mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-27 02:30:10 +08:00
20150427-1 选题
This commit is contained in:
parent
1e64ea0c0b
commit
944c76f2cf
@ -0,0 +1,298 @@
|
||||
15 Things to Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.04 Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
This tutorial is intended for beginners and covers some basic steps on what to do after you have installed Ubuntu 15.04 “Vivid Vervet” Desktop version on your computer in order to customize the system and install basic programs for daily usage.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
15 Things to Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.04
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Enable Ubuntu Extra Repositories and Update the System ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing you should take care of after a fresh installation of Ubuntu is to enable Ubuntu Extra Repositories provided by official Canonical Partners and keep an up-to-date system with the last security patches and software updates.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to accomplish this step, open from the left Launcher System Settings -> Software and Updates utility and check all Ubuntu Software and Other Software (Canonical Partners) repositories. After you finish hit the Close button and wait for the utility to Reload the cache sources tree.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Software Updates
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Other Software (Canonical Partners)
|
||||
|
||||
For a fast and smooth update process, open a Terminal and issue the following command in order to update the system using the new software repositories:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get upgrade
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Ubuntu Upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Additional Drivers ###
|
||||
|
||||
In order for the system to scan and install additional hardware proprietary drivers, open Software and Updates utility from System Settings, go to Additional Drivers tab and wait for the utility to scan for drivers.
|
||||
|
||||
If some drivers matching your hardware are found, check the drivers you want to install and hit the Apply Changes button to install it. In case the proprietary drivers are not working as expected, uninstall them using the Revert button or check Do not use the device and Apply Changes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Drivers
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Install Synaptic and Gdebi Package Tools ###
|
||||
|
||||
Besides Ubuntu Software Center, Synaptic is a Graphical utility for apt command line through which you can manage repositories or install, remove, search, upgrade and configure software packages. Similar way, Gdebi has the same functionality for local .deb packages. To install this two package managers on your system issue the following command on Terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install synaptic gdebi
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Synaptic and Gdebi
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Synaptic Package Manager
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Change System Appearance and Behavior ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to change Desktop Background or Launcher Icon Size, open System Settings –> Appearance –> Look and personalize the desktop. To move the menu to window title bar, enable workspaces and desktop icons or auto-hide the Launcher visit Behavior tab.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
System Appearances
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Improve System Security and Privacy ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
System Security Enhancement
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
System Security Options
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Disable Unneeded Startup Applications ###
|
||||
|
||||
To improve system login speed, reveal hidden Startup Applications by issuing the below command on Terminal, open Startup Applications utility by searching it in Dash and uncheck the unneeded applications during login process.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo sed -i ‘s/NoDisplay=true/NoDisplay=false/g’ /etc/xdg/autostart/*.desktop
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Disable Unwanted Applications
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Add Extended Multimedia Support ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Ubuntu comes with a minimal support for media files. In order to play various media formats or manipulate video files, install the following multimedia applications:
|
||||
|
||||
- VLC
|
||||
- Smplayer
|
||||
- Audacious
|
||||
- QMMP
|
||||
- Mixxx
|
||||
- XBMC
|
||||
- Handbrake
|
||||
- Openshot
|
||||
|
||||
Use the following command line to install all with one shot:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install vlc smplayer audacious qmmp mixxx xbmc handbrake openshot
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Media Players
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Media Player Playlist
|
||||
|
||||
Besides this multimedia players also install ubuntu-restricted-extras and Java support packages in order to decode and support other restricted media formats.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras openjdk-8-jdk
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Ubuntu Extras
|
||||
|
||||
To enable DVD Playback and other multimedia codecs issue the following command on Terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install ffmpeg gstreamer0.10-plugins-bad lame libavcodec-extra
|
||||
$ sudo /usr/share/doc/libdvdread4/install-css.sh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enable Video Codes
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Install Image Applications ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you are a photography enthusiast and you want to handle and manipulate images on Ubuntu, probably you want to install the following imaging programs:
|
||||
|
||||
- GIMP (alternative for Adobe Photoshop)
|
||||
- Darktable
|
||||
- Rawtherapee
|
||||
- Pinta
|
||||
- Shotwell
|
||||
- Inkscape (alternative for Adobe Illustrator)
|
||||
- Digikam
|
||||
- Cheese
|
||||
|
||||
This applications can be installed from Ubuntu Software Center or all at once by using the following command line on Terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install gimp gimp-plugin-registry gimp-data-extras darktable rawtherapee pinta shotwell inkscape
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Image Applications
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Rawtherapee Tool
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Install Media Burners ###
|
||||
|
||||
To mount ISO images or burn a CDs or a DVD, you can choose and install from the following software:
|
||||
|
||||
- Brasero Disk Burner
|
||||
- K3b
|
||||
- Xfburn
|
||||
- Furius ISO Mount
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install brasero
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install k3b
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install xfburn
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install furiusisomount
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Media Burners
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Install Archive Applications ###
|
||||
|
||||
To handle most of archive formatted files (zip, tar.gz, zip, 7zip rar etc) install the following packages by issuing the below command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install unace unrar zip unzip p7zip-full p7zip-rar sharutils rar uudeview mpack arj cabextract file-roller
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Archive Applications
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Install Chat Application ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to talk to people all over the world, here is a list of the most popular chat applications for Linux:
|
||||
|
||||
- Pidgin
|
||||
- Skype
|
||||
- Xchat
|
||||
- Telegram
|
||||
- aMSN
|
||||
- Viber
|
||||
|
||||
You can install most of them from Ubuntu Software Center or by using the command line:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install pidgin
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install skype
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install xchat
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install amsn
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:atareao/telegram -y
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install telegram
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Chat Applications
|
||||
|
||||
To install Viber application on Ubuntu visit [Viber official webpage][1], download the Debian package locally and install the viber.deb application using Gdebi package manager (left click – > Open with -> GDebi Package Installer).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Viber
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. Install Torrent Software ###
|
||||
|
||||
The most popular torrent applications and peer-to-peer file sharing programs for Ubuntu are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Deluge
|
||||
- Transmission
|
||||
- Qbittorrent
|
||||
- LinuxDC++
|
||||
|
||||
To install your favorite peer-to-peer file sharing application on Ubuntu issue the following command on Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install deluge
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install transmission
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install qbittorrent
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install linuxdcpp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Torrent
|
||||
|
||||
### 12. Install Windows Emulator -Wine and Gaming Support – Steam ###
|
||||
|
||||
Wine emulator allows you to install and run Windows applications on Linux. On the other hand, Steam is a popular gaming platform for Linux based systems developed by Valve. To install both of them on your machine issue the following command on Terminal or use Ubuntu Software Center.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install steam wine winetricks
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Wine
|
||||
|
||||
### 13. Install Cairo-Dock and Enable Desktop Visual Effects ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cairo-Dock is a beautiful and flexible launcher bar for Linux desktops similar to the Mac OS X dock. To install it on Ubuntu, run the following command on Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install cairo-dock cairo-dock-plug-ins
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Cairo Dock
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Add Cairo Dock at Startup
|
||||
|
||||
To enable a set of Desktop Effects, such as Cube effect, install Compiz package with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install compiz compizconfig-settings-manager compiz-plugins-extra
|
||||
|
||||
To activate the Desktop Cube effect, search for ccsm on Dash, open CompizConfig Settings Manager, go to General Options – > Desktop Size and set Horizontal Virtual Size value to 4 and Vertical Virtual Size to 1. Then go back and check Desktop Cube (Disable Desktop Wall) and Rotate Cube boxes (Resolve Conflicts ->Disable Switch to Viewport 1) and press Ctrl+Alt+Left Mouse Click to view the cube effect.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enable Compiz
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Compiz Settings
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Compiz Settings Addons
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Desktop Window Rotating
|
||||
|
||||
### 14. Add Extra Browser Support ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04 comes by default with Mozilla Firefox Web Browser. To install other browsers such as Google Chrome or Opera, visit their official web pages, download the provided .deb packages and install them on your system using the Gdebi Package Installer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enable Browser Support
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Opera Browser Support
|
||||
|
||||
To install Chromium Open Source browser issue the following command on Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install chromium-browser
|
||||
|
||||
### 15. Install Tweak Tools ###
|
||||
|
||||
Want extra applications for customizing Ubuntu? Then install Unity Tweak Tool and Gnome Tweak Tool by issuing the following commands on Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install unity-tweak-tool gnome-tweak-tool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Tweak Tool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Tweak Tool Settings
|
||||
|
||||
Another interesting tweak tool is represented by the Ubuntu Tweak package which can be obtained and installed by visiting the webpage: [http://ubuntu-tweak.com/][2].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Tweak Tool: System Information
|
||||
|
||||
After you have installed all this bunch of software, you might want to clean your system in order to free some space on the hard drive, by issuing the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -y autoremove
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -y autoclean
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -y clean
|
||||
|
||||
This are just a few tweaks and programs that an average user might install and use on Ubuntu 15.04 Desktop for daily basic utilization. For more advanced programs, features and utilities use Ubuntu Software Center or consult Ubuntu Wiki webpage.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-15-04-desktop/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.viber.com/en/products/linux
|
||||
[2]:http://ubuntu-tweak.com/
|
||||
165
sources/tech/20150427 How to set up NTP server in CentOS.md
Normal file
165
sources/tech/20150427 How to set up NTP server in CentOS.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,165 @@
|
||||
How to set up NTP server in CentOS
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Network Time Protocol (NTP) is used to synchronize system clocks of different hosts over network. All managed hosts can synchronize their time with a designated time server called an NTP server. An NTP server on the other hand synchronizes its own time with any public NTP server, or any server of your choice. The system clocks of all NTP-managed devices are synchronized to the millisecond precision.
|
||||
|
||||
In a corporate environment, if they do not want to open up their firewall for NTP traffic, it is necessary to set up in-house NTP server, and let employees use the internal server as opposed to public NTP servers. In this tutorial, we will describe how to configure a CentOS system as an NTP server. Before going into the detail, let's go over the concept of NTP first.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Do We Need NTP? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Due to manufacturing variances, all (non-atomic) clocks do not run at the exact same speed. Some clocks tend to run faster, while some run slower. So over a large timeframe, the time of one clock gradually drifts from another, causing what is known as "clock drift" or "time drift". To minimize the effect of clock drift, the hosts using NTP should periodically communicate with a designated NTP server to keep their clock in sync.
|
||||
|
||||
Time synchrony across different hosts is important for things like scheduled backup, [intrusion detection][1] logging, [distributed job scheduling ][2]or transaction bookkeeping. It may even be required as part of regulatory compliance.
|
||||
|
||||
### NTP Hierarchy ###
|
||||
|
||||
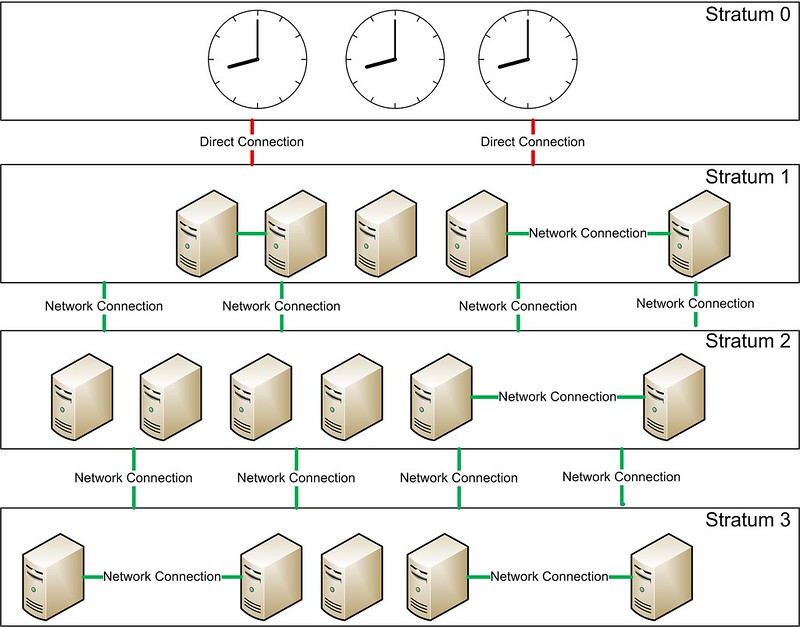
NTP clocks are organized in a layered hierarchy. Each level of the hierarchy is called a *stratum*. The notion of stratum describes how many NTP hops away a machine is from an authoritative time source.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Stratum 0 is populated with clocks that have virtually no time drifts, such as atomic clocks. These clocks cannot be directly used over the network. Stratum N (N > 1) servers synchronize their time against Stratum N-1 servers. Stratum N clocks may be connected with each other over network.
|
||||
|
||||
NTP supports up to 15 stratums in the hierarchy. Stratum 16 is considered unsynchronized and unusable.
|
||||
|
||||
### Preparing CentOS Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's proceed to set up an NTP server on CentOS.
|
||||
|
||||
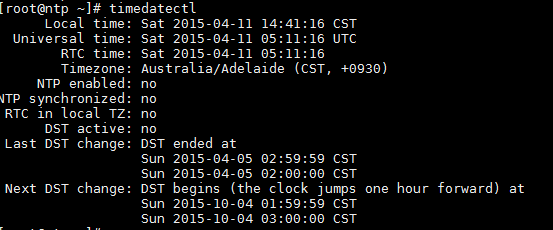
First of all, we need to make sure that the time zone of the server is set up correctly. In CentOS 7, we can use the timedatectl command to view and change the server time zone (e.g., "Australia/Adelaide")
|
||||
|
||||
# timedatectl list-timezones | grep Australia
|
||||
# timedatectl set-timezone Australia/Adelaide
|
||||
# timedatectl
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Go ahead and set up necessary software using yum.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install ntp
|
||||
|
||||
Then we will add the global NTP servers to synchronize time with.
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/ntp.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
server 0.oceania.pool.ntp.org
|
||||
server 1.oceania.pool.ntp.org
|
||||
server 2.oceania.pool.ntp.org
|
||||
server 3.oceania.pool.ntp.org
|
||||
|
||||
By default, NTP server logs are saved in /var/log/messages. If you want to use a custom log file, that can be specified as well.
|
||||
|
||||
logfile /var/log/ntpd.log
|
||||
|
||||
If you opt for a custom log file, make sure to change its ownership and SELinux context.
|
||||
|
||||
# chown ntp:ntp /var/log/ntpd.log
|
||||
# chcon -t ntpd_log_t /var/log/ntpd.log
|
||||
|
||||
Now initiate NTP service and make sure it's added to startup.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart ntp
|
||||
# systemctl enable ntp
|
||||
|
||||
### Verifying NTP Server Clock ###
|
||||
|
||||
We can use the ntpq command to check how the local server's clock is synchronized via NTP.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The following table explains the output columns.
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table id="content">
|
||||
<tbody><tr>
|
||||
<td>remote</td>
|
||||
<td>The sources defined at ntp.conf. '*' indicates the current and best source; '+' indicates that these sources are available as NTP source. Sources with - are considered unusable.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>refid</td>
|
||||
<td>The IP address of the clock with which the remote server clock is synchronized with.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>st</td>
|
||||
<td>Stratum</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>t</td>
|
||||
<td>Type. 'u' is for unicast. Other values may include local, multicast, broadcast.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>when</td>
|
||||
<td>The time elapsed (in seconds) since the last contact with the server.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>poll</td>
|
||||
<td>Polling frequency with the server in seconds.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>reach</td>
|
||||
<td>An octal value that indicates whether there are any errors in communication with the server. The value 377 indicates 100% success.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>delay</td>
|
||||
<td>The round trip time between our server and the remote server.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>offset</td>
|
||||
<td>The time difference between our server and the remote server in milliseconds.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>jitter</td>
|
||||
<td>The average time difference in milliseconds between two samples.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody></table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Controlling Access to NTP Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default, NTP server allows incoming queries from all hosts. If you want to filter incoming NTP synchronization connections, you could add a rule in your firewall to filter the traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -s 192.168.1.0/24 -p udp --dport 123 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
# iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 123 -j DROP
|
||||
|
||||
The rule will allow NTP traffic (on port UDP/123) from 192.168.1.0/24, and deny traffic from all other networks. You can update the rule to match your requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring NTP Clients ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Linux ####
|
||||
|
||||
NTP client hosts need the ntpdate package to synchronize time against the server. The package can be easily installed using yum or apt-get. After installing the package, run the command with the IP address of the server.
|
||||
|
||||
# ntpdate <server-IP-address>
|
||||
|
||||
The command is identical for RHEL and Debian based systems.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Windows ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using Windows, look for 'Internet Time' under Date and Time settings.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Cisco Devices ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to synchronize the time of a Cisco device, you can use the following command from the global configuration mode.
|
||||
|
||||
# ntp server <server-IP-address>
|
||||
|
||||
NTP enabled devices from other vendors have their own parameters for Internet time. Please check the documentation of the device if you want to synchronize its time with the NTP server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
To sum up, NTP is a protocol that keeps the clocks across all your hosts in sync. We have demonstrated how we can set up an NTP server, and let NTP enabled devices synchronize their time against the server.
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/setup-ntp-server-centos.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sarmed Rahman][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-compile-and-install-snort-from-source-code-on-ubuntu.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-hdfs-and-hadoop-using.html
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user