs. BSD "flame wars" from the '80s and early '90s, saying that the open source movement brought more technology and less "ideology" to the sector. "Which is not to say that a lot of people aren't around because they believe it's the 'ethical' thing to do (I do myself too)," Torvalds added, "but you don't have to believe that, and you can just do it because it's the most fun, or the most efficient way to do technology development."
|
||||
|
||||
### “This ‘you have to be nice’ seems very popular in the US” ###
|
||||
|
||||
He then sent a second e-mail to Ars about the topic of "niceness" that came up during the keynote. He said that his return to his Auckland hotel was delayed by "like three hours" because of hallway conversations about this very topic.
|
||||
|
||||
"I don't know where you happen to be based, but this 'you have to be nice' seems to be very popular in the US," Torvalds continued, calling the concept an "ideology."
|
||||
|
||||
"The same way we have developers and marketing people and legal people who speak different languages, I think we can have some developers who are used to—and prefer—a more confrontational style, and still **also** have people who don't," he wrote.
|
||||
|
||||
He lambasted the "brainstorming" model of having a criticism-free bubble to bounce ideas off of. "Maybe it works for some people, but I happen to simply not believe in it," he said. "I'd rather be really confrontational, and bad ideas should be [taken] down aggressively. Even good ideas need to be vigorously defended."
|
||||
|
||||
"Maybe it's just because I like arguing," Torvalds added. "I'm just not a huge believer in politeness and sensitivity being preferable over bluntly letting people know your feelings. But I also understand that other people are driven away by cursing and crass language when it all gets a bit too carried away." To that point, Torvalds said that the open source movement might simply need more "people who are good at mediating," as opposed to asking developers to calm their own tone or attitude.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://arstechnica.com/business/2015/01/linus-torvalds-responds-to-ars-about-diversity-niceness-in-open-source/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sam Machkovech][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/samred/
|
||||
[1]:https://secure.flickr.com/photos/12693492@N04/1338136415/in/photolist-33fikv-3jXFce-3ALpLy-4m6Shj-4pADUg-4pHwcW-4rNTR7-4GMhKc-4HM2qp-4JSHKa-4PomQo-4SKxMo-58LBYf-5iVNX6-5tXbB8-5xi67A-5A8rRc-5C8fAT-5Ccxjw-5EcYvx-5UoNTc-5UoVJK-5Uti6q-5UuiX2-5UuE2B-5UyEJu-5UyHMf-5UyJ2G-5UFbXP-5UFg8Z-5UFhwV-5UKDkG-5UKDP9-5UTHGv-5XM2s2-5YFmLu-65N31L-6pSwh7-6trmfx-6H2uZP-6JVV4V-71qkot-71BBbk-72vuYo-73j9yB-79aQ2a-79bfqe-79EKPH-79EXvD-79PuG5-7a4BxF
|
||||
[2]:http://arstechnica.com/business/2015/01/linus-torvalds-on-why-he-isnt-nice-i-dont-care-about-you/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,91 @@
|
||||
Did this JavaScript break the console?
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
#Q:
|
||||
|
||||
Just doing some JavaScript stuff in google chrome (don't want to try in other browsers for now, in case this is really doing real damage) and I'm not sure why this seemed to break my console.
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
>var x = "http://www.foo.bar/q?name=%%this%%";
|
||||
<undefined
|
||||
>x
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After x (and enter) the console stops working... I restarted chrome and now when I do a simple
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
console.clear();
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It's giving me
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
Console was cleared
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And not clearing the console. Now in my scripts console.log's do not register and I'm wondering what is going on. 99% sure it has to do with the double percent signs (%%).
|
||||
|
||||
Anyone know what I did wrong or better yet, how to fix the console?
|
||||
|
||||
[A bug report for this issue has been filed here.][1]
|
||||
Edit: Feeling pretty dumb, but I had Preserve log checked... That's why the console wasn't clearing.
|
||||
|
||||
#A:
|
||||
|
||||
As discussed in the comments, there are actually many different ways of constructing a string that causes this issue, and it is not necessary for there to be two percent signs in most cases.
|
||||
|
||||
```TXT
|
||||
http://example.com/%
|
||||
http://%%%
|
||||
http://ab%
|
||||
http://%ab
|
||||
http://%zz
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
However, it's not just the presence of a percent sign that breaks the Chrome console, as when we enter the following well-formed URL, the console continues to work properly and produces a clickable link.
|
||||
|
||||
```TXT
|
||||
http://ab%20cd
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, the strings `http://%`, and `http://%%` will also print properly, since Chrome will not auto-link a URL-link string unless the [`http://`][2] is followed by at least 3 characters.
|
||||
|
||||
From here I hypothesized that the issue must be in the process of linking a URL string in the console, likely in the process of decoding a malformed URL. I remembered that the JavaScript function `decodeURI` will throw an exception if given a malformed URL, and since Chrome's developer tools are largely written in JavaScript, could this be the issue that is evidently crashing the developer console?
|
||||
|
||||
To test this theory, I ran Chrome by the command link, to see if any errors were being logged.
|
||||
|
||||
Indeed, the same error you would see if you ran decodeURI on a malformed URL (i.e. decodeURI('http://example.com/%')) was being printed to the console:
|
||||
|
||||
>[4810:1287:0107/164725:ERROR:CONSOLE(683)] "Uncaught URIError: URI malformed", source: chrome-devtools://devtools/bundled/devtools.js (683)
|
||||
>So, I opened the URL 'chrome-devtools://devtools/bundled/devtools.js' in Chrome, and on line 683, I found the following.
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
{var parsedURL=new WebInspector.ParsedURL(decodeURI(url));var origin;var folderPath;var name;if(parsedURL.isValid){origin=parsedURL.scheme+"://"+parsedURL.host;if(parsedURL.port)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As we can see, `decodeURI(url)` is being called on the URL without any error checking, thus throwing the exception and crashing the developer console.
|
||||
|
||||
A real fix for this issue will come from adding error handling to the Chrome console code, but in the meantime, one way to avoid the issue would be to wrap the string in a complex data type like an array to prevent parsing when logging.
|
||||
|
||||
```javascript
|
||||
var x = "http://example.com/%";
|
||||
console.log([x]);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Thankfully, the broken console issue does not persist once the tab is closed, and will not affect other tabs.
|
||||
|
||||
###Update:
|
||||
|
||||
Apparently, the issue can persist across tabs and restarts if Preserve Log is checked. Uncheck this if you are having this issue.
|
||||
|
||||
via:[stackoverflow](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/27828804/did-this-javascript-break-the-console/27830948#27830948)
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Alexander O'Mara][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://stackoverflow.com/users/3155639/alexander-omara
|
||||
[1]:https://code.google.com/p/chromium/issues/detail?id=446975
|
||||
[2]:https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/decodeURI
|
||||
95
sources/talk/20150121 If a 32-bit integer overflows.md
Normal file
95
sources/talk/20150121 If a 32-bit integer overflows.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
If a 32-bit integer overflows, can we use a 40-bit structure instead of a 64-bit long one?
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
#Q:
|
||||
|
||||
If, say, a 32-bit integer is overflowing, instead of upgrading int to long, can we make use of some 40-bit type if we need a range only within 240, so that we save 24 (64-40) bits for every integer?
|
||||
|
||||
If so, how?
|
||||
|
||||
I have to deal with billions and space is a bigger constraint.
|
||||
|
||||
#A:
|
||||
|
||||
##Yes, but...
|
||||
|
||||
It is certainly possible, but it is usually nonsensical (for any program that doesn't use billions of these numbers):
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
#include <stdint.h> // don't want to rely on something like long long
|
||||
struct bad_idea
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint64_t var : 40;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, var will indeed have a width of 40 bits at the expense of much less efficient code generated (it turns out that "much" is very much wrong -- the measured overhead is a mere 1-2%, see timings below), and usually to no avail. Unless you have need for another 24-bit value (or an 8 and 16 bit value) which you wish to pack into the same structure, alignment will forfeit anything that you may gain.
|
||||
|
||||
In any case, unless you have billions of these, the effective difference in memory consumption will not be noticeable (but the extra code needed to manage the bit field will be noticeable!).
|
||||
|
||||
###Note:
|
||||
|
||||
The question has in the mean time been updated to reflect that indeed billions of numbers are needed, so this may be a viable thing to do, presumed that you take measures not to lose the gains due to structure alignment and padding, i.e. either by storing something else in the remaining 24 bits or by storing your 40-bit values in structures of 8 each or multiples thereof).
|
||||
Saving three bytes a billion times is worthwhile as it will require noticeably fewer memory pages and thus cause fewer cache and TLB misses, and above all page faults (a single page fault weighting tens of millions instructions).
|
||||
|
||||
While the above snippet does not make use of the remaining 24 bits (it merely demonstrates the "use 40 bits" part), something akin to the following will be necessary to really make the approach useful in a sense of preserving memory -- presumed that you indeed have other "useful" data to put in the holes:
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
struct using_gaps
|
||||
{
|
||||
uint64_t var : 40;
|
||||
uint64_t useful_uint16 : 16;
|
||||
uint64_t char_or_bool : 8;
|
||||
};
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Structure size and alignment will be equal to a 64 bit integer, so nothing is wasted if you make e.g. an array of a billion such structures (even without using compiler-specific extensions). If you don't have use for an 8-bit value, you could also use an 48-bit and a 16-bit value (giving a bigger overflow margin).
|
||||
Alternatively you could, at the expense of usability, put 8 40-bit values into a structure (least common multiple of 40 and 64 being 320 = 8*40). Of course then your code which accesses elements in the array of structures will become much more complicated (though one could probably implement an operator[] that restores the linear array functionality and hides the structure complexity).
|
||||
|
||||
Update:
|
||||
Wrote a quick test suite, just to see what overhead the bitfields (and operator overloading with bitfield refs) would have. Posted code (due to length) at gcc.godbolt.org, test output from my Win7-64 machine is:
|
||||
|
||||
```TXT
|
||||
Running test for array size = 1048576
|
||||
what alloc seq(w) seq(r) rand(w) rand(r) free
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
uint32_t 0 2 1 35 35 1
|
||||
uint64_t 0 3 3 35 35 1
|
||||
bad40_t 0 5 3 35 35 1
|
||||
packed40_t 0 7 4 48 49 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Running test for array size = 16777216
|
||||
what alloc seq(w) seq(r) rand(w) rand(r) free
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
uint32_t 0 38 14 560 555 8
|
||||
uint64_t 0 81 22 565 554 17
|
||||
bad40_t 0 85 25 565 561 16
|
||||
packed40_t 0 151 75 765 774 16
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Running test for array size = 134217728
|
||||
what alloc seq(w) seq(r) rand(w) rand(r) free
|
||||
-----------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
uint32_t 0 312 100 4480 4441 65
|
||||
uint64_t 0 648 172 4482 4490 130
|
||||
bad40_t 0 682 193 4573 4492 130
|
||||
packed40_t 0 1164 552 6181 6176 130
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
What one can see is that the extra overhead of bitfields is neglegible, but the operator overloading with bitfield reference as a convenience thing is rather drastic (about 3x increase) when accessing data linearly in a cache-friendly manner. On the other hand, on random access it barely even matters.
|
||||
|
||||
These timings suggest that simply using 64-bit integers would be better since they are still faster overall than bitfields (despite touching more memory), but of course they do not take into account the cost of page faults with much bigger datasets. It might look very different once you run out of physical RAM (I didn't test that).
|
||||
|
||||
------
|
||||
|
||||
via:[stackoverflow](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/27705409/if-a-32-bit-integer-overflows-can-we-use-a-40-bit-structure-instead-of-a-64-bit/27705562#27705562)
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Damon][a][Michael Kohne][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://stackoverflow.com/users/572743/damon
|
||||
[b]:http://stackoverflow.com/users/5801/michael-kohne
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
How are C data types “supported directly by most computers”?
|
||||
---------
|
||||
|
||||
#Q:
|
||||
|
||||
I am reading K&R's *The C Programming Language*” and came across this statement [Introduction, p. 3]:
|
||||
|
||||
>Because the data types and control structures provided by C are supported directly by most computers, the run-time library required to implement self-contained programs is tiny.
|
||||
|
||||
What does the bolded statement mean? Is there an example of a data type or a control structure that isn't supported directly by a computer?
|
||||
|
||||
#A:
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, there are data types not directly supported.
|
||||
|
||||
On many embedded systems, there is no hardware floating point unit. So, when you write code like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
float x = 1.0f, y = 2.0f;
|
||||
return x + y;
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It gets translated into something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```C
|
||||
unsigned x = 0x3f800000, y = 0x40000000;
|
||||
return _float_add(x, y);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then the compiler or standard library has to supply an implementation of `_float_add()`, which takes up memory on your embedded system. If you're counting bytes on a really tiny system, this can add up.
|
||||
|
||||
Another common example is 64-bit integers (`long long` in the C standard since 1999), which are not directly supported by 32-bit systems. Old SPARC systems didn't support integer multiplication, so multiplication had to be supplied by the runtime. There are other examples.
|
||||
|
||||
##Other languages
|
||||
|
||||
By comparison, other languages have more complicated primitives.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, a Lisp symbol requires a lot of runtime support, just like tables in Lua, strings in Python, arrays in Fortran, et cetera. The equivalent types in C are usually either not part of the standard library at all (no standard symbols or tables) or they are much simpler and don't require much runtime support (arrays in C are basically just pointers, nul-terminated strings are almost as simple).
|
||||
|
||||
##Control structures
|
||||
|
||||
A notable control structure missing from C is exception handling. Nonlocal exit is limited to `setjmp()` and `longjmp()`, which just save and restore certain parts of processor state. By comparison, the C++ runtime has to walk the stack and call destructors and exception handlers.
|
||||
|
||||
----
|
||||
via:[stackoverflow](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/27977522/how-are-c-data-types-supported-directly-by-most-computers/27977605#27977605)
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dietrich Epp][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://stackoverflow.com/users/82294/dietrich-epp
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
Top 10 FOSS legal developments of 2014
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Image by : opensource.com
|
||||
|
||||
The year 2014 continued the trend of the increasing importance of legal issues for the FOSS community. Continuing [the tradition of looking back][1] over the top ten legal developments in FOSS, my selection of the top ten issues for 2014 is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Courts interpret General Public License version 2 (GPLv2) ###
|
||||
|
||||
The GPLv2 continues to be the most widely used and most important license for free and open source software. Black Duck Software estimates that 16 billion lines of code are licensed under the GPLv2. Despite its importance, the GPLv2 has been the subject of very few court decisions, and virtually all of the most important terms of the GPLv2 have not been interpreted by courts. This lack of court decisions is about to change due to the five interrelated cases arising from an attempt by Versata Software, Inc. (Versata) to terminate its software license to Ameriprise Financial, Inc. Versata’s product included software licensed by Ximpleware, Inc. (Ximpleware) under the GPLv2, but Versata had not complied with the terms of the GPLv2. Ximpleware sued Versata and eight of its customers for both copyright and patent infringement. (For a more detailed description of the facts [read this article][2].) This dispute is important because Ximpleware is the first commercial enforcer of the GPLv2 in which the courts are likely to issue decisions and Ximpleware is seeking monetary damages rather than compliance.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. GPL guides ###
|
||||
|
||||
Two of the most important organizations enforcing the GPL family of licenses recently provided [guidance on compliance][3]: On October 31, the Software Freedom Law Center published the second version of their Practical Guide to GPL Compliance. Several days later, the Software Conservancy and the Free Software Foundation published the first version of their guide, the Copyleft, and the GNU General Public License: [A Comprehensive Tutorial and Guide][4]. These guides are required reading for anyone managing FOSS.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. EU Commission (EC) to revise FOSS policy ###
|
||||
|
||||
Governments are one of the most important users of software but have had a mixed record in using and contributing to FOSS (free and open source software). The EC recently announced that it intends to remove the barriers that may hinder code contributions to FOSS projects. In particular, the EC wants to clarify legal aspects, including intellectual property rights, copyright, and which author or authors to name when submitting code to the upstream repositories. Pierre Damas, Head of Sector at the Directorate General for IT, [hopes that such clarification][5] will motivate many of the EC’s software developers and functionaries to promote the use of FOSS at the EC.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Validation of FOSS business model by Hortonworks IPO ###
|
||||
|
||||
Hortonworks provides services and support for the Hadoop data analysis software managed by the Apache Software Foundation. Hortonworks is one of three venture backed companies based on the Hadoop software. Hortonworks went public this fall and immediately rose 65% in share price, valuing the company at over $1 billion. The market for Hadoop products, software, and services is projected to reach $50.2 billion in 2020, up from $1.5 billion in 2012.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Core Infrastructure Initiative ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux Foundation put together [a consortium of companies][6] to support the many smaller open source projects that are critical to software ecosystem, such as OpenSSL. This effort was a response to the Heartbleed problem with OpenSSL in 2013, which I described in last year’s summary. This consortium is a great example of the ability of the FOSS community to come together to solve community problems.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Linux SCO case terminated again ###
|
||||
|
||||
The lawsuit by Santa Cruz Operations, Inc. (SCO) against IBM claiming that Linux includes Unix code was once a potentially major challenge to FOSS. Despite losing its suit against Novell, the bankruptcy court allowed SCO to continue its suit against IBM. I thought this case [had been concluded in 2008][7], but Judge Nuffer appears to have put the case to rest on December 15, 2014. He dismissed the case against IBM based on the decisions in the Novell case (although SCO could still appeal once again):
|
||||
|
||||
*It is further ORDERED that, with respect to all remaining claims and counterclaims, SCO is bound by, and may not here re-litigate, the rulings in the Novell Judgment that Novell (not SCO) owns the copyrights to the pre-1996 UNIX source code, and that Novell waived SCO’s contract claims against IBM for alleged breaches of the licensing agreements pursuant to which IBM licensed such source code.*
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. FOSS trademark issues ###
|
||||
|
||||
The use of trademarks in FOSS projects continues to raise issues. This year brought the settlement of the dispute over the “Python” mark between the Python Software Foundation and Veber, a small hosting company in the UK. Veber had decided to use "Python" in branding certain of its products and services. In addition, the OpenStack Foundation is working through the application of trademarks to the OpenStack project through its [DefCore committee][8].
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Use of FOSS by commercial companies expands ###
|
||||
|
||||
We have discussed in the past how many large companies are using FOSS as an explicit strategy to build their software. Jim Zemlin, Executive Director of the Linux Foundation, has described this strategic use of FOSS as external “research and development.” His conclusions are supported by Gartner who noted that “the top tech companies are still spending tens of billions of dollars on software research and development, the smart ones are leveraging open source for 80 percent of the code and spending their money on the remaining 20 percent, which represents their program’s ‘special sauce.’” The scope of this trend was emphasized by Microsoft’s announcement that it was “open sourcing” the .NET software framework (this software is used by millions of developers to build and operate websites and other large online applications).
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Rockstar Consortium threat evaporates ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Rockstar Consortium was formed by Microsoft, Blackberry, Ericsson, Sony, and Apple to exploit the 6,000 patents from Nortel Networks. The Rockstar Consortium sued Google for infringement of the Android operating system. This litigation was aimed at fundamental functions of the Android operating system and could have had a significant effect on the Android ecosystem. The Rockstar Consortium settled its litigation with Google this year, but then sold 4,000 of its patents to RPX, the patent defense firm (financed by a number of companies as well as RPX). The remaining patents were distributed to the members of the Rockstar Consortium.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Android litigation ###
|
||||
|
||||
The litigation surrounding Android continued this year, with significant developments in the patent litigation between Apple Computer, Inc. (Apple) and Samsung Electronics, Inc. (Samsung) and the copyright litigation over the Java APIs between Oracle Corporation (Oracle) and Google, Inc. (Google). Apple and Samsung have agreed to end patent disputes in nine countries, but they will continue the litigation in the US. As I stated last year, the Rockstar Consortium was a wild card in this dispute. However, the Rockstar Consortium settled its litigation with Google this year and sold off its patents, so it will no longer be a risk to the Android ecosystem.
|
||||
|
||||
The copyright litigation regarding the copyrightability of the Java APIs was brought back to life by the Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit (CAFC) decision which overturned [the District Court decision][9]. The District Court had found that Google was not liable for copyright infringement for its admitted copying of the Java APIs: the court found that the Java APIs were either not copyrightable or their use by Google was protected by various defenses to copyright. The CAFC overturned both the decision and the analysis and remanded the case to the District Court for a review of the fair use defense raised by Google. Subsequently, Google filed an appeal to the Supreme Court. The impact of a finding that Google was liable for copyright infringement in this case would have a dramatic effect on Android and, depending on the reasoning, would have a ripple effect across the interpretation of the scope of the “copyleft” terms of the GPL family of licenses which use APIs.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://opensource.com/law/15/1/top-foss-legal-developments-2014
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Mark Radcliffe][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://opensource.com/users/mradcliffe
|
||||
[1]:http://lawandlifesiliconvalley.com/blog/?p=853
|
||||
[2]:http://opensource.com/law/14/12/gplv2-court-decisions-versata
|
||||
[3]:http://www.softwarefreedom.org/resources/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.copyleft.org/guide/
|
||||
[5]:https://joinup.ec.europa.eu/community/osor/news/european-commission-update-its-open-source-policy
|
||||
[6]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/programs/core-infrastructure-initiative
|
||||
[7]:http://lawandlifesiliconvalley.com/blog/?m=200812
|
||||
[8]:https://wiki.openstack.org/wiki/Governance/CoreDefinition
|
||||
[9]:http://law.justia.com/cases/federal/appellate-courts/cafc/13-1021/13-1021-2014-05-09.html
|
||||
126
sources/talk/20150122 Top 10 open source projects of 2014.md
Normal file
126
sources/talk/20150122 Top 10 open source projects of 2014.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
||||
Top 10 open source projects of 2014
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Image credits : [CC0 Public Domain][1], modifications by Jen Wike Huger
|
||||
|
||||
Every year we collect the best of the best open source projects covered on Opensource.com. [Last year's list of 10 projects][2] guided people working and interested in tech throughout 2014. Now, we're setting you up for 2015 with a brand new list of accomplished open source projects.
|
||||
|
||||
Some faces are new. Some have been around and just keep rocking it. Let's dive in!
|
||||
|
||||
## Top 10 open source projects in 2014 ##
|
||||
|
||||
### Docker ###
|
||||
|
||||
[application container platform][3]
|
||||
|
||||
"In the same way that power management and virtualisation has allowed us to get maximum engineering benefit from our server utilisation, the problem of how to really solve first world problems in virtualisation has remained prevalent. Docker's open sourcing in 2013 can really align itself with these pivotal moments in the evolution of open source—providing the extensible building blocks allowing us as engineers and architects to extend distributed platforms like never before." —Richard Morrell, [Senior software engineer Petazzoni on the breathtaking growth of Docker][4].
|
||||
|
||||
**Interview**: VP of Services for Docker talks to Jodi Biddle in [Why is Docker the new craze in virtualization and cloud computing?][5] "I think it's the lightweight nature of Docker combined with the workflow. It's fast, easy to use and a developer-centric DevOps-ish tool. Its mission is basically: make it easy to package and ship code." —James Turnbull.
|
||||
|
||||
### Kubernetes ###
|
||||
|
||||
[orchestration system for containers][6]
|
||||
|
||||
"One of the projects you're starting to hear a lot about in the orchestration space is [Kubernetes][7], which came out of Google's internal container work. It aims to provide features such as high availability and replication, service discovery, and service aggregation." —Gordon Haff, [Open source accelerating the pace of software][8].
|
||||
|
||||
### Taiga ###
|
||||
|
||||
[project management platform][9]
|
||||
|
||||
"It’s almost always the case that the project management tool doesn’t reflect the actual project scenario. One solution to this is using a tool that is intuitive and fits alongside the developer's normal workflow. Additionally, a tool that is quick to update and attracts users to use it. [Taiga][10] is an open source project management tool that aims to solve the basic problem of software usability." —Nitish Tiwari, [Taiga, a new open source project management tool with focus on usability][11].
|
||||
|
||||
### Apache Mesos ###
|
||||
|
||||
[cluster manager][12]
|
||||
|
||||
"[Apache Mesos][13] is a cluster manager that provides efficient resource isolation and sharing across distributed applications or frameworks. It sits between the application layer and the operating system and makes it easier to deploy and manage applications in large-scale clustered environments more efficiently. It can run many applications on a dynamically shared pool of nodes. Prominent users of Mesos include Twitter, Airbnb, MediaCrossing, Xogito and Categorize. —Sachin P Bappalige, [Open source datacenter computing with Apache Mesos][14].
|
||||
|
||||
Interview: Head of Open Source at Twitter talks to Jason Hibbets in [Scale like Twitter with Apache Mesos][15]. "As of today, Twitter has over 270 million active users which produces 500+ million tweets a day, up to 150k+ tweets per second, and more than 100TB+ of compressed data per day. Architecturally, Twitter is mostly composed of services, mostly written in the open source project [Finagle][16], representing the core nouns of the platform such as the user service, timeline service, and so on. Mesos allows theses services to scale to tens of thousands of bare-metal machines and leverage a shared pool of servers across data centers." —Chris Aniszczyk
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenStack ###
|
||||
|
||||
[cloud computing platform][17]
|
||||
|
||||
"As OpenStack continues to mature and slowly make its way into production environments, the focus on the user is continuing to grow. And so, to better meet the needs of users, the community is working hard to get users to meet the next step of engagement by highlighting those users who are change agents both in their organization and within the OpenStack community at large: the superusers." —Jason Baker, [What is an OpenStack superuser][18]?
|
||||
|
||||
**Interview**: Infrastructure manager at CERN talks to Jason Hibbets in [How OpenStack powers the research at CERN][19]. "At CERN, the European Organization for Nuclear Research physicists and engineers are probing the fundamental structure of the universe. In order to do this, we use some of the world's largest and most complex scientific instruments such as the Large Hadron Collider, a 27 KM ring 100m underground on the border between France and Switzerland. OpenStack provides the infrastructure cloud which is used to provide much of the compute resources for this processing." —Tim Bell.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ansible ###
|
||||
|
||||
[IT automation tool][20]
|
||||
|
||||
"A lot of what I want to do is enable people to not only have more free time for beer, but to have more free time for their own projects, their own ideas, and to do new an interesting things." —[Michael DeHaan, Making your IT infrastructure boring with Ansible][21].
|
||||
|
||||
**Interview**: CTO of Ansible talks to Jen Krieger in [Behind the scenes with CTO Michael DeHaan of Ansible][22]. "I like to quote Star Trek 2 a lot. We definitely optimize for 'the needs of the many'. I know Spock dies after he says that, but he does get to come back." —Michael DeHaan
|
||||
|
||||
### ownCloud ###
|
||||
|
||||
[cloud storage tool][23]
|
||||
|
||||
"I was looking for an easy way how to have all my online storage services, such as Google Drive and Dropbox, integrated with my Linux desktop without using some nasty hack, and I finally have a solution that works. I'm here to share it with you. This is not rocket science really, all I did was a little bit of documentation reading, and a couple of clicks." —Jiri Folta, [Using ownCloud to integrate Dropbox, Google Drive, and more in Gnome][24].
|
||||
|
||||
**Listed**: Top 5 open source alternatives: "ownCloud does most everything that the proprietary names do and it keeps control of your information in your hands." —Scott Nesbitt, [Five open source alternatives to popular web apps][25].
|
||||
|
||||
### Apache Hadoop ###
|
||||
|
||||
[framework for big data][26]
|
||||
|
||||
"Apache Hadoop is an open source software framework for storage and large scale processing of data-sets on clusters of commodity hardware. Hadoop is an Apache top-level project being built and used by a global community of contributors and users. It is licensed under the Apache License 2.0." —Sachin P Bappalige, [An introduction to Apache Hadoop for big data][27].
|
||||
|
||||
### Drupal ###
|
||||
|
||||
[content management system (CMS)][28]
|
||||
|
||||
"When it was released in 2011, Drupal 7 was the most accessible open source content management system (CMS) available. I expect that this will be true until the release of Drupal 8. Web accessibility requires constant vigilance and will be something that will always need attention in any piece of software striving to meet the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) 2.0 guidelines." —Mike Gifford, [Drupal 8's accessibility advantage][29].
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenDaylight ###
|
||||
|
||||
[foundation for software defined networking][30]
|
||||
|
||||
"We are seeing more and more that the networking functions traditionally done in the datacenter by dedicated, almost exclusively proprietary hardware and software combinations, are now being defined through software. Leading that charge within the open source community has been the [OpenDaylight Project][31], a collaborative project through the [Linux Foundation][32] working to define the needs which software defined networking may fill and coordinating the efforts of individuals and companies worldwide to create an open source solution to software defined networking (SDN)." —Jason Baker, [Define your network in software with OpenDaylight][33].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://opensource.com/business/14/12/top-10-open-source-projects-2014
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jen Wike Huger][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://opensource.com/users/jen-wike
|
||||
[1]:http://pixabay.com/en/lightbulb-lamp-light-hotspot-336193/
|
||||
[2]:http://opensource.com/life/13/12/top-open-source-projects-2013
|
||||
[3]:https://www.docker.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://opensource.com/business/14/7/interview-jerome-petazzoni-docker
|
||||
[5]:https://opensource.com/business/14/7/why-docker-new-craze-virtualization-and-cloud-computing
|
||||
[6]:http://kubernetes.io/
|
||||
[7]:https://cloud.google.com/compute/docs/containers
|
||||
[8]:http://opensource.com/business/14/11/open-source-accelerating-pace-software
|
||||
[9]:https://taiga.io/
|
||||
[10]:https://github.com/taigaio
|
||||
[11]:https://opensource.com/business/14/10/taiga-open-source-project-management-tool
|
||||
[12]:http://mesos.apache.org/
|
||||
[13]:http://mesos.apache.org/
|
||||
[14]:https://opensource.com/business/14/9/open-source-datacenter-computing-apache-mesos
|
||||
[15]:https://opensource.com/business/14/8/interview-chris-aniszczyk-twitter-apache-mesos
|
||||
[16]:https://twitter.github.io/finagle/
|
||||
[17]:http://www.openstack.org/
|
||||
[18]:https://opensource.com/business/14/5/what-is-openstack-superuser
|
||||
[19]:https://opensource.com/business/14/10/interview-tim-bell-cern-it-operating-systems
|
||||
[20]:http://www.ansible.com/home
|
||||
[21]:https://opensource.com/business/14/12/ansible-it-infrastructure
|
||||
[22]:https://opensource.com/business/14/10/interview-michael-dehaan-ansible
|
||||
[23]:http://owncloud.org/
|
||||
[24]:https://opensource.com/life/14/12/using-owncloud-integrate-dropbox-google-drive-gnome
|
||||
[25]:https://opensource.com/life/14/10/five-open-source-alternatives-popular-web-apps
|
||||
[26]:http://hadoop.apache.org/
|
||||
[27]:http://opensource.com/life/14/8/intro-apache-hadoop-big-data
|
||||
[28]:https://www.drupal.org/
|
||||
[29]:http://opensource.com/business/14/5/new-release-drupal-8-accessibility-advantage
|
||||
[30]:http://www.opendaylight.org/
|
||||
[31]:http://www.opendaylight.org/
|
||||
[32]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[33]:http://opensource.com/business/14/5/defining-your-network-software-opendaylight
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
translating by alim0x
|
||||
|
||||
The history of Android
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Android 2.1—the discovery (and abuse) of animations ###
|
||||
@ -88,11 +90,11 @@ The oft-neglected Music app got a minor update. The four-button home screen was
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:
|
||||
via:
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,180 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How To Recover Windows 7 And Delete Ubuntu In 3 Easy Steps
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Introduction ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is a strange article for me to write as I am normally in a position where I would advocate installing Ubuntu and getting rid of Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
What makes writing this article today doubly strange is that I am choosing to write it on the day that Windows 7 mainstream support comes to an end.
|
||||
|
||||
So why am I writing this now?
|
||||
|
||||
I have been asked on so many occasions now how to remove Ubuntu from a dual booting Windows 7 or a dual booting Windows 8 system and it just makes sense to write the article.
|
||||
|
||||
I spent the Christmas period looking through the comments that people have left on articles and it is time to write the posts that are missing and update some of those that have become old and need attention.
|
||||
|
||||
I am going to spend the rest of January doing just that. This is the first step. If you have Windows 7 dual booting with Ubuntu and you want Windows 7 back without restoring to factory settings follow this guide. (Note there is a separate guide required for Windows 8)
|
||||
|
||||
### The Steps Required To Remove Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. Remove Grub By Fixing The Windows Boot Record
|
||||
1. Delete The Ubuntu Partitions
|
||||
1. Expand The Windows Partition
|
||||
|
||||
### Back Up Your System ###
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin I recommend taking a backup of your system.
|
||||
|
||||
I also recommend not leaving this to chance nor Microsoft's own tools.
|
||||
|
||||
[Click here for a guide showing how to backup your drive using Macrium Reflect.][1]
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any data you wish to save within Ubuntu log into it now and back up the data to external hard drives, USB drives or DVDs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1 - Remove The Grub Boot Menu ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
When you boot your system you will see a menu similar to the one in the image.
|
||||
|
||||
To remove this menu and boot straight into Windows you have to fix the master boot record.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this I am going to show you how to create a system recovery disk, how to boot to the recovery disk and how to fix the master boot record.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Press the "Start" button and search for "backup and restore". Click the icon that appears.
|
||||
|
||||
A window should open as shown in the image above.
|
||||
|
||||
Click on "Create a system repair disc".
|
||||
|
||||
You will need a [blank DVD][2].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Insert the blank DVD in the drive and select your DVD drive from the dropdown list.
|
||||
|
||||
Click "Create Disc".
|
||||
|
||||
Restart your computer leaving the disk in and when the message appears to boot from CD press "Enter" on the keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
A set of "Systems Recovery Options" screens will appear.
|
||||
|
||||
You will be asked to choose your keyboard layout.
|
||||
|
||||
Choose the appropriate options from the lists provided and click "Next".
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The next screen lets you choose an operating system to attempt to fix.
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively you can restore your computer using a system image saved earlier.
|
||||
|
||||
Leave the top option checked and click "Next".
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You will now see a screen with options to repair your disk and restore your system etc.
|
||||
|
||||
All you need to do is fix the master boot record and this can be done from the command prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
Click "Command Prompt".
|
||||
|
||||
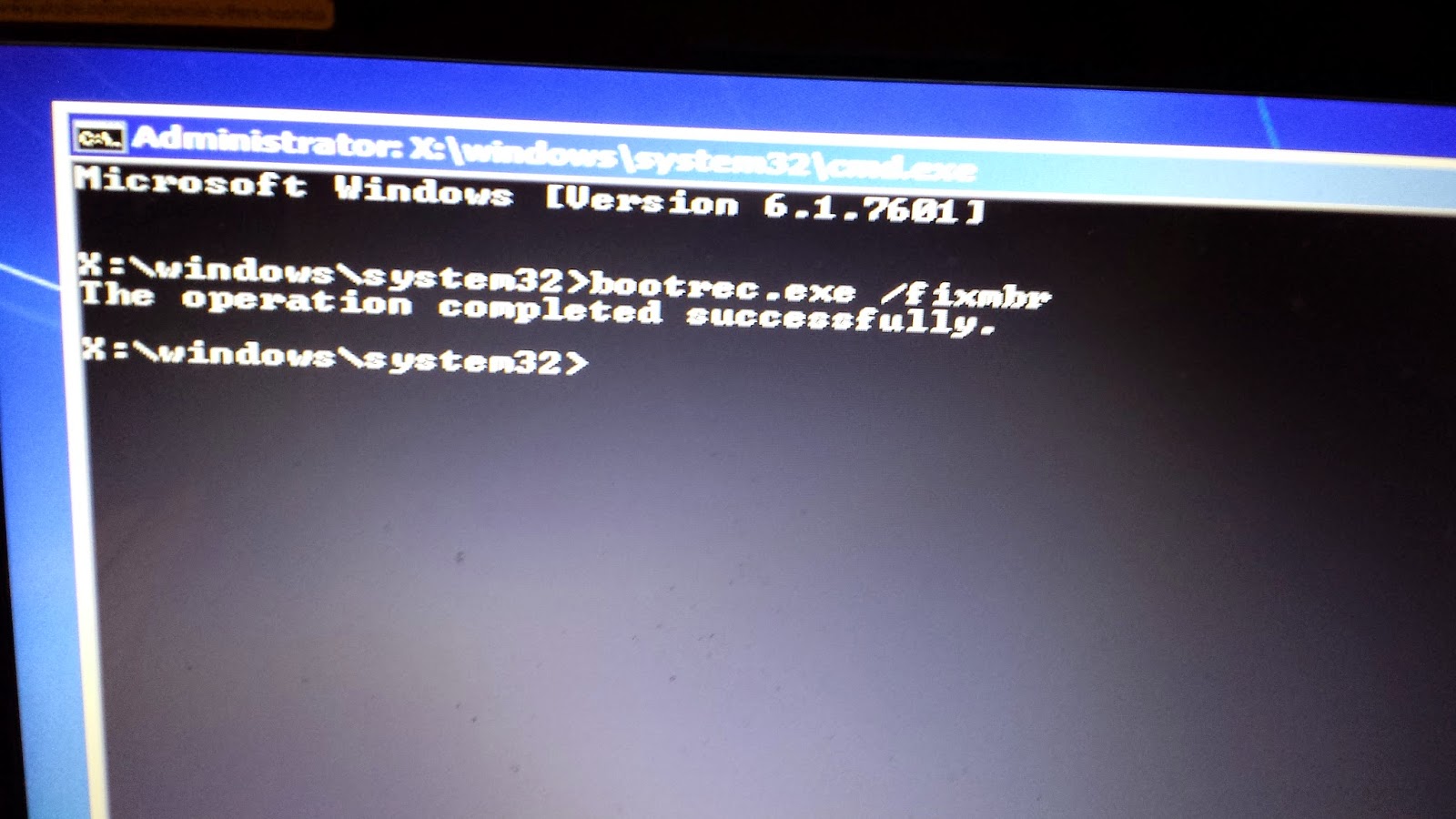
|
||||
|
||||
Now simply type the following command into the command prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
bootrec.exe /fixmbr
|
||||
|
||||
A message will appear stating that the operation has completed successfully.
|
||||
|
||||
You can now close the command prompt window.
|
||||
|
||||
Click the "Restart" button and remove the DVD.
|
||||
|
||||
Your computer should boot straight into Windows 7.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2 - Delete The Ubuntu Partitions ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To delete Ubuntu you need to use the "Disk Management" tool from within Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
Press "Start" and type "Create and format hard disk partitions" into the search box. A window will appear similar to the image above.
|
||||
|
||||
Now my screen above isn't going to be quite the same as yours but it won't be much different. If you look at disk 0 there is 101 MB of unallocated space and then 4 partitions.
|
||||
|
||||
The 101 MB of space is a mistake I made when installing Windows 7 in the first place. The C: drive is Windows 7, the next partition (46.57 GB) is Ubuntu's root partition. The 287 GB partition is the /HOME partition and the 8 GB partition is the SWAP space.
|
||||
|
||||
The only one we really need for Windows is the C: drive so the rest can be deleted.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: Be careful. You may have recovery partitions on the disk. Do not delete the recovery partitions. They should be labelled and will have file systems set to NTFS or FAT32**
|
||||
|
||||
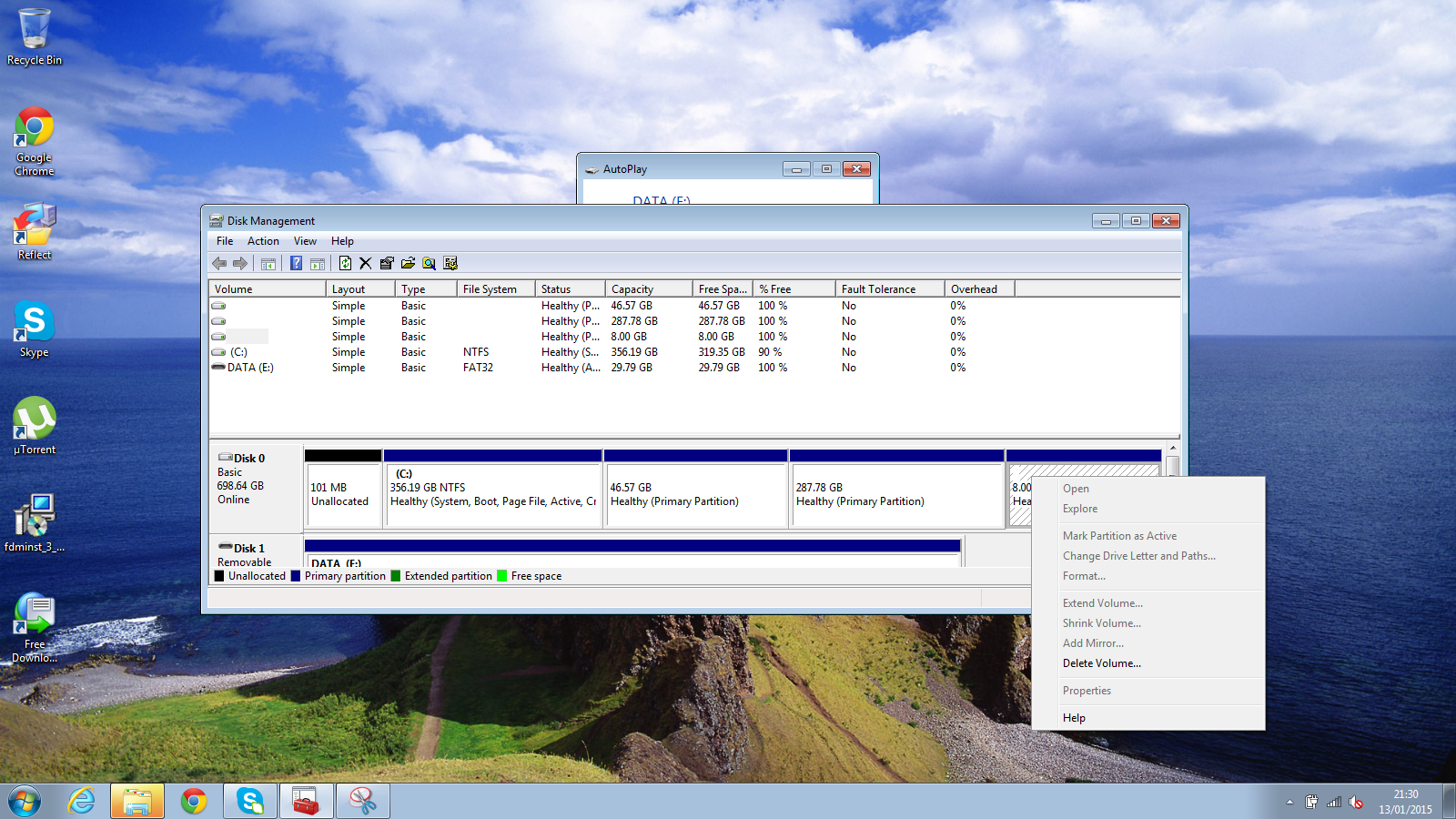
|
||||
|
||||
Right click on one of the partitions you wish to delete (i.e. the root, home and swap partitions) and from the menu click "Delete Volume".
|
||||
|
||||
**(Do not delete any partitions that have a file system of NTFS or FAT32)**
|
||||
|
||||
Repeat this process for the other two partitions.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After the partitions have been deleted you will have a large area of free space. Right click the free space and choose delete.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Your disk will now contain your C drive and a large amount of unallocated space.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3 - Expand The Windows Partition ###
|
||||
|
||||
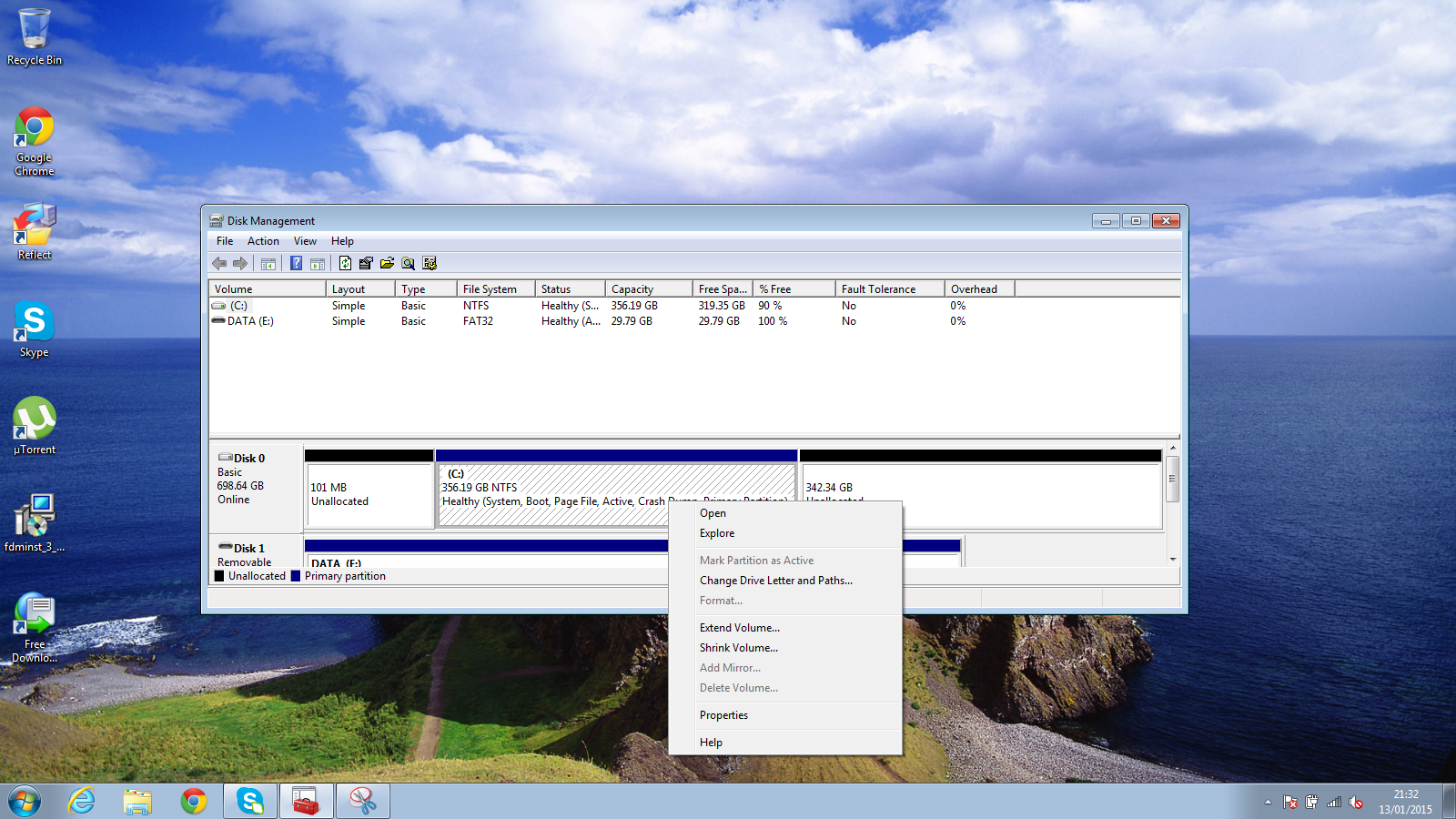
|
||||
|
||||
The final step is to expand Windows so that it is one large partition again.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this right click on the Windows partition (C: drive) and choose "Extend Volume".
|
||||
|
||||
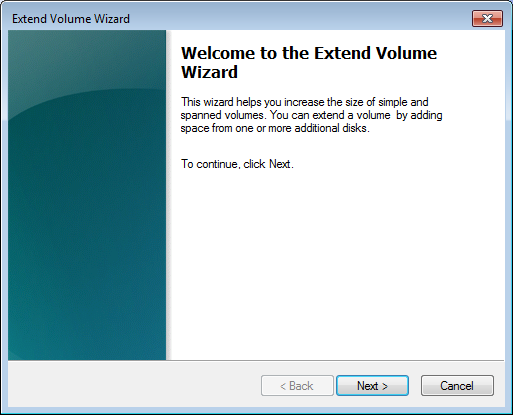
|
||||
|
||||
When the Window to the left appears click "Next",
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The next screen shows a wizard whereby you can select the disks to expand to and change the size to expand to.
|
||||
|
||||
By default the wizard shows the maximum amount of disk space it can claim from unallocated space.
|
||||
|
||||
Accept the defaults and click "Next".
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The final screen shows the settings that you chose from the previous screen.
|
||||
|
||||
Click "Finish" to expand the disk.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see from the image above my Windows partition now takes up the entire disk (except for the 101 MB that I accidentally created before installing Windows in the first place).
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
That is all folks. A site dedicated to Linux has just shown you how to remove Linux and replace it with Windows 7.
|
||||
|
||||
Any questions? Use the comments section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.everydaylinuxuser.com/2015/01/how-to-recover-windows-7-and-delete.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Gary Newell
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.about.com/od/LinuxNewbieDesktopGuide/ss/Create-A-Recovery-Drive-For-All-Versions-Of-Windows.htm
|
||||
[2]:http://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/B0006L2HTK/ref=as_li_qf_sp_asin_il_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=B0006L2HTK&linkCode=as2&tag=evelinuse-21&linkId=3R363EA63XB4Z3IL
|
||||
@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Vic020
|
||||
|
||||
Tips for Apache Migration From 2.2 to 2.4 on Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you do a distribution upgrade from **Ubuntu** 12.04 to 14.04, the upgrade will bring among other things an important update to **Apache**, from [version 2.2][1] to version 2.4. The update brings many improvements but it may cause some errors when used with the old configuration file from 2.2.
|
||||
|
||||
### Access control in Apache 2.4 Virtual Hosts ###
|
||||
|
||||
Starting with **Apache 2.4** authorization is applied in a way that is much more flexible then just a single check against a single data store like it was in 2.2. In the past it was tricky to figure how and in what order authorization is applied but with the introduction of authorization container directives such as and , the configuration also has control over when the authorization methods are called and what criteria determines when access is granted.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the point where most upgrades fail because of wrong configuration because in 2.2 access control based on IP address, hostname or other characteristic was done using the directives Order, Allow, Deny or Satisfy, but in 2.4 this is done with authorization checks using the new modules.
|
||||
|
||||
To be clear let's see some virtual host examples, this can be found in your /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/default or /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/YOUR_WEBSITE_NAME:
|
||||
|
||||
Old 2.2 virtual host configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow from all
|
||||
|
||||
New 2.4 virtual host configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
Require all granted
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### .htaccess problems ###
|
||||
|
||||
If after the upgrade some settings don't work or you get redirect errors, check if those settings are in a .htaccess file. If settings in the .htaccess file are not used by Apache it's because in 2.4 AllowOverride directive is set to None by default, thus ignoring the .htaccess files. All you have to do is to either change or add the AllowOverride All directive to your site configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
You also see the AllowOverride All directive set in the screenshot above.
|
||||
|
||||
### Missing config file or module ###
|
||||
|
||||
From my experience another problem during upgrades is that your configuration file includes an old module or configuration file that is no longer needed or supported in 2.4, you will get a clear warning that Apache can't include the respective file and all you have to do is go to your configuration file and remove the line that causes problem. Afterwards you can search or install a similar module.
|
||||
|
||||
### Other small changes you shound know about ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are a few other changes that you should consider, although they generally result in an warning and not an error:
|
||||
|
||||
- MaxClients has been renamed to MaxRequestWorkers, which describes more accurately what it does. For async MPMs, like event, the maximum number of clients is not equivalent than the number of worker threads. The old name is still supported.
|
||||
- The DefaultType directive no longer has any effect, other than to emit a warning if it's used with any value other than none. You need to use other configuration settings to replace it in 2.4.
|
||||
- EnableSendfile now defaults to Off.
|
||||
- FileETag now defaults to "MTime Size" (without INode).
|
||||
- KeepAlive only accepts values of On or Off. Previously, any value other than "Off" or "0" was treated as "On".
|
||||
- Directives AcceptMutex, LockFile, RewriteLock, SSLMutex, SSLStaplingMutex, and WatchdogMutexPath have been replaced with a single Mutex directive. You will need to evaluate any use of these removed directives in your 2.2 configuration to determine if they can just be deleted or will need to be replaced using Mutex.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/apache-migration-2-2-to-2-4-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/adriand/
|
||||
[1]:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/
|
||||
@ -1,95 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How To Disable IPv6 In CentOS 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Recently, one of my friend asked me how to disable IPv6. After searching a bit, I found the following solution. Here is the steps that I followed to disable IPv6 in my CentOS 7 minimal server.
|
||||
|
||||
You can do it in two methods.
|
||||
|
||||
### Method 1 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Edit file **/etc/sysctl.conf**,
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Add the following lines:
|
||||
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to disable IPV6 for particular network card, for example enp0s3, add the following entry.
|
||||
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.enp0s3.disable_ipv6 = 1
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit the file.
|
||||
|
||||
Execute the following command to reflect the changes.
|
||||
|
||||
sysctl -p
|
||||
|
||||
### Method 2: ###
|
||||
|
||||
To IPv6 disable in the running system, enter the following commands one by one:
|
||||
|
||||
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/all/disable_ipv6
|
||||
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/default/disable_ipv6
|
||||
|
||||
or,
|
||||
|
||||
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1
|
||||
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6=1
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. Now IPv6 has been disabled.
|
||||
|
||||
### What If I get issues after disabling IPv6? ###
|
||||
|
||||
You may get problems after disabling IPv6.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Issue 1: ####
|
||||
|
||||
if you get issues with SSH after disabling IPv6, do the following.
|
||||
|
||||
Edit **/etc/ssh/sshd_config** file,
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
|
||||
Find the line;
|
||||
|
||||
#AddressFamily any
|
||||
|
||||
And. change it to:
|
||||
|
||||
AddressFamily inet
|
||||
|
||||
or,
|
||||
|
||||
Remove the hash mark **(#)** in front of the line:
|
||||
|
||||
#ListenAddress 0.0.0.0
|
||||
|
||||
Then, restart ssh to reflect the changes.
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl restart sshd
|
||||
|
||||
#### Issue 2: ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you get problems with starting postfix after disabling IPv6, edit **/etc/postfix/main.cf** file;
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/postfix/main.cf
|
||||
|
||||
and comment out the localhost part of the config and use ipv4 loopback.
|
||||
|
||||
#inet_interfaces = localhost
|
||||
inet_interfaces = 127.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. Cheers!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/disable-ipv6-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[Quick Tip] How To Restart Cinnamon After Crash
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Cinnamon is a Linux desktop environment which provides advanced innovative features and a traditional user experience. The desktop layout is similar to Gnome 2. The underlying technology is similar from Gnome Shell. The emphasis is put on making users feel at home and providing them with an easy to use and comfortable desktop experience.
|
||||
|
||||
In this post, we’re going to look at a quick way to restart Cinnamon without logging out or rebooting when it crashes.
|
||||
|
||||
The image below is an example of Cinnamon crashed desktop where text and icons vanish from Menu and panel.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To restart Cinnamon
|
||||
|
||||
Press **Alt + F2** this brings out a command menu. Type **r** and press Enter.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon should restart displaying icons and text in panel and menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/quick-tip-restart-cinnamon-crash/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Enock Seth Nyamador][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/seth/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,206 @@
|
||||
How to Monitor Network Usage with nload in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
nload is a free linux utility that can help the linux user or sysadmin to monitor network traffic and bandwidth usage in real time by providing two simple graphs: one per incoming traffic and one for outgoing traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
I really like to use **nload** to display information on my screen about the current download speed, the total incoming traffic, and the average download speed. The graphs reported by nload tool are very easy to interpret and what is the most important thing they are very helpful.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the manual pages it monitors all network devices by default, but you can easily specify the device you want to monitor and also switch between different network devices using the arrow keys. There are many options avaliable such as -t to determine refresh interval of the display in milliseconds (the default value of interval is 500), -m to show multiple devices at the same time(traffic graphs are not shown when this option is used), -u to set the type of unit used for the display of traffic numbers and many others that we are going to explore and practise in this tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to install nload on your linux machine ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu** and **Fedora** users can easily install nload from the default repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
Install nload on Ubuntu by using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install nload
|
||||
|
||||
Install nload on Fedora by using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install nload
|
||||
|
||||
What about **CentOS** users? Just type the following command on your machine and you will get nload installed.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install nload
|
||||
|
||||
The following command will help you to install nload on OpenBSD systems.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo pkg_add -i nload
|
||||
|
||||
A very effective way to install software on linux machine is to compile by source as you can download and install the latest version which usually means better performance, cool features and less bugs.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to install nload from source ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing you need to do before installing nload from source you need to download it and to do this I like to use the wget uility which is available by default on many linux machines. This free utility helps linux users to download files from the web in a non-interactive way and has support for the following protocols.
|
||||
|
||||
- HTTP
|
||||
- HTTPS
|
||||
- FTP
|
||||
|
||||
Change directory to **/tmp** by using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
cd /tmp
|
||||
|
||||
Now type the following command in your terminal to download the latest version of nload on your linux machine.
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't like to use the linux wget utility you can easily download it from the [official][1] source by just a mouse click.
|
||||
|
||||
The download will finish in no time as it is a small software. The next step is to untar the file you downloaded with the help of the **tar** utility.
|
||||
|
||||
The tar archiving utility can be used to store and extract files from a tape or disk archive. There are many options available in this tool but we need the followings to perform our operation:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **-x** to extract files from an archive
|
||||
1. **-v** to run in verbose mode
|
||||
1. **-f** to specify the files
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
tar xvf example.tar
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you learned how to use the tar utility I am very sure you know how to untar .tar archives from the commandline.
|
||||
|
||||
tar xvf nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Then use the cd command to change directory to nload*.
|
||||
|
||||
cd nload*
|
||||
|
||||
It looks like this on my system.
|
||||
|
||||
oltjano@baby:/tmp/nload-0.7.4$
|
||||
|
||||
Now run the command
|
||||
|
||||
./configure
|
||||
|
||||
to to configure the package for your system.
|
||||
|
||||
./configure
|
||||
|
||||
Alot of stuff is going to be displayed on your screen. The following screenshot demonstrates how it is going to look like.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then compile the nload with the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
make
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
And finally install nload on your linux machine with the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now that the installation of nload is finished it is time for you to learn how to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to use nload ###
|
||||
|
||||
I like to explore so type the following command on your terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
nload
|
||||
|
||||
What do you see?
|
||||
|
||||
I get the following.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see from the above screenshot I get information on:
|
||||
|
||||
### Incoming Traffic ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Current download speed ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Average download speed ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Minimum download speed ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Maximum download speed ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Total incoming traffic in bytes by default ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Outgoing Traffic ###
|
||||
|
||||
The same goes for outgoing traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Some useful options of nload ####
|
||||
|
||||
Use the option
|
||||
|
||||
-u
|
||||
|
||||
to set set the type of unit used for the display of traffic numbers.
|
||||
|
||||
The following command will help you to use the MBit/s unit.
|
||||
|
||||
nload -u m
|
||||
|
||||
The following screenshot shows the result of the above command.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Try the following command and see the results.
|
||||
|
||||
nload -u g
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There is also the option **-U**. According to the manual pages it is same as the option -u but only for an amount of data. I tested this option and to be honest it very helpful when you want to check the total amount of traffic be it incoming or outgoing.
|
||||
|
||||
nload -U G
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see from the above screenshot the command **nload -U G** helps to display the total amount of data (incoming or outgoing) in Gbyte.
|
||||
|
||||
Another useful option I like to use with nload is the option **-t**. This option is used to refresh interval of display in milliseconds which is 500 by default.
|
||||
|
||||
I like to experiment a little by using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
nload -t 130
|
||||
|
||||
So what the above command does is that it sets the display to refresh every 130 milliseconds. It is recommended to no specify refresh intervals shorter than about 100 milliseconds as nload will generate reports with mistakes during the calculations.
|
||||
|
||||
Another option is **-a**. It is used when you want to set the length in seconds of the time window for average calculation which is 300 seconds by default.
|
||||
|
||||
What if you want to monitor a specific network device? It is very easy to do that, just specify the device or the list of devices you want to monitor like shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
nload wlan0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The following syntax can help to monitor specific multiple devices.
|
||||
|
||||
nload [options] device1 device2 devicen
|
||||
|
||||
For example use the following command to monitor eth0 and wlan0.
|
||||
|
||||
nload wlan0 eth0
|
||||
|
||||
And if you run the command nload without any option it will monitor all auto-detected devices, you can display graphs for each one of them by using the right and left arrow keys.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/monitor-network-usage-nload/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Oltjano Terpollari][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/oltjano/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
How to apply image effects to pictures on Raspberry Pi
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Like a common pocket camera which has a built-in function to add various effects on captured photos, [Raspberry Pi camera board][1] ("raspi cam") can actually do the same. With the help of raspistill camera control options, we can add the image effects function like we have in a pocket camera.
|
||||
|
||||
There are [three comman-line applications][2] which can be utilized for [taking videos or pictures][3] with raspi cam, and one of them is the raspistill application. The raspistill tool offers various camera control options such as sharpness, contrast, brightness, saturation, ISO, exposure, automatic white balance (AWB), image effects.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article I will show how to apply exposure, AWB, and other image effects with raspistill while capturing pictures using raspi cam. To automate the process, I wrote a simple Python script which takes pictures and automatically applies a series of image effects to the pictures. The raspi cam documentation describes available types of the exposure, AWB, and image effects. In total, the raspi cam offers 16 types of image effects, 12 types of exposure, and 10 types of AWB values.
|
||||
|
||||
The simple Python script looks like the following.
|
||||
|
||||
#!/usb/bin/python
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import time
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
list_ex=['auto','night']
|
||||
list_awb=['auto','cloud',flash']
|
||||
list_ifx=['blur','cartoon','colourswap','emboss','film','gpen','hatch','negative','oilpaint','posterise','sketch','solarise','watercolour']
|
||||
x=0
|
||||
for ex in list_ex:
|
||||
for awb in list_awb:
|
||||
for ifx in list_ifx:
|
||||
x=x+1
|
||||
filename='img_'+ex+'_'+awb+'_'+ifx+'.jpg'
|
||||
cmd='raspistill -o '+filename+' -n -t 1000 -ex '+ex+' -awb '+awb+' -ifx '+ifx+' -w 640 -h 480'
|
||||
pid=subprocess.call(cmd,shell=True)
|
||||
print "["+str(x)+"]-"+ex+"_"+awb+"_"+ifx+".jpg"
|
||||
time.sleep(0.25)
|
||||
print "End of image capture"
|
||||
|
||||
The Python script operates as follows. First, create three array/list variable for the exposure, AWB and image effects. In the example, we use 2 types of exposure, 3 types of AWB, and 13 types of image effects values. Then make nested loops for applying the value of the three variables that we have. Inside the nested loop, execute the raspistill application. We specify (1) the output filename; (2) exposure value; (3) AWB value; (4) image effect value; (5) the time to take a photo, which is set to 1 second; and (6) the size of the photo, which is set to 640x480px. This Python script will create 78 different versions of a captured photo with a combination of 2 types of exposure, 3 types of AWB, and 13 types of image effects.
|
||||
|
||||
To execute the Python script, simply type:
|
||||
|
||||
$ python name_of_this_script.py
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the first round of the sample result.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Bonus ###
|
||||
|
||||
For those who are more interested, there is another way to access and control the raspi cam besides raspistill. [Picamera][4] a pure Python interface which provides APIs for accessing and controlling raspi cam, so that one can build a complex program for utilizing raspi cam according to their needs. If you are skilled at Python, picamera is a good feature-complete interface for implementing your raspi cam project. The picamera interface is included by default in the recent image of Raspbian. If your [Raspberry Pi][5] operating system is not new or not Raspbian, you can install it on your system as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
First, install pip on your system by following [this guideline][6].
|
||||
|
||||
Then, install picamera as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pip install picamera
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the [official documentation][7] on how to use picamera.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/apply-image-effects-pictures-raspberrypi.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kristophorus Hadiono][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/kristophorus
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/go/picam
|
||||
[2]:http://www.raspberrypi.org/documentation/usage/camera/raspicam/
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/install-raspberry-pi-camera-board.html
|
||||
[4]:https://pypi.python.org/pypi/picamera
|
||||
[5]:http://xmodulo.com/go/raspberrypi
|
||||
[6]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-pip-linux.html
|
||||
[7]:http://picamera.readthedocs.org/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,115 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to check CPU info on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I would like to know detailed information about the CPU processor of my computer. What are the available methods to check CPU information on Linux?
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on your need, there are various pieces of information you may need to know about the CPU processor(s) of your computer, such as CPU vendor name, model name, clock speed, number of sockets/cores, L1/L2/L3 cache configuration, available processor capabilities (e.g., hardware virtualization, AES, MMX, SSE), and so on. In Linux, there are many command line or GUI-based tools that are used to show detailed information about your CPU hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. /proc/cpuinfo ###
|
||||
|
||||
The simpliest method is to check /proc/cpuinfo. This virtual file shows the configuration of available CPU hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
$ more /proc/cpuinfo
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
By inspecting this file, you can [identify][1] the number of physical processors, the number of cores per CPU, available CPU flags, and a number of other things.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. cpufreq-info ###
|
||||
|
||||
The cpufreq-info command (which is part of **cpufrequtils** package) collects and reports CPU frequency information from the kernel/hardware. The command shows the hardware frequency that the CPU currently runs at, as well as the minimum/maximum CPU frequency allowed, CPUfreq policy/statistics, and so on. To check up on CPU #0:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cpufreq-info -c 0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. cpuid ###
|
||||
|
||||
The cpuid command-line utility is a dedicated CPU information tool that displays verbose information about CPU hardware by using [CPUID functions][2]. Reported information includes processor type/family, CPU extensions, cache/TLB configuration, power management features, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cpuid
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. dmidecode ###
|
||||
|
||||
The dmidecode command collects detailed information about system hardware directly from DMI data of the BIOS. Reported CPU information includes CPU vendor, version, CPU flags, maximum/current clock speed, (enabled) core count, L1/L2/L3 cache configuration, and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dmidecode
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. hardinfo ###
|
||||
|
||||
The hardinfo is a GUI-based system information tool which can give you an easy-to-understand summary of your CPU hardware, as well as other hardware components of your system.
|
||||
|
||||
$ hardinfo
|
||||
|
||||
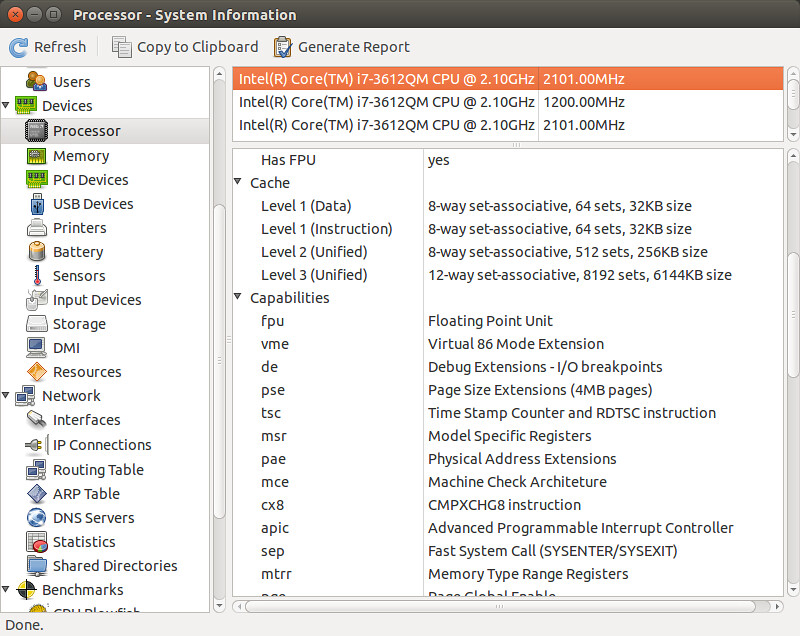
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. i7z ###
|
||||
|
||||
i7z is a real-time CPU reporting tool dedicated to Intel Core i3, i5 and i7 CPUs. It can display various per-core information in real time, such as Turbo Boost states, CPU frequencies, CPU power states, temperature measurements, and so on. i7z runs in either ncurses-based console mode or QT based GUI.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo i7z
|
||||
|
||||
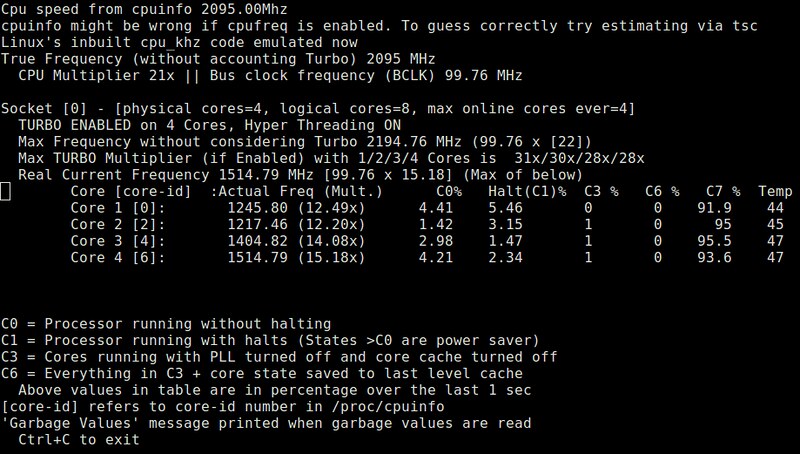
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. likwid-topology ###
|
||||
|
||||
[likwid][3] (Like I Knew What I'm Doing) is a collection of command-line tools to measure, configure and display hardware related properties. Among them is likwid-topology which shows CPU hardware (thread/cache/NUMA) topology information. It can also identify processor families (e.g., Intel Core 2, AMD Shanghai).
|
||||
|
||||
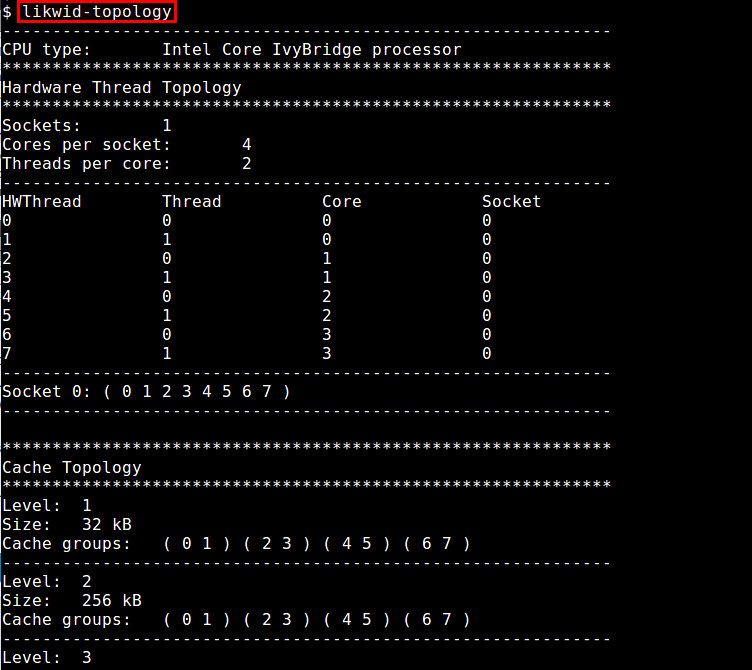
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. lscpu ###
|
||||
|
||||
The lscpu command summarizes /etc/cpuinfo content in a more user-friendly format, e.g., the number of (online/offline) CPUs, cores, sockets, NUMA nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
$ lscpu
|
||||
|
||||
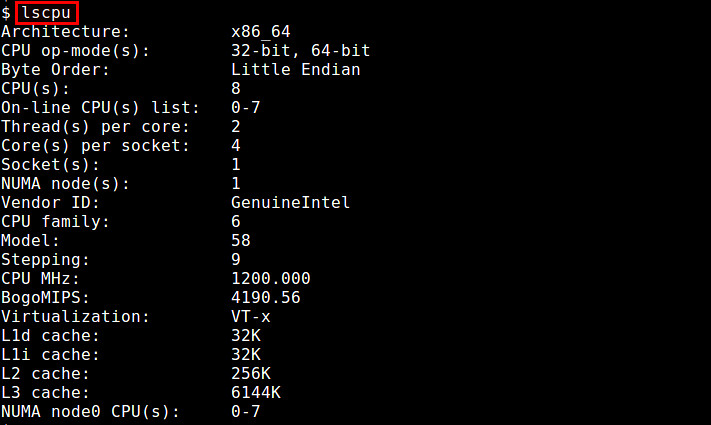
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. lshw ###
|
||||
|
||||
The **lshw** command is a comprehensive hardware query tool. Unlike other tools, lshw requires root privilege because it query DMI information in system BIOS. It can report the total number of cores and enabled cores, but miss out on information such as L1/L2/L3 cache configuration. The GTK version lshw-gtk is also available.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo lshw -class processor
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 11. lstopo ###
|
||||
|
||||
The lstopo command (contained in [hwloc][4] package) visualizes the topology of the system which is composed of CPUs, cache, memory and I/O devices. This command is useful to identify the processor architecture and NUMA topology of the system.
|
||||
|
||||
$ lstopo
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 12. numactl ###
|
||||
|
||||
Originally developed to set the NUMA scheduling and memeory placement policy of Linux processes, the numactl command can also show information about NUMA topology of the CPU hardware from the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
$ numactl --hardware
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 13. x86info ###
|
||||
|
||||
x86info is a command-line tool for showing x86-based CPU information. Reported information includes CPU model, number of threads/cores, clock speed, TLB cache configuration, supported feature flags, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
$ x86info --all
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/check-cpu-info-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-find-number-of-cpu-cores-on.html
|
||||
[2]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CPUID
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/identify-cpu-processor-architecture-linux.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/identify-cpu-processor-architecture-linux.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,158 @@
|
||||
translating by mtunique
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to check disk space on Linux with df command
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I know I can use df command to check a file system's disk space usage on Linux. Can you show me practical examples of the df command so that I can make the most out of it?
|
||||
|
||||
As far as disk storage is concerned, there are many command-line or GUI-based tools that can tell you about current disk space usage. These tools report on detailed disk utilization in various human-readable formats, such as easy-to-understand summary, detailed statistics, or [intuitive visualization][1]. If you simply want to know how much free disk space is available for different file systems, then df command is probably all you need.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The df command can report on disk utilization of any "mounted" file system. There are different ways this command can be invoked. Here are some **useful** df **command examples**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Display in Human-Readable Format ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the df command reports disk space in 1K blocks, which is not easily interpretable. The "-h" parameter will make df print disk space in a more human-readable format (e.g., 100K, 200M, 3G).
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
|
||||
/dev/mapper/ubuntu-root 909G 565G 299G 66% /
|
||||
none 4.0K 0 4.0K 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
|
||||
udev 3.9G 4.0K 3.9G 1% /dev
|
||||
tmpfs 785M 1.2M 784M 1% /run
|
||||
none 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
|
||||
none 3.9G 63M 3.8G 2% /run/shm
|
||||
none 100M 48K 100M 1% /run/user
|
||||
/dev/sda1 228M 98M 118M 46% /boot
|
||||
|
||||
### Display Inode Usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
When you monitor disk usage, you must watch out for not only disk space, but also "inode" usage. In Linux, inode is a data structure used to store metadata of a particular file, and when a file system is created, a pre-defined number of inodes are allocated. This means that a file system can run out of space not only because big files use up all available space, but also because many small files use up all available inodes. To display inode usage, use "-i" option.
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -i
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on
|
||||
/dev/mapper/ubuntu-root 60514304 1217535 59296769 3% /
|
||||
none 1004417 13 1004404 1% /sys/fs/cgroup
|
||||
udev 1000623 552 1000071 1% /dev
|
||||
tmpfs 1004417 608 1003809 1% /run
|
||||
none 1004417 11 1004406 1% /run/lock
|
||||
none 1004417 288 1004129 1% /run/shm
|
||||
none 1004417 28 1004389 1% /run/user
|
||||
/dev/sda1 124496 346 124150 1% /boot
|
||||
|
||||
### Display Disk Usage Grant Total ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the df command shows disk utilization of individual file systems. If you want to know the total disk usage over all existing file systems, add "--total" option.
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h --total
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
|
||||
/dev/mapper/ubuntu-root 909G 565G 299G 66% /
|
||||
none 4.0K 0 4.0K 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
|
||||
udev 3.9G 4.0K 3.9G 1% /dev
|
||||
tmpfs 785M 1.2M 784M 1% /run
|
||||
none 5.0M 0 5.0M 0% /run/lock
|
||||
none 3.9G 62M 3.8G 2% /run/shm
|
||||
none 100M 48K 100M 1% /run/user
|
||||
/dev/sda1 228M 98M 118M 46% /boot
|
||||
total 918G 565G 307G 65% -
|
||||
|
||||
### Display File System Types ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the df command does not show file system type information. Use "-T" option to add file system types to the output.
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -T
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem Type 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
|
||||
/dev/mapper/ubuntu-root ext4 952893348 591583292 312882844 66% /
|
||||
none tmpfs 4 0 4 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
|
||||
udev devtmpfs 4002492 4 4002488 1% /dev
|
||||
tmpfs tmpfs 803536 1196 802340 1% /run
|
||||
none tmpfs 5120 0 5120 0% /run/lock
|
||||
none tmpfs 4017668 60176 3957492 2% /run/shm
|
||||
none tmpfs 102400 48 102352 1% /run/user
|
||||
/dev/sda1 ext2 233191 100025 120725 46% /boot
|
||||
|
||||
### Include or Exclude a Specific File System Type ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to know free space of a specific file system type, use "-t <type>" option. You can use this option multiple times to include more than one file system types.
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -t ext2 -t ext4
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
|
||||
/dev/mapper/ubuntu-root 952893348 591583380 312882756 66% /
|
||||
/dev/sda1 233191 100025 120725 46% /boot
|
||||
|
||||
To exclude a specific file system type, use "-x <type>" option. You can use this option multiple times as well.
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -x tmpfs
|
||||
|
||||
### Display Disk Usage of a Specific Mount Point ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you specify a mount point with df, it will report disk usage of the file system mounted at that location. If you specify a regular file (or a directory) instead of a mount point, df will display disk utilization of the file system which contains the file (or the directory).
|
||||
|
||||
$ df /
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
|
||||
/dev/mapper/ubuntu-root 952893348 591583528 312882608 66% /
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
$ df /home/dev
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
|
||||
/dev/mapper/ubuntu-root 952893348 591583528 312882608 66% /
|
||||
|
||||
### Display Information about Dummy File Systems ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to display disk space information for all existing file systems including dummy file systems, use "-a" option. Here, dummy file systems refer to pseudo file systems which do not have corresponding physical devices, e.g., tmpfs, cgroup virtual file system or FUSE file systems. These dummy filesystems have size of 0, and are not reported by df without "-a" option.
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -a
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
|
||||
/dev/mapper/ubuntu-root 952893348 591578716 312887420 66% /
|
||||
proc 0 0 0 - /proc
|
||||
sysfs 0 0 0 - /sys
|
||||
none 4 0 4 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
|
||||
none 0 0 0 - /sys/fs/fuse/connections
|
||||
none 0 0 0 - /sys/kernel/debug
|
||||
none 0 0 0 - /sys/kernel/security
|
||||
udev 4002492 4 4002488 1% /dev
|
||||
devpts 0 0 0 - /dev/pts
|
||||
tmpfs 803536 1196 802340 1% /run
|
||||
none 5120 0 5120 0% /run/lock
|
||||
none 4017668 58144 3959524 2% /run/shm
|
||||
none 102400 48 102352 1% /run/user
|
||||
none 0 0 0 - /sys/fs/pstore
|
||||
cgroup 0 0 0 - /sys/fs/cgroup/cpuset
|
||||
cgroup 0 0 0 - /sys/fs/cgroup/hugetlb
|
||||
/dev/sda1 233191 100025 120725 46% /boot
|
||||
vmware-vmblock 0 0 0 - /run/vmblock-fuse
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/check-disk-space-linux-df-command.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/visualize-disk-usage-linux.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,207 @@
|
||||
Syncthing: A Private, And Secure Tool To Sync Files/Folders Between Computers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Introduction ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Syncthing** is a free, Open Source tool that can be used to sync files/folders between your networked computers. Unlike other sync tools, such as **BitTorrent Sync** or **Dropbox**, Syncthing transfers data directly from one system to another system, and It is completely open source, secure and private. All of your precious data will be stored in your system so that you can have full control over your files and folders, and none of them are stored in any third party systems. Also, you deserve to choose where it is stored, if it is shared with some third party and how it’s transmitted over the Internet.
|
||||
|
||||
All communication is encrypted using TLS, so your data is very secure from the prying eyes. Syncthing has a responsive and powerful WebGUI which will help the users to easily add, delete and manage directories to be synced over network. Using Syncthing, you can sync multiple folders to multiple systems at a time. Syncthing is very simple, portable, yet powerful tool in terms of installation and usage. Since all files/folders are directly transferred from one computer to another computer, you don’t have to worry about purchasing extra space from your Cloud provider. All you need is very stable LAN/WAN connection and enough disk space on your systems. It supports all modern operating systems, including GNU/Linux, Windows, Mac OS X, and ofcourse Android.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation ###
|
||||
|
||||
For the purpose of this tutorial, We will be using two systems, one is running with Ubuntu 14.04 LTS, and another one is running with Ubuntu 14.10 server. To easily recognize these two systems, we will be calling them using names **system1**, and **system2**.
|
||||
|
||||
### System1 Details: ###
|
||||
|
||||
- **OS**: Ubuntu 14.04 LTS server;
|
||||
- **Hostname**: server1.unixmen.local;
|
||||
- **IP Address**: 192.168.1.150.
|
||||
- **System user**: sk (You can use your own)
|
||||
- **Sync Directory**: /home/Sync/ (Will be created by default by Syncthing)
|
||||
|
||||
### System2 Details: ###
|
||||
|
||||
- **OS**: Ubuntu 14.10 server;
|
||||
- **Hostname**: server.unixmen.local;
|
||||
- **IP Address**: 192.168.1.151.
|
||||
- **System user**: sk (You can use your own)
|
||||
- **Sync Directory**: /home/Sync/ (Will be created by default by Syncthing)
|
||||
|
||||
### Creating User For Syncthing On System 1 & System2: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following commands on both system to create the user for Syncthing and the directory to be synced between two systems:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo useradd sk
|
||||
sudo passwd sk
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Syncthing On System1 And System2: ###
|
||||
|
||||
You should do the following steps on both System 1 and System 2.
|
||||
|
||||
Download the latest version from the [official download page][1]. As I am using 64bit system, I downloaded the 6bbit package.
|
||||
|
||||
wget https://github.com/syncthing/syncthing/releases/download/v0.10.20/syncthing-linux-amd64-v0.10.20.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Extract the download file:
|
||||
|
||||
tar xzvf syncthing-linux-amd64-v0.10.20.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Cd to the extracted folder:
|
||||
|
||||
cd syncthing-linux-amd64-v0.10.20/
|
||||
|
||||
Copy the excutable file “syncthing” to **$PATH**:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cp syncthing /usr/local/bin/
|
||||
|
||||
Now, run the following command to run the syncthing for the first time.
|
||||
|
||||
syncthing
|
||||
|
||||
When you run the above command, syncthing will generate a configuration and some keys and then start the admin GUI in your browser. You should see something like below.
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
[monitor] 15:40:27 INFO: Starting syncthing
|
||||
15:40:27 INFO: Generating RSA key and certificate for syncthing...
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:40:34 INFO: syncthing v0.10.20 (go1.4 linux-386 default) unknown-user@syncthing-builder 2015-01-13 16:27:47 UTC
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:40:34 INFO: My ID: BQXVO3D-VEBIDRE-MVMMGJI-ECD2PC3-T5LT3JB-OK4Z45E-MPIDWHI-IRW3NAZ
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:40:34 INFO: No config file; starting with empty defaults
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:40:34 INFO: Edit /home/sk/.config/syncthing/config.xml to taste or use the GUI
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:40:34 INFO: Starting web GUI on http://127.0.0.1:8080/
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:40:34 INFO: Loading HTTPS certificate: open /home/sk/.config/syncthing/https-cert.pem: no such file or directory
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:40:34 INFO: Creating new HTTPS certificate
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:40:34 INFO: Generating RSA key and certificate for server1...
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:41:01 INFO: Starting UPnP discovery...
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:41:07 INFO: Starting local discovery announcements
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:41:07 INFO: Starting global discovery announcements
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:41:07 OK: Ready to synchronize default (read-write)
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:41:07 INFO: Device BQXVO3D-VEBIDRE-MVMMGJI-ECD2PC3-T5LT3JB-OK4Z45E-MPIDWHI-IRW3NAZ is "server1" at [dynamic]
|
||||
[BQXVO] 15:41:07 INFO: Completed initial scan (rw) of folder default
|
||||
|
||||
Syncthing has been successfully initialized, and the Web admin interface can be accessed using URL: **http://localhost:8080** from your browser. As you see in the above output, syncthing has automatically created a folder called **default** for you, in a directory called **Sync** in your **home** directory.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Syncthing WebGUI will only be accessed from the localhost itself. To access the WebGUI from the remote systems, you need to do the following changes on both systems.
|
||||
|
||||
First, stop the Syncthing initialization process by pressing the CTRL+C. Now, you will be returned back to the Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
Edit file **config.xml**,
|
||||
|
||||
sudo nano ~/.config/syncthing/config.xml
|
||||
|
||||
Find this directive:
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
<gui enabled="true" tls="false">
|
||||
<address>127.0.0.1:8080</address>
|
||||
<apikey>-Su9v0lW80JWybGjK9vNK00YDraxXHGP</apikey>
|
||||
</gui>
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
In the **<address>** field, change **127.0.0.1:8080** to **0.0.0.0:8080**. So, your config.xml will look like below.
|
||||
|
||||
<gui enabled="true" tls="false">
|
||||
<address>0.0.0.0:8080</address>
|
||||
<apikey>-Su9v0lW80JWybGjK9vNK00YDraxXHGP</apikey>
|
||||
</gui>
|
||||
|
||||
Save and close the file.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, start again the Syncthing initialization on both systems by entering the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
syncthing
|
||||
|
||||
### Access the WebGUI ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, open your browser **http://ip-address:8080/**. You will see the following screen,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The WebGUI has two panes. In the left pane, you may see the list of folders to be synced. As I mentioned before, the folder **default** has been automatically created for you while initializing Syncthing. If you want to sync more folders, you can add using **Add Folder** button.
|
||||
|
||||
In the right pane, you see the number of devices connected. Currently there is only one device, the computer you are running this on.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure Syncthing Web GUI ###
|
||||
|
||||
For the security enhancement, let us enable TLS, and setup administrative user and password to access the WebGUI. To od that, click on the gear button and select **Settings** on the top right corner.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enter the admin username/password. In my case it is admin/ubuntu. You should use some strong password. And, check the box that says: **Use HTTPS for GUI**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click Save button. Now, you’ll be asked to restart the Syncthing to activate the changes. Click Restart.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Selection_005Refresh you web browser. You’ll see the SSL warning like below. Click on the button that says: **I understand the Risks**. And, click Add Exception button to add this page to the browser trusted lists.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enter the administrative user and password which we configured in the previous steps. In my case it’s **admin/ubuntu**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We have secured the WebGUI now. Don’t forget to do the same steps on both server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Connect Servers To Each Other ###
|
||||
|
||||
To sync folders between systems, you must told them about each other. This is accomplished by exchanging “device IDs”. You can find it in the web GUI by selecting the “gear menu” (top right) and “Show ID”.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, here is my System 1 ID.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Copy the ID, and go to the another system (system 2) WebGUI. From the second system (system 2) WebGUI window, click on the Add Device on the right side.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The following screen should appear. Paste the **System 1 ID** in the Device section. Enter the Device name(optional). In the Addresses field, you can either enter the IP address of the other system or leave it as default. The default value is **dynamic**. Finally, select the folder to be synced. In our case, the sync folder is **default**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once you done, click on the save button. You’ll be asked to restart the Syncthing. Click Restart button to activate the changes.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, go to the **System 1** WebUI, you’ll see a request has been sent from the System 2 to connect and sync. Click **Add** button. Now, the System 2 will ask the System 1 to share and sync the folder called “default”. Click **Share** button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Next restart the Syncthing service on the System 1 to activate the changes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Wait for few seconds, approximately 60 seconds, and you’ll see the two systems have been successfully connected and synced to each other.
|
||||
|
||||
You can verify it under the Add Device section of the WebGUI.
|
||||
|
||||
System 1 WebGUI console after adding System 2:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
System 2 WebGUI console after adding System 1:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, put any file or folder in any one of the systems “**default**” folder. You may see the file/folder will be synced to the other system automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it! Happy Sync’ing!!
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!!!
|
||||
|
||||
- [Syncthing Website][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/syncthing-private-secure-tool-sync-filesfolders-computers/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/syncthing/syncthing/releases/tag/v0.10.20
|
||||
[2]:http://syncthing.net/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to check memory usage on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I would like to monitor memory usage on my Linux system. What are the available GUI-based or command-line tools for checking current memory usage of Linux?
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes to optimizing the performance of a Linux system, physical memory is the single most important factor. Naturally, Linux offers a wealth of options to monitor the usage of the precious memory resource. Different tools vary in terms of their monitoring granularity (e.g., system-wide, per-process, per-user), interface (e.g., GUI, command-line, ncurses) or running mode (e.g., interactive, batch mode).
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a non-exhaustive list of GUI or command-line tools to choose from to check used and free memory on Linux platform.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. /proc/meminfo ###
|
||||
|
||||
The simpliest method to check RAM usage is via /proc/meminfo. This dynamically updated virtual file is actually the source of information displayed by many other memory related tools such as free, top and ps tools. From the amount of available/free physical memory to the amount of buffer waiting to be or being written back to disk, /proc/meminfo has everything you want to know about system memory usage. Process-specific memory information is also available from /proc/<pid>/statm and /proc/<pid>/status
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat /proc/meminfo
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. atop ###
|
||||
|
||||
The atop command is an ncurses-based interactive system and process monitor for terminal environments. It shows a dynamically-updated summary of system resources (CPU, memory, network, I/O, kernel), with colorized warnings in case of high system load. It also offers a top-like view of processes (or users) along with their resource usage, so that system admin can tell which processes or users are responsible for system load. Reported memory statistics include total/free memory, cached/buffer memory and committed virtual memory.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo atop
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. free ###
|
||||
|
||||
The free command is a quick and easy way to get an overview of memory usage gleaned from /proc/meminfo. It shows a snapshot of total/free physical memory and swap space of the system, as well as used/free buffer space in the kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
$ free -h
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. GNOME System Monitor ###
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME System Monitor is a GUI application that shows a short history of system resource utilization for CPU, memory, swap space and network. It also offers a process view of CPU and memory usage.
|
||||
|
||||
$ gnome-system-monitor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. htop ###
|
||||
|
||||
The htop command is an ncurses-based interactive processor viewer which shows per-process memory usage in real time. It can report resident memory size (RSS), total program size in memory, library size, shared page size, and dirty page size for all running processes. You can scroll the (sorted) list of processes horizontally or vertically.
|
||||
|
||||
$ htop
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 6. KDE System Monitor ###
|
||||
|
||||
While GNOME desktop has GNOME System Monitor, KDE desktop has its own counterpart: KDE System Monitor. Its functionality is mostly similar to GNOME version, i.e., showing a real-time history of system resource usage, as well as a process list along with per-process CPU/memory consumption.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ksysguard
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. memstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
The memstat utility is useful to identify which executable(s), process(es) and shared libraries are consuming virtual memory. Given a process ID, memstat identifies how much virtual memory is used by the process' associated executable, data, and shared libraries.
|
||||
|
||||
$ memstat -p <PID>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. nmon ###
|
||||
|
||||
The nmon utility is an ncurses-based system benchmark tool which can monitor CPU, memory, disk I/O, kernel, filesystem and network resources in interactive mode. As for memory usage, it can show information such as total/free memory, swap space, buffer/cached memory, virtual memory page in/out statistics, all in real time.
|
||||
|
||||
$ nmon
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 9. ps ###
|
||||
|
||||
The ps command can show per-process memory usage in real-time. Reported memory usage information includes %MEM (percent of physical memory used), VSZ (total amount of virtual memory used), and RSS (total amount of physical memory used). You can sort the process list by using "--sort" option. For example, to sort in the decreasing order of RSS:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps aux --sort -rss
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 10. smem ###
|
||||
|
||||
The [smem][1] command allows you to measure physical memory usage by different processes and users based on information available from /proc. It utilizes proportional set size (PSS) metric to accurately quantify effective memory usage of Linux processes. Memory usage analysis can be exported to graphical charts such as bar and pie graphs.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo smem --pie name -c "pss"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. top ###
|
||||
|
||||
The top command offers a real-time view of running processes, along with various process-specific resource usage statistics. Memory related information includes %MEM (memory utilization percentage), VIRT (total amount of virtual memory used), SWAP (amount of swapped-out virtual memory), CODE (amount of physical memory allocated for code execution), DATA (amount of physical memory allocated to non-executable data), RES (total amount of physical memory used; CODE+DATA), and SHR (amount of memory potentially shared with other processes). You can sort the process list based on memory usage or size.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 12. vmstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
The vmstat command-line utility displays instantaneous and average statistics of various system activities covering CPU, memory, interrupts, and disk I/O. As for memory information, the command shows not only physical memory usage (e.g., tota/used memory and buffer/cache memory), but also virtual memory statistics (e.g., memory paged in/out, swapped in/out).
|
||||
|
||||
$ vmstat -s
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/check-memory-usage-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/visualize-memory-usage-linux.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create and configure a MySQL user from the command line
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I would like to create a new user account on MySQL server, and apply appropriate permissions and resource limits to the account. How can I create and configure a MySQL user from the command line?
|
||||
|
||||
To access a MySQL server, you need to log in to the server using a user account. Each MySQL user account has a number of attributes associated with it, such as user name, password, as well as privileges and resource limits. Privileges are user-specific permissions defining what you can do inside a MySQL server, while resource limits set the limitations on the amount of server resource allowed for for the user. Creating or updating a MySQL user involves managing all these attributes of the user account.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how to create and configure a MySQL user on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
You first log in to MySQL server as the root.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -p
|
||||
|
||||
When prompted for authentication, enter the MySQL root password.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a MySQL User ###
|
||||
|
||||
To create a new user with username 'myuser' and password 'mypassword', use the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> CREATE USER 'myuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'mypassword';
|
||||
|
||||
Once a user is created, all its account details including an encrypted password, privileges and resource limits are stored in a table called **user** in a special database named **mysql**.
|
||||
|
||||
To verify that the account is created successfully, run:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SELECT host, user, password FROM mysql.user WHERE user='myuser';
|
||||
|
||||
### Grant Privileges to MySQL User ###
|
||||
|
||||
A newly created MySQL user comes with zero access privilege, which means that you cannot do anything inside MySQL server. You need to grant necessary privileges to the user. Some of available privileges are the following.
|
||||
|
||||
- **ALL**: all privileges available.
|
||||
- **CREATE**: create databases, tables or indices.
|
||||
- **LOCK_TABLES**: lock databases.
|
||||
- **ALTER**: alter tables.
|
||||
- **DELETE**: delete tables.
|
||||
- **INSERT**: insert tables or columns.
|
||||
- **SELECT**: select tables or columns.
|
||||
- **CREATE_VIEW**: create views.
|
||||
- **SHOW_DATABASES**: show databases.
|
||||
- **DROP**: drop daabases, tables or views.
|
||||
|
||||
To grant a particular privilege to user 'myuser', use the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> GRANT <privileges> ON <database>.<table> TO 'myuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
|
||||
In the above, <privileges> is expressed as a comma-separated list of privileges. If you want to grant privileges for any database (or table), place an asterisk (*) in the database (or table) name.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to grant CREATE and INSERT privileges for all databases/tables:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> GRANT CREATE, INSERT ON *.* TO 'myuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
|
||||
To verify the granted privileges of the user:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SHOW GRANTS FOR 'myuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
To grant all privileges to all databases/tables:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'myuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
|
||||
You can also remove existing privileges from a user. To revoke existing privileges from the account 'myuser', use the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> REVOKE <privileges> ON <database>.<table> FROM 'myuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
|
||||
### Add Resource Limits to MySQL User ###
|
||||
|
||||
In MySQL, you can place limits on MySQL resource usage for individual users. The available resource limits are the following.
|
||||
|
||||
- **MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR**: number of allowed queries per hour.
|
||||
- **MAX_UPDATES_PER_HOUR**: number of allowed updates per hour.
|
||||
- **MAX_CONNECTIONS_PER_HOUR**: number of allowed logins per hour.
|
||||
- **MAX_USER_CONNECTIONS**: number of simultaneous connections to the server.
|
||||
|
||||
To add a resource limit to the account 'myuser', use the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> GRANT USAGE ON <database>.<table> TO 'myuser'@'localhost' WITH <resource-limits>;
|
||||
|
||||
In <resource-limits>, you can specify multiple resource limits separated by space.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to add MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR and MAX_CONNECTIONS_PER_HOUR resource limits:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO 'myuser'@'localhost' WITH MAX_QUERIES_PER_HOUR 30 MAX_CONNECTIONS_PER_HOUR 6;
|
||||
|
||||
To verify the resource limits of the user:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SHOW GRANTS FOR 'myuser'@'localhost;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The last important step after creating and configuring a MySQL user is to run:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
|
||||
|
||||
so that the changes take effect. Now the MySQL user account is good to go!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/create-configure-mysql-user-command-line.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to download and install ixgbe driver on Ubuntu or Debian
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I want to download and install the latest ixgbe driver for my Intel 10 Gigabit Ethernet card. How can I install ixgbe driver on Ubuntu (or Debian)?
|
||||
|
||||
Intel's PCI Express 10 Gigabit (10G) network inerface cards (e.g., 82598, 82599, x540) are supported by ixgbe driver. The stock kernel of the modern Linux distributions already comes with ixgbe driver as a loadable module. However, there are cases where you may want to compile and install ixgbe driver on your own. For example, you may want to try the new features of the latest ixgbe driver. Also, the problem of the default ixgbe driver in the stock kernel is that it does not allow you to customize many of its driver parameters. If you want to fully customize ixgbe device driver (e.g., RSS, multi-queue, interrupt throttling, etc), you need to manually compile ixgbe driver from the source.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how to download and install ixgbe driver on Ubuntu, Debian or their derivatives.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step One: Install Prerequites ###
|
||||
|
||||
As prerequisites, install matching kernel headers and development packages.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install linux-headers-$(uname -r)
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install gcc make
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Two: Compile Ixgbe Driver ###
|
||||
|
||||
Download the source code of the [latest ixgbe driver][1].
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/e1000/files/ixgbe%20stable/3.23.2/ixgbe-3.23.2.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Compile ixgbe driver as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ tar xvfvz ixgbe-3.23.2.tar.gz
|
||||
$ cd ixgbe-3.23.2/src
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Three: Check Ixgbe Driver ###
|
||||
|
||||
After compilation, you will see **ixgbe.ko** created in ixgbe-3.23.2/src directory. This is the ixgbe device driver which will be loaded into the kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
Check the information of this kernel module with modinfo command. Note that you need to specify an absolute path to the module (e.g., ./ixgbe.ko or /home/xmodulo/ixgbe/ixgbe-3.23.2/src/ixgbe.ko). The output will show the version of ixgbe driver.
|
||||
|
||||
$ modinfo ./ixgbe.ko
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
filename: /home/xmodulo/ixgbe/ixgbe-3.23.2/src/ixgbe.ko
|
||||
version: 3.23.2
|
||||
license: GPL
|
||||
description: Intel(R) 10 Gigabit PCI Express Network Driver
|
||||
author: Intel Corporation,
|
||||
srcversion: 2ADA5E537923E983FA9DAE2
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d00001560sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d00001558sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d0000154Asv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d00001557sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d0000154Fsv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d0000154Dsv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d00001528sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010F8sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d0000151Csv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d00001529sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d0000152Asv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010F9sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d00001514sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d00001507sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010FBsv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d00001517sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010FCsv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010F7sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d00001508sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010DBsv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010F4sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010E1sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010F1sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010ECsv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010DDsv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d0000150Bsv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010C8sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010C7sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010C6sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
alias: pci:v00008086d000010B6sv*sd*bc*sc*i*
|
||||
depends: ptp,dca
|
||||
vermagic: 3.11.0-19-generic SMP mod_unload modversions
|
||||
parm: InterruptType:Change Interrupt Mode (0=Legacy, 1=MSI, 2=MSI-X), default IntMode (deprecated) (array of int)
|
||||
parm: IntMode:Change Interrupt Mode (0=Legacy, 1=MSI, 2=MSI-X), default 2 (array of int)
|
||||
parm: MQ:Disable or enable Multiple Queues, default 1 (array of int)
|
||||
parm: DCA:Disable or enable Direct Cache Access, 0=disabled, 1=descriptor only, 2=descriptor and data (array of int)
|
||||
parm: RSS:Number of Receive-Side Scaling Descriptor Queues, default 0=number of cpus (array of int)
|
||||
parm: VMDQ:Number of Virtual Machine Device Queues: 0/1 = disable, 2-16 enable (default=8) (array of int)
|
||||
parm: max_vfs:Number of Virtual Functions: 0 = disable (default), 1-63 = enable this many VFs (array of int)
|
||||
parm: VEPA:VEPA Bridge Mode: 0 = VEB (default), 1 = VEPA (array of int)
|
||||
parm: InterruptThrottleRate:Maximum interrupts per second, per vector, (0,1,956-488281), default 1 (array of int)
|
||||
parm: LLIPort:Low Latency Interrupt TCP Port (0-65535) (array of int)
|
||||
parm: LLIPush:Low Latency Interrupt on TCP Push flag (0,1) (array of int)
|
||||
parm: LLISize:Low Latency Interrupt on Packet Size (0-1500) (array of int)
|
||||
parm: LLIEType:Low Latency Interrupt Ethernet Protocol Type (array of int)
|
||||
parm: LLIVLANP:Low Latency Interrupt on VLAN priority threshold (array of int)
|
||||
parm: FdirPballoc:Flow Director packet buffer allocation level:
|
||||
1 = 8k hash filters or 2k perfect filters
|
||||
2 = 16k hash filters or 4k perfect filters
|
||||
3 = 32k hash filters or 8k perfect filters (array of int)
|
||||
parm: AtrSampleRate:Software ATR Tx packet sample rate (array of int)
|
||||
parm: FCoE:Disable or enable FCoE Offload, default 1 (array of int)
|
||||
parm: LRO:Large Receive Offload (0,1), default 1 = on (array of int)
|
||||
parm: allow_unsupported_sfp:Allow unsupported and untested SFP+ modules on 82599 based adapters, default 0 = Disable (array of int)
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Four: Test Ixgbe Driver ###
|
||||
|
||||
Before testing the new module, you need to remove an old ersion of ixgbe module if it exists in the kernel:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo rmmod ixgbe
|
||||
|
||||
Go ahead and insert the newly built ixgbe module into the kernel with insmod command. Make sure to specify an absolute path to the module.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo insmod ./ixgbe.ko
|
||||
|
||||
If the above command runs successfully, it will not show any message.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want, you can try passing additional prameter(s). For example, to set the number of RSS queues to 16:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo insmod ./ixgbe.ko RSS=16
|
||||
|
||||
Check out **/var/log/kern.log** to see if ixgbe driver is successfully activated. Look for "Intel(R) 10 Gigabit PCI Express Network Driver" in the log. The ixgbe version should be matched with the output of modinfo shown earlier.
|
||||
|
||||
Sep 18 14:48:52 spongebob kernel: [684717.906254] Intel(R) 10 Gigabit PCI Express Network Driver - version 3.22.3
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Five: Install Ixgbe Driver ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once you verify that a new ixgbe driver is successfully loaded, the last step is to install the driver on your system.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
**ixgbe.ko** will then be installed under /lib/modules/<kernel-version>/kernel/drivers/net/ethernet/intel/ixgbe.
|
||||
|
||||
From this point on, you can load ixgbe driver with modprobe command as follows. Note that you no longer need to specify an absolute path.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo modprobe ixgbe
|
||||
|
||||
If you want ixgbe driver to be loaded automatically upon boot, you can add "ixgbe" to the end of /etc/modules.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/download-install-ixgbe-driver-ubuntu-debian.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/e1000/files/ixgbe%20stable/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to set a custom HTTP header in curl
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I am trying to fetch a URL with curl command, but want to set a few custom header fields in the outgoing HTTP request. How can I use a custom HTTP header with curl?
|
||||
|
||||
curl is a powerful command-line tool that can transfer data to and from a server over network. It supports a number of transfer protocols, notably HTTP/HTTPS, and many others such as FTP/FTPS, RTSP, POP3/POP3S, SCP, IMAP/IMAPS, etc. When you send out an HTTP request for a URL with curl, it uses a default HTTP header with only essential header fields (e.g., User-Agent, Host, and Accept).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
In some cases, however, you may want to override the default header or even add a custom header field in an HTTP request. For example, you may want to override "Host" field to test a [load balancer][1], or spoof "User-Agent" string to get around browser-specific access restriction. In other cases, you may be accessing a website which requires a specific cookie, or testing a REST-ful API with various custom parameters in the header.
|
||||
|
||||
To handle all these cases, curl provides an easy way to fully control the HTTP header of outgoing HTTP requests. The parameter you want to use is "-H" or equivalently "--header".
|
||||
|
||||
The "-H" option can be specified multiple times with curl command to define more than one HTTP header fields.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, the following command sets three HTTP header fields, i.e., overriding "Host" field, and add two fields ("Accept-Language" and "Cookie").
|
||||
|
||||
$ curl -H 'Host: 157.166.226.25' -H 'Accept-Language: es' -H 'Cookie: ID=1234' http://cnn.com
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For standard HTTP header fields such as "User-Agent", "Cookie", "Host", there is actually another way to setting them. The curl command offers designated options for setting these header fields:
|
||||
|
||||
- **-A (or --user-agent)**: set "User-Agent" field.
|
||||
- **-b (or --cookie)**: set "Cookie" field.
|
||||
- **-e (or --referer)**: set "Referer" field.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, the following two commands are equivalent. Both of them change "User-Agent" string in the HTTP header.
|
||||
|
||||
$ curl -H "User-Agent: my browser" http://cnn.com
|
||||
$ curl -A "my browser" http://cnn.com
|
||||
|
||||
wget is another command-line tool which you can use to fetch a URL similar to curl, and wget also allows you to use a custom HTTP header. Check out [this post][2] for details on wget command.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/custom-http-header-curl.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/haproxy-http-load-balancer-linux.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-use-custom-http-headers-with-wget.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to use yum to download a RPM package without installing it
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I want to download a RPM package from Red Hat's standard repositories. Can I use yum command to download a RPM package without installing it?
|
||||
|
||||
yum is the default package manager for Red Hat based systems, such as CentOS, Fedora or RHEL. Using yum, you can install or update a RPM package while resolving its package dependencies automatically. What if you want to download a RPM package without installing it on the system? For example, you may want to archive some RPM packages for later use or to install them on another machine.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how to download a RPM package from yum repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
### Method One: Yum ###
|
||||
|
||||
The yum command itself can be used to download a RPM package. The standard yum command offers '--downloadonly' option for this purpose.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install --downloadonly <package-name>
|
||||
|
||||
By default, a downloaded RPM package will be saved in:
|
||||
|
||||
/var/cache/yum/x86_64/[centos/fedora-version]/[repository]/packages
|
||||
|
||||
In the above, [repository] is the name of the repository (e.g., base, fedora, updates) from which the package is downloaded.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to download a package to a specific directory (e.g., /tmp):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install --downloadonly --downloaddir=/tmp <package-name>
|
||||
|
||||
Note that if a package to download has any unmet dependencies, yum will download all dependent packages as well. None of them will be installed.
|
||||
|
||||
One important thing is that on CentOS/RHEL 6 or earlier, you will need to install a separate yum plugin (called yum-plugin-downloadonly) to be able to use '--downloadonly' command option:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install yum-plugin-downloadonly
|
||||
|
||||
Without this plugin, you will get the following error with yum:
|
||||
|
||||
Command line error: no such option: --downloadonly
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Method Two: Yumdownloader ###
|
||||
|
||||
Another method to download a RPM package is via a dedicated package downloader tool called yumdownloader. This tool is part of yum-utils package which contains a suite of helper tools for yum package manager.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install yum-utils
|
||||
|
||||
To download a RPM package:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yumdownloader <package-name>
|
||||
|
||||
The downloaded package will be saved in the current directory. You need to use root privilege because yumdownloader will update package index files during downloading. Unlike yum command above, none of the dependent package(s) will be downloaded.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/yum-download-rpm-package.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
||||
How to Boot Linux ISO Images Directly From Your Hard Drive
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hi all, today we'll teach you an awesome interesting stuff related with the Operating System Disk Image and Booting. Now, try many OS you like without installing them in your Physical Hard Drive and without burning DVDs or USBs.
|
||||
|
||||
We can boot Linux ISO files directly from your hard drive with Linux’s GRUB2 boot loader. We can boot any Linux Distribution's using this method without creating bootable USBs, Burn DVDs, etc but the changes made will be temporary.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Get the ISO of the Linux Distributions: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we're gonna create Menu of Ubuntu 14.04 LTS "Trusty" and Linux Mint 17.1 LTS "Rebecca" so, we downloaded them from their official site:
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu from : [http://ubuntu.com/][1] And Linux Mint from: [http://linuxmint.com/][2]
|
||||
|
||||
You can download ISO files of required linux distributions from their respective websites. If you have mirror of the iso files hosted near your area or country, it is recommended if you have no sufficient internet download speed.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Determine the Hard Drive Partition’s Path ###
|
||||
|
||||
GRUB uses a different “device name” scheme than Linux does. On a Linux system, /dev/sda0 is the first partition on the first hard disk — **a** means the first hard disk and **0** means its first partition. In GRUB, (hd0,1) is equivalent to /dev/sda0. The **0** means the first hard disk, while **1** means the first partition on it. In other words, in a GRUB device name, the disk numbers start counting at 0 and the partition numbers start counting at 1. For example, (hd3,6) refers to the sixth partition on the fourth hard disk.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the **fdisk -l** command to view this information. On Ubuntu, open a Terminal and run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fdisk -l
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You’ll see a list of Linux device paths, which you can convert to GRUB device names on your own. For example, below we can see the system partition is /dev/sda1 — so that’s (hd0,1) for GRUB.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Adding boot menu to Grub2 ###
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to add a custom boot entry is to edit the /etc/grub.d/40_custom script. This file is designed for user-added custom boot entries. After editing the file, the contents of your /etc/defaults/grub file and the /etc/grub.d/ scripts will be combined to create a /boot/grub/grub.cfg file. You shouldn't edit this file by hand. It’s designed to be automatically generated from settings you specify in other files.
|
||||
|
||||
So we’ll need to open the /etc/grub.d/40_custom file for editing with root privileges. On Ubuntu, you can do this by opening a Terminal window and running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/grub.d/40_custom
|
||||
|
||||
Unless we’ve added other custom boot entries, we should see a mostly empty file. We'll need to add one or more ISO-booting sections to the file below the commented lines.
|
||||
|
||||
=====
|
||||
menuentry “Ubuntu 14.04 ISO” {
|
||||
set isofile=”/home/linoxide/Downloads/ubuntu-14.04.1-desktop-amd64.iso”
|
||||
loopback loop (hd0,1)$isofile
|
||||
linux (loop)/casper/vmlinuz.efi boot=casper iso-scan/filename=${isofile} quiet splash
|
||||
initrd (loop)/casper/initrd.lz
|
||||
}
|
||||
menuentry "Linux Mint 17.1 Cinnamon ISO" {
|
||||
set isofile=”/home/linoxide/Downloads/mint-17.1-desktop-amd64.iso”
|
||||
loopback loop (hd0,1)$isofile
|
||||
linux (loop)/casper/vmlinuz.efi boot=casper iso-scan/filename=${isofile} quiet splash
|
||||
initrd (loop)/casper/initrd.lz
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Important Note**: Different Linux distributions require different boot entries with different boot options. The GRUB Live ISO Multiboot project offers a variety of [menu entries for different Linux distributions][3]. You should be able to adapt these example menu entries for the ISO file you want to boot. You can also just perform a web search for the name and release number of the Linux distribution you want to boot along with “boot from ISO in GRUB” to find more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Updating Grub2 ###
|
||||
|
||||
To make the custom menu entries active, we'll run "sudo update-grub"
|
||||
|
||||
sudo update-grub
|
||||
|
||||
Hurray, we have successfully added our brand new linux distribution's ISO to our GRUB Menu. Now, we'll be able to boot them and enjoy trying them. You can add many distributions and try them all. Note that the changes made in those OS will don't be kept preserved, which means you'll loose changes made in that distros after the restart.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/boot-linux-iso-images-directly-hard-drive/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://linuxmint.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://git.marmotte.net/git/glim/tree/grub2
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
How to make a file immutable on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Suppose you want to write-protect some important files on Linux, so that they cannot be deleted or tampered with by accident or otherwise. In other cases, you may want to prevent certain configuration files from being overwritten automatically by software. While changing their ownership or permission bits on the files by using chown or chmod is one way to deal with this situation, this is not a perfect solution as it cannot prevent any action done with root privilege. That is when chattr comes in handy.
|
||||
|
||||
chattr is a Linux command which allows one to set or unset attributes on a file, which are separate from the standard (read, write, execute) file permission. A related command is lsattr which shows which attributes are set on a file. While file attributes managed by chattr and lsattr are originally supported by EXT file systems (EXT2/3/4) only, this feature is now available on many other native Linux file systems such as XFS, Btrfs, ReiserFS, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I am going to demonstrate how to use chattr to make files immutable on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
chattr and lsattr commands are a part of e2fsprogs package which comes pre-installed on all modern Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
Basic syntax of chattr is as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ chattr [-RVf] [operator][attribute(s)] files...
|
||||
|
||||
The operator can be '+' (which adds selected attributes to attribute list), '-' (which removes selected attributes from attribute list), or '=' (which forces selected attributes only).
|
||||
|
||||
Some of available attributes are the following.
|
||||
|
||||
- **a**: can be opened in append mode only.
|
||||
- **A**: do not update atime (file access time).
|
||||
- **c**: automatically compressed when written to disk.
|
||||
- **C**: turn off copy-on-write.
|
||||
- **i**: set immutable.
|
||||
- **s**: securely deleted with automatic zeroing.
|
||||
|
||||
### Immutable Attribute ###
|
||||
|
||||
To make a file immutable, you can add "immutable" attribute to the file as follows. For example, to write-protect /etc/passwd file:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chattr +i /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you must use root privilege to set or unset "immutable" attribute on a file. Now verify that "immutable" attribute is added to the file successfully.
|
||||
|
||||
$ lsattr /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
Once the file is set immutable, this file is impervious to change for any user. Even the root cannot modify, remove, overwrite, move or rename the file. You will need to unset the immutable attribute before you can tamper with the file again.
|
||||
|
||||
To unset the immutable attribute, use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chattr -i /etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you want to make a whole directory (e.g., /etc) including all its content immutable at once recursively, use "-R" option:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chattr -R +i /etc
|
||||
|
||||
### Append Only Attribute ###
|
||||
|
||||
Another useful attribute is "append-only" attribute which forces a file to grow only. You cannot overwrite or delete a file with "append-only" attribute set. This attribute can be useful when you want to prevent a log file from being cleared by accident.
|
||||
|
||||
Similar to immutable attribute, you can turn a file into "append-only" mode by:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chattr +a /var/log/syslog
|
||||
|
||||
Note that when you copy an immutable or append-only file to another file, those attributes will not be preserved on the newly created file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I showed how to use chattr and lsattr commands to manage additional file attributes to prevent (accidental or otherwise) file tampering. Beware that you cannot rely on chattr as a security measure as one can easily undo immutability. One possible way to address this limitation is to restrict the availability of chattr command itself, or drop kernel capability CAP_LINUX_IMMUTABLE. For more details on chattr and available attributes, refer to its man page.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/make-file-immutable-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
Keep History Of Notifications With Recent Notifications AppIndicator
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Most of the desktop environments like Unity and Gnome have notification featured. Something which I like a lot. It specially helps me when I am listening to [streaming radio on Ubuntu][1]. But by default the notification is displayed on the top of the desktop for a couple of seconds and then it fades in disappearance. Now, what if you hear the notification sound but did not see it in time? How do you know what notification was it?
|
||||
|
||||
If somehow you could have a history of all recent notifications, would it not be great? Yes, I know it would be great. You can easily keep track of all recent notifications in Ubuntu Unity or GNOME using Recent **Notifications applet indicator**.
|
||||
|
||||
Recent Notifications sits in the top panel and keeps the history of all recent notifications. When there are new notifications captured by it, the indicator turns green to notify you of unread notifications.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When you click on it, you will see all the recent notifications. You can either choose to clear all of the notifications or remove some of those.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately there are no configuration options here. Therefore you cannot block notifications from specific applications. All kind of notifications will be saved here.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Recent Notifications in Ubuntu 14.04 and 14.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Normally this Recent Notification applet indicator should also work in Linux Mint Cinnamon edition. You can give it a try. Use the following commands to install Recent Notifications applet indicator in Ubuntu 14.04 and 14.10:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:jconti/recent-notifications
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install indicator-notifications
|
||||
|
||||
After installation, log out, log back in and you are good to go. Now none of the recent notifications will go unnoticed. Hand applet indicator, isn’t it?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/notifications-appindicator/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/apps-internet-streaming-radio-ubuntu/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
|
||||
手把手教你安装Xubuntu Linux
|
||||
==============================================
|
||||
|
||||
### 简介 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个教程会一步一步的教你如何安装Xubuntu Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
为什么你会想要安装Xubuntu呢?这里有三个原因:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 你有一台安装Windows XP的计算机,但是微软已经不再对Windows XP提供支持
|
||||
2. 你的[电脑运行很慢][1],并且你想要一个轻量级并且跟得上时代潮流的操作系统
|
||||
3. 你想要增加一些DIY经验
|
||||
|
||||
首先,你需要[下载Xubuntu,并且创建一个启动优盘][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
完成以后,用优盘启动到Xubuntu,然后点击安装Xubuntu图标。
|
||||
|
||||
### 选择你的安装语言 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
第一步,选择你的安装语言。
|
||||
|
||||
在左边的列表中选择语言,然后单击“Continue”。
|
||||
|
||||
### 选择无线网络链接 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
第二步,需要你来选择你的网络链接。这个步骤不是必须的。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你[网络状况十分糟糕][3],直接跳过是一个明智的选择,因为安装程序会在安装过程中从网络上下载一些更新包。那么可想而知,你的安装过程就会花费很长的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,如果你的[网速很快][4],选择一个无线网,然后输入密码就行了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 准备安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这时候,你将会看到一个列表,显示安装Xubuntu的一些准备条件:
|
||||
|
||||
- 是否拥有至少6.2G的磁盘空间
|
||||
- 是否链接到互联网
|
||||
- 是否连接了电源
|
||||
|
||||
只有磁盘空间是必要条件。
|
||||
|
||||
在上一个步骤中提到过,你可以在安装Xubuntu的过程中不安装更新包。在系统安装完成以后再安装更新包也是可以的。
|
||||
|
||||
安装过程中,如果电池电量耗完的话,你才必须要链接到到电源。
|
||||
|
||||
这里还有一个复选框,提示你是否安装用于[播放MP3][5]或者[Flash视频][6]的第三方软件,当然,这些内容也可以在安装完成以后进行。
|
||||
|
||||
### 选择安装类型 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
接下来的步骤是选择安装类型。显示那些选项,取决于之前电脑上安装了什么系统。
|
||||
|
||||
在我的示例中,我已经安装了[Ubuntu MATE][7],所以,我的选项是重装Ubuntu、删除并且重装、Xubuntu和Ubuntu双系统、以及其他。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的计算机上安装了Windows,那么你得到的选项就是,安装双系统、使用Xubuntu替换Windows以及其他。
|
||||
|
||||
这个教程只是用来说明如何在计算机上安装Xubuntu,而不是怎么安装双系统,那将是一个完全不同的教程。
|
||||
|
||||
选择使用Xubuntu替换当前系统,然后点击“Continue”。
|
||||
|
||||
> 备注:这会导致你的磁盘被完全清除,在继续安装之前,你应该备份你的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
### 选择安装磁盘 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
选择你要在那个磁盘上安装的Xubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“Install Now”。
|
||||
|
||||
这时候会弹出一个警告窗口,会提示你,选择的磁盘驱动器会被完全清除,然后会显示一个新创建的分区列表。
|
||||
|
||||
> 备注:这是你改变主意的最后一个机会,如果你点击继续,磁盘就会被完全清除,然后开始安装Xubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“Continue”来安装Xubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
### 选择地区 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个步骤中,你需要通过点击底图来选择你的地区。系统根据你的选择来设置时区,这样,你的时钟就可以显示正确的时间了。
|
||||
|
||||
选择以后点击“Continue”。
|
||||
|
||||
### 选择键盘布局 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
选择你的键盘布局。
|
||||
|
||||
在左边的列表中选择键盘语言,然后在右边的列表显示确切的键盘布局。
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以点击“Detect Keyboard Layout”让系统选择最适合的键盘布局。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要确认键盘布局是否正确,可以在“Type here to test your keyboard”输入字符。你需要特别注意fn键和一些符号,例如英镑和美元符号。
|
||||
|
||||
如果在安装过程中没有设对也没关系,安装完成以后在Xubuntu系统设置中也可以进行调整。
|
||||
|
||||
### 新增用户 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
为了使用Xubuntu,你至少需要设置一个用户,因此安装程序需要你设置一个默认用户。
|
||||
|
||||
在前两个输入框里面,输入你的名字以及用来识别你的计算机的名字。
|
||||
|
||||
为用户选择一个用户名并且[创建一个密码][8]。为了保证你的密码输入正确,你需要输入两遍。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要系统自动登入,而不是在每次启动的时候输入密码,选择“Log in automatically”。尽管对于我来说,我肯定不会选择这个选项。
|
||||
|
||||
更好的选项是“Require my password to log in”,并且如果你想要更高的安全等级,勾选“Encrypt my home fodler”选项。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“Continue”然后继续。
|
||||
|
||||
### 等待安装完成 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个步骤中,将会会拷贝文件到你的电脑,并且安装Xubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
在这个过程中,你会看到一个简短的幻灯片。在这个时候你可以去[泡一杯咖啡][9]或者放松一下什么的。
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成以后,会弹出提示告诉你是否重新启动,并且开始体验一下新安装的Xubuntu系统。
|
||||
|
||||
准备好了么?拔掉启动盘重新启动吧。
|
||||
|
||||
> 备注:在UEFI机器上面安装Xubuntu的话,需要一些额外的步骤,在这个教程里面没有提到。关于这方面的内容,且听下回分解。
|
||||
|
||||
via : http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/A-Step-By-Step-Guide-To-Installing-Xubuntu-Linux.htm#step-heading
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gary Newell][a]
|
||||
译者:[zhouj-sh](https://github.com/zhouj-sh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linux.about.com/bio/Gary-Newell-132058.htm
|
||||
[1]:http://windows.about.com/od/maintainandfix/a/8ways2speedup.htm
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-Persistent-Bootable-Xubuntu-Linux-USB-Drive.htm
|
||||
[3]:http://netforbeginners.about.com/od/basicinternethardware/f/Why-Internet-Connections-Can-Be-Slow.htm
|
||||
[4]:http://netforbeginners.about.com/b/2011/09/07/test-your-internet-connection-speed-here.htm
|
||||
[5]:http://mp3.about.com/od/freebies/tp/freemusictp.htm
|
||||
[6]:http://animation.about.com/od/2danimationtutorials/ss/2d_fla_lesson1.htm
|
||||
[7]:http://www.everydaylinuxuser.com/2014/11/ubuntu-mate-vs-lubuntu-on-old-netbook.html
|
||||
[8]:http://netsecurity.about.com/cs/generalsecurity/a/aa112103b.htm
|
||||
[9]:http://coffeetea.about.com/od/preparationandrecipes/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
|
||||
3种创建轻量、持久化的Xubuntu Linux USB系统盘的方法
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用Universal USB Install创建持久化USB Xubuntu系统盘 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个教程为你介绍如何使用Xubuntu Linux创建一个轻量并且[持久化][1]的Linux USB系统盘。
|
||||
|
||||
> 译者注:持久化Linux USB系统盘(Persistent Linux USB drive),安装在优盘的Linux系统,允许用户保存数据到优盘而不是仅仅将这些修改留在内存中。这些数据可以在重启后恢复并且重新使用,甚至是在其他的机器上面启动也没有关系。一般情况下,持久化系统盘会安装一个压缩过的Linux操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
为什么你需要做这些事情呢,这里有5个很好的理由:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 你想要在你的电脑上安装一个轻量的并且功能完善的Linux版本。
|
||||
2. 你的电脑没有硬盘,那么一个Linux USB系统盘就可以让这台电脑摆脱被扔到垃圾堆的命运。
|
||||
3. 你想体验一下Linux,但是你却不想花太多的时间去准备。
|
||||
4. 你想创建一个USB系统恢复盘,并且在优盘上安装一些特定的应用程序。
|
||||
5. 你想要一个可以装在屁股口袋或者可以挂在钥匙圈上面的可定制的Linux版本。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们有了充足的理由,那么开始做一些准备工作吧。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你使用的是Windows:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 下载Xubuntu。
|
||||
2. 下载Universal USB Installer。
|
||||
3. 插入一个空的优盘。
|
||||
4. 使用Universal USB Installer创建一个常驻系统启动盘。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你使用的是Ubuntu:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 下载Xubuntu。
|
||||
2. 使用Ubuntu Startup Creator。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你使用的是其他版本的Linux:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 下载Xubuntu。
|
||||
2. 使用UNetbootin。
|
||||
|
||||
还有一些场景,可能需要使用命令行,会更难一些,但是上面列的三种应该已经可以满足大部分的情况。
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载Xubuntu和Universal USB Installer ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
访问[Xubuntu网站][2],然后选一个你喜欢的版本下载。
|
||||
|
||||
目前有两个版本可供使用:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Trusty Tahr (14.04 LTS)][3]
|
||||
- [Utopic Unicorn (14.10)][4]
|
||||
|
||||
14.04版是一个长期维护的版本,维护周期会持续3年。14.10是最新版本,但是只提供9个月的维护。
|
||||
|
||||
你选择了下载站点以后,会提示你选择32位版本或者64位版本。如果你的电脑是32位,就选32位版本,同样,如果你的电脑是64位选64位版本就行了。
|
||||
|
||||
[点击这里,有一个教程来教你辨别你的电脑是32位还是64位][5]。
|
||||
|
||||
可以从[Pendrive Linux网站][6]下载Universal USB Installer,点击download链接,过一会下载页面就会弹出来了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用Universal USB Installer创建一个Xubuntu启动优盘 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下载完Universal USB Installer和Xubuntu以后,运行Universal USB Installer,出现安全警告时,点击“Accept”。
|
||||
|
||||
Universal USB Installer用来创建一个持久化的Xubuntu启动优盘。
|
||||
|
||||
第一屏是许可协议。点击“I Agree”继续。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Universal USB Installer主界面出现以后,从下拉列表中选择你想要的配置(i.e Xubuntu),第二步,点击“Browse”选择你下载的ISO文件的路径。
|
||||
|
||||
在电脑上插入一个空的优盘,然后选中“Showing all drives”复选框。
|
||||
|
||||
在下拉列表中选中你的优盘(一定要确定选的是正确的盘符哦)。如果优盘不是空的,选中格式化复选框。
|
||||
|
||||
> 注:格式化优盘会清除优盘上的所有数据,首先一定要确认是否以及备份过相关的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
在第四步中选择用于保存“持久化”系统数据的存储空间大小。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“Create”按钮继续。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后一个界面提示你如果点击“Yes”,那么将会直接应用你的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
这是停止安装的最后一个机会,一定要确定你选了正确的优盘盘符,并且优盘上没有需要备份的其他文件。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“Yes”,然后耐心等待优盘创建完成。
|
||||
|
||||
> 注:创建持久化保存空间会花费一些时间,并且这时候进度条不会继续滚动。
|
||||
|
||||
这个过程完成以后,重启电脑,如果从优盘启动,就会加载Xubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用Ubuntu的Startup Disk Creator创建Xubuntu启动优盘 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经安装了Ubuntu,那么创建持久化USB Xubuntu系统盘的最简单的办法就是使用Startup Disk Creator。
|
||||
|
||||
按下超级键(Windows键),打开Dash,搜索“Startup Disk Creator”,图标出现以后点击它。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你对Ubuntu Dash不太熟悉,你可以[点击这里,查看一个完整的教程][7]。
|
||||
|
||||
Startup Disk Creator使用起来很简单。
|
||||
|
||||
界面被划分成两个部分。在上面部分指定下载的系统盘路径,在下面指定安装的优盘。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,点击“Other”按钮,第二步,选择你所下载的Xubuntu ISO文件。
|
||||
|
||||
然后插入优盘,点击“Erase”按钮清除优盘数据。
|
||||
|
||||
> 注:点击“Erase”会删除优盘中所有的数据,记得先备份数据。
|
||||
|
||||
选中“Stored in reserved extra sapce”单选按钮,然后拖动“How much”来确定你想要用来存储“持久化”数据的空间。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“Make Startup Disk”。
|
||||
|
||||
你创建的过程中,你可能需要输入几次你的系统密码,USB系统盘创建完成以后,你就可以使用它启动到Xubuntu了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用UNetbootin创建持久化Xubuntu系统盘 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我要介绍的最后一个工具是UNetbootin,这个工具在Windows和Linux上都可以使用。
|
||||
|
||||
个人来说,在Windows系统上面我喜欢用Universal USB Installer,但Linux的话,UNetbootin更合适一些。
|
||||
|
||||
> 注:UNetbootin并不是100%完美的,它并不支持所有的Linux发行版。
|
||||
|
||||
Windows平台可以点击[这里][8]下载UNetbootin。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux平台可以使用package manager安装UNetbootin。
|
||||
|
||||
确认你的优盘已经连接到电脑上,确认优盘已经格式化,并且在优盘上没有其他的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
在Windows平台上运行UNetbootin只需要双击可执行程序即可,在Linux运行的话则需要提升权限。
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux上如何运行取决于你使用的是何种桌面环境以及Linux发行版。从命令行运行的话,输入下列命令:
|
||||
|
||||
> sudo unetbootin
|
||||
|
||||
UNetbootin的界面分为两个部分。你可以在上面的部分选择一个Linux发行版,然后下载它,如果已经下载了某个发行版,可以在下半部分选择已经下载的系统盘。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“Diskimage”单选框,然后点击三个点的按钮。找到已经下载的Xubuntu ISO文件。路径会显示到按钮旁边的文本框里面。
|
||||
|
||||
修改“Space used to preserve files across reboots”的值,来指定你想要用来存储“持久化”数据的空间大小。
|
||||
|
||||
类型选择USB drive,然后选择优盘的盘符。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“OK”来创建一个持久化Xubuntu启动优盘。
|
||||
|
||||
创建的过程要花一些时间,创建完成以后,你就可以通过优盘启动到Xubuntu系统了。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要创建一个支持UEFI的Xubuntu启动优盘,[照着这个教程来做][8],只需要把Ubuntu ISO替换为Xubuntu ISO就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
via : http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-Persistent-Bootable-Xubuntu-Linux-USB-Drive.htm
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gary Newell][a]
|
||||
译者:[zhouj-sh](https://github.com/Zhouj-sh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linux.about.com/bio/Gary-Newell-132058.htm
|
||||
[1]:http://www.pendrivelinux.com/what-is-persistent-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://xubuntu.org/getxubuntu/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/xubuntu-trusty.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/xubuntu-utopic.html
|
||||
[5]:http://pcsupport.about.com/od/fixtheproblem/f/32-bit-64-bit-windows.htm
|
||||
[6]:http://www.pendrivelinux.com/universal-usb-installer-easy-as-1-2-3/
|
||||
[7]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/fl/Learn-Ubuntu-The-Unity-Dash.htm
|
||||
[8]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-UEFI-Bootable-Ubuntu-USB-Drive-Using-Windows.htm
|
||||
161
translated/share/20150119 Ubuntu With XFCE vs Xubuntu Linux.md
Normal file
161
translated/share/20150119 Ubuntu With XFCE vs Xubuntu Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu With XFCE vs Xubuntu Linux
|
||||
=========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu vs Xubuntu。Ubuntu拥有漂亮的桌面体验以及强大的应用程序。Xubuntu轻量、快速并且可定制,哪个更适合你?
|
||||
---------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
首先,这篇文章不是用来说明Ubuntu比Xubuntu更好或者Xubuntu比Ubuntu更好之类的东西。
|
||||
|
||||
并且,我同时也会在这篇文章中介绍Ubuntu用户如何获取基本的XFCE桌面,以及如何安装完整的Xubuntu桌面。
|
||||
|
||||
[Ubuntu][1]以及[Xubuntu][2]是针对不同目的开发的操作系统,为什么我会强调这一点,是为了说明什么时候或者为什么你应该使用Ubuntu以及什么时候应该使用Xubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
比较这两个操作系统就像比较[劳斯莱斯][3]与[保时捷][4]。这两个都是很棒的车,但是如果把劳斯莱斯给一个赛车迷,他们也许会卖掉它买个其他的车,同样,如果把保时捷给舒格勋爵或者休·海夫纳这类人可能也不那么合适。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu拥有一个适用性很强的桌面环境,叫做Unity,并且默认会安装一些很棒的Linux应用程序,包括Rhythmbox以及[LibreOffic][5]。Ubuntu就像是劳斯莱斯。它为舒适而生,并且尽可能的提供从A到B的最时髦的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个Ubuntu用户,就像汽车里面的乘客。你在到达目的地的过程中就可以同时把事情搞定,并且所有的事看起来都很漂亮并且很简单。
|
||||
|
||||
另一方面,Xubuntu采用了轻量的[XFCE桌面环境][6]。内置的应用自然也是轻量级的,使用它们也可以完成工作,但是不像Ubuntu自带的应用那么完整。
|
||||
|
||||
XFCE桌面环境可以高度定制化,你可以把你的桌面搞成任何你想要的形式。
|
||||
|
||||
Xubuntu就像一个改装过的跑车。你可以把它改装成任何你想要的样子。但不是做为一名乘客,而更像是驾驶员开着它快速漂移过弯,或者小心翼翼的通过狭小的弯角。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不关心如何美化或者定制桌面,并且你发现Ubuntu用起来很顺手,那么你没必要切换到Xubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,如果你发现Unity没办法满足你的要求,并且感觉你的计算机在运行Ubuntu时或多或少有一些性能压力,那么当然就可以考虑考虑Xubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
上周我发了一篇文章介绍怎么[创建Xubuntu启动优盘][c],并且也写了一篇[安装Xubuntu的教程][b](译者注:链接为github地址)。
|
||||
|
||||
不过,如果你已经安装了Ubuntu,就不用这么费事照着教程再来一遍了。你只需要继续读完这篇文章,就可以在Ubuntu里面安装一个更合适的解决方案。
|
||||
|
||||
那么如果你已经装了Ubuntu,如何切换到Xubuntu呢?
|
||||
|
||||
你需要做一个选择题。问题是,你是仅仅需要一个更轻量的、可定制化的XFCE桌面,还是同时也需要那些Xubuntu内置的轻量级应用。
|
||||
|
||||
先来看看这些应用吧。下面有一个列表,列出了Ubuntu和Xubuntu内置的应用程序。如果你只需要几个Xubuntu应用程序,那么我建议你只安装XFCE然后单独安装这些应用。如果你需要一半以上的应用,那就安装整个Xubuntu桌面环境吧。
|
||||
|
||||
<table class="table table-bordered table-striped table-condensed">
|
||||
<caption>
|
||||
<strong>Ubuntu与Xubuntu内置应用对比</strong>
|
||||
</caption>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><strong>应用类型</strong></td>
|
||||
<td><strong>Ubuntu</strong></td>
|
||||
<td><strong>Xubuntu</strong></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>音频</td>
|
||||
<td>Rhythmbox</td>
|
||||
<td>gmusicbrowser</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>视频</td>
|
||||
<td>Totem</td>
|
||||
<td>Parole</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>照片管理</td>
|
||||
<td>Shotwell</td>
|
||||
<td>Ristretto</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>办公</td>
|
||||
<td>LibreOffice</td>
|
||||
<td>Abiword/Gnumeric</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>浏览器</td>
|
||||
<td>FireFox</td>
|
||||
<td>FireFox</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>Email</td>
|
||||
<td> </td>
|
||||
<td>Thunderbird</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>即时通讯</td>
|
||||
<td>Empathy</td>
|
||||
<td>Pidgin</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在Ubuntu安装XFCE桌面环境 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
接下来,我会使用命令行工具[apt-get][7]介绍在Ubuntu安装XFCE桌面的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
打开一个终端窗口,在Unity环境,你可以在[Dash][8]中搜索“TERM”,或者使用组合键 CTRL+ALT+T。
|
||||
|
||||
安装XFCE桌面十分简单,输入下列命令就可以了:
|
||||
|
||||
>sudo apt-get update
|
||||
>sudo apt-get install xfce4
|
||||
|
||||
点击右上角设置图标然后登出,来切换到[XFCE桌面环境][9]。
|
||||
|
||||
切换到登入界面以后,点击在你用户名旁边的小Ubuntu图标,就会出现Unity桌面和XFCE桌面的选项。切换到XFCE然后正常登录。
|
||||
|
||||
系统会显示一个消息,提示你是否使用默认的面板布局或者使用单独的面板。
|
||||
|
||||
[最新版本的Xubuntu][10]在顶部包含一个单独的面板,不过我更喜欢两个面板,顶部一个标准面板,底部一个常用程序的停靠面板。
|
||||
|
||||
需要注意的是,XFCE桌面菜单系统和Xubuntu的菜单有些差异,除非你安装[一个更好的菜单系统][11],设置两个面板或许是个更好的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
这取决与选择的是哪个选项,不过没关系,如果后面你改变了主意,也可以很容易重新设置。XFCE可以进行深度的自定义。
|
||||
|
||||
### 不重新安装的情况下,如何从Ubuntu切换到Xubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你想全都使用Xubuntu的东西,但是又不想按照那些介绍重新安装系统的话,看看下面的东西。
|
||||
|
||||
通过搜索“TERM”,或者组合键CTRL+ALT+T,打开一个终端窗口。
|
||||
|
||||
在终端输入如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
>sudo apt-get update
|
||||
>sudo apt-get install xubuntu-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
花费的时间会比安装XFCE桌面长一些,但是要比重新安装Xubuntu系统要快。
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成以后,点击右上角图标,然后登出。
|
||||
|
||||
在登录界面,点击Ubuntu图标。会出现Unity和Xubuntu选项。点击Xubuntu,然后正常登入。
|
||||
|
||||
Xubuntu桌面就会显示出来啦。
|
||||
|
||||
这里会有一些差异。菜单仍然是XFCE菜单,而不是Xubuntu菜单。某些图标也不会出现在顶部面板中。但是这些问题都不足以让我们花时间卸载Ubuntu然后重装Xubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
下一篇文章中,我会介绍如何自定义Xubuntu以及XFCE桌面。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
via : http://linux.about.com/od/dist/fl/Ubuntu-With-XFCE-vs-Xubuntu-Linux.htm
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gary Newell][a]
|
||||
译者:[zhouj-sh](https://github.com/Zhouj-sh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linux.about.com/bio/Gary-Newell-132058.htm
|
||||
[b]:https://github.com/ZhouJ-sh/TranslateProject/blob/0c4ad0bc8e79e28c1f7f8ccf805708829baa8ea9/translated/share/20150116%20A%20Step%20By%20Step%20Guide%20To%20Installing%20Xubuntu%20Linux.md
|
||||
[c]:https://github.com/ZhouJ-sh/TranslateProject/blob/d91316c19c6668b82cfabf9f89e4ad07c7193202/translated/share/20150119%203%20Ways%20To%20Create%20A%20Lightweight%20And%20Persistent%20Xubuntu%20Linux%20USB%20Drive.md
|
||||
[1]:http://www.everydaylinuxuser.com/2014/11/an-everyday-linux-user-review-of-ubuntu.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.everydaylinuxuser.com/2015/01/an-everyday-linux-user-review-of.html
|
||||
[3]:http://exoticcars.about.com/od/overviewsofmaker1/p/RollsHistory.htm
|
||||
[4]:http://exoticcars.about.com/od/overviewsofmaker1/p/PorscheHistory.htm
|
||||
[5]:http://office.about.com/od/FreeOpenSourceOfficeSoftware/a/All-About-Libreoffice-4-0.htm
|
||||
[6]:http://linux.about.com/cs/linux101/g/xfce.htm
|
||||
[7]:http://linux.about.com/od/ubusrv_doc/a/ubusg11t01.htm
|
||||
[8]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/fl/Learn-Ubuntu-The-Unity-Dash.htm
|
||||
[9]:http://linux.about.com/cs/linux101/g/xfce.htm
|
||||
[10]:http://www.everydaylinuxuser.com/2015/01/an-everyday-linux-user-review-of.html
|
||||
[11]:http://xubuntugeek.blogspot.co.uk/2013/12/how-to-install-whisker-menu-in-xubuntu.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
2015:开源已经完胜,但还在继续
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 在 2014 年的完胜后,接下来会如何?
|
||||
|
||||
新年伊始,习惯上都是回顾已经走过的一年。但只要观注我们的这个栏目,就会很容易获得过去一年的总结:开源已经全胜。让我们从头开始说起吧:
|
||||
|
||||
**超级计算机**: Linux 在超级计算机系统 500 强的名单上占据绝对的主导地位这本身就令人很尴尬。[2014年11月的数据][1]显示前500系统中的485个系统都在运行着 Linux 的发布系统,而仅仅只有一台运行着 Windows 系统。如果您查询相关的核心数据,这问题更是让人触目惊心。截止到目前,Linux 系统有 22,851,693 之多而 windows 系统仅仅只有 30,720。这意味着什么?Linux 不仅仅是占据主导地位,在大型系统中已经是绝对的霸主了。
|
||||
|
||||
**云计算**: 去年, Linux 基金会撰写了一个有趣的[报告][2],是关于大公司在云端使用 Linux 的情况的。它发现 75% 的大公司在使用 Linux 系统作为他们的主要平台,相对的使用 Windows 系统的只占 23%。因为需要考虑云端和非云端的因素,它们已经混淆在一起了,所以很难把这比例对应到真实的市场份额里。但是,鉴于当前云计算的流行度,可以很确定的说明 Linux 使用的高速增长。事实上,同样的调查发现,在云端的 Linux 部署率已经从 45% 增长到 79%,而对于 Windows 来说已经从 45% 下降到 36%。当然了,某些人可能认为 Linux 基金会在这块上并不是完全公正无私的,但即使是有私心或是统计的不确定性而有失公允,事情也正朝着预料的正确方向迈进。
|
||||
|
||||
**Web 服务器**: 开源已经统治这个行业近20年 - 取得了一份很惊人的成绩。然而,最近在市场份额上出现了一些有趣的变动:一点就是,在 Web 服务器的总计数上,微软的 IIS 服务已经超越了 Apache 服务。但正如 Netcraft 公司其最近的[分析][3]解释所说的那样,这儿还有很多令人大饱眼福的地方呢:
|
||||
|
||||
> 这是网站总数持续大幅回落以来的第二个月,从一月份以来,创造了一个月的最低点。由于在十一月份的时候,损失的仅仅只是集中在主机提供商中的一小部分,只占了5200万主机名数的十大点。这点损失相比于激活的站点和网站来说不是一个数据级的,所以造不成什么影响,但激活的这些站点大部分都是广告类的链接页面,基本上没有原创的内容。大多数这些站点都是运行在微软的 IIS 服务器上的,所以在2014年7月份的调查中 IIS 的使用数就超过的 Apache 的。然而,近期跌势已导致其市场份额下降到 29.8%,现在已经低于Apache 10个百分点了。
|
||||
|
||||
这表明,微软的所谓“激增”更多的是表象,而事实并非如此,它的大多数增加都是基于链接页面站点,其内容很少有用。事实上,Netcraft公司的关于活动网站的数据给我们描绘了一幅完全不同的图表:Apache 拥有 50.57% 的市场份额,nginx 的是 14.73% 位居第二;微软的 IIS 很无力,占到了相当微弱的 11.72%。这意味着在活跃 Web 服务器市场上开源大约有65%的份额 - 虽然没有超级计算机那么高的水平,但也还不错。
|
||||
|
||||
**移动设备系统**. 目前,开源的大军主要是 Andriod 为基础在继续着。最新数据表明,在2014年第三季度的智能手机出货量中,Andriod 设备的市场份额从去年同期的 81.4% 上升到了 [83.6%][4]。苹果的从去年同期的 13.4% 下降到 12.3%。对于平板电脑来说,Android 平板遵循同样的轨迹:在2014年第二季度,Android 平板的占有率达到[全球平板电脑的销量的75%][5]左右,而苹果的只有25%。
|
||||
|
||||
**嵌入式系统**: 虽然很难量化 Linux 在的重要的嵌入式系统市场的市场份额,但来一个自 2013 年的研究数字表明,[计划大约一半的嵌入式系统][6]将会采用 Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
**物联网**: 在很多方面上可以把它们简单的认为是嵌入式系统的另外一个化身,不同之处在于它们被设计为一直在线的。虽然现在谈论它的市场份额还有点为时过早,但如我在[讨论栏目][7]里的,AllSeen 的物联网开源框架正进行的如火如荼。他们所缺少的也最引入注目的事情是要让任何可信任的闭源项目把其当做对手。因此,很有可能物联网将会通过开源的方式来达到 Linux 在超级计算机中的占有率这样的水平。
|
||||
|
||||
当然了,这个阶段的成功也带来了一些问题:我们将何去何从?鉴于开源将会使很多成功的行业达到饱和点,想必唯一的办法就是下跌吗?要回答这个问题,我建议浏览下 Christopher Kelty 于2013年写的一篇供同行参阅、发人深省的文章,有个耐人寻味的标题“[天下没有免费的软件][8]”。下面是他的开头段:
|
||||
|
||||
> 免费软件并不存在。在我写了一整本书后,我莫名的忧伤。但这也是我写进文章的一个观点。免费软件和它的分身开源正在不断的变化着。它并不是一直持续不变的,不稳定、不固定、不持久,这正是它的特色的一部分。
|
||||
|
||||
换句话说,无论2014年带给我们多少惊人的免费软件,我们也确信2015年会更多更丰富,因为进化是永无止境的。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.computerworlduk.com/blogs/open-enterprise/open-source-has-won-3592314/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[lyn Moody][a]
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.computerworlduk.com/author/glyn-moody/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.top500.org/statistics/list/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/publications/linux-foundation/linux-end-user-trends-report-2014
|
||||
[3]:http://news.netcraft.com/archives/2014/12/18/december-2014-web-server-survey.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.cnet.com/news/android-stays-unbeatable-in-smartphone-market-for-now/
|
||||
[5]:http://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/tech/tech-news/Android-tablet-market-share-hits-70-in-Q2-iPads-slip-to-25-Survey/articleshow/38966512.cms
|
||||
[6]:http://linuxgizmos.com/embedded-developers-prefer-linux-love-android/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.computerworlduk.com/blogs/open-enterprise/allseen-3591023/
|
||||
[8]:http://peerproduction.net/issues/issue-3-free-software-epistemics/debate/there-is-no-free-software/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 14.04 Apache2.2迁移2.4问题解决
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如果你进行了一次**Ubuntu**从12.04到14.04的升级,那么这次升级还包括了一个重大的升级--**Apache**从2.2版本到2.4版本。**Apache**的这次升级带来了许多性能提升,但是如果继续使用2.2的配置会导致很多错误。
|
||||
|
||||
### 访问控制的改变 ###
|
||||
|
||||
从**Apache 2.4**起,授权(authorization)开始启用,比起2.2的一个检查一个数据存储,授权更加灵活。过去很难确定那些命令授权应用了,但是授权(authorization)的引入解决了这些问题,现在,配置可以控制什么时候授权方法被调用,什么条件决定何时授权访问。
|
||||
|
||||
这就是为什么大多数的升级失败是由于错误配置,2.2的访问控制基于IP地址,主机名和其他字符通过使用指令Order,来设置Allow, Deny或 Satisfy,但是2.4,这些一切被新模板授权(authorization)来替代检查。
|
||||
|
||||
为了弄清楚这些,可以来看一些虚拟主机的例子,这些可以在/etc/apache2/sites-enabled/default 或者 /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/网页名称 中找到:
|
||||
|
||||
老2.2虚拟主机配置:
|
||||
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow from all
|
||||
|
||||
新2.4虚拟主机配置:
|
||||
|
||||
Require all granted
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### .htaccess 问题 ###
|
||||
|
||||
升级后如果一些设置不执行或者得到重定向错误,检查是否这些设置是在.htaccess文件中。如果是,2.4已经不再使用.htaccess文件,在2.4中默认使用AllowOverride指令来设置,因此忽略了.htaccess文件。你需要做的就是改变和增加AllowOverride All命令到你的页面配置文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
上面截图中,可以看见AllowOverride All指令。
|
||||
|
||||
### 丢失配置文件或者模块 ###
|
||||
|
||||
根据我的经验,这次升级带了其他问题就是老模块和配置文件不再需要或者不被支持了。所以你必须十分清楚Apache不再支持的各种文件,并且在老配置中移除这些老模块来解决问题。之后你可以搜索和安装相似的模块来替代。
|
||||
|
||||
### 其他需要的知道的小改变 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里还有一些其他改变的需要考虑,虽然这些通常只会发生警告,而不是错误。
|
||||
|
||||
- MaxClients重命名为MaxRequestWorkers,使之有更准确的描述。而异步MPM,如event,客服端最大连接数不量比与工作线程数。老名字依然支持。
|
||||
- DefaultType命令无效,使用它已经没有任何效果了。需要使用其他配置设定来替代它
|
||||
- EnableSendfile默认关闭
|
||||
- FileETag 默认"MTime Size"(没有INode)
|
||||
- KeepAlive 只接受On或Off值。之前的任何值不是Off或者0都认为是On
|
||||
- Mutex 替代 Directives AcceptMutex, LockFile, RewriteLock, SSLMutex, SSLStaplingMutex, 和 WatchdogMutexPath 。需要删除或者替代所有2.2老配置的设置。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/apache-migration-2-2-to-2-4-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
|
||||
译者:[Vic020/VicYu](http://vicyu.net)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/adriand/
|
||||
[1]:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/
|
||||
96
translated/tech/20150119 How To Disable IPv6 In CentOS 7.md
Normal file
96
translated/tech/20150119 How To Disable IPv6 In CentOS 7.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
如何在CentOS 7中禁止IPv6
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
最近,我的一位朋友问我该如何禁止IPv6。在搜索了一番之后,我找到了下面的方案。下面就是我在CentOS 7迷你版中禁止IPv6的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以用两个方法做到这个。
|
||||
|
||||
### 方法 1 ###
|
||||
|
||||
编辑文件**/etc/sysctl.conf**,
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
|
||||
|
||||
添加下面的行:
|
||||
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要为特定的网卡禁止IPv6,比如,对于enp0s3,添加下面的行。
|
||||
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.enp0s3.disable_ipv6 = 1
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出文件。
|
||||
|
||||
执行下面的命令来使设置生效。
|
||||
|
||||
sysctl -p
|
||||
|
||||
### 方法 2 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要在运行的系统中禁止IPv6,依次输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/all/disable_ipv6
|
||||
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/default/disable_ipv6
|
||||
|
||||
或者,
|
||||
|
||||
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1
|
||||
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6=1
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样。现在IPv6已经禁止了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 我在禁止IPv6后遇到问题怎么办 ###
|
||||
|
||||
You may get problems after disabling IPv6.
|
||||
你可能在禁止IPv6后遇到一些问题
|
||||
|
||||
#### 问题1: ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在禁止IPv6后SSH遇到问题,按照下面的做。
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 **/etc/ssh/sshd_config** 文件
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
|
||||
找到下面的行:
|
||||
|
||||
#AddressFamily any
|
||||
|
||||
把它改成:
|
||||
|
||||
AddressFamily inet
|
||||
|
||||
或者,
|
||||
|
||||
在这行的前面去掉注释**(#)**:
|
||||
|
||||
#ListenAddress 0.0.0.0
|
||||
|
||||
接着重启ssh来使改变生效。
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl restart sshd
|
||||
|
||||
#### 问题2: ####
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在禁止Ipv6后启动postfix遇到问题,编辑**/etc/postfix/main.cf**:
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/postfix/main.cf
|
||||
|
||||
注释掉配置中的localhost部分,并且使用ipv4回环。
|
||||
|
||||
#inet_interfaces = localhost
|
||||
inet_interfaces = 127.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样,干杯!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/disable-ipv6-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
如何在崩溃后重启Cinnamon
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Cinnamon是一个提供了高级创新特性和传统用户体验的Linux桌面环境。桌面布局和Gnome 2相似。底层的技术与Gnome Shell相似。它的重点是让用户有宾至如归的感觉并提供一个简单和舒适的桌面体验。
|
||||
|
||||
本篇中我们会展示一个快速的方法来重启Cinnamon而不用在崩溃后登出或者重启。
|
||||
|
||||
下图是Cinnamon桌面崩溃后,文本和图标从菜单和面板消失了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要重启Cinnamon
|
||||
|
||||
按下**Alt + F2** 将会打开一个命令菜单,输入**r**并按下回车。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon应该会重新在面板和菜单中显示图标和文本了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
享受吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/quick-tip-restart-cinnamon-crash/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Enock Seth Nyamador][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/seth/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
Linux 有问必答:如何在Ubuntu或者Debian中启动进入命令行
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**:我运行的是Ubuntu桌面,但是我希望启动后临时进入命令行。有什么简便的方法可以启动进入终端?
|
||||
|
||||
Linux桌面自带了一个显示管理器(比如:GDM、KDM、LightDM),它们可以让计算机启动自动进入一个基于GUI的登录环境。然而,如果你要直接启动进入终端怎么办? 比如,你在排查桌面相关的问题或者想要运行一个不需要GUI的发行程序。
|
||||
|
||||
注意你可以通过按下Ctrl+Alt+F1到F6临时从桌面GUI切换到虚拟终端。然而,在本例中你的桌面GUI仍在后台运行,这不同于纯文本模式启动。
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu或者Debian桌面中,你可以通过传递合适的内核参数在启动时启动文本模式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动临时进入命令行 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要禁止桌面GUI并只有一次进入文本模式,你可以使用GRUB菜单。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,打开你的电脑。当你看到初始的GRUB菜单时,按下‘e’。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
接着会进入下一屏,这里你可以修改内核启动选项。向下滚动到以“linux”开始的行,这里就是内核参数的列表。删除列表中的“quiet”和“splash”。在列表中添加“text”。
|
||||
|
||||
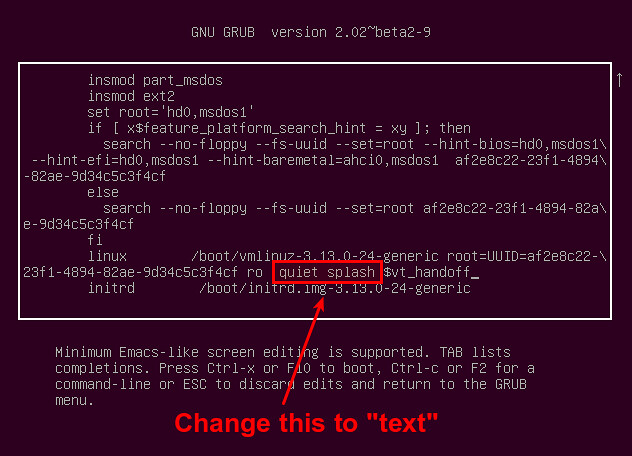
|
||||
|
||||
升级的内核选项列表看上去像这样。按下Ctrl+x继续启动。这会一次性以详细模式启动控制台。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
永久启动进入命令行。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要永久启动进入命令行,你需要[更新定义了内核启动参数GRUB设置][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
在文本编辑器中打开默认的GRUB配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/default/grub
|
||||
|
||||
查找以GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT开头的行,并用“#”注释这行。这会禁止初始屏幕,而启动详细模式(也就是说显示详细的的启动过程)。
|
||||
|
||||
更改GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="" 成:
|
||||
|
||||
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="text"
|
||||
|
||||
接下来取消“#GRUB_TERMINAL=console”的注释。
|
||||
|
||||
更新后的GRUB配置看上去像下面这样。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后,使用update-grub命令来基于这些更改重新生成/boot下的GRUB2配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo update-grub
|
||||
|
||||
这时,你的桌面应该从GUI启动切换到控制台启动了。可以通过重启验证。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/boot-into-command-line-ubuntu-debian.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/add-kernel-boot-parameters-via-grub-linux.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
Linux 有问必答: 如何在Linux中加入cron任务
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**: 我想在我的Linux中安排一个计划任务,该任务在固定时间周期性地运行。我该如何在Linux中添加一个cron任务?
|
||||
|
||||
cron是Linux中默认的计划任务。使用cron,你可以安排一个计划(比如:命令或者shell脚本)周期性地运行或者在指定的小时、天、周、月等特定时间运行。cron在你安排不同的常规维护任务时是很有用的,比如周期性地备份、日志循环、检查文件系统、监测磁盘空间等等。
|
||||
|
||||
### 从命令行中添加cron任务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要添加cron任务,你可以使用称为crontab的命令行工具。
|
||||
|
||||
输入下面的命令会创建一个以当前用户运行的新cron任务。
|
||||
|
||||
$ crontab -e
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要以其他用户运行cron任务,输入下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo crontab -u <username> -e
|
||||
|
||||
你将会看见一个文本编辑窗口,这里你可以添加或者编辑cron任务。默认使用nono编辑器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
每个cron任务的格式如下。
|
||||
|
||||
<minute> <hour> <day-of-month> <month-of-year> <day-of-week> <command>
|
||||
|
||||
前5个元素定义了任务的计划,最后一个元素是命令或者脚本的完整路径。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下面是一些cron任务示例。
|
||||
|
||||
- *** * * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 每分钟运行。
|
||||
- **0 * * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 每小时运行。
|
||||
- **0 0 * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 每12小时运行。
|
||||
- **0 9,18 * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 在每天的9AM和6PM运行。
|
||||
- **0 9-18 * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 在9AM到6PM的每个小时运行。
|
||||
- **0 9-18 * * 1-5 /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 周一到周五的9AM到6PM每小时运行。
|
||||
- ***/10 * * * * /home/dan/bin/script.sh**: 每10分钟运行。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦完成上面的设置步骤后,按下Ctrl+X来保存并退出编辑器。此时,新增的计划任务应该已经激活了。
|
||||
|
||||
要查看存在的计划任务,使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ crontab -l
|
||||
|
||||
### 从GUI添加计划任务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在Linux桌面环境中,你可以使用crontab的更加友好的GUI前端来添加或者添加一个cron任务。
|
||||
|
||||
在Gnome桌面中,有一个Gnome Schedule(gnome-schedule包)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在KDE桌面中,有一个Task Scheduler(kcron包)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/add-cron-job-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,181 @@
|
||||
如何通过简单的3步恢复Windows7同时删除Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### 说明 ###
|
||||
|
||||
写这篇文章对我来说是一件奇怪的事情,因为我通常都是提倡安装Ubuntu而卸载Windows的。
|
||||
|
||||
让今天写这篇文章更加奇怪的是,我决定在微软决定终止对Windows7的主流支持的这一天来写。
|
||||
|
||||
那么为什么我现在要写这篇文章呢?
|
||||
|
||||
到目前为止我曾经在很多场合被问到如何从一个装有Windows7或Windows8的双系统中删除Unbuntu系统,因此写这篇文章就变得有意义了。
|
||||
|
||||
我在圣诞节期间浏览了人们在我文章中的留言,感觉是时候把缺失的文章写完同时更新一下那些比较老的又需要关注的文章了。
|
||||
|
||||
我打算把一月份剩下的时间都用在这上面。这是第一步。如果你的电脑上安装了Windown7和Ubuntu双系统,同时你不想通过恢复出厂设置的方式恢复Windows7系统,那么请参考该教程。(注意:对于Windows8系统,有一个独立的教程)
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除Ubuntu系统需要的步骤 ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. 通过修复Windows启动项来删除Grub
|
||||
1. 删除Ubuntu系统所在分区
|
||||
1. 扩展Windows系统分区
|
||||
|
||||
### 备份系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在你开始之前,我建议为你的系统保留一个备份。
|
||||
|
||||
我也建议不要放弃这样的机会也不要使用微软自带的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
[点击查看如何使用Macrinum Reflect备份你的驱动][1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果Ubuntu中有你希望保存的数据,现在就登录进去然后将数据保存到外部硬盘驱动器,USB驱动器或者DVD中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤1 - 删除Grub启动菜单 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当你启动系统的时候你会看见一个与上图类似的菜单。
|
||||
|
||||
要想删除这个菜单直接进入Windows系统,你必须修复主引导记录。
|
||||
|
||||
要达到这个目的,我将向你展示如何创建一个系统恢复盘,如何从恢复盘中启动以及如何修复主引导记录。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
按下“开始”按钮,搜索“备份和还原”。点击出现的图标。
|
||||
|
||||
将会打开一个与上图一样的窗口。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“创建系统修复光盘”。
|
||||
|
||||
你需要一个[空的DVD盘][2]。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
将空的DVD盘插入到驱动器中然后从下拉列表中选择你的DVD驱动器。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“创建光盘”。
|
||||
|
||||
将光盘留在电脑中重启电脑,当出现从CD中启动的消息的时候按下键盘上的“回车”键。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
屏幕上会出现“系统恢复选项”。
|
||||
|
||||
它会要求你选择你的键盘布局方式。
|
||||
|
||||
从列表中选择合适的选项,然后点击“下一步”。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下一个界面让你选择你想修复的操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
或者你可以使用早先保存的系统镜像恢复系统。
|
||||
|
||||
选中上面的选项然后点击“下一步”。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在你将会看到一个有修复硬盘和恢复您的系统等选项的界面。
|
||||
|
||||
你需要做的是修复主引导记录,而这可以通过领命提示符来完成。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“命令提示符”。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在只需要把下面的命令输入到命令提示符中:
|
||||
|
||||
bootrec.exe /fixmbr
|
||||
|
||||
接下来将会出现一条消息,提示操作已经成功完成。
|
||||
|
||||
你现在就可以关闭命令提示符窗口了。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“重启”按钮然后取出DVD。
|
||||
|
||||
你的电脑就会直接启动进入Windows7系统了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 2 - 删除Ubuntu分区 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要删除Ubuntu你需要使用Windows系统提供的“磁盘管理”工具。
|
||||
|
||||
按下“开始”按钮然后在搜索框中输入“创建和格式化磁盘分区”。将会出现一个与上图类似的窗口。
|
||||
|
||||
现在上面我的屏幕将不再和你的一模一样了,不过也不会相差太多。你会看到第0块磁盘有101MB的未分配空间,另外还有4个分区。
|
||||
|
||||
这101MB的空间是之前我安装Windows7时犯的一个错误。驱动器C是Windows7系统,下一个分区(46.57GB)是Ubuntu的根分区。287G的分区是/HOME分区,8G的分区是交换空间。
|
||||
|
||||
对于Windows系统来说,我们真正需要的只有驱动器C,所以剩下的是可以删掉的。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意: 注意一下.你的磁盘上可能有恢复分区。 不要删除恢复分区.。它们应该会被标记,将文件系统设置为NTFS或FAT32**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在你希望删除的分区上单击右键(例如:root,home和swap分区),然后从弹出的菜单中点击“删除卷”。
|
||||
|
||||
**(不要删除任何NTFS或者FAT32文件系统的分区)**
|
||||
|
||||
对于剩下的两个分区重复执行上面的操作。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
分区被删除后你将会有很大的一片空闲区域。右键点击空闲区域然后选择删除。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在你的磁盘将包含驱动器C和一大片没有分配的空间。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 3 - 扩展Windows分区 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后一步是扩展Windows以便于将它再变成一个大的分区。
|
||||
右键点击Windows分区(C盘),然后选择“扩展卷”。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当出现左面的窗口的时候点击“下一步”,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
接下来是一个向导界面,在这里你可以选择扩展到那个盘,同时修改扩展的大小。
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,向导界面将显示它能从未分配区域中获取的最大的磁盘空间数。
|
||||
|
||||
接受默认的选项,然后点击“下一步”。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后的界面展示了你在前一个界面中的选择结果。
|
||||
|
||||
点击“结束”进行磁盘扩展。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
从上图中你可以看到,我的Windows分区占据了整个磁盘(除了我之前安装Windows的时候偶然创建的101MB的空间)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这就是全部内容。一个致力于Linux的网站刚刚向你展示了如何移除Linux然后用Windows7取而代之。
|
||||
|
||||
有任何疑问可以在下面评论区留言。
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.everydaylinuxuser.com/2015/01/how-to-recover-windows-7-and-delete.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Gary Newell
|
||||
译者:[Medusar](https://github.com/Medusar)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.about.com/od/LinuxNewbieDesktopGuide/ss/Create-A-Recovery-Drive-For-All-Versions-Of-Windows.htm
|
||||
[2]:http://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/B0006L2HTK/ref=as_li_qf_sp_asin_il_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=B0006L2HTK&linkCode=as2&tag=evelinuse-21&linkId=3R363EA63XB4Z3IL
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user