mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-25 23:11:02 +08:00
20150309-1 选题
This commit is contained in:
parent
3b5b71641a
commit
9bde39c07d
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
New App Brings Android Notifications to The GNOME Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
Fancy seeing your Android alerts here? You can.
|
||||
|
||||
**You’ll shortly be able to view your Android notifications on the GNOME desktop thanks to a new application in development.**
|
||||
|
||||
The new project is called ‘Nuntius’ and lets notifications received on an Android phone appear on the GNOME desktop. It’s with GNOME 3.16 and its (wonderfully) [redesigned notification system][1] that the app and its features will be used by more.
|
||||
|
||||
The app, which developers are hoping will be ready in time for this month’s release of GNOME 3.16, will work over Bluetooth to ensure that nothing is passed to external servers or stored online. This does mean that your phone will need to be in a certain proximity to your GNOME desktop for the feature to work.
|
||||
|
||||
It also isn’t yet possible to reply to a text message or act on a news alert.
|
||||
|
||||
The development team do caution that **this is an early release** and those planning on diving in to use it should expect minimum functionality for now.
|
||||
|
||||
The mobile app required to see Android notifications in GNOME’s new notification shade is already available [from the Google Play Store][2] and the GNOME application is already available in the Fedora repos.
|
||||
|
||||
The developers have open-sourced both the Android app and the GNOME application receiver and hosted them (where else) on GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
A similar tool [has been available for KDE desktops][3] – ‘KDE Connect’ – for a year or two, while the ever-gaining Pushbullet offers similar features on Windows, Mac and Linux desktops for iOS and Android platforms using Google Chrome.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Nuntius for Android & GNOME on GitHub][4]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/03/new-app-brings-android-notifications-to-the-gnome-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/02/4-reason-why-gnome-3-16-might-be-the-best-version-yet-gallery
|
||||
[2]:https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=org.holylobster.nuntius
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/06/kde-connect-android-notifications-linux-desktop
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/holylobster
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
10 best uses for open source software in the business world
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Open source offers some compelling benefits for businesses large and small -- but you might be surprised at some of the ways it's being used.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Certain inevitabilities occur in technology. For instance, open source software will make its way into your business. Ten years ago, this could easily have been called into question. Now? There's no way to avoid it -- and there's no reason to. With so many powerful (and necessary) pieces of technology, open source has become, in various cases, the savior of tech. But what areas of your business are best suited for open source? The answer to that question is, of course, will be different from one company to the next. But some applications can apply in almost every circumstance.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a look at 10 possible best-case uses for open source software that can help make your business grow, bring you a level of flexibility and reliability you haven't experienced, or just save you a welcome percentage of your budget.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1: Server software ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you're still battling Microsoft's IIS platform, you need to experience Apache. The flagship open source web server software is one of the most widely used on the planet. It's free, incredibly reliable, easy to manage, and doesn't require the enormous overhead needed for IIS. But open source isn't limited to just web servers. If you need SMB sharing across your company, consider Samba. Samba 4 even integrates with Active Directory, so you don't have to worry about setting up separate user accounts on the Samba server.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2: Development ###
|
||||
|
||||
Developing with open source is a no-brainer. PHP, Rails, Perl -- there are as many languages to develop with as there are tools (from IDEs to bug tracking). There are a lot of options for developing for open source or with open source tools (as are there with proprietary development). The biggest difference between open source and proprietary is the access you have to the software code. Within the world of FOSS (free open source software) the code is readily available. For many developers, the Linux operating system has everything they need to develop, built right in (especially those who code without a full-blown IDE). If you do require GUI development tools, open source has you covered.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3: Security ###
|
||||
|
||||
The route to security is a challenging one, but there are many paths to success. You can opt for the "security in a box" solution and go with the likes of Cisco (a solid solution) or you can craft your security to perfectly fit your needs with the likes of iptables. Yes, the open source security route will take a bit more time to deploy (with a much higher learning curve), but the end results are generally incredible. This doesn't even address the idea that using open source on the desktop is, generally speaking, a more secure platform than most proprietary systems. Deploy Linux on the desktops and your security woes will drop dramatically.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4: Desktops ###
|
||||
|
||||
This area is where most of the pushback happens. However, you must take into consideration the fact that the daily workflow has undergone a major paradigm shift. Most of what we do now is done via a web browser. So why not deploy Linux on the desktop? Not only does it work with the majority of today's tasks, it will do so without suffering from viruses, malware, and updates that cripple a system. It's not perfect -- what platform is? But it's solid, and in the end, it can save you money. That's a win-win.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5: Workflow ###
|
||||
|
||||
Every business depends upon workflow. For some businesses, a smooth workflow depends upon tools. Open source has this arena covered. CRM, HRM, ERP, BI, BPM... you name it, open source handles just about every possible acronym you can think of -- and it does it very well. With the likes of [Pentaho][1], [Collabtive][2], and [SugarCRM][3], open source can keep up with closed source tools any day.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6: Collaboration ###
|
||||
|
||||
Without the ability to work together on projects, your staff wouldn't be able to get the job done. So the collaboration tools you choose are crucial. You'll find plenty of quality collaboration tools within the world of open source. [Cyn.in community edition][4], [Zimbra Open Source Edition][5], and [Kolab][6] are just three examples of the excellent collaboration tools that exist within the open source world.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7: Big data ###
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes to big data, open source can't be matched. Thanks to the likes of [SUSE][7], big data and open source now go hand in hand. Innovations like in-memory data and live kernel patching make open source an ideal solution for big data. It can be perfectly tuned to meet the massive demands big data places on the platform. Closed source software can't touch this level of flexibility.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8: Cloud ###
|
||||
|
||||
The major players in the cloud are open source. [Red Hat][8], [Ubuntu][9], [SUSE][10], [Amazon][11], [Rackspace][12] -- they all get it and know that open source is the best solution for cloud deployments. But if you don't want to go with the larger companies, there are always up and coming tools like [ownCloud][12], where you can either take advantage of its hosted cloud solutions or build your own.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9: Multimedia ###
|
||||
|
||||
If your company does podcasting or video for PR, open source has you covered. With tools like [Audacity][14] and [OpenShot][15], you can do just about anything with audio or video you need -- and do so on the cheap. In fact, you'll be hard-pressed to find a better podcasting tool than Audacity or an easier-to-use video editor than OpenShot. Both pieces of software do an outstanding job of creating professional-quality results without the steep learning curves or the high prices often associated with closed source tools
|
||||
|
||||
### 10: E-commerce ###
|
||||
|
||||
If your business sells products online, you'd be remiss not to give a tool like [PrestaShop][16] a try. PrestaShop is, hands down, one of the most powerful e-commerce solutions available -- regardless of license. With just about every feature you could possible want (and some you probably haven't even thought of), the open source platform excels at e-commerce on every level.
|
||||
|
||||
### FOSS for business ###
|
||||
|
||||
Open source is no longer hanging around the periphery of the business conversation. In many instances, FOSS leads and dominates that conversation. If you've been looking for areas to consider deploying open source solutions, look no further than these 10.
|
||||
|
||||
### Your turn ###
|
||||
|
||||
Have you added open source software to your business? If so, in what way?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.techrepublic.com/blog/10-things/10-best-uses-for-open-source-software-in-the-business-world/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jack Wallen][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.techrepublic.com/search/?a=jack+wallen
|
||||
[1]:http://community.pentaho.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://collabtive.o-dyn.de/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.sugarcrm.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://cynapse.com/cyn-in/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.zimbra.com/open-source
|
||||
[6]:http://kolab.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.suse.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.redhat.com/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.suse.com/
|
||||
[11]:http://aws.amazon.com/ec2/
|
||||
[12]:http://www.rackspace.com/cloud
|
||||
[13]:https://owncloud.org/
|
||||
[14]:http://audacity.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.openshot.org/
|
||||
[16]:https://www.prestashop.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
Comparative Introduction To FreeBSD For Linux Users
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Introduction ###
|
||||
|
||||
BSD was originally derived from UNIX and currently, there are various number of Unix-like operating systems descended from the BSD. While, FreeBSD is the most widely used open source Berkeley Software Distribution (BSD distribution). As it is implicitly said it is a free and open source Unix-like-operating system and a public server platform. FreeBSD source code is generally released under a permissive BSD license. It is true that it has similarities with Linux but we cannot deny that they differs in other points.
|
||||
|
||||
The remainder of this article is organized as follows: the description of FreeBSD will be treated in our first section. The similarities between FreeBSD and Linux will be briefly described in the second section. While their differences will be discussed in the third section. And a comparison of their features will be summarized in our last section.
|
||||
|
||||
### FreeBSD description ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### History ####
|
||||
|
||||
- The first version of FreeBSD was released in 1993, while its first CD-ROM distributed was FreeBSD1.0 on December 1993. Then, FreeBSD 2.1.0 was released in 1995 which gained the satisfaction of all users. Actually, many IT companies use FreeBSD and are satisfied where we can list those companies: IBM, Nokia, NetApp and Juniper Networks.
|
||||
|
||||
#### License ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Concerning its license, FreeBSD is released under various source licenses. Its newest code called Kernel is released under the two-clause BSD license, offering the possibility to use and redistribute FreeBSD with absolute freedom. Other codes are released three- and four-clause BSD license and some others are released under GPL and CDDL.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Users ####
|
||||
|
||||
- One of the important feature of FreeBSD, we can mention the various categories of its users. In fact, it is possible to use FreeBSD as a mail server, web server, FTP server and as a router due to the significant set of server-related software accompanied with it. Furthermore, ARM, PowerPC and MIPS are supported by FreeBSD so it is possible to use x86 and s86-64.
|
||||
|
||||
### FreeBSD and Linux similarities ###
|
||||
|
||||
FreeBSD and Linux are two free and open source systems. Indeed, their users can easily check and modify the source code with an absolute freedom. To add, FreeBSD and Linux, both of them are derived from Unix.-like because they have a kernel, internals, and libraries programmed using algorithms derived from historic AT&T Unix. While FreeBSD’s roots are similar to Unix systems, Linux is released as a free Unix-like option. Various tools and applications can be found either in FreeBSD or in Linux in fact, they almost share the same functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
Furthermore, FreeBSD can run big number of Linux applications. It has a Linux compatibility layer that can be installed. This Linux compatibility layer can be installed while compiling FreeBSD with AAC Compact Linux or downloading compiled FreeBSD systems with a Linux compatibility program such as: aac_linux.ko. Which is not the same case with Linux, Linux cannot run FreeBSD software.
|
||||
|
||||
At the end, we can mention that both of them have the same goal but have also some differences which we will outline in the next section.
|
||||
|
||||
### FreeBSD and Linux differences ###
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, no criteria of choice between FreeBSD and Linux is clear for most users. Since, they share almost the same applications. Those two operating systems are as mentioned previously UNIX-like.
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we will list the most important differences of those two systems.
|
||||
|
||||
#### License ####
|
||||
|
||||
- The first difference point between those two compared systems consist on their license. To start by Linux license, it is released under the GPL license which offers the possibility to view, distribute and change the source code with an absolute freedom. The GPL license helps users to prevent the distribution of binary-only source. Which is the case with FreeBSD, which is licensed under BSD license. This kind of license is more restrictive and easily allows the distribution of binary-only source. The BSD license is more permissive that the GPL since no derivative work is required to maintain the licensing terms. Means any user can use, distribute and modify the code without need to have the previous version of code before changing made. They only need to have the original license of BSD.
|
||||
- Depending on the needs of each user, a selection can be made between those two types of license. Starting by BSD license which is more preferred by many users due to its special features. In fact, this license gives the possibility to sell each software licensed under it and retain the source code. Passing now to the GPL license, which requires some care of each user has a software released under it.
|
||||
- To be able to choose between those two software, it is required to understand the licensing of both of them to more understand the methodology used in their development, to distinguish between their features and know which one will fit user’s need.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Control ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Since FreeBSD and Linux are released under two different type of license, the Linux Torvalds control the Linux kernel which is not the same case with FreeBSD which is not controlled. Personally, I prefer to use FreeBSD instead of Linux since it is an absolute free software, no control permission exists. But it is not enough there is other differences between Linux and FreeBSD, help you to choose between both of them. As an advice don’t choose one of them, follow us and then give us your choice.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Operating system ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Linux concentrates only on the kernel system which is not the case with FreeBSD while the whole operating system is maintained. The kernel and a set of software, some of them are developed by the FreeBSD team, are maintained as one unit. Indeed, the FreeBSD developers have the possibility to manage the essential operating systems remotely and efficiently.
|
||||
- With Linux, there is some difficulties while managing a system. Since, the different components maintained will be from different sources so the Linux developers need to assemble them into groups having the same functionality.
|
||||
- FreeBSD and Linux both of them give the possibility to have a big set of optional software and distributions but they differ on the way they are managed. With FreeBSD, they are managed together while with Linux they will be maintained separately.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Hardware support ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Concerning the hardware support, Linux is better than FreeBSD. It doesn’t mean that FreeBSD hasn’t the capability to support hardware as Linux. They differ just on the manner. It depends on your need as usual. So if you are searching for the newest solution, the FreeBSD will fit your needs but if you are looking for greatest graphs, it is better to use Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
#### FreeBSD origin Vs Linux origin ####
|
||||
|
||||
- The origin of each system is also another point of distinction between both of them. As I said previously Linux is an alternative of the operating system Unix, written by Linus Trovalds and assisted by a special group of hackers across the Net. Linux has all the needed features in a modern Unix, such as virtual memory, shared libraries, demand loading, proper memory management and many others. It is released under the General Public License.
|
||||
- FreeBSD also shared many important features of its Unix heritage. FreeBSD as a type of the Berkeley Software Distribution, the distribution of the Unix developed at the University of California. The most important reason under developing BSD is to replace the AT&T operating system by an open source alternative giving the user the ability to use BSD without carry about the obtaining of the AT&T license.
|
||||
- The problem of licensing, is the most important worry of developers. They try to offer the maximum open source clone of Unix. Which influences the choice of users regarding the degree of open source of each system as FreeBSD gives more freedom than Linux regarding its use since it is released under BSD license.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Supported Package ####
|
||||
|
||||
- From the user’s perspective, another difference between our two compared systems, is their availability and support of the packaged software and source installed software. The Linux distributions provide just the pre-compiled binary packages which is not the same case with FreeBSD, which has the pre-built packages and the build system for the compilation and installation through their available open source. Due to its ports, FreeBSD gives you the possibility to choose between the default making of pre-compiled packages and your ability to customize your software while it is compiled.
|
||||
- Those ports enable you to build all the software available with FreeBSD. Furthermore, there is an hierarchy of organization all of them due to the directories /usr/ports where you can find the location of the source files and some documentation about the way to use FreeBSD correctly.
|
||||
- The ports as mentioned give the possibility produce the packages version of software. Instead of having just the pre-compiled packages using Linux, FreeBSD gives you the possibility to have the source-built and the pre-packages software. You can manage your system using the two installation methods.
|
||||
|
||||
#### FreeBSD Vs Linux common Tools ####
|
||||
|
||||
- A huge number of common tools are available while using FreeBSD and are fully own made by the FreeBSD team. In contrast, the Linux tools are from the GNU that is why there is some control during their usage.
|
||||
- The fact that FreeBSD is released under BSD license is so beneficial and useful. Since, you have the ability to maintain the core operating system, control the development of these applications. Same of those tools are similar to BSD and Unix tools from where they were derived which is not the same case with GNU suite, which want to just make them less backwards compatible.
|
||||
|
||||
#### The Standard Shell ####
|
||||
|
||||
- The tcsh shell is used by default with FreeBSD. Which is an evaluated version fo csh. Since, the FreeBSD is released under the BSD license, it is not recommended to use the bash shell which is a GNU component. The only difference between bash and tcsh shell consists on the scripting feature which can’t be made by tcsh. Indeed, the sh shell is more recommended for the FreeBSD use since it is more reliable and prevents some issues of scripting can be occurred using the tcsh or csh shell.
|
||||
|
||||
#### A More Stratified Filesystem ####
|
||||
|
||||
- As it was mentioned previously, base operating system and optional components can be easily distinguished using the FreeBSD system. Which causes some specification of their organization. In Linux, /bin, /sbin, /usr/bin, or usr/sbin are the directories for executable systems. With FreeBSD it is not the case. There are some additional specifications concerning their organization. The base system are putted in one of the directories mentioned above while the ports and packages are placed in /usr/local/bin or /usr/local/sbin. This methodology helps to recognize and distinguish between an application considered as a base system or a port.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
FreeBSD and Linux those two free and open source systems, share various similarities but they also differ in several points. The list giving above isn’t given to say that one of them is better than the other. In fact, FreeBSD and Linux, each one of them has its features and specifications that make it a special regarding the other. And you what is your opinion? Have you already used one on them or both? If yes what is your feedback and if no after reading our description what do you think? Sound off and give us and the fellow readers your opinion.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.unixmen.com/comparative-introduction-freebsd-linux-users/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[anismaj][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.unixmen.com/author/anis/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
||||
List Of Free Windows SSH Client Tools To Connect To Your Linux Server
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
You have Windows as operating system and you need to connect to Linux server to transfer files from Linux to Windows and inversely. So you need to have Secure Shell known as SSH. In fact, SSH is a network protocol which enables you to connect to Linux and Unix servers over the network. It uses public key cryptography to authenticate the remote computer. You can use SSH by several ways, either by using it automatically or by using a password authentication to log in.
|
||||
|
||||
This article provides a list of SSH clients let you to connect SSH to your Linux servers.
|
||||
|
||||
let’s start.
|
||||
|
||||
### PuTTY ###
|
||||
|
||||
**PuTTY** is the most famous SSH and telnet client, developed originally by Simon Tatham for the Windows platform. PuTTY is open source software that is available with source code and is developed and supported by a group of volunteers.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Putty is very easy to install and to use.You don’t usually need to change most of the configuration options. To start the simplest kind of session, all you need to do is to enter a few basic parameters.You can download PuTTY [here][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### Bitvise SSH Client ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Bitvise SSH** Client is an SSH and SFTP client for Windows. It is developed and supported professionally by Bitvise. The SSH Client is robust, easy to install, easy to use. Bitvise SSH Client is a feature-rich graphical SSH/SFTP client for windows and allow you dynamic port forwarding through an integrated proxy with auto-reconnecting capability.
|
||||
|
||||
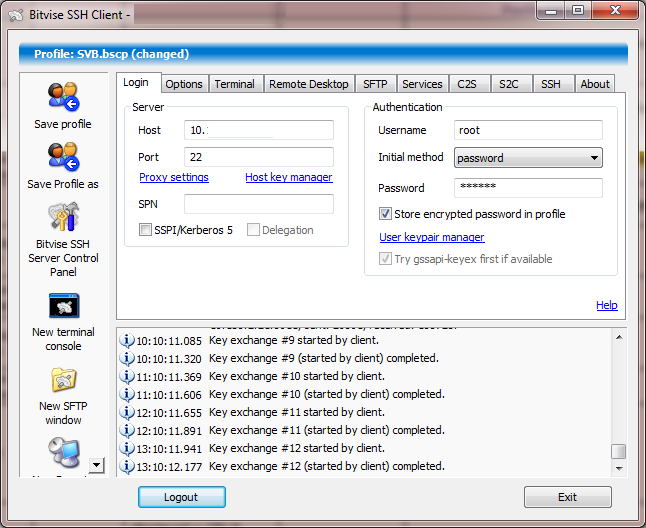
|
||||
|
||||
Bitvise SSH Client is **free for personal use**, as well as for individual commercial use inside organizations. You can [download Bitvise SSH Client here][2].
|
||||
|
||||
### MobaXterm ###
|
||||
|
||||
**MobaXterm** is your **ultimate toolbox for remote computing**. In a single Windows application, it provides loads of functions that are tailored for programmers, webmasters, IT administrators and pretty much all users who need to handle their remote jobs in a more simple fashion.
|
||||
|
||||
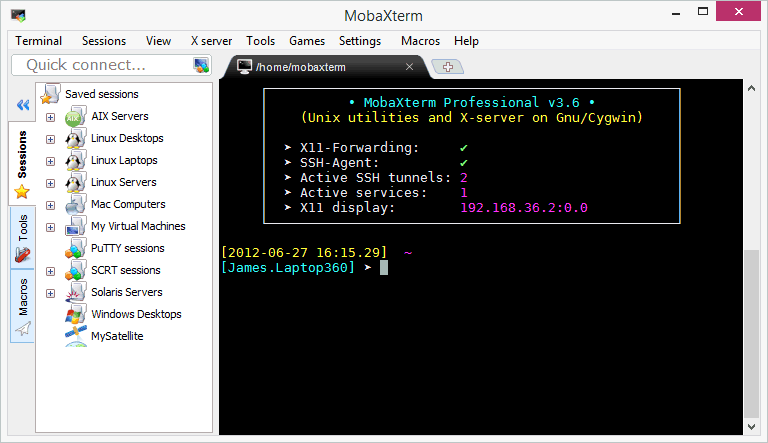
|
||||
|
||||
MobaXterm provides all the important **remote network tools** (SSH, X11, RDP, VNC, FTP, MOSH, …) and **Unix commands** (bash, ls, cat, sed, grep, awk, rsync, …) to Windows desktop, in a **single portable exe file** which works out of the box. MobaXterm is **free for personal use**. You can download MobaXterm [from here][3].
|
||||
|
||||
### DameWare SSH ###
|
||||
|
||||
I think that **DameWare SSH** is the best free ssh client.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This free tool is a terminal emulator that lets you make multiple telnet and SSH connections from one easy-to-use console.
|
||||
|
||||
- Manage multiple sessions from one console with a tabbed interface
|
||||
- Save favorite sessions within the Windows file system
|
||||
- Access multiple sets of saved credentials for easy log-in to different devices
|
||||
- Connect to computers and devices using telnet, SSH1, and SSH2 protocols
|
||||
|
||||
You can download **DameWare SSH** from [this link][4].
|
||||
|
||||
### SmarTTY ###
|
||||
|
||||
SmarTTY is a free multi-tabbed SSH client that supports copying files and directories with SCP on-the-fly.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Most SSH servers support up to 10 sub-sessions per connection. SmarTTY makes the best of it: no annoying multiple windows, no need to relogin, just open a new tab and go!
|
||||
|
||||
### Cygwin ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cygwin is a large collection of GNU and Open Source tools which provide functionality similar to a Linux distribution on Windows.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Cygwin** consists of a Unix system call emulation library, cygwin1.dll, together with a [vast set][5] of GNU and other free software applications organized into a large number of optional packages. Among these packages are high-quality compilers and other software development tools, an X11 server, a complete X11 development toolkit, GNU emacs, TeX and LaTeX, OpenSSH (client and server), and much more, including everything needed to compile and use PhysioToolkit software under MS-Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
After reading our article, which is your favorite SSH client? You can leave a comment describing your favorite system and the reasons of your choice. And of course if there is another SSH client doesn’t appear in this article, you can help us to add it.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.unixmen.com/list-free-windows-ssh-client-tools-connect-linux-server/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[anismaj][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.unixmen.com/author/anis/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/download.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.bitvise.com/download-area
|
||||
[3]:http://mobaxterm.mobatek.net/download.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.dameware.com/downloads/registration.aspx?productType=ssh&AppID=17471&CampaignID=70150000000PcNM
|
||||
[5]:http://cygwin.com/packages/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user