mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-30 02:40:11 +08:00
Merge pull request #3571 from ivo-wang/master
20150410 How to Install and Configure Multihomed ISC DHCP Server on Debian Linux.md翻译完毕 辛苦啦,不过下回不需要保留英文原文,校对时会根据版本记录进行校对的。
This commit is contained in:
commit
98e742d370
@ -1,159 +1,238 @@
|
||||
How to Install and Configure Multihomed ISC DHCP Server on Debian Linux
|
||||
debian linux上安装配置 ISC DHCP Server
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) offers an expedited method for network administrators to provide network layer addressing to hosts on a constantly changing, or dynamic, network. One of the most common server utilities to offer DHCP functionality is ISC DHCP Server. The goal of this service is to provide hosts with the necessary network information to be able to communicate on the networks in which the host is connected. Information that is typically served by this service can include: DNS server information, network address (IP), subnet mask, default gateway information, hostname, and much more.
|
||||
动态主机控制协议(DHCP)给网络管理员提供一种便捷的方式,为不断变化的网络主机或是动态网络提供网络层地址。其中最常用的DHCP服务工具是 ISC DHCP Server。DHCP服务的目的是给给主机提供必要的网络信息以便能够和其他连接在网络中的主机互相通信。DHCP服务一般包括以下信息:DNS服务器信息,网络地址(IP),子网掩码,默认网关信息,主机名等等。
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will cover ISC-DHCP-Server version 4.2.4 on a Debian 7.7 server that will manage multiple virtual local area networks (VLAN) but can very easily be applied to a single network setup as well.
|
||||
本节教程介绍4.2.4版的ISC-DHCP-Server如何在Debian7.7上管理多个虚拟局域网(VLAN),但是它也可以非常简单的用于单一网络。
|
||||
|
||||
The test network that this server was setup on has traditionally relied on a Cisco router to manage the DHCP address leases. The network currently has 12 VLANs needing to be managed by one centralized server. By moving this responsibility to a dedicated server, the router can regain resources for more important tasks such as routing, access control lists, traffic inspection, and network address translation.
|
||||
测试用的网络是通过思科路由器依赖传统的方式来管DHCP租约地址,目前有12个VLANs需要通过路由器的集中式服务器来管理。把DHCP这个责任转移到一个专用的服务器上面,路由器可以回收资源去用到更重要的任务上,比如路由寻址,访问控制列表,流量监测以及网络地址转换等。
|
||||
|
||||
The other benefit to moving DHCP to a dedicated server will, in a later guide, involve setting up Dynamic Domain Name Service (DDNS) so that new host’s host-names will be added to the DNS system when the host requests a DHCP address from the server.
|
||||
|
||||
另一个将DHCP服务移动到专用服务器的好处,后续会讲到,建立动态域名服务器(DDNS)这样当主机从服务器请求DHCP地址的时候,新主机的主机名将被添加到DNS系统里面。
|
||||
### Step 1: Installing and Configuring ISC DHCP Server ###
|
||||
### 安装和配置ISC DHCP Server###
|
||||
|
||||
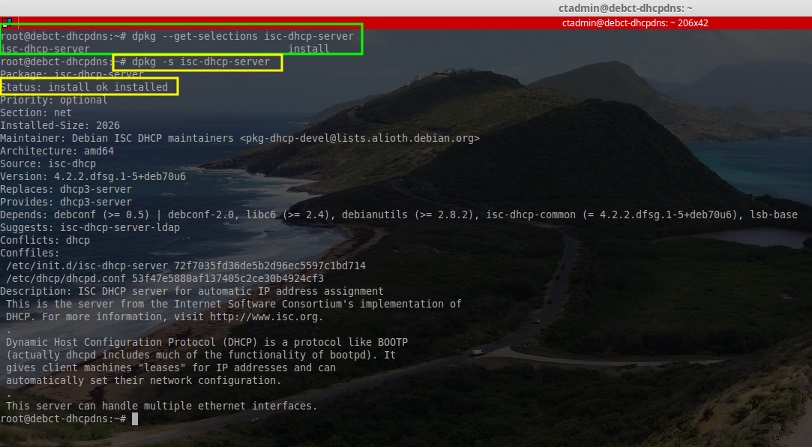
1. To start the process of creating this multi-homed server, the ISC software needs to be installed via the Debian repositories using the ‘apt‘ utility. As with all tutorials, root or sudo access is assumed. Please make the appropriate modifications to the following commands.
|
||||
1. 创建这个多宿主服务器的过程中,需要用apt工具来安装Debian软件仓库中的ISC软件。与其他教程一样需要使用root或者sudo访问权限。请适当的修改以使用下面的命令。(译者注:下面中括号里面是注释,使用的时候请删除,#表示使用的root权限)
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install isc-dhcp-server [Installs the ISC DHCP Server software]
|
||||
# dpkg --get-selections isc-dhcp-server [Confirms successful installation]
|
||||
# dpkg -s isc-dhcp-server [Alternative confirmation of installation]
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install isc-dhcp-server [安装 the ISC DHCP Server 软件]
|
||||
# dpkg --get-selections isc-dhcp-server [确认软件已经成功安装]
|
||||
# dpkg -s isc-dhcp-server [用另一种方式确认成功安装]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. Now that the server software is confirmed installed, it is now necessary to configure the server with the network information that it will need to hand out. At the bare minimum, the administrator needs to know the following information for a basic DHCP scope:
|
||||
|
||||
2. 现在已经确认服务软件安装完毕,现在需要配置服务器,它将分发网络信息。作为管理员你最起码应该了解DHCP的信息如下:
|
||||
- The network addresses
|
||||
- 网络地址
|
||||
- The subnet masks
|
||||
- 子网掩码
|
||||
- The range of addresses to be dynamically assigned
|
||||
- 动态分配的地址范围
|
||||
|
||||
Other useful information to have the server dynamically assign includes:
|
||||
|
||||
其他一些使服务器动态分配的有用信息包括:
|
||||
- Default gateway
|
||||
- 默认网关
|
||||
- DNS server IP addresses
|
||||
- DNS服务器IP地址
|
||||
- The Domain Name
|
||||
- 域名
|
||||
- Host name
|
||||
- 主机名
|
||||
- Network Broadcast addresses
|
||||
- 网络广播地址
|
||||
|
||||
These are merely a few of the many options that the ISC DHCP server can handle. To get a complete list as well as a description of each option, enter the following command after installing the package:
|
||||
|
||||
这只是很少一部分能让ISC DHCP server处理的选项。完整的查看所有选项及其描述需要在安装好软件后输入以下命令:
|
||||
# man dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
3. Once the administrator has concluded all the necessary information for this server to hand out it is time to configure the DHCP server as well as the necessary pools. Before creating any pools or server configurations though, the DHCP service must be configured to listen on one of the server’s interfaces.
|
||||
|
||||
3. 一旦管理员已经确定了这台服务器需要分发出去的必要信息,那么是时候配置它和分配必要的地址池了。在配置任何地址池或服务器配置之前,DHCP服务必须配置好,来监听这台服务器上面的一个接口。
|
||||
|
||||
On this particular server, a NIC team has been setup and DHCP will listen on the teamed interfaces which were given the name `'bond0'`. Be sure to make the appropriate changes given the server and environment in which everything is being configured. The defaults in this file are okay for this tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
在这台特定的服务器上,一个网卡设置好后,DHCP会监听命名为`'bond0'`的接口。请适确保适当的更改服务器以及网络环境。下面默认的配置都是针对于本次教程的。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This line will instruct the DHCP service to listen for DHCP traffic on the specified interface(s). At this point, it is time to modify the main configuration file to enable the DHCP pools on the necessary networks. The main configuration file is located at /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf. Open the file with a text editor to begin:
|
||||
|
||||
这行指定的是DHCP服务监听接口(一个或多个)上的DHCP流量。修改主要的配置文件分派DHCP池配置在所需要的网络上。主要的配置文件的位置在/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf。用文本编辑器打开这个文件
|
||||
# nano /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
This file is the configuration for the DHCP server specific options as well as all of the pools/hosts one wishes to configure. The top of the file starts of with a ‘ddns-update-style‘ clause and for this tutorial it will remain set to ‘none‘ however in a future article, Dynamic DNS will be covered and ISC-DHCP-Server will be integrated with BIND9 to enable host name to IP address updates.
|
||||
|
||||
这个配置文件可以配置我们想的地址池/主机。文件顶部有‘ddns-update-style‘这样一句,在本教程中它设置为‘none‘。在以后的教程中动态DNS, ISC-DHCP-Server 将被整合到 BIND9为了能够使主机名更新到IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
4. The next section is typically the area where and administrator can configure global network settings such as the DNS domain name, default lease time for IP addresses, subnet-masks, and much more. Again to know more about all the options be sure to read the man page for the dhcpd.conf file.
|
||||
|
||||
4. 接下来的部分 是管理员配置全局网络设置,如DNS域名,默认的租约时间,IP地址,子网的掩码,以及更多的区域。想更多地了解所有的选项,阅读man手册dhcpd.conf文件,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# man dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
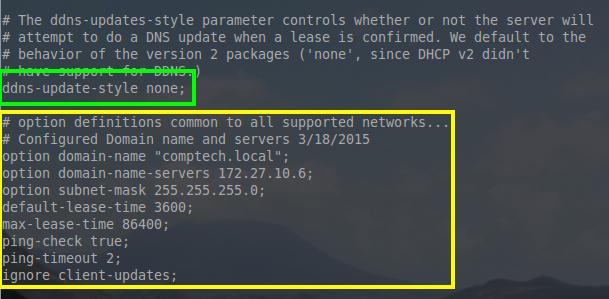
For this server install, there were a couple of global network options that were configured at the top of the configuration file so that they wouldn’t have to be implemented in every single pool created.
|
||||
|
||||
对于这台服务器,我们需要在顶部配置一些全局网络设置,这腰就不用到每个地址池中单独去设置了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Lets take a moment to explain some of these options. While they are configured globally in this example, all of them can be configured on a per pool basis as well.
|
||||
下面我们花一点时间来解释一下这些选项,在本例中虽然它们是一些全局,但是也可以为每一个地址池配置。
|
||||
|
||||
- option domain-name “comptech.local”; – All hosts that this DHCP server hosts, will be a member of the DNS domain name “comptech.local”
|
||||
- option domain-name “comptech.local”; – 所有使用这台DHCP服务器的主机,将成为DNS域名“comptech.local”的一员
|
||||
- option domain-name-servers 172.27.10.6; DHCP will hand out DNS server IP of 172.27.10.6 to all of the hosts on all of the networks it is configured to host.
|
||||
- option domain-name-servers 172.27.10.6; DHCP 将向所有配置好的网络主机分发DNS服务器地址172.27.10.6
|
||||
- option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0; – The subnet mask handed out to every network will be a 255.255.255.0 or a /24
|
||||
- option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0; – 分派子网掩码到每一个网络设备 255.255.255.0 或a /24
|
||||
- default-lease-time 3600; – This is the time in seconds that a lease will automatically be valid. The host can re-request the same lease if time runs out or if the host is done with the lease, they can hand the address back early.
|
||||
- default-lease-time 3600; – 有效的地址租约时间,单位是秒。如果租约时间耗尽主机可以重新申请租约。如果租约完成那么相应的地址也将被尽快回收。
|
||||
- max-lease-time 86400; – This is the maximum amount of time in seconds a lease can be held by a host.
|
||||
- max-lease-time 86400; – 这是一个主机最大的租约时间,单位为秒。
|
||||
- ping-check true; – This is an extra test to ensure that the address the server wants to assign out isn’t in use by another host on the network already.
|
||||
- ping-check true; – 这是一个额外的测试,以确保服务器分配出的地址不是一个网络内另一台主机已使用的网络地址。
|
||||
- ping-timeout; – This is how long in second the server will wait for a response to a ping before assuming the address isn’t in use.
|
||||
- ping-timeout; – 假设地址以前没有使用,用这个来检测2个ping值回应之间的时间长度。
|
||||
- ignore client-updates; For now this option is irrelevant since DDNS has been disabled earlier in the configuration file but when DDNS is operating, this option will ignore a hosts to request to update its host-name in DNS.
|
||||
- ignore client-updates; 现在这个选项是可以忽略的,因为DDNS在前面已在配置文件中被禁用,但是当DDNS运行,此选项会忽略一个主机请求的DNS更新其主机名。
|
||||
|
||||
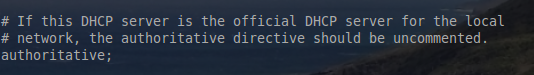
5. The next line in this file is the authoritative DHCP server line. This line means that if this server is to be the server that hands out addresses for the networks configured in this file, then uncomment the authoritative stanza.
|
||||
5. 文件中的下面一行是权威DHCP所在行。这行的意义是如果服务器是为文件中所配置的网络分发地址的服务器,那么就取消注释权威节(uncomment the authoritative stanza.)。
|
||||
|
||||
This server will be the only authority on all the networks it manages so the global authoritative stanza was un-commented by removing the ‘#’ in front of the keyword authoritative.
|
||||
|
||||
通过去掉关键字authoritative 前面的‘#’,取消注释全局权威节。那么该服务器将是它管理网络里面的唯一权威。
|
||||
|
||||
Enable ISC Authoritative
|
||||
开启 ISC Authoritative
|
||||
|
||||
By default the server is assumed to NOT be an authority on the network. The rationale behind this is security. If someone unknowingly configures the DHCP server improperly or on a network they shouldn’t, it could cause serious connectivity issues. This line can also be used on a per network basis. This means that if the server is not the entire network’s DHCP server, the authoritative line can instead be used on a per network basis rather than in the global configuration as seen in the above screen-shot.
|
||||
默认情况下服务器被假定为不是网络上的权威。这样做的理由是为了安全。如果有人因为不了解DHCP服务的配置导致配置不当或在一个不该出现的网络里面,这都将会造成非常严重的重连接问题。这行还可用在每个网络中单独使用。这意味着如果该服务器不是整个网络的DHCP服务器,authoritative行可以用在每个单独的网络中,而不是像上面截图显示中的全局配置那样。
|
||||
|
||||
6. The next step is to configure all of the DHCP pools/networks that this server will manage. For brevities sake, this guide will only walk through one of the pools configured. The administrator will need to have gathered all of the necessary network information (ie domain name, network addresses, how many addresses can be handed out, etc).
|
||||
|
||||
6. 下一步是配置所有的服务器将要管理的DHCP地址池/网络。简短起见,这个教程将只配置地址池。作为管理员需要收集所有必要的网络信息(比如域名,网络地址,有多少地址能够被分发等等)
|
||||
For this pool the following information was obtained from the network administrator: network id of 172.27.60.0, subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 or a /24, the default gateway for the subnet is 172.27.60.1, and a broadcast address of 172.27.60.255.
|
||||
This information is important to building the appropriate network stanza in the dhcpd.conf file. Without further ado, let’s open the configuration file again using a text editor and then add the new network to the server. This must be done with root/sudo!
|
||||
|
||||
以下这个地址池所用到的信息都是管理员收集整理的:网络id 172.27.60.0, 子网掩码 255.255.255.0 or a /24, 默认网关172.27.60.1,广播地址 172.27.60.255.
|
||||
# nano /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Configure DHCP Pools and Networks
|
||||
配置DHCP的地址池和网络
|
||||
|
||||
This is the sample created to hand out IP addresses to a network that is used for the creation of VMWare virtual practice servers. The first line indicates the network as well as the subnet mask for that network. Then inside the brackets are all the options that the DHCP server should provide to hosts on this network.
|
||||
|
||||
这例子是分配IP地址给用VMWare创建的虚拟服务器。第一行标明是该网络的子网掩码。括号里面是DHCP服务器应该提供给当前网络上主机的所有选项。
|
||||
|
||||
The first stanza, range 172.27.60.50 172.27.60.254;, is the range of dynamically assignable addresses that the DHCP server can hand out to hosts on this network. Notice that the first 49 addresses aren’t in the pool and can be assigned statically to hosts if needed.
|
||||
|
||||
第一节, range 172.27.60.50 172.27.60.254;是DHCP服务在这个网络上能够给主机动态分发的地址范围。
|
||||
|
||||
The second stanza, option routers 172.27.60.1; , hands out the default gateway address for all hosts on this network.
|
||||
|
||||
第二节,option routers 172.27.60.1;给网络里面所有的主机分发默认网关地址。
|
||||
|
||||
The last stanza, option broadcast-address 172.27.60.255;, indicates what the network’s broadcast address. This address SHOULD NOT be a part of the range stanza as the broadcast address can’t be assigned to a host.
|
||||
|
||||
最后一节, option broadcast-address 172.27.60.255;,说明当前网络的广播地址。这个地址不能被包含在要分发放的地址范围内,因为广播地址不能分配到一个主机上面。
|
||||
Some pointers, be sure to always end the option lines with a semi-colon (;) and always make sure each network created is enclosed in curly braces { }.
|
||||
|
||||
必须要强调的是每行的结尾必须要用(;)来结束,所有创建的网络必须要在{}里面。
|
||||
|
||||
7. If there are more networks to create, continue creating them with their appropriate options and then save the text file. Once all configurations have been completed, the ISC-DHCP-Server process will need to be restarted in order to apply the new changes. This can be accomplished with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
7. 如果是创建多个网络,持续的创建它们的相应选项最终保存文本文件。一旦配置完成, ISC-DHCP-Server进程需要重启来使新的更改生效。可以通过下面的命令来完成:
|
||||
# service isc-dhcp-server restart
|
||||
|
||||
This will restart the DHCP service and then the administrator can check to see if the server is ready for DHCP requests several different ways. The easiest is to simply see if the server is listening on port 67 via the [lsof command][1]:
|
||||
|
||||
这条命令将重启DHCP服务,管理员能够使用几种不同的方式来检查服务器是否已经可以处理dhcp请求。最简单的方法是通过lsof命令[1]来查看服务器是否在监听67端口,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# lsof -i :67
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check DHCP Listening Port
|
||||
检查DHCP监听端口
|
||||
|
||||
This output indicates that the DHCPD (DHCP Server daemon) is running and listening on port 67. Port 67 in this output was actually converted to ‘bootps‘ due to a port number mapping for port 67 in /etc/services file.
|
||||
|
||||
这里的输出表明DHCPD(DHCP服务守护进程)正在运行并且监听67端口。由于/etc/services文件中67端口的端口映射,输出中的67端口实际上被转换成了“bootps”。
|
||||
|
||||
This is very common on most systems. At this point, the server should be ready for network connectivity and can be confirmed by connecting a machine to the network and having it request a DHCP address from the server.
|
||||
|
||||
在大多数的系统中这是非常普遍的,此时,服务器应该已经为网络连接做好准备,可以通过将一台主机接入网络请求DHCP地址来验证服务是否正常。
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Testing Client Connectivity ###
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试客户端连接 ###
|
||||
8. Most systems now-a-days are using Network Manager to maintain network connections and as such the device should be pre-configured to pull DHCP when the interface is active.
|
||||
|
||||
8. 现在许多系统使用网络管理器来维护网络连接状态,因此这个装置应该预先配置,当接口是活跃的时候来获取DHCP。
|
||||
|
||||
However on machines that aren’t using Network Manager, it may be necessary to manually attempt to pull a DHCP address. The next few steps will show how to do this as well as how to see whether the server is handing out addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
然而当一台设备无法使用网络管理器时,它可能需要手动获取DHCP地址。下面的几步将展示如何做到这一点以及如何查看服务器是否分发地址。
|
||||
|
||||
The ‘[ifconfig][2]‘ utility can be used to check an interface’s configuration. The machine used to test the DHCP server only has one network adapter and it is called ‘eth0‘.
|
||||
|
||||
‘[ifconfig][2]‘工具能够用来检查接口配置。这台设备被用来监测DHCP服务它只有一个网络适配器(网卡),这块网卡被命名为‘eth0‘。
|
||||
|
||||
# ifconfig eth0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check Network Interface IP Address
|
||||
检查网络接口IP地址
|
||||
|
||||
From this output, this machine currently doesn’t have an IPv4 address, great! Let’s instruct this machine to reach out to the DHCP server and request an address. This machine has the DHCP client utility known as ‘dhclient‘ installed. The DHCP client utility may very from system to system.
|
||||
|
||||
从输出结果上看,这台设备目前没有一个IPv4地址,很好这样便于测试。让这台设备连接到DHCP服务器并发出一个请求。这台设备上安装了一个名为‘dhclient‘ 的DHCP客户端工具。这个客户端工具会因为系统不同而不同。
|
||||
# dhclient eth0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Request IP Address from DHCP
|
||||
从DHCP请求IP地址
|
||||
|
||||
Now the `'inet addr:'` field shows an IPv4 address that falls within the scope of what was configured for the 172.27.60.0 network. Also notice that the proper broadcast address was handed out as well as subnet mask for this network.
|
||||
|
||||
现在 `'inet addr:'` 字段显示了属于172.27.60.0网络地址范围内的IPv4地址。另外要注意:目前该网络配置了正确的子网掩码并且分发了广播地址。
|
||||
|
||||
Things are looking promising but let’s check the server to see if it was actually the place where this machine received this new IP address. To accomplish this task, the server’s system log file will be consulted. While the entire log file may contain hundreds of thousands of entries, only a few are necessary for confirming that the server is working properly. Rather than using a full text editor, this time a utility known as ‘tail‘ will be used to only show the last few lines of the log file.
|
||||
|
||||
看起来还不错,让我们来测试一下,看看它是不是这台设备收到新IP地址的地方。我们参照服务器的日志文件来完成这个任务。虽然这个日志的内容有几十万条,但是里面只有几条是用来确定服务器是否正常工作的。这里我们使用一个工具‘tail’,它只显示日志文件的最后几行,而不是使用一个完整的文本编辑器去查看日志文件。命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# tail /var/log/syslog
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check DHCP Logs
|
||||
检查DHCP日志文件
|
||||
|
||||
Voila! The server recorded handing out an address to this host (HRTDEBXENSRV). It is a safe assumption at this point that the server is working as intended and handing out the appropriate addresses for the networks that it is an authority. At this point the DHCP server is up and running. Configure the other networks, troubleshoot, and secure as necessary.
|
||||
|
||||
OK!服务器记录表明它分发了一个地址给这台主机(HRTDEBXENSRV)。服务器按预期运行,给它充当权威的网络分发适合的网络地址。到这里DHCP服务器搭建成功并且运行起来了。配置其他的网络,排查故障,确保安全。
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy the newly functioning ISC-DHCP-Server and tune in later for more Debian tutorials. In the not too distant future there will be an article on Bind9 and DDNS that will tie into this article.
|
||||
|
||||
更多新的 ISC-DHCP-Server 的功能在以后的Debian教程中会被提及。不久以后将写一篇关于Bind9和DDNS的教程,插入到这篇文章里面。
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-and-configure-multihomed-isc-dhcp-server-on-debian-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Rob Turner][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[ivo-wang](https://github.com/ivo-wang)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/robturner/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-lsof-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/ifconfig-command-examples/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/ifconfig-command-examples/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user