mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-27 02:30:10 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject
This commit is contained in:
commit
8b6f342a3e
sources
share
20141106 Exaile 3.4.1 Overview--A Feature-Complete GNOME Music Player.md20150323 Red Hat Developer Toolset 3.1 beta arrives.md20150330 Picty--Managing Photos Made Easy.md20150410 This tool can alert you about evil twin access points in the area.md
talk
20150407 10 Years of Git--An Interview with Git Creator Linus Torvalds.md20150410 10 Famous IT Skills in Demand That Will Get You Hired.md20150410 10 Top Distributions in Demand to Get Your Dream Job.md
tech
20150331 Linux Email App Geary Updated--How To Install It In Ubuntu.md20150407 5 Linux Command Line Based Tools for Downloading Files and Browsing Websites.md20150409 4 Tools Send Email with Subject, Body and Attachment in Linux.md20150409 Install Inkscape - Open Source Vector Graphic Editor.md20150410 7 Command Line Tools for Browsing Websites and Downloading Files in Linux.md20150410 How to Install and Configure Multihomed ISC DHCP Server on Debian Linux.md20150410 How to run Ubuntu Snappy Core on Raspberry Pi 2.md20150410 What is a good alternative to wget or curl on Linux.md
translated
@ -1,76 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by ictlyh
|
||||
Exaile 3.4.1 Overview – A Feature-Complete GNOME Music Player
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Exaile** has been a bit quiet in the past two years with maybe only one or two stable releases, but nevertheless, it’s one of the full-featured music players for GNOME which are on par with applications like [Rhythmbox][1] or [Banshee][2] in terms of features. However, over the past two months a new stable release, 3.4, has been put out under the slogan “We’re not dead yet”, as well as an incremental 3.4.1 release, which shipped on November 1. To be honest, Exaile has so many features that I could go on writing a lot more than an article to cover them all, so let’s have a look at some of the most notable ones.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
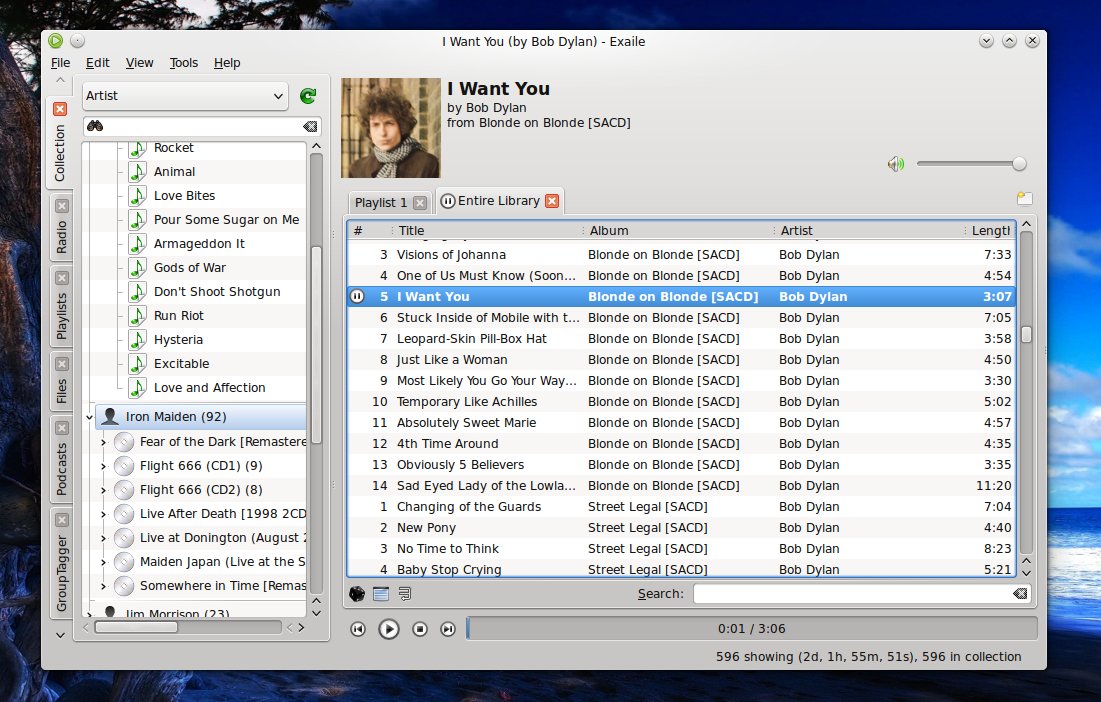
[Exaile][3] is a GTK2-based music player written in Python which fits well into GNOME, has an interface which pretty much resembles the one of the old Amarok 1.4 or actual Clementine, and ships with some great features. The interface is composed mainly of two panels, both with support for tabs. The left panel provides access to the collection, Internet radio, smart and custom playlists, file browser, podcasts, Group Tagger and lyrics while the main area of the window is taken by the playlists (with multiple, tabbed playlist support) and control buttons.
|
||||
|
||||
Exaile’s interface is very similar to the one of Clementine or Amarok 1.4 and the tabs on the left can be shown or hidden:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Version 3.4 shipped with a big number of major new features and changes while 3.4.1 was a small bug fix release. The major new features in 3.4 include new plugins like Icecast, Lyricsmania, Playlist Analyzer, Soma.fm, a new, simpler plugin API. Changes were done to the user interface and the general behavior as well, with the possibility to show playlists in multiple panels, close left panels, better BPM UI integration.
|
||||
|
||||
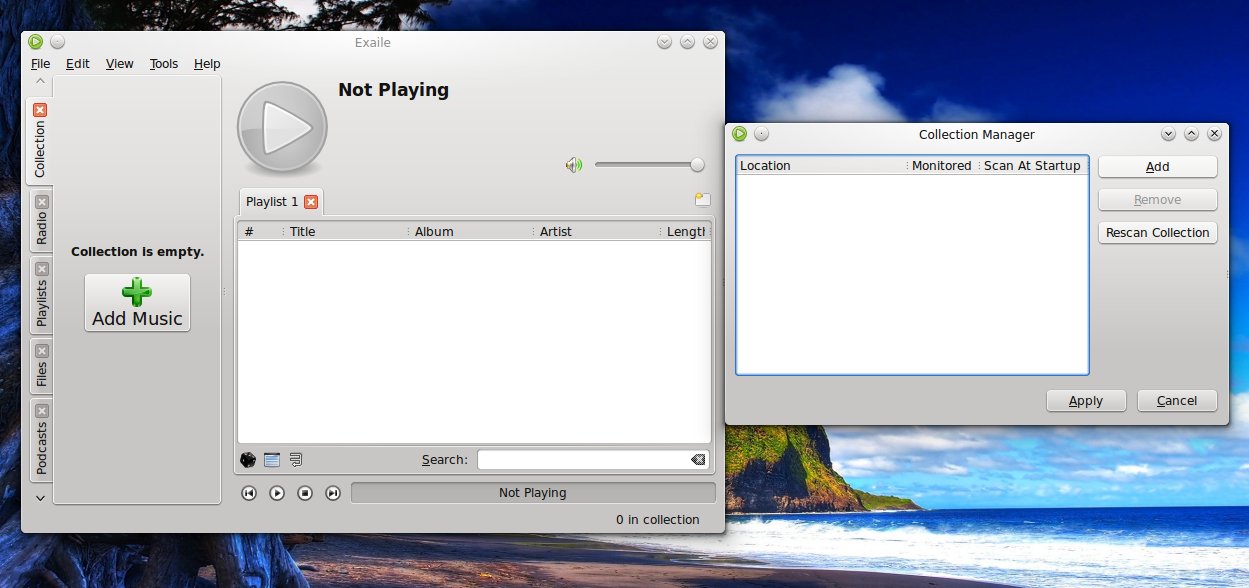
The first time it starts you can add music folders to the collection – you can also choose to add directories and enable or disable monitoring or scanning them at start-up:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Exaile’s features are practically countless. You can organize your music in a collection, listen to podcasts, set song ratings, edit tags, view file properties, queue tracks, view lyrics and covers, sort the playlist by a huge number of criteria, change playback behavior or appearance style.
|
||||
|
||||
Equalizer, cover manager and listening to Internet radio:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
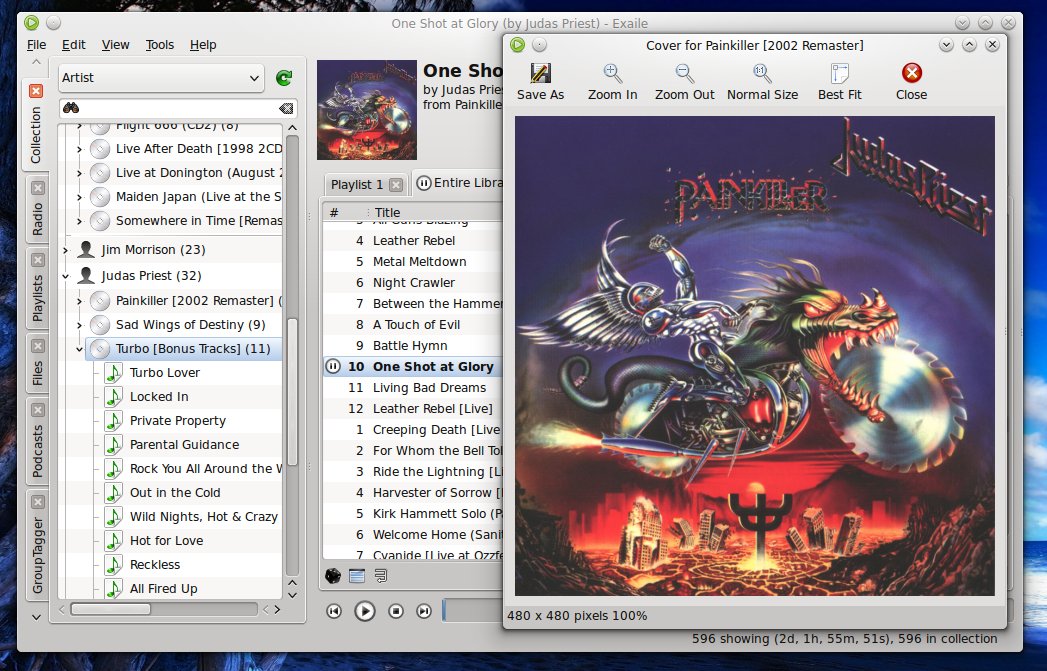
Local album covers are detected automatically and can be shown in full size, with the possibility to zoom in or out:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
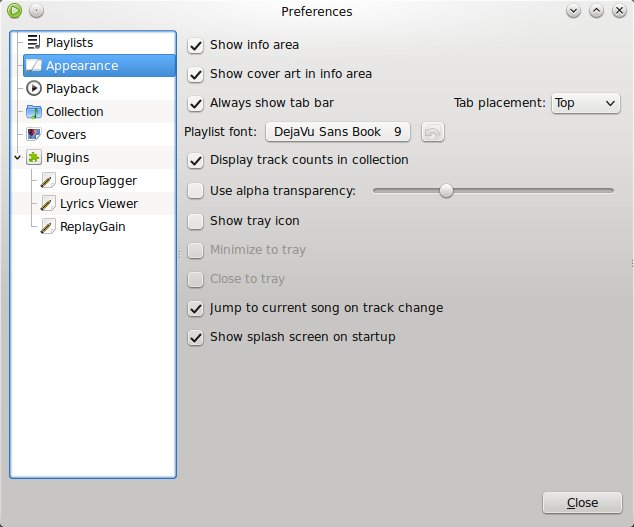
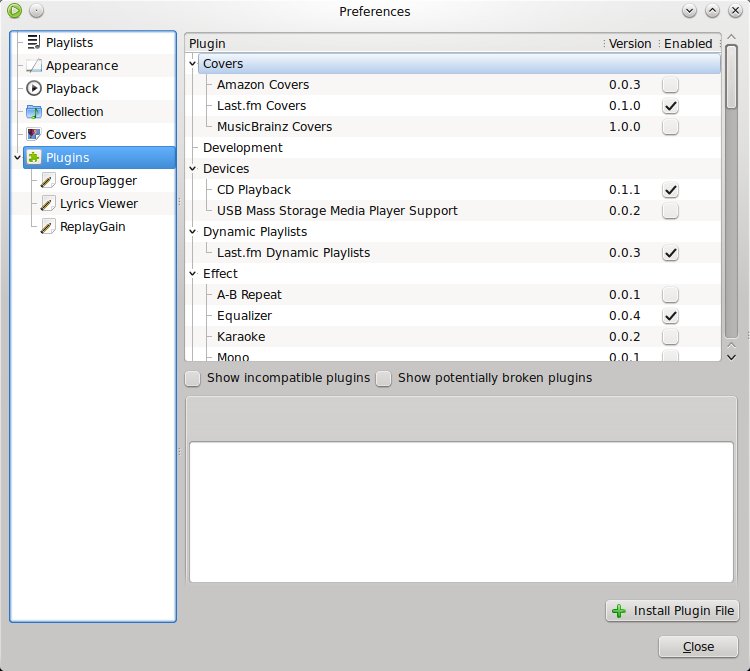
The preferences window allows to configure various aspects of Exaile, including enable or disable plugins, appearance, system tray integration, or playback. The appearance settings will allow you to change the tabs placement, show/hide the tab bar, enable or disable transparency, or disable the start-up splash screen.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
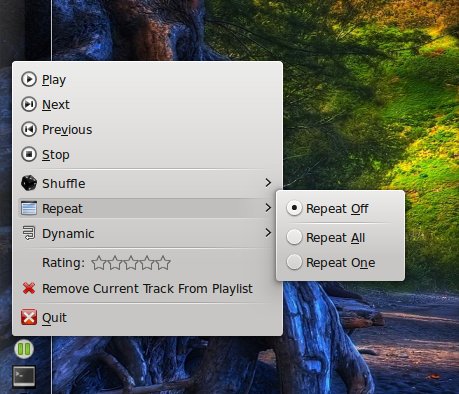
The system tray integration offers a menu to quickly play/pause songs, set a song rating or change the way the playlist handles playback (shuffle, repeat or dynamic).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The countless features in Exaile I believe make it the perfect choice as a music player, especially for GNOME users. Any user should be satisfied with the wealth of options and the highly configurable approach.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Exaile 3.4.1 in Ubuntu 14.04 and 14.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Compiling and installing from source should be pretty straightforward. First, get the dependencies:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get build-dep exaile
|
||||
sudo apt-get install python-gst0.10
|
||||
|
||||
Download the source tarball from the [downloads page][4] (direct link [here][5]), then uncompress it:
|
||||
|
||||
tar -xf exaile-3.4.1.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Change the working directory to exaile-3.4.1 and issue the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
make
|
||||
sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
The binary will be installed as **/usr/local/bin/exaile**.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tuxarena.com/2014/11/exaile-3-4-1-overview-a-feature-complete-gnome-music-player/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Craciun Dan
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Rhythmbox
|
||||
[2]:http://banshee.fm/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.exaile.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.exaile.org/download/
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/exaile-dev/exaile/archive/3.4.1.tar.gz
|
||||
@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Red Hat Developer Toolset 3.1 beta arrives
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Summary**:Want the newest developer tools for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 6 or 7? The beta's ready for you now.
|
||||
|
||||
It's one of those eternal problems between developers and operators that even [DevOps][1] can't entirely solve. System administrators want the most stable operating system possible, while programmers want the latest and greatest development tools. [Red Hat][2]'s solution for this dilemma has been to take those brand spanking-new tools, test them out on the latest stable [Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)][3], and then release them to developers.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Red Hat Developer Toolset
|
||||
|
||||
So it is that Red Hat has just announced its latest toys for developers, [Red Hat Developer Toolset 3.1][4]. This packaging of the hottest new tools is now available in beta.
|
||||
|
||||
This update includes:
|
||||
|
||||
[GNUCompiler Collection (GCC) 4.9][5]: the latest stable upstream version of GCC, which provides numerous improvements and bug fixes
|
||||
|
||||
[Eclipse 4.4.1][6]: with support for Java 8 and updated versions of Eclipse CDT (8.5), Eclipse Linux Tools (3.1), Eclipse Mylyn (3.14), and Eclipse Egit/Jgit (3.6.1)
|
||||
|
||||
Numerous additional updated packages: These include GDB 7.8.2, elfutils 0.161, memstomp 0.1.5, SystemTap 2.6, Valgrind 3.10.1, Dyninst 8.2.1, and ltrace 0.7.91.
|
||||
|
||||
With these development programs, you'll be able to create applications for RHEL 6 and 7.x. These apps will then run on RHEL regardless of whether you're running it on a physical, virtual or cloud environments. They will also run on Red Hat's [OpenShift][7], its Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) offering.
|
||||
|
||||
This new set of developer programs includes packages for both RHEL 7 and 7 running on [AMD64 and Intel 64 architectures][8]. Although the tools are 64-bit you can use them to create and modify 32-bit binaries.
|
||||
|
||||
Before you try running any of these programs, you should patch RHEL with all the latest updates. To install the beta Toolset, your systems need to be subscribed to the Optional channel to access all the required Red Hat Developer Toolset tool-chain packages.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, if you've installed earlier Toolkits you may run into some [problems while installing Toolkit 3.1][9]. While these difficulties are easy enough to fix, you should go over these possible hiccups before trying to install the new Toolkit.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, you may notice that some of the most exciting of the new tools, such as Docker, Kubernetes, and other container tools aren't here. That's because they're in the newly released [RHEL 7.1][10] and [Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Atomic Host (RHELAH)][11]. [Red Hat has partnered with Docker][12], but you'll need to move to a Docker-friendly version of RHEL to get at these container-friendly programs.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.zdnet.com/article/red-hat-developer-toolset-3-1-beta-arrives/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.zdnet.com/meet-the-team/us/sjvn/
|
||||
[1]:http://blogs.csc.com/2015/02/03/devops-theory-for-beginners/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.redhat.com/en
|
||||
[3]:http://www.redhat.com/en/technologies/linux-platforms/enterprise-linux
|
||||
[4]:http://www.redhat.com/en/about/blog/red-hat-developer-toolset-31-beta-now-available
|
||||
[5]:https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-4.9/
|
||||
[6]:https://projects.eclipse.org/projects/eclipse/releases/4.4.1
|
||||
[7]:https://www.openshift.com/
|
||||
[8]:https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Developer_Toolset/3-Beta/html/3.1_Release_Notes/System_Requirements.html
|
||||
[9]:https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Developer_Toolset/3-Beta/html/3.1_Release_Notes/DTS3.1_Release.html#Known_Issues
|
||||
[10]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/red-hat-7-1-is-here-centos-7-1-is-coming-soon/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/red-hat-buys-into-docker-containers-with-atomic-host/
|
||||
[12]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/red-hat-partners-with-docker-to-create-linuxdocker-software-stack/
|
||||
@ -1,103 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by H-mudcup
|
||||
Picty: Managing Photos Made Easy
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### About Picty ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Picty** is a free, simple, yet powerful photo collection manager that will help you to manage your photos. It is designed around managing **metadata** and a **lossless** approach to image handling. Picty currently supports both online(web-based) and offline(local) collections. In local collections, the images will be stored in a local folder and it’s sub-folders. A database will be maintained to speed up the image queries in the user’s home folder. In online(web-based) collections, you can upload and share images through a web browser. Ant user with proper rights can share photos to any persons, and each user can have multiple collections open at once and collections can be shared by multiple users. There is a simple interface for transferring images between collections using a transfer plugin.
|
||||
|
||||
You can download any number of photos from your Camera or any devices. Also, Picty allows you to browse photo collections from your Camera before downloading it. Picty is lightweight application, and has snappy interface. It supports Linux, and Windows platforms.
|
||||
|
||||
### Features ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Supports big photo collections (20,000 plus images).
|
||||
- Open more than one collection at a time and transfer images between them.
|
||||
- Collections are:
|
||||
- Folders of images in your local file system.
|
||||
- Images on cameras, phones and other media devices.
|
||||
- Photo hosting services (Flickr currently supported).
|
||||
- picty does not “Import” photos into its own database, it simply provides an interface for accessing them wherever they are. To keep things snappy and to allow you to browse even if you are offline, picty maintains a cache of thumbnails and metadata.
|
||||
- Reads and writes metadata in industry standard formats Exif, IPTC and Xmp
|
||||
- Lossless approach:
|
||||
- picty writes all changes including image edits as metadata. e.g. an image crop is stored as any instruction, the original pixels remain in the file
|
||||
- Changes are stored in picty’s collection cache until you save your metadata changes to the images. You can easily revert unsaved changes that you don’t like.
|
||||
- Basic image editing:
|
||||
- Current support for basic image enhancements such as brightness, contrast, color, cropping, and straightening.
|
||||
- Improvements to those tools and other tools coming soon (red eye reduction, levels, curves, noise reduction)
|
||||
- Image tagging:
|
||||
- Use standard IPTC and Xmp keywords for image tags
|
||||
- A tag tree view lets you easily manage your tags and navigate your collection
|
||||
- Folder view:
|
||||
- Navigate the directory heirarchy of your image collection
|
||||
- Multi-monitor support
|
||||
- picty can be configured to let you browse your collection on one screen and view full screen images on another.
|
||||
- Customizable
|
||||
- Create launchers for external tools
|
||||
- Supports plugins – many of the current features (tagging and folder views, and all of the image editing tools) are provided by plugins
|
||||
- Written in python – batteries included!
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Install from PPA ####
|
||||
|
||||
Picty developers has a PPA for Debian based distributions, like Ubuntu, to make the installation much easier.
|
||||
|
||||
To install in Ubuntu and derivatives, run:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:damien-moore/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install picty
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Install from Source ####
|
||||
|
||||
Also, you can install it from Source files. First, install the following dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install bzr python-pyinotify python-pyexiv2 python-gtk2 python-gnome2 dcraw python-osmgpsmap python-flickrapi
|
||||
|
||||
Then, get the latest version using command:
|
||||
|
||||
bzr branch lp:picty
|
||||
|
||||
To run picty, change to the picty directory, and enter:
|
||||
|
||||
cd picty
|
||||
bin/picty
|
||||
|
||||
To update to the latest version, run:
|
||||
|
||||
cd picty
|
||||
bzr pull
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
Launch Picty either from Menu or Unity Dash.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can either choose existing collection, device or directory. Let us create a **new collection**. To do that, create New Collection button. Enter the collection, and browse to the path where you have the images stored. Finally, click **Create** button.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can modify, rotate, add/remove tags, set descriptive info of each images. To do that, just right click any image and do the actions of your choice.
|
||||
|
||||
Visit the following Google group to get more information and support about Picty Photo manager.
|
||||
|
||||
- [http://groups.google.com/group/pictyphotomanager][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/picty-managing-photos-made-easy/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:http://groups.google.com/group/pictyphotomanager
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
This tool can alert you about evil twin access points in the area
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**EvilAP_Defender can even attack rogue Wi-Fi access points for you, the developer says**
|
||||
|
||||
A new open-source tool can periodically scan an area for rogue Wi-Fi access points and can alert network administrators if any are found.
|
||||
|
||||
The tool, called EvilAP_Defender, was designed specifically to detect malicious access points that are configured by attackers to mimic legitimate ones in order to trick users to connect to them.
|
||||
|
||||
These access points are known as evil twins and allow hackers to intercept Internet traffic from devices connected to them. This can be used to steal credentials, spoof websites, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
Most users configure their computers and devices to automatically connect to some wireless networks, like those in their homes or at their workplace. However, when faced with two wireless networks that have the same name, or SSID, and sometimes even the same MAC address, or BSSID, most devices will automatically connect to the one that has the stronger signal.
|
||||
|
||||
This makes evil twin attacks easy to pull off because both SSIDs and BSSIDs can be spoofed.
|
||||
|
||||
[EvilAP_Defender][1] was written in Python by a developer named Mohamed Idris and was published on GitHub. It can use a computer's wireless network card to discover rogue access points that duplicate a real access point's SSID, BSSID, and even additional parameters like channel, cipher, privacy protocol, and authentication.
|
||||
|
||||
The tool will first run in learning mode, so that the legitimate access point [AP] can be discovered and whitelisted. It can then be switched to normal mode to start scanning for unauthorized access points.
|
||||
|
||||
If an evil AP is discovered, the tool can alert the network administrator by email, but the developer also plans to add SMS-based alerts in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
There is also a preventive mode in which the tool can launch a denial-of-service [DoS] attack against the evil AP to buy the administrator some time to take defensive measures.
|
||||
|
||||
"The DoS will only be performed for evil APs which have the same SSID but a different BSSID (AP's MAC address) or run on a different channel," Idris said in the tool's documentation. "This is to avoid attacking your legitimate network."
|
||||
|
||||
However, users should remember that attacking someone else's access point, even a likely malicious one operated by an attacker, is most likely illegal in many countries.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to run, the tool needs the Aircrack-ng wireless suite, a wireless card supported by Aircrack-ng, MySQL and the Python runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2905725/security0/this-tool-can-alert-you-about-evil-twin-access-points-in-the-area.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Lucian Constantin][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.infoworld.com/author/Lucian-Constantin/
|
||||
[1] https://github.com/moha99sa/EvilAP_Defender/blob/master/README.TXT
|
||||
@ -1,134 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by ZTinoZ
|
||||
10 Years of Git: An Interview with Git Creator Linus Torvalds
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Linus Torvalds explains why he created Git
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Thanks to Linus' Git today GitHub is the world's biggest code hoster in the world with over 9 million users and over 21.1 million repositories.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> By Swapnil Bhartiya -
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Git will be celebrating it’s 10 anniversary this month. It’s yet another contribution of Linus Torvalds to the world in addition to Sub Surface and Linux. [Jennifer Cloer of The Linux Foundation interviewed the father of Linux][2] and presented us with a very comprehensive story behind Git.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> When Cloer asked Linus why he created Git, his answer was:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> “I really never wanted to do source control management at all and felt that it was just about the least interesting thing in the computing world (with the possible exception of databases ;^), and I hated all SCM’s with a passion.”
|
||||
>
|
||||
> He then played with BitKeeper which he initially liked as in his own words:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> “BK got most things right and having a local copy of the repository and distributed merging was a big deal.”
|
||||
>
|
||||
> But he was not satisfied:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> “I had performance requirements that were not even remotely satisfied by what was available, and I also worried about integrity of the code and the whole workflow, so I ended up just deciding to write my own.”
|
||||
>
|
||||
> And the rest is history. Today GitHub is the world’s biggest code hoster in the world with over 9 million users and over 21.1 million repositories.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> via:http://www.linuxveda.com/2015/04/06/linus-torvalds-explains-why-he-created-git/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ten years ago this week, the Linux kernel community faced a daunting challenge: They could no longer use their revision control system BitKeeper and no other Software Configuration Management (SCMs) met their needs for a distributed system. Linus Torvalds, the creator of Linux, took the challenge into his own hands and disappeared over the weekend to emerge the following week with Git. Today Git is used for thousands of projects and has ushered in a new level of social coding among programmers.
|
||||
|
||||
To celebrate this milestone, we asked Linus to share the behind-the-scenes story of Git and tell us what he thinks of the project and its impact on software development. You'll find his comments in the story below. We'll follow this Q&A with a week of Git in which we profile a different project each day that is using the revision control system. Look for the stories behind KVM, Qt, Drupal, Puppet and Wine, among others.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why did you create Git? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Torvalds**: I really never wanted to do source control management at all and felt that it was just about the least interesting thing in the computing world (with the possible exception of databases ;^), and I hated all SCM's with a passion. But then BitKeeper came along and really changed the way I viewed source control. BK got most things right and having a local copy of the repository and distributed merging was a big deal. The big thing about distributed source control is that it makes one of the main issues with SCM's go away - the politics around "who can make changes." BK showed that you can avoid that by just giving everybody their own source repository. But BK had its own problems, too; there were a few technical choices that caused problems (renames were painful), but the biggest downside was the fact that since it wasn't open source, there was a lot of people who didn't want to use it. So while we ended up having several core maintainers use BK - it was free to use for open source projects - it never got ubiquitous. So it helped kernel development, but there were still pain points.
|
||||
|
||||
That then came to a head when Tridge (Andrew Tridgell) started reverse-engineering the (fairly simply) BK protocol, which was against the usage rules for BK. I spent a few weeks (months? It felt that way) trying to mediate between Tridge and Larry McVoy, but in the end it clearly wasn't working. So at some point I decided that I can't continue using BK, but that I really didn't want to go back to the bad old pre-BK days. Sadly, at the time, while there were some other SCM's that kind of tried to get the whole distributed thing, none of them did it remotely well. I had performance requirements that were not even remotely satisfied by what was available, and I also worried about integrity of the code and the whole workflow, so I ended up just deciding to write my own.
|
||||
|
||||
### How did you approach it? Did you stay up all weekend to write it or was it just during regular hours? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Torvalds**: Heh. You can actually see how it all took shape in the git source code repository, except for the very first day or so. It took about a day to get to be "self-hosting" so that I could start committing things into git using git itself, so the first day or so is hidden, but everything else is there. The work was clearly mostly during the day, but there's a few midnight entries and a couple of 2 a.m. ones. The most interesting part is how quickly it took shape ; the very first commit in the git tree is not a lot of code, but it already did the basics - enough to commit itself. The trick wasn't really so much the coding but coming up with how it organizes the data.
|
||||
|
||||
So I'd like to stress that while it really came together in just about ten days or so (at which point I did my first *kernel* commit using git), it wasn't like it was some kind of mad dash of coding. The actual amount of that early code is actually fairly small, it all depended on getting the basic ideas right. And that I had been mulling over for a while before the whole project started. I'd seen the problems others had. I'd seen what I wanted to avoid doing.
|
||||
|
||||
### Has it lived up to your expectations? How is it working today in your estimation? Are there any limitations? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Torvalds**: I'm very happy with git. It works remarkably well for the kernel and is still meeting all my expectations. What I find interesting is how it took over so many other projects, too. Surprisingly quickly, in the end. There is a lot of inertia in switching source control systems; just look at how long CVS and even RCS have stayed around, but at some point git just took over.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why do you think it's been so widely adopted? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Torvalds**: I think that many others had been frustrated by all the same issues that made me hate SCM's, and while there have been many projects that tried to fix one or two small corner cases that drove people wild, there really hadn't been anything like git that really ended up taking on the big problems head on. Even when people don't realize how important that "distributed" part was (and a lot of people were fighting it), once they figure out that it allows those easy and reliable backups, and allows people to make their own private test repositories without having to worry about the politics of having write access to some central repository, they'll never go back.
|
||||
|
||||
### Does Git last forever, or do you foresee another revision control system in another 10 years? Will you be the one to write it? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Torvalds**: I'm not going to be the one writing it, no. And maybe we'll see something new in ten years, but I guarantee that it will be pretty "git-like." It's not like git got everything right, but it got all the really basic issues right in a way that no other SCM had ever done before.
|
||||
|
||||
No false modesty ;)
|
||||
|
||||
### Why does Git work so well for Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Torvalds**: Well, it was obviously designed for our workflow, so that is part of it. I've already mentioned the whole "distributed" part many times, but it bears repeating. But it was also designed to be efficient enough for a biggish project like Linux, and it was designed to do things that people considered "hard" before git - because those are the things *I* do every day.
|
||||
|
||||
Just to pick an example: the concept of "merging" was generally considered to be something really quite painful and hard in most SCM's. You'd plan your merges, because they were big deals. That's not acceptable to me, since I commonly do tens of merges a day when in the merge window, and even then, the biggest overhead shouldn't be the merge itself, it should be testing the result. The "git" part of the merge is just a couple of seconds, it should take me much longer just to write the merge explanation message.
|
||||
|
||||
So git was basically designed and written for my requirements, and it shows.
|
||||
|
||||
### People have said that Git is only for super smart people. Even Andrew Morton said Git is "expressly designed to make you feel less intelligent than you thought you were." What's your response to this? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Torvalds**: So I think it used to be true but isn't any more. There is a few reasons people feel that way, but I think only one of them remains. The one that remains is fairly simple: "you can do things so many ways."
|
||||
|
||||
You can do a lot of things with git, and many of the rules of what you *should* do are not so much technical limitations but are about what works well when working together with other people. So git is a very powerful set of tools, and that can not only be overwhelming at first, it also means that you can often do the same (or similar) things different ways, and they all "work." Generally, the best way to learn git is probably to first only do very basic things and not even look at some of the things you can do until you are familiar and confident about the basics.
|
||||
|
||||
There's a few historical reasons for why git was considered complicated. One of them is that it was complicated. The people who started using git very early on in order to work on the kernel really had to learn a very rough set of scripts to make everything work. All the effort had been on making the core technology work and very little on making it easy or obvious. So git (deservedly) had a reputation for requiring you to know exactly what you did early on. But that was mainly true for the first 6 months or a year.
|
||||
|
||||
The other big reason people thought git was hard is that git is very different. There are people who used things like CVS for a decade or two, and git is not CVS. Not even close. The concepts are different. The commands are different. Git never even really tried to look like CVS, quite the reverse. And if you've used a CVS-like system for a long time, that makes git appear complicated and needlessly different. People were put off by the odd revision numbers. Why is a git revision not "1.3.1" with nice incrementing numbers like it was in CVS? Why is it that odd scary 40-character HEX number?
|
||||
|
||||
But git wasn't "needlessly different." The differences are required. It's just that it made some people really think it was more complicated than it is, because they came from a very different background. The "CVS background" thing is going away. By now there are probably lots of programmers out there who have never used CVS in their lives and would find the CVS way of doing things very confusing, because they learned git first.
|
||||
|
||||
### Do you think the rate of Linux kernel development would have been able to grow at its current rate without Git? Why or why not? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Torvalds**: Well, "without git," sure. But it would have required that somebody else wrote something git-equivalent: a distributed SCM that is as efficient as git is. We definitely needed something *like* git.
|
||||
|
||||
### What's your latest opinion of GitHub? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Torvalds**: Github is an excellent hosting service; I have nothing against it at all. Now, the complaints I've had is that GitHub as a development platform - making commits, pull requests, keeping track of issues etc - doesn't work very well at all. It's not even close, not for something like the kernel. It's much too limited.
|
||||
|
||||
That's partly because of how the kernel is developed, but part of it was that the GitHub interfaces were actively encouraging bad behavior. Commits done on GitHub had bad commit messages etc, because the web interfaces at GitHub were actively encouraging bad behavior. They did fix some of that, so it probably works better, but it will never be appropriate for something like the Linux kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is the most interesting use you've seen for Git and/or GitHub? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Torvalds**: I'm just happy that it made it so easy to start a new project. Project hosting used to be painful, and with git and GitHub it's just so trivial to do a random small project. It doesn't matter what the project is; what matters is that you can do it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Do you have side projects up your sleeve today? Any more brilliant software projects that will dominate software development for years to come? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Torvalds**: Nothing planned. But I'll let you know if that changes.
|
||||
|
||||
Atlassian is also helping to celebrate the anniversary of Git. Click on the image below to [take a walk down memory lane][1].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/185-jennifer-cloer/821541-10-years-of-git-an-interview-with-git-creator-linus-torvalds
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jennifer Cloer][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linux.com/community/forums/person/714/catid/185-jennifer-cloer
|
||||
[1]:https://www.atlassian.com/git/articles/10-years-of-git/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linux.com/news/featured-blogs/185-jennifer-cloer/821541-10-years-of-git-an-interview-with-git-creator-linus-torvalds
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
[13]:
|
||||
[14]:
|
||||
[15]:
|
||||
[16]:
|
||||
[17]:
|
||||
[18]:
|
||||
[19]:
|
||||
[20]:
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
|
||||
10 Famous IT Skills in Demand That Will Get You Hired
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In continuation of our last article [[Top 10 Operating Systems in demand][1]] which was highly appreciated by the Tecmint community, we here in this article aims at throwing light on top IT skills that will help you land to your dream job.
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned in the first article these data and statistics are supposed to be change with the change in demand and market. We will try our best to update the list whenever there is any major changes. All the statistics are produced on the basis of close study of Job boards, postings and requirements by several IT companies across the globe.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. VMware ###
|
||||
|
||||
The visualization and cloud computing software designed by Vmware Inc. tops the List. Vmware claims to commercially virtualize x86 architecture for the first time. VMware demand has increased upto 16% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest stable Release: 11.0
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. MySQL ###
|
||||
|
||||
The open source Relational Database Management System falls second in the list. Until 2013 it was the second most widely used RDBMS. MySQL demand has increased upto 11% in the last quarter. The very famous MariaDB has been forked out of MySQL after Oracle Corp. Owned it.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : 5.6.23
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Apache ###
|
||||
|
||||
The open source cross platform web (HTTP) server stands third in the list. Apache demand has increased to more than 13% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : 2.4.12
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. AWS ###
|
||||
|
||||
Amazon web services is a collection of remote computing services offered by Amazon.com. Aws made to the list at number four. AWS demand has shown a growth of nearly 14% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Puppet ###
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration Management System used in setting up IT Infrastructure comes at number five. It is written in Ruby and follows Client-server architecture. The demand of puppet has grown above 9% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : 3.7.3
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Hadoop ###
|
||||
|
||||
Hadoop is a open source software framework written in Java to process big data. It stands at position six in the list. The demand of Hadoop has gone upto 0.2% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : 2.6.0
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Git ###
|
||||
|
||||
The famous distributed control system written initially by Linus Torvalds made to the list at number seven. The demand of Git has gone above 7% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : 2.3.4
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Oracle PL/SQL ###
|
||||
|
||||
The procedural extension for SQL by Oracle corp. stands at position eight. PL/SQL is included in Oracle Database since Oracle 7. It has shown a decline of nearly 8% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Tomcat ###
|
||||
|
||||
Open source web server and servlet container comes at position number nine. It has shown a growth in demand of nearly 15% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : 8.0.15
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. SAP ###
|
||||
|
||||
The most famous Enterprise Resource Planning Software stands at position ten. The demand of SAP has shown a growth of nearly 3.5% in last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格数据,不需要翻译-开始
|
||||
<table cellspacing="0" cellpadding="5" style="width: 804px;">
|
||||
<colgroup>
|
||||
<col width="88">
|
||||
<col width="427">
|
||||
<col width="257">
|
||||
</colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="88" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: 1px solid #000000; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0.1cm;">1.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="427" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: 1px solid #000000; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0.1cm;">VMware</td>
|
||||
<td width="257" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border: 1px solid #000000; padding: 0.1cm;"><span style="color: #006600;"><b>16% +</b></span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top" class="alt">
|
||||
<td width="88" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">2.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="427" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">MySQL</td>
|
||||
<td width="257" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: 1px solid #000000; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0.1cm; padding-top: 0cm;"><span style="color: #006600;"><b>11% +</b></span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="88" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">3.</td>
|
||||
<td width="427" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">Apache</td>
|
||||
<td width="257" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: 1px solid #000000; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0.1cm; padding-top: 0cm;"><span style="color: #006600;"><b>13% +</b></span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top" class="alt">
|
||||
<td width="88" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">4.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="427" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">Amazon web services (AWS)</td>
|
||||
<td width="257" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: 1px solid #000000; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0.1cm; padding-top: 0cm;"><span style="color: #006600;"><b>14% +</b></span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="88" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">5.
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td width="427" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">Puppet</td>
|
||||
<td width="257" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: 1px solid #000000; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0.1cm; padding-top: 0cm;"><span style="color: #006600;"><b>9% +</b></span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top" class="alt">
|
||||
<td width="88" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">6.</td>
|
||||
<td width="427" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">Hadoop</td>
|
||||
<td width="257" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: 1px solid #000000; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0.1cm; padding-top: 0cm;"><span style="color: #006600;"><b>0.2% +</b></span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="88" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">7.</td>
|
||||
<td width="427" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">Git</td>
|
||||
<td width="257" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: 1px solid #000000; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0.1cm; padding-top: 0cm;"><span style="color: #006600;"><b>7% +</b></span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top" class="alt">
|
||||
<td width="88" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">8.</td>
|
||||
<td width="427" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">Oracle PL/SQL</td>
|
||||
<td width="257" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: 1px solid #000000; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0.1cm; padding-top: 0cm;"><span style="color: red;"><b>8% -</b></span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top">
|
||||
<td width="88" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">9.</td>
|
||||
<td width="427" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">Tomcat</td>
|
||||
<td width="257" bgcolor="#eeeeee" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: 1px solid #000000; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0.1cm; padding-top: 0cm;"><span style="color: #006600;"><b>15% +</b></span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr valign="top" class="alt">
|
||||
<td width="88" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">10.</td>
|
||||
<td width="427" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: none; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0cm; padding-top: 0cm;">SAP</td>
|
||||
<td width="257" style="border-bottom: 1px solid #000000; border-left: 1px solid #000000; border-right: 1px solid #000000; border-top: none; padding-bottom: 0.1cm; padding-left: 0.1cm; padding-right: 0.1cm; padding-top: 0cm;"><span style="color: #006600;"><b>3.5% +</b></span></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
注:表格数据,不需要翻译-结束
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I’ll be here with the next part of the series following. Till then stay tuned. Stay Connected. Stay Commenting. Don’t forget to provide us with your feedback. Like and share us and help us get spread.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/famous-it-skills-in-demand-that-will-get-you-hired/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/top-distributions-in-demand-to-get-your-dream-job/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,149 @@
|
||||
10 Top Distributions in Demand to Get Your Dream Job
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
We are coming up with a series of five articles which aims at making you aware of the top skills which will help you in getting yours dream job. In this competitive world you can not rely on one skill. You need to have balanced set of skills. There is no measure of a balanced skill set except a few conventions and statistics which changes from time-to-time.
|
||||
|
||||
The below article and remaining to follow is the result of close study of job boards, posting and requirements of various IT Companies across the globe of last three months. The statistics keeps on changing as the demand and market changes. We will try our best to update the list when there is any major changes.
|
||||
The Five articles of this series are…
|
||||
|
||||
- 10 Distributions in Demand to Get Your Dream Job
|
||||
- [10 Famous IT Skills in Demand That Will Get You Hired][1]
|
||||
- 10 Programming Skills That Will Help You to Get Dream Job
|
||||
- 10 IT Networking Protocols Skills to Land Your Dream Job
|
||||
- 10 Professional Certifications in Demand That Will Get You Hired
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Windows ###
|
||||
|
||||
The operating System developed by Microsoft not only dominates the PC market but it is also the most sought OS skill from job perspective irrespective of all the odds and criticism that follows. It has shown a growth in demand which equals to 0.1% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : Windows 8.1
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Red Hat Enterprise Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat Enterprise Linux is a commercial Linux Distribution developed by Red Hat Inc. It is one of the Most widely used Linux distribution specially in corporates and production. It comes at number two having a overall growth in demand which equals to 17% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : RedHat Enterprise Linux 7.1
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Solaris ###
|
||||
|
||||
The UNIX Operating System developed by Sun Microsystems and now owned by Oracle Inc. comes at number three. It has shown a growth in demand which equals to 14% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : Oracle Solaris 10 1/13
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. AIX ###
|
||||
|
||||
Advanced Interactive eXecutive is a Proprietary Unix Operating System by IBM stands at number four. It has shown a growth in demand which equals to 11% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : AIX 7
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Android ###
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most widely used open source operating system designed specially for mobile, tablet computers and wearable gadgets is now owned by Google Inc. comes at number five. It has shown a growth in demand which equals to 4% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : Android 5.1 aka Lollipop
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. CentOS ###
|
||||
|
||||
Community Enterprise Operating System is a Linux distribution derived from RedHat Enterprise Linux. It comes at sixth position in the list. Market has shown a growth in demand which is nearly 22% for CentOS, in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : CentOS 7
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux Operating System designed for Humans and designed by Canonicals Ltd. Ubuntu comes at position seventh. It has shown a growth in demand which equals to 11% in the last quarter.
|
||||
Latest Stable Release :
|
||||
|
||||
- Ubuntu 14.10 (9 months security and maintenance update).
|
||||
- Ubuntu 14.04.2 LTS
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Suse ###
|
||||
|
||||
Suse is a Linux operating System owned by Novell. The Linux distribution is famous for YaST configuration tool. It comes at position eight. It has shown a growth in demand which equals to 8% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : 13.2
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Debian ###
|
||||
|
||||
The very famous Linux Operating System, mother of 100’s of Distro and closest to GNU comes at number nine. It has shown a decline in demand which is nearly 9% in the last quarter.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : Debian 7.8
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. HP-UX ###
|
||||
|
||||
The Proprietary UNIX Operating System designed by Hewlett-Packard comes at number ten. It has shown a decline in the last quarter by 5%.
|
||||
|
||||
Latest Stable Release : 11i v3 Update 13
|
||||
|
||||
注:表格数据--不需要翻译--开始
|
||||
<table border="0" cellspacing="0">
|
||||
<colgroup width="107"></colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="92"></colgroup>
|
||||
<colgroup width="80"></colgroup>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" bgcolor="#DDDDDD" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: #111111; font-size: small;">1</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#DDDDDD" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="color: #111111; font-size: small;">Windows</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#DDDDDD" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: #111111; font-size: small;">0.1% +</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">2</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">RedHat</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: #007826; font-size: small;">17% +</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">3</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">Solaris</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: #007826; font-size: small;">14% +</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">4</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">AIX</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: #007826; font-size: small;">11% +</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">5</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">Android</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: #007826; font-size: small;">4% +</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">6</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">CentOS</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: #007826; font-size: small;">22% +</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">7</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">Ubuntu</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: #007826; font-size: small;">11% +</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">8</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">Suse</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: #007826; font-size: small;">8% +</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td height="25" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">9</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">Debian</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: #ff3300; font-size: small;">9% -</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr class="alt">
|
||||
<td height="25" bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">10</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><span style="font-size: small;">HP-UX</span></td>
|
||||
<td bgcolor="#FFFFFF" align="center" style="border: 1px solid #000000;"><b><span style="color: #ff3300; font-size: small;">5% -</span></b></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
注:表格数据--不需要翻译--结束
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I’ll be coming up with the next article of this series very soon. Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below. Like and share us and help us get spread.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/top-distributions-in-demand-to-get-your-dream-job/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/top-distributions-in-demand-to-get-your-dream-job/www.tecmint.com/famous-it-skills-in-demand-that-will-get-you-hired/
|
||||
@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by ictlyh
|
||||
Linux Email App Geary Updated — How To Install It In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Geary, the popular desktop email client for Linux, has been updated to version 0.10 — and it gains a glut of new features in the process.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
An older version of Geary running in elementary OS
|
||||
|
||||
Geary 0.100 features some welcome user interface improvements and additional UI options, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- New: Ability to ‘Undo’ Archive, Trash and Move actions
|
||||
- New: Option to switch between a 2 column or 2 column layout
|
||||
- New “split header bar” — improves message list, composer layouts
|
||||
- New shortcut keys — use j/k to navigate next/previous conversations
|
||||
|
||||
This update also introduces a **brand new full-text search algorithm** designed to improve the search experience in Geary, according to Yorba.
|
||||
|
||||
This introduction should calm some complaints of the app’s search prowess, which often sees Geary return a slew of search results that are, to quote software outfit themselves, “…seemingly unrelated to the search query.”
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘Yorba recommends that all users of the client upgrade to this release’
|
||||
|
||||
*“Although not all search problems are fixed in 0.10, Geary should be more conservative about displaying results that match the user’s query,” [the team notes][1]. *
|
||||
|
||||
Last but by no means least on the main feature front is something sure to find favour with power users: **support for multiple/alternate e-mail addresses per account**.
|
||||
|
||||
If your main Gmail account is set-up in Geary to pull in your Yahoo, Outlook and KittyMail messages too then you should now see them all kept neatly together and be given the option of picking which identity you send from when using the composer ‘From’ field. No, it’s not the sexiest feature but it is one that has been requested often.
|
||||
|
||||
Rounding out this release of the popular Linux email client is the usual gamut of bug fixes, performance optimisations and miscellaneous improvements.
|
||||
|
||||
Yorba recommends that all users of the client upgrade to this release.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Geary 0.10 in Ubuntu 14.04, 14.10 & 15.04 ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The latest version of Yorba is available to download as source, ready for compiling from the GNOME Git. But let’s be honest: that’s a bit of a hassle, right?
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu users wondering how to install Geary 0.10 in **14.04, 14.10** and (for early birds) **15.04** have things easy.
|
||||
|
||||
The official Yorba PPA contains the **latest versions of Geary** as well as those for Shotwell (photo manager) and [California][2] (calendar app). Be aware that any existing versions of these apps installed on your computer may/will be upgraded to a more recent version by adding this PPA.
|
||||
|
||||
Capiche? Coolio.
|
||||
|
||||
To install Geary in Ubuntu you first need to add the Yorba PPA your Softwares Sources. To do this just open a new Terminal window and carefully enter the following two commands:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yorba/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install geary
|
||||
|
||||
After hitting return/enter on the last you’ll be prompted to enter your password. Do this, and then let the installation complete.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once done, open your desktop environment’s app launcher and seek out the ‘Geary’ icon. Click it, add your account(s) and discover [what the email mail man has dropped off through the information superhighway][3] and into the easy to use graphical interface.
|
||||
|
||||
**Don’t forget: you can always tip us with news, app suggestions, and anything else you’d like to see us cover by using the power of electronic mail. Direct your key punches to joey [at] oho [dot] io.**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/03/install-geary-ubuntu-linux-email-update
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Geary/FullTextSearchStrategy
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/10/california-calendar-natural-language-parser
|
||||
[3]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rxM8C71GB8w
|
||||
@ -1,156 +0,0 @@
|
||||
5 Linux Command Line Based Tools for Downloading Files and Browsing Websites
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux command-line, the most adventurous and fascinating part of GNU/Linux is very cool and powerful tool. Command line itself is very productive and the availability of various inbuilt and third party command line application makes Linux robust and powerful. The Linux Shell supports a variety of web application of various kind be it torrent downloader, dedicated downloader or Internet Surfing.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
5 Command Line Internet Tools
|
||||
|
||||
Here we are presenting 5 great command line Internet tools, which are very useful and proves to be very handy.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. rTorrent ###
|
||||
|
||||
rTorrent is a text-based Torrent Client which is written in C++ aimed at high performance. It is available for most of the standard Linux Distributions including FreeBSD and Mac OS X.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Installation of rTorrent ####
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install rtorrent (on APT based System)
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install rtorrent (on YUM based System)
|
||||
|
||||
Check if rtorrent is installed correctly by running the following command in the terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
# rtorrent
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
rTorrent Command Line Tool
|
||||
|
||||
#### Functioning of rTorrent ####
|
||||
|
||||
Some of the useful Key-bindings and their use.
|
||||
|
||||
- CTRL+ q – Quit rTorrent Application
|
||||
- CTRL+ s – Start Download
|
||||
- CTRL+ d – Stop an active Download or Remove an already stopped Download.
|
||||
- CTRL+ k – Stop and Close an active Download.
|
||||
- CTRL+ r – Hash Check a torrent before Upload/Download Begins.
|
||||
- CTRL+ q – When this key combination is executed twice, rTorrent shutdown without sending a stop Signal.
|
||||
- Left Arrow Key – Redirect to Previous screen.
|
||||
- Right Arrow Key – Redirect to Next Screen
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Wget ###
|
||||
|
||||
Wget, is a part of GNU Project, the name is derived from World Wide Web (WWW). Wget is a brilliant tool which is useful for recursive download, offline viewing of HTML from local Server and is available for most of the platforms be it Windows, Mac, Linux. Wget makes it possible to download files over HTTP, HTTPS and FTP. Moreover it can be useful in mirroring the whole website as well as support for proxy browsing, pausing/resuming Downloads.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Installation of Wget ####
|
||||
|
||||
Wget being a GNU project comes bundled with Most of the Standard Linux Distributions and there is no need to download and install it separately. If in-case, it’s not installed by default, you can still install it using apt or yum.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install wget (on APT based System)
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install wget (on YUM based System)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Some Basic Usage of Wget ####
|
||||
|
||||
Download a single file using wget.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://www.website-name.com/file
|
||||
|
||||
Download a whole website, recursively.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget -r http://www.website-name.com
|
||||
|
||||
Download specific type of file (say pdf and png) from a website.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget -r -A png,pdf http://www.website-name.com
|
||||
|
||||
Wget is a wonderful tool which enables custom and filtered download even on limited resource Machine. A screen shot of wget download, where we are mirroring a website (Yahoo.com).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Wget Command Line File Download
|
||||
|
||||
For more such wget download examples, read our article that shows [10 Wget Download Command Examples][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. cURL ###
|
||||
|
||||
cURL is a command line tool for transferring data over a number of protocols. cURL is a client side application which support protocols like FTP, HTTP, FTPS, TFTP, TELNET, IMAP, POP3, etc. cURL is a simple downloader which is different from wget in supporting LDAP, POP3 as compared to others. Moreover Proxy Downloading, pausing download, resuming download are well supported in cURL.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Installation of cURL ####
|
||||
|
||||
By default cURL is available in most of the distribution either in repository or installed. if it’s not installed, just do a apt or yum to get a required package from the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install curl (on APT based System)
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install curl (on YUM based System)
|
||||
|
||||
Basic Usage of cURL
|
||||
|
||||
# curl www.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Curl Data Download
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Curl Download
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. w3m ###
|
||||
|
||||
The w3m is a text based web browser released under GPL. W3m support tables, frames, color, SSL connection and inline images. W3m is known for fast browsing.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Installation of w3m ####
|
||||
|
||||
Again w3m is available by default in most of the Linux Distribution. If incase, it is not available you can always apt or yum the required package.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install w3m (on APT based System)
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install w3m (on YUM based System)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Basic Usage of w3m ####
|
||||
|
||||
# w3m www.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
w3m Text Based Web Browser
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Elinks ###
|
||||
|
||||
Elinks is a free text-based web browser for Unix and Unix based System. Elinks support HTTP, HTTP Cookies and also support browsing script in Perl and Ruby. Tab based browsing is well supported. The best thing is that it supports Mouse, Display Colours and support a number of Protocols like HTTP, FTP, SMB, Ipv4 and Ipv6.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Installation of Elinks ####
|
||||
|
||||
By default elinks also available in most of the Linux distributions. If not, install it via apt or yum.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install elinks (on APT based System)
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install elinks (on YUM based System)
|
||||
|
||||
Basic Usage of Elinks
|
||||
|
||||
# elinks www.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Elinks Command Line Web Browsing
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I’ll be here again with an interesting article which you people will love to read. Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint and don’t forget to give your valuable feedback in comment section.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-command-line-tools-for-downloading-files/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,261 @@
|
||||
4 Tools Send Email with Subject, Body and Attachment in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In today's article we will cover a few ways you can use to send emails with attachments from the command line interface on Linux. It can have quite a few uses, for example to send an archive with an application from an application server to email or you can use the commands in scripts to automate some process. For our examples,we will use the file foo.tar.gz as our attachment.
|
||||
|
||||
There are various ways to send emails from command line using different mail clients but here I am sharing few mail client utility used by most users like mailx, mutt and swaks.
|
||||
|
||||
All the tools we will present to you are very popular and present in the repositories of most Linux distributions, you can install them using the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
For **Debian / Ubuntu** systems
|
||||
|
||||
apt-get install mutt
|
||||
apt-get install swaks
|
||||
apt-get install mailx
|
||||
apt-get install sharutils
|
||||
|
||||
For Red Hat based systems like **CentOS** or **Fedora**
|
||||
|
||||
yum install mutt
|
||||
yum install swaks
|
||||
yum install mailx
|
||||
yum install sharutils
|
||||
|
||||
### 1) Using mail / mailx ###
|
||||
|
||||
The mailx utility found as the default mailer application in most Linux distributions now includes the support to attach file. If it is not available you can easily install using the following commands please take note that this may not be supported in older versions, to check this you can use the command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ man mail
|
||||
|
||||
And the first line should look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
mailx [-BDdEFintv~] [-s subject] [-a attachment ] [-c cc-addr] [-b bcc-addr] [-r from-addr] [-h hops] [-A account] [-S variable[=value]] to-addr . . .
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see it supports the -a attribute to add a file to the email and -s attribute to subject to the email. Use few of below examples to send mails.
|
||||
|
||||
**a) Simple Mail**
|
||||
|
||||
Run the mail command, and then mailx would wait for you to enter the message of the email. You can hit enter for new lines. When done typing the message, press Ctrl+D and mailx would display EOT.
|
||||
|
||||
After than mailx automatically delivers the email to the destination.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mail user@example.com
|
||||
|
||||
HI,
|
||||
Good Morning
|
||||
How are you
|
||||
EOT
|
||||
|
||||
**b) To send email with subject**
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo "Email text" | mail -s "Test Subject" user@example.com
|
||||
|
||||
-s is used for defining subject for email.
|
||||
|
||||
**c) To send message from a file**
|
||||
|
||||
$ mail -s "message send from file" user@example.com < /path/to/file
|
||||
|
||||
**d) To send message piped using the echo command**
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo "This is message body" | mail -s "This is Subject" user@example.com
|
||||
|
||||
**e) To send email with attachment**
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo “Body with attachment "| mail -a foo.tar.gz -s "attached file" user@example.com
|
||||
|
||||
-a is used for attachments
|
||||
|
||||
### 2) mutt ###
|
||||
|
||||
Mutt is a text-based email client for Unix-like systems. It was developed over 20 years ago and it's an important part of Linux history, one of the first clients to support scoring and threading capabilities. Use few of below examples to send email.
|
||||
|
||||
**a) Send email with subject & body message from a file**
|
||||
|
||||
$ mutt -s "Testing from mutt" user@example.com < /tmp/message.txt
|
||||
|
||||
**b) To send body message piped using the echo command**
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo "This is the body" | mutt -s "Testing mutt" user@example.com
|
||||
|
||||
**c) To send email with attachment**
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo "This is the body" | mutt -s "Testing mutt" user@example.com -a /tmp/foo.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
**d) To send email with multiple attachments**
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo "This is the body" | mutt -s "Testing" user@example.com -a foo.tar.gz –a bar.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
### 3) swaks ###
|
||||
|
||||
Swaks stands for Swiss Army Knife for SMTP and it is a featureful, flexible, scriptable, transaction-oriented SMTP test tool written and maintained by John Jetmore. You can use the following syntax to send an email with attachment:
|
||||
|
||||
$ swaks -t "foo@bar.com" --header "Subject: Subject" --body "Email Text" --attach foo.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
The important thing about Swaks is that it will also debug the full mail transaction for you, so it is a very useful tool if you also wish to debug the mail sending process:
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see it gives you full details about the sending process including what capabilities the receiving mail server supports, each step of the transaction between the 2 servers.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4) uuencode ###
|
||||
|
||||
Email transport systems were originally designed to transmit characters with a seven-bit encoding -- like ASCII. This meant they could send messages with plain text but not "binary" text, such as program files or image files that used all of an eight-bit byte. The program is used to solve this limitation is “uuencode”( "UNIX to UNIX encoding") which encode the mail from binary format to text format that is safe to transmit & program is used to decode the data is called “uudecode”
|
||||
|
||||
We can easily send binary text such as a program files or image files using uuencode with mailx or mutt email client is shown by following example:
|
||||
|
||||
$ uuencode example.jpeg example.jpeg | mail user@example.com
|
||||
|
||||
### Shell Script : Explain how to send email ###
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
FROM=""
|
||||
SUBJECT=""
|
||||
ATTACHMENTS=""
|
||||
TO=""
|
||||
BODY=""
|
||||
|
||||
# Function to check if entered file names are really files
|
||||
function check_files()
|
||||
{
|
||||
output_files=""
|
||||
for file in $1
|
||||
do
|
||||
if [ -s $file ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
output_files="${output_files}${file} "
|
||||
fi
|
||||
done
|
||||
echo $output_files
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
echo "*********************"
|
||||
echo "E-mail sending script."
|
||||
echo "*********************"
|
||||
echo
|
||||
|
||||
# Getting the From address from user
|
||||
while [ 1 ]
|
||||
do
|
||||
if [ ! $FROM ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
echo -n -e "Enter the e-mail address you wish to send mail from:\n[Enter] "
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo -n -e "The address you provided is not valid:\n[Enter] "
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
read FROM
|
||||
echo $FROM | grep -E '^.+@.+$' > /dev/null
|
||||
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
break
|
||||
fi
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
echo
|
||||
|
||||
# Getting the To address from user
|
||||
while [ 1 ]
|
||||
do
|
||||
if [ ! $TO ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
echo -n -e "Enter the e-mail address you wish to send mail to:\n[Enter] "
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo -n -e "The address you provided is not valid:\n[Enter] "
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
read TO
|
||||
echo $TO | grep -E '^.+@.+$' > /dev/null
|
||||
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
break
|
||||
fi
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
echo
|
||||
|
||||
# Getting the Subject from user
|
||||
echo -n -e "Enter e-mail subject:\n[Enter] "
|
||||
read SUBJECT
|
||||
|
||||
echo
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "$SUBJECT" == "" ]
|
||||
then
|
||||
echo "Proceeding without the subject..."
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
# Getting the file names to attach
|
||||
echo -e "Provide the list of attachments. Separate names by space.
|
||||
If there are spaces in file name, quote file name with \"."
|
||||
read att
|
||||
|
||||
echo
|
||||
|
||||
# Making sure file names are poiting to real files
|
||||
attachments=$(check_files "$att")
|
||||
echo "Attachments: $attachments"
|
||||
|
||||
for attachment in $attachments
|
||||
do
|
||||
ATTACHMENTS="$ATTACHMENTS-a $attachment "
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
echo
|
||||
|
||||
# Composing body of the message
|
||||
echo "Enter message. To mark the end of message type ;; in new line."
|
||||
read line
|
||||
|
||||
while [ "$line" != ";;" ]
|
||||
do
|
||||
BODY="$BODY$line\n"
|
||||
read line
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
SENDMAILCMD="mutt -e \"set from=$FROM\" -s \"$SUBJECT\" \
|
||||
$ATTACHMENTS -- \"$TO\" <<< \"$BODY\""
|
||||
echo $SENDMAILCMD
|
||||
|
||||
mutt -e "set from=$FROM" -s "$SUBJECT" $ATTACHMENTS -- $TO <<< $BODY
|
||||
|
||||
**Script Output**
|
||||
|
||||
$ bash send_mail.sh
|
||||
*********************
|
||||
E-mail sending script.
|
||||
*********************
|
||||
|
||||
Enter the e-mail address you wish to send mail from:
|
||||
[Enter] test@gmail.com
|
||||
|
||||
Enter the e-mail address you wish to send mail to:
|
||||
[Enter] test@gmail.com
|
||||
|
||||
Enter e-mail subject:
|
||||
[Enter] Message subject
|
||||
|
||||
Provide the list of attachments. Separate names by space.
|
||||
If there are spaces in file name, quote file name with ".
|
||||
send_mail.sh
|
||||
|
||||
Attachments: send_mail.sh
|
||||
|
||||
Enter message. To mark the end of message type ;; in new line.
|
||||
This is a message
|
||||
text
|
||||
;;
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are many ways of send emails from command line / shell script but here we have shared 4 tools available for unix / linux based distros. Hope you enjoyed reading our article and please provide your valuable comments and also let us know if you know about any new tools.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-shell-script/send-email-subject-body-attachment-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Bobbin Zachariah][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/bobbin/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,95 @@
|
||||
Install Inkscape - Open Source Vector Graphic Editor
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Inkscape is an open source vector graphic editing tool which uses Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) and that makes it different from its competitors like Xara X, Corel Draw and Adobe Illustrator etc. SVG is a widely-deployed royalty-free graphics format developed and maintained by the W3C SVG Working Group. It is a cross platform tool which runs fine on Linux, Windows and Mac OS.
|
||||
|
||||
Inkscape development was started in 2003, Inkscape's bug tracking system was hosted on Sourceforge initially but it was migrated to Launchpad afterwards. Its current latest stable version is 0.91. It is under continuous development and bug fixes and we will be reviewing its prominent features and installing process in the article.
|
||||
|
||||
### Salient Features ###
|
||||
|
||||
Lets review the outstanding features of this application categorically.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Creating Objects ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Drawing different colored sized and shaped freehand lines through pencil tool, straight lines and curves through Bezier (pen) tool, applying freehand calligraphic strokes through calligraphic tool etc
|
||||
- Creating, selecting, editing and formatting text through text tool. Manipulating text in plain text boxes, on paths or in shapes
|
||||
- Helps draw various shapes like rectangles, ellipses, circles, arcs, polygons, stars, spirals etc and then resize, rotate and modify (turn sharp edges round) them
|
||||
- Create and embed bitmaps with simple commands
|
||||
|
||||
#### Object manipulation ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Skewing, moving, scaling, rotating objects through interactive manipulations and pacifying the numeric values
|
||||
- Performing raising and lowering Z-order operations
|
||||
- Grouping and ungrouping objects to create a virtual scope for editing or manipulation
|
||||
- Layers form a hierarchal tree and can be locked or rearranged for various manipulations
|
||||
- Distribution and alignment commands
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fill and Stroke ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Copy/paste styles
|
||||
- Pick Color tool
|
||||
- Selecting colors on a continuous plot based on vectors of RGB, HSL, CMS, CMYK and color wheel
|
||||
- Gradient editor helps creating and managing multi-stop gradients
|
||||
- Define an image or selection and use it to pattern fill
|
||||
- Dashed Strokes can be used with few predefined dashed patterns
|
||||
- Beginning, middle and ending marks through path markers
|
||||
|
||||
#### Operation on Paths ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Node Editing: Moving nodes and Bezier handles, node alignment and distribution etc
|
||||
- Boolean operations like yes or no conditions
|
||||
- Simplifying paths with variable levels or thresholds
|
||||
- Path insetting and outsetting along with link and offset objects
|
||||
- Converting bitmap images into paths (color and monochrome paths) through path tracing
|
||||
|
||||
#### Text manipulation ####
|
||||
|
||||
- All installed outlined fonts can be used even for right to left align objects
|
||||
- Formatting text, letter spacing, line spacing or kerning
|
||||
- Text on path and on shapes where both text and path or shapes can be edited or modified
|
||||
|
||||
#### Rendering ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Inkscape fully support anti-aliased display which is a technique that reduces or eliminates aliasing by shading the pixels along the border.
|
||||
- Support for alpha transparency display and PNG export
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Inkscape on Ubuntu 14.04 and 14.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||
In order to install Inkscape on Ubuntu, we will need to first [add its stable Personal Package Archive][1] (PPA) to Advanced Package Tool (APT) repository. Launch the terminal and run following command to add its PPA.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:inkscape.dev/stable
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once the PPA has been added to the APT repository we need to update it using following command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After updating the repository we are ready to install inkscape which is accomplished using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install inkscape
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Congratulation, Inkscape has been installed now and all set for image editing and making full use of feature rich application.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Inkscape is a feature rich graphic editing tool which empowers its user with state of the art capabilities. It is an open source application which is freely available for installation and customizations and supports wide range of file formats including but not limited to JPEG, PNG, GIF and PDF. Visit its [official website][2] for more news and updates regarding this application.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/tools/install-inkscape-open-source-vector-graphic-editor/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aun Raza][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunrz/
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/~inkscape.dev/+archive/ubuntu/stable
|
||||
[2]:https://inkscape.org/en/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,152 @@
|
||||
7 Command Line Tools for Browsing Websites and Downloading Files in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In the last article, we have covered few useful tools like ‘rTorrent‘, ‘wget‘, ‘cURL‘, ‘w3m‘, and ‘Elinks‘. We got lots of response to cover few other tools of same genre, if you’ve missed the first part you can go through it..
|
||||
|
||||
- [5 Command Line Tools for Downloading Files and Browsing Websites][1]
|
||||
|
||||
This article aims at making you aware of several other Linux command Line browsing and downloading applications, which will help you to browse and download files within the Linux shell.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. links ###
|
||||
|
||||
Links is an open source web browser written in C programming Language. It is available for all major platforms viz., Linux, Windows, OS X and OS/2. This browser is text based as well as graphical. The text based links web browser is shipped by most of the standard Linux distributions by default. If links is not installed in your system by default you may install it from the repo. Elinks is a fork of links.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install links
|
||||
# yum install links
|
||||
|
||||
After installing links, you can browse any websites within the terminal as shown below in the screen cast..
|
||||
|
||||
# links www.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to navigate. Right arrow Key on a link will redirect you to that link and Left arrow key will bring you back to the last page. To QUIT press q.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how it seems to access Tecmint using links tool.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you are interested in installing GUI of links, you may need to download latest source tarball (i.e. version 2.9) from [http://links.twibright.com/download/][2].
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you may use following wget command to download and install as suggested below.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://links.twibright.com/download/links-2.9.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar -xvf links-2.9.tar.gz
|
||||
# cd links-2.9
|
||||
# ./configure –enable-graphics
|
||||
# make
|
||||
# make install
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: You need to install packages (libpng, libjpeg, TIFF library, SVGAlib, XFree86, C Compiler and make), if not already installed to successfully compile the package.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. links2 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Links2 is a graphical web browser version of Twibright Labs Links web browser. This browser has support for mouse and clicks. Designed specially for speed without any CSS support, fairly good HTML and JavaScript support with limitations.
|
||||
|
||||
To install links2.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install links2
|
||||
# yum install links2
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. lynx ###
|
||||
|
||||
A text based web browser released under GNU GPLv2 license and written in ISO C. lynx is highly configurable web browser and Savior for many SYSAdmin. It has the reputation of being the oldest web browser that is being used and still actively developed.
|
||||
|
||||
To install lynx.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install lynx
|
||||
# yum install lynx
|
||||
|
||||
After installing lynx, type the following command to browse the website as shown below in the screen cast..
|
||||
|
||||
# lynx www.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you are interested in knowing a bit more about links and lynx web browser, you may like to visit the below link:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Web Browsing with Lynx and Links Command Line Tools][3]
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. youtube-dl ###
|
||||
|
||||
youtube-dl is a platform independent application which can be used to download videos from youtube and a few other sites. Written primarily in python and released under GNU GPL License, the application works out of the box. (Since youtube don’t allow you to download videos, it may be illegal to use it. Check the laws before you start using this.)
|
||||
|
||||
To install youtube-dl.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install youtube-dl
|
||||
# yum install youtube-dl
|
||||
|
||||
After installing, try to download files from the Youtube site, as shown in the below screen cast.
|
||||
|
||||
# youtube-dl https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ql4SEy_4xws
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you are interested in knowing more about youtube-dl you may like to visit the below link:
|
||||
|
||||
- [YouTube-DL – A Command Line Youtube Video Downloader for Linux][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. fetch ###
|
||||
|
||||
It is a command utility for unix-like operating system that is used for URL retrieval. It supports a lot of options like fetching ipv4 only address, ipv6 only address, no redirect, exit after successful file retrieval request, retry, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Fetch can be Downloaded and installed from the link below
|
||||
|
||||
- [http://sourceforge.net/projects/fetch/?source=typ_redirect][5]
|
||||
|
||||
But before you compile and run it, you should install HTTP Fetcher. Download HTTP Fetcher from the link below.
|
||||
|
||||
- [http://sourceforge.net/projects/http-fetcher/?source=typ_redirect][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Axel ###
|
||||
|
||||
Axel is a command-line based download accelerator for Linux. Axel makes it possible to download a file at much faster speed through single connection request for multiple copies of files in small chunks through multiple http and ftp connections.
|
||||
|
||||
To install Axel.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install axel
|
||||
# yum install axel
|
||||
|
||||
After axel installed, you may use following command to download any given file, as shown in the screen cast.
|
||||
|
||||
# axel http://mirror.cse.iitk.ac.in/archlinux/iso/2015.04.01/archlinux-2015.04.01-dual.iso
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 7. aria2 ###
|
||||
|
||||
aria2 is a command-line based download utility that is lightweight and support multi-protocol (HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, BitTorrent and Metalink). It can use metalinks files to simultaneously download ISO files from more than one server. It can serve as a Bit torrent client as well.
|
||||
|
||||
To install aria2.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install aria2
|
||||
# yum install aria2
|
||||
|
||||
Once aria2 installed, you can fire up the following command to download any given file…
|
||||
|
||||
# aria2c http://cdimage.debian.org/debian-cd/7.8.0/multi-arch/iso-cd/debian-7.8.0-amd64-i386-netinst.iso
|
||||
|
||||
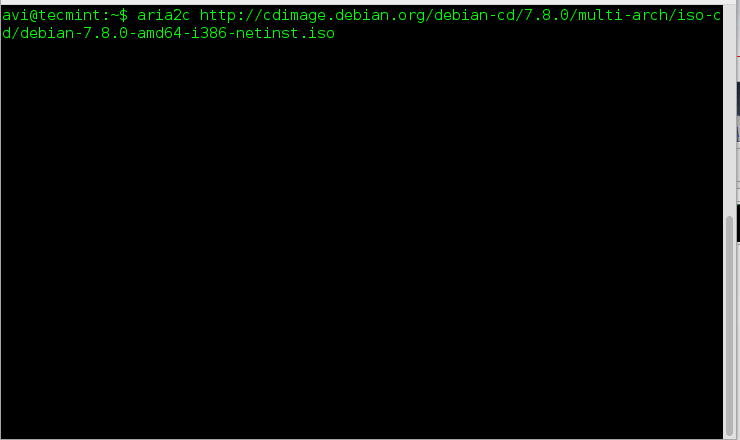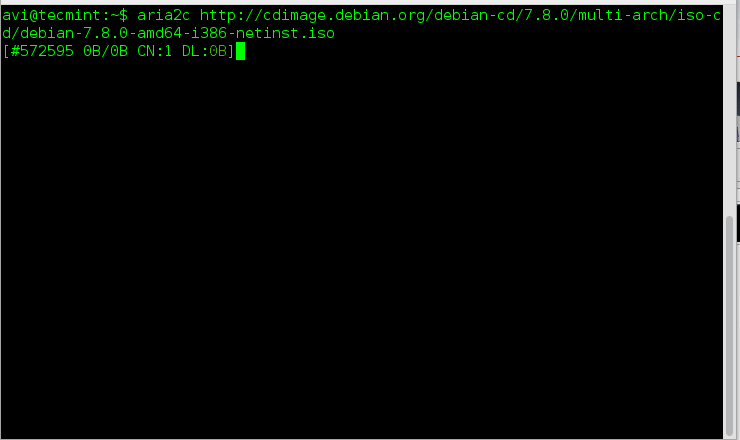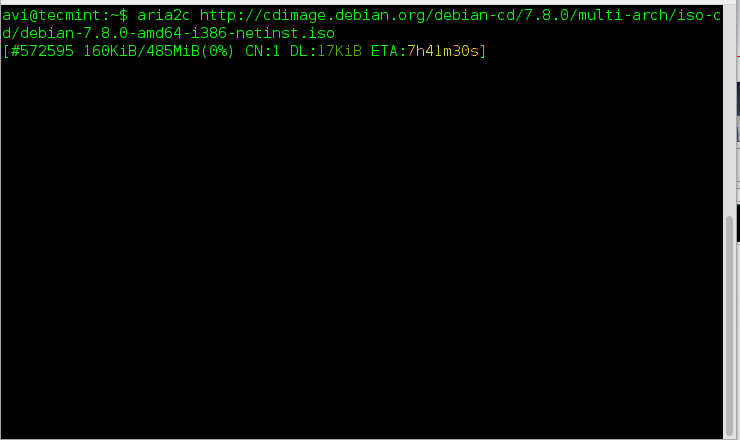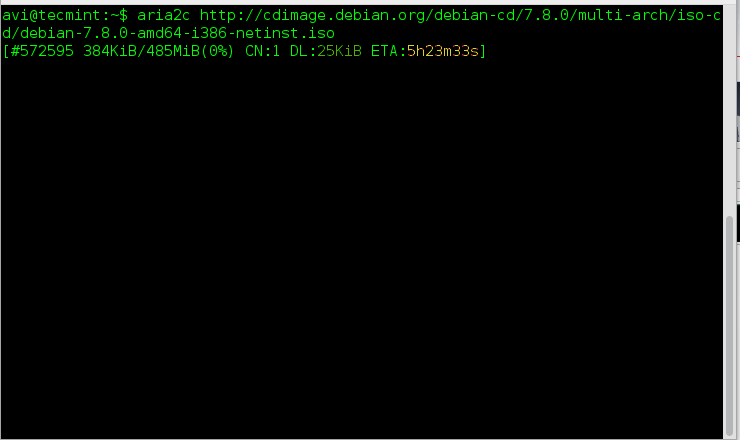
|
||||
Aria2: Command Line Download Manager for Linux
|
||||
|
||||
If you’re interested to know more at aria2 and their switches, read the following article.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Aria2 – A Multi-Protocol Command-Line Download Manager for Linux][7]
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I’ll be here again with another interesting topic you people will love to read. Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comments below. Like and share us and help us get spread.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/command-line-web-browser-download-file-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-command-line-tools-for-downloading-files/
|
||||
[2]:http://links.twibright.com/download/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/command-line-web-browsers/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-youtube-dl-command-line-video-download-tool/
|
||||
[5]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/fetch/?source=typ_redirect
|
||||
[6]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/http-fetcher/?source=typ_redirect
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-aria2-a-multi-protocol-command-line-download-manager-in-rhel-centos-fedora/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,159 @@
|
||||
How to Install and Configure Multihomed ISC DHCP Server on Debian Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Dynamic Host Control Protocol (DHCP) offers an expedited method for network administrators to provide network layer addressing to hosts on a constantly changing, or dynamic, network. One of the most common server utilities to offer DHCP functionality is ISC DHCP Server. The goal of this service is to provide hosts with the necessary network information to be able to communicate on the networks in which the host is connected. Information that is typically served by this service can include: DNS server information, network address (IP), subnet mask, default gateway information, hostname, and much more.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will cover ISC-DHCP-Server version 4.2.4 on a Debian 7.7 server that will manage multiple virtual local area networks (VLAN) but can very easily be applied to a single network setup as well.
|
||||
|
||||
The test network that this server was setup on has traditionally relied on a Cisco router to manage the DHCP address leases. The network currently has 12 VLANs needing to be managed by one centralized server. By moving this responsibility to a dedicated server, the router can regain resources for more important tasks such as routing, access control lists, traffic inspection, and network address translation.
|
||||
|
||||
The other benefit to moving DHCP to a dedicated server will, in a later guide, involve setting up Dynamic Domain Name Service (DDNS) so that new host’s host-names will be added to the DNS system when the host requests a DHCP address from the server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Installing and Configuring ISC DHCP Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. To start the process of creating this multi-homed server, the ISC software needs to be installed via the Debian repositories using the ‘apt‘ utility. As with all tutorials, root or sudo access is assumed. Please make the appropriate modifications to the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install isc-dhcp-server [Installs the ISC DHCP Server software]
|
||||
# dpkg --get-selections isc-dhcp-server [Confirms successful installation]
|
||||
# dpkg -s isc-dhcp-server [Alternative confirmation of installation]
|
||||
|
||||
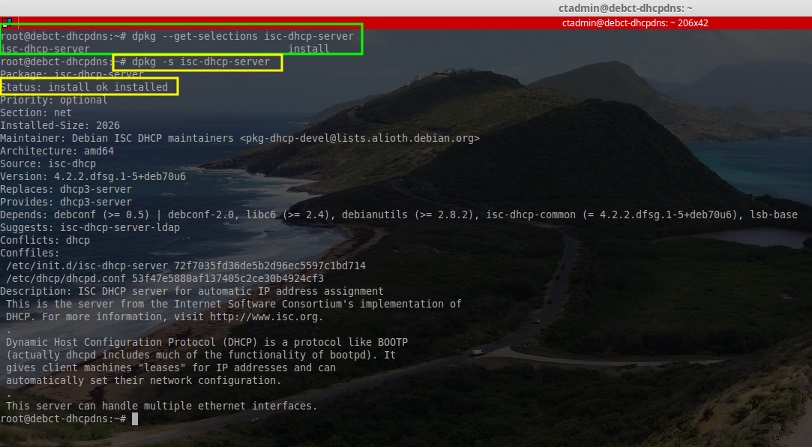
|
||||
|
||||
2. Now that the server software is confirmed installed, it is now necessary to configure the server with the network information that it will need to hand out. At the bare minimum, the administrator needs to know the following information for a basic DHCP scope:
|
||||
|
||||
- The network addresses
|
||||
- The subnet masks
|
||||
- The range of addresses to be dynamically assigned
|
||||
|
||||
Other useful information to have the server dynamically assign includes:
|
||||
|
||||
- Default gateway
|
||||
- DNS server IP addresses
|
||||
- The Domain Name
|
||||
- Host name
|
||||
- Network Broadcast addresses
|
||||
|
||||
These are merely a few of the many options that the ISC DHCP server can handle. To get a complete list as well as a description of each option, enter the following command after installing the package:
|
||||
|
||||
# man dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
3. Once the administrator has concluded all the necessary information for this server to hand out it is time to configure the DHCP server as well as the necessary pools. Before creating any pools or server configurations though, the DHCP service must be configured to listen on one of the server’s interfaces.
|
||||
|
||||
On this particular server, a NIC team has been setup and DHCP will listen on the teamed interfaces which were given the name `'bond0'`. Be sure to make the appropriate changes given the server and environment in which everything is being configured. The defaults in this file are okay for this tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This line will instruct the DHCP service to listen for DHCP traffic on the specified interface(s). At this point, it is time to modify the main configuration file to enable the DHCP pools on the necessary networks. The main configuration file is located at /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf. Open the file with a text editor to begin:
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
This file is the configuration for the DHCP server specific options as well as all of the pools/hosts one wishes to configure. The top of the file starts of with a ‘ddns-update-style‘ clause and for this tutorial it will remain set to ‘none‘ however in a future article, Dynamic DNS will be covered and ISC-DHCP-Server will be integrated with BIND9 to enable host name to IP address updates.
|
||||
|
||||
4. The next section is typically the area where and administrator can configure global network settings such as the DNS domain name, default lease time for IP addresses, subnet-masks, and much more. Again to know more about all the options be sure to read the man page for the dhcpd.conf file.
|
||||
|
||||
# man dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
For this server install, there were a couple of global network options that were configured at the top of the configuration file so that they wouldn’t have to be implemented in every single pool created.
|
||||
|
||||
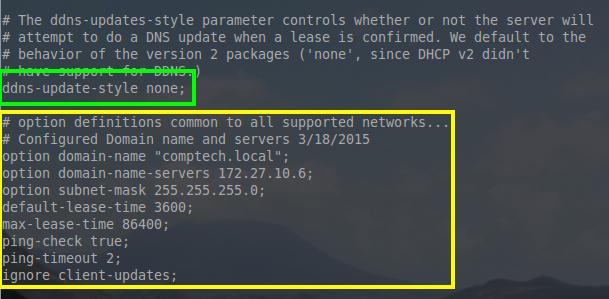
|
||||
|
||||
Lets take a moment to explain some of these options. While they are configured globally in this example, all of them can be configured on a per pool basis as well.
|
||||
|
||||
- option domain-name “comptech.local”; – All hosts that this DHCP server hosts, will be a member of the DNS domain name “comptech.local”
|
||||
- option domain-name-servers 172.27.10.6; DHCP will hand out DNS server IP of 172.27.10.6 to all of the hosts on all of the networks it is configured to host.
|
||||
- option subnet-mask 255.255.255.0; – The subnet mask handed out to every network will be a 255.255.255.0 or a /24
|
||||
- default-lease-time 3600; – This is the time in seconds that a lease will automatically be valid. The host can re-request the same lease if time runs out or if the host is done with the lease, they can hand the address back early.
|
||||
- max-lease-time 86400; – This is the maximum amount of time in seconds a lease can be held by a host.
|
||||
- ping-check true; – This is an extra test to ensure that the address the server wants to assign out isn’t in use by another host on the network already.
|
||||
- ping-timeout; – This is how long in second the server will wait for a response to a ping before assuming the address isn’t in use.
|
||||
- ignore client-updates; For now this option is irrelevant since DDNS has been disabled earlier in the configuration file but when DDNS is operating, this option will ignore a hosts to request to update its host-name in DNS.
|
||||
|
||||
5. The next line in this file is the authoritative DHCP server line. This line means that if this server is to be the server that hands out addresses for the networks configured in this file, then uncomment the authoritative stanza.
|
||||
|
||||
This server will be the only authority on all the networks it manages so the global authoritative stanza was un-commented by removing the ‘#’ in front of the keyword authoritative.
|
||||
|
||||
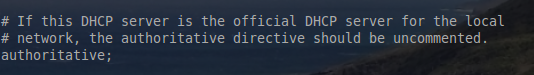
|
||||
Enable ISC Authoritative
|
||||
|
||||
By default the server is assumed to NOT be an authority on the network. The rationale behind this is security. If someone unknowingly configures the DHCP server improperly or on a network they shouldn’t, it could cause serious connectivity issues. This line can also be used on a per network basis. This means that if the server is not the entire network’s DHCP server, the authoritative line can instead be used on a per network basis rather than in the global configuration as seen in the above screen-shot.
|
||||
|
||||
6. The next step is to configure all of the DHCP pools/networks that this server will manage. For brevities sake, this guide will only walk through one of the pools configured. The administrator will need to have gathered all of the necessary network information (ie domain name, network addresses, how many addresses can be handed out, etc).
|
||||
|
||||
For this pool the following information was obtained from the network administrator: network id of 172.27.60.0, subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 or a /24, the default gateway for the subnet is 172.27.60.1, and a broadcast address of 172.27.60.255.
|
||||
This information is important to building the appropriate network stanza in the dhcpd.conf file. Without further ado, let’s open the configuration file again using a text editor and then add the new network to the server. This must be done with root/sudo!
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/dhcp/dhcpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Configure DHCP Pools and Networks
|
||||
|
||||
This is the sample created to hand out IP addresses to a network that is used for the creation of VMWare virtual practice servers. The first line indicates the network as well as the subnet mask for that network. Then inside the brackets are all the options that the DHCP server should provide to hosts on this network.
|
||||
|
||||
The first stanza, range 172.27.60.50 172.27.60.254;, is the range of dynamically assignable addresses that the DHCP server can hand out to hosts on this network. Notice that the first 49 addresses aren’t in the pool and can be assigned statically to hosts if needed.
|
||||
|
||||
The second stanza, option routers 172.27.60.1; , hands out the default gateway address for all hosts on this network.
|
||||
|
||||
The last stanza, option broadcast-address 172.27.60.255;, indicates what the network’s broadcast address. This address SHOULD NOT be a part of the range stanza as the broadcast address can’t be assigned to a host.
|
||||
|
||||
Some pointers, be sure to always end the option lines with a semi-colon (;) and always make sure each network created is enclosed in curly braces { }.
|
||||
|
||||
7. If there are more networks to create, continue creating them with their appropriate options and then save the text file. Once all configurations have been completed, the ISC-DHCP-Server process will need to be restarted in order to apply the new changes. This can be accomplished with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# service isc-dhcp-server restart
|
||||
|
||||
This will restart the DHCP service and then the administrator can check to see if the server is ready for DHCP requests several different ways. The easiest is to simply see if the server is listening on port 67 via the [lsof command][1]:
|
||||
|
||||
# lsof -i :67
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check DHCP Listening Port
|
||||
|
||||
This output indicates that the DHCPD (DHCP Server daemon) is running and listening on port 67. Port 67 in this output was actually converted to ‘bootps‘ due to a port number mapping for port 67 in /etc/services file.
|
||||
|
||||
This is very common on most systems. At this point, the server should be ready for network connectivity and can be confirmed by connecting a machine to the network and having it request a DHCP address from the server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Testing Client Connectivity ###
|
||||
|
||||
8. Most systems now-a-days are using Network Manager to maintain network connections and as such the device should be pre-configured to pull DHCP when the interface is active.
|
||||
|
||||
However on machines that aren’t using Network Manager, it may be necessary to manually attempt to pull a DHCP address. The next few steps will show how to do this as well as how to see whether the server is handing out addresses.
|
||||
|
||||
The ‘[ifconfig][2]‘ utility can be used to check an interface’s configuration. The machine used to test the DHCP server only has one network adapter and it is called ‘eth0‘.
|
||||
|
||||
# ifconfig eth0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check Network Interface IP Address
|
||||
|
||||
From this output, this machine currently doesn’t have an IPv4 address, great! Let’s instruct this machine to reach out to the DHCP server and request an address. This machine has the DHCP client utility known as ‘dhclient‘ installed. The DHCP client utility may very from system to system.
|
||||
|
||||
# dhclient eth0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Request IP Address from DHCP
|
||||
|
||||
Now the `'inet addr:'` field shows an IPv4 address that falls within the scope of what was configured for the 172.27.60.0 network. Also notice that the proper broadcast address was handed out as well as subnet mask for this network.
|
||||
|
||||
Things are looking promising but let’s check the server to see if it was actually the place where this machine received this new IP address. To accomplish this task, the server’s system log file will be consulted. While the entire log file may contain hundreds of thousands of entries, only a few are necessary for confirming that the server is working properly. Rather than using a full text editor, this time a utility known as ‘tail‘ will be used to only show the last few lines of the log file.
|
||||
|
||||
# tail /var/log/syslog
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Check DHCP Logs
|
||||
|
||||
Voila! The server recorded handing out an address to this host (HRTDEBXENSRV). It is a safe assumption at this point that the server is working as intended and handing out the appropriate addresses for the networks that it is an authority. At this point the DHCP server is up and running. Configure the other networks, troubleshoot, and secure as necessary.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy the newly functioning ISC-DHCP-Server and tune in later for more Debian tutorials. In the not too distant future there will be an article on Bind9 and DDNS that will tie into this article.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-and-configure-multihomed-isc-dhcp-server-on-debian-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Rob Turner][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/robturner/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-lsof-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/ifconfig-command-examples/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
||||
How to run Ubuntu Snappy Core on Raspberry Pi 2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The Internet of Things (IoT) is upon us. In a couple of years some of us might ask ourselves how we ever survived without it, just like we question our past without cellphones today. Canonical is a contender in this fast growing, but still wide open market. The company wants to claim their stakes in IoT just as they already did for the cloud. At the end of January, the company launched a small operating system that goes by the name of [Ubuntu Snappy Core][1] which is based on Ubuntu Core.
|
||||
|
||||
Snappy, the new component in the mix, represents a package format that is derived from DEB, is a frontend to update the system that lends its idea from atomic upgrades used in CoreOS, Red Hat's Atomic and elsewhere. As soon as the Raspberry Pi 2 was marketed, Canonical released Snappy Core for that plattform. The first edition of the Raspberry Pi was not able to run Ubuntu because Ubuntu's ARM images use the ARMv7 architecture, while the first Raspberry Pis were based on ARMv6. That has changed now, and Canonical, by releasing a RPI2-Image of Snappy Core, took the opportunity to make clear that Snappy was meant for the cloud and especially for IoT.
|
||||
|
||||
Snappy also runs on other platforms like Amazon EC2, Microsofts Azure, and Google's Compute Engine, and can also be virtualized with KVM, Virtualbox, or Vagrant. Canonical has embraced big players like Microsoft, Google, Docker or OpenStack and, at the same time, also included small projects from the maker scene as partners. Besides startups like Ninja Sphere and Erle Robotics, there are board manufacturers like Odroid, Banana Pro, Udoo, PCDuino and Parallella as well as Allwinner. Snappy Core will also run in routers soon to help with the poor upgrade policy that vendors perform.
|
||||
|
||||
In this post, let's see how we can test Ubuntu Snappy Core on Raspberry Pi 2.
|
||||
|
||||
The image for Snappy Core for the RPI2 can be downloaded from the [Raspberry Pi website][2]. Unpacked from the archive, the resulting image should be [written to an SD card][3] of at least 8 GB. Even though the OS is small, atomic upgrades and the rollback function eat up quite a bit of space. After booting up your Raspberry Pi 2 with Snappy Core, you can log into the system with the default username and password being 'ubuntu'.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
sudo is already configured and ready for use. For security reasons you should change the username with:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo usermod -l <new name> <old name>
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can add a new user with the command `adduser`.
|
||||
|
||||
Due to the lack of a hardware clock on the RPI, that the Snappy Core image does not take account of, the image has a small bug that will throw a lot of errors when processing commands. It is easy to fix.
|
||||
|
||||
To find out if the bug affects you, use the command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ date
|
||||
|
||||
If the output is "Thu Jan 1 01:56:44 UTC 1970", you can fix it with:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo date --set="Sun Apr 04 17:43:26 UTC 2015"
|
||||
|
||||
adapted to your actual time.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now you might want to check if there are any updates available. Note that the usual commands:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get distupgrade
|
||||
|
||||
will not get you very far though, as Snappy uses its own simplified package management system which is based on dpkg. This makes sense, as Snappy will run on a lot of embedded appliances, and you want things to be as simple as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's dive into the engine room for a minute to understand how things work with Snappy. The SD card you run Snappy on has three partitions besides the boot partition. Two of those house a duplicated file system. Both of those parallel file systems are permanently mounted as "read only", and only one is active at any given time. The third partition holds a partial writable file system and the users persistent data. With a fresh system, the partition labeled 'system-a' holds one complete file system, called a core, leaving the parallel partition still empty.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If we run the following command now:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo snappy update
|
||||
|
||||
the system will install the update as a complete core, similar to an image, on 'system-b'. You will be asked to reboot your device afterwards to activate the new core.
|
||||
|
||||
After the reboot, run the following command to check if your system is up to date and which core is active.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo snappy versions -a
|
||||
|
||||
After rolling out the update and rebooting, you should see that the core that is now active has changed.
|
||||
|
||||
As we have not installed any apps yet, the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo snappy update ubuntu-core
|
||||
|
||||
would have been sufficient, and is the way if you want to upgrade just the underlying OS. Should something go wrong, you can rollback by:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo snappy rollback ubuntu-core
|
||||
|
||||
which will take you back to the system's state before the update.
|
||||
|
||||
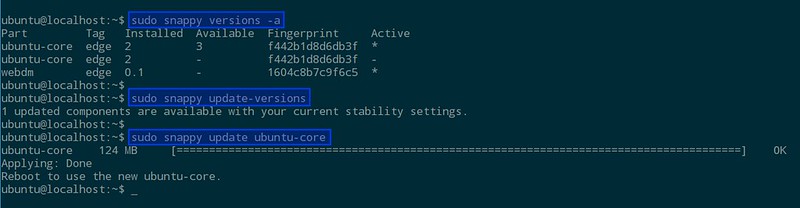
|
||||
|
||||
Speaking of apps, they are what makes Snappy useful. There are not that many at this point, but the IRC channel #snappy on Freenode is humming along nicely and with a lot of people involved, the Snappy App Store gets new apps added on a regular basis. You can visit the shop by pointing your browser to http://<ip-address>:4200, and you can install apps right from the shop and then launch them with http://webdm.local in your browser. Building apps yourself for Snappy is not all that hard, and [well documented][4]. You can also port DEB packages into the snappy format quite easily.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Snappy Core, due to the limited number of available apps, is not overly useful in a productive way at this point in time, although it invites us to dive into the new Snappy package format and play with atomic upgrades the Canonical way. Since it is easy to set up, this seems like a good opportunity to learn something new.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/ubuntu-snappy-core-raspberry-pi-2.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ferdinand Thommes][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/ferdinand
|
||||
[1]:http://www.ubuntu.com/things
|
||||
[2]:http://www.raspberrypi.org/downloads/
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/write-raspberry-pi-image-sd-card.html
|
||||
[4]:https://developer.ubuntu.com/en/snappy/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,145 @@
|
||||
wangjiezhe translating...
|
||||
What is a good alternative to wget or curl on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you often need to access a web server non-interactively in a terminal environment (e.g., download a file from the web, or test REST-ful web service APIs), chances are that wget or curl is your go-to tool. With extensive command-line options, both of these tools can handle a variety of non-interactive web access use cases (examples [here][1], [here][2] and [here][3]). However, even powerful tools like these are only as good as your knowledge of how to use them. Unless you are well versed in the nitty and gritty details of their syntax, these tools are nothing more than simple web downloaders for you.
|
||||
|
||||
Billed as a "curl-like tool for humans," [HTTPie][4] is designed to improve on wget and curl in terms of usability. Its main goal is to make command-line interaction of a web server as human-friendly as possible. For that, HTTPie comes with expressive, yet very simple and intuitive syntax. It also displays responses in colorized formats for readability, and offers nice goodies like excellent JSON support and persistent sessions to streamline your workflows.
|
||||
|
||||
I know some of you will be skeptical about replacing a ubiquitously available, perfectly good tool such as wget or curl with totally unheard of software. This view has merit especially if you are a system admin who works with many different hardware boxes. For developers or end-users, however, I would say it's all about productivity. If I've found a user-friendly alternative of a tool, I don't see any problem adopting the easy to use version in my work environment to save my precious time. No need to be loyal and religious about what's being replaced. After all, choice is the best thing about Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
In this post, let me review HTTPie, and show you what I mean by HTTPie being a user-friendly alternative of wget and curl.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Install HTTPie on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
HTTPie is written in Python, so you can install it pretty much everywhere (Linux, MacOSX, Windows). Even better, it comes as a prebuilt package on most Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint: ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install httpie
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fedora: ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install httpie
|
||||
|
||||
#### CentOS/RHEL: ####
|
||||
|
||||
First, enable [EPEL repository][5] and then run:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install httpie
|
||||
|
||||
For any Linux distribution, an alternative installation method is to use [pip][6].
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pip install --upgrade httpie
|
||||
|
||||
### HTTPie Examples ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once you install HTTPie, you can invoke it by typing http command. In the rest of this article, let me show several useful examples of http command.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example 1: Custom Headers ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can set custom headers in the format of <header:value>. For example, let's send an HTTP GET request to www.test.com, with custom user-agent and referer, as well as a custom header (e.g., MyParam).
|
||||
|
||||
$ http www.test.com User-Agent:Xmodulo/1.0 Referer:http://xmodulo.com MyParam:Foo
|
||||
|
||||
Note that when HTTP GET method is used, you don't need to specify any HTTP method.
|
||||
|
||||
The HTTP request will look like:
|
||||
|
||||
GET / HTTP/1.1
|
||||
Host: www.test.com
|
||||
Accept: */*
|
||||
Referer: http://xmodulo.com
|
||||
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, compress
|
||||
MyParam: Foo
|
||||
User-Agent: Xmodulo/1.0
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example 2: Download a File ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can use http as a file downloader tool. You will need to redirect output to a file as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ http www.test.com/my_file.zip > my_file.zip
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively:
|
||||
|
||||
$ http --download www.test.com/my_file.zip
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example 3: Custom HTTP Method ####
|
||||
|
||||
Besides the default GET method, you can use other methods (e.g., PUT, POST, HEAD). For example, to sent an HTTP PUT request:
|
||||
|
||||
$ http PUT www.test.com name='Dan Nanni' email=dan@email.com
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example 4: Submit a Form ####
|
||||
|
||||
Submitting a form with http command is as easy as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ http -f POST www.test.com name='Dan Nanni' comment='Hi there'
|
||||
|
||||
The '-f' option lets http command serialize data fields, and set 'Content-Type' to "application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8".
|
||||
|
||||
The HTTP POST request will look like:
|
||||
|
||||
POST / HTTP/1.1
|
||||
Host: www.test.com
|
||||
Content-Length: 31
|
||||
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, compress
|
||||
Accept: */*
|
||||
User-Agent: HTTPie/0.8.0
|
||||
|
||||
name=Dan+Nanni&comment=Hi+there
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example 5: JSON Support ####
|
||||
|
||||
HTTPie comes with built-in JSON support, which is nice considering its growing popularity as a data exchange format. In fact, the default content-type used by HTTPie is JSON. So if you send data fields without specifying any content-type, they will automatically be serialized as a JSON object.
|
||||
|
||||
$ http POST www.test.com name='Dan Nanni' comment='Hi there'
|
||||
|
||||
The HTTP POST request will look like:
|
||||
|
||||
POST / HTTP/1.1
|
||||
Host: www.test.com
|
||||
Content-Length: 44
|
||||
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
|
||||
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, compress
|
||||
Accept: application/json
|
||||
User-Agent: HTTPie/0.8.0
|
||||
|
||||
{"name": "Dan Nanni", "comment": "Hi there"}
|
||||
|
||||
#### Example 6: Input Redirect ####
|
||||
|
||||
Another nice user-friendly feature of HTTPie is input redirection, where you can feed an HTTP request body with buffered data. For example, you can do things like:
|
||||
|
||||
$ http POST api.test.com/db/lookup < my_info.json
|
||||
|
||||
or:
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo '{"name": "Dan Nanni"}' | http POST api.test.com/db/lookup
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, I introduce to you HTTPie, a possible alternative to wget or curl. Besides these simple examples presented here, you can find a lot of interesting use cases of HTTPie at the [official site][7]. Again, a powerful tool is only as good as your knowledge about the tool. Personally I am sold on HTTPie, as I was looking for a way to test complicated web APIs more easily.
|
||||
|
||||
What's your thought?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/wget-curl-alternative-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[wangjiezhe](https://github.com/wangjiezhe)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-download-multiple-files-with-wget.html
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-use-custom-http-headers-with-wget.html
|
||||
[3]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/custom-http-header-curl.html
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/jakubroztocil/httpie
|
||||
[5]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[6]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-pip-linux.html
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/jakubroztocil/httpie
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
||||
Exaile 3.4.1 概述 — 一个全功能的GNOME音乐播放器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Exaile** 在过去两年显得有些平静,也许只有一个或者两个稳定版发布,但尽管如此,在功能方面,它是一个和[Rhythmbox][1]或者[Banshee][2]相匹敌的全功能GNOME音乐播放器。然而,在过去的两个月,在"We’re not dead yet"的口号下,推出了一个新的稳定版3.4,同时在11月1日还推出了3.4.1增量版本。事实上,Exaile有很多的功能,我可以继续写很多的文章而不是在一篇文章里全部介绍到,就让我们来看一下一些最显著的特点吧。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Exaile][3]是基于GTK-2,用Python写的音乐播放器,它能很好地兼容GNOME,有和旧的Amarok1.4或者Clementine非常类似的界面,以及一些很好的功能。界面主要由两个面板组成,两个都支持标签。左边的面板提供对音乐集,网络音频,只能和自定义播放列表,文件浏览,播客,组标签以及歌词的访问,窗口的主要部分是播放列表(支持多种,带标签的播放列表)和控制按钮。
|
||||
|
||||
Exaile的界面和Clementine或者Amarok1.4非常相似,可以显示或者隐藏左边的标签。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
版本3.4增加了很多新的主要功能和更改,而3.4.1是一个小的bug修复版本。版本3.4的新功能包括类似Icecast的新插件,歌词同步,播放列表分析器,Soma.fm,以及新的更简单的插件API。用户界面和一般操作也作了修改,包括可以在多个面板显示播放列表,关闭左边的面板以及更好的BPM用户界面集成。
|
||||
|
||||
第一次打开Exaile你可以添加歌曲文件夹到音乐集中-你也可以选择添加文件夹并设置在打开Exaile的时候是否监视或者扫描这些文件夹:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Exaile的功能几乎不尽其数。你可以在音乐集中组织音乐,听播客,对音乐进行评分,编辑标签,查看文件属性,排列歌曲,查看歌曲和封面,按照多种方式排序播放列表,更改播放行为和外观风格。
|
||||
|
||||
均衡器,封面管理以及收听网络电台:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
自动检测本地专辑封面,可以全尺寸显示,放大或者缩小:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
首选项窗口允许多个方面配置Exaile,包括启用或者禁用插件,外观,系统托盘集成或者播放模式。外观设置允许你更改标签的布局,显示或者隐藏便签栏,启用或者禁用透明性或者禁用启动画面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
系统托盘集成提供了一个快速播放或者暂停音乐,对音乐评分或者更改音乐列表播放模式(随机,重复或者动态)的菜单。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我相信Exaile数不尽的功能使它成为音乐播放器的完美选择,尤其是对于GNOME用户。每个用户都会对丰富多样的选项和高度可配置的方式感到满意。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu 14.04 和 14.10上安装Exaile 3.4.1 ###
|
||||
|
||||
从源码编译并安装和简单明了。首先获取依赖包:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get build-dep exaile
|
||||
sudo apt-get install python-gst0.10
|
||||
|
||||
从[下载页面][4](或者直接点击[这里][5])下载源码包,然后解压:
|
||||
|
||||
tar -xf exaile-3.4.1.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
更改工作目录到exaile-3.4.1然后运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
make
|
||||
sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
二进制可执行文件将被安装为 **/usr/local/bin/exaile**.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tuxarena.com/2014/11/exaile-3-4-1-overview-a-feature-complete-gnome-music-player/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Craciun Dan
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Rhythmbox
|
||||
[2]:http://banshee.fm/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.exaile.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.exaile.org/download/
|
||||
[5]:https://github.com/exaile-dev/exaile/archive/3.4.1.tar.gz
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
红帽开发者工具集3.1测试版发布了
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Summary**:想要最新的红帽企业版Linux6或者7开发者工具?测试版已经发布啦.
|
||||
|
||||
这是[DevOps][1]也不能完全解决的开发商和运营商之间永恒的问题之一。系统管理员想要最稳定的操作系统,而程序员想要最新最棒的开发工具。[红帽公司][2]对这个两难问题的解决方法就是用最新的稳定版[Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)][3]去测试这些新品牌工具,然后向开发者发布。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
红帽开发者工具集
|
||||
|
||||
基于此红帽刚刚公布了给开发者的最新玩具,[红帽开发者工具集 3.1][4]。现在可以获得这些最热门工具包的测试版了。
|
||||
|
||||
这次更新包括:
|
||||
|
||||
[GNUCompiler Collection (GCC) 4.9][5]: 最新的GCC上游稳定版本,提供多处改进和bug修复
|
||||
|
||||
[Eclipse 4.4.1][6]: 支持Java 8 以及更新了的Eclipse CDT(8.5)版本,Eclipse Linux Tools (3.1), Eclipse Mylyn (3.14), 和 Eclipse Egit/Jgit (3.6.1)
|
||||
|
||||
众多额外的更新包: 包括 GDB 7.8.2, elfutils 0.161, memstomp 0.1.5, SystemTap 2.6, Valgrind 3.10.1, Dyninst 8.2.1, 以及 ltrace 0.7.91.
|
||||
|
||||
用这些开发工具,你可以给RHEL 6 和 7.x 开发应用程序。这些应用程序可以在RHEL上运行,不管是物理机,虚拟机还是云环境。它们也可以在红帽提供的Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)服务[OpenShift][7]上运行。
|
||||
|
||||
这些新的开发者程序集有RHEL 7 以及 运行在[AMD64 和 Intel 64 架构][8]上的安装包。尽管这些工具都是64位的,你也可以用它们创建或者更改32位的二进制文件。
|
||||
|
||||
在运行任何这些程序之前,你应该安装RHEL所有最近的更新。要安装这个测试工具集,你的系统需要选中可选渠道来获取所有红帽开发者工具集需要的工具链包。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,如果已经安装了早期版本的工具集,可能会遇到[安装Toolkit 3.1 时的一些问题][9]。尽管这些问题很容易解决,在安装新的工具集之前还是应该大概看一下这些可能出现的问题。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,你可能注意到一些最令人激动的工具,例如Docker,Kubernetes以及其它这里没有的容器工具。因为它们在最新的发行版[RHEL 7.1][10] 和 [Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 Atomic Host (RHELAH)][11]中。[红帽和Docker已成为合作伙伴][12],要获取这些容器友好的程序,你需要转换到Docker友好的RHEL版本上来。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.zdnet.com/article/red-hat-developer-toolset-3-1-beta-arrives/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.zdnet.com/meet-the-team/us/sjvn/
|
||||
[1]:http://blogs.csc.com/2015/02/03/devops-theory-for-beginners/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.redhat.com/en
|
||||
[3]:http://www.redhat.com/en/technologies/linux-platforms/enterprise-linux
|
||||
[4]:http://www.redhat.com/en/about/blog/red-hat-developer-toolset-31-beta-now-available
|
||||
[5]:https://gcc.gnu.org/gcc-4.9/
|
||||
[6]:https://projects.eclipse.org/projects/eclipse/releases/4.4.1
|
||||
[7]:https://www.openshift.com/
|
||||
[8]:https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Developer_Toolset/3-Beta/html/3.1_Release_Notes/System_Requirements.html
|
||||
[9]:https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Developer_Toolset/3-Beta/html/3.1_Release_Notes/DTS3.1_Release.html#Known_Issues
|
||||
[10]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/red-hat-7-1-is-here-centos-7-1-is-coming-soon/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/red-hat-buys-into-docker-containers-with-atomic-host/
|
||||
[12]:http://www.zdnet.com/article/red-hat-partners-with-docker-to-create-linuxdocker-software-stack/
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux上安装Telegram Messenger应用
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Telegram是和whatsapp类似的及时通讯应用。它有一个非常庞大的用户群。它有很多能和其他通讯应用区分开来的特性。
|
||||
Telegram是和whatsapp类似的及时通讯应用。它有一个庞大的用户群,并且很多能和其他通讯应用区分开来的特性。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Telegram Messenger for Linux
|
||||
@ -13,19 +13,19 @@ Telegram Messenger for Linux
|
||||
- 有桌面版本
|
||||
- 第三方开发者可以访问Telegram的应用程序接口(API)。
|
||||
- 支持Android, iphone/ipad, Windows Phone, Web-Version, PC, Mac 和 Linux。
|
||||
- 以上应用支持重度加密和自销毁信息。
|
||||
- 以上应用支持高度加密和自销毁信息。
|
||||
- 可以让你从多种设备和平台查看你的信息。
|
||||
- 整体的处理和消息传送都非常快
|
||||
- 为了安全和效率,在全球有分布式服务器
|
||||
- 开放的API和自由协议
|
||||
- 没有广告,没有认购费用。-永久免费
|
||||
- 强大-没有媒体和聊天限制
|
||||
- 功能强大-没有媒体和聊天限制
|
||||
- 多种安全措施使其免受黑客侵害
|
||||
- 在群组中回复特定信息。使用@username提醒群组里的多个用户
|
||||
|
||||
#### 为什么使用Telegram? ####
|
||||
|
||||
当像WhatsApp的和其他的及时通讯应用都提供了几乎同样的功能的情况下,为什么要选择Telegram?
|
||||
在像WhatsApp以及其他及时通讯应用都提供了几乎同样的功能的情况下,为什么要选择Telegram?
|
||||
|
||||
第三方开发者可以使用API这一点就足够了。更多PC的可用性意味着你不必再纠结在你的移动设备上打字,你可以使用你的PC,这样更具有可用性。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -65,12 +65,12 @@ Telegram Messenger for Linux
|
||||

|
||||
Telegram验证码
|
||||
|
||||
4. 输入你的姓名,昵称并点击“SIGNUP”.
|
||||
4. 输入你的姓名,昵称并点击“SIGN UP”.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
输入账户详细信息
|
||||
|
||||
5. 新建账户之后,我看到这个界面。一切准备就绪,尽管我是Telegram的新用户。这个界面真的很简洁。
|
||||
5. 新建账户之后,我看到这个界面。一切准备就绪,尽管我对Telegram还不熟悉。这个界面真的很简洁。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Telegram界面
|
||||
@ -87,7 +87,7 @@ Telegram联系人提示
|
||||
|
||||
8. 当联系人加入Telegram的时候,你会收到信息(类似弹出提示)显示[YOUR_CONTACT]加入了Telegram。
|
||||
|
||||
9. 在Linux系统上正式的聊天窗口。 很好的体验…
|
||||
9. 在Linux系统上正式的聊天窗口。很好的体验…
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
联系人加入Telegram消息
|
||||
@ -113,7 +113,7 @@ Telegram联系人提示
|
||||
- 一开始在2013年(8月14号)发布iPhone版
|
||||
- 惊人项目背后的人物:Pavel and Nikolai Durov..
|
||||
|
||||
就是这些了。我还会有你喜欢阅读的其它有趣的文章。很高兴能代表Tecmint感谢我们尊贵的读者以及使得我们通过不断的自我进步走到这里的批评者。保持联系!继续评论。如果你关注我们就请和我们分享吧。
|
||||
就是这些了。我还会为大家带来你们喜欢阅读的其它有趣文章。很高兴能代表Tecmint,感谢我们尊贵的读者以及使得我们通过不断的自我提升走到这里的批评者。保持联系!继续评论。如果你关注我们那就请分享吧。
|
||||
|
||||
- [https://telegram.org/][2]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -123,10 +123,10 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-telegram-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:https://tdesktop.com/linux
|
||||
[2]:https://telegram.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://telegram.org/
|
||||
|
||||
104
translated/share/20150330 Picty--Managing Photos Made Easy.md
Normal file
104
translated/share/20150330 Picty--Managing Photos Made Easy.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
|
||||
Translated by H-mudcup
|
||||
|
||||
Picty:让图片管理变简单
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 关于Picty ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Picty**是个免费,简单,却强大的照片收藏管理器,它可以帮助你管理你的照片。它的设计围绕着管理**元数据**和**无损**的处理图像的方法。Picty目前同时支持在线(基于网页的)和离线(本地的)收藏集。在本地的收藏集中,图片将被保存在一个本地的文件夹和它的子文件夹中。为了加快用户主目录里图片的查询速度,它会维持一个数据库。在在线(基于网页的)收藏集中,你可以通过网页浏览器上传并分享图片。拥有适当权限的个人用户可以把图片分享给任何人,而且每个用户可以同时开放多个收藏集,收藏集也可以被多个用户分享。通过一个转载插件在收藏集间传递图片就有了个简单的交互界面。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以从你的相机或任何设备中下载任何数量的照片。除此之外,Picty允许你在下载前浏览在你相机里的图片集。Picty是个轻量级的应用,还有着清爽的界面。它支持Linux和Windows平台。
|
||||
|
||||
### 功能 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 支持大相片集(20000张以上)。
|
||||
- 同时开放多个收藏集还可以在它们之间传照片。
|
||||
- 收藏集包括:
|
||||
- 本地文件系统中保存图片的文件夹。
|
||||
- 相机、电话及其他媒体设备中的图片。
|
||||
- 图片保存服务(目前支持Flickr)
|
||||
- Picty不是把相片“导入”到它的数据库中,它仅仅提供了一个界面来访问它们,不管它们保存在哪。为了保持迅速的反应以及能使你在离线时浏览图片的能力,Picty会保存缩略图和元数据的缓存。
|
||||
- 以业界标准格式Exif、IPTC和Xmp读写元数据。
|
||||
- 无损的方法:
|
||||
- Picty把所有改变包括图像编辑以元数据写入。例如,一个图片可以以任何方式剪切保存,原来的像素仍然保存在该文件里。
|
||||
- 修改会保存在Picty的收藏集缓存中直到你把你对元数据的修改保存到图片中。你能很容易撤销你不喜欢的未保存的修改。
|
||||
- 基本图片编辑:
|
||||
- 目前支持基本的图像增强,如亮度、对比度、色彩、剪切以及矫正。
|
||||
- Improvements to those tools and other tools coming soon (red eye reduction, levels, curves, noise reduction)对这些工具的改善和其他的工具即将到来。(红眼消除、拉伸、弯曲、噪声消除)
|
||||
- 图片标签:
|
||||
- 使用标准的IPTC和Xmp关键词为图片做标签。
|
||||
- 一个树状标签图让你能很容易的管理标签和对你的收藏集进行导航。
|
||||
- 文件夹视图:
|
||||
- 按照目录的结构对你的图片收藏进行导航
|
||||
- 支持多屏显示
|
||||
- Picty可以设置成让你在一个屏幕上浏览你的收藏集同时在另一个屏幕上全屏显示图片。
|
||||
- 可个性化
|
||||
- 可以为外部工具创建快捷方式
|
||||
- 支持插件——目前提供的功能中有许多(标签和文件夹视图以及所有的图片编辑工具)都可以通过插件提供。
|
||||
- 使用Python编写——自带batteries!(python的这个特点使它可在mac、Linux和windows上直接安装使用,无需复杂的设置。)
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装方法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1、从PPA安装 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Picty开发人员为基于Debian的发行版,如Ubuntu,创建了一个PPA,让安装更简单。
|
||||
|
||||
要在Ubuntu和它的衍生版上安装,请运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:damien-moore/ppa
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install picty
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2、从源文件安装 ####
|
||||
|
||||
此外,你还可以从源文件安装。首先安装如下依赖项。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install bzr python-pyinotify python-pyexiv2 python-gtk2 python-gnome2 dcraw python-osmgpsmap python-flickrapi
|
||||
|
||||
然后,使用下面这个命令得到最新版本:
|
||||
|
||||
bzr branch lp:picty
|
||||
|
||||
要运行Picty,先转到Picty所在的目录,然后输入:
|
||||
|
||||
cd picty
|
||||
bin/picty
|
||||
|
||||
要想更新到最新版,请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
cd picty
|
||||
bzr pull
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用方法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
可以从目录或Unity Dash启动Picty。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以选择已存在的收藏集、设备或目录。让我们创建一个**新收藏集** 。要这样做,得先点击新收藏集(New Collection)按钮。进入收藏集,然后浏览都你保存图片的地方。最后,点击**创建(Create)**按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你可以修改,旋转,添加/移除标签,设置每个图片的描述。要这么做,只需右击任何一个图片然后爱做什么做什么。
|
||||
|
||||
访问下面这个Google组可以得到更多关于Picty相片管理器的信息和支持。
|
||||
|
||||
- [http://groups.google.com/group/pictyphotomanager][1]
|
||||
|
||||
干杯!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/picty-managing-photos-made-easy/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
译者:[H-mudcup](https://github.com/H-mudcup)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/sk/
|
||||
[1]:http://groups.google.com/group/pictyphotomanager
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
||||
如何在Docker容器中运行GUI程序
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
各位,今天我们将学习如何在[Docker][1]之中运行GUI程序。我们可以轻易地在Docker容器中运行大多数GUI程序且不出错。Docker是一个开源项目,提供了一个打包、分发和运行任意程序的轻量级容器的开放平台。它没有语言支持、框架或者打包系统的限制并可以在任何地方、任何时候,从小型的家用电脑到高端的服务器都可以运行。这让人们可以打包不同的包用于部署和扩展网络应用,数据库和后端服务而不必依赖于特定的栈或者提供商。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是我们该如何在Docker容器中运行GUI程序的简单步骤。本教程中,我们会用Firefox作为例子。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 安装 Docker ###
|
||||
|
||||
在开始事前,我们首先得确保在Linux主机中已经安装了Docker。这里,我运行的是CentOS 7 主机,我们将运行yum管理器和下面的命令来安装Docker。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install docker
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart docker.service
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 创建 Dockerfile ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,Docker守护进程已经在运行中了,我们现在准备创建自己的Firefox Docker容器。我们要创建一个Dockerfile,这里我们要输入需要的配置来创建一个可以工作的Firefox容器。我们取下CentOS中最新的Docker镜像。至此,我们需要用文本编辑器创建一个名为Dockerfile的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano Dockerfile
|
||||
|
||||
接着,在Dockerfile中添加下面的行并保存。
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
FROM centos:7
|
||||
RUN yum install -y firefox
|
||||
# Replace 0 with your user / group id
|
||||
RUN export uid=0 gid=0
|
||||
RUN mkdir -p /home/developer
|
||||
RUN echo "developer:x:${uid}:${gid}:Developer,,,:/home/developer:/bin/bash" >> /etc/passwd
|
||||
RUN echo "developer:x:${uid}:" >> /etc/group
|
||||
RUN echo "developer ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" > /etc/sudoers
|
||||
RUN chmod 0440 /etc/sudoers
|
||||
RUN chown ${uid}:${gid} -R /home/developer
|
||||
|
||||
USER developer
|
||||
ENV HOME /home/developer
|
||||
CMD /usr/bin/firefox
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**注意:在第四行的配置中,用你自己的用户和组id来替换0。 我们可以用下面的命令在shell或者终端中得到uid和gid。**
|
||||
|
||||
# id $USER
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 构造Docker容器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下面我们就要根据上面的Dockerfile构建一个容器。它会安装firefox浏览器和它需要的包。它接着会设置用户权限并让它可以工作。这里镜像名是firefox,你可以根据你的需要命名。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker build --rm -t firefox .
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 运行Docker容器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,如果一切顺利,我们现在可以在运行着CentOS 7镜像的Docker容器中运行我们的GUI程序也就是Firefox浏览器了。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -ti --rm -e DISPLAY=$DISPLAY -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix firefox
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在Dcoker容器中运行GUI程序是一次很棒的体验,它对你的主机文件系统没有任何的伤害。它完全依赖你的Docker容器。本教程中,我尝试了CentOS 7 Docker中的Firefox。我们可以用这个技术尝试更多的GUI程序。如果你有任何问题、建议、反馈请在下面的评论栏中写下来,这样我们可以提升或更新我们的内容。谢谢!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/run-gui-apps-docker-container/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://docker.io/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
Linux Email应用 Geary 更新了 — 如何在Ubuntu上安装
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Geary,Linux上流行的桌面email客户端,更新到版本0.10了 — 并且有了很多新的功能。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
elementary OS上运行的旧版本的Geary
|
||||
|
||||
Geary 0.10有一些可惜的用户界面改进以及额外的UI选项,包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 新增: 可以对归档,删除以及移动做'Undo'操作
|
||||
- 新增: 在2列或者2列布局之间切换
|
||||
- 新的 “split header bar” — 改进邮件列表,发件人布局
|
||||
- 新的快捷键 — 使用j/k切换到上/下一封邮件
|
||||
|
||||
根据Yorba介绍,这次更新还提出了一个 **全新的全文检索算法** ,用来改进Geary的搜索体验。
|
||||
|
||||
这个更新应该能平息一下对应用搜索能力的抱怨,那些经常觉得Geary返回的搜索结果仅仅是包装软件自身"看起来和查询语句毫不相关"的观点。
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘Yorba 建议所有这个软件客户端的用户升级到这个版本’
|
||||
|
||||
*“尽管并不是所有的搜索问题在0.10版本中都解决了,但Geary能确保显示的结果能和更好的匹配用户的查询,”[团队表示][1]。*
|
||||
|
||||
最后同样重要的是,专业用户会喜欢的主要功能:**支持一个账户有多个或者备用的email地址**。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在Geary中设置Gmail账户来收取你的Yahoo,Outlook和KittyMail信件,你可以看到现在它们都整齐地放在一起,当你写信时在'From'栏你可以选择指定账户作为发送人。这并不是最重要,但是却是最经常被人要求的的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
这个流行的Linux电子邮件客户端的这次发布主要是bug修复,性能优化以及一些杂项改进。
|
||||
|
||||
Yorba建议所有这个客户端的用户都升级到这个发行版。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu 14.04, 14.10 & 15.04安装Geary 0.10 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Yorba的最新版本可以从GNOME的Git账户下载可编译的源代码。但说实话:这不是有点麻烦吗?
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu用户想知道如何在 **14.04,14.10** 以及 **15.04**(那些更新爱好者) 上安装Geary 0.10。
|
||||
|
||||
官方的Youba PPA包括了 **Geary最新版本** 以及Shotwell(照片管理器)和[California][2](日历应用)。请注意添加这个PPA会使你电脑上任何已经安装的这些应用更新到最近的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
Capiche? Coolio.
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu上安装Geary你首先需要添加Yorba PPA和你的软件源。做这些你只需要打开终端窗口并小心地输入下面的两条命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yorba/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install geary
|
||||
|
||||
在输入最后一条命令并敲击回车键后会提示输入你的密码。输入密码让安装完成。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
完成后,打开你的桌面环境应用启动面板并查找‘Geary’图标。点击它,添加你的账户并查看[通过信息高速公路下载了什么][3],开始使用简单的图形界面吧。
|
||||
|
||||
**别忘记:你可以通过电子邮件告诉我们你想看的新闻,应用建议,以及任何你想我们包括的东西,直接点击joey@oho.io**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/03/install-geary-ubuntu-linux-email-update
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Apps/Geary/FullTextSearchStrategy
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/10/california-calendar-natural-language-parser
|
||||
[3]:https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rxM8C71GB8w
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
|
||||
5个基于Linux命令行的文件下载和网站浏览工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
GNU/Linux最冒险迷人的部分,Linux命令行,是非常强大的工具。命令行本身功能多样,多种内建或者第三方的命令行应用使得Linux变得更加健壮和强大。Linux Shell支持多种不同类型的网络应用,无论是BT下载软件,专用下载器或者互联网冲浪。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
5个命令行互联网工具
|
||||
|
||||
这里我们介绍了5个很好的命令行互联网工具,它们非常有用,也很容易上手。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. rTorrent ###
|
||||
|
||||
rTorrent是基于文本,用C++编写,追求高性能的Torrent客户端。支持大部分标准的Linux发行版,包括FreeBSD和Mac OS X。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 安装rTorrent ####
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install rtorrent (基于 APT 的系统)
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install rtorrent (基于 YUM 的系统)
|
||||
|
||||
在终端中用下面的命令检查rtorrent是否正确安装
|
||||
|
||||
# rtorrent
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
rTorrent命令行工具
|
||||
|
||||
#### rTorrent的功能 ####
|
||||
|
||||
一些有用的快捷键和使用方法
|
||||
|
||||
- CTRL+ q – 退出rTorrent应用程序
|
||||
- CTRL+ s – 开始下载
|
||||
- CTRL+ d – 停止运行中的下载或者移除已完成的下载
|
||||
- CTRL+ k – 停止并关闭运行中的下载
|
||||
- CTRL+ r – 在上传/下载torrent之前进行Hash检查
|
||||
- CTRL+ q – 执行两次这个命令,rTorrent会直接退出而不发送停止信号
|
||||
- Left Arrow Key – 跳到上一屏幕
|
||||
- Right Arrow Key – 跳到下一屏幕
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Wget ###
|
||||
|
||||
Wget是GNU项目的一部分,名字由World Wide Web (WWW)衍生而来。Wget是用来递归下载,离线查看本地服务器HTML文件一个很好的工具,它可用于Windows, Max,以及Linux等大部分平台。Wget能通过HTTP,HTTPS和FTP下载文件。另外,能镜像整个网站,支持代理浏览以及暂停/回复下载使得它更为有用。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 安装Wget ####
|
||||
|
||||
由于是GNE项目的一部分,Wget在大部分标准Linux发行版中都绑定发布,不再需要独立下载安装。如果默认没有安装,你也可以使用apt或者yum安装。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install wget (基于 APT 的系统)
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install wget (基于 YUM 的系统)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Wget的一些基本用法 ####
|
||||
|
||||
使用wget下载一个单独的文件.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://www.website-name.com/file
|
||||
|
||||
递归下载整个网站.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget -r http://www.website-name.com
|
||||
|
||||
从一个网站下载指定类型的文件(例如 pdf 和 png).
|
||||
|
||||
# wget -r -A png,pdf http://www.website-name.com
|
||||
|
||||
Wget是一个很棒的工具,它允许在资源有限的机器上自定义或者过滤下载。这是镜像一个网站(Yahoo.com)的wget下载截图。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Wget 命令行文件下载
|
||||
|
||||
要获取更多wget下载的例子,可以阅读我们的文章[10个Wget下载命令例子][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. cURL ###
|
||||
|
||||
cURL是在多种协议上传输数据的命令行工具。cURL是支持FTP, HTTP, FTPS, TFTP, TELNET, IMAP, POP3等协议的客户端应用。和其它相对比,在支持LDAP,POP3方面,cURL是和wget不同的简单下载器。cURL也很好的支持代理下载,暂停下载以及恢复下载。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 安装cURL ####
|
||||
|
||||
在软件仓库或者已安装软件中,cURL在大部分发行版中默认是可用的。如果没有安装,运行apt或者yum从软件仓库中获取需要的安装包。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install curl (基于 APT 的系统)
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install curl (基于 YUM 的系统)
|
||||
|
||||
cURL的基本使用方法
|
||||
|
||||
# curl www.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Curl 下载数据
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Curl 下载
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. w3m ###
|
||||
|
||||
W3m是GPL协议下发布的基于文本的web浏览器。W3m支持表格,帧,颜色,SSL连接以及内联图像。W3m由于快速浏览而出名。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 安装w3m ####
|
||||
|
||||
W3m在大部分Linux发行版中也是默认可用的。如果不可用的话可以用apt或者yum获取需要的安装包。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install w3m (基于 APT 的系统)
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install w3m (基于 YUM 的系统)
|
||||
|
||||
#### w3m的基本使用方法 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# w3m www.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
基于文本的web浏览器w3m
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Elinks ###
|
||||
|
||||
Elinks是基于文本,给基于Unix和基于Unix的系统使用的免费web浏览器。Elinks支持 HTTP,HTTP Cookies以及支持浏览Pery和Ruby脚本。也很好的支持基于标签的浏览。最棒的是它支持鼠标,颜色显示以及支持一系列的协议,例如HTTP, FTP, SMB, Ipv4 和 Ipv6。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 安装Elinks ####
|
||||
|
||||
Elinks在大部分Linux发行版上是默认可用的。如果不是的话,可以通过apt或者yum安装。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install elinks (基于 APT 的系统)
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install elinks (基于 YUM 的系统)
|
||||
|
||||
Elinks的基本使用方法
|
||||
|
||||
# elinks www.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Elinks命令行浏览互联网
|
||||
|
||||
就是这些了。有你们喜欢读的有趣的文章,我会再次来到这里。到那时尽请关注并保持和Tecmint的联系,别忘了在评论部分给我们你的宝贵的反馈。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-command-line-tools-for-downloading-files/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user