mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject
This commit is contained in:
commit
968e9fd0e1
@ -0,0 +1,162 @@
|
||||
在 Debian Linux 上安装配置 ISC DHCP 服务器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
动态主机控制协议(Dynamic Host Control Protocol,DHCP)给网络管理员提供了一种便捷的方式,为不断变化的网络主机或是动态网络提供网络层地址。其中最常用的 DHCP 服务工具是 ISC DHCP Server。DHCP 服务的目的是给主机提供必要的网络信息以便能够和其他连接在网络中的主机互相通信。DHCP 服务提供的信息包括:DNS 服务器信息,网络地址(IP),子网掩码,默认网关信息,主机名等等。
|
||||
|
||||
本教程介绍运行在 Debian 7.7 上 4.2.4 版的 ISC-DHCP-Server 如何管理多个虚拟局域网(VLAN),也可以非常容易应用到单一网络上。
|
||||
|
||||
测试用的网络是通过思科路由器使用传统的方式来管理 DHCP 租约地址的。目前有 12 个 VLAN 需要通过集中式服务器来管理。把 DHCP 的任务转移到一个专用的服务器上,路由器可以收回相应的资源,把资源用到更重要的任务上,比如路由寻址,访问控制列表,流量监测以及网络地址转换等。
|
||||
|
||||
另一个将 DHCP 服务转移到专用服务器的好处,以后会讲到,它可以建立动态域名服务器(DDNS),这样当主机从服务器请求 DHCP 地址的时候,这样新主机的主机名就会被添加到 DNS 系统里面。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装和配置 ISC DHCP 服务器###
|
||||
|
||||
1、使用 apt 工具用来安装 Debian 软件仓库中的 ISC 软件,来创建这个多宿主服务器。与其他教程一样需要使用 root 或者 sudo 访问权限。请适当的修改,以便使用下面的命令。(LCTT 译注:下面中括号里面是注释,使用的时候请删除,#表示使用的 root 权限)
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install isc-dhcp-server [安装 the ISC DHCP Server 软件]
|
||||
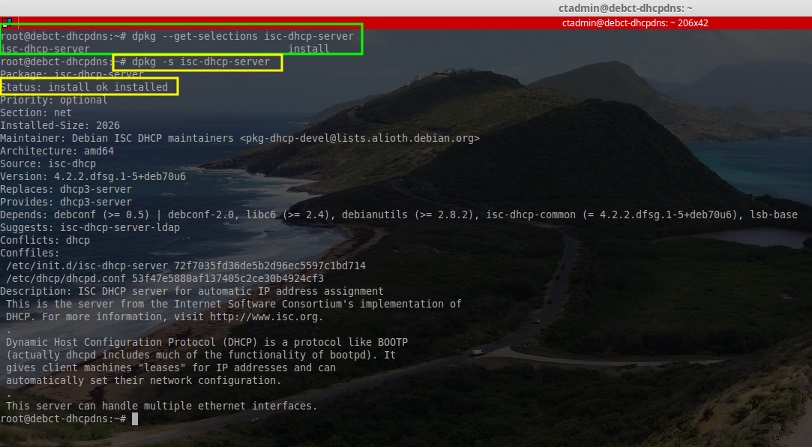
# dpkg --get-selections isc-dhcp-server [确认软件已经成功安装]
|
||||
# dpkg -s isc-dhcp-server [用另一种方式确认成功安装]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2、 确认服务软件已经安装完成,现在需要提供网络信息来配置服务器,这样服务器才能够根据我们的需要来分发网络信息。作为管理员最起码需要了解的 DHCP 信息如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 网络地址
|
||||
- 子网掩码
|
||||
- 动态分配的地址范围
|
||||
|
||||
其他一些服务器动态分配的有用信息包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 默认网关
|
||||
- DNS 服务器 IP 地址
|
||||
- 域名
|
||||
- 主机名
|
||||
- 网络广播地址
|
||||
|
||||
这只是能让 ISC DHCP 服务器处理的选项中非常少的一部分。如果你想查看所有选项及其描述需要在安装好软件后输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# man dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
3、 一旦管理员已经确定了这台服务器分发的所有必要信息,那么是时候配置服务器并且分配必要的地址池了。在配置任何地址池或服务器配置之前,必须配置 DHCP 服务器侦听这台服务器上面的一个接口。
|
||||
|
||||
在这台特定的服务器上,设置好网卡后,DHCP 会侦听名称名为`'bond0'`的接口。请适根据你的实际情况来更改服务器以及网络环境。下面的配置都是针对本教程的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这行指定的是 DHCP 服务侦听接口(一个或多个)上的 DHCP 流量。修改主配置文件,分配适合的 DHCP 地址池到所需要的网络上。主配置文件在 /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf。用文本编辑器打开这个文件
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
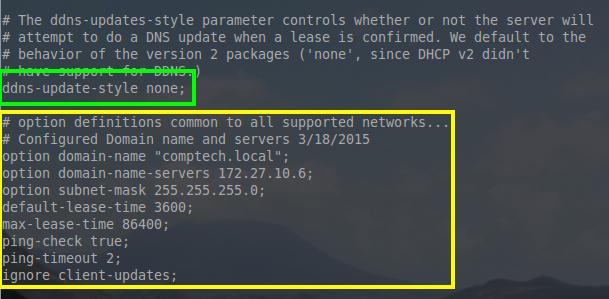
这个配置文件可以配置我们所需要的地址池/主机。文件顶部有 ‘ddns-update-style‘ 这样一句,在本教程中它设置为 ‘none‘。在以后的教程中会讲到动态 DNS,ISC-DHCP-Server 将会与 BIND9 集成,它能够使主机名更新指向到 IP 地址。
|
||||
|
||||
4、 接下来的部分是管理员配置全局网络设置,如 DNS 域名,默认的租约时间,IP地址,子网的掩码,以及其它。如果你想了解所有的选项,请阅读 man 手册中的 dhcpd.conf 文件,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# man dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
对于这台服务器,我们需要在配置文件顶部配置一些全局网络设置,这样就不用到每个地址池中去单独设置了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们花一点时间来解释一下这些选项,在本教程中虽然它们是一些全局设置,但是也可以单独的为某一个地址池进行配置。
|
||||
|
||||
- option domain-name “comptech.local”; – 所有使用这台 DHCP 服务器的主机,都将成为 DNS 域 “comptech.local” 的一员
|
||||
|
||||
- option domain-name-servers 172.27.10.6; DHCP 向所有配置这台 DHCP 服务器的的网络主机分发 DNS 服务器地址为 172.27.10.6
|
||||
|
||||
- option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0; – 每个网络设备都分配子网掩码 255.255.255.0 或 /24
|
||||
|
||||
- default-lease-time 3600; – 默认有效的地址租约时间(单位是秒)。如果租约时间耗尽,那么主机可以重新申请租约。如果租约完成,那么相应的地址也将被尽快回收。
|
||||
|
||||
- max-lease-time 86400; – 这是一台主机所能租用的最大的租约时间(单位为秒)。
|
||||
|
||||
- ping-check true; – 这是一个额外的测试,以确保服务器分发出的网络地址不是当前网络中另一台主机已使用的网络地址。
|
||||
|
||||
- ping-timeout; – 在判断地址以前没有使用过前,服务器将等待 ping 响应多少秒。
|
||||
|
||||
- ignore client-updates; 现在这个选项是可以忽略的,因为 DDNS 在前面已在配置文件中已经被禁用,但是当 DDNS 运行时,这个选项会忽略主机更新其 DNS 主机名的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
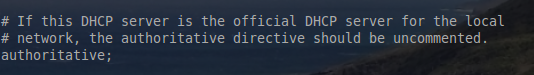
5、 文件中下面一行是权威 DHCP 所在行。这行的意义是如果服务器是为文件中所配置的网络分发地址的服务器,那么取消对该权威关键字(authoritative stanza) 的注释。
|
||||
|
||||
通过去掉关键字 authoritative 前面的 ‘#’,取消注释全局权威关键字。这台服务器将是它所管理网络里面的唯一权威。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下服务器被假定为**不是**网络上的权威服务器。之所以这样做是出于安全考虑。如果有人因为不了解 DHCP 服务的配置,导致配置不当或配置到一个不该出现的网络里面,这都将带来非常严重的连接问题。这行还可用在每个网络中单独配置使用。也就是说如果这台服务器不是整个网络的 DHCP 服务器,authoritative 行可以用在每个单独的网络中,而不是像上面截图中那样的全局配置。
|
||||
|
||||
6、 这一步是配置服务器将要管理的所有 DHCP 地址池/网络。简短起见,本教程只讲到配置的地址池之一。作为管理员需要收集一些必要的网络信息(比如域名,网络地址,有多少地址能够被分发等等)
|
||||
|
||||
以下这个地址池所用到的信息都是管理员收集整理的:网络 ID 172.27.60.0, 子网掩码 255.255.255.0 或 /24, 默认子网网关 172.27.60.1,广播地址 172.27.60.255.0 。
|
||||
|
||||
以上这些信息对于构建 dhcpd.conf 文件中新网络非常重要。使用文本编辑器修改配置文件添加新网络进去,这里我们需要使用 root 或 sudo 访问权限。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当前这个例子是给用 VMWare 创建的虚拟服务器分配 IP 地址。第一行显示是该网络的子网掩码。括号里面的内容是 DHCP 服务器应该提供给网络上面主机的所有选项。
|
||||
|
||||
第一行, range 172.27.60.50 172.27.60.254; 这一行显示的是,DHCP 服务在这个网络上能够给主机动态分发的地址范围。
|
||||
|
||||
第二行,option routers 172.27.60.1; 这里显示的是给网络里面所有的主机分发的默认网关地址。
|
||||
|
||||
最后一行, option broadcast-address 172.27.60.255; 显示当前网络的广播地址。这个地址不能被包含在要分发放的地址范围内,因为广播地址不能分配到一个主机上面。
|
||||
|
||||
必须要强调的是每行的结尾必须要用(;)来结束,所有创建的网络必须要在 {} 里面。
|
||||
|
||||
7、 如果要创建多个网络,继续创建完它们的相应选项后保存文本文件即可。配置完成以后如果有更改,ISC-DHCP-Server 进程需要重启来使新的更改生效。重启进程可以通过下面的命令来完成:
|
||||
|
||||
# service isc-dhcp-server restart
|
||||
|
||||
这条命令将重启 DHCP 服务,管理员能够使用几种不同的方式来检查服务器是否已经可以处理 dhcp 请求。最简单的方法是通过 [lsof 命令][1]来查看服务器是否在侦听67端口,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# lsof -i :67
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这里输出的结果表明 dhcpd(DHCP 服务守护进程)正在运行并且侦听67端口。由于在 /etc/services 文件中67端口的映射,所以输出中的67端口实际上被转换成了 “bootps”。
|
||||
|
||||
在大多数的系统中这是非常常见的,现在服务器应该已经为网络连接做好准备,我们可以将一台主机接入网络请求DHCP地址来验证服务是否正常。
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试客户端连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
8、 现在许多系统使用网络管理器来维护网络连接状态,因此这个设备应该预先配置好的,只要对应的接口处于活跃状态就能够获取 DHCP。
|
||||
|
||||
然而当一台设备无法使用网络管理器时,它可能需要手动获取 DHCP 地址。下面的几步将演示怎样手动获取以及如何查看服务器是否已经按需要分发地址。
|
||||
|
||||
‘[ifconfig][2]‘工具能够用来检查接口的配置。这台被用来测试的 DHCP 服务器的设备,它只有一个网络适配器(网卡),这块网卡被命名为 ‘eth0‘。
|
||||
|
||||
# ifconfig eth0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
从输出结果上看,这台设备目前没有 IPv4 地址,这样很便于测试。我们把这台设备连接到 DHCP 服务器并发出一个请求。这台设备上已经安装了一个名为 ‘dhclient‘ 的DHCP客户端工具。因为操作系统各不相同,所以这个客户端软件也是互不一样的。
|
||||
|
||||
# dhclient eth0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当前 `'inet addr:'` 字段中显示了属于 172.27.60.0 网络地址范围内的 IPv4 地址。值得欣慰的是当前网络还配置了正确的子网掩码并且分发了广播地址。
|
||||
|
||||
到这里看起来还都不错,让我们来测试一下,看看这台设备收到新 IP 地址是不是由服务器发出的。这里我们参照服务器的日志文件来完成这个任务。虽然这个日志的内容有几十万条,但是里面只有几条是用来确定服务器是否正常工作的。这里我们使用一个工具 ‘tail’,它只显示日志文件的最后几行,这样我们就可以不用拿一个文本编辑器去查看所有的日志文件了。命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# tail /var/log/syslog
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
OK!服务器记录表明它分发了一个地址给这台主机 (HRTDEBXENSRV)。服务器按预期运行,给它充当权威服务器的网络分发了适合的网络地址。至此 DHCP 服务器搭建成功并且运行。如果有需要你可以继续配置其他的网络,排查故障,确保安全。
|
||||
|
||||
在以后的Debian教程中我会讲一些新的 ISC-DHCP-Server 功能。有时间的话我将写一篇关于 Bind9 和 DDNS 的教程,融入到这篇文章里面。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-and-configure-multihomed-isc-dhcp-server-on-debian-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Rob Turner][a]
|
||||
译者:[ivo-wang](https://github.com/ivo-wang)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/robturner/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-lsof-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/ifconfig-command-examples/
|
||||
220
published/20150917 A Repository with 44 Years of Unix Evolution.md
Executable file
220
published/20150917 A Repository with 44 Years of Unix Evolution.md
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,220 @@
|
||||
一个涵盖 Unix 44 年进化史的版本仓库
|
||||
=============================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html
|
||||
|
||||
This is an HTML rendering of a working paper draft that led to a publication. The publication should always be cited in preference to this draft using the following reference:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Diomidis Spinellis**. [A repository with 44 years of Unix evolution](http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html). In MSR '15: Proceedings of the 12th Working Conference on Mining Software Repositories, pages 13-16. IEEE, 2015. Best Data Showcase Award. ([doi:10.1109/MSR.2015.6](http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/MSR.2015.6))
|
||||
|
||||
This document is also available in [PDF format](http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.pdf).
|
||||
|
||||
The document's metadata is available in [BibTeX format](http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c-bibtex.html).
|
||||
|
||||
This material is presented to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work. Copyright and all rights therein are retained by authors or by other copyright holders. All persons copying this information are expected to adhere to the terms and constraints invoked by each author's copyright. In most cases, these works may not be reposted without the explicit permission of the copyright holder.
|
||||
|
||||
[Diomidis Spinellis Publications](http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/)
|
||||
|
||||
© 2015 IEEE. Personal use of this material is permitted. However, permission to reprint/republish this material for advertising or promotional purposes or for creating new collective works for resale or redistribution to servers or lists, or to reuse any copyrighted component of this work in other works must be obtained from the IEEE.
|
||||
|
||||
### 摘要 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Unix 操作系统的进化历史,可以从一个版本控制仓库中窥见,时间跨度从 1972 年的 5000 行内核代码开始,到 2015 年成为一个含有 26,000,000 行代码的被广泛使用的系统。该仓库包含 659,000 条提交,和 2306 次合并。仓库部署了被普遍采用的 Git 系统用于储存其代码,并且在时下流行的 GitHub 上建立了存档。它由来自贝尔实验室(Bell Labs),伯克利大学(Berkeley University),386BSD 团队所开发的系统软件的 24 个快照综合定制而成,这包括两个老式仓库和一个开源 FreeBSD 系统的仓库。总的来说,可以确认其中的 850 位个人贡献者,更早些时候的一批人主要做基础研究。这些数据可以用于一些经验性的研究,在软件工程,信息系统和软件考古学领域。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1、介绍 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Unix 操作系统作为一个主要的工程上的突破而脱颖而出,得益于其模范的设计、大量的技术贡献、它的开发模型及广泛的使用。Unix 编程环境的设计已经被视为一个提供非常简洁、强大而优雅的设计 [[1][1]] 。在技术方面,许多对 Unix 有直接贡献的,或者因 Unix 而流行的特性就包括 [[2][2]] :用高级语言编写的可移植部署的内核;一个分层式设计的文件系统;兼容的文件,设备,网络和进程间 I/O;管道和过滤架构;虚拟文件系统;和作为普通进程的可由用户选择的不同 shell。很早的时候,就有一个庞大的社区为 Unix 贡献软件 [[3][3]] ,[[4][4],pp. 65-72] 。随时间流逝,这个社区不断壮大,并且以现在称为开源软件开发的方式在工作着 [[5][5],pp. 440-442] 。Unix 和其睿智的晚辈们也将 C 和 C++ 编程语言、分析程序和词法分析生成器(*yacc*,*lex*)、文档编制工具(*troff*,*eqn*,*tbl*)、脚本语言(*awk*,*sed*,*Perl*)、TCP/IP 网络、和配置管理系统(configuration management system)(*SCSS*,*RCS*,*Subversion*,*Git*)发扬广大了,同时也形成了现代互联网基础设施和网络的最大的部分。
|
||||
|
||||
幸运的是,一些重要的具有历史意义的 Unix 材料已经保存下来了,现在保持对外开放。尽管 Unix 最初是由相对严格的协议发行,但在早期的开发中,很多重要的部分是通过 Unix 的版权拥有者之一(Caldera International) (LCTT 译注:2002年改名为 SCO Group)以一个自由的协议发行。通过将这些部分再结合上由加州大学伯克利分校(University of California, Berkeley)和 FreeBSD 项目组开发或发布的开源软件,贯穿了从 1972 年六月二十日开始到现在的整个系统的开发。
|
||||
|
||||
通过规划和处理这些可用的快照以及或旧或新的配置管理仓库,将这些可用数据的大部分重建到一个新合成的 Git 仓库之中。这个仓库以数字的形式记录了过去44年来最重要的数字时代产物的详细的进化。下列章节描述了该仓库的结构和内容(第[2][6]节)、创建方法(第[3][7]节)和该如何使用(第[4][8]节)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2、数据概览 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这 1GB 的 Unix 历史仓库可以从 [GitHub][9] 上克隆^[1][10] 。如今^[2][11] ,这个仓库包含来自 850 个贡献者的 659,000 个提交和 2,306 个合并。贡献者有来自贝尔实验室(Bell Labs)的 23 个员工,伯克利大学(Berkeley University)的计算机系统研究组(Computer Systems Research Group)(CSRG)的 158 个人,和 FreeBSD 项目的 660 个成员。
|
||||
|
||||
这个仓库的生命始于一个 *Epoch* 的标签,这里面只包含了证书信息和现在的 README 文件。其后各种各样的标签和分支记录了很多重要的时刻。
|
||||
|
||||
- *Research-VX* 标签对应来自贝尔实验室(Bell Labs)六个研究版本。从 *Research-V1* (4768 行 PDP-11 汇编代码)开始,到以 *Research-V7* (大约 324,000 行代码,1820 个 C 文件)结束。
|
||||
- *Bell-32V* 是第七个版本 Unix 在 DEC/VAX 架构上的移植。
|
||||
- *BSD-X* 标签对应伯克利大学(Berkeley University)释出的 15 个快照。
|
||||
- *386BSD-X* 标签对应该系统的两个开源版本,主要是 Lynne 和 William Jolitz 写的适用于 Intel 386 架构的内核代码。
|
||||
- *FreeBSD-release/X* 标签和分支标记了来自 FreeBSD 项目的 116 个发行版。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,以 *-Snapshot-Development* 为后缀的分支,表示该提交由来自一个以时间排序的快照文件序列而合成;而以一个 *-VCS-Development* 为后缀的标签,标记了有特定发行版出现的历史分支的时刻。
|
||||
|
||||
仓库的历史包含从系统开发早期的一些提交,比如下面这些。
|
||||
|
||||
commit c9f643f59434f14f774d61ee3856972b8c3905b1
|
||||
Author: Dennis Ritchie <research!dmr>
|
||||
Date: Mon Dec 2 18:18:02 1974 -0500
|
||||
Research V5 development
|
||||
Work on file usr/sys/dmr/kl.c
|
||||
|
||||
两个发布之间的合并代表着系统发生了进化,比如 BSD 3 的开发来自 BSD2 和 Unix 32/V,它在 Git 仓库里正是被表示为带两个父节点的图形节点。
|
||||
|
||||
更为重要的是,以这种方式构造的仓库允许 **git blame**,就是可以给源代码行加上注释,如版本、日期和它们第一次出现相关联的作者,这样可以知道任何代码的起源。比如说,检出 **BSD-4** 这个标签,并在内核的 *pipe.c* 文件上运行一下 git blame,就会显示出由 Ken Thompson 写于 1974,1975 和 1979年的代码行,和 Bill Joy 写于 1980 年的。这就可以自动(尽管计算上比较费事)检测出任何时刻出现的代码。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
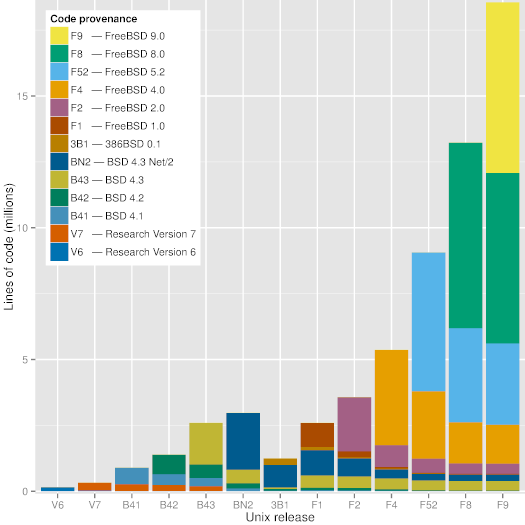
*图1:各个重大 Unix 发行版的代码来源*
|
||||
|
||||
如[上图][12]所示,现代版本的 Unix(FreeBSD 9)依然有相当部分的来自 BSD 4.3,BSD 4.3 Net/2 和 BSD 2.0 的代码块。有趣的是,这图片显示有部分代码好像没有保留下来,当时激进地要创造一个脱离于伯克利(386BSD 和 FreeBSD 1.0)所释出代码的开源操作系统。FreeBSD 9 中最古老的代码是一个 18 行的队列,在 C 库里面的 timezone.c 文件里,该文件也可以在第七版的 Unix 文件里找到,同样的名字,时间戳是 1979 年一月十日 - 36 年前。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3、数据收集和处理 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个项目的目的是以某种方式巩固从数据方面说明 Unix 的进化,通过将其并入一个现代的版本仓库,帮助人们对系统进化的研究。项目工作包括收录数据,分类并综合到一个单独的 Git 仓库里。
|
||||
|
||||
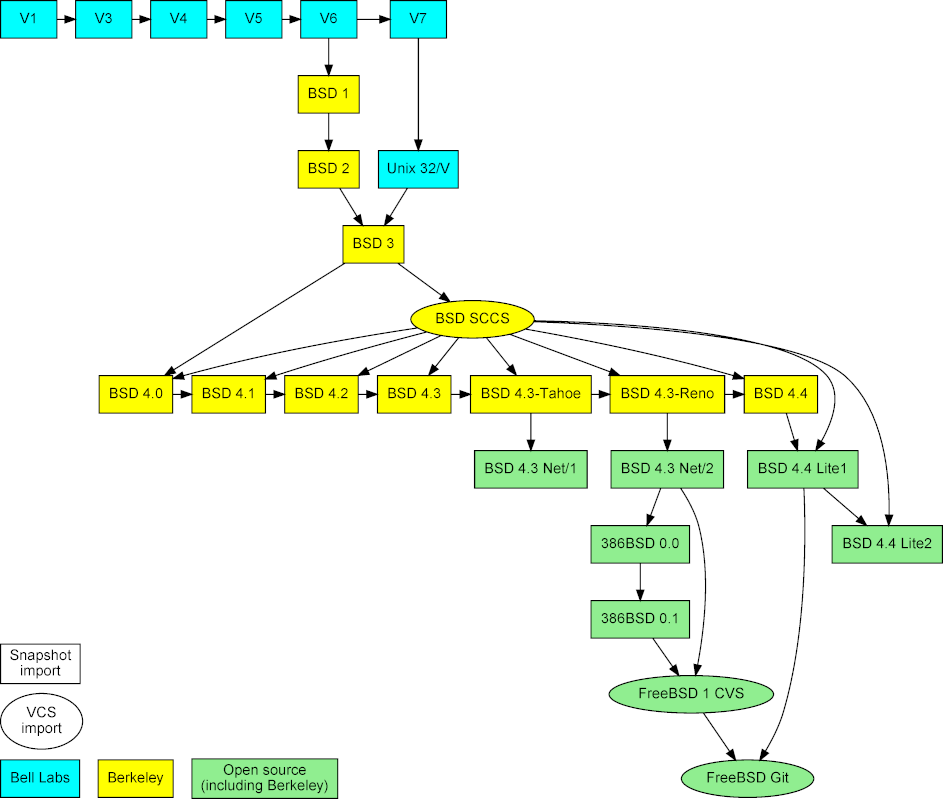
|
||||
|
||||
*图2:导入 Unix 快照、仓库及其合并*
|
||||
|
||||
项目以三种数据类型为基础(见[图2][13])。首先,早期发布版本的快照,获取自 [Unix 遗产社会归档(Unix Heritage Society archive)][14]^[3][15] 、包括了 CSRG 全部的源代码归档的 [CD-ROM 镜像][16]^[4][17] , [Oldlinux 网站][18]^[5][19] 和 [FreeBSD 归档][20]^[6][21] 。 其次,以前的和现在的仓库,即 CSRG SCCS [[6][22]] 仓库,FreeBSD 1 CVS 仓库,和[现代 FreeBSD 开发的 Git 镜像][23]^[7][24] 。前两个都是从和快照相同的来源获得的。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,也是最费力的数据源是 **初步研究(primary research)**。释出的快照并没有提供关于它们的源头和每个文件贡献者的信息。因此,这些信息片段需要通过初步研究(primary research)验证。至于作者信息主要通过作者的自传,研究论文,内部备忘录和旧文档扫描件;通过阅读并且自动处理源代码和帮助页面补充;通过与那个年代的人用电子邮件交流;在 *StackExchange* 网站上贴出疑问;查看文件的位置(在早期的内核版本的源代码,分为 `usr/sys/dmr` 和 `/usr/sys/ken` 两个位置);从研究论文和帮助手册披露的作者找到源代码,从一个又一个的发行版中获取。(有趣的是,第一和第二的研究版(Research Edition)帮助页面都有一个 “owner” 部分,列出了作者(比如,*Ken*)及对应的系统命令、文件、系统调用或库函数。在第四版中这个部分就没了,而在 BSD 发行版中又浮现了 “Author” 部分。)关于作者信息更为详细地写在了项目的文件中,这些文件被用于匹配源代码文件和它们的作者和对应的提交信息。最后,关于源代码库之间的合并信息是获取自[ NetBSD 项目所维护的 BSD 家族树][25]^[8][26] 。
|
||||
|
||||
作为本项目的一部分而开发的软件和数据文件,现在可以[在线获取][27]^[9][28] ,并且,如果有合适的网络环境,CPU 和磁盘资源,可以用来从头构建这样一个仓库。关于主要发行版的作者信息,都存储在本项目的 `author-path` 目录下的文件里。它们的内容中带有正则表达式的文件路径后面指出了相符的作者。可以指定多个作者。正则表达式是按线性处理的,所以一个文件末尾的匹配一切的表达式可以指定一个发行版的默认作者。为避免重复,一个以 `.au` 后缀的独立文件专门用于映射作者的识别号(identifier)和他们的名字及 email。这样一个文件为每个与该系统进化相关的社区都建立了一个:贝尔实验室(Bell Labs),伯克利大学(Berkeley University),386BSD 和 FreeBSD。为了真实性的需要,早期贝尔实验室(Bell Labs)发行版的 emails 都以 UUCP 注释(UUCP notation)方式列出(例如, `research!ken`)。FreeBSD 作者的识别映射,需要导入早期的 CVS 仓库,通过从如今项目的 Git 仓库里拆解对应的数据构建。总的来说,由 1107 行构成了注释作者信息的文件(828 个规则),并且另有 640 行用于映射作者的识别号到名字。
|
||||
|
||||
现在项目的数据源被编码成了一个 168 行的 `Makefile`。它包括下面的步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
**Fetching** 从远程站点复制和克隆大约 11GB 的镜像、归档和仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
**Tooling** 从 2.9 BSD 中为旧的 PDP-11 归档获取一个归档器,并调整它以在现代的 Unix 版本下编译;编译 4.3 BSD 的 *compress* 程序来解压 386BSD 发行版,这个程序不再是现代 Unix 系统的组成部分了。
|
||||
|
||||
**Organizing** 用 *tar* 和 *cpio* 解压缩包;合并第六个研究版的三个目录;用旧的 PDP-11 归档器解压全部一个 BSD 归档;挂载 CD-ROM 镜像,这样可以作为文件系统处理;合并第 8 和 62 的 386BSD 磁盘镜像为两个独立的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
**Cleaning** 恢复第一个研究版的内核源代码文件,这个可以通过 OCR 从打印件上得到近似其原始状态的的格式;给第七个研究版的源代码文件打补丁;移除发行后被添加进来的元数据和其他文件,为避免得到错误的时间戳信息;修复毁坏的 SCCS 文件;用一个定制的 Perl 脚本移除指定到多个版本的 CVS 符号、删除与现在冲突的 CVS *Attr* 文件、用 *cvs2svn* 将 CVS 仓库转换为 Git 仓库,以处理早期的 FreeBSD CVS 仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
在仓库再现(representation)中有一个很有意思的部分就是,如何导入那些快照,并以一种方式联系起来,使得 *git blame* 可以发挥它的魔力。快照导入到仓库是基于每个文件的时间戳作为一系列的提交实现的。当所有文件导入后,就被用对应发行版的名字给标记了。然后,可以删除那些文件,并开始导入下一个快照。注意 *git blame* 命令是通过回溯一个仓库的历史来工作的,并使用启发法(heuristics)来检测文件之间或文件内的代码移动和复制。因此,删除掉的快照间会产生中断,以防止它们之间的代码被追踪。
|
||||
|
||||
相反,在下一个快照导入之前,之前快照的所有文件都被移动到了一个隐藏的后备目录里,叫做 `.ref`(引用)。它们保存在那,直到下个快照的所有文件都被导入了,这时候它们就会被删掉。因为 `.ref` 目录下的每个文件都精确对应一个原始文件,*git blame* 可以知道多少源代码通过 `.ref` 文件从一个版本移到了下一个,而不用显示出 `.ref` 文件。为了更进一步帮助检测代码起源,同时增加再现(representation)的真实性,每个发行版都被再现(represented)为一个有增量文件的分支(*-Development*)与之前发行版之间的合并。
|
||||
|
||||
上世纪 80 年代时期,只有伯克利(Berkeley) 开发的文件的一个子集是用 SCCS 版本控制的。在那个期间,我们的统一仓库里包含了来自 SCCS 的提交和快照的增量文件的导入数据。对于每个发行版,可用最近的时间戳找到该 SCCS 提交,并被标记为一个与发行版增量导入分支的合并。这些合并可以在[图2][29] 的中间看到。
|
||||
|
||||
将各种数据资源综合到一个仓库的工作,主要是用两个脚本来完成的。一个 780 行的 Perl 脚本(`import-dir.pl`)可以从一个单独的数据源(快照目录、SCCS 仓库,或者 Git 仓库)中,以 *Git fast export* 格式导出(真实的或者综合的)提交历史。输出是一个简单的文本格式,Git 工具用这个来导入和导出提交。其他方面,这个脚本以一些东西为参数,如文件到贡献者的映射、贡献者登录名和他们的全名间的映射、哪个导入的提交会被合并、哪些文件要处理和忽略、以及“引用”文件的处理。一个 450 行的 Shell 脚本创建 Git 仓库,并调用带适当参数的 Perl 脚本,来导入 27 个可用的历史数据资源。Shell 脚本也会运行 30 个测试,比较特定标签的仓库和对应的数据源,核对查看的目录中出现的和没出现的,并回溯查看分支树和合并的数量,*git blame* 和 *git log* 的输出。最后,调用 *git* 作垃圾收集和仓库压缩,从最初的 6GB 降到分发的 1GB 大小。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4、数据使用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
该数据可以用于软件工程、信息系统和软件考古学(software archeology)领域的经验性研究。鉴于它从不间断而独一无二的存在了超过了 40 年,可以供软件进化和跨代更迭参考。从那时以来,处理速度已经成千倍地增长、存储容量扩大了百万倍,该数据同样可以用于软件和硬件技术交叉进化(co-evolution)的研究。软件开发从研究中心到大学,到开源社区的转移,可以用来研究组织文化对于软件开发的影响。该仓库也可以用于学习著名人物的实际编程,比如 Turing 奖获得者(Dennis Ritchie 和 Ken Thompson)和 IT 产业的大佬(Bill Joy 和 Eric Schmidt)。另一个值得学习的现象是代码的长寿,无论是单行的水平,或是作为那个时代随 Unix 发布的完整的系统(Ingres、 Lisp、 Pascal、 Ratfor、 Snobol、 TMP),和导致代码存活或消亡的因素。最后,因为该数据让 Git 感到了压力,底层的软件仓库存储技术达到了其极限,这会推动版本管理系统领域的工程进度。
|
||||
|
||||
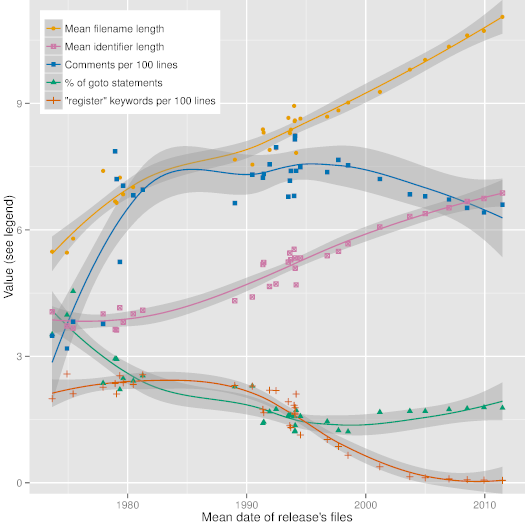
|
||||
|
||||
*图3:Unix 发行版的代码风格进化*
|
||||
|
||||
[图3][30] 根据 36 个主要 Unix 发行版描述了一些有趣的代码统计的趋势线(用 R 语言的局部多项式回归拟合函数生成),验证了代码风格和编程语言的使用在很长的时间尺度上的进化。这种进化是软硬件技术的需求和支持、软件构筑理论,甚至社会力量所驱动的。图片中的日期计算了出现在一个给定发行版中的所有文件的平均日期。正如可以从中看到,在过去的 40 年中,标示符和文件名字的长度已经稳步从 4 到 6 个字符增长到 7 到 11 个字符。我们也可以看到注释数量的少量稳步增加,以及 *goto* 语句的使用量减少,同时 *register* 这个类型修饰符的消失。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5、未来的工作 ###
|
||||
|
||||
可以做很多事情去提高仓库的正确性和有效性。创建过程以开源代码共享了,通过 GitHub 的拉取请求(pull request),可以很容易地贡献更多代码和修复。最有用的社区贡献将使得导入的快照文件的覆盖面增长,以便归属于某个具体的作者。现在,大约 90,000 个文件(在 160,000 总量之外)通过默认规则指定了作者。类似地,大约有 250 个作者(最初 FreeBSD 那些)仅知道其识别号。两个都列在了 build 仓库的 unmatched 目录里,欢迎贡献数据。进一步,BSD SCCS 和 FreeBSD CVS 的提交共享相同的作者和时间戳,这些可以结合成一个单独的 Git 提交。导入 SCCS 文件提交的支持会被添加进来,以便引入仓库对应的元数据。最后,也是最重要的,开源系统的更多分支会添加进来,比如 NetBSD、 OpenBSD、DragonFlyBSD 和 *illumos*。理想情况下,其他历史上重要的 Unix 发行版,如 System III、System V、 NeXTSTEP 和 SunOS 等的当前版权拥有者,也会在一个允许他们的合作伙伴使用仓库用于研究的协议下释出他们的系统。
|
||||
|
||||
### 鸣谢 ###
|
||||
|
||||
本文作者感谢很多付出努力的人们。 Brian W. Kernighan, Doug McIlroy 和 Arnold D. Robbins 在贝尔实验室(Bell Labs)的登录识别号方面提供了帮助。 Clem Cole, Era Erikson, Mary Ann Horton, Kirk McKusick, Jeremy C. Reed, Ingo Schwarze 和 Anatole Shaw 在 BSD 的登录识别号方面提供了帮助。BSD SCCS 的导入代码是基于 H. Merijn Brand 和 Jonathan Gray 的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
这次研究由欧盟 ( 欧洲社会基金(European Social Fund,ESF)) 和 希腊国家基金(Greek national funds)通过国家战略参考框架( National Strategic Reference Framework ,NSRF) 的 Operational Program " Education and Lifelong Learning" - Research Funding Program: Thalis - Athens University of Economics and Business - Software Engineering Research Platform ,共同出资赞助。
|
||||
|
||||
### 引用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
[[1]][31]
|
||||
M. D. McIlroy, E. N. Pinson, and B. A. Tague, "UNIX time-sharing system: Foreword," *The Bell System Technical Journal*, vol. 57, no. 6, pp. 1899-1904, July-August 1978.
|
||||
|
||||
[[2]][32]
|
||||
D. M. Ritchie and K. Thompson, "The UNIX time-sharing system," *Bell System Technical Journal*, vol. 57, no. 6, pp. 1905-1929, July-August 1978.
|
||||
|
||||
[[3]][33]
|
||||
D. M. Ritchie, "The evolution of the UNIX time-sharing system," *AT&T Bell Laboratories Technical Journal*, vol. 63, no. 8, pp. 1577-1593, Oct. 1984.
|
||||
|
||||
[[4]][34]
|
||||
P. H. Salus, *A Quarter Century of UNIX*. Boston, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1994.
|
||||
|
||||
[[5]][35]
|
||||
E. S. Raymond, *The Art of Unix Programming*. Addison-Wesley, 2003.
|
||||
|
||||
[[6]][36]
|
||||
M. J. Rochkind, "The source code control system," *IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering*, vol. SE-1, no. 4, pp. 255-265, 1975.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
#### 脚注 ####
|
||||
|
||||
[1][37] - [https://github.com/dspinellis/unix-history-repo][38]
|
||||
|
||||
[2][39] - Updates may add or modify material. To ensure replicability the repository's users are encouraged to fork it or archive it.
|
||||
|
||||
[3][40] - [http://www.tuhs.org/archive_sites.html][41]
|
||||
|
||||
[4][42] - [https://www.mckusick.com/csrg/][43]
|
||||
|
||||
[5][44] - [http://www.oldlinux.org/Linux.old/distributions/386BSD][45]
|
||||
|
||||
[6][46] - [http://ftp-archive.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD-Archive/old-releases/][47]
|
||||
|
||||
[7][48] - [https://github.com/freebsd/freebsd][49]
|
||||
|
||||
[8][50] - [http://ftp.netbsd.org/pub/NetBSD/NetBSD-current/src/share/misc/bsd-family-tree][51]
|
||||
|
||||
[9][52] - [https://github.com/dspinellis/unix-history-make][53]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Diomidis Spinellis
|
||||
译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#MPT78
|
||||
[2]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#RT78
|
||||
[3]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#Rit84
|
||||
[4]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#Sal94
|
||||
[5]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#Ray03
|
||||
[6]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#sec:data
|
||||
[7]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#sec:dev
|
||||
[8]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#sec:use
|
||||
[9]:https://github.com/dspinellis/unix-history-repo
|
||||
[10]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAB
|
||||
[11]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAC
|
||||
[12]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#fig:provenance
|
||||
[13]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#fig:branches
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tuhs.org/archive_sites.html
|
||||
[15]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAD
|
||||
[16]:https://www.mckusick.com/csrg/
|
||||
[17]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAE
|
||||
[18]:http://www.oldlinux.org/Linux.old/distributions/386BSD
|
||||
[19]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAF
|
||||
[20]:http://ftp-archive.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD-Archive/old-releases/
|
||||
[21]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAG
|
||||
[22]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#SCCS
|
||||
[23]:https://github.com/freebsd/freebsd
|
||||
[24]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAH
|
||||
[25]:http://ftp.netbsd.org/pub/NetBSD/NetBSD-current/src/share/misc/bsd-family-tree
|
||||
[26]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAI
|
||||
[27]:https://github.com/dspinellis/unix-history-make
|
||||
[28]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAJ
|
||||
[29]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#fig:branches
|
||||
[30]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#fig:metrics
|
||||
[31]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#CITEMPT78
|
||||
[32]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#CITERT78
|
||||
[33]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#CITERit84
|
||||
[34]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#CITESal94
|
||||
[35]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#CITERay03
|
||||
[36]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#CITESCCS
|
||||
[37]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAB
|
||||
[38]:https://github.com/dspinellis/unix-history-repo
|
||||
[39]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAC
|
||||
[40]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAD
|
||||
[41]:http://www.tuhs.org/archive_sites.html
|
||||
[42]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAE
|
||||
[43]:https://www.mckusick.com/csrg/
|
||||
[44]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAF
|
||||
[45]:http://www.oldlinux.org/Linux.old/distributions/386BSD
|
||||
[46]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAG
|
||||
[47]:http://ftp-archive.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD-Archive/old-releases/
|
||||
[48]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAH
|
||||
[49]:https://github.com/freebsd/freebsd
|
||||
[50]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAI
|
||||
[51]:http://ftp.netbsd.org/pub/NetBSD/NetBSD-current/src/share/misc/bsd-family-tree
|
||||
[52]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAJ
|
||||
[53]:https://github.com/dspinellis/unix-history-make
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,15 @@
|
||||
|
||||
如何在树莓派2 B型上安装 FreeBSD
|
||||
如何在树莓派 2B 上安装 FreeBSD
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在树莓派2 B型上如何安装 FreeBSD 10 或 FreeBSD 11(current)?怎么在 Linux,OS X,FreeBSD 或类 Unix 操作系统上烧录 SD 卡?
|
||||
在树莓派 2B 上如何安装 FreeBSD 10 或 FreeBSD 11(current)?怎么在 Linux,OS X,FreeBSD 或类 Unix 操作系统上烧录 SD 卡?
|
||||
|
||||
在树莓派2 B型上安装 FreeBSD 10或 FreeBSD 11(current)很容易。使用 FreeBSD 操作系统可以打造一个非常易用的 Unix 服务器。FreeBSD-CURRENT 自2012年十一月以来一直支持树莓派,2015年三月份后也开始支持树莓派2了。在这个快速教程中我将介绍如何在 RPI2 上安装 FreeBSD 11 current arm 版。
|
||||
在树莓派 2B 上安装 FreeBSD 10 或 FreeBSD 11(current)很容易。使用 FreeBSD 操作系统可以打造一个非常易用的 Unix 服务器。FreeBSD-CURRENT 自2012年十一月以来一直支持树莓派,2015年三月份后也开始支持树莓派2了。在这个快速教程中我将介绍如何在树莓派 2B 上安装 FreeBSD 11 current arm 版。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 下载 FreeBSD-current 的 arm 镜像 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以 [访问这个页面来下载][1] 树莓派2的镜像。使用 wget 或 curl 命令来下载镜像:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget ftp://ftp.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD/snapshots/arm/armv6/ISO-IMAGES/11.0/FreeBSD-11.0-CURRENT-arm-armv6-RPI2-20151016-r289420.img.xz
|
||||
|
||||
或
|
||||
@ -45,52 +44,51 @@
|
||||
1024+0 records out
|
||||
1073741824 bytes transferred in 661.669584 secs (1622776 bytes/sec)
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 Linux/FreeBSD 或者 类 Unix 系统来烧录 FreeBSD-current ####
|
||||
#### 使用 Linux/FreeBSD 或者类 Unix 系统来烧录 FreeBSD-current ####
|
||||
|
||||
语法是这样:
|
||||
|
||||
$ dd if=FreeBSD-11.0-CURRENT-arm-armv6-RPI2-20151016-r289420.img of=/dev/sdb bs=1M
|
||||
|
||||
确保使用实际 SD 卡的设备名称来替换 /dev/sdb 。
|
||||
**确保使用实际的 SD 卡的设备名称来替换 /dev/sdb**(LCTT 译注:千万注意不要写错了)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 引导 FreeBSD ###
|
||||
|
||||
在树莓派2 B型上插入 SD 卡。你需要连接键盘,鼠标和显示器。我使用的是 USB 转串口线来连接显示器的:
|
||||
在树莓派 2B 上插入 SD 卡。你需要连接键盘,鼠标和显示器。我使用的是 USB 转串口线来连接显示器的:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
图01 RPI 基于 USB 的串行连接
|
||||
*图01 基于树莓派 USB 的串行连接*
|
||||
|
||||
在下面的例子中,我使用 screen 命令来连接我的 RPI:
|
||||
|
||||
## Linux version ##
|
||||
## Linux 上 ##
|
||||
screen /dev/tty.USB0 115200
|
||||
|
||||
## OS X version ##
|
||||
## OS X 上 ##
|
||||
screen /dev/cu.usbserial 115200
|
||||
|
||||
## Windows user use Putty.exe ##
|
||||
## Windows 请使用 Putty.exe ##
|
||||
|
||||
FreeBSD RPI 启动输出样例:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
图01: 在 RPi 2上引导 FreeBSD-current
|
||||
*图02: 在树莓派 2上引导 FreeBSD-current*
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. FreeBSD 在 RPi 2上的用户名和密码 ###
|
||||
|
||||
默认的密码是 freebsd/freebsd 和 root/root。
|
||||
|
||||
到此为止, FreeBSD-current 已经安装并运行在 RPi 2上。
|
||||
到此为止, FreeBSD-current 已经安装并运行在树莓派 2上。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/how-to-install-freebsd-on-raspberry-pi-2-model-b/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Vivek Gite][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/strugglingyouth)
|
||||
译者:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/strugglingyouth)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
||||
黑客利用 Wi-Fi 攻击你的七种方法
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 黑客利用 Wi-Fi 侵犯你隐私的七种方法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Wi-Fi — 啊,你是如此的方便,却又如此的危险!
|
||||
|
||||
这里给大家介绍一下通过Wi-Fi连接“慷慨捐赠”你的身份信息的七种方法和反制措施。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 利用免费热点 ###
|
||||
|
||||
它们似乎无处不在,而且它们的数量会在[接下来四年里增加三倍][1]。但是它们当中很多都是不值得信任的,从你的登录凭证、email 甚至更加敏感的账户,都能被黑客用“嗅探器(sniffers)”软件截获 — 这种软件能截获到任何你通过该连接提交的信息。防止被黑客盯上的最好办法就是使用VPN(虚拟私有网virtual private network),它加密了你所输入的信息,因此能够保护你的数据隐私。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 网上银行 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可能认为没有人需要被提醒不要使用免费 Wi-Fi 来操作网上银行, 但网络安全厂商卡巴斯基实验室表示**[全球超过100家银行因为网络黑客而损失9亿美元][2]**,由此可见还是有很多人因此受害。如果你确信一家咖啡店的免费 Wi-Fi 是正规的,想要连接它,那么你应该向服务员确认网络名称。[其他人在店里用路由器设置一个开放的无线连接][3],并将它的网络名称设置成店名是一件相当简单的事。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 始终开着 Wi-Fi 开关 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你手机的 Wi-Fi 开关一直开着的,你会自动被连接到一个不安全的网络中去,你甚至都没有意识到。你可以利用你手机中[基于位置的 Wi-Fi 功能][4],如果有这种功能的话,那它会在你离开你所保存的网络范围后自动关闭你的 Wi-Fi 开关并在你回去之后再次开启。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 不使用防火墙 ###
|
||||
|
||||
防火墙是你的第一道抵御恶意入侵的防线,它能有效地让你的电脑网络保持通畅并阻挡黑客和恶意软件。你应该时刻开启它除非你的杀毒软件有它自己的防火墙。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 浏览非加密网页 ###
|
||||
|
||||
说起来很难过,**[世界上排名前100万个网站中55%是不加密的][5]**,一个未加密的网站会让一切传输数据暴露在黑客的眼中。如果一个网页是安全的,你的浏览器则会有标明(比如说火狐浏览器是一把灰色的挂锁,Chrome 浏览器则是个绿锁图标)。但是即使是安全的网站不能让你免于被劫持的风险,他们能通过公共网络从你访问过的网站上窃取 cookies,无论是不是正规网站。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 不更新你的安全防护软件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要确保你自己的网络是受保护的,就更新路由器固件。你要做的就是进入你的路由器管理页面去检查,通常你能在厂商的官方网页上下载到最新的固件版本。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 不保护你的家用 Wi-Fi ###
|
||||
|
||||
不用说,设置一个复杂的密码和更改无线连接的默认名都是非常重要的。你还可以过滤你的 MAC 地址来让你的路由器只识别那些确认过的设备。
|
||||
|
||||
本文作者 **Josh Althuser** 是一个开源支持者、网络架构师和科技企业家。在过去12年里,他花了很多时间去倡导使用开源软件来管理团队和项目,同时为网络应用程序提供企业级咨询并帮助它们把产品推向市场。你可以通过[他的推特][6]联系他。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.networkworld.com/article/3003170/mobile-security/7-ways-hackers-can-use-wi-fi-against-you.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Josh Althuser][a]
|
||||
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://twitter.com/JoshAlthuser
|
||||
[1]:http://www.pcworld.com/article/243464/number_of_wifi_hotspots_to_quadruple_by_2015_says_study.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.nytimes.com/2015/02/15/world/bank-hackers-steal-millions-via-malware.html?hp&action=click&pgtype=Homepage&module=first-column-region%C2%AEion=top-news&WT.nav=top-news&_r=3
|
||||
[3]:http://news.yahoo.com/blogs/upgrade-your-life/banking-online-not-hacked-182159934.html
|
||||
[4]:http://pocketnow.com/2014/10/15/should-you-leave-your-smartphones-wifi-on-or-turn-it-off
|
||||
[5]:http://www.cnet.com/news/chrome-becoming-tool-in-googles-push-for-encrypted-web/
|
||||
[6]:https://twitter.com/JoshAlthuser
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu 中安装最新的 Arduino IDE 1.6.6
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> 本篇教程会教你如何在当前的 Ubuntu 发行版中安装最新的 Arduino IDE 1.6.6。
|
||||
|
||||
开源的 Arduino IDE 发布了1.6.6,并带来了很多的改变。新的发布已经切换到 Java 8,它与 IDE 绑定并且用于编译所需。具体见 [发布说明][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
对于那些不想使用软件中心的 1.0.5 旧版本的人而言,你可以使用下面的步骤在所有的 Ubuntu 发行版中安装 Arduino。
|
||||
|
||||
> **请用正确版本号替换软件包的版本号**
|
||||
|
||||
**1、** 从下面的官方链接下载最新的包 **Linux 32-bit 或者 Linux 64-bit**。
|
||||
|
||||
- [https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software][2]
|
||||
|
||||
如果不知道你系统的类型?进入系统设置->详细->概览。
|
||||
|
||||
**2、** 从Unity Dash、App Launcher 或者使用 Ctrl+Alt+T 打开终端。打开后,一个个运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
进入下载文件夹:
|
||||
|
||||
cd ~/Downloads
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用 tar 命令解压:
|
||||
|
||||
tar -xvf arduino-1.6.6-*.tar.xz
|
||||
|
||||
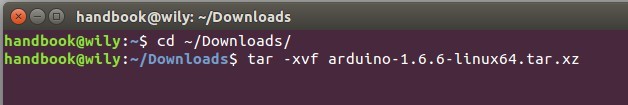
|
||||
|
||||
将解压后的文件移动到**/opt/**下:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo mv arduino-1.6.6 /opt
|
||||
|
||||
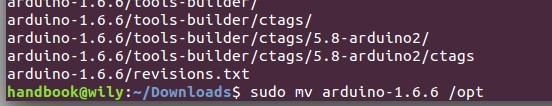
|
||||
|
||||
**3、** 现在 IDE 已经与最新的 Java 绑定使用了。但是最好为程序设置一个桌面图标/启动方式:
|
||||
|
||||
进入安装目录:
|
||||
|
||||
cd /opt/arduino-1.6.6/
|
||||
|
||||
在这个目录给 install.sh 可执行权限
|
||||
|
||||
chmod +x install.sh
|
||||
|
||||
最后运行脚本同时安装桌面快捷方式和启动图标:
|
||||
|
||||
./install.sh
|
||||
|
||||
下图中我用“&&”同时运行这三个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
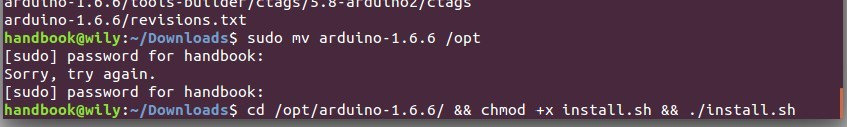
|
||||
|
||||
最后从 Unity Dash、程序启动器或者桌面快捷方式运行 Arduino IDE。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/2015/11/install-arduino-ide-1-6-6-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ji m][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/about/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/ReleaseNotes
|
||||
[2]:https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
可以在 Linux 下试试苹果编程语言 Swift
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
是的,你知道的,苹果编程语言 Swift 已经开源了。其实我们并不应该感到意外,因为[在六个月以前苹果就已经宣布了这个消息][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
苹果宣布推出开源 Swift 社区。一个专用于开源 Swift 社区的[新网站][2]已经就位,网站首页显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
> 我们对 Swift 开源感到兴奋。在苹果推出了编程语言 Swift 之后,它很快成为历史上增长最快的语言之一。Swift 可以编写出难以置信的又快又安全的软件。目前,Swift 是开源的,你可以将这个最好的通用编程语言用在各种地方。
|
||||
|
||||
[swift.org][2] 这个网站将会作为一站式网站,它会提供各种资料的下载,包括各种平台,社区指南,最新消息,入门教程,为开源 Swift 做贡献的说明,文件和一些其他的指南。 如果你正期待着学习 Swift,那么必须收藏这个网站。
|
||||
|
||||
在苹果的这次宣布中,一个用于方便分享和构建代码的包管理器已经可用了。
|
||||
|
||||
对于所有的 Linux 使用者来说,最重要的是,源代码已经可以从 [Github][3]获得了.你可以从以下链接 Checkout 它:
|
||||
|
||||
- [苹果 Swift 源代码][3]
|
||||
|
||||
除此之外,对于 ubuntu 14.04 和 15.10 版本还有预编译的二进制文件。
|
||||
|
||||
- [ubuntu 系统的 Swift 二进制文件][4]
|
||||
|
||||
不要急着在产品环境中使用它们,因为这些都是开发分支而不适合于产品环境。因此现在应避免使用在产品环境中,一旦发布了 Linux 下 Swift 的稳定版本,我希望 ubuntu 会把它包含在 [umake][5]中,和 [Visual Studio Code][6] 放一起。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/swift-open-source-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[Flowsnow](https://github.com/Flowsnow)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/apple-open-sources-swift-programming-language-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://swift.org/
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/apple
|
||||
[4]:https://swift.org/download/#latest-development-snapshots
|
||||
[5]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-make
|
||||
[6]:http://itsfoss.com/install-visual-studio-code-ubuntu/
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
|
||||
自定义Ubuntu面板时间日期显示格式
|
||||
如何深度定制 Ubuntu 面板的时间日期显示格式
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
尽管设置里已经有一些选项可以用了,这个快速教程会向你展示如何更加深入地自定义 Ubuntu 面板上的时间和日期指示器。
|
||||
尽管设置页面里已经有一些选项可以用了,这个快速教程会向你展示如何更加深入地自定义 Ubuntu 面板上的时间和日期指示器。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在开始之前,在 Ubuntu 软件中心搜索并安装 **dconf Editor**。然后启动该软件并按以下步骤执行:
|
||||
|
||||
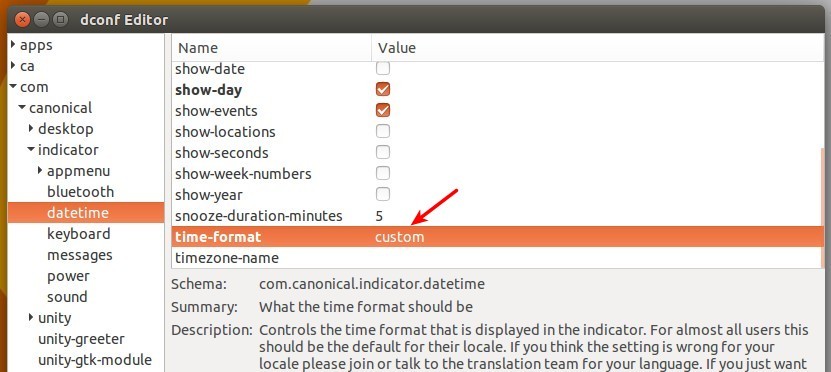
**1.** 当 dconf Editor 启动后,导航至 **com -> canonical -> indicator -> datetime**。将 **time-format** 的值设置为 **custom**。
|
||||
**1、** 当 dconf Editor 启动后,导航至 **com -> canonical -> indicator -> datetime**。将 **time-format** 的值设置为 **custom**。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,11 +16,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
gsettings set com.canonical.indicator.datetime time-format 'custom'
|
||||
|
||||
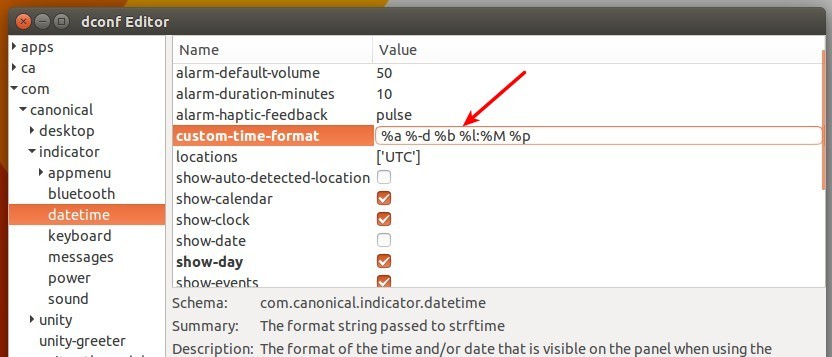
**2.** 现在你可以通过编辑 **custom-time-format** 的值来自定义时间和日期的格式。
|
||||
**2、** 现在你可以通过编辑 **custom-time-format** 的值来自定义时间和日期的格式。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以通过命令完成:(译注:将 FORMAT_VALUE_HERE 替换为所需要的格式值)
|
||||
你也可以通过命令完成:(LCTT 译注:将 FORMAT_VALUE_HERE 替换为所需要的格式值)
|
||||
|
||||
gsettings set com.canonical.indicator.datetime custom-time-format 'FORMAT_VALUE_HERE'
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,29 +30,28 @@
|
||||
- %A = 星期名完整拼写
|
||||
- %b = 月份名缩写
|
||||
- %B = 月份名完整拼写
|
||||
- %d = 按月计日期
|
||||
- %d = 每月的日期
|
||||
- %l = 小时 ( 1..12), %I = 小时 (01..12)
|
||||
- %k = 小时 ( 1..23), %H = 小时 (01..23)
|
||||
- %M = 分钟 (00..59)
|
||||
- %p = 午别,AM 或 PM, %P = am 或 pm.
|
||||
- %S = 秒 (00..59)
|
||||
- 打开终端键入命令 `man date` 并执行以了解更多细节。
|
||||
|
||||
一些例子:
|
||||
可以打开终端键入命令 `man date` 并执行以了解更多细节。
|
||||
|
||||
自定义时间日期显示格式值:
|
||||
一些自定义时间日期显示格式值的例子:
|
||||
|
||||
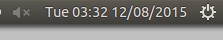
**%a %H:%M %m/%d/%Y**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
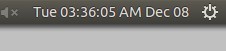
**%a %r %b %d or %a %I:%M:%S %p %b %d**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**%a %-d %b %l:%M %P %z**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,7 +59,7 @@ via: http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/2015/12/time-date-format-ubuntu-panel/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ji m][a]
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,100 @@
|
||||
如何在 CentOS 上启用 软件集 Software Collections(SCL)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
红帽企业版 linux(RHEL)和它的社区版分支——CentOS,提供10年的生命周期,这意味着 RHEL/CentOS 的每个版本会提供长达10年的安全更新。虽然这么长的生命周期为企业用户提供了迫切需要的系统兼容性和可靠性,但也存在一个缺点:随着底层的 RHEL/CentOS 版本接近生命周期的结束,核心应用和运行时环境变得陈旧过时。例如 CentOS 6.5,它的生命周期结束时间是2020年11月30日,其所携带的 Python 2.6.6和 MySQL 5.1.73,以今天的标准来看已经非常古老了。
|
||||
|
||||
另一方面,在 RHEL/CentOS 上试图手动升级开发工具链和运行时环境存在使系统崩溃的潜在可能,除非所有依赖都被正确解决。通常情况下,手动升级都是不推荐的,除非你知道你在干什么。
|
||||
|
||||
[软件集(Software Collections)][1](SCL)源出现了,以帮助解决 RHEL/CentOS 下的这种问题。SCL 的创建就是为了给 RHEL/CentOS 用户提供一种以方便、安全地安装和使用应用程序和运行时环境的多个(而且可能是更新的)版本的方式,同时避免把系统搞乱。与之相对的是第三方源,它们可能会在已安装的包之间引起冲突。
|
||||
|
||||
最新的 SCL 提供了:
|
||||
|
||||
- Python 3.3 和 2.7
|
||||
- PHP 5.4
|
||||
- Node.js 0.10
|
||||
- Ruby 1.9.3
|
||||
- Perl 5.16.3
|
||||
- MariaDB 和 MySQL 5.5
|
||||
- Apache httpd 2.4.6
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇教程的剩余部分,我会展示一下如何配置 SCL 源,以及如何安装和启用 SCL 中的包。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置 SCL 源
|
||||
|
||||
SCL 可用于 CentOS 6.5 及更新的版本。要配置 SCL 源,只需执行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install centos-release-SCL
|
||||
|
||||
要启用和运行 SCL 中的应用,你还需要安装下列包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install scl-utils-build
|
||||
|
||||
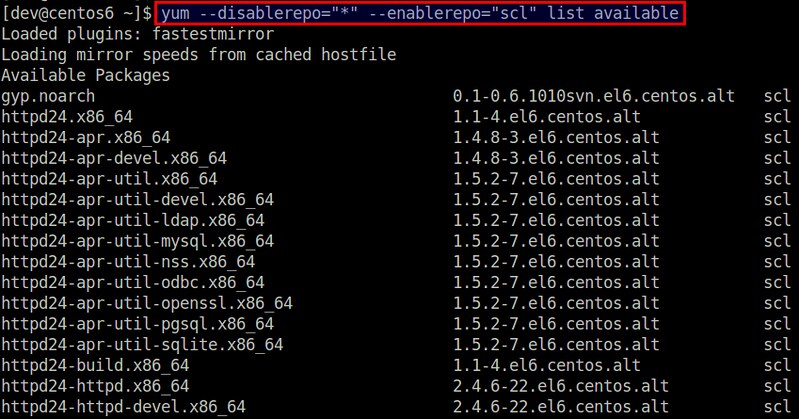
执行下面的命令可以查看 SCL 中可用包的完整列表:
|
||||
|
||||
$ yum --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo="scl" list available
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 从 SCL 中安装和启用包
|
||||
|
||||
既然你已配置好了 SCL,你可以继续并从 SCL 中安装包了。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以搜索 SCL 中的包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ yum --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo="scl" search <keyword>
|
||||
|
||||
我们假设你要安装 Python 3.3。
|
||||
|
||||
继续,就像通常安装包那样使用 yum 安装:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install python33
|
||||
|
||||
任何时候你都可以查看从 SCL 中安装的包的列表,只需执行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ scl --list
|
||||
|
||||
python33
|
||||
|
||||
SCL 的优点之一是安装其中的包不会覆盖任何系统文件,并且保证不会引起与系统中其它库和应用的冲突。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,如果在安装 python33 包后检查默认的 python 版本,你会发现默认的版本并没有改变:
|
||||
|
||||
$ python --version
|
||||
|
||||
Python 2.6.6
|
||||
|
||||
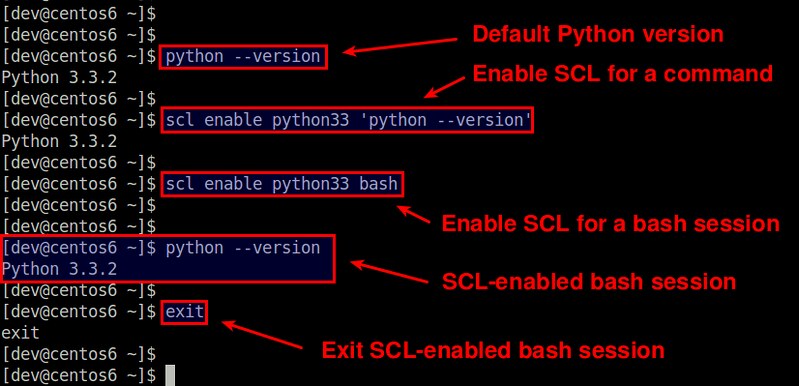
如果想使用一个已经安装的 SCL 包,你需要在每个命令中使用 `scl` 命令显式启用它(LCTT 译注:即想在哪条命令中使用 SCL 中的包,就得通过`scl`命令执行该命令)
|
||||
|
||||
$ scl enable <scl-package-name> <command>
|
||||
|
||||
例如,要针对`python`命令启用 python33 包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ scl enable python33 'python --version'
|
||||
|
||||
Python 3.3.2
|
||||
|
||||
如果想在启用 python33 包时执行多条命令,你可以像下面那样创建一个启用 SCL 的 bash 会话:
|
||||
|
||||
$ scl enable python33 bash
|
||||
|
||||
在这个 bash 会话中,默认的 python 会被切换为3.3版本,直到你输入`exit`,退出会话。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
简而言之,SCL 有几分像 Python 的虚拟环境,但更通用,因为你可以为远比 Python 更多的应用启用/禁用 SCL 会话。
|
||||
|
||||
更详细的 SCL 指南,参考官方的[快速入门指南][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/enable-software-collections-centos.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[bianjp](https://github.com/bianjp)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:https://www.softwarecollections.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.softwarecollections.org/docs/
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,17 @@
|
||||
Linux/Unix桌面趣事:让桌面下雪
|
||||
Linux/Unix 桌面趣事:让桌面下雪
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在这个节日里感到孤独么?试一下Xsnow吧。它是一个可以在Unix/Linux桌面下下雪的app。圣诞老人和他的驯鹿会在屏幕中奔跑,伴随着雪片让你感受到节日的感觉。
|
||||
|
||||
我第一次是再13、4年前安装的它。它最初是在1984年Macintosh系统中创造的。你可以用下面的方法来安装:
|
||||
在这个节日里感到孤独么?试一下 Xsnow 吧。它是一个可以在 Unix/Linux 桌面下下雪的应用。圣诞老人和他的驯鹿会在屏幕中奔跑,伴随着雪片让你感受到节日的感觉。
|
||||
|
||||
我第一次安装它还是在 13、4 年前。它最初是在 1984 年 Macintosh 系统中创造的。你可以用下面的方法来安装:
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 xsnow ###
|
||||
|
||||
Debian/Ubuntu/Mint用户用下面的命令:
|
||||
Debian/Ubuntu/Mint 用户用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install xsnow
|
||||
|
||||
Freebsd用户输入下面的命令:
|
||||
Freebsd 用户输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /usr/ports/x11/xsnow/
|
||||
# make install clean
|
||||
@ -21,13 +22,13 @@ Freebsd用户输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 其他发行版的方法 ####
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fedora/RHEL/CentOS在[rpmfusion][1]仓库中找找。
|
||||
2. Gentoo用户试下Gentoo portage也就是[emerge -p xsnow][2]
|
||||
3. Opensuse用户使用yast搜索xsnow
|
||||
1. Fedora/RHEL/CentOS 在 [rpmfusion][1] 仓库中找找。
|
||||
2. Gentoo 用户试下 Gentoo portage,也就是[emerge -p xsnow][2]
|
||||
3. Opensuse 用户使用 yast 搜索 xsnow
|
||||
|
||||
### 我该如何使用xsnow? ###
|
||||
### 我该如何使用 xsnow? ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端(程序 > 附件 > 终端),输入下面的额命令启动xsnow:
|
||||
打开终端(程序 > 附件 > 终端),输入下面的额命令启动 xsnow:
|
||||
|
||||
$ xsnow
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,13 +36,13 @@ Freebsd用户输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
图01: 在Linux和Unix桌面中显示雪花
|
||||
*图01: 在 Linux 和 Unix 桌面中显示雪花*
|
||||
|
||||
你可以设置背景位蓝色,并让它下白雪,输入:
|
||||
你可以设置背景为蓝色,并让它下白雪,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ xsnow -bg blue -sc snow
|
||||
|
||||
设置最大的雪片数量,并让它尽可能快地运行,输入:
|
||||
设置最大的雪片数量,并让它尽可能快地掉下,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ xsnow -snowflakes 10000 -delay 0
|
||||
|
||||
@ -49,14 +50,14 @@ Freebsd用户输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ xsnow -notrees -nosanta
|
||||
|
||||
关于xsnow更多的信息和选项,在命令行下输入man xsnow查看手册:
|
||||
关于 xsnow 更多的信息和选项,在命令行下输入 man xsnow 查看手册:
|
||||
|
||||
$ man xsnow
|
||||
|
||||
建议阅读
|
||||
|
||||
- 官网[下载 Xsnow][1]
|
||||
- 注意[MS-Windows][2]和[Mac OS X version][3]有一次性的共享软件费用。
|
||||
- 注意 [MS-Windows][2] 和 [Mac OS X][3] 版本有一次性的共享软件费用。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,7 +65,7 @@ via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-unix-xsnow.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,30 +1,31 @@
|
||||
Linux/Unix 桌面趣事:蒸汽火车
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
一个[最常见的错误][1]是把ls输入成了sl。我已经设置了[一个alias][2],也就是alias sl=ls。但是你也许就错过了带汽笛的蒸汽小火车了。
|
||||
一个你[经常犯的错误][1]是把 ls 输入成了 sl。我已经设置了[一个别名][2],也就是 `alias sl=ls`。但是这样你也许就错过了这辆带汽笛的蒸汽小火车了。
|
||||
|
||||
sl是一个玩笑软件或是一个Unix游戏。它会在你错误地把“ls”输入成“sl”(Steam Locomotive)后出现一辆蒸汽火车穿过你的屏幕。
|
||||
sl 是一个搞笑软件或,也是一个 Unix 游戏。它会在你错误地把“ls”输入成“sl”(Steam Locomotive)后出现一辆蒸汽火车穿过你的屏幕。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 sl ###
|
||||
|
||||
在Debian/Ubuntu下输入下面的命令:
|
||||
在 Debian/Ubuntu 下输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install sl
|
||||
|
||||
它同样也在Freebsd和其他类Unix的操作系统上存在。下面把ls输错成sl:
|
||||
它同样也在 Freebsd 和其他类Unix的操作系统上存在。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,让我们把 ls 输错成 sl:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sl
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
图01: 如果你把“ls”输入成“sl”蒸汽火车会穿过你的屏幕。
|
||||
*图01: 如果你把 “ls” 输入成 “sl” ,蒸汽火车会穿过你的屏幕。*
|
||||
|
||||
It also supports the following options:
|
||||
它同样支持下面的选项:
|
||||
|
||||
- **-a** : 似乎发生了意外。你会哭喊求助的人们感到难过。
|
||||
- **-a** : 似乎发生了意外。你会为那些哭喊求助的人们感到难过。
|
||||
- **-l** : 显示小一点的火车
|
||||
- **-F** : 它飞走
|
||||
- **-e** : 允许被Ctrl+C终端
|
||||
- **-F** : 它居然飞走了
|
||||
- **-e** : 允许被 Ctrl+C 中断
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,7 +33,7 @@ via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/displays-animations-when-accidentally-you-typ
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
||||
Linux/Unix桌面趣事:终端ASCII水族箱
|
||||
Linux/Unix 桌面趣事:终端 ASCII 水族箱
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
你可以在你的终端中使用ASCIIQuarium安全地欣赏海洋的神秘了。它是一个用perl写的ASCII艺术水族箱/海洋动画。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在你的终端中使用 ASCIIQuarium 安全地欣赏海洋的神秘了。它是一个用 perl 写的 ASCII 艺术水族箱/海洋动画。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 Term::Animation ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
首先你需要安装名为Term-Animation的perl模块。打开终端(选择程序 > 附件 > 终端),并输入:
|
||||
首先你需要安装名为 Term-Animation 的perl模块。打开终端(选择程序 > 附件 > 终端),并输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install libcurses-perl
|
||||
$ cd /tmp
|
||||
@ -15,9 +15,9 @@ Linux/Unix桌面趣事:终端ASCII水族箱
|
||||
$ perl Makefile.PL && make && make test
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载安装ASCIIQuarium ###
|
||||
### 下载安装 ASCIIQuarium ###
|
||||
|
||||
接着再终端中输入:
|
||||
接着在终端中输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /tmp
|
||||
$ wget http://www.robobunny.com/projects/asciiquarium/asciiquarium.tar.gz
|
||||
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ Linux/Unix桌面趣事:终端ASCII水族箱
|
||||
$ sudo cp asciiquarium /usr/local/bin
|
||||
$ sudo chmod 0755 /usr/local/bin/asciiquarium
|
||||
|
||||
### 我怎么浏览ASCII水族箱? ###
|
||||
### 我怎么观赏 ASCII 水族箱? ###
|
||||
|
||||
输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,8 @@ Linux/Unix桌面趣事:终端ASCII水族箱
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*ASCII 水族箱*
|
||||
|
||||
### 相关媒体 ###
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
@ -45,9 +47,9 @@ Linux/Unix桌面趣事:终端ASCII水族箱
|
||||
|
||||
[视频01: ASCIIQuarium - Linux/Unix桌面上的海洋动画][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载:ASCII Aquarium的KDE和Mac OS X版本 ###
|
||||
### 下载:ASCII Aquarium 的 KDE 和 Mac OS X 版本 ###
|
||||
|
||||
[下载asciiquarium][2]。如果你运行的是Mac OS X,试下一个可以直接使用已经打包好的[版本][3]。对于KDE用户,试试基于Asciiquarium的[KDE屏幕保护程序][4]
|
||||
[点此下载 asciiquarium][2]。如果你运行的是 Mac OS X,试下这个可以直接使用的已经打包好的[版本][3]。对于 KDE 用户,试试基于 Asciiquarium 的[KDE 屏幕保护程序][4]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -55,7 +57,7 @@ via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-unix-apple-osx-terminal-ascii-aquarium.
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
Linux/Unix桌面趣事:猫和老鼠在屏幕中追逐
|
||||
Linux/Unix桌面趣事:显示器里的猫和老鼠
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Oneko是一个有趣的app。它会把你的光标变成一直老鼠,并在后面创建一个可爱的小猫,并且始终在老鼠光标后面追着。单词“neko”再日语中的意思是老鼠。它最初是作为Macintosh桌面附件由一位日本人开发的。
|
||||
Oneko 是一个有趣的应用。它会把你的光标变成一只老鼠,并在后面创建一个可爱的小猫,并且始终追逐着老鼠光标。单词“neko”在日语中的意思是老鼠。它最初是一位日本人开发的 Macintosh 桌面附件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 oneko ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -29,19 +29,18 @@ Oneko是一个有趣的app。它会把你的光标变成一直老鼠,并在后
|
||||
Setting up oneko (1.2.sakura.6-7) ...
|
||||
Processing triggers for menu ...
|
||||
|
||||
FreeBSD用户输入下面的命令安装oneko:
|
||||
FreeBSD 用户输入下面的命令安装 oneko:
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /usr/ports/games/oneko
|
||||
# make install clean
|
||||
|
||||
### 我该如何使用oneko? ###
|
||||
### 我该如何使用 oneko? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Simply type the following command:
|
||||
输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ oneko
|
||||
|
||||
你可以把猫变成“tora-neko”,一只像白老虎条纹的猫:
|
||||
你可以把猫变成 “tora-neko”,一只像白老虎条纹的猫:
|
||||
|
||||
$ oneko -tora
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,19 +65,18 @@ Simply type the following command:
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
<iframe width="596" height="335" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/Nm3SkXThL0s"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
(Video.01: 示例 - 在Linux下安装和使用oneko)
|
||||
(Video.01: 示例 - 在 Linux 下安装和使用 oneko)
|
||||
|
||||
### 其他选项 ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can pass the following options:
|
||||
你可以传入下面的选项
|
||||
|
||||
1.**-tofocus**:让猫再聚焦的窗口顶部奔跑。当聚焦的窗口不在视野中时,猫像平常那样追逐老鼠。
|
||||
1. **-tofocus**:让猫在获得焦点的窗口顶部奔跑。当获得焦点的窗口不在视野中时,猫像平常那样追逐老鼠。
|
||||
2. **-position 坐标** :指定X和Y来调整猫相对老鼠的位置
|
||||
3. **-rv**:将前景色和背景色对调
|
||||
4. **-fg 颜色** : 前景色 (比如 oneko -dog -fg red)。
|
||||
5. **-bg 颜色** : 背景色 (比如 oneko -dog -bg green)。
|
||||
6. 查看oneko的手册获取更多信息。
|
||||
6. 查看 oneko 的手册获取更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -86,6 +84,6 @@ via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/open-source/oneko-app-creates-cute-cat-chasing-aro
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,229 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by H-mudcup
|
||||
Great Open Source Collaborative Editing Tools
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In a nutshell, collaborative writing is writing done by more than one person. There are benefits and risks of collaborative working. Some of the benefits include a more integrated / co-ordinated approach, better use of existing resources, and a stronger, united voice. For me, the greatest advantage is one of the most transparent. That's when I need to take colleagues' views. Sending files back and forth between colleagues is inefficient, causes unnecessary delays and leaves people (i.e. me) unhappy with the whole notion of collaboration. With good collaborative software, I can share notes, data and files, and use comments to share thoughts in real-time or asynchronously. Working together on documents, images, video, presentations, and tasks is made less of a chore.
|
||||
|
||||
There are many ways to collaborate online, and it has never been easier. This article highlights my favourite open source tools to collaborate on documents in real time.
|
||||
|
||||
Google Docs is an excellent productivity application with most of the features I need. It serves as a collaborative tool for editing documents in real time. Documents can be shared, opened, and edited by multiple users simultaneously and users can see character-by-character changes as other collaborators make edits. While Google Docs is free for individuals, it is not open source.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is my take on the finest open source collaborative editors which help you focus on writing without interruption, yet work mutually with others.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Hackpad ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Hackpad is an open source web-based realtime wiki, based on the open source EtherPad collaborative document editor.
|
||||
|
||||
Hackpad allows users to share your docs realtime and it uses color coding to show which authors have contributed to which content. It also allows in line photos, checklists and can also be used for coding as it offers syntax highlighting.
|
||||
|
||||
While Dropbox acquired Hackpad in April 2014, it is only this month that the software has been released under an open source license. It has been worth the wait.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Very rich set of functions, similar to those offered by wikis
|
||||
- Take collaborative notes, share data and files, and use comments to share your thoughts in real-time or asynchronously
|
||||
- Granular privacy permissions enable you to invite a single friend, a dozen teammates, or thousands of Twitter followers
|
||||
- Intelligent execution
|
||||
- Directly embed videos from popular video sharing sites
|
||||
- Tables
|
||||
- Syntax highlighting for most common programming languages including C, C#, CSS, CoffeeScript, Java, and HTML
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [hackpad.com][1]
|
||||
- Source code: [github.com/dropbox/hackpad][2]
|
||||
- Developer: [Contributors][3]
|
||||
- License: Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
- Version Number: -
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Etherpad ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Etherpad is an open source web-based collaborative real-time editor, allowing authors to simultaneously edit a text document leave comments, and interact with others using an integrated chat.
|
||||
|
||||
Etherpad is implemented in JavaScript, on top of the AppJet platform, with the real-time functionality achieved using Comet streaming.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Well designed spartan interface
|
||||
- Simple text formatting features
|
||||
- "Time slider" - explore the history of a pad
|
||||
- Download documents in plain text, PDF, Microsoft Word, Open Document, and HTML
|
||||
- Auto-saves the document at regular, short intervals
|
||||
- Highly customizable
|
||||
- Client side plugins extend the editor functionality
|
||||
- Hundreds of plugins extend Etherpad including support for email notifications, pad management, authentication
|
||||
- Accessibility enabled
|
||||
- Interact with Pad contents in real time from within Node and from your CLI
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [etherpad.org][4]
|
||||
- Source code: [github.com/ether/etherpad-lite][5]
|
||||
- Developer: David Greenspan, Aaron Iba, J.D. Zamfiresc, Daniel Clemens, David Cole
|
||||
- License: Apache License Version 2.0
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.5.7
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Firepad ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Firepad is an open source, collaborative text editor. It is designed to be embedded inside larger web applications with collaborative code editing added in only a few days.
|
||||
|
||||
Firepad is a full-featured text editor, with capabilities like conflict resolution, cursor synchronization, user attribution, and user presence detection. It uses Firebase as a backend, and doesn't need any server-side code. It can be added to any web app. Firepad can use either the CodeMirror editor or the Ace editor to render documents, and its operational transform code borrows from ot.js.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to extend your web application capabilities by adding the simple document and code editor, Firepad is perfect.
|
||||
|
||||
Firepad is used by several editors, including the Atlassian Stash Realtime Editor, Nitrous.IO, LiveMinutes, and Koding.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- True collaborative editing
|
||||
- Intelligent OT-based merging and conflict resolution
|
||||
- Support for both rich text and code editing
|
||||
- Cursor position synchronization
|
||||
- Undo / redo
|
||||
- Text highlighting
|
||||
- User attribution
|
||||
- Presence detection
|
||||
- Version checkpointing
|
||||
- Images
|
||||
- Extend Firepad through its API
|
||||
- Supports all modern browsers: Chrome, Safari, Opera 11+, IE8+, Firefox 3.6+
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.firepad.io][6]
|
||||
- Source code: [github.com/firebase/firepad][7]
|
||||
- Developer: Michael Lehenbauer and the team at Firebase
|
||||
- License: MIT
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.1.1
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### OwnCloud Documents ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ownCloud Documents is an ownCloud app to work with office documents alone and/or collaboratively. It allows up to 5 individuals to collaborate editing .odt and .doc files in a web browser.
|
||||
|
||||
ownCloud is a self-hosted file sync and share server. It provides access to your data through a web interface, sync clients or WebDAV while providing a platform to view, sync and share across devices easily.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Cooperative edit, with multiple users editing files simultaneously
|
||||
- Document creation within ownCloud
|
||||
- Document upload
|
||||
- Share and edit files in the browser, and then share them inside ownCloud or through a public link
|
||||
- ownCloud features like versioning, local syncing, encryption, undelete
|
||||
- Seamless support for Microsoft Word documents by way of transparent conversion of file formats
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [owncloud.org][8]
|
||||
- Source code: [github.com/owncloud/documents][9]
|
||||
- Developer: OwnCloud Inc.
|
||||
- License: AGPLv3
|
||||
- Version Number: 8.1.1
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Gobby ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Gobby is a collaborative editor supporting multiple documents in one session and a multi-user chat. All users could work on the file simultaneously without the need to lock it. The parts the various users write are highlighted in different colours and it supports syntax highlighting of various programming and markup languages.
|
||||
|
||||
Gobby allows multiple users to edit the same document together over the internet in real-time. It integrates well with the GNOME environment. It features a client-server architecture which supports multiple documents in one session, document synchronisation on request, password protection and an IRC-like chat for communication out of band. Users can choose a colour to highlight the text they have written in a document.
|
||||
|
||||
A dedicated server called infinoted is also provided.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Full-fledged text editing capabilities including syntax highlighting using GtkSourceView
|
||||
- Real-time, lock-free collaborative text editing through encrypted connections (including PFS)
|
||||
- Integrated group chat
|
||||
- Local group undo: Undo does not affect changes of remote users
|
||||
- Shows cursors and selections of remote users
|
||||
- Highlights text written by different users with different colors
|
||||
- Syntax highlighting for most programming languages, auto indentation, configurable tab width
|
||||
- Zeroconf support
|
||||
- Encrypted data transfer including perfect forward secrecy (PFS)
|
||||
- Sessions can be password-protected
|
||||
- Sophisticated access control with Access Control Lists (ACLs)
|
||||
- Highly configurable dedicated server
|
||||
- Automatic saving of documents
|
||||
- Advanced search and replace options
|
||||
- Internationalisation
|
||||
- Full Unicode support
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [gobby.github.io][10]
|
||||
- Source code: [github.com/gobby][11]
|
||||
- Developer: Armin Burgmeier, Philipp Kern and contributors
|
||||
- License: GNU GPLv2+ and ISC
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.5.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### OnlyOffice ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ONLYOFFICE (formerly known as Teamlab Office) is a multifunctional cloud online office suite integrated with CRM system, document and project management toolset, Gantt chart and email aggregator.
|
||||
|
||||
It allows you to organize business tasks and milestones, store and share your corporate or personal documents, use social networking tools such as blogs and forums, as well as communicate with your team members via corporate IM.
|
||||
|
||||
Manage documents, projects, team and customer relations in one place. OnlyOffice combines text, spreadsheet and presentation editors that include features similar to Microsoft desktop editors (Word, Excel and PowerPoint), but then allow to co-edit, comment and chat in real time.
|
||||
|
||||
OnlyOffice is written in ASP.NET, based on HTML5 Canvas element, and translated to 21 languages.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- As powerful as a desktop editor when working with large documents, paging and zooming
|
||||
- Document sharing in view / edit modes
|
||||
- Document embedding
|
||||
- Spreadsheet and presentation editors
|
||||
- Co-editing
|
||||
- Commenting
|
||||
- Integrated chat
|
||||
- Mobile applications
|
||||
- Gantt charts
|
||||
- Time management
|
||||
- Access right management
|
||||
- Invoicing system
|
||||
- Calendar
|
||||
- Integration with file storage systems: Google Drive, Box, OneDrive, Dropbox, OwnCloud
|
||||
- Integration with CRM, email aggregator and project management module
|
||||
- Mail server
|
||||
- Mail aggregator
|
||||
- Edit documents, spreadsheets and presentations of the most popular formats: DOC, DOCX, ODT, RTF, TXT, XLS, XLSX, ODS, CSV, PPTX, PPT, ODP
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.onlyoffice.com][12]
|
||||
- Source code: [github.com/ONLYOFFICE/DocumentServer][13]
|
||||
- Developer: Ascensio System SIA
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- Version Number: 7.7
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150823085112605/CollaborativeEditing.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://hackpad.com/
|
||||
[2]:https://github.com/dropbox/hackpad
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/dropbox/hackpad/blob/master/CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
[4]:http://etherpad.org/
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/ether/etherpad-lite
|
||||
[6]:http://www.firepad.io/
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/firebase/firepad
|
||||
[8]:https://owncloud.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://github.com/owncloud/documents/
|
||||
[10]:https://gobby.github.io/
|
||||
[11]:https://github.com/gobby
|
||||
[12]:https://www.onlyoffice.com/free-edition.aspx
|
||||
[13]:https://github.com/ONLYOFFICE/DocumentServer
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
translating by fw8899
|
||||
Optimize Web Delivery with these Open Source Tools
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Web proxy software forwards HTTP requests without modifying traffic in any way. They can be configured as a transparent proxy with no client-side configuration required. They can also be used as a reverse proxy front-end to websites; here the cache serves an unlimited number of clients for one or some web servers.
|
||||
@ -192,4 +193,4 @@ via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20151101020309690/WebDelivery.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.privoxy.org/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.varnish-cache.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.pps.univ-paris-diderot.fr/%7Ejch/software/polipo/
|
||||
[5]:https://banu.com/tinyproxy/
|
||||
[5]:https://banu.com/tinyproxy/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
bazz2222222222222222222222222222222222222222222
|
||||
Review EXT4 vs. Btrfs vs. XFS
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
|
||||
StdioA translating
|
||||
|
||||
Ten Biggest Linux Stories Of The Year 2015
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Year 2015 is coming to an end and I am here with Year 2015 special series on It’s FOSS. First in this series is the biggest Linux stories of the year 2015. These stories are the ones that had the most impact on the Linux world, both positive and negative.
|
||||
|
||||
I have summarized ten of such stories which created the most buzz in 2015. Here we go!
|
||||
|
||||
### Biggest Linux and Open Source stories of the year 2015 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Just to add, the listed items are not ordered chronologically.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Microsoft’s partnering with Linux ####
|
||||
|
||||
In late September, everyone was shocked to hear that [Microsoft created its own Linux distribution][1]. It was later revealed that [it was a software][2] developed for its Azur cloud switches.
|
||||
|
||||
But the story did not end up just there. Microsoft indeed partnered with Canonical (parent company of Ubuntu Linux) for [HDInsight][3], Microsoft’s big data Hadoop-on-Azure service. Ubuntu was the first Linux on which [Microsoft deployed this software][4].
|
||||
|
||||
Will Microsoft continue its affair with Linux? Or will it dump it after Linux has served its purpose (Azur). Only time will tell.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Microsoft releases Visual Studio Code for Linux ####
|
||||
|
||||
Before Microsoft-Linux distribution uproar, Microsoft has dropped another bomb by releasing Visual Studio Code for Linux, along with Windows and OS X versions. Though Visual Studio Code is not open source, releasing a Linux version was somehow a win for Linux users. After all, Linus Torvalds had famously said, “if Microsoft ever does an application for Linux, it means I’ve won”.
|
||||
|
||||
You can follow this tutorial to see [how to install Visual Studio Code in Ubuntu][5].
|
||||
|
||||
#### Apple open sources Swift programming language ####
|
||||
|
||||
Apple was not behind in showing off its ‘love’ for Linux and Open Source. Apple’s flagship programming language Swift which is used for making iOS apps, [is now open source][6] with Linux ports available. Though in beta, you can easily [install Swift in Ubuntu][7].
|
||||
|
||||
But Apple is Apple and it [started bragging itself][8] as the “first major computer company to make Open Source development a key part of its software strategy…(sic)”.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu Phone finally launched ####
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Phone was finally launched earlier this year. Intended for early adopters and developers, Ubuntu was welcomed with open heart by the Ubuntu community. Mainstream smartphone users are still shying away from it, mainly [because the OS is still under heavy development][9]. Year 2016 will be deciding for the existence of Ubuntu Phone.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Financial crisis hits Jolla ####
|
||||
|
||||
Jolla, the company behind Linux based smartphone operating system Sailfish OS, hit a major financial hurdle. It resulted in [half of Jolla employees being laid off][10].
|
||||
|
||||
Jolla had a very [successful crowdfunding campaign][11] in 2014 for its tablet. Apparently, they spent most of the budget on the development of Sailfish OS and when the lead investor backed off, company struggled for its survival.
|
||||
|
||||
Good news is that Jolla has managed to get some solid funding and its ]back in business][12].
|
||||
|
||||
#### Firefox OS is dead ####
|
||||
|
||||
One of the open source alternatives to Android, Mozilla’s mobile operating system Firefox OS died a slow death earlier this month. Intended at developing countries with smartphones as cheap as $25, Firefox OS based smartphones could never gained popularity. I think lack of popular apps and cheap hardware was the main reason.
|
||||
|
||||
In December, [Mozilla announced][13] that it will stop developing Firefox OS and also stop the sale of Firefox smartphones.
|
||||
|
||||
Though it is never announced, I think even [Tizen][14], Linux foundation’s own Linux based mobile OS, is dead as well. I don’t see any development news on Tizen and Linux Foundation never promotes it. It is just the matter of time when we will be invited to the funeral of Tizen.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Infighting in “Ubuntu family” ####
|
||||
|
||||
There were lots of heated discussion in May this year when Kubuntu project lead, [Jonathan Riddell was forced out by Ubuntu Community Council][15]. Jonathan had asked questions about how the donations received by Ubuntu is being spent. He had complained that Kubuntu never saw the money.
|
||||
|
||||
This led to an exchange of accusation between both sides. Ultimately, big daddy of Ubuntu, [Mark Shuttleworth asked Jonathan to step down][16].
|
||||
|
||||
#### Female Linux Kernel developer quits citing ‘brutal communication style’ ####
|
||||
|
||||
Linux creator Linux Torvalds is known for the use of abusive language. Linux Kernel dev [Sarah Sharp][17] is also known for being out spoken.
|
||||
|
||||
Sarah Sharp had earlier locked horns with Linus Torvalds in 2013 when she publicly [advised Linus to keep “verbal violence” off the mailing list][18]. Linus did not take it [lightly][19] as well.
|
||||
|
||||
That was in 2013. In 2015, Sarah announced that she is [stepping down from her work in Kernel community][20] because the communication style lacks basic decency and is brutal and profane.
|
||||
|
||||
This move left people discussing if Linux Kernel community should really change the way they behave or if Sarah took things too far.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Unity gaming editor ported to Linux ####
|
||||
|
||||
While [gaming on Linux][21] is still the Achilles heel for Linux users, the community got excited when gaming engine Unity announced that it is testing its [game editor on Linux][22]. As Linux is used very well for rendering, it is speculated that this move will bring game developers to Linux. It is not confirmed yet if Unity will actually bring a final Linux version of its game editor though.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Open Source adoption in government organization ####
|
||||
|
||||
Administration in several [European cities decided to ditch proprity software][23] and opt for open source alternatives. Most city administration replaced Microsoft Office with LibreOffice or OpenOffice. Few cities and [government][24] schools also went ahead and replaced Microsoft Windows with Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Cost cutting was one of the major factor in this decision as the city administration saved hundreds of thousands of Euro by adopting Open Source.
|
||||
|
||||
Universities were not far behind in adopting open source as well. All year round, we get to hear how a [university dropped Photoshop for Krita][25] or [university using open source office][26].
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
As with any other year, 2015 also had some positive and some negative moments for Linux lovers. We saw competitors like Microsoft and Apple coming close to Linux, government organizations adopting to open source. At the same time, we witnessed the failure of Firefox smartphone OS. A mixed year, I would say.
|
||||
|
||||
What do you think? I let you share what you think was the most important news for Linux-ers in the year 2015 and your overall feel about it.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/biggest-linux-stories-2015/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.theregister.co.uk/2015/09/18/microsoft_has_developed_its_own_linux_repeat_microsoft_has_developed_its_own_linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2015/09/microsoft-has-built-software-but-not-a-linux-distribution-for-its-software-switches/
|
||||
[3]:https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/services/hdinsight/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/microsoft-deploys-first-major-server-application-on-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/install-visual-studio-code-ubuntu/
|
||||
[6]:http://itsfoss.com/swift-open-source-linux/
|
||||
[7]:http://itsfoss.com/use-swift-linux/
|
||||
[8]:https://business.facebook.com/itsfoss/photos/pb.115098615297581.-2207520000.1450817108./634288916711879/?type=3&theater
|
||||
[9]:http://www.engadget.com/2015/07/24/ubuntu-phone-review/
|
||||
[10]:http://techcrunch.com/2015/11/20/jolla-running-out-of-runway-for-its-android-alternative/
|
||||
[11]:https://www.indiegogo.com/projects/jolla-tablet-world-s-first-crowdsourced-tablet#/
|
||||
[12]:https://blog.jolla.com/jolla-back-business/
|
||||
[13]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2015/12/firefox-os-smartphones-are-dead/
|
||||
[14]:https://www.tizen.org/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/05/kubuntu-project-lead-asked-to-step-down-by-ubuntu-community-council
|
||||
[16]:http://www.cio.com/article/2926838/linux/mark-shuttleworth-ubuntu-community-council-ask-kubuntu-developer-to-step-down-as-leader.html
|
||||
[17]:http://sarah.thesharps.us/
|
||||
[18]:http://www.techeye.net/chips/linus-torvalds-and-intel-woman-in-sweary-spat
|
||||
[19]:http://marc.info/?l=linux-kernel&m=137392506516022&w=2
|
||||
[20]:http://www.networkworld.com/article/2988850/opensource-subnet/linux-kernel-dev-sarah-sharp-quits-citing-brutal-communications-style.html
|
||||
[21]:http://itsfoss.com/linux-gaming-guide/
|
||||
[22]:http://itsfoss.com/unity-gaming-engine-linux/
|
||||
[23]:http://itsfoss.com/tag/open-source-adoption/
|
||||
[24]:http://itsfoss.com/spanish-school-ditches-windows-ubuntu/
|
||||
[25]:http://itsfoss.com/french-university-dumps-adobe-photoshop-open-source-app-krita/
|
||||
[26]:http://itsfoss.com/hungarian-universities-switch-eurooffice/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,96 @@
|
||||
What’s the Best File System for My Linux Install?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
File systems: they’re not the most exciting things in the world, but important nonetheless. In this article we’ll go over the popular choices for file systems on Linux – what they’re about, what they can do, and who they’re for.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ext4 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you’ve ever installed Linux before, chances are you’ve seen the “Ext4” during installation. There’s a good reason for that: it’s the file system of choice for just about every Linux distribution available right now. Sure, there are some that choose other options, but there’s no denying that Extended 4 is the file system of choice for almost all Linux users.
|
||||
|
||||
#### What can it do? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Extended 4 has all of the goodness that you’ve come to expect from past file system iterations (Ext2/Ext3) but with enhancements. There’s a lot to dig into, but here are the best parts of what Ext4 can do for you:
|
||||
|
||||
- file system journaling
|
||||
- journal checksums
|
||||
- multi-block file allocation
|
||||
- backwards compatibility support for Extended 2 and 3
|
||||
- persistent pre-allocation of free space
|
||||
- improved file system checking (over previous versions)
|
||||
- and of course, support for larger files
|
||||
|
||||
#### Who is it for? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Extended 4 is for those looking for a super-stable foundation to build upon, or for those looking for something that just works. This file system won’t snapshot your system; it doesn’t even have the greatest SSD support, but If your needs aren’t too extravagant, you’ll get along with it just fine.
|
||||
|
||||
### BtrFS ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The B-tree file system (also known as butterFS) is a file system for Linux developed by Oracle. It’s a new file system and is in heavy development stages. The Linux community considers it unstable to use for some. The core principle of BtrFS is based around the principle of copy-on-write. **Copy on write** basically means that the system has one single copy of a bit of data before the data has been written. When the data has been written, a copy of it is made.
|
||||
|
||||
#### What can it do? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Besides supporting copy-on-write, BtrFS can do many other things – so many things, in fact, that it’d take forever to list everything. Here are the most notable features: The file system supports read-only snapshots, file cloning, subvolumes, transparent compression, offline file system check, in-place conversion from ext3 and 4 to Btrfs, online defragmentation, anew has support for RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6 and RAID 10.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Who is it for? ####
|
||||
|
||||
The developers of BtrFS have promised that this file system is the next-gen replacement for other file systems out there. That much is true, though it certainly is a work in progress. There are many killer features for advanced users and basic users alike (including great performance on SSDs). This file system is for those looking to get a little bit more out of their file system and who want to try the copy-on-write way of doing things.
|
||||
|
||||
### XFS ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Developed and created by Silicon Graphics, XFS is a high-end file system that specializes in speed and performance. XFS does extremely well when it comes to parallel input and output because of its focus on performance. The XFS file system can handle massive amounts of data, so much in fact that some users of XFS have close to 300+ terabytes of data.
|
||||
|
||||
#### What can it do? ####
|
||||
|
||||
XFS is a well-tested data storage file system created for high performance operations. Its features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- striped allocation of RAID arrays
|
||||
- file system journaling
|
||||
- variable block sizes
|
||||
- direct I/O
|
||||
- guaranteed-rate I/O
|
||||
- snapshots
|
||||
- online defragmentation
|
||||
- online resizing
|
||||
|
||||
#### Who is it for? ####
|
||||
|
||||
XFS is for those looking for a rock-solid file solution. The file system has been around since 1993 and has only gotten better and better with time. If you have a home server and you’re perplexed on where you should go with storage, consider XFS. A lot of the features the file system comes with (like snapshots) could aid in your file storage system. It’s not just for servers, though. If you’re a more advanced user and you’re interested in a lot of what was promised in BtrFS, check out XFS. It does a lot of the same stuff and doesn’t have stability issues.
|
||||
|
||||
### Reiser4 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Reiser4, the successor to ReiserFS, is a file system created and developed by Namesys. The creation of Reiser4 was backed by the Linspire project as well as DARPA. What makes Reiser4 special is its multitude of transaction models. There isn’t one single way data can be written; instead, there are many.
|
||||
|
||||
#### What can it do? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Reiser4 has the unique ability to use different transaction models. It can use the copy-on-write model (like BtrFS), write-anywhere, journaling, and the hybrid transaction model. It has a lot of improvements upon ReiserFS, including better file system journaling via wandering logs, better support for smaller files, and faster handling of directories. Reiser4 has a lot to offer. There are a lot more features to talk about, but suffice it to say it’s a huge improvement over ReiserFS with tons of added features.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Who is it for? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Resier4 is for those looking to stretch one file system across multiple use-cases. Maybe you want to set up one machine with copy-on-write, another with write-anywhere, and another with hybrid transaction, and you don’t want to use different types of file systems to accomplish this task. Reiser4 is perfect for this type of use-case.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are many file systems available on Linux. Each serves a unique purpose for unique users looking to solve different problems.This post focuses on the most popular choices for the platform. There is no doubt there are other choices out there for other use-cases.
|
||||
|
||||
What’s your favorite file system to use on Linux? Tell us why below!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/best-file-system-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Derrik Diener][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/derrikdiener/
|
||||
66
sources/talk/20151227 Upheaval in the Debian Live project.md
Normal file
66
sources/talk/20151227 Upheaval in the Debian Live project.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
While the event had a certain amount of drama surrounding it, the [announcement][1] of the end for the [Debian Live project][2] seems likely to have less of an impact than it first appeared. The loss of the lead developer will certainly be felt—and the treatment he and the project received seems rather baffling—but the project looks like it will continue in some form. So Debian will still have tools to create live CDs and other media going forward, but what appears to be a long-simmering dispute between project founder and leader Daniel Baumann and the Debian CD and installer teams has been "resolved", albeit in an unfortunate fashion.
|
||||
|
||||
The November 9 announcement from Baumann was titled "An abrupt End to Debian Live". In that message, he pointed to a number of different events over the nearly ten years since the [project was founded][3] that indicated to him that his efforts on Debian Live were not being valued, at least by some. The final straw, it seems, was an "intent to package" (ITP) bug [filed][4] by Iain R. Learmonth that impinged on the namespace used by Debian Live.
|
||||
|
||||
Given that one of the main Debian Live packages is called "live-build", the new package's name, "live-build-ng", was fairly confrontational in and of itself. Live-build-ng is meant to be a wrapper around the [vmdebootstrap][5] tool for creating live media (CDs and USB sticks), which is precisely the role Debian Live is filling. But when Baumann [asked][6] Learmonth to choose a different name for his package, he got an "interesting" [reply][7]:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
It is worth noting that live-build is not a Debian project, it is an external project that claims to be an official Debian project. This is something that needs to be fixed.
|
||||
There is no namespace issue, we are building on the existing live-config and live-boot packages that are maintained and bringing these into Debian as native projects. If necessary, these will be forks, but I'm hoping that won't have to happen and that we can integrate these packages into Debian and continue development in a collaborative manner.
|
||||
live-build has been deprecated by debian-cd, and live-build-ng is replacing it. In a purely Debian context at least, live-build is deprecated. live-build-ng is being developed in collaboration with debian-cd and D-I [Debian Installer].
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Whether or not Debian Live is an "official" Debian project (or even what "official" means in this context) has been disputed in the thread. Beyond that, though, Neil Williams (who is the maintainer of vmdebootstrap) [provided some][8] explanation for the switch away from Debian Live:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
vmdebootstrap is being extended explicitly to provide support for a replacement for live-build. This work is happening within the debian-cd team to be able to solve the existing problems with live-build. These problems include reliability issues, lack of multiple architecture support and lack of UEFI support. vmdebootstrap has all of these, we do use support from live-boot and live-config as these are out of the scope for vmdebootstrap.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Those seem like legitimate complaints, but ones that could have been fixed within the existing project. Instead, though, something of a stealth project was evidently undertaken to replace live-build. As Baumann [pointed out][9], nothing was posted to the debian-live mailing list about the plans. The ITP was the first notice that anyone from the Debian Live project got about the plans, so it all looks like a "secret plan"—something that doesn't sit well in a project like Debian.
|
||||
|
||||
As might be guessed, there were multiple postings that supported Baumann's request to rename "live-build-ng", followed by many that expressed dismay at his decision to stop working on Debian Live. But Learmonth and Williams were adamant that replacing live-build is needed. Learmonth did [rename][10] live-build-ng to a perhaps less confrontational name: live-wrapper. He noted that his aim had been to add the new tool to the Debian Live project (and "bring the Debian Live project into Debian"), but things did not play out that way.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
I apologise to everyone that has been upset by the ITP bug. The software is not yet ready for use as a full replacement for live-build, and it was filed to let people know that the work was ongoing and to collect feedback. This sort of worked, but the feedback wasn't the kind I was looking for.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The backlash could perhaps have been foreseen. Communication is a key aspect of free-software communities, so a plan to replace the guts of a project seems likely to be controversial—more so if it is kept under wraps. For his part, Baumann has certainly not been perfect—he delayed the "wheezy" release by [uploading an unsuitable syslinux package][11] and [dropped down][12] from a Debian Developer to a Debian Maintainer shortly thereafter—but that doesn't mean he deserves this kind of treatment. There are others involved in the project as well, of course, so it is not just Baumann who is affected.
|
||||
|
||||
One of those other people is Ben Armstrong, who has been something of a diplomat during the event and has tried to smooth the waters. He started with a [post][13] that celebrated the project and what Baumann and the team had accomplished over the years. As he noted, the [list of downstream projects][14] for Debian Live is quite impressive. In another post, he also [pointed out][15] that the project is not dead:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
If the Debian CD team succeeds in their efforts and produces a replacement that is viable, reliable, well-tested, and a suitable candidate to replace live-build, this can only be good for Debian. If they are doing their job, they will not "[replace live-build with] an officially improved, unreliable, little-tested alternative". I've seen no evidence so far that they operate that way. And in the meantime, live-build remains in the archive -- there is no hurry to remove it, so long as it remains in good shape, and there is not yet an improved successor to replace it.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
On November 24, Armstrong also [posted][16] an update (and to [his blog][17]) on Debian Live. It shows some good progress made in the two weeks since Baumann's exit; there are even signs of collaboration between the project and the live-wrapper developers. There is also a [to-do list][18], as well as the inevitable call for more help. That gives reason to believe that all of the drama surrounding the project was just a glitch—avoidable, perhaps, but not quite as dire as it might have seemed.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
---------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://lwn.net/Articles/665839/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Jake Edge
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[1]: https://lwn.net/Articles/666127/
|
||||
[2]: http://live.debian.net/
|
||||
[3]: https://www.debian.org/News/weekly/2006/08/
|
||||
[4]: https://bugs.debian.org/cgi-bin/bugreport.cgi?bug=804315
|
||||
[5]: http://liw.fi/vmdebootstrap/
|
||||
[6]: https://lwn.net/Articles/666173/
|
||||
[7]: https://lwn.net/Articles/666176/
|
||||
[8]: https://lwn.net/Articles/666181/
|
||||
[9]: https://lwn.net/Articles/666208/
|
||||
[10]: https://lwn.net/Articles/666321/
|
||||
[11]: https://bugs.debian.org/cgi-bin/bugreport.cgi?bug=699808
|
||||
[12]: https://nm.debian.org/public/process/14450
|
||||
[13]: https://lwn.net/Articles/666336/
|
||||
[14]: http://live.debian.net/project/downstream/
|
||||
[15]: https://lwn.net/Articles/666338/
|
||||
[16]: https://lwn.net/Articles/666340/
|
||||
[17]: http://syn.theti.ca/2015/11/24/debian-live-after-debian-live/
|
||||
[18]: https://wiki.debian.org/DebianLive/TODO
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,10 @@
|
||||
alim0x translating
|
||||
|
||||
The history of Android
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Android 4.2, Jelly Bean—new Nexus devices, new tablet interface ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Android Platform was rapidly maturing, and with Google hosting more and more apps in the Play Store, there was less and less that needed to go out in the OS update. Still, the relentless march of updates must continue, and in November 2012 Android 4.2 was released. 4.2 was still called "Jelly Bean," a nod to the relatively small amount of changes that were present in this release.
|
||||
The Android Platform was rapidly maturing, and with Google hosting more and more apps in the Play Store, there was less and less that needed to go out in the OS update. Still, the relentless march of updates must continue, and in November 2012 Android 4.2 was released. 4.2 was still called "Jelly Bean," a nod to the relatively small amount of changes that were present in this release.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
The LG-made Nexus 4 and Samsung-made Nexus 10.
|
||||
@ -81,4 +83,4 @@ via: http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/building-android-a-40000-word-histor
|
||||
[1]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/01/hands-on-with-samsungs-notepro-and-tabpro-new-screen-sizes-and-magazine-ui/
|
||||
[2]:http://cdn.arstechnica.net/wp-content/uploads/2013/12/device-2013-12-26-11016071.png
|
||||
[a]:http://arstechnica.com/author/ronamadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
[t]:https://twitter.com/RonAmadeo
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,12 @@
|
||||
taichirain 翻译中
|
||||
|
||||
5 great Raspberry Pi projects for the classroom
|
||||
5 伟大的树莓派项目教室
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Image by : opensource.com
|
||||
图片来源 : opensource.com
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Minecraft Pi ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -93,4 +97,4 @@ via: https://opensource.com/education/15/12/5-great-raspberry-pi-projects-classr
|
||||
[11]:https://www.piborg.org/4borg
|
||||
[12]:https://www.piborg.org/diddyborg
|
||||
[13]:https://www.piborg.org/doodleborg
|
||||
[14]:http://camjam.me/?page_id=1035#worksheets
|
||||
[14]:http://camjam.me/?page_id=1035#worksheets
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Top 5 open source community metrics to track
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
So you decided to use metrics to track your free, open source software (FOSS) community. Now comes the big question: Which metrics should I be tracking?
|
||||
|
||||
To answer this question, you must have an idea of what information you need. For example, you may want to know about the sustainability of the project community. How quickly does the community react to problems? How is the community attracting, retaining, or losing contributors? Once you decide which information you need, you can figure out which traces of community activity are available to provide it. Fortunately, FOSS projects following an open development model tend to leave loads of public data in their software development repositories, which can be analyzed to gather useful data.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, I'll introduce metrics that help provide a multi-faceted view of your project community.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Activity ###
|
||||
|
||||
The overall activity of the community and how it evolves over time is a useful metric for all open source communities. Activity provides a first view of how much the community is doing, and can be used to track different kinds of activity. For example, the number of commits gives a first idea about the volume of the development effort. The number of tickets opened provides insight into how many bugs are reported or new features are proposed. The number of messages in mailing lists or posts in forums gives an idea of how much discussion is being held in public.
|
||||
|
||||
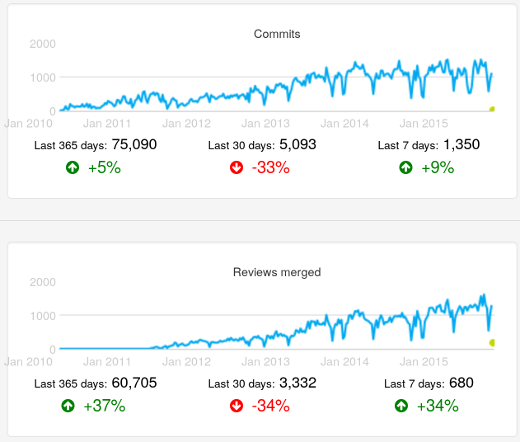
|
||||
|
||||
Number of commits and number of merged changes after code review in the OpenStack project, as found in the [OpenStack Activity Dashboard][1]. Evolution over time (weekly data).
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Size ###
|
||||
|
||||
The size of the community is the number of people participating in it, but, depending on the kind of participation, size numbers may vary. Usually you're interested in active contributors, which is good news. Active people may leave traces in the repositories of the project, which means you can count contributors who are active in producing code by looking at the **Author** field in git repositories, or count people participating in the resolution of tickets by looking at who is contributing to them.
|
||||
|
||||
This basic idea of activity" (somebody did something) can be extended in many ways. One common way to track activity is to look at how many people did a sizable chunk of the activity. Generally most of a project's code contributions, for example, are from a small fraction of the people in the project's community. Knowing about that fraction helps provide an idea of the core group (i.e., the people who help lead the community).
|
||||
|
||||
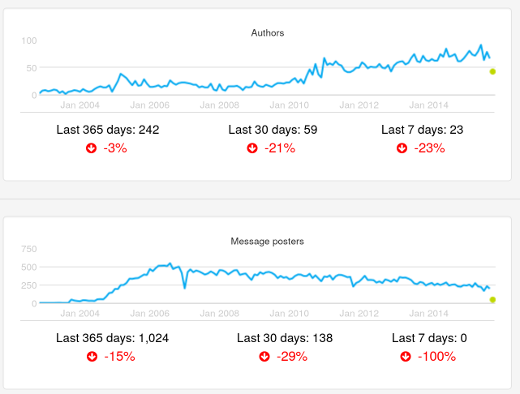
|
||||
|
||||
Number of authors and number of posters in mailing lists in the Xen project, as found in the [Xen Project Development Dashboard][2]. Evolution over time (monthly data).
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Performance ###
|
||||
|
||||
So far, I have focused on measuring quantities of activities and contributors. You also can analyze how processes and people are performing. For example, you can measure how long processes take to finish. Time to resolve or close tickets shows how the project is reacting to new information that requires action, such as fixing a reported bug or implementing a requested new feature. Time spent in code review—from the moment when a change to the code is proposed to the moment it is accepted—shows how long upgrading a proposed change to the quality standards expected by the community takes.
|
||||
|
||||
Other metrics deal with how well the project is coping with pending work, such as the ratio of new to closed tickets, or the backlog of still non-completed code reviews. Those parameters tell us, for example, whether or not the resources put into solving issues is enough.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Ratio of tickets closed by tickets opened, and ratio of change proposals accepted or abandoned by new change proposals per quarter. OpenStack project, as shown in the [OpenStack Development Report, 2015-Q3][3] (PDF).
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Demographics ###
|
||||
|
||||
Communities change as contributors move in and out. Depending on how people enter and leave a community over time, the age (time since members joined the community) of the community varies. The [community aging chart][4] nicely illustrates these exchanges over time. The chart is structured as a set of horizontal bars, two per "generation" of people joining the community. For each generation, the attracted bar shows how many new people joined the community during the corresponding period of time. The retained bar shows how many people are still active in the community.
|
||||
|
||||
The relationship between the two bars for each generation is the retention rate: the fraction of people of that generation who are still in the project. The complete set of attracted bars show how attractive the project was in the past. And the complete set of the retention bars shows the current age structure of the community.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Community aging chart for the Eclipse community, as shown in the [Eclipse Development Dashboard][5]. Generations are defined every six months.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Diversity ###
|
||||
|
||||
Diversity is an important factor in the resiliency of communities. In general, the more diverse communities are—in terms of people or organizations participating—the more resilient they are. For example, when a company decides to leave a FOSS community, the potential problems the departure may cause are much smaller if its employees were contributing 5% of the work rather than 85%.
|
||||
|
||||
The [Pony Factor][6], a term defined by [Daniel Gruno][7] for the minimum number of developers performing 50% of the commits. Based on the Pony Factor, the Elephant Factor is the minimum number of companies whose employees perform 50% of the commits. Both numbers provide an indication of how many people or companies the community depends on.
|
||||
|
||||
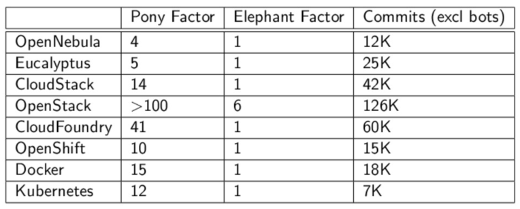
|
||||
|
||||
Pony and Elephant Factor for several FOSS projects in the area of cloud computing, as presented in [The quantitative state of the open cloud 2015][8] (slides).
|
||||
|
||||
There are many other metrics to help measure a community. When determing which metrics to collect, think about the goals of your community, and which metrics will help you reach them.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/business/15/12/top-5-open-source-community-metrics-track
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jesus M. Gonzalez-Barahona][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://opensource.com/users/jgbarah
|
||||
[1]:http://activity.openstack.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://projects.bitergia.com/xen-project-dashboard/
|
||||
[3]:http://activity.openstack.org/dash/reports/2015-q3/pdf/2015-q3_OpenStack_report.pdf
|
||||
[4]:http://radar.oreilly.com/2014/10/measure-your-open-source-communitys-age-to-keep-it-healthy.html
|
||||
[5]:http://dashboard.eclipse.org/demographics.html
|
||||
[6]:https://ke4qqq.wordpress.com/2015/02/08/pony-factor-math/
|
||||
[7]:https://twitter.com/humbedooh
|
||||
[8]:https://speakerdeck.com/jgbarah/the-quantitative-state-of-the-open-cloud-2015-edition
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
translating By Bestony
|
||||
Remember sed and awk? All Linux admins should
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translation by bestony
|
||||
DFileManager: Cover Flow File Manager
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A real gem of a file manager absent from the standard Ubuntu repositories but sporting a unique feature. That’s DFileManager in a twitterish statement.
|
||||
|
||||
A tricky question to answer is just how many open source Linux applications are available. Just out of curiosity, you can type at the shell:
|
||||
|
||||
~$ for f in /var/lib/apt/lists/*Packages; do printf ’%5d %s\n’ $(grep ’^Package: ’ “$f” | wc -l) ${f##*/} done | sort -rn
|
||||
|
||||
On my Ubuntu 15.04 system, it produces the following results:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As the screenshot above illustrates, there are approximately 39,000 packages in the Universe repository, and around 8,500 packages in the main repository. These numbers sound a lot. But there is a smorgasbord of open source applications, utilities, and libraries that don’t have an Ubuntu team generating a package. And more importantly, there are some real treasures missing from the repositories which can only be discovered by compiling source code. DFileManager is one such utility. It is a Qt based cross-platform file manager which is in an early stage of development. Qt provides single-source portability across all major desktop operating systems.
|
||||
|
||||
In the absence of a binary package, the user needs to compile the code. For some tools, this can be problematic, particularly if the application depends on any obscure libraries, or specific versions which may be incompatible with other software installed on a system.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation ###
|
||||
|
||||
Fortunately, DFileManager is simple to compile. The installation instructions on the developer’s website provide most of the steps necessary for my creaking Ubuntu box, but a few essential packages were missing (why is it always that way however many libraries clutter up your filesystem?) To prepare my system, download the source code from GitHub and then compile the software, I entered the following commands at the shell:
|
||||
|
||||
~$ sudo apt-get install qt5-default qt5-qmake libqt5x11extras5-dev
|
||||
~$ git clone git://git.code.sf.net/p/dfilemanager/code dfilemanager-code
|
||||
~$ cd dfilemananger-code
|
||||
~$ mkdir build
|
||||
~$ cd build
|
||||
~$ cmake ../ -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr
|
||||
~$ make
|
||||
~$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
You can then start the application by typing at the shell:
|
||||
|
||||
~$ dfm
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a screenshot of DFileManager in action, with the main attraction in full view; the Cover Flow view. This offers the ability to slide through items in the current folder with an attractive feel. It’s ideal for viewing photos. The file manager bears a resemblance to Finder (the default file manager and graphical user interface shell used on all Macintosh operating systems), which may appeal to you.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Features: ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 4 views: Icons, Details, Columns, and Cover Flow
|
||||
- Categorised bookmarks with Places and Devices
|
||||
- Tabs
|
||||
- Simple searching and filtering
|
||||
- Customizable thumbnails for filetypes including multimedia files
|
||||
- Information bar which can be undocked
|
||||
- Open folders and files with one click
|
||||
- Option to queue IO operations
|
||||
- Remembers some view properties for each folder
|
||||
- Show hidden files
|
||||
|
||||
DFileManager is not a replacement for KDE’s Dolphin, but do give it a go. It’s a file manager that really helps the user browse files. And don’t forget to give feedback to the developer; that’s a contribution anyone can offer.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://gofk.tumblr.com/post/131014089537/dfilemanager-cover-flow-file-manager-a-real-gem
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[gofk][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://gofk.tumblr.com/
|
||||
@ -1,317 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Setup Drone - a Continuous Integration Service in Linux
|
||||
==============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Are you tired of cloning, building, testing, and deploying codes time and again? If yes, switch to continuous integration. Continuous Integration aka CI is practice in software engineering of making frequent commits to the code base, building, testing and deploying as we go. CI helps to quickly integrate new codes into the existing code base. If this process is made automated, then this will speed up the development process as it reduces the time taken for the developer to build and test things manually. [Drone][1] is a free and open source project which provides an awesome environment of continuous integration service and is released under Apache License Version 2.0. It integrates with many repository providers like Github, Bitbucket and Google Code and has the ability to pull codes from the repositories enabling us to build the source code written in number of languages including PHP, Node, Ruby, Go, Dart, Python, C/C++, JAVA and more. It is made such a powerful platform cause it uses containers and docker technology for every build making users a complete control over their build environment with guaranteed isolation.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Installing Docker ###
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, we'll gonna install Docker as its the most vital element for the complete workflow of Drone. Drone does a proper utilization of docker for the purpose of building and testing application. This container technology speeds up the development of the applications. To install docker, we'll need to run the following commands with respective the distribution of linux. In this tutorial, we'll cover the steps with Ubuntu 14.04 and CentOS 7 linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
To install Docker in Ubuntu, we can simply run the following commands in a terminal or console.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
# apt-get install docker.io
|
||||
|
||||
After the installation is done, we'll restart our docker engine using service command.
|
||||
|
||||
# service docker restart
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll make docker start automatically in every system boot.
|
||||
|
||||
# update-rc.d docker defaults
|
||||
|
||||
Adding system startup for /etc/init.d/docker ...
|
||||
/etc/rc0.d/K20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
/etc/rc1.d/K20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
/etc/rc6.d/K20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
/etc/rc2.d/S20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
/etc/rc3.d/S20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
/etc/rc4.d/S20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
/etc/rc5.d/S20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
First, we'll gonna update every packages installed in our centos machine. We can do that by running the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# sudo yum update
|
||||
|
||||
To install docker in centos, we can simply run the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
# curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh
|
||||
|
||||
After our docker engine is installed in our centos machine, we'll simply start it by running the following systemd command as systemd is the default init system in centos 7.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start docker
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll enable docker to start automatically in every system startup.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable docker
|
||||
|
||||
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/docker.service'
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Installing SQlite Driver ###
|
||||
|
||||
It uses SQlite3 database server for storing its data and information by default. It will automatically create a database file named drone.sqlite under /var/lib/drone/ which will handle database schema setup and migration. To setup SQlite3 drivers, we'll need to follow the below steps.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 14.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
As SQlite3 is available on the default respository of Ubuntu 14.04, we'll simply install it by running the following apt command.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install libsqlite3-dev
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
To install it on CentOS 7 machine, we'll need to run the following yum command.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install sqlite-devel
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Installing Drone ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, after we have installed those dependencies successfully, we'll now go further towards the installation of drone in our machine. In this step, we'll simply download the binary package of it from the official download link of the respective binary formats and then install them using the default package manager.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
We'll use wget to download the debian package of drone for ubuntu from the [official Debian file download link][2]. Here is the command to download the required debian package of drone.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget downloads.drone.io/master/drone.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Resolving downloads.drone.io (downloads.drone.io)... 54.231.48.98
|
||||
Connecting to downloads.drone.io (downloads.drone.io)|54.231.48.98|:80... connected.
|
||||
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
|
||||
Length: 7722384 (7.4M) [application/x-debian-package]
|
||||
Saving to: 'drone.deb'
|
||||
100%[======================================>] 7,722,384 1.38MB/s in 17s
|
||||
2015-11-06 14:09:28 (456 KB/s) - 'drone.deb' saved [7722384/7722384]
|
||||
|
||||
After its downloaded, we'll gonna install it with dpkg package manager.
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -i drone.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Selecting previously unselected package drone.
|
||||
(Reading database ... 28077 files and directories currently installed.)
|
||||
Preparing to unpack drone.deb ...
|
||||
Unpacking drone (0.3.0-alpha-1442513246) ...
|
||||
Setting up drone (0.3.0-alpha-1442513246) ...
|
||||
Your system ubuntu 14: using upstart to control Drone
|
||||
drone start/running, process 9512
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
In the machine running CentOS, we'll download the RPM package from the [official download link for RPM][3] using wget command as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget downloads.drone.io/master/drone.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
--2015-11-06 11:06:45-- http://downloads.drone.io/master/drone.rpm
|
||||
Resolving downloads.drone.io (downloads.drone.io)... 54.231.114.18
|
||||
Connecting to downloads.drone.io (downloads.drone.io)|54.231.114.18|:80... connected.
|
||||
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
|
||||
Length: 7763311 (7.4M) [application/x-redhat-package-manager]
|
||||
Saving to: ‘drone.rpm’
|
||||
100%[======================================>] 7,763,311 1.18MB/s in 20s
|
||||
2015-11-06 11:07:06 (374 KB/s) - ‘drone.rpm’ saved [7763311/7763311]
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll install the download rpm package using yum package manager.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum localinstall drone.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Configuring Port ###
|
||||
|
||||
After the installation is completed, we'll gonna configure drone to make it workable. The configuration of drone is inside **/etc/drone/drone.toml** file. By default, drone web interface is exposed under port 80 which is the default port of http, if we wanna change it, we can change it by replacing the value under server block as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
[server]
|
||||
port=":80"
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Integrating Github ###
|
||||
|
||||
In order to run Drone we must setup at least one integration points between GitHub, GitHub Enterprise, Gitlab, Gogs, Bitbucket. In this tutorial, we'll only integrate github but if we wanna integrate other we can do that from the configuration file. In order to integrate github, we'll need to create a new application in our [github settings][4].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To create, we'll need to click on Register a New Application then fill out the form as shown in the following image.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We should make sure that **Authorization callback URL** looks like http://drone.linoxide.com/api/auth/github.com under the configuration of the application. Then, we'll click on Register application. After done, we'll note the Client ID and Client Secret key as we'll need to configure it in our drone configuration.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After thats done, we'll need to edit our drone configuration using a text editor by running the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/drone/drone.toml
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll find the [github] section and append the section with the above noted configuration as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
[github]
|
||||
client="3dd44b969709c518603c"
|
||||
secret="4ee261abdb431bdc5e96b19cc3c498403853632a"
|
||||
# orgs=[]
|
||||
# open=false
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Configuring SMTP server ###
|
||||
|
||||
If we wanna enable drone to send notifications via emails, then we'll need to specify the SMTP configuration of our SMTP server. If we already have an SMTP server, we can use its configuration but as we don't have an SMTP server, we'll need to install an MTA ie Postfix and then specify the SMTP configuration in the drone configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
We can install postfix in ubuntu by running the following apt command.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install postfix
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
We can install postfix in CentOS by running the following yum command.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install postfix
|
||||
|
||||
After installing, we'll need to edit the configuration of our postfix configuration using a text editor.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/postfix/main.cf
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll need to replace the value of myhostname parameter to our FQDN ie drone.linoxide.com .
|
||||
|
||||
myhostname = drone.linoxide.com
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll gonna finally configure the SMTP section of our drone configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/drone/drone.toml
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll find the [stmp] section and then we'll need to append the setting as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
[smtp]
|
||||
host = "drone.linoxide.com"
|
||||
port = "587"
|
||||
from = "root@drone.linoxide.com"
|
||||
user = "root"
|
||||
pass = "password"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note: Here, **user** and **pass** parameters are strongly recommended to be changed according to one's user configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Configuring Worker ###
|
||||
|
||||
As we know that drone utilizes docker for its building and testing task, we'll need to configure docker as the worker for our drone. To do so, we'll need to edit the [worker] section in the drone configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/drone/drone.toml
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll uncomment the following lines and append as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
[worker]
|
||||
nodes=[
|
||||
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock",
|
||||
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we have set only 2 node which means the above configuration is capable of executing only 2 build at a time. In order to increase concurrency, we can increase the number of nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
[worker]
|
||||
nodes=[
|
||||
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock",
|
||||
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock",
|
||||
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock",
|
||||
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
Here, in the above configuration, drone is configured to process four builds at a time, using the local docker daemon.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Restarting Drone ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, after everything is done regarding the installation and configuration, we'll now start our drone server in our linux machine.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
To start drone in our Ubuntu 14.04 machine, we'll simply run service command as the default init system of Ubuntu 14.04 is SysVinit.
|
||||
|
||||
# service drone restart
|
||||
|
||||
To make drone start automatically in every boot of the system, we'll run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# update-rc.d drone defaults
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
To start drone in CentOS machine, we'll simply run systemd command as CentOS 7 is shipped with systemd as init system.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart drone
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll enable drone to start automatically in every system boot.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable drone
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Allowing Firewalls ###
|
||||
|
||||
As we know drone utilizes port 80 by default and we haven't changed the port, we'll gonna configure our firewall programs to allow port 80 (http) and be accessible from other machines in the network.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 14.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Iptables is a popular firewall program which is installed in the ubuntu distributions by default. We'll make iptables to expose port 80 so that we can make our Drone web interface accessible in the network.
|
||||
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
# /etc/init.d/iptables save
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
As CentOS 7 has systemd installed by default, it contains firewalld running as firewall problem. In order to open the port 80 (http service) on firewalld, we'll need to execute the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Accessing Web Interface ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll gonna open the web interface of drone using our favourite web browser. To do so, we'll need to point our web browser to our machine running drone in it. As the default port of drone is 80 and we have also set 80 in this tutorial, we'll simply point our browser to http://ip-address/ or http://drone.linoxide.com according to our configuration. After we have done that correctly, we'll see the first page of it having options to login into our dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As we have configured Github in the above step, we'll simply select github and we'll go through the app authentication process and after its done, we'll be forwarded to our Dashboard.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Here, it will synchronize all our github repository and will ask us to activate the repo which we want to build with drone.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After its activated, it will ask us to add a new file named .drone.yml in our repository and define the build process and configuration in that file like which image to fetch and which command/script to run while compiling, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
We'll need to configure our .drone.yml as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
image: python
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- python helloworld.py
|
||||
- echo "Build has been completed."
|
||||
|
||||
After its done, we'll be able to build our application using the configuration YAML file .drone.yml in our drone appliation. All the commits made into the repository is synced in realtime. It automatically syncs the commit and changes made to the repository. Once the commit is made in the repository, build is automatically started in our drone application.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After the build is completed, we'll be able to see the output of the build with the output console.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we learned to completely setup a workable Continuous Intergration platform with Drone. If we want, we can even get started with the services provided by the official Drone.io project. We can start with free service or paid service according to our requirements. It has changed the world of Continuous integration with its beautiful web interface and powerful bunches of features. It has the ability to integrate with many third party applications and deployment platforms. If you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below so that we can improve or update our contents. Thank you !
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/setup-drone-continuous-integration-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://drone.io/
|
||||
[2]:http://downloads.drone.io/master/drone.deb
|
||||
[3]:http://downloads.drone.io/master/drone.rpm
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/settings/developers
|
||||
@ -1,135 +0,0 @@
|
||||
taichirain 翻译中
|
||||
|
||||
How to Configure Apache Solr on Ubuntu 14 / 15
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hello and welcome to our today's article on Apache Solr. The brief description about Apache Solr is that it is an Open Source most famous search platform with Apache Lucene at the back end for Web sites that enables you to easily create search engines which searches websites, databases and files. It can index and search multiple sites and return recommendations for related contents based on the searched text.
|
||||
|
||||
Solr works with HTTP Extensible Markup Language (XML) that offers application program interfaces (APIs) for Javascript Object Notation, Python, and Ruby. According to the Apache Lucene Project, Solr offers capabilities that have made it popular with administrators including it many featuring like:
|
||||
|
||||
- Full Text Search
|
||||
- Faceted Navigation
|
||||
- Snippet generation/highting
|
||||
- Spell Suggestion/Auto complete
|
||||
- Custom document ranking/ordering
|
||||
|
||||
#### Prerequisites: ####
|
||||
|
||||
On a fresh Linux Ubuntu 14/15 with minimal packages installed, you only have to take care of few prerequisites in order to install Apache Solr.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1)System Update ###
|
||||
|
||||
Login to your Ubuntu server with a non-root sudo user that will be used to perform all the steps to install and use Solr.
|
||||
|
||||
After successful login, issue the following command to update your system with latest updates and patches.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
### 2) JRE Setup ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Solr setup needs Java Runtime Environment to be installed on the system as its basic requirement because solr and tomcat both are the Java based applications. So, we need to install and configure its home environment with latest Java.
|
||||
|
||||
To install the latest version on Oracle Java 8, we need to install Python Software Properties using the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install python-software-properties
|
||||
|
||||
Upon completion, run the setup its the repository for the latest version of Java 8.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
|
||||
|
||||
Now you are able to install the latest version of Oracle Java 8 with 'wget' by issuing the below commands to update the packages source list and then to install Java.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install oracle-java8-installer
|
||||
|
||||
Accept the Oracle Binary Code License Agreement for the Java SE Platform Products and JavaFX as you will be asked during the Java installation and configuration process by a click on the 'OK' button.
|
||||
|
||||
When the installation process complete, run the below command to test the successful installation of Java and check its version.
|
||||
|
||||
kash@solr:~$ java -version
|
||||
java version "1.8.0_66"
|
||||
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_66-b17)
|
||||
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.66-b17, mixed mode)
|
||||
|
||||
The output indicates that we have successfully fulfilled the basic requirement of Solr by installing the Java. Now move to the next step to install Solr.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Solr ###
|
||||
|
||||
Installing Solr on Ubuntu can be done by using two different ways but in this article we prefer to install its latest package from the source.
|
||||
|
||||
To install Solr from its source, download its available package with latest version from there Official [Web Page][1], copy the link address and get it using 'wget' command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://www.us.apache.org/dist/lucene/solr/5.3.1/solr-5.3.1.tgz
|
||||
|
||||
Run the command below to extract the archived service into '/bin' folder.
|
||||
|
||||
$ tar -xzf solr-5.3.1.tgz solr-5.3.1/bin/install_solr_service.sh --strip-components=2
|
||||
|
||||
Then run the script to start Solr service that will creates a new 'solr' user and then installs solr as a service.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo bash ./install_solr_service.sh solr-5.3.1.tgz
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To check the status of Solr service, you use the below command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ service solr status
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Creating Solr Collection: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can create multiple collections using Solr user. To do so just run the below command by mentioning the name of the collection you want to create and by specifying its configuration set as shown.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo su - solr -c "/opt/solr/bin/solr create -c myfirstcollection -n data_driven_schema_configs"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We have successfully created the new core instance directory for our our first collection where we can add new data in it. To view its default schema file in directory '/opt/solr/server/solr/configsets/data_driven_schema_configs/conf' .
|
||||
|
||||
### Using Solr Web ###
|
||||
|
||||
Apache Solr can be accessible on the default port of Solr that 8983. Open your favorite browser and navigate to http://your_server_ip:8983/solr or http://your-domain.com:8983/solr. Make sure that the port is allowed in your firewall.
|
||||
|
||||
http://172.25.10.171:8983/solr/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
From the Solr Web Console click on the 'Core Admin' button from the left bar, then you will see your first collection that we created earlier using CLI. While you can also create new cores by pointing on the 'Add Core' button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can also add the document and query from the document as shown in below image by selecting your particular collection and pointing the document. Add the data in the specified format as shown in the box.
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"number": 1,
|
||||
"Name": "George Washington",
|
||||
"birth_year": 1989,
|
||||
"Starting_Job": 2002,
|
||||
"End_Job": "2009-04-30",
|
||||
"Qualification": "Graduation",
|
||||
"skills": "Linux and Virtualization"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
After adding the document click on the 'Submit Document' button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
You are now able to insert and query data using the Solr web interface after its successful installation on Ubuntu. Now add more collections and insert you own data and documents that you wish to put and manage through Solr. We hope you have got this article much helpful and enjoyed reading this.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/configure-apache-solr-ubuntu-14-15/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kashif][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/kashifs/
|
||||
[1]:http://lucene.apache.org/solr/
|
||||
@ -1,176 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by NearTan
|
||||
How to Install Laravel PHP Framework on CentOS 7 / Ubuntu 15.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hi All, In this article we are going to setup Laravel on CentOS 7 and Ubuntu 15.04. If you are a PHP web developer then you don't need to worry about of all modern PHP frameworks, Laravel is the easiest to get up and running that saves your time and effort and makes web development a joy. Laravel embraces a general development philosophy that sets a high priority on creating maintainable code by following some simple guidelines, you should be able to keep a rapid pace of development and be free to change your code with little fear of breaking existing functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
Laravel's PHP framework installation is not a big deal. You can simply follow the step by step guide in this article for your CentOS 7 or Ubuntu 15 server.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1) Server Requirements ###
|
||||
|
||||
Laravel depends upon a number of prerequisites that must be setup before installing it. Those prerequisites includes some basic tuning parameter of server like your system update, sudo rights and installation of required packages.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you are connected to your server make sure to configure the fully qualified domain name then run the commands below to enable EPEL Repo and update your server.
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS-7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install epel-release
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -Uvh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
|
||||
# rpm -Uvh https://mirror.webtatic.com/yum/el7/webtatic-release.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install python-software-properties
|
||||
# add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php5
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install -y php5 mcrypt php5-mcrypt php5-gd
|
||||
|
||||
### 2) Firewall Setup ###
|
||||
|
||||
System Firewall and SELinux setup is an important part regarding the security of your applications in production. You can make firewall off if you are working on test server and keep SELinux to permissive mode using the below command, so that you installing setup won't be affected by it.
|
||||
|
||||
# setenforce 0
|
||||
|
||||
### 3) Apache, MariaDB, PHP Setup ###
|
||||
|
||||
Laravel installation requires a complete LAMP stack with OpenSSL, PDO, Mbstring and Tokenizer PHP Extensions. If you are already running LAMP server then you can skip this step to move on and just make sure that the required PHP extensions are installed.
|
||||
|
||||
To install AMP stack you can use the below commands on your respective server.
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install httpd mariadb-server php56w php56w-mysql php56w-mcrypt php56w-dom php56w-mbstring
|
||||
|
||||
To start and enable Apache web and MySQL/Mariadb services at bootup on CentOS 7 , we will use below commands.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start httpd
|
||||
# systemctl enable httpd
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
#systemctl start mysqld
|
||||
#systemctl enable mysqld
|
||||
|
||||
After starting MariaDB service, we will configure its secured password with below command.
|
||||
|
||||
#mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install mysql-server apache2 libapache2-mod-php5 php5-mysql
|
||||
|
||||
### 4) Install Composer ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now we are going to install composer that is one of the most important requirement before starting the Laravel installation that helps in installing Laravel's dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS/Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
Run the below commands to setup 'composer' in CentOS/Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
# curl -sS https://getcomposer.org/installer | php
|
||||
# mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composer
|
||||
# chmod +x /usr/local/bin/composer
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 5) Installing Laravel ###
|
||||
|
||||
Laravel's installation package can be downloaded from github using the command below.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget https://github.com/laravel/laravel/archive/develop.zip
|
||||
|
||||
To extract the archived package and move into the document root directory use below commands.
|
||||
|
||||
# unzip develop.zip
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# mv laravel-develop /var/www/
|
||||
|
||||
Now use the following compose command that will install all required dependencies for Laravel within its directory.
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /var/www/laravel-develop/
|
||||
# composer install
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 6) Key Encryption ###
|
||||
|
||||
For encrypter service, we will be generating a 32 digit encryption key using the command below.
|
||||
|
||||
# php artisan key:generate
|
||||
|
||||
Application key [Lf54qK56s3qDh0ywgf9JdRxO2N0oV9qI] set successfully
|
||||
|
||||
Now put this key into the 'app.php' file as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /var/www/laravel-develop/config/app.php
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 7) Virtua Host and Ownership ###
|
||||
|
||||
After composer installation assign the permissions and apache user ownership to the document root directory as shown.
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod 775 /var/www/laravel-develop/app/storage
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# chown -R apache:apache /var/www/laravel-develop
|
||||
|
||||
Open the default configuration file of apache web server using any editor to add the following lines at the end file for new virtual host entry.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
ServerName laravel-develop
|
||||
DocumentRoot /var/www/laravel/public
|
||||
|
||||
start Directory /var/www/laravel
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
Directory close
|
||||
|
||||
Now the time is to restart apache web server services as shown below and then open your web browser to check your localhost page.
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart httpd
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
# service apache2 restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 8) Laravel 5 Web Access ###
|
||||
|
||||
Open your web browser and give your server IP or Fully Qualified Domain name and you will see the default web page of Laravel 5 frame work.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Laravel Framework is a great tool to develop your web applications. So, at the end of this article you have learned its installation setup on Ubuntu 15 and CentOS 7 , Now start using this awesome PHP framework that provides you a lot of more features and comfort in your development work. Feel free to comment us back for your valuable suggestions an feedback to guide you in more specific and easiest way.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-laravel-php-centos-7-ubuntu-15-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kashif][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/kashifs/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
How to Setup SSH Login Without Password CentOS / RHEL
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As a system administrator, you plan on using OpenSSH for Linux and automate your daily tasks such as transferring files or database dump file for the backup to another server. To achieve this goal, you need to log in automatically from the host A to host B. Login automatically mean you do not want to enter any password because you want to use ssh from a shell script.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we’ll show you how to Setup SSH Login without Password on CentOS / RHEL. After automatic login has been configured, you can use it to move the file using SSH (Secure Shell) and secure copy (SCP).
|
||||
|
||||
SSH is open source and the most trusted network protocol which is used to login to the remote server. It is used by system administrators to execute commands, also used to transfer files from one computer to another over a network using SCP protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
After you setup SSH login without password, you can get the following advantages :
|
||||
|
||||
a) Automate your daily task via scripts.
|
||||
b) Enhance security of your linux server. This is one of the recommended method to prevent a brute force attack on virtual private server (VPS), SSH keys are nearly impossible to decipher by brute force alone.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is ssh-keygen ###
|
||||
|
||||
ssh-keygen is a Unix utility that is used to generate, create, manage the public and private keys for ssh authentication. With the help of the ssh-keygen tool, a user can create passphrase keys for both SSH protocol version 1 and version 2. ssh-keygen creates RSA keys for SSH protocol version 1 and RSA or DSA keys for use by SSH protocol version 2.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is ssh-copy-id ###
|
||||
|
||||
ssh-copy-id is a script that copies the local-host’s public key to the remote-host’s authorized_keys file. ssh-copy-id also append the indicated identity file to that machine’s ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file and assigns proper permission to the remote-host’s home.
|
||||
|
||||
### SSH keys ###
|
||||
|
||||
SSH keys provide better and secure way of logging into a linux server with SSH. After you run ssh-keygen, you will generate public key and private key. You can place the public key on any server, and then unlock it by connecting to it with a client that already has the private key. When the two match up, the system unlocks without the need for a password.
|
||||
|
||||
### Setup SSH Login Without Password on CentOS and RHEL. ###
|
||||
|
||||
This steps tested on CentOS 5/6/7, RHEL 5/6/7 and Oracle Linux 6/7.
|
||||
|
||||
Node1 : 192.168.0.9
|
||||
Node2 : 192.168.l.10
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step One : ####
|
||||
|
||||
Test the connection and access from node1 to node2 :
|
||||
|
||||
[root@node1 ~]# ssh root@192.168.0.10
|
||||
The authenticity of host '192.168.0.10 (192.168.0.10)' can't be established.
|
||||
RSA key fingerprint is 6d:8f:63:9b:3b:63:e1:72:b3:06:a4:e4:f4:37:21:42.
|
||||
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
|
||||
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.0.10' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
|
||||
root@192.168.0.10's password:
|
||||
Last login: Thu Dec 10 22:04:55 2015 from 192.168.0.1
|
||||
[root@node2 ~]#
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Two : ####
|
||||
|
||||
Generate public and private keys using ssh-key-gen. Please take note that you can increase security by protecting the private key with a passphrase.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@node1 ~]# ssh-keygen
|
||||
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
|
||||
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
|
||||
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
|
||||
Enter same passphrase again:
|
||||
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
|
||||
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
|
||||
The key fingerprint is:
|
||||
b4:51:7e:1e:52:61:cd:fb:b2:98:4b:ad:a1:8b:31:6d root@node1.ehowstuff.local
|
||||
The key's randomart image is:
|
||||
+--[ RSA 2048]----+
|
||||
| . ++ |
|
||||
| o o o |
|
||||
| o o o . |
|
||||
| . o + .. |
|
||||
| S . . |
|
||||
| . .. .|
|
||||
| o E oo.o |
|
||||
| = ooo. |
|
||||
| . o.o. |
|
||||
+-----------------+
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Three : ####
|
||||
|
||||
Copy or transfer the public key to remote-host using ssh-copy-id command. It will append the indicated identity file to ~/.ssh/authorized_keys on node2 :
|
||||
|
||||
[root@node1 ~]# ssh-copy-id -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub 192.168.0.10
|
||||
root@192.168.0.10's password:
|
||||
Now try logging into the machine, with "ssh '192.168.0.10'", and check in:
|
||||
|
||||
.ssh/authorized_keys
|
||||
|
||||
to make sure we haven't added extra keys that you weren't expecting.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Step Four : ####
|
||||
|
||||
Try SSH login without Password to node2 :
|
||||
|
||||
[root@node1 ~]# ssh root@192.168.0.10
|
||||
Last login: Sun Dec 13 14:03:20 2015 from www.ehowstuff.local
|
||||
|
||||
I hope this article gives you some ideas and quick guide on how to setup SSH login without password on Linux CentOS / RHEL.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ehowstuff.com/ssh-login-without-password-centos/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[skytech][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ehowstuff.com/author/skytech/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
translating by bianjp
|
||||
|
||||
How to Use Glances to Monitor System on Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Glances is a cross-platform command-line text-based tool to monitor your system. It is written in Python language and uses the `psutil` library to get information from the system. Using it you can monitor CPU, Load Average, Memory, Network Interfaces, Disk I/O, File System spaces utilization, mounted devices, total number of active processes and top processes. There are many interesting options available in Glances. One of the main features is that you can set thresholds (careful, warning and critical) in a configuration file, and information will be shown in colors which indicates the bottleneck in the system.
|
||||
|
||||
### Glances Features ###
|
||||
|
||||
- the average CPU load
|
||||
- total number of processes like active, sleeping processes, etc.
|
||||
- total memory information like RAM, swap, free memory, etc.
|
||||
- CPU information
|
||||
- Network download and upload speed of connections
|
||||
- Disk I/O read/write speed details
|
||||
- Currently mounted devices’ disk usages
|
||||
- Top processes with their CPU/memory usages
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Glances ###
|
||||
|
||||
Installing Glances on Ubuntu is easy, as it is available on Ubuntu’s repository. You can install Glances by running the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install glances
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage of Glances ###
|
||||
|
||||
After installation has been finished, you can launch Glances by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
glances
|
||||
|
||||
You will see an output like the following:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Press ESC or “Ctrl + C” to quit from the Glances terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the interval time is set to 1 second, but you can define the custom interval time while running glances from the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
To set the interval time to 5 seconds, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
glances -t 5
|
||||
|
||||
### Glances Color Codes ###
|
||||
|
||||
Glances color code meanings:
|
||||
|
||||
- `GREEN` : OK
|
||||
- `BLUE` : CAREFUL
|
||||
- `VIOLET` : ALERT
|
||||
- `RED` : CRITICAL
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Glances thresholds set is: careful=50, warning=70, critical=90. You can customize the threshold by using the default configuration file glances.conf located at the “/etc/glances/” directory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Glances Options ###
|
||||
|
||||
Glances provides sever so hot keys to find output information while it is running.
|
||||
|
||||
Below are the list of several hot keys.
|
||||
|
||||
- `m` : sort processes by MEM%
|
||||
- `p` : sort processes by name
|
||||
- `c` : sort processes by CPU%
|
||||
- `d` : show/hide disk I/O stats
|
||||
- `a` : sort processes automatically
|
||||
- `f` : show/hide file system statshddtemp
|
||||
- `i` : sort processes by I/O rate
|
||||
- `s` : show/hide sensors’ stats
|
||||
- `y` : show/hide hddtemp stats
|
||||
- `l` : show/hide logs
|
||||
- `n` : show/hide network stats
|
||||
- `x` : delete warning and critical logs
|
||||
- `h` : show/hide help screen
|
||||
- `q` : quit
|
||||
- `w` : delete warning logs
|
||||
|
||||
### Use Glances to Monitor Remote Systems ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can also monitor remote systems using Glances. To use it on a remote system, use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
glances -s
|
||||
|
||||
You will see an output like the following:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You will see Glances running on port 61209.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, go to the remote machine and execute the following command to connect to a Glances server by specifying the IP address as shown below. For example, 192.168.1.10 is your Glances server IP address.
|
||||
|
||||
glances -c -P 192.168.1.10
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Glances is a very useful tool for every Linux system administrator. Using it, you can easily monitor your Linux system in less time. Feel free to comment if you have any questions.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/glances-monitor-system-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Hitesh Jethva][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/hiteshjethva/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
Monitor Linux System Performance Using Nmon
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Nmon (also known as Nigel’s Monitor) is a computer performance system monitor tool for the AIX and Linux operating systems developed by IBM employee Nigel Griffiths. The tool displays onscreen or saves to a data file the operating system statistics to aid in the understanding of computer resource use, tuning options and bottlenecks. This system benchmark tool gives you a huge amount of important performance information in one go with a single command. You can easily monitor your system’s CPU, memory, network, disks, file systems, NFS, top processes, resources and power micro-partition information using Nmon.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Nmon ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default nmon is available in the Ubuntu repository. You can easily install nmon by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install nmon
|
||||
|
||||
How to Use Nmon to Monitor Linux Performance
|
||||
|
||||
Once the installation has been finished, you can launch it by typing the `nmon` command in the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
nmon
|
||||
|
||||
You wI’ll see the following output:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can see from the above screenshot that the nmon command-line utility runs completely in interactive mode, and you can easily toggle statistics using shortcut keys.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the following nmon keyboard shortcuts to display different system stats:
|
||||
|
||||
- `q` : to stop and exit Nmon
|
||||
- `h` : to see help screen
|
||||
- `c` : see CPU stats
|
||||
- `m` : see memory stats
|
||||
- `d` : see disk stats
|
||||
- `k` : see kernel stats
|
||||
- `n` : see network stats
|
||||
- `N` : see NFS stats
|
||||
- `j` : see file system stats
|
||||
- `t` : see top process
|
||||
- `V` : see virtual memory stats
|
||||
- `v` : verbose mode
|
||||
|
||||
### Check CPU by Processor ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you would like to collect some statistics on CPU performance, you should hit the c key on the keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
After hitting the c key you wI’ll see the following output.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Check Top Process Statistics ###
|
||||
|
||||
To get stats on top processes that are running on your system, press the t key on your keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the following output.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Check Network Statistics ###
|
||||
|
||||
To get the network stats of your Linux system, just press the n key on your keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
You wI’ll see the following output:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Disk I/O Graphs ###
|
||||
|
||||
Use the `d` key to get information about disks.
|
||||
|
||||
You wI’ll see the following output:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Check Kernel Information ###
|
||||
|
||||
A most important key to use with this tool is `k;` it is used to display some brief information on the kernel of your system.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the following output after hitting the `k` key on your keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Get System Information ###
|
||||
|
||||
A very useful key for every system admin is the `r` key which is used to give information on different resources such as machine architecture, operating system version, Linux version and CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
You will see the following output by hitting the `r` key.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are many other tools that can do the same job of the Nmon, but Nmon is so usee friendly for a Linux beginner. Please feel free to comment if you have any questions.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/monitor-linux-system-performance/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Hitesh Jethva][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/hiteshjethva/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
||||
What are the best plugins to increase productivity on Emacs
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Over a year ago now, I went looking for the best plugins to [turn Vim into a full-fledged IDE][1]. Interestingly, a lot of the comments on that post were about how Emacs already has most of these plugins built in, and was already a great IDE. Although I can only agree about Emacs' incredible versatility, it is still not the ultimate editor when it comes out of the box. Thankfully, its vast plugin library is here to fix that. But among the plethora of options available to you, it is sometimes hard to know where to start. So for now, let me try to assemble a short list of the indispensable plugins to increase your productivity while using Emacs. Although I am heavily geared towards programming related productivity, most of these plugins would be useful to anyone for any usage.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Ido-mode ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Maybe one of the most useful plugin for beginners, Ido stands for interactively do. It replaces most of the dry prompts with a fancy character matching menu. For example, it will replace the normal prompt to open a file with a list of all the files in the current directory. Type any string, and Ido will try to match it with the most appropriate file. It makes it really easy to visualize your actions, and also to quickly get through a folder where all files are named with the same prefix.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Smex ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Not the most famous one, but a good place to complete what Ido-mode started: Smex can be a fancy replacement to the normal 'M-x' prompt, with a heavy inspiration from Ido-mode. It brings the same interactive search for the commands you would normally have to type after calling 'M-x'. It is simple and efficient, and a great way to save those additional few fractions of a second you normally need.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Auto Complete ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Before knowing the existence of this plugin, I spent half of my time on Emacs pressing ‘M-/’ to complete my words. Now, I have a fancy pop-up to do it for me. There is not much more to say about it, except that we all need it.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. YASnippet ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This one is really for the coders. There is always some piece of code that we feel we use all the time. For me, it's 'var_dump(...); exit;' to debug PHP. After a while of typing it over and over, it just occurred to me that I could have it pre-recorded and easily accessible as a snippet of code. With YASnippets, it's easy to import snippet files or make your own. After that, a simple press on the tabulation key will expand a small keyword into a chunk of pre-written code easy to navigate through and modify.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Org-mode ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For disclaimer, I have only recently started using Org-mode. But it has already blown me away. From the hundreds of written pieces I have seen around, Org-mode can change your life. The idea behind it is simple: it is a mode that simplifies note taking while keeping a plain text format, making it easy to navigate through lists of tasks and various data, and perform operations such as filtering by priority or due date, or setting a recurrence. Yet, from this simple idea, you can accomplish a lot, and it is easy to get overwhelmed with all the options. Rather than a long explanation, I urge you to go through [available tutorials][2], watch a lot of videos, and see by yourself how powerful Org-mode is.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Helm ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Some love it, but others are not such a big fan of it. I am part of the later. But with such a huge following, it is impossible to avoid it. Helm aims to transform your Emacs experience completely. Simply described, Helm is a framework that will help you find a file or a command quickly from within Emacs. Based on your input, it will try to use word completion to guide you to the action you have in mind. The feeling is a bit weird at first, but for some, Helm is a religion of its own. Although I am not its fan, I do appreciate helm-occur which a great tool to search for strings in a large document as it shows all occurrences in a separate buffer, making it easy to navigate through them. If you are looking for a quick demo to understand what Helm can do, I recommend [this post][3].
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. ace-jump-mode ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Another plugin with a big following that I am trying to get on board with is ace-jump-mode. Master this plugin, and you will be promised to transcend the usage of a mouse. Simply described, by triggering ace-jump-mode with a shortcut of your choice, you will be prompted for a character. Enter one, and all words starting with that character will be highlighted with a unique letter. Enter one of the letters on screen, and your cursor will jump straight to the word it is highlighting. I have to admit that it is pretty hard to get the reflex to use it, but once you have it, it will increase your movement speed in a document by a lot.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. find-file-in-project ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you like Sublime text and its very handy 'Ctrl-p' fuzzy search to open any file in a project, then you will love find-file-in-project (or ffip). After setting it up by declaring the root of your version control folder, you can summon easily a cool text bar that quickly scans and searches through your code base for a matching file based on the name you input. I like to have it bound to the F6 key on my keyboard. It is simple and very handy if you do not know the complicate directory structure from the top of your head.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Flymake ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For IDE lovers, I think that syntax checker is one of the most powerful features. It is great for beginners and handy for tired programmers. And thanks to Flymake, Emacs users can enjoy it too. Since I work in PHP a lot, Flymake does not need any extra configuration. As I write my code, it will automatically check my code and highlight any line that contains a problem. For compiled languages, Flymake will look for a Makefile that it will use to check your code. Absolutely magical.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. electric-pair ###
|
||||
|
||||
Last, but not least, electric-pair is one of the simplest yet most powerful plugin in my opinion. It just automatically closes whatever parenthesis or bracket you open. It doesn't look like much at first, but trust me. After struggling for the hundredth time to find that matching parenthesis, you will be glad to have a plugin to ensure that all your expressions are balanced.
|
||||
|
||||
To conclude, Emacs is a fantastic tool. Probably not a shocker. Try these plugins and watch as your productivity goes through the roof. This list is of course not exhaustive at all. If you want to bring your contribution, feel free to do so in the comments. I am myself always looking for new plugins to try and new ways to experience Emacs.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/best-plugins-to-increase-productivity-on-emacs.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/adrien
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/turn-vim-full-fledged-ide.html
|
||||
[2]:http://orgmode.org/worg/org-tutorials/
|
||||
[3]:http://tuhdo.github.io/helm-intro.html
|
||||
68
sources/tech/20151227 Ubuntu Touch, three years later.md
Normal file
68
sources/tech/20151227 Ubuntu Touch, three years later.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
Back in early 2013, your editor [dedicated a sacrificial handset][2] to the testing of the then-new Ubuntu Touch distribution. At that time, things were so unbaked that the distribution came with mocked-up data for unready apps; it even came with a set of fake tweets. Nearly three years later, it seemed time to give Ubuntu Touch another try on another sacrificial device. This distribution has certainly made some progress in those years, but, sadly, it still seems far from being a competitive offering in this space.
|
||||
In particular, your editor tested version 16.04r3 from the testing channel on a Nexus 4 handset. The Nexus 4 is certainly past its prime at the end of 2015, but it still functions as a credible Android device. It is, in any case, the only phone handset on [the list of supported devices][1] other than the three that were sold (in locations far from your editor's home) with Ubuntu Touch pre-installed. It is a bit discouraging that Ubuntu Touch is not supported on a more recent device; the Nexus 4 was discontinued over two years ago.
|
||||
|
||||
People who are accustomed to putting strange systems on Nexus devices know the drill fairly well: unlock the bootloader, install a new recovery image if necessary, then use the **fastboot** tool to flash a new image. Ubuntu Touch does not work that way; instead, one must use a set of tools available only on the Ubuntu desktop distribution. Your editor's current menagerie of systems does not include any of those, but, fortunately, running the Ubuntu 15.10 distribution off a USB drive works just fine. It must be said, though, that Ubuntu appears not to have gotten the memo regarding high-DPI laptop displays; 15.10 is an exercise in eyestrain on such a device.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the requisite packages have been installed, the **ubuntu-device-flash** command can be used to install Ubuntu Touch on the phone. It finds the installation image wherever Canonical hides them (it's not obvious where that is) and puts it onto the phone; the process, on the Nexus 4, took about three hours — a surprisingly long time. Among other things, it installs a Ubuntu-specific recovery image, regardless of whether that should be necessary or not. The installation takes up about 4.5GB of space on the device. At the end, the phone reboots and comes up with the Ubuntu Touch lock screen, which has changed little in the last three years. The first boot takes a discouragingly long time, but subsequent reboots are faster, perhaps faster than Android on the same device.
|
||||
|
||||
Alas, that's about the only thing that is faster than Android. The phone starts sluggish and gets worse as time goes on. At one point it took a solid minute to get the dialer screen up on the running device. Scrolling can be jerky and unpleasant to work with. At least once, the phone bogged down to the point that there was little alternative to shutting it down and starting over.
|
||||
|
||||
Logging into the device over the USB connection offers some clues as to why that might be. There were no less than 258 processes running on the system. A number of them have "evolution" in their name, which is never a good sign even on a heftier system. Daemons like NetworkManager and pulseaudio are running. In general, Ubuntu Touch seems to have a large number of relatively large moving parts, leading, seemingly, to memory pressure and a certain amount of thrashing.
|
||||
|
||||
Three years ago, Ubuntu Touch was built on an Android chassis. There are still bits of Android that show up here and there (it uses binder, for example), but a number of those components have been replaced. This release runs an Android-derived kernel that identifies itself as "3.4.0-7 #39-Ubuntu". 3.4.0 was released in May 2012, so it is getting a bit long in the tooth; the 3.4.0 number suggests this kernel hasn't even gotten the stable updates that followed that release. Finding the source for the kernel in this distribution is not easy; it must almost certainly be hidden somewhere in this Gerrit repository, but your editor ran out of time while trying to find it. The SurfaceFlinger display manager has been replaced by Ubuntu's own Mir, with Unity providing the interface. Upstart is the init system, despite the fact that Ubuntu has moved to systemd on desktop systems.
|
||||
|
||||
When one moves beyond the command-line interface and starts playing with the touchscreen, one finds that the basics of the interface resemble what was demonstrated three years ago. Swiping from the left edge brings the [Overview screen] Unity icon bar (but no longer switches to a home screen; the "home screen" concept doesn't really seem to exist anymore). Swiping from the right will either switch to another application or produce an overview of running applications; it's not clear how it decides which. The overview provides a cute oblique view of the running applications; it's sufficient to choose one, but seems somewhat wasteful of screen space. Swiping up from the bottom produces an application-specific menu — usually.
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The swipe gestures work well enough once one gets used to them, but there is scope for confusion. The camera app, for example, will instruct the user to "swipe left for photo roll," but, unless one is careful to avoid [Swipe left] the right edge of the screen, that gesture will yield the overview screen instead. One can learn subtleties like "swipes involving the edge" and "swipes avoiding the edge," but one could argue that such an interface is more difficult than it needs to be and less discoverable than it could be.
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Speaking of the camera app, it takes pictures as one might expect, and it has gained a high-dynamic-range mode in recent years. It still has no support for stitching together photos in a panorama or "photo sphere" mode, though.
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
The base distribution comes with a fairly basic set of apps. Many of them appear to be interfaces to an associated web page; the Amazon, GMail, and Facebook apps, for example. Something called "Shorts" appears to be an RSS reader, though it seems impervious to the addition of arbitrary feeds. There is a terminal app, but it prompts for a password — a bit surprising [Terminal emulator] given that no password had ever been supplied for the device (it turns out that one should use the screen-lock PIN here). It's not clear that this extra level of "security" is helpful, given that the user involved is already able to install, launch, and run applications on the device, but so it goes.
|
||||
|
||||
Despite the presence of all those evolution processes, there is no IMAP-capable email app; there are also no mapping apps. There is a rudimentary web browser with Ubuntu branding; it appears that this browser is based on Chromium. The weather app is limited to a few dozen hardwired locations worldwide; the closest supported location to LWN headquarters was Houston, which, one assumes, is unlikely to be dealing with the foot of snow your editor had to shovel while partway through this article. One suspects we would have heard about that.
|
||||
|
||||
![][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Inevitably, there is a store from which one can obtain other apps. There are, for example, a couple of seemingly capable, OpenStreetMap-based mapping apps there, including one that claims turn-by-turn navigation, but nothing requiring GPS access worked in your editor's tests. Games abound, of course, but [Maps] there is little in the way of apps that are well known in the Android or iOS worlds. The store will refuse to allow the installation of apps until one creates a "Ubuntu One" account; that is unfortunate, but most Android users never get anywhere near that far before having to create or supply a Google account.
|
||||
|
||||
![][7]
|
||||
|
||||
Canonical puts a fair amount of energy into promoting its "scopes," which are said to be better than apps for the aggregation of content. In truth, they seem to just be another type of app with a focus on gathering information from more than one source. Although, with "branded scopes," the "more than one source" part is often deliberately put by the wayside. Your editor played around with scopes for a while, but, in truth, could not find what was supposed to make them special.
|
||||
|
||||
Permissions management in Ubuntu Touch resembles that found in recent Android releases: the user will be prompted the first time an application tries to exercise a specific privilege. As with Android, the number of [Permissions request] actions requiring privilege is relatively small, and "connect to any arbitrary site on the Internet" is not among them. Access to location information or the camera, though, will generate a prompt. There is also, again as with Android, a way to control which applications are allowed to place notifications on the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Touch still seems to drain the battery far more quickly than Android does on the same device. Indeed, it is barely able to get through the night while sitting idle. There is a cute battery app that offers a couple of "ways to reduce battery use," but it lacks Android's ability to say which apps are actually draining the battery (though, it must be said, that information from Android is often less helpful than one might hope).
|
||||
|
||||
![][8]
|
||||
|
||||
The keyboard now has proper multi-lingual support (though there is no visual indication of which language is currently in effect) and, as with Android, one can switch between languages on the fly. It offers word suggestions, does [Keyboard] spelling correction, and all the usual things. One missing feature, though, is "swipe" typing which, your editor has found, can speed the process of inputting text on a small keyboard considerably. There is also no voice input; no major loss from your editor's point of view, but others will probably see that differently.
|
||||
|
||||
There is a lot to like in Ubuntu Touch. There is some appeal to running something that looks like a proper Linux system, even if it still has a number of Ubuntu-specific components. One does not get the sense that the device is watching quite as closely as Android devices do, though it's not entirely clear, for example, what happens with location data or where it might be stored. In any case, a Ubuntu device clearly has more free software on it than most alternatives do; there is no proprietary "play services" layer maintaining control over the system.
|
||||
|
||||
Sadly, though, this distribution still is not up to the capabilities and the performance of the big alternatives. Switching to Ubuntu Touch means settling for a much slower system, running on a severely limited set of devices, with a relative scarcity of apps to choose from. Your editor would very much like to see a handset distribution that is more free and more open than the alternatives, but that distribution must also be competitive with those alternatives, and that does not seem to be the case here. Unless Canonical can find a way to close the performance and feature gaps with Android, it seems unlikely to have much hope of achieving uptake that is within a few orders of magnitude of Android's.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://lwn.net/Articles/667983/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Jonathan Corbet
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]: https://developer.ubuntu.com/en/start/ubuntu-for-devices/devices/
|
||||
[2]: https://lwn.net/Articles/540138/
|
||||
[3]: https://static.lwn.net/images/2015/utouch/overview-sm.png
|
||||
[4]: https://static.lwn.net/images/2015/utouch/camera-swipe-sm.png
|
||||
[5]: https://static.lwn.net/images/2015/utouch/terminal.png
|
||||
[6]: https://static.lwn.net/images/2015/utouch/gps-sm.png
|
||||
[7]: https://static.lwn.net/images/2015/utouch/camera-perm.png
|
||||
[8]: https://static.lwn.net/images/2015/utouch/schifo.png
|
||||
@ -1,387 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Part 2 - LFCS: How to Install and Use vi/vim as a Full Text Editor
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A couple of months ago, the Linux Foundation launched the LFCS (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin) certification in order to help individuals from all over the world to verify they are capable of doing basic to intermediate system administration tasks on Linux systems: system support, first-hand troubleshooting and maintenance, plus intelligent decision-making to know when it’s time to raise issues to upper support teams.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Learning VI Editor in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Please take a look at the below video that explains The Linux Foundation Certification Program.
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
<iframe width="720" height="405" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="allowfullscreen" src="//www.youtube.com/embed/Y29qZ71Kicg"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
This post is Part 2 of a 10-tutorial series, here in this part, we will cover the basic file editing operations and understanding modes in vi/m editor, that are required for the LFCS certification exam.
|
||||
|
||||
### Perform Basic File Editing Operations Using vi/m ###
|
||||
|
||||
Vi was the first full-screen text editor written for Unix. Although it was intended to be small and simple, it can be a bit challenging for people used exclusively to GUI text editors, such as NotePad++, or gedit, to name a few examples.
|
||||
|
||||
To use Vi, we must first understand the 3 modes in which this powerful program operates, in order to begin learning later about the its powerful text-editing procedures.
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that most modern Linux distributions ship with a variant of vi known as vim (“Vi improved”), which supports more features than the original vi does. For that reason, throughout this tutorial we will use vi and vim interchangeably.
|
||||
|
||||
If your distribution does not have vim installed, you can install it as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
- Ubuntu and derivatives: aptitude update && aptitude install vim
|
||||
- Red Hat-based distributions: yum update && yum install vim
|
||||
- openSUSE: zypper update && zypper install vim
|
||||
|
||||
### Why should I want to learn vi? ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are at least 2 good reasons to learn vi.
|
||||
|
||||
1. vi is always available (no matter what distribution you’re using) since it is required by POSIX.
|
||||
|
||||
2. vi does not consume a considerable amount of system resources and allows us to perform any imaginable tasks without lifting our fingers from the keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, vi has a very extensive built-in manual, which can be launched using the :help command right after the program is started. This built-in manual contains more information than vi/m’s man page.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
vi Man Pages
|
||||
|
||||
#### Launching vi ####
|
||||
|
||||
To launch vi, type vi in your command prompt.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Start vi Editor
|
||||
|
||||
Then press i to enter Insert mode, and you can start typing. Another way to launch vi/m is.
|
||||
|
||||
# vi filename
|
||||
|
||||
Which will open a new buffer (more on buffers later) named filename, which you can later save to disk.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Understanding Vi modes ####
|
||||
|
||||
1. In command mode, vi allows the user to navigate around the file and enter vi commands, which are brief, case-sensitive combinations of one or more letters. Almost all of them can be prefixed with a number to repeat the command that number of times.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, yy (or Y) copies the entire current line, whereas 3yy (or 3Y) copies the entire current line along with the two next lines (3 lines in total). We can always enter command mode (regardless of the mode we’re working on) by pressing the Esc key. The fact that in command mode the keyboard keys are interpreted as commands instead of text tends to be confusing to beginners.
|
||||
|
||||
2. In ex mode, we can manipulate files (including saving a current file and running outside programs). To enter this mode, we must type a colon (:) from command mode, directly followed by the name of the ex-mode command that needs to be used. After that, vi returns automatically to command mode.
|
||||
|
||||
3. In insert mode (the letter i is commonly used to enter this mode), we simply enter text. Most keystrokes result in text appearing on the screen (one important exception is the Esc key, which exits insert mode and returns to command mode).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
vi Insert Mode
|
||||
|
||||
#### Vi Commands ####
|
||||
|
||||
The following table shows a list of commonly used vi commands. File edition commands can be enforced by appending the exclamation sign to the command (for example, <b.:q! enforces quitting without saving).
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table cellspacing="0" border="0">
|
||||
<colgroup width="290">
|
||||
</colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="781">
|
||||
</colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#999999" height="19" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="font-size: small;"> Key command</span></b></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#999999" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="font-size: small;"> Description</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> h or left arrow</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Go one character to the left</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> j or down arrow</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Go down one line</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> k or up arrow</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Go up one line</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> l (lowercase L) or right arrow</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Go one character to the right</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> H</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Go to the top of the screen</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> L</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Go to the bottom of the screen</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> G</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Go to the end of the file</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> w</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Move one word to the right</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> b</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Move one word to the left</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> 0 (zero)</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Go to the beginning of the current line</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> ^</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Go to the first nonblank character on the current line</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> $</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Go to the end of the current line</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> Ctrl-B</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Go back one screen</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> Ctrl-F</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Go forward one screen</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> i</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Insert at the current cursor position</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> I (uppercase i)</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Insert at the beginning of the current line</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> J (uppercase j)</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Join current line with the next one (move next line up)</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> a</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Append after the current cursor position</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> o (lowercase O)</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Creates a blank line after the current line</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> O (uppercase o)</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Creates a blank line before the current line</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> r</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Replace the character at the current cursor position</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> R</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Overwrite at the current cursor position</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> x</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Delete the character at the current cursor position</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> X</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Delete the character immediately before (to the left) of the current cursor position</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> dd</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Cut (for later pasting) the entire current line</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="20" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> D</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Cut from the current cursor position to the end of the line (this command is equivalent to d$)</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="20" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> yX</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Give a movement command X, copy (yank) the appropriate number of characters, words, or lines from the current cursor position</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> yy or Y</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Yank (copy) the entire current line</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> p</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Paste after (next line) the current cursor position</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> P</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Paste before (previous line) the current cursor position</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> . (period)</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Repeat the last command</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> u</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Undo the last command</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> U</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Undo the last command in the last line. This will work as long as the cursor is still on the line.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> n</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Find the next match in a search</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> N</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Find the previous match in a search</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> :n</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Next file; when multiple files are specified for editing, this commands loads the next file.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="20" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> :e file</td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Load file in place of the current file.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="20" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> :r file</td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Insert the contents of file after (next line) the current cursor position</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> :q</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Quit without saving changes.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="20" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> :w file</td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Write the current buffer to file. To append to an existing file, use :w >> file.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> :wq</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Write the contents of the current file and quit. Equivalent to x! and ZZ</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="20" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> :r! command</td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> Execute command and insert output after (next line) the current cursor position.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
#### Vi Options ####
|
||||
|
||||
The following options can come in handy while running vim (we need to add them in our ~/.vimrc file).
|
||||
|
||||
# echo set number >> ~/.vimrc
|
||||
# echo syntax on >> ~/.vimrc
|
||||
# echo set tabstop=4 >> ~/.vimrc
|
||||
# echo set autoindent >> ~/.vimrc
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
vi Editor Options
|
||||
|
||||
- set number shows line numbers when vi opens an existing or a new file.
|
||||
- syntax on turns on syntax highlighting (for multiple file extensions) in order to make code and config files more readable.
|
||||
- set tabstop=4 sets the tab size to 4 spaces (default value is 8).
|
||||
- set autoindent carries over previous indent to the next line.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Search and replace ####
|
||||
|
||||
vi has the ability to move the cursor to a certain location (on a single line or over an entire file) based on searches. It can also perform text replacements with or without confirmation from the user.
|
||||
|
||||
a). Searching within a line: the f command searches a line and moves the cursor to the next occurrence of a specified character in the current line.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, the command fh would move the cursor to the next instance of the letter h within the current line. Note that neither the letter f nor the character you’re searching for will appear anywhere on your screen, but the character will be highlighted after you press Enter.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, this is what I get after pressing f4 in command mode.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Search String in Vi
|
||||
|
||||
b). Searching an entire file: use the / command, followed by the word or phrase to be searched for. A search may be repeated using the previous search string with the n command, or the next one (using the N command). This is the result of typing /Jane in command mode.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Vi Search String in File
|
||||
|
||||
c). vi uses a command (similar to sed’s) to perform substitution operations over a range of lines or an entire file. To change the word “old” to “young” for the entire file, we must enter the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
:%s/old/young/g
|
||||
|
||||
**Notice**: The colon at the beginning of the command.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Vi Search and Replace
|
||||
|
||||
The colon (:) starts the ex command, s in this case (for substitution), % is a shortcut meaning from the first line to the last line (the range can also be specified as n,m which means “from line n to line m”), old is the search pattern, while young is the replacement text, and g indicates that the substitution should be performed on every occurrence of the search string in the file.
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, a c can be added to the end of the command to ask for confirmation before performing any substitution.
|
||||
|
||||
:%s/old/young/gc
|
||||
|
||||
Before replacing the original text with the new one, vi/m will present us with the following message.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Replace String in Vi
|
||||
|
||||
- y: perform the substitution (yes)
|
||||
- n: skip this occurrence and go to the next one (no)
|
||||
- a: perform the substitution in this and all subsequent instances of the pattern.
|
||||
- q or Esc: quit substituting.
|
||||
- l (lowercase L): perform this substitution and quit (last).
|
||||
- Ctrl-e, Ctrl-y: Scroll down and up, respectively, to view the context of the proposed substitution.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Editing Multiple Files at a Time ####
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s type vim file1 file2 file3 in our command prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim file1 file2 file3
|
||||
|
||||
First, vim will open file1. To switch to the next file (file2), we need to use the :n command. When we want to return to the previous file, :N will do the job.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to switch from file1 to file3.
|
||||
|
||||
a). The :buffers command will show a list of the file currently being edited.
|
||||
|
||||
:buffers
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Edit Multiple Files
|
||||
|
||||
b). The command :buffer 3 (without the s at the end) will open file3 for editing.
|
||||
|
||||
In the image above, a pound sign (#) indicates that the file is currently open but in the background, while %a marks the file that is currently being edited. On the other hand, a blank space after the file number (3 in the above example) indicates that the file has not yet been opened.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Temporary vi buffers ####
|
||||
|
||||
To copy a couple of consecutive lines (let’s say 4, for example) into a temporary buffer named a (not associated with a file) and place those lines in another part of the file later in the current vi section, we need to…
|
||||
|
||||
1. Press the ESC key to be sure we are in vi Command mode.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Place the cursor on the first line of the text we wish to copy.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Type “a4yy to copy the current line, along with the 3 subsequent lines, into a buffer named a. We can continue editing our file – we do not need to insert the copied lines immediately.
|
||||
|
||||
4. When we reach the location for the copied lines, use “a before the p or P commands to insert the lines copied into the buffer named a:
|
||||
|
||||
- Type “ap to insert the lines copied into buffer a after the current line on which the cursor is resting.
|
||||
- Type “aP to insert the lines copied into buffer a before the current line.
|
||||
|
||||
If we wish, we can repeat the above steps to insert the contents of buffer a in multiple places in our file. A temporary buffer, as the one in this section, is disposed when the current window is closed.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
As we have seen, vi/m is a powerful and versatile text editor for the CLI. Feel free to share your own tricks and comments below.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Reference Links ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [About the LFCS][1]
|
||||
- [Why get a Linux Foundation Certification?][2]
|
||||
- [Register for the LFCS exam][3]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/vi-editor-usage/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:https://training.linuxfoundation.org/certification/LFCS
|
||||
[2]:https://training.linuxfoundation.org/certification/why-certify-with-us
|
||||
[3]:https://identity.linuxfoundation.org/user?destination=pid/1
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
GHLandy Translateing
|
||||
|
||||
Part 3 - LFCS: How to Archive/Compress Files & Directories, Setting File Attributes and Finding Files in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Recently, the Linux Foundation started the LFCS (Linux Foundation Certified Sysadmin) certification, a brand new program whose purpose is allowing individuals from all corners of the globe to have access to an exam, which if approved, certifies that the person is knowledgeable in performing basic to intermediate system administration tasks on Linux systems. This includes supporting already running systems and services, along with first-level troubleshooting and analysis, plus the ability to decide when to escalate issues to engineering teams.
|
||||
@ -379,4 +381,4 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/compress-files-and-finding-files-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/35-practical-examples-of-linux-find-command/
|
||||
[4]:https://training.linuxfoundation.org/certification/LFCS
|
||||
[5]:https://training.linuxfoundation.org/certification/why-certify-with-us
|
||||
[6]:https://identity.linuxfoundation.org/user?destination=pid/1
|
||||
[6]:https://identity.linuxfoundation.org/user?destination=pid/1
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,156 +0,0 @@
|
||||
bazz2
|
||||
Learn with Linux: Learning Music
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Linux 学习系列][1]的所有文章:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之教你练打字][2]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之物理模拟][3]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之教你玩音乐][4]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之两款地理软件][5]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之掌握数学][6]
|
||||
|
||||
引言:Linux 提供大量的教学软件和工具,面向各个年级段以及年龄段,提供大量学科的练习实践,其中大多数是可以与用户进行交互的。本“Linux 教学”系列就来介绍一些教学软件。
|
||||
|
||||
Learning music is a great pastime. Training your ears to identify scales and chords and mastering an instrument or your own voice requires lots of practise and could become difficult. Music theory is extensive. There is much to memorize, and to turn it into a “skill” you will need diligence. Linux offers exceptional software to help you along your musical journey. They will not help you become a professional musician instantly but could ease the process of learning, being a great aide and reference point.
|
||||
|
||||
### Gnu Solfège ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Solfège][7] is a popular music education method that is used in all levels of music education all around the world. Many popular methods (like the Kodály method) use Solfège as their basis. GNU Solfège is a great software aimed more at practising Solfège than learning it. It assumes the student has already acquired the basics and wishes to practise what they have learned.
|
||||
|
||||
As the developer states on the GNU website:
|
||||
|
||||
> “When you study music on high school, college, music conservatory, you usually have to do ear training. Some of the exercises, like sight singing, is easy to do alone [sic]. But often you have to be at least two people, one making questions, the other answering. […] GNU Solfège tries to help out with this. With Solfege you can practise the more simple and mechanical exercises without the need to get others to help you. Just don’t forget that this program only touches a part of the subject.”
|
||||
|
||||
The software delivers its promise; you can practise essentially everything with audible and visual aids.
|
||||
|
||||
GNU solfege is in the Debian (therefore Ubuntu) repositories. To get it just type the following command into a terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install solfege
|
||||
|
||||
When it loads, you find yourself on a simple starting screen/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The number of options is almost overwhelming. Most of the links will open sub-categories
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
from where you can select individual exercises.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There are practice sessions and tests. Both will be able to play the tones through any connected MIDI device or just your sound card’s MIDI player. The exercises often have visual notation and the ability to play back the sequence slowly.
|
||||
|
||||
One important note about Solfège is that under Ubuntu you might not be able to hear anything with the default setup (unless you have a MIDI device connected). If that is the case, head over to “File -> Preferences,” select sound setup and choose the appropriate option for your system (choosing ALSA would probably work in most cases).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Solfège could be very helpful for your daily practise. Use it regularly and you will have trained your ear before you can sing do-re-mi.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tete (ear trainer) ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Tete][8] (This ear trainer ‘ere) is a Java application for simple, yet efficient, [ear training][9]. It helps you identify a variety of scales by playing thhm back under various circumstances, from different roots and on different MIDI sounds. [Download it from SourceForge][10]. You then need to unzip the downloaded file.
|
||||
|
||||
unzip Tete-*
|
||||
|
||||
Enter the unpacked directory:
|
||||
|
||||
cd Tete-*
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming you have Java installed in your system, you can run the java file with
|
||||
|
||||
java -jar Tete-[your version]
|
||||
|
||||
(To autocomplete the above command, just press the Tab key after typing “Tete-“.)
|
||||
|
||||
Tete has a simple, one-page interface with everything on it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can choose to play scales (see above), chords,
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
or intervals.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can “fine tune” your experience with various options including the midi instrument’s sound, what note to start from, ascending or descending scales, and how slow/fast the playback should be. Tete’s SourceForge page includes a very useful tutorial that explains most aspects of the software.
|
||||
|
||||
### JalMus ###
|
||||
|
||||
Jalmus is a Java-based keyboard note reading trainer. It works with attached MIDI keyboards or with the on-screen virtual keyboard. It has many simple lessons and exercises to train in music reading. Unfortunately, its development has been discontinued since 2013, but the software appears to still be functional.
|
||||
|
||||
To get Jalmus, head over to the [sourceforge page][11] of its last version (2.3) to get the Java installer, or just type the following command into a terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://garr.dl.sourceforge.net/project/jalmus/Jalmus-2.3/installjalmus23.jar
|
||||
|
||||
Once the download finishes, load the installer with
|
||||
|
||||
java -jar installjalmus23.jar
|
||||
|
||||
You will be guided through a simple Java-based installer that was made for cross-platform installation.
|
||||
|
||||
Jalmus’s main screen is plain.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can find lessons of varying difficulty in the Lessons menu. It ranges from very simple ones, where one notes swims in from the left, and the corresponding key lights up on the on screen keyboard …
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
… to difficult ones with many notes swimming in from the right, and you are required to repeat the sequence on your keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Jalmus also includes exercises of note reading single notes, which are very similar to the lessons, only without the visual hints, where your score will be displayed after you finished. It also aids rhythm reading of varying difficulty, where the rhythm is both audible and visually marked. A metronome (audible and visual) aids in the understanding
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
and score reading where multiple notes will be played
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
All these options are configurable; you can switch features on and off as you like.
|
||||
|
||||
All things considered, Jalmus probably works best for rhythm training. Although it was not necessarily its intended purpose, the software really excelled in this particular use-case.
|
||||
|
||||
### Notable mentions ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### TuxGuitar ####
|
||||
|
||||
For guitarists, [TuxGuitar][12] works much like Guitar Pro on Windows (and it can also read guitar-pro files).
|
||||
PianoBooster
|
||||
|
||||
[Piano Booster][13] can help with piano skills. It is designed to play MIDI files, which you can play along with on an attached keyboard, watching the core roll past on the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux offers many great tools for learning, and if your particular interest is music, your will not be left without software to aid your practice. Surely there are many more excellent software tools available for music students than were mentioned above. Do you know of any? Please let us know in the comments below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/series/learn-with-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-to-type-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-physics-simulation/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-geography-apps/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-linux-maths/
|
||||
[7]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solf%C3%A8ge
|
||||
[8]:http://tete.sourceforge.net/index.shtml
|
||||
[9]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ear_training
|
||||
[10]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/tete/files/latest/download
|
||||
[11]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/jalmus/files/Jalmus-2.3/
|
||||
[12]:http://tuxguitar.herac.com.ar/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20090517041840856/PianoBooster.html
|
||||
@ -1,43 +0,0 @@
|
||||
|
||||
苹果编程语言Swift开始支持Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
苹果也开源了?是的,苹果编程语言Swift已经开源了。其实我们并不应该感到意外,因为[在六个月以前苹果就已经宣布了这个消息][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
苹果宣布这周将推出开源Swift社区。一个专用于开源Swift社区的[新网站][2]已经就位,网站首页显示以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
> 我们对Swift开源感到兴奋。在苹果推出了编程语言Swift之后,它很快成为历史上增长最快的语言之一。Swift可以编写出难以置信的又快又安全的软件。目前,Swift是开源的,你能帮助做出随处可用的最好的通用编程语言。
|
||||
|
||||
[swift.org][2]这个网站将会作为一站式网站,它会提供各种资料的下载,包括各种平台,社区指南,最新消息,入门教程,贡献开源Swift的说明,文件和一些其他的指南。 如果你正期待着学习Swift,那么必须收藏这个网站。
|
||||
|
||||
在苹果的这次宣布中,一个用于方便分享和构建代码的包管理器已经可用了。
|
||||
|
||||
对于所有的Linux使用者来说,最重要的是,源代码已经可以从[Github][3]获得了.你可以从以下链接Checkout它:
|
||||
Most important of all for Linux users, the source code is now available at [Github][3]. You can check it out from the link below:
|
||||
|
||||
- [苹果Swift源代码][3]
|
||||
|
||||
除此之外,对于ubuntu 14.04和15.10版本还有预编译的二进制文件。
|
||||
|
||||
- [ubuntu系统的Swift二进制文件][4]
|
||||
|
||||
不要急着去使用它们,因为这些都是发展分支而且不适合于专用机器。因此现在避免使用,一旦发布了Linux下Swift的稳定版本,我希望ubuntu会把它包含在[umake][5]中靠近[Visual Studio][6]的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/swift-open-source-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[Flowsnow](https://github.com/Flowsnow)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/apple-open-sources-swift-programming-language-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://swift.org/
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/apple
|
||||
[4]:https://swift.org/download/#latest-development-snapshots
|
||||
[5]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-make
|
||||
[6]:http://itsfoss.com/install-visual-studio-code-ubuntu/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,228 @@
|
||||
优秀的开源合作编辑工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
一句话,合作编著就是多个人进行编著。合作有好处也有风险。好处包括更加全面/协调的方式,更好的利用现有资源和一个更加有力的、团结的声音。对于我来说,最大的好处是极大的透明度。那是当我需要采纳同事的观点。同事之间来来回回地传文件效率非常低,导致不必要的延误还让人(比如,我)对整个合作这件事都感到不满意。有个好的合作软件,我就能实时地或异步地分享笔记,数据和文件,并用评论来分享自己的想法。这样在文档、图片、视频、演示文稿上合作就不会那么的琐碎而无聊。
|
||||
|
||||
有很多种方式能在线进行合作,简直不能更简便了。这篇文章表明了我最喜欢的开源实时文档合作编辑工具。
|
||||
|
||||
Google Docs 是个非常好的高效应用,有着大部分我所需要的功能。它可以作为一个实时地合作编辑文档的工具提供服务。文档可以被分享、打开并被多位用户同时编辑,用户还能看见其他合作者一个字母一个字母的编辑过程。虽然 Google Docs 对个人是免费的,但并不开源。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是我带来的最棒的开源合作编辑器,它们能帮你不被打扰的集中精力进行写作,而且是和其他人协同完成。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Hackpad ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Hackpad 是个开源的基于网页的实时 wiki,基于开源 EtherPad 合作文档编辑器。
|
||||
|
||||
Hackpad 允许用户实时分享你的文档,它还用彩色编码显示各个作者分别贡献了哪部分。它还允许插入图片、清单,由于提供了语法高亮功能,它还能用来写代码。
|
||||
|
||||
当2014年4月 Dropbox 获得了 Hackpad 后,这款软件就以开源的形式在本月发行。让我们经历的等待非常值得。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 有类似 wiki 所提供的,一套非常完善的功能
|
||||
- 实时或者异步地记合作笔记,共享数据和文件,或用评论分享你们的想法
|
||||
- 细致的隐私许可让你可以邀请单个朋友,一个十几人的团队或者上千的 Twitter 粉丝
|
||||
- 智能执行
|
||||
- 直接从流行的视频分享网站上插入视频
|
||||
- 表格
|
||||
- 可对使用广泛的包括 C, C#, CSS, CoffeeScript, Java, 以及 HTML 在内的编程语言进行语法高亮
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[hackpad.com][1]
|
||||
- 源代码:[github.com/dropbox/hackpad][2]
|
||||
- 开发者:[Contributors][3]
|
||||
- 许可:Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
- 版本号: -
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Etherpad ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Etherpad 是个基于网页的开源实时合作编辑器,允许多个作者同时编辑一个文本文档,写评论,并与其他作者用群聊方式进行交流。
|
||||
|
||||
Etherpad 是用 JavaScript 运行的,在 AppJet 平台的顶端,通过 Comet 流实现实时的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 尽心设计的斯巴达界面
|
||||
- 简单的格式化文本功能
|
||||
- “滑动时间轴”——浏览一个工程历史版本
|
||||
- 可以下载纯文本、 PDF、微软的 Word 文档、Open Document 和 HTML 格式的文档
|
||||
- 每隔一段很短的时间就会自动保存
|
||||
- 可个性化程度高
|
||||
- 有客户端插件可以扩展编辑的功能
|
||||
- 几百个支持 Etherpad 的扩展包括支持 email 提醒,pad 管理,授权
|
||||
- 可访问性开启
|
||||
- 可从 Node 里或通过 CLI(命令行界面)和 Pad 目录实时交互
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [etherpad.org][4]
|
||||
- 源代码:[github.com/ether/etherpad-lite][5]
|
||||
- 开发者:David Greenspan, Aaron Iba, J.D. Zamfiresc, Daniel Clemens, David Cole
|
||||
- 许可:Apache License, Version 2.0
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.5.7
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Firepad ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Firepad 是个开源的合作文本编辑器。它的设计目的是被嵌入到更大的网页应用中对几天内新加入的代码进行批注。
|
||||
|
||||
Firepad 是个全功能的文本编辑器,有解决冲突,光标同步,用户属性,用户在线状态检测功能。它使用 Firebase 作为后台,而且不需要任何服务器端的代码。他可以被加入到任何网页应用中。Firepad 可以使用 CodeMirror 编辑器或者 Ace 编辑器提交文本,它的操作转换代码是从 ot.js 上借鉴的。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要通过添加简单的文档和代码编辑器来扩展你的网页应用能力,Firepad 最适合不过了。
|
||||
|
||||
Firepad 已被多个编辑器使用,包括Atlassian Stash Realtime Editor、Nitrous.IO、LiveMinutes 和 Koding。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 纯正的合作编辑
|
||||
- 基于 OT 的智能合并及解决冲突
|
||||
- 支持多种格式的文本和代码的编辑
|
||||
- 光标位置同步
|
||||
- 撤销/重做
|
||||
- 文本高亮
|
||||
- 用户属性
|
||||
- 在线检测
|
||||
- 版本检查点
|
||||
- 图片
|
||||
- 通过它的 API 拓展 Firepad
|
||||
- 支持所有现代浏览器:Chrome、Safari、Opera 11+、IE8+、Firefox 3.6+
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.firepad.io][6]
|
||||
- 源代码:[github.com/firebase/firepad][7]
|
||||
- 开发者:Michael Lehenbauer and the team at Firebase
|
||||
- 许可:MIT
|
||||
- 版本号:1.1.1
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### OwnCloud Documents ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ownCloud Documents 是个可以单独并/或合作进行办公室文档编辑 ownCloud 应用。它允许最多5个人同时在网页浏览器上合作进行编辑 .odt 和 .doc 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
ownCloud 是个自托管文件同步和分享服务器。他通过网页界面,同步客户端或 WebDAV 提供你数据的使用权,同时提供一个容易在设备间进行浏览、同步和分享的平台。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 合作编辑,多个用户同时进行文件编辑
|
||||
- 在 ownCloud 里创建文档
|
||||
- 上传文档
|
||||
- 在浏览器里分享和编辑文件,然后在 ownCloud 内部或通过公共链接进行分享这些文件
|
||||
- 有类似 ownCloud 的功能,如版本管理、本地同步、加密、恢复被删文件
|
||||
- 通过透明转换文件格式的方式无缝支持微软 Word 文档
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[owncloud.org][8]
|
||||
- 源代码: [github.com/owncloud/documents][9]
|
||||
- 开发者:OwnCloud Inc.
|
||||
- 许可:AGPLv3
|
||||
- 版本号:8.1.1
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Gobby ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Gobby 是个支持在一个会话内进行多个用户聊天并打开多个文档的合作编辑器。所有的用户都能同时在文件上进行工作,无需锁定。不同用户编写的部分用不同颜色高亮显示,它还支持多个编程和标记语言的语法高亮。
|
||||
|
||||
Gobby 允许多个用户在互联网上实时共同编辑同一个文档。他很好的整合了 GNOME 环境。它拥有一个客户端-服务端结构,这让它能支持一个会话开多个文档,文档同步请求,密码保护和 IRC 式的聊天方式可以在多个频道进行交流。用户可以选择一个颜色对他们在文档中编写的文本进行高亮。
|
||||
|
||||
还供有一个叫做 infinoted 的专用服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 成熟的文本编辑能力包括使用 GtkSourceView 的语法高亮功能
|
||||
- 实时、无需锁定、通过加密(包括PFS)连接的合作文本编辑
|
||||
- 整合了群聊
|
||||
- 本地组撤销:撤销不会影响远程用户的修改
|
||||
- 显示远程用户的光标和选择区域
|
||||
- 用不同颜色高亮不同用户编写的文本
|
||||
- 适用于大多数编程语言的语法高亮,自动缩进,可配置 tab 宽度
|
||||
- 零冲突
|
||||
- 加密数据传输包括完美的正向加密(PFS)
|
||||
- 会话可被密码保护
|
||||
- 通过 Access Control Lists (ACLs) 进行精密的权限保护
|
||||
- 高度个性化的专用服务器
|
||||
- 自动保存文档
|
||||
- 先进的查找和替换功能
|
||||
- 国际化
|
||||
- 完整的 Unicode 支持
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[gobby.github.io][10]
|
||||
- 源代码: [github.com/gobby][11]
|
||||
- 开发者: Armin Burgmeier, Philipp Kern and contributors
|
||||
- 许可: GNU GPLv2+ and ISC
|
||||
- 版本号:0.5.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### OnlyOffice ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ONLYOFFICE(从前叫 Teamlab Office)是个多功能云端在线办公套件,整合了 CRM(客户关系管理)系统、文档和项目管理工具箱、甘特图以及邮件整合器
|
||||
|
||||
它能让你整理商业任务和时间表,保存并分享你的合作或个人文档,使用网络社交工具如博客和论坛,还可以和你的队员通过团队的即时聊天工具进行交流。
|
||||
|
||||
能在同一个地方管理文档、项目、团队和顾客关系。OnlyOffice 结合了文本,电子表格和电子幻灯片编辑器,他们的功能跟微软桌面应用(Word、Excel 和 PowerPoint)的功能相同。但是他允许实时进行合作编辑、评论和聊天。
|
||||
|
||||
OnlyOffice 是用 ASP.NET 编写的,基于 HTML5 Canvas 元素,并且被翻译成21种语言。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 当在大文档里工作、翻页和缩放时,它能与桌面应用一样强大
|
||||
- 文档可以在浏览/编辑模式下分享
|
||||
- 文档嵌入
|
||||
- 电子表格和电子幻灯片编辑器
|
||||
- 合作编辑
|
||||
- 评论
|
||||
- 群聊
|
||||
- 移动应用
|
||||
- 甘特图
|
||||
- 时间管理
|
||||
- 权限管理
|
||||
- Invoicing 系统
|
||||
- 日历
|
||||
- 整合了文件保存系统:Google Drive、Box、OneDrive、Dropbox、OwnCloud
|
||||
- 整合了 CRM、电子邮件整合器和工程管理模块
|
||||
- 邮件服务器
|
||||
- 邮件整合器
|
||||
- 可以编辑流行格式的文档、电子表格和电子幻灯片:DOC、DOCX、ODT、RTF、TXT、XLS、XLSX、ODS、CSV、PPTX、PPT、ODP
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站:[www.onlyoffice.com][12]
|
||||
- 源代码:[github.com/ONLYOFFICE/DocumentServer][13]
|
||||
- 开发者:Ascensio System SIA
|
||||
- 许可:GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- 版本号:7.7
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150823085112605/CollaborativeEditing.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[H-mudcup](https://github.com/H-mudcup)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://hackpad.com/
|
||||
[2]:https://github.com/dropbox/hackpad
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/dropbox/hackpad/blob/master/CONTRIBUTORS
|
||||
[4]:http://etherpad.org/
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/ether/etherpad-lite
|
||||
[6]:http://www.firepad.io/
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/firebase/firepad
|
||||
[8]:https://owncloud.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://github.com/owncloud/documents/
|
||||
[10]:https://gobby.github.io/
|
||||
[11]:https://github.com/gobby
|
||||
[12]:https://www.onlyoffice.com/free-edition.aspx
|
||||
[13]:https://github.com/ONLYOFFICE/DocumentServer
|
||||
@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
|
||||
黑客利用Wi-Fi侵犯你隐私的七种方法
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 黑客利用Wi-Fi侵犯你隐私的七种方法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Wi-Fi — 既然方便又危险的东西!这里给大家介绍一下通过Wi-Fi连接泄露身份信息的七种方法和预防措施。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 利用免费热点 ###
|
||||
|
||||
它们似乎无处不在,而且它们的数量会在[下一个四年里增加四倍][1]。但是它们当中很多都是不值得信任的,从你的登录凭证、email甚至更加敏感的账户,都能被黑客用一款名叫“sniffers”的软件截获 — 这款软件能截获到任何你通过该连接提交的信息。防止被黑客盯上的最好办法就是使用VPN(virtual private network),它能保护你的数据隐私它会加密你所输入的信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 网上银行 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可能认为没有人需要自己被提醒不要使用免费Wi-Fi来操作网上银行, 但网络安全厂商卡巴斯基实验室表示[全球超过100家银行因为网络黑客而损失9亿美元][2],由此可见还是有很多人因此受害。如果你真的想要在一家咖吧里使用免费真实的Wi-Fi,那么你应该向服务员确认网络名称。[在店里用路由器设置一个开放的无线连接][3]并将它的网络名称设置成店名是一件相当简单的事。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 始终开着Wi-Fi开关 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你手机的Wi-Fi开关一直开着的,你会自动被连接到一个不安全的网络中去,你甚至都没有意识到。你可以利用你手机的[基于位置的Wi-Fi功能][4],如果它是可用的,那它会在你离开你所保存的网络范围后自动关闭你的Wi-Fi开关并在你回去之后再次开启。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 不使用防火墙 ###
|
||||
|
||||
防火墙是你的第一道抵御恶意入侵的防线,它能有效地让你的电脑网络通畅并阻挡黑客和恶意软件。你应该时刻开启它除非你的杀毒软件有它自己的防火墙。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 浏览非加密网页 ###
|
||||
|
||||
说起来很难过,[世界上排名前100万个网站中55%是不加密的][5],一个未加密的网站则会让传输的数据暴露在黑客的眼下。如果一个网页是安全的,你的浏览器则会有标明(比如说火狐浏览器是一把绿色的挂锁、Chrome蓝旗则是个绿色的图标)。但是一个安全的网站不能让你免于被劫持的风险,它能通过公共网络从你访问过的网站上窃取cookies,无论是不是正当网站与否。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 不更新你的安全防护软件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要确保你自己的网络是受保护的,就更新的路由器固件。你要做的就是进入你的路由器管理页面去检查,通常你能在厂商的官方网页上下载到最新的固件版本。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 不保护你的家用Wi-Fi ###
|
||||
|
||||
不用说,设置一个复杂的密码和更改无线连接的默认名都是非常重要的。你还可以过滤你的MAC地址来让你的路由器只承认那些确认过的设备。
|
||||
|
||||
**Josh Althuser**是一个开源支持者、网络架构师和科技企业家。在过去12年里,他花了很多时间去倡导使用开源软件来管理团队和项目,同时为网络应用程序提供企业级咨询并帮助它们走向市场。你可以联系[他的推特][6].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.networkworld.com/article/3003170/mobile-security/7-ways-hackers-can-use-wi-fi-against-you.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Josh Althuser][a]
|
||||
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://twitter.com/JoshAlthuser
|
||||
[1]:http://www.pcworld.com/article/243464/number_of_wifi_hotspots_to_quadruple_by_2015_says_study.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.nytimes.com/2015/02/15/world/bank-hackers-steal-millions-via-malware.html?hp&action=click&pgtype=Homepage&module=first-column-region%C2%AEion=top-news&WT.nav=top-news&_r=3
|
||||
[3]:http://news.yahoo.com/blogs/upgrade-your-life/banking-online-not-hacked-182159934.html
|
||||
[4]:http://pocketnow.com/2014/10/15/should-you-leave-your-smartphones-wifi-on-or-turn-it-off
|
||||
[5]:http://www.cnet.com/news/chrome-becoming-tool-in-googles-push-for-encrypted-web/
|
||||
[6]:https://twitter.com/JoshAlthuser
|
||||
@ -1,24 +1,24 @@
|
||||
eSpeak: Linux文本转语音工具
|
||||
eSpeak: Linux 文本转语音工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[eSpeak][1]是Linux的命令行工具,能把文本转变成语音。这是一款用C语言写就的精致的语音合成器,提供英语和其它多种语言支持。
|
||||
[eSpeak][1]是一款 Linux 命令行工具,能把文本转换成语音。它是一款简洁的语音合成器,用C语言编写而成,它支持英语和其它多种语言。
|
||||
|
||||
eSpeak从标准输入或者输入文件中读取文本。虽然语音输出与真人声音相去甚远,但是,在你项目有用得到的地方,eSpeak仍不失为一个精致快捷的工具。
|
||||
eSpeak 从标准输入或者输入文件中读取文本。虽然语音输出与真人声音相去甚远,但是,在你项目需要的时候,eSpeak 仍不失为一个简便快捷的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
eSpeak部分主要特性如下:
|
||||
eSpeak 部分主要特性如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 为Linux和Windows准备的命令行工具
|
||||
- 提供给 Linux 和 Windows 的命令行工具
|
||||
- 从文件或者标准输入中把文本读出来
|
||||
- 提供给其它程序使用的共享库版本
|
||||
- 为Windows提供SAPI5版本,在screen-readers或者其它支持Windows SAPI5接口程序的支持下,eSpeak仍然能正常使用
|
||||
- 为 Windows 提供SAPI5版本,在screen-readers或者其它支持Windows SAPI5接口程序的支持下,eSpeak仍然能正常使用
|
||||
- 可移植到其它平台,包括安卓,OSX等
|
||||
- 多种特色声音提供选择
|
||||
- 提供多种声音特性选择
|
||||
- 语音输出可保存为[.WAV][2]格式的文件
|
||||
- 部分SSML([Speech Synthesis Markup Language][3])能为HTML所支持
|
||||
- 体积小巧,整个程序包括语言支持等占用不足2MB
|
||||
- 可以实现文本到音素编码的转化,能被其它语音合成引擎吸纳为前端工具
|
||||
- 可作为生成和调制音素数据的开发工具
|
||||
- 部分SSML([Speech Synthesis Markup Language][3]语音合成标记语言)能为HTML所支持
|
||||
- 体积小巧,整个程序连同语言支持等占用小于2MB
|
||||
- 可以实现文本到音素编码的转化,因此能适应成为其它语音合成引擎的前端工具
|
||||
- 开发工具可用于生产和调整音素数据
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装eSpeak ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,35 +26,35 @@ eSpeak部分主要特性如下:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install espeak
|
||||
|
||||
eSpeak is an old tool and I presume that it should be available in the repositories of other Linux distributions such as Arch Linux, Fedora etc. You can install eSpeak easily using dnf, pacman etc.eSpeak是一个古老的工具,我推测它应该能在其它众多Linux发行版如Arch,Fedora中运行。使用dnf,pacman等命令就能轻易安装。
|
||||
eSpeak 是一个古老的工具,我推测它应该能在其它众多 Linux 发行版中运行,比如 Arch,Fedora。使用 dnf,pacman 等命令就能轻松安装。
|
||||
|
||||
eSpeak用法如下:输入espeak按enter键运行程序。输入字符按enter转换为语音输出(译补)。使用Ctrl+C来关闭运行中的程序。
|
||||
eSpeak 用法如下:输入 espeak 按 enter 键运行程序。输入字符按 enter 转换为语音输出(译补)。使用 Ctrl+C 来关闭运行中的程序。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
还有其它可以的选项,可以通过程序帮助进行查看。
|
||||
还有一些其他的选项可用,可以通过程序帮助进行查看。
|
||||
|
||||
### GUI版本:Gespeaker ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你更倾向于使用GUI版本,可以安装Gespeaker,它为eSpeak提供了GTK界面。
|
||||
如果你更倾向于使用 GUI 版本,可以安装 Gespeaker,它为 eSpeak 提供了 GTK 界面。
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令来安装Gespeaker:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gespeaker
|
||||
|
||||
操作接口简明易用,你完全可以自行探索。
|
||||
操作界面简明易用,你完全可以自行探索。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
虽然这个工具不能为大部分计算所用,但是当你的项目需要把文本转换成语音,espeak还是挺方便使用的。需则用之吧~
|
||||
虽然这些工具不能为大部分计算所用,但是当你的项目需要把文本转换成语音时,使用 espeak 还是挺方便的。是否使用 espeak 这款语音合成器,选择权就交给你们啦。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/espeak-text-speech-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/soooogreen)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[soooogreen](https://github.com/soooogreen)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,164 +0,0 @@
|
||||
debian linux上安装配置 ISC DHCP Server
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
动态主机控制协议(DHCP)给网络管理员提供一种便捷的方式,为不断变化的网络主机或是动态网络提供网络层地址。其中最常用的DHCP服务工具是 ISC DHCP Server。DHCP服务的目的是给主机提供必要的网络信息以便能够和其他连接在网络中的主机互相通信。DHCP服务一般包括以下信息:DNS服务器信息,网络地址(IP),子网掩码,默认网关信息,主机名等等。
|
||||
|
||||
本教程介绍4.2.4版的ISC-DHCP-Server如何在Debian7.7上管理多个虚拟局域网(VLAN),它也可以非常容易的配置的用于单一网络。
|
||||
|
||||
测试用的网络是通过思科路由器使用传统的方式来管理DHCP租约地址的,目前有12个VLANs需要通过路由器的集中式服务器来管理。把DHCP的任务转移到一个专用的服务器上面,路由器可以收回相应的资源,把资源用到更重要的任务上,比如路由寻址,访问控制列表,流量监测以及网络地址转换等。
|
||||
|
||||
另一个将DHCP服务转移到专用服务器的好处,以后会讲到,它可以建立动态域名服务器(DDNS)这样当主机从服务器请求DHCP地址的时候,新主机的主机名将被添加到DNS系统里面。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装和配置ISC DHCP Server###
|
||||
|
||||
1. 使用apt工具用来安装Debian软件仓库中的ISC软件,来创建这个多宿主服务器。与其他教程一样需要使用root或者sudo访问权限。请适当的修改,以便使用下面的命令。(译者注:下面中括号里面是注释,使用的时候请删除,#表示使用的root权限)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install isc-dhcp-server [安装 the ISC DHCP Server 软件]
|
||||
# dpkg --get-selections isc-dhcp-server [确认软件已经成功安装]
|
||||
# dpkg -s isc-dhcp-server [用另一种方式确认成功安装]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2. 确认服务软件已经安装完成,现在需要一些网络的需求来配置服务器,这样服务器才能够根据我们的需要来分发网络信息。作为管理员最起码需要了解的DHCP信息如下:
|
||||
- 网络地址
|
||||
- 子网掩码
|
||||
- 动态分配的地址范围
|
||||
|
||||
其他一些服务器动态分配的有用信息包括:
|
||||
- 默认网关
|
||||
- DNS服务器IP地址
|
||||
- 域名
|
||||
- 主机名
|
||||
- 网络广播地址
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这只是能让ISC DHCP server处理的选项中非常少的一部分。如果你想查看所有选项及其描述需要在安装好软件后输入以下命令:
|
||||
# man dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
3. 一旦管理员已经确定了这台服务器需要分发的需求信息,那么是时候配置服务器并且分配必要的地址池了。在配置任何地址池或服务器配置之前,DHCP服务必须配置好,来侦听这台服务器上面的一个接口。
|
||||
|
||||
在这台特定的服务器上,设置好网卡后,DHCP会侦听名称名为`'bond0'`的接口。请适根据你的实际情况来更改服务器以及网络环境。下面的配置都是针对本教程的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这行指定的是DHCP服务侦听接口(一个或多个)上的DHCP流量。修改主要的配置文件分配适合的DHCP地址池到所需要的网络上。配置文件所在置/etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf。用文本编辑器打开这个文件
|
||||
# nano /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
这个配置文件可以配置我们所需要的地址池/主机。文件顶部有‘ddns-update-style‘这样一句,在本教程中它设置为‘none‘。在以后的教程中动态DNS,ISC-DHCP-Server 将被整合到 BIND9,它能够使主机名更新到IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
4. 接下来的部分是管理员配置全局网络设置,如DNS域名,默认的租约时间,IP地址,子网的掩码,以及更多的区域。如果你想了解所有的选项,请阅读man手册中的dhcpd.conf文件,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# man dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
对于这台服务器,我们需要在顶部配置一些全局网络设置,这样就不用到每个地址池中去单独设置了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们花一点时间来解释一下这些选项,在本教程中虽然它们是一些全局设置,但是也可以为单独的为某一个地址池进行配置。
|
||||
|
||||
- option domain-name “comptech.local”; – 所有使用这台DHCP服务器的主机,都将成为DNS域名为“comptech.local”的一员
|
||||
|
||||
- option domain-name-servers 172.27.10.6; DHCP向所有配置这台DHCP服务器的的网络主机分发DNS服务器地址为172.27.10.6
|
||||
|
||||
- option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0; – 分派子网掩码到每一个网络设备 255.255.255.0 或a /24
|
||||
|
||||
- default-lease-time 3600; – 默认有效的地址租约时间(单位是秒)。如果租约时间耗尽,那么主机可以重新申请租约。如果租约完成,那么相应的地址也将被尽快回收。
|
||||
|
||||
- max-lease-time 86400; – 这是一台主机最大的租约时间(单位为秒)。
|
||||
|
||||
- ping-check true; – 这是一个额外的测试,以确保服务器分发出的网络地址不是当前网络中另一台主机已使用的网络地址。
|
||||
|
||||
- ping-timeout; – 如果地址以前没有使用过,可以用这个选项来检测2个ping返回值之间的时间长度。
|
||||
|
||||
- ignore client-updates; 现在这个选项是可以忽略的,因为DDNS在前面已在配置文件中已经被禁用,但是当DDNS运行时,这个选项会忽略更新其DNS主机名的请求。
|
||||
|
||||
5. 文件中下面一行是权威DHCP所在行。这行的意义是如果服务器是为文件中所配置的网络分发地址的服务器,那么取消注释权威字节(authoritative stanza)来实现。
|
||||
|
||||
通过去掉关键字authoritative 前面的‘#’,取消注释全局权威字节。这台服务器将是它所管理网络里面的唯一权威。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
开启 ISC Authoritative
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下服务器被假定为不是网络上的权威。之所以这样做是出于安全考虑。如果有人因为不了解DHCP服务的配置,导致配置不当或配置到一个不该出现的网络里面,这都将带来非常严重的重连接问题。这行还可用在每个网络中单独配置使用。也就是说如果这台服务器不是整个网络的DHCP服务器,authoritative行可以用在每个单独的网络中,而不是像上面截图中那样的全局配置。
|
||||
|
||||
6. 这一步是配置服务器将要管理的所有DHCP地址池/网络。简短起见,本教程只配置了地址池。作为管理员需要收集一些必要的网络信息(比如域名,网络地址,有多少地址能够被分发等等)
|
||||
|
||||
以下这个地址池所用到的信息都是管理员收集整理的:网络id 172.27.60.0, 子网掩码 255.255.255.0 or a /24, 默认子网网关172.27.60.1,广播地址 172.27.60.255.0
|
||||
|
||||
以上这些信息用于构建hcpd.conf文件中新的网络非常重要。使用文本编辑器修改配置文件添加新的网络进去,这里我们需要使用root或sudo访问权限。网络非常重要。使用文本编辑器修改配置文件添加新的网络进去,这里我们需要使用root或sudo访问权限。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
配置DHCP的地址池和网络
|
||||
|
||||
当前这个例子是给用VMWare创建的虚拟服务器分配IP地址。第一行显示是该网络的子网掩码。括号里面的内容是DHCP服务器应该提供给网络上面主机的所有选项。
|
||||
|
||||
第一节, range 172.27.60.50 172.27.60.254;这一行显示的是,DHCP服务在这个网络上能够给主机动态分发的地址范围。
|
||||
|
||||
第二节,option routers 172.27.60.1;这里显示的是网络里面所有的主机分发默认网关地址。
|
||||
|
||||
最后一节, option broadcast-address 172.27.60.255;,显示当前网络的广播地址。这个地址不能被包含在要分发放的地址范围内,因为广播地址不能分配到一个主机上面。
|
||||
|
||||
必须要强调的是每行的结尾必须要用(;)来结束,所有创建的网络必须要在{}里面。
|
||||
|
||||
7. 如果是创建多个网络,连续的创建完它们的相应选项后保存文本文件即可。配置完成以后如果有更改,ISC-DHCP-Server进程需要重启来使新的更改生效。重启进程可以通过下面的命令来完成:
|
||||
# service isc-dhcp-server restart
|
||||
|
||||
这条命令将重启DHCP服务,管理员能够使用几种不同的方式来检查服务器是否已经可以处理dhcp请求。最简单的方法是通过lsof命令[1]来查看服务器是否在侦听67端口,命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# lsof -i :67
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
检查DHCP侦听端口
|
||||
|
||||
这里输出的结果表明DHCPD(DHCP服务守护进程)正在运行并且侦听67端口。由于/etc/services文件中67端口是端口映射,所以输出中的67端口实际上被转换成了“bootps”。
|
||||
|
||||
在大多数的系统中这是非常常见的,现在服务器应该已经为网络连接做好准备,我们可以将一台主机接入网络请求DHCP地址来验证服务是否正常。
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试客户端连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
8. 现在许多系统使用网络管理器来维护网络连接状态,因此这个设备应该预先配置好的,只要对应的接口处于活跃状态就能够获取DHCP。
|
||||
|
||||
然而当一台设备无法使用网络管理器时,它可能需要手动获取DHCP地址。下面的几步将演示怎样手动获取以及如何查看服务器是否已经按需要分发地址。
|
||||
|
||||
‘[ifconfig][2]‘工具能够用来检查接口的配置。这台被用来测试的DHCP服务器的设备,它只有一个网络适配器(网卡),这块网卡被命名为‘eth0‘。
|
||||
|
||||
# ifconfig eth0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
检查网络接口IP地址
|
||||
|
||||
从输出结果上看,这台设备目前没IPv4地址,这样很好便于测试。我们把这台设备连接到DHCP服务器并发出一个请求。这台设备上已经安装了一个名为‘dhclient‘ 的DHCP客户端工具。因为操作系统各不相同,所以这个客户端软件也是互不一样的。
|
||||
# dhclient eth0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
从DHCP请求IP地址
|
||||
|
||||
当前 `'inet addr:'` 字段中显示了属于172.27.60.0网络地址范围内的IPv4地址。值得欣慰的是当前网络还配置了正确的子网掩码并且分发了广播地址。
|
||||
|
||||
到这里看起来还都不错,让我们来测试一下,看看这台设备收到新IP地址是不是由服务器发出的。这里我们参照服务器的日志文件来完成这个任务。虽然这个日志的内容有几十万条,但是里面只有几条是用来确定服务器是否正常工作的。这里我们使用一个工具‘tail’,它只显示日志文件的最后几行,这样我们就可以不用拿一个文本编辑器去查看所有的日志文件了。命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# tail /var/log/syslog
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
检查DHCP日志文件
|
||||
|
||||
OK!服务器记录表明它分发了一个地址给这台主机(HRTDEBXENSRV)。服务器按预期运行,给它充当权威的网络分发适合的网络地址。至此DHCP服务器搭建成功并且运行。如果有需要你可以继续配置其他的网络,排查故障,确保安全。
|
||||
|
||||
在以后的Debian教程中我会讲一些新的 ISC-DHCP-Server 功能。有时间的话我将写一篇关于Bind9和DDNS的教程,融入到这篇文章里面。
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-and-configure-multihomed-isc-dhcp-server-on-debian-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Rob Turner][a]
|
||||
译者:[ivo-wang](https://github.com/ivo-wang)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/robturner/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-lsof-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/ifconfig-command-examples/
|
||||
@ -1,202 +0,0 @@
|
||||
一个涵盖 Unix 44 年进化史的仓库
|
||||
=============================================================================
|
||||
### 摘要 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Unix 操作系统的进化历史,可以从一个版本控制的仓库中窥见,时间跨越从 1972 年以 5000 行内核代码的出现,到 2015 年成为一个含有 26,000,000 行代码的被广泛使用的系统。该仓库包含 659,000 条提交,和 2306 次合并。仓库部署被普遍采用的 Git 系统储存其代码,并且在时下流行的 GitHub 上建立了档案。它综合了系统定制软件的 24 个快照,都是开发自贝尔实验室,伯克利大学,386BSD 团队,两个传统的仓库 和 开源 FreeBSD 系统的仓库。总的来说,850 位个人贡献者已经确认,更早些时候的一批人主要做基础研究。这些数据可以用于一些经验性的研究,在软件工程,信息系统和软件考古学领域。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1 介绍 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Unix 操作系统作为一个主要的工程上的突破而脱颖而出,得益于其模范的设计,大量的技术贡献,它的开发模型和广泛的使用。Unix 编程环境的设计已经被标榜为一个能提供非常简洁,功能强大并且优雅的设计[[1][1]]。在技术方面,许多对 Unix 有直接贡献的,或者因 Unix 而流行的特性就包括[[2][2]]:用高级语言编写的可移植部署的内核;一个分层式设计的文件系统;兼容的文件,设备,网络和进程间 I/O;管道和过滤架构;虚拟文件系统;和用户可选的 shell。很早的时候,就有一个庞大的社区为 Unix 贡献软件[[3][3]],[[4][4]],pp. 65-72]。随时间流走,这个社区不断壮大,并且以现在称为开源软件开发的方式在工作着[[5][5],pp. 440-442]。Unix 和其睿智的晚辈们也将 C 和 C++ 编程语言,分析程序和词法分析生成器(*yacc,lex*),发扬光大了,文档编制工具(*troff,eqn,tbl*),脚本语言(*awk,sed,Perl*),TCP/IP 网络,和配置管理系统(*SCSS,RCS,Subversion,Git*)发扬广大了,同时也形成了大部分的现代互联网基础设施和网络。
|
||||
|
||||
幸运的是,一些重要的具有历史意义的 Unix 材料已经保存下来了,现在保持对外开放。尽管 Unix 最初是由相对严格的协议发行,但在早期的开发中,很多重要的部分是通过 Unix 的某个版权拥有者以一个自由的协议发行。然后将这些部分再结合开发的软件或者以开源发行的软件,Berkeley,Californai 大学和 FreeBSD 项目组从 1972 年六月二十日开始到现在,提供了涵盖整个系统的开发。
|
||||
|
||||
Curating and processing available snapshots as well as old and modern configuration management repositories allows the reconstruction of a new synthetic Git repository that combines under a single roof most of the available data. This repository documents in a digital form the detailed evolution of an important digital artefact over a period of 44 years. The following sections describe the repository's structure and contents (Section [II][6]), the way it was created (Section [III][7]), and how it can be used (Section [IV][8]).
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 数据概览 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这 1GB 的 Unix 仓库可以从 [GitHub][9] 克隆。[1][10]如今[2][11],这个仓库包含来自 850 个贡献者的 659,000 个提交和 2306 个合并。贡献者有来自 Bell 实验室的 23 个员工,Berkeley 计算机系统研究组(CSRG)的 158 个人,和 FreeBSD 项目的 660 个成员。
|
||||
|
||||
这个仓库的生命始于一个 *Epoch* 的标签,这里面只包含了证书信息和现在的 README 文件。其后各种各样的标签和分支记录了很多重要的时刻。
|
||||
|
||||
- *Research-VX* 标签对应来自 Bell 实验室六次的研究版本。从 *Research-V1* (PDP-11 4768 行汇编代码)开始,到以 *Research-V7* (大约 324,000 行代码,1820 个 C 文件)结束。
|
||||
- *Bell-32V* 是 DEC/VAX 架构的 Unix 第七个版本的一部分。
|
||||
- *BSD-X* 标签对应 Berkeley 释出的 15 个快照。
|
||||
- *386BSD-X* 标签对应系统的两个开源版本,主要是 Lynne 和 William Jolitz 写的 适用于 Intel 386 架构的内核代码。
|
||||
- *FreeBSD-release/X* 标签和分支标记了来自 FreeBSD 项目的 116 个发行版。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,以 *-Snapshot-Development* 为后缀的分支,表示一个被综合的以时间排序的快照文件序列的一些提交,而以一个 *-VCS-Development* 为后缀的标签,标记了有特别发行版出现的历史分支的时刻。
|
||||
|
||||
仓库的历史包含从系统开发早期的一些提交,比如下面这些。
|
||||
|
||||
commit c9f643f59434f14f774d61ee3856972b8c3905b1
|
||||
Author: Dennis Ritchie <research!dmr>
|
||||
Date: Mon Dec 2 18:18:02 1974 -0500
|
||||
Research V5 development
|
||||
Work on file usr/sys/dmr/kl.c
|
||||
|
||||
释出间隙的合并随着系统进化而发生,比如 从 BSD 2 到 BSD 3 的开发,Unix 32/V 也是正确地代表了 Git 仓库里带两个父节点的图形节点。(这太莫名其妙了)
|
||||
|
||||
更为重要的是,该仓库的构造方式允许 **git blame**,就是可以给源代码加上注释,如版本,日期和它们第一次出现相关联的作者,这样可以知道任何代码的起源。比如说 **BSD-4** 这个标签,在内核的 *pipe.c* 文件上运行一下 git blame,就会显示代码行由 Ken Thompson 写于 1974,1975 和 1979年,Bill Joy 写于 1980 年。这就可以自动(尽管计算上比较费事)检测出任何时刻出现的代码。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Figure 1: Code provenance across significant Unix releases.
|
||||
|
||||
如上图[12]所示,现代版本的 Unix(FreeBSD 9)依然有来自 BSD 4.3,BSD 4.3 Net/2 和 BSD 2.0 的代码块。有趣的是,这图片显示有部分代码好像没有保留下来,当时激进地要创造一个脱离于 Berkeyel(386BSD 和 FreeBSD 1.0)释出代码的开源操作系统,其所开发的代码。FreeBSD 9 中最古老的代码是一个 18 行的队列,在 C 库里面的 timezone.c 文件里,该文件也可以在第七版的 Unix 文件里找到,同样的名字,时间戳是 1979 年一月十日 - 36 年前。
|
||||
|
||||
### 数据收集和处理 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个项目的目的是以某种方式巩固从数据方面说明 Unix 的进化,通过将其并入一个现代的修订仓库,帮助人们对系统进化的研究。项目工作包括收录数据,分类并综合到一个单独的 Git 仓库里。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Figure 2: Imported Unix snapshots, repositories, and their mergers.
|
||||
|
||||
项目以三种数据类型为基础(见 Figure [2][13])。首先,早些发布的版本快照,是从 [Unix Heritage Society archive][14] 中获得,[2][15] 在 [CD-ROM 镜像][16] 中包括 CSRG 全部的源包,[4][17] [Oldlinux site],[5][19] 和 [FreeBSD 包][20]。[6][21] 其次,以前的,现在的仓库,也就是 CSRG SCCS [[6][22]] 仓库,FreeBSD 1 CVS 仓库,和[现代 FreeBSD 开发的 Git 镜像][23]。[7][24]前两个都是从相同的源获得而作为对应的快照。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,也是最费力的数据源是 **primary research**。释出的快照并没有提供关于它们的源头和每个文件贡献者的信息。因此,这些信息片段需要通过 primary research 验证。至于作者信息主要通过作者的自传,研究论文,内部备忘录和旧文档扫描;通过阅读并且自动处理源代码和帮助页面补充;通过与那个年代的人用电子邮件交流;在 *StackExchange* 网站上贴出疑问;查看文件的位置(在早期的内核源代码版本中,分为 `usr/sys/dmr` 和 `/usr/sys/ken`);从研究论文和帮助手册到源代码,从一个发行版到另一个发行版地宣传中获取。(有趣的是,第一和第二的研究版帮助页面都有一个 “owner” 部分,列出了作者(比如,*Ken*)与对应的系统命令,文件,系统调用,或者功能库。在第四版中这个部分就没了,而在 BSD 发行版中又浮现了 “Author” 部分。)关于作者信息更为详细地写在了项目的文件中,这些文件被用于匹配源代码文件和它们的作者和对应的提交信息。最后,information regarding merges between source code bases was obtained from a [BSD family tree maintained by the NetBSD project][25].[8][26](不好组织这个语言)
|
||||
|
||||
作为该项目的一部分而开发的软件和数据文件,现在可以[在线获取][27],[9][28],并且,如果有合适的网络环境,CPU 和磁盘资源,可以用来从头构建这样一个仓库。关于主要发行版的所有者信息,都存储在该项目 `author-path` 目录下的文件里。These contain lines with a regular expressions for a file path followed by the identifier of the corresponding author.(这句单词都认识,但是不理解具体意思)也可以制定多个作者。正则表达式是按线性处理的,所以一个文件末尾的匹配一切的表达式可以指定一个发行版的默认作者。为避免重复,一个以 `.au` 后缀的独立文件专门用于映射作者身份到他们的名字和 email。这样一个文件为每个社区建立了一个,以关联系统的进化:Bell 实验室,Berkeley,386BSD 和 FreeBSD。为了真实性的需要,早期 Bell 实验室发行版的 emails 都以 UUCP 注释列出了(e.g. `research!ken`)。FreeBSD 作者的鉴定人图谱,需要导入早期的 CVS 仓库,通过从如今项目的 Git 仓库里解压对应的数据构建。总的来说,注释作者信息的文件(828 rules)包含 1107 行,并且另外 640 映射作者鉴定人到名字。
|
||||
|
||||
现在项目的数据源被编码成了一个 168 行的 `Makefile`。它包括下面的步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
**Fetching** 从远程站点复制和克隆大约 11GB 的镜像,档案和仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
**Tooling** 从 2.9 BSD 中为旧的 PDP-11 档案获取一个归档器,并作出调整来在现代的 Unix 版本下编译;编译 4.3 BSD *compress* 程序来解压 386BSD 发行版,这个程序不再是现代 Unix 系统的组成部分了。
|
||||
|
||||
**Organizing** 用 tar 和 *cpio* 解压缩包;结合第六版的三个目录;用旧的 PDP-11 归档器解压所有的 1 BSD 档案;挂载 CD-ROM 镜像,这样可以作为文件系统处理;组合 8 和 62 386BSD 散乱的磁盘镜像为两个独立的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
**Cleaning** 重新存储第一版的内核源代码文件,这个可以通过合适的字符识别从打印输出用获取;给第七版的源代码文件打补丁;移除一个发行版后被添加进来的元数据和其他文件,为避免得到错误的时间戳信息;修复毁坏的 SCCS 文件;通过移除 CVS symbols assigned to multiple revisions with a custom Perl script,删除 CVS *Attr* 文件和用 *cvs2svn* 将 CVS 仓库转换为 Git 仓库,来处理早期的 FreeBSD CVS 仓库。
|
||||
|
||||
在仓库表述中有一个很有意思的部分就是,如何导入那些快照,并以一种方式联系起来,使得 *git blame* 可以发挥它的魔力。快照导入到仓库是作为一系列的提交实现的,根据每个文件的时间戳。当所有文件导入后,就被用对应发行版的名字给标记了。在这点上,一个人可以删除那些文件,并开始导入下一个快照。注意 *git blame* 命令是通过回溯一个仓库的历史来工作的,并使用启发法来检测文件之间或内部的代码移动和复制。因此,删除掉的快照间会产生中断,防止它们之间的代码被追踪。
|
||||
|
||||
相反,在下一个快照导入之前,之前快照的所有文件都被移动到了一个隐藏的后备目录里,叫做 `.ref`(引用)。它们保存在那,直到下个快照的所有文件都被导入了,这时候它们就会被删掉。因为 `.ref` 目录下的每个文件都完全配对一个原始文件,*git blame* 可以知道多少源代码通过 `.ref` 文件从一个版本移到了下一个,而不用显示出 `.ref` 文件。为了更进一步帮助检测代码起源,同时增加表述的真实性,每个发行版都被表述成了一个合并,介于有增加文件的分支(*-Development*)与之前发行版之间的合并。
|
||||
|
||||
上世纪 80 年代这个时期,只有 Berkeley 开发文件的一个子集是用 SCCS 版本控制的。整个时期内,我们统一的仓库里包含了来自 SCCS 的提交和快照增加的文件。在每个发行版的时间点上,可以发现 SCCS 最近的提交,被标记成一个发行版中增加的导入分支的合并。这些合并可以在 Figure [2][29] 中间看到。
|
||||
|
||||
将各种数据资源综合到一个仓库的工作,主要是用两个脚本来完成的。一个 780 行的 Perl 脚本(`import-dir.pl`)可以从一个单独的数据源(快照目录,SCCS 仓库,或者 Git 仓库)中,以 *Git fast export* 格式导出(真实的或者综合的)提交历史。输出是一个简单的文本格式,Git 工具用这个来导入和导出提交。其他方面,这个脚本以一些东西为参数,如文件到贡献者的映射,贡献者登录名和他们的全名间的映射,导入的提交会被合并,哪些文件要处理,哪些文件要忽略,和“引用”文件的处理。一个 450 行的 Shell 脚本创建 Git 仓库,并调用带适当参数的 Perl 脚本,导入 27 个可用的历史数据资源。Shell 脚本也会跑 30 遍测试,比较特定标签的仓库和对应的数据源,确认出现的和没出现的备用目录,并查看分支树和合并的数量,*git blame* 和 *git log* 的输出中的退化。最后,*git* 被调用来作垃圾收集和压缩仓库,从最初的 6GB 降到发行的 1GB。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4 数据使用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
数据可以用于软件工程,信息系统和软件考古学领域的经验性研究。鉴于它从不间断而独一无二的存在了超过了 40 年,可以供软件的进化和代代更迭参考。伴随那个时代以来在处理速度千倍地增长,存储容量百万倍的扩大,数据同样可以用于软件和硬件技术交叉进化的研究。软件开发从研究中心到大学,到开源社区的转移,可以用来研究组织文化对于软件开发的影响。仓库也可以用于学习开发者编程的影响力,比如 Turing 奖获得者(Dennis Ritchie 和 Ken Thompson)和 IT 产业的大佬(Bill Joy 和 Eric Schmidt)。另一个值得学习的现象是代码的长寿,无论是单行的水平,或是作为那个时代随 Unix 发行的完整的系统(Ingres, Lisp, Pascal, Ratfor, Snobol, TMP),和导致代码存活或消亡的因素。最后,因为数据使 Git 底层软件仓库存储技术感到压力,到了它的限度,这会加速修正管理系统领域的工程进度。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Figure 3: Code style evolution along Unix releases.
|
||||
|
||||
Figure [3][30] 描述了一些有趣的代码统计,根据 36 个主要 Unix 发行版,验证了代码风格和编程语言的使用在很长的时间尺度上的进化。这种进化是软硬件技术的需求和支持驱动的,软件构筑理论,甚至社会力量。图片中的数据已经计算了在一个所给发行版中出现的文件的平均时间。正如可以从中看到,在过去的 40 年中,验证器和文件名字的长度已经稳定从 4 到 6 个字符增长到 7 到 11 个字符。我们也可以看到在评论数量的少量稳定增加,和 *goto* 表达的使用量减少,同时 *register* 这个类型修改器的消失。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5 未来的工作 ###
|
||||
|
||||
可以做很多事情去提高仓库的正确性和有效性。创建进程作为源代码开源了,通过 GitHub 的拉取请求,可以很容易地贡献更多代码和修复。最有用的社区贡献会使得导入的快照文件的覆盖增长,这曾经是隶属于一个具体的作者。现在,大约 90,000 个文件(在 160,000 总量之外)被指定了作者,根据一个默认的规则。类似地,大约有 250 个作者(最初 FreeBSD 那些)是验证器确认的。两个都列在了 build 仓库无配对的目录里,也欢迎贡献数据。进一步,BSD SCCS 和 FreeBSD CVS 的提交,共享相同的作者和时间戳,这些可以结合成一个单独的 Git 提交。导入 SCCS 文件提交的支持会被添加进来,为了引入仓库对应的元数据。最后,最重要的,开源系统的更多分支会添加进来,比如 NetBSD OpenBSD, DragonFlyBSD 和 *illumos*。理想地,其他重要的历史上的 Unix 发行版,它们的版权拥有者,如 System III, System V, NeXTSTEP 和 SunOS,也会在一个协议下释出他们的系统,允许他们的合作伙伴使用仓库用于研究。
|
||||
|
||||
### 鸣谢 ###
|
||||
|
||||
本人感谢很多付出努力的人们。 Brian W. Kernighan, Doug McIlroy 和 Arnold D. Robbins 帮助 Bell 实验室开发了登录验证器。 Clem Cole, Era Erikson, Mary Ann Horton, Kirk McKusick, Jeremy C. Reed, Ingo Schwarze 和 Anatole Shaw 开发了 BSD 的登录验证器。BSD SCCS 导入了 H. Merijn Brand 和 Jonathan Gray 的开发工作的代码。
|
||||
|
||||
这次研究通过 National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF) 的 Operational Program " Education and Lifelong Learning" - Research Funding Program: Thalis - Athens University of Economics and Business - Software Engineering Research Platform,由 European Union ( European Social Fund - ESF) 和 Greek national funds 出资赞助。
|
||||
|
||||
### 引用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
[[1]][31]
|
||||
M. D. McIlroy, E. N. Pinson, and B. A. Tague, "UNIX time-sharing system: Foreword," *The Bell System Technical Journal*, vol. 57, no. 6, pp. 1899-1904, July-August 1978.
|
||||
|
||||
[[2]][32]
|
||||
D. M. Ritchie and K. Thompson, "The UNIX time-sharing system," *Bell System Technical Journal*, vol. 57, no. 6, pp. 1905-1929, July-August 1978.
|
||||
|
||||
[[3]][33]
|
||||
D. M. Ritchie, "The evolution of the UNIX time-sharing system," *AT&T Bell Laboratories Technical Journal*, vol. 63, no. 8, pp. 1577-1593, Oct. 1984.
|
||||
|
||||
[[4]][34]
|
||||
P. H. Salus, *A Quarter Century of UNIX*. Boston, MA: Addison-Wesley, 1994.
|
||||
|
||||
[[5]][35]
|
||||
E. S. Raymond, *The Art of Unix Programming*. Addison-Wesley, 2003.
|
||||
|
||||
[[6]][36]
|
||||
M. J. Rochkind, "The source code control system," *IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering*, vol. SE-1, no. 4, pp. 255-265, 1975.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
#### Footnotes: ####
|
||||
|
||||
[1][37] - [https://github.com/dspinellis/unix-history-repo][38]
|
||||
|
||||
[2][39] - Updates may add or modify material. To ensure replicability the repository's users are encouraged to fork it or archive it.
|
||||
|
||||
[3][40] - [http://www.tuhs.org/archive_sites.html][41]
|
||||
|
||||
[4][42] - [https://www.mckusick.com/csrg/][43]
|
||||
|
||||
[5][44] - [http://www.oldlinux.org/Linux.old/distributions/386BSD][45]
|
||||
|
||||
[6][46] - [http://ftp-archive.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD-Archive/old-releases/][47]
|
||||
|
||||
[7][48] - [https://github.com/freebsd/freebsd][49]
|
||||
|
||||
[8][50] - [http://ftp.netbsd.org/pub/NetBSD/NetBSD-current/src/share/misc/bsd-family-tree][51]
|
||||
|
||||
[9][52] - [https://github.com/dspinellis/unix-history-make][53]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[wi-cuckoo](https://github.com/wi-cuckoo)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#MPT78
|
||||
[2]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#RT78
|
||||
[3]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#Rit84
|
||||
[4]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#Sal94
|
||||
[5]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#Ray03
|
||||
[6]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#sec:data
|
||||
[7]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#sec:dev
|
||||
[8]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#sec:use
|
||||
[9]:https://github.com/dspinellis/unix-history-repo
|
||||
[10]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAB
|
||||
[11]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAC
|
||||
[12]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#fig:provenance
|
||||
[13]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#fig:branches
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tuhs.org/archive_sites.html
|
||||
[15]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAD
|
||||
[16]:https://www.mckusick.com/csrg/
|
||||
[17]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAE
|
||||
[18]:http://www.oldlinux.org/Linux.old/distributions/386BSD
|
||||
[19]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAF
|
||||
[20]:http://ftp-archive.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD-Archive/old-releases/
|
||||
[21]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAG
|
||||
[22]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#SCCS
|
||||
[23]:https://github.com/freebsd/freebsd
|
||||
[24]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAH
|
||||
[25]:http://ftp.netbsd.org/pub/NetBSD/NetBSD-current/src/share/misc/bsd-family-tree
|
||||
[26]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAI
|
||||
[27]:https://github.com/dspinellis/unix-history-make
|
||||
[28]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFtNtAAJ
|
||||
[29]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#fig:branches
|
||||
[30]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#fig:metrics
|
||||
[31]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#CITEMPT78
|
||||
[32]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#CITERT78
|
||||
[33]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#CITERit84
|
||||
[34]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#CITESal94
|
||||
[35]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#CITERay03
|
||||
[36]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#CITESCCS
|
||||
[37]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAB
|
||||
[38]:https://github.com/dspinellis/unix-history-repo
|
||||
[39]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAC
|
||||
[40]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAD
|
||||
[41]:http://www.tuhs.org/archive_sites.html
|
||||
[42]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAE
|
||||
[43]:https://www.mckusick.com/csrg/
|
||||
[44]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAF
|
||||
[45]:http://www.oldlinux.org/Linux.old/distributions/386BSD
|
||||
[46]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAG
|
||||
[47]:http://ftp-archive.freebsd.org/pub/FreeBSD-Archive/old-releases/
|
||||
[48]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAH
|
||||
[49]:https://github.com/freebsd/freebsd
|
||||
[50]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAI
|
||||
[51]:http://ftp.netbsd.org/pub/NetBSD/NetBSD-current/src/share/misc/bsd-family-tree
|
||||
[52]:http://www.dmst.aueb.gr/dds/pubs/conf/2015-MSR-Unix-History/html/Spi15c.html#tthFrefAAJ
|
||||
[53]:https://github.com/dspinellis/unix-history-make
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
DFileManager:文件流文件管理器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
一个像宝石一样的文件管理器从Ubuntu标准库中缺失,但是有器自己的独特的特色。DFileManager是一个推特一样的产品
|
||||
|
||||
一个很棘手的问题是,如何知道有多少个Linux开源软件可以被使用。出于好奇,你可以在Shell里输入如下命令
|
||||
|
||||
~$ for f in /var/lib/apt/lists/*Packages; do printf ’%5d %s\n’ $(grep ’^Package: ’ “$f” | wc -l) ${f##*/} done | sort -rn
|
||||
|
||||
在我的Ubuntu15.04系统上,会产生如下结果
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
正如上面的截图所示,在所有的库中,大约有39000个包,在主库中有8500个包。这听起来很少.但是这些自助形式的开源软件、组件、支持库有很多不是由Ubuntu开发者打包的。重要的是,有很多重要的组件不在库中,只能通过源代码编译。DFileManager就是这样一个组件。他是仍处在早期阶段的一个QT跨平台文件管理器.QT提供单一源码的跨平台可移植性。
|
||||
|
||||
在缺失二进制文件的包里,用户需要编译源代码。对于一些工具来说,这个可能会产生很大的问题,特别是如果这个应用依赖于任何一个含糊不清的依赖库,或者某个没有被编译在系统中的特殊软件版本。
|
||||
### 安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
幸运的是,DFileManager非常容易编译。对于我的老Ubutnu来说,这个在开发者网站上的安装介绍提供了大部分的重要步骤,不过,少量的基础包没有在上面(为什么总是这样?虽然支持库会让文件系统变得一团糟!)。在我的系统上,为了做好准备,从github上下载源代码并且编译这个软件,我在Shell里输入了以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
~$ sudo apt-get install qt5-default qt5-qmake libqt5x11extras5-dev
|
||||
~$ git clone git://git.code.sf.net/p/dfilemanager/code dfilemanager-code
|
||||
~$ cd dfilemananger-code
|
||||
~$ mkdir build
|
||||
~$ cd build
|
||||
~$ cmake ../ -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr
|
||||
~$ make
|
||||
~$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过在shell中输入如下命令来启动它
|
||||
|
||||
~$ dfm
|
||||
|
||||
下面是在最吸引人的操作界面下操作的DFileManager,文件流视图.这提供了一个拥有相当有吸引力的体验的滑动当前文件夹下的文件的能力。这是看图片的理想选择。这个文件管理器酷似Finder(Macintosh 操作系统下的默认文件管理器),可能会对你有吸引力。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 特点: ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 4种视图:图标、详请、列和文件流
|
||||
- 通过位置和设备归类书签
|
||||
- 标签页
|
||||
- 简单的搜索和过滤
|
||||
- 自定义文件类型的缩略图,包括多媒体文件
|
||||
- 可以移动的信息栏
|
||||
- 单击打开文件和目录
|
||||
- 控制队列IO操作
|
||||
- 记住每个文件夹的视图属性
|
||||
- 显示隐藏文件
|
||||
|
||||
DFileManager 不是KDE 的Dolphin,但是能做相同的事情。这个是一个真正能够帮助人们的浏览文件的文件管理器。还有,别忘了反馈信息给开发者,任何人都可以做出这样的贡献
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://gofk.tumblr.com/post/131014089537/dfilemanager-cover-flow-file-manager-a-real-gem
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[gofk][a]
|
||||
译者:[bestony](https://github.com/bestony)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://gofk.tumblr.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,317 @@
|
||||
如何在linux 上配置持续集成服务 - Drone
|
||||
==============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
如果你对一次又一次的克隆、构建、测试和部署代码感到厌倦了,可以考虑一下持续集成。持续集成也就是CI,是软件工程的像我们一样的频繁提交的代码库,构建、测试和部署的实践。CI 帮助我们快速的集成新代码到已有的代码基线。如果这个过程是自动化进行的,那么就会提高开发的速度,因为这可以减少开发人员手工构建和测试的时间。[Drone][1] 是一个免费的开源项目,用来提供一个非常棒的持续集成服务的环境,采用了Apache 2.0 协议。它已经集成近很多代码库提供商,比如Github、Bitbucket 以及Google COde,并且它可以从代码库提取代码,使我们可以编译多种语言,包括PHP, Node, Ruby, Go, Dart, Python, C/C++, JAVA 等等。它是如此一个强大的平台是因为它每次构建都使用了容器和docker 技术,这让用户可以在保证隔离的条件下完全控制他们自己的构建环境。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 安装 Docker ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们要安装docker,因为这是Drone 的工作流的最关键的元素。Drone 合理的利用了docker 来构建和测试应用。容器技术提高了应用部署的效率。要安装docker ,我们需要在不同的linux 发行版本运行下面对应的命令,我们这里会说明Ubuntu 14.04 和CentOS 7 两个版本。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
要在Ubuntu 上安装Docker ,我们只需要运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
# apt-get install docker.io
|
||||
|
||||
安装之后我们需要使用`service` 命令重启docker 引擎。
|
||||
|
||||
# service docker restart
|
||||
|
||||
然后我们让docker 在系统启动时自动启动。
|
||||
|
||||
# update-rc.d docker defaults
|
||||
|
||||
Adding system startup for /etc/init.d/docker ...
|
||||
/etc/rc0.d/K20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
/etc/rc1.d/K20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
/etc/rc6.d/K20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
/etc/rc2.d/S20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
/etc/rc3.d/S20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
/etc/rc4.d/S20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
/etc/rc5.d/S20docker -> ../init.d/docker
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
第一,我们要更新机器上已经安装的软件包。我们可以使用下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# sudo yum update
|
||||
|
||||
要在centos 上安装docker,我们可以简单的运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# curl -sSL https://get.docker.com/ | sh
|
||||
|
||||
安装好docker 引擎之后我么只需要简单实用下面的`systemd` 命令启动docker,因为centos 7 的默认init 系统是systemd。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start docker
|
||||
|
||||
然后我们要让docker 在系统启动时自动启动。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable docker
|
||||
|
||||
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/docker.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/docker.service'
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 安装 SQlite 驱动 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Drone 默认使用SQLite3 数据库服务器来保存数据和信息。它会在/var/lib/drone/ 自动创建名为drone.sqlite 的数据库来处理数据库模式的创建和迁移。要安装SQLite3 我们要完成以下几步。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu 14.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
因为SQLite3 存在于Ubuntu 14.04 的默认软件库,我们只需要简单的使用apt 命令安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install libsqlite3-dev
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
要在Centos 7 上安装选哟使用下面的yum 命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install sqlite-devel
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 安装 Drone ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,我们安装好依赖的软件,我们现在更进一步的接近安装Drone。在这一步里我们值简单的从官方链接下载对应的二进制软件包,然后使用默认软件包管理器安装Drone。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
我们将使用wget 从官方的[Debian 文件下载链接][2]下载drone 的debian 软件包。下面就是下载命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# wget downloads.drone.io/master/drone.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Resolving downloads.drone.io (downloads.drone.io)... 54.231.48.98
|
||||
Connecting to downloads.drone.io (downloads.drone.io)|54.231.48.98|:80... connected.
|
||||
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
|
||||
Length: 7722384 (7.4M) [application/x-debian-package]
|
||||
Saving to: 'drone.deb'
|
||||
100%[======================================>] 7,722,384 1.38MB/s in 17s
|
||||
2015-11-06 14:09:28 (456 KB/s) - 'drone.deb' saved [7722384/7722384]
|
||||
|
||||
下载好之后,我们将使用dpkg 软件包管理器安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
# dpkg -i drone.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Selecting previously unselected package drone.
|
||||
(Reading database ... 28077 files and directories currently installed.)
|
||||
Preparing to unpack drone.deb ...
|
||||
Unpacking drone (0.3.0-alpha-1442513246) ...
|
||||
Setting up drone (0.3.0-alpha-1442513246) ...
|
||||
Your system ubuntu 14: using upstart to control Drone
|
||||
drone start/running, process 9512
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS 机器上我们要使用wget 命令从[下载链接][3]下载RPM 包。
|
||||
|
||||
# wget downloads.drone.io/master/drone.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
--2015-11-06 11:06:45-- http://downloads.drone.io/master/drone.rpm
|
||||
Resolving downloads.drone.io (downloads.drone.io)... 54.231.114.18
|
||||
Connecting to downloads.drone.io (downloads.drone.io)|54.231.114.18|:80... connected.
|
||||
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
|
||||
Length: 7763311 (7.4M) [application/x-redhat-package-manager]
|
||||
Saving to: ‘drone.rpm’
|
||||
100%[======================================>] 7,763,311 1.18MB/s in 20s
|
||||
2015-11-06 11:07:06 (374 KB/s) - ‘drone.rpm’ saved [7763311/7763311]
|
||||
|
||||
然后我们使用yum 安装rpm 包。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum localinstall drone.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 配置端口 ###
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成之后,我们要使它工作要先进行配置。drone 的配置文件在**/etc/drone/drone.toml** 。默认情况下drone 的web 接口使用的是80,而这也是http 默认的端口,如果我们要下面所示的修改配置文件里server 块对应的值。
|
||||
|
||||
[server]
|
||||
port=":80"
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 集成 Github ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了运行Drone 我们必须设置最少一个和GitHub、GitHub 企业版,Gitlab,Gogs,Bitbucket 关联的集成点。在本文里我们只集成了github,但是如果哦我们要集成其他的我们可以在配置文件做修改。为了集成github 我们需要在[github setting] 创建一个新的应用。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要创建一个应用,我们需要在`New Application` 页面点击`Register`,然后如下所示填表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我们应该保证在应用的配置项里设置了**授权了的回调链接**,链接看起来像`http://drone.linoxide.com/api/auth/github.com`。然后我们点击注册应用。所有都做好之后我们会看到我们需要在我们的Drone 配置文件里配置的客户端ID 和客户端密钥。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在这些都完成之后我们需要使用文本编辑器编辑drone 配置文件,比如使用下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/drone/drone.toml
|
||||
|
||||
然后我们会在drone 的配置文件里面找到`[github]` 部分,紧接着的是下面所示的配置内容
|
||||
|
||||
[github]
|
||||
client="3dd44b969709c518603c"
|
||||
secret="4ee261abdb431bdc5e96b19cc3c498403853632a"
|
||||
# orgs=[]
|
||||
# open=false
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 配置 SMTP 服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们想让drone 使用email 发送通知,那么我们需要在SMTP 配置里面设置我们的SMTP 服务器。如果我们已经有了一个SMTP 服务,那就只需要简单的使用它的配置文件就行了,但是因为我们没有一个SMTP 服务器,我们需要安装一个MTA 比如Postfix,然后在drone 配置文件里配置好SMTP。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
在ubuntu 里使用下面的apt 命令安装postfix。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install postfix
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS 里使用下面的yum 命令安装postfix。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install postfix
|
||||
|
||||
安装好之后,我们需要编辑我们的postfix 配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/postfix/main.cf
|
||||
|
||||
然后我们要把myhostname 的值替换为我们自己的FQDN,比如drone.linoxide.com。
|
||||
|
||||
myhostname = drone.linoxide.com
|
||||
|
||||
现在开始配置drone 配置文件里的SMTP 部分。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/drone/drone.toml
|
||||
|
||||
找到`[smtp]` 部分补充上下面的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
[smtp]
|
||||
host = "drone.linoxide.com"
|
||||
port = "587"
|
||||
from = "root@drone.linoxide.com"
|
||||
user = "root"
|
||||
pass = "password"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
注意:这里的**user** 和 **pass** 参数强烈推荐一定要改成一个用户的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 配置 Worker ###
|
||||
|
||||
如我们所知的drone 利用了docker 完成构建、测试任务,我们需要把docker 配置为drone 的worker。要完成这些需要修改drone 配置文件里的`[worker]` 部分。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/drone/drone.toml
|
||||
|
||||
然后取消底下几行的注释并且补充上下面的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
[worker]
|
||||
nodes=[
|
||||
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock",
|
||||
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
这里我们只设置了两个节点,这意味着上面的配置文件只能同时执行2 个构建操作。要提高并发性可以增大节点的值。
|
||||
|
||||
[worker]
|
||||
nodes=[
|
||||
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock",
|
||||
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock",
|
||||
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock",
|
||||
"unix:///var/run/docker.sock"
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
使用上面的配置文件drone 被配置为使用本地的docker 守护程序可以同时构建4个任务。
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. 重启 Drone ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,当所有的安装和配置都准备好之后,我们现在要在本地的linux 机器上启动drone 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
因为ubuntu 14.04 使用了sysvinit 作为默认的init 系统,所以只需要简单执行下面的service 命令就可以启动drone 了。
|
||||
|
||||
# service drone restart
|
||||
|
||||
要让drone 在系统启动时也自动运行,需要运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# update-rc.d drone defaults
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
因为CentOS 7使用systemd 作为init 系统,所以只需要运行下面的systemd 命令就可以重启drone。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart drone
|
||||
|
||||
要让drone 自动运行只需要运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable drone
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. 添加防火墙例外 ###
|
||||
|
||||
众所周知drone 默认使用了80 端口而我们又没有修改他,所以我们需要配置防火墙程序允许80 端口(http)开发并允许其他机器可以通过网络连接。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu 14.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
iptables 是最流行的防火墙程序,并且ubuntu 默认安装了它。我们需要修改iptable 暴露端口80,这样我们才能让drone 的web 界面在网络上被大家访问。
|
||||
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
# /etc/init.d/iptables save
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
因为CentOS 7 默认安装了systemd,它使用firewalld 作为防火墙程序。为了在firewalld 上打开80端口(http 服务),我们需要执行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. 访问web 界面 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们将在我们最喜欢的浏览器上通过web 界面打开drone。要完成这些我们要把浏览器指向运行drone 的服务器。因为drone 默认使用80 端口而我们有没有修改过,所以我们只需要在浏览器里根据我们的配置输入`http://ip-address/` 或 `http://drone.linoxide.com` 就行了。在我们正确的完成了上述操作后,我们就可以看到登陆界面了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
因为在上面的步骤里配置了Github,我们现在只需要简单的选择github然后进入应用授权步骤,这些完成后我们就可以进入工作台了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这里它会同步我们在github 上的代码库,然后询问我们要在drone 上构建那个代码库。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这一步完成后,它会询问我们在代码库里添加`.drone.yml` 文件的新名称,并且在这个文件里定义构建的过程和配置项,比如使用那个docker 镜像,执行那些命令和脚本来编译,等等。
|
||||
|
||||
我们按照下面的内容来配置我们的`.drone.yml`。
|
||||
|
||||
image: python
|
||||
script:
|
||||
- python helloworld.py
|
||||
- echo "Build has been completed."
|
||||
|
||||
这一步完成后我们就可以使用drone 应用里的YAML 格式的配置文件来构建我们的应用了。所有对代码库的提交和改变此时都会同步到这个仓库。一旦提交完成了,drone 就会自动开始构建。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
所有操作都完成后,我们就能在终端看到构建的结果了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在本文中我们学习了如何安装一个可以工作的使用drone 的持续集成平台。如果我们愿意我们甚至可以从drone.io 官方提供的服务开始工作。我们可以根据自己的需求从免费的服务或者收费服务开始。它通过漂亮的web界面和强大的功能改变了持续集成的世界。它可以集成很多第三方应用和部署平台。如果你有任何问题、建议可以直接反馈给我们,谢谢。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/setup-drone-continuous-integration-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[ezio](https://github.com/oska874)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://drone.io/
|
||||
[2]:http://downloads.drone.io/master/drone.deb
|
||||
[3]:http://downloads.drone.io/master/drone.rpm
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/settings/developers
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 15.10 上为单个网卡设置多个 IP 地址
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
有时候你可能想在你的网卡上使用多个 IP 地址。遇到这种情况你会怎么办呢?买一个新的网卡并分配一个新的 IP?不,这没有必要(至少在小网络中)。现在我们可以在 Ubuntu 系统中为一个网卡分配多个 IP 地址。想知道怎么做到的?跟着我往下看,其实并不难。
|
||||
有时候你可能想在你的网卡上使用多个 IP 地址。遇到这种情况你会怎么办呢?买一个新的网卡并分配一个新的 IP?不,没有这个必要(至少在小型网络中)。现在我们可以在 Ubuntu 系统中为一个网卡分配多个 IP 地址。想知道怎么做到的?跟着我往下看,其实并不难。
|
||||
|
||||
这个方法也适用于 Debian 以及它的衍生版本。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ip addr
|
||||
|
||||
**事例输出:**
|
||||
**样例输出:**
|
||||
|
||||
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default
|
||||
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
|
||||
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ifconfig
|
||||
|
||||
**事例输出:**
|
||||
**样例输出:**
|
||||
|
||||
enp0s3 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:2a:03:4b
|
||||
inet addr:192.168.1.103 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
|
||||
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@
|
||||
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
|
||||
RX bytes:38793 (38.7 KB) TX bytes:38793 (38.7 KB)
|
||||
|
||||
正如你在上面看到的,我的网卡名称是 **enp0s3**,它的 IP 地址是 **192.168.1.103**。
|
||||
正如你在上面输出中看到的,我的网卡名称是 **enp0s3**,它的 IP 地址是 **192.168.1.103**。
|
||||
|
||||
现在让我们来为网卡添加一个新的 IP 地址,例如说 **192.168.1.104**。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,7 +73,7 @@
|
||||
inet6 fe80::a00:27ff:fe2a:34e/64 scope link
|
||||
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
|
||||
|
||||
类似地,你可以添加想要的任意多的 IP 地址。
|
||||
类似地,你可以添加任意数量的 IP 地址,只要你想要。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们 ping 一下这个 IP 地址验证一下。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -108,7 +108,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
可以看到已经没有了!!
|
||||
|
||||
也许你已经知道,你重启系统后会丢失这些设置。那么怎么设置才能永久有效呢?这也很简单。
|
||||
正如你所知,重启系统后这些设置会失效。那么怎么设置才能永久有效呢?这也很简单。
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加永久 IP 地址 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -154,7 +154,7 @@ Ubuntu 系统的网卡配置文件是 **/etc/network/interfaces**。
|
||||
|
||||
保存并关闭文件。
|
||||
|
||||
无需重启运行下面的命令使更改生效。
|
||||
运行下面的命令使更改无需重启即生效。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ifdown enp0s3 && sudo ifup enp0s3
|
||||
|
||||
@ -182,7 +182,7 @@ Ubuntu 系统的网卡配置文件是 **/etc/network/interfaces**。
|
||||
DHCPACK of 192.168.1.103 from 192.168.1.1
|
||||
bound to 192.168.1.103 -- renewal in 35146 seconds.
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:如果你从远程连接到服务器,把上面的两个命令放到**一行**中**非常重要**,因为第一个命令会断掉你的连接。而采用这种方式可以存活你的 ssh 会话。
|
||||
**注意**:如果你从远程连接到服务器,把上面的两个命令放到**一行**中**非常重要**,因为第一个命令会断掉你的连接。而采用这种方式可以保留你的 ssh 会话。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,让我们用下面的命令来检查一下是否添加了新的 IP:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -228,9 +228,9 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/assign-multiple-ip-addresses-to-one-interface-on-ubu
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](http://mutouxiaogui.cn/blog/)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/linux-basics-assign-multiple-ip-addresses-single-network-interface-card-centos-7/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/linux-basics-assign-multiple-ip-addresses-single-network-interface-card-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,134 @@
|
||||
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu 14/15上配置Apache Solr
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
大家好,欢迎来阅读我们今天Apache Solr的文章。Apache Solr是一个最有名的开源搜索平台,基于在网站后端运行的Apache Lucene,能够让你轻松创建搜索引擎来搜索网站、数据库和文件。它能够索引和搜索多个网站并根据搜索文本的相关内容返回搜索建议.
|
||||
|
||||
Solr工作在可扩展标记语言(XML),并可以为JSON、Python和Ruby提供应用程序接口(APIs)。根据Apache Lucene项目,Solr提供了非常多的功能,让它很受管理员们的欢迎:
|
||||
- 全文检索
|
||||
- 分面导航
|
||||
- 拼写建议/自动完成
|
||||
- 自定义文档排序/排列
|
||||
|
||||
#### 前提条件: ####
|
||||
|
||||
在一个使用最小化安装包的全新 Ubuntu 14/15 系统上,你仅仅需要少量的准备,就开始安装 Apache Solor.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1)System Update 系统更新###
|
||||
|
||||
使用一个具有sudo权限的非root用户登录你的Ubuntu服务器,这将会在接下来的所有安装和使用Solr的步骤中使用。
|
||||
|
||||
登录成功后,使用下面的命令,升级你的系统到最新的更新及补丁
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
### 2) JRE Setup 安装JRE###
|
||||
|
||||
要安装Solr,首先需要安装JRE(Java Runtime Environment)作为基础环境,因为solr和tomcat都是基于Java.所以,我们需要安装最新版的Java和配置Java本地环境.
|
||||
|
||||
要想安装最新版的Java 8,我们需要通过以下命令安装Python Software Properties工具包
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install python-software-properties
|
||||
|
||||
完成后,配置最新版Java 8的仓库
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以通过以下命令更新包源列表,使用‘wget’来安装最新版本的Oracle Java 8,然后安装Java。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install oracle-java8-installer
|
||||
|
||||
在安装和配置Java SE Platform 和 JavaFX 过程中点击'OK'按钮接受 Oracle二进制代码许可协议(Oracle Binary Code License Agreement)。
|
||||
|
||||
在安装完成后,运行下面的命令,检查是否安装成功以及查看安装的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
kash@solr:~$ java -version
|
||||
java version "1.8.0_66"
|
||||
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_66-b17)
|
||||
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.66-b17, mixed mode)
|
||||
|
||||
执行结果表明我们已经成功安装了Java,并达到安装Solr最基本的要求了,接着我们进行下一步。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Solr###
|
||||
|
||||
有两种不同的方式可以在Ubuntu上安装Solr,在本文中我们只用最新的源码包来演示源码安装。
|
||||
|
||||
要使用源码安装Solr,先要从官网 [Web Page][1] 下载最新的可用安装包。复制以下链接,然后使用 'wget'命令来下载。
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://www.us.apache.org/dist/lucene/solr/5.3.1/solr-5.3.1.tgz
|
||||
|
||||
运行下面的命令,将已存档的服务解压到 /bin目录。
|
||||
|
||||
$ tar -xzf solr-5.3.1.tgz solr-5.3.1/bin/install_solr_service.sh --strip-components=2
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
运行脚本来启动Solr服务,这将会先创建一个solr的用户,然后将Solr安装成服务。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo bash ./install_solr_service.sh solr-5.3.1.tgz
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令来检查Solr服务的状态。
|
||||
|
||||
$ service solr status
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 创建Solr集合: ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们现在可以使用Solr用户添加多个集合。就像下图所示的那样,我们只需要在命令行中指定集合名称和指定其配置集就可以创建多个集合了。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo su - solr -c "/opt/solr/bin/solr create -c myfirstcollection -n data_driven_schema_configs"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我们已经成功的为我们的第一个集合创建了新的内核实例目录,并可以将数据添加到里面。
|
||||
查看库中的默认模式文件 '/opt/solr/server/solr/configsets/data_driven_schema_configs/conf'
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用Solr页面###
|
||||
|
||||
可以使用默认的端口8983连接Apache Solr.打开浏览器,输入 http://your_server_ip:8983/solr 或者 http://your-domain.com:8983/solr. 确保你的防火墙允许8983端口.
|
||||
|
||||
http://172.25.10.171:8983/solr/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在Solr的Web控制台左侧菜单点击'Core Admin'按钮,你将会看见我们之前使用CLI方式创建的集合。你可以点击'Add Core'按钮来创建新的内核。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
就像下图中所示,你可以选择某个集合和指向文档向里面添加内容或从文档中查询数据。像方框中显示的那样添加指定格式的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
"number": 1,
|
||||
"Name": "George Washington",
|
||||
"birth_year": 1989,
|
||||
"Starting_Job": 2002,
|
||||
"End_Job": "2009-04-30",
|
||||
"Qualification": "Graduation",
|
||||
"skills": "Linux and Virtualization"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
添加文件后点击'Submit Document'按钮.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 总结###
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu上安装成功后,你就可以使用Solr WEB接口插入或查询数据。如果你想通过Solr来管理更多的数据和文件,可以创建更多的集合。希望你能喜欢这篇文章并且希望它能够帮到你。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/configure-apache-solr-ubuntu-14-15/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kashif][a]
|
||||
译者:[taichirain](https://github.com/taichirain)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/kashifs/
|
||||
[1]:http://lucene.apache.org/solr/
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
||||
Linux 中如何从命令行访问 Dropbox
|
||||
Linux 中如何通过命令行访问 Dropbox
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在当今这个多设备的环境下,云存储无处不在。无论身处何方,人们都想通过多种设备来从云存储中获取所需的内容。由于优雅的 UI 和完美的跨平台兼容性,Dropbox 已成为最为广泛使用的云存储服务。 Dropbox 的流行已引发了一系列官方或非官方 Dropbox 客户端的出现,它们支持不同的操作系统平台。
|
||||
在当今这个多设备的环境下,云存储无处不在。无论身处何方,人们都想通过多种设备来从云存储中获取所需的内容。由于拥有漂亮的 UI 和完美的跨平台兼容性,Dropbox 已成为最为广泛使用的云存储服务。 Dropbox 的流行已引发了一系列官方或非官方 Dropbox 客户端的出现,它们支持不同的操作系统平台。
|
||||
|
||||
当然 Linux 平台下也有着自己的 Dropbox 客户端: 既有命令行的,也有图形界面。[Dropbox Uploader][1] 是一个简单易用的 Dropbox 命令行客户端,它是用 BASH 脚本语言所编写的。在这篇教程中,我将描述 **在 Linux 中如何使用 Dropbox Uploader 通过命令行来访问 Dropbox**。
|
||||
当然 Linux 平台下也有着自己的 Dropbox 客户端: 既有命令行的,也有图形界面客户端。[Dropbox Uploader][1] 是一个简单易用的 Dropbox 命令行客户端,它是用 BASH 脚本语言所编写的。在这篇教程中,我将描述 **在 Linux 中如何使用 Dropbox Uploader 通过命令行来访问 Dropbox**。
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux 中安装和配置 Dropbox Uploader ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Linux 中如何从命令行访问 Dropbox
|
||||
|
||||
请确保你已经在系统中安装了 `curl`,因为 Dropbox Uploader 通过 curl 来运行 Dropbox 的 API。
|
||||
|
||||
要配置 Dropbox Uploader,只需运行 dropbox_uploader.sh 即可。当你第一次运行这个脚本时,它将询问你,以使得它可以访问你的 Dropbox 账户。
|
||||
要配置 Dropbox Uploader,只需运行 dropbox_uploader.sh 即可。当你第一次运行这个脚本时,它将请求得到授权以使得脚本可以访问你的 Dropbox 账户。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./dropbox_uploader.sh
|
||||
|
||||
@ -88,7 +88,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/access-dropbox-command-line-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu 15.04 / CentOS 7 上安装 Android Studio
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
随着最近几年智能手机的进步,安卓成为了最大的手机平台之一,也有很多免费的用于开发安卓应用的工具。Android Studio 是基于 [IntelliJ IDEA][1] 用于开发安卓应用的集成开发环境。它是 Google 2014 年发布的免费开源软件,继 Eclipse 之后成为主要的 IDE。
|
||||
随着最近几年智能手机的进步,安卓成为了最大的手机平台之一,所有用于开发安卓应用的工具都是免费提供。Android Studio 是基于 [IntelliJ IDEA][1] 用于开发安卓应用的集成开发环境(IDE)。它是 Google 2014 年发布的免费开源软件,继 Eclipse 之后成为主要的 IDE。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章,我们一起来学习如何在 Ubuntu 15.04 和 CentOS 7 上安装 Android Studio。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 15.04 上安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以用两种方式安装 Android Studio。第一种是配置必须的库然后再安装它;另一种是从 Android 官方网站下载然后再本地编译安装。在下面的例子中,我们会使用命令行设置库并安装它。在继续下一步之前,我们需要确保我们已经安装了 JDK 1.6 或者更新版本。
|
||||
我们可以用两种方式安装 Android Studio。第一种是配置必须的库然后再安装它;另一种是从 Android 官方网站下载然后在本地编译安装。在下面的例子中,我们会使用命令行设置库并安装它。在继续下一步之前,我们需要确保我们已经安装了 JDK 1.6 或者更新版本。
|
||||
|
||||
这里,我打算安装 JDK 1.8。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,7 +32,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
上面的安装命令会在 /opt 目录下面安装 Android Studio。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,运行下面的命令启动安装窗口:
|
||||
现在,运行下面的命令启动安装向导:
|
||||
|
||||
$ /opt/android-studio/bin/studio.sh
|
||||
|
||||
@ -121,7 +121,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
虽然发布不到一年,但是 Android Studio 已经替代 Eclipse 成为了安装开发最主要的 IDE。它是唯一一个能支持之后 Google 提供的 Android SDKs 和其它 Android 特性的官方 IDE 工具。那么,你还在等什么呢?赶快安装 Android Studio 然后体验开发安装应用的乐趣吧。
|
||||
虽然发布不到一年,但是 Android Studio 已经替代 Eclipse 成为了Android开发最主要的 IDE。它是唯一能支持 Google 之后将要提供的 Android SDKs 和其它 Android 特性的官方 IDE 工具。那么,你还在等什么呢?赶快安装 Android Studio 来体验开发 Android 应用的乐趣吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -129,11 +129,11 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/tools/install-android-studio-ubuntu-15-04-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[B N Poornima][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](http://mutouxiaogui.cn/blog/)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/bnpoornima/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.jetbrains.com/idea/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downloads-2133151.html
|
||||
[3]:http://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://developer.android.com/sdk/index.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +1,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如何在FreeBSD 10.2上安装Nginx作为Apache的反向代理
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Nginx是一款免费的,开源的HTTP和反向代理服务器, 以及一个代理POP3/IMAP的邮件服务器. Nginx是一款高性能的web服务器,其特点是丰富的功能,简单的结构以及低内存的占用. 第一个版本由 Igor Sysoev在2002年发布,然而到现在为止很多大的科技公司都在使用,包括 Netflix, Github, Cloudflare, WordPress.com等等
|
||||
Nginx是一款免费的开源HTTP和反向代理服务器, 以及一个POP3/IMAP的邮件代理服务器。Nginx是一款高性能的web服务器,其特点是丰富的功能,简单的结构以及低内存的占用. 第一个版本由 Igor Sysoev在2002年发布,迄今为止很多大的科技公司依然在使用,包括 Netflix, Github, Cloudflare, WordPress.com等等。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇教程里我们会 "**在freebsd 10.2系统上,安装和配置Nginx网络服务器作为Apache的反向代理**". Apache 会用PHP在8080端口上运行,并且我们需要在80端口配置Nginx的运行,用来接收用户/访问者的请求.如果网页的用户请求来自于浏览器的80端口, 那么Nginx会用Apache网络服务器和PHP来通过这个请求,并运行在8080端口.
|
||||
在这篇教程里我们会 "**在freebsd 10.2系统上,安装和配置Nginx网络服务器作为Apache的反向代理**". Apache 会用PHP在8080端口上运行,并且我们需要在80端口配置Nginx的运行,用来接收用户/访问者的请求.如果网页的用户请求来自于浏览器的80端口, 那么Nginx会用Apache网络服务器和PHP来通过这个请求,并运行在8080端口。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 前提条件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ Nginx是一款免费的,开源的HTTP和反向代理服务器, 以及一个代
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 2 - 安装 Apache ###
|
||||
|
||||
Apache是现在使用范围最广的网络服务器以及开源的HTTP服务器.在FreeBSD里Apache是未被默认安装的, 但是我们可以直接从端口下载,或者解压包在"/usr/ports/www/apache24" 目录下,再或者直接从PKG命令的FreeBSD系统信息库安装。在本教程中,我们将使用PKG命令从FreeBSD的库中安装:
|
||||
Apache是现在使用范围最广的web服务器以及开源的HTTP服务器.在FreeBSD里Apache是未被默认安装的, 但是我们可以直接通过端口或者在"/usr/ports/www/apache24" 目录下的解压包安装,再或者直接从PKG命令的FreeBSD系统信息库安装。在本教程中,我们将使用PKG命令从FreeBSD的库中安装:
|
||||
|
||||
pkg install apache24
|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ Apache是现在使用范围最广的网络服务器以及开源的HTTP服务器.
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 4 - 配置 Apache 和 PHP ###
|
||||
|
||||
一旦所有都安装好了, 我们将会配置Apache在8080端口上运行, 并让PHP与Apache一同工作. 为了配置Apache,我们可以编辑 "httpd.conf"这个配置文件, 然而PHP我们只需要复制PHP的配置文件 php.ini 在 "/usr/local/etc/"目录下.
|
||||
一旦所有都安装好了, 我们将会配置Apache在8080端口上运行, 并让PHP与Apache一同工作. 要想配置Apache,我们可以编辑 "httpd.conf"这个配置文件, 然而PHP我们只需要复制"/usr/local/etc/"目录下的PHP配置文件 php.ini 。
|
||||
|
||||
进入到 "/usr/local/etc/" 目录 并且复制 php.ini-production 文件到 php.ini :
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ Apache是现在使用范围最广的网络服务器以及开源的HTTP服务器.
|
||||
SetHandler application/x-httpd-php-source
|
||||
</FilesMatch>
|
||||
|
||||
保存然后退出.
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
现在用sysrc命令,来添加Apache作为开机启动项目 :
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,7 +78,7 @@ Apache是现在使用范围最广的网络服务器以及开源的HTTP服务器.
|
||||
|
||||
service apache24 start
|
||||
|
||||
如果全部完毕, 在"/usr/local/www/apache24/data" 目录下,创建一个phpinfo文件是验证PHP在Apache下完美运行的好方法 :
|
||||
如果全部完毕, 在"/usr/local/www/apache24/data" 目录下创建一个phpinfo文件来验证PHP在Apache下完美运行:
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/local/www/apache24/data
|
||||
echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" > info.php
|
||||
@ -87,17 +87,17 @@ Apache是现在使用范围最广的网络服务器以及开源的HTTP服务器.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Apache 是使用 PHP 在 8080端口下运行的.
|
||||
Apache 是使用 PHP 在 8080 端口下运行的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 5 - 安装 Nginx ###
|
||||
|
||||
Nginx 以低内存的占用作为一款高性能的web服务器以及反向代理服务器.在这个步骤里,我们将会使用Nginx作为Apache的反向代理, 因此让我们用pkg命令来安装它吧 :
|
||||
Nginx 以低内存的占用作为一款高性能的web服务器以及反向代理服务器。在这个步骤里,我们将会使用Nginx作为Apache的反向代理, 因此让我们用pkg命令来安装它吧 :
|
||||
|
||||
pkg install nginx
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 6 - 配置 Nginx ###
|
||||
|
||||
一旦 Nginx 安装完毕, 在 "**nginx.conf**" 文件里,我们需要做一个新的配置文件来替换掉原来的nginx文件. 更改到 "/usr/local/etc/nginx/"目录下 并且默认备份到 nginx.conf 文件:
|
||||
一旦 Nginx 安装完毕, 在 "**nginx.conf**" 文件里,我们需要做一个新的配置文件来替换掉原来的nginx文件。更改到 "/usr/local/etc/nginx/"目录下,并且备份默认 nginx.conf 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/local/etc/nginx/
|
||||
mv nginx.conf nginx.conf.oroginal
|
||||
@ -164,7 +164,7 @@ Nginx 以低内存的占用作为一款高性能的web服务器以及反向代
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
保存退出.
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
下一步, 在nginx目录下面,创建一个 **proxy.conf** 文件,使其作为反向代理 :
|
||||
|
||||
@ -186,7 +186,7 @@ Nginx 以低内存的占用作为一款高性能的web服务器以及反向代
|
||||
proxy_buffers 100 8k;
|
||||
add_header X-Cache $upstream_cache_status;
|
||||
|
||||
保存退出.
|
||||
保存并退出.
|
||||
|
||||
最后一步, 为 nginx 的高速缓存创建一个 "/var/nginx/cache"的新目录 :
|
||||
|
||||
@ -194,14 +194,14 @@ Nginx 以低内存的占用作为一款高性能的web服务器以及反向代
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 7 - 配置 Nginx 的虚拟主机 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这个步骤里面,我们需要创建一个新的虚拟主机域 "saitama.me", 以跟文件 "/usr/local/www/saitama.me" 和日志文件一同放在 "/var/log/nginx" 目录下.
|
||||
在这个步骤里面,我们需要创建一个新的虚拟主机域 "saitama.me", 以跟文件 "/usr/local/www/saitama.me" 和日志文件一同放在 "/var/log/nginx" 目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
我们必须做的第一件事情就是创建新的目录来存放虚拟主机文件, 在这里我们将用到一个"**vhost**"的新文件. 并创建它 :
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/local/etc/nginx/
|
||||
mkdir vhost
|
||||
|
||||
创建好vhost 目录, 那么我们就进入这个目录并创建一个新的虚拟主机文件. 这里我取名为 "**saitama.conf**" :
|
||||
创建好vhost 目录, 那么我们就进入这个目录并创建一个新的虚拟主机文件。这里我取名为 "**saitama.conf**" :
|
||||
|
||||
cd vhost/
|
||||
nano -c saitama.conf
|
||||
@ -252,7 +252,7 @@ Nginx 以低内存的占用作为一款高性能的web服务器以及反向代
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
保存退出.
|
||||
保存并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
下一步, 为nginx和虚拟主机创建一个新的日志目录 "/var/log/" :
|
||||
|
||||
@ -265,7 +265,7 @@ Nginx 以低内存的占用作为一款高性能的web服务器以及反向代
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 8 - 测试 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这个步骤里面,我们只是测试我们的nginx和虚拟主机的配置.
|
||||
在这个步骤里面,我们只是测试我们的nginx和虚拟主机的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
用如下命令测试nginx的配置 :
|
||||
|
||||
@ -282,37 +282,37 @@ Nginx 以低内存的占用作为一款高性能的web服务器以及反向代
|
||||
cd /usr/local/www/saitama.me
|
||||
echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" > info.php
|
||||
|
||||
然后便访问这个文档 : **www.saitama.me/info.php**.
|
||||
然后访问这个域名 : **www.saitama.me/info.php**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Nginx 作为Apache的反向代理正在运行了,PHP也同样在进行工作了.
|
||||
Nginx 作为Apache的反向代理正在运行了,PHP也同样在进行工作了。
|
||||
|
||||
这是另一种结果 :
|
||||
|
||||
Test .html 文件无缓存.
|
||||
无缓存的 Test .html 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
curl -I www.saitama.me
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Test .css 文件只有三十天的缓存.
|
||||
有三十天缓存的 Test .css 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
curl -I www.saitama.me/test.css
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Test .php 文件正常缓存 :
|
||||
正常缓存的 Test .php 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
curl -I www.saitama.me/info.php
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
全部完成.
|
||||
全部完成。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Nginx 是最广泛的 HTTP 和反向代理的服务器. 拥有丰富的高性能和低内存/RAM的使用功能. Nginx使用了太多的缓存, 我们可以在网络上缓存静态文件使得网页加速, 并且在用户需要的时候再缓存php文件. 这样Nginx 的轻松配置和使用,可以让它用作HTTP服务器 或者 apache的反向代理.
|
||||
Nginx 是最受欢迎的 HTTP 和反向代理服务器,拥有丰富的高性能和低内存/RAM的使用功能。Nginx使用了太多的缓存, 我们可以在网络上缓存静态文件使得网页加速,并且在用户需要的时候再缓存php文件。这样 Nginx 的轻松配置和使用可以让它用作HTTP服务器或者 apache的反向代理。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -320,8 +320,8 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-nginx-reverse-proxy-apache-freebsd
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arul][a]
|
||||
译者:[KnightJoker](https://github.com/KnightJoker)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline(https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arulm/
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arulm/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,10 @@
|
||||
# 使用SystemBack备份你的Ubuntu/Linux Mint(系统还原)
|
||||
# 使用 SystemBack 备份你的 Ubuntu/Linux Mint(系统还原)
|
||||
|
||||
系统还原对于任何一款允许用户还原电脑到之前状态(包括文件系统,安装的应用,以及系统设置)的操作系统来说,都是必备功能,可以处理系统故障以及其他的问题。有的时候安装一个程序或者驱动可能让你的系统黑屏。系统还原则让你电脑里面的系统文件(译者注:是系统文件,并非普通文件,详情请看**注意**部分)和程序恢复到之前工作正常时候的状态,进而让你远离那让人头痛的排障过程了。而且它也不会影响你的文件,照片或者其他数据。简单的系统备份还原工具[Systemback](https://launchpad.net/systemback)让你很容易地创建系统备份以及用户配置文件。如果遇到问题,你可以傻瓜式还原。它还有一些额外的特征包括系统复制,系统安装以及Live系统创建。
|
||||
对于任何一款允许用户还原电脑到之前状态(包括文件系统,安装的应用,以及系统设置)的操作系统来说,系统还原都是必备功能,可以恢复系统故障以及其他的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
有的时候安装一个程序或者驱动可能让你的系统黑屏。系统还原则让你电脑里面的系统文件(译者注:是系统文件,并非普通文件,详情请看**注意**部分)和程序恢复到之前工作正常时候的状态,进而让你远离那让人头痛的排障过程了。而且它也不会影响你的文件,照片或者其他数据。
|
||||
|
||||
简单的系统备份还原工具[Systemback](https://launchpad.net/systemback)让你很容易地创建系统备份以及用户配置文件。一旦遇到问题,你可以简单地恢复到系统先前的状态。它还有一些额外的特征包括系统复制,系统安装以及Live系统创建。
|
||||
|
||||
截图
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +16,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:使用系统还原不会还原你的文件,音乐,电子邮件或者其他任何类型的私人文件。对不同用户来讲,这既是优点又是缺点。坏消息是它不会还原你意外删除的文件,不过你可以通过一个文件恢复程序来解决这个问题。如果你的计算机上没有系统还原点,那么系统还原工具就不会奏效了。(最后一句没有太理解)
|
||||
**注意**:使用系统还原不会还原你的文件,音乐,电子邮件或者其他任何类型的私人文件。对不同用户来讲,这既是优点又是缺点。坏消息是它不会还原你意外删除的文件,不过你可以通过一个文件恢复程序来解决这个问题。如果你的计算机没有还原点,那么系统恢复就无法奏效,所以这个工具就无法帮助你(还原系统),如果你尝试恢复一个主要问题,你将需要移步到另外的步骤来进行故障排除。
|
||||
|
||||
> > >适用于Ubuntu 15.10 Wily/16.04/15.04 Vivid/14.04 Trusty/Linux Mint 14.x/其他Ubuntu衍生版,打开终端,将下面这些命令复制过去:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,7 +36,7 @@ sudo apt-get install systemback
|
||||
via: http://www.noobslab.com/2015/11/backup-system-restore-point-your.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[DongShuaike](https://github.com/DongShuaike)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
|
||||
如何再Ubuntu中安装最新的Arduino IDE 1.6.6
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> 本篇教程会教你如何在现在的Ubuntu发布版中安装最新的 Arduino IDE,目前的版本为1.6.6。
|
||||
|
||||
开源的Arduino IDE发布了1.6.6,并带来了很多的改变。新的发布已经切换到Java 8,它与IDE绑定并且再编译时需要它。具体见[RELEASE NOTE][1]。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
对于那些不想使用软件中心的1.0.5旧版本的人而言,你可以使用下面的步骤再所有的Ubuntu发行版中安装Ardunino。
|
||||
|
||||
注:下面这个说明下面的代码颜色,这个发布的时候要对照一下原文,写点说明,因为颜色在md里标识不出来
|
||||
> **用红字替换将来的版本**
|
||||
|
||||
**1.** Download the latest packages, **Linux 32-bit or Linux 64-bit**, from the official link below:
|
||||
**1.** 从下面的官方链接下载最新的包 **Linux 32-bit 或者 Linux 64-bit**。
|
||||
|
||||
- [www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software][2]
|
||||
|
||||
不知道你系统的类型?进入系统设置->详细->概览。
|
||||
|
||||
**2.** 从Unity Dash、App Launcher或者Ctrl+Alt+T打开终端。打开后,一个个运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
进入下载文件夹:
|
||||
|
||||
cd ~/Downloads
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
使用tar命令解压
|
||||
|
||||
注:arduino-1.6.6-*.tar.xz 为红色部分
|
||||
tar -xvf arduino-1.6.6-*.tar.xz
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
将解压后的文件移动到**/opt/**下:
|
||||
|
||||
注:arduino-1.6.6 为红色部分
|
||||
sudo mv arduino-1.6.6 /opt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**3.** 现在IDE已经与最新的Java绑定使用了。但是最好位程序设置一个桌面图标/启动方式:
|
||||
|
||||
进入安装目录
|
||||
|
||||
注:arduino-1.6.6 为红色部分
|
||||
cd /opt/arduino-1.6.6/
|
||||
|
||||
在这个目录给install.sh可执行权限
|
||||
|
||||
chmod +x install.sh
|
||||
|
||||
最后运行脚本同事安装桌面快捷方式和启动图标:
|
||||
|
||||
./install.sh
|
||||
|
||||
下图中我用“&&”同事运行这三个命令:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后从Unity Dash、程序启动器或者桌面快捷方式运行Arduino IDE。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/2015/11/install-arduino-ide-1-6-6-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ji m][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/about/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/ReleaseNotes
|
||||
[2]:https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,176 @@
|
||||
|
||||
如何在 CentOS 7 / Ubuntu 15.04 上安装 PHP 框架 Framework
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
大家好,这篇文章将要讲述如何在 CentOS 7 / Ubuntu 15.04 上安装 PHP 框架 Laravel。如果你是一个 PHP Web 的开发者,你并不需要关心各种琳琅满目的现代 PHP 框架,Laravel 是最易用同时也是最能节省你时间的一个框架,能让你享受到 web 开发的乐趣。一个好的框架能让你在简单的使用指导下能快速开发出最核心的代码,Laravel 拥抱这一普世的开发哲学。你能抱持很高的开发效率并且无痛重构你现有的代码。
|
||||
|
||||
Laravel 安装极其容易,你只要跟着本文章一步步操作就能在 CentOS 7 或者 Ubuntu 15 服务器上安装。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1) 服务器要求 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在安装 Laravel 前需要安装一些它的依赖和先决条件,这些包括升级系统到最新版本,sudo 权限,和安装依赖包。
|
||||
|
||||
当你连接到你的服务器时,请确保你能通以下命令能成功的使用 EPEL 仓库并且升级你的服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS-7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install epel-release
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# rpm -Uvh https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
|
||||
# rpm -Uvh https://mirror.webtatic.com/yum/el7/webtatic-release.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install python-software-properties
|
||||
# add-apt-repository ppa:ondrej/php5
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install -y php5 mcrypt php5-mcrypt php5-gd
|
||||
|
||||
### 2) Firewall Setup ###
|
||||
|
||||
系统防火墙和 SELinux 设置对于用于生产的服务器安全来说非常重要,你可以关闭防火墙和用以下命令行设置 SELinux 成宽容模式(permissive)模式来保证安装程序不受他们的影响。
|
||||
|
||||
# setenforce 0
|
||||
|
||||
### 3) Apache, MariaDB, PHP Setup ###
|
||||
|
||||
Laravel 安装程序需要完成安装 LAMP 整个环境,需要额外安装 OpenSSL, PDO, Mbstring 和 Tokenizer PHP Extensions。如果 LAMP 已经运行在你的服务器上你可以跳过这部,但是需要注意一些必要的 PHP 插件是否安装好。
|
||||
|
||||
要安装完整 AMP 你需要在自己的服务器上运行以下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install httpd mariadb-server php56w php56w-mysql php56w-mcrypt php56w-dom php56w-mbstring
|
||||
|
||||
要在 CentOS 7 上实现 MySQL / Mariadb 服务开机自动启动,你需要运行以下命令
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start httpd
|
||||
# systemctl enable httpd
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
#systemctl start mysqld
|
||||
#systemctl enable mysqld
|
||||
|
||||
在启动 MariaDB 服务之后,你需要运行以下命令配置一个足够安全的密码
|
||||
|
||||
#mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install mysql-server apache2 libapache2-mod-php5 php5-mysql
|
||||
|
||||
### 4) 安装 Composer ###
|
||||
|
||||
在我们安装 Laravel 前,先让我们开始安装 composer。安装 composer 对于安装 Laravel 是最重要的步骤之一,因为 composer 能帮我们安装 Laravel 的各种依赖。
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS/Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
在 CentOS / Ubuntu 下运行以下命令来配置 composer
|
||||
|
||||
# curl -sS https://getcomposer.org/installer | php
|
||||
# mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composer
|
||||
# chmod +x /usr/local/bin/composer
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 5) Installing Laravel ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以运行以下命令从 github 上下载 Laravel 的安装包
|
||||
|
||||
# wget https://github.com/laravel/laravel/archive/develop.zip
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令解压安装包并且移动 document 的根目录
|
||||
|
||||
# unzip develop.zip
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# mv laravel-develop /var/www/
|
||||
|
||||
现在使用 compose 命令来安装目录下所有 Laravel 所需要的依赖
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /var/www/laravel-develop/
|
||||
# composer install
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 6) Key Encryption ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了加密服务器,我们使用以下命令来生成一个加密后的 32 位的密钥
|
||||
|
||||
# php artisan key:generate
|
||||
|
||||
Application key [Lf54qK56s3qDh0ywgf9JdRxO2N0oV9qI] set successfully
|
||||
|
||||
现在把这个密钥放到 'app.php' 文件,如以下所示
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /var/www/laravel-develop/config/app.php
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 7) 虚拟 Host 和 所属用户 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在 composer 安装好后,分配 document 根目录的权限和所属用户,如下所示
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod 775 /var/www/laravel-develop/app/storage
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# chown -R apache:apache /var/www/laravel-develop
|
||||
|
||||
用任意一款编辑器打开 apache 服务器的默认配置文件,在文件最后加上虚拟 host 入口
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
ServerName laravel-develop
|
||||
DocumentRoot /var/www/laravel/public
|
||||
|
||||
start Directory /var/www/laravel
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
Directory close
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们用以下命令重启 apache 服务器,打开浏览器查看 localhost 页面
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart httpd
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
# service apache2 restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 8) Laravel 5 Web Access ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开浏览器然后输入你的配置的 IP 地址或者绝对域名(to 校对:「绝对域名」译自 https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%AE%8C%E6%95%B4%E7%B6%B2%E5%9F%9F%E5%90%8D%E7%A8%B1#cite_note-1)你将会看到 Laravel 5 的默认页面
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Laravel 框架对于开发网页应用来说是一个绝好的的工具。所以,看了这篇文章你将学会在 Ubuntu 15 和 CentOS 7 上安装 Laravel 之后你就能开始使用这超棒的框架提供的各种功能来舒服的来进行你的开发工作。如果你有什么意见或者建议请发表在评论内容上,我们将根据您宝贵的反馈来使我们的文章更加浅显易懂。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-laravel-php-centos-7-ubuntu-15-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kashif][a]
|
||||
译者:[NearTan](https://github.com/NearTan)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/kashifs/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
||||
五大开源社区指标追踪
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你决定使用指标来追踪你的免费开源的软件社区。那么问题来了:我应该去追踪哪些指标呢?
|
||||
|
||||
要回答这个问题,你必须知道你需要什么信息。比如,你可能想要知道一个项目社区的可持续性。一个社区对问题的应对速度有多快。一个社区怎么吸引、维护或者流失贡献者。一旦你知道需要哪类信息,你就可以找出哪些社区活动可以提供你想要知道的内容。幸运的是,免费开源软件社区(FOSS)一些遵从开放式开发模型的项目在其软件开发仓库里留下了大量的公共数据,我们可以对这些数据进行分析,并从中收集到一些有用的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我会介绍一些指标,从而为你的项目社区提供一个多方位的视角分析。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 社区活动 ###
|
||||
|
||||
一个社区的总体活动和这个社区怎样随着时间演变,是度量所有社区好坏的非常有用的指标。社区活动是评价一个社区工作量的第一印象,也可以用来追踪不同种类的活动。比如,提交次数,给人的第一印象就是跟开发工作量挂钩。通过开放的投票数我们可以大概知道提交了多少bug或者又提出了多少新特性。邮件列表的数量或者论坛帖子的数量可以让我们了解到有过多少次公开的讨论。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[OpenStack活动看板][1]上面显示的项目代码提交次数和代码评审之后代码合并次数随时间变化的趋势图(周数据)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 社区规模 ###
|
||||
|
||||
社区的规模指的是参与到这个社区的人数,但是,基于不同形式的参与人数也有很大的差别。好消息是,通常你只对积极活跃的贡献者比较感兴趣。活跃的贡献者会在项目的仓库留下一些线索。这意味着你可以通过查看git仓库存放的代码中**author**字段来统计积极贡献代码的人数,或者通过看积极参与问题解决的人的得票数来统计活跃人数。
|
||||
|
||||
所谓活跃(某些人做了某些事)可以扩展到很多方面。一种常见的跟踪活动的方式是看有多少人做了工作量相当可观的任务。比如,通常一个项目代码的贡献者是来自这个项目社区的一小部分人。了解了这一小部分人,就对核心的工作组(比如,领导这个社区的人)有一个基本的认识了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Xen项目开发看板][2]上展示的该项目邮件列表上作者人数和提交人数随时间的变化趋势(每月数据)
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 社区表现 ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
到目前为止,关注点主要集中在活动数量和贡献者数量的统计上了。你也可以分析流程还有用户的表现如何。比如,你可以测量某流程需要多久才能执行完成。解决或者关闭投票的时间可以表明一个需要及时响应的项目对新信息的应对如何,比如修复一个已经提出的bug或者实现一个新需求。代码评审花费的时间,即从代码修改提交到被通过的时间,可以看出更新一个提出的改变要达到社区期望的标准需要多久。
|
||||
|
||||
其他的一些指标主要与项目处理挂起的工作表现如何有关,比如新的和被关闭投票的比例,或者仍然没有关闭的代码评审的后台日志。这些参数能告诉我们像投入到解决这些问题的资源是否充足这样的一些信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在[2015第三季度OpenStack开发报告][3]上显示的,每季度关闭与打开状态的投票数之比,接受与放弃的改变提案与最新的改变提案之比。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 社区人口统计 ###
|
||||
|
||||
随着贡献者的参与或者退出,社区也在不断改变。社区的年龄(从社区成员加入时算起)取决于随着时间变化,人们怎么加入和退出社区。[社区年龄统计图表][4]很直观的展现了这些改变随时间的变化。图标是由一系列的水平条组成,每两条水平条代表加入到社区的一代人。对于每一代,Attracted水平条表示在相应的时间里有多少人加入到了社区。Retained水平条表示有多少人目前仍然活跃在社区。
|
||||
|
||||
代表一代人的两个水平条的关系就是滞留比例:依然在这个项目中的那一代人的一部分。Attracted水平条的完整集合表示这个项目在过去有多么受欢迎。Retained水平条的完整集合则表示社区目前的年龄结构。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Eclipse开发看板][5]上显示的Eclipse社区的社区年龄表。每六个月定义一次。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 社区多样性 ###
|
||||
|
||||
多样性是一个社区保持弹性的很关键的因素。通常来说,一个社区越具有多样性(人或者组织参与的多元化),那么这个社区的弹性也就越大。比如,如果一个公司要决定离开一个免费开源社区,那么这个公司的员工贡献5%要远比贡献85%所可能引起的潜在问题要小很多。
|
||||
|
||||
[小马因素][6],是[Daniel Gruno][7] 为“最少的开发者贡献了50%的代码提交量”这一现象定义的术语。基于这一小马因素,大象因素则是指最少量的公司其员工贡献了50%的代码提交量。这两个数据提供了一种指示,即这个社区依赖多少人或者公司。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[2015开发云数量状态统计][8]显示的在云计算领域的几个免费开源社区项目的小马和大象因素。
|
||||
|
||||
还有许多其他的指标来衡量一个社区。在决定收集哪些指标时,可以考虑一下社区的目标,还有哪些指标能帮到你。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/business/15/12/top-5-open-source-community-metrics-track
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jesus M. Gonzalez-Barahona][a]
|
||||
译者:[sonofelice](https://github.com/sonofelice)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://opensource.com/users/jgbarah
|
||||
[1]:http://activity.openstack.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://projects.bitergia.com/xen-project-dashboard/
|
||||
[3]:http://activity.openstack.org/dash/reports/2015-q3/pdf/2015-q3_OpenStack_report.pdf
|
||||
[4]:http://radar.oreilly.com/2014/10/measure-your-open-source-communitys-age-to-keep-it-healthy.html
|
||||
[5]:http://dashboard.eclipse.org/demographics.html
|
||||
[6]:https://ke4qqq.wordpress.com/2015/02/08/pony-factor-math/
|
||||
[7]:https://twitter.com/humbedooh
|
||||
[8]:https://speakerdeck.com/jgbarah/the-quantitative-state-of-the-open-cloud-2015-edition
|
||||
@ -1,106 +0,0 @@
|
||||
如何在CentOS上启用Software Collections(SCL)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
红帽企业版linux(RHEL)和它的社区版分支——CentOS,提供10年的生命周期,这意味着RHEL/CentOS的每个版本会提供长达10年的安全更新。虽然这么长的生命周期为企业用户提供了更需要的系统兼容性和可靠性,但也存在一个缺点:随着底层的RHEL/CentOS版本接近生命周期的结束,核心应用和运行时环境变得陈旧过时。例如CentOS 6.5,它的生命周期结束时间是2020年11月30日,携带Python 2.6.6和MySQL 5.1.73,以今天的标准来看已经非常古老了。
|
||||
|
||||
另一方面,在RHEL/CentOS上试图手动升级开发工具链和运行时环境存在潜在的可能使系统崩溃,除非所有依赖都被正确解决。通常情况下,手动升级都是不推荐的,除非你知道你在干什么。
|
||||
|
||||
[Software Collections][1](SCL)源出现了,以帮助解决RHEL/CentOS下的这种问题。SCL的创建就是为了给RHEL/CentOS用户提供一种方式以方便、安全地安装和使用应用程序和运行时环境的多个(而且可能更新的)版本,同时避免把系统搞乱。与之相对的是第三方源,它们可能会在已安装的包之间引起冲突。
|
||||
|
||||
最新的SCL提供:
|
||||
|
||||
- Python 3.3 和 2.7
|
||||
- PHP 5.4
|
||||
- Node.js 0.10
|
||||
- Ruby 1.9.3
|
||||
- Perl 5.16.3
|
||||
- MariaDB 和 MySQL 5.5
|
||||
- Apache httpd 2.4.6
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇教程的剩余部分,我会展示一下如何配置SCL源,以及如何安装和启用SCL中的包。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置SCL源
|
||||
|
||||
SCL可用于CentOS 6.5及更新的版本。要配置SCL源,只需执行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install centos-release-SCL
|
||||
|
||||
要启用和运行SCL中的应用,你还需要安装下列包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install scl-utils-build
|
||||
|
||||
执行下面的命令可以查看SCL中可用包的完整列表:
|
||||
|
||||
$ yum --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo="scl" list available
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 从SCL中安装和启用包
|
||||
|
||||
既然你已配置好了SCL,你可以继续并从SCL中安装包了。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以搜索SCL中的包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ yum --disablerepo="*" --enablerepo="scl" search <keyword>
|
||||
|
||||
我们假设你要安装Python 3.3。
|
||||
|
||||
继续,就像通常安装包那样使用yum安装:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install python33
|
||||
|
||||
任何时候你都可以查看从SCL中安装的包的列表,只需执行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ scl --list
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
python33
|
||||
|
||||
SCL的优点之一是安装其中的包不会覆盖任何系统文件,并且保证了不会引起系统中其它库和应用的冲突。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,若果在安装python33包后检查默认的python版本,你会发现默认的版本并没有改变:
|
||||
|
||||
$ python --version
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Python 2.6.6
|
||||
|
||||
如果想使用一个已经安装的SCL包,你需要在每个命令中使用scl命令显式启用它(译注:即想在哪条命令中使用SCL中的包,就得通过scl命令执行该命令)
|
||||
|
||||
$ scl enable <scl-package-name> <command>
|
||||
|
||||
例如,要针对python命令启用python33包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ scl enable python33 'python --version'
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
Python 3.3.2
|
||||
|
||||
如果想在启用python33包时执行多条命令,你可以像下面那样创建一个启用SCL的bash会话:
|
||||
|
||||
$ scl enable python33 bash
|
||||
|
||||
在这个bash会话中,默认的python会被切换为3.3版本,直到你输入exit,退出会话。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
简而言之,SCL有几分像Python的虚拟环境,但更通用,因为你可以为远远更多的应用启用/禁用SCL会话,而不仅仅是Python。
|
||||
|
||||
更详细的SCL指南,参考官方的[快速入门指南][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/enable-software-collections-centos.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[bianjp](https://github.com/bianjp)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:https://www.softwarecollections.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.softwarecollections.org/docs/
|
||||
86
translated/tech/20151222 Turn Tor socks to http.md
Normal file
86
translated/tech/20151222 Turn Tor socks to http.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
将Tor socks转换成http
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
使用tor服务你可以使用不同的工具像Tor浏览器、Foxyproxy和其他事情,有些下载管理器像wget和aria2不能直接直接使用tor socks开始匿名下载,因此我们需要一些工具来将tor socks转换成http代理这样就能用它来下载了。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:本教程基于Debian下,其他发行版会有些不同,因此如果你的发行版是基于Debian的,就可以直接使用下面的配置了。
|
||||
|
||||
**Polipo** : 这个服务会使用8123端口和127.0.0.1的IP,使用下面的命令来在计算机上安装Polipo:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt install polipo
|
||||
|
||||
现在使用这个命令打开Polipo的配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo nano /etc/polipo/config
|
||||
|
||||
在文件最后加入下面的行:
|
||||
|
||||
proxyAddress = "::0"
|
||||
allowedClients = 192.168.1.0/24
|
||||
socksParentProxy = "localhost:9050"
|
||||
socksProxyType = socks5
|
||||
|
||||
用下面的命令来重启Polipo:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo service polipo restart
|
||||
|
||||
现在Polipo已经安装好了!在匿名的世界里做你想做的吧!下面是使用的例子:
|
||||
|
||||
pdmt -l "link" -i 127.0.01 -p 8123
|
||||
|
||||
用上面的命令PDMT(Persian下载器)会匿名地下载你的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
**Proxychains** : 在此服务中你可以设置使用tor或者Lantern代理,但是在使用上它和Polipo和Privoxy有点不同,它不需要使用任何端口!使用下面的命令来安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt install proxychains
|
||||
|
||||
用这条命令来打开配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo nano /etc/proxychains.conf
|
||||
|
||||
现在添加下面的代码到文件底部,这里是tor的端口和IP:
|
||||
|
||||
socks5 127.0.0.1 9050
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在命令的前面加上“proxychains”并运行,它就能通过tor代理来运行:
|
||||
|
||||
proxychains firefoxt
|
||||
proxychains aria2c
|
||||
proxychains wget
|
||||
|
||||
**Privoxy** : Privoxy使用8118端口,并且首次可以很轻松地通过privoxy包来安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt install privoxy
|
||||
|
||||
我们现在要修改配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo nano /etc/pivoxy/config
|
||||
|
||||
在文件底部加入下面的行:
|
||||
|
||||
forward-socks5 / 127.0.0.1:9050 .
|
||||
forward-socks4a / 127.0.0.1:9050 .
|
||||
forward-socks5t / 127.0.0.1:9050 .
|
||||
forward 192.168.*.*/ .
|
||||
forward 10.*.*.*/ .
|
||||
forward 127.*.*.*/ .
|
||||
forward localhost/ .
|
||||
|
||||
重启服务:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo service privoxy restart
|
||||
|
||||
服务已经好了!端口是8118,IP是127.0.0.1,就尽情使用吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/turn-tor-socks-http/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Hossein heydari][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/hossein/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,392 @@
|
||||
GHLandy Translated
|
||||
|
||||
LFCS系列第二讲:如何安装和使用纯文本编辑器vi/vim
|
||||
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
几个月前, Linux 基金会发起了 LFCS (Linux Foundation Certified System administrator,Linux 基金会认证系统管理员)认证,以帮助世界各地的人来验证他们能够在 Linux 系统上做基本的中间系统管理任务:如系统支持,第一手的故障诊断和处理,以及何时向上游支持团队提出问题的智能决策。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中学习 vi 编辑器
|
||||
|
||||
请简要看看一下视频,里边介绍了 Linux 基金会认证的程序。
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe width="720" height="405" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="allowfullscreen" src="//www.youtube.com/embed/Y29qZ71Kicg"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章是《十个教程》系列的第二部分,在这个部分,我们会介绍 vi/vim 基本的文件编辑操作,帮助读者理解编辑器中的三个模式,这是LFCS认证考试中必须掌握的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 vi/vim 执行基本的文件编辑操作 ###
|
||||
|
||||
vi 是为 Unix 而生的第一个全屏文本编辑器。它的设计小巧简单,对于仅仅使用过诸如 NotePad++ 或 gedit 等图形界面的文本编辑器的用户来说,使用起来可能存在一些困难。
|
||||
|
||||
为了使用 vi,我们必须首先理解这个强大的程序操作中的三种模式,方便我们后边学习这个强大的文本处理软件的相关操作。
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,大多数的现代 Linux 发行版都集成了 vi 的变种——— vim(Vi IMproved,VI 的改进),相比于 vi,它有更多新功能。所以,我们会在本教程中交替使用 vi 和 vim。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的发行版还没有安装 vim,你可以通过以下方法来安装:
|
||||
|
||||
- Ubuntu 及其衍生版:apt-get update && apt-get install vim
|
||||
- 以 Red-Hat 为基础的发行版:yum update && yum install vim
|
||||
- openSUSE :zypper update && zypper install vim
|
||||
|
||||
### 我为什么要学习 vi ###
|
||||
|
||||
至少有以下两个理由:
|
||||
|
||||
1.因为它是 POSIX 标准的一部分,所以不管你使用什么发行版 vi 总是可用的。
|
||||
|
||||
2.vi 基本不消耗多少系统资源,并且允许我们仅仅通过键盘来完成任何可能的任务。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,vi 有的非常丰富的内置帮助手册,程序打开后就可以通过 :help 命令来查看。这个内置帮助手册比 vi/vim 的 man 页面包含了更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
vi Man 页面
|
||||
|
||||
#### 启动 vi ####
|
||||
|
||||
可以通过在命令提示符下输入 vi 来启动。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
使用 vi 编辑器
|
||||
|
||||
然后按下字母 i,你就可以开始输入了。或者通过下面的方法来启动 vi:
|
||||
|
||||
# vi filename
|
||||
|
||||
这样会打开一个名为 filename 的 buffer(稍后详细介绍 buffer),在你编辑完成之后就可以存储在磁盘中了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 理解 vi 的三个模式 ####
|
||||
|
||||
1.在命令模式中,vi 允许用户浏览该文件并输入由一个或多个字母组成简短的、大小写敏感的 vi 命令。这些命令的大部分都可以增加一个前缀数字表示执行次数。
|
||||
|
||||
比如:yy(或Y) 复制当前的整行,3yy(或3Y) 复制当前整行和下边紧接着的两行(总共3行)。通过 Esc 键可以随时进入命令模式(而不管当前工作在什么模式下)。事实上,在命令模式下,键盘上所有的输入都被解释为命令而非文本,这往往使得初学者困惑不已。
|
||||
|
||||
2.在末行模式中,我们可以处理文件(包括保存当前文件和运行外部程序)。我们必须在命令模式下输入一个冒号(:),才能进入这个模式,紧接着是需要使用的末行模式下的命令。执行之后 vi 自动回到命令模式。
|
||||
|
||||
3.在文本输入模式(通常使用字母 i 进入这个模式)中,我们可以随意输入文本。大多数的键入将以文本形式输出到屏幕(一个重要的例外是Esc键,它将退出文本编辑模式并回到命令模式)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
vi 文本插入模式
|
||||
|
||||
#### vi 命令 ####
|
||||
|
||||
下面的表格列出常用的 vi 命令。文件版本的命令可以通过添加叹号的命令强制执行(如,:q! 命令强制退出编辑器而不保存文件)。
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table cellspacing="0" border="0">
|
||||
<colgroup width="290">
|
||||
</colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="781">
|
||||
</colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#999999" height="19" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="font-size: small;"> 关键命令</span></b></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#999999" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="font-size: small;"> 描述</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> h 或 ←</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标左移一个字符</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> j 或 ↓</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标下移一行</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> k 或 ↑</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标上移一行</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> l (小写 L) 或 →</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标右移一个字符</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> H</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标移至屏幕顶行</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> L</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标移至屏幕末行</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> G</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标移至文件末行</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> w</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标右移一个词</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> b</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标左移一个词</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> 0 (零)</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标移至行首</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> ^</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标移至当前行第一个非空格字符</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> $</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标移至当前行行尾</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> Ctrl-B</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 向后翻页</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> Ctrl-F</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 向前翻页</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> i</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 在光标所在位置插入文本</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> I (大写 i)</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 在当前行首插入文本</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> J (大写 j)</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 将下一行与当前行合并(下一行上移到当前行)</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> a</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 在光标所在位置后追加文本</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> o (小写 O)</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 在当前行下边插入空白行</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> O (大写 o)</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 在当前行上边插入空白行</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> r</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 替换光标所在位置的字符</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> R</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 光标所在位置覆盖插入文本</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> x</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 删除光标所在位置的字符</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> X</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 立即删除光标所在位置之前(左边)的一个字符</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> dd</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 剪切当前整行文本(为了之后进行粘贴)</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="20" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> D</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 剪切光标所在位置到行末的文本(该命令等效于 d$)</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="20" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> yX</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 给 X 命令一个移动长度,复制适当数量的字符、单词或者从光标开始到一定数量的行</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> yy 或 Y</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 复制当前整行</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> p</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 粘贴在光标所在位置之后(下一行)</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> P</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 粘贴在光标所在位置之前(上一行)</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> . (句点)</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 重复最后一个命令</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> u</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 撤销最后一个命令</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> U</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 撤销最后一行的最后一个命令,只有光标仍在最后一行才能执行。</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> n</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 在查找中跳到下一个匹配项</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> N</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 在查找中跳到前一个匹配项</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> :n</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 下一个文件,编辑多个指定文件时,该命令加载下一个文件。</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="20" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> :e file</td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 加载新文件来替代当前文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="20" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> :r file</td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 将新文件的内容插入到光标所在位置的下一行</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> :q</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 退出并放弃更改</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="20" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> :w file</td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 将当期打开的buffer保存为file。如果是追加到已存在的文件中,则使用 :w >> file 命令</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="18" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-family: Courier New;"> :wq</span></td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 保存当前文件的内容并退出。等效于 x! 和 ZZ</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="20" align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> :r! command</td>
|
||||
<td align="LEFT" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"> 执行 command 命令,并将命令的输出插入到光标所在位置的下一行</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
#### vi 选项 ####
|
||||
|
||||
下列选项将会在启动 Vim 的时候进行加载(需要写入到~/.vimrc文件):
|
||||
|
||||
# echo set number >> ~/.vimrc
|
||||
# echo syntax on >> ~/.vimrc
|
||||
# echo set tabstop=4 >> ~/.vimrc
|
||||
# echo set autoindent >> ~/.vimrc
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
vi编辑器选项
|
||||
|
||||
- set number 当 vi 打开或新建文件时,显示行号。
|
||||
- syntax on 打开语法高亮(对应多个文件扩展名),以便源码文件和配置文件更具可读性。
|
||||
- set tabstop=4 设置制表符间距为 4 个空格(默认为 8)。
|
||||
- set autoindent 将前一行的缩进应用于下一行。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 查找和替换 ####
|
||||
|
||||
vi 具有通过查找将光标移动到(在单独一行或者整个文件中的)指定位置。它还可自动或者通过用户确认来执行文本替换。
|
||||
|
||||
a) 在行内查找。f 命令在当前行查找指定字符,并将光标移动到指定字符出现的位置。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,命令 fh 会在本行中将光标实例字母h出现的位置。注意,字母 f 和你要查找的字符都不会出现在屏幕上,但是当你按下回车的时候,要查找的字符会被高亮显示。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,以下是在命令模式按下 f4 之后的结果。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 vi 中查找字符。
|
||||
|
||||
b) 在整个文件内查找。使用 / 命令,紧接着需要查找的单词或短语。这个查找可以通过使用 n 命令或者 N 重复查找上一个查找的字符串。以下是在命令模式键入 /Jane 的查找结果。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在vi中查找字符
|
||||
|
||||
c) vi 通过使用命令来完成多行或者整个文件的替换操作(类似于 sed)。我们可以使用以下命令,使得整个文件中的单词 “old” 替换为 “young”。
|
||||
|
||||
:%s/old/young/g
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:冒号位于命令的最前面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
vi 的查找和替换
|
||||
|
||||
冒号 (:) 进入末行模式,在本例中 s 表示替换,% 是从第一行到最后一行的表示方式(也可以使用 nm 表示范围,即第 n 行到第 m 行),old 是查找模式,young 是用来替换的文本,g 表示在每个查找出来的字符串都进行替换。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,在命令最后增加一个 c,可以在每一个匹配项替换前进行确认。
|
||||
|
||||
:%s/old/young/gc
|
||||
|
||||
将就文本替换为新文本前,vi/vim 会想我们显示一下信息:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
vi 中替换字符串
|
||||
|
||||
- y: 执行替换(yes)
|
||||
- n: 跳过这个匹配字符的替换并转到下一个(no)
|
||||
- a: 在当前匹配字符及后边的相同项全部执行替换
|
||||
- q 或 Esc: 取消替换
|
||||
- l (小写 L): 执行本次替换并退出
|
||||
- Ctrl-e, Ctrl-y: 下翻页,上翻页,查看相应的文本来进行替换
|
||||
|
||||
#### 同时编辑多个文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
我们在命令提示符输入 vim file1 file2 file3 如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# vim file1 file2 file3
|
||||
|
||||
vim 会首先打开 file1,要跳到 file2 需用 :n 命令。当需要打开前一个文件时,:N 就可以了。
|
||||
|
||||
为了从 file1 跳到 file3
|
||||
|
||||
a) :buffers 命令会显示当前正在编辑的文件列表
|
||||
|
||||
:buffers
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
编辑多个文件
|
||||
|
||||
b) :buffer 3 命令(后边没有 s)会打开 file 进行编辑。
|
||||
|
||||
在上边的图片中,标记符号 # 表示该文件当前已被打开在后台,而 %a 标记的文件是正在被编辑的。另外,文件号(如上边例子的 3)后边的空格表示该文件还没有被打开。
|
||||
|
||||
#### vi 的临时 buffers ####
|
||||
|
||||
为了复制连续的多行(比如,假设为 4 行)到一个名为 a 的临时 buffer(与文件无关),并且还要将这些行粘贴到在当前 vi 会话文件中的其它位置,我们需要:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 按下 Esc 键以确认 vi 处在命令模式
|
||||
|
||||
2. 将光标放在我们希望复制的第一行文本
|
||||
|
||||
3. 输入 a4yy 复制当前行和接下来的 3 行,进入一个名为 a 的 buffer。我们一继续编辑我们的文件————我们不需要立即插入刚刚复制的行。
|
||||
|
||||
4. 当到了需要使用刚刚复制行的位置,在 p(小写)或 P(大写)命令来讲复制行插入到名为 a 的 buffer:
|
||||
|
||||
- 输入 ap,复制行将插入到光标位置所在行的下一行。
|
||||
- 输入 aP,复制行将插入到光标位置所在行的上一行。
|
||||
|
||||
如果愿意,我们可以重复上述步骤,将 buffer a 中的内容插入到我们文件的多个位置。一个临时 buffer,像本次会话中的一样,会在当前窗口关闭时释放掉。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
像我们看到的一样,vi/vim 在命令接口下是一个强大而灵活的文本编辑器。通过以下链接,随时分享你自己的技巧和评论。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 参考链接 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- [About the LFCS][1]
|
||||
- [Why get a Linux Foundation Certification?][2]
|
||||
- [Register for the LFCS exam][3]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/vi-editor-usage/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[GHLandy](https://github.com/GHLandy)
|
||||
校对:[东风唯笑](https://github.com/dongfengweixiao)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:https://training.linuxfoundation.org/certification/LFCS
|
||||
[2]:https://training.linuxfoundation.org/certification/why-certify-with-us
|
||||
[3]:https://identity.linuxfoundation.org/user?destination=pid/1
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,153 @@
|
||||
Linux 教学之教你玩音乐
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Linux 学习系列][1]的所有文章:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之教你练打字][2]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之物理模拟][3]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之教你玩音乐][4]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之两款地理软件][5]
|
||||
- [Linux 教学之掌握数学][6]
|
||||
|
||||
引言:Linux 提供大量的教学软件和工具,面向各个年级段以及年龄段,提供大量学科的练习实践,其中大多数是可以与用户进行交互的。本“Linux 教学”系列就来介绍一些教学软件。
|
||||
|
||||
学习音乐是一个很好的消遣方式。训练你的耳朵能识别音阶与和弦、掌握一门乐器、控制自己的嗓音,这些都需要大量的练习,以及会遇到很多困难。音乐理论非常博大精深,有太多东西需要记忆,你需要非常勤奋才能讲这些东西变成你的“技术”。在你的音乐之路上,Linux 提供了杰出的软件来帮助你前行。它们不能让你立刻成为一个音乐家,但可以作为一个降低学习难度的好助手。
|
||||
|
||||
### Gnu Solfège ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Solfège][7] 是一个世界流行的音乐教学工具,适用于各个级别的音乐教育。很多流行的教学方法(比如著名的柯达伊教学法)就使用 Solfège 作为它们的基础。相比于学到音乐知识,Solfège 更关注于让用户不断练习音乐。它假想的用户是那些已经有一些音乐基础,并且想不断练习音乐技巧的学生。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是 GNU 网站的开发者声明:
|
||||
|
||||
> “当你在高校、学院、音乐学校中学习音乐,你一般要进行的一些听力训练,比如视唱,会比较简单,但是通常需要两个人配合,一个问,一个答。[...] GNU Solfège 尝试着解决这个问题,你可以在没有其他人的帮助下完成更多的简单机械式练习。只是别忘了这些练习只是整个音乐训练过程的一部分。”
|
||||
|
||||
这款软件兑现了它的承诺,你可以在试听帮手的帮助下练习几乎所有音乐技巧。
|
||||
|
||||
Debian 和 Ubuntu 的远端库上有这款软件,在终端运行下面命令安装软件:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install solfege
|
||||
|
||||
它开启的时候会出现一个简单的开始界面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这些选项几乎包含了所有种类,大多数链接里面都有子类,你可以从中选择独立的练习。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
软件提供多种练习和测试项目,都能通过外接的 MIDI 设备(LCTT 译注:MIDI,Musical Instrument Digital Interface,乐器数字接口)或者声卡来播放音乐。这些练习还配合音符播放,以及支持慢动作回放功能。
|
||||
|
||||
很重要的一点是如果你在 Ubuntu 下使用 Solfège,默认情况下你可能没法听到声音(除非你有外接 MIDI 设备)。如果出现了这种情况,点击“File -> Prefernces -> Sound Setup”,选择合适的设备(一般情况下选 ALSA 都能解决问题)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Solfège 对你的日常练习非常有帮助,经常使用它,可以在你开始唱 do-re-mi 之前练好你的音乐听觉。
|
||||
|
||||
### Tete (听力训练) ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Tete][8] (这款听力训练软件)是一款简单但有效的 JAVA 软件,用于[训练听力][9]。它通过在不同背景下播放不同和弦以及不同 MIDI 声音来训练你分辨不同的音阶。[从 SourceForge 下载][10],然后解压它。
|
||||
|
||||
unzip Tete-*
|
||||
|
||||
进入解压出来的目录:
|
||||
|
||||
cd Tete-*
|
||||
|
||||
这里假设你的系统已经安装好了 JAVA,你可以使用下面的命令执行 Java 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
java -jar Tete-[版本号]
|
||||
|
||||
(可以在输入“Tete-”后按 Tab 键进行自动补全。)
|
||||
|
||||
Tete 只有一个简单的界面,所有内容都在这里了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以选择表演音阶(见上图),和弦(下图),
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
或音程。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以“精调”很多选项,包括 midi 乐器的声音、提升或降低音阶以及回放的快慢等等。SourceForge 网站上有关于 Tete 的非常有用的教程,介绍了这个软件的各个方面。
|
||||
|
||||
### JalMus ###
|
||||
|
||||
Jalmus 是用 JAVA 写的键盘音符阅读训练器。可以外接 MIDI 键盘,也可以使用虚拟键盘。它提供很多简单的课程练习来训练你的音符阅读能力。这个软件在2013年之后就不再更新了,但还是比较实用的。
|
||||
|
||||
进入[sourceforge 页面][11]下载最后版本(v2.3)的 JAVA 安装器,或者在终端输入下面的命令下载:
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://garr.dl.sourceforge.net/project/jalmus/Jalmus-2.3/installjalmus23.jar
|
||||
|
||||
下载完成后,加载安装器:
|
||||
|
||||
java -jar installjalmus23.jar
|
||||
|
||||
跨平台的 JAVA 安装器会一步一步引导你完成安装的。
|
||||
|
||||
Jalmus 的主界面非常朴素。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以在“Lessons”菜单中找到各种不同难度的课程,从非常简单(一行音符从左边向右滑过,键盘上相应的按键会高亮显示),
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
到非常困难(有多行音符从右向左滑过,你需要按顺序键入音符)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Jalmus 也包含一些训练,内容和课程相似,只是没有那些视觉上的提示了。当完成训练后,屏幕上会显示你的乐谱。它还提供不同难度的节拍训练,你能听到看到这些训练里面播放的旋律。在多行乐谱同时播放时,一个节拍器(能听见能看见)可以帮你理解
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
和阅读乐谱。(LCTT 写给王老板的话:我特么实在编不下去了,这段你得帮我改改。)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
所有这些功能都是可配置的,你可以选择打开或者关闭它们。
|
||||
|
||||
总的来说,Jalmus 可能是节奏训练软件中属于功能最强的,虽然它不是学音乐必备的软件,但在节奏训练这个特殊的领域,它做得很出色。
|
||||
|
||||
### 号外 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### TuxGuitar ####
|
||||
|
||||
对于吉他练习者,[TuxGuitar][12] 看起来很像 Windows 下面的 Guitar Pro 软件(它也可以读 Guitar Pro 格式的文件)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### PianoBooster ####
|
||||
[Piano Booster][13] 可以练习钢琴技巧,它能播放 MIDI 文件,你可以使用外接键盘来弹钢琴,同时还能查看屏幕上滑过的乐谱。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 提供很多优秀的工具供你学习,如果你对音乐感兴趣,你完全不用担心没有软件能帮你练习音乐技术。实际上,可供学习音乐的学生选择的优秀软件数量远比上面介绍的要多。如果你还知道其他的音乐训练软件,请在写下你的评论,让我们能够知道。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/series/learn-with-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-to-type-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-physics-simulation/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-learning-music/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/linux-geography-apps/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/learn-linux-maths/
|
||||
[7]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Solf%C3%A8ge
|
||||
[8]:http://tete.sourceforge.net/index.shtml
|
||||
[9]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ear_training
|
||||
[10]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/tete/files/latest/download
|
||||
[11]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/jalmus/files/Jalmus-2.3/
|
||||
[12]:http://tuxguitar.herac.com.ar/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20090517041840856/PianoBooster.html
|
||||
@ -1,17 +1,19 @@
|
||||
Linux / UNIX View Only Configuration File Directives ( Uncommented Lines of a Config File )
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Most Linux and UNIX-like system configuration files are documented using comments, but some time I just need to see line of configuration text in a config file. How can I view just the uncommented configuration file directives from squid.conf or httpd.conf file? How can I strip out comments and blank lines on a Linux or Unix-like systems?
|
||||
Linux / UNIX 下只查看配置文件的有效配置行(配置文件中未被注释的命令行)
|
||||
=========================================================
|
||||
|
||||
To view just the uncommented lines of text in a config file use the grep, sed, awk, perl or any other text processing utility provided by UNIX / BSD / OS X / Linux operating systems.
|
||||
大多数的Linux和类Unix系统的配置文件中都有许多的注释行,但是有时候我只想看其中的有效配置行。那我怎么才能只看到quid.conf或httpd.conf这样的配置文件中的非注释命令行呢?怎么去掉这些注释或者空行呢?
|
||||
|
||||
### grep command example to strip out command ###
|
||||
我们可以使用UNIX / BSD / OS X / Linux 这些操作系统自身提供的grep,sed,awk,perl或者其他文本处理工具来查看配置文件中的有效配置命令行。
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the gerp command as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
### grep 命令示例——去掉注释 ###
|
||||
|
||||
可以按照如下示例使用grep命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ grep -v "^#" /path/to/config/file
|
||||
$ grep -v "^#" /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
ServerRoot "/etc/apache2"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -98,7 +100,7 @@ Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
Include /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/
|
||||
|
||||
To suppress blank lines use [egrep command][1], run:
|
||||
想要跳过空行,可以使用 [egrep 命令][1], 示例:
|
||||
|
||||
egrep -v "^#|^$" /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
|
||||
## or pass it to the page such as more or less ##
|
||||
@ -113,35 +115,34 @@ To suppress blank lines use [egrep command][1], run:
|
||||
[ -f "$1" ] && command egrep -v "^#|^$" "$f" || echo "Error $1 file not found."
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Fig.01: Unix/Linux Egrep Strip Out Comments Blank Lines
|
||||
Fig.01: Unix/Linux Egrep 除去注释行和空行
|
||||
|
||||
### Understanding grep/egrep command line options ###
|
||||
### 理解 grep/egrep 命令行选项 ###
|
||||
|
||||
The -v option invert the sense of matching, to select non-matching lines. This option should work under all posix based systems. The regex ^$ matches and removes all blank lines and ^# matches and removes all comments that starts with a "#".
|
||||
-v 选项,选择出不匹配的命令行。该选项适用于所有基于posix的系统。正则表达式 ^$ 匹配出所有的非空行, ^#匹配出所有的不以“#”开头的非注释行。
|
||||
|
||||
### sed Command example ###
|
||||
### sed 命令示例 ###
|
||||
|
||||
GNU / sed command can be used as follows:
|
||||
可以按照如下示例使用 GNU / sed 命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sed '/ *#/d; /^ *$/d' /path/to/file
|
||||
$ sed '/ *#/d; /^ *$/d' /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
|
||||
|
||||
GNU or BSD sed can update your config file too. The syntax is as follows to edit files in-place, saving backups with the specified extension such as .bak:
|
||||
GNU or BSD sed 也可以修改配置文件。下面的语法是编辑文件,修改扩展名(比如 .bak)进行文件备份:
|
||||
|
||||
sed -i'.bak.2015.12.27' '/ *#/d; /^ *$/d' /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
|
||||
|
||||
For more info see man pages - [grep(1)][2], [sed(1)][3]
|
||||
更多信息见参考手册 - [grep(1)][2], [sed(1)][3]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/shell-display-uncommented-lines-only/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[sonofelice](https://github.com/sonofelice)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user