mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-12 01:40:10 +08:00
commit
93a9c1690a
@ -0,0 +1,166 @@
|
||||
文件轻松比对,伟大而自由的比较软件们
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
文件比较工具用于比较计算机上的文件的内容,找到他们之间相同与不同之处。比较的结果通常被称为diff。
|
||||
|
||||
diff同时也是一个基于控制台的、能输出两个文件之间不同之处的著名的文件比较程序的名字。diff是于二十世纪70年代早期,在Unix操作系统上被开发出来的。diff将会把两个文件之间不同之处的部分进行输出。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux拥有很多不错的GUI工具,能使你能清楚的看到两个文件或同一文件不同版本之间的不同之处。这次我从自己最喜欢的GUI比较工具中选出了五个推荐给大家。除了其中的一个,其他的都是开源的。
|
||||
|
||||
这些应用程序可以让你更清楚的看到文件或目录的差别,能合并有差异的文件,可以解决冲突并将其输出成一个新的文件或补丁,其也用于那些预览和备注文件改动的产品上(比如,在源代码合并到源文件树之前,要先接受源代码的改变)。因此它们是非常重要的软件开发工具。它们可以帮助开发人员们对文件进行处理,不停的把文件转来转去。这些比较工具不仅仅能用于显示源代码文件中的不同之处;他们还适用于很多种的文本文件。可视化的特性使文件比较变得容易、简单。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Meld
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Meld是一个适用于Gnome桌面的、开源的、图形化的文件差异查看和合并的应用程序。它支持2到3个文件的同时比较、递归式的目录比较、处于版本控制(Bazaar, Codeville, CVS, Darcs, Fossil SCM, Git, Mercurial, Monotone, Subversion)之下的目录比较。还能够手动或自动合并文件差异。
|
||||
|
||||
Meld的重点在于帮助开发人员比较和合并多个源文件,并在他们最喜欢的版本控制系统下能直观的浏览改动过的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
功能包括
|
||||
|
||||
- 原地编辑文件,即时更新
|
||||
- 进行两到三个文件的比较及合并
|
||||
- 在显示的差异和冲突之间的导航
|
||||
- 使用插入、改变和冲突这几种标记可视化展示本地和全局的差异
|
||||
- 内置正则表达式文本过滤器,可以忽略不重要的差异
|
||||
- 语法高亮度显示(使用可选的gtksourceview)
|
||||
- 将两到三个目录中的文件逐个进行比较,显示新建,缺失和替换过的文件
|
||||
- 对任何有冲突或差异的文件直接打开比较界面
|
||||
- 可以过滤文件或目录以避免以忽略某些差异
|
||||
- 被改动区域的自动合并模式使合并更容易
|
||||
- 也有一个简单的文件管理
|
||||
- 支持多种版本控制系统,包括Git, Mercurial, Bazaar 和 SVN
|
||||
- 在提交前开启文件比较来检查改动的地方和内容
|
||||
- 查看文件版本状态
|
||||
- 还能进行简单的版本控制操作(例如,提交、更新、添加、移动或删除文件)
|
||||
- 继承自同一文件的两个文件进行自动合并
|
||||
- 标注并在中间的窗格显示所有有冲突的变更的基础版本
|
||||
- 显示并合并同一文件的无关的独立修改
|
||||
- 锁定只读性质的基础文件以避免出错
|
||||
- 可以整合到已有的命令行界面中,包括gitmergetool
|
||||
- 国际化支持
|
||||
- 可视化使文件比较更简单
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址: [meldmerge.org][1]
|
||||
- 开发人员: Kai Willadsen
|
||||
- 证书: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.8.5
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
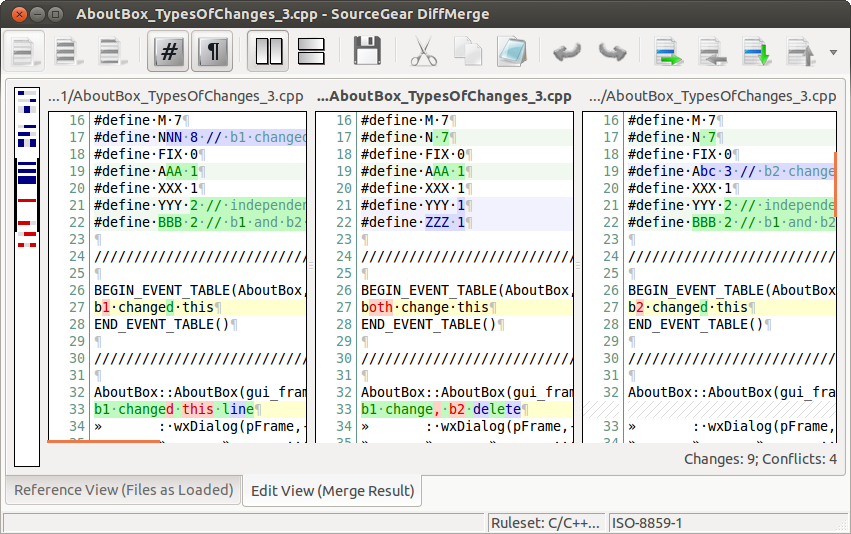
###DiffMerge
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
DiffMerge是一个可以在Linux、Windows和OS X上运行的,可以可视化文件的比较和合并的应用软件。
|
||||
|
||||
功能包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 图形化显示两个文件之间的差别。包括插入行,高亮标注以及对编辑的全面支持
|
||||
- 图形化显示三个文件之间的差别。(安全的前提下)允许自动合并,并对最终文件可以随意编辑
|
||||
- 并排显示两个文件夹的比较,显示哪一个文件只存在于其中一个文件夹而不存在于另外的一个文件夹,还能一对一的将完全相同的、等价的或不同的文件配对
|
||||
- 规则设置和选项让你可以个性化它的外观和行为
|
||||
- 基于Unicode,可以导入多种编码的字符
|
||||
- 跨平台工具
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址: [sourcegear.com/diffmerge][2]
|
||||
- 开发人员: SourceGear LLC
|
||||
- 证书: Licensed for use free of charge (not open source)
|
||||
- 版本号: 4.2
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###xxdiff
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
xxdiff是个开源的图形化的可进行文件、目录比较及合并的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
xxdiff可以用于显示两到三个文件或两个目录的差别,还能产生一个合并后的版本。被比较的两到三个文件会并排显示,并将有区别的文字内容用不同颜色高亮显示以便于识别。
|
||||
|
||||
这个程序是个非常重要的软件开发工具。他可以图形化的显示两个文件或目录之间的差别,合并有差异的文件,其也用于那些预览和备注文件改动的产品上(比如,在源代码合并到源文件树之前,要先接受源代码的改变)
|
||||
|
||||
功能包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 比较两到三个文件,或是两个目录(浅层或递归)
|
||||
- 横向高亮显示差异
|
||||
- 交互式的文件合并,可视化的输出和保存
|
||||
- 可以辅助合并的评论/监管
|
||||
- 自动合并文件中时不合并 CVS 冲突,并以两个文件显示以便于解决冲突
|
||||
- 可以用其它的比较程序计算差异:适用于GNU diff、SGI diff和ClearCase的cleardiff,以及所有与这些程序输出相似的文件比较程序。
|
||||
- 可以使用资源文件实现完全的个性化设置
|
||||
- 用起来感觉和Rudy Wortel或SGI的xdiff差不多,与桌面系统无关
|
||||
- 功能和输出可以和脚本轻松集成
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址: [furius.ca/xxdiff][3]
|
||||
- 开发人员: Martin Blais
|
||||
- 证书: GNU GPL
|
||||
- 版本号: 4.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Diffuse
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Diffuse是个开源的图形化工具,可用于合并和比较文本文件。Diffuse能够比较任意数量的文件,并排显示,并提供手动行匹配调整,能直接编辑文件。Diffuse还能从bazaar、CVS、darcs, git, mercurial, monotone, Subversion和GNU RCS 库中获取版本用于比较及合并。
|
||||
|
||||
功能包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 比较任意数量的文件,并排显示(多方合并)
|
||||
- 行匹配可以被用户人工矫正
|
||||
- 直接编辑文件
|
||||
- 语法高亮
|
||||
- 支持Bazaar, CVS, Darcs, Git, Mercurial, Monotone, RCS, Subversion和SVK
|
||||
- 支持Unicode
|
||||
- 可无限撤销
|
||||
- 易用的键盘导航
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址: [diffuse.sourceforge.net][]
|
||||
- 开发人员: Derrick Moser
|
||||
- 证书: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.4.7
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Kompare
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Kompare是个开源的GUI前端程序,可以对不同源文件之间差异的可视化和合并。Kompare可以比较文件或文件夹内容的差异。Kompare支持很多种diff格式,并提供各种选项来设置显示的信息级别。
|
||||
|
||||
不论你是个想比较源代码的开发人员,还是只想比较一下研究论文手稿与最终文档的差异,Kompare都是个有用的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
Kompare是KDE桌面环境的一部分。
|
||||
|
||||
功能包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 比较两个文本文件
|
||||
- 递归式比较目录
|
||||
- 显示diff产生的补丁
|
||||
- 将补丁合并到一个已存在的目录
|
||||
- 可以让你在编译时更轻松
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址: [www.caffeinated.me.uk/kompare/][5]
|
||||
- 开发者: The Kompare Team
|
||||
- 证书: GNU GPL
|
||||
- 版本号: Part of KDE
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/2014062814400262/FileComparisons.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[H-mudcup](https://github.com/H-mudcup)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://meldmerge.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://sourcegear.com/diffmerge/
|
||||
[3]:http://furius.ca/xxdiff/
|
||||
[4]:http://diffuse.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.caffeinated.me.uk/kompare/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
Linux上几款好用的字幕编辑器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如果你经常看国外的大片,你应该会喜欢带字幕版本而不是有国语配音的版本。我在法国长大,童年的记忆里充满了迪斯尼电影。但是这些电影因为有了法语的配音而听起来很怪。如果现在有机会能看原始的版本,我想,对于大多数的人来说,字幕还是必须的。我很高兴能为家人制作字幕。给我带来希望的是,Linux 也不乏有很多花哨、开源的字幕编辑器。总之一句话,文中Linux上字幕编辑器的列表并不详尽,你可以告诉我哪一款是你认为最好的字幕编辑器。
|
||||
|
||||
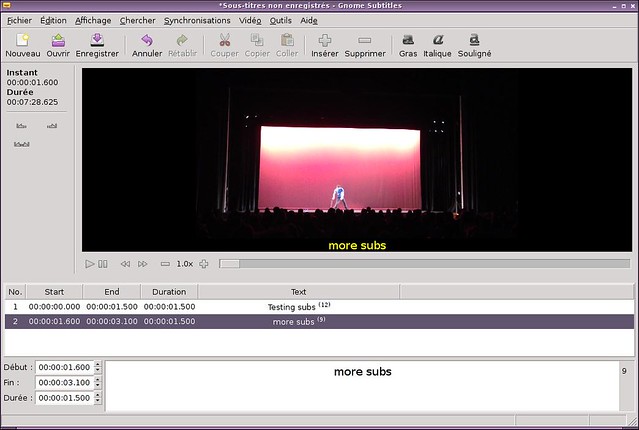
### 1. Gnome Subtitles ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
当有现有字幕需要快速编辑时,[Gnome Subtitles][1] 是我的一个选择。你可以载入视频,载入字幕文本,然后就可以即刻开始了。我很欣赏其对于易用性和高级特性之间的平衡。它带有一个同步工具以及一个拼写检查工具。最后但同样重要的的一点,这么好用最主要的是因为它的快捷键:当你编辑很多的台词的时候,你最好把你的手放在键盘上,使用其内置的快捷键来移动。
|
||||
|
||||
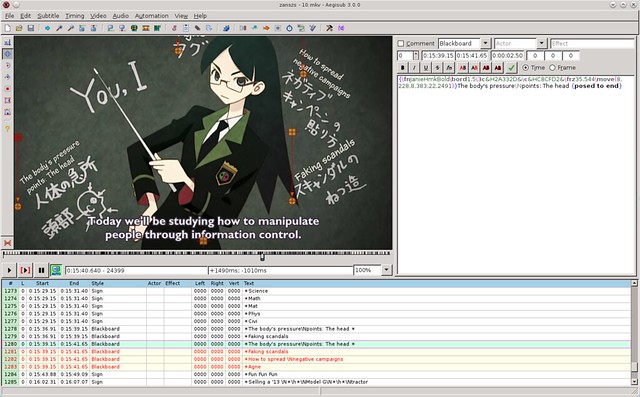
### 2. Aegisub ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[Aegisub][2] 已经是一款高级别的复杂字幕编辑器。仅仅是界面就反映出了一定的学习曲线。但是,除了它吓人的样子以外,Aegisub 是一个非常完整的软件,提供的工具远远超出你能想象的。和Gnome Subtitles 一样,Aegisub也采用了所见即所得(WYSIWYG:what you see is what you get)的处理方式。但是是一个全新的高度:可以再屏幕上任意拖动字幕,也可以在另一边查看音频的频谱,并且可以利用快捷键做任何的事情。除此以外,它还带有一个汉字工具,有一个kalaok模式,并且你可以导入lua 脚本让它自动完成一些任务。我希望你在用之前,先去阅读下它的[指南][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Gaupol ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
另一个操作复杂的软件是[Gaupol][4],不像Aegisub ,Gaupol 很容易上手而且采用了一个和Gnome Subtitles 很像的界面。但是在这些相对简单背后,它拥有很多很必要的工具:快捷键、第三方扩展、拼写检查,甚至是语音识别(由[CMU Sphinx][5]提供)。这里也提一个缺点,我注意到有时候在测试的时候也,软件会有消极怠工的表现,不是很严重,但是也足以让我更有理由喜欢Gnome Subtitles了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Subtitle Editor ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Subtitle Editor][6]和 Gaupol 很像,但是它的界面有点不太直观,特性也只是稍微的高级一点点。我很欣赏的一点是,它可以定义“关键帧”,而且提供所有的同步选项。然而,多一点的图标,或者是少一点的文字都能提供界面的特性。作为一个值得称赞的字幕编辑器,Subtitle Editor 可以模仿“作家”打字的效果,虽然我不确定它是否特别有用。最后但同样重要的一点,重定义快捷键的功能很实用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Jubler ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Jubler][7]是一个用Java编写并有多平台支持的字幕编辑器。我对它的界面印象特别深刻。在上面我确实看出了Java特点的东西,但是,它仍然是经过精心的构造和构思的。像Aegisub 一样,你可以再屏幕上任意的拖动字幕,让你有愉快的体验而不单单是打字。它也可以为字幕自定义一个风格,在另外的一个轨道播放音频,翻译字幕,或者是是做拼写检查。不过,要注意的是,你需要事先安装好媒体播放器并且正确的配置,如果你想完整的使用Jubler。我把这些归功于在[官方页面][8]下载了脚本以后其简便的安装方式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Subtitle Composer ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Subtitle Composer][9]被视为“KDE里的字幕作曲家”,它能够唤起对很多传统功能的回忆。伴随着KDE界面,我们充满了期待。我们自然会说到快捷键,我特别喜欢这个功能。除此之外,Subtitle Composer 与上面提到的编辑器最大的不同地方就在于,它可以执行用JavaScript,Python,甚至是Ruby写成的脚本。软件带有几个例子,肯定能够帮助你很好的学习使用这些特性的语法。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,不管你是否喜欢,都来为你的家庭编辑几个字幕吧,重新同步整个轨道,或者是一切从头开始,那么Linux 有很好的工具给你。对我来说,快捷键和易用性使得各个工具有差异,想要更高级别的使用体验,脚本和语音识别就成了很便利的一个功能。
|
||||
|
||||
你会使用哪个字幕编辑器,为什么?你认为还有没有更好用的字幕编辑器这里没有提到的?在评论里告诉我们吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/good-subtitle-editor-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/adrien
|
||||
[1]:http://gnomesubtitles.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.aegisub.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://docs.aegisub.org/3.2/Main_Page/
|
||||
[4]:http://home.gna.org/gaupol/
|
||||
[5]:http://cmusphinx.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[6]:http://home.gna.org/subtitleeditor/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.jubler.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.jubler.org/download.html
|
||||
[9]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/subcomposer/
|
||||
@ -1,22 +1,22 @@
|
||||
Linux用户应该了解一下开源硬件
|
||||
Linux用户,你们真的了解开源硬件吗?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Linux用户不了解一点开源硬件制造相关的事情,他们将会很失望。
|
||||
> Linux用户不了解一点开源硬件制造相关的事情,他们就会经常陷入失望的情绪中。
|
||||
|
||||
商业软件和免费软件已经互相纠缠很多年了,但是这俩经常误解对方。这并不奇怪 -- 对一方来说是生意,而另一方只是一种生活方式。但是,这种误解会给人带来痛苦,这也是为什么值得花精力去揭露这里面的内幕。
|
||||
|
||||
一个逐渐普遍的现象:对开源硬件的不断尝试,不管是Canonical,Jolla,MakePlayLive,或者其他几个。不管是评论员或终端用户,一般的免费软件用户会为新的硬件平台发布表现出过分的狂热,然后因为不断延期有所醒悟,最终放弃整个产品。
|
||||
一个逐渐普遍的现象:对开源硬件的不断尝试,不管是Canonical,Jolla,MakePlayLive,或者其他公司。无论是评论员或是终端用户,通常免费软件用户都会为新的硬件平台发布表现出过分的狂热,然后因为不断延期有所醒悟,直到最终放弃整个产品。
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个没有人获益的怪圈,而且滋生出不信任 - 都是因为一般的Linux用户根本不知道这些新闻背后发生的事情。
|
||||
这是一个没有人获益的怪圈,而且常常滋生出不信任 - 都是因为一般的Linux用户根本不知道这些新闻背后发生的事情。
|
||||
|
||||
我个人对于把产品推向市场的经验很有限。但是,我还不知道谁能有所突破。推出一个开源硬件或其他产品到市场仍然不仅仅是个残酷的生意,而且严重不利于新加入的厂商。
|
||||
我个人对于把产品推向市场的经验很有限。但是,我还没听说谁能有所突破。推出一个开源硬件或其他产品到市场仍然不仅仅是个残酷的生意,而且严重不利于新进厂商。
|
||||
|
||||
### 寻找合作伙伴 ###
|
||||
|
||||
不管是数码产品的生产还是分销都被相对较少的一些公司控制着,有时需要数月的预订。利润率也会很低,所以就像那些购买古老情景喜剧的电影工作室一样,生成商一般也希望复制当前热销产品的成功。像Aaron Seigo在谈到他花精力开发Vivaldi平板时告诉我的,生产商更希望能由其他人去承担开发新产品的风险。
|
||||
不管是数码产品的生产还是分销都被相对较少的一些公司控制着,有时需要数月的预订。利润率也会很低,所以就像那些购买古老情景喜剧的电影工作室一样,生产商一般也希望复制当前热销产品的成功。像Aaron Seigo在谈到他花精力开发Vivaldi平板时告诉我的,生产商更希望能由其他人去承担开发新产品的风险。
|
||||
|
||||
不仅如此,他们更希望和那些有现成销售记录的有可能带来可复制生意的人合作。
|
||||
不仅如此,他们更希望和那些有现成销售记录的有可能带来长期客户生意的人合作。
|
||||
|
||||
而且,一般新加入的厂商所关心的产品只有几千的量。芯片制造商更愿意和苹果或三星合作,因为它们的订单很可能是几百K。
|
||||
而且,一般新加入的厂商所关心的产品只有几千的量。芯片制造商更愿意和苹果或三星这样的公司合作,因为它们的订单很可能是几十上百万的量。
|
||||
|
||||
面对这种情形,开源硬件制造者们可能会发现他们在工厂的列表中被淹没了,除非能找到二线或三线厂愿意尝试一下小批量生产新产品。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,9 +28,9 @@ Linux用户应该了解一下开源硬件
|
||||
|
||||
这样必然会引起潜在用户的批评,但是开源硬件制造者没得选,只能折中他们的愿景。寻找其他生产商也不能解决问题,有一个原因是这样做意味着更多延迟,但是更多的是因为完全免授权费的硬件是不存在的。像三星这样的业内巨头对免费硬件没有任何兴趣,而作为新人,开源硬件制造者也没有影响力去要求什么。
|
||||
|
||||
更何况,就算有免费硬件,生产商也不能保证会用在下一批生产中。制造者们会轻易地发现他们每次需要生产的时候都要重打一样的仗。
|
||||
更何况,就算有免费硬件,生产商也不能保证会用在下一批生产中。制造者们会轻易地发现他们每次需要生产的时候都要重打一次一模一样的仗。
|
||||
|
||||
这些都还不够,这个时候开源硬件制造者们也许已经花了6-12个月时间来讨价还价。机会来了,产业标准已经变更,他们也许为了升级产品规格又要从头来过。
|
||||
这些都还不够,这个时候开源硬件制造者们也许已经花了6-12个月时间来讨价还价。等机会终于来了,产业标准却已经变更,于是他们可能为了升级产品规格又要从头来过。
|
||||
|
||||
### 短暂而且残忍的货架期 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,15 +42,15 @@ Linux用户应该了解一下开源硬件
|
||||
|
||||
### 衡量整件怪事 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这里我只是粗略地概括了一下,但是任何涉足过制造的人会认出我形容成标准的东西。而更糟糕的是,开源硬件制造者们通常在这个过程中才会有所觉悟。不可避免,他们也会犯错,从而带来更多的延迟。
|
||||
在这里我只是粗略地概括了一下,但是任何涉足过制造的人会认同我形容为行业标准的东西。而更糟糕的是,开源硬件制造者们通常只有在亲身经历过后才会有所觉悟。不可避免,他们也会犯错,从而带来更多的延迟。
|
||||
|
||||
但重点是,一旦你对整个过程有所了解,你对另一个开源硬件进行尝试的消息的反应就会改变。这个过程意味着,除非哪家公司处于严格的保密模式,对于产品将于六个月内发布的声明会很快会被证实是过期的推测。很可能是12-18个月,而且面对之前提过的那些困难很可能意味着这个产品永远不会真正发布。
|
||||
但重点是,一旦你对整个过程有所了解,你对另一个开源硬件进行尝试的新闻的反应就会改变。这个过程意味着,除非哪家公司处于严格的保密模式,对于产品将于六个月内发布的声明会很快会被证实是过期的推测。很可能是12-18个月,而且面对之前提过的那些困难很可能意味着这个产品永远都不会真正发布。
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子,就像我写的,人们等待第一代Steam Machines面世,它是一台基于Linux的游戏主机。他们相信Steam Machines能彻底改变Linux和游戏。
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个市场分类,Steam Machines也许比其他新产品更有优势,因为参与开发的人员至少有开发软件产品的经验。然而,整整一年过去了Steam Machines的开发成果都还只有原型机,而且直到2015年中都不一定能买到。面对硬件生产的实际情况,就算有一半能见到阳光都是很幸运了。而实际上,能发布2-4台也许更实际。
|
||||
|
||||
我做出这个预测并没有考虑个体努力。但是,对硬件生产的理解,比起那些Linux和游戏的黄金年代之类的预言,我估计这个更靠谱。如果我错了也会很开心,但是事实不会改变:让人吃惊的不是如此多的Linux相关硬件产品失败了,而是那些即使是短暂的成功的产品。
|
||||
我做出这个预测并没有考虑个体努力。但是,对硬件生产的理解,比起那些Linux和游戏的黄金年代之类的预言,我估计这个更靠谱。如果我错了也会很开心,但是事实不会改变:让人吃惊的不是如此多的Linux相关硬件产品失败了,而是那些虽然短暂但却成功的产品。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/what-linux-users-should-know-about-op
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Bruce Byfield][a]
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Mr小眼儿](https://github.com/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,10 @@
|
||||
“ntpq -p”命令输出详解
|
||||
网络时间的那些事情及 ntpq 详解
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Gentoo][1](也许其他发行版也是?)中 ["ntp -q" 的 man page][2] 只有简短的描述:“*打印出服务器已知的节点列表和它们的状态概要信息。*”
|
||||
[Gentoo][1](也许其他发行版也是?)中 ["ntpq -p" 的 man page][2] 只有简短的描述:“*打印出该服务器已知的节点列表和它们的状态概要信息。*”
|
||||
|
||||
我还没见到关于这个命令的说明文档,因此这里对此作一个总结,可以补充进 "[man ntpq][3]" man page 中。更多的细节见这里 “[ntpq – standard NTP query program][4]”(原作者),和 [其他关于 man ntpq 的例子][5].
|
||||
我还没见到关于这个命令的说明文档,因此这里对此作一个总结,可以补充进 "[man ntpq][3]" man page 中。更多的细节见这里 “[ntpq – 标准 NTP 请求程序][4]”(原作者),和 [其他关于 man ntpq 的例子][5].
|
||||
|
||||
[NTP][6] 是一个设计用于通过 [udp][9] 网络 ([WAN][7] 或者 [LAN][8]) 来同步计算机时钟的协议。引用 [Wikipedia – NTP][10]:
|
||||
[NTP][6] is a protocol designed to synchronize the clocks of computers over a ([WAN][7] or [LAN][8]) [udp][9] network. From [Wikipedia – NTP][10]:
|
||||
|
||||
> 网络时间协议(英语:Network Time Protocol,NTP)一种协议和软件实现,用于通过使用有网络延迟的报文交换网络同步计算机系统间的时钟。最初由美国特拉华大学的 David L. Mills 设计,现在仍然由他和志愿者小组维护,它于 1985 年之前开始使用,是因特网中最老的协议之一。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,10 +27,10 @@
|
||||
- **st** – 远程节点或服务器的 [Stratum][17](级别,NTP 时间同步是分层的)
|
||||
- **t** – 类型 (u: [unicast(单播)][18] 或 [manycast(选播)][19] 客户端, b: [broadcast(广播)][20] 或 [multicast(多播)][21] 客户端, l: 本地时钟, s: 对称节点(用于备份), A: 选播服务器, B: 广播服务器, M: 多播服务器, 参见“[Automatic Server Discovery][22]“)
|
||||
- **when** – 最后一次同步到现在的时间 (默认单位为秒, “h”表示小时,“d”表示天)
|
||||
- **poll** – 同步的频率:[rfc5905][23]建议在 NTPv4 中这个值的范围在 4 (16s) 至 17 (36h) 之间(2的指数次秒),然而观察发现这个值的实际大小在一个小的多的范围内 :64 (2的6次方)秒 至 1024 (2的10次方)秒
|
||||
- **poll** – 同步的频率:[rfc5905][23]建议在 NTPv4 中这个值的范围在 4 (16秒) 至 17 (36小时) 之间(即2的指数次秒),然而观察发现这个值的实际大小在一个小的多的范围内 :64 (2^6 )秒 至 1024 (2^10 )秒
|
||||
- **reach** – 一个8位的左移移位寄存器值,用来测试能否和服务器连接,每成功连接一次它的值就会增加,以 [8 进制][24]显示
|
||||
- **delay** – 从本地到远程节点或服务器通信的往返时间(毫秒)
|
||||
- **offset** – 主机与远程节点或服务器时间源的时间偏移量,offset 越接近于0,主机和 NTP 服务器的时间越接近([方均根][25]表示,单位为毫秒)
|
||||
- **offset** – 主机与远程节点或服务器时间源的时间偏移量,offset 越接近于0,主机和 NTP 服务器的时间越接近(以[方均根][25]表示,单位为毫秒)
|
||||
- **jitter** – 与远程节点同步的时间源的平均偏差(多个时间样本中的 offset 的偏差,单位是毫秒),这个数值的绝对值越小,主机的时间就越精确
|
||||
|
||||
#### 字段的统计代码 ####
|
||||
@ -47,7 +46,7 @@
|
||||
- “**-**” – 已不再使用
|
||||
- “**#**” – 良好的远程节点或服务器但是未被使用 (不在按同步距离排序的前六个节点中,作为备用节点使用)
|
||||
- “**+**” – 良好的且优先使用的远程节点或服务器(包含在组合算法中)
|
||||
- “*****” – 当前作为优先主同步对象的远程节点或服务器
|
||||
- “*” – 当前作为优先主同步对象的远程节点或服务器
|
||||
- “**o**” – PPS 节点 (当优先节点是有效时)。实际的系统同步是源于秒脉冲信号(pulse-per-second,PPS),可能通过PPS 时钟驱动或者通过内核接口。
|
||||
|
||||
参考 [Clock Select Algorithm][27].
|
||||
@ -74,9 +73,9 @@
|
||||
- **.WWV.** – [WWV][46] (HF, Ft. Collins, CO, America) 标准时间无线电接收器
|
||||
- **.WWVB.** – [WWVB][47] (LF, Ft. Collins, CO, America) 标准时间无线电接收器
|
||||
- **.WWVH.** – [WWVH][48] (HF, Kauai, HI, America) 标准时间无线电接收器
|
||||
- **.GOES.** – 美国 [静止环境观测卫星][49];
|
||||
- **.GOES.** – 美国[静止环境观测卫星][49];
|
||||
- **.GPS.** – 美国 [GPS][50];
|
||||
- **.GAL.** – [伽利略定位系统][51] 欧洲 [GNSS][52];
|
||||
- **.GAL.** – [伽利略定位系统][51]欧洲 [GNSS][52];
|
||||
- **.ACST.** – 选播服务器
|
||||
- **.AUTH.** – 认证错误
|
||||
- **.AUTO.** – Autokey (NTP 的一种认证机制)顺序错误
|
||||
@ -105,7 +104,7 @@ NTP 协议是高精度的,使用的精度小于纳秒(2的 -32 次方)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### “ntpq -c rl”输出参数 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- **precision** 为四舍五入值,且为 2 的幂数。因此精度为 2 的 *precision* 此幂(秒)
|
||||
- **precision** 为四舍五入值,且为 2 的幂数。因此精度为 2^precision (秒)
|
||||
- **rootdelay** – 与同步网络中主同步服务器的总往返延时。注意这个值可以是正数或者负数,取决于时钟的精度。
|
||||
- **rootdisp** – 相对于同步网络中主同步服务器的偏差(秒)
|
||||
- **tc** – NTP 算法 [PLL][59] (phase locked loop,锁相环路) 或 [FLL][60] (frequency locked loop,锁频回路) 时间常量
|
||||
@ -122,20 +121,20 @@ Jitter (也叫 timing jitter) 表示短期变化大于10HZ 的频率, wander
|
||||
|
||||
NTP 软件维护一系列连续更新的频率变化的校正值。对于设置正确的稳定系统,在非拥塞的网络中,现代硬件的 NTP 时钟同步通常与 UTC 标准时间相差在毫秒内。(在千兆 LAN 网络中可以达到何种精度?)
|
||||
|
||||
对于 UTC 时间,[闰秒][62] 可以每两年插入一次用于同步地球自传的变化。注意本地时间为[夏令时][63]时时间会有一小时的变化。在重同步之前客户端设备会使用独立的 UTC 时间,除非客户端使用了偏移校准。
|
||||
对于 UTC 时间,[闰秒 leap second ][62] 可以每两年插入一次用于同步地球自传的变化。注意本地时间为[夏令时][63]时时间会有一小时的变化。在重同步之前客户端设备会使用独立的 UTC 时间,除非客户端使用了偏移校准。
|
||||
|
||||
#### [闰秒发生时会怎样][64] ####
|
||||
|
||||
> 闰秒发生时,会对当天时间增加或减少一秒。闰秒的调整在 UTC 时间当天的最后一秒。如果增加一秒,UTC 时间会出现 23:59:60。即 23:59:59 到 0:00:00 之间实际上需要 2 秒钟。如果减少一秒,时间会从 23:59:58 跳至 0:00:00 。另见 [The Kernel Discipline][65].
|
||||
|
||||
好了… 间隔阈值(step threshold)的真实值是多少: 125ms 还是 128ms? PLL/FLL tc 的单位是什么 (log2 s? ms?)?在非拥塞的千兆 LAN 中时间节点间的精度能达到多少?
|
||||
那么… 间隔阈值(step threshold)的真实值是多少: 125ms 还是 128ms? PLL/FLL tc 的单位是什么 (log2 s? ms?)?在非拥塞的千兆 LAN 中时间节点间的精度能达到多少?
|
||||
|
||||
感谢 Camilo M 和 Chris B的评论。 欢迎校正错误和更多细节的探讨。
|
||||
|
||||
谢谢
|
||||
Martin
|
||||
|
||||
### 外传 ###
|
||||
### 附录 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [NTP 的纪元][66] 从 1900 开始而 UNIX 的从 1970开始.
|
||||
- [时间校正][67] 是逐渐进行的,因此时间的完全同步可能会画上几个小时。
|
||||
@ -152,7 +151,7 @@ Martin
|
||||
|
||||
- [ntpq – 标准 NTP 查询程序][77]
|
||||
- [The Network Time Protocol (NTP) 分布][78]
|
||||
- NTP 的简明 [历史][79]
|
||||
- NTP 的简明[历史][79]
|
||||
- 一个更多细节的简明历史 “Mills, D.L., A brief history of NTP time: confessions of an Internet timekeeper. Submitted for publication; please do not cite or redistribute” ([pdf][80])
|
||||
- [NTP RFC][81] 标准文档
|
||||
- Network Time Protocol (Version 3) RFC – [txt][82], or [pdf][83]. Appendix E, The NTP Timescale and its Chronometry, p70, 包含了对过去 5000 年我们的计时系统的变化和关系的有趣解释。
|
||||
@ -165,7 +164,7 @@ Martin
|
||||
|
||||
### 其他 ###
|
||||
|
||||
SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol, [RFC 4330][91],简单未落协议)基本上也是NTP,但是缺少一些基于 [RFC 1305][92] 实现的 NTP 的一些不再需要的内部算法。
|
||||
SNTP (Simple Network Time Protocol, [RFC 4330][91],简单网络协议)基本上也是NTP,但是少了一些基于 [RFC 1305][92] 实现的 NTP 的一些不再需要的内部算法。
|
||||
|
||||
Win32 时间 [Windows Time Service][93] 是 SNTP 的非标准实现,没有精度的保证,并假设精度几乎有 1-2 秒的范围。(因为没有系统时间变化校正)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -184,7 +183,7 @@ via: http://nlug.ml1.co.uk/2012/01/ntpq-p-output/831
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Martin L
|
||||
译者:[Liao](https://github.com/liaosishere)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
66
published/20141108 When hackers grow old.md
Normal file
66
published/20141108 When hackers grow old.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
ESR:黑客年暮
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
近来我一直在与某资深开源开发团队中的多个成员缠斗,尽管密切关注我的人们会在读完本文后猜到是哪个组织,但我不会在这里说出这个组织的名字。
|
||||
|
||||
怎么让某些人进入 21 世纪就这么难呢?真是的...
|
||||
|
||||
我快 56 岁了,也就是大部分年轻人会以为的我将时不时朝他们发出诸如“滚出我的草坪”之类歇斯底里咆哮的年龄。但事实并非如此 —— 我发现,尤其是在技术背景之下,我变得与我的年龄非常不相称。
|
||||
|
||||
在我这个年龄的大部分人确实变成了爱发牢骚、墨守成规的老顽固。并且,尴尬的是,偶尔我会成为那个打断谈话的人,我会指出他们某个在 1995 年(或者在某些特殊情况下,1985 年)时很适合的方法... 几十年后的今天就不再是好方法了。
|
||||
|
||||
为什么是我?因为年轻人在我的同龄人中很难有什么说服力。如果有人想让那帮老头改变主意,首先他得是自己同龄人中具有较高思想觉悟的佼佼者。即便如此,在与习惯做斗争的过程中,我也比看起来花费了更多的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
年轻人犯下无知的错误是可以被原谅的。他们还年轻。年轻意味着缺乏经验,缺乏经验通常会导致片面的判断。我很难原谅那些经历了足够多本该有经验的人,却被*长期的固化思维*蒙蔽,无法发觉近在咫尺的东西。
|
||||
|
||||
(补充一下:我真的不是保守党拥护者。那些和我争论政治的,无论保守党还是非保守党都没有注意到这点,我觉得这颇有点嘲讽的意味。)
|
||||
|
||||
那么,现在我们来讨论下 GNU 更新日志文件(ChangeLog)这件事。在 1985 年的时候,这是一个不错的主意,甚至可以说是必须的。当时的想法是用单独的更新日志条目来记录多个相关文件的变更情况。用这种方式来对那些存在版本缺失或者非常原始的版本进行版本控制确实不错。当时我也*在场*,所以我知道这些。
|
||||
|
||||
不过即使到了 1995 年,甚至 21 世纪早期,许多版本控制系统仍然没有太大改进。也就是说,这些版本控制系统并非对批量文件的变化进行分组再保存到一条记录上,而是对每个变化的文件分别进行记录并保存到不同的地方。CVS,当时被广泛使用的版本控制系统,仅仅是模拟日志变更 —— 并且在这方面表现得很糟糕,导致大多数人不再依赖这个功能。即便如此,更新日志文件的出现依然是必要的。
|
||||
|
||||
但随后,版本控制系统 Subversion 于 2003 年发布 beta 版,并于 2004 年发布 1.0 正式版,Subversion 真正实现了更新日志记录功能,得到了人们的广泛认可。它与一年后兴起的分布式版本控制系统(Distributed Version Control System,DVCS)共同引发了主流世界的激烈争论。因为如果你在项目上同时使用了分布式版本控制与更新日志文件记录的功能,它们将会因为争夺相同元数据的控制权而产生不可预料的冲突。
|
||||
|
||||
有几种不同的方法可以折衷解决这个问题。一种是继续将更新日志作为代码变更的授权记录。这样一来,你基本上只能得到简陋的、形式上的提交评论数据。
|
||||
|
||||
另一种方法是对提交的评论日志进行授权。如果你这样做了,不久后你就会开始思忖为什么自己仍然对所有的日志更新条目进行记录。提交元数据与变化的代码具有更好的相容性,毕竟这才是当初设计它的目的。
|
||||
|
||||
(现在,试想有这样一个项目,同样本着把项目做得最好的想法,但两拨人却做出了完全不同的选择。因此你必须同时阅读更新日志和评论日志以了解到底发生了什么。最好在矛盾激化前把问题解决....)
|
||||
|
||||
第三种办法是尝试同时使用以上两种方法 —— 在更新日志条目中,以稍微变化后的的格式复制一份评论数据,将其作为评论提交的一部分。这会导致各种你意想不到的问题,最具代表性的就是它不符合“真理的单点性(single point of truth)”原理;只要其中有拷贝文件损坏,或者日志文件条目被修改,这就不再是同步时数据匹配的问题,它将导致在其后参与进来的人试图搞清人们是怎么想的时候变得非常困惑。(LCTT 译注:《[程序员修炼之道][1]》(The Pragmatic Programmer):任何一个知识点在系统内都应当有一个唯一、明确、权威的表述。根据Brian Kernighan的建议,把这个原则称为“真理的单点性(Single Point of Truth)”或者SPOT原则。)
|
||||
|
||||
或者,正如这个*我就不说出具体名字的特定项目*所做的,它的高层开发人员在电子邮件中最近声明说,提交可以包含多个更新日志条目,并且提交的元数据与更新日志是无关的。这导致我们直到现在还得不断进行记录。
|
||||
|
||||
当时我读到邮件的时候都要吐了。什么样的傻瓜才会意识不到这是自找麻烦 —— 事实上,在 DVCS 中针对可靠的提交日志有很好的浏览工具,围绕更新日志文件的整个定制措施只会成为负担和拖累。
|
||||
|
||||
唉,这是比较特殊的笨蛋:变老的并且思维僵化了的黑客。所有的合理化改革他都会极力反对。他所遵循的行事方法在几十年前是有效的,但现在只能适得其反。如果你试图向他解释这些不仅仅和 git 的摘要信息有关,同时还为了正确适应当前的工具集,以便实现更新日志的去条目化... 呵呵,那你就准备好迎接无法忍受、无法想象的疯狂对话吧。
|
||||
|
||||
的确,它成功激怒了我。这样那样的胡言乱语使这个项目变成了很难完成的工作。而且,同样的糟糕还体现在他们吸引年轻开发者的过程中,我认为这是真正的问题。相关 Google+ 社区的人员数量已经达到了 4 位数,他们大部分都是孩子,还没有成长起来。显然外界已经接受了这样的信息:这个项目的开发者都是部落中地位根深蒂固的崇高首领,最好的崇拜方式就是远远的景仰着他们。
|
||||
|
||||
这件事给我的最大触动就是每当我要和这些部落首领较量时,我都会想:有一天我也会这样吗?或者更糟的是,我看到的只是如同镜子一般对我自己的真实写照,而我自己却浑然不觉?我的意思是,我所得到的印象来自于他的网站,这个特殊的笨蛋要比我年轻。年轻至少 15 岁呢。
|
||||
|
||||
我总是认为自己的思路很清晰。当我和那些比我聪明的人打交道时我不会受挫,我只会因为那些思路跟不上我、看不清事实的人而沮丧。但这种自信也许只是邓宁·克鲁格效应(Dunning-Krueger effect)在我身上的消极影响,我并不确定这意味着什么。很少有什么事情会让我感到害怕;而这件事在让我害怕的事情名单上是名列前茅的。
|
||||
|
||||
另一件让人不安的事是当我逐渐变老的时候,这样的矛盾发生得越来越频繁。不知怎的,我希望我的黑客同行们能以更加优雅的姿态老去,即使身体老去也应该保持一颗年轻的心灵。有些人确实是这样;但可惜绝大多数人都不是。真令人悲哀。
|
||||
|
||||
我不确定我的职业生涯会不会完美收场。假如我最后成功避免了思维僵化(注意我说的是假如),我想我一定知道其中的部分原因,但我不确定这种模式是否可以被复制 —— 为了达成目的也许得在你的头脑中发生一些复杂的化学反应。尽管如此,无论对错,请听听我给年轻黑客以及其他有志青年的建议。
|
||||
|
||||
你们——对的,也包括你——一定无法在你中年老年的时候保持不错的心灵,除非你能很好的控制这点。你必须不断地去磨练你的内心、在你还年轻的时候完成自己的种种心愿,你必须把这些行为养成一种习惯直到你老去。
|
||||
|
||||
有种说法是中年人锻炼身体的最佳时机是 30 岁以前。我以为同样的方法,坚持我以上所说的习惯能让你在 56 岁,甚至 65 岁的时候仍然保持灵活的头脑。挑战你的极限,使不断地挑战自己成为一种习惯。立刻离开安乐窝,由此当你以后真正需要它的时候你可以建立起自己的安乐窝。
|
||||
|
||||
你必须要清楚的了解这点;还有一个可选择的挑战是你选择一个可以实现的目标并且为了这个目标不断努力。这个月我要学习 Go 语言。不是指游戏,我早就玩儿过了(虽然玩儿的不是太好)。并不是因为工作需要,而是因为我觉得是时候来扩展下我自己了。
|
||||
|
||||
保持这个习惯。永远不要放弃。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://esr.ibiblio.org/?p=6485
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Eric Raymond][a]
|
||||
译者:[Stevearzh](https://github.com/Stevearzh)
|
||||
校对:[Mr小眼儿](https://github.com/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://esr.ibiblio.org/?author=2
|
||||
[1]:http://book.51cto.com/art/200809/88490.htm
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
你能快速定位CPU性能回退的问题么? 如果你的工作环境非常复杂且变化快速,那么使用现有的工具是来定位这类问题是很具有挑战性的。当你花掉数周时间把根因找到时,代码已经又变更了好几轮,新的性能问题又冒了出来。
|
||||
|
||||
辛亏有了[CPU火焰图][1](flame graphs),CPU使用率的问题一般都比较好定位。但要处理性能回退问题,就要在修改前后的火焰图间,不断切换对比,来找出问题所在,这感觉就是像在太阳系中搜寻冥王星。虽然,这种方法可以解决问题,但我觉得应该会有更好的办法。
|
||||
幸亏有了[CPU火焰图][1](flame graphs),CPU使用率的问题一般都比较好定位。但要处理性能回退问题,就要在修改前后的火焰图之间,不断切换对比,来找出问题所在,这感觉就是像在太阳系中搜寻冥王星。虽然,这种方法可以解决问题,但我觉得应该会有更好的办法。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,下面就隆重介绍**红/蓝差分火焰图(red/blue differential flame graphs)**:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
这张火焰图中各火焰的形状和大小都是和第二次抓取的profile文件对应的CPU火焰图是相同的。(其中,y轴表示栈的深度,x轴表示样本的总数,栈帧的宽度表示了profile文件中该函数出现的比例,最顶层表示正在运行的函数,再往下就是调用它的栈)
|
||||
|
||||
在下面这个案例展示了,在系统升级后,一个工作负载的CPU使用率上升了。 下面是对应的CPU火焰图([SVG格式][4])
|
||||
在下面这个案例展示了,在系统升级后,一个工作载荷的CPU使用率上升了。 下面是对应的CPU火焰图([SVG格式][4])
|
||||
|
||||
<p><object data="http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/images/2014/zfs-flamegraph-after.svg" type="image/svg+xml" width=720 height=296>
|
||||
<img src="http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/images/2014/zfs-flamegraph-after.svg" width=720 />
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
通常,在标准的火焰图中栈帧和栈塔的颜色是随机选择的。 而在红/蓝差分火焰图中,使用不同的颜色来表示两个profile文件中的差异部分。
|
||||
|
||||
在第二个profile中deflate_slow()函数以及它后续调用的函数运行的次数要比前一次更多,所以在上图中这个栈帧被标为了红色。可以看出问题的原因是ZFS的压缩功能被使能了,而在系统升级前这项功能是关闭的。
|
||||
在第二个profile中deflate_slow()函数以及它后续调用的函数运行的次数要比前一次更多,所以在上图中这个栈帧被标为了红色。可以看出问题的原因是ZFS的压缩功能被启用了,而在系统升级前这项功能是关闭的。
|
||||
|
||||
这个例子过于简单,我甚至可以不用差分火焰图也能分析出来。但想象一下,如果是在分析一个微小的性能下降,比如说小于5%,而且代码也更加复杂的时候,问题就为那么好处理了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -69,7 +69,9 @@ difffolded.p只能对“折叠”过的堆栈profile文件进行操作,折叠
|
||||
在上面的例子中"func_a()->func_b()->func_c()" 代表调用栈,这个调用栈在profile1文件中共出现了31次,在profile2文件中共出现了33次。然后,使用flamegraph.pl脚本处理这3列数据,会自动生成一张红/蓝差分火焰图。
|
||||
|
||||
### 其他选项 ###
|
||||
|
||||
再介绍一些有用的选项:
|
||||
|
||||
**difffolded.pl -n**:这个选项会把两个profile文件中的数据规范化,使其能相互匹配上。如果你不这样做,抓取到所有栈的统计值肯定会不相同,因为抓取的时间和CPU负载都不同。这样的话,看上去要么就是一片红(负载增加),要么就是一片蓝(负载下降)。-n选项对第一个profile文件进行了平衡,这样你就可以得到完整红/蓝图谱。
|
||||
|
||||
**difffolded.pl -x**: 这个选项会把16进制的地址删掉。 profiler时常会无法将地址转换为符号,这样的话栈里就会有16进制地址。如果这个地址在两个profile文件中不同,这两个栈就会认为是不同的栈,而实际上它们是相同的。遇到这样的问题就用-x选项搞定。
|
||||
@ -77,6 +79,7 @@ difffolded.p只能对“折叠”过的堆栈profile文件进行操作,折叠
|
||||
**flamegraph.pl --negate**: 用于颠倒红/蓝配色。 在下面的章节中,会用到这个功能。
|
||||
|
||||
### 不足之处 ###
|
||||
|
||||
虽然我的红/蓝差分火焰图很有用,但实际上还是有一个问题:如果一个代码执行路径完全消失了,那么在火焰图中就找不到地方来标注蓝色。你只能看到当前的CPU使用情况,而不知道为什么会变成这样。
|
||||
|
||||
一个办法是,将对比顺序颠倒,画一个相反的差分火焰图。例如:
|
||||
@ -95,12 +98,13 @@ difffolded.p只能对“折叠”过的堆栈profile文件进行操作,折叠
|
||||
|
||||
这样,把前面生成diff2.svg一并使用,我们就能得到:
|
||||
|
||||
- **diff1.svg**: 宽度是以修改前profile文件为基准, 颜色表明将要发生的情况
|
||||
- **diff2.svg**: 宽度以修改后的profile文件为基准,颜色表明已经发生的情况
|
||||
- **diff1.svg**: 宽度是以修改前profile文件为基准,颜色表明将要发生的情况
|
||||
- **diff2.svg**: 宽度是以修改后profile文件为基准,颜色表明已经发生的情况
|
||||
|
||||
如果是在做功能验证测试,我会同时生成这两张图。
|
||||
|
||||
### CPI 火焰图 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这些脚本开始是被使用在[CPI火焰图][8]的分析上。与比较修改前后的profile文件不同,在分析CPI火焰图时,可以分析CPU工作周期与停顿周期的差异变化,这样可以凸显出CPU的工作状态来。
|
||||
|
||||
### 其他的差分火焰图 ###
|
||||
@ -110,6 +114,7 @@ difffolded.p只能对“折叠”过的堆栈profile文件进行操作,折叠
|
||||
也有其他人做过类似的工作。[Robert Mustacchi][10]在不久前也做了一些尝试,他使用的方法类似于代码检视时的标色风格:只显示了差异的部分,红色表示新增(上升)的代码路径,蓝色表示删除(下降)的代码路径。一个关键的差别是栈帧的宽度只体现了差异的样本数。右边是一个例子。这个是个很好的主意,但在实际使用中会感觉有点奇怪,因为缺失了完整profile文件的上下文作为背景,这张图显得有些难以理解。
|
||||
|
||||
[][12]
|
||||
|
||||
Cor-Paul Bezemer也制作了一种差分显示方法[flamegraphdiff][13],他同时将3张火焰图放在同一张图中,修改前后的标准火焰图各一张,下面再补充了一张差分火焰图,但栈帧宽度也是差异的样本数。 上图是一个[例子][14]。在差分图中将鼠标移到栈帧上,3张图中同一栈帧都会被高亮显示。这种方法中补充了两张标准的火焰图,因此解决了上下文的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
我们3人的差分火焰图,都各有所长。三者可以结合起来使用:Cor-Paul方法中上方的两张图,可以用我的diff1.svg 和 diff2.svg。下方的火焰图可以用Robert的方式。为保持一致性,下方的火焰图可以用我的着色方式:蓝->白->红。
|
||||
@ -128,7 +133,7 @@ via: http://www.brendangregg.com/blog/2014-11-09/differential-flame-graphs.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Brendan Gregg][a]
|
||||
译者:[coloka](https://github.com/coloka)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,11 +24,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
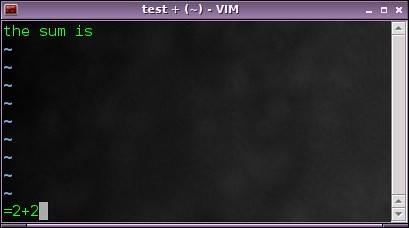
然后 4 会被插入到文件中。
|
||||
然后计算结果“4 ”会被插入到文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 查找重复的连续的单词 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当你很快地打字时,很有可能会连续输入同一个单词两次,就像 this this。这种错误可能骗过任何一个人,即使是你自己重新阅读一边也不可避免。幸运的是,有一个简单的正则表达式可以用来预防这个错误。使用搜索命令(默认时 `/`)然后输入:
|
||||
当你很快地打字时,很有可能会连续输入同一个单词两次,就像 this this。这种错误可能骗过任何一个人,即使是你自己重新阅读一遍也不可避免。幸运的是,有一个简单的正则表达式可以用来预防这个错误。使用搜索命令(默认时 `/`)然后输入:
|
||||
|
||||
\(\<\w\+\>\)\_s*\1
|
||||
|
||||
@ -72,7 +72,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
`gg` 把光标移动到 Vim 缓冲区的第一行,`V` 进入可视模式,`G` 把光标移动到缓冲区的最后一行。因此,`ggVG` 使可视模式覆盖这个当前缓冲区。最后 `g?` 使用 ROT13 对整个区域进行编码。
|
||||
|
||||
注意它应该被映射到一个最长使用的键。它对字母符号也可以很好地工作。要对它进行撤销,最好的方法就是使用撤销命令:`u`。
|
||||
注意它可以被映射到一个最常使用的键。它对字母符号也可以很好地工作。要对它进行撤销,最好的方法就是使用撤销命令:`u`。
|
||||
|
||||
###自动补全 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -110,7 +110,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 按时间回退文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Vim 会记录文件的更改,你很容易可以回退到之前某个时间。该命令时相当直观的。比如:
|
||||
Vim 会记录文件的更改,你很容易可以回退到之前某个时间。该命令是相当直观的。比如:
|
||||
|
||||
:earlier 1m
|
||||
|
||||
@ -122,7 +122,7 @@ Vim 会记录文件的更改,你很容易可以回退到之前某个时间。
|
||||
|
||||
### 删除标记内部的文字 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当我开始使用 Vim 时一件我总是想很方便做的事情是如何轻松的删除方括号或圆括号里的内容。转到开始的标记,然后使用下面的语法:
|
||||
当我开始使用 Vim 时,一件我总是想很方便做的事情是如何轻松的删除方括号或圆括号里的内容。转到开始的标记,然后使用下面的语法:
|
||||
|
||||
di[标记]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -164,11 +164,11 @@ Vim 会记录文件的更改,你很容易可以回退到之前某个时间。
|
||||
|
||||
### 把光标下的文字置于屏幕中央 ###
|
||||
|
||||
所有要做的事情都包含在标题中。如果你想强制滚动屏幕来把光标下的文字置于屏幕的中央,在可视模式中使用命令(译者注:在普通模式中也可以):
|
||||
我们所要做的事情如标题所示。如果你想强制滚动屏幕来把光标下的文字置于屏幕的中央,在可视模式中使用命令(译者注:在普通模式中也可以):
|
||||
|
||||
zz
|
||||
|
||||
### 跳到上一个/下一个 位置 ###
|
||||
### 跳到上一个/下一个位置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当你编辑一个很大的文件时,经常要做的事是在某处进行修改,然后跳到另外一处。如果你想跳回之前修改的地方,使用命令:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -196,7 +196,7 @@ Vim 会记录文件的更改,你很容易可以回退到之前某个时间。
|
||||
|
||||
总的来说,这一系列命令是在我读了许多论坛主题和 [Vim Tips wiki][3](如果你想学习更多关于编辑器的知识,我非常推荐这篇文章) 之后收集起来的。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你还知道哪些非常有用但你认为大多数人并不知道的命令,可以随意在评论中分享出来。就像引言中所说的,一个“鲜为人知但很有用的”命令是很主观的,但分享出来总是好的。
|
||||
如果你还知道哪些非常有用但你认为大多数人并不知道的命令,可以随意在评论中分享出来。就像引言中所说的,一个“鲜为人知但很有用的”命令也许只是你自己的看法,但分享出来总是好的。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -204,7 +204,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/useful-vim-commands.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[wangjiezhe](https://github.com/wangjiezhe)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,7 +1,6 @@
|
||||
用Grub启动ISO镜像
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如果你需要使用多个Linux发行版,你没有那么多的选项。你可以安装到你的物理机或虚拟机中,也可以以live模式从ISO文件启动。第二个选择,如果对硬盘空间需求更少,就有点麻烦,因为你需要将ISO文件写入到USB棒或CD来启动。但是,这里有另外一个可选的折中方案:把ISO镜像放在硬盘中,然后以live模式来启动。该方案比完全安装更省空间,但是功能完备,这对于缓慢的虚拟机而言是个不错的替代方案。下面我将介绍怎样使用流行的Grub启动加载器来实现该方案。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要使用多个Linux发行版,你没有那么多的选择。你要么安装到你的物理机或虚拟机中,要么以live模式从ISO文件启动。第二个选择,对硬盘空间需求较小,只是有点麻烦,因为你需要将ISO文件写入到U盘或CD/DVD中来启动。不过,这里还有另外一个可选的折中方案:把ISO镜像放在硬盘中,然后以live模式来启动。该方案比完全安装更省空间,而且功能也完备,这对于缓慢的虚拟机而言是个不错的替代方案。下面我将介绍怎样使用流行的Grub启动加载器来实现该方案。
|
||||
|
||||
很明显,你将需要使用到Grub,这是几乎所有现代Linux发行版都使用的。你也需要你所想用的Linux版本的ISO文件,将它下载到本地磁盘。最后,你需要知道启动分区在哪里,并怎样在Grub中描述。对于此,请使用以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,7 +30,7 @@
|
||||
[some specific] arguments
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
例如,如果你想要从ISO文件启动Ubuntu,那么你就是想要添加该行到40_custom文件:
|
||||
例如,如果你想要从ISO文件启动Ubuntu,那么你就是想要添加如下行到40_custom文件:
|
||||
|
||||
menuentry "Ubuntu 14.04 (LTS) Live Desktop amd64" {
|
||||
set isofile="/boot/ubuntu-14.04-desktop-amd64.iso"
|
||||
@ -62,7 +61,7 @@
|
||||
initrd (loop)/isolinux/initrd0.img
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
注意,参数可根据发行版进行修改。有幸的是,有许多地方你可以查阅。我喜欢这一个,但是还有很多其它的。同时,请考虑你放置ISO文件的地方。如果你的家目录被加密或者无法被访问到,你可能更喜欢将这些文件放到像例子中的启动分区。但是,请首先确保有足够的空间。
|
||||
注意,参数可根据发行版进行修改。幸运的是,有许多地方你可以查阅到。我喜欢这个发行版,但是还有很多其它的发行版你可以启动。同时,请注意你放置ISO文件的地方。如果你的家目录被加密或者无法被访问到,你可能更喜欢将这些文件放到像例子中的启动分区。但是,请首先确保启动分区有足够的空间。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,不要忘了保存40_custom文件并使用以下命令来更新grub:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -92,7 +91,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
可以显示DBAN选项,让你选择清除驱动器。**当心,因为它仍然十分危险**。
|
||||
|
||||
小结一下,对于ISO文件和Grub有很多事情可做:从快速live会话到用你的指尖来破坏一切,都可以满足你。下一步是启动一些关注隐私的发行版如[Tails][2]。
|
||||
小结一下,对于ISO文件和Grub有很多事情可做:从快速live会话到一键毁灭,都可以满足你。之后,你也可以试试启动一些针对隐私方面的发行版,如[Tails][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
你认为从Grub启动一个ISO这个主意怎样?这是不是你想要做的呢?为什么呢?请在下面留言。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -102,7 +101,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/boot-iso-image-from-grub.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,30 +1,34 @@
|
||||
硬盘监控和分析神器——Smartctl
|
||||
硬盘监控和分析工具——Smartctl
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Smartctl**(自监控,分析和报告技术)是类Unix系统下实施SMART任务命令行套件或工具,它用于打印SMART**自检**和**错误日志**,启用并禁用SMRAT**自动检测**,以及初始化设备自检。
|
||||
**Smartctl**(S.M.A.R.T 自监控,分析和报告技术)是类Unix系统下实施SMART任务命令行套件或工具,它用于打印SMART**自检**和**错误日志**,启用并禁用SMRAT**自动检测**,以及初始化设备自检。
|
||||
|
||||
Smartctl对于Linux物理服务器十分有用,在这些服务器上,可以对智能磁盘进行错误检查,并将与**硬件RAID**上相关的磁盘信息摘录下来。
|
||||
Smartctl对于Linux物理服务器十分有用,在这些服务器上,可以对智能磁盘进行错误检查,并将与**硬件RAID**相关的磁盘信息摘录下来。
|
||||
|
||||
在本帖中,我们将讨论smartctl命令的一些实用样例。如果你的Linux上海没有安装smartctl,请按以下步骤来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu中smartctl的安装 ###
|
||||
### 安装 Smartctl ###
|
||||
|
||||
**对于 Ubuntu**
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install smartmontools
|
||||
|
||||
### Redhat / CentOS中smartctl的安装 ###
|
||||
**对于 CentOS & RHEL**
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install smartmontools
|
||||
|
||||
**启动Smartctl服务**
|
||||
###启动Smartctl服务###
|
||||
|
||||
**对于Ubuntu**
|
||||
**对于 Ubuntu**
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/smartmontools start
|
||||
|
||||
**对于CentOS & RHEL**
|
||||
**对于 CentOS & RHEL**
|
||||
|
||||
# service smartd start ; chkconfig smartd on
|
||||
|
||||
**样例:1 检查针对磁盘的Smart负载量**
|
||||
### 样例 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 样例:1 检查磁盘的 Smart 功能是否启用
|
||||
|
||||
root@linuxtechi:~# smartctl -i /dev/sdb
|
||||
smartctl 6.2 2013-07-26 r3841 [x86_64-linux-3.13.0-32-generic] (local build)
|
||||
@ -46,9 +50,9 @@ Smartctl对于Linux物理服务器十分有用,在这些服务器上,可以
|
||||
SMART support is: Available - device has SMART capability.
|
||||
SMART support is: Enabled
|
||||
|
||||
这里‘/dev/sdb’是你的硬盘。上面输出中的最后两行显示了SMART负载量已启用。
|
||||
这里‘/dev/sdb’是你的硬盘。上面输出中的最后两行显示了SMART功能已启用。
|
||||
|
||||
**样例:2 为磁盘启用Smart负载量**
|
||||
#### 样例:2 启用磁盘的 Smart 功能
|
||||
|
||||
root@linuxtechi:~# smartctl -s on /dev/sdb
|
||||
smartctl 6.2 2013-07-26 r3841 [x86_64-linux-3.13.0-32-generic] (local build)
|
||||
@ -57,7 +61,7 @@ Smartctl对于Linux物理服务器十分有用,在这些服务器上,可以
|
||||
=== START OF ENABLE/DISABLE COMMANDS SECTION ===
|
||||
SMART Enabled.
|
||||
|
||||
**样例:3 为磁盘禁用Smart负载量**
|
||||
#### 样例:3 禁用磁盘的 Smart 功能
|
||||
|
||||
root@linuxtechi:~# smartctl -s off /dev/sdb
|
||||
smartctl 6.2 2013-07-26 r3841 [x86_64-linux-3.13.0-32-generic] (local build)
|
||||
@ -66,12 +70,12 @@ Smartctl对于Linux物理服务器十分有用,在这些服务器上,可以
|
||||
=== START OF ENABLE/DISABLE COMMANDS SECTION ===
|
||||
SMART Disabled. Use option -s with argument 'on' to enable it.
|
||||
|
||||
**样例:4 为磁盘显示详细Smart信息**
|
||||
#### 样例:4 显示磁盘的详细 Smart 信息
|
||||
|
||||
root@linuxtechi:~# smartctl -a /dev/sdb // For IDE drive
|
||||
root@linuxtechi:~# smartctl -a -d ata /dev/sdb // For SATA drive
|
||||
|
||||
**样例:5 显示磁盘总体健康状况**
|
||||
#### 样例:5 显示磁盘总体健康状况
|
||||
|
||||
root@linuxtechi:~# smartctl -H /dev/sdb
|
||||
smartctl 6.2 2013-07-26 r3841 [x86_64-linux-3.13.0-32-generic] (local build)
|
||||
@ -84,7 +88,7 @@ Smartctl对于Linux物理服务器十分有用,在这些服务器上,可以
|
||||
ID# ATTRIBUTE_NAME FLAG VALUE WORST THRESH TYPE UPDATED WHEN_FAILED RAW_VALUE
|
||||
190 Airflow_Temperature_Cel 0x0022 067 045 045 Old_age Always In_the_past 33 (Min/Max 25/33)
|
||||
|
||||
**样例:6 使用long和short选项测试硬盘**
|
||||
#### 样例:6 使用long和short选项测试硬盘
|
||||
|
||||
**Long测试**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -126,7 +130,7 @@ Smartctl对于Linux物理服务器十分有用,在这些服务器上,可以
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:short测试将花费最多2分钟,而在long测试中没有时间限制,因为它会读取并验证磁盘的每个段。
|
||||
|
||||
**样例:7 查看驱动器的自检结果**
|
||||
#### 样例:7 查看驱动器的自检结果
|
||||
|
||||
root@linuxtechi:~# smartctl -l selftest /dev/sdb
|
||||
smartctl 6.2 2013-07-26 r3841 [x86_64-linux-3.13.0-32-generic] (local build)
|
||||
@ -138,7 +142,7 @@ Smartctl对于Linux物理服务器十分有用,在这些服务器上,可以
|
||||
# 1 Short offline Completed: read failure 90% 492 210841222
|
||||
# 2 Extended offline Completed: read failure 90% 492 210841222
|
||||
|
||||
**样例:8 计算测试时间估值**
|
||||
#### 样例:8 计算测试时间估值
|
||||
|
||||
root@linuxtechi:~# smartctl -c /dev/sdb
|
||||
smartctl 6.2 2013-07-26 r3841 [x86_64-linux-3.13.0-32-generic] (local build)
|
||||
@ -178,7 +182,7 @@ Smartctl对于Linux物理服务器十分有用,在这些服务器上,可以
|
||||
SCT Feature Control supported.
|
||||
SCT Data Table supported.
|
||||
|
||||
**样例:9 显示磁盘错误日志**
|
||||
#### 样例:9 显示磁盘错误日志
|
||||
|
||||
root@linuxtechi:~# smartctl -l error /dev/sdb
|
||||
|
||||
@ -219,7 +223,7 @@ via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/smartctl-monitoring-analysis-tool-hard-drive/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ Postfix邮件服务器的配置与安全加固
|
||||
service sendmail stop
|
||||
yum remove sendmail
|
||||
|
||||
Postfix包含了**两个配置文件main.cf和master.cf**,对于基本的配置,你需要修改main.cf。同时,postfix可以像shell变量一样定义参数,并通过美元符号来调用。这些参数不需要再使用前定义,Postfix只在运行中需要时才会查询某个参数。
|
||||
Postfix包含了**两个配置文件main.cf和master.cf**,对于基本的配置,你需要修改main.cf。同时,postfix可以像shell变量一样定义参数,并通过$来调用。这些参数不需要再使用前定义,Postfix只在运行中需要时才会查询某个参数。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置postfix ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,23 +21,23 @@ Postfix包含了**两个配置文件main.cf和master.cf**,对于基本的配
|
||||
|
||||
去掉以下行的注释
|
||||
|
||||
#Add the hostname of your machine
|
||||
# 你的主机名
|
||||
myhostname = yourhostname.com
|
||||
|
||||
#From Domain to be used when mail is sent from this linux machine
|
||||
# 你的发件域
|
||||
myorigin = $myhostname
|
||||
|
||||
#The network interface to receive mail on, I prefer localhost as I only want emails from this system to be delivered
|
||||
# 指定用于接收邮件的网络接口,这里指定 localhost 是因为我们只用来接受本地的程序投递
|
||||
inet_interfaces = localhost
|
||||
|
||||
# The protocol to use when postfix will make or accept a connection. You can use “all” if you want to enable IPv6 support
|
||||
# 指定所使用的协议,可以使用“all”来增加 IPv6 支持
|
||||
inet_protocols = ipv4
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#Domains to receive email for
|
||||
# 指定所接受的邮件域
|
||||
mydestination = $myhostname, localhost.$mydomain, localhost
|
||||
|
||||
#Only forward emails for the local machine and not machines on the network.
|
||||
# 仅转发本地主机的邮件,而不是主机所在的网络
|
||||
mynetworks_style = host
|
||||
|
||||
启动postfix
|
||||
@ -48,13 +48,13 @@ Postfix包含了**两个配置文件main.cf和master.cf**,对于基本的配
|
||||
|
||||
echo test mail | mail -s "test" leo@techarena51.com && sudo tail -f /var/log/maillog
|
||||
|
||||
#Logs should output the following
|
||||
# 输出的日志类似如下
|
||||
Aug 25 14:16:21 vps postfix/smtp[32622]: E6A372DC065D: to=, relay=smtp.mailserver.org[50.56.21.176], delay=0.8, delays=0.1/0/0.43/0.27, dsn=2.0.0, status=sent (250 Great success)
|
||||
Aug 25 14:16:21 vps postfix/qmgr[5355]: E6A372DC065D: removed
|
||||
|
||||
但是,上述配置并不够,因为邮件服务大多数时候都会被垃圾邮件挤满,你需要添加SPF、PTR和DKIM记录。你的邮件仍然可能被当作垃圾邮件来投递,因为你的IP地址被列入了黑名单,大多数时候是因为你的vps先前被入侵了。
|
||||
但是,上述配置并不够,因为邮件服务大多数时候都会被垃圾邮件挤满,你需要添加SPF、PTR和DKIM记录。即便如此,你的邮件仍然可能被当作垃圾邮件来投递,因为你的IP地址被列入了黑名单,大多数时候是因为你的vps先前被入侵了。
|
||||
|
||||
另外一种选择,或者说是更好的方式是使用第三方邮件提供商提供的邮件服务,如Gmail,或者甚至是Mailgun。我使用Mailgun,因为它们提供了每个月10000封免费电子邮件,而Gmail则提供了每天100封左右的邮件。
|
||||
还有另外一种选择,或者说是更好的方式是使用第三方邮件提供商提供的邮件服务,如Gmail,或者甚至是Mailgun。我使用Mailgun,因为它们提供了每个月10000封免费电子邮件,而Gmail则提供了每天100封左右的邮件。
|
||||
|
||||
在“/etc/postfix/main.cf”中,你需要添加“smtp.mailgun.com”作为你的“转发主机”,并启用“SASL”验证,这样postfix就可以连接并验证到远程Mailgun服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -77,21 +77,21 @@ Postfix本身不会实施“SASL”验证,因此你需要安装“cyrus-sasl-p
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用TLS加固Postfix安全 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Postfix支持TLS,它是SSL的后继者,允许你使用基于密钥的验证来加密数据。我推荐你阅读http://www.postfix.org/TLS_README.html,以了解tls是怎么和postfix一起工作的。
|
||||
Postfix支持TLS,它是SSL的后继者,允许你使用基于密钥的验证来加密数据。我推荐你阅读 http://www.postfix.org/TLS_README.html ,以了解TLS是怎么和postfix一起工作的。
|
||||
|
||||
为了使用TLS,你需要生成一个私钥和一个由证书授权机构颁发的证书。在本例中,我将使用自颁发的证书。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install mod_ssl openssl
|
||||
# Generate private key
|
||||
# 生成私钥
|
||||
openssl genrsa -out smtp.key 2048
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate CSR
|
||||
# 生成 CSR
|
||||
openssl req -new -key smtp.key -out smtp.csr
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate Self Signed Key
|
||||
# 生成自签名的钥匙
|
||||
openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in smtp.csr -signkey smtp.key -out smtp.crt
|
||||
|
||||
# Copy the files to the correct locations
|
||||
# 将文件复制到正确的位置
|
||||
cp smtp.crt /etc/pki/tls/certs
|
||||
cp smtp.key /etc/pki/tls/private/smtp.key
|
||||
cp smtp.csr /etc/pki/tls/private/smtp.csr
|
||||
@ -109,10 +109,10 @@ Postfix支持TLS,它是SSL的后继者,允许你使用基于密钥的验证
|
||||
smtp_tls_CAfile = /etc/ssl/certs/ca.crt
|
||||
smtp_tls_loglevel = 1
|
||||
|
||||
安全级别“may”意味着宣告对远程SMTP客户端上的STARTTLS的支持,但是客户端不需要使用加密。我在这里用它作为每个[mailgun文档][1],但是如果你想要强制使用TLS加密,可以使用“encrypt”。
|
||||
安全级别“may”意味着宣告对远程SMTP客户端上的STARTTLS的支持,但是客户端不需要使用加密。我在这里按照[mailgun文档][1]提示使用“may”,但是如果你想要强制使用TLS加密,可以使用“encrypt”。
|
||||
|
||||
service postfix restart
|
||||
#Send a test email
|
||||
# 发送一封测试邮件
|
||||
echo test mail | mail -s "test" test@yourdomain.com && sudo tail -f /var/log/maillog
|
||||
|
||||
你应该会看到以下信息
|
||||
@ -122,7 +122,7 @@ Postfix支持TLS,它是SSL的后继者,允许你使用基于密钥的验证
|
||||
|
||||
如果一切正常,你可以注释掉以下参数。
|
||||
|
||||
“smtp_tls_loglevel = 1”
|
||||
“smtp\_tls\_loglevel = 1”
|
||||
|
||||
对于故障排除,我推荐你阅读[Postfix小建议和排障命令][2]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ via: http://techarena51.com/index.php/configure-secure-postfix-email-server/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Leo G][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,37 +1,40 @@
|
||||
四招搞定Linux内核热补丁
|
||||
不重启不当机!Linux内核热补丁的四种技术
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
Credit: Shutterstock
|
||||
|
||||
多种技术在竞争成为实现inux内核热补丁的最优方案。
|
||||
供图: Shutterstock
|
||||
|
||||
有多种技术在竞争成为实现Linux内核热补丁的最优方案。
|
||||
|
||||
没人喜欢重启机器,尤其是涉及到一个内核问题的最新补丁程序。
|
||||
为达到不重启的目的,目前有3个项目在朝这方面努力,将为大家提供对内核进行运行时打热补丁的机制,这样就可以做到完全不重启机器。
|
||||
|
||||
为达到不重启的目的,目前有3个项目在朝这方面努力,将为大家提供内核升级时打热补丁的机制,这样就可以做到完全不重启机器。
|
||||
|
||||
### Ksplice项目 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先要介绍的项目是Ksplice,它是热补丁技术的创始者,并于2008年建立了与项目同名的公司。Ksplice在替换新内核时,不需要预先修改;只需要一个diff文件,将内核的修改点列全即可。Ksplice公司免费提供软件,但技术支持是需要收费的,目前能够支持大部分常用的Linux发行版本。
|
||||
首先要介绍的项目是Ksplice,它是热补丁技术的创始者,并于2008年建立了与项目同名的公司。Ksplice在替换新内核时,不需要预先修改;只需要一个diff文件,列出内核即将接受的修改即可。Ksplice公司免费提供软件,但技术支持是需要收费的,目前能够支持大部分常用的Linux发行版本。
|
||||
|
||||
但在2011年[Oracle收购了这家公司][1]后,情况发生了变化。 这项功能被合入到Oracle的Linux发行版本中,且只对Oralcle的版本提供技术更新。 这就导致,其他内核hacker们开始寻找替代Ksplice的方法,以避免缴纳Oracle税。
|
||||
但在2011年[Oracle收购了这家公司][1]后,情况发生了变化。 这项功能被合入到Oracle自己的Linux发行版本中,只对Oralcle自己提供技术更新。 这就导致,其他内核hacker们开始寻找替代Ksplice的方法,以避免缴纳Oracle税。
|
||||
|
||||
### Kgraft项目 ###
|
||||
|
||||
2014年2月,Suse提供了一个很好的解决方案:[Kgraft][2],该技术以GPLv2/GPLv3混合许可证发布,且Suse不会将其作为一个专有的实现。Kgraft被[提交][3]到Linux内核主线,很有可能被内核主线采用。目前Suse已经把此技术集成到[Suse Linux Enterprise Server 12][4]。
|
||||
2014年2月,Suse提供了一个很好的解决方案:[Kgraft][2],该内核更新技术以GPLv2/GPLv3混合许可证发布,且Suse不会将其作为一个专有发明封闭起来。Kgraft被[提交][3]到Linux内核主线,很有可能被内核主线采用。目前Suse已经把此技术集成到[Suse Linux Enterprise Server 12][4]。
|
||||
|
||||
Kgraft和Ksplice在工作原理上很相似,都是使用一组diff文件来计算内核中需要修改的部分。但与Ksplice不同的是,Kgraft在做替换时,不需要完全停止内核。 在打补丁时,正在运行的函数可以先使用老版本中对应的部分,当补丁打完后就可以切换新的版本。
|
||||
Kgraft和Ksplice在工作原理上很相似,都是使用一组diff文件来计算内核中需要修改的部分。但与Ksplice不同的是,Kgraft在做替换时,不需要完全停止内核。 在打补丁时,正在运行的函数可以先使用老版本或新内核中对应的部分,当补丁打完后就可以完全切换新的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
### Kpatch项目 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat也提出了他们的内核热补丁技术。同样是在今年年初 -- 与Suse在这方面的工作差不多 -- [Kpatch][5]的工作原理也和Kgraft相似。
|
||||
Red Hat也提出了他们的内核热补丁技术。同样是在2014年初 -- 与Suse在这方面的工作差不多 -- [Kpatch][5]的工作原理也和Kgraft相似。
|
||||
|
||||
主要的区别点在于,正如Red Hat的Josh Poimboeuf[总结][6]的那样,Kpatch不能将内核调用重定向到老版本。相反,它会等待所有函数调用都停止时,再切换到新内核。Red Hat的工程师认为这种方法更为安全,且更容易维护,缺点就是在打补丁的过程中会带来更大的延迟。
|
||||
主要的区别点在于,正如Red Hat的Josh Poimboeuf[总结][6]的那样,Kpatch并不将内核调用重定向到老版本。相反,它会等待所有函数调用都停止时,再切换到新内核。Red Hat的工程师认为这种方法更为安全,且更容易维护,缺点就是在打补丁的过程中会带来更大的延迟。
|
||||
|
||||
和Kgraft一样,Kpatch不仅仅能在Red Hat的发行版本上可以使用,同时也被提交到了内核主线,作为一个可能的候选。 坏消息是Red Hat还未将此技术集成到产品中。 它只是被合入到了Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7的技术预览版中。
|
||||
和Kgraft一样,Kpatch不仅仅可以在Red Hat的发行版本上使用,同时也被提交到了内核主线,作为一个可能的候选。 坏消息是Red Hat还未将此技术集成到产品中。 它只是被合入到了Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7的技术预览版中。
|
||||
|
||||
### ...也许 Kgraft + Kpatch更合适? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat的工程师Seth Jennings在2014年11月初,提出了[第四种解决方案][7]。将Kgraft和Kpatch结合起来, 补丁包用这两种方式都可以。在新的方法中,Jennings提出,“热补丁核心为其他内核模块提供了热补丁的注册机制”, 通过这种方法,打补丁的过程 -- 更准确的说,如何处理运行时内核调用 --可以被更加有序的进行。
|
||||
Red Hat的工程师Seth Jennings在2014年11月初,提出了[第四种解决方案][7]。将Kgraft和Kpatch结合起来, 补丁包用这两种方式都可以。在新的方法中,Jennings提出,“热补丁核心为其他内核模块提供了一个热补丁的注册接口”, 通过这种方法,打补丁的过程 -- 更准确的说,如何处理运行时内核调用 --可以被更加有序的组织起来。
|
||||
|
||||
这项新建议也意味着两个方案都还需要更长的时间,才能被linux内核正式采纳。尽管Suse步子迈得更快,并把Kgraft应用到了最新的enterprise版本中。让我们也关注一下Red Hat和Linux官方近期的动态。
|
||||
这项新建议也意味着两个方案都还需要更长的时间,才能被linux内核正式采纳。尽管Suse步子迈得更快,并把Kgraft应用到了最新的enterprise版本中。让我们也关注一下Red Hat和Canonical近期是否会跟进。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
@ -40,7 +43,7 @@ via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2851028/linux/four-ways-linux-is-headed-fo
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Serdar Yegulalp][a]
|
||||
译者:[coloka](https://github.com/coloka)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[tinyeyeser](https://github.com/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,4 +54,4 @@ via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2851028/linux/four-ways-linux-is-headed-fo
|
||||
[4]:http://www.infoworld.com/article/2838421/linux/suse-linux-enterprise-12-goes-light-on-docker-heavy-on-reliability.html
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/dynup/kpatch
|
||||
[6]:https://lwn.net/Articles/597123/
|
||||
[7]:http://lkml.iu.edu/hypermail/linux/kernel/1411.0/04020.html
|
||||
[7]:http://lkml.iu.edu/hypermail/linux/kernel/1411.0/04020.html
|
||||
@ -1,38 +1,39 @@
|
||||
How to install Cacti (Monitoring tool) on ubuntu 14.10 server
|
||||
怎样在 Ubuntu 14.10 Server 上安装 Cacti(监控工具)
|
||||
怎样在 Ubuntu 14.10 Server 上安装 Cacti
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Cacti 是一个网络绘图解决方案,它被设计用来管理 RRDTool (一个 Linux 数据存储和绘图工具)的数据存储和绘图的强大功能。Cacti 提供一个快速的轮询器,高级的绘图模版,多种数据获取方法和用户管理功能,并且可以开箱即用。所有的这些都被打包进一个直观,易用的界面,可用于监控简单的 LAN 网络,乃至包含成百上千设备的复杂网络。
|
||||
|
||||
Cacti 是一个完善的网络监控的图形化解决方案,它被设计用来发挥 RRDTool (一个 Linux 数据存储和绘图工具)的数据存储和绘图的强大功能。Cacti 提供一个快速的轮询器,高级的绘图模版,多种数据获取方法和用户管理功能,并且可以开箱即用。所有的这些都被打包进一个直观,易用的界面,可用于监控简单的 LAN 网络,乃至包含成百上千设备的复杂网络。
|
||||
|
||||
### 功能 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 绘图 ####
|
||||
|
||||
无上限的监控图条目(graph item),每个图形可以视情况使用 Cacti 中的 CDEFs (Calculation Define,可以对图形输出结果进行计算)或者数据源。
|
||||
没有数量限制的监控图条目(graph item),每个图形可以视情况使用 Cacti 中的 CDEFs (Calculation Define,可以对图形输出结果进行计算)或者数据源。
|
||||
|
||||
自动将 GPRINT 条目分组至 AREA,STACK 和 LINE[1-3] 中,可以对图形进行快速重排序。
|
||||
自动将 GPRINT 条目分组至 AREA,STACK 和 LINE[1-3] 中,来对监控图条目进行快速重排序。
|
||||
|
||||
自动填充功能使得图形的说明整齐排列。
|
||||
自动填充功能支持整齐排列图形内的说明项。
|
||||
|
||||
可以使用 RRDTool 中内置的 CDEF 数学函数对图形数据进行处理。这些 CDEF 函数可以定义在 Cacti 中,并且每一个图形都可以使用它们。
|
||||
|
||||
支持所有的 RRDTool 图形类型包括 AREA,STACK,LINE[1-3],GPRINT,COMMENT,VRULE 和 HRULE。
|
||||
支持所有的 RRDTool 图形类型,包括 AREA,STACK,LINE[1-3],GPRINT,COMMENT,VRULE 和 HRULE。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 数据源 ####
|
||||
|
||||
数据源可以使用 RRDTool 的 "create" 和 "update" 功能创建。每一个数据源可以用来收集本地或者远程的数据,并将数据输出给图形。
|
||||
数据源可以使用 RRDTool 的 "create" 和 "update" 功能创建。每一个数据源可以用来收集本地或者远程的数据,并将数据输出成图形。
|
||||
|
||||
支持包含多个数据源的 RRD 文件,并可以使用存储在本地文件系统中任何位置的 RRD 文件。
|
||||
可以自定义轮询归档(RRA)设置,用户可以在存储数据时使用非标准的时间间隔(标准时间间隔是5分钟,30分钟,2小时 和 1天)。
|
||||
|
||||
可以自定义轮询归档(RRA)设置,用户可以在存储数据时使用非标准的时间间隔(标准时间间隔是5分钟,30分钟,2小时和 1天)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 数据收集 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Cacti 包含一个 "data input" 机制,可以让用户定义自定义的脚本用来收集数据。每个脚本可以包含调用参数,每次创建调用此脚本的数据源时输入相应的调用参数(如 IP 地址)。
|
||||
Cacti 包含一个 "data input" 机制,可以让用户定义自定义的脚本用来收集数据。每个脚本可以包含调用参数,每次调用此脚本的创建数据源时必须输入相应的调用参数(如 IP 地址)。
|
||||
|
||||
支持 SNMP 功能,可以使用 php-snmp,ucd-snmp 或者 net-snmp。
|
||||
|
||||
可以基于索引来使用 SNMP 或者脚本收集数据。例如,可以列出一个服务器上所有网卡接口或者已挂载分区的索引列表。集成的绘图模版可以用来一键为主机创建图形。
|
||||
可以基于索引来使用 SNMP 或者脚本收集数据。例如,可以列出一个服务器上所有网卡接口或者已挂载分区的索引列表。其集成的绘图模版可以用来为主机一键创建图形。
|
||||
|
||||
提供一个基于 PHP 的轮询器用于执行脚本,收集 SNMP数据并更新数据至 RRD 文件中。
|
||||
提供了一个基于 PHP 的轮询器执行脚本,可以收集 SNMP数据并更新数据至 RRD 文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 模版 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -44,7 +45,7 @@ Cacti 包含一个 "data input" 机制,可以让用户定义自定义的脚本
|
||||
|
||||
#### 图形展示 ####
|
||||
|
||||
图形树允许用户创建「图形层次结构」并将图形放至树中。这种方法可以方便的管理大量图形。
|
||||
图形树模式允许用户创建「图形层次结构」并将图形放至树中。这种方法可以方便的管理大量图形。
|
||||
|
||||
列表模式将所有图形的链接在一个大列表中展示出来,链接指向用户创建的图形。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -55,7 +56,10 @@ Cacti 包含一个 "data input" 机制,可以让用户定义自定义的脚本
|
||||
用户管理功能允许管理员创建用户并分配给用户访问 Cacti 接口的不同级别的权限。
|
||||
|
||||
权限可以为每个用户指定其对每个图形的权限,这适用于主机租用的场景。
|
||||
|
||||
每个用户可以保存他自己的图形显示模式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 系统准备 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -123,7 +127,7 @@ via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/how-to-install-cacti-monitoring-tool-on-ubuntu-14
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[Liao](https://github.com/liaoishere)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,17 +2,18 @@ Linux 下五款出色的流媒体客户端
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
数字流媒体这几天几乎占据了我音乐收听的全部时间。近年来我为了收藏 CD 花费了数量可观的费用;但它们中的大部分现在正静静地躺在满是灰尘的角落里。基本上所有的音乐流媒体服务所提供的的音质都不如 CD 的,但它们受欢迎的原因很大程度上在于其便捷性,而非高度保真的音质再现。音乐流媒体不仅造成了 CD 销量的大幅减少;也使数字音乐的下载开始缓慢下滑。这种趋势还会继续下去。音乐发烧友现在或许也想要拥抱音乐流媒体服务了,某些音乐流媒体服务商如 Tidal 提供了无损的音乐流媒体服务,其中包含了 25 万首比特率为 1411kbps 的 FLAC 格式的音乐。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管 CD 暂时不会消失,但音乐流媒体服务商却无法协调和那些不满从音乐托管服务中收取的租金的唱片公司及音乐家之间的问题。这一切仍然处于变化之中;我们看到了今年 Led Zeppelin, Pink Floyd, Metallica 签名支持流媒体服务,但仍然有部分知名的老牌乐队如 Beatles, Radiohead 以及 AC/DC 拒绝将自己的作品放到流媒体上供粉丝收听。即使当某个唱片公司或者音乐家已经授权给流媒体服务商访问自己的作品,但只要音乐家发表声明就可以在第一时间将其作品从流媒体服务下架。本月(2014 年 11 月),Taylor Swift 请求将她的所有音乐作品从 Spotify 的流媒体服务下架。有些人还是更偏向于“拥有”他们的音乐,但这看起来像是一种快要过时了的欣赏音乐的方式。
|
||||
尽管 CD 暂时不会消失,但音乐流媒体服务商却无法调和那些不满从音乐托管服务中收取的租金的唱片公司及音乐家之间的问题。这一切仍然处于变化之中;我们看到了今年 Led Zeppelin, Pink Floyd, Metallica 签名支持流媒体服务,但仍然有部分知名的老牌乐队如 Beatles, Radiohead 以及 AC/DC 拒绝将自己的作品放到流媒体上供粉丝收听。即使当某个唱片公司或者音乐家已经授权给流媒体服务商访问自己的作品,但只要音乐家发表声明就可以在第一时间将其作品从流媒体服务下架。本月(2014 年 11 月),Taylor Swift 请求将她的所有音乐作品从 Spotify 的流媒体服务下架。有些人还是更偏向于“拥有”他们的音乐,但这看起来像是一种快要过时了的欣赏音乐的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 Linux 平台来收听流媒体音乐服务的方法已经逐渐成熟。在 Linux 平台下,你可以找到许多客户端,通过它们你可以使用大部分的音乐流媒体服务;我希望 TIDAL 能在今后合适的时候发行 Linux 桌面客户端,而不是仅仅依赖 web 播放器。本文精选的这些应用都是非常出色的。另外 Amarok,pianobar 还有 Tomahawk 也表现得很不错。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
### Spotify
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Spotify 是一种专有的 P2P 音乐流媒体服务,允许用户收听点播曲目或专辑。Spotify 将自己描述为“音乐圣殿。快捷、简易、免费的服务”。Spotify 分别为普通的移动端和桌面端用户提供了 96kbps 和 160kbps 比特率的流媒体服务,并且为高级用户提供了 Ogg Vorbis 格式的 320kbps 比特率的流媒体服务。Spotify 为普通用户提供了免费但是有广告的服务,以及无广告的订阅账户服务。
|
||||
|
||||
Spotify 是很奇妙的服务,向用户们提供了涵盖各种类型的数量众多的音乐,如:流行乐、另类摇滚、古典乐、铁克诺电音、摇滚乐等。这是发现新音乐的好方法。Spotify 得到了包括 Sony BMG,EMI,Universal 以及 Warner Music 在内的主流唱片公司,以及 Labrador Records,The Orchard,Alligator Records,Merlin,CD Baby,INgrooves 等独立唱片唱片公司和分销网络,甚至 Chandos,Naxos,EMI Classic,Warner Classics,Denon Essentials 这些古典唱片公司的支持,还有更多的公司在这里就不一一列举了。
|
||||
|
||||
Spotify 的音乐涵盖范围还在继续以惊人的步伐扩张着。
|
||||
|
||||
Spotify 现在并没有发行官方版的 Linux 客户端。不过,开发团队已经推出了针对 Linux 的客户端预览版,并且表现得还不错。因为仍然是预览版,所以没有得到官方的支持。
|
||||
@ -34,9 +35,8 @@ Spotify 流媒体服务现已支持以下地区/国家:安道尔,阿根廷
|
||||
- 许可证:专有许可证
|
||||
- 当前版本:预览版
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
### Pithos
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -69,9 +69,8 @@ Pandora 音乐服务只能通过美国的 IP 地址使用。不过,非美国
|
||||
- 许可证:GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- 当前版本:1.0.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
### Clementine
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -80,6 +79,7 @@ Clementine 基于 Amarok 开发,是一款跨平台的轻量级现代化音乐
|
||||
Clementine 在 Amarok 1.4 的基础上开发。
|
||||
|
||||
**特色包括:**
|
||||
|
||||
- 检索、播放本地音乐库
|
||||
- 从 Last.fm 和 SomaFM 收听互联网电台
|
||||
- 标签式播放列表,支持导入导出 M3U,XSPF,PLS 及 ASX 格式的播放列表
|
||||
@ -110,9 +110,8 @@ Clementine 在 Amarok 1.4 的基础上开发。
|
||||
- 许可证:GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- 当前版本:1.2
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
### Nuvola Player
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -151,9 +150,8 @@ Nuvola Player 是一个免费的开源项目,能够整合云端音乐到你的
|
||||
- 许可证:2-Clause BSD license
|
||||
- 当前版本:2.4.3
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
### Atraci
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -185,7 +183,7 @@ via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20141116052055674/MusicStreaming.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[Stevearzh](https://github.com/Stevearzh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu上使用MultiSystem创建多启动USB
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu上使用MultiSystem创建多启动USB盘
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
### 介绍 ###
|
||||
|
||||
一些人并不知道**MultiSystem**是一个小型的开源软件来在Linux系统中创建多启动usb盘。使用这个工具,我们可以在USB中创建任意多的可启动Linux发行版。你所要的只是网络链接(之在MultiSystem安装的时候需要),以及一个足够大的USB盘,这取决于你想在USB盘中放入发行版的数量。
|
||||
也许还有不少人不知道**MultiSystem**,它是一个用来在Linux系统中创建多启动usb盘的小型的开源软件。使用这个工具,我们可以在USB中创建任意多的可启动Linux发行版。你所需要的只是网络链接(只在MultiSystem安装的时候需要),以及一个足够大的USB盘,这取决于你想在USB盘中放入发行版的数量。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 14.10/14.04 安装MultiSystem ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,18 +15,18 @@
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 PPA 安装: ####
|
||||
|
||||
相应地,你可以用下面的命令来更简单地使用PPA来安装MultiSystem。
|
||||
当然,你也可以用下面的命令来更简单地使用PPA来安装MultiSystem。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-add-repository 'deb http://liveusb.info/multisystem/depot all main'
|
||||
wget -q -O - http://liveusb.info/multisystem/depot/multisystem.asc | sudo apt-key add -
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install multisystem
|
||||
|
||||
安装玩之后,它会自动打开。只要点击关闭按钮退出。
|
||||
安装完之后,它会自动打开MultiSystem。只要点击关闭按钮退出。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装之后 ###
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,插入你的USB,并通过Unity Dash或者菜单运行MultiSystem。
|
||||
MultiSystem 安装完成后,可以插入你的USB,并通过Unity Dash或者菜单运行MultiSystem。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,7 +34,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
选择USB设备,点击**确认**按钮。你可能会看到下面的错误窗口。不必担心,它说的是USB设备没有标签。点击OK让MultiSystem自动设置标签。
|
||||
选择USB设备,点击**确认**按钮。如果你看到下面的错误窗口,不必担心,它说的是USB设备没有标签。点击OK让MultiSystem自动设置标签。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,7 +48,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用 ###
|
||||
|
||||
MultiSystem非常容易使用。将ISO文件拖入MultiSystem窗口中。如果这不能用,点击底部的**cd 按钮**来选择ISO文件。
|
||||
MultiSystem非常容易使用。将ISO文件拖入MultiSystem窗口中。如果不行的话,点击底部的**cd 按钮**来选择ISO文件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -65,24 +66,24 @@ MultiSystem非常容易使用。将ISO文件拖入MultiSystem窗口中。如果
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
额外地,MultiSystem含有一些额外的选项:
|
||||
此外,MultiSystem含有一些其它的选项:
|
||||
|
||||
- Grub 设置;
|
||||
- Grub 和 Burg 的bootloader更新;
|
||||
- 下载 LiveCD;
|
||||
- VirtualBox 安装;
|
||||
- 格式化USB盘;
|
||||
- 还有更多选项。
|
||||
- Grub 设置
|
||||
- Grub 和 Burg 的bootloader更新
|
||||
- 下载 LiveCD
|
||||
- VirtualBox 安装
|
||||
- 格式化USB盘
|
||||
- 还有更多选项
|
||||
|
||||
要浏览额外的选项列表,进入MultiSystem的**菜单**标签。
|
||||
这些额外选项可以在MultiSystem的**菜单**标签里面看到。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
同样,你可以在Ubuntu中使用QEMU或者Oracle VirtualBox测试多启动USB盘。
|
||||
同样,你也可以在Ubuntu中使用QEMU或者Oracle VirtualBox测试多启动USB盘。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
MultiSystem工具是我测试到现在最棒和最有用的一款工具。这款工具对那些想要在他们的机器上安装多个系统的人是非常有用的。在你外出的时候,你不必再携带CD/DVD袋了。只要买一个16GB或者32GB的USB就行,并把所有你想要的系统都放在里面,就像老板一样安装系统。
|
||||
MultiSystem工具是我测试到现在最棒和最有用的一款工具。这款工具对那些想要在他们的机器上安装多个系统的人是非常有用的。在你外出的时候,你不必再携带CD/DVD袋了。只要买一个16GB或者32GB的USB就行,并下载所有你想要的系统,随心所欲的安装系统即可。
|
||||
|
||||
并且,一个对于Windows系统用户的好消息是它也支持Windows系统。我在Windows 7上测试过,它可以工作!
|
||||
|
||||
@ -94,7 +95,7 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/create-multiboot-usb-ubuntu-using-multisystem/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
如何手动删除Oracle 11g数?据库
|
||||
如何手动删除Oracle 11g数据库
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
下面的步骤会家你如何在Linux环境下手动删除Oracle 11g数据库。
|
||||
下面的步骤会教你如何在Linux环境下手动删除Oracle 11g数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
我在Centos 6上安装了Oralce 11G数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
**在SQL*Plus中关闭数据库,接着退出SQL*Plus**
|
||||
|
||||
sqlplus " / as sysdba'
|
||||
sqlplus "/ as sysdba"
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
在Oralce Linux账户中:
|
||||
|
||||
lsnrctl stop
|
||||
lsnrctl stop
|
||||
|
||||
回忆一下之前的文件路径;在删除这些文件的时候作为一个检查项。记住:你备份了数据库了么?当准备好之后,就删除你的数据文件吧,同样还有你的日志文件、控制文件和临时文件。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -44,7 +44,7 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/manually-delete-oracle-11g-database/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[M.el Khamlichi][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,28 +1,29 @@
|
||||
在 Mac OS X 系统中创建可启动的 Ubuntu USB 驱动盘
|
||||
在 Mac OS X 系统中创建用于 Mac 的 Ubuntu USB 启动盘
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
上个月,在戴尔的服务中心丢失我的笔记本后,我买了一台 Macbook Air 笔记本。买回来后我首先做的一些事就是给机器装上双系统,使 Ubuntu Linux 和 Mac OS X 都可用。随后的文章我会介绍如何在 Macbook 上安装 Linux ,刚开始我们需要学习 **如何在 Mac 的 OS X 系统中创建可启动的 Ubuntu USB 驱动盘**。
|
||||
上个月,在戴尔的服务中心丢失我的笔记本后,我买了一台 Macbook Air 笔记本。买回来后我首先做的一些事就是给机器装上双系统,使 Ubuntu Linux 和 Mac OS X 都可用。随后的文章我会介绍如何在 Macbook 上安装 Linux ,刚开始我们需要学习 **如何在 Mac OS X 系统中创建用于 Mac 的 Ubuntu USB 启动盘**。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 系统或 Windows 系统中创建可启动的 USB 是非常容易的,但在 Mac OS X 系统中就没这么简单了。这就是为什么 Ubuntu 的官方指南上,在 Mac 中安装 live Ubuntu 推荐使用磁盘安装而不是 USB 的原因。考虑到我的 Macbook Air 既没有 CD 驱动也没有 DVD 驱动,所以我更愿意在 Mac OS X 下创建一个 live USB.
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 系统或 Windows 系统中创建可启动的 USB 是非常容易的,但在 Mac OS X 系统中就没这么简单了。这就是为什么 Ubuntu 的官方指南上,在 Mac 中安装 live Ubuntu 推荐使用光盘安装而不是 USB 的原因。考虑到我的 Macbook Air 既没有 CD 驱动也没有 DVD 驱动,所以我更愿意在 Mac OS X 下创建一个 live USB。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Mac OS X 下创建可启动 USB 驱动盘###
|
||||
|
||||
如前所述,在 Mac OS X 上创建对于像 Ubuntu 或任何其它可引导的操作系统这样的可启动 USB 盘是个极其麻烦的过程。但请别担心,按照下面的步骤一步一步操作就行。让我们就开始创建一个可启动的 USB 盘的操作吧:
|
||||
如前所述,在 Mac OS X 上创建对于像 Ubuntu 或任何其它可引导的操作系统这样的可启动 USB 盘是个比较麻烦的过程。但请别担心,按照下面的步骤一步一步操作就行。让我们就开始创建一个可启动的 USB 盘的操作吧:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤 1: 格式化 USB 驱动盘 ####
|
||||
|
||||
苹果是以它自定义的标准而闻名的,所以 Mac OS X 系统有自己的文件系统类型就好不奇怪了,它的文件系统叫做 Mac OS 扩展或 [HFS 插件][1]。因此,您需要做的第一件事就是用 Mac OS 扩展文件系统来格式化您的 USB 驱动盘。
|
||||
苹果是以它自定义的标准而闻名的,所以 Mac OS X 系统有自己的文件系统类型就毫不奇怪了,它的文件系统叫做 Mac OS 扩展或 [HFS 插件][1]。因此,您需要做的第一件事就是用 Mac OS 扩展文件系统来格式化您的 USB 驱动盘。
|
||||
|
||||
要格式化 USB 盘,插入 USB 钥匙链。从 Launchpad(在底部面板上的一个火箭形状的图标)上前往**磁盘工具**应用程序。
|
||||
要格式化 USB 盘,请先插入 USB 盘。从 Launchpad(在底部面板上的一个火箭形状的图标)上前往**磁盘工具**应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- 在磁盘工具中,从左手边的面板上选择 USB 驱动盘来格式化。
|
||||
- 在磁盘工具中,从左手边的面板上选择你的 USB 盘来格式化。
|
||||
- 点击右边面板的**分区**标签。
|
||||
- 从下拉菜单中,选择 **1 分区**。
|
||||
- 给这驱动盘起个您想要的名字。
|
||||
- 接下来,切换来**格式化成 Mac OS 扩展 (日志型)**
|
||||
- 接下来,切换分区格式为**格式化成 Mac OS 扩展 (日志型)**
|
||||
|
||||
下面的截屏将会对您有所帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,7 +33,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当所有的都已经设置完了后,仅仅只需点击**应用**按纽。它会弹出一个要格式化 USB 驱动盘的警告消息,当然是要点击分区按纽来格式化 USB 驱动盘拉。
|
||||
当所有都已经设置完了后,仅仅只需点击**应用**按纽。它会弹出一个要格式化 USB 驱动盘的警告消息,当然是要点击分区按纽来格式化 USB 驱动盘拉。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤 2: 下载 Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,15 +51,15 @@
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
您可能已经注意到我并没有新转换出的文件加上 IMG 后缀。这是没问题的,因为后缀只是个标志,它代表的是文件类型并不是文件的扩展名。转换出来的文件可能会被 Mac OS X 系统自动加上个 .dmg 后缀。别担心,这是正常的。
|
||||
您可能已经注意到我并没有新转换出的文件加上 IMG 后缀。这是没问题的,因为后缀只是个标志,重要的是文件类型并不是文件的扩展名。转换出来的文件可能会被 Mac OS X 系统自动加上个 .dmg 后缀。别担心,这是正常的。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤 4: 获得 USB 驱动盘的设备号 ####
|
||||
#### 步骤 4: 获得 USB 盘的设备号 ####
|
||||
|
||||
接下来的事情就是获得 USB 驱动盘的设备号。在终端中运行如下命令:
|
||||
接下来的事情就是获得 USB 盘的设备号。在终端中运行如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
diskutil list
|
||||
|
||||
它会列出系统中当前可用的所有‘磁盘’信息。从它的大小上您应该能识别出此 USB 驱动盘。为了避免混淆,我建议您只插入一个 USB 盘。我的示例中,设置号是 2 (一个大小为 8G 的 USB): /dev/disk2
|
||||
它会列出系统中当前可用的所有‘磁盘’信息。从它的大小上您应该能识别出此 USB 盘。为了避免混淆,我建议您只插入一个 USB 盘。我的示例中,设置号是 2 (一个大小为 8G 的 USB): /dev/disk2
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -110,11 +111,11 @@ N 当然指的是我们前面使用过的设备号,在我的示例中是 2 :
|
||||
|
||||
diskutil eject /dev/disk2
|
||||
|
||||
一旦弹出,点击前面出现那对话框上的**忽略**按纽。现在您的可启动 USB 磁盘已经创建好了,把它从系统中移除。
|
||||
一旦弹出,点击前面出现那对话框上的**忽略**按纽。现在您的可启动 USB 磁盘已经创建好了,把它拔下来吧。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 步骤 7: 检查您新创建的可启动 USB 盘 ####
|
||||
|
||||
一旦您在 Mac OS X 中完成了创建一个 live USB 这么重大的任务,是时候测试您的幸成果了。
|
||||
一旦您在 Mac OS X 中完成了创建一个 live USB 这么重大的任务,是时候测试您的新成果了。
|
||||
|
||||
- 插入可启动 USB 盘,重启系统。
|
||||
- 在苹果启动的时候,一直按着 option (或 alt)键。
|
||||
@ -128,7 +129,7 @@ N 当然指的是我们前面使用过的设备号,在我的示例中是 2 :
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我希望这篇教程对您想要在 Mac OS X 下创建可启动的 Ubuntu 系统 USB 驱动盘。在接下来的一篇文章中您会学到怎么样安装 OS X 和 Ubuntu 双系统。请继续关注。
|
||||
我希望这篇教程对您想要在 Mac OS X 下创建可启动的 Ubuntu 系统 USB 驱动盘有所帮助。在接下来的一篇文章中您会学到怎么样安装 OS X 和 Ubuntu 双系统。请继续关注。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -136,7 +137,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/create-bootable-ubuntu-usb-drive-mac-os/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,20 +1,19 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to disable Apport internal error reporting on Ubuntu
|
||||
有问必答--如何禁止Ubuntu的Apport内部错误报告程序
|
||||
Linux有问必答:如何禁止Ubuntu的Apport内部错误报告程序
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:在桌面版Ubuntu中,我经常遇到一些弹窗窗口,警告我Ubuntu发生了内部错误,问我要不要发送错误报告。每次软件崩溃都要烦扰我,我如何才能关掉这个错误报告功能呢?
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu桌面版预安装了Apport,它是一个错误收集系统,会收集软件崩溃、未处理异常和其他,包括程序bug,并为调试目的生成崩溃报告。当一个应用程序崩溃或者出现Bug时候,Apport就会通过弹窗警告用户并且询问用户是否提交崩溃报告。你也许也看到过下面的消息。
|
||||
Ubuntu桌面版预装了Apport,它是一个错误收集系统,会收集软件崩溃、未处理异常和其他,包括程序bug,并为调试目的生成崩溃报告。当一个应用程序崩溃或者出现Bug时候,Apport就会通过弹窗警告用户并且询问用户是否提交崩溃报告。你也许也看到过下面的消息。
|
||||
|
||||
- "Sorry, the application XXXX has closed unexpectedly."
|
||||
- "对不起,应用程序XXXX意外关闭了"
|
||||
- "对不起,应用程序XXXX意外关闭了。"
|
||||
- "Sorry, Ubuntu XX.XX has experienced an internal error."
|
||||
- "对不起,Ubuntu XX.XX 经历了一个内部错误"
|
||||
- "对不起,Ubuntu XX.XX 发生了一个内部错误。"
|
||||
- "System program problem detected."
|
||||
- "系统程序问题发现"
|
||||
- "检测到系统程序问题。"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
也许因为应用一直崩溃,频繁的错误报告会使人心烦。也许你担心Apport会收集和上传你的Ubuntu系统的敏感信息。无论什么原因,你需要关掉Apport的错误报告功能。
|
||||
也许因为应用一直崩溃,频繁的错误报告会使人心烦。也许你担心Apport会收集和上传你的Ubuntu系统的敏感信息。无论什么原因,你想关掉Apport的错误报告功能。
|
||||
|
||||
### 临时关闭Apport错误报告 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,6 +40,6 @@ Ubuntu桌面版预安装了Apport,它是一个错误收集系统,会收集
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/disable-apport-internal-error-reporting-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[VicYu/Vic020](http://www.vicyu.net/)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,9 @@
|
||||
NetHack
|
||||
也许是有史以来最好的游戏:NetHack
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
## 一直以来最好的游戏? ##
|
||||
|
||||
**这款游戏非常容易让你上瘾。你可能需要花费一生的时间来掌握它。许多人玩了几十年也没有通关。欢迎来到 NetHack 的世界...**
|
||||
|
||||
不管你信不信,在 NetHack 里你见到字母 D 的时候你会被吓着。但是当你看见一个 % 的时候,你将会欣喜若狂。(忘了说 ^,你看见它将会更激动)在你寻思我们的脑子是不是烧坏了并准备关闭浏览器标签之前,请给我们一点时间解释:这些符号分别代表龙、食物以及陷阱。欢迎来到 NetHack 的世界,在这里你的想象力需要发挥巨大的作用。
|
||||
不管你信不信,在 NetHack 里你见到字母 **D** 的时候你会被吓着。但是当你看见一个 **%** 的时候,你将会欣喜若狂。(忘了说 **\^**,你看见它将会更激动)在你寻思我们的脑子是不是烧坏了并准备关闭浏览器标签之前,请给我们一点时间解释:这些符号分别代表龙、食物以及陷阱。欢迎来到 NetHack 的世界,在这里你的想象力需要发挥巨大的作用。
|
||||
|
||||
如你所见,NetHack 是一款文字模式的游戏:它仅仅使用标准终端字符集来刻画玩家、敌人、物品还有环境。游戏的图形版是存在的,不过 NetHack 的骨灰级玩家们都倾向于不去使用它们,问题在于假如你使用图形界面,当你通过 SSH 登录到你的古董级的运行着 NetBSD 的 Amiga 3000 上时,你还能进行游戏吗?在某些方面,NetHack 和 Vi 非常相似 - 几乎被移植到了现存的所有的操作系统上,并且依赖都非常少。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,68 +15,68 @@ NetHack
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
NetHack 界面
|
||||
*NetHack 界面*
|
||||
|
||||
### 也许是最古老的仍在开发的游戏里 ###
|
||||
|
||||
名非其实,NetHack 并不是一款网络游戏。它只不过是基于一款出现较早的名为 Hack 的地牢探险类游戏开发出来的,而这款 Hack 游戏是 1980 年的游戏 Rogue 的后代。NetHack 在 1987 年发布了第一个版本,并于 2003 年发布了 3.4.3 版本,尽管在这期间一直没有加入新的功能,但各种补丁、插件,以及衍生作品还是在网络上疯狂流传。这使得它可以说是最古老的、拥有众多对游戏乐此不疲的粉丝的游戏。当你访问 [www.reddit.com/r/nethack][1] 之后,你就会了解我们的意思了 - 骨灰级的 NetHack 的玩家们仍然聚集在一起讨论新的策略、发现和技巧。偶尔你也可以发现 NetHack 的元老级玩家在历经千辛万苦终于通关之后发出的欢呼。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
但怎样才能通关呢?首先,NetHack 被设定在既大又深的地牢中。游戏开始时你在最顶层 - 第 1 层 - 你的目标是不断往下深入直到你找到一个非常宝贵的物品,护身符 Yendor。通常来说 Yendor 在 第 20 层或者更深的地方,但它是可以变化的。随着你在地牢的不断深入,你会遇到各种各样的怪物、陷阱以及 NPC;有些会试图杀掉你,有些会挡在你前进的路上,还有些... 总而言之,在你靠近 TA 们之前你永远不知道 TA 们会怎样。
|
||||
|
||||
> 要学习的有太多太多,绝大多数物品只有在和其他物品同时使用的情况下才会发挥最好的效果。
|
||||
|
||||
是 NetHack 如此引人入胜的原因是游戏中所加入的大量物品。武器、盔甲、附魔书、戒指、宝石 - 要学习的有太多太多,绝大多数物品只有在和其他物品同时使用的情况下才会发挥最好的效果。怪物在死亡后经常会掉落一些有用的物品,以及某些物品如果你不正确使用的话会产生及其不良的作用。你可以在地牢找到商店,里面有许多看似平凡实则非常有用的物品,,不过别指望店主能给你详细的描述。你只能靠自己的经验来了解各个物品的用途。有些物品确实没有太大用处,NetHack 中有很多的恶搞元素 - 比如你可以把一块奶油砸到自己的脸上。
|
||||
使 NetHack 如此引人入胜的原因是游戏中所加入的大量物品。武器、盔甲、附魔书、戒指、宝石 - 要学习的有太多太多,绝大多数物品只有在和其他物品同时使用的情况下才会发挥最好的效果。怪物在死亡后经常会掉落一些有用的物品,以及某些物品如果你不正确使用的话会产生及其不良的作用。你可以在地牢找到商店,里面有许多看似平凡实则非常有用的物品,不过别指望店主能给你详细的描述。你只能靠自己的经验来了解各个物品的用途。有些物品确实没有太大用处,NetHack 中有很多的恶搞元素 - 比如你可以把一块奶油砸到自己的脸上。
|
||||
|
||||
不过在你踏入地牢之前,NetHack 会询问你要选择哪种角色进行游戏。你可以为你接下来的地牢之行选择骑士、修道士、巫师,或者卑微的旅者,还有许多其他的角色类型。每种角色都有其独特的优势与弱点,NetHack 的重度玩家喜欢选择那些相对较弱的角色来挑战游戏。你懂的,这样可以向其他玩家炫耀自己的实力。
|
||||
|
||||
> ## 情报不会降低游戏的乐趣 ##
|
||||
> **情报不会降低游戏的乐趣**
|
||||
|
||||
> 用 NetHack 的说法来讲,“情报员”给指其他玩家提供关于怪物、物品、武器和盔甲信息的玩家。理论上来说,完全可以不借助任何外来信息而通关,但几乎没有几个玩家能做到,游戏实在是太难了。因此使用情报并不会被视为一件糟糕的事情 - 但是一开始由你自己来探索游戏和解决难题,这样才会获得更多的乐趣,只有当你遇到瓶颈的时候再去使用那些情报。
|
||||
|
||||
> 在这里给出一个比较有名的情报站点 [www.statslab.cam.ac.uk/~eva/nethack/spoilerlist.html][2],其中的情报被分为了不同的类别。游戏中随机发生的事,比如在喷泉旁饮水可能导致的不同结果,从这里你可以得知已确定的不同结果的发生概率。
|
||||
>
|
||||
> ### 你的首次地牢之行 ###
|
||||
|
||||
NetHack 几乎可以在所有的主流操作系统以及 Linux 发行版上运行,因此你可以通过 "apt-get install nethack" 或者 "yum install nethack" 等适合你用的发行版的命令来安装游戏。安装完毕后,在一个命令行窗口中键入 "nethack" 就可以开始游戏了。游戏开始时系统会询问是否为你随机挑选一位角色 - 但作为一个新手,你最好自己从里面挑选一位比较强的角色。所以,你应该点 "n",然后点 "v" 以选取女武神(Valkyrie),最后点 "d" 选择成为侏儒(dwarf)。
|
||||
### 你的首次地牢之行 ###
|
||||
|
||||
NetHack 几乎可以在所有的主流操作系统以及 Linux 发行版上运行,因此你可以通过 "apt-get install nethack" 或者 "yum install nethack" 等适合你用的发行版的命令来安装游戏。安装完毕后,在一个命令行窗口中键入 "nethack" 就可以开始游戏了。游戏开始时系统会询问是否为你随机挑选一位角色 - 但作为一个新手,你最好自己从里面挑选一位比较强的角色。所以,你应该点 "n",然后点 "v" 以选取女武神(Valkyrie),而点 "d" 会选择成为侏儒(dwarf)。
|
||||
|
||||
接着 NetHack 上会显示出剧情,说你的神正在寻找护身符 Yendor,你的目标就是找到它并将它带给神。阅读完毕后点击空格键(其他任何时候当你见到屏幕上的 "-More-" 时都可以这样)。接着就让我们出发 - 开始地牢之行吧!
|
||||
|
||||
先前已经介绍过了,你的角色用 @ 来表示。你可以看见角色所出房间周围的墙壁,房间里显示点的那些地方是你可以移动的空间。首先,你得明白怎样移动角色:h、j、k 以及 l。(是的,和 Vim 中移动光标的操作相同)这些操作分别会使角色向向左、向下、向上以及向右移动。你也可以通过 y、u、b 和 n 来使角色斜向移动。在你熟悉如何控制角色移动前你最好在房间里来回移动你的角色。
|
||||
先前已经介绍过了,你的角色用 @ 来表示。你可以看见角色所出房间周围的墙壁,房间里显示“点”的那些地方是你可以移动的空间。首先,你得明白怎样移动角色:h、j、k 以及 l。(是的,和 Vim 中移动光标的操作相同)这些操作分别会使角色向向左、向下、向上以及向右移动。你也可以通过 y、u、b 和 n 来使角色斜向移动。在你熟悉如何控制角色移动前你最好在房间里来回移动你的角色。
|
||||
|
||||
NetHack 采用了回合制,因此即使你不进行任何动作,游戏仍然在进行。这是你可以提前计划你的行动。你可以看见一个 "d" 字符或者 "f" 字符在房间里来回移动:这是你的宠物狗/猫,(通常情况下)它们 不会伤害你而是帮助你击杀怪物。但是宠物也会被惹怒 - 它们偶尔也会抢在你接近食物或者怪物尸体之前吃掉它们。
|
||||
NetHack 采用了回合制,因此即使你不进行任何动作,游戏仍然在进行。这是你可以提前计划你的行动。你可以看见一个 "d" 字符或者 "f" 字符在房间里来回移动:这是你的宠物狗/猫,(通常情况下)它们不会伤害你而是帮助你击杀怪物。但是宠物也会被惹怒 - 它们偶尔也会抢在你接近食物或者怪物尸体之前吃掉它们。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
点击 “i” 列出你当前携带的物品清单
|
||||
*点击 “i” 列出你当前携带的物品清单*
|
||||
|
||||
### 门后有什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,让我们离开房间。房间四周的墙壁某处会有缝隙,可能是 "+" 号。"+" 号表示一扇关闭的门,这时你应该靠近它然后点击 "o" 来开门。接着系统会询问你开门的方向,假如门在你的左方,就点击 "h"。(如果门被卡住了,就多试几次)然后你就可以看见门后的走廊了,它们由 "#" 号表示,沿着走廊前进直到你找到另一个房间。
|
||||
|
||||
地牢之行中你会见到各种各样的物品。某些物品,比如金币(由 "$" 号表示)会被自动捡起来;至于另一些物品,你只能站在上面按下逗号键手动拾起。如果同一位置有多个物品,系统会给你显示一个列表,你只要通过合适的案件选择列表中你想要的物品最后按下 "Enter" 键即可。任何时间你都可以点击 "i" 键在屏幕上列出你当前携带的物品清单。
|
||||
地牢之行中你会见到各种各样的物品。某些物品,比如金币(由 "$" 号表示)会被自动捡起来;至于另一些物品,你只能站在上面按下逗号键手动拾起。如果同一位置有多个物品,系统会给你显示一个列表,你只要通过合适的按键选择列表中你想要的物品最后按下 "Enter" 键即可。任何时间你都可以点击 "i" 键在屏幕上列出你当前携带的物品清单。
|
||||
|
||||
如果看见了怪物该怎么办?在游戏早期,你可能会遇到的怪物会用符号 "d"、"x" 和 ":" 表示。想要攻击的话,只要简单地朝怪物的方向移动即可。系统会在屏幕顶部通过信息显示来告诉你你的攻击是否成功 - 以及怪物做出了何种反应。早期的怪物很容易击杀,所以你可以毫不费力地打败他们,但请留意底部状态栏里显示的角色的 HP 值。
|
||||
如果看见了怪物该怎么办?在游戏早期,你可能会遇到的怪物会用符号 "d"、"x" 和 ":" 表示。想要攻击的话,只要简单地朝怪物的方向移动即可。系统会在屏幕顶部通过信息显示来告诉你攻击是否成功 - 以及怪物做出了何种反应。早期的怪物很容易击杀,所以你可以毫不费力地打败他们,但请留意底部状态栏里显示的角色的 HP 值。
|
||||
|
||||
> 早期的怪物很容易击杀,但请留意角色的 HP 值。
|
||||
|
||||
如果怪物死后掉落了一具尸体("%"),你可以点击逗号进行拾取,并点击 "e" 来食用。(在任何时候系统提示你选择一件物品,你都可以从物品列表中点击相应的按键,或者点击 "?" 来查询迷你菜单。)主意!有些尸体是有毒的,这些知识你将在日后的冒险中逐渐学会掌握。
|
||||
如果怪物死后掉落了一具尸体("%"),你可以点击逗号进行拾取,并点击 "e" 来食用。(在任何时候系统提示你选择一件物品,你都可以从物品列表中点击相应的按键,或者点击 "?" 来查询迷你菜单。)注意!有些尸体是有毒的,这些知识你将在日后的冒险中逐渐学会掌握。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在走廊里行进时遇到了死胡同,你可以点击 "s" 进行搜寻直到找到一扇门。这会花费时间,但是你由此加速了游戏进程:输入 "10" 并点击 "s" 你将一下搜索 10 次。这将花费游戏中进行 10 次动作的时间,不过如果你正在饥饿状态,你将有可能会被饿死。
|
||||
如果你在走廊里行进时遇到了死胡同,你可以点击 "s" 进行搜寻直到找到一扇门。这会花费时间,但是你可以这样加速游戏进程:输入 "10" 并点击 "s" 你将一下搜索 10 次。这将花费游戏中进行 10 次动作的时间,不过如果你正在饥饿状态,你将有可能会被饿死!
|
||||
|
||||
通常你可以在地牢顶部找到 "{"(喷泉)以及 "!"(药水)。当你找到喷泉的时候,你可以站在上面并点击 "q" 键开始 “畅饮(quaff)” - 引用后会得到积极的到致命的多种效果。当你找到药水的时候,将其拾起并点击 "q" 来引用。如果你找到一个商店,你可以拾取其中的物品并在离开前点击 "p" 键进行支付。当你负重过大时,你可以点击 "d" 键丢掉一些东西。
|
||||
通常你可以在地牢顶部找到 "{"(喷泉)以及 "!"(药水)。当你找到喷泉的时候,你可以站在上面并点击 "q" 键开始 “畅饮(quaff)” - 引用后会得到从振奋的到致命的多种效果。当你找到药水的时候,将其拾起并点击 "q" 来饮用。如果你找到一个商店,你可以拾取其中的物品并在离开前点击 "p" 键进行支付。当你负重过大时,你可以点击 "d" 键丢掉一些东西。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在已经有带音效的 3D 版 Nethack 了,如:Falcon’s Eye
|
||||
*现在已经有带音效的 3D 版 Nethack 了,如:Falcon’s Eye*
|
||||
|
||||
> ## 愚蠢的死法 ##
|
||||
> **愚蠢的死法**
|
||||
|
||||
> 在 NetHack 玩家中流行着一个缩写词 "YASD" - 又一种愚蠢的死法(Yet Another Stupid Death)。这个缩写词表示了玩家由于自身的的愚蠢或者粗心大意导致了角色的死亡。我们搜集了很多这类死法,但我们最喜欢的是下面描述的:
|
||||
> 在 NetHack 玩家中流行着一个缩写词 "YASD" - 又一种愚蠢的死法(Yet Another Stupid Death)。这个缩写词表示了玩家由于自身的的愚蠢或者粗心大意导致了角色的死亡。我们搜集了很多这类死法,但我们最喜欢的是下面这种死法:
|
||||
|
||||
> 我们正在商店浏览商品,这时一条蛇突然从药剂后面跳了出来。在杀死蛇之后,系统弹出一条信息提醒我们角色饥饿值过低了,因此我们顺手食用了蛇的尸体。坏事了!这使得我们的角色失明,导致我们的角色再也不能看见商店里的其他角色及地上的商品了。我们试图离开商店,但在慌乱中却撞在了店主身上并攻击了他。这种做法激怒了店主:他立即向我们的角色使用了火球术。我们试图逃到商店外的走廊上,但却在逃亡的过程中被烧死。
|
||||
|
||||
> 如果你有类似的死法,一定要来我们的论坛告诉我们。不要担心 - 没有人会嘲笑你。经历这样的死法也是你在 NetHack 的世界里不断成长的一部分。
|
||||
> 如果你有类似的死法,一定要来我们的论坛告诉我们。不要担心 - 没有人会嘲笑你。经历这样的死法也是你在 NetHack 的世界里不断成长的一部分。哈哈。
|
||||
|
||||
### 武装自己 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,7 +84,7 @@ NetHack 采用了回合制,因此即使你不进行任何动作,游戏仍然
|
||||
|
||||
在靠近掉在地下的装备之前最好检查一下身上的东西。点击 ";"(分号)后,"Pick an object"(选择一样物品)选项将出现在屏幕顶部。选择该选项,使用移动键直到选中你想要检查的物品,然后点击 ":"(冒号)。接着屏幕顶部将出现这件物品的描述。
|
||||
|
||||
因为你的目标是不断深入地牢直到找到护身符 Yendor,所以请随时留意周围的 "<" 和 ">" 符号。这两个符号分别表示向上和向下的楼梯,你可以用与之对应的按键来上楼或下楼。注意!如果你想让宠物跟随你进入下/上一层地牢,下/上楼前请确保你的宠物在你邻近的方格内。若果你想退出,点击 "S"(大写的 s)来保存进度,输入 #quit 退出游戏。当你再次运行 NetHack 时,系统将会自动读取你上次退出时的游戏进度。
|
||||
因为你的目标是不断深入地牢直到找到护身符 Yendor,所以请随时留意周围的 "<" 和 ">" 符号。这两个符号分别表示向上和向下的楼梯,你可以用与之对应的按键来上楼或下楼。注意!如果你想让宠物跟随你进入下/上一层地牢,下/上楼前请确保你的宠物在你邻近的方格内。若果你想退出,点击 "S"(大写的)来保存进度,输入 #quit 退出游戏。当你再次运行 NetHack 时,系统将会自动读取你上次退出时的游戏进度。
|
||||
|
||||
我们就不继续剧透了,地牢深处还有更多的神秘细节、陌生的 NPC 以及不为人知的秘密等着你去发掘。那么,我们再给你点建议:当你遇到了让你困惑不已的物品时,你可以尝试去 NetHack 维基 [http://nethack.wikia.com][3] 进行搜索。你也可以在 [www.nethack.org/v343/Guidebook.html][4] 找到一本非常不错(尽管很长)的指导手册。最后,祝游戏愉快!
|
||||
|
||||
@ -95,7 +94,7 @@ via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/nethack/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Mike Saunders][a]
|
||||
译者:[Stevearzh](https://github.com/Stevearzh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,64 @@
|
||||
Calife:一个轻量级的sudo替代品
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Calife会在登录为另外一个用户前输入自己的密码(如果没有提供登录名,默认是登录为root),在验证具有正确的权限后,就会切换到该用户及其组身份,并就会执行一个shell。如果 calife 是由 root 执行的,不需要密码,会执行一个所需的用户ID的shell。
|
||||
|
||||
所用的shell是用户自身所用的,除非在calife.auth配置文件中指定了某个shell。如果在命令行指定了“-”选项,就会读取该用户的环境文件,该shell就像是一个登录shell。这和su的惯常用法不同。
|
||||
|
||||
只有在calife.auth中指定的用户才能使用此方法通过calife成为另外一个用户。calife.auth安装位置处于/etc/calife.auth。
|
||||
|
||||
### Calife特性 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里给出了一个关于calife特性的扩展列表:
|
||||
|
||||
- 你可以完整保留你的环境变量和shell别名
|
||||
- 它可以全程记录会话的开始到结束
|
||||
- 你可以列出每个许可使用calife的用户,那样,你就可以用户赋予主管权限而不必提供root密码
|
||||
- 你可以在配置文件中指定哪个组可以使用:只要使用@staff或者%staff,那么所有staff组中的成员都将具有访问calife的权限
|
||||
- 通过calife也可以登录成为那些没有家目录或甚至没有shell的用户。如果你想要成为uucp或者甚至是bin,那会很方便
|
||||
- 你可以让calife在会话结束时运行一个指定的系统级的脚本(例如,发送一封邮件告知以root身份做了哪些事)
|
||||
|
||||
### ubuntu中安装calife ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端,然后运行以下命令
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install calife
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用Calife ###
|
||||
|
||||
### 语法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
calife [-] [login]
|
||||
|
||||
详情请参与calife手册页
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/calife-a-lightweight-alternative-to-sudo.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
|
||||
[1]:
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
[13]:
|
||||
[14]:
|
||||
[15]:
|
||||
[16]:
|
||||
[17]:
|
||||
[18]:
|
||||
[19]:
|
||||
[20]:
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
||||
Linux 有问必答--Linux 中如何安装 7zip
|
||||
Linux有问必答:Linux 中如何安装 7zip
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**: 我需要要从 ISO 映像中获取某些文件,为此我想要使用 7zip 程序。那么我应该如何安装 7zip 软件呢,[在 Linux 发布版本上完全安装]?
|
||||
|
||||
7zip 是一款开源的归档应用程序,开始是为 Windows 系统而开发的。它能对多种格式的档案文件进行打包或解包处理,除了支持原生的 7z 格式的文档外,还支持包括 XZ、GZIP、TAR、ZIP 和 BZIP2 等这些格式。 一般地,7zip 也常用来解压 RAR、DEB、RPM 和 ISO 等格式的文件。除了简单的归档功能,7zip 还具有支持 AES-256 算法加密以及自解压和建立多卷存档功能。在以 POSIX 协议为标准的系统上(Linux、Unix、BSD),原生的 7zip 程序被移植过来并被命名为 p7zip(“POSIX 7zip” 的简称)。
|
||||
7zip 是一款开源的归档应用程序,开始是为 Windows 系统而开发的。它能对多种格式的档案文件进行打包或解包处理,除了支持其原生的 7z 格式的文档外,还支持包括 XZ、GZIP、TAR、ZIP 和 BZIP2 等这些格式。 通常,7zip 也用来解压 RAR、DEB、RPM 和 ISO 等格式的文件。除了简单的归档功能,7zip 还具有支持 AES-256 算法加密以及自解压和建立多卷存档功能。在支持 POSIX 标准的系统上(Linux、Unix、BSD),原生的 7zip 程序被移植过来并被命名为 p7zip(“POSIX 7zip” 的简称)。
|
||||
|
||||
下面介绍如何在 Linux 中安装 7zip (或 p7zip)。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ Linux 有问必答--Linux 中如何安装 7zip
|
||||
基于红帽的发布系统上提供了两个 7zip 的软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
- **p7zip**: 包含 7za 命令,支持 7z、ZIP、GZIP、CAB、ARJ、BZIP2、TAR、CPIO、RPM 和 DEB 格式。
|
||||
- **p7zip-plugins**: 包含 7z 命令,额外的插件,它扩展了 7za 命令(例如 支持 ISO 格式的抽取)。
|
||||
- **p7zip-plugins**: 包含 7z 命令,额外的插件,它扩展了 7za 命令(例如支持 ISO 格式的抽取)。
|
||||
|
||||
在 CentOS/RHEL 系统中,在运行下面命令前您需要确保 [EPEL 资源库][1] 可用,但在 Fedora 系统中就不需要额外的资源库了。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,11 +37,11 @@ Linux 有问必答--Linux 中如何安装 7zip
|
||||
|
||||
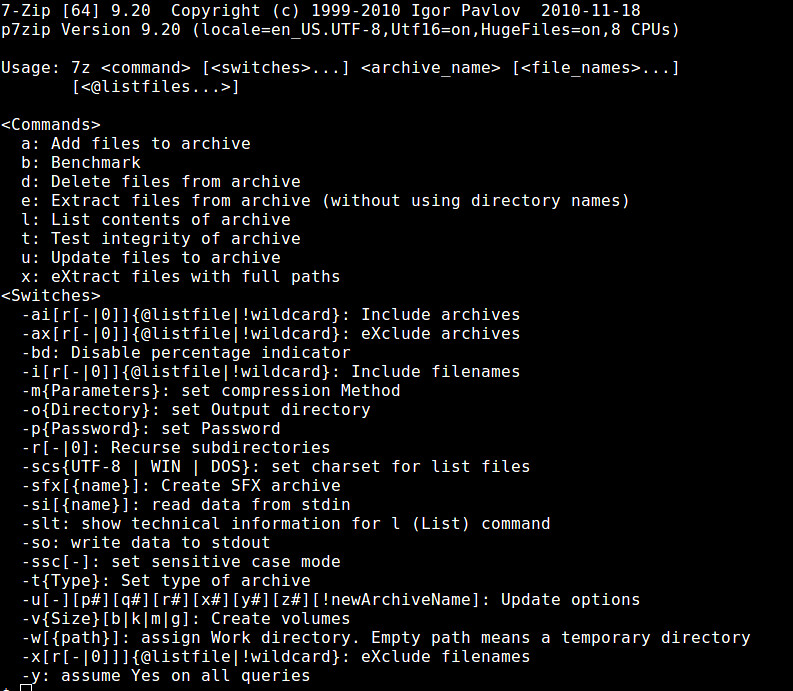
|
||||
|
||||
使用 “a” 选项就可以创建一个归档文件,它可以创建 7z、XZ、GZIP、TAR、 ZIP 和 BZIP2 这几种格式的文件。如果指定的归档文件已经存在的话,它会把文件“添加”到存在的归档中,而不是覆盖原有归档文件。
|
||||
使用 “a” 选项就可以创建一个归档文件,它可以创建 7z、XZ、GZIP、TAR、 ZIP 和 BZIP2 这几种格式的文件。如果指定的归档文件已经存在的话,它会把文件“附加”到存在的归档中,而不是覆盖原有归档文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ 7z a <archive-filename> <list-of-files>
|
||||
|
||||
使用 “e” 选项可以抽取出一个归档文件,抽取出的文件会放在当前目录。抽取支持的格式比创建时支持的格式要多的多,包括 7z、XZ、GZIP、TAR、ZIP、BZIP2、LZMA2、CAB、ARJ、CPIO、RPM、ISO 和 DEB 这些格式。
|
||||
使用 “e” 选项可以抽取一个归档文件,抽取出的文件会放在当前目录。抽取支持的格式比创建时支持的格式要多的多,包括 7z、XZ、GZIP、TAR、ZIP、BZIP2、LZMA2、CAB、ARJ、CPIO、RPM、ISO 和 DEB 这些格式。
|
||||
|
||||
$ 7z e <archive-filename>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -67,8 +67,8 @@ Linux 有问必答--Linux 中如何安装 7zip
|
||||
via:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-7zip-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-2324-1.html
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,8 @@
|
||||
Translated by H-mudcup
|
||||
|
||||
2014年Linux界发生的好事,坏事和丑事
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2014年已经接近尾声,现在正是盘点**2014年Linux大事件**的时候。整整一年,我们关注了有关Linux和开源的一些好事,坏事和丑事。让我们来快速回顾一下2014对于Linux是怎样的一年。
|
||||
2014年已经过去,现在正是盘点**2014年Linux大事件**的时候。整整一年,我们关注了有关Linux和开源的一些好事,坏事和丑事。让我们来快速回顾一下2014对于Linux是怎样的一年。
|
||||
|
||||
### 好事 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +12,7 @@ Translated by H-mudcup
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
从使用Wine到[使用Chrome的测试功能][1],为了能让Netflix能在Linux上工作,Linux用户曾尝试了各种方法。好消息是Netflix终于在2014年带来了Linux的本地支持。这让所有能使用Netflix的地区的Linux用户的脸上浮现出了微笑。想在[美国以外的地区使用Netflix][2](或其他官方授权使用Netflix的国家之外)的人还是得靠其他的方法。
|
||||
从使用Wine到[使用Chrome的测试功能][1],为了能让Netflix能在Linux上工作,Linux用户曾尝试了各种方法。好消息是Netflix终于在2014年带来了Linux的本地支持。这让所有能使用Netflix的地区的Linux用户的脸上浮现出了微笑。不过,想在[美国以外的地区使用Netflix][2](或其他官方授权使用Netflix的国家之外)的人还是得靠其他的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 欧洲国家采用开源/Linux ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,19 +28,19 @@ Translated by H-mudcup
|
||||
|
||||
### 坏事 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux在2014年并不是一帆风顺。某些事件的发生损坏了Linux/开源的形象。
|
||||
Linux在2014年并不是一帆风顺。某些事件的发生败坏了Linux/开源的形象。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Heartbleed心血 ####
|
||||
#### Heartbleed 心血漏洞 ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在今年的四月份,检测到[OpenSSL][8]有一个缺陷。这个漏洞被命名为[Heartbleed心血][9]。他影响了包括Facebook和Google在内的50多万个“安全”网站。这项漏洞可以真正的允许任何人读取系统的内存,并能因此给予用于加密数据流的密匙的访问权限。[xkcd上的漫画以更简单的方式解释了心血][10]。不必说,这个漏洞在OpenSSL的更新中被修复了。
|
||||
在今年的四月份,检测到[OpenSSL][8]有一个缺陷。这个漏洞被命名为[Heartbleed心血漏洞][9]。他影响了包括Facebook和Google在内的50多万个“安全”网站。这项漏洞可以真正的允许任何人读取系统的内存,并能因此给予用于加密数据流的密匙的访问权限。[xkcd上的漫画以更简单的方式解释了心血漏洞][10]。自然,这个漏洞在OpenSSL的更新中被修复了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Shellshock ####
|
||||
#### Shellshock 破壳漏洞 ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
好像有个心血还不够似的,在Bash里的一个缺陷更严重的震撼了Linux世界。这个漏洞被命名为[Shellshock][11]。这个漏洞把Linux往远程攻击的危险深渊又推了一把。这项漏洞是通过黑客的DDoS攻击暴露出来的。升级一下Bash版本应该能修复这个问题。
|
||||
好像有个心血漏洞还不够似的,在Bash里的一个缺陷更严重的震撼了Linux世界。这个漏洞被命名为[Shellshock 破壳漏洞][11]。这个漏洞把Linux往远程攻击的危险深渊又推了一把。这项漏洞是通过黑客的DDoS攻击暴露出来的。升级一下Bash版本应该能修复这个问题。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu Phone和Steam控制台 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,13 +50,13 @@ Linux在2014年并不是一帆风顺。某些事件的发生损坏了Linux/开
|
||||
|
||||
### 丑事 ###
|
||||
|
||||
systemd的归属战变得不知廉耻。
|
||||
是否采用 systemd 的争论变得让人羞耻。
|
||||
|
||||
### systemd大论战 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
用init还是systemd的争吵已经进行了一段时间了。但是在2014年当systemd准备在包括Debian, Ubuntu, OpenSUSE, Arch Linux and Fedora几个主流Linux分布中替代init时,事情变得不知廉耻了起来。它是如此的一发不可收拾,以至于它已经不限于boycottsystemd.org这类网站了。Lennart Poettering(systemd的首席开发人员及作者)在一条Google Plus状态上声明,说那些反对systemd的人在“收集比特币来雇杀手杀他”。Lennart还声称开源社区“是个恶心得不能待的地方”。人们吵得越来越离谱以至于把Debian分裂成了一个新的操作系统,称为[Devuan][15]。
|
||||
用init还是systemd的争吵已经进行了一段时间了。但是在2014年当systemd准备在包括Debian, Ubuntu, OpenSUSE, Arch Linux 和 Fedora几个主流Linux分布中替代init时,事情变得不知廉耻了起来。它是如此的一发不可收拾,以至于它已经不限于boycottsystemd.org这类网站了。Lennart Poettering(systemd的首席开发人员及作者)在一条Google Plus状态上声明,说那些反对systemd的人在“收集比特币来雇杀手杀他”。Lennart还声称开源社区“是个恶心得不能待的地方”。人们吵得越来越离谱以至于把Debian分裂成了一个新的操作系统,称为[Devuan][15]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 还有诡异的事 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -81,10 +79,10 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/biggest-linux-stories-2014/
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/watch-netflix-in-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-3024-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/easiest-watch-netflix-hulu-usa/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/french-city-toulouse-saved-1-million-euro-libreoffice/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/italian-city-turin-open-source/
|
||||
[3]:http://linux.cn/article-3575-1.html
|
||||
[4]:http://linux.cn/article-3602-1.html
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/170-primary-public-schools-geneva-switch-ubuntu/
|
||||
[6]:http://itsfoss.com/german-town-gummersbach-completes-switch-open-source/
|
||||
[7]:http://itsfoss.com/windows-10-inspired-linux/
|
||||
@ -95,8 +93,8 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/biggest-linux-stories-2014/
|
||||
[12]:http://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-phone-specification-release-date-pricing/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/systemd-replaces-init-in-linux/
|
||||
[14]:https://plus.google.com/+LennartPoetteringTheOneAndOnly/posts/J2TZrTvu7vd
|
||||
[15]:http://debianfork.org/
|
||||
[16]:http://thenewstack.io/microsoft-professes-love-for-linux-adds-support-for-coreos-cloudera-and-host-of-new-features/
|
||||
[15]:http://linux.cn/article-4512-1.html
|
||||
[16]:http://linux.cn/article-4056-1.html
|
||||
[17]:http://www.theregister.co.uk/2001/06/02/ballmer_linux_is_a_cancer/
|
||||
[18]:http://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/
|
||||
[19]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/top-five-linux-contributor-microsoft/
|
||||
@ -4,7 +4,9 @@ Windows和Ubuntu双系统,修复UEFI引导的两种办法
|
||||
|
||||
这里有两种修复EFI启动引导的方法,使Ubuntu可以正常启动
|
||||
|
||||
 "将GRUB2设置为启动引导"
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*将GRUB2设置为启动引导*
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 启用GRUB引导 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,22 +20,22 @@ Windows和Ubuntu双系统,修复UEFI引导的两种办法
|
||||
|
||||
可以按照以下几个步骤将GRUB2设置为默认的引导程序:
|
||||
|
||||
1.登录Windows 8
|
||||
2.转到桌面
|
||||
3.右击开始按钮,选择管理员命令行
|
||||
4.输入 mountvol g: (将你的EFI目录结构映射到G盘)
|
||||
5.输入 cd g:\EFI
|
||||
6.当你输入 dir 列出文件夹内容时,你可以看到一个Ubuntu的文件夹
|
||||
7.这里的参数可以是grubx64.efi或者shimx64.efi
|
||||
8.运行下列命令将grub64.efi设置为启动引导程序:
|
||||
1. 登录Windows 8
|
||||
2. 转到桌面
|
||||
3. 右击开始按钮,选择管理员命令行
|
||||
4. 输入 mountvol g: /s (这将你的EFI目录结构映射到G盘)
|
||||
5. 输入 cd g:\EFI
|
||||
6. 当你输入 dir 列出文件夹内容时,你可以看到一个Ubuntu的文件夹
|
||||
7. 这里的参数可以是grubx64.efi或者shimx64.efi
|
||||
8. 运行下列命令将grub64.efi设置为启动引导程序:
|
||||
bcdedit /set {bootmgr} path \EFI\ubuntu\grubx64.efi
|
||||
9.重启你的电脑
|
||||
10.你将会看到一个包含Ubuntu和Windows选项的GRUB菜单
|
||||
11.如果你的电脑仍然直接启动到Windows,重复步骤1到7,但是这次输入:
|
||||
9. 重启你的电脑
|
||||
10. 你将会看到一个包含Ubuntu和Windows选项的GRUB菜单
|
||||
11. 如果你的电脑仍然直接启动到Windows,重复步骤1到7,但是这次输入:
|
||||
bcdedit /set {bootmgr} path \EFI\ubuntu\shimx64.efi
|
||||
12.重启你的电脑
|
||||
12. 重启你的电脑
|
||||
|
||||
这里你做的事情是登录Windows管理员命令行,将EFI引导区映射到磁盘上,来查看Ubuntu的引导程序是否安装成功,然后选择grubx64.efi或者shimx64.efi作为引导程序。
|
||||
这里你做的事情就是登录Windows管理员命令行,将EFI引导区映射到磁盘上,来查看Ubuntu的引导程序是否安装成功,然后选择grubx64.efi或者shimx64.efi作为引导程序。
|
||||
|
||||
那么[grubx64.efi和shimx64.efi有什么区别呢][4]?在安全启动(serureboot)关闭的情况下,你可以使用grubx64.efi。如果安全启动打开则需要选择shimx64.efi。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,28 +43,30 @@ bcdedit /set {bootmgr} path \EFI\ubuntu\shimx64.efi
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.使用rEFInd引导Ubuntu和Windows双系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[rEFInd引导程序][5]会以图标的方式列出你所有的操作系统。因此,你可以通过点击相应的图标来启动Windows、Ubuntu或者优盘中的操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
[点击这里][6]下载rEFInd for Windows 8。
|
||||
|
||||
下载和解压以后,按照以下的步骤安装rEFInd。
|
||||
|
||||
1.返回桌面
|
||||
2.右击开始按钮,选择管理员命令行
|
||||
3.输入 mountvol g: (将你的EFI目录结构映射到G盘)
|
||||
4.进入解压的rEFInd目录。例如:
|
||||
cd c:\users\gary\downloads\refind-bin-0.8.4\refind-bin-0.8.4
|
||||
1. 返回桌面
|
||||
2. 右击开始按钮,选择管理员命令行
|
||||
3. 输入 mountvol g: /s (这将你的EFI目录结构映射到G盘)
|
||||
4. 进入解压的rEFInd目录。例如:
|
||||
cd c:\users\gary\downloads\refind-bin-0.8.4\refind-bin-0.8.4 。
|
||||
当你输入 dir 命令,你可以看到一个refind目录
|
||||
5.输入如下命令将refind拷贝到EFI引导区
|
||||
5. 输入如下命令将refind拷贝到EFI引导区
|
||||
xcopy /E refind g:\EFI\refind\
|
||||
6.输入如下命令进入refind文件夹
|
||||
6. 输入如下命令进入refind文件夹
|
||||
cd g:\EFI\refind
|
||||
7.重命名示例配置文件
|
||||
7. 重命名示例配置文件
|
||||
rename refind.conf-sample refind.conf
|
||||
8.运行如下命令将rEFind设置为引导程序
|
||||
8. 运行如下命令将rEFind设置为引导程序
|
||||
bcdedit /set {bootmgr} path \EFI\refind\refind_x64.efi
|
||||
9.重启你的电脑
|
||||
10.你将会看到一个包含Ubuntu和Windows的图形菜单
|
||||
9. 重启你的电脑
|
||||
10. 你将会看到一个包含Ubuntu和Windows的图形菜单
|
||||
|
||||
这个过程和选择GRUB引导程序十分相似。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -72,17 +76,20 @@ bcdedit /set {bootmgr} path \EFI\refind\refind_x64.efi
|
||||
|
||||
希望这篇文章可以解决有些人在安装Ubuntu和Windows 8.1双系统时出现的问题。如果你仍然有问题,可以通过上面的电邮和我进行交流。
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
via: http://linux.about.com/od/LinuxNewbieDesktopGuide/tp/3-Ways-To-Fix-The-UEFI-Bootloader-When-Dual-Booting-Windows-And-Ubuntu.htm
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gary Newell][a]
|
||||
译者:[zhouj-sh](https://github.com/zhouj-sh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://linux.about.com/od/LinuxNewbieDesktopGuide/tp/3-Ways-To-Fix-The-UEFI-Bootloader-When-Dual-Booting-Windows-And-Ubuntu.htm
|
||||
[a]:http://linux.about.com/bio/Gary-Newell-132058.htm
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.about.com/od/LinuxNewbieDesktopGuide/ss/The-Ultimate-Windows-81-And-Ubuntu-
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-UEFI-Bootable-Ubuntu-USB-Drive-Using-Windows_3.htm#step-heading
|
||||
[3]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-UEFI-Bootable-Ubuntu-USB-Drive-Using-Windows.htm
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-3178-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.cn/article-3178-1.html#4_3289
|
||||
[3]:http://linux.cn/article-3178-1.html#4_1717
|
||||
[4]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/SecurityTeam/SecureBoot
|
||||
[5]:http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/installing.html#windows
|
||||
[6]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/refind/files/0.8.4/refind-bin-0.8.4.zip/download
|
||||
@ -2,13 +2,13 @@
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
这里,我们将展示如何在一台Ubuntu 14.04或CentOS 6.5/7上安装Bugzilla。Bugzilla是一款基于web,用来记录跟踪缺陷数据库的bug跟踪软件,它同时是一款免费及开源软件(FOSS),它的bug跟踪系统允许个人和开发团体有效地记录下他们产品的一些突出问题。尽管是"免费"的,Bugzilla依然有很多其它同类产品所没有的“珍贵”特性。因此,Bugzilla很快就变成了全球范围内数以千计的组织最喜欢的bug管理工具。
|
||||
|
||||
Bugzilla对于不同状况的适应能力非常强。如今它们应用在各个不同的IT领域,系统管理员部署管理、芯片设计和部署问题跟踪(制作前后),还有为那些诸如Redhat,NASA,Linux-Mandrake和VA Systems这些名家提供软硬件bug跟踪。
|
||||
Bugzilla对于不同使用场景的适应能力非常强。如今它们应用在各个不同的IT领域,如系统管理中的部署管理、芯片设计及部署的问题跟踪(制造前期和后期),还有为那些诸如Redhat,NASA,Linux-Mandrake和VA Systems这些著名公司提供软硬件bug跟踪。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 安装依赖程序 ###
|
||||
|
||||
安装Bugzilla相当**简单**。这篇文章特别针对Ubuntu 14.04和CentOS 6.5两个版本(不过也适用于更老的版本)。
|
||||
|
||||
为了获取并能在Ubuntu或CentOS系统中运行Bugzilla,我们要安装Apache网络服务器(允许SSL),MySQL数据库服务器和一些需要来安装并配置Bugzilla的工具。
|
||||
为了获取并能在Ubuntu或CentOS系统中运行Bugzilla,我们要安装Apache网络服务器(启用SSL),MySQL数据库服务器和一些需要来安装并配置Bugzilla的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
要在你的服务器上安装使用Bugzilla,你需要安装好以下程序:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -29,14 +29,13 @@ Bugzilla对于不同状况的适应能力非常强。如今它们应用在各个
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu版本:**
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install apache2 mysql-server libapache2-mod-perl2
|
||||
libapache2-mod-perl2-dev libapache2-mod-perl2-doc perl postfix make gcc g++
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install apache2 mysql-server libapache2-mod-perl2 libapache2-mod-perl2-dev libapache2-mod-perl2-doc perl postfix make gcc g++
|
||||
|
||||
**CentOS版本:**
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install httpd mod_ssl mysql-server mysql php-mysql gcc perl* mod_perl-devel
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:请在shell或者终端下运行所有的命令并且确保你用root用户(sudo)连接机器。**
|
||||
**注意:请在shell或者终端下运行所有的命令并且确保你用root用户(sudo)操作机器。**
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 启动Apache服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -115,7 +114,6 @@ CentOS 6.5和Ubuntu 14.04 Trusty两个版本:
|
||||
# cd /var/www/html/
|
||||
|
||||
# mv -v bugzilla-4.5.2 bugzilla
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:这里,**/var/www/html/bugzilla/**就是**Bugzilla主目录**.
|
||||
@ -194,7 +192,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/tools/install-bugzilla-ubuntu-centos/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ Docker的镜像并不安全!
|
||||
|
||||
起初我以为这条信息引自Docker[大力推广][1]的镜像签名系统,因此也就没有继续跟进。后来,研究加密摘要系统的时候——Docker用这套系统来对镜像进行安全加固——我才有机会更深入的发现,逻辑上整个与镜像安全相关的部分具有一系列系统性问题。
|
||||
|
||||
Docker所报告的,一个已下载的镜像经过“验证”,它基于的仅仅是一个标记清单(signed manifest),而Docker却从未根据清单对镜像的校验和进行验证。一名攻击者以此可以提供任意所谓具有标记清单的镜像。一系列严重漏洞的大门就此敞开。
|
||||
Docker所报告的,一个已下载的镜像经过“验证”,它基于的仅仅是一个标记清单(signed manifest),而Docker却从未据此清单对镜像的校验和进行验证。一名攻击者以此可以提供任意所谓具有标记清单的镜像。一系列严重漏洞的大门就此敞开。
|
||||
|
||||
镜像经由HTTPS服务器下载后,通过一个未加密的管道流进入Docker守护进程:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ Docker所报告的,一个已下载的镜像经过“验证”,它基于的
|
||||
|
||||
这条管道的性能没有问题,但是却完全没有经过加密。不可信的输入在签名验证之前是不应当进入管道的。不幸的是,Docker在上面处理镜像的三个步骤中,都没有对校验和进行验证。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,不论Docker如何[声明][2],实际上镜像的校验和从未经过校验。下面是Docker与镜像校验和的验证相关的代码[片段][3],即使我提交了校验和不匹配的镜像,都无法触发警告信息。
|
||||
然而,不论Docker如何[声明][2],实际上镜像的校验和(Checksum)从未经过校验。下面是Docker与镜像校验和的验证相关的代码[片段][3],即使我提交了校验和不匹配的镜像,都无法触发警告信息。
|
||||
|
||||
if img.Checksum != "" && img.Checksum != checksum {
|
||||
log.Warnf("image layer checksum mismatch: computed %q,
|
||||
@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ Docker支持三种压缩算法:gzip、bzip2和xz。前两种使用Go的标准
|
||||
|
||||
第三种压缩算法,xz,比较有意思。因为没有现成的Go实现,Docker 通过[执行(exec)][5]`xz`二进制命令来实现解压缩。
|
||||
|
||||
xz二进制程序来自于[XZ Utils][6]项目,由[大概][7]2万行C代码生成而来。而C语言不是一门内存安全的语言。这意味着C程序的恶意输入,在这里也就是Docker镜像的XZ Utils解包程序,潜在地可能会执行任意代码。
|
||||
xz二进制程序来自于[XZ Utils][6]项目,由[大概][7]2万行C代码生成而来。而C语言不是一门内存安全的语言。这意味着C程序的恶意输入,在这里也就是Docker镜像的XZ Utils解包程序,潜在地存在可能会执行任意代码的风险。
|
||||
|
||||
Docker以root权限*运行* `xz` 命令,更加恶化了这一潜在威胁。这意味着如果在`xz`中出现了一个漏洞,对`docker pull`命令的调用就会导致用户整个系统的完全沦陷。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,7 +39,6 @@ Docker以root权限*运行* `xz` 命令,更加恶化了这一潜在威胁。
|
||||
|
||||
由于其生成校验和的步骤固定,它解码不可信数据的过程就有可能被设计成[攻破tarsum的代码][9]。这里潜在的攻击既包括拒绝服务攻击,还有逻辑上的漏洞攻击,可能导致文件被感染、忽略、进程被篡改、植入等等,这一切攻击的同时,校验和可能都是不变的。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**解包**
|
||||
|
||||
解包的过程包括tar解码和生成硬盘上的文件。这一过程尤其危险,因为在解包写入硬盘的过程中有另外三个[已报告的漏洞][10]。
|
||||
@ -60,8 +59,7 @@ Docker的工具包[libtrust][11],号称“通过一个分布式的信任图表
|
||||
|
||||
### 补救 ###
|
||||
|
||||
研究结束前,我[报告][15]了一些在tarsum系统中发现的问题,但是截至目前我报告的这些问题仍然
|
||||
没有修复。
|
||||
研究结束前,我[报告][15]了一些在tarsum系统中发现的问题,但是截至目前我报告的这些问题仍然没有修复。
|
||||
|
||||
要改进Docker镜像下载系统的安全问题,我认为应当有以下措施:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -79,16 +77,18 @@ Docker的工具包[libtrust][11],号称“通过一个分布式的信任图表
|
||||
|
||||
作为将更新框架加入Docker的一部分,还应当加入一个本地密钥存储池,将root密钥与registry的地址进行映射,这样用户就可以拥有他们自己的签名密钥,而不必使用Docker公司的了。
|
||||
|
||||
我注意到使用Docker公司非官方的宿主仓库往往会是一种非常糟糕的用户体验。当没有技术上的原因时,Docker也会将第三方的仓库内容降为二等地位来看待。这个问题不仅仅是生态问题,还是一个终端用户的安全问题。针对第三方仓库的全方位、去中心化的安全模型即必须又迫切。我希望Docker公司在重新设计他们的安全模型和镜像认证系统时能采纳这一点。
|
||||
我注意到使用非Docker公司官方的第三方仓库往往会是一种非常糟糕的用户体验。Docker也会将第三方的仓库内容降为二等地位来看待,即使不因为技术上的原因。这个问题不仅仅是生态问题,还是一个终端用户的安全问题。针对第三方仓库的全方位、去中心化的安全模型既必须又迫切。我希望Docker公司在重新设计他们的安全模型和镜像认证系统时能采纳这一点。
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker用户应当意识到负责下载镜像的代码是非常不安全的。用户们应当只下载那些出处没有问题的镜像。目前,这里的“没有问题”并不包括Docker公司的“可信(trusted)”镜像,例如官方的Ubuntu和其他基础镜像。
|
||||
Docker用户应当意识到负责下载镜像的代码是非常不安全的。用户们应当只下载那些出处没有问题的镜像。目前,这里的“没有问题”并**不**包括Docker公司的“可信(trusted)”镜像,例如官方的Ubuntu和其他基础镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
最好的选择就是在本地屏蔽 `index.docker.io`,然后使用`docker load`命令在导入Docker之前手动下载镜像并对其进行验证。Red Hat的安全博客有一篇[很好的文章][18],大家可以看看。
|
||||
|
||||
感谢Lewis Marshall指出tarsum从未真正验证。
|
||||
|
||||
参考
|
||||
|
||||
- [校验和的代码][19]
|
||||
- [cloc][20]介绍了18141行没有空格没有注释的C代码,以及5900行的header代码,版本号为v5.2.0。
|
||||
- [Android中也发现了][21]类似的bug,能够感染已签名包中的任意文件。同样出现问题的还有[Windows的Authenticode][22]认证系统,二进制文件会被篡改。
|
||||
@ -101,7 +101,7 @@ via: https://titanous.com/posts/docker-insecurity
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[titanous][a]
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
systemd-nspawn 指南
|
||||
systemd-nspawn 快速指南
|
||||
===========================
|
||||
我目前已从 chroot(译者注:chroot可以构建类似沙盒的环境,建议各位同学先了解chroot) 迁移到 systemd-nspawn,同时我写了一篇快速指南。简单的说,我强烈建议正在使用 systemd 的用户从 chroot 转为 systemd-nspawn,因为只要你的内核配置正确的话,它几乎没有什么缺点。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,11 +6,11 @@ systemd-nspawn 指南
|
||||
|
||||
###chroot 面临的挑战
|
||||
|
||||
大多数交互环境下,仅运行chroot还不够。通常还要挂载 /proc, /sys,另外为了确保不会出现类似“丢失 ptys”之类的错误,我们还得 bind(译者注:bind 是 mount 的一个选项) 挂载 /dev。如果你使用 tmpfs,你可能想要以 tmpfs 类型挂载新的 tmp, var/tmp。接下来你可能还想将其他的挂载点 bind 到 chroot 中。这些都不是特别难,但是一般情况下要写一个脚本来管理它。
|
||||
大多数交互环境下,仅运行chroot还不够。通常还要挂载 /proc, /sys,另外为了确保不会出现类似“丢失 ptys”之类的错误,我们还得 bind(译者注:bind 是 mount 的一个选项) 挂载 /dev。如果你使用 tmpfs,你可能想要以 tmpfs 类型挂载新的 tmp、 var/tmp。接下来你可能还想将其他的挂载点 bind 到 chroot 中。这些都不是特别难,但是一般情况下要写一个脚本来管理它。
|
||||
|
||||
现在我按照日常计划执行备份操作,当然有一些不必备份的数据如 tmp 目录,或任何 bind 挂载的内容。当我配置了一个新的 chroot 意味着我要更新我的备份配置了,但我经常忘记这点,因为大多数时间里 chroot 挂载点并没有运行。当这些挂载点任然存在的情况下执行备份的话,那么备份中会多出很多不需要的内容。
|
||||
现在我按照日常计划执行备份操作,当然有一些不必备份的数据如 tmp 目录,或任何 bind 挂载的内容。当我配置了一个新的 chroot 后就意味着我要更新我的备份配置了,但我经常忘记这点,因为大多数时间里 chroot 挂载点并没有运行。当这些挂载点仍然存在的情况下执行备份的话,那么备份中会多出很多不需要的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
当 bind 挂载点包含其他挂载点时(比如挂载时使用 -rbind 选项),这种情况下 systemd 的默认处理方式略有不同。在 bind 挂载中卸载一些东西时,systemd 会将处于 bind 另一边的目录也卸载掉。想像一下,如果我卸载了 chroot 中以bind 挂载 /dev 的某个目录后发现主机上的 /dev/pts 与 /dev/shm 也不见了,我肯定会很吃惊。不过好像有其他方法可以避免,但是这不是我们此次讨论的重点。
|
||||
当 bind 挂载点包含其他挂载点时(比如挂载时使用 -rbind 选项),这种情况下 systemd 的默认处理方式略有不同。在 bind 挂载中卸载一些东西时,systemd 会将处于 bind 另一边的目录也卸载掉。想像一下,如果我卸载了 chroot 中以 bind 挂载 /dev 的某个目录后,发现主机上的 /dev/pts 与 /dev/shm 也不见了,我肯定会很吃惊。不过好像有其他方法可以避免,但是这不是我们此次讨论的重点。
|
||||
|
||||
### Systemd-nspawn 优点
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,25 +39,25 @@ Systemd-nspawn 用于启动一个容器,并且它的最简模式就可以像 c
|
||||
|
||||
像 chroot 那样启动 namespace 是非常简单的:
|
||||
|
||||
systemd-nspawn -D .
|
||||
systemd-nspawn -D .
|
||||
|
||||
也可以像 chroot 那样退出。在内部可以运行 mount 并且可以看到默认它已将 /dev 与 /tmp 准备好了。 ”.“就是 chroot 的路径,也就是当前路径。在它内部运行的是 bash。
|
||||
|
||||
如果要添加一些 bind 挂载点也非常简便:
|
||||
|
||||
systemd-nspawn -D . --bind /usr/portage
|
||||
systemd-nspawn -D . --bind /usr/portage
|
||||
|
||||
现在,容器中的 /usr/portage 就与主机的对应目录绑定起来了,我们无需 sync /etc。如果想要绑定到指定的路径,只要在原路径后添加 ”:dest“,相当于 chroot 的 root(--bind foo 与 --bind foo:foo是一样的)。
|
||||
现在,容器中的 /usr/portage 就与主机的对应目录绑定起来了,我们无需 sync /etc。如果想要绑定到指定的路径,只要在原路径后添加 ”:dest“,相当于 chroot 的 root(--bind foo 与 --bind foo:foo是一样的)。
|
||||
|
||||
如果容器具有 init 功能并且可以在内部运行,可以通过添加 -b 选项启动它:
|
||||
|
||||
systemd-nspawn -D . --bind /usr/portage -b
|
||||
systemd-nspawn -D . --bind /usr/portage -b
|
||||
|
||||
可以观察到 init 的运作。关闭容器会自动退出。
|
||||
|
||||
如果容器内运行了 systemd ,你可以使用 -h 选项将它的日志重定向到主机的systemd日志:
|
||||
|
||||
systemd-nspawn -D . --bind /usr/portage -j -b
|
||||
systemd-nspawn -D . --bind /usr/portage -j -b
|
||||
|
||||
使用 nspawn 注册容器以便它能够在 machinectl 中显示。如此可以方便的在主机上对它进行操作,如启动新的 getty, ssh 连接,关机等。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -68,8 +68,8 @@ Systemd-nspawn 用于启动一个容器,并且它的最简模式就可以像 c
|
||||
via: http://rich0gentoo.wordpress.com/2014/07/14/quick-systemd-nspawn-guide/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[rich0][a]
|
||||
译者:[SPccman](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[SPccman](https://github.com/SPccman)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Turla espionage operation infects Linux systems with malware
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> A newly identified Linux backdoor program is tied to the Turla cyberespionage campaign, researchers from Kaspersky Lab said
|
||||
|
||||
A newly discovered malware program designed to infect Linux systems is tied to a sophisticated cyberespionage operation of Russian origin dubbed Epic Turla, security researchers found.
|
||||
|
||||
The Turla campaign, also known as Snake or Uroburos, [was originally uncovered in February][1], but goes back several years. The massive operation infected computers at government organizations, embassies, military installations, education and research institutions and pharmaceutical companies in over 45 countries.
|
||||
|
||||
The newly identified Turla component for Linux was uploaded recently to a multi-engine antivirus scanning service and was described by security researchers from antivirus vendor Kaspersky Lab as "a previously unknown piece of a larger puzzle."
|
||||
|
||||
"So far, every single Turla sample we've encountered was designed for the Microsoft Windows family, 32 and 64 bit operating systems," the Kaspersky researchers said Monday in a [blog post][2]. "The newly discovered Turla sample is unusual in the fact that it's the first Turla sample targeting the Linux operating system that we have discovered."
|
||||
|
||||
The Turla Linux malware is based on an open-source backdoor program called cd00r developed in 2000. It allows attackers to execute arbitrary commands on a compromised system, but doesn't require elevated privileges or root access to function and listens to commands received via hidden TCP/UDP packets, making it stealthy.
|
||||
|
||||
"It can't be discovered via netstat, a commonly used administrative tool," said the Kaspersky researchers, who are still analyzing the malware's functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
"We suspect that this component was running for years at a victim site, but do not have concrete data to support that statement just yet," they said.
|
||||
|
||||
Since their blog post Monday, the Kaspersky researchers also found a second Turla Linux component that appears to be a separate malware program.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.computerworld.com/article/2857129/turla-espionage-operation-infects-linux-systems-with-malware.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Lucian Constantin][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.computerworld.com/author/Lucian-Constantin/
|
||||
[1]:http://news.techworld.com/security/3505688/invisible-russian-cyberweapon-stalked-us-and-ukraine-since-2005-new-research-reveals/
|
||||
[2]:https://securelist.com/blog/research/67962/the-penquin-turla-2/
|
||||
@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Git 2.2.1 Released To Fix Critical Security Issue
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Git 2.2.1 was released this afternoon to fix a critical security vulnerability in Git clients. Fortunately, the vulnerability doesn't plague Unix/Linux users but rather OS X and Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
Today's Git vulnerability affects those using the Git client on case-insensitive file-systems. On case-insensitive platforms like Windows and OS X, committing to .Git/config could overwrite the user's .git/config and could lead to arbitrary code execution. Fortunately with most Phoronix readers out there running Linux, this isn't an issue thanks to case-sensitive file-systems.
|
||||
|
||||
Besides the attack vector from case insensitive file-systems, Windows and OS X's HFS+ would map some strings back to .git too if certain characters are present, which could lead to overwriting the Git config file. Git 2.2.1 addresses these issues.
|
||||
|
||||
More details via the [Git 2.2.1 release announcement][1] and [GitHub has additional details][2].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTg2ODA
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Michael Larabel][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.michaellarabel.com/
|
||||
[1]:http://article.gmane.org/gmane.linux.kernel/1853266
|
||||
[2]:https://github.com/blog/1938-git-client-vulnerability-announced
|
||||
@ -1,28 +0,0 @@
|
||||
New 64-bit Linux Kernel Vulnerabilities Disclosed This Week
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For those that didn't hear the news yet, multiple Linux x86_64 vulnerabilities were made public this week.
|
||||
|
||||
With CVE-2014-9322 that's now public, there's a local privilege escalation issue affecting all kernel versions prior to Linux 3.17.5. CVE-2014-9322 is described as "privilege escalation due to incorrect handling of a #SS fault caused
|
||||
by an IRET instruction. In particular, if IRET executes on a writeable kernel stack (this was always the case before 3.16 and is sometimes the case on 3.16 and newer), the assembly function general_protection will execute with the user's gsbase and the kernel's gsbase swapped. This is likely to be easy to exploit for privilege escalation, except on systems with SMAP or UDEREF. On those systems, assuming that the mitigation works correctly, the impact of this bug may be limited to massive memory corruption and an eventual crash or reboot."
|
||||
|
||||
Fortunately, it's fixed [in Linux kernel Git since late November][1]. CVE-2014-9322 is linked to CVE-2014-9090, which is also corrected by the fixes in Git.
|
||||
|
||||
There's also two x86_64 kernel bugs related to espfix. "The next two bugs are related to espfix. The IRET instruction has IMO a blatant design flaw: IRET to a 16-bit user stack segment will leak bits 31:16 of the kernel stack pointer. This flaw exists on 32-bit and 64-bit systems. 32-bit Linux kernels have mitigated this leak for a long time, and 64-bit Linux kernels have mitigated this leak since 3.16. The mitigation is called espfix."
|
||||
|
||||
Fixes for CVE-2014-8133 and CVE-2014-8134 are in KVM and Linux kernel Git as of a few days ago. More details on these x86_64 vulnerabilities via [this oss-sec posting][2]. These issues were uncovered by Andy Lutomirski at AMA Capital Management.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTg2NzY
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Michael Larabel][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.michaellarabel.com/
|
||||
[1]:https://git.kernel.org/cgit/linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux.git/commit/arch/x86/kernel/entry_64.S?id=6f442be2fb22be02cafa606f1769fa1e6f894441
|
||||
[2]:http://seclists.org/oss-sec/2014/q4/1052
|
||||
@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[zhouj-sh translating...]
|
||||
2 Ways To Fix The UEFI Bootloader When Dual Booting Windows And Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The main problem that users experience after following my [tutorials for dual booting Ubuntu and Windows 8][1] is that their computer continues to boot directly into Windows 8 with no option for running Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are two ways to fix the EFI boot loader to get the Ubuntu portion to boot correctly.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Make GRUB The Active Bootloader ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are a few things that may have gone wrong during the installation.
|
||||
|
||||
In theory if you have managed to install Ubuntu in the first place then you will have [turned off fast boot][2].
|
||||
|
||||
Hopefully you [followed this guide to create a bootable UEFI Ubuntu USB drive][3] as this installs the correct UEFI boot loader.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have done both of these things as part of the installation, the bit that may have gone wrong is the part where you set GRUB2 as the boot manager.
|
||||
|
||||
To set GRUB2 as the default bootloader follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1.Login to Windows 8
|
||||
2.Go to the desktop
|
||||
3.Right click on the start button and choose administrator command prompt
|
||||
4.Type mountvol g: /s (This maps your EFI folder structure to the G drive).
|
||||
5.Type cd g:\EFI
|
||||
6.When you do a directory listing you will see a folder for Ubuntu. Type dir.
|
||||
7.There should be options for grubx64.efi and shimx64.efi
|
||||
8.Run the following command to set grubx64.efi as the bootloader:
|
||||
|
||||
bcdedit /set {bootmgr} path \EFI\ubuntu\grubx64.efi
|
||||
|
||||
9:Reboot your computer
|
||||
10:You should now have a GRUB menu appear with options for Ubuntu and Windows.
|
||||
11:If your computer still boots straight to Windows repeat steps 1 through 7 again but this time type:
|
||||
|
||||
bcdedit /set {bootmgr} path \EFI\ubuntu\shimx64.efi
|
||||
|
||||
12:Reboot your computer
|
||||
|
||||
What you are doing here is logging into the Windows administration command prompt, mapping a drive to the EFI partition so that you can see where the Ubuntu bootloaders are installed and then either choosing grubx64.efi or shimx64.efi as the bootloader.
|
||||
|
||||
So [what is the difference between grubx64.efi and shimx64.efi][4]? You should choose grubx64.efi if secureboot is turned off. If secureboot is turned on you should choose shimx64.efi.
|
||||
|
||||
In my steps above I have suggested trying one and then trying another. The other option is to install one and then turn secure boot on or off within the UEFI firmware for your computer depending on the bootloader you chose.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Use rEFInd To Dual Boot Windows 8 And Ubuntu ###
|
||||
The [rEFInd boot loader][5] works by listing all of your operating systems as icons. You will therefore be able to boot Windows, Ubuntu and operating systems from USB drives simply by clicking the appropriate icon.
|
||||
|
||||
To download rEFInd for Windows 8 [click here][6].
|
||||
|
||||
After you have downloaded the file extract the zip file.
|
||||
|
||||
Now follow these steps to install rEFInd.
|
||||
|
||||
1.Go to the desktop
|
||||
2.Right click on the start button and choose administrator command prompt
|
||||
3.Type mountvol g: /s (This maps your EFI folder structure to the G drive)
|
||||
4.Navigate to the extracted rEFInd folder. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
cd c:\users\gary\downloads\refind-bin-0.8.4\refind-bin-0.8.4
|
||||
|
||||
When you type dir you should see a folder for refind
|
||||
5.Type the following to copy refind to the EFI partition:
|
||||
|
||||
xcopy /E refind g:\EFI\refind\
|
||||
|
||||
6.Type the following to navigate to the refind folder
|
||||
|
||||
cd g:\EFI\refind
|
||||
|
||||
7.Rename the sample configuration file:
|
||||
|
||||
rename refind.conf-sample refind.conf
|
||||
8.Run the following command to set rEFInd as the bootloader
|
||||
|
||||
bcdedit /set {bootmgr} path \EFI\refind\refind_x64.efi
|
||||
|
||||
9.Reboot your computer
|
||||
10.You should now have a menu similar to the image above with options to boot Windows and Ubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
This process is fairly similar to choosing the GRUB bootloader.
|
||||
|
||||
Basically it involves downloading rEFInd, extracting the files. copying the files to the EFI partition, renaming the configuration file and then setting rEFInd as the boot loader.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
Hopefully this guide has solved the issues that some of you have been having with dual booting Ubuntu and Windows 8.1. If you are still having issues feel free to get back in touch using the email link above.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gary Newell][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://linux.about.com/od/LinuxNewbieDesktopGuide/tp/3-Ways-To-Fix-The-UEFI-Bootloader-When-Dual-Booting-Windows-And-Ubuntu.htm
|
||||
[a]:http://linux.about.com/bio/Gary-Newell-132058.htm
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.about.com/od/LinuxNewbieDesktopGuide/ss/The-Ultimate-Windows-81-And-Ubuntu-
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-UEFI-Bootable-Ubuntu-USB-Drive-Using-Windows_3.htm#step-heading
|
||||
[3]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-UEFI-Bootable-Ubuntu-USB-Drive-Using-Windows.htm
|
||||
[4]:https://wiki.ubuntu.com/SecurityTeam/SecureBoot
|
||||
[5]:http://www.rodsbooks.com/refind/installing.html#windows
|
||||
[6]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/refind/files/0.8.4/refind-bin-0.8.4.zip/download
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
Best GNOME Shell Themes For Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Themes are the best way to customize your Linux desktop. If you [install GNOME on Ubuntu 14.04][1] or 14.10, you might want to change the default theme and give it a different look. To help you in this task, I have compiled here a **list of best GNOME shell themes for Ubuntu** or any other Linux OS that has GNOME shell installed on it. But before we see the list, let’s first see how to change install new themes in GNOME Shell.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install themes in GNOME Shell ###
|
||||
|
||||
To install new themes in GNOME with Ubuntu, you can use Gnome Tweak Tool which is available in software repository in Ubuntu. Open a terminal and use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnome-tweak-tool
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can use themes by putting them in ~/.themes directory. I have written a detailed tutorial on [how to install and use themes in GNOME Shell][2], in case you need it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Best GNOME Shell themes ###
|
||||
|
||||
The themes listed here are tested on GNOME Shell 3.10.4 but it should work for all version of GNOME 3 and higher. For the sake of mentioning, the themes are not in any kind of priority order. Let’s have a look at the best GNOME themes:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Numix ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
No list can be completed without the mention of [Numix themes][3]. These themes got so popular that it encouraged [Numix team to work on a new Linux OS, Ozon][4]. Considering their design work with Numix theme, it won’t be exaggeration to call it one of the [most beautiful Linux OS][5] releasing in near future.
|
||||
|
||||
To install Numix theme in Ubuntu based distributions, use the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-add-repository ppa:numix/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install numix-icon-theme-circle
|
||||
|
||||
#### Elegance Colors ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Another beautiful theme from Satyajit Sahoo, who is also a member of Numix team. [Elegance Colors][6] has its own PPA so that you can easily install it:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:satyajit-happy/themes
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gnome-shell-theme-elegance-colors
|
||||
|
||||
#### Moka ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Moka][7] is another mesmerizing theme that is always included in the list of beautiful themes. Designed by the same developer who gave us Unity Tweak Tool, Moka is a must try:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:moka/stable
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install moka-gnome-shell-theme
|
||||
|
||||
#### Viva ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Based on Gnome’s default Adwaita theme, Viva is a nice theme with shades of black and oranges. You can download Viva from the link below.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Viva GNOME Shell Theme][8]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ciliora-Prima ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Previously known as Zukitwo Dark, Ciliora-Prima has square icons theme. Theme is available in three versions that are slightly different from each other. You can download it from the link below.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Ciliora-Prima GNOME Shell Theme][9]
|
||||
|
||||
#### Faience ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Faience has been a popular theme for quite some time and rightly so. You can install Faience using the PPA below for GNOME 3.10 and higher.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:tiheum/equinox
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install faience-theme
|
||||
|
||||
#### Paper [Incomplete] ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ever since Google talked about Material Design, people have been going gaga over it. Paper GTK theme, by Sam Hewitt (of Moka Project), is inspired by Google Material design and currently under development. Which means you will not have the best experience with Paper at the moment. But if your a bit experimental, like me, you can definitely give it a try.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:snwh/pulp
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install paper-gtk-theme
|
||||
|
||||
That concludes my list. If you are trying to give a different look to your Ubuntu, you should also try the list of [best icon themes for Ubuntu 14.04][10].
|
||||
|
||||
How do you find this list of **best GNOME Shell themes**? Which one is your favorite among the one listed here? And if it’s not listed here, do let us know which theme you think is the best GNOME Shell theme.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/gnome-shell-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-gnome-in-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/install-switch-themes-gnome-shell/
|
||||
[3]:https://numixproject.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/numix-linux-distribution/
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/new-beautiful-linux-2015/
|
||||
[6]:http://satya164.deviantart.com/art/Gnome-Shell-Elegance-Colors-305966388
|
||||
[7]:http://mokaproject.com/
|
||||
[8]:https://github.com/vivaeltopo/gnome-shell-theme-viva
|
||||
[9]:http://zagortenay333.deviantart.com/art/Ciliora-Prima-Shell-451947568
|
||||
[10]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
What is a good IDE for C/C++ on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
"A real coder doesn't use an IDE, a real coder uses [insert a text editor name here] with such and such plugins." We all heard that somewhere. Yet, as much as one can agree with that statement, an IDE remains quite useful. An IDE is easy to set up and use out of the box. Hence there is no better way to start coding a project from scratch. So for this post, let me present you with my list of good IDEs for C/C++ on Linux. Why is C/C++ specifically? Because C is my favorite language, and we need to start somewhere. Also note that there are in general a lot of ways to code in C, so in order to trim down the list, I only selected "real out-of-the-box IDE", not text editors like Gedit or Vim pumped with [plugins][1]. Not that this alternative is bad in any way, just that the list will go on forever if I include text editors.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Code::Blocks ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Starting all out with my personal favorite, [Code::Blocks][2] is a simple and fast IDE for C/C++ exclusively. Like any respectable IDE, it integrates syntax highlighting, bookmarking, word completion, project management, and a debugger. Where it shines is via its simple plugin system which adds indispensable tools like Valgrind and CppCheck, and less indispensable like a Tetris mini-game. But my reason for liking it particularly is for its coherent set of handy shortcuts, and the large number of options that never feel too overwhelming.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Eclipse ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
I know that I said only "real out-of-the-box IDE" and not a text editor pumped with plugins, but [Eclipse][3] is a "real out-of-the-box IDE." It's just that Eclipse needs a little [plugin][4] (or a variant) to code in C. So I technically did not contradict myself. And it would have been impossible to make an IDE list without mentioning the behemoth that is Eclipse. Like it or not, Eclipse remains a great tool to code in Java. And thanks to the [CDT Project][5], it is possible to program in C/C++ too. You will benefit from all the power of Eclipse and its traditional features like word completion, code outline, code generator, and advanced refactoring. What it lacks in my opinion is the lightness of Code::Blocks. It is still very heavy and takes time to load. But if your machine can take it, or if you are a hardcore Eclipse fan, it is a very safe option.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Geany ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
With a lot less features but a lot more flexibility, [Geany][6] is at the opposite of Eclipse. But what it lacks (like a debugger for example), Geany makes it up with nice little features: a space for note taking, creation from template, code outline, customizable shortcuts, and plugins management. Geany is still closer to an extensive text editor than an IDE here. However I keep it in the list for its lightness and its well designed interface.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. MonoDevelop ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Another monster to add to the list, [MonoDevelop][7] has a very unique feel derived from its look and interface. I personally love its project management and its integrated version control system. The plugin system is also pretty amazing. But for some reason, all the options and the support for all kind of programming languages make it feel a bit overwhelming to me. It remains a great tool that I used many times in the past, but just not my number one when dealing with "simplistic" C.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Anjuta ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
With a very strong "GNOME feeling" attached to it, [Anjuta][8]'s appearance is a hit or miss. I tend to see it as an advanced version of Geany with a debugger included, but the interface is actually a lot more elaborate. I do enjoy the tab system to switch between the project, folders, and code outline view. I would have liked maybe a bit more shortcuts to move around in a file. However, it is a good tool, and offers outstanding compilation and build options, which can support the most specific needs.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Komodo Edit ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
I was not very familiar with [Komodo Edit][9], but after trying it a few days, it surprised me with many many good things. First, the tab-based navigation is always appreciable. Then the fancy looking code outline reminds me a lot of Sublime Text. Furthermore, the macro system and the file comparator make Komodo Edit very practical. Its plugin library makes it almost perfect. "Almost" because I do not find the shortcuts as nice as in other IDEs. Also, I would enjoy more specific C/C++ tools, and this is typically the flaw of general IDEs. Yet, very enjoyable software.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. NetBeans ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Just like Eclipse, impossible to avoid this beast. With navigation via tabs, project management, code outline, change history tracking, and a plethora of tools, [NetBeans][10] might be the most complete IDE out there. I could list for half a page all of its amazing features. But that will tip you off too easily about its main disadvantage, it might be too big. As great as it is, I prefer plugin based software because I doubt that anyone will need both Git and Mercurial integration for the same project. Call me crazy. But if you have the patience to master all of its options, you will be pretty much become the master of IDEs everywhere.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. KDevelop ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For all KDE fans out there, [KDevelop][11] might be the answer to your prayers. With a lot of configuration options, KDevelop is yours if you manage to seize it. Call me superficial but I never really got past the interface. But it's too bad for me as the editor itself packs quite a punch with a lot of navigation options and customizable shortcuts. The debugger is also very advanced and will take a bit of practice to master. However, this patience will be rewarded with this very flexible IDE's full power. And it gets special credits for its amazing embedded documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. CodeLite ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Finally, last for not least, [CodeLite][12] shows that you can take a traditional formula and still get something with its own feeling attached to it. If the interface really reminded me of Code::Blocks and Anjuta at first, I was just blown away by the extensive plugin library. Whether you want to diff a file, insert a copyright block, define an abbreviation, or push your work on Git, there is a plugin for you. If I had to nitpick, I would say that it lacks a few navigation shortcuts for my taste, but that's really it.
|
||||
|
||||
To conclude, I hope that this list had you discover new IDEs for coding in your favorite language. While Code::Blocks remains my favorite, it has some serious challengers. Also we are far from covering all the ways to code in C/C++ using an IDE on Linux. So if you have another one to propose, let us know in the comments. Also if you would like me to cover IDEs for a different language next, also let us know in the comment section.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/good-ide-for-c-cpp-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/adrien
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/turn-vim-full-fledged-ide.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.codeblocks.org/
|
||||
[3]:https://eclipse.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-c-cpp-development-environment-in-eclipse.html
|
||||
[5]:https://eclipse.org/cdt/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.geany.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.monodevelop.com/
|
||||
[8]:http://anjuta.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://komodoide.com/komodo-edit/
|
||||
[10]:https://netbeans.org/
|
||||
[11]:https://www.kdevelop.org/
|
||||
[12]:http://codelite.org/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,157 @@
|
||||
A Step By Step Guide To Installing Xubuntu Linux
|
||||
================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
### Introduction To Installing Xubuntu Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This guide shows how to install Xubuntu Linux using step by step instructions.
|
||||
|
||||
Why would you want to install Xubuntu? Here are three reasons:
|
||||
|
||||
1. You have a computer running Windows XP that is out of support
|
||||
2. You have [a computer that is running really slowly][1] and you want a lightweight but modern operating system
|
||||
3. You want to be able to customise your computing experience
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing you need to do is download Xubuntu and create a bootable USB drive.
|
||||
|
||||
After you have done this boot into a live version of Xubuntu and click on the install Xubuntu icon.
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose Your Installation Language ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The first step is to choose your language.
|
||||
|
||||
Click on the language in the left pane and then click "Continue"
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose Wireless Connection ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The second step requires you to choose your internet connection. This is not a required step and there are reasons why you might choose not to set up your internet connection at this stage.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a [poor internet connection][3] it is a good idea not to choose a wireless network because the installer will attempt to download updates as part of the installation. Your installation will therefore take a long time to complete.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a really [good internet connection][4] choose your wireless network and enter the security key.
|
||||
|
||||
### Be Prepared ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You will now see a checklist which shows how well prepared you are for installing Xubuntu:
|
||||
|
||||
- Do you have at least 6.2 gigabytes of disk space
|
||||
- Are you connected to the internet
|
||||
- Are you connected to a power source
|
||||
|
||||
The only one that is a necessity is the disk space.
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned in the previous step you can install Xubuntu without being connected to the internet. You can install updates once the installation is complete.
|
||||
|
||||
You only need to be connected to a power source if you are likely to run out of battery power during the installation.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that if you are connected to the internet there is a checkbox to turn off the option to download updates while installing.
|
||||
|
||||
There is also a checkbox that lets you install third party software to enable you to [play MP3s][5] and watch [Flash videos][6]. This is a step that can be completed post installation as well.
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose Your Installation Type ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The next step is to choose the installation type. The options available will depend on what is already installed on the computer.
|
||||
|
||||
In my case I was installing Xubuntu on a netbook over the top of [Ubuntu MATE][7] and so I had options to reinstall Ubuntu, erase and reinstall, install Xubuntu alongside Ubuntu or something else.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have Windows on your computer you will have options to install alongside, replace Windows with Xubuntu or something else.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide shows how to install Xubuntu on a computer and not how to dual boot. That is a completely different guide altogether.
|
||||
|
||||
Choose the option to replace your operating system with Xubuntu and click "Continue"
|
||||
|
||||
Note: This will cause your disk to be wiped and you should backup all of your data before continuing
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose The Disk To Install To ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Select the drive you wish to install Xubuntu to.
|
||||
|
||||
Click "Install Now".
|
||||
|
||||
A warning will appear telling you that the drive will be wiped and you will be shown a list of partitions that will be created.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: This is the very last chance to change your mind. If you click continue the disk will be wiped and Xubuntu will be installed
|
||||
|
||||
Click "Continue" to install Xubuntu
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose Your Location ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You are now required to choose your location by clicking on the map. This sets your timezone so that your clock is set to the right time.
|
||||
|
||||
After you have selected the correct location click "Continue".
|
||||
|
||||
### Choose Your Keyboard Layout ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Choose your keyboard layout.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this select the language of your keyboard in the left hand pane and then choose the exact layout in the right pane such as dialect, number of keys etc.
|
||||
|
||||
You can click the "Detect Keyboard Layout" button to automatically select the best keyboard layout.
|
||||
|
||||
To make sure the keyboard layout is set correctly enter text into the "Type here to test your keyboard". Pay close attention to function keys and symbols such as pound and dollar symbols.
|
||||
|
||||
Don't worry if you don't get this right during installation. You can set the keyboard layout again within Xubuntu's system settings post installation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Add A User ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
n order to use Xubuntu you will need to have at least one user set up and so the installer requires you to create a default user.
|
||||
|
||||
Enter your name and a name to distinguish the computer into the first two boxes.
|
||||
|
||||
Choose a username and [set up a password][8] for the user. You will need to type the password in twice to make sure you have set the password correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want Xubuntu to automatically login without having to enter a password check the box marked "Log in automatically". Personally I would never recommend doing this though.
|
||||
|
||||
The better option is to check the "Require my password to log in" radio button and if you want to be completely secure check the "Encrypt my home folder" option.
|
||||
|
||||
Click "Continue" to move on.
|
||||
|
||||
### Wait For Installation To Complete ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The files will now be copied to your computer and Xubuntu will be installed.
|
||||
|
||||
During this process you will see a short slide show. You can go and [make some coffee][9] at this point and relax.
|
||||
|
||||
A message will appear stating that you can continue to try Xubuntu or reboot to start using the newly installed Xubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
When you are ready, reboot and remove the USB drive.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: To install Xubuntu on a UEFI based machine requires some extra steps not included here. These instructions will be added as a separate guide
|
||||
|
||||
via : http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/A-Step-By-Step-Guide-To-Installing-Xubuntu-Linux.htm#step-heading
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gary Newell][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linux.about.com/bio/Gary-Newell-132058.htm
|
||||
[1]:http://windows.about.com/od/maintainandfix/a/8ways2speedup.htm
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/ss/How-To-Create-A-Persistent-Bootable-Xubuntu-Linux-USB-Drive.htm
|
||||
[3]:http://netforbeginners.about.com/od/basicinternethardware/f/Why-Internet-Connections-Can-Be-Slow.htm
|
||||
[4]:http://netforbeginners.about.com/b/2011/09/07/test-your-internet-connection-speed-here.htm
|
||||
[5]:http://mp3.about.com/od/freebies/tp/freemusictp.htm
|
||||
[6]:http://animation.about.com/od/2danimationtutorials/ss/2d_fla_lesson1.htm
|
||||
[7]:http://www.everydaylinuxuser.com/2014/11/ubuntu-mate-vs-lubuntu-on-old-netbook.html
|
||||
[8]:http://netsecurity.about.com/cs/generalsecurity/a/aa112103b.htm
|
||||
[9]:http://coffeetea.about.com/od/preparationandrecipes/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
Cutegram: A Better Telegram Client For GNU/Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
No need for a introduction to **Telegram**, right? Telegram is a popular free Instant messenger application that can be used to chat with your friends all over the world. Unlike Whatsapp, Telegram is free forever, no ads, no subscription fees. And, the Telegram client is open source too. Telegram is available for many different platforms, including Linux, Android, iOS, Windows Phone, Windows, and Mac OS X. The messages which are sending using telegram are highly encrypted and self-destructive. It is very secure, and there is no limit on the size of your media and chats.
|
||||
|
||||
You can install and use Telegram desktop on your Debian/Ubuntu systems as mentioned in [our previous tutorial][1]. However, a new telegram client called **Cutegram** is available now to make your chat experience more fun and easy.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is Cutegram? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cutegram is a free and opensource telegram clients for GNU/Linux focusing on user friendly, compatibility with Linux desktop environments and easy to use. Cutegram using Qt5, QML, libqtelegram, libappindication, AsemanQtTools technologies and Faenza icons and Twitter emojies graphic sets. It’s free and released under GPLv3 license.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Cutegram ###
|
||||
|
||||
Head over to the Cutegram homepage and download the latest version of your distribution’s choice. As I use Ubuntu 64 bit, I downloaded the .deb file.
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://aseman.co/downloads/cutegram/cutegram_1.0.2-1-amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Now, Install Cutegram as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install gdebi
|
||||
sudo gdebi cutegram_1.0.2-1-amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
For other distributions, run the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
**64bit:**
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://aseman.co/downloads/cutegram/cutegram-1.0.2-linux-x64-installer.run
|
||||
|
||||
**32 bit:**
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://aseman.co/downloads/cutegram/cutegram-1.0.2-linux-installer.run
|
||||
|
||||
Set executable permission:
|
||||
|
||||
chmod + cutegram-1.0.2-linux*.run
|
||||
|
||||
And, install it as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ./cutegram-1.0.2-linux*.run
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
Launch Cutegram either from Menu or Unity dash. From the login screen, select your country, and enter your mobile number, finally click **Login**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A code will be sent to your mobile number. Enter the code and click **Sign in**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There you go.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Start Chatting!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
And, you can set a profile picture, start new chat/group chat, or secret chat from using the buttons on the left pane.
|
||||
|
||||
Stay happy! Cheers!!
|
||||
|
||||
For more details, check the [Cutegram website][2].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/cutegram-better-telegram-client-gnulinux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/install-telegram-desktop-via-ppa/
|
||||
[2]:http://aseman.co/en/products/cutegram/
|
||||
@ -1,116 +0,0 @@
|
||||
The awesomely epic guide to KDE
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Everything you ever wanted to know about KDE (but were too afraid of the number of possible solutions to ask).**
|
||||
|
||||
Desktops on Linux. They’re a concept completely alien to users of other operating systems because they never having to think about them. Desktops must feel like the abstract idea of time to the Amondawa tribe, a thought that doesn’t have any use until you’re in a different environment. But here it is – on Linux you don’t have to use the graphical environment lurking beneath your mouse cursor. You can change it for something completely different. If you don’t like windows, switch to xmonad. If you like full-screen apps, try Gnome. And if you’re after the most powerful and configurable point-and-click desktop, there’s KDE.
|
||||
|
||||
KDE is wonderful, as they all are in their own way. But in our opinion, KDE in particular suffers from poor default configuration and a rather allusive learning curve. This is doubly frustrating, firstly because it has been quietly growing more brilliant over the last couple of years, and secondly, because KDE should be the first choice for users unhappy with their old desktop – in particular, Windows 8 users pining for an interface that makes sense.
|
||||
|
||||
But fear not. We’re going to use a decade’s worth of KDE firefighting to bring you the definitive guide to making KDE look good and function slightly more like how you might expect it to. We’re not going to look at KDE’s applications, other than perhaps Dolphin; we’re instead going to look at the functionality in the desktop environment itself. And while our guinea pig distribution is going to be Mageia, this guide will be equally applicable to any recent KDE desktop running from almost any distribution, so don’t let the default Mageia background put you off.
|
||||
|
||||
### Fonts ###
|
||||
|
||||
A great first target for getting your system looking good is its selection of fonts. It used to be the case that many of us would routinely copy fonts across from a Windows installation, getting the professional Ariel and Helvetica font rendering that was missing from Linux at the time. But thanks to generic quality fonts such as DejaVu and Nimbus Sans/Roman, this isn’t a problem any more. But it’s still worth finding a font you prefer, as there are now so many great alternatives to choose between.
|
||||
|
||||
The best source of free fonts we’ve found is [www.fontsquirrel.com][1] – it hosts the Roboto, Roboto Slab (Hello!) and Roboto Condensed (Hello!) typefaces used throughout our magazine, and also on the Nexus 5 smartphone (Roboto was developed for use in the Ice Cream Sandwich version of the Android mobile operating system).
|
||||
|
||||
TrueType fonts, with their **.ttf** file extensions, are incredibly easy to install from KDE. Download the zip file, right-click and select something from the Extract menu. Now all you need to do is drag a selection across the TrueType fonts you want to install and select ‘Install’ from the right-click Actions menu. KDE will take care of the rest.
|
||||
|
||||
Another brilliant thing about KDE is that you can change all the fonts at once. Open the System Settings panel and click on Application Appearances, followed by the fonts tab, and click on Adjust All Fonts. Now just select a font from the requester. Most KDE applications will update with your choice immediately, while other applications, such as Firefox, will require a restart. Either way, it’s a quick and effective way of experimenting with your desktop’s usability and appearance. We’d recommend either Open Sans or the thinner Aller fonts.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Most distributions don’t include decent fonts. But KDE enables you to quickly install new ones and apply them to your desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
### Eye candy ###
|
||||
|
||||
One of KDE’s most secret features is that backgrounds can be dynamic. We don’t find much use for this when it comes to the desktops that tells us the weather outside the window, but we do like backgrounds that dynamically grab images from the internet. With most distributions you’ll need to install something for this to work. Just search for **plasma-wallpaper** in your distribution’s package manager. Our favourite is **plasma-wallpaper-potd**, as this installs easy access to update-able wallpaper images from a variety of sources.
|
||||
|
||||
Changing a desktop background is easy with KDE, but it’s not intuitive. Mageia, for example, defaults to using ‘Folder’ view, as this is closer to the traditional desktop where files from the Desktop folder in your home directory are displayed on the background, and the whole desktop works like a file manager. Right-click and select ‘Folder Settings’ if this is the view you’re using. Alternatively, KDE defaults to ‘Desktop’, where the background is clear apart from any widgets you add yourself, and files and folders are considered links to the sources. The menu item in this mode is labelled Desktop Settings. The View Configuration panel that changes the background is the same, however, and you need to make your changes in the Wallpaper drop-down menu. We’d recommend Picture Of The Day as the wallpaper, and the Astronomy Picture Of The Day as the image source.
|
||||
|
||||
Another default option we think is crazy is the blue glow that surrounds the active window. While every other desktop uses a slightly deeper drop-shadow, KDE’s active window looks like it’s bathed in radioactive light. The solution to this lies in the default theme, and this can be changed by going to KDE’s System Settings control panel and selecting Workspace Appearance. On the first page, which is labelled Window Decorations, you’ll find that Oxygen is nearly always selected, and it’s this theme that contains the option to change the blue glow. Just click on the Configure Decoration button, flip to the Shadows tab and disable Active Window Glow’. Alternatively, if you’d like active windows to have a more pronounced shadow, change the inner and outer colours to black.
|
||||
|
||||
You may have seen the option to download wallpapers, for example, from within a KDE window, and you can see this now by clicking on the Get New Decorations button. Themes are subjective, but our favourite combination is currently the Chrome window decoration (it looks identical to Google’s default theme for its browser) with the Aya desktop theme. The term ‘desktop theme’ is a bit of a misnomer, as it doesn’t encapsulate every setting as you might expect. Instead it controls how generic desktop elements are rendered. The most visible of these elements is the launch panel, and changing the desktop theme will usually have a dramatic effect on its appearance, but you’ll also notice a difference in the widgets system.
|
||||
|
||||
The final graphical flourish we’d suggest is to change the icon set that KDE uses. There’s nothing wrong with the default Oxygen set, but there are better options. Unfortunately, this is where the ‘Get New Themes’ download option often fails, probably because icon packages are large and can overwhelm the personal storage space often reserved for projects like these. We’d suggest going to [kde-look.org][2] and browsing its icon collections. Open up the Icons panel from KDE’s System Settings, click on the Icons tab followed by Install Theme File and point the requester at the location of the archive you just downloaded. KDE will take it from there and add the icon set to the list in the panel. Try Kotenza for a flat theme, or keep an eye on Nitrux development.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Remove the blue glow and change a few of the display options, and KDE starts to look pretty good in our opinion.
|
||||
|
||||
### The panel ###
|
||||
|
||||
Our next target is going to be the panel at the bottom of the screen. This has become a little dated, especially if you’re using KDE on a large or high-resolution display, so our first suggestion is to re-scale and centre it for your screen. The key to moving screen components in KDE is making sure they’re unlocked, and this accomplished by right-clicking on the ‘plasma’ cashew in the top-right of the display where the current activity is listed. Only when widgets are unlocked can you re-size the panel, and even add new applications from the launch menu.
|
||||
|
||||
With widgets unlocked, click on the cashew on the side of the panel followed by More Settings and select Centre for panel alignment. With this enabled you can re-size the panel using the sliders on either side and the panel itself will always stay in the middle of your screen. Just pretend you’re working on indentation on a word processor and you’ll get the idea. You can also change its height when the sliders are visible by dragging the central height widget, and to the left of this, you can drag the panel to a different edge on your screen. The top edge works quite well, but many of KDE’s applets don’t work well when stacked vertically on the left or right edges of the display.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two different kinds of task manager applets that come with KDE. The default displays each running application as a title bar in the panel, but this takes up quite a bit of space. The alternative task manager displays only the icon of the application, which we think is much more useful. Mageia defaults to the icon version, but most others – and KDE itself – prefer the title bar applet. To change this, click on the cashew again and hover over the old applet so that the ‘X’ appears, then click on this ‘X’ to remove the applet from the panel. Now click on Add Widgets, find the two task managers and drag the icon version on to your panel. You can re-arrange any other applets in this mode by dragging them to the left and right.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the Icon-Only task manager will only display icons for tasks running on the current desktop, which we think is counterintuitive, as it’s more convenient to see all of the applications you may have running and to quickly switch between whatever desktops on which they may be running with a simple click. To change this behaviour, right-click on the applet and select the Settings menu option and the Behaviour tab in the next window. Deselect ‘Only Show Tasks From The Current Desktop’, and perhaps ‘Only Show Tasks From The Current Activity’ if you use KDE’s activities.
|
||||
|
||||
Another alteration we like to make is to reconfigure the virtual desktops applet from showing four desktops as a 2×2, which doesn’t look too good on a small panel, to 4×1. This can be done by right-clicking on the applet, selecting Pager Settings and then clicking on the Virtual Desktops tabs and changing the number of rows to ‘1’.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, there’s the launch menu. Mageia has switched this from the new style of application launcher to the old style originally seen in Microsoft Windows. We prefer the former because of its search field, but the two can be switched by right-clicking the icon and selecting the Switch To… menu option.
|
||||
|
||||
If you find the hover-select action of this mode annoying, where moving the mouse over one of the categories automatically selects it, you can disable it by right-clicking on the launcher, selecting Launcher Settings from the menu and disabling ‘Switch Tabs On Hover’ from the General settings page. It’s worth reiterating that many of these menu options are only available when widgets are unlocked, so don’t despair if you don’t see the correct menu entry at first.
|
||||
|
||||
> ### Activities ###
|
||||
>
|
||||
> No article on KDE would be complete without some discussion of what KDE calls Activities. In many ways, Activities are a solution waiting for a problem. They’re meta-virtual desktops that allow you to group desktop configuration and applications together. You may have an activity for photo editing, for example, or one for working and another for the internet. If you’ve got a touchscreen laptop, activities could be used to switch between an Android-style app launcher (the Search and Launch mode from the Desktop Settings panel), and the regular desktop mode. We use a single activity as a default for screenshots, for instance, while another activity switches everything to the file manager desktop mode. But the truth is that you have to understand what they are before you can find a way of using them.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Some installations of KDE will include the Activity applet in the toolbar. Its red, blue and green dots can be clicked on to open the activity manager, or you can click on the Plasma cashew in the top-right and select Activities. This will open the bar at the bottom of the screen, which lists activities installed and primed on your system. Clicking on any will switch between them; as will pressing the meta key (usually the Windows key) and Tab.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> We’d suggest that finding a fast way to switch between activities, such as with a keyboard shortcut or with the Activity Bar widget is the key to using them more. With the Activity Manager open, clicking on Create Activity lets you either clone the current desktop, add a blank desktop or create a new activity from a list of templates. Clone works well if you want to add some default applications to the desktop for your current setup. To remove an activity, switch to another one and press the Stop and Delete buttons from the Activity Manager.
|
||||
|
||||
### Upgraded launch menu ###
|
||||
|
||||
You may want to look into replacing the default launch menu entirely. If you open the Add Widgets view, for instance, and search for menus, you’ll see several results. Our current favourite is called Application Launcher (QML). It provides the same kind of functionality as the default menu, but has a cleaner interface after you’ve enlarged the initial window. But if we’re being honest, we don’t use the launcher that much. We prefer to do most launching through KRunner, which is the seemingly simple requester that appears when you hold Alt+F2.
|
||||
|
||||
KRunner is better than the default launcher, because you can type this shortcut from anywhere, regardless of which applications are running or where your mouse is located. When you start to type the name of the application you want to run into KRunner, you’ll see the results filtered in real time beneath the entry field – press Enter to launch the top choice.
|
||||
|
||||
KRunner is capable of so much more. You can type in calculations like **=sin(90)**, for example, and see the result in real time. You can search Google with **gg**: or Wikipedia with **wp**: followed by the search terms, and add many other operations through installable modules. To make best use of this awesome KDE feature, make sure you’ve got the **plasma-addons** package installed, and search for **runner** on your distribution’s package manager. When you next launch KRunner and click on the tool icon to the left of the search bar, you’ll see a wide variety of plugins that can do all kinds of things with the text you type in. In classic KDE style, many don’t include instructions on how to use them, so here’s our breakdown of the most useful things you can do with KRunner:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### File management ###
|
||||
|
||||
File management may not be the most exciting subject in Linux, but it is one we all seem to spend a lot of time doing, whether that’s moving a download into a better folder, or copying photos from a camera. The old file manager, Konqueror, was one of the best reasons for using KDE in the first place, and while Konqueror has been superseded by Dolphin in KDE 4.x, it’s still knocking around – even if it is labelled a web browser.
|
||||
|
||||
If you open Konqueror and enter the URL as **file:/**, it turns back into that file manager of old, with many of its best features intact. You can click on the lower status bar, for example, and split the view vertically or horizontally, into other views. You can fill the view with proportionally sized blocks by selecting Preview File Size View from the right-click menu, and preview many other file types without ever leaving Konqueror.
|
||||
|
||||
Mageia uses a double-click for most options, whereas we prefer a single click. This can be changed from the System-Settings panel by opening Input Devices, clicking on Mouse and enabling ‘Single-click To Open Files And Folders’. If you’ve become used to Apple’s reverse scroll, you’ll also find an option here to reverse the scroll direction on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Konqueror is a great application, but it hasn’t been a focus of KDE development for a considerable period of time. Dolphin has replaced it, and while this is a much simplified file manager, it does inherit some of Konqueror’s best features. You can still split the view, for instance, albeit one only once, and only horizontally, from the toolbar. You can also view lots of metadata. Select the Details View and right-click on the column headings for the files, and you can add columns that list the word counts in text files, or an image’s size and orientation, or the artist, title and duration of an audio file, all from within the contents of the data. This is KDE’s semantic desktop in action, and it’s been growing in functionality for the last couple of years. Apple’s OS X, for example, has only just started pushing its ability to tag files and applications – we’ve been able to do this from KDE for a long time. We don’t know any other desktop that comes close to providing that level of control.
|
||||
|
||||
### Window management ###
|
||||
|
||||
KDE has a comprehensive set of windowing functions as well as graphical effects. They’re all part of the window manager, KWin, rather than the desktop, which is what we’ve been dealing with so far. It’s the window manager’s job to handle the positioning, moving and rendering of your windows, which is why they can be replaced without switching the whole desktop. You might want to try KWin on the RazorQt desktop, for example, to get the best of both the minimal environment RazorQt offers and the power of KDE’s window manager.
|
||||
|
||||
The easiest way to get to KWin’s configuration settings is to right-click on the title bar of any window (this is usually the most visible element of any window manager), and select Window Manager Settings from the More Actions menu.
|
||||
|
||||
The Task Switcher is the tool that appears when you press Alt+Tab, and continually pressing those two keys will switch between all running applications on the current desktop. You can also use cursor keys to move left and right through the list. These settings are mostly sensibly configured, but you may want to include All Other Desktops in the Filter Windows By section, as that will allow you to quickly switch to applications running on other desktops. We also like the Cover Switch visualisation rather than the Thumbnails view, and you can even configure the perceived distance of the windows by clicking on the toolbar icon.
|
||||
|
||||
The next page on the window manager control module handles what happens at the edges of your screen. At the very least, we prefer to enable Switch Desktop On Edge by selecting Only When Moving Windows from the drop-down list. This means that when you drag a window to one edge, the virtual desktop will switch beneath, effectively dragging the window on to a new virtual desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
The great thing about enabling this only for dragged windows is that it doesn’t interfere with KDE’s fantastic window snapping feature. When you drag a window close to the left or right edge, for instance, KDE displays a ghosted window where your window will snap to if you release the mouse. This is a great way of turning KDE into a tiling window manager, where you can easily have two windows split down the middle of the screen area. Moving a window into any of the corners will also give you the ability to neatly arrange your windows to occupy a quarter of the screen, which is ideal for large displays.
|
||||
|
||||
We also enable a mode similar to Mission Control on OS X when the cursor is in the region of the top-left corner of the screen. On the screen edge layout, click on the dot in the top-right of the screen (or any other point you’d prefer) and select Desktop Grid from the drop-down menu that appears. Now when you move to the top-right of your display, you’ll get an overview of all your virtual desktops, any of which can be chosen with a click.
|
||||
|
||||
Two pages down in the configuration module, there’s a page called Focus. This is an old idea where you can change whether a window becomes active when you click on it, or when you roll your mouse cursor over it. KDE adds another twist to this by providing a slider that progresses from click to a strict hover policy, where the window under the cursor always becomes active. We prefer to use one of the middle options – Focus Follows Mouse – as this chooses the most obvious window to activate for us without making too many mistakes, and it means we seldom click to focus. We also reduce the focus delay to 200ms, but this will depend on how you feel about the feature after using it for a while.
|
||||
|
||||
KDE has so many features, many of which only come to light when you start to use the desktop. It really is a case of developers often adding things and then telling no one. But we feel KDE is worth the effort, and unlikely some other desktops, is unlikely to change too much in the transition from 4.x to 5. That means the time you spend learning how to use KDE now is an investment. Dive in!.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
KDE visual effects (click for larger)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/desktops/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ben Everard][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/author/ben_everard/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.fontsquirrel.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://kde-look.org/
|
||||
@ -1,119 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Interview: Thomas Voß of Mir
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Mir was big during the space race and it’s a big part of Canonical’s unification strategy. We talk to one of its chief architects at mission control.**
|
||||
|
||||
Not since the days of 2004, when X.org split from XFree86, have we seen such exciting developments in the normally prosaic realms of display servers. These are the bits that run behind your desktop, making sure Gnome, KDE, Xfce and the rest can talk to your graphics hardware, your screen and even your keyboard and mouse. They have a profound effect on your system’s performance and capabilities. And where we once had one, we now have two more – Wayland and Mir, and both are competing to win your affections in the battle for an X replacement.
|
||||
|
||||
We spoke to Wayland’s Daniel Stone in issue 6 of Linux Voice, so we thought it was only fair to give equal coverage to Mir, Canonical’s own in-house X replacement, and a project that has so far courted controversy with some of its decisions. Which is why we headed to Frankfurt and asked its Technical Architect, Thomas Voß, for some background context…
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Linux Voice: Let’s go right back to the beginning, and look at what X was originally designed for. X solved the problems that were present 30 years ago, where people had entirely different needs, right?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Thomas Voß**: It was mainframes. It was very expensive mainframe computers with very cheap terminals, trying to keep the price as low as possible. And one of the first and foremost goals was: “Hey, I want to be able to distribute my UI across the network, ideally compressed and using as little data as possible”. So a lot of the decisions in X were motivated by that.
|
||||
|
||||
A lot of the graphics languages that X supports even today have been motivated by that decision. The X developers started off in a 2D world; everything was a 2D graphics language, the X way of drawing rectangles. And it’s present today. So X is not necessarily bad in that respect; it still solves a lot of use cases, but it’s grown over time.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the reasons is that X is a protocol, in essence. So a lot of things got added to the protocol. The problem with adding things to a protocol is that they tend to stick. To use a 2D graphics language as an example, XVideo is something that no-one really likes today. It’s difficult to support and the GPU vendors actually cry out in pain when you start talking about XVideo. It’s somewhat bloated, and it’s just old. It’s an old proven technology – and I’m all for that. I actually like X for a lot of things, and it was a good source of inspiration. But then when you look at your current use cases and the current setup we are in, where convergence is one of the buzzwords – massively overrated obviously – but at the heart of convergence lies the fact that you want to scale across different form factors.
|
||||
|
||||
**LV: And convergence is big for Canonical isn’t it?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Thomas**: It’s big, I think, for everyone, especially over time. But convergence is a use case that was always of interest to us. So we always had this idea that we want one codebase. We don’t want a situation like Apple has with OS X and iOS, which are two different codebases. We basically said “Look, whatever we want to do, we want to do it from one codebase, because it’s more efficient.” We don’t want to end up in the situation where we have to be maintaining two, three or four separate codebases.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s where we were coming from when we were looking at X, and it was just too bloated. And we looked at a lot of alternatives. We started looking at how Mac OS X was doing things. We obviously didn’t have access to the source code, but if you see the transition from OS 9 to OS X, it was as if they entirely switched to one graphics language. It was pre-PostScript at that time. But they chose one graphics language, and that’s it. From that point on, when you choose a graphics language, things suddenly become more simple to do. Today’s graphics language is EGL ES, so there was inspiration for us to say we were converged on GL and EGL. From our perspective, that’s the least common denominator.
|
||||
|
||||
> We basically said: whatever we want to do, we want to do it from one codebase, because it’s more efficient.
|
||||
|
||||
Obviously there are disadvantages to having only one graphics language, but the benefits outweigh the disadvantages. And I think that’s a common theme in the industry. Android made the same decision to go that way. Even Wayland to a certain degree has been doing that. They have to support EGL and GL, simply because it’s very convenient for app developers and toolkit developers – an open graphics language. That was the part that inspired us, and we wanted to have this one graphics language and support it well. And that takes a lot of craft.
|
||||
|
||||
So, once you can say: no more weird 2D API, no more weird phong API, and everything is mapped out to GL, you’re way better off. And you can distill down the scope of the overall project to something more manageable. So it went from being impossible to possible. And then there was me, being very opinionated. I don’t believe in extensibility from the beginning – traditionally in Linux everything is super extensible, which has got benefits for a certain audience.
|
||||
|
||||
If you think about the audience of the display server, it’s one of the few places in the system where you’ve got three audiences. So you’ve got the users, who don’t care, or shouldn’t care, about the display server.
|
||||
|
||||
**LV: It’s transparent to them.**
|
||||
|
||||
**Thomas**: Yes, it’s pixels, right? That’s all they care about. It should be smooth. It should be super nice to use. But the display server is not their main concern. It obviously feeds into a user experience, quite significantly, but there are a lot of other parts in the system that are important as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you’ve got developers who care about the display server in terms of the API. Obviously we said we want to satisfy this audience, and we want to provide a super-fast experience for users. It should be rock solid and stable. People have been making fun of us and saying “yeah, every project wants to be rock solid and stable”. Cool – so many fail in doing that, so let’s get that down and just write out what we really want to achieve.
|
||||
|
||||
And then you’ve got developers, and the moment you expose an API to them, or a protocol, you sign a contract with them, essentially. So they develop to your API – well, many app developers won’t directly because they’ll be using toolkits – but at some point you’ve got developers who sign up to your API.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**LV: The developers writing the toolkits, then?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Thomas**: We do a lot of work in that arena, but in general it’s a contract that we have with normal app developers. And we said: look, we don’t want the API or contract to be super extensible and trying to satisfy every need out there. We want to understand what people really want to do, and we want to commit to one API and contract. Not five different variants of the contract, but we want to say: look, this is what we support and we, as Canonical and as the Mir maintainers, will sign up to.
|
||||
|
||||
So I think that’s a very good thing. You can buy into specific shells sitting on top of Mir, but you can always assume a certain base level of functionality that we will always provide in terms of window management, in terms of rendering capabilities, and so on and so forth. And funnily enough, that also helps with convergence. Because once you start thinking about the API as very important, you really start thinking about convergence. And what happens if we think about form factor and we transfer from a phone to a tablet to a desktop to a fridge?
|
||||
|
||||
**LV: And whatever might come!**
|
||||
|
||||
**Thomas**: Right, right. How do we account for future developments? And we said we don’t feel comfortable making Mir super extensible, because it will just grow. Either it will just grow and grow, or you will end up with an organisation that just maintains your protocol and protocol extensions.
|
||||
|
||||
**LV: So that’s looking at Mir in relation to X. The obvious question is comparing Mir to Wayland – so what is it that Mir does, that Wayland doesn’t?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Thomas**: This might sound picky, but we have to distinguish what Wayland really is. Wayland is a protocol specification which is interesting because the value proposition is somewhat difficult. You’ve got a protocol and you’ve got a reference implementation. Specifically, when we started, Weston was still a test bed and everything being developed ended up in there.
|
||||
|
||||
No one was buying into that; no one was saying, “Look, we’re moving this to production-level quality with a bona fide protocol layer that is frozen and stable for a specific version that caters to application authors”. If you look at the Ubuntu repository today, or in Debian, there’s Wayland-cursor-whatever, so they have extensions already. So that’s a bit different from our approach to Mir, from my perspective at least.
|
||||
|
||||
There was this protocol that the Wayland developers finished and back then, before we did Mir and I looked into all of this, I wrote a Wayland compositor in Go, just to get to know things.
|
||||
|
||||
**LV: As you do!**
|
||||
|
||||
**Thomas**: And I said: you know, I don’t think a protocol is a good way of approaching this because versioning a protocol in a packaging scenario is super difficult. But versioning a C API, or any sort of API that has a binary stability contract, is way easier and we are way more experienced at that. So, in that respect, we are different in that we are saying the protocol is an implementation detail, at least up to a certain point.
|
||||
|
||||
I’m pretty sure for version 1.0, which we will call a golden release, we will open up the protocol for communication purposes. Under the covers it’s Google buffers and sockets. So we’ll say: this is the API, work against that, and we’re committed to it.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s one thing, and then we said: OK, there’s Weston, but we cannot use Weston because it’s not working on Android, the driver model is not well defined, and there’s so much work that we would have to do to actually implement a Wayland compositor. And then we are in a situation where we would have to cut out a set of functionality from the Wayland protocol and commit to that, no matter what happens, and ultimately that would be a fork, over time, right?.
|
||||
|
||||
**LV: It’s a difficult concept for many end users, who just want to see something working.**
|
||||
|
||||
**Thomas**: Right, and even from a developer’s perspective – and let’s jump to the political part – I find it somewhat difficult to have a party owning a protocol definition and another party building the reference implementations. Now, Gnome and KDE do two different Wayland compositors. I don’t see the benefit in that, to be quite frank, so the value proposition is difficult to my mind.
|
||||
|
||||
The driver model in Mir and Wayland is ultimately not that different – it’s GL/EGL based. That is kind of the denominator that you will find in both things, which is actually a good thing, because if you look at the contract to application developers and toolkit developers, most of them don’t want Mir or Wayland. They talk ELG and GL, and at that point, it’s not that much of a problem to support both.
|
||||
|
||||
> If there had been a full reference implementation of Wayland, our decision might have been different.
|
||||
|
||||
So we did this work for porting the Chromium browser to Mir. We actually took the Chromium Wayland back-end, factored out all the common pieces to EGL and GL ES, and split it up into Wayland and Mir.
|
||||
|
||||
And I think from a user’s or application developer’s perspective, the difference is not there. I think, in retrospect, if there would have been something like a full reference implementation of Wayland, where a company had signed up to provide something that is working, and committed to a certain protocol version, our decision might have been different. But there just wasn’t. It was five years out there, Wayland, Wayland, Wayland, and there was nothing that we could build upon.
|
||||
|
||||
**LV: The main experience we’ve had is with RebeccaBlackOS, which has Weston and Wayland, because, like you say, there’s no that much out there running it.**
|
||||
|
||||
**Thomas**: Right. I find Wayland impressive, obviously, but I think Mir will be significantly more relevant than Wayland in two years time. We just keep on bootstrapping everything, and we’ve got things working across multiple platforms. Are there issues, and are there open questions to solve? Most likely. We never said we would come up with the perfect solution in version 1. That was not our goal. I don’t think software should be built that way. So it just should be iterated.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**LV: When was Mir originally planned for? Which Ubuntu release? Because it has been pushed back a couple of times.**
|
||||
|
||||
**Thomas**: Well, we originally planned to have it by 14.04. That was the kind of stretch goal, because it highly depends on the availability of proprietary graphics drivers. So you can’t ship an LTS [Long Term Support] release of Ubuntu on a new display server without supporting the hardware of the big guys.
|
||||
|
||||
**LV: We thought that would be quite ambitious anyway – a Long Term Support release with a whole new display server!**
|
||||
|
||||
**Thomas**: Yes, it was ambitious – but for a reason. If you don’t set a stretch goal, and probably fail in reaching it, and then re-evaluate how you move forward, it’s difficult to drive a project. So if you just keep it evolving and evolving and evolving, and you don’t have a checkpoint at some point…
|
||||
|
||||
**LV: That’s like a lot of open source projects. Inkscape is still on 0.48 or something, and it works, it’s reliable, but they never get to 1.0. Because they always say: “Oh let’s add this feature, and that feature”, and the rest of us are left thinking: just release 1.0 already!.**
|
||||
|
||||
**Thomas**: And I wouldn’t actually tie it to a version number. To me, that is secondary. To me, the question is whether we call this ready for broad public consumption on all of the hardware versions we want to support?
|
||||
|
||||
In Canonical, as a company, we have OEM contracts and we are enabling Ubuntu on a host of devices, and laptops and whatever, so we have to deliver on those contracts. And the question is, can we do that? No. Well, you never like a ‘no’.
|
||||
|
||||
> The question is whether we call this ready for broad public consumption on the hardware we want to support.
|
||||
|
||||
Usually, when you encounter a problem and you tackle it, and you start thinking how to solve the problem, that’s more beneficial than never hearing a no. That’s kind of what we were aiming for. Ubuntu 14.04 was a stretch goal – everyone was aware of that and we didn’t reach it. Fine, cool. Let’s go on.
|
||||
|
||||
So how do we stage ourself for the next cycle, until an LTS? Now we have this initiative where we have a daily testable image with Unity 8 and Mir. It’s not super usable because it’s just essentially the tethered UI that you are seeing there, but still it’s something that we didn’t have a year ago. And for me, that’s a huge gain.
|
||||
|
||||
And ultimately, before we can ship something, before any new display server can ship in an LTS release, you need to have buy-in from the GPU vendors. That’s what you need.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/interview-thomas-vos-of-mir/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Mike Saunders][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/author/mike/
|
||||
@ -1,131 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FOSS and the Fear Factor
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> "'Many eyes' is a complete and total myth," said SoylentNews' hairyfeet. "I bet my last dollar that if you looked at every.single.package. that makes up your most popular distros and then looked at how many have actually downloaded the source for those various packages, you'd find that there is less than 30 percent ... that are downloaded by anybody but the guys that actually maintain the things."
|
||||
|
||||
In a world that's been dominated for far too long by the [Systemd Inferno][1], Linux fans will have to be forgiven if they seize perhaps a bit too gleefully upon the scraps of cheerful news that come along on any given day.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, for cheerful news, there's never any better place to look than the [Reglue][2] effort. Run by longtime Linux advocate and all-around-hero-for-kids Ken Starks, as alert readers [may recall][3], Reglue just last week launched a brand-new [fundraising effort][4] on Indiegogo to support its efforts over the coming year.
|
||||
|
||||
Since 2005, Reglue has placed more than 1,600 donated and then refurbished computers into the homes of financially disadvantaged kids in Central Texas. Over the next year, it aims to place 200 more, as well as paying for the first 90 days of Internet connection for each of them.
|
||||
|
||||
"As overused as the term is, the 'Digital Divide' is alive and well in some parts of America," Starks explained. "We will bridge that divide where we can."
|
||||
|
||||
How's that for a heaping helping of hope and inspiration?
|
||||
|
||||
### Windows as Attack Vector ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Offering discouraged FOSS fans a bit of well-earned validation, meanwhile -- and perhaps even a bit of levity -- is the news that Russian hackers apparently have begun using Windows as a weapon against the rest of the world.
|
||||
|
||||
"Russian hackers use Windows against NATO" is the [headline][5] over at Fortune, making it plain for all the world to see that Windows isn't the bastion of security some might say it is.
|
||||
|
||||
The sarcasm is [knee-deep][6] in the comments section on Google+ over that one.
|
||||
|
||||
### 'Hackers Shake Confidence' ###
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, malicious hacking is no laughing matter, and the FOSS world has gotten a bitter taste of the effects for itself in recent months with the Heartbleed and Shellshock flaws, to name just two.
|
||||
|
||||
Has it been enough to scare Linux aficionados away?
|
||||
|
||||
That essentially is [the suggestion][7] over at Bloomberg, whose story, entitled "Hackers Shake Confidence in 1980s Free Software Idealism," has gotten more than a few FOSS fans' knickers in a twist.
|
||||
|
||||
### 'No Software Is Perfect' ###
|
||||
|
||||
"None of this has shaken my confidence in the slightest," asserted [Linux Rants][8] blogger Mike Stone down at the blogosphere's Broken Windows Lounge, for instance.
|
||||
|
||||
"I remember a time when you couldn't put a Windows machine on the network without firewall software or it would be infected with viruses/malware in seconds," he explained. "I don't recall the articles claiming that confidence had been shaken in Microsoft.
|
||||
|
||||
"The fact of the matter is that no software is perfect, not even FOSS, but it comes closer than the alternatives," Stone opined.
|
||||
|
||||
### 'My Faith Is Just Fine' ###
|
||||
|
||||
"It is hard to even begin to get into where the Bloomberg article fails," began consultant and [Slashdot][9] blogger Gerhard Mack.
|
||||
|
||||
"For one, decompilers have existed for ages and allow black hats to find flaws in proprietary software, so the black-hats can find problems but cannot admit they found them let alone fix them," Mack explained. "Secondly, it has been a long time since most open source was volunteer-written, and most contributions need to be paid.
|
||||
|
||||
"The author goes on to rip into people who use open source for not contributing monetarily, when most of the listed companies are already Linux Foundation members, so they are already contributing," he added.
|
||||
|
||||
In short, "my faith in open source is just fine, and no clickbait Bloomberg article will change that," Mack concluded.
|
||||
|
||||
### 'The Author Is Wrong' ###
|
||||
|
||||
"Clickbait" is also the term Google+ blogger Alessandro Ebersol chose to describe the Bloomberg account.
|
||||
|
||||
"I could not see the point the author was trying to make, except sensationalism and views," he told Linux Girl.
|
||||
|
||||
"The author is wrong," Ebersol charged. "He should educate himself on the topic. The flaws are results of lack of funding, and too many corporations taking advantage of free software and giving nothing back."
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover, "I still believe that a piece of code that can be studied and checked by many is far more secure than a piece made by a few," Google+ blogger Gonzalo Velasco C. chimed in.
|
||||
|
||||
"All the rumors that FLOSS is as weak as proprietary software are only [FUD][10] -- period," he said. "It is even more sad when it comes from private companies that drink in the FLOSS fountain."
|
||||
|
||||
### 'Source Helps Ensure Security' ###
|
||||
|
||||
Chris Travers, a [blogger][11] who works on the [LedgerSMB][12] project, had a similar view.
|
||||
|
||||
"I do think that having the source available helps ensure security for well-designed, well-maintained software," he began.
|
||||
|
||||
"Those of us who do development on such software must necessarily approach the security process under a different set of constraints than proprietary vendors do," Travers explained.
|
||||
|
||||
"Since our code changes are public, when we release a security fix this also provides effectively full disclosure," he said, "ensuring that the concerns for unpatched systems are higher than they would be for proprietary solutions absent full disclosure."
|
||||
|
||||
At the same time, "this disclosure cuts both ways, as software security vendors can use this to provide further testing and uncover more problems," Travers pointed out. "In the long run, this leads to more secure software, but in the short run it has security costs for users."
|
||||
|
||||
Bottom line: "If there is good communication with the community, if there is good software maintenance and if there is good design," he said, "then the software will be secure."
|
||||
|
||||
### 'Source Code Isn't Magic Fairy Dust' ###
|
||||
|
||||
SoylentNews blogger hairyfeet had a very different view.
|
||||
|
||||
"'Many eyes' is a complete and total myth," hairyfeet charged. "I bet my last dollar that if you looked at every.single.package. that makes up your most popular distros and then looked at how many have actually downloaded the source for those various packages, you'd find that there is less than 30 percent of the packages that are downloaded by anybody but the guys that actually maintain the things.
|
||||
|
||||
"How many people have done a code audit on Firefox? [LibreOffice][13]? Gimp? I bet you won't find a single one, because everybody ASSUMES that somebody else did it," he added.
|
||||
|
||||
"At the end of the day, Wall Street is finding out what guys like me have been saying for years: Source code isn't magic fairy dust that makes the bugs go away," hairyfeet observed.
|
||||
|
||||
### 'No One Actually Looked at It' ###
|
||||
|
||||
"The problem with [SSL][14] was that everyone assumed the code was good, but almost no one had actually looked at, so you never had the 'many eyeballs' making the bugs shallow," Google+ blogger Kevin O'Brien conceded.
|
||||
|
||||
Still, "I think the methodology and the idealism are separable," he suggested. "Open source is a way of writing software in which the value created for everyone is much greater than the value captured by any one entity, which is why it is so powerful.
|
||||
|
||||
"The idea that corporate contributions somehow sully the purity is a stupid idea," added O'Brien. "Corporate involvement is not inherently bad; what is bad is trying to lock other people out of the value created. Many companies handle this well, such as Red Hat."
|
||||
|
||||
### 'The Right Way to Do IT' ###
|
||||
|
||||
Last but not least, "my confidence in FLOSS is unshaken," blogger [Robert Pogson][15] declared.
|
||||
|
||||
"After all, I need software to run my computers, and as bad as some flaws are in FLOSS, that vulnerability pales into insignificance compared to the flaws in that other OS -- you know, the one that thinks images are executable and has so much complexity that no one, not even M$ with its $billions, can fix."
|
||||
|
||||
FOSS is "the right way to do IT," Pogson added. "The world can and does make its own software, and the world has more and better programmers than the big corporations.
|
||||
|
||||
"Those big corporations use FLOSS and should support FLOSS," he maintained, offering "thanks to the corporations who hire FLOSS programmers; sponsor websites, mirrors and projects; and who give back code -- the fuel in the FLOSS economy."
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/FOSS-and-the-Fear-Factor-81221.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Katherine Noyes
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.linuxinsider.com/perl/story/80980.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.reglue.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/78422.html
|
||||
[4]:https://www.indiegogo.com/projects/deleting-the-digital-divide-one-computer-at-a-time
|
||||
[5]:http://fortune.com/video/2014/10/14/russian-hackers-use-windows-against-nato/
|
||||
[6]:https://plus.google.com/+KatherineNoyes/posts/DQvRMekLHV4
|
||||
[7]:http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-10-14/hackers-shake-confidence-in-1980s-free-software-idealism.html
|
||||
[8]:http://linuxrants.com/
|
||||
[9]:http://slashdot.org/
|
||||
[10]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fear,_uncertainty_and_doubt
|
||||
[11]:http://ledgersmbdev.blogspot.com/
|
||||
[12]:http://www.ledgersmb.org/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.libreoffice.org/
|
||||
[14]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security
|
||||
[15]:http://mrpogson.com/
|
||||
@ -1,115 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Calculate Linux Provides Consistency by Design
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> Calculate Linux has a rather interesting strategy for desktop environments. It is characterized by two flavors with the same look and feel. That does not mean that the inherent functionality of the KDE and Xfce desktops are compromised. Rather, the Calculate Linux developers did what you seldom see within a Linux distribution with more than one desktop option: They unified the design.
|
||||
|
||||
Calculate Linux 14 is a distribution designed with home and SMB users in mind. It is optimized for rapid deployment in corporate environments as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Calculate gives users something no other Linux distro makes possible. The Xfce desktop session is customized to imitate the look of the [KDE][1] desktop environment.
|
||||
|
||||
This design approach goes a long way toward making Calculate Linux a one-distro-fits-all solution. Individual users or entire departments within an organization can fine-tune user preferences and features without changing the common appearance or performance.
|
||||
|
||||
Calculate Linux 14, developed by Alexander Tratsevskiy in Russia, is not your typical cookie-cutter type of Linux OS. This latest version, released Sept. 5, is a rolling-release distribution that provides a number of preconfigured features.
|
||||
|
||||
It uses a source-based approach to package management to optimize the software. This in part comes from its roots as a Gentoo Linux-based distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
Calculate Linux comes in three more versions to expand its reach. Calculate Directory Server is for servers, and Calculate Linux Scratch for building customized systems. The Calculate Media Center is a distro to run a home multimedia center.
|
||||
|
||||
### What's New ###
|
||||
|
||||
This latest version of Calculate ships with a few new features, including notification of software updates and an improved administration panel.
|
||||
|
||||
This release adds an improved graphical user interface for Calculate Utilities. It also provides various kernel and other software package updates.
|
||||
|
||||
It comes in 32-bit or 64-bit builds that include two desktop options for personal/business use: KDE and Xfce. A boot menu lets users choose to run the Calculate live desktop environment from RAM for added performance or with a command line interface only.
|
||||
|
||||
Why two choices? Users get better performance on low-end computers using the lightweight desktop environment that comes with Xfce. This is the second release containing this option. It solves the problem of not being able to run the KDE edition of Calculate Linux on underpowered hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
### Designing Details ###
|
||||
|
||||
Calculate Linux has a rather interesting strategy for desktop environments. It is characterized by two flavors with one common design.
|
||||
|
||||
That does not mean that the inherent functionality of the KDE and Xfce desktops are compromised. Rather, the Calculate Linux developers did what you seldom see within a Linux distribution with more than one desktop option.
|
||||
|
||||
Typically, KDE by design is much more animation based. By design, Xfce has fewer visual frills in keeping with its lightweight philosophy. Most KDE distributions place the panel bar at the bottom and do not have a Docky-style launcher anywhere in the desktop decor.
|
||||
|
||||
In Calculate Linux, a classic style application menu, task switcher and system tray are configured at the top of the screen in both desktop versions. At the bottom of the display, there is a hidden quick-launch bar that pops up when the mouse pointer strays toward the lower edge of the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
> 
|
||||
> Calculate Linux has a unified design that makes KDE and Xfce desktops look nearly the same. The panel and menu display are very nontraditional as seen in this KDE desktop view.
|
||||
|
||||
This duality ties the two desktops together. Both the KDE and the Xfce versions have right-click access to some of the most commonly used system commands and features.
|
||||
|
||||
### Look and Feel ###
|
||||
|
||||
Whether you run the KDE or the Xfce desktops, the panel design is the same. The menu falls from the top left corner as a single box with the same categories in both versions.
|
||||
|
||||
> 
|
||||
> The Xfce desktop in Calculate Linux is almost totally indistinguishable from its KDE counterpart.
|
||||
|
||||
Hover the mouse over the right edge of the menu box to see the category contents slide out to the right of the box. Only then do you see a varying range of applications to launch with a click.
|
||||
|
||||
The same operation governs the popup launcher bar hidden at the bottom of the screen. Some of the offerings are desktop-specific, however.
|
||||
|
||||
> 
|
||||
> Calculate Linux embeds a popup launch dock in both the KDE and Xfce desktop editions.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, the bottom dock in both desktop versions launches the Chromium Web browser, [LibreOffice][3], GIMP, SMPlayer and Leafpad (simple text editor). The KDE dock launches kcalc, digikam, Amarok and k3b disk burner. Xfce launches Galculator, Clementine and xfburn.
|
||||
|
||||
### Designed to Differ ###
|
||||
|
||||
One difference is the KDE version has an added button where expected along the upper right edge of the screen. It also has a Widgets button near the far right end of the top panel.
|
||||
|
||||
These provide access to the activities layout where you choose the style of desktop typical of KDE. These are: Grid, Newspaper, Folder, Grouping and Search & Launch.
|
||||
|
||||
A second style difference between the two desktop versions is the inclusion of widgets with the KDE version. These desktop widgets personalize the desktop items.
|
||||
|
||||
### Feature Folly ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Calculate Desktop edition, both KDE and Xfce, creates a user profile when it loads. This profile is fully integrated with Calculate Directory Server. Roaming profiles also are supported. Auto-tuning applications at logon are based on the server settings.
|
||||
|
||||
The approach greatly simplifies the setup and maintenance roles for users with no IT department to support the computer system. The desktop version functions simply as a standalone operating system. No server is needed. However, enterprise and SMB environments can pair the desktop version with the server version for seamless integration.
|
||||
|
||||
Either way, the common set of toolbars, desktop applications and basic settings are easier to configure for desktop and server use, regardless of the desktop environment choice.
|
||||
|
||||
You can install Calculate Linux on a USB thumb drive or a USB hard drive with a choice of these volume formats: ext4, ext3, ext2, reiserfs, btrfs, xfs, jfs, nilfs2 or fat32.
|
||||
|
||||
### Gentler Gentoo ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Gentoo distro in its own right installs applications compiled from source. It uses a software packaging system called "Portage" to semi-automate this process. It also uses the command-line compiling system run by Emerge.
|
||||
|
||||
Calculate's developers soften this Gentoo-based software compiling process somewhat, but it is still more complex than using a community-managed automated software binary repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Calculate Linux is fully compatible with Gentoo repositories and support for binary repository updates. System files are updated via Portage throughout the distribution life cycle.
|
||||
|
||||
### Bottom Line ###
|
||||
|
||||
Calculate Linux is a well-tooled Linux distro that makes consistency in design job number one. It is highly configurable and is optimized for nearly every computing circumstance.
|
||||
|
||||
It runs a full-blown KDE desktop on upper-end hardware, and provides the same look and feel with Xfce on low-end gear. Calculate Linux runs from a hard drive installation or by loading directly into RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
It could offer home and SMB users an effective distro alternative. However, typical for Gentoo-based distros, Calculate Linux's weak point is the lack of a full-fledged binary software repository system.
|
||||
|
||||
### Want to Suggest a Review? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Is there a Linux software application or distro you'd like to suggest for review? Something you love or would like to get to know?
|
||||
|
||||
Please [email your ideas to me][4], and I'll consider them for a future Linux Picks and Pans column.
|
||||
|
||||
And use the Talkback feature below to add your comments!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/Calculate-Linux-Provides-Consistency-by-Design-81242.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Jack M. Germain
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.calculate-linux.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.kde.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.libreoffice.org/
|
||||
[4]:jack.germain@newsroom.ectnews.com
|
||||
@ -1,136 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Debian's Civil War: Has It Really Come to This?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**"The 'new' Debian would be rather weak," said blogger Robert Pogson. "Would it have the hundreds of mirrors that make Debian wonderful? I doubt that. Debian is a great distro. Disemboweling it out of spite is just wrong. Why can't we come to some amicable agreement? Why do we have to race at full speed to the edge of a cliff when we don't know if we can stop?"**
|
||||
|
||||
Well it seems no matter how loudly we here in the Linux blogosphere try to hum a happy tune or discuss [cheerful FOSS matters][1], we just can't seem to drown out the shouts and screams coming from those standing too close to the Systemd Inferno.
|
||||
|
||||
Stand back, people! It's dangerous!
|
||||
|
||||
The embers, of course, [had been hot][2] for some time already before the blaze [flared sky-high][3] a few months ago. Now, the conflagration appears to be completely out of control.
|
||||
|
||||
Need proof? Two words: [Debian fork][4].
|
||||
|
||||
That's right: Debian, the granddaddy of Linux distributions and embodiment of everything so many FOSS fans hold dear, may be forked, and it's apparently all because of Systemd.
|
||||
|
||||
A more upsetting development would be hard to conceive.
|
||||
|
||||
### 'Roll Up Your Sleeves' ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
"Debian today is haunted by the tendency to betray its own mandate, a base principle of the Free Software movement: put the user's rights first," explained the anonymous developers behind the Debian Fork site. "What is happening now instead is that through a so-called 'do-ocracy,' developers and package maintainers are imposing their choices on users."
|
||||
|
||||
Their conclusion: "Roll up your sleeves, we may need to fork Debian."
|
||||
|
||||
Quick as a flash, [word traveled][5] to [Slashdot][6], [LXer][7] and beyond.
|
||||
|
||||
Down at the Linux blogosphere's Punchy Penguin Saloon, a profound hush fell as soon as the news arrived. Fortunately, it lasted only a fraction of a second.
|
||||
|
||||
### 'I Say Go for It' ###
|
||||
|
||||
"Freedom of choice implies the freedom to be a complete idiot, and clearly Free Software has its share," Google+ blogger Kevin O'Brien said.
|
||||
|
||||
"I have been skeptical about Systemd, but I have trouble believing there are enough people this crazy to actually pull off a fork of Debian," O'Brien added. "I predict a year from now we won't remember what this was all about."
|
||||
|
||||
On the other hand: "I say go for it if you're that passionate about it," offered [Linux Rants][8] blogger Mike Stone. "This is Linux we're talking about, after all, and Linux is open source. Anybody should always feel free to do what they want with Linux, as long as they're willing to share.
|
||||
|
||||
"The fact that SysVinit will still be available on standard Debian kind of makes forking it over Systemd seem a little silly, but I'm not going to stand in the way of anybody that wants to fork any FOSS for their own use," Stone added.
|
||||
|
||||
Indeed, "Linux's strength is also its Achilles' Heel," Google+ blogger Rodolfo Saenz opined. 'In the Linux world, forking is inevitable. It is part of Linux's evolution."
|
||||
|
||||
### 'A Lot of Misinformation' ###
|
||||
|
||||
At the same time, "I think if they were likely to actually fork Debian, they would have just gone and done it rather than throw a massive public temper tantrum," consultant and Slashdot blogger Gerhard Mack suggested.
|
||||
|
||||
"Secondly, I think there is a lot of misinformation out there about what Systemd does and how it works," Mack added. 'At the beginning of all of this I was very worried about the stability and security of the systems I maintain after reading the nerd rage on Slashdot, The Register, and sites like [Boycott Systemd][9], so I looked into Systemd for myself.
|
||||
|
||||
"What I have discovered is that they seem to be confusing Systemd with things that are bundled with Systemd but run separately using a 'least privilege needed for the task' type design," he explained. "There are things I don't like, such as the binary logs, but then I can just configure it to run through syslogd as usual and ignore the binary logs."
|
||||
|
||||
Particularly "hilarious," Mack added, is that people "suggest that only desktops need to boot quickly," he said. "I have seen some automated systems that load VMs on demand, and they would be much more effective if they booted faster."
|
||||
|
||||
### 'I'm Really Confused' ###
|
||||
|
||||
It will be "a sad day if Debian forks over this Systemd thing," longtime Debian user [Robert Pogson][10] told Linux Girl.
|
||||
|
||||
"I am one of the haters, I guess," Pogson said. "I see adopting Systemd as something that kept Jessie's bug count high for months. I just don't see the need for it. I've read that some desktop users complain that Systemd is all for server users and I've read that some server users complain that Systemd is all for desktop users. I'm both and I'm really confused."
|
||||
|
||||
Meanwhile, "do I need to learn a lot about Systemd to use it?" Pogson wondered. "I'm too old to learn too many new tricks. Does it give me any benefits, or is it just a nuisance?
|
||||
|
||||
"I see faster booting as a rather small benefit for a lot of nuisance value like binary logs... what's with that?" he added. "I've learned to use grep on current logs to get what I need. Hiding them is just making GNU/Linux more like that other OS. Yuck!"
|
||||
|
||||
### 'Nonfree Software Is the Real Enemy' ###
|
||||
|
||||
Debian is an organization of roughly a thousand developers, Pogson pointed out.
|
||||
|
||||
"They work hard and make the world a better place," he said. "Forcing them to choose which fork to take is really cruel and unusual punishment for such generous people. If the fork is 50/50, Debian might take years of recruitment to recover. That does no one any good.
|
||||
|
||||
"The 'new' Debian would be rather weak," Pogson added. "Would it have the hundreds of mirrors that make Debian wonderful? I doubt that. Debian is a great distro. Disemboweling it out of spite is just wrong. Why can't we come to some amicable agreement? Why do we have to race at full speed to the edge of a cliff when we don't know if we can stop?"
|
||||
|
||||
Bottom line: "If this civil war gets any worse, I may switch back to Debian Stable/Wheezy, my 'bomb shelter,' in the hope that I can wait for peace to break out," he concluded. "I don't need the drama. Bill Gates must be laughing at this waste of energy. Nonfree software is the real enemy -- not folks building/using Debian GNU/Linux."
|
||||
|
||||
### 'It Is What Happens' ###
|
||||
|
||||
It is a sad development, Google+ blogger Gonzalo Velasco C. agreed.
|
||||
|
||||
At the same time, "it is what happens in the FLOSS world when you don't listen to your peers and users and listen to others that have their own (commercial) agenda and 'suggest' you use a tool as hungry as Systemd, regardless of its merits and modernism comparing to old sisVinit," he said.
|
||||
|
||||
"There are a lot of technical discussions and arguments out there, and Debian must show it is neither deaf nor blind and re-discuss the issue," he added.
|
||||
|
||||
### Red Hat's Influence ###
|
||||
|
||||
"Do the users wish to be beholden to [Red Hat's][11] corporate roadmap? If the answer is 'no,' then a fork is the only choice left open, as it's pretty plain to see that Debian will go Systemd whether their users like it or not," SoylentNews blogger hairyfeet said.
|
||||
|
||||
"It all comes down to cloud computing, and RH intends to foist its version of SVCHOSTS for Linux onto Debian and Ubuntu," he added. "The reason why is obvious: it gives them pretty much every major Linux distro, as they are nearly all built on RH, Debian or Ubuntu."
|
||||
|
||||
So, the answer is simple, hairyfeet said: "If you want RH calling the shots, then stay; if not, fork."
|
||||
|
||||
### 'Seems Like a Lot of Work' ###
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, there's nothing to prevent a fork, Google+ blogger Brett Legree pointed out.
|
||||
|
||||
"If someone wants to do it, that's their choice," he noted.
|
||||
|
||||
"Seems like a lot of work, though," Legree added. "I mean, I figure that most people wouldn't care either way what init system is being used, and those who do know can probably figure out how to configure Debian (or whatever) to use a different init system. That's been possible up to now, and I'd expect it will continue to be so."
|
||||
|
||||
Forks are a lot of work to maintain, agreed Chris Travers, a [blogger][12] who works on the [LedgerSMB][13] project.
|
||||
|
||||
"Trust me -- I know from experience, as LedgerSMB began life as a fork of SQL-Ledger," Travers said.
|
||||
|
||||
Still, "there are huge differences in philosophy between init scripts and Systemd, and this is an area where there is probably room for a good Unix-like distro to keep the old ways," Travers said. "There are certainly worse things than forks developing. This being said, I wonder if people who really want Unix should instead switch to the BSDs."
|
||||
|
||||
### 'Like Killing Mosquitoes With Shotguns' ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Debian community was not aware of everything the changes in the init system would bring, Google+ blogger Alessandro Ebersol suggested. "They thought it was a non-issue."
|
||||
|
||||
Now that "a large number of Debian sysadmins are not pleased," however, forking would be "an extreme measure," he said, "and a last resort. There are still a lot of things that can be done."
|
||||
|
||||
After all, Debian is "the GNU/Linux that runs on anything, in any *nix setup -- remember the Debian BSD flavor, and that Debian BSD will have to be accommodated to work with the new init system," Ebersol pointed out.
|
||||
|
||||
"So, I believe all is not lost for Debian, but a fork, right now, is too extreme, like killing mosquitoes with shotguns," he concluded. "There's still time and place to make peace and amendments in the Debian community."
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/81262.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Katherine Noyes][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://twitter.com/noyesk
|
||||
[1]:http://www.reglue.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/80472.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/80980.html
|
||||
[4]:http://debianfork.org/
|
||||
[5]:http://linux.slashdot.org/story/14/10/20/1944226/debians-systemd-adoption-inspires-threat-of-fork
|
||||
[6]:http://slashdot.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://lxer.com/module/forums/t/35625/
|
||||
[8]:http://linuxrants.com/
|
||||
[9]:http://boycottsystemd.org/
|
||||
[10]:http://mrpogson.com/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.redhat.com/
|
||||
[12]:http://ledgersmbdev.blogspot.com/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.ledgersmb.org/
|
||||
@ -1,92 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[translating by KayGuoWhu]
|
||||
A brief history of Linux malware
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A look at some of the worms and viruses and Trojans that have plagued Linux throughout the years.
|
||||
|
||||
### Nobody’s immune ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Although not as common as malware targeting Windows or even OS X, security threats to Linux have become both more numerous and more severe in recent years. There are a couple of reasons for that – the mobile explosion has meant that Android (which is Linux-based) is among the most attractive targets for malicious hackers, and the use of Linux as a server OS for and in the data center has also grown – but Linux malware has been around in some form since well before the turn of the century. Have a look.
|
||||
|
||||
### Staog (1996) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The first recognized piece of Linux malware was Staog, a rudimentary virus that tried to attach itself to running executables and gain root access. It didn’t spread very well, and it was quickly patched out in any case, but the concept of the Linux virus had been proved.
|
||||
|
||||
### Bliss (1997) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If Staog was the first, however, Bliss was the first to grab the headlines – though it was a similarly mild-mannered infection, trying to grab permissions via compromised executables, and it could be deactivated with a simple shell switch. It even kept a neat little log, [according to online documentation from Ubuntu][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### Ramen/Cheese (2001) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cheese is the malware you actually want to get – certain Linux worms, like Cheese, may actually have been beneficial, patching the vulnerabilities the earlier Ramen worm used to infect computers in the first place. (Ramen was so named because it replaced web server homepages with a goofy image saying that “hackers looooove noodles.”
|
||||
|
||||
### Slapper (2002) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The Slapper worm struck in 2002, infecting servers via an SSL bug in Apache. That predates Heartbleed by 12 years, if you’re keeping score at home.
|
||||
|
||||
### Badbunny (2007) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Badbunny was an OpenOffice macro worm that carries a sophisticated script payload that worked on multiple platforms – even though the only effect of a successful infection was to download a raunchy pic of a guy in a bunny suit, er, doing what bunnies are known to do.
|
||||
|
||||
### Snakso (2012) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Image courtesy [TechWorld UK][2]
|
||||
|
||||
The Snakso rootkit targeted specific versions of the Linux kernel to directly mess with TCP packets, injecting iFrames into traffic generated by the infected machine and pushing drive-by downloads.
|
||||
|
||||
### Hand of Thief (2013) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Hand of Thief is a commercial (sold on Russian hacker forums) Linux Trojan creator that made quite a splash when it was introduced last year. RSA researchers, however, discovered soon after that [it wasn’t quite as dangerous as initially thought][3].
|
||||
|
||||
### Windigo (2014) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Image courtesy [freezelight][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Windigo is a complex, large-scale cybercrime operation that targeted tens of thousands of Linux servers, causing them to produce spam and serve drive-by malware and redirect links. It’s still out there, according to ESET security, [so admins should tread carefully][5].
|
||||
|
||||
### Shellshock/Mayhem (2014) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Striking at the terminal strikes at the heart of Linux, which is why the recent Mayhem attacks – which targeted the so-called Shellshock vulnerabilities in Linux’s Bash command-line interpreter using a specially crafted ELF library – were so noteworthy. Researchers at Yandex said that the network [had snared 1,400 victims as of July][6].
|
||||
|
||||
### Turla (2014) ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A large-scale campaign of cyberespionage emanating from Russia, called Epic Turla by researchers, was found to have a new Linux-focused component earlier this week. It’s apparently [based on a backdoor access program from all the way back in 2000 called cd00r][7].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.networkworld.com/article/2858742/linux/a-brief-history-of-linux-malware.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jon Gold][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.networkworld.com/author/Jon-Gold/
|
||||
[1]:https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Linuxvirus
|
||||
[2]:http://news.techworld.com/security/3412075/linux-users-targeted-by-mystery-drive-by-rootkit/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.networkworld.com/article/2168938/network-security/dangerous-linux-trojan-could-be-sign-of-things-to-come.html
|
||||
[4]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/63056612@N00/155554663
|
||||
[5]:http://www.welivesecurity.com/2014/04/10/windigo-not-windigone-linux-ebury-updated/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.pcworld.com/article/2825032/linux-botnet-mayhem-spreads-through-shellshock-exploits.html
|
||||
[7]:http://www.computerworld.com/article/2857129/turla-espionage-operation-infects-linux-systems-with-malware.html
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
Translating by ZTinoZ
|
||||
20 Linux Commands Interview Questions & Answers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Q:1 How to check current run level of a linux server ?**
|
||||
@ -140,4 +141,4 @@ via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/20-linux-commands-interview-questions-answers/
|
||||
[17]:
|
||||
[18]:
|
||||
[19]:
|
||||
[20]:
|
||||
[20]:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Docker CTO Solomon Hykes to Devs: Have It Your Way
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**"We made a very conscious effort with Docker to insert the technology into an existing toolbox. We did not want to turn the developer's world upside down on the first day. ... We showed them incremental improvements so that over time the developers discovered more things they could do with Docker. So the developers could transition into the new architecture using the new tools at their own pace."**
|
||||
|
||||
[Docker][1] in the last two years has moved from an obscure Linux project to one of the most popular open source technologies in cloud computing.
|
||||
|
||||
Project developers have witnessed millions of Docker Engine downloads. Hundreds of Docker groups have formed in 40 countries. Many more companies are announcing Docker integration. Even Microsoft will ship Windows 10 with Docker preinstalled.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Solomon Hykes
|
||||
Founder and CTO of Docker
|
||||
|
||||
"That caught a lot of people by surprise," Docker founder and CTO Solomon Hykes told LinuxInsider.
|
||||
|
||||
Docker is an open platform for developers and sysadmins to build, ship and run distributed applications. It uses a Docker engine along with a portable, lightweight runtime and packaging tool. It also needs the Docker Hub and a cloud service for sharing applications and automating workflows.
|
||||
|
||||
Docker provides a vehicle for developers to quickly assemble their applications from components. It eliminates the friction between development, quality assurance and production environments. Thus, IT can ship applications faster and run them unchanged on laptops, on data center virtual machines, and in any cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
In this exclusive interview, LinuxInsider discusses with Solomon Hykes why Docker is revitalizing Linux and the cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
**LinuxInsider: You have said that Docker's success is more the result of being in the right place at the right time for a trend that's much bigger than Docker. Why is that important to users?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Solomon Hykes**: There is always an element of being in the right place at the right time. We worked on this concept for a long time. Until recently, the market was not ready for this kind of technology. Then it was, and we were there. Also, we were very deliberate to make the technology flexible and very easy to get started using.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: Is Docker a new cloud technology or merely a new way to do cloud storage?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: Containers in themselves are just an enabler. The really big story is how it changes the software model enormously. Developers are creating new kinds of applications. They are building applications that do not run on only one machine. There is a need for completely new architecture. At the heart of that is independence from the machine.
|
||||
|
||||
The problem for the developer is to create the kind of software that can run independently on any kind of machine. You need to package it up so it can be moved around. You need to cross that line. That is what containers do.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: How analogous is the software technology to traditional cargo shipping in containers?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: That is a very apt example. It is the same thing for shipping containers. The innovation is not in the box. It is in how the automation handles millions of those boxes moving around. That is what is important.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: How is Docker affecting the way developers build their applications?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: The biggest way is it helps them structure their applications for a better distributive system. Another distributive application is Gmail. It does not run on just one application. It is distributive. Developers can package the application as a series of services. That is their style of reasoning when they design. It brings the tooling up to the level of design.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: What led you to this different architecture approach?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: What is interesting about this process is that we did not invent this model. It was there. If you look around, you see this trend where developers are increasingly building distributive applications where the tooling is inadequate. Many people have tried to deal with the existing tooling level. This is a new architecture. When you come up with tools that support this new model, the logical thing to do is tell the developer that the tools are out of date and are inadequate. So throw away the old tools and here are the new tools.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: How much friction did you encounter from developers not wanting to throw away their old tools?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: That approach sounds perfectly reasonable and logical. But in fact it is very hard to get developers to throw away their tools. And for IT departments the same thing is very true. They have legacy performance to support. So most of these attempts to move into next-generation tools have failed. They ask too much of the developers from day one.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: How did you combat that reaction from developers?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: We made a very conscious effort with Docker to insert the technology into an existing toolbox. We did not want to turn the developer's world upside down on the first day. Instead, we showed them incremental improvements so that over time the developers discovered more things they could do with Docker. So the developers could transition into the new architecture using the new tools at their own pace. That makes all the difference in the world.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: What reaction are you seeing from this strategy?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: When I ask people using Docker today how revolutionary it is, some say they are not using it in a revolutionary way. It is just a little improvement in my toolbox. That is the point. Others say that they jumped all in on the first day. Both responses are OK. Everyone can take their time moving toward that new model.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: So is it a case of integrating Docker into existing platforms, or is a complete swap of technology required to get the full benefit?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: Developers can go either way. There is a lot of demand for Docker native. But there is a whole ecosystem of new tools and companies competing to build brand new platforms entirely build on top of Docker. Over time the world is trending towards Docker native, but there is no rush. We totally support the idea of developers using bits and pieces of Docker in their existing platform forever. We encourage that.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: What about Docker's shared Linux kernel architecture?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: There are two steps involved in answering that question. What Docker does is become a layer on top of the Linux kernel. It exposes an abstraction function. It takes advantage of the underlying system. It has access to all of the Linux features. It also takes advantage of the networking stack and the storage subsystem. It uses the abstraction feature to map what developers need.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: How detailed a process is this for developers?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: As a developer, when I make an application I need a run-time that can run my application in a sandbox environment. I need a packaging system that makes it easy to move it around to other machines. I need a networking model that allows my application to talk to the outside world. I need storage, etc. We abstract ... the gritty details of whatever the kernel does right now.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: Why does this benefit the developer?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: There are two really big advantages to that. The first is simplicity. Developers can actually be productive now because that abstraction is easier for them to comprehend and is designed for that. The system APIs are designed for the system. What the developer needs is a consistent abstraction that works everywhere.
|
||||
|
||||
The second advantage is that over time you can support more systems. For example, early on Docker could only work on a single distribution of Linux under very narrow versions of the kernel. Over time, we expanded the surface area for the number of systems out there that Docker supports natively. So now you can run Docker on every major Linux distribution and in combination with many more networking and storage features.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: Does this functionality trickle down to nondevelopers, or is the benefit solely targeting developers?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: Every time we expand that surface area, every single developer that uses the Docker abstraction benefits from that too. So every application running Docker gets the added functionality every time the Docker community adds to the expansion. That is the thing that benefits all users. Without that universal expansion, every single developer would not have time to invest to update. There is just too much to support.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: What about Microsoft's recent announcement that it was shipping Docker support with Windows?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: If you think of Docker as a very narrow and very simple tool, then why would you roll out support for Windows? The whole point is that over time, you can expand the reach of that abstraction. Windows works very differently, obviously. But now that Microsoft has committed to adding features to Windows 10, it exposes the functionality required to run Docker. That is real exciting.
|
||||
|
||||
Docker still has to be ported to Windows, but Microsoft has committed to contributing in a major way to the port. Realize how far Microsoft has come in doing this. Microsoft is doing this fully upstream in a completely native, open source way. Everyone installing Windows 10 will get Docker preinstalled.
|
||||
|
||||
**LI: What lies ahead for growing Docker's feature set and user base?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Hykes**: The community has a lot of features on the drawing board. Most of them have to do with more improved tools for developers to build better distributive applications. A toolkit implies having a series of tools with each tool designed for one job.
|
||||
|
||||
In each of these subsystems, there is a need for new tools. In each of these areas, you will see an enormous amount of activity in the community in terms of contributions and designs. In that regard, the Docker project is enormously ambitious. The ability to address each of these areas will ensure that developers have a huge array of choices without fragmentation.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxinsider.com/story/Docker-CTO-Solomon-Hykes-to-Devs-Have-It-Your-Way-81504.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Jack M. Germain
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://www.docker.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
Linus Tells Wired Leap Second Irrelevant
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Two larger publications today featured Linux and the effect of the upcoming leap second. The Register today said that the leap second effects of the past are no longer an issue. Coincidentally, Wired talked to Linus Torvalds about the same issue today as well.
|
||||
|
||||
**Linus Torvalds** spoke with Wired's Robert McMillan about the approaching leap second due to be added in June. The Register said the last leap second in 2012 took out Mozilla, StumbleUpon, Yelp, FourSquare, Reddit and LinkedIn as well as several major airlines and travel reservation services that ran Linux. Torvalds told Wired today that the kernel is patched and he doesn't expect too many issues this time around. [He said][1], "Just take the leap second as an excuse to have a small nonsensical party for your closest friends. Wear silly hats, get a banner printed, and get silly drunk. That’s exactly how relevant it should be to most people."
|
||||
|
||||
**However**, The Register said not everyone agrees with Torvalds' sentiments. They quote Daily Mail saying, "The year 2015 will have an extra second — which could wreak havoc on the infrastructure powering the Internet," then remind us of the Y2K scare that ended up being a non-event. The Register's Gavin [Clarke concluded][2]:
|
||||
|
||||
> No reason the Penguins were caught sans pants.
|
||||
|
||||
> Now they've gone belt and braces.
|
||||
|
||||
The take-away is: move along, nothing to see here.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/linus-tells-wired-leap-second-irrelevant
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Susan Linton][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ostatic.com/member/susan-linton
|
||||
[1]:http://www.wired.com/2015/01/torvalds_leapsecond/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.theregister.co.uk/2015/01/09/leap_second_bug_linux_hysteria/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
diff -u: What's New in Kernel Development
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**David Drysdale** wanted to add Capsicum security features to Linux after he noticed that FreeBSD already had Capsicum support. Capsicum defines fine-grained security privileges, not unlike filesystem capabilities. But as David discovered, Capsicum also has some controversy surrounding it.
|
||||
|
||||
Capsicum has been around for a while and was described in a USENIX paper in 2010: [http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/research/security/capsicum/papers/2010usenix-security-capsicum-website.pdf][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Part of the controversy is just because of the similarity with capabilities. As Eric Biderman pointed out during the discussion, it would be possible to implement features approaching Capsicum's as an extension of capabilities, but implementing Capsicum directly would involve creating a whole new (and extensive) abstraction layer in the kernel. Although David argued that capabilities couldn't actually be extended far enough to match Capsicum's fine-grained security controls.
|
||||
|
||||
Capsicum also was controversial within its own developer community. For example, as Eric described, it lacked a specification for how to revoke privileges. And, David pointed out that this was because the community couldn't agree on how that could best be done. David quoted an e-mail sent by Ben Laurie to the cl-capsicum-discuss mailing list in 2011, where Ben said, "It would require additional book-keeping to find and revoke outstanding capabilities, which requires knowing how to reach capabilities, and then whether they are derived from the capability being revoked. It also requires an authorization model for revocation. The former two points mean additional overhead in terms of data structure operations and synchronisation."
|
||||
|
||||
Given the ongoing controversy within the Capsicum developer community and the corresponding lack of specification of key features, and given the existence of capabilities that already perform a similar function in the kernel and the invasiveness of Capsicum patches, Eric was opposed to David implementing Capsicum in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
But, given the fact that capabilities are much coarser-grained than Capsicum's security features, to the point that capabilities can't really be extended far enough to mimic Capsicum's features, and given that FreeBSD already has Capsicum implemented in its kernel, showing that it can be done and that people might want it, it seems there will remain a lot of folks interested in getting Capsicum into the Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes it's unclear whether there's a bug in the code or just a bug in the written specification. Henrique de Moraes Holschuh noticed that the Intel Software Developer Manual (vol. 3A, section 9.11.6) said quite clearly that microcode updates required 16-byte alignment for the P6 family of CPUs, the Pentium 4 and the Xeon. But, the code in the kernel's microcode driver didn't enforce that alignment.
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, Henrique's investigation uncovered the fact that some Intel chips, like the Xeon X5550 and the second-generation i5 chips, needed only 4-byte alignment in practice, and not 16. However, to conform to the documented specification, he suggested fixing the kernel code to match the spec.
|
||||
|
||||
Borislav Petkov objected to this. He said Henrique was looking for problems where there weren't any. He said that Henrique simply had discovered a bug in Intel's documentation, because the alignment issue clearly wasn't a problem in the real world. He suggested alerting the Intel folks to the documentation problem and moving on. As he put it, "If the processor accepts the non-16-byte-aligned update, why do you care?"
|
||||
|
||||
But, as H. Peter Anvin remarked, the written spec was Intel's guarantee that certain behaviors would work. If the kernel ignored the spec, it could lead to subtle bugs later on. And, Bill Davidsen said that if the kernel ignored the alignment requirement, and "if the requirement is enforced in some future revision, and updates then fail in some insane way, the vendor is justified in claiming 'I told you so'."
|
||||
|
||||
The end result was that Henrique sent in some patches to make the microcode driver enforce the 16-byte alignment requirement.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/diff-u-whats-new-kernel-development-6
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Zack Brown][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/user/801501
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cl.cam.ac.uk/research/security/capsicum/papers/2010usenix-security-capsicum-website.pdf
|
||||
81
sources/talk/20150114 Why Mac users don't switch to Linux.md
Normal file
81
sources/talk/20150114 Why Mac users don't switch to Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
||||
Why Mac users don’t switch to Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux and Mac users share at least one common thing: they prefer not to use Windows. But after that the two groups part company and tend to go their separate ways. But why don’t more Mac users switch to Linux? Is there something that prevents Mac users from making the jump?
|
||||
|
||||
[Datamation took a look at these questions][1] and tried to answer them. Datamation’s conclusion was that it’s really about the applications and workflow, not the operating system:
|
||||
|
||||
> …there are some instances where replacing existing applications with new options isn’t terribly practical – both in workflow and in overall functionality. This is an area where, sadly, Apple has excelled in. So while it’s hardly “impossible” to get around these issues, they are definitely a large enough challenge that it will give the typical Mac enthusiast pause.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> But outside of Web developers, honestly, I don’t see Mac users “en masse,” seeking to disrupt their workflows for the mere idea of avoiding the upgrade to OS X Yosemite. Granted, having seen Yosemite up close – Mac users who are considered power users will absolutely find this change-up to be hideous. However, despite poor OS X UI changes, the core workflow for existing Mac users will remain largely unchanged and unchallenged.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> No, I believe Linux adoption will continue to be sporadic and random. Ever-growing, but not something that is easily measured or accurately calculated.
|
||||
|
||||
I agree to a certain extent with Datamation’s take on the importance of applications and workflows, both things are important and matter in the choice of a desktop operating system. But I think there’s something more going on with Mac users than just that. I believe that there’s a different mentality that exists between Linux and Mac users, and I think that’s the real reason why many Mac users don’t switch to Linux.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### It’s all about control for Linux users ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux users tend to want control over their computing experience, they want to be able to change things to make them the way that they want them. One simply cannot do that in the same way with OS X or any other Apple products. With Apple you get what they give you for the most part.
|
||||
|
||||
For Mac (and iOS) users this is fine, they seem mostly content to stay within Apple’s walled garden and live according to whatever standards and options Apple gives them. But this is totally unacceptable to most Linux users. People who move to Linux usually come from Windows, and it’s there that they develop their loathing for someone else trying to define or control their computing experiences.
|
||||
|
||||
And once someone like that has tasted the freedom that Linux offers, it’s almost impossible for them to want to go back to living under the thumb of Apple, Microsoft or anyone else. You’d have to pry Linux from their cold, dead fingers before they’d accept the computing experience created for them Apple or Microsoft.
|
||||
|
||||
But you won’t find that same determination to have control among most Mac users. For them it’s mostly about getting the most out of whatever Apple has done with OS X in its latest update. They tend to adjust fairly quickly to new versions of OS X and even when unhappy with Apple’s changes they seem content to continue living within Apple’s walled garden.
|
||||
|
||||
So the need for control is a huge difference between Mac and Linux users. I don’t see it as a problem though since it just reflects the reality of two very different attitudes toward using computers.
|
||||
|
||||
### Mac users need Apple’s support mechanisms ###
|
||||
|
||||
Linux users are also different in the sense that they don’t mind getting their hands dirty by getting “under the hood” of their computers. Along with control comes the personal responsibility of making sure that their Linux systems work well and efficiently, and digging into the operating system is something that many Linux users have no problem doing.
|
||||
|
||||
When a Linux user needs to fix something, chances are they will attempt to do so immediately themselves. If that doesn’t work then they’ll seek additional information online from other Linux users and work through the problem until it has been resolved.
|
||||
|
||||
But Mac users are most likely not going to do that to the same extent. That is probably one of the reasons why Apple stores are so popular and why so many Mac users opt to buy Apple Care when they get a new Mac. A Mac user can simply take his or her computer to the Apple store and ask someone to fix it for them. There they can belly up to the Genius Bar and have their computer looked at by someone Apple has paid to fix it.
|
||||
|
||||
Most Linux users would blanche at the thought of doing such a thing. Who wants some guy you don’t even know to lay hands on your computer and start trying to fix it for you? Some Linux users would shudder at the very idea of such a thing happening.
|
||||
|
||||
So it would be hard for a Mac user to switch to Linux and suddenly be bereft of the support from Apple that he or she was used to getting in the past. Some Mac users might feel very vulnerable and uncertain if they were cut off from the Apple mothership in terms of support.
|
||||
|
||||
### Mac users love Apple’s hardware ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Datamation article focused on software, but I believe that hardware also matters to Mac users. Most Apple customers tend to love Apple’s hardware. When they buy a Mac, they aren’t just buying it for OS X. They are also buying Apple’s industrial design expertise and that can be an important differentiator for Mac users. Mac users are willing to pay more because they perceive that the overall value they are getting from Apple for a Mac is worth it.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux users, on the other hand, seem less concerned by such things. I think they tend to focus more on cost and less on the looks or design of their computer hardware. For them it’s probably about getting the most value from the hardware at the lowest cost. They aren’t in love with the way their computer hardware looks in the same way that some Mac users probably are, and so they don’t make buying decisions based on it.
|
||||
|
||||
I think both points of view on hardware are equally valid. It ultimately gets down to the needs of the individual user and what matters to them when they choose to buy or, in the case of some Linux users, build their computer. Value is the key for both groups, and each has its own perceptions of what constitutes real value in a computer.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course it is [possible to run Linux on a Mac][2], directly or indirectly via virtual machine. So a user that really liked Apple’s hardware does have the option of keeping their Mac but installing Linux on it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Too many Linux distros to choose from? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Another reason that might make it hard for a Mac user to move to Linux is the sheer number of distributions to choose from in the world of Linux. While most Linux users probably welcome the huge diversity of distros available, it could also be very confusing for a Mac user who hasn’t learned to navigate those choices.
|
||||
|
||||
Over time I think a Mac user would learn and adjust by figuring out which distribution worked best for him or her. But in the short term it might be a very daunting hurdle to overcome after being used to OS X for a long period of time. I don’t think it’s insurmountable, but it’s definitely something that is worth mentioning here.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course we do have helpful resources like [DistroWatch][3] and even my own [Desktop Linux Reviews][4] blog that can help people find the right Linux distribution. Plus there are many articles available about “the best Linux distro” and that sort of thing that Mac users can use as resources when trying to figure out the distribution they want to use.
|
||||
|
||||
But one of the reasons why Apple customers buy Macs is the simplicity and all-in-one solution that they offer in terms of the hardware and software being unified by Apple. So I am not sure how many Mac users would really want to spend the time trying to find the right Linux distribution. It might be something that puts them off really considering the switch to Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### Mac users are apples and Linux users are oranges ###
|
||||
|
||||
I see nothing wrong with Mac and Linux users going their separate ways. I think we’re just talking about two very different groups of people, and it’s a good thing that both groups can find and use the operating system and software that they prefer. Let Mac users enjoy OS X and let Linux users enjoy Linux, and hopefully both groups will be happy and content with their computers.
|
||||
|
||||
Every once in a while a Mac user might stray over to Linux or vice versa, but for the most part I think the two groups live in different worlds and mostly prefer to stay separate and apart from one another. I generally don’t compare the two because when you get right down to it, it’s really just a case of apples and oranges.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://jimlynch.com/linux-articles/why-mac-users-dont-switch-to-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jim Lynch][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://jimlynch.com/author/Jim/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.datamation.com/open-source/why-linux-isnt-winning-over-mac-users-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.howtogeek.com/187410/how-to-install-and-dual-boot-linux-on-a-mac/
|
||||
[3]:http://distrowatch.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://desktoplinuxreviews.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04 Finally Lets You Set Menus To ‘Always Show’
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**If you hate the way that Unity’s global menus fade out of view after you mouse away, Ubuntu 15.04 has a little extra to win you around.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The latest build of Unity for Ubuntu 15.04, currently sitting in the ‘proposed’ channel, offers an option to **make app menus visible in Ubuntu**.
|
||||
|
||||
No fading, no timeout, no missing menus.
|
||||
|
||||
The drawback for now is that it can currently only be enabled through a dconf switch and not a regular user-facing option.
|
||||
|
||||
I’d hope (if not expect) that an option to set the feature is added to the Ubuntu System Settings > Appearance section as development continues.
|
||||
|
||||
Right now, if you’re on Ubuntu 15.04 and have the “Proposed” update channel enabled, you should find this switch waiting in **com > canonical > unity >** ‘always show menus’.
|
||||
|
||||
### Better Late Than Never? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Developers plan to backport the option to Ubuntu 14.04 LTS in the next SRU (assuming nothing unexpected crops up during testing).
|
||||
|
||||
Locally Integrated Menus (LIM) debuted in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS to much appreciation, being widely seen as the best compromise between those who liked the simplicity of the “hidden” approach and those who disliked the mouse and trackpad aerobics using it required.
|
||||
|
||||
While locally integrated menus brought us half way to silencing the criticisms levelled at this aspect of Unity, the default “fade in/fade out” behaviour left an itch unscratched.
|
||||
|
||||
The past few releases of Ubuntu has seen proactive addressing of concerns and issues experienced by its earlier UX decisions. After several years on the ‘to do’ list [we finally got Locally Integrated Menus last year][1], as well as an unsupported [option to minimise and restore apps to the Unity Launcher][2] by clicking on their icon.
|
||||
|
||||
A year on from that we finally get an option to make application menus always show, no matter where our mouse is. Better late than never, right?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/01/ubuntu-15-04-always-show-menu-bar-option
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/02/locally-integrated-menus-ubuntu-14-04
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/03/minimize-click-launcher-option-ubuntu-14-04
|
||||
@ -1,86 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to convert image, audio and video formats on Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you need to work with a variety of image, audio and video files encoded in all sorts of different formats, you are probably using more than one tools to convert among all those heterogeneous media formats. If there is a versatile all-in-one media conversion tool that is capable of dealing with all different image/audio/video formats, that will be awesome.
|
||||
|
||||
[Format Junkie][1] is one such all-in-one media conversion tool with an extremely user-friendly GUI. Better yet, it is free software! With Format Junkie, you can convert image, audio, video and archive files of pretty much all the popular formats simply with a few mouse clicks.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Format Junkie on Ubuntu 12.04, 12.10 and 13.04 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Format Junkie is available for installation via Ubuntu PPA format-junkie-team. This PPA supports Ubuntu 12.04, 12.10 and 13.04. To install Format Junkie on one of those Ubuntu releases, simply run the following.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:format-junkie-team/release
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install formatjunkie
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /opt/extras.ubuntu.com/formatjunkie/formatjunkie /usr/bin/formatjunkie
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Format Junkie on Ubuntu 13.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you are running Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander), you can download and install .deb package for Ubuntu 13.04 as follows. Since the .deb package for Format Junkie requires quite a few dependent packages, install it using [gdebi deb installer][2].
|
||||
|
||||
On 32-bit Ubuntu 13.10:
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget https://launchpad.net/~format-junkie-team/+archive/release/+files/formatjunkie_1.07-1~raring0.2_i386.deb
|
||||
$ sudo gdebi formatjunkie_1.07-1~raring0.2_i386.deb
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /opt/extras.ubuntu.com/formatjunkie/formatjunkie /usr/bin/formatjunkie
|
||||
|
||||
On 64-bit Ubuntu 13.10:
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget https://launchpad.net/~format-junkie-team/+archive/release/+files/formatjunkie_1.07-1~raring0.2_amd64.deb
|
||||
$ sudo gdebi formatjunkie_1.07-1~raring0.2_amd64.deb
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /opt/extras.ubuntu.com/formatjunkie/formatjunkie /usr/bin/formatjunkie
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Format Junkie on Ubuntu 14.04 or Later ###
|
||||
|
||||
The currently available official Format Junkie .deb file requires libavcodec-extra-53 which has become obsolete starting from Ubuntu 14.04. Thus if you want to install Format Junkie on Ubuntu 14.04 or later, you can use the following third-party PPA repositories instead.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:jon-severinsson/ffmpeg
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install formatjunkie
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Use Format Junkie ###
|
||||
|
||||
To start Format Junkie after installation, simply run:
|
||||
|
||||
$ formatjunkie
|
||||
|
||||
#### Convert audio, video, image and archive formats with Format Junkie ####
|
||||
|
||||
The user interface of Format Junkie is pretty simple and intuitive, as shown below. To choose among audio, video, image and iso media, click on one of four tabs at the top. You can add as many files as you want for batch conversion. After you add files, and select output format, simply click on "Start Converting" button to convert.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Format Junkie supports conversion among the following media formats:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Audio**: mp3, wav, ogg, wma, flac, m4r, aac, m4a, mp2.
|
||||
- **Video**: avi, ogv, vob, mp4, 3gp, wmv, mkv, mpg, mov, flv, webm.
|
||||
- **Image**: jpg, png, ico, bmp, svg, tif, pcx, pdf, tga, pnm.
|
||||
- **Archive**: iso, cso.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Subtitle encoding with Format Junkie ####
|
||||
|
||||
Besides media conversion, Format Junkie also provides GUI for subtitle encoding. Actual subtitle encoding is done by MEncoder. In order to do subtitle encoding via Format Junkie interface, first you need to install MEencoder.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install mencoder
|
||||
|
||||
Then click on "Advanced" tab on Format Junkie. Choose AVI/subtitle files to use for encoding, as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Overall, Format Junkie is an extremely easy-to-use and versatile media conversion tool. One drawback, though, is that it does not allow any sort of customization during conversion (e.g., bitrate, fps, sampling frequency, image quality, size). So this tool is recommended for newbies who are looking for an easy-to-use simple media conversion tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoyed this post? I will appreciate your like/share buttons on Facebook, Twitter and Google+.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/how-to-convert-image-audio-and-video-formats-on-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/format-junkie
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-deb-file-with-dependencies.html
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,8 @@
|
||||
What is good audio editing software on Linux
|
||||
Translating by ly0
|
||||
|
||||
Linux下一些蛮不错的音频编辑软件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Whether you are an amateur musician or just a student recording his professor, you need to edit and work with audio recordings. If for a long time such task was exclusively attributed to Macintosh, this time is over, and Linux now has what it takes to do the job. In short, here is a non-exhaustive list of good audio editing software, fit for different tasks and needs.
|
||||
无论你是一个业余的音乐家或者仅仅是一个上课撸教授音的学,你总是需要和录音打交道。如果你有很长的时间仅仅用Mac干这种事情,那么可以和这个过程说拜拜了,现在Linux也可以干同样的事情。简而言之,这里有一个简单但是不错的音频编辑软件列表,来满足你对不同任务和需求。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Audacity ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,4 +80,4 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/good-audio-editing-software-linux.html
|
||||
[17]:
|
||||
[18]:
|
||||
[19]:
|
||||
[20]:
|
||||
[20]:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,207 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to configure fail2ban to protect Apache HTTP server
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
An Apache HTTP server in production environments can be under attack in various different ways. Attackers may attempt to gain access to unauthorized or forbidden directories by using brute-force attacks or executing evil scripts. Some malicious bots may scan your websites for any security vulnerability, or collect email addresses or web forms to send spams to.
|
||||
|
||||
Apache HTTP server comes with comprehensive logging capabilities capturing various abnormal events indicative of such attacks. However, it is still non-trivial to systematically parse detailed Apache logs and react to potential attacks quickly (e.g., ban/unban offending IP addresses) as they are perpetrated in the wild. That is when `fail2ban` comes to the rescue, making a sysadmin's life easier.
|
||||
|
||||
`fail2ban` is an open-source intrusion prevention tool which detects various attacks based on system logs and automatically initiates prevention actions e.g., banning IP addresses with `iptables`, blocking connections via /etc/hosts.deny, or notifying the events via emails. fail2ban comes with a set of predefined "jails" which use application-specific log filters to detect common attacks. You can also write custom jails to deter any specific attack on an arbitrary application.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial, I am going to demonstrate how you can configure fail2ban to protect your Apache HTTP server. I assume that you have Apache HTTP server and fail2ban already installed. Refer to [another tutorial][1] for fail2ban installation.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is a Fail2ban Jail ###
|
||||
|
||||
Let me go over more detail on fail2ban jails. A jail defines an application-specific policy under which fail2ban triggers an action to protect a given application. fail2ban comes with several jails pre-defined in /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf, for popular applications such as Apache, Dovecot, Lighttpd, MySQL, Postfix, [SSH][2], etc. Each jail relies on application-specific log filters (found in /etc/fail2ban/fileter.d) to detect common attacks. Let's check out one example jail: SSH jail.
|
||||
|
||||
[ssh]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = ssh
|
||||
filter = sshd
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/auth.log
|
||||
maxretry = 6
|
||||
banaction = iptables-multiport
|
||||
|
||||
This SSH jail configuration is defined with several parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
- **[ssh]**: the name of a jail with square brackets.
|
||||
- **enabled**: whether the jail is activated or not.
|
||||
- **port**: a port number to protect (either numeric number of well-known name).
|
||||
- **filter**: a log parsing rule to detect attacks with.
|
||||
- **logpath**: a log file to examine.
|
||||
- **maxretry**: maximum number of failures before banning.
|
||||
- **banaction**: a banning action.
|
||||
|
||||
Any parameter defined in a jail configuration will override a corresponding `fail2ban-wide` default parameter. Conversely, any parameter missing will be assgined a default value defined in [DEFAULT] section.
|
||||
|
||||
Predefined log filters are found in /etc/fail2ban/filter.d, and available actions are in /etc/fail2ban/action.d.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to overwrite `fail2ban` defaults or define any custom jail, you can do so by creating **/etc/fail2ban/jail.local** file. In this tutorial, I am going to use /etc/fail2ban/jail.local.
|
||||
|
||||
### Enable Predefined Apache Jails ###
|
||||
|
||||
Default installation of `fail2ban` offers several predefined jails and filters for Apache HTTP server. I am going to enable those built-in Apache jails. Due to slight differences between Debian and Red Hat configurations, let me provide fail2ban jail configurations for them separately.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Enable Apache Jails on Debian or Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
To enable predefined Apache jails on a Debian-based system, create /etc/fail2ban/jail.local as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# detect password authentication failures
|
||||
[apache]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-auth
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/apache*/*error.log
|
||||
maxretry = 6
|
||||
|
||||
# detect potential search for exploits and php vulnerabilities
|
||||
[apache-noscript]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-noscript
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/apache*/*error.log
|
||||
maxretry = 6
|
||||
|
||||
# detect Apache overflow attempts
|
||||
[apache-overflows]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-overflows
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/apache*/*error.log
|
||||
maxretry = 2
|
||||
|
||||
# detect failures to find a home directory on a server
|
||||
[apache-nohome]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-nohome
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/apache*/*error.log
|
||||
maxretry = 2
|
||||
|
||||
Since none of the jails above specifies an action, all of these jails will perform a default action when triggered. To find out the default action, look for "banaction" under [DEFAULT] section in /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf.
|
||||
|
||||
banaction = iptables-multiport
|
||||
|
||||
In this case, the default action is iptables-multiport (defined in /etc/fail2ban/action.d/iptables-multiport.conf). This action bans an IP address using iptables with multiport module.
|
||||
|
||||
After enabling jails, you must restart fail2ban to load the jails.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service fail2ban restart
|
||||
|
||||
#### Enable Apache Jails on CentOS/RHEL or Fedora ####
|
||||
|
||||
To enable predefined Apache jails on a Red Hat based system, create /etc/fail2ban/jail.local as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# detect password authentication failures
|
||||
[apache]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-auth
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
|
||||
maxretry = 6
|
||||
|
||||
# detect spammer robots crawling email addresses
|
||||
[apache-badbots]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-badbots
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*access_log
|
||||
bantime = 172800
|
||||
maxretry = 1
|
||||
|
||||
# detect potential search for exploits and php <a href="http://xmodulo.com/recommend/penetrationbook" style="" target="_blank" rel="nofollow" >vulnerabilities</a>
|
||||
[apache-noscript]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-noscript
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
|
||||
maxretry = 6
|
||||
|
||||
# detect Apache overflow attempts
|
||||
[apache-overflows]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-overflows
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
|
||||
maxretry = 2
|
||||
|
||||
# detect failures to find a home directory on a server
|
||||
[apache-nohome]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-nohome
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
|
||||
maxretry = 2
|
||||
|
||||
# detect failures to execute non-existing scripts that
|
||||
# are associated with several popular web services
|
||||
# e.g. webmail, phpMyAdmin, WordPress
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-botsearch
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
|
||||
maxretry = 2
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the default action for all these jails is iptables-multiport (defined as "banaction" under [DEFAULT] in /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf). This action bans an IP address using iptables with multiport module.
|
||||
|
||||
After enabling jails, you must restart fail2ban to load the jails in fail2ban.
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora or CentOS/RHEL 7:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart fail2ban
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS/RHEL 6:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service fail2ban restart
|
||||
|
||||
### Check and Manage Fail2ban Banning Status ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once jails are activated, you can monitor current banning status with fail2ban-client command-line tool.
|
||||
|
||||
To see a list of active jails:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fail2ban-client status
|
||||
|
||||
To see the status of a particular jail (including banned IP list):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fail2ban-client status [name-of-jail]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can also manually ban or unban IP addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
To ban an IP address with a particular jail:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fail2ban-client set [name-of-jail] banip [ip-address]
|
||||
|
||||
To unban an IP address blocked by a particular jail:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fail2ban-client set [name-of-jail] unbanip [ip-address]
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial explains how a fail2ban jail works and how to protect an Apache HTTP server using built-in Apache jails. Depending on your environments and types of web services you need to protect, you may need to adapt existing jails, or write custom jails and log filters. Check outfail2ban's [official Github page][3] for more up-to-date examples of jails and filters.
|
||||
|
||||
Are you using fail2ban in any production environment? Share your experience.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/configure-fail2ban-apache-http-server.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-protect-ssh-server-from-brute-force-attacks-using-fail2ban.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-protect-ssh-server-from-brute-force-attacks-using-fail2ban.html
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/fail2ban/fail2ban
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
What are useful command-line network monitors on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Network monitoring is a critical IT function for businesses of all sizes. The goal of network monitoring can vary. For example, the monitoring activity can be part of long-term network provisioning, security protection, performance troubleshooting, network usage accounting, and so on. Depending on its goal, network monitoring is done in many different ways, such as performing packet-level sniffing, collecting flow-level statistics, actively injecting probes into the network, parsing server logs, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
While there are many dedicated network monitoring systems capable of 24/7/365 monitoring, you can also leverage command-line network monitors in certain situations, where a dedicated monitor is an overkill. If you are a system admin, you are expected to have hands-on experience with some of well known CLI network monitors. Here is a list of **popular and useful command-line network monitors on Linux**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Packet-Level Sniffing ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this category, monitoring tools capture individual packets on the wire, dissect their content, and display decoded packet content or packet-level statistics. These tools conduct network monitoring from the lowest level, and as such, can possibly do the most fine-grained monitoring at the cost of network I/O and analysis efforts.
|
||||
|
||||
1. **dhcpdump**: a comman-line DHCP traffic sniffer capturing DHCP request/response traffic, and displays dissected DHCP protocol messages in a human-friendly format. It is useful when you are troubleshooting DHCP related issues.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **[dsniff][1]**: a collection of command-line based sniffing, spoofing and hijacking tools designed for network auditing and penetration testing. They can sniff various information such as passwords, NSF traffic, email messages, website URLs, and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **[httpry][2]**: an HTTP packet sniffer which captures and decode HTTP requests and response packets, and display them in a human-readable format.
|
||||
|
||||
4. **IPTraf**: a console-based network statistics viewer. It displays packet-level, connection-level, interface-level, protocol-level packet/byte counters in real-time. Packet capturing can be controlled by protocol filters, and its operation is full menu-driven.
|
||||
|
||||
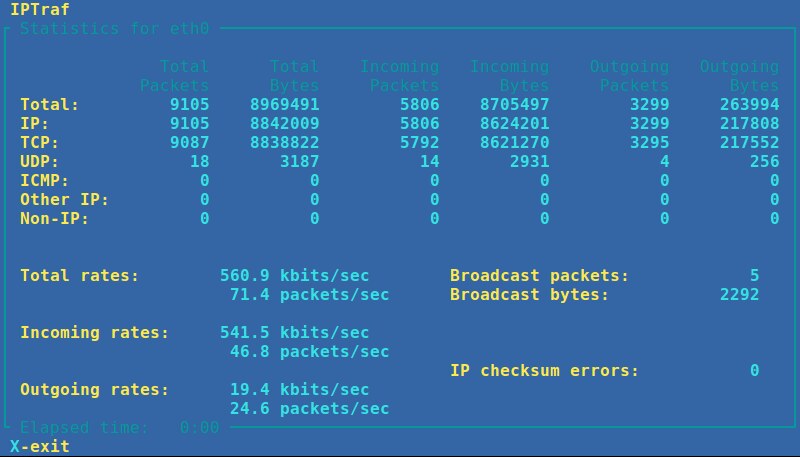
|
||||
|
||||
5. **[mysql-sniffer][3]**: a packet sniffer which captures and decodes packets associated with MySQL queries. It displays the most frequent or all queries in a human-readable format.
|
||||
|
||||
6. **[ngrep][4]**: grep over network packets. It can capture live packets, and match (filtered) packets against regular expressions or hexadecimal expressions. It is useful for detecting and storing any anomalous traffic, or for sniffing particular patterns of information from live traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
7. **[p0f][5]**: a passive fingerprinting tool which, based on packet sniffing, reliably identifies operating systems, NAT or proxy settings, network link types and various other properites associated with an active TCP connection.
|
||||
|
||||
8. **pktstat**: a command-line tool which analyzes live packets to display connection-level bandwidth usages as well as descriptive information of protocols involved (e.g., HTTP GET/POST, FTP, X11).
|
||||
|
||||
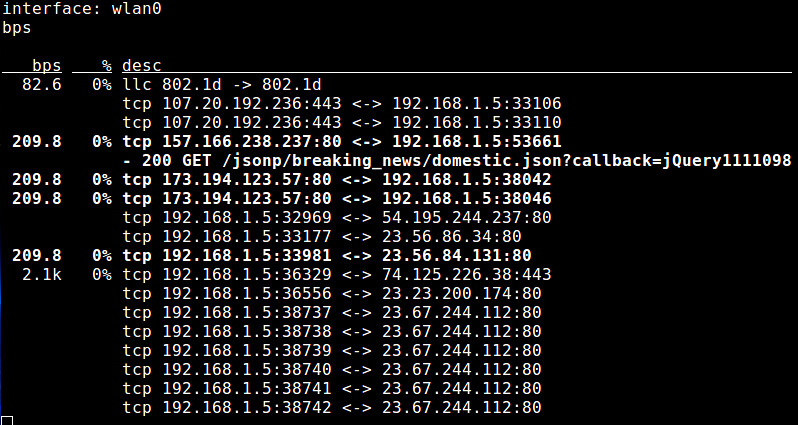
|
||||
|
||||
9. **Snort**: an intrusion detection and prevention tool which can detect/prevent a variety of backdoor, botnets, phishing, spyware attacks from live traffic based on rule-driven protocol analysis and content matching.
|
||||
|
||||
10. **tcpdump**: a command-line packet sniffer which is capable of capturing nework packets on the wire based on filter expressions, dissect the packets, and dump the packet content for packet-level analysis. It is widely used for any kinds of networking related troubleshooting, network application debugging, or [security][6] monitoring.
|
||||
|
||||
11. **tshark**: a command-line packet sniffing tool that comes with Wireshark GUI program. It can capture and decode live packets on the wire, and show decoded packet content in a human-friendly fashion.
|
||||
|
||||
### Flow-/Process-/Interface-Level Monitoring ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this category, network monitoring is done by classifying network traffic into flows, associated processes or interfaces, and collecting per-flow, per-process or per-interface statistics. Source of information can be libpcap packet capture library or sysfs kernel virtual filesystem. Monitoring overhead of these tools is low, but packet-level inspection capabilities are missing.
|
||||
|
||||
12. **bmon**: a console-based bandwidth monitoring tool which shows various per-interface information, including not-only aggregate/average RX/TX statistics, but also a historical view of bandwidth usage.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
13. **[iftop][7]**: a bandwidth usage monitoring tool that can shows bandwidth usage for individual network connections in real time. It comes with ncurses-based interface to visualize bandwidth usage of all connections in a sorted order. It is useful for monitoring which connections are consuming the most bandwidth.
|
||||
|
||||
14. **nethogs**: a process monitoring tool which offers a real-time view of upload/download bandwidth usage of individual processes or programs in an ncurses-based interface. This is useful for detecting bandwidth hogging processes.
|
||||
|
||||
15. **netstat**: a command-line tool that shows various statistics and properties of the networking stack, such as open TCP/UDP connections, network interface RX/TX statistics, routing tables, protocol/socket statistics. It is useful when you diagnose performance and resource usage related problems of the networking stack.
|
||||
|
||||
16. **[speedometer][8]**: a console-based traffic monitor which visualizes the historical trend of an interface's RX/TX bandwidth usage with ncurses-drawn bar charts.
|
||||
|
||||
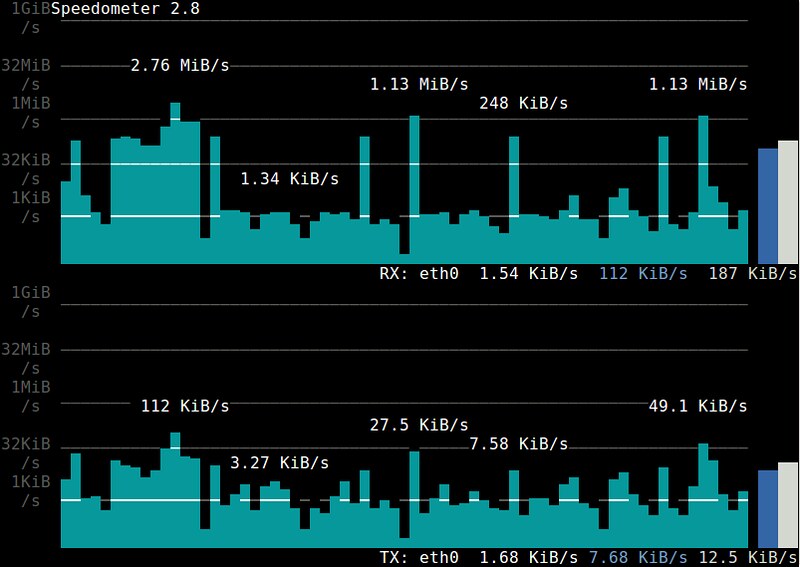
|
||||
|
||||
17. **[sysdig][9]**: a comprehensive system-level debugging tool with a unified interface for investigating different Linux subsystems. Its network monitoring module is capable of monitoring, either online or offline, various per-process/per-host networking statistics such as bandwidth usage, number of connections/requests, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
18. **tcptrack**: a TCP connection monitoring tool which displays information of active TCP connections, including source/destination IP addresses/ports, TCP state, and bandwidth usage.
|
||||
|
||||
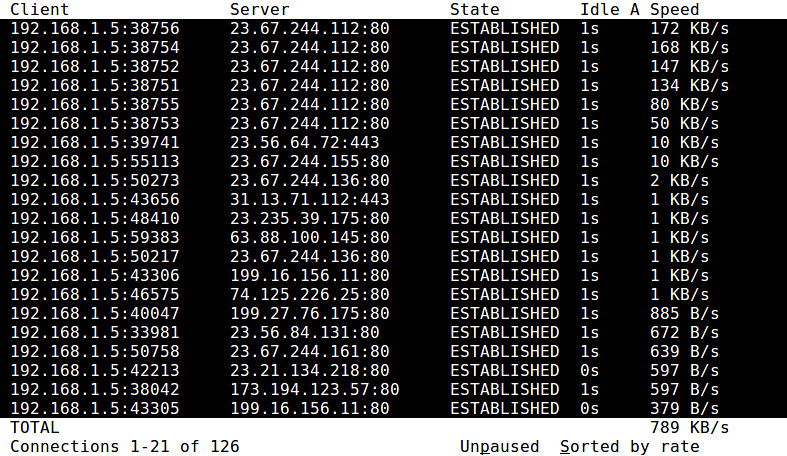
|
||||
|
||||
19. **vnStat**: a command-line traffic monitor which maintains a historical view of RX/TX bandwidh usage (e.g., current, daily, monthly) on a per-interface basis. Running as a background daemon, it collects and stores interface statistics on bandwidth rate and total bytes transferred.
|
||||
|
||||
### Active Network Monitoring ###
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike passive monitoring tools presented so far, tools in this category perform network monitoring by actively "injecting" probes into the network and collecting corresponding responses. Monitoring targets include routing path, available bandwidth, loss rates, delay, jitter, system settings or vulnerabilities, and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
20. **[dnsyo][10]**: a DNS monitoring tool which can conduct DNS lookup from open resolvers scattered across more than 1,500 different networks. It is useful when you check DNS propagation or troubleshoot DNS configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
21. **[iperf][11]**: a TCP/UDP bandwidth measurement utility which can measure maximum available bandwidth between two end points. It measures available bandwidth by having two hosts pump out TCP/UDP probe traffic between them either unidirectionally or bi-directionally. It is useful when you test the network capacity, or tune the parameters of network stack. A variant called [netperf][12] exists with more features and better statistics.
|
||||
|
||||
22. **[netcat][13]/socat**: versatile network debugging tools capable of reading from, writing to, or listen on TCP/UDP sockets. They are often used alongside with other programs or scripts for backend network transfer or port listening.
|
||||
|
||||
23. **nmap**: a command-line port scanning and network discovery utility. It relies on a number of TCP/UDP based scanning techniques to detect open ports, live hosts, or existing operating systems on the local network. It is useful when you audit local hosts for vulnerabilities or build a host map for maintenance purpose. [zmap][14] is an alernative scanning tool with Internet-wide scanning capability.
|
||||
|
||||
24. ping: a network testing tool which works by exchaning ICMP echo and reply packets with a remote host. It is useful when you measure round-trip-time (RTT) delay and loss rate of a routing path, as well as test the status or firewall rules of a remote system. Variations of ping exist with fancier interface (e.g., [noping][15]), multi-protocol support (e.g., [hping][16]) or parallel probing capability (e.g., [fping][17]).
|
||||
|
||||
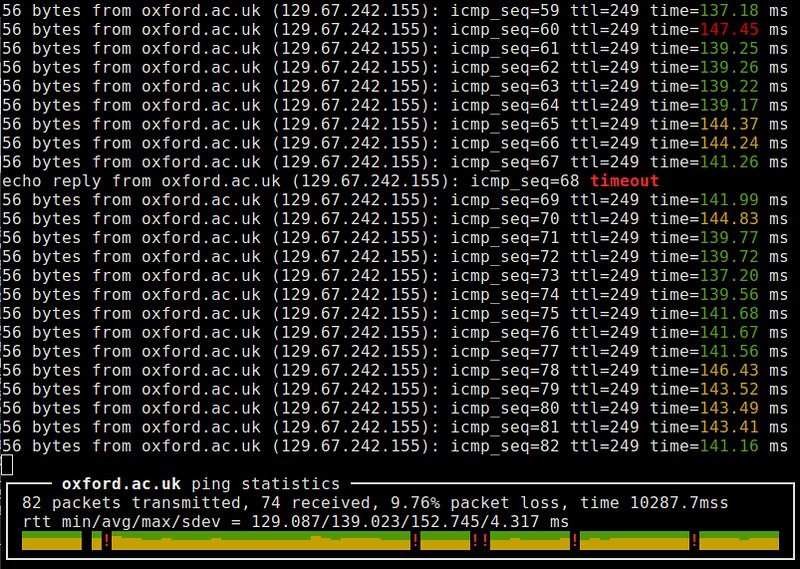
|
||||
|
||||
25. **[sprobe][18]**: a command-line tool that heuristically infers the bottleneck bandwidth between a local host and any arbitrary remote IP address. It uses TCP three-way handshake tricks to estimate the bottleneck bandwidth. It is useful when troubleshooting wide-area network performance and routing related problems.
|
||||
|
||||
26. **traceroute**: a network discovery tool which reveals a layer-3 routing/forwarding path from a local host to a remote host. It works by sending TTL-limited probe packets and collecting ICMP responses from intermediate routers. It is useful when troubleshooting slow network connections or routing related problems. Variations of traceroute exist with better RTT statistics (e.g., [mtr][19]).
|
||||
|
||||
### Application Log Parsing ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this category, network monitoring is targeted at a specific server application (e.g., web server or database server). Network traffic generated or consumed by a server application is monitored by analyzing its log file. Unlike network-level monitors presented in earlier categories, tools in this category can analyze and monitor network traffic from application-level.
|
||||
|
||||
27. **[GoAccess][20]**: a console-based interactive viewer for Apache and Nginx web server traffic. Based on access log analysis, it presents a real-time statistics of a number of metrics including daily visits, top requests, client operating systems, client locations, client browsers, in a scrollable view.
|
||||
|
||||
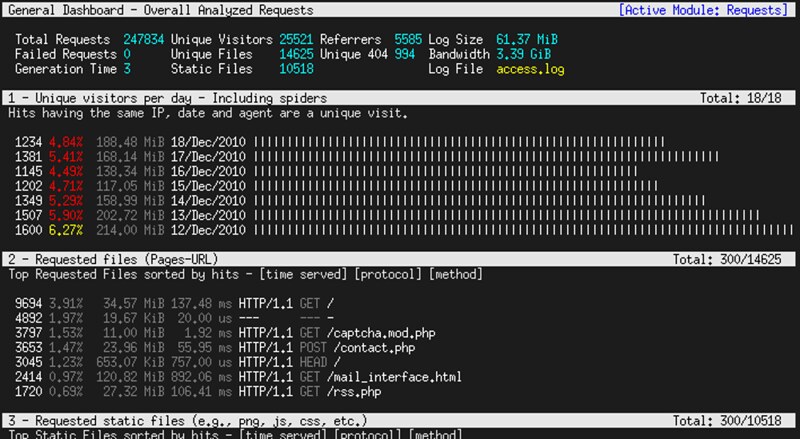
|
||||
|
||||
28. **[mtop][21]**: a command-line MySQL/MariaDB server moniter which visualizes the most expensive queries and current database server load. It is useful when you optimize MySQL server performance and tune server configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
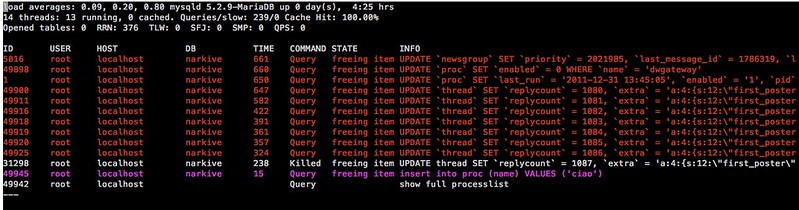
|
||||
|
||||
29. **[ngxtop][22]**: a traffic monitoring tool for Nginx and Apache web server, which visualizes web server traffic in a top-like interface. It works by parsing a web server's access log file and collecting traffic statistics for individual destinations or requests.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, I presented a wide variety of command-line network monitoring tools, ranging from the lowest packet-level monitors to the highest application-level network monitors. Knowing which tool does what is one thing, and choosing which tool to use is another, as any single tool cannot be a universal solution for your every need. A good system admin should be able to decide which tool is right for the circumstance at hand. Hopefully the list helps with that.
|
||||
|
||||
You are always welcome to improve the list with your comment!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/useful-command-line-network-monitors-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://www.monkey.org/~dugsong/dsniff/
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-http-traffic-command-line-linux.html
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/zorkian/mysql-sniffer
|
||||
[4]:http://ngrep.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[5]:http://lcamtuf.coredump.cx/p0f3/
|
||||
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/recommend/firewallbook
|
||||
[7]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-iftop-on-linux.html
|
||||
[8]:https://excess.org/speedometer/
|
||||
[9]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-troubleshoot-linux-server-sysdig.html
|
||||
[10]:http://xmodulo.com/check-dns-propagation-linux.html
|
||||
[11]:https://iperf.fr/
|
||||
[12]:http://www.netperf.org/netperf/
|
||||
[13]:http://xmodulo.com/useful-netcat-examples-linux.html
|
||||
[14]:https://zmap.io/
|
||||
[15]:http://noping.cc/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.hping.org/
|
||||
[17]:http://fping.org/
|
||||
[18]:http://sprobe.cs.washington.edu/
|
||||
[19]:http://xmodulo.com/better-alternatives-basic-command-line-utilities.html#mtr_link
|
||||
[20]:http://goaccess.io/
|
||||
[21]:http://mtop.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[22]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-nginx-web-server-command-line-real-time.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,180 @@
|
||||
How To Recover Windows 7 And Delete Ubuntu In 3 Easy Steps
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Introduction ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is a strange article for me to write as I am normally in a position where I would advocate installing Ubuntu and getting rid of Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
What makes writing this article today doubly strange is that I am choosing to write it on the day that Windows 7 mainstream support comes to an end.
|
||||
|
||||
So why am I writing this now?
|
||||
|
||||
I have been asked on so many occasions now how to remove Ubuntu from a dual booting Windows 7 or a dual booting Windows 8 system and it just makes sense to write the article.
|
||||
|
||||
I spent the Christmas period looking through the comments that people have left on articles and it is time to write the posts that are missing and update some of those that have become old and need attention.
|
||||
|
||||
I am going to spend the rest of January doing just that. This is the first step. If you have Windows 7 dual booting with Ubuntu and you want Windows 7 back without restoring to factory settings follow this guide. (Note there is a separate guide required for Windows 8)
|
||||
|
||||
### The Steps Required To Remove Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. Remove Grub By Fixing The Windows Boot Record
|
||||
1. Delete The Ubuntu Partitions
|
||||
1. Expand The Windows Partition
|
||||
|
||||
### Back Up Your System ###
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin I recommend taking a backup of your system.
|
||||
|
||||
I also recommend not leaving this to chance nor Microsoft's own tools.
|
||||
|
||||
[Click here for a guide showing how to backup your drive using Macrium Reflect.][1]
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any data you wish to save within Ubuntu log into it now and back up the data to external hard drives, USB drives or DVDs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1 - Remove The Grub Boot Menu ###
|
||||
|
||||
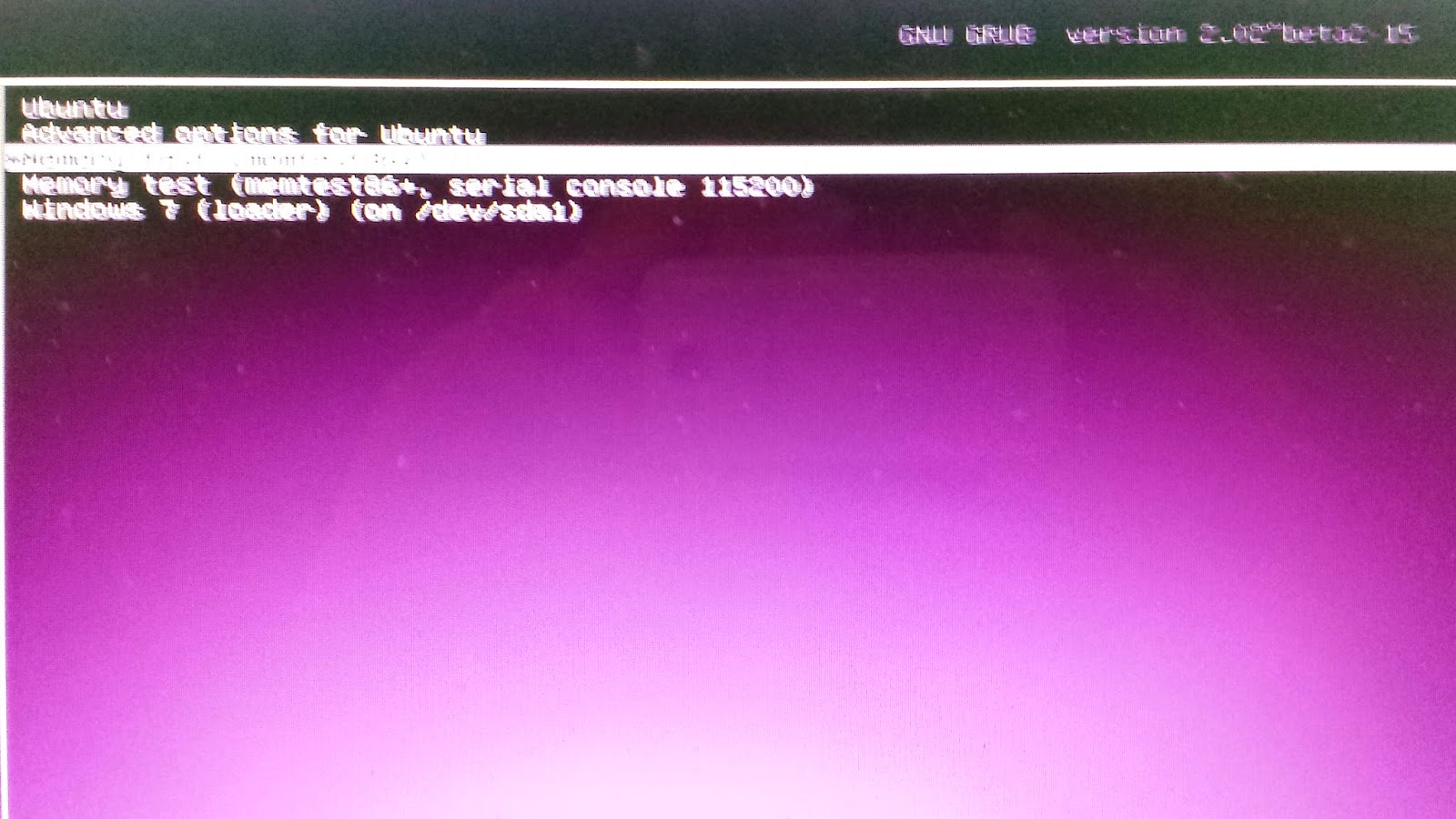
|
||||
|
||||
When you boot your system you will see a menu similar to the one in the image.
|
||||
|
||||
To remove this menu and boot straight into Windows you have to fix the master boot record.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this I am going to show you how to create a system recovery disk, how to boot to the recovery disk and how to fix the master boot record.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Press the "Start" button and search for "backup and restore". Click the icon that appears.
|
||||
|
||||
A window should open as shown in the image above.
|
||||
|
||||
Click on "Create a system repair disc".
|
||||
|
||||
You will need a [blank DVD][2].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Insert the blank DVD in the drive and select your DVD drive from the dropdown list.
|
||||
|
||||
Click "Create Disc".
|
||||
|
||||
Restart your computer leaving the disk in and when the message appears to boot from CD press "Enter" on the keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
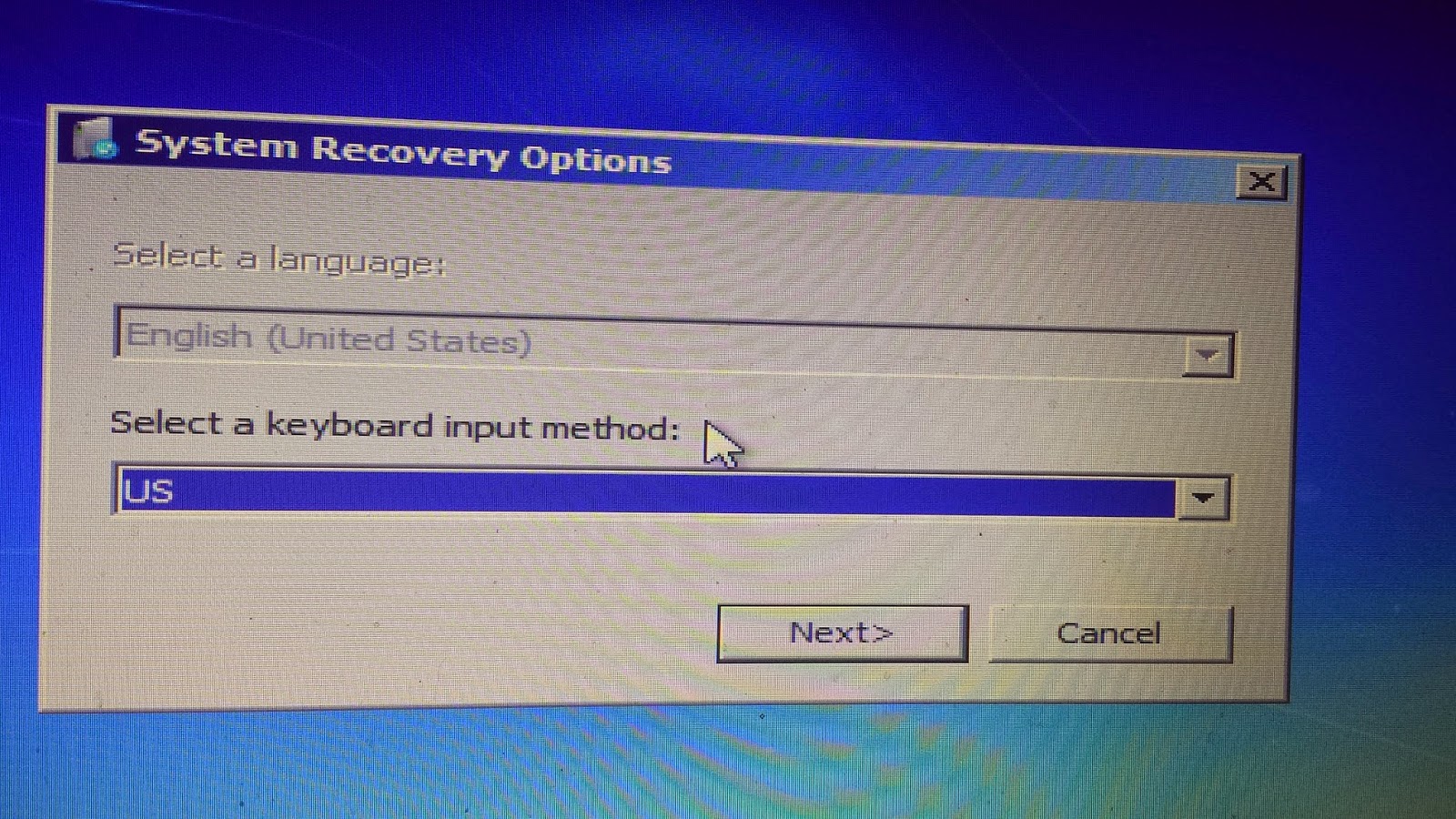
|
||||
|
||||
A set of "Systems Recovery Options" screens will appear.
|
||||
|
||||
You will be asked to choose your keyboard layout.
|
||||
|
||||
Choose the appropriate options from the lists provided and click "Next".
|
||||
|
||||
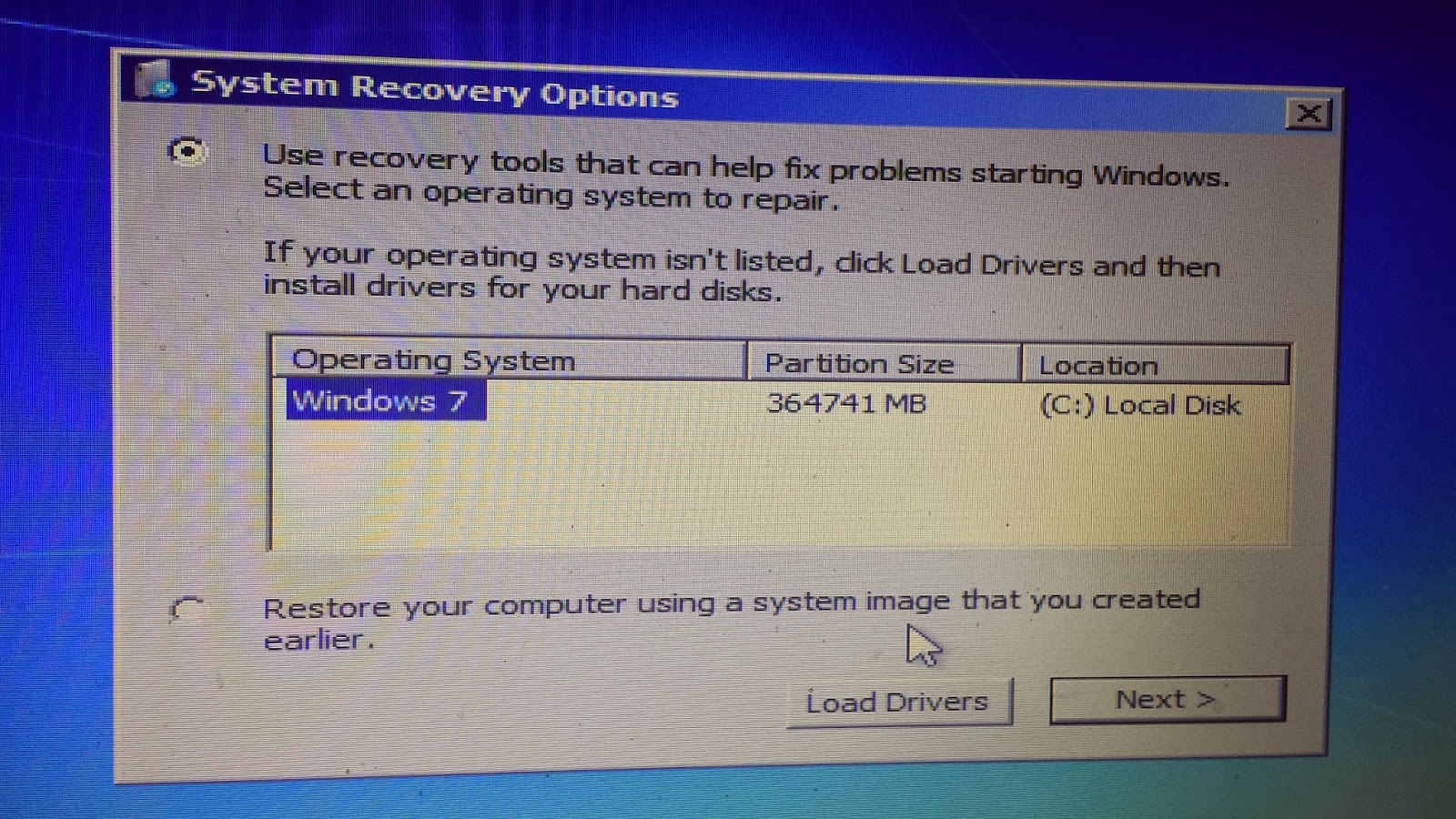
|
||||
|
||||
The next screen lets you choose an operating system to attempt to fix.
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively you can restore your computer using a system image saved earlier.
|
||||
|
||||
Leave the top option checked and click "Next".
|
||||
|
||||
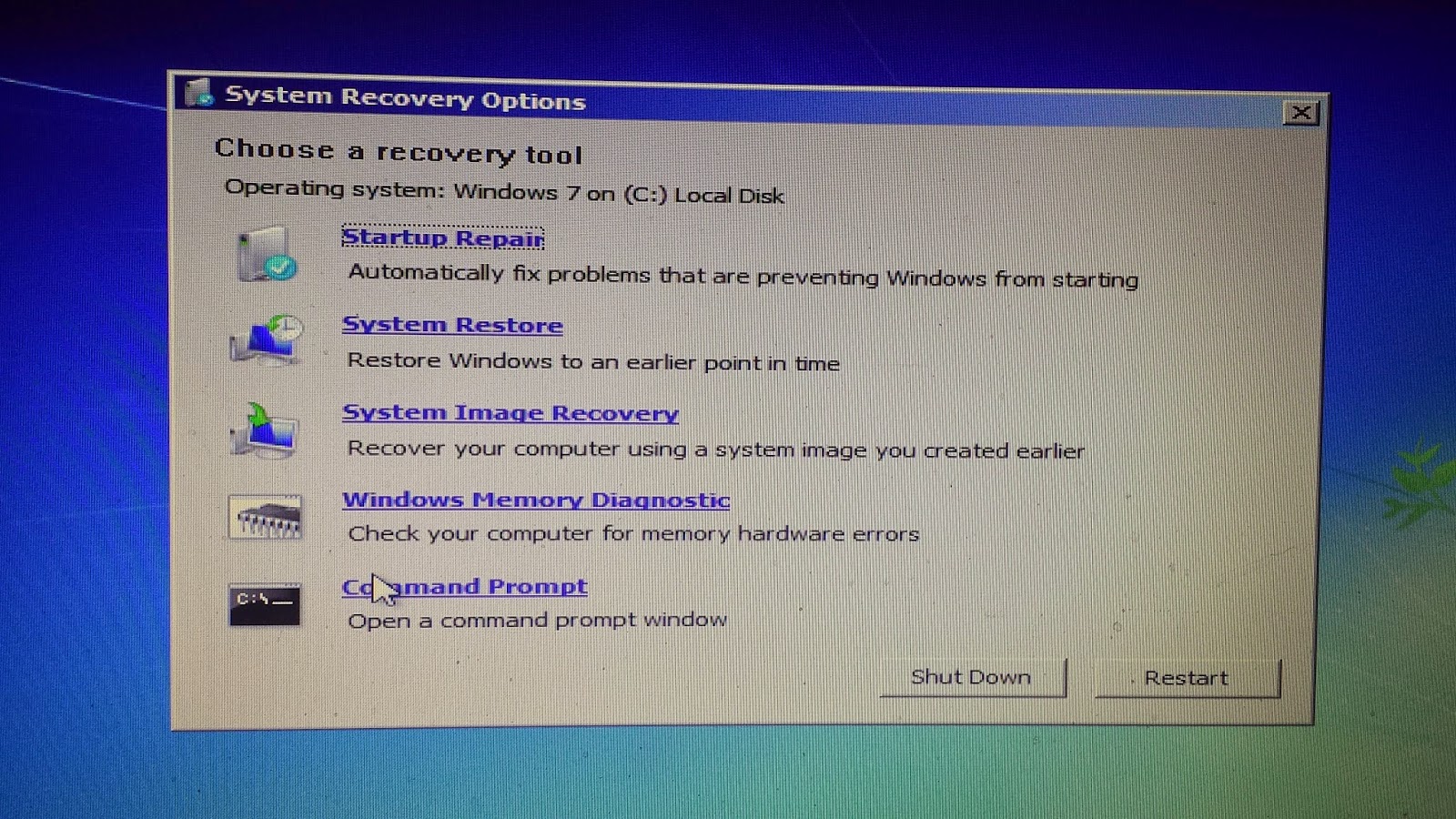
|
||||
|
||||
You will now see a screen with options to repair your disk and restore your system etc.
|
||||
|
||||
All you need to do is fix the master boot record and this can be done from the command prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
Click "Command Prompt".
|
||||
|
||||
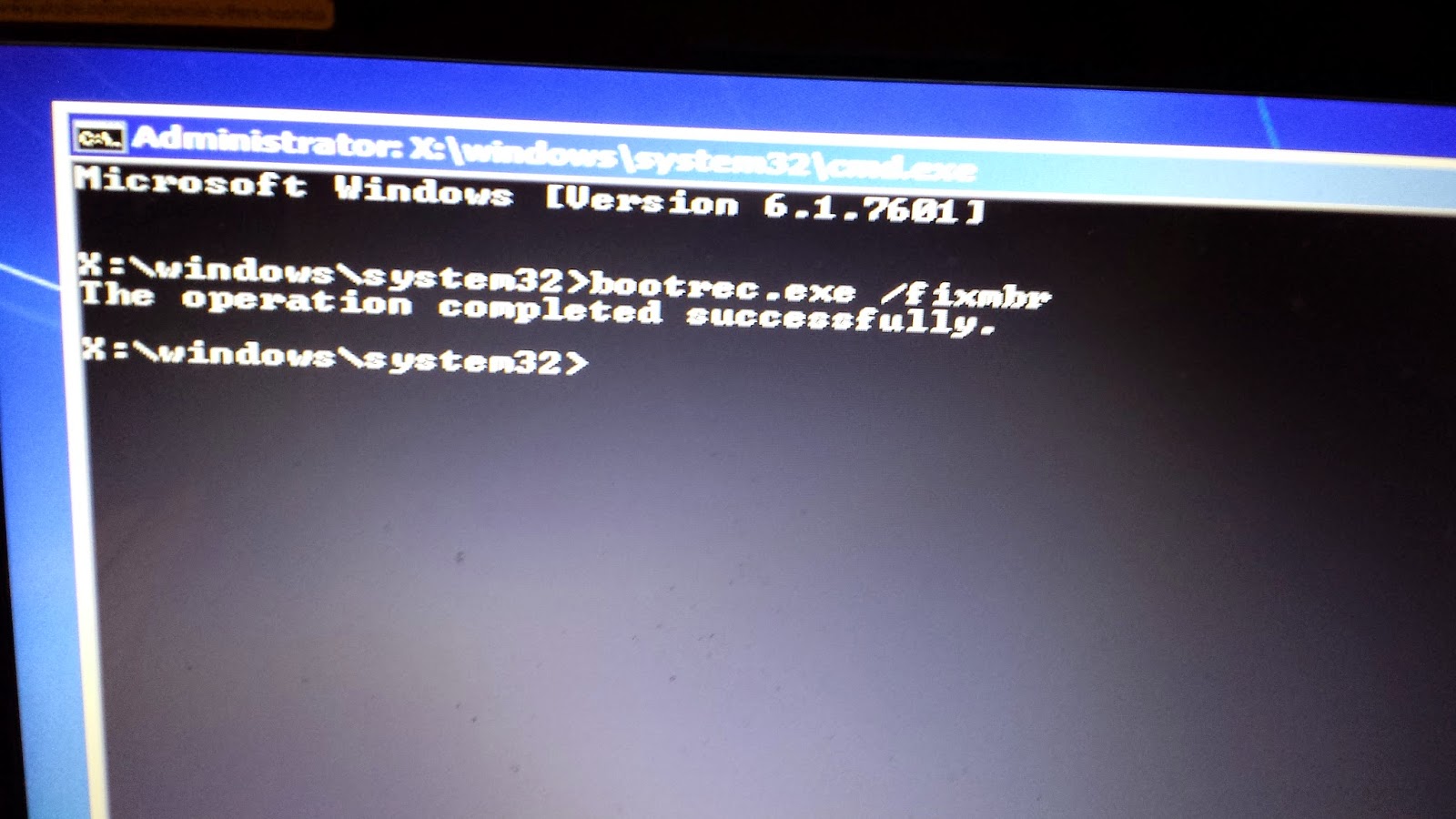
|
||||
|
||||
Now simply type the following command into the command prompt:
|
||||
|
||||
bootrec.exe /fixmbr
|
||||
|
||||
A message will appear stating that the operation has completed successfully.
|
||||
|
||||
You can now close the command prompt window.
|
||||
|
||||
Click the "Restart" button and remove the DVD.
|
||||
|
||||
Your computer should boot straight into Windows 7.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2 - Delete The Ubuntu Partitions ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To delete Ubuntu you need to use the "Disk Management" tool from within Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
Press "Start" and type "Create and format hard disk partitions" into the search box. A window will appear similar to the image above.
|
||||
|
||||
Now my screen above isn't going to be quite the same as yours but it won't be much different. If you look at disk 0 there is 101 MB of unallocated space and then 4 partitions.
|
||||
|
||||
The 101 MB of space is a mistake I made when installing Windows 7 in the first place. The C: drive is Windows 7, the next partition (46.57 GB) is Ubuntu's root partition. The 287 GB partition is the /HOME partition and the 8 GB partition is the SWAP space.
|
||||
|
||||
The only one we really need for Windows is the C: drive so the rest can be deleted.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: Be careful. You may have recovery partitions on the disk. Do not delete the recovery partitions. They should be labelled and will have file systems set to NTFS or FAT32**
|
||||
|
||||
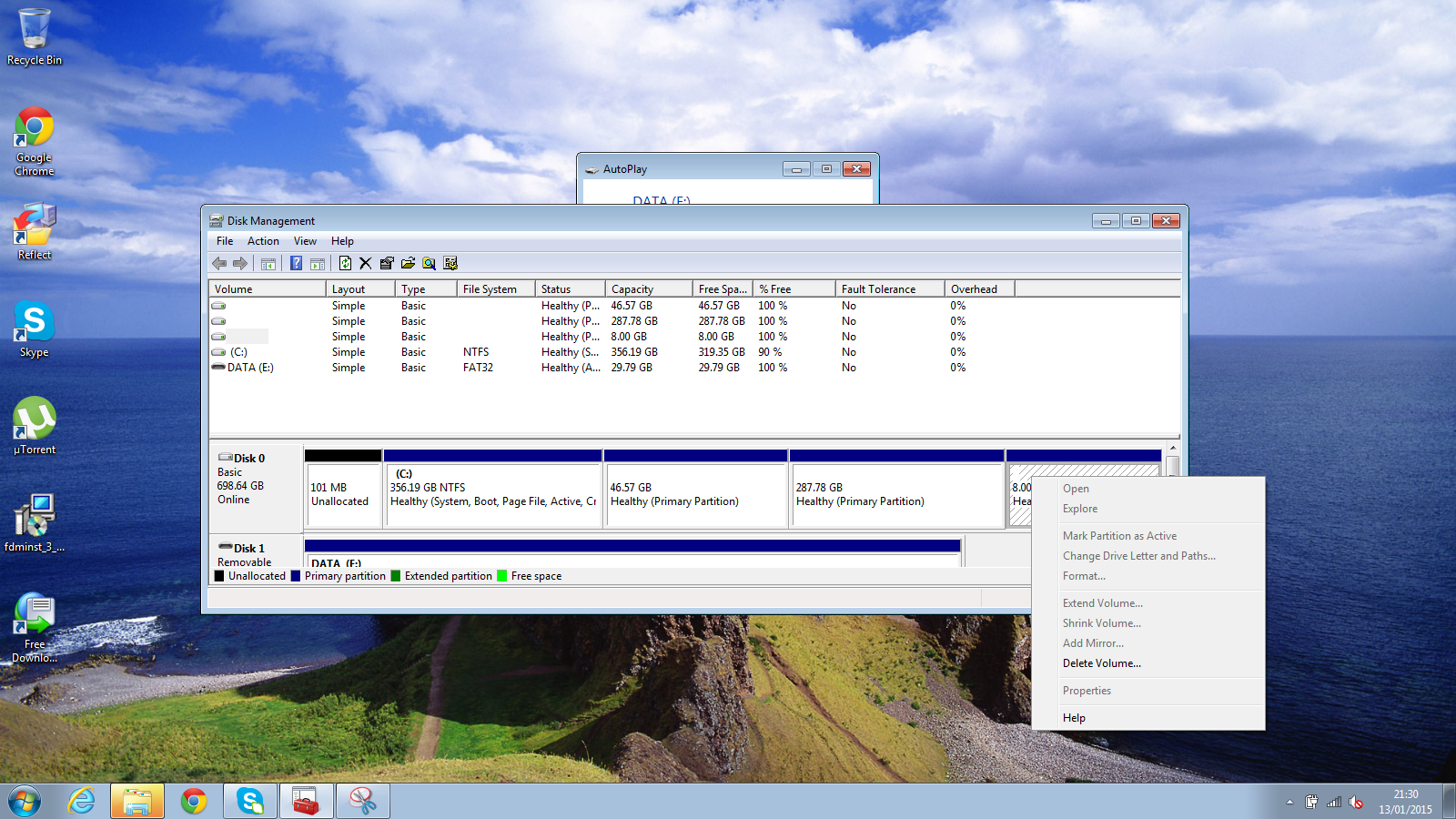
|
||||
|
||||
Right click on one of the partitions you wish to delete (i.e. the root, home and swap partitions) and from the menu click "Delete Volume".
|
||||
|
||||
**(Do not delete any partitions that have a file system of NTFS or FAT32)**
|
||||
|
||||
Repeat this process for the other two partitions.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After the partitions have been deleted you will have a large area of free space. Right click the free space and choose delete.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Your disk will now contain your C drive and a large amount of unallocated space.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3 - Expand The Windows Partition ###
|
||||
|
||||
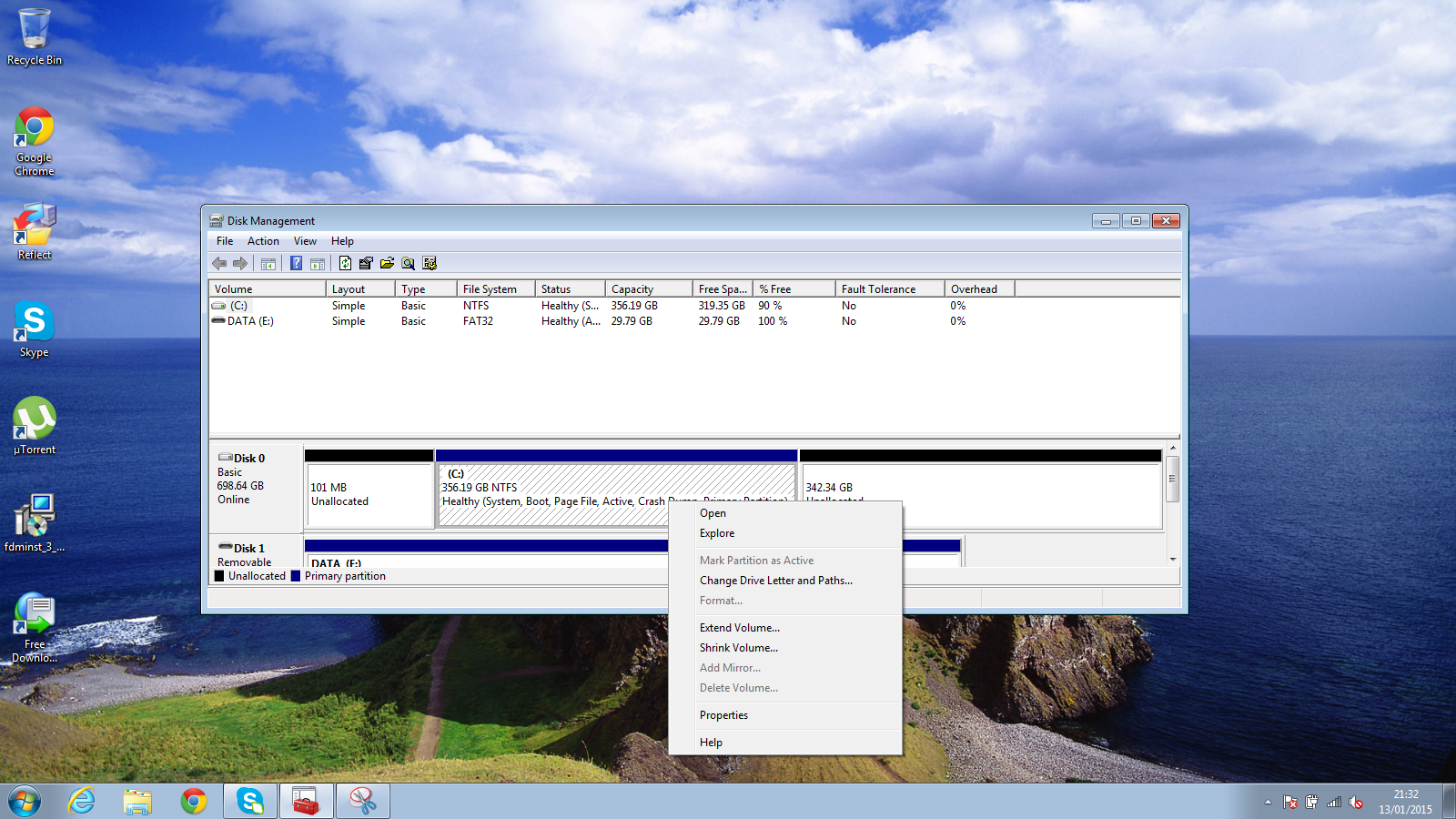
|
||||
|
||||
The final step is to expand Windows so that it is one large partition again.
|
||||
|
||||
To do this right click on the Windows partition (C: drive) and choose "Extend Volume".
|
||||
|
||||
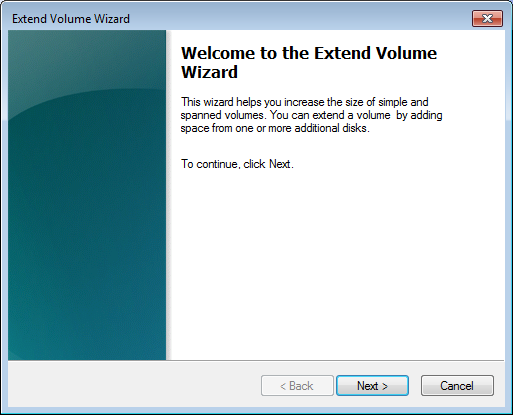
|
||||
|
||||
When the Window to the left appears click "Next",
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The next screen shows a wizard whereby you can select the disks to expand to and change the size to expand to.
|
||||
|
||||
By default the wizard shows the maximum amount of disk space it can claim from unallocated space.
|
||||
|
||||
Accept the defaults and click "Next".
|
||||
|
||||
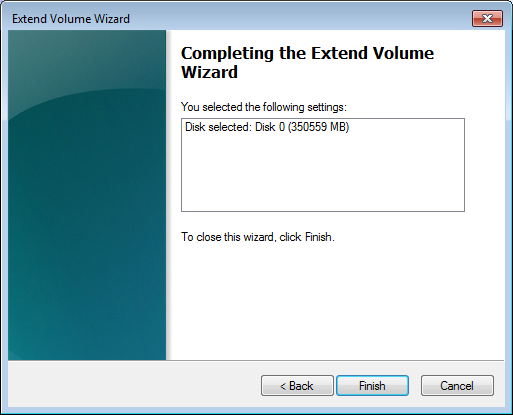
|
||||
|
||||
The final screen shows the settings that you chose from the previous screen.
|
||||
|
||||
Click "Finish" to expand the disk.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see from the image above my Windows partition now takes up the entire disk (except for the 101 MB that I accidentally created before installing Windows in the first place).
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
That is all folks. A site dedicated to Linux has just shown you how to remove Linux and replace it with Windows 7.
|
||||
|
||||
Any questions? Use the comments section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.everydaylinuxuser.com/2015/01/how-to-recover-windows-7-and-delete.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Gary Newell
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.about.com/od/LinuxNewbieDesktopGuide/ss/Create-A-Recovery-Drive-For-All-Versions-Of-Windows.htm
|
||||
[2]:http://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/B0006L2HTK/ref=as_li_qf_sp_asin_il_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=B0006L2HTK&linkCode=as2&tag=evelinuse-21&linkId=3R363EA63XB4Z3IL
|
||||
1113
sources/tech/20150115 Get back your privacy and control.md
Normal file
1113
sources/tech/20150115 Get back your privacy and control.md
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
Vic020
|
||||
|
||||
Tips for Apache Migration From 2.2 to 2.4 on Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you do a distribution upgrade from **Ubuntu** 12.04 to 14.04, the upgrade will bring among other things an important update to **Apache**, from [version 2.2][1] to version 2.4. The update brings many improvements but it may cause some errors when used with the old configuration file from 2.2.
|
||||
|
||||
### Access control in Apache 2.4 Virtual Hosts ###
|
||||
|
||||
Starting with **Apache 2.4** authorization is applied in a way that is much more flexible then just a single check against a single data store like it was in 2.2. In the past it was tricky to figure how and in what order authorization is applied but with the introduction of authorization container directives such as and , the configuration also has control over when the authorization methods are called and what criteria determines when access is granted.
|
||||
|
||||
This is the point where most upgrades fail because of wrong configuration because in 2.2 access control based on IP address, hostname or other characteristic was done using the directives Order, Allow, Deny or Satisfy, but in 2.4 this is done with authorization checks using the new modules.
|
||||
|
||||
To be clear let's see some virtual host examples, this can be found in your /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/default or /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/YOUR_WEBSITE_NAME:
|
||||
|
||||
Old 2.2 virtual host configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow from all
|
||||
|
||||
New 2.4 virtual host configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
Require all granted
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### .htaccess problems ###
|
||||
|
||||
If after the upgrade some settings don't work or you get redirect errors, check if those settings are in a .htaccess file. If settings in the .htaccess file are not used by Apache it's because in 2.4 AllowOverride directive is set to None by default, thus ignoring the .htaccess files. All you have to do is to either change or add the AllowOverride All directive to your site configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
You also see the AllowOverride All directive set in the screenshot above.
|
||||
|
||||
### Missing config file or module ###
|
||||
|
||||
From my experience another problem during upgrades is that your configuration file includes an old module or configuration file that is no longer needed or supported in 2.4, you will get a clear warning that Apache can't include the respective file and all you have to do is go to your configuration file and remove the line that causes problem. Afterwards you can search or install a similar module.
|
||||
|
||||
### Other small changes you shound know about ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are a few other changes that you should consider, although they generally result in an warning and not an error:
|
||||
|
||||
- MaxClients has been renamed to MaxRequestWorkers, which describes more accurately what it does. For async MPMs, like event, the maximum number of clients is not equivalent than the number of worker threads. The old name is still supported.
|
||||
- The DefaultType directive no longer has any effect, other than to emit a warning if it's used with any value other than none. You need to use other configuration settings to replace it in 2.4.
|
||||
- EnableSendfile now defaults to Off.
|
||||
- FileETag now defaults to "MTime Size" (without INode).
|
||||
- KeepAlive only accepts values of On or Off. Previously, any value other than "Off" or "0" was treated as "On".
|
||||
- Directives AcceptMutex, LockFile, RewriteLock, SSLMutex, SSLStaplingMutex, and WatchdogMutexPath have been replaced with a single Mutex directive. You will need to evaluate any use of these removed directives in your 2.2 configuration to determine if they can just be deleted or will need to be replaced using Mutex.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/apache-migration-2-2-to-2-4-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/adriand/
|
||||
[1]:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/
|
||||
95
sources/tech/20150119 How To Disable IPv6 In CentOS 7.md
Normal file
95
sources/tech/20150119 How To Disable IPv6 In CentOS 7.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
How To Disable IPv6 In CentOS 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Recently, one of my friend asked me how to disable IPv6. After searching a bit, I found the following solution. Here is the steps that I followed to disable IPv6 in my CentOS 7 minimal server.
|
||||
|
||||
You can do it in two methods.
|
||||
|
||||
### Method 1 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Edit file **/etc/sysctl.conf**,
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Add the following lines:
|
||||
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to disable IPV6 for particular network card, for example enp0s3, add the following entry.
|
||||
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.enp0s3.disable_ipv6 = 1
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit the file.
|
||||
|
||||
Execute the following command to reflect the changes.
|
||||
|
||||
sysctl -p
|
||||
|
||||
### Method 2: ###
|
||||
|
||||
To IPv6 disable in the running system, enter the following commands one by one:
|
||||
|
||||
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/all/disable_ipv6
|
||||
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/default/disable_ipv6
|
||||
|
||||
or,
|
||||
|
||||
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1
|
||||
sysctl -w net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6=1
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. Now IPv6 has been disabled.
|
||||
|
||||
### What If I get issues after disabling IPv6? ###
|
||||
|
||||
You may get problems after disabling IPv6.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Issue 1: ####
|
||||
|
||||
if you get issues with SSH after disabling IPv6, do the following.
|
||||
|
||||
Edit **/etc/ssh/sshd_config** file,
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
|
||||
Find the line;
|
||||
|
||||
#AddressFamily any
|
||||
|
||||
And. change it to:
|
||||
|
||||
AddressFamily inet
|
||||
|
||||
or,
|
||||
|
||||
Remove the hash mark **(#)** in front of the line:
|
||||
|
||||
#ListenAddress 0.0.0.0
|
||||
|
||||
Then, restart ssh to reflect the changes.
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl restart sshd
|
||||
|
||||
#### Issue 2: ####
|
||||
|
||||
If you get problems with starting postfix after disabling IPv6, edit **/etc/postfix/main.cf** file;
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/postfix/main.cf
|
||||
|
||||
and comment out the localhost part of the config and use ipv4 loopback.
|
||||
|
||||
#inet_interfaces = localhost
|
||||
inet_interfaces = 127.0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. Cheers!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/disable-ipv6-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
How to Install Cherokee Lightweight Web Server on Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Cherokee** is an free and open source high performance, lightweight, full-featured web server and running on major platform (Linux, Mac OS X, Solaris, and BSD). It is compatible with TLS/SSL,FastCGI, SCGI, PHP, uWSGI, SSI, CGI, LDAP, HTTP proxying, video streaming, content caching, traffic shaping, virtual hosts, Apache compatible log files, and load balancing.
|
||||
|
||||
Today we'll explains how to install and configure the Light Weight Cherokeeweb server on Ubuntu Server edition 14.04 LTS (Trusty) and should also work with 12.04, 12.10 and 13. 04, just skip the modification of source list.
|
||||
|
||||
Step by step install and configure the Cherokee web server on Ubuntu Server edition
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Updating Ubuntu Package Index ###
|
||||
|
||||
First, Login into Ubuntu Server and make sure your ubuntu server update, run the following commands one by one, and install any available updates:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Adding PPA ###
|
||||
|
||||
Add the PPA cherokee webserver. by running the following commands
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:cherokee-webserver
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
Now, only for servers running Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty) follow this step below
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/apt/sources.list.d
|
||||
|
||||
nano cherokee-webserver-ppa-trusty.list
|
||||
|
||||
replace:
|
||||
|
||||
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/cherokee-webserver/ppa/ubuntu trusty main
|
||||
|
||||
to:
|
||||
|
||||
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/cherokee-webserver/ppa/ubuntu saucy main
|
||||
|
||||
**then again run:**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Installing Cherokee Web Server using apt-get ###
|
||||
|
||||
Enter the following command to install the Cherokee web server including Module SSL
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install cherokee cherokee-admin cherokee-doc libcherokee-mod-libssl libcherokee-mod-streaming libcherokee-mod-rrd
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Configuring Cherokee ###
|
||||
|
||||
sudo service cherokee start
|
||||
|
||||
The best part about using its Web Server is being able to manage all of its configurations through a simple to use web interface. This interface, known as cherokee-admin, is the recommended means of administering cherokee web server through web browser. Start cherokee-admin by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cherokee-admin
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: The cherokee-admin will display the administration user name, One-time Password and administration web interface.**
|
||||
|
||||
**Note down your One-Time password. You will need this when you login to its admin web interface.**
|
||||
|
||||
By default, cherokee-admin can only accessed from localhost. If you need to access the admin for other network address using the parameter ‘**-b**’. If you doesn’t mention any ip address, it will automatically listen to all network interfaces. Then you can connect to cherokee-admin from other network address.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cherokee-admin -b
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to access its admin from specific network address
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cherokee-admin -b 192.168.1.102
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Browse your Cherokee Admin Panel ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can access the administration panel from you favorite browser by typing http://hostname_or_IP:9090/ for me its http://127.0.0.1:9090/, it will appear on your browser like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Hurray, we have successfully installed and configured Cherokee Web Server in our Ubuntu Server.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-cherokee-lightweight-web-server-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
|
||||
How to Remember and Restore Running Applications on Next Logon
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
You have made some apps running in your Ubuntu and don't want to stop the process, just managed your windows and opened your stuffs needed to work. Then, something else demands your attention or you have battery low in your machine and you have to shut down. No worries. You can have Ubuntu remember all your running applications and restore them the next time you log in.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, to make our Ubuntu remember the applications you have running in our current session and restore them the next time our log in, We will use the dconf-editor. This tool replaces the gconf-editor available in previous versions of Ubuntu but is not available by default. To install the dconf-editor, you need to run sudo apt-get install dconf-editor.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install dconf-tools
|
||||
|
||||
Once the dconf-editor is installed, you can open dconf-editor from Application Menu. Or you can run it from terminal or run command (alt+f2):
|
||||
|
||||
$ dconf-editor
|
||||
|
||||
In the “dconf Editor” window, click the right arrow next to “org” in the left pane to expand that branch of the tree.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Under “org”, click the right arrow next to “gnome.”
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Under “gnome,” click “gnome-session”. In the right pane, select the “auto-save-session” check box to turn on the option.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After you check or tick it, close the “Dconf Editor” by clicking the close button (X) in the upper-left corner of the window which is by default.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The next time you log out and log back in, all of your running applications will be restored.
|
||||
|
||||
Hurray, we have successfully configured our Ubuntu 14.04 LTS "Trusty" to remember automatically running applications from our last session.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, on this same tutorial, we'll gonna also learn **how to enable hibernation in our Ubuntu 14.04 LTS**:
|
||||
|
||||
Before getting started, press Ctrl+ALt+T on your keyboard to open the terminal. When it opens, run:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo pm-hibernate
|
||||
|
||||
After your computer turns off, switch it back on. Did your open applications re-open? If hibernate doesn’t work, check if your swap partition is at least as large as your available RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
You can check your Swap Area Partition Size from System Monitor, you can get it from the App Menu or run command in terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ gnome-system-monitor
|
||||
|
||||
### Enable Hibernate in System Tray Menu: ###
|
||||
|
||||
The indicator-session was updated to use logind instead of upower. Hibernate is disabled by default in both upower and logind.
|
||||
|
||||
To re-enable hibernate, run the commands below one by one to edit the config file:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo -i
|
||||
|
||||
cd /var/lib/polkit-1/localauthority/50-local.d/
|
||||
|
||||
gedit com.ubuntu.enable-hibernate.pkla
|
||||
|
||||
**Tips: if the config file does not work for you, try another one by changing /var/lib to /etc in the code.**
|
||||
|
||||
Copy and paste below lines into the file and save it.
|
||||
|
||||
[Re-enable hibernate by default in upower]
|
||||
Identity=unix-user:*
|
||||
Action=org.freedesktop.upower.hibernate
|
||||
ResultActive=yes
|
||||
|
||||
[Re-enable hibernate by default in logind]
|
||||
Identity=unix-user:*
|
||||
Action=org.freedesktop.login1.hibernate
|
||||
ResultActive=yes
|
||||
|
||||
Restart your computer and done.
|
||||
|
||||
### Hibernate your laptop when lid is closed: ###
|
||||
|
||||
1.Edit “/etc/systemd/logind.conf” via command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/systemd/logind.conf
|
||||
|
||||
2. Change the line **#HandleLidSwitch=suspend to HandleLidSwitch=hibernate** and save the file.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Run command below or just restart your computer to apply changes:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo restart systemd-logind
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. Enjoy! Now, we have both dconf and hibernation on :) Now, your Ubuntu will completely remember your opened apps and stuffs.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/remember-running-applications-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
[Quick Tip] How To Restart Cinnamon After Crash
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Cinnamon is a Linux desktop environment which provides advanced innovative features and a traditional user experience. The desktop layout is similar to Gnome 2. The underlying technology is similar from Gnome Shell. The emphasis is put on making users feel at home and providing them with an easy to use and comfortable desktop experience.
|
||||
|
||||
In this post, we’re going to look at a quick way to restart Cinnamon without logging out or rebooting when it crashes.
|
||||
|
||||
The image below is an example of Cinnamon crashed desktop where text and icons vanish from Menu and panel.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To restart Cinnamon
|
||||
|
||||
Press **Alt + F2** this brings out a command menu. Type **r** and press Enter.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon should restart displaying icons and text in panel and menu.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/quick-tip-restart-cinnamon-crash/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Enock Seth Nyamador][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/seth/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
‘Unity Greeter Badges’ Brings Missing Session Icons to Ubuntu Login Screen
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**A new package available in Ubuntu 15.04 solves a petty gripe I have with the Unity Greeter: the lack of branded icons for alternative desktop sessions like Cinnamon.**
|
||||
|
||||
I know it’s a minor quibble; it’s a visual paper cut with minimal impact for most. But the inconsistency niggles me because Ubuntu ships with icons for a number of sessions, including Unity, GNOME and KDE. Other DEs, including some of its own flavors like Xubuntu, default to showing a plain white dot in the session switcher list and the main user pod.
|
||||
|
||||
The inconsistency these dots create jars, even if it is only for a fleeting moment, not just in design. It’s in usability too. Branded glyphs are helpful in letting us know what session we’re about to log in to.
|
||||
|
||||
For instance, can you tell what session this is?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Budgie? Maybe MATE? Could be Cinnamon…I’d have to click on it and check first.
|
||||
|
||||
It doesn’t have to be this way. The Unity Greeter is built such that the developers of desktop environments can ship badges that appear in the Greeter (and some do). But in many cases, like MATE whose packages are imported from upstream Debian, the inclination to carry an “Ubuntu-specific patch” is either not desirable or not possible.
|
||||
|
||||
### A Solution Is Badged ###
|
||||
|
||||
Experienced Debian maintainer [Doug Torrance][1] has a solution to fix this usability paper cut. Rather than rely on desktop makers themselves to add branded badges to their packages, and rather than burden Ubuntu with the responsibility of maintaining it, Torrance has created a separate ‘unity-greeter-badges’ package to house them.
|
||||
|
||||
In assuming responsibility for providing the session glyphs directly, this package ensure that new and old window managers, session and desktops alike are catered for.
|
||||
|
||||
Among the 30 or so desktop environments it bundles new session badges for are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Xubuntu
|
||||
- Cinnamon
|
||||
- MATE
|
||||
- Cairo-Dock
|
||||
- Xmonad
|
||||
- Awesome
|
||||
- OpenBox
|
||||
- Pantheon
|
||||
|
||||
The best part is that ‘**Unity-Greeter-Badges**’ has been accepted into Ubuntu 15.04. That means Torrance’s package will be available to install directly, no PPAs or downloads needed. In not being part of a core package like the Unity Greeter it can be updated with newer icons in a more efficient and timely manner.
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re running Ubuntu 15.04 you will find the package available to install from the Software Center in the coming days.
|
||||
|
||||
Don’t want to wait until 15.04? Torrance has made .deb installers for Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and Ubuntu 14.10 users.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download unity-greeter-badges for Ubuntu 14.04][2]
|
||||
- [Download unity-greeter-badges for Ubuntu 14.10][3]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/01/unity-greeter-badges-brings-missing-session-icons-ubuntu-login-screen
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/~profzoom
|
||||
[2]:https://launchpad.net/~profzoom/+archive/ubuntu/misc/+files/unity-greeter-badges_0.1-0ubuntu1%7E201412111501%7Eubuntu14.04.1_all.deb
|
||||
[3]:https://launchpad.net/~profzoom/+archive/ubuntu/misc/+files/unity-greeter-badges_0.1-0ubuntu1%7E201412111501%7Eubuntu14.10.1_all.deb
|
||||
@ -1,168 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translated By H-mudcup
|
||||
|
||||
文件轻松比对,伟大而自由的比较软件们
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
作者 Frazer Kline
|
||||
|
||||
文件比较工具用于比较电脑文件的内容,找到他们之间相同与不同之处。比较的结果通常被称为diff。
|
||||
|
||||
diff同时也是一个著名的,基于控制台的,能输出两个文件之间不同之处的,文件比较程序的名字。diff是二十世纪70年代早期,在Unix操作系统上被开发出来的。diff将会把两个文件之间不同之处的部分进行输出。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux拥有很多不错的,能使你能清楚的看到两个文件或同一文件不同版本之间的不同之处的,很棒的GUI工具。这次我从自己最喜欢的GUI比较工具中选出了五个推荐给大家。除了其中的一个,其他的都有开源许可证。
|
||||
|
||||
这些应用程序可以让文件或目录的差别变得可见,能合并有差异的文件,可以解决冲突并将其输出成一个新的文件或补丁,还能帮助回顾文件被改动过的地方并评论最终产品(比如,在源代码合并到源文件树之前,要先批准源代码的改变)。因此它们是非常重要的软件开发工具。它们不停的把文件传来传,帮助开发人员们在同一个文件上工作。这些比较工具不仅仅能用于显示源代码文件中的不同之处;他们还适用于很多种文本类文件。可视化的特性使文件比较变得容易、简单。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Meld是一个适用于Gnome桌面的,开源的,图形化的文件差异查看和合并的应用程序。它支持2到3个文件的同时比较,递归式的目录比较,版本控制(Bazaar, Codeville, CVS, Darcs, Fossil SCM, Git, Mercurial, Monotone, Subversion)之下的目录比较。还能够手动或自动合并文件差异。
|
||||
|
||||
eld的重点在于帮助开发人员比较和合并多个源文件,并在他们最喜欢的版本控制系统下能直观的浏览改动过的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
功能包括
|
||||
|
||||
- 原地编辑文件,即时更新
|
||||
- 进行两到三个文件的比较及合并
|
||||
- 差异和冲突之间的导航
|
||||
- 可视化本地和总体间的插入、改变和冲突这几种不同之处。
|
||||
- 内置正则表达式文本过滤器,可以忽略不重要的差异
|
||||
- 语法高亮度显示(可选择gtksourceview)
|
||||
- 将两到三个目录一个文件一个文件的进行比较,显示新建,缺失和替换过的文件。
|
||||
- 可直接开启任何有冲突或差异的文件的比较
|
||||
- 可以过滤文件或目录以避免出现假差异
|
||||
- 被改动区域的自动合并模式使合并更容易
|
||||
- 简单的文件管理
|
||||
- 支持多种版本控制系统,包括Git, Mercurial, Bazaar and SVN
|
||||
- 在提交前开启文件比较来检查改动的地方和内容
|
||||
- 查看文件版本状态
|
||||
- 还能进行简单的版本控制操作(例如,提交、更新、添加、移动或删除文件)
|
||||
- 继承自同一文件的两个文件进行自动合并
|
||||
- 标注并在中间的窗格显示所有有冲突的变更的基础版本
|
||||
- 显示并合并同一文件的各自独立的修改
|
||||
- 锁定只读性质的基础文件以避免出错
|
||||
- 可以整合到已有的命令行界面中,包括gitmergetool
|
||||
- 国际化支持
|
||||
- 可视化使文件比较更简单
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址: [meldmerge.org][1]
|
||||
- 开发人员: Kai Willadsen
|
||||
- 证书: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.8.5
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
注:上面这个图访问不到,图的地址是原文地址的小图的链接地址,发布的时候在验证一下,如果还访问不到,不行先采用小图或者网上搜一下看有没有大图
|
||||
|
||||
DiffMerge是一个可以在Linux、Windows和OS X上运行的,可以可视化文件的比较和合并的应用软件。
|
||||
|
||||
功能包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 图形化的显示两个文件之间的差别。包括插入行,高亮标注以及对编辑的全面支持。
|
||||
- 图形化的显示三个文件之间的差别。(安全的前提下)允许自动合并还完全拥有最终文件的编辑权。
|
||||
- 并排显示两个文件夹的比较,显示哪一个文件只存在于其中一个文件夹而不存在于与之相比较的那个文件夹,还能一对一的将完全相同的、等价的或不同的文件配对。
|
||||
- 规则设置和选项让你可以个性化它的外观和行为
|
||||
- 基于Unicode,可以导入多种编码的字符
|
||||
- 跨平台工具
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址: [sourcegear.com/diffmerge][2]
|
||||
- 开发人员: SourceGear LLC
|
||||
- 证书: Licensed for use free of charge (not open source)
|
||||
- 版本号: 4.2
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
xxdiff是个开源的图形化的,可进行文件、目录比较及合并的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
xxdiff可以用于显示两到三个文件或两个目录的差别,还能产生一个合并后的版本。被比较的两到三个文件会并排显示,并将有区别的文字内容用不同颜色高亮显示以便于识别。
|
||||
|
||||
这个程序是个非常重要的软件开发工具。他可以图形化的显示两个文件或目录之间的差别,合并有差异的文件,解决冲突并评论结果(例如在源代码合并到一个源文件树里之前必须先允许其改变)
|
||||
|
||||
功能包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 比较两到三个文件,或是两个目录(浅层或递归)
|
||||
- 水平差别高亮显示
|
||||
- 文件可以被交互式的合并,可视化的输出和保存
|
||||
- 可以可视化合并的评论/监管
|
||||
- 保留自动合并文件中的冲突,并以两个文件显示以便于解决冲突
|
||||
- 用额外的比较程序估算差异:适用于GNU diff、SGI diff和ClearCase的cleardiff,以及所有与这些程序输出相似的文件比较程序。
|
||||
- 可以在源文件上实现完全的个性化设置
|
||||
- 用起来感觉和Rudy Wortel或SGI的xdiff差不多, it is desktop agnostic
|
||||
- 功能和输出可以和脚本轻松集成
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址: [furius.ca/xxdiff][3]
|
||||
- 开发人员: Martin Blais
|
||||
- 证书: GNU GPL
|
||||
- 版本号: 4.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Diffuse是个开源的图形化工具,可用于合并和比较文本文件。Diffuse能够比较任意数量的文件,并排显示,并提供手动行匹配调整,能直接编辑文件。Diffuse还能从bazaar、CVS、darcs, git, mercurial, monotone, Subversion和GNU矫正控制系统(GNU Revision Control System ,RCS)这些关于比较及合并的资源中对文件进行恢复和矫正。
|
||||
|
||||
功能包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 比较任意数量的文件,并排显示(多方合并)
|
||||
- 行匹配可以被用户人工矫正
|
||||
- 直接编辑文件
|
||||
- 语法高亮
|
||||
- 支持Bazaar, CVS, Darcs, Git, Mercurial, Monotone, RCS, Subversion和SVK
|
||||
- 支持Unicode
|
||||
- 可无限撤销
|
||||
- 简易键盘导航
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址: [diffuse.sourceforge.net][]
|
||||
- 开发人员: Derrick Moser
|
||||
- 证书: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.4.7
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Kompare是个开源的GUI前端程序,可以开启不同源文件之间差异的可视化和合并。Kompare可以比较文件或文件夹内容的差异。Kompare支持很多种diff格式,并提供各种选项来设置显示的信息级别。
|
||||
|
||||
不论你是个想比较源代码的开发人员,还是只想比较一下研究论文手稿与最终文档的差异,Kompare都是个有用的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
Kompare是KDE桌面环境的一部分。
|
||||
|
||||
功能包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 比较两个文本文件
|
||||
- 递归式比较目录
|
||||
- 显示diff产生的补丁
|
||||
- 将补丁合并到一个已存在的目录
|
||||
- 在无聊的编译时刻,逗你玩
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址: [www.caffeinated.me.uk/kompare/][5]
|
||||
- 开发者: The Kompare Team
|
||||
- 证书: GNU GPL
|
||||
- 版本号: Part of KDE
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/2014062814400262/FileComparisons.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[H-mudcup](https://github.com/H-mudcup) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://meldmerge.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://sourcegear.com/diffmerge/
|
||||
[3]:http://furius.ca/xxdiff/
|
||||
[4]:http://diffuse.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.caffeinated.me.uk/kompare/
|
||||
@ -1,22 +0,0 @@
|
||||
开始使用Ubuntu 14.04(PDF指南)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
开始熟悉每天的任务,像上网冲浪,听听音乐,还有扫描文档之类。
|
||||
|
||||
好好享受这份全面而综合的Ubuntu操作系统初学者指南吧。本教程适用于任何经验等级的人,跟着傻瓜式的指令一步一步操作吧。好好探索Ubuntu系统的潜力吧,你不会因为技术细节而陷入困境。
|
||||
|
||||
- [**开始使用Ubuntu 14.04 (PDF指南)**][1]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/getting-started-with-ubuntu-14-04-pdf-guide.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
|
||||
[1]:http://ubuntugeek.tradepub.com/free/w_ubun06/
|
||||
@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Calife —— 一个轻量级的sudo替代方案
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Calife要求用户用户以自己的密码登录(或者root,如果没有提供登录),在验证具有正确的权限后,就会切换到该用户以及组身份,然后就会执行一个shell。如果calife是由root执行的,不需要密码,一个具有恰当用户ID的shell就会被执行。
|
||||
|
||||
唤醒的shell是用户自身的,除非在calife.auth配置文件中指定了某个shell。
|
||||
|
||||
如果在命令行指定了“-”选项,就会读取该用户的环境文件,该shell就像是一个登陆shell。
|
||||
|
||||
这不是su的惯用操作。
|
||||
|
||||
只有在calife.auth中指定的用户才能使用此方法通过calife成为另外一个用户。
|
||||
|
||||
calife.auth安装位置处于/etc/calife.auth。
|
||||
|
||||
### Calife特性 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里给出了一个关于calife特性的扩展列表:
|
||||
|
||||
你可以完整保留环境变量和shell别名
|
||||
|
||||
它可以全程记录会话开始到结束
|
||||
|
||||
你可以为每个calife用户许可的登录制作列表,那样,你就可以用户赋予主管权限而不必提供root密码
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在配置文件中指定一个组来取代所有管理员登录:只要使用@staff或者%staff,那么所有staff组中的成员都将具有访问calife的权限
|
||||
|
||||
calife也可以成为那些没有家目录或甚至没有shell的用户。如果你想要成为uucp或者甚至是bin,那会很实用
|
||||
|
||||
你可以让calife在会话结束时运行一个指定的系统范围的脚本(例如,发送一封邮件告知以root身份做了哪些事)
|
||||
|
||||
### ubuntu中安装calife ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端,然后运行以下命令
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install calife
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用Calife ###
|
||||
|
||||
### 语法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
calife [-] [login]
|
||||
|
||||
详情请参与calife手册页
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.ubuntugeek.com/calife-a-lightweight-alternative-to-sudo.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ruchi][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.ubuntugeek.com/author/ubuntufix
|
||||
[1]:
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
[13]:
|
||||
[14]:
|
||||
[15]:
|
||||
[16]:
|
||||
[17]:
|
||||
[18]:
|
||||
[19]:
|
||||
[20]:
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
||||
如何在终端使用后台运行模式启动一个Linux应用程序
|
||||
========================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这是一个篇幅不长但是十分有用的教程,可以帮助你在终端启动一个Linux应用程序,并且使终端窗口不会丢失焦点。
|
||||
|
||||
我们有很多方法可以在Linux系统中打开一个终端窗口,这取决与你的选择以及你的桌面环境。
|
||||
|
||||
如果是使用Ubuntu的话,你可以利用CTRL+ALT+T组合键打开终端。当然你也可以使用超级键(Windows键)[打开Dash][1],搜索“TERM”,然后点击“Term”图标来打开终端窗口。
|
||||
|
||||
对于其他的桌面环境来说,例如XFCE、KDE、LXDE、Cinnamon以及MATE,你可以在菜单中找到终端。有些环境会在停靠栏或者面板上面包含终端图标。
|
||||
|
||||
通常情况下,你可以在终端里面直接输入应用程序名来启动一个应用程序。比如说,你可以通过输入“firefox”来启动Firefox。
|
||||
|
||||
在终端启动应用程序的好处是,你可以包含一些额外的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,你可以通过下列命令来打开一个Firefox浏览窗口,然后利用默认的搜索引擎搜索相关信息:
|
||||
|
||||
firefox -search "linux.cn"
|
||||
|
||||
你可能会注意到,当你启动Firefox的时候,如果程序打开以后,焦点重新会到终端窗口的话,你就可以继续在终端进行工作。
|
||||
|
||||
通常情况下,如果你在终端启动了应用程序,焦点会切换到新启动的应用程序,只有程序被关闭以后焦点才会重新切换到终端。这是因为你在前台启动了这个程序。
|
||||
|
||||
如果要实现焦点仍然保持在终端窗口的目的,那么你需要将应用程序启动为后台进程。
|
||||
|
||||
向下面所列的命令一样,我们可以通过增加一个(&)符号,将应用程序在后台启动。
|
||||
|
||||
libreoffice &
|
||||
|
||||
>译者注:如果需要加参数的话,记得把&符号放在最后。
|
||||
|
||||
>译者注:一般情况下,关闭终端时,在这个终端启动的后台程序也会被终止,要使终端关闭以后,后台程序依然保持执行可以使用下列命令
|
||||
|
||||
> nohup command [arg...] &
|
||||
|
||||
如果应用程序目录没有安装在PATH变量包含的目录里面的话,我们就没有办法直接通过应用程序名来启动程序,必须输入应用程序的整个路径来启动它。
|
||||
|
||||
/path/to/yourprogram &
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不确定程序输入哪个Linux目录结构的话,可以使用[find][2]或者[location][3]命令来定位它。
|
||||
|
||||
可以输入下列符号来找到一个文件:
|
||||
|
||||
find /path/to/start/from -name programname
|
||||
|
||||
例如,你可以输入下列命令来找到Firefox:
|
||||
|
||||
find / -name firefox
|
||||
|
||||
命令运行的结果会嗖的一下输出一大堆,别担心,你也可以通过[less][4]或者[more][5]来进行分页查看。
|
||||
|
||||
find / -name firefox | more
|
||||
|
||||
find / -name firefox | less
|
||||
|
||||
当find命令查找到没有权限访问的文件夹时,会报出一条拒绝访问错误,
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过[sudo命令来提示权限][6]。当然,如果你没有安装sudo的话,就只能切换到一个拥有权限的用户了。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo find / -name firefox | more
|
||||
|
||||
如果你知道你要查找的文件在你的当前目录及其子目录中,那么你可以使用点来代替斜杠:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo find . -name firefox | more
|
||||
|
||||
你可能需要sudo来提升权限,也可能根本就不需要,如果这个文件在你的跟目录里面,那么就不需要使用sudo。
|
||||
|
||||
有些应用程序则必须要提升权限才能运行,否则你就会得到一大堆拒绝访问错误,除非你使用一个具有权限的用户,或者使用sudo提升权限。
|
||||
|
||||
这里有个小窍门。如果你运行了一个程序,但是它报了权限错误以后,输入下面命令试试:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo !!
|
||||
|
||||
via : http://linux.about.com/od/commands/fl/How-To-Run-Linux-Programs-From-The-Terminal-In-Background-Mode.htm
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gary Newell][a]
|
||||
译者:[zhouj-sh](https://github.com/zhouj-sh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linux.about.com/bio/Gary-Newell-132058.htm
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.about.com/od/howtos/fl/Learn-Ubuntu-The-Unity-Dash.htm
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.about.com/od/commands/l/blcmdl1_find.htm
|
||||
[3]:http://linux.about.com/od/commands/l/blcmdl1_locate.htm
|
||||
[4]:http://linux.about.com/library/cmd/blcmdl1_less.htm
|
||||
[5]:http://linux.about.com/library/cmd/blcmdl1_more.htm
|
||||
[6]:http://linux.about.com/od/commands/l/blcmdl8_sudo.htm
|
||||
@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux 上好用的几款字幕编辑器介绍
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如果你经常看国外的大片,你应该会喜欢带字幕版本而不是有国语配音的版本。在法国长大,我的童年记忆里充满了迪斯尼电影。但是这些电影因为有了法语的配音而听起来很怪。如果现在有机会能看原始的版本,我知道,对于大多数的人来说,字幕还是必须的。我很高兴能为家人制作字幕。最让我感到希望的是,Linux 也不无花哨,而且有很多开源的字幕编辑器。总之一句话,这篇文章并不是一个详尽的Linux上字幕编辑器的列表。你可以告诉我那一款是你认为最好的字幕编辑器。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Gnome Subtitles ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Gnome Subtitles][1] 我的一个选择,当有字幕需要快速编辑时。你可以载入视频,载入字幕文本,然后就可以即刻开始了。我很欣赏其对于易用性和高级特性之间的平衡性。它带有一个同步工具以及一个拼写检查工具。最后,虽然最后,但并不是不重要,这么好用最主要的是因为它的快捷键:当你编辑很多的台词的时候,你最好把你的手放在键盘上,使用其内置的快捷键来移动。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Aegisub ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Aegisub][2] 有更高级别的复杂性。接口仅仅反映了学习曲线。但是,除了它吓人的样子以外,Aegisub 是一个非常完整的软件,提供的工具远远超出你能想象的。和Gnome Subtitles 一样,Aegisub也采用了所见即所得(WYSIWYG:what you see is what you get)的处理方式。但是是一个全新的高度:可以再屏幕上任意拖动字幕,也可以在另一边查看音频的频谱,并且可以利用快捷键做任何的事情。除此以外,它还带有一个汉字工具,有一个kalaok模式,并且你可以导入lua 脚本让它自动完成一些任务。我希望你在用之前,先去阅读下它的[指南][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Gaupol ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
另一个操作复杂的软件是[Gaupol][4],不像Aegisub ,Gaupol 很容易上手而且采用了一个和Gnome Subtitles 很像的界面。但是在这些相对简单背后,它拥有很多很必要的工具:快捷键、第三方扩展、拼写检查,甚至是语音识别(由[CMU Sphinx][5]提供)。这里也提一个缺点,我注意到有时候在测试的时候也,软件会有消极怠工的表现,不是很严重,但是也足以让我更有理由喜欢Gnome Subtitles了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Subtitle Editor ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Subtitle Editor][6]和Gaupol 很像。但是,它的界面有点不太直观,特性也只是稍微的高级一点点。我很欣赏的一点是,它可以定义“关键帧”,而且提供所有的同步选项。然而,多一点的图标,或者是少一点的文字都能提供界面的特性。作为一个好人,我认为,Subtitle Editor 可以模仿“作家”打字的效果,虽然我不知道它是否有用。最后但并非不重要。重定义快捷键的功能很实用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Jubler ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
用Java 写的,[Jubler][7]是一个多平台支持的字幕编辑器。我对它的界面印象特别深刻。在上面我确实看出了Java-ish 方面的东西,但是,它仍然是经过精心的构造和构思的。像Aegisub 一样,你可以再屏幕上任意的拖动字幕,让你有愉快的体验而不单单是打字。它也可以为字幕自定义一个风格,在另外的一个轨道播放音频,翻译字幕,或者是是做拼写检查,然而,你必须要注意的是,你必须事先安装好媒体播放器并且正确的配置,如果你想完整的使用Jubler。我把这些归功于在[官方页面][8]下载了脚本以后其简便的安装方式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Subtitle Composer ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
被视为“KDE里的字幕作曲家”,[Subtitle Composer][9]能够唤起对很多传统功能的回忆。伴随着KDE界面,我们很期望。很自然的我们就会说到快捷键,我特别喜欢这个功能。除此之外,Subtitle Composer 与上面提到的编辑器最大的不同地方就在于,它可以执行用JavaScript,Python,甚至是Ruby写成的脚本。软件带有几个例子,肯定能够帮助你很好的学习使用这些特性的语法。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,不管你喜不喜欢我,都要为你的家庭编辑几个字幕,重新同步整个轨道,或者是一切从头开始,那么Linux 有很好的工具给你。对我来说,快捷键和易用性使得各个工具有差异,想要更高级别的使用体验,脚本和语音识别就成了很便利的一个功能。
|
||||
|
||||
你会使用哪个字幕编辑器,为什么?你认为还有没有更好用的字幕编辑器这里没有提到的?在评论里告诉我们。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/good-subtitle-editor-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/adrien
|
||||
[1]:http://gnomesubtitles.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.aegisub.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://docs.aegisub.org/3.2/Main_Page/
|
||||
[4]:http://home.gna.org/gaupol/
|
||||
[5]:http://cmusphinx.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[6]:http://home.gna.org/subtitleeditor/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.jubler.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.jubler.org/download.html
|
||||
[9]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/subcomposer/
|
||||
@ -1,65 +0,0 @@
|
||||
黑客年暮
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
近来我一直在与某资深开源组织的各成员进行争斗,尽管密切关注我的人们会在读完本文后猜到是哪个组织,但我不会在这里说出这个组织的名字。
|
||||
|
||||
怎么让某些人进入 21 世纪就这么难呢?真是的...
|
||||
|
||||
我快56 岁了,也就是大部分年轻人会以为的我将时不时朝他们发出诸如“滚出我的草坪”之类歇斯底里咆哮的年龄。但事实并非如此 —— 我发现,尤其是在技术背景之下,我变得与我的年龄非常不相称。
|
||||
|
||||
在我这个年龄的大部分人确实变成了爱发牢骚、墨守成规的老顽固。并且,尴尬的是,偶尔我会成为那个打断谈话的人,然后提出在 1995 年(或者在某些特殊情况下,1985 年)时很适合的方法... 但十年后就不是个好方法了。
|
||||
|
||||
为什么是我?因为我的同龄人里大部分人在孩童时期都没有什么名气。任何想要改变自己的人,就必须成为他们中具有较高思想觉悟的佼佼者。即便如此,在与习惯做斗争的过程中,我也比实际上花费了更多的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
年轻人犯下无知的错误是可以被原谅的。他们还年轻。年轻意味着缺乏经验,缺乏经验通常会导致片面的判断。我很难原谅那些经历了足够多本该有经验的人,却被<em>长期的固化思维</em>蒙蔽,无法发觉近在咫尺的东西。
|
||||
|
||||
(补充一下:我真的不是老顽固。那些和我争论政治的,无论保守派还是非保守派都没有注意到这点,我觉得这颇有点嘲讽的意味。)
|
||||
|
||||
那么,现在我们来讨论下 GNU 更新日志文件这件事。在 1985 年的时候,这是一个不错的主意,甚至可以说是必须的。当时的想法是用单独的更新日志文件来记录相关文件的变更情况。用这种方式来对那些存在版本缺失或者非常原始的版本进行版本控制确实不错。当时我也在场,所以我知道这些。
|
||||
|
||||
不过即使到了 1995 年,甚至 21 世纪早期,许多版本控制系统仍然没有太大改进。也就是说,这些版本控制系统并非对批量文件的变化进行分组再保存到一条记录上,而是对每个变化的文件分别进行记录并保存到不同的地方。CVS,当时被广泛使用的版本控制系统,仅仅是模拟日志变更 —— 并且在这方面表现得很糟糕,导致大多数人不再依赖这个功能。即便如此,更新日志文件的出现依然是必要的。
|
||||
|
||||
但随后,版本控制系统 Subversion 于 2003 年发布 beta 版,并于 2004 年发布 1.0 正式版,Subversion 真正实现了更新日志记录功能,得到了人们的广泛认可。它与一年后兴起的分散式版本控制系统(Distributed Version Control System,DVCS)共同引发了主流世界的激烈争论。因为如果你在项目上同时使用了分散式版本控制与更新日志文件记录的功能,它们将会因为争夺相同元数据的控制权而产生不可预料的冲突。
|
||||
|
||||
另一种方法是对提交的评论日志进行授权。如果你这样做了,不久后你就会开始思忖为什么自己仍然对所有的日志更新条目进行记录。提交的元数据与变化的代码具有更好的相容性,毕竟这就是它当初设计的目的。
|
||||
|
||||
(现在,试想有这样一个项目,同样本着把项目做得最好的想法,但两拨人却做出了完全不同的选择。因此你必须同时阅读更新日志和评论日志以了解到底发生了什么。最好在矛盾激化前把问题解决....)
|
||||
|
||||
第三种办法是尝试同时使用两种方法 —— 以另一种格式再次提交评论数据,作为更新日志提交的一部分。这解决了所有你期待的有代表性的问题,并且没有任何缺陷遗留下来;只要其中有拷贝文件损坏,日志文件就会修改,因此这不再是同步时数据匹配的问题,而且导致在其后参与进来的人试图搞清人们是怎么想的时候将会变得非常困惑。
|
||||
|
||||
或者,如某个<em>我就不说出具体名字的特定项目</em>的高层开发只是通过电子邮件来完成这些,声明提交可以包含多个更新日志,以及提交的元数据与更新日志是无关的。这导致我们直到现在还得不断进行记录。
|
||||
|
||||
当我读到那条的时候我的眼光停在了那个地方。什么样的傻瓜才会没有意识到这是在自找麻烦 —— 事实上,针对更新日志文件采取的定制措施完全是不必要的,尤其是在分散式版本控制系统中
|
||||
有很好的浏览工具来阅读可靠的提交日志的时候。
|
||||
|
||||
唉,这是比较特殊的笨蛋:变老的并且思维僵化了的黑客。所有的合理化改革他都会极力反对。他所遵循的行事方法在十年前是有效的,但现在只能使得其反了。如果你试图解释不只是git的总摘要,还得正确掌握当前的各种工具才能完全弃用更新日志... 呵呵,准备好迎接无法忍受、无法想象的疯狂对话吧。
|
||||
|
||||
幸运的是这激怒了我。因为这点还有其他相关的胡言乱语使这个项目变成了很难完成的工作。而且,这类糟糕的事时常发生在年轻的开发者身上,这才是问题所在。相关 G+ 社群的数量已经达到了 4 位数,他们大部分都是孩子,他们也没有紧张起来。显然消息已经传到了外面;这个项目的开发者都是被莫名关注者的老牌黑客,同时还有很多对他们崇拜的人。
|
||||
|
||||
这件事给我的最大触动就是每当我要和这些老牌黑客较量时,我都会想:有一天我也会这样吗?或者更糟的是,我看到的只是如同镜子一般对我自己的真实写照,而我自己却浑然不觉吗?我的意思是,我的印象来自于他的网站,这个特殊的样本要比我年轻。通过十五年的仔细观察得出的结论。
|
||||
|
||||
我觉得思路很清晰。当我和那些比我聪明的人打交道时我不会受挫,我只会因为那些不能跟上我的人而
|
||||
沮丧,这些人也不能看见事实。但这种自信也许只是邓宁·克鲁格效应的消极影响,至少我明白这点。很少有什么事情会让我感到害怕;而这件事在让我害怕的事情名单上是名列前茅的。
|
||||
|
||||
另一件让人不安的事是当我逐渐变老的时候,这样的矛盾发生得越来越频繁。不知怎的,我希望我的黑客同行们能以更加优雅的姿态老去,即使身体老去也应该保持一颗年轻的心灵。有些人确实是这样;但可是绝大多数人都不是。真令人悲哀。
|
||||
|
||||
我不确定我的职业生涯会不会完美收场。假如我最后成功避免了思维僵化(注意我说的是假如),我想我一定知道其中的部分原因,但我不确定这种模式是否可以被复制 —— 为了达成目的也许得在你的头脑中发生一些复杂的化学反应。尽管如此,无论对错,请听听我给年轻黑客以及其他有志青年的建议。
|
||||
|
||||
你们 —— 对的,也包括你 —— 一定无法在你中年老年的时候保持不错的心灵,除非你能很好的控制这点。你必须不断地去磨练你的内心、在你还年轻的时候完成自己的种种心愿,你必须把这些行为养成一种习惯直到你老去。
|
||||
|
||||
有种说法是中年人锻炼身体的最佳时机是他进入中年的 30 年前。我以为同样的方法,坚持我以上所说的习惯能让你在 56 岁,甚至 65 岁的时候仍然保持灵活的头脑。挑战你的极限,使不断地挑战自己成为一种习惯。立刻离开安乐窝,由此当你以后真正需要它的时候你可以建立起自己的安乐窝。
|
||||
|
||||
你必须要清楚的了解这点;还有一个可选择的挑战是你选择一个可以实现的目标并且为了这个目标不断努力。这个月我要学习 Go 语言。不是指游戏,我早就玩儿过了(虽然玩儿的不是太好)。并不是因为工作需要,而是因为我觉得是时候来扩展下我自己了。
|
||||
|
||||
保持这个习惯。永远不要放弃。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://esr.ibiblio.org/?p=6485
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Eric Raymond][a]
|
||||
译者:[Stevearzh](https://github.com/Stevearzh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://esr.ibiblio.org/?author=2
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu上转换图片音频和视频格式
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的工作中需要接触到各种不同编码格式的图片、音频和视频,那么你或许正在使用多个工具来转换这些不同的媒介格式。如果存在一个能够处理所有文件/音频/视频格式的多和一的转换工具,那就太好了。
|
||||
|
||||
[Format Junkie][1] 就是这样一个有着极其友好的用户界面的多和一的媒介转换工具。更棒的是它是一个免费软件。你可以使用 Format Junkie 来转换几乎所有的流行格式的图像、音频、视频和归档文件(或称压缩文件),所有这些只需要简单地点击几下鼠标而已。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu 12.04, 12.10 和 13.04 上安装 Format Junkie ###
|
||||
|
||||
Format Junkie 可以通过 Ubuntu PPA format-junkie-team 进行安装。这个PPA支持Ubuntu 12.04, 12.10 和 13.04。在以上任意一种Ubuntu版本中安装Format Junkie的话,简单的执行一下命令即可:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:format-junkie-team/release
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install formatjunkie
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /opt/extras.ubuntu.com/formatjunkie/formatjunkie /usr/bin/formatjunkie
|
||||
|
||||
### 将 Format Junkie 安装到 Ubuntu 13.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你正在运行Ubuntu 13.10 (Saucy Salamander),你可以按照以下步骤下载 .deb 安装包来进行安装。由于Format Junkie 的 .deb 安装包只有很少的依赖包,所以使用 [gdebi deb installer][2] 来按安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
在32位版Ubuntu 13.10上:
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget https://launchpad.net/~format-junkie-team/+archive/release/+files/formatjunkie_1.07-1~raring0.2_i386.deb
|
||||
$ sudo gdebi formatjunkie_1.07-1~raring0.2_i386.deb
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /opt/extras.ubuntu.com/formatjunkie/formatjunkie /usr/bin/formatjunkie
|
||||
|
||||
在32位版Ubuntu 13.10上:
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget https://launchpad.net/~format-junkie-team/+archive/release/+files/formatjunkie_1.07-1~raring0.2_amd64.deb
|
||||
$ sudo gdebi formatjunkie_1.07-1~raring0.2_amd64.deb
|
||||
$ sudo ln -s /opt/extras.ubuntu.com/formatjunkie/formatjunkie /usr/bin/formatjunkie
|
||||
|
||||
### 将 Format Junkie 安装到 Ubuntu 14.04 或 之后版本 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现有的可供使用的官方 Format Junkie .deb 文件 需要 libavcodec-extra-53,这个东西从Ubuntu 14.04开始就已经过时了。所以如果你想在Ubuntu 14.04或之后版本上安装Format Junkie的话,可以使用以下的第三方PPA来代替。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:jon-severinsson/ffmpeg
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install formatjunkie
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何使用 Format Junkie ###
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,只需运行以下命令即可启动 Format Junkie:
|
||||
|
||||
$ formatjunkie
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 Format Junkie 来转换音频、视频、图像和归档格式 ####
|
||||
|
||||
就像下方展示的一样,Format Junkie 的用户界面简单而且直观。在音频、视频、图像和iso媒介之间进行选择,在顶部四个标签当中点击你需要的那个。你可以根据需要添加无限量的文件用于批量转换。添加文件后,选择输出格式,直接点击 "Start Converting" 按钮进行转换。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Format Junkie支持以下媒介媒介媒介格式间的转换:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Audio**: mp3, wav, ogg, wma, flac, m4r, aac, m4a, mp2.
|
||||
- **Video**: avi, ogv, vob, mp4, 3gp, wmv, mkv, mpg, mov, flv, webm.
|
||||
- **Image**: jpg, png, ico, bmp, svg, tif, pcx, pdf, tga, pnm.
|
||||
- **Archive**: iso, cso.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 用 Format Junkie 进行字幕编码 ####
|
||||
|
||||
除了媒介转换,Format Junkie 可提供了字幕编码的图形界面。实际的字幕编码是由MEncoder来完成的。为了使用Format Junkie的字幕编码接口,首先你需要安装MEencoder。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install mencoder
|
||||
|
||||
然后点击Format Junkie 中的 "Advanced"标签。选择 AVI/subtitle 文件来进行编码,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
总而言之,Format Junkie 是一个非常易于使用和多才多艺的媒介转换工具。但也有一个缺陷,它不允许对转换进行任何定制化(例如:比特率,帧率,采样频率,图像质量,尺寸)。所以这个工具推荐正在寻找一个简单易用的媒介转换工具的新手使用。
|
||||
|
||||
喜欢这篇文章吗?在facebook、twitter和google+上给我点赞吧。多谢!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/how-to-convert-image-audio-and-video-formats-on-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[Ping](https://github.com/mr-ping)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/format-junkie
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-deb-file-with-dependencies.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,207 @@
|
||||
如何配置fail2ban来保护Apache服务器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
生产环境中的Apache服务器可能会受到不同的攻击。攻击者或许试图通过暴力攻击或者执行恶意脚本来获取未经授权或者禁止访问的目录。一些恶意爬虫或许会扫描你网站下的任意安全漏洞,或者手机email地址或者web表格来发送垃圾邮件。
|
||||
|
||||
Apache服务器具有综合的日志功能来捕捉不同表明是攻击的异常事件。然而,它还不能系统地解析具体的apache日志并迅速地反应到潜在的攻击(比如,禁止/解禁IP地址)。这时候`fail2ban`可以解救这一切,解放了系统管理员的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
`fail2ban`是一款入侵防御工具,可以基于系统日志检测不同的工具并且可以自动采取保护措施比如:通过`iptables`禁止ip、阻止/etc/hosts.deny中的连接、或者通过邮件通知事件。fail2ban具有一系列预定义的“监狱”,它使用特定程序日志过滤器来检测通常的攻击。你也可以编写自定义的规则来检测来自任意程序的攻击。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我会演示如何配置fail2ban来保护你的apache服务器。我假设你已经安装了apache和fail2ban。对于安装,请参考[另外一篇教程][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 Fail2ban 监狱 ###
|
||||
|
||||
让我们更深入地了解fail2ban监狱。监狱定义了具体的应用策略,它会为指定的程序触发一个保护措施。fail2ban在/etc/fail2ban/jail.conf 下为一些流行程序如Apache、Dovecot、Lighttpd、MySQL、Postfix、[SSH][2]等预定义了一些监狱。每个依赖于特定的程序日志过滤器(在/etc/fail2ban/fileter.d 下面)来检测通常的攻击。让我看一个例子监狱:SSH监狱。
|
||||
|
||||
[ssh]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = ssh
|
||||
filter = sshd
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/auth.log
|
||||
maxretry = 6
|
||||
banaction = iptables-multiport
|
||||
|
||||
SSH监狱的配置定义了这些参数:
|
||||
|
||||
- **[ssh]**: 方括号内是监狱的名字。
|
||||
- **enabled**:是否启用监狱
|
||||
- **port**: 端口的数字 (或者数字对应的名称).
|
||||
- **filter**: 检测攻击的检测规则
|
||||
- **logpath**: 检测的日志文件
|
||||
- **maxretry**: 禁止前失败的最大数字
|
||||
- **banaction**: 禁止操作
|
||||
|
||||
定义配置文件中的任意参数都会覆盖相应的默认配置`fail2ban-wide` 中的参数。相反,任意缺少的参数都会使用定义在[DEFAULT]字段的值。
|
||||
|
||||
预定义日志过滤器都必须在/etc/fail2ban/filter.d,可以采取的操作在/etc/fail2ban/action.d。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要覆盖`fail2ban`的默认操作或者定义任何自定义监狱,你可以创建*/etc/fail2ban/jail.local**文件。本篇教程中,我会使用/etc/fail2ban/jail.local。
|
||||
|
||||
### 启用预定义的apache监狱 ###
|
||||
|
||||
`fail2ban`的默认安装为Apache服务提供了一些预定义监狱以及过滤器。我要启用这些内建的Apache监狱。由于Debian和红买配置的稍微不同,我会分别它们的配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Debian 或者 Ubuntu启用Apache监狱 ####
|
||||
|
||||
要在基于Debian的系统上启用预定义的apache监狱,如下创建/etc/fail2ban/jail.local。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# detect password authentication failures
|
||||
[apache]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-auth
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/apache*/*error.log
|
||||
maxretry = 6
|
||||
|
||||
# detect potential search for exploits and php vulnerabilities
|
||||
[apache-noscript]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-noscript
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/apache*/*error.log
|
||||
maxretry = 6
|
||||
|
||||
# detect Apache overflow attempts
|
||||
[apache-overflows]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-overflows
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/apache*/*error.log
|
||||
maxretry = 2
|
||||
|
||||
# detect failures to find a home directory on a server
|
||||
[apache-nohome]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-nohome
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/apache*/*error.log
|
||||
maxretry = 2
|
||||
|
||||
由于上面的监狱没有指定措施,这些监狱都将会触发默认的措施。要查看默认的措施,在/etc/fail2ban/jail.conf中的[DEFAULT]下找到“banaction”。
|
||||
|
||||
banaction = iptables-multiport
|
||||
|
||||
本例中,默认的操作是iptables-multiport(定义在/etc/fail2ban/action.d/iptables-multiport.conf)。这个措施使用iptable的多端口模块禁止一个IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
在启用监狱后,你必须重启fail2ban来加载监狱。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service fail2ban restart
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在CentOS/RHEL 或者 Fedora中启用Apache监狱 ####
|
||||
|
||||
要在基于红帽的系统中启用预定义的监狱,如下创建/etc/fail2ban/jail.local。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/fail2ban/jail.local
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# detect password authentication failures
|
||||
[apache]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-auth
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
|
||||
maxretry = 6
|
||||
|
||||
# detect spammer robots crawling email addresses
|
||||
[apache-badbots]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-badbots
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*access_log
|
||||
bantime = 172800
|
||||
maxretry = 1
|
||||
|
||||
# detect potential search for exploits and php <a href="http://xmodulo.com/recommend/penetrationbook" style="" target="_blank" rel="nofollow" >vulnerabilities</a>
|
||||
[apache-noscript]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-noscript
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
|
||||
maxretry = 6
|
||||
|
||||
# detect Apache overflow attempts
|
||||
[apache-overflows]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-overflows
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
|
||||
maxretry = 2
|
||||
|
||||
# detect failures to find a home directory on a server
|
||||
[apache-nohome]
|
||||
enabled = true
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-nohome
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
|
||||
maxretry = 2
|
||||
|
||||
# detect failures to execute non-existing scripts that
|
||||
# are associated with several popular web services
|
||||
# e.g. webmail, phpMyAdmin, WordPress
|
||||
port = http,https
|
||||
filter = apache-botsearch
|
||||
logpath = /var/log/httpd/*error_log
|
||||
maxretry = 2
|
||||
|
||||
注意这些监狱文件默认的操作是iptables-multiport(定义在/etc/fail2ban/jail.conf中[DEFAULT]字段下的“banaction”中)。这个措施使用iptable的多端口模块禁止一个IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
启用监狱后,你必须重启fail2ban来加载监狱。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Fedora 或者 CentOS/RHEL 7中:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl restart fail2ban
|
||||
|
||||
在 CentOS/RHEL 6中:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service fail2ban restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 检查和管理fail2ban禁止状态 ###
|
||||
|
||||
监狱一旦激活后,你可以用fail2ban的客户端命令行工具来监测当前的禁止状态。
|
||||
|
||||
查看激活的监狱列表:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fail2ban-client status
|
||||
|
||||
查看特定监狱的状态(包含禁止的IP列表):
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fail2ban-client status [监狱名]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你也可以手动禁止或者解禁IP地址
|
||||
|
||||
要用制定监狱禁止IP:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fail2ban-client set [name-of-jail] banip [ip-address]
|
||||
|
||||
要解禁指定监狱屏蔽的IP:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fail2ban-client set [name-of-jail] unbanip [ip-address]
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
本篇教程解释了fail2ban监狱如何工作以及如何使用内置的监狱来保护Apache服务器。依赖于你的环境以及要保护的web服务器类型,你或许要适配已存在的监狱或者编写自定义监狱和日志过滤器。查看outfail2ban的[官方Github页面][3]来获取最新的监狱和过滤器示例。
|
||||
|
||||
你有在生产环境中使用fail2ban么?分享一下你的经验吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/configure-fail2ban-apache-http-server.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-protect-ssh-server-from-brute-force-attacks-using-fail2ban.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-protect-ssh-server-from-brute-force-attacks-using-fail2ban.html
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/fail2ban/fail2ban
|
||||
@ -1,54 +1,54 @@
|
||||
Managing Linux server configs with the SaltStack
|
||||
SaltStack:Linux服务器配置管理神器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I came across Salt while searching for an alternative to [Puppet][1]. I like puppet, but I am falling in love with Salt :). This maybe a personal opinion but I found Salt easier to configure and get started with as compared to Puppet. Another reason I like Salt is that it let’s you manage your server configurations from the command line, for example:
|
||||
我在搜索[Puppet][1]的替代品时,偶然间碰到了Salt。我喜欢puppet,但是我又爱上Salt了:)。我发现Salt在配置和使用上都要比Puppet简单,当然这只是一家之言,你大可不必介怀。另外一个爱上Salt的理由是,它可以让你从命令行管理服务器配置,比如:
|
||||
|
||||
To update all your servers with Salt, just run
|
||||
要通过Salt来更新所有服务器,你只需运行以下命令
|
||||
|
||||
salt ‘*’ pkg.upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
**Installing the SaltStack on Linux.**
|
||||
**安装SaltStack到Linux上。**
|
||||
|
||||
Salt is available in the EPEL repo if you are installing it on CentOS 6/7, Pi and Ubuntu linux users can add the Salt Repository from [here][2]. Since Salt is python based you can also use ‘pip’ to install it but you have take care of dependencies like yum-utils and other packages yourself.
|
||||
如果你是在CentOS 6/7上安装的话,那么Salt可以通过EPEL仓库获取到。而对于Pi和Ubuntu Linux用户,你可以从[这里][2]添加Salt仓库。Salt是基于python的,所以你也可以使用‘pip’来安装,但是你得用yum-utils或是其它包管理器来自己处理它的依赖关系哦。
|
||||
|
||||
Salt follows the Server-Client model, The Server is known as the master whereas clients are called minions.
|
||||
Salt遵循服务器-客户端模式,服务器端称为领主,而客户端则称为下属。
|
||||
|
||||
**Installation and Configuration of a Salt Master**
|
||||
**安装并配置Salt领主**
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master~]# yum install salt-master
|
||||
|
||||
Salt configurations files are stored in /etc/salt and /srv/salt. Salt is good to go out of the box, but I would recommend you configure a bit more verbose logging to help your troubleshoot.
|
||||
Salt配置文件位于/etc/salt和/srv/salt。Salt虽然可以开箱即用,但我还是建议你将日志配置得更详细点,以方便日后排除故障。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
|
||||
#Default is warning change to the following
|
||||
# 默认是warning,修改如下
|
||||
log_level: debug
|
||||
log_level_logfile: debug
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master ~]# systemctl start salt-master
|
||||
|
||||
**Installation and Configuration of a Salt minion**
|
||||
**安装并配置Salt下属**
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-minion~]#yum install salt-minion
|
||||
|
||||
#Add the hostname of your Salt Master
|
||||
# 添加你的Salt领主的主机名
|
||||
[root@salt-minion~]#vim /etc/salt/minion
|
||||
master: salt-master.com
|
||||
#start the minion
|
||||
# 启动下属
|
||||
[root@salt-minion~] systemctl start salt-minion
|
||||
|
||||
On Startup, a minion will generate a cryptographic key and an id. It will then connect to the Salt Master and identify itself. The Salt Master must accept the minion’s key before allowing the minion to download a configuration.
|
||||
在启动时,下属客户机会生成一个密钥和一个id。然后,它会连接到Salt领主服务器并验证自己的身份。Salt领主服务器在允许下属客户机下载配置之前,必须接受下属的密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
**Listing and Accepting keys on the Salt Master**
|
||||
**在Salt领主服务器上列出并接受密钥**
|
||||
|
||||
#List all keys
|
||||
# 列出所有密钥
|
||||
[root@salt-master~] salt-key -L
|
||||
Accepted Keys:
|
||||
Unaccepted Keys:
|
||||
minion.com
|
||||
Rejected Keys:
|
||||
|
||||
#Accept key with id ‘minion.com’
|
||||
# 使用id 'minion.com'命令接受密钥
|
||||
[root@salt-master~]salt-key -a minion.com
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master~] salt-key -L
|
||||
@ -57,43 +57,45 @@ On Startup, a minion will generate a cryptographic key and an id. It will then c
|
||||
Unaccepted Keys:
|
||||
Rejected Keys:
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have accepted a minions keys, you can get information on it immediately using the ‘salt’ command.
|
||||
在接受下属客户机的密钥后,你可以使用‘salt’命令来立即获取信息。
|
||||
|
||||
**Salt command line examples**
|
||||
**Salt命令行实例**
|
||||
|
||||
#Check if a minion is up and running
|
||||
# 检查下属是否启动并运行
|
||||
[root@salt-master~] salt 'minion.com' test.ping
|
||||
minion.com:
|
||||
True
|
||||
# run shell commands on the minion
|
||||
# 在下属客户机上运行shell命令
|
||||
[root@salt-master~]# salt 'minion.com' cmd.run 'ls -l'
|
||||
minion.com:
|
||||
total 2988
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1024 Jul 31 08:24 1g.img
|
||||
-rw-------. 1 root root 940 Jul 14 15:04 anaconda-ks.cfg
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 1024 Aug 14 17:21 test
|
||||
#install/update a software on all your servers
|
||||
# 安装/更新所有服务器上的软件
|
||||
[root@salt-master ~]# salt '*' pkg.install git
|
||||
|
||||
The salt command needs a few components to send information. One of these components is the minion id and another is the function to be called on the minion.
|
||||
In the first example I used the ‘ping’ function of the ‘test’ module to check if the system is up. This function does not perform an actual ping, it just return’s ‘true’ if the minion responds.
|
||||
‘cmd.run’ is used to execute remote commands and ‘pkg’ module contains functions for package management. The full list of builin modules is at the end of this post.
|
||||
salt命令需要一些组件来发送信息,其中之一是mimion id,而另一个是下属客户机上要调用的函数。
|
||||
|
||||
**Grains example**
|
||||
在第一个实例中,我使用‘test’模块的‘ping’函数来检查系统是否启动。该函数并不是真的实施一次ping,它仅仅是在下属客户机作出回应时返回‘真’。
|
||||
|
||||
Salt uses an interface called **Grains** to get system information. You can use grains to run commands on systems with particular properties.
|
||||
‘cmd.run’用于执行远程命令,而‘pkg’模块包含了包管理的函数。本文结尾提供了全部内建模块的列表。
|
||||
|
||||
**颗粒实例**
|
||||
|
||||
Salt使用一个名为**颗粒**的界面来获取系统信息。你可以使用颗粒在指定属性的系统上运行命令。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@vps4544 ~]# salt -G 'os:Centos' test.ping
|
||||
minion:
|
||||
True
|
||||
|
||||
More grain examples are available at http://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/targeting/grains.html
|
||||
更多颗粒实例,请访问http://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/targeting/grains.html
|
||||
|
||||
**Package Management via the State File System.**
|
||||
**通过状态文件系统进行包管理。**
|
||||
|
||||
In order to automate software configurations you will need to use the state system and create a state file. These files use the YAML format and python dictionaries, lists, strings and numbers for data structure. Reading up on them will help you understand the configurations better.
|
||||
为了是软件配置自动化,你需要使用状态系统,并创建状态文件。这些文件使用YAML格式和python字典、列表、字符串以及编号来构成数据结构。将这些文件从头到尾研读一遍,这将有助于你更好地理解它的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
**VIM state file example**
|
||||
**VIM状态文件实例**
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master~]# vim /srv/salt/vim.sls
|
||||
vim-enhanced:
|
||||
@ -104,11 +106,10 @@ In order to automate software configurations you will need to use the state syst
|
||||
- user: root
|
||||
- group: root
|
||||
- mode: 644
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The first and third line in this file are called state id. They must contain the exact name or path of the package or file to be managed. After the state ids are state and function declaration. ‘pkg’ and file are state declarations whereas ‘installed’ and ‘managed’ are function declarations. Functions accept arguments, user,group,mode and source are all arguments to the function ‘managed’.
|
||||
该文件的第一和第三行成为状态id,它们必须包含有需要管理的包或文件的确切名称或路径。在状态id之后是状态和函数声明,‘pkg’和‘file’是状态声明,而‘installed’和‘managed’是函数声明。函数接受参数,用户、组、模式和源都是函数‘managed’的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
To apply this configuration to a minion move your ‘vimrc’ file to ‘/srv/salt’ and run.
|
||||
要将该配置应用到下属客户端,请移动你的‘vimrc’文件到‘/src/salt’,然后运行以下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master~]# salt 'minion.com' state.sls vim
|
||||
minion.com:
|
||||
@ -134,8 +135,8 @@ To apply this configuration to a minion move your ‘vimrc’ file to ‘/srv/sa
|
||||
Failed: 0
|
||||
------------
|
||||
Total states run: 1
|
||||
|
||||
You can also add dependencies to your configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以添加依赖关系到你的配置中。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master~]# vim /srv/salt/ssh.sls
|
||||
openssh-server:
|
||||
@ -154,9 +155,9 @@ You can also add dependencies to your configurations.
|
||||
- require:
|
||||
- pkg: openssh-server
|
||||
|
||||
The ‘require’ statement here is a requisite declaration, it creates a dependency between the ‘service’ and ‘pkg’ states. This declaration will first check if the package is installed and then run the service.
|
||||
这里的‘require’声明是必须的,它在‘service’和‘pkg’状态之间创建依赖关系。该声明将首先检查包是否安装,然后运行服务。
|
||||
|
||||
However, I prefer using the ‘watch’ statement as it also checks for file modifications and restarts the service.
|
||||
但是,我更偏向于使用‘watch’声明,因为它也可以检查文件是否修改和重启服务。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master~]# vim /srv/salt/ssh.sls
|
||||
openssh-server:
|
||||
@ -228,7 +229,7 @@ However, I prefer using the ‘watch’ statement as it also checks for file mod
|
||||
------------
|
||||
Total states run: 4
|
||||
|
||||
Maintaining all config files in single directory can make scaling a complex task, hence you can create sub-directories and add your configuration in them with a init.sls file
|
||||
在单一目录中维护所有的配置文件是一项复杂的大工程,因此,你可以创建子目录并在其中添加配置文件init.sls文件。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master~]# mkdir /srv/salt/ssh
|
||||
[root@salt-master~]# vim /srv/salt/ssh/init.sls
|
||||
@ -252,13 +253,13 @@ Maintaining all config files in single directory can make scaling a complex task
|
||||
[root@vps4544 ssh]# cp /etc/ssh/sshd_config /srv/salt/ssh/
|
||||
[root@vps4544 ssh]# salt 'minion.com' state.sls ssh
|
||||
|
||||
**Top File and Environments.**
|
||||
**Top文件和环境。**
|
||||
|
||||
A Top file (top.sls) is where you define your environments. A top file allows you to map minions to packages. The default environment is ‘base’. You need to define which packages will be installed on which server under the base environment.
|
||||
top文件(top.sls)是用来定义你的环境的文件,它允许你映射下属客户机到包,默认环境是‘base’。你需要定义在基本环境下,哪个包会被安装到哪台服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
If there are multiple environments and more than one definitions for a particular minion is used then by default the base environment will supersede the others.
|
||||
如果对于一台特定的下属客户机而言,有多个环境,并且有多于一个的定义,那么默认情况下,基本环境将取代其它环境。
|
||||
|
||||
To define an environment you need to add it to the ‘file_roots’ directive in the master configuration file.
|
||||
要定义环境,你需要将它添加到领主配置文件的‘file_roots’指针。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master ~]# vim /etc/salt/master
|
||||
file_roots:
|
||||
@ -267,7 +268,7 @@ To define an environment you need to add it to the ‘file_roots’ directive in
|
||||
dev:
|
||||
- /srv/salt/dev
|
||||
|
||||
Now add a top.sls file in /srv/salt
|
||||
现在,添加一个top.sls文件到/src/salt
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master ~]# vim /srv/salt/top.sls
|
||||
base:
|
||||
@ -276,7 +277,7 @@ Now add a top.sls file in /srv/salt
|
||||
'minion.com':
|
||||
- ssh
|
||||
|
||||
Apply the top file configuration with
|
||||
应用top文件配置
|
||||
|
||||
[root@salt-master~]# salt '*' state.highstate
|
||||
minion.com:
|
||||
@ -296,29 +297,29 @@ Apply the top file configuration with
|
||||
Started: 13:10:55.
|
||||
Duration: 2.156 ms
|
||||
|
||||
The minion will download the top file and search for it’s configuration. It will also apply the configuration for all minions.
|
||||
下属客户机将下载top文件并搜索用于它的配置,领主服务器也会将配置应用到所有下属客户机。
|
||||
|
||||
This is just a brief introduction to Salt, for in depth understanding you can go through the links below and if you are already using Salt and have any recommendations do let me know.
|
||||
这仅仅是一个Salt的简明教程,如果你想要深入学习并理解,你可以访问以下链接。如果你已经在使用Salt,那么请告诉我你的建议和意见吧。
|
||||
|
||||
Update: [Foreman][3] has support for salt via [plugins][4].
|
||||
更新: [Foreman][3] 已经通过[插件][4]支持salt。
|
||||
|
||||
Read
|
||||
阅读链接
|
||||
|
||||
- http://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/states/top.html#how-top-files-are-compiled
|
||||
- http://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/tutorials/states_pt1.html
|
||||
- http://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/states/highstate.html#state-declaration
|
||||
|
||||
Grains
|
||||
颗粒
|
||||
|
||||
- http://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/targeting/grains.html
|
||||
|
||||
List of Salt Modules
|
||||
Salt模块列表
|
||||
|
||||
Good comparison of Salt and puppet
|
||||
Salt和Puppet的充分比较
|
||||
|
||||
- https://mywushublog.com/2013/03/configuration-management-with-salt-stack/
|
||||
|
||||
Full list of builtin execution modules
|
||||
内建执行模块的完全列表
|
||||
|
||||
- http://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/ref/modules/all/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -327,7 +328,7 @@ Full list of builtin execution modules
|
||||
via: http://techarena51.com/index.php/getting-started-with-saltstack/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Leo G][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -336,4 +337,4 @@ via: http://techarena51.com/index.php/getting-started-with-saltstack/
|
||||
[1]:http://techarena51.com/index.php/a-simple-way-to-install-and-configure-a-puppet-server-on-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://docs.saltstack.com/en/latest/topics/installation/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://techarena51.com/index.php/using-foreman-opensource-frontend-puppet/
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/theforeman/foreman_salt/wiki
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/theforeman/foreman_salt/wiki
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,93 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux上找出并删除重复的文件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
大家好,今天我们会学习如何在Linux PC或者服务器上找出和删除重复文件。这里有一款工具你可以工具自己的需要使用。
|
||||
|
||||
无论你是否正在使用Linux桌面或者服务器,有一些很好的工具能一帮你扫描系统中的重复文件并删除它们来释放空间。图形界面和命令行界面的都有。重复文件是磁盘空间不必要的浪费。毕竟,如果你的确需要在不同的位置享有同一个文件,你可以使用软链接或者硬链接,这样就可以这样就可以在磁盘的一处地方存储数据了。
|
||||
|
||||
### FSlint ###
|
||||
|
||||
[FSlint][1] 在不同的Linux发行办二进制仓库中都有,包括Ubuntu、Debian、Fedora和Red Hat。只需你运行你的包管理器并安装“fslint”包就行。这个工具默认提供了一个简单的图形化界面,同样也有包含各种功能的命令行版本。
|
||||
|
||||
不要让它让你害怕使用FSlint的图形化界面。默认情况下,它会自动选中Duplicate窗格,并以你的家目录作为搜索路径。
|
||||
|
||||
要安装fslint,若像我这样运行的是Ubuntu,这里是默认的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install fslint
|
||||
|
||||
这里还有针对其他发行版的安装命令:
|
||||
|
||||
Debian:
|
||||
|
||||
svn checkout http://fslint.googlecode.com/svn/trunk/ fslint-2.45
|
||||
cd fslint-2.45
|
||||
dpkg-buildpackage -I.svn -rfakeroot -tc
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i ../fslint_2.45-1_all.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Fedora:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install fslint
|
||||
|
||||
For OpenSuse:
|
||||
|
||||
[ -f /etc/mandrake-release ] && pkg=rpm
|
||||
[ -f /etc/SuSE-release ] && pkg=packages
|
||||
wget http://www.pixelbeat.org/fslint/fslint-2.42.tar.gz
|
||||
sudo rpmbuild -ta fslint-2.42.tar.gz
|
||||
sudo rpm -Uvh /usr/src/$pkg/RPMS/noarch/fslint-2.42-1.*.noarch.rpm
|
||||
|
||||
对于其他发行版:
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://www.pixelbeat.org/fslint/fslint-2.44.tar.gz
|
||||
tar -xzf fslint-2.44.tar.gz
|
||||
cd fslint-2.44
|
||||
(cd po && make)
|
||||
./fslint-gui
|
||||
|
||||
要在Ubuntu中运行fslint的GUI版本fslint-gui, 使用Alt+F2运行命令或者在终端输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ fslint-gui
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,它会自动选中Duplicate窗格,并以你的家目录作为搜索路径。你要做的就是点击Find按钮,FSlint会自动在你的家目录下找出重复文件列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
使用按钮来删除任何你要删除的文件,并且可以双击预览。
|
||||
|
||||
完成这一切后,我们就成功地删除你系统中的重复文件了。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意** 的是命令行工具默认不在环境的路径中,你不能像典型的命令那样运行它。在Ubuntu中,你可以在/usr/share/fslint/fslint下找到它。因此,如果你要在一个单独的目录运行fslint完整扫描,下面是Ubuntu中的运行命令:
|
||||
|
||||
cd /usr/share/fslint/fslint
|
||||
|
||||
./fslint /path/to/directory
|
||||
|
||||
**这个命令实际上并不会删除任何文件。它只会打印出重复文件的列表-你需要自己做接下来的事。**
|
||||
|
||||
$ /usr/share/fslint/fslint/findup --help
|
||||
find dUPlicate files.
|
||||
Usage: findup [[[-t [-m|-d]] | [--summary]] [-r] [-f] paths(s) ...]
|
||||
|
||||
If no path(s) specified then the current directory is assumed.
|
||||
|
||||
When -m is specified any found duplicates will be merged (using hardlinks).
|
||||
When -d is specified any found duplicates will be deleted (leaving just 1).
|
||||
When -t is specfied, only report what -m or -d would do.
|
||||
When --summary is specified change output format to include file sizes.
|
||||
You can also pipe this summary format to /usr/share/fslint/fslint/fstool/dupwaste
|
||||
to get a total of the wastage due to duplicates.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/file-system/find-remove-duplicate-files-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.pixelbeat.org/fslint/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.pixelbeat.org/fslint/fslint-2.42.tar.gz
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS(Trusty) 上安装Ghost
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
今天我们将会在Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS (Trusty)上安装一个博客平台Ghost。
|
||||
|
||||
Ghost是一款设计优美的发布平台,很容易使用且对任何人都免费。它是免费的开源软件(FOSS),它的源码在Github上。截至2014年1月,它的界面很简单还有分析面板。编辑使用的是分屏显示。
|
||||
|
||||
因此有了这篇步骤明确的在Ubuntu Server上安装Ghost的教程:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 升级Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
第一步是运行Ubuntu软件升级并安装一系列需要的额外包。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get upgrade -y
|
||||
sudo aptitude install -y build-essential zip vim wget
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 下载并安装 Node.js 源码 ###
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://nodejs.org/dist/node-latest.tar.gz
|
||||
tar -xzf node-latest.tar.gz
|
||||
cd node-v*
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们使用下面的命令安装Node.js:
|
||||
|
||||
./configure
|
||||
make
|
||||
sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 下载并安装Ghost ###
|
||||
|
||||
sudo mkdir -p /var/www/
|
||||
cd /var/www/
|
||||
sudo wget https://ghost.org/zip/ghost-latest.zip
|
||||
sudo unzip -d ghost ghost-latest.zip
|
||||
cd ghost/
|
||||
sudo npm install --production
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 配置Ghost ###
|
||||
|
||||
sudo nano config.example.js
|
||||
|
||||
在“Production”字段,将:
|
||||
|
||||
host: '127.0.0.1',
|
||||
|
||||
修改成
|
||||
|
||||
host: '0.0.0.0',
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建Ghost用户 ###
|
||||
|
||||
sudo adduser --shell /bin/bash --gecos 'Ghost application' ghost
|
||||
sudo chown -R ghost:ghost /var/www/ghost/
|
||||
|
||||
现在启动Ghost,你需要以“ghsot”用户登录。
|
||||
|
||||
su - ghost
|
||||
cd /var/www/ghost/
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你已经以“ghsot”用户登录,并可启动Ghost:
|
||||
|
||||
npm start --production
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-ghost-ubuntu-server-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
||||
如何在RedHat/CentOS 7.x中使用nmcli管理网络
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[**Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7**][1]和**CentOS 7**的一个新特性是默认的网络服务由**NetworkManager**提供,这是一个动态的网络控制和配置守护进程,它在网络设备和连接可用时保持链接正常,同时也提供了典型的ifcfg类型的配置文件。NetworkManager可以用于下面这些连接:Ethernet、 VLANs、桥接、Bonds、Teams、 Wi-Fi、 移动宽带 (比如 3G)和IP-over-InfiniBand(IPoIB)。
|
||||
|
||||
NetworkManager可以由命令行工具**nmcli**控制。
|
||||
|
||||
### nmcli的通常用法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
nmcli的通常语法是:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli [ OPTIONS ] OBJECT { COMMAND | help }
|
||||
|
||||
一件很酷的事情是你可以使用tab键来补全操作,这样你在何时忘记了语法你都可以用tab来看到可用的选项了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
nmcli通常用法的一些例子:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli general status
|
||||
|
||||
会显示NetworkManager的整体状态。
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection show
|
||||
|
||||
会显示所有的连接
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection show -a
|
||||
|
||||
仅显示活跃的连接
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli device status
|
||||
|
||||
显示NetworkManager识别的设备列表和它们当前的状态。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 启动/停止网络设备 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用nmcli从命令行启动或者停止网络设备,这等同于ifconfig中的up和down。
|
||||
|
||||
停止网络设备使用下面的语法:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli device disconnect eno16777736
|
||||
|
||||
要启动它使用下面的语法:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli device connect eno16777736
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用静态IP添加一个以太网连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要用静态IP添加一个以太网连接可以使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NAME_OF_CONNECTION ifname interface-name ip4 IP_ADDRESS gw4 GW_ADDRESS
|
||||
|
||||
将NAME_OF_CONNECTION替换成新的连接名,IP_ADDRESS替换成你要的IP地址,GW_ADDRESS替换成你使用的网关地址(如果你并不使用网关,你可以忽略这部分)。
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NEW ifname eno16777736 ip4 192.168.1.141 gw4 192.168.1.1
|
||||
|
||||
=要设置这个连接的DNS服务器使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection modify NEW ipv4.dns "8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4"
|
||||
|
||||
要启用新的以太网连接,使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection up NEW ifname eno16777736
|
||||
|
||||
要查看新配置连接的详细信息,使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli -p connection show NEW
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 添加一个使用DHCP的连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要添加一个使用DHCP来配置接口IP地址、网关地址和dns服务器地址的新的连接,你要做的就是忽略命令中的ip/gw部分,NetworkManager会自动使用DHCP来获取配置细节。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,要创建一个新的叫NEW_DHCP的DHCP连接,在设备eno16777736上你可以使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NEW_DHCP ifname eno16777736
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/nmcli-tool-red-hat-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/adriand/
|
||||
[1]:https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/7/html/7.0_Release_Notes/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,149 @@
|
||||
在Ubuntu/Fedora/CentOS中安装Gitblit
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Git**是一款注重速度、数据完整性、分布式支持和非线性工作流的分布式版本控制工具。Git最初由Linus Torvalds在2005年为Linux内核开发而设计,如今已经成为被广泛接受的版本控制系统。
|
||||
|
||||
和其他大多数分布式版本控制系统比起来,不像大多数客户端-服务端的系统,每个Git工作目录是一个完整的仓库,带有完整的历史记录和完整的版本跟踪能力,不需要依赖网络或者中心服务器。像Linux内核一样,Git意识在GPLv2许可证下的免费软件。
|
||||
|
||||
本篇教程我会演示如何安装gitlit服务器。gitlit的最新稳定版是1.6.2。[Gitblit][1]是一款开源、纯Java开发的用于管理浏览和服务的[Git][2]仓库。它被设计成一款为希望托管中心仓库的小工作组服务的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p /opt/gitblit; cd /opt/gitblit; wget http://dl.bintray.com/gitblit/releases/gitblit-1.6.2.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
### 列出目录: ###
|
||||
|
||||
root@vps124229 [/opt/gitblit]# ls
|
||||
./ docs/ gitblit-stop.sh* LICENSE service-ubuntu.sh*
|
||||
../ ext/ install-service-centos.sh* migrate-tickets.sh*
|
||||
add-indexed-branch.sh* gitblit-1.6.2.tar.gz install-service-fedora.sh* NOTICE
|
||||
authority.sh* gitblit.jar install-service-ubuntu.sh* reindex-tickets.sh*
|
||||
data/ gitblit.sh* java-proxy-config.sh* service-centos.sh*
|
||||
|
||||
默认配置文件在data/gitblit.properties,你可以根据需要自己修改。
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动gitlit服务: ###
|
||||
|
||||
### 通过service命令: ###
|
||||
|
||||
root@vps124229 [/opt/gitblit]# cp service-centos.sh /etc/init.d/gitblit
|
||||
root@vps124229 [/opt/gitblit]# chkconfig --add gitblit
|
||||
root@vps124229 [/opt/gitblit]# service gitblit start
|
||||
Starting gitblit server
|
||||
.
|
||||
|
||||
### 手动启动: ###
|
||||
|
||||
root@vps124229 [/opt/gitblit]# java -jar gitblit.jar --baseFolder data
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:53 [INFO ] *****************************************************************
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:53 [INFO ] _____ _ _ _ _ _ _
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:53 [INFO ] | __ \(_)| | | | | |(_)| |
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:53 [INFO ] | | \/ _ | |_ | |__ | | _ | |_
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:53 [INFO ] | | __ | || __|| '_ \ | || || __|
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:53 [INFO ] | |_\ \| || |_ | |_) || || || |_
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:53 [INFO ] \____/|_| \__||_.__/ |_||_| \__|
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:53 [INFO ] Gitblit v1.6.2
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:53 [INFO ]
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:53 [INFO ] *****************************************************************
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:53 [INFO ] Running on Linux (3.8.13-xxxx-grs-ipv6-64-vps)
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:53 [INFO ] Logging initialized @842ms
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:54 [INFO ] Using JCE Unlimited Strength Jurisdiction Policy files
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:54 [INFO ] Setting up HTTPS transport on port 8443
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:54 [INFO ] certificate alias = localhost
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:54 [INFO ] keyStorePath = /opt/gitblit/data/serverKeyStore.jks
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:54 [INFO ] trustStorePath = /opt/gitblit/data/serverTrustStore.jks
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:54 [INFO ] crlPath = /opt/gitblit/data/certs/caRevocationList.crl
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:54 [INFO ] Shutdown Monitor listening on port 8081
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:54 [INFO ] jetty-9.2.3.v20140905
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] NO JSP Support for /, did not find org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ]
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] ----[com.gitblit.manager.IRuntimeManager]----
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Basefolder : /opt/gitblit/data
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Settings : /opt/gitblit/data/gitblit.properties
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] JVM timezone: America/Montreal (EST -0500)
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] App timezone: America/Montreal (EST -0500)
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] JVM locale : en_US
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] App locale : <client>
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] PF4J runtime mode is 'deployment'
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Enabled plugins: []
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Disabled plugins: []
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ]
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] ----[com.gitblit.manager.INotificationManager]----
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [WARN ] Mail service disabled.
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ]
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] ----[com.gitblit.manager.IUserManager]----
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] ConfigUserService(/opt/gitblit/data/users.conf)
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ]
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] ----[com.gitblit.manager.IAuthenticationManager]----
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] External authentication disabled.
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ]
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] ---- [com.gitblit.transport.ssh.IPublicKeyManager]----
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] FileKeyManager (/opt/gitblit/data/ssh)
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ]
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] ----[com.gitblit.manager.IRepositoryManager]----
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Repositories folder : /opt/gitblit/data/git
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Identifying repositories...
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] 0 repositories identified with calculated folder sizes in 11 msecs
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Lucene will process indexed branches every 2 minutes.
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Garbage Collector (GC) is disabled.
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Mirror service is disabled.
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Alias UTF-9 & UTF-18 encodings as UTF-8 in JGit
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Preparing 14 day commit cache. please wait...
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] 0 repositories identified with calculated folder sizes in 0 msecs
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] built 14 day commit cache of 0 commits across 0 repositories in 2 msecs
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ]
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] ----[com.gitblit.manager.IProjectManager]----
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ]
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] ----[com.gitblit.manager.IFederationManager]----
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ]
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] ----[com.gitblit.manager.IGitblit]----
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Starting services manager...
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Federation passphrase is blank! This server can not be PULLED from.
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Fanout PubSub service is disabled.
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] Git Daemon is listening on 0.0.0.0:9418
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] SSH Daemon (NIO2) is listening on 0.0.0.0:29418
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [WARN ] No ticket service configured.
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ]
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] ----[com.gitblit.manager.IPluginManager]----
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] No plugins
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ]
|
||||
2015-01-10 09:16:55 [INFO ] All managers started.
|
||||
|
||||
打开浏览器,依据你的配置进入**http://localhost:8080** 或者 **https://localhost:8443**。 输入默认的管理员授权:**admin / admin** 并点击**Login** 按钮
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 添加用户: ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
添加仓库:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 用命令行创建新的仓库: ###
|
||||
|
||||
touch README.md
|
||||
git init
|
||||
git add README.md
|
||||
git commit -m "first commit"
|
||||
git remote add origin ssh://admin@142.4.202.70:29418/Programming.git
|
||||
git push -u origin master
|
||||
|
||||
### 从命令行推送已有的仓库: ###
|
||||
|
||||
git remote add origin ssh://admin@142.4.202.70:29418/Programming.git
|
||||
git push -u origin master
|
||||
|
||||
完成!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-gitblit-ubuntu-fedora-centos/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[M.el Khamlichi][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/pirat9/
|
||||
[1]:http://gitblit.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://git-scm.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
|
||||
在CentOS/RHEL/Scientific Linux 6 & 7 上安装Telnet
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
#### 声明: ####
|
||||
|
||||
在安装和使用Telnet之前,需要记住以下几点。
|
||||
|
||||
- 在公网(WAN)中使用Telnet是非常不好的想法。它会以明文的格式传输登入数据。每个人都可以看到明文。
|
||||
- 如果你还是需要Telnet,强烈建议你只在局域网内部使用。
|
||||
- 你可以使用**SSH**作为替代方法。但是确保不要用root用户登录。
|
||||
|
||||
### Telnet是什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Telnet][1] 是用于通过TCP/IP网络远程登录计算机的协议。一旦与远程计算机建立了连接,它就会成为一个虚拟终端且允许你与远程计算机通信。
|
||||
|
||||
在本篇教程中,我们会展示如何安装Telnet并且如何通过Telnet访问远程系统。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端并输入下面的命令来安装telnet:
|
||||
|
||||
yum install telnet telnet-server -y
|
||||
|
||||
现在telnet已经安装在你的服务器上了。接下来编辑文件**/etc/xinetd.d/telnet**:
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/xinetd.d/telnet
|
||||
|
||||
设置 **disable = no**:
|
||||
|
||||
# default: on
|
||||
# description: The telnet server serves telnet sessions; it uses \
|
||||
# unencrypted username/password pairs for authentication.
|
||||
service telnet
|
||||
{
|
||||
flags = REUSE
|
||||
socket_type = stream
|
||||
wait = no
|
||||
user = root
|
||||
server = /usr/sbin/in.telnetd
|
||||
log_on_failure += USERID
|
||||
disable = no
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出文件。记住我们不必在CentOS 7做这步。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来使用下面的命令重启telnet服务:
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS 6.x 系统中:
|
||||
|
||||
service xinetd start
|
||||
|
||||
让这个服务在每次重启时都会启动:
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS 6上:
|
||||
|
||||
chkconfig telnet on
|
||||
chkconfig xinetd on
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS 7上:
|
||||
|
||||
systemctl start telnet.socket
|
||||
systemctl enable telnet.socket
|
||||
|
||||
让telnet的默认端口**23**可以通过防火墙和路由器。要让telnet端口可以通过防火墙,在CentOS 6.x系统中编辑下面的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
vi /etc/sysconfig/iptables
|
||||
|
||||
加入红色显示的行:
|
||||
|
||||
# Firewall configuration written by system-config-firewall
|
||||
# Manual customization of this file is not recommended.
|
||||
*filter
|
||||
:INPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
|
||||
:FORWARD ACCEPT [0:0]
|
||||
:OUTPUT ACCEPT [0:0]
|
||||
-A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
-A INPUT -p icmp -j ACCEPT
|
||||
-A INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT
|
||||
-A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW --dport 23 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
-A INPUT -m state --state NEW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 22 -j ACCEPT
|
||||
-A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
|
||||
-A FORWARD -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-host-prohibited
|
||||
COMMIT
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出文件。重启iptables服务:
|
||||
|
||||
service iptables restart
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS 7中,运行下面的命令让telnet服务可以通过防火墙。
|
||||
|
||||
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=23/tcp
|
||||
firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样。现在telnet服务就可以使用了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 创建用户 ####
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个测试用户,比如用户名是“**sk**”,密码是“**centos**“:
|
||||
|
||||
useradd sk
|
||||
passwd sk
|
||||
|
||||
#### 客户端配置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
安装telnet包:
|
||||
|
||||
yum install telnet
|
||||
|
||||
在基于DEB的系统中:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install telnet
|
||||
|
||||
现在,打开终端,尝试访问你的服务器(远程主机)。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的客户端是Linux系统,打开终端并输入下面的命令来连接到telnet服务器上。
|
||||
|
||||
telnet 192.168.1.150
|
||||
|
||||
输入服务器上已经创建的用户名和密码:
|
||||
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
Trying 192.168.1.150...
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.1.150.
|
||||
Escape character is '^]'.
|
||||
|
||||
Kernel 3.10.0-123.13.2.el7.x86_64 on an x86_64
|
||||
server1 login: sk
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
[sk@server1 ~]$
|
||||
|
||||
如你所见,已经成功从本地访问远程主机了。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的系统是windows,进入**开始 -> 运行 -> 命令提示符**。
|
||||
|
||||
在命令提示符中,输入命令:
|
||||
|
||||
telnet 192.168.1.150
|
||||
|
||||
**192.168.1.150**是远程主机IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
现在你就可以连接到你的服务器上了。
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样。
|
||||
|
||||
干杯!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/installing-telnet-centosrhelscientific-linux-6-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Telnet
|
||||
305
translated/tech/20150115 20 Unix Command Line Tricks--Part I.md
Normal file
305
translated/tech/20150115 20 Unix Command Line Tricks--Part I.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,305 @@
|
||||
20个Unix命令技巧 - 第一部分
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
让我们用**这些Unix命令技巧**开启新的一年,提高在终端下的生产力。我已经找了很久了,现在就与你们分享。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 删除一个大文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我在生产服务器上有一个很大的200GB的日志文件需要删除。我的rm和ls命令已经崩溃,我担心这是由于巨大的磁盘IO造成的,要删除这个大文件,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
> /path/to/file.log
|
||||
# or use the following syntax
|
||||
: > /path/to/file.log
|
||||
|
||||
# finally delete it
|
||||
rm /path/to/file.log
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何缓存终端输出? ###
|
||||
|
||||
尝试使用script命令行工具来为你的终端输出创建typescript。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
script my.terminal.sessio
|
||||
|
||||
输入命令:
|
||||
|
||||
ls
|
||||
date
|
||||
sudo service foo stop
|
||||
|
||||
要退出(结束script绘画),输入*exit* 或者 *logout* 或者按下 *control-D*
|
||||
|
||||
exit
|
||||
|
||||
要浏览输入:
|
||||
|
||||
more my.terminal.session
|
||||
less my.terminal.session
|
||||
cat my.terminal.session
|
||||
|
||||
### 还原删除的 /tmp 文件夹 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我在文章[Linux和Unix shell,我犯了一些错误][1]。我意外地删除了/tmp文件夹。要还原它,我需要这么做:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir /tmp
|
||||
chmod 1777 /tmp
|
||||
chown root:root /tmp
|
||||
ls -ld /tmp
|
||||
|
||||
### 锁定一个文件夹 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了我的数据隐私,我想要锁定我文件服务器下的/downloads文件夹。因此我运行:
|
||||
|
||||
chmod 0000 /downloads
|
||||
|
||||
root用户仍旧可以访问,但是ls和cd命令还不可用。要还原它用:
|
||||
|
||||
chmod 0755 /downloads
|
||||
|
||||
### 在vim中用密码保护文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
害怕root用户或者其他人偷窥你的个人文件么?尝试在vim中用密码保护,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
vim +X filename
|
||||
|
||||
或者,在退出vim之前使用:X 命令来加密你的文件,vim会提示你输入一个密码。
|
||||
|
||||
### 清除屏幕上的输出 ###
|
||||
|
||||
只要输入:
|
||||
|
||||
reset
|
||||
|
||||
### 成为人类 ###
|
||||
|
||||
传递*-h*或者*-H*(和其他选项)选项给GNU或者BSD工具来获取像ls、df、du等命令以人类可读的格式输出:
|
||||
|
||||
ls -lh
|
||||
# 以人类可读的格式 (比如: 1K 234M 2G)
|
||||
df -h
|
||||
df -k
|
||||
# 已字节输出如: KB, MB, or GB
|
||||
free -b
|
||||
free -k
|
||||
free -m
|
||||
free -g
|
||||
# 以人类可读的格式打印 (比如 1K 234M 2G)
|
||||
du -h
|
||||
# 以人类可读的格式获取系统perms
|
||||
stat -c %A /boot
|
||||
# 比较人类可读的数字
|
||||
sort -h -a file
|
||||
# 在Linux上以人类可读的形式显示cpu信息
|
||||
lscpu
|
||||
lscpu -e
|
||||
lscpu -e=cpu,node
|
||||
# 以人类可读的形式显示每个文件的大小
|
||||
tree -h
|
||||
tree -h /boot
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux系统中显示已知用户的信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
只要输入:
|
||||
|
||||
## linux 版本 ##
|
||||
lslogins
|
||||
|
||||
## BSD 版本 ##
|
||||
logins
|
||||
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||
UID USER PWD-LOCK PWD-DENY LAST-LOGIN GECOS
|
||||
0 root 0 0 22:37:59 root
|
||||
1 bin 0 1 bin
|
||||
2 daemon 0 1 daemon
|
||||
3 adm 0 1 adm
|
||||
4 lp 0 1 lp
|
||||
5 sync 0 1 sync
|
||||
6 shutdown 0 1 2014-Dec17 shutdown
|
||||
7 halt 0 1 halt
|
||||
8 mail 0 1 mail
|
||||
10 uucp 0 1 uucp
|
||||
11 operator 0 1 operator
|
||||
12 games 0 1 games
|
||||
13 gopher 0 1 gopher
|
||||
14 ftp 0 1 FTP User
|
||||
27 mysql 0 1 MySQL Server
|
||||
38 ntp 0 1
|
||||
48 apache 0 1 Apache
|
||||
68 haldaemon 0 1 HAL daemon
|
||||
69 vcsa 0 1 virtual console memory owner
|
||||
72 tcpdump 0 1
|
||||
74 sshd 0 1 Privilege-separated SSH
|
||||
81 dbus 0 1 System message bus
|
||||
89 postfix 0 1
|
||||
99 nobody 0 1 Nobody
|
||||
173 abrt 0 1
|
||||
497 vnstat 0 1 vnStat user
|
||||
498 nginx 0 1 nginx user
|
||||
499 saslauth 0 1 "Saslauthd user"
|
||||
|
||||
### 我如何删除意外在当前文件夹下解压的文件? ###
|
||||
|
||||
我意外在/var/www/html/而不是/home/projects/www/current下解压了一个tarball。它混乱了/var/www/html下的文件。最简单修复这个问题的方法是:
|
||||
|
||||
cd /var/www/html/
|
||||
/bin/rm -f "$(tar ztf /path/to/file.tar.gz)"
|
||||
|
||||
### 对top命令的输出感到疑惑? ###
|
||||
|
||||
正经地说,你应该试一下用htop代替top:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo htop
|
||||
|
||||
### 想要再次运行相同的命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
只需要输入!!。比如:
|
||||
|
||||
/myhome/dir/script/name arg1 arg2
|
||||
|
||||
# 要再次运行相同的命令
|
||||
!!
|
||||
|
||||
## 以root用户运行最后运行的命令
|
||||
sudo !!
|
||||
|
||||
!!会运行最近使用的命令。要运行最近运行的“foo”命令:
|
||||
|
||||
!foo
|
||||
# 以root用户运行上一次以“service”开头的命令
|
||||
sudo !service
|
||||
|
||||
!$用于运行带上最后一个参数的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# 编辑 nginx.conf
|
||||
sudo vi /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
|
||||
|
||||
# 测试 nginx.conf
|
||||
/sbin/nginx -t -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
|
||||
|
||||
# 测试完 "/sbin/nginx -t -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf"你可以用vi编辑了
|
||||
sudo vi !$
|
||||
|
||||
### 在你要离开的时候留下一个提醒 ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you need a reminder to leave your terminal, type the following command:
|
||||
如果你需要提醒离开你的终端,输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
leave +hhmm
|
||||
|
||||
这里:
|
||||
|
||||
- **hhmm** - 时间是以hhmm的形式,hh表示小时(12时制或者24小时制),mm代表分钟。所有的时间都转化成12时制,并且假定发生在接下来的12小时。
|
||||
|
||||
### 甜蜜的家 ###
|
||||
|
||||
想要进入刚才进入的地方?运行:
|
||||
|
||||
cd -
|
||||
|
||||
需要快速地回到家目录?输入:
|
||||
|
||||
cd
|
||||
|
||||
变量*CDPATH*定义了含有这个目录的搜索目录路径:
|
||||
|
||||
export CDPATH=/var/www:/nas10
|
||||
|
||||
现在,不用输入cd */var/www/html/ ,我可以直接输入下面的命令进入/var/www/html:
|
||||
|
||||
cd html
|
||||
|
||||
### 编辑一个用less浏览的文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要编辑一个用less浏览的文件,按下v。你就可以用变量$EDITOR下的编辑器来编辑了:
|
||||
|
||||
less *.c
|
||||
less foo.html
|
||||
## 下载v编辑文件 ##
|
||||
## 退出编辑器,你可以继续用less浏览了 ##
|
||||
|
||||
### 列出你系统中的所有文件和目录 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要看到你系统中的所有目录,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
find / -type d | less
|
||||
|
||||
# 列出$HOME 所有目录
|
||||
find $HOME -type d -ls | less
|
||||
|
||||
要看到所有的文件,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
find / -type f | less
|
||||
|
||||
# 列出 $HOME 中所有的文件
|
||||
find $HOME -type f -ls | less
|
||||
|
||||
### 用一条命令构造命令树 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以用mkdir加上-p选项一次创建目录树:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p /jail/{dev,bin,sbin,etc,usr,lib,lib64}
|
||||
ls -l /jail/
|
||||
|
||||
### 复制文件到多个目录中 ###
|
||||
|
||||
不必运行:
|
||||
|
||||
cp /path/to/file /usr/dir1
|
||||
cp /path/to/file /var/dir2
|
||||
cp /path/to/file /nas/dir3
|
||||
|
||||
运行下面的命令来复制文件到多个目录中:
|
||||
|
||||
echo /usr/dir1 /var/dir2 /nas/dir3 | xargs -n 1 cp -v /path/to/file
|
||||
|
||||
留下[创建一个shell函数][2]作为读者的练习。
|
||||
|
||||
### 快速找出两个目录的不同 ###
|
||||
|
||||
diff命令会按行比较文件。它也可以比较两个目录:
|
||||
|
||||
ls -l /tmp/r
|
||||
ls -l /tmp/s
|
||||
# Compare two folders using diff ##
|
||||
diff /tmp/r/ /tmp/s/
|
||||
|
||||
[][3]
|
||||
|
||||
图片: 找出目录之间的不同
|
||||
|
||||
### 文本格式化 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以用fmt命令重新格式化每个段落。在本例中,我要用分割超长的行并且填充短行:
|
||||
|
||||
fmt file.txt
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以分割长的行,但是不重新填充,也就是说分割长行,但是不填充短行:
|
||||
|
||||
fmt -s file.txt
|
||||
|
||||
### 看见输出并写入到一个文件中 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如下使用tee命令在屏幕上看见输出并同样写入到日志文件my.log中:
|
||||
|
||||
mycoolapp arg1 arg2 input.file | tee my.log
|
||||
|
||||
tee可以保证你同时在屏幕上看到mycoolapp的输出和写入文件。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/open-source/command-line-hacks/20-unix-command-line-tricks-part-i/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[nixCraft][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/about-us
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/my-10-unix-command-line-mistakes.html
|
||||
[2]:http://bash.cyberciti.biz/guide/Writing_your_first_shell_function
|
||||
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/open-source/command-line-hacks/20-unix-command-line-tricks-part-i/attachment/differences-between-folders/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
使用Mate Tweak配置Mate桌面
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[在Ubuntu中安装Mate桌面][1]是一码事但是你或许想要知道如何**配置Mate桌面**? 大多数桌面环境都有它们自己的调整工具。比如Unity有Unity Tweak,Gnome有Gnome Tweak,Elementary OS有 Elementary OS Teweak。好消息是Mate桌面也有它自己的调整工具,叫Mate Tweak][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
Mate Tweak是[mintDesktop][3]的克隆分支,一款Linux Mint的配置工具。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Mate Tweak来配置Mate桌面 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Mate Tweak可以通过官方的PPA很简单地在Ubuntu和基于Ubuntu的系统中安装。打开终端,输入下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ubuntu-mate-dev/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install mate-tweak
|
||||
|
||||
你可以控制桌面的显示、按钮的布局和其他界面微调和窗口行为。与Unity和Gnome的调整工具比起来,Mate Tweak没有提供太多的调整选项。比如你还不能用它[改变主题][4],但是至少它提供了一个简单的方法来改变一些配置。我希望它可以在不久的将来提供更多的特性。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/configure-mate-desktop-mate-tweak/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/install-mate-desktop-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
[2]:https://bitbucket.org/flexiondotorg/mate-tweak
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/linuxmint/mintdesktop
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-themes-in-ubuntu-13-10/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux/类Unix系统中解压tar文件到不同的目录中
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我想要解压一个tar文件到一个指定的目录叫/tmp/data。我该如何在Linux或者类Unix的系统中使用tar命令解压一个tar文件到不同的目录中?
|
||||
|
||||
你不必使用cd名切换到其他的目录并解压。可以使用下面的语法解压一个文件:
|
||||
|
||||
### 语法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
典型Unix tar语法:
|
||||
|
||||
tar -xf file.name.tar -C /path/to/directory
|
||||
|
||||
GNU/tar 语法:
|
||||
|
||||
tar xf file.tar -C /path/to/directory
|
||||
|
||||
tar xf file.tar --directory /path/to/directory
|
||||
|
||||
### 示例:解压文件到另一个文件夹中 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在本例中。我解压$HOME/etc.backup.tar到文件夹/tmp/data中。首先,你需要手动创建这个目录,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir /tmp/data
|
||||
|
||||
要解压$HOME/etc.backup.tar 到/tmp/data中,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
tar -xf $HOME/etc.backup.tar -C /tmp/data
|
||||
|
||||
要看到进度,使用-v选项:
|
||||
|
||||
tar -xvf $HOME/etc.backup.tar -C /tmp/data
|
||||
|
||||
示例输出:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Gif 01: tar命令解压文件到不同的目录
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以指定解压的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
tar -xvf $HOME/etc.backup.tar file1 file2 file3 dir1 -C /tmp/data
|
||||
|
||||
要解压foo.tar.gz(.tgz扩展文件)包到/tmp/bar中,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir /tmp/bar
|
||||
tar -zxvf foo.tar.gz -C /tmp/bar
|
||||
|
||||
要解压foo.tar.bz2(.tbz, .tbz2 和 .tb2 扩展文件)包到/tmp/bar中,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir /tmp/bar
|
||||
tar -jxvf foo.tar.bz2 -C /tmp/bar
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-extract-tar-file-to-specific-directory-on-unixlinux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[nixCraft][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/about-us
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
|
||||
在 RedHat/CentOS 7.x 中使用 cmcli 命令管理网络
|
||||
===============
|
||||
[**Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7** 与 **CentOS 7**][1] 中默认的网络服务由 **NetworkManager** 提供,这是动态控制及配置网络的守护进程,它用于保持当前网络设备及连接处于工作状态,同时也支持传统的 ifcfg 类型的配置文件。
|
||||
NetworkManager 可以用于以下类型的连接:
|
||||
Ethernet,VLANS,Bridges,Bonds,Teams,Wi-Fi,mobile boradband(如移动3G)以及 IP-over-InfiniBand。针对与这些网络类型,NetworkManager 可以配置他们的网络别名,IP 地址,静态路由,DNS,VPN连接以及很多其它的特殊参数。
|
||||
|
||||
可以用命令行工具 nmcli 来控制 NetworkManager。
|
||||
|
||||
###nmcli 用法###
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli [ OPTIONS ] OBJECT { COMMAND | help }
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以通过 TAB 键补全命令,当你忘记这个命令的语法时只需要按下 TAB 就可以看到选项列表。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
使用 nmcli 的一些例子:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli general status
|
||||
|
||||
这条命令将 NetworkManager 的所有状态都打印出来。
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection show
|
||||
|
||||
显示所有连接。
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection show -a
|
||||
|
||||
仅显示当前活动的连接。
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli device status
|
||||
|
||||
列出通过 NetworkManager 验证的设备列表及他们的状态。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 启动/停止 网络接口###
|
||||
|
||||
使用 nmcli 工具启动或停止网络接口,与 ifconfig 的 up/down 是一样的。使用下列命令停止某个接口:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli device disconnect eno16777736
|
||||
|
||||
下列命令用来启动接口:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli device connect eno16777736
|
||||
|
||||
###添加静态IP的以太网连接
|
||||
|
||||
以下命令可以添加一个静态IP地址的以太网连接:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NAME_OF_CONNECTION ifname interface-name ip4 IP_ADDRESS gw4 GW_ADDRESS
|
||||
|
||||
根据你需要的配置更改 NAME_OF_CONNECTION,IP_ADDRESS, GW_ADDRESS参数(如果不需要网关的话可以省略最后一部分)。
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NEW ifname eno16777736 ip4 192.168.1.141 gw4 192.168.1.1
|
||||
|
||||
使用下列命令设置DNS服务器:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection modify NEW ipv4.dns "8.8.8.8 8.8.4.4"
|
||||
|
||||
下列命令启动新的 Ethernet 连接:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection up NEW ifname eno16777736
|
||||
|
||||
查看新连接的配置信息:
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli -p connection show NEW
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
增加新的连接,使用DHCP自动分配IP地址,网关,DNS等,你要做的就是将命令行后 ip/gw 地址部分去掉就行了,DHCP会自动分配这些参数。
|
||||
|
||||
例,在 eno 16777736 设备上配置一个 名为 NEW_DHCP 的 DHCP 连接
|
||||
|
||||
# nmcli connection add type ethernet con-name NEW_DHCP ifname eno16777736
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/nmcli-tool-red-hat-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrian Dinu][a]
|
||||
译者:[SPccman](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/adriand/
|
||||
[1]:https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/7/html/7.0_Release_Notes/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user