mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-25 00:50:15 +08:00
翻译完成:20141120 How to visualize memory usage on Linux.md
翻译中:20141117 Restricting process CPU usage using nice cpulimit and cgroups.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
68a784d630
commit
8ee9eb4893
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
翻译中 by coloka
|
||||
Restricting process CPU usage using nice, cpulimit, and cgroups
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
注:本文中的图片似乎都需要翻墙后才能看到,发布的时候注意
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
|
||||
翻译中 by coloka
|
||||
How to visualize memory usage on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Lack of sufficient physical memory can significantly hamper the performance of Linux desktop and server environments. When your desktop is sluggish, one of the first things to do is to free up RAMs. Memory usage is even more critical in multi-user shared hosting or mission-critical server environments, where different users or application threads constantly compete for more memory.
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes to monitoring any type of system resources such as memory or CPUs, visualization is an effective means to help understand quickly how they are consumed by different processes and users. In this tutorial, I describe **how to visualize memory usage in Linux environment** using a command-line tool called [smem][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### Physical Memory Usage: RSS vs. PSS vs. USS ###
|
||||
|
||||
In the presence of virtual memory abstraction, accurately quantifying physical memory usage of a process is actually not straightforward. The virtual memory size of a process is not meaningful because it does not tell how much of it is actually allocated physical memory.
|
||||
|
||||
**Resident set size (RSS)**, reported by top command, is one popular metric which captures what portion of a process' reported memory is residing in RAM. However, aggregating RSS of existing processes can easily overestimate the overall physical memory usage of the Linux system because the same physical memory page can be shared by different processes. **Proportional set size (PSS)** is a more accurate measurement of effective memory usage of Linux processes since PSS properly discounts the memory page shared by more than one process. **Unique set size (USS)** of a process is a subset of the process' PSS, which is not shared by any other processes.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Smem on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
The command-line tool smem can generate a variety of reports related to memory PSS/USS usage by pulling information from /proc. It comes with built-in graphical chart generation capabilities, so one can easily visualize overall memory consumption status.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install Smem on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install smem
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install Smem on Fedora or CentOS/RHEL ####
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS/RHEL, you need to [enable][2] EPEL repository first.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install smem python-matplotlib
|
||||
|
||||
### Check Memory Usage with Smem ###
|
||||
|
||||
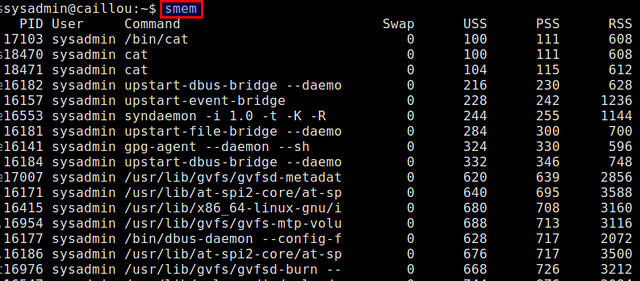
When you run smem as a unprivileged user, it will report physical memory usage of every process launched by the current user, in an increasing order of PSS.
|
||||
|
||||
$ smem
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to check the overall system memory usage for all users, run smem as the root.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo smem
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To view per-user memory usage:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo smem -u
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
smem allows you to filter memory usage results based on mapping, processes or users in the following format:
|
||||
|
||||
- -M <mapping-filtering-regular-expression>
|
||||
- -P <process-filtering-regular-expression>
|
||||
- -U <user-filtering-regular-expression>
|
||||
|
||||
For a complete usage of smem, refer to its man page.
|
||||
|
||||
### Visualize Memory Usage with Smem ###
|
||||
|
||||
Visualized reports are often easier to read to identify the memory hogs of your system quickly. smem supports two kinds of graphical reports for memory usage visualization: bar and pie graphs.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are examples of memory usage visualization.
|
||||
|
||||
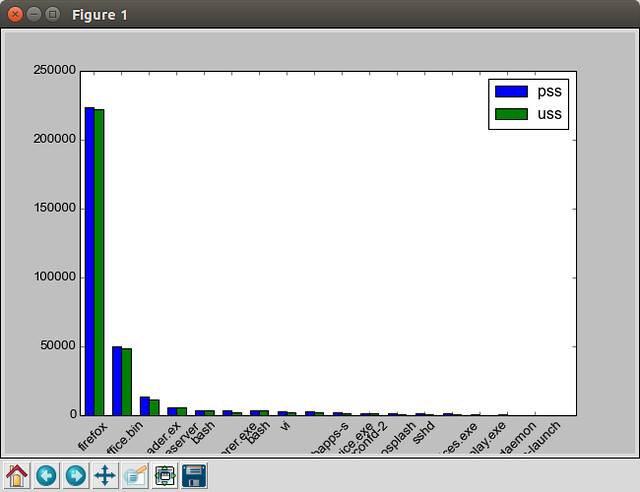
The following command will generate a bar graph that visualizes the PSS/USS memory usage of a user alice.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo smem --bar name -c "pss uss" -U alice
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
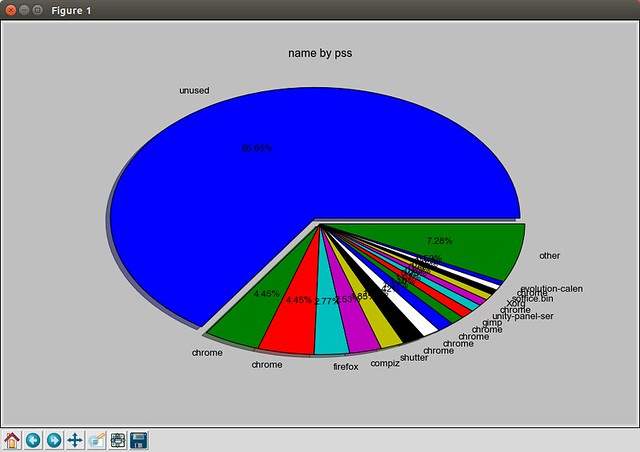
The next command will plot a pie graph of the overall PSS memory usage of different processes.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo smem --pie name -c "pss"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
As a summary, smem is a simple and effective memory analysis tool that comes in handy in various circumstances. Using its formatted output, you can run smem to identify any memory issues and take an action in an automatic fashion. If you know of any good memory monitoring tool, share it in the comment.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/visualize-memory-usage-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://www.selenic.com/smem/
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
图形化显示Linux内存使用情况
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
物理内存不足对Linux桌面系统和服务器系统的性能影响都很大。当你的电脑变慢时,要做的第一件事就是释放内存。尤其是在多用户环境以及执行关键任务的服务器环境下,内存消耗会变得更加关键,因为多个用户和应用线程会同时争用更多的内存空间。
|
||||
|
||||
如果要监测系统内各种资源的使用情况(比如说CPU或内存),图形化显示是一种高效的方法,通过图形界面可以快速分析各用户和进程的资源消耗情况。本教程将给大家介绍**在linux下图形化分析内存使用情况**的方法,使用到命令行工具是[smem][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### 物理内存使用情况: RSS vs. PSS vs. USS ###
|
||||
|
||||
由于Linux使用到了虚拟内存(virtual memory),因此要准确的计算一个进程实际使用的物理内存就不是那么简单。 只知道进程的虚拟内存大小也并没有太大的用处,因为还是无法获取到实际分配的物理内存大小。
|
||||
|
||||
**RSS(Resident set size)**,使用top命令可以查询到,是最常用的内存指标,表示进程占用的物理内存大小。但是,将各进程的RSS值相加,通常会超出整个系统的内存消耗,这是因为RSS中包含了各进程间共享的内存。**PSS(Proportional set size)**会更准确一些,它将共享内存的大小进行平均后,再分摊到各进程上去。**USS(Unique set size )**是PSS的自己,它只计算了进程独自占用的内存大小,不包含任何共享的部分。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装Smem ###
|
||||
|
||||
smem是一个能够生成多种内存耗用报告的命令行工具,它从/proc文件系统中提取各进程的PSS/USS信息,并进行汇总输出。它还内建了图表的生成能力,所以能够方便地分析整个系统的内存使用情况。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Debian, Ubuntu 或 Linux Mint 上安装smem ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install smem
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Fedora 或 CentOS/RHEL上安装Smem ####
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS/RHEL上,你首先得[使能][2]EPEL仓。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install smem python-matplotlib
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用smem检查内存使用情况 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在非特权模式下使用smem,它能够显示当前用户运行的所有进程的内存使用情况,并按照PSS的大小进行排序。
|
||||
|
||||
$ smem
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如有你想得到整个系统中所有用户的内存使用情况,就需要使用root权限来运行smem。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo smem
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
也可以按用户维度来输出报告:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo smem -u
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
smem提供了以下选项来对输出结果进行筛选,支持按映射方式(mapping),进程和用户三个维度的筛选:
|
||||
|
||||
- -M <mapping-filtering-regular-expression>
|
||||
- -P <process-filtering-regular-expression>
|
||||
- -U <user-filtering-regular-expression>
|
||||
|
||||
想了解smem更多的使用方式,可以查询用户手册(man page)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用smem图形化显示内存使用情况 ###
|
||||
|
||||
图形化的报告使用起来会更加方便快捷。smem支持支持两种格式的图形显示方式:直方图和饼图。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一些图形化显示的实例。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令行会基于PSS/RSS值,生成直方图,以用户alice为例。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo smem --bar name -c "pss uss" -U alice
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个例子会生成一张饼图,图中显示了系统中各进程的PSS内存使用量:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo smem --pie name -c "pss"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
概括来说,smem是一个方便易用的内存分析工具。利用smem的格式化输出,你可以对内存使用报告进行自动化分析,并执行一些自动化的处理措施。如果你还知道其他的一些优秀的内存检测工具,请在留言区告诉我。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/visualize-memory-usage-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[coloka](https://github.com/coloka)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://www.selenic.com/smem/
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user