mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
[Translated] sources/tech/RHCE/Part 9 - How to Setup Postfix Mail Server (SMTP) using null-client Configuration.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
7165293ca0
commit
98f2d70679
@ -1,153 +0,0 @@
|
||||
ictlyh Translating
|
||||
How to Setup Postfix Mail Server (SMTP) using null-client Configuration – Part 9
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Regardless of the many online communication methods that are available today, email remains a practical way to deliver messages from one end of the world to another, or to a person sitting in the office next to ours.
|
||||
|
||||
The following image illustrates the process of email transport starting with the sender until the message reaches the recipient’s inbox:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
How Mail Setup Works
|
||||
|
||||
To make this possible, several things happen behind the scenes. In order for an email message to be delivered from a client application (such as [Thunderbird][1], Outlook, or webmail services such as Gmail or Yahoo! Mail) to a mail server, and from there to the destination server and finally to its intended recipient, a SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) service must be in place in each server.
|
||||
|
||||
That is the reason why in this article we will explain how to set up a SMTP server in RHEL 7 where emails sent by local users (even to other local users) are forwarded to a central mail server for easier access.
|
||||
|
||||
In the exam’s requirements this is called a null-client setup.
|
||||
|
||||
Our test environment will consist of an originating mail server and a central mail server or relayhost.
|
||||
|
||||
Original Mail Server: (hostname: box1.mydomain.com / IP: 192.168.0.18)
|
||||
Central Mail Server: (hostname: mail.mydomain.com / IP: 192.168.0.20)
|
||||
|
||||
For name resolution we will use the well-known /etc/hosts file on both boxes:
|
||||
|
||||
192.168.0.18 box1.mydomain.com box1
|
||||
192.168.0.20 mail.mydomain.com mail
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Postfix and Firewall / SELinux Considerations ###
|
||||
|
||||
To begin, we will need to (in both servers):
|
||||
|
||||
**1. Install Postfix:**
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install postfix
|
||||
|
||||
**2. Start the service and enable it to run on future reboots:**
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start postfix
|
||||
# systemctl enable postfix
|
||||
|
||||
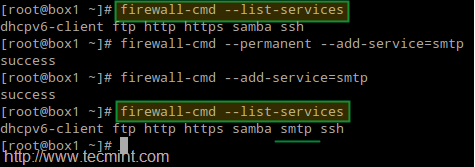
**3. Allow mail traffic through the firewall:**
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=smtp
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --add-service=smtp
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Open Mail Server SMTP Port in Firewall
|
||||
|
||||
**4. Configure Postfix on box1.mydomain.com.**
|
||||
|
||||
Postfix’s main configuration file is located in /etc/postfix/main.cf. This file itself is a great documentation source as the included comments explain the purpose of the program’s settings.
|
||||
|
||||
For brevity, let’s display only the lines that need to be edited (yes, you need to leave mydestination blank in the originating server; otherwise the emails will be stored locally as opposed to in a central mail server which is what we actually want):
|
||||
|
||||
**Configure Postfix on box1.mydomain.com**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
myhostname = box1.mydomain.com
|
||||
mydomain = mydomain.com
|
||||
myorigin = $mydomain
|
||||
inet_interfaces = loopback-only
|
||||
mydestination =
|
||||
relayhost = 192.168.0.20
|
||||
|
||||
**5. Configure Postfix on mail.mydomain.com.**
|
||||
|
||||
**Configure Postfix on mail.mydomain.com**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
myhostname = mail.mydomain.com
|
||||
mydomain = mydomain.com
|
||||
myorigin = $mydomain
|
||||
inet_interfaces = all
|
||||
mydestination = $myhostname, localhost.$mydomain, localhost, $mydomain
|
||||
mynetworks = 192.168.0.0/24, 127.0.0.0/8
|
||||
|
||||
And set the related SELinux boolean to true permanently if not already done:
|
||||
|
||||
# setsebool -P allow_postfix_local_write_mail_spool on
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Set Postfix SELinux Permission
|
||||
|
||||
The above SELinux boolean will allow Postfix to write to the mail spool in the central server.
|
||||
|
||||
**6. Restart the service on both servers for the changes to take effect:**
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart postfix
|
||||
|
||||
If Postfix does not start correctly, you can use following commands to troubleshoot.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl –l status postfix
|
||||
# journalctl –xn
|
||||
# postconf –n
|
||||
|
||||
### Testing the Postfix Mail Servers ###
|
||||
|
||||
To test the mail servers, you can use any Mail User Agent (most commonly known as MUA for short) such as [mail or mutt][2].
|
||||
|
||||
Since mutt is a personal favorite, I will use it in box1 to send an email to user tecmint using an existing file (mailbody.txt) as message body:
|
||||
|
||||
# mutt -s "Part 9-RHCE series" tecmint@mydomain.com < mailbody.txt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Test Postfix Mail Server
|
||||
|
||||
Now go to the central mail server (mail.mydomain.com), log on as user tecmint, and check whether the email was received:
|
||||
|
||||
# su – tecmint
|
||||
# mail
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Check Postfix Mail Server Delivery
|
||||
|
||||
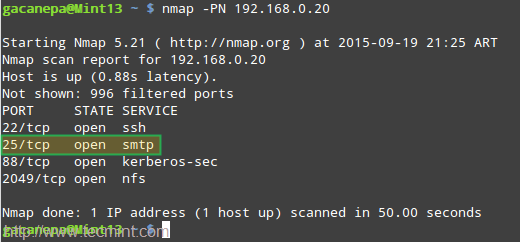
If the email was not received, check root’s mail spool for a warning or error notification. You may also want to make sure that the SMTP service is running on both servers and that port 25 is open in the central mail server using [nmap command][3]:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmap -PN 192.168.0.20
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Troubleshoot Postfix Mail Server
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
Setting up a mail server and a relay host as shown in this article is an essential skill that every system administrator must have, and represents the foundation to understand and install a more complex scenario such as a mail server hosting a live domain for several (even hundreds or thousands) of email accounts.
|
||||
|
||||
(Please note that this kind of setup requires a DNS server, which is out of the scope of this guide), but you can use following article to setup DNS Server:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Setup Cache only DNS Server in CentOS/RHEL 07][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, I highly recommend you become familiar with Postfix’s configuration file (main.cf) and the program’s man page. If in doubt, don’t hesitate to drop us a line using the form below or using our forum, Linuxsay.com, where you will get almost immediate help from Linux experts from all around the world.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/setup-postfix-mail-server-smtp-using-null-client-on-centos/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-thunderbird-17-in-ubuntu-xubuntu-linux-mint/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/send-mail-from-command-line-using-mutt-command/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/nmap-command-examples/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/setup-dns-cache-server-in-centos-7/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,153 @@
|
||||
第九部分 - 如果使用零客户端配置 Postfix 邮件服务器(SMTP)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
尽管现在有很多在线联系方式,邮件仍然是一个人传递信息给远在世界尽头或办公室里坐在我们旁边的另一个人的有效方式。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的图描述了邮件从发送者发出直到信息到达接收者收件箱的传递过程。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
邮件如何工作
|
||||
|
||||
要使这成为可能,背后发生了好多事情。为了使邮件信息从一个客户端应用程序(例如 [Thunderbird][1]、Outlook,或者网络邮件服务,例如 Gmail 或 Yahoo 邮件)到一个邮件服务器,并从其到目标服务器并最终到目标接收人,每个服务器上都必须有 SMTP(简单邮件传输协议)服务。
|
||||
|
||||
这就是为什么我们要在这篇博文中介绍如何在 RHEL 7 中设置 SMTP 服务器,从中本地用户发送的邮件(甚至发送到本地用户)被转发到一个中央邮件服务器以便于访问。
|
||||
|
||||
在实际需求中这称为零客户端安装。
|
||||
|
||||
在我们的测试环境中将包括一个原始邮件服务器和一个中央服务器或中继主机。
|
||||
|
||||
原始邮件服务器: (主机名: box1.mydomain.com / IP: 192.168.0.18)
|
||||
中央邮件服务器: (主机名: mail.mydomain.com / IP: 192.168.0.20)
|
||||
|
||||
为了域名解析我们在两台机器中都会使用有名的 /etc/hosts 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
192.168.0.18 box1.mydomain.com box1
|
||||
192.168.0.20 mail.mydomain.com mail
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 Postfix 和防火墙/SELinux 注意事项 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们需要(在两台机器上):
|
||||
|
||||
**1. 安装 Postfix:**
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install postfix
|
||||
|
||||
**2. 启动服务并启用开机自动启动:**
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start postfix
|
||||
# systemctl enable postfix
|
||||
|
||||
**3. 允许邮件流量通过防火墙:**
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=smtp
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --add-service=smtp
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在防火墙中开通邮件服务器端口
|
||||
|
||||
**4. 在 box1.mydomain.com 配置 Postfix**
|
||||
|
||||
Postfix 的主要配置文件是 /etc/postfix/main.cf。这个文件本身是一个很大的文本,因为其中包含的注释解析了程序设置的目的。
|
||||
|
||||
为了简洁,我们只显示了需要编辑的行(是的,在原始服务器中你需要保留 mydestination 为空;否则邮件会被保存到本地而不是我们实际想要的中央邮件服务器):
|
||||
|
||||
**在 box1.mydomain.com 配置 Postfix**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
myhostname = box1.mydomain.com
|
||||
mydomain = mydomain.com
|
||||
myorigin = $mydomain
|
||||
inet_interfaces = loopback-only
|
||||
mydestination =
|
||||
relayhost = 192.168.0.20
|
||||
|
||||
**5. 在 mail.mydomain.com 配置 Postfix**
|
||||
|
||||
** 在 mail.mydomain.com 配置 Postfix **
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
myhostname = mail.mydomain.com
|
||||
mydomain = mydomain.com
|
||||
myorigin = $mydomain
|
||||
inet_interfaces = all
|
||||
mydestination = $myhostname, localhost.$mydomain, localhost, $mydomain
|
||||
mynetworks = 192.168.0.0/24, 127.0.0.0/8
|
||||
|
||||
如果还没有设置,还要设置相关的 SELinux 布尔值永久为真:
|
||||
|
||||
# setsebool -P allow_postfix_local_write_mail_spool on
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
设置 Postfix SELinux 权限
|
||||
|
||||
上面的 SELinux 布尔值会允许 Postfix 在中央服务器写入邮件池。
|
||||
|
||||
**6. 在两台机子上重启服务以使更改生效:**
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart postfix
|
||||
|
||||
如果 Postfix 没有正确启动,你可以使用下面的命令进行错误处理。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl –l status postfix
|
||||
# journalctl –xn
|
||||
# postconf –n
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试 Postfix 邮件服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了测试邮件服务器,你可以使用任何邮件用户代理(最常见的简称为 MUA)例如 [mail 或 mutt][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
由于我个人喜欢 mutt,我会在 box1 中使用它发送邮件给用户 tecmint,并把现有文件(mailbody.txt)作为信息内容:
|
||||
|
||||
# mutt -s "Part 9-RHCE series" tecmint@mydomain.com < mailbody.txt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
测试 Postfix 邮件服务器
|
||||
|
||||
现在到中央邮件服务器(mail.mydomain.com)以 tecmint 用户登录,并检查是否收到了邮件:
|
||||
|
||||
# su – tecmint
|
||||
# mail
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查 Postfix 邮件服务器发送
|
||||
|
||||
如果没有收到邮件,检查 root 用户的邮件池查看警告或者错误提示。你也需要使用 [nmap 命令][3]确保两台服务器运行了 SMTP 服务,并在中央邮件服务器中 打开了 25 号端口:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmap -PN 192.168.0.20
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Postfix 邮件服务器错误处理
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
像本文中展示的设置邮件服务器和中继主机是每个系统管理员必须拥有的重要技能,也代表了理解和安装更复杂情景的基础,例如一个邮件服务器托管有多个邮件账户(甚至成百上千)的域名。
|
||||
|
||||
(请注意这种类型的设置需要有 DNS 服务器,这不在本文的介绍范围),但你可以参照下面的文章设置 DNS 服务器:
|
||||
|
||||
- [在 CentOS/RHEL 07 上配置仅缓存的 DNS 服务器][4]
|
||||
|
||||
最后,我强烈建议你熟悉 Postfix 的配置文件(main.cf)和这个程序的帮助手册。如果有任何疑问,别犹豫,使用下面的评论框或者我们的论坛 Linuxsay.com 告诉我们吧,你会从世界各地的 Linux 高手中获得几乎及时的帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/setup-postfix-mail-server-smtp-using-null-client-on-centos/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https//www.mutouxiaogui.cn/blog/)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-thunderbird-17-in-ubuntu-xubuntu-linux-mint/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/send-mail-from-command-line-using-mutt-command/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/nmap-command-examples/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/setup-dns-cache-server-in-centos-7/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user