mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
Merge pull request #3552 from ictlyh/master
Translated sources/tech/20151125 The tar command explained.md
This commit is contained in:
commit
924502bc42
@ -1,138 +0,0 @@
|
||||
ictlyh Translating
|
||||
The tar command explained
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The Linux [tar][1] command is the swiss army of the Linux admin when it comes to archiving or distributing files. Gnu Tar archives can contain multiple files and directories, file permissions can be preserved and it supports multiple compression formats. The name tar stands for "**T**ape **Ar**chiver", the format is an official POSIX standard.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tar file formats ###
|
||||
|
||||
A short introduction into tar compression levels.
|
||||
|
||||
- **No compression** Uncompressed files have the file ending .tar.
|
||||
- **Gzip Compression** The Gzip format is the most widely used compression format for tar, it is fast for creating and extracting files. Files with gz compression have normally the file ending .tar.gz or .tgz. Here some examples on how to [create][2] and [extract][3] a tar.gz file.
|
||||
- **Bzip2 Compression** The Bzip2 format offers a better compression then the Gzip format. Creating files is slower, the file ending is usually .tar.bz2.
|
||||
- **Lzip (LZMA) Compression** The Lzip compression combines the speed of Gzip with a compression level that is similar to Bzip2 (or even better). Independently from these good attributes, this format is not widely used.
|
||||
- **Lzop Compression** This compress option is probably the fastest compression format for tar, it has a compression level similar to gzip and is not widely used.
|
||||
|
||||
The common formats are tar.gz and tar.bz2. If you goal is fast compression, then use gzip. When the archive file size is critical, then use tar.bz2.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is the tar command used for? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Here a few common use cases of the tar command.
|
||||
|
||||
- Backup of Servers and Desktops.
|
||||
- Document archiving.
|
||||
- Software Distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing tar ###
|
||||
|
||||
The command is installed on most Linux Systems by default. Here are the instructions to install tar in case that the command is missing.
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
Execute the following command as root user on the shell to install tar on CentOS.
|
||||
|
||||
yum install tar
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
This command will install tar on Ubuntu. The "sudo" command ensures that the apt command is run with root privileges.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install tar
|
||||
|
||||
#### Debian ####
|
||||
|
||||
The following apt command installs tar on Debian.
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install tar
|
||||
|
||||
#### Windows ####
|
||||
|
||||
The tar command is available for Windows as well, you can download it from the Gunwin project. [http://gnuwin32.sourceforge.net/packages/gtar.htm][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### Create tar.gz Files ###
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the [tar command][5] that has to be run on the shell. I will explain the command line options below.
|
||||
|
||||
tar pczf myarchive.tar.gz /home/till/mydocuments
|
||||
|
||||
This command creates the archive myarchive.tar.gz which contains the files and folders from the path /home/till/mydocuments. **The command line options explained**:
|
||||
|
||||
- **[p]** This option stand for "preserve", it instructs tar to store details on file owner and file permissions in the archive.
|
||||
- **[c]** Stands for create. This option is mandatory when a file is created.
|
||||
- **[z]** The z option enables gzip compression.
|
||||
- **[f]** The file option tells tar to create an archive file. Tar will send the output to stdout if this option is omitted.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tar command examples ####
|
||||
|
||||
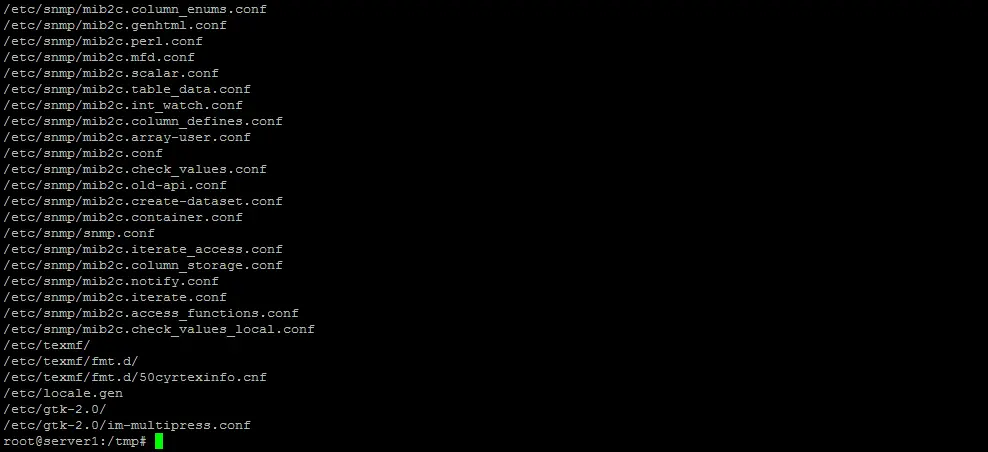
**Example 1: Backup the /etc Directory** Create a backup of the /etc config directory. The backup is stored in the root folder.
|
||||
|
||||
tar pczvf /root/etc.tar.gz /etc
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The command should be run as root to ensure that all files in /etc are included in the backup. This time, I've added the [v] option in the command. This option stands for verbose, it tells tar to show all file names that get added into the archive.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 2: Backup your /home directory** Create a backup of your home directory. The backup will be stored in a directory /backup.
|
||||
|
||||
tar czf /backup/myuser.tar.gz /home/myuser
|
||||
|
||||
Replace myuser with your username. In this command, I've omitted the [p] switch, so the permissions get not preserved.
|
||||
|
||||
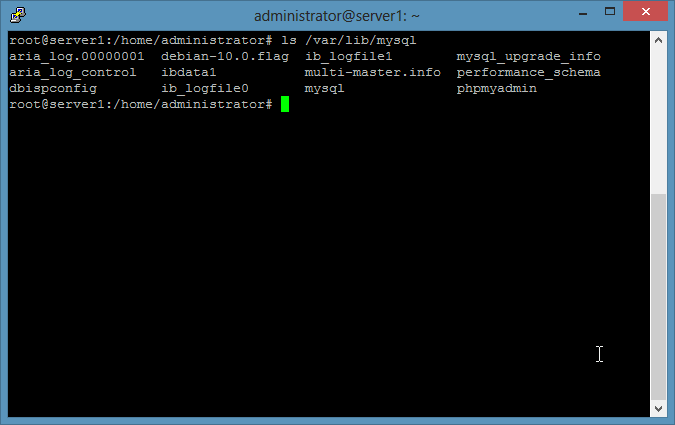
**Example 3: A file-based backup of MySQL databases** The MySQL databases are stored in /var/lib/mysql on most Linux distributions. You can check that with the command:
|
||||
|
||||
ls /var/lib/mysql
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Stop the database server to get a consistent MySQL file backup with tar. The backup will be written to the /backup folder.
|
||||
|
||||
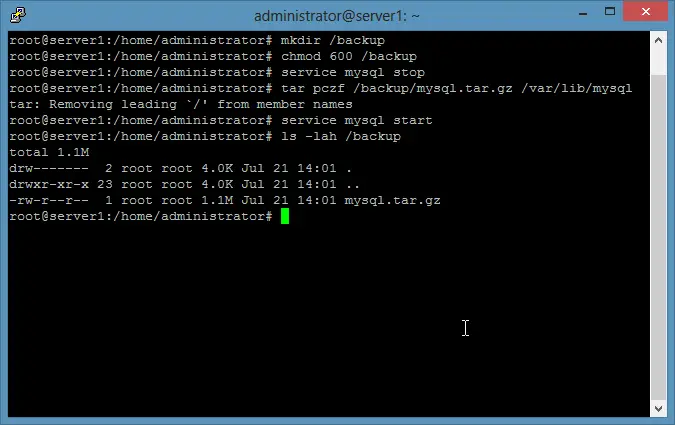
1) Create the backup folder
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir /backup
|
||||
chmod 600 /backup
|
||||
|
||||
2) Stop MySQL, run the backup with tar and start the database server again.
|
||||
|
||||
service mysql stop
|
||||
tar pczf /backup/mysql.tar.gz /var/lib/mysql
|
||||
service mysql start
|
||||
ls -lah /backup
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Extract tar.gz Files ###
|
||||
|
||||
The command to extract tar.gz files is:
|
||||
|
||||
tar xzf myarchive.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
#### The tar command options explained ####
|
||||
|
||||
- **[x]** The x stand for extract, it is mandatory when a tar file shall be extracted.
|
||||
- **[z]** The z option tells tar that the archive that shall be unpacked is in gzip format.
|
||||
- **[f]** This option instructs tar to read the archive content from a file, in this case the file myarchive.tar.gz.
|
||||
|
||||
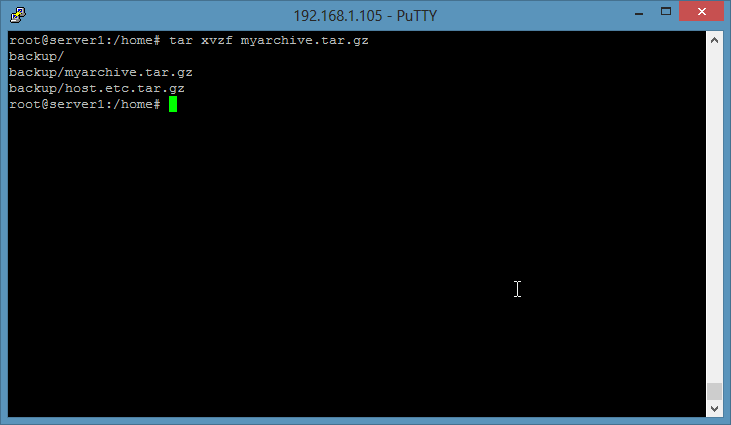
The above tar command will silently extract that tar.gz file, it will show only error messages. If you like to see which files get extracted, then add the "v" option.
|
||||
|
||||
tar xzvf myarchive.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
The **[v]** option stands for verbose, it will show the file names while they get unpacked.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/linux-tar-command/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[howtoforge][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.howtoforge.com/
|
||||
[1]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tar_(computing)
|
||||
[2]:http://www.faqforge.com/linux/create-tar-gz/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.faqforge.com/linux/extract-tar-gz/
|
||||
[4]:http://gnuwin32.sourceforge.net/packages/gtar.htm
|
||||
[5]:http://www.faqforge.com/linux/tar-command/
|
||||
137
translated/tech/20151125 The tar command explained.md
Normal file
137
translated/tech/20151125 The tar command explained.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
|
||||
tar 命令详解
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux [tar][1] 命令是归档或分发文件时的强大武器。GNU tar 归档包可以包含多个文件和目录,还能保留权限,它还支持多种压缩格式。Tar 表示 "**T**ape **Ar**chiver",这是一种 POSIX 标准。
|
||||
|
||||
### Tar 文件格式 ###
|
||||
|
||||
tar 压缩等级简介。
|
||||
|
||||
- **无压缩** 没有压缩的文件用 .tar 结尾。
|
||||
- **Gzip 压缩** Gzip 格式是 tar 使用最广泛的压缩格式,它能快速压缩和提取文件。用 gzip 压缩的文件通常用 .tar.gz 或 .tgz 结尾。这里有一些如何[创建][2]和[解压][3] tar.gz 文件的例子。
|
||||
- **Bzip2 压缩** 和 Gzip格式相比 Bzip2 提供了更好的压缩比。创建压缩文件也比较慢,通常采用 .tar.bz2 结尾。
|
||||
- **Lzip(LAMA)压缩** Lizp 压缩结合了 Gzip 快速的优势,以及和 Bzip2 类似(甚至更好) 的压缩率。尽管有这些好处,这个格式并没有得到广泛使用。
|
||||
- **Lzop 压缩** 这个压缩选项也许是 tar 最快的压缩格式,它的压缩率和 gzip 类似,也没有广泛使用。
|
||||
|
||||
常见的格式是 tar.gz 和 tar.bz2。如果你想快速压缩,那么就是用 gzip。如果归档文件大小比较重要,就是用 tar.bz2。
|
||||
|
||||
### tar 命令用来干什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一些使用 tar 命令的常见情形。
|
||||
|
||||
- 备份服务器或桌面系统
|
||||
- 文档归档
|
||||
- 软件分发
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 tar ###
|
||||
|
||||
大部分 Linux 系统默认都安装了 tar。如果没有,这里有安装 tar 的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS ####
|
||||
|
||||
在 CentOS 中,以 root 用户在 shell 中执行下面的命令安装 tar。
|
||||
|
||||
yum install tar
|
||||
|
||||
#### Ubuntu ####
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令会在 Ubuntu 上安装 tar。“sudo” 命令确保 apt 命令是以 root 权限运行的。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install tar
|
||||
|
||||
#### Debian ####
|
||||
|
||||
下面的 apt 命令在 Debian 上安装 tar。
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install tar
|
||||
|
||||
#### Windows ####
|
||||
|
||||
tar 命令在 Windows 也可以使用,你可以从 Gunwin 项目[http://gnuwin32.sourceforge.net/packages/gtar.htm][4]中下载它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建 tar.gz 文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下面是在 shell 中运行 [tar 命令][5] 的一些例子。下面我会解释这些命令行选项。
|
||||
|
||||
tar pczf myarchive.tar.gz /home/till/mydocuments
|
||||
|
||||
这个命令会创建归档文件 myarchive.tar.gz,其中包括了路径 /home/till/mydocuments 中的文件和目录。**命令行选项解释**:
|
||||
|
||||
- **[p]** 这个选项表示 “preserve”,它指示 tar 在归档文件中保留文件属主和权限信息。
|
||||
- **[c]** 表示创建。要创建文件时不能缺少这个选项。
|
||||
- **[z]** z 选项启用 gzip 压缩。
|
||||
- **[f]** file 选项告诉 tar 创建一个归档文件。如果没有这个选项 tar 会把输出发送到 stdout。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tar 命令事例 ####
|
||||
|
||||
**事例 1: 备份 /etc 目录** 创建 /etc 配置目录的一个备份。备份保存在 root 目录。
|
||||
|
||||
tar pczvf /root/etc.tar.gz /etc
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要以 root 用户运行命令确保 /etc 中的所有文件都会被包含在备份中。这次,我在命令中添加了 [v] 选项。这个选项表示 verbose,它告诉 tar 显示所有被包含到归档文件中的文件名。
|
||||
|
||||
**事例 2: 备份你的 /home 目录** 创建你的 home 目录的备份。备份会被保存到 /backup 目录。
|
||||
|
||||
tar czf /backup/myuser.tar.gz /home/myuser
|
||||
|
||||
用你的用户名替换 myuser。这个命令中,我省略了 [p] 选项,也就不会保存权限。
|
||||
|
||||
**事例 3: 基于文件的 MySQL 数据库备份** 在大部分 Linux 发行版中,MySQL 数据库保存在 /var/lib/mysql。你可以使用下面的命令检查:
|
||||
|
||||
ls /var/lib/mysql
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
用 tar 备份 MySQL 文件时为了保持一致性,首先停用数据库服务器。备份会被写到 /backup 目录。
|
||||
|
||||
1) 创建 backup 目录
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir /backup
|
||||
chmod 600 /backup
|
||||
|
||||
2) 停止 MySQL,用 tar 进行备份并重新启动数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
service mysql stop
|
||||
tar pczf /backup/mysql.tar.gz /var/lib/mysql
|
||||
service mysql start
|
||||
ls -lah /backup
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 提取 tar.gz 文件###
|
||||
|
||||
提取 tar.gz 文件的命令是:
|
||||
|
||||
tar xzf myarchive.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
#### tar 命令选项解释 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- **[x]** x 表示提取,提取 tar 文件时这个命令不可缺少。
|
||||
- **[z]** z 选项告诉 tar 要解压的归档文件时 gzip 格式。
|
||||
- **[f]** 该选项告诉 tar 从一个文件中读取归档内容,本例中是 myarchive.tar.gz。
|
||||
|
||||
上面的 tar 命令会安静地提取 tar.gz 文件,它只会显示错误信息。如果你想要看提取了哪些文件,那么添加 “v” 选项。
|
||||
|
||||
tar xzvf myarchive.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
**[v]** 选项表示 verbose,它会向你显示解压的文件名。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.howtoforge.com/tutorial/linux-tar-command/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[howtoforge][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](http://mutouxiaogui.cn/blog/)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.howtoforge.com/
|
||||
[1]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tar_(computing)
|
||||
[2]:http://www.faqforge.com/linux/create-tar-gz/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.faqforge.com/linux/extract-tar-gz/
|
||||
[4]:http://gnuwin32.sourceforge.net/packages/gtar.htm
|
||||
[5]:http://www.faqforge.com/linux/tar-command/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user