mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-03 01:10:13 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject
This commit is contained in:
commit
9a60927a6b
@ -1,15 +1,16 @@
|
||||
示例说明10个Linux中常用又好用的链接操作符
|
||||
Linux中命令链接操作符的十个最佳实例
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux命令中的链接的意思是,通过操作符的行为将几个命令组合执行。Linux中的链接命令,有些像你在shell中写[短小的shell脚本][1],并直接在终端中执行。链接使得自动处理变得可能。不仅如此,一个无人看管的机器在链接操作符的帮助下能够十分有条理地运行。
|
||||
Linux命令中的链接的意思是,通过操作符的行为将几个命令组合执行。Linux中的链接命令,有些像你在shell中写[短小的shell脚本][1],并直接在终端中执行。链接使得自动处理变得更方便。不仅如此,一个无人看管的机器在链接操作符的帮助下能够十分有条理地运行。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Linux中的10个链接操作符*
|
||||
|
||||
本文旨在介绍一些常用的**链接操作符**,通过简短的描述和相关的例子帮助读者提高生产力、降低系统负载、写出更加简短有意义的代码。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 和号操作符 (&) ###
|
||||
|
||||
‘**&**‘的作用是使命令在后台运行。只要在命令后面跟上一个空格和 ‘**&**。你可以一口气在后台运行多个命令。
|
||||
‘**&**’的作用是使命令在后台运行。只要在命令后面跟上一个空格和 ‘**&**’。你可以一口气在后台运行多个命令。
|
||||
|
||||
在后台运行一个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,7 +18,7 @@ Linux命令中的链接的意思是,通过操作符的行为将几个命令组
|
||||
|
||||
同时在后台运行两个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# apt-get update & apt-get upgrade &
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# apt-get update & mkdit test &
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 分号操作符 (;) ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,19 +26,19 @@ Linux命令中的链接的意思是,通过操作符的行为将几个命令组
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# apt-get update ; apt-get upgrade ; mkdir test
|
||||
|
||||
上述命令先后执行了update和upgrade,最后在当前工作目录下创建了一个‘**test**‘文件夹
|
||||
上述命令先后执行了update和upgrade,最后在当前工作目录下创建了一个‘**test**’文件夹
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 与操作符 (&&) ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果第一个命令执行成功,**与操作符 (&&)**会执行第二个命令,也就是说,第一个命令退出状态是**0**。(译注:原文的这里明显写错了,我们进行了改译,有兴趣的读者可以参看原文以及原文下面的评论)。这个命令在检查最后一个命令的执行状态时很有用。
|
||||
如果第一个命令执行成功,**与操作符 (&&)**才会执行第二个命令,也就是说,第一个命令退出状态是**0**。(译注:原文的这里明显写错了,我们进行了改译,有兴趣的读者可以参看原文以及原文下面的评论。在UNIX里面,0表示无错误,而所有非0返回值都是各种错误)。这个命令在检查最后一个命令的执行状态时很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,我想使用**[links command][2]**在终端中访问网站**tecmint.com**,但在这之前我需要检查主机是否**在线**或**不在线**。
|
||||
比如,我想使用**[links 命令][2]**在终端中访问网站**tecmint.com**,但在这之前我需要检查主机是否**在线**或**不在线**。
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# ping -c3 www.tecmint.com && links www.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 或操作符 (||) ###
|
||||
|
||||
**或操作符 (||)**很像编程中的**else**语句。上面的操作符允许你在第一个命令失败的情况下执行第二个命令,也就是说,第一个命令的退出状态是**1**。
|
||||
**或操作符 (||)**很像编程中的**else**语句。上面的操作符允许你在第一个命令失败的情况下执行第二个命令,比如,第一个命令的退出状态是**1**。
|
||||
|
||||
举例来说,我想要在非root帐户中执行‘**apt-get update**‘,如果第一个命令失败了,接着会执行第二个命令‘**links www.tecmint.com**‘。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -53,22 +54,22 @@ Linux命令中的链接的意思是,通过操作符的行为将几个命令组
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 非操作符 (!) ###
|
||||
|
||||
**非操作符 (!)**很像**except**语句。这个命令会执行除了提供的条件外的所有的语句。要理解这点,在你的家目录创建一个目录‘**tecmint**‘,并‘**cd**‘到它这里。
|
||||
**非操作符 (!)**很像**except**语句。这个命令会执行除了提供的条件外的所有的语句。要理解这点,在你的主目录创建一个目录‘**tecmint**’,并‘**cd**’到它这里。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ mkdir tecmint
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ cd tecmint
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,在文件夹‘**tecmint**‘下创建不同类型的文件。
|
||||
接下来,在文件夹‘**tecmint**’下创建不同类型的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ touch a.doc b.doc a.pdf b.pdf a.xml b.xml a.html b.html
|
||||
|
||||
看一下我们在文件夹‘**tecmint**‘创建的新文件。
|
||||
看一下我们在文件夹‘**tecmint**’创建的新文件。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ls
|
||||
|
||||
a.doc a.html a.pdf a.xml b.doc b.html b.pdf b.xml
|
||||
|
||||
用一种聪明的办法马上删除除了 ‘**html**‘之外的所有文件。
|
||||
用一种聪明的办法马上删除除了 ‘**html**’之外的所有文件。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ rm -r !(*.html)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,11 +79,11 @@ Linux命令中的链接的意思是,通过操作符的行为将几个命令组
|
||||
|
||||
a.html b.html
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 与 – 或 操作符 (&& – ||) ###
|
||||
### 6. 与或操作符 (&& – ||) ###
|
||||
|
||||
上面的操作符实际上是‘**与**‘和‘**或**‘操作符的组合。它很像‘**if-else**‘语句。
|
||||
上面的操作符实际上是‘**与**’和‘**或**’操作符的组合。它很像‘**if-else**‘语句。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,我们ping **tecmint.com**,如果成功打印‘**已验证**‘,否则打印‘**主机故障**‘。
|
||||
比如,我们ping **tecmint.com**,如果成功打印‘**已验证**’,否则打印‘**主机故障**’。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ping -c3 www.tecmint.com && echo "Verified" || echo "Host Down"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -109,7 +110,7 @@ Linux命令中的链接的意思是,通过操作符的行为将几个命令组
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 管道操作符 (|) ###
|
||||
|
||||
**PIPE**在将第一个命令的输出作为第二个命令的输入时很有用。比如,‘**ls -l**‘的输出通过管道到‘**less**‘,并看一下输出。
|
||||
**PIPE**在将第一个命令的输出作为第二个命令的输入时很有用。比如,‘**ls -l**’的输出通过管道到‘**less**’,并看一下输出。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ ls -l | less
|
||||
|
||||
@ -117,15 +118,17 @@ Linux命令中的链接的意思是,通过操作符的行为将几个命令组
|
||||
|
||||
合并两个或多个命令,第二个命令依赖于第一个命令的执行。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,检查一下文件‘**xyz.txt**‘和‘**xyz1.txt**‘是否在**Downloads**目录下,并输出相关的输出。
|
||||
比如,检查一下文件‘**xyz.txt**’是否在**Downloads**目录下,如果不存在则创建之并输出提示信息。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ [ -f /home/tecmint/Downloads/xyz.txt ] || echo “The file does not exist”
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ [ -f /home/tecmint/Downloads/xyz.txt ] || touch /home/tecmint/Downloads/xyz.txt; echo "The file does not exist"
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ [ -f /home/tecmint/Downloads/xyz1.txt ] || echo “The file does not exist”
|
||||
但是这样的命令的运行结果并不如我们预期的运行,会始终都输出提示信息。因此需要使用{}操作符来合并命令:
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ [ -f /home/tecmint/Downloads/xyz1.txt ] || {touch /home/tecmint/Downloads/xyz.txt; echo "The file does not exist"}
|
||||
|
||||
“The file does not exist”
|
||||
|
||||
(LCTT注:原文这里应该也是复制或书写的时候,出现了一些问题,例子中并没有出现小标题中的"{}"操作符,这里我们原文翻译了,关于这里,有兴趣的同学请在评论中和我们交流~)
|
||||
(译注:原文这里应该也是复制或书写的时候,出现了一些问题,例子中并没有出现小标题中的"{}"操作符,所以这里我们进行了修改)
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. 优先操作符 () ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -141,11 +144,10 @@ Linux命令中的链接的意思是,通过操作符的行为将几个命令组
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. 连接符 (\) ###
|
||||
|
||||
**连接符 (\)**如它名字所说,被用于连接shell中跨越多行的命令。比如,下面的命令会打开文本文件**test(1).txt**。
|
||||
**连接符 (\)**如它名字所说,被用于连接shell中那些太长而需要分成多行的命令。可以在输入一个“\”之后就回车,然后继续输入命令行,直到输入完成。比如,下面的命令会打开文本文件**test(1).txt**。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/Downloads$ nano test\
|
||||
(1\
|
||||
).txt
|
||||
1.txt
|
||||
|
||||
今天就到这里,我会近日开始另外一个有趣的文章。不要走开,继续关注**Tecmint**。不要忘记在评论栏里提出有价值的反馈。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,13 @@
|
||||
如何在 Linux 中合并照片
|
||||
如何在 Linux 中生成全景照片
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如果你是一位狂热的摄影爱好者,那么你的摄影集中可能会有一些令人叹为观止的全景摄影作品。事实上,制作这些照片既不需要专业的摄影技术,也不需要什么特别的设备,利用一些照片合并软件(在线或者是离线,桌面设备或者移动设备)就可以将两幅或者多幅有重叠部分的照片轻松合成一幅全景照片。
|
||||
这篇教程里,我将会解释 **如何在 Linux 中完成照片的合并工作**。在这儿,我将会使用一款叫做 [Hugin][1] 的照片合并软件。
|
||||
|
||||
这篇教程里,我将会解释 **如何在 Linux 中完成全景照片的合并工作**。在这儿,我将会使用一款叫做 [Hugin][1] 的照片合并软件。
|
||||
|
||||
Hugin 是一款开源(GPLv2)并可以免费使用的照片合并工具。它目前支持多个平台,包括 Linux,Windows,OS X 和 FreeBSD。 尽管作为一款开源软件,但是不论在功能上还是质量上,Hugin 都丝毫不逊色于商业软件。相反,Hugin 非常强大,不仅可以用来创建360度全景照片,还支持多种高级测光修正和优化。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 中安装 Hugin
|
||||
|
||||
在 Debian,Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint 中安装 Hugin:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install hugin
|
||||
@ -13,57 +17,76 @@ Hugin 是一款开源(GPLv2)并可以免费使用的照片合并工具。它
|
||||
$ sudo yum install hugin
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动 Hugin
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用命令来启动Hugin。
|
||||
|
||||
$ hugin
|
||||
|
||||
在这儿,我们要做的第一件事就是导入我们想要合并的照片。我们先来点击Load images 按钮,然后导入(两张或者多张)图片。当然了,这些照片应该需要相互有一些重叠的部分。
|
||||
在这儿(Assistant页),我们要做的第一件事就是导入我们想要合并的照片。我们先来点击Load images 按钮,然后导入(两张或者多张)图片。当然了,这些照片应该需要相互有一些重叠的部分(我们这里载入了三张)。
|
||||
|
||||
[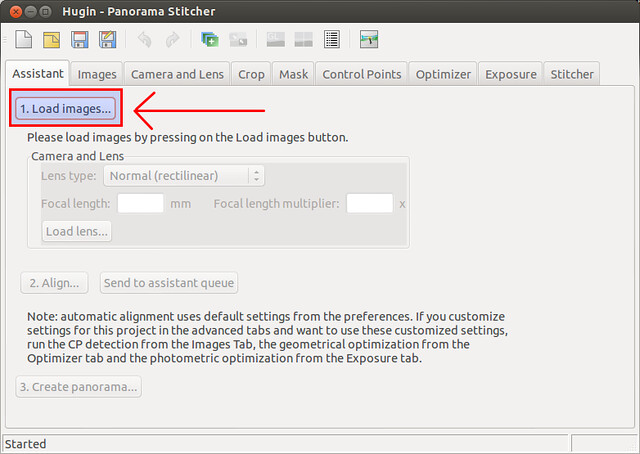][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一次照片合并
|
||||
|
||||
在导入照片之后,点击 Align 按钮来开始我们的第一次合并
|
||||
|
||||
[][3]
|
||||
|
||||
为了正确合并照片,Hugin 将会在一个单独的窗口中启动合并助手,用来分析照片之间的关键点(控制点)。分析完毕之后,呈现在你眼前的将会是一幅全景照片的预览图。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来让我们切换回 Hugin 的主窗口。在 Align 按钮的下方,你将会看见照片合并的状态(比如控制点的数量,错误情况)。当然,还会有合并好坏的相关提示。
|
||||
|
||||
[][4]
|
||||
|
||||
如果合并提示显示 bad 或者 really bad,你可以继续按照下面的办法来进行排列的调整。
|
||||
### 添加活着删除控制点
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加或者删除控制点
|
||||
|
||||
在主窗口中,进入 Control Points 标签页。在这儿,Hugin 展现在组合照片中常用的的控制点。我们看到,在左右面板中展现了一对照片,上面的一些同色的小方盒表示的是常用的控制点。你可以手动来添加或者删除这些控制点。这些控制点匹配的越精确,我们得到的合并质量也就越高。除此之外,如果这些控制点分散得比较均匀,得到的效果将会更好。
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
使用顶部中间的左右箭头按钮来找到拥有最少控制点的两幅照片。对这样的两幅照片,我们可以试图按照下面的办法来手动增加控制点。
|
||||
使用顶部中间的左右箭头按钮来找到拥有最少控制点的两幅照片。如这样的两幅照片,我们可以试图按照下面的办法来手动增加控制点。
|
||||
|
||||
首先我们点击左边照片中的某个点,然后再来点击右边照片中对应的点。Hugin 将会试图自动调整。接下来,我们继续点击底部的 Add 按钮来添加匹配对。重复上面的操作来添加更多的控制点。
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### 其他优化
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以试图进行重新优化,比如点击工具栏中的 Re-optimize 按钮,或者去 Optimizer 标签中重新调整之前的优化。
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
接下来回到 Hugin 主窗口中的 Assistant 标签,再次点击 Align 按钮来看看是否能得到一个更棒的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
倘若合并的全景照片的水平线参差不齐,我们可以试图将它拉直。首先点击工具栏上的 Preview panorama 按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
然后点击预览窗口中的 Straighten 按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
[][7]
|
||||
|
||||
一旦你对合并的结果感到满意,你可以继续将它导出为图片文件。只需要到 Hugin 主窗口中 Sticher 标签页里进行下面的操作:
|
||||
|
||||
调整画布大小,剪切数量。当然,还需要选择输出格式(比如 TIFF,JPEG,PNG)。最后,点击 Stitch!按钮来完成。
|
||||
|
||||
[][8]
|
||||
|
||||
之后会有提示保存当前项目文件(*.pto),设定保存好输出的文件名即可。
|
||||
|
||||
导出过程可能会需要花费几秒钟的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
这里有一张我利用 Hugin 的实验输出结果。画面中是墨西哥坎昆迷人海滩的全景。:-)
|
||||
[][9]
|
||||
|
||||
[][9]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/stitch-photos-together-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/ailurus1991) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[ailurus1991](https://github.com/ailurus1991) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
|
||||
Linux vmstat 命令 - 报告虚拟内存统计的工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
众所周知,计算机必须有称之为RAM(随机访问内存)的存储器使得计算机工作。RAM指的是插在计算机主板上的物理存储。这里的RAM被用于加载像浏览器、文字处理器这类的程序、实际上,你使用的程序都运行在内存上。
|
||||
众所周知,计算机必须有称之为RAM(随机访问内存)的存储器使得计算机工作。RAM指的是插在计算机主板上的物理存储。这里的RAM被用于加载像浏览器、文字处理器这类的程序,实际上,你使用的程序都运行在内存上。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们假设你有2GB的内存。当你在运行操作系统时,你的可用内存可能只有1.5GB。接着你使用了大量的程序。当内存使用满之后,你可能再也无法加载更多的程序。浅显地说,计算机可能会说:"抱歉,你不能在运行更多的程序了,如果你还要运行其他的程序请先关闭一些程序。"
|
||||
|
||||
为了解决这个问题,操作系统包括Linux使用了一个方法称之为虚拟内存。这个方法会搜索最近不在使用的程序的内存区域,接着将它们拷贝到计算机硬盘上。这会腾出一些剩余内存空间给你有机会运行更多的程序。
|
||||
为了解决这个问题,包括Linux在内的各种操作系统使用了一个称之为虚拟内存的方法。这个方法会搜索最近不在使用的程序的内存区域,接着将它们拷贝到计算机硬盘上。这会腾出一些剩余内存空间给你有机会运行更多的程序。
|
||||
|
||||
为了监视虚拟内存的活动,我们使用**vmstat**工具。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么事 vmstat ###
|
||||
### 什么是 vmstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
vmstat是一个提供报告虚拟内存统计的工具。他/她覆盖了系统内存、交换和实时处理器利用率。
|
||||
vmstat是一个提供报告虚拟内存统计的工具。它包括了系统内存、交换和实时处理器利用率。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何运行 vmstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,39 +20,39 @@ vmstat是一个提供报告虚拟内存统计的工具。他/她覆盖了系统
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
让我们看下如何读取vmstat提供的信息:
|
||||
让我们看下如何了解vmstat提供的信息:
|
||||
|
||||
### Procs ###
|
||||
#### Procs ####
|
||||
|
||||
procs有 **r**列和**b**列。**r**列代表等待访问CPU进程的数量。而b列意味着睡眠进程的数量。在这些列的下面,是它们的值。从上面的截图中,我门有2个进程正在等待访问CPU,0个睡眠进程。
|
||||
|
||||
### Memory ###
|
||||
#### Memory ####
|
||||
|
||||
memory有**swpd、 free、 buff** 和 **cache** 这些列.这些信息和命令**free -m**相同。**swpd列**显示了有多少内存已经被交换到了交换文件或者磁盘。**free列**显示了未分配的可用内存。**buff列**显示了使用中的内存。**cache列**显示了有多少内存可以被交换到交换文件或者磁盘上如果一些应用需要他们。
|
||||
memory有**swpd、 free、 buff** 和 **cache** 这些列。这些信息和命令**free -m**相同。**swpd列**显示了有多少内存已经被交换到了交换文件或者磁盘。**free列**显示了未分配的可用内存。**buff列**显示了使用中的内存。**cache列**显示了有多少内存可以被交换到交换文件或者磁盘上如果一些应用需要他们。
|
||||
|
||||
### Swap ###
|
||||
#### Swap ####
|
||||
|
||||
swap显示了从交换系统上发送或取回了多少内存。**si**列告诉我们每秒有多少内存被**从swap移到真实内存**中。**so**列告诉我们每秒有多少内存被**从真实内存移到swap**中。
|
||||
swap显示了从交换系统上发送或取回了多少内存。**si**列告诉我们每秒有多少内存被**从swap移到真实内存**中(In)。**so**列告诉我们每秒有多少内存被**从真实内存移到swap**中(Out)。
|
||||
|
||||
### I/O ###
|
||||
#### I/O ####
|
||||
|
||||
**io**依据块的读写显示了每秒输入输出的活动。**bi**列告诉我们块收到的数量,**bo**列告诉我们块发送的数量。
|
||||
**io**依据块的读写显示了每秒输入输出的活动。**bi**列告诉我们收到的块数量,**bo**列告诉我们发送的块数量。
|
||||
|
||||
### System ###
|
||||
#### System ####
|
||||
|
||||
system显示了每秒的系统操作数量。**in**列显示了系统每秒被中断的数量。**cs**列显示了系统为了处理所以任务而上下文切换的数量。
|
||||
|
||||
### CPU ###
|
||||
#### CPU ####
|
||||
|
||||
CPU告诉了我们CPU资源的使用情况。**us列**显示了处理器在非内核程序消耗的时间。**sy列**显示了处理器在内核相关任务上消耗的时间。**id列**显示了处理器的空闲时间。**wa列**显示了处理器在等待IO操作完成以继续处理任务上的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
### 代延迟使用vmstat ###
|
||||
### 按间隔时间运行vmstat ###
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个统计工具,使用vmstat最好的方法是使用**延迟**。你可以间断地捕捉活动。让我假设以5秒的延迟使用vmstat。只需要在你的控制台中输入**vmstat 5**就行。
|
||||
作为一个统计工具,使用vmstat最好的方法是使用**间隔时间**。你可以间断地捕捉系统状态。让我假设以5秒的间隔运行vmstat。只需要在你的控制台中输入**vmstat 5**就行。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
命令将会每5秒运行一次**直到**你按下Ctrl-C来终止它。你可以使用**count**来显示vmstat运行的次数。
|
||||
命令将会每5秒运行一次,**直到**你按下Ctrl-C来终止它。你也可以使用第二个参数来控制vmstat运行的次数。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,17 +66,17 @@ CPU告诉了我们CPU资源的使用情况。**us列**显示了处理器在非
|
||||
|
||||
### 显示磁盘统计数据总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想,vmstat可以打印系统磁盘统计。使用**-D**选项就行。
|
||||
如果你想,vmstat也可以打印系统磁盘活动统计。使用**-D**选项就行。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 显示单位 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以选择你想打印的显示单位字符。在**-S后跟上k (1000)、 K (1024)、 m (1000000)、 M (1048576)** 字节. 如果你不想选择单位,默认使用的是K (1024)。
|
||||
你可以选择你想打印的显示单位字符。在**-S后跟上k (小写,1000)、 K (大写,1024)、 m (小写,1000000)、 M (大写,1048576)** 字节. 如果你不想选择单位,默认使用的是K (1024)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 为特定分区打印详细统计数据 ###
|
||||
### 显示某个磁盘分区的详细统计数据 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要这么做,你可以使用**-p选项跟上设备名**。这里有个例子。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ CPU告诉了我们CPU资源的使用情况。**us列**显示了处理器在非
|
||||
|
||||
### 文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
vmstat使用这些文件工作。
|
||||
vmstat实际上是使用这些文件获取的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
/proc/meminfo
|
||||
/proc/stat
|
||||
@ -92,14 +92,13 @@ vmstat使用这些文件工作。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
vmstat** on your console. It will bring you to vmstat manual page.
|
||||
如果你感觉系统运行超出内存了,在你增加物理内存前,这个工具可以帮助你确定问题的根本原因。通常上,你可以在控制台中输入**man vmstat**获取更多的关于vmstat的详细信息。这会带你进入vmstat的手册页。
|
||||
如果你感觉系统运行超出内存了,在你增加物理内存前,这个工具可以帮助你确定问题的根本原因。通常上,你可以在控制台中输入**man vmstat**获取更多的关于vmstat的详细信息,这会为你显示vmstat的手册页。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-vmstat-command-tool-report-virtual-memory-statistics/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,32 +1,39 @@
|
||||
新版Ubuntu 14.01图标美轮美奂,可能不会发布桌面版
|
||||
新版Ubuntu 14.04图标美轮美奂,不过可能不会发布桌面版
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**Canonical正在为Ubuntu 14.04准备一次改版,正在设计中的新版图标会超越之前所有的。**
|
||||
|
||||
在上一次UDS(Ubuntu开发者提交)中,詹姆斯·马修,一位一直热情地在为Ubuntu设计外观的设计师,展示了一组非常漂亮的图标,没有一个更好的词语来形容了。现在他正在为我们展示他一直所进行的工作的更多细节。
|
||||
在上一次UDS(Ubuntu开发者提交)中,詹姆斯·马修,一位一直热情地在为Ubuntu设计外观的设计师,展示了一组美轮美奂的图标,没有一个更好的词语来形容了。现在他正在为我们展示他一直所进行的工作的更多细节。
|
||||
|
||||
”这个项目的主要目标是为桌面环境和触屏设备创建一个现代化,高分辨率的图标主题,它能够适应各种各样的屏幕像素密度,增强Ubuntu的用户体验。我们想要我们的图标传达出我们的价值,用一种独特的方式传达出Ubuntu的个性化。“
|
||||
>“这个项目的主要目标是为桌面环境和触屏设备创建一个现代化,高分辨率的图标主题,它能够适应各种各样的屏幕像素密度,增强Ubuntu的用户体验。我们想要我们的图标传达出我们的价值观,用一种独特的方式传达出Ubuntu的个性化。”
|
||||
|
||||
詹姆斯·马修在Ubuntu官方站点的一片文章中提到:”我们已经为应用程序和标识(symbol不知如何翻译恰当)设计了移动图标,但是,因为它们在时间的演变中并没有明确的指引方向,所以没有形成一致的集合。在桌面上,虽然风格是简洁一致的,但图标看起来过时了,也需要更新。“
|
||||
詹姆斯·马修在Ubuntu官方站点的一篇文章中提到:“我们已经为应用程序和标识(symbol)设计了移动图标,但是,因为它们在时间的演变中并没有明确的指引方向,所以没有形成一致的风格。在桌面上,虽然风格是简洁一致的,但图标看起来过时了,也需要更新。“
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical现在的目标是为包括手机和平板在内的所有平台更新掉陈旧的图标,使它们在不丢失辨识度的情况下达到出最新的标准。用户只需要看一眼图标,然后什么都不做,就能识别这是Ubuntu系统。
|
||||
Canonical现在的目标是为包括手机和平板在内的所有平台更新掉陈旧的图标,使它们在不丢失原来辨识度的情况下达到出最新的标准。用户只需要看一眼图标,不需要思考,就能识别这是Ubuntu系统。
|
||||
|
||||
迄今为止仍在使用的老旧图标看起来并非那么糟糕,但已经展示出来的新图标则是倾国倾城。
|
||||
迄今为止仍在使用的老旧图标看起来并非那么糟糕,但已经展示出来的新图标则是美轮美奂。
|
||||
|
||||
马修在他的文章中[也][1]提到:”过去一年我们都在为这个进行中的项目工作。我们已经集中精力在如何最好地分类图标这个问题上进行了广泛的研究;我们也经历了数次的设计迭代和探索“。
|
||||
马修在他的文章中[也提到][1]:“过去一年我们都在为这个进行中的项目工作。我们已经集中精力在如何最好地分类图标这个问题上进行了广泛的研究;我们也经历了数次的设计迭代和探索。”
|
||||
|
||||
这些并不是图标的最终版本,设计可能会继续修改。还有一种可能性是这些新图标可能还没有为桌面版本而准备好,但是我们只有希望它们准备好了。
|
||||
这些并不是图标的最终版本,设计可能会继续修改。还有一种可能性是这些新图标可能没有时间为桌面版本准备好,但是我们只有希望它们能。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Ubuntu 14.04 icon set*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Ubuntu 14.04 symbolic icons*
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Ubuntu 14.04 icons in context*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/New-Ubuntu-14-04-Icons-Are-Drop-dead-Gorgeous-Might-Not-Arrive-in-Desktop-Version-410435.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ look: Linux 下验证拼写并显示以某字符串开头的行的命令
|
||||
|
||||
#### 下载/安装/配置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
下面是关于look命令的一些终于链接:
|
||||
下面是关于look命令的一些链接:
|
||||
|
||||
- 主页 [*如果你知道这个工具的主页的话让我知道一下*]
|
||||
- 下载链接
|
||||
@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ look命令成了**util-linux**包的一部分,它在大多数Linux发行版中
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://mylinuxbook.com/look-verify-spellings-and-display-lines/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
33
sources/10 Useful Open Source Web Based File Managers.md
Normal file
33
sources/10 Useful Open Source Web Based File Managers.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
10 Useful Open Source Web Based File Managers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
File managers have recently been more useful than ever before. Increase in the usage of the internet is a big reason for this. Having an application that can effectively manage your files over the internet is an imperative for many. So, here is a list of 10 of the best open source file managers that you can use!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. **eXtplorer**: This application provides you with move, copy, edit, search, delete, download and upload capabilities. In addition, you can also create and extract archives, directories and new files using eXtplorer. It’s key feature is that it lets you access files through FTP. You can either opt to use it under the Mozilla Public License or the GNU Public License. A minimum of PHP 4.3 is required on the server and JavaScript on the browser must be updated in order to use this file manager.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **AjaXplorer**: This explorer is supported by all major browsers and can adapt to smaller screens likes those in mobile phones very easily. While the iOS application for this file manager is already live, the Android application is supposedly coming soon. All you need is a web-server with PHP 5.1 or above to run the AjaXplorer. It allows you to directly stream video content from the server.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **KFM**: This free and open source file manager can be used as a plugin for rich text editors like FCKedition, CKeditor and Tiny MCE. If you’re using a Linux-based operating system, then you need PHP 5.2 or above, while Mac OS X and Windows need MySQL 4.1 or above and MySQL 5.0 or above respectively. It has a search engine of its own and comes with a text editor that can highlight syntax. It also brings mp3 playback and video playback options.
|
||||
|
||||
4. **PAFM**: This file manager gives the user complete control over the files and also allows source code editing using CodePress. The key feature of the file manager comes through Code Press, which provides as-you-type syntax highlighting.
|
||||
|
||||
5. **QuiXplorer**: This file manager can be used for management and sharing over the internet and intranets. It also provides a multi-user mode, where each individual user can have their own settings.
|
||||
|
||||
6. **BytesFall** Explorer: This explorer was released under the GNU GLU license and has been written using PHP and JavaScript. It’s UI is very similar to the Windows Explorer but it has used projects like GeSHi, LiveTree, Shell Commander, FCKeditor etc. because of which it has a varied set of functions.
|
||||
|
||||
7. **NavPHP**: This file manager was written using PHP and AJAX and offers Windows XP style navigation. Like the QuiXplorer, this one also has a multi-user mode and comes with a code editor of its own. In addition, it can also Deflate and Gzip a webpage. You can also download a file or folder as a zip file using this.
|
||||
|
||||
8. **iDC File Manager**: This is a multi-user system that can be installed on Linux or Windows-based web servers. It provides the Hotlink function with social network support and can also monitor user activity on it. It is driven by the MySQL database.
|
||||
|
||||
9. **FileMan**: This file manager comes with a what-you-see-is-what-you-get editor, which allows editing and creation of HTML files. Apart from the HTML editor, it has various other options that can be very useful.
|
||||
|
||||
10. **Relay**: This file manager is used under the GNU Public License and is AJAX enabled. If you use large sets of directories and files, then this manager is ideal for you.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=126569
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
|
||||
@yechunxiao19 翻译中
|
||||
2013: The Golden Year for Linux – 10 Biggest Linux Achievements
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The **Year 2013** is about to end. This Year witnessed many milestones and can be called as a **Golden Year for Linux**. Some of the remarkable achievements from the perspective of **FOSS** and **Linux** are.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Rising Trends of Android ###
|
||||
|
||||
Year 2013 marked a record of Android phone activation with a figure of **1.5 Million** everyday. Need not mention, Android usage **Linux Kernel** and such an enthusiastic approach regarding Android was notable landmark, which will continue to increase in the years to come.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Raspberry pi ###
|
||||
|
||||
One of the greatest development ever in the history of Low cost, single board computer was **Raspberry pi**. Raspberry pi was intended to promote Linux computing in schools and elsewhere and the board was highly welcomed by the FOSS Community and still continuing.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Debian in Space ###
|
||||
|
||||
Debian, one of the upper state of the art Linux distribution was controlling an experiment on a **Space Shuttle** mission in late march of year 2013. The experiment which was controlled by Debian was to test the way to grow plants without soil that could eventually provide oxygen and food to astronauts.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Rise of SteamOS ###
|
||||
|
||||
SteamOS, a debian based distribution was designed for **Stream Machine Game Console** and released in the mid of **December 2013**. With the trend of GNU/Linux into gaming environment is certainly a very welcome act.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Linux on Tablets ###
|
||||
|
||||
Seeing the Tablet sales at **Amazon**, Top ten tablets were running on Android Linux. Apple and Microsoft were far behind in the List on Number 11 and 12, certainly an enthusiastic news for FOSS community.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Chromebooks ###
|
||||
|
||||
Chromebooks wins the market of notebook computers, with a lot of high-end manufacturer viz., Samsung, ASUS giving place to GNU/Linux OS over Proprietary OS’s.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. The Firefox OS ###
|
||||
|
||||
Firefox OS, the Linux based FOSS Operating System for Smart phones and Tablets, was released in late **April 2013**. The **ARM** based Linux distribution for mobile devices, shows promising future.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. The Release of Kali ###
|
||||
|
||||
From the developers of BackTrack Linux comes **Kali Linux**. Kali is a Linux distribution based on Debian, the mother OS which is Primarily developed for Penetration testing and shares a lot of repository of Debian, one of the most rich Distro. Kali Linux holds the record download, in a very less time of its release.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Android Kitkat ###
|
||||
|
||||
One of the Most awaited release was named **Kitkat**. Google Announced **Android 4.4** aka **KitKat in September of 2013**. Although the release had been expected to be number **5.0** aka **Key Lime Pie**. Kitkat has been optimised to run on a large variety of devices having a minimum of **512 MB RAM**.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Linux in Cars ###
|
||||
|
||||
Till now Linux were in a variety of devices ranging from wrist-watches, Remote Controls to Space ship, so ‘**Linux in Cars**’ were not very unexpected still it was surprising when the role of Linux was demonstrated in **Motor Trends Magazines**, car of the year. Both of the Candidate whose model was selected as Winner, in the year 2013, were running on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
The story is endless and it will continue in the future. We might have missed a few major landmark which you can tell us in our comment section. With all these we are giving our readers the last article of the great year for us (**Tecmint**) as well.
|
||||
|
||||
We need your appreciation and Love in the next year as we got in year **2013**. We promise to keep providing you knowledgeable articles in future. Till then, keep connected to **Tecmint**.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/2013-the-golden-year-for-linux-and-foss/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Vic020的WC
|
||||
29 Practical Examples of Nmap Commands for Linux System/Network Administrators
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The **Nmap** aka **Network Mapper** is an open source and a very versatile tool for Linux system/network administrators. **Nmap** is used for **exploring networks, perform security scans, network audit** and **finding open ports** on remote machine. It scans for Live hosts, Operating systems, packet filters and open ports running on remote hosts.
|
||||
|
||||
37
sources/5 Things To Love And Hate About Ubuntu 13.10.md
Normal file
37
sources/5 Things To Love And Hate About Ubuntu 13.10.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
5 Things To Love And Hate About Ubuntu 13.10
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu 13.10 made a lot of noise before and after its arrival. The OS takes Canonical to a whole new level, especially with the big year that Linux has had in 2013. But now that the dust has settled and there's less talk, let us take a look at five things that you might like and five things that you may hate in the OS.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### LOVE ###
|
||||
|
||||
**OpenStack APIs**: Ubuntu 13.10 is compatible with them. In fact, both internal and external Ubuntu-hoster clouds are compatible with OpenStack APIs now.
|
||||
|
||||
**Graphical User Interface**: The Unity GUI is now going from PCs to smartphones and tablets as well.
|
||||
|
||||
**Upgraded Dashboard**: Ubuntu Dash has been upgraded, which offers users the option to search even the Ubuntu One cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
**Good Juju**: In Saucy Salamander, you can use Juju in order to create app instances within Linux containers or LXC.
|
||||
|
||||
**GUI is smoother**: Perhaps because of its versatility, the GUI for Saucy Salamander is much smoother than older GUIs.
|
||||
|
||||
### HATE ###
|
||||
|
||||
**No Mir**: The Unity interface hasn’t moved from X.org to the Mir translator. This was a major let down for many.
|
||||
|
||||
**No MariaDB**: The forked MySQL database, MariaDB, has not been introduced by Canonical. This is more surprising than disappointing as most other vendors have already made the move. Canonical’s Ubuntu 13.10 still has MySQL as the default LAMP database.
|
||||
|
||||
**Old landscape management tool**: Canonical’s landscape service is not advanced enough. In fact, it is old compared to even the Microsoft System Center that comes with Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
**Only two supported phones**: Only the Nexus 4 and the Galaxy Nexus smartphones support Ubuntu 13.10 right now. In addition, only core and shell apps are available for the devices.
|
||||
|
||||
**LXC is still beta**: We talked about Juju being used alongside LXC, but LXC itself is still in beta mode. It is supposedly going to get a stable build in February this year.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.networkworld.com/slideshow/134353/ubuntu-1310-5-things-we-love-5-things-we-hate.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
6 Unusual Yet Great Linux Operating Systems For Your Netbook!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> The beauty of Linux-based operating systems is that they can be customised as per the requirements. So, here we present top 6 unusual yet interesting distros for netbooks!
|
||||
|
||||
A good netbook operating system is one that can fully utilise its resources. The memory usage should be minimal when it is on the idle mode and as the screen is smaller, you need to have a very good navigation system to avoid cluttering the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
And what better for a Linux enthusiast than having a netbook optimised operating system, based on open source technology.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1.**AntiX** – This utilises the iceWM window manager that assists in keeping the initial memory footprint low. Although it’s not as stylish as Ubuntu, Mint or Elementary, it is fully functional. There is a taskbar for navigation at the bottom and icons on the desktop that has been standard across operating systems over a number of years. AntiX is accompanied with an array of applications with a few that won’t necessarily fit well with a netbook.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **SparkyLinux** - The appearance and feel of Razor-Qt is extremely traditional and comes with a panel at the bottom and a menu in the bottom left corner. SparkyLinux is accompanied with an array of applications. The developers once again have plumped for the LibreOffice suite over the lighter Abiword and Gnumeric tools.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **Lubuntu** - The LXDE desktop is extremely light and nearly as easy to customise as Xubuntu. The desktop is quite familiar having a panel at the bottom with a menu and system tray icons. However, you can customise Lubuntu to appear the way you want it to with multiple panels if you so wish. The applications are quite well adapted to a netbook with the Sylpheed email client, the Firefox web browser as well as Abiword and Gnumeric.
|
||||
|
||||
4. **OS4** – This is based on Xubuntu. It makes use of the XFCE desktop that is wonderful for customizing and can work any way you want it to. XFCE being a lightweight desktop environment performs grealty on a netbook. However, you will need to install the restricted extras package to get Flash videos and MP3s to play but with OS4 these things work straight away. It comes with a Commodore Amiga Emulator installed so if you like to retro game on your netbook this is definitely an option.
|
||||
|
||||
5. **Point Linux** – This is unique as it uses the MATE desktop. The MATE desktop was initially taken from Gnome 2 but it has evolved to be a really good desktop environment in its own right. Point Linux appears quite stylish. The menus appear great and the performance on the netbook is really good. Similar to LXDE and XFCE desktops, it is highly customizable. Point Linux comes with four virtual workspaces by default allowing you to use these again to maximize the usage of your netbook so that it is limited by memory and processor power over display issues.
|
||||
|
||||
6. **Elementary OS** – This is great if you are looking for something very stylish. It doesn’t have an office suite on installation but you have the option to pick and select tools you want to use. For web browsing you have Midori and the email client is Geary. It comes installed with Totem for viewing movies and the audio application is a compact tool called Noise.
|
||||
|
||||
Source: everydaylinuxuser.com
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=126643
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
(whatever1992 ing)
|
||||
Built in Audit Trail Tool – Last Command in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,375 @@
|
||||
Collectl is a powerful tool to monitor system resources on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Monitoring system resources ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux system admins often need to monitor system resources like cpu, memory, disk, network etc to make sure that the system is in a good condition. And there are plenty of commands like iotop, top, free, htop, sar etc to do the task. Today we shall take a look at a tool called collectl that can be used to measure, monitor and analyse system performance on linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Collectl is a nifty little program that does a lot more than most other tools. It comes with a extensive set of options that allow users to not only measure the values of multiple different system metrics but also save the data for later analysis. Unlike other tools, which are designed to measure only a specific system parameter, collectl can monitor different parameters at the same time and report them in a suitable manner.
|
||||
|
||||
From the [project website][1] ...
|
||||
|
||||
> Unlike most monitoring tools that either focus on a small set of statistics, format their output in only one way, run either interatively or as a daemon but not both, collectl tries to do it all. You can choose to monitor any of a broad set of subsystems which currently include buddyinfo, cpu, disk, inodes, infiniband, lustre, memory, network, nfs, processes, quadrics, slabs, sockets and tcp.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a peek at the command before we start digging deeper.
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
#<--------CPU--------><----------Disks-----------><----------Network---------->
|
||||
#cpu sys inter ctxsw KBRead Reads KBWrit Writes KBIn PktIn KBOut PktOut
|
||||
0 0 864 1772 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
|
||||
5 2 1338 2734 0 0 8 2 0 0 0 1
|
||||
1 0 1222 2647 0 0 92 3 0 2 0 1
|
||||
1 0 763 1722 0 0 80 3 0 1 0 2
|
||||
|
||||
The cpu usage, disk io, and network activity is being logged every second. The data is not difficult to read for those who understand it. The list keeps growing at a defined time interval and is easily loggable to a file. And collectl provides necessary options to record, search and do other useful things with the data.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install collectl ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu/Debian and the likes have Collectl is available in the default repositories, so just apt it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install collectl
|
||||
|
||||
Fedora/CentOS too have it in the repos, so grab it with yum.
|
||||
|
||||
$ yum install collectl
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Essential theory - Collectl subsystems ####
|
||||
|
||||
Different types of system resources that can be measured are called subsystems. Like cpu, memory, network bandwidth and so on. If you just run the collectl command, it will show the cpu, disk and network subsystems in a batch mode output. That has already been shown above.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the man page, collectl identifies the following subsystems.
|
||||
|
||||
SUMMARY SUBSYSTEMS
|
||||
|
||||
b - buddy info (memory fragmentation)
|
||||
c - CPU
|
||||
d - Disk
|
||||
f - NFS V3 Data
|
||||
i - Inode and File System
|
||||
j - Interrupts
|
||||
l - Lustre
|
||||
m - Memory
|
||||
n - Networks
|
||||
s - Sockets
|
||||
t - TCP
|
||||
x - Interconnect
|
||||
y - Slabs (system object caches)
|
||||
|
||||
DETAIL SUBSYSTEMS
|
||||
|
||||
This is the set of detail data from which in most cases the corresponding summary data is derived. There are currently 2 types that
|
||||
do not have corresponding summary data and those are "Environmental" and "Process". So, if one has 3 disks and chooses -sd, one
|
||||
will only see a single total taken across all 3 disks. If one chooses -sD, individual disk totals will be reported but no totals.
|
||||
Choosing -sdD will get you both.
|
||||
|
||||
C - CPU
|
||||
D - Disk
|
||||
E - Environmental data (fan, power, temp), via ipmitool
|
||||
F - NFS Data
|
||||
J - Interrupts
|
||||
L - Lustre OST detail OR client Filesystem detail
|
||||
M - Memory node data, which is also known as numa data
|
||||
N - Networks
|
||||
T - 65 TCP counters only available in plot format
|
||||
X - Interconnect
|
||||
Y - Slabs (system object caches)
|
||||
Z - Processes
|
||||
|
||||
To monitor and measure a particular subsystem use the "-s" option and add the subsytem identifier to it. Now lets try out a few examples.
|
||||
|
||||
##$# 1. Monitor cpu usage ####
|
||||
|
||||
To monitor just the summary of cpu usage use "-sc"
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -sc
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
#<--------CPU-------->
|
||||
#cpu sys inter ctxsw
|
||||
3 0 1800 3729
|
||||
3 0 1767 3599
|
||||
|
||||
To observe each cpu individually, use "C". It will output multiple lines together, one for each cpu.
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -sC
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
|
||||
# SINGLE CPU STATISTICS
|
||||
# Cpu User Nice Sys Wait IRQ Soft Steal Idle
|
||||
0 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 96
|
||||
1 3 0 0 0 0 0 0 96
|
||||
2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 97
|
||||
3 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 98
|
||||
0 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 97
|
||||
1 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 95
|
||||
2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 98
|
||||
3 4 0 1 0 0 0 0 95
|
||||
|
||||
Using the C and c option together will fetch you both individual measures and the summary stats in a mmore comprehensive manner, if you need.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Monitor memory ####
|
||||
|
||||
Use the m subsystem to check the memory
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -sm
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
#<-----------Memory----------->
|
||||
#Free Buff Cach Inac Slab Map
|
||||
2G 220M 1G 1G 210M 3G
|
||||
2G 220M 1G 1G 210M 3G
|
||||
2G 220M 1G 1G 210M 3G
|
||||
|
||||
Should not be difficult to interpret.
|
||||
The M option would give further details about the memory.
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -sM
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
|
||||
# MEMORY STATISTICS
|
||||
# Node Total Used Free Slab Mapped Anon Locked Inact Hit%
|
||||
0 7975M 5939M 2036M 215720K 372184K 0 6652K 1434M 0
|
||||
0 7975M 5939M 2036M 215720K 372072K 0 6652K 1433M 0
|
||||
|
||||
Does that look similar to what free reports ?
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Check disk usage ####
|
||||
|
||||
The d and D options provide the summary and details on disk usage.
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -sd
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
#<----------Disks----------->
|
||||
#KBRead Reads KBWrit Writes
|
||||
4 1 136 24
|
||||
0 0 80 13
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -sD
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
|
||||
# DISK STATISTICS (/sec)
|
||||
# <---------reads---------><---------writes---------><--------averages--------> Pct
|
||||
#Name KBytes Merged IOs Size KBytes Merged IOs Size RWSize QLen Wait SvcTim Util
|
||||
sda 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
|
||||
sda 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
|
||||
sda 1 0 2 1 17 1 5 3 2 2 6 2 1
|
||||
sda 0 0 0 0 92 11 5 18 18 1 12 12 5
|
||||
|
||||
Another option that provides extended information is the "--verbose" option. It expands the summary to include more information but is not identical to using D.
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -sd --verbose
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. Report multiple systems together ####
|
||||
|
||||
So lets say you want a report of cpu, memory and disk io together, then use the subsystems together.
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -scmd
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
#<--------CPU--------><-----------Memory-----------><----------Disks----------->
|
||||
#cpu sys inter ctxsw Free Buff Cach Inac Slab Map KBRead Reads KBWrit Writes
|
||||
4 0 2187 4334 1G 221M 1G 1G 210M 3G 0 0 0 0
|
||||
3 0 1896 4065 1G 221M 1G 1G 210M 3G 0 0 20 5
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. Display time with the stats ####
|
||||
|
||||
To display the time in each line along with the measurements, use the T option. And over that, to specify options, you need to use the "-o" switch.
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -scmd -oT
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
# <--------CPU--------><-----------Memory-----------><----------Disks----------->
|
||||
#Time cpu sys inter ctxsw Free Buff Cach Inac Slab Map KBRead Reads KBWrit Writes
|
||||
12:03:05 3 0 1961 4013 1G 225M 1G 1G 212M 3G 0 0 0 0
|
||||
12:03:06 3 0 1884 3810 1G 225M 1G 1G 212M 3G 0 0 0 0
|
||||
12:03:07 3 0 2011 4060 1G 225M 1G 1G 212M 3G 0 0 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
You could also display the time in milliseconds with "-oTm".
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. Change sample count ####
|
||||
|
||||
Every row the collectl reports is a snapshot or sample. And it takes these snapshots at regular intervals, say 1 second. The i option sets the interval and c option sets the sample count.
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -c1 -sm
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
#<-----------Memory----------->
|
||||
#Free Buff Cach Inac Slab Map
|
||||
1G 261M 1G 1G 228M 3G
|
||||
|
||||
To change interval use the i options
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -sm -i2
|
||||
waiting for 2 second sample...
|
||||
#<-----------Memory----------->
|
||||
#Free Buff Cach Inac Slab Map
|
||||
1G 261M 1G 1G 229M 3G
|
||||
|
||||
The above command would collect memory stats every 2 seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7. Use collectl like iotop ####
|
||||
|
||||
Out of the plenty options, the "top" option makes collectl report process-wise statistics much like iostat/top commands. The list is continuously updated and can be sorted on a number of fields.
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl --top iokb
|
||||
|
||||
The output looks like this
|
||||
|
||||
# TOP PROCESSES sorted by iokb (counters are /sec) 09:44:57
|
||||
# PID User PR PPID THRD S VSZ RSS CP SysT UsrT Pct AccuTime RKB WKB MajF MinF Command
|
||||
3104 enlighte 20 2683 3 S 938M 33M 0 0.00 0.00 0 00:09.16 0 4 0 0 /usr/bin/ktorrent
|
||||
1 root 20 0 0 S 26M 3M 2 0.00 0.00 0 00:01.30 0 0 0 0 /sbin/init
|
||||
2 root 20 0 0 S 0 0 3 0.00 0.00 0 00:00.00 0 0 0 0 kthreadd
|
||||
3 root 20 2 0 S 0 0 0 0.00 0.00 0 00:00.02 0 0 0 0 ksoftirqd/0
|
||||
4 root 20 2 0 S 0 0 0 0.00 0.00 0 00:00.00 0 0 0 0 kworker/0:0
|
||||
5 root 0 2 0 S 0 0 0 0.00 0.00 0 00:00.00 0 0 0 0 kworker/0:0H
|
||||
7 root RT 2 0 S 0 0 0 0.00 0.00 0 00:00.08 0 0 0 0 migration/0
|
||||
8 root 20 2 0 S 0 0 2 0.00 0.00 0 00:00.00 0 0 0 0 rcu_bh
|
||||
9 root 20 2 0 S 0 0 0 0.00 0.00 0 00:00.00 0 0 0 0 rcuob/0
|
||||
|
||||
The output is very similar to the top command and it sorts the process by the amount of disk io in descending order.
|
||||
|
||||
To display only top 5 processes use it as follows
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl --top iokb,5
|
||||
|
||||
To learn about what fields the above list can be sorted, use the following command
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl --showtopopts
|
||||
The following is a list of --top's sort types which apply to either
|
||||
process or slab data. In some cases you may be allowed to sort
|
||||
by a field that is not part of the display if you so desire
|
||||
|
||||
TOP PROCESS SORT FIELDS
|
||||
|
||||
Memory
|
||||
vsz virtual memory
|
||||
rss resident (physical) memory
|
||||
|
||||
Time
|
||||
syst system time
|
||||
usrt user time
|
||||
time total time
|
||||
accum accumulated time
|
||||
|
||||
I/O
|
||||
rkb KB read
|
||||
wkb KB written
|
||||
iokb total I/O KB
|
||||
|
||||
rkbc KB read from pagecache
|
||||
wkbc KB written to pagecache
|
||||
iokbc total pagecacge I/O
|
||||
ioall total I/O KB (iokb+iokbc)
|
||||
|
||||
rsys read system calls
|
||||
wsys write system calls
|
||||
iosys total system calls
|
||||
|
||||
iocncl Cancelled write bytes
|
||||
|
||||
Page Faults
|
||||
majf major page faults
|
||||
minf minor page faults
|
||||
flt total page faults
|
||||
|
||||
Context Switches
|
||||
vctx volunary context switches
|
||||
nctx non-voluntary context switches
|
||||
|
||||
Miscellaneous (best when used with --procfilt)
|
||||
cpu cpu number
|
||||
pid process pid
|
||||
thread total process threads (not counting main)
|
||||
|
||||
TOP SLAB SORT FIELDS
|
||||
|
||||
numobj total number of slab objects
|
||||
actobj active slab objects
|
||||
objsize sizes of slab objects
|
||||
numslab number of slabs
|
||||
objslab number of objects in a slab
|
||||
totsize total memory sizes taken by slabs
|
||||
totchg change in memory sizes
|
||||
totpct percent change in memory sizes
|
||||
name slab names
|
||||
|
||||
#### 8. Use collectl like top ####
|
||||
|
||||
To make collectl report like top, we just have to report processes ordered by the cpu usage.
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl --top
|
||||
|
||||
The output should be like this
|
||||
|
||||
# TOP PROCESSES sorted by time (counters are /sec) 14:08:46
|
||||
# PID User PR PPID THRD S VSZ RSS CP SysT UsrT Pct AccuTime RKB WKB MajF MinF Command
|
||||
9471 enlighte 20 9102 0 R 63M 22M 3 0.03 0.10 13 00:00.81 0 0 0 3 /usr/bin/perl
|
||||
3076 enlighte 20 2683 2 S 521M 40M 2 0.00 0.03 3 00:55.14 0 0 0 2 /usr/bin/yakuake
|
||||
3877 enlighte 20 3356 41 S 1G 218M 1 0.00 0.03 3 10:10.50 0 0 0 0 /opt/google/chrome/chrome
|
||||
4625 enlighte 20 2895 36 S 1G 241M 2 0.00 0.02 2 08:24.39 0 0 0 12 /usr/lib/firefox/firefox
|
||||
5638 enlighte 20 3356 3 S 1G 265M 1 0.00 0.02 2 09:55.04 0 0 0 2 /opt/google/chrome/chrome
|
||||
1186 root 20 1152 4 S 502M 76M 0 0.00 0.01 1 03:02.96 0 0 0 0 /usr/bin/X
|
||||
1334 www-data 20 1329 0 S 87M 1M 2 0.00 0.01 1 00:00.85 0 0 0 0 nginx:
|
||||
|
||||
You can also display sub system information along with the above
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl --top -scm
|
||||
|
||||
#### 9. List processes like ps ####
|
||||
|
||||
To just list out the processes like ps command, without updating continously, just set the sample count to 1 with the "c" options
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -c1 -sZ -i:1
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will list out all the processes much like "ps -e". The 'procfilt' option can be used to filter out specific processes from the process. The 'procopts' option can be used to specify another set of options for fine tune the process list display.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 10. Use collectl like vmstat ####
|
||||
|
||||
Collectl has got a direct option to make it behave like vmstat
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl --vmstat
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
#procs ---------------memory (KB)--------------- --swaps-- -----io---- --system-- ----cpu-----
|
||||
# r b swpd free buff cache inact active si so bi bo in cs us sy id wa
|
||||
1 0 0 1733M 242M 1922M 1137M 710M 0 0 0 108 1982 3918 2 0 95 1
|
||||
1 0 0 1733M 242M 1922M 1137M 710M 0 0 0 0 1906 3886 1 0 98 0
|
||||
1 0 0 1733M 242M 1922M 1137M 710M 0 0 0 0 1739 3480 3 0 96 0
|
||||
|
||||
#### 11. Detailed information about subsystems ####
|
||||
|
||||
The following command would collect "5 samples" of CPU statistics at "1 second" interval and print detailed information (verbose) along with the time.
|
||||
|
||||
$ collectl -sc -c5 -i1 --verbose -oT
|
||||
waiting for 1 second sample...
|
||||
|
||||
# CPU SUMMARY (INTR, CTXSW & PROC /sec)
|
||||
#Time User Nice Sys Wait IRQ Soft Steal Idle CPUs Intr Ctxsw Proc RunQ Run Avg1 Avg5 Avg15 RunT BlkT
|
||||
14:22:10 11 0 0 0 0 0 0 87 4 1312 2691 0 866 1 0.78 0.86 0.78 1 0
|
||||
14:22:11 15 0 0 0 0 0 0 84 4 1283 2496 0 866 1 0.78 0.86 0.78 1 0
|
||||
14:22:12 17 0 0 0 0 0 0 82 4 1342 2658 0 866 0 0.78 0.86 0.78 0 0
|
||||
14:22:13 15 0 0 0 0 0 0 84 4 1241 2429 0 866 1 0.78 0.86 0.78 1 0
|
||||
14:22:14 11 0 0 0 0 0 0 88 4 1270 2488 0 866 0 0.80 0.87 0.78 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
Change the "-s" parameter to view a different subsystem.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
The post so far was just a bird's view of this amazing tool called collectl. It should have given a fair idea of how flexible it is. The discussion however leaves out various other features of collectl which include the ability to record and "playback" the captured data, export data for various file formats and data formats that can be used with external tools for analysis etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Another major feature that collectl supports is running as a service that allows for remote monitoring making it a perfect tool for keeping a watch on resources of remote linux machines or an entire server cluster.
|
||||
|
||||
Collectl is accompanied with an additional set of tools named [Collectl Utils][2] (colmux, colgui, colplot) that can be used to process and analyse the data collected. May be we shall take a look at those in another post.
|
||||
|
||||
Check the man page to learn more about the options. I would also recommend checking out the [FAQs][3] to get a quick idea about collectl. Next, read up the [collectl documentation][4] for more indepth examples to get beyond the basics. There is also a [command equivalence matrix][5] which maps the more common commands like sar, iostat, netstat, top with their collectl equivalents.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.binarytides.com/collectl-monitor-system-resources-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://collectl.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[2]:http://collectl-utils.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[3]:http://collectl.sourceforge.net/FAQ-collectl.html
|
||||
[4]:http://collectl.sourceforge.net/Documentation.html
|
||||
[5]:http://collectl.sourceforge.net/Matrix.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Linux Kernel 3.12.7 Released – Here’s How To Upgrade In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux Kernel version 3.12.7 mainline has just been released and this brief tutorial is going to show you how to easily upgrade in Ubuntu. If you’re running Ubuntu 13.10 and below, chances are your system doesn’t have this latest kernel installed.
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux Kernel is the core of the Linux Operating System that includes Ubuntu. The kernel makes it possible for Ubuntu to communicate with your system hardware (Memory, CPU, Drives, etc). The kernel manages resources and handles all essential the parts of your machine.
|
||||
|
||||
Without the Linux Kernel, Ubuntu is only bunch of fancy applications without access to the hardware or essential parts of your machine. That’s why the Linux Kernel is so important.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Upgrade Your Ubuntu Kernel? ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing to understand before upgrading your system’s kernel is that it could break your system and make it unusable. In fact, it’s not recommended to upgrade the kernel on your own. Canonical, the parent company of Ubuntu does a great job updating the kernel in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
They test and make sure the kernel installed is compatible with that edition of Ubuntu before releasing it. So, if your machine is working fine without issues, you should keep the current installed kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
On the other hand, if Ubuntu isn’t able to recognize all your system’s components or your machines isn’t functioning correctly, upgrading the Linux Kernel might just help.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s because newer kernels add newer drivers and features for newer machines.. If the current installed kernel doesn’t support some features on your machine, you should upgrade.
|
||||
|
||||
For more about kernel 2.12.7, [read the ChangeLog here][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### Upgrading The Linux Kernel. ###
|
||||
|
||||
To upgrade your kernel, run the commands below to update all packages and existing kernels.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade && sudo apt-get autoremove
|
||||
|
||||
After updating your machine, restart your machine. It’s always good to restart after upgrading your system packages and kernel. Doing so allows for newer kernels to be applied.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, run the commands below to download Linux Kernel 3.12.7.
|
||||
|
||||
#### For 32-bit Machines, run the commands below. ####
|
||||
|
||||
cd /tmp && wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v3.12.7-trusty/linux-headers-3.12.7-031207-generic_3.12.7-031207.201401091657_i386.deb http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v3.12.7-trusty/linux-headers-3.12.7-031207_3.12.7-031207.201401091657_all.deb http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v3.12.7-trusty/linux-image-3.12.7-031207-generic_3.12.7-031207.201401091657_i386.deb
|
||||
|
||||
#### For 64-bit System, run the commands below ####
|
||||
|
||||
cd /tmp && wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v3.12.7-trusty/linux-headers-3.12.7-031207-generic_3.12.7-031207.201401091657_amd64.deb http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v3.12.7-trusty/linux-headers-3.12.7-031207_3.12.7-031207.201401091657_all.deb http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v3.12.7-trusty/linux-image-3.12.7-031207-generic_3.12.7-031207.201401091657_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
After downloading the version for your system, run the commands below to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i *.deb
|
||||
|
||||
After installing, restart your machine and if everything went as described above, your system should have the latest stable kernel version installed.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To uninstall kernel version 3.12.7, run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove linux-headers-3.12.7-* linux-image-3.13.7-*
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2014/01/daily-ubuntu-tips-linux-kernel-3-12-7-released-heres-how-to-upgrade-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v3.x/ChangeLog-3.12.7
|
||||
@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
|
||||
翻译ing Luox
|
||||
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Mount Partitions In Ubuntu From Your Desktop GUI
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Not very long ago if you had asked a seasoned Linux user how to mount partitions in Ubuntu, they would’ve told you to use the fstab file in the **/etc/** directory. It seemed like this was the only way to mount partitions in Linux systems, including Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Well, not anymore thanks to [GNOME Disk Utility][1]. With Disks, you can now mount partitions easily from the GUI without ever touching the fstab file from the command line. The fstab file is a Linux file that lists available disks and partitions, and indicates how they are mounted.
|
||||
|
||||
The mount command looks in the fstab file and determine how and where these devices should be mounted. It’s only accessed by the system administrator or root.
|
||||
|
||||
This brief tutorial is going to show you how to easily mount partitions in Ubuntu without touching the fstab file. For new users and those who are just starting out with Ubuntu, they should find this method easy to use when mounting external partitions or drives.
|
||||
|
||||
There are some tools that may help you build the fstab file, but few can do it as efficiently as Disks in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
If you open the fstab file in Ubuntu, you’ll see something like what’s below.
|
||||
|
||||
#<File System> <Mount Point> <type> <options> <dump> <pass>
|
||||
/dev/fd0 /media/floppy0 vfat rw,user,noauto 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
These line above are just a sample of how partitions are mounted in Ubuntu. Each device gets its own file types and mount points. For those starting out with Ubuntu, this can be intimidating.
|
||||
|
||||
For seasoned Linux users, administering the fstab file isn’t difficult. If you’ve done it once, the next should be easy.
|
||||
|
||||
So, here you go. To add an entry in the fstab file or mount a partition, go to Unity Dash and open **Disk app**. When it opens, select the drive you wish to mount and format it. After formatting it, select **Option –> Edit Mount Options**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Finally, turn off auto mount options and manually specify your mount options. The Disk will automatically inserts these options in the fstab file so the mount command can read and mount the partition.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Save your settings and restart or hit the mount command to mount the partition.
|
||||
|
||||
The options above will look like this in the fstab file.
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/sdb /media/richard/ExtPartition ntfs-3g rw,auto,user,fmask=0111,dmask=0000 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
Yep, that’s it! The new partition will be mounted every time you start your machine.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2014/01/daily-ubuntu-tips-mount-partitions-in-ubuntu-from-your-desktop-gui/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Design/Apps/Disks
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
先来篇儿短的练练手儿
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Support For Ubuntu 13.04 Ends January 27, 2014
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you’re currently Ubuntu 13.04 Raring Ringtail, it may be time to upgrade to the next version because support for it will end January 27 of this year.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
【scusjs占】Daily Ubuntu Tips – Take Screenshots Of your Desktop
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Take Screenshots Of your Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu, a powerful and modern operating system allows you to perform many tasks. From creating and editing documents using LibreOffice Productivity Suite to enhancing an image with GIMP, Ubuntu is super!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
||||
翻译中 by TImeszoro
|
||||
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips — Windows Disk Management Equivalent In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
For new users just starting out with Ubuntu who have some knowledge of Microsoft Windows, one question keeps coming up in most Ubuntu forums online. One of our readers asked us the same questions few days ago.
|
||||
|
||||
> What is Windows Disk Management Equivalent in Ubuntu?
|
||||
|
||||
For those who don’t know about Disk Management, here’s a brief summary.
|
||||
|
||||
Disk Management is a tool that comes with Windows by default beginning with Windows XP. It performs disk-related task such as creating and formatting volumes, initializing disks, resizing partitions, assigning drive letters and deleting partitions.
|
||||
|
||||
It uses the DiskPart command along with related command-line tools to perform disk management task from the command-line in Windows. It is a very powerful tool in Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
The question is, is there a Ubuntu equivalent? The answer is Yes.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu comes with similar tool called GNOME Disk Utility. It’s a tool to view / manage disk drives, modify partitions, create and restore disk images and more. You can also use it to format and create partitions, mount and unmount volumes, and other disk related tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
Although it similar to Disk Management in Windows, it doesn’t allow you to resize partitions and volumes. Since Ubuntu doesn’t support drive letters, it doesn’t do that as well.
|
||||
|
||||
So, for disk management equivalent in Ubuntu, look at GNOME Disk Utility.
|
||||
|
||||
To access it, open Unity Dash and search for Disks. When it opens, it should automatically recognize external drives or additional hard drives that are attached to your machine.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once the drive is selected, you can then perform disk-related tasks such as formatting, creating partitions and managing your drives. Other settings you can configure is standby mode for your disk where it puts the drive in standby mode after timeouts.
|
||||
|
||||
Something to remember is when you’re formatting a drive to use on both Ubuntu and Windows, use NTFS file system.
|
||||
|
||||
So, use Disks to configure you drives in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy! And Happy New Year!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2014/01/daily-ubuntu-tips-windows-disk-management-equivalent-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Find Saved WiFi Password In Linux Mint 16 [Beginner]
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
When you connect to a wireless network using WEP, WPA or WPA2-PSK, the password is saved in Linux Mint (or any other OS) when you use “connect automatically”. Imagine a situation where you need to know the WiFi password and you have not noted it down somewhere for e.g., if you need to provide the password to a visitor. You can easily retrieve the password of an earlier connected wireless network.
|
||||
|
||||
In this **beginner’s tutorial**, we shall see **how to find the saved WiFi passwords in Linux Mint 16 Petra**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Find saved WiFi password in Linux Mint: ###
|
||||
|
||||
The procedure to find the saved WiFi password is very simple. Click on the Menu button and type network. Choose **Network Connections** in there:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In Network Connections, you’ll see all the WiFi networks you have been connected to recently. Select the one for which you want to know the password and click on **Edit**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In here, under the **Wi-Fi Security** tab, check the **Show password** to reveal the password.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
And that’s all you had to do to get the saved password. You can do similar steps to [get the stored WiFi passwords in Ubuntu][1]. I hope the article helped you.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/find-wifi-password-linux-mint-16/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-find-saved-wireless-wifi-passwords-ubuntu/
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
coolpigs translating
|
||||
|
||||
Here are Facebook’s 9 top open-source projects from 2013
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Facebook and open-source software go together like Jay-Z and Beyoncé — you just can’t have one without the other.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How To Install Icon Themes In Linux Mint 16 [Beginner Tip]
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you think the default Mint themes and icons are not good enough for you, why not change it? In this quick tip for beginners, we shall see how to **install icon themes in Linux Mint 16** and more than that **how to change the icons in Linux Mint**. We shall see this quick tutorial by installing gorgeous Moka icon themes.
|
||||
|
||||
Just a quick note, if you do not know it already, there is a difference between ‘themes’ and ‘icon themes’. An icon theme just changes the look of icons while a theme changes a lot of other things along with the looks of icons.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install icon themes in Linux Mint 16: ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are two ways to install icon themes in Linux Mint (and many other Linux distributions, if not all). If you download the icon theme in a zipped folder, you can extract it in ~/.icons directory. Usually this directory does not exist. Feel free to create it.
|
||||
|
||||
Second way to install an icon theme is using a [PPA][1]. Most of the standard and popular icon themes have their own PPA. Lets see how to install Moka icons set in Mint using PPA.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Moka icon set in Linux Mint 16: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Open a terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and use the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:moka/moka-icon-theme
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install moka-icon-theme
|
||||
|
||||
### Change icons in Linux Mint 16: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Changing an [icon theme in Ubuntu][2] was straight forward. It is slightly hidden in Linux Mint though. Once you have installed the icon themes, go to **Settings** from the Menu. And then go to **Themes**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now you might have realized why I said that changing the icon is slightly hidden in Linux Mint. You’ll not find an option to change just the icons here, at least not in the first look. To change only the icon, go to **Other settings** and click on **Icons** there. You’ll see all the icons set available here. Choose the one you like.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The changes will be reflected immediately. No need of a restart. Here is how my Linux Mint desktop looks after applying Moka icon themes:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I hope you find this quick to install and change icon themes in Linux Mint helpful. Don’t forget to check 5 best icon themes in Ubuntu 13.10, you’ll find some beautiful icons there to make your desktop prettier. Any questions, suggestion, thoughts? Feel free to drop a comment.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-icon-linux-mint/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Personal_Package_Archive
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-themes-in-ubuntu-13-10/
|
||||
@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How To Properly Install Ubuntu One In Linux Mint 16
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Linux Mint][1] is based on Ubuntu so I was thinking that Ubuntu One would be one of the pre-installed programs. I was wrong. So, I installed Ubuntu One from Software Manager and surprisingly, it did not work. In this quick tip we shall see **how to install Ubuntu One in Linux Mint 16** and how to make it work as well.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Ubuntu One in Linux Mint 16: ###
|
||||
|
||||
You have just installed the Ubuntu One client from Software Manager and when you look for it to open and configure it, you will not even find it in the menu search. It’s as if it was never installed. But if you look in Software Manager, it will be marked as installed. So what went wrong here, then?
|
||||
|
||||
The problem here is that **Ubuntu One installer** has been referred by **ubuntuone-control-panel-qt** package. Since this package is not installed, your Ubuntu One installation fails to load. To fix this issue, open a terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ubuntuone-control-panel-qt
|
||||
|
||||
Now when you search in the menu, you will see Ubuntu One present there. You can configure the account and choose what to sync and what not to sync. And when you start to think that you have over come all the issues, you’ll notice that **Ubuntu One indicator is not present in the panel**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Ubuntu One indicator in Linux Mint 16: ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can add the following PPA to get the Ubuntu One indicator applet in Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:rye/ubuntuone-extras
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install indicator-ubuntuone
|
||||
|
||||
Log out and when you log back in, you can see the indicator in the panel. And with this, we are done with installing and setting Ubuntu One completely. I hope this post helped you to **install Ubuntu One in Linux Mint**. Questions, suggestions are always welcomed.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-one-linux-mint-16/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxmint.com/
|
||||
34
sources/How to Dual Boot Ubuntu and Windows Properly.md
Normal file
34
sources/How to Dual Boot Ubuntu and Windows Properly.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
How to Dual Boot Ubuntu and Windows Properly
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Despite what Microsoft would have you believe, a Linux and a Windows operating system can coexist peacefully on the same PC. This is a tutorial that will teach you how to get an Ubuntu system to run in parallel with a Windows OS.**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
There are two situations that you must consider, and you have to decide which one applies to you. This has to do with the order of the installation. Installing Windows after you already have an Ubuntu system is a little bit problematic, because Microsoft doesn't really care about other users.
|
||||
|
||||
If you install Ubuntu after you already have Windows installed, things are a lot simpler and virtually no work or preparation is required.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s get on with the more difficult problem. If you have an Ubuntu system and you want to install Windows, you will lose GRUB, which is the default bootloader. Windows doesn’t really care and will erase it.
|
||||
|
||||
If you made this mistake and you didn't overwrite the Linux partition, don't despair. The data is still there and all you need is a bootable live CD with Ubuntu (up until 13.10). You will need to install an application called Boot-Repair. This is done with a PPA.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember, if you use a USB stick, it's quite easy to install applications because Ubuntu is a hybrid image. Boot the live Ubuntu session, open a terminal, and enter the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair && sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install -y boot-repair && (boot-repair &)
|
||||
|
||||
Open the application, click recommended repair, and wait. When it's finished, reboot, and you will get GRUB back and dual boot.
|
||||
|
||||
On the other hand, if you already have Windows and you want to install Ubuntu, things are a lot easier. Start the Ubuntu installation, choose to install on a partition that's not Windows, format to EXT4, choose the location of the bootloader, and it's done.
|
||||
|
||||
If you choose to place the bootloader on the same hard drive as the Windows installation, it will erase the Microsoft's bootloader. This is ok because GRUB recognizes the Windows OS and you won't miss it. If you place it somewhere else, on another hard-drive for example, you will get both of them when you choose to boot from different hard drives.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy your Ubuntu and Windows dual boot system.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Dual-Boot-Ubuntu-and-Windows-Properly-415377.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
45
sources/How to Replace GRUB with Syslinux on Arch Linux.md
Normal file
45
sources/How to Replace GRUB with Syslinux on Arch Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
How to Replace GRUB with Syslinux on Arch Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The following tutorial will teach existing Arch Linux users how to install replace the GRUB boot loader in their operating systems with Syslinux, which offers a simple, fast, and more modern boot loader.**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Actually, Syslinux is not a single boot loader, as it’s comprised of multiple boot loaders that are capable of booting from local drives, over the network via PXE, as well as removable media. In addition, it supports both MBR and GPT disks, as well as RAID setups.
|
||||
|
||||
Before you jump to the actual installation process, you should know that Syslinux supports the following filesystems: FAT, EXT2, EXT3, EXT4, and Btrfs. You should also know that Syslinux can boot from both UEFI and BIOS machines, and it is not capable (at the moment) of accessing files from partitions other than its own.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, keep in mind that replacing GRUB with Syslinux is an optional thing, not something that you should really do because “something else will happen.” Only people who want to try something new, who are bored with the look of the GRUB boot loader should install Syslinux, otherwise keep running GRUB.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Syslinux on your Arch box ###
|
||||
|
||||
Knowing all of the above, we should proceed with the installation of Syslinux, replacing your old GRUB Legacy or GRUB2 boot loader. Open a terminal and execute the following command to install Syslinux
|
||||
|
||||
sudo pacman -S syslinux
|
||||
|
||||
After installation, you should notice a message that will instruct you how to deploy the Syslinux boot loader on a BIOS or a UEFI system. BIOS users are the luckiest ones, as they will only have to run the syslinux-install_update script created by Matthew Gyurgyik in order to successfully deploy Syslinux on their systems.
|
||||
|
||||
### Deploying Syslinux on your Arch box ###
|
||||
|
||||
Those of you who have a separate /boot partition should make sure that it is mounted before executing the script above. In the same terminal window, execute the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo syslinux-install_update -i -a -m
|
||||
|
||||
The script will install the necessary files, mark the partition with the boot flag, and install the MBR boot code.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring Syslinux ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is a very important step and no one should ignore it, because your computer will no longer boot if Syslinux is not configured properly. You have been warned!
|
||||
|
||||
Syslinux can now be configured via the /boot/syslinux/syslinux.cfg file. Take a look at [the official Arch Linux page of Syslinux][1] for detailed configuration instructions. When done, reboot your system to see the new boot loader.
|
||||
|
||||
Do not hesitate to use our commenting system below in case you encounter any issues with the tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Replace-GRUB-with-Syslinux-on-Arch-Linux-415394.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/syslinux#Configuration
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
翻译中by Linux-pdz
|
||||
How to convert video to animated gif image on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Once thought of as outdated art forms, animated GIF images have now come back. If you haven't noticed, quite a few online sharing and social networking sites are now supporting animated GIF images, for example, on [Tumblr][1], [Flickr][2], [Google+][3], and [partly on Facebook][4]. Due to their ease of consumption and sharing, GIF-ed animations are now part of mainstream Internet culture.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[Translate by SteveArcher]
|
||||
Juju ice-cream icon design
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Who doesn’t like ice-cream? Here in the design team we sure do! In the last few weeks we’ve been preparing a special Juju demo for the OpenStack Summit in Hong Kong and we’ve created some very ‘tasty’ icons for it. We thought it would be nice to show you how those icons were created, so here’s a little insight on the design process.
|
||||
|
||||
### The brief ###
|
||||
|
||||
We wanted to replace the normal Juju icons for something a little bit more special in order to explain to people that visited the Ubuntu stand what kind of things Juju can do. We decided to use the idea of an ice-cream with toppings and sauce which you can build in the same way that you can build services in Juju.
|
||||
|
||||
The best part of this demo is that people would actually get the ice-cream they had ‘built’ in Juju in real life!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*The Juju interface, with its default icons*
|
||||
|
||||
### Finding good concepts ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing I needed to do was to find good concepts to present ice-creams and toppings in an icon format. Toppings were going to be especially tricky, as they can be very small and therefore hard to make out at small sizes.
|
||||
|
||||
I initially sketched and designed some ideas that were using a kind of flat look. This worked well for the ice-cream, but not so much for the toppings — I soon noticed they had to be semi-realistic to be recognisable.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Initial sketches and designs following a flat and more simplified look*
|
||||
|
||||
At a second stage, I added perspective to the icons; it was important that the icons kept the same perspective for consistency.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Another set of sketches with added perspective*
|
||||
|
||||
The shape of the sauce bottles was also something that needed a bit of trial and error. The initial design looked too much like a ketchup bottle, so we’ve decided to try a different approach.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Before and after shape of the sauce*
|
||||
|
||||
For the backgrounds, I chose to use vibrant colours for the ice-cream icons, to contrast with the ice-creams’ monochrome palette, but paler colours for the toppings, as these are already quite colourful.
|
||||
|
||||
The amount of detail added to the icons is just enough for what we needed to show and for them to be recognised. I’ve also added larger pieces to the side of the toppings, to make them easier to be identified.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*The Oreo topping icon, with a side of Oreos*
|
||||
|
||||
### Working out the detail ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Oreo pieces were created from a single biscuit, which I cut into 9 different parts and then distributed in different layers — I guess in a similar way to what happens in real life.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*The 9 pieces used to create the icon*
|
||||
|
||||
The clone tool in Inkscape came in handy: repeating the same small set of different pieces made the final SVG file much lighter, and also Inkscape faster.
|
||||
|
||||
The whole process took 4 days from brief to final icons, which is quite a tight deadline, but it was a really fun project to work on.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*The final icon set*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://design.canonical.com/2013/11/juju-ice-cream-icon-design/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
[marked stduolc]
|
||||
Linux iostat Command to Report CPU Statistics and I/O Statistics
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A Central Processing Unit or CPU is the brain of the computer. All of processing command is run here. Input / Ouput or I/O also play critical roles. The disks is used to provide data to processor and keeps the data which has been processed by CPU. One of the methods for measuring processor utilization and I/O utilization is to use **iostat** command. From its utilization we can decide do we need to add more resources or not.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
[翻译中 by KayGuoWhu]
|
||||
Solving HIPPA, HITECH, SSAE16 Server Compliance Issues with Next Generation Datacenters
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,21 @@
|
||||
The Fedora Project Will No Longer Name Its Linux Distributions
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The Fedora Project has a very colorful history of naming its distributions, but that will come to an end with Fedora 21.**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The Fedora developers have decided that it was time to end the naming policy and process of their Fedora operating system. It's unclear whether the process will be carried out by the community instead, but one thing is certain: the Fedora people will no longer choose the names.
|
||||
|
||||
“What will be the code name for Fedora 21. And again short answer: null. Not null as null string but null. Fedora Board decided to end release names process. It does not mean ‘no more release names’ but it's up to community or working groups, if anyone wants to step into the role of Name Wrangler and helps running this process. Or reform it in any way,” said Red Hat's Jaroslav Reznik in a blog [post][1].
|
||||
|
||||
This information was made available quite a while ago on an obscure mailing list, but the Fedora Project hasn't been the best communicator possible so far.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/The-Fedora-Project-Will-No-Longer-Name-Their-Linux-Distributions-416156.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://borntobeopen.blogspot.ru/2014/01/wheres-fedora-21-schedule.html
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
hyaocuk is TRANSLATING
|
||||
|
||||
Top 10 Linux Games of 2013
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**With 2013 wrapping up, we’ve brought together 10 of our favourite Linux games of the past year.**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
乌龙茶 翻译中
|
||||
Ubuntu Will Reach True Convergence Before Microsoft, Says Shuttleworth
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The traditional six-monthly Ubuntu release cycle could become a thing of the past, Ubuntu’s founder has suggested.**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
2013:Linux的黄金年-十大杰出成就
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**2013年**快结束了。这一年发生很多里程碑事件使得今年可以称得上**Linux的黄金年**。一些成果从**FOSS**和**Linux**的角度来看可以说是举世瞩目的成就。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 1.Android的上升趋势 ###
|
||||
|
||||
2013年标志着Android手机的日活跃数量为**150万**。不用说,Android使用**Linux内核**是Android著名的标志,并受到大家的热情推崇,这将在未来的日子里继续。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Raspberry pi ###
|
||||
|
||||
一个曾经在低成本史上最伟大的开发,单板计算机**Raspberry pi**。Raspberry Pi的目的就是为了通过FOSS社区在学校和其他地方推广Linux,并仍在继续。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Debian的空间应用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Debian,最新Linux发行版被用于在2013年的三月下旬的**航天飞机**实验中的控制使命。这个实验的主要内容是通过Debian控制系统来尝试通过无土栽培来为宇航员提供空气和实物的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. SteamOS的崛起 ###
|
||||
|
||||
SteamOS,一个基于Debian发行版被设计用于**Stream Machine Game Console**并将在**2013年12月**中旬发布。GNU/Linux的潮流应用于游戏环境无疑是一个非常受欢迎的行为。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Linux的平板应用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
查看**亚马逊**的平板销量,前十的平板都是Android操作系统。苹果和微软的平板则排在第11和12位,对于FOSS社区来说确实是个好消息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Chromebooks ###
|
||||
|
||||
Chromebooks通过很多高端制造商赢得了笔记本电脑市场,三星,华硕推出GNU/Linux操作系统的电脑比例超过专有操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. The Firefox OS ###
|
||||
|
||||
Firefox OS,用于智能手机和平板的基于Linux的开源操作系统,在**2013年4月**下旬发布了。智能手机基于**ARM**构架的Linux发行版,显示出广阔的前景。
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Kali发布 ###
|
||||
|
||||
来自开发者的BackTrack Linux成为**Kali Linux**。Kali是是基于Debian的Linux发行版,母系统主要开发用于渗透测试,并分享了大量的Debian版本库,一个最丰富的发行版。Kail保持着在很短时间内超高下载记录。
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Android Kitkat ###
|
||||
|
||||
最新发布的最受期待的android版本被命名为**Kitkat**,Google宣布**Android 4.4**又名**KitKat 4于2013年9月发布**.虽然之前预测的发布版本是**5.0 Key Lime Pie**。Kitkat进行了优化,能在具有最小的**512 MB内存**的设备上运行。
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Linux 在汽车上的应用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
截至目前,Linux被应用于各种可穿戴设备,从手腕的手表,遥控器到飞船,所以**Linux在汽车上的应用**不是很意外但当Linux的作用表现在**汽车趋势杂志**的年度车上仍然是令人惊讶。2013年被选为优胜候选的两个型号,都运行Linux系统。
|
||||
|
||||
这个故事会在未来继续下去。我们可能错过了一些重要的里程碑,你可以在评论部分告诉我们。以上是我们(**Tecmint**)给读者在这黄金一年的最后一篇文章。
|
||||
|
||||
希望您能在新的一年里一如既往的支持我们。我们会在以后的日子里继续为您提供科技文章。继续关注**Tecmint**。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/2013-the-golden-year-for-linux-and-foss/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[乌龙茶](https://github.com/yechunxiao19) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 每日小贴士 - 在Ubuntu下用桌面图形界面挂载分区
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果在不久前你询问过一位经验丰富的 Linux 用户如何在 Ubuntu 下挂载磁盘分区,他们可能会告诉你使用在 **/etc** 目录里的fstab文件。这似乎是 Linux 系统包括 Ubuntu 挂载分区的唯一方式。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
呵呵,幸亏有了[GNOME Disk Utility][1],让挂载分区变得更加多样化。使用这个磁盘工具,你就可以在图形界面下轻松的挂载分区,不需要再在命令行下修改 fstab 文件。fstab 文件是一个用来列出可用磁盘和分区的 Linux 文件,同时指示出他们的挂载情况。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
mount 命令与 fstab 文件很相似,它决定了设备挂载的方式和位置。这只能通过系统管理员或 root 来修改。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这个简短的教程将会展示给你如何在 Ubuntu 下轻松的挂载分区,在不主动修改 fstab 文件的前提下。对于新手和那些刚开始使用 Ubuntu 的用户,他们会发现这个方法易于挂载额外的分区和设备。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
虽然有一些工具也许能帮助你构建 fstab 文件,但是在 Ubuntu 下很少有像这个磁盘工具那么高效的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在 Ubuntu 下打开了fstab 文件, 你会看到类似下面的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
#<File System> <Mount Point> <type> <options> <dump> <pass>
|
||||
/dev/fd0 /media/floppy0 vfat rw,user,noauto 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
上列只是 Ubuntu 分区挂载的一个样例。每一个设备都有它自己的文件类型和挂载点。对于刚接触 Ubuntu 的用户,可能会感到生畏。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
对于经验丰富的 Linux 用户来说,管理 fstab 并不困难。如果你已经做个一次了,那么下次会更加的轻松。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
所以,接下来动手吧。在 fstab 文件中添加一个条目或挂载一个分区,打开 Unity Dash 搜索**Disk app**并打开。当程序打开后,选择你想要挂载和格式化的驱动器。在格式完后,选择**选项 -> Mount 编辑选项**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
最后,关闭自动关在选项并手动指定你的挂载选项。磁盘会自动的将这些选项写入到 fstab 文件中,这样 mount 命令才可以读取挂载的分区。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
保存你的设置并重启,或用 mount 命令挂载分区。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
上面的选项在 fstab 文件中会像这样显示。
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/sdb /media/richard/ExtPartition ntfs-3g rw,auto,user,fmask=0111,dmask=0000 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
好了,这些就是今天全部内容!每当你启动你的机子是新分区将会自动挂载上。
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
好好享受吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2014/01/daily-ubuntu-tips-mount-partitions-in-ubuntu-from-your-desktop-gui/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Design/Apps/Disks
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧:Ubuntu下一款和Windows磁盘管理一样的工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
对于一些用惯了Windows的用户来说,刚开始接触Ubuntu的时候会面临这样的一个问题,这个问题在很多论坛里面也经常出现,前段时间也有位读者问到相同的问题:
|
||||
|
||||
>在 Ubuntu 中有和 Windows 下的磁盘管理一样的工具么?
|
||||
|
||||
对于那些不太清楚磁盘管理的用户,下面有个简单介绍。
|
||||
|
||||
磁盘管理是一个从 Windows XP 起就有的默认工具,其主要负责磁盘相关的任务,比如:创建和格式化磁盘、初始化磁盘,重新划分磁盘大小和指定分区号以及删除分区。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Windows 下用户使用和磁盘分区管理相关的命令行工具进行磁盘操作,这个工具很高大上。
|
||||
|
||||
问题是在 Ubuntu 系统下有这样的工具么,答案是肯定滴。
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 下有个很相似的软件叫做 GNOME Disk Utility ,这个工具同样能尽心查看/管理你的磁盘分区,以及创建和恢复分区。你同样可以用它进行创建和格式化分区,挂载和卸载卷组以及其它相关的磁盘操作。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管这和Windows下的管理工具相似,但是它不允许用户重新定义分区和卷组大小,因为 ubuntu 不支持驱动器号。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,想在 Ubuntu 系统下使用类似 windows 下的磁盘管理工具,那就试试 GNOME Disk Utility 吧。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 Unity Dash 中搜索 **硬盘** ,打开时,它会自己识别你电脑上的外部硬盘和额外的硬盘驱动器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
一旦驱动器被选择你就可以进行磁盘相关的操作了,比如:格式化、创建分区,管理驱动器。另外在磁盘访问超时情况下一些待机模式的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
需要注意的是,当你格式化一个磁盘让它既可以在 Windows 下又可以在 Ubuntu 下使用时,一定要选择 NTFS 文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
那么,在 Ubuntu 下使用磁盘配置你的驱动器吧。
|
||||
|
||||
慢慢享用,新年快乐!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2014/01/daily-ubuntu-tips-windows-disk-management-equivalent-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Timeszoro](https://github.com/Timeszoro) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
在Linux Mint 16中找到保存的WiFi密码[新手教程]
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
当你使用WEP,WPA或WPA2-PSK连接到无线网络时,选择“自动连接”后密码将保存在Linux Mint(或任何其他的操作系统)中。试想一个情况,你需要知道WiFi密码,例如你需要提供密码给访问者,你有没有注意到它保存在哪。您可以轻松地找到之前连接的WiFi密码。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇**新手教程**中,我们将会告诉你**如何在Linux Mint 16中找到保存的WiFi密码**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux Mint中找到保存的WiFi密码: ###
|
||||
|
||||
找到保存的WiFi密码的过程其实非常简单。点击Menu输入network。在其中选择**Network Connections**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Network Connections中,你可以看到所有你曾经链接过的WiFi网络。选择你希望知道密码的一个,点击**Edit**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
到了这一步,在 **Wi-Fi Security**选项卡下,选中**Show password**来显示密码。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
通过以上的步骤,你就可以得到保存的WiFi密码。你也可以通过相同的步骤来[在Ubuntu中获取保存的WiFi密码][1]。希望这篇文章能够帮到你。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/find-wifi-password-linux-mint-16/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[乌龙茶](https://github.com/yechunxiao19) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-find-saved-wireless-wifi-passwords-ubuntu/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux Mint 16中安装图标主题[新手教程]
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
你是否想过默认的Mint主题和图标并不足以满足你,为何不来点改变那?在这篇初学者快速教程中,我们会告诉你如何**在Linux Mint 16中安装图标主题**以及**如何改变图标**。通过这篇快速教程你将安装上Moka图标主题。
|
||||
|
||||
小小提一下,可能你以前不知道,主题和图标主题之间是有区别的。图标主题只是改变图标的外观,而主题则是改变了包括图标在内其余很多东西的外观。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux Mint 16中安装图标主题: ###
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux Mint(以及其他大部分的Linux发行版)中有个两种方法来安装图标主题。如果你下载了图标主题的压缩包,你可以在~/.icons目录下解压它。通常这个目录并不存在。你可以随意创建它。
|
||||
|
||||
安装图标主题的第二种方法是使用[PPA][1]。大多数流行的图标主题都有自己的PPA。让我们来看看如何使用PPA在Mint中安装Moka图标。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux Mint 16中安装Moka图标主题: ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开terminal(Ctrl+Alt+T)并输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:moka/moka-icon-theme
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install moka-icon-theme
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux Mint 16中改变图标: ###
|
||||
|
||||
改变一个[在Ubuntu的图标主题][2]是非常直接简单地。不过在Linux Mint中稍微隐藏了一下。你安装了图标主题后,在菜单中选择**Setting**,然后选择**Themes**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在你可能已经意识到为什么我说在Linux Mint的图标更改稍微隐藏了。至少第一眼,你不会找到一个选项来改变图标。只改变图标,选择**Other settings**并点击**Icons**。你会在这找到所有的图标设置。选择你喜欢的一个。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
改变会立即生效,并不需要重启。下面是我的Linux Mint使用Moka图标主题后的桌面:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我希望这篇教程能帮助你实现图标主题的修改。不要忘记Ubuntu 13.10的5个最好图标主题,你可以使用任何你喜欢的图标主题来使你的桌面变得更漂亮。有任何问题,建议,想法?随时联系。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/install-icon-linux-mint/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[乌龙茶](https://github.com/yechunxiao19) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Personal_Package_Archive
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-themes-in-ubuntu-13-10/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux Mint 16中正确安装Ubuntu One
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
由于[Linux Mint][1]是基于 Ubuntu 的,所以我认为 Ubuntu One 应该是预装程序之一。不过我错了。我自行从 Software Manager 安装了 Ubuntu One,令我惊讶的是,它居然无法正常运行。在这篇教程中我们会告诉你**如何在 Linux Mint 16中安装 Ubuntu One** 以及如何正常运行它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux Mint 16 中安装 Ubuntu One: ###
|
||||
|
||||
当你通过 Software Manager 安装 Ubuntu One 客户端以后,你准备打开并配置它时,你甚至都无法在菜单搜索里面找到它。就像是完全没有安装过一样。但你查看 Software Manager,又显示它已经安装完成了。问题到底出在哪了?
|
||||
|
||||
问题的关键是 **Ubuntu One installer** 已经转交 **ubuntuone-control-panel-qt** 包了。这个包没有安装,你的 Ubuntu One 就无法运行。要解决这个问题,打开终端 (Ctrl+Alt+T)并运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install ubuntuone-control-panel-qt
|
||||
|
||||
现在你在菜单里面搜索,你会发现 Ubuntu One 已经存在了。现在你可以配置账户,进行同步。现在你可能觉得你已经解决了所有的问题,这时你会发现 **Ubuntu One indicator 并没出现在面板上**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux Mint 16 中安装 Ubuntu One indicator: ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过添加以下的 PPA 在 Linux Mint 中获取 Ubuntu One indicator 程序:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:rye/ubuntuone-extras
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install indicator-ubuntuone
|
||||
|
||||
注销并重新登录后,你会看到 indicator 出现在面板中。与此同时,你的 Ubuntu One 也全部安装完成了。我希望这篇 **在 Linux Mint 中安装 Ubuntu One** 会对你有所帮助。欢迎提出问题和建议。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-one-linux-mint-16/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[乌龙茶](https://github.com/yechunxiao19) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxmint.com/
|
||||
70
translated/Juju ice-cream icon design.md
Normal file
70
translated/Juju ice-cream icon design.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
Juju 冰淇淋图标设计
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
有哪个人会不喜欢冰淇淋?作为设计团队我们当然喜欢!在过去几周的时间里我们一直在为香港举办的开源架构会议准备一场特别的 Juju 演示,并且我们已经为之设计了一些非常“美味的”图标。我们认为向大家展示这些图标的创作过程是很美妙的,以下是这个设计流程的一些简介。
|
||||
|
||||
### 摘要 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们想要用一些稍微有点特别的图标去替换常规的 Juju 图标,向人们阐述独立访问 Ubuntu 时 Juju 可以做些什么事情。我们决定用带有点缀物和酱调味的冰淇淋这个想法,你可以用同样的方法打造在 Juju 上打造的服务。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这场演示最棒的环节是人们将在现实中真实地得到他们在 Juju 中'打造'的冰淇淋!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*使用默认图标的 Juju 界面*
|
||||
|
||||
### 寻找好的想法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我需要做的第一件事情是找到一个好的想法以图标的形式表现带有点缀物的冰淇淋。点缀物将被设计的非常精巧,以致它们将非常小并且很难制作成较小的尺寸。
|
||||
|
||||
最初我以缩略图和设计思想的方式使用一种扁平外观的图标。这种方式对冰激凌来说很有用,但是对点缀物作用不大 —— 不久之后我发现它们变成半分离的现代主义,很难辨认。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*扁平简洁化外观的初始缩略图与设计理念*
|
||||
|
||||
在第二阶段,我给图标添加了透视效果;图标保持一样的透视连贯性是很重要的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*另一套添加透视效果的缩略图*
|
||||
|
||||
酱调味瓶的外观也有些误差,需要一定的试验。最初的设计看起来非常像是瓶装番茄酱,于是我们决定尝试另一种不同的风格。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*调味酱外观变化前后*
|
||||
|
||||
至于背景,我选择用闪亮的颜色来搭配冰淇淋图标,以此与冰淇淋单色调形成对比,点缀物使用稍淡颜色,这全部整合起来就非常多彩艳丽了。
|
||||
|
||||
为图标添加的众多细节对于我们需要展示的以及图标本身的辨认来说已经足够了。我同样添加了更大尺寸的点缀物,以使它们变得更加容易辨认。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*带有破碎奥利奥的点缀物图标*
|
||||
|
||||
### 编制细节 ###
|
||||
|
||||
破碎的奥利奥由单一的饼干而来,我将之分成 9 个不同的部分然后散布在不同层 —— 我猜在现实生活中也是这样的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*创立图标所使用的 9 个分布层*
|
||||
|
||||
Inkscape 中的克隆工具得到了用武之地:在不同分布层上重复同样的小尺寸使得最后的 SVG 文件更加轻巧,也使 Inkscape 运行得更快。
|
||||
|
||||
从最初设计到最后图标完成整个过程花费了 4 天的时间,差点超过预订的限期,但这确实是一个应该继续下去的有趣项目。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*最终图标设计*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://design.canonical.com/2013/11/juju-ice-cream-icon-design/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[SteveArcher](https://github.com/SteveArcher) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,30 +1,30 @@
|
||||
Linus Torvalds发布了2013年的最后一个Linux内核3.13RC版本
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Linux Torvalds已经发布了内核3.13分支中最新的一个候选版本 —— 第6版**
|
||||
**Linux Torvalds宣布Linux内核3.13分支中的第六个候选版本已发布,即时可用。**
|
||||
|
||||
Linux内核3.13 RC6按时发布了,但是仅包含了很小数量的一些提交,使得此次候选版本成为了体积最小的一个,至少在这一个开发周期中如此。
|
||||
Linux内核3.13 RC6按时发布了,但是仅包含了很小数量的一些提交,使得此次候选版本成为了迄今体积最小的一个,至少在这一个开发周期中如此。
|
||||
|
||||
Linus Torvalds在官方发布中说道:“正如我们之前期望的那样,整个假期一周都没有什么大的bug出现。因此,我们这次只有一些小的随机更新:驱动方面(例如无限宽带、GPU、CPUfreg、libata、块设备等),一些小的文件系统修复(ext4/jdb2),以及一些ARM SoC方面的更新。x86、perCPU和cgroup方面的更新很少。没什么值得特别注意的,只是总共81个很平常的小提交。”
|
||||
Linus Torvalds在官方发布中说道:“正如我们之前期望的那样,整个一周假期都没有什么大的bug出现。因此,我们这次只有一些小的随机更新:驱动方面(例如无限宽带、GPU、CPUfreg、libata、块设备等),一些小的文件系统修复(ext4/jdb2),以及一些ARM SoC方面的更新。x86、perCPU 和 cgroup 方面的更新很少。甚至没什么值得注意的,只有81个很平常的小提交。”
|
||||
|
||||
大神平常是非常健谈的,但年底前的这次小发布却这么惜字如金,估计是为了避免更多的非议,打算过个好年。
|
||||
大神平常是非常健谈的,但是对于年底的这次小发布却如此惜字如金,估计是为了避免更多的非议,打算过个好年。
|
||||
|
||||
Linus Torvalds还在[12月18号庆祝了自己的生日][1],但并没有大操大办。
|
||||
|
||||
###Linux内核 3.13 RC6 的亮点###
|
||||
|
||||
• 修正了音频pins的数目(drm/radeon/dce6)
|
||||
• 在Cayman上禁用了SS(drm/radeon/dpm)
|
||||
• 检查了扬声器分配和SAD代码中的0计数(drm/radeon)
|
||||
• 修复了热插拔块设备时的内存泄露问题
|
||||
• 修复了SDHI资源的大小
|
||||
• 修复了执行缓存中分配内存失败后仍然释放引用的问题(drm/i9150)
|
||||
• 修复了reset_status中对batch_obj的错误引用释放
|
||||
• Sandybridge+启用了正确的GMCH_CTRL注册
|
||||
• 对废弃的消息JBD->JBD2进行了重命名
|
||||
• 增加对ValleyView Soc的支持
|
||||
• 增加对PWM背光电源的支持
|
||||
- 修正了音频pins的数目(drm/radeon/dce6)
|
||||
- 在Cayman上禁用了SS(drm/radeon/dpm)
|
||||
- 检查了扬声器分配和SAD代码中的0计数(drm/radeon)
|
||||
- 修复了拔掉块设备时的内存泄露问题
|
||||
- 修复了SDHI资源的大小
|
||||
- 修复了执行缓存中分配内存失败后仍然释放引用的问题(drm/i9150)
|
||||
- 修复了 reset_status 中对 batch_obj 的错误引用释放
|
||||
- Sandybridge+ 启用了正确的 GMCH_CTRL 注册
|
||||
- 对废弃的消息 JBD->JBD2 进行了重命名
|
||||
- 增加对 ValleyView Soc 的支持
|
||||
- 增加对 PWM 背光电源的支持
|
||||
|
||||
完整的修改、改进、修复列表请参看官方[修改日志][2]。
|
||||
完整的修改、改进以及修复列表请参看官方[修改日志][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
下载Linux内核3.13 RC6:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ Linus Torvalds还在[12月18号庆祝了自己的生日][1],但并没有大操
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Linus-Torvalds-Releases-Last-Linux-Kernel-3-13-RC-for-2013-412622.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](https://github.com/tinyeyeser) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](https://github.com/tinyeyeser) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,38 +1,38 @@
|
||||
Linux id 命令 - 打印用户id和组id信息
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
要登入一台计算机,我们需要一个用户名。用户名是一个被计算机识别的身份。基于此,计算机会对使用这个用户名的登陆的人应用一系列的规则。在Linux系统下,我们可以使用**id**命令。
|
||||
要登入一台计算机,我们需要一个用户名。用户名是一个可以被计算机识别的身份。基于此,计算机会对使用这个用户名的登陆的人应用一系列的规则。在Linux系统下,我们可以使用 **id** 命令。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 id 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**id** 命令可以打印真实并有效的用户ID(UID)和组ID(GID)。UID是对一个用户的唯一标识。组ID(GID)可以包含多个UID。
|
||||
**id** 命令可以打印真实有效的用户 ID(UID) 和组 ID(GID)。UID 是对一个用户的单一身份标识。组 ID(GID)可以包含多个UID。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何使用 ###
|
||||
### 如何使用 id 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
默认上,**id**命令已经预装在大多数Linux系统中。要使用它,只需要在你的控制台输入id。不带选项输入id会显示如下。结果会使用活跃用户。
|
||||
**id** 命令已经默认预装在大多数 Linux 系统中。要使用它,只需要在你的控制台输入id。不带选项输入 id 会显示如下。结果会使用活跃用户。
|
||||
|
||||
$ id
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 如何读取输出t : ####
|
||||
#### 如何读取输出: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 用户 **pungki** 的 **UID** 号码= **1000**, **GID** 号码= **1000**
|
||||
- 用户 **pungki ** 是下面的组成员 :
|
||||
|
||||
**pungki** with GID = **1000**
|
||||
**adm** with GID = **4**
|
||||
**cdrom** with GID = **24**
|
||||
**sudo** with GID = **27**
|
||||
**dip** with GID = **30**
|
||||
**plugdev** with GID = **46**
|
||||
**lpadmin** with GID = **108**
|
||||
**sambashare** with GID = **124**
|
||||
**pungki** 的 GID 号码= **1000**
|
||||
**adm** 的 GID 号码= **4**
|
||||
**cdrom** 的 GID 号码= **24**
|
||||
**sudo** 的 GID 号码= **27**
|
||||
**dip** 的 GID 号码= **30**
|
||||
**plugdev** 的 GID 号码= **46**
|
||||
**lpadmin** 的 GID 号码= **108**
|
||||
**sambashare** 的 GID 号码= **124**
|
||||
|
||||
### 带选项使用id ###
|
||||
|
||||
id 命令可以使用一些选项。下面有一些在日常使用中有用的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 打印用户名, 该UID所属的所有组 ####
|
||||
#### 打印用户名、UID 和该用户所属的所有组 ####
|
||||
|
||||
要这么做,我们可以使用 **-a** 选项
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ id命令可以使用一些选项。下面有一些在日常使用中有用的选
|
||||
|
||||
#### 输出所有不同的组ID (有效的,真实的和补充的) ####
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以使用 **-G**选项实现这个。
|
||||
我们可以使用 **-G** 选项来实现。
|
||||
|
||||
$ id -G
|
||||
|
||||
@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ id命令可以使用一些选项。下面有一些在日常使用中有用的选
|
||||
|
||||
#### 只输出有效的组ID ####
|
||||
|
||||
使用 **-g** 选项来只输出有效组ID。
|
||||
通过使用 **-g** 选项来只输出有效组ID。
|
||||
|
||||
$ id -g
|
||||
|
||||
@ -94,12 +94,12 @@ id命令可以使用一些选项。下面有一些在日常使用中有用的选
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当我们想知道某个用户的UID和GID时是非常有用的。一些程序可能需要UID/GID来运行。id使我们更加容易地找出用户的UID以GID而不必在/etc/group文件中搜寻。像往常一样,你可以在控制台输入**man id**进入id的手册页来获取更多的细节。
|
||||
当我们想知道某个用户的 UID 和 GID 时 id 命令是非常有用的。一些程序可能需要 UID/GID 来运行。id 使我们更加容易地找出用户的 UID 以 GID 而不必在 /etc/group 文件中搜寻。如往常一样,你可以在控制台输入 **man id** 进入 id 的手册页来获取更多的详情。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-id-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user