mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-12 01:40:10 +08:00
commit
8a40b9e051
@ -1,8 +1,7 @@
|
||||
10款专为嵌入式系统打造的Linux平台
|
||||
|
||||
==========================================
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 有着广泛的用途。该平台被许多简单的家用电器所使用,同时它也深受程序员和黑客们的青睐。此外,Linux 还广泛地应用在嵌入式系统中,有一系列专门适用于此类系统的发行版。我们将为大家推荐十个非常优秀的专为嵌入式系统发行的linux版本!
|
||||
Linux 有着广泛的用途。该平台用于很多家庭的简单使用,同时它也深受程序员和黑客们的青睐。此外,Linux 还广泛地应用在嵌入式系统中,有一系列专门适用于此类系统的发行版。我们将为大家推荐十个非常优秀的专为嵌入式系统发行的linux版本!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
![] (http://www.efytimes.com/admin/useradmin/photo/UJVP24130PM532014.jpeg)
|
||||
@ -10,61 +9,49 @@ Linux 有着广泛的用途。该平台被许多简单的家用电器所使用
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.[Ampro 嵌入式 Linux][1] ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个自由和开放源代码的从Ubuntu派生来的轻量级操作系统。
|
||||
这是一个自由和开放源代码的从Ubuntu精简来的轻量级操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. [BlueCat Linux from Lynx][2] ###
|
||||
这个基于 Linux 的发行版是Lynx套件的一部分,并为嵌入式系统打造。
|
||||
|
||||
这个基于 Linux 的发行版是Lynx套件的一部分,并为嵌入式系统打造。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. [CacheGuard OS][3] ###
|
||||
|
||||
CacheGuard OS 是一个从零开始建立的集成了安全解决方案的基于Linux的可自定义版本 ,专门为网络管理设计的。
|
||||
|
||||
CacheGuard OS 是一个从零开始建立的集成了安全解决方案的基于Linux的版本,专门为网络管理设计的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. [Darma NAS OS][4] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个发行版有一个基于 SSL 的加密客户端服务器和基于 Java 的图形用户界面。
|
||||
|
||||
这个发行版有一个基于 SSL 的加密客户端的服务器和基于 Java 的图形用户界面。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. [DIET-PC][5] ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这是开源的瘦客户端软件 kitset,它允许用户建立网络设备。
|
||||
|
||||
这是开源的瘦客户端软件 kitset,它允许用户建立网络应用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. [ELinOS][6] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个发行版为在嵌入式系统上工作的用户提供大量的技术。它是一个相当受欢迎的嵌入式 Linux 平台。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. [eLux][7] ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这个发行版有一个非常简单和容易使用的界面,适用于用户和管理员都不具有任何有关 Linux 的知识的特殊情况下。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. [eLux NG][8] ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
这一个发行版为支持 eLux 的列表中的处理器添加了新的模式。
|
||||
|
||||
这个发行版为支持 eLux 的处理器列表中添加了新的型号。
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. [Embedded Coyote Linux][9] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这种基于 Coyote Linux的防火墙和 VPN 服务器一直为很多人选择的平台。
|
||||
|
||||
这种基于 Coyote Linux的防火墙和 VPN 服务器 一直为很多人选择的平台。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# # # 10。[嵌入式 Debian 项目][10] # # #
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. [嵌入式 Debian 项目][10] ###
|
||||
|
||||
这个项目的目的是使 Debian GNU/Linux 成为嵌入式系统的第一选择。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=137612
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[owen-carter](https://github.com/owen-carter) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[owen-carter](https://github.com/owen-carter) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,39 +2,39 @@
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
MacBook Pros拥有非常强大的配置,有些人想强上加强,他们想用Linux系统。
|
||||
MacBook Pros拥有非常强大的配置,但是有些人想强上加强,他们想用Linux系统。
|
||||
|
||||
不管您是想要更开放和个性化的操作系统又或者您只想要需要用某些在Linux特有的软件,您都会想要把Linux装载您的MacBook上。 可惜的是MacBook Pros们可是一块块密不透风砖头,让您想装其他系统又无从下手。尤其是Linux,比在MacBooks上装Windows还难。 Boot Camp在此时对于Linux来说也是手无对策。 虽然如此,但并不代表您完全不能做到,装机走起!
|
||||
不管您是想要更开放和个性化的操作系统又或者是您只想要使用某些在Linux特有的软件,您都会想要在您的MacBook上安装Linux。 可惜的是MacBook Pro们可是一块块密不透风砖头,让您想装其他系统又无从下手。尤其是Linux,比在MacBook上装Windows还难。 Boot Camp对于Linux来说也没有什么用处。 虽然如此,但并不代表您完全不能做到,装机走起!
|
||||
|
||||
### 为什么要在MacBook Pro Retina上装Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
买MacBook不就是为了OS X吗?为何要装Linux? 其实买MacBook的原因不必须只是因为它的系统, 其极致的性能,极其耐用的电池以及高大上的持久力都是购买它的原因。 这些这么好的硬件再加上一块能让您体验到HiDPI的清晰度Retina显示屏,其不皆是买入的理由乎?
|
||||
买MacBook不就是为了OS X吗?为何要装Linux? 其实买MacBook的原因不仅仅只是因为它的操作系统, 其极致的硬件性能,超长的电池寿命,以及抗操抗造都是购买它的原因。 这些这么好的硬件再加上一块能让您体验到HiDPI的清晰度Retina显示屏,其不皆是买入的理由乎?
|
||||
|
||||
但是如果您对OS X无爱,又或者您真心需要使用Linux,为何不将这自由,开源,小巧,个性化的Linux塞进您的高大上硬件呢?苹果可能有话要说了,可谁在乎呢~
|
||||
但是如果您对OS X无爱,又或者您真心想要使用Linux,为何不将这自由、开源、小巧、个性化的Linux塞进您的高大上的硬件呢?苹果可能有话要说了,可谁在乎呢~
|
||||
|
||||
注:在本期教程我们将会使用[最流行的Linux发行版][1] - Ubuntu来作为我们这次安装的选择。您也可以用自己想用的的Linux发行版,但相关的步骤会和本教程有出入。 如果您把自己的系统玩坏了,我们将不承担任何责任。 本教程将教您如何Linux 和 OS X 双系统启动,另外只有在OS X 才能升级固件,所以我们建议您不要将OS X 删除。
|
||||
注:在本期教程我们将会使用[最流行的Linux发行版][1] - Ubuntu来作为我们这次安装的选择。您也可以用自己想用的的Linux发行版,但相关的步骤会和本教程略有出入。 如果您把自己的系统玩坏了,我们将不承担任何责任。 本教程将教您如何 Linux 和 OS X 双系统启动,另外只有在OS X才能升级固件,所以我们建议您不要将OS X 删除。
|
||||
|
||||
但在我们开始之前,请您用您喜欢的方法(比如Time Machine 或 CrashPlan)将您的电脑彻底备份,以防万一。
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载 Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先您需要下载一份[copy of the Ubuntu desktop ISO image][2] 。 该镜像在BIOS和EFI模式下都能启动,而Mac版的只能在BIOS启动。 可是我们需要在EFI模式启动,所以请确保您选择的是64-bit(64位),而不是Mac版的64-bit。
|
||||
首先您需要下载一份[Ubuntu桌面版安装镜像][2] 。 务必选择64位的桌面版,虽然该镜像并不是为Mac提供的。该镜像在BIOS和EFI模式下都能启动,而Mac的镜像却只能在BIOS启动。Mac是专门设计成这样的,但是我们要使之以EFI模式下启动。
|
||||
|
||||
### 存入U盘(USB) ###
|
||||
### 写到U盘(USB) ###
|
||||
|
||||
其次第二步, 找个2GB以上的USB, 我们将会用该USB作为Ubuntu的安装启动盘。 你可以按照 [the official Ubuntu steps][3] 或者 [use the dedicated GUI tool for the job][4] 的步骤来准备安装盘.
|
||||
其次, 找个2GB以上的USB, 我们将会用该USB作为Ubuntu的安装启动盘。 你可以按照 [Ubuntu官方指导的步骤][3] 或者 [使用专用的图形化工具][4] 来准备安装盘.
|
||||
|
||||
### 调整分区大小 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当你这一步也完成的时候,你的大Mac就做好安装的准备了。 打开Disk Utility(磁盘工具), 点击左边选择你的硬盘, 选择Partitions(分区)标签页。 把分区调整到你喜欢的大小 - 我们将会用新创建的空间来安装Ubuntu。
|
||||
当你完成上一步后,你的Mac Book Pro就做好安装的准备了。 打开Disk Utility(磁盘工具), 点击左边选择你的硬盘, 选择Partitions(分区)标签页。 把Mac分区缩小到你喜欢的大小 - 我们将会用新创建的可用空间来安装Ubuntu。
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动Ubuntu镜像 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当关机之后屏幕一黑时,请按住Option键(alt)知道你看到不同的启动选项。选择EFI选项(如果有两个的话选择左边的哪一个)来从USB启动Ubuntu.
|
||||
上述步骤完成后,将U盘插入并重启Mac Book Pro。当关机之后屏幕一黑时,请按住Option键(alt)直到你看到不同的启动选项。选择EFI选项(如果有两个的话选择左边的哪一个)来从USB启动Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
当你看到“Try Ubuntu" 和 "Install Ubuntu" 两个选项的时候, 选择 "Try Ubuntu" 因为我们需要在安装完成之后重启之前弄一些其他的东西。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -44,11 +44,11 @@ MacBook Pros拥有非常强大的配置,有些人想强上加强,他们想
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
一路来到分区这个步骤之后, 选择 "Do Something else" 这个选项。 然后请确保那块大约128MB左右的分区已经设置成EFI启动分区(你可以按他一下然后选择Option来确定一下; 另外,那一块盘应该是 /dev/sda1). 下一步, 你要在新建的空间里创建一个 ext4分区,用“/”路径来安装它。 如果你知道你自己在干嘛的话也可以创建几个不同的分区(切记这不是Windows啊孩纸)。
|
||||
到分区这个步骤之后, 选择 "Do Something else" 这个选项。 然后请确保那块大约128MB左右的分区已经被识别为EFI启动分区(你可以点击它然后选择Option来确定一下; 另外,那个分区应该是 /dev/sda1)。下一步, 你要在新建的空间里创建一个 ext4分区,在其上挂载“/”路径。 如果你知道你自己在干嘛的话也可以创建几个不同的分区(切记这不是Windows啊孩纸)。
|
||||
|
||||
在你开始下一步之前,请确保你的安装引导程序(boot loader)是选择了 /dev/sda1,GRUB也是装到该分区的。 然后按照平常一样该咋装咋装。
|
||||
|
||||
### EFI Boot Fix ###
|
||||
### 修改 EFI 引导 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,9 +60,9 @@ MacBook Pros拥有非常强大的配置,有些人想强上加强,他们想
|
||||
|
||||
sudo efibootmgr
|
||||
|
||||
这个将会列印出当前的启动设置, 你应该看到的是 "ubuntu" 和 "Boot0000", 当前的EFI设置是把系统指向 Boot0080, 这样的话就会跳过GRUB然后直接跳入OS X,所以我们要用一下指令来修复它:
|
||||
这个将会显示出当前的启动设置, 你应该看到的是 "ubuntu" 和 "Boot0000*",当前的EFI设置是把系统指向 Boot0080*,这样的话就会跳过GRUB然后直接跳入OS X,所以我们要用以下指令来修复它:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo efibootmgr -o 0,80`
|
||||
sudo efibootmgr -o 0,80
|
||||
|
||||
现在就可以重启了!
|
||||
|
||||
@ -70,21 +70,21 @@ MacBook Pros拥有非常强大的配置,有些人想强上加强,他们想
|
||||
|
||||
### 坑爹地调整设置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先你需要改一下GRUB的设置,这样你的SSD盘才不会偶尔死机, 输入:
|
||||
首先你需要改一下GRUB的设置,这样你的SSD盘才不会偶尔死机, 在Terminal输入:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo nano /etc/default/grub
|
||||
|
||||
在Terminal找到 **GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX** , 把他改成 **GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="libata.force=noncq"** 。 按下CTRL + X保存,然后按Y来确定保存。 接下来你要输入:
|
||||
找到 **GRUB\_CMDLINE\_LINUX**那一行 , 把它改成 **GRUB\_CMDLINE\_LINUX="libata.force=noncq"** 。 按下CTRL + X保存,然后按Y来确定保存。 接下来你要在Terminal输入:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo nano /etc/grub.d/40_custom
|
||||
|
||||
在Terminal会打开一个新的文件,请使用真丶精准手指准确地一字一字输入:
|
||||
打开一个新的文件,请使用真丶精准手指准确地一字一字输入:
|
||||
|
||||
menuentry "Mac OS X" {
|
||||
exit
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
这将会让你boot到你的Mac OS X安装程序(GRUB的32-bit和64bit项不能用)。然后CTRL+X 和 Y 保存退出,然后输入:
|
||||
这将会让你boot到你安装好的Mac OS X(GRUB的32-bit和64-bit项不能用)。然后CTRL+X 和 Y 保存退出,然后输入:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo update-grub
|
||||
|
||||
@ -94,11 +94,11 @@ MacBook Pros拥有非常强大的配置,有些人想强上加强,他们想
|
||||
|
||||
在极其高清的Retina显示屏上神马都这么小,坑爹啊啊? 去Setting -> Display 里把 Scaling Factor弄大一点吧,不然妈妈又要担心你的近视眼了。
|
||||
|
||||
你也可能觉得在边边改变窗口大小是一件极其困难的事情,坑爹啊啊? 去Terminal输入:
|
||||
你也可能觉得在边边上改变窗口大小是一件极其困难的事情,坑爹啊啊? 去Terminal输入:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo nano /usr/share/themes/Ambiance/metacity-1/metacity-theme-1.xml
|
||||
|
||||
然后在里面修改下面的参数:
|
||||
然后在里面修改成下面的参数:
|
||||
|
||||
<distance name="left_width" value="4"/>
|
||||
<distance name="right_width" value="4"/>
|
||||
@ -110,15 +110,14 @@ MacBook Pros拥有非常强大的配置,有些人想强上加强,他们想
|
||||
|
||||
/Library/ColorSync/Profiles/Displays/Color LCD-xxxxxx.icc
|
||||
|
||||
xxxxxx只是一串随机的字符,不过这路径应该只有一个文件。把他搬到你Ubuntu的Home folder, 然后到 System Settings –> Color 选择 Add New Profile 并选择你那刚弄过来的icc文件
|
||||
xxxxxx只是一串随机的字符,不过这路径应该只有一个文件。把他搬到你Ubuntu的Home folder, 然后到 System Settings –> Color 选择 Add New Profile 并选择你那刚弄过来的icc文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
恭喜你啦, 现在终于有一台属于你的Linux MacBook Pro Retina啦!如果你想把你的Ubuntu弄得更手熟,请按 [make Ubuntu feel more like home][5] 尽情地修改配置吧! 该教程也弄用于其他的Mac系统,当然每个release都不由不同的好处和坏处。 如果你用的是其他的电脑,请翻一翻[这篇为Ubuntu写的文档][6]
|
||||
恭喜你啦, 现在终于有一台属于你的Linux MacBook Pro Retina啦!如果你想把你的Ubuntu弄得更手熟,请按 [让你的Ubuntu 像家一样舒服][5] 尽情地修改配置吧! 该教程也可用于其他的Mac系统,当然每种Mac都有不同的好处和坏处。 如果你用的是其他的Mac,请翻一翻[这篇为Ubuntu写的文档][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, feel free to check out [other great Linux distros][7] that you can install to your Mac!
|
||||
另外,你还可以看一下其他可以在Mac安装的[Linux 发行包][7]哦!
|
||||
|
||||
Image Credits: [K?rlis Dambr?ns][8] Via Flickr
|
||||
@ -127,7 +126,7 @@ Image Credits: [K?rlis Dambr?ns][8] Via Flickr
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.makeuseof.com/tag/install-linux-macbook-pro/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[213edu](https://github.com/213edu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[213edu](https://github.com/213edu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,15 +8,15 @@ APP Grid:一个优秀的Ubuntu软件中心替代品
|
||||
|
||||
### App Grid:Ubuntu软件中心替代品 ###
|
||||
|
||||
自从2011年的彻底改造后,Ubuntu的旗舰应用商店的界面就没怎么变过。这并不是说它在此期间被完全忽略了,12.04的开发周期中可以看到[在启动时间上的工作][1]已经做了一些。
|
||||
自从2011年的彻底改造后,Ubuntu的旗舰应用商店的界面就没怎么变过。这并不是说它在此期间被完全忽略了,在12.04的开发周期中可以看到已经做了一些[减少打开耗时的工作][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
撇开那个不算,ol’ USC还是一如既往:一篮子的潜力还没被开发。
|
||||
撇开那个不算,Ubuntu软件中心还是一如既往,还有许多潜在功能还没被开发。
|
||||
|
||||
App Grid的目标时解决这些问题。从零开始,它要求更快的启动时间,更快的反应时间,而且“不感觉混乱,不让人失望”。
|
||||
App Grid的目标是解决这些问题。从零开始,它要求更快的启动时间,更快的反应时间,而且“不感觉混乱,不让人失望”。
|
||||
|
||||
在大部分这些方面,App Grid取得了成功。它几乎可以立即打开,而在界面上点击也确实反应迅速。“不感觉混乱”这一承诺,或许有一点小小的争议。该应用有时候要你横向滚动,而另外的时候,又要你纵向滚动。也有人禁不住会想,如果这个应用能把它的网格背景样式扔了,可能看起来会显得更专业一些。
|
||||
|
||||
作为在Ubuntu上从筛选应用程序的一个方式,App Grid做出了极大的努力。它支持Ubuntu One上的订购、评级和评论,作为Ubuntu默认应用商店的替代品,它更好用。
|
||||
作为在Ubuntu上筛选应用程序的一个方式,App Grid做出了极大的努力。它支持Ubuntu One上的订购、评级和评论,作为Ubuntu默认应用商店的替代品,它更好用。
|
||||
|
||||
如果非要说点什么缺点的话,那就是它不是一个开源的应用程序,第一次运行时会显示以下免责声明:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,18 +27,19 @@ App Grid的目标时解决这些问题。从零开始,它要求更快的启动
|
||||
App Grid可运行在Ubuntu 12.04 LTS,13.10以及14.04 LTS版本下。可以通过添加以下PPA软件源来安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:appgrid/stable
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install app grid
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install appgrid
|
||||
|
||||
或者,也可以[从项目网站][2]抓取一个.deb安装包来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载用于Ubuntu 14.04的App Grid安装包][3]
|
||||
|
||||
试试吧,试过后请到我们开的空间里来发表一下你的看法吧……
|
||||
试试吧,试过后请发表一下你的看法吧……
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/05/appgrid-ubuntu-software-centre-alternative
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
370
published/20140603 Write your first Linux Kernel module.md
Normal file
370
published/20140603 Write your first Linux Kernel module.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,370 @@
|
||||
黑客内核:编写属于你的第一个Linux内核模块
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 曾经多少次想要在内核游荡?曾经多少次茫然不知方向?你不要再对着它迷惘,让我们指引你走向前方……
|
||||
|
||||
内核编程常常看起来像是黑魔法,而在亚瑟 C 克拉克的眼中,它八成就是了。Linux内核和它的用户空间是大不相同的:抛开漫不经心,你必须小心翼翼,因为你编程中的一个bug就会影响到整个系统。浮点运算做起来可不容易,堆栈固定而狭小,而你写的代码总是异步的,因此你需要想想并发会导致什么。而除了所有这一切之外,Linux内核只是一个很大的、很复杂的C程序,它对每个人开放,任何人都去读它、学习它并改进它,而你也可以是其中之一。
|
||||
|
||||
学习内核编程的最简单的方式也许就是写个内核模块:一段可以动态加载进内核的代码。模块所能做的事是有限的——例如,他们不能在类似进程描述符这样的公共数据结构中增减字段(LCTT译注:可能会破坏整个内核及系统的功能)。但是,在其它方面,他们是成熟的内核级的代码,可以在需要时随时编译进内核(这样就可以摒弃所有的限制了)。完全可以在Linux源代码树以外来开发并编译一个模块(这并不奇怪,它称为树外开发),如果你只是想稍微玩玩,而并不想提交修改以包含到主线内核中去,这样的方式是很方便的。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我们将开发一个简单的内核模块用以创建一个**/dev/reverse**设备。写入该设备的字符串将以相反字序的方式读回(“Hello World”读成“World Hello”)。这是一个很受欢迎的程序员面试难题,当你利用自己的能力在内核级别实现这个功能时,可以使你得到一些加分。在开始前,有一句忠告:你的模块中的一个bug就会导致系统崩溃(虽然可能性不大,但还是有可能的)和数据丢失。在开始前,请确保你已经将重要数据备份,或者,采用一种更好的方式,在虚拟机中进行试验。
|
||||
|
||||
### 尽可能不要用root身份 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> 默认情况下,**/dev/reverse**只有root可以使用,因此你只能使用**sudo**来运行你的测试程序。要解决该限制,可以创建一个包含以下内容的**/lib/udev/rules.d/99-reverse.rules**文件:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> SUBSYSTEM=="misc", KERNEL=="reverse", MODE="0666"
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 别忘了重新插入模块。让非root用户访问设备节点往往不是一个好主意,但是在开发其间却是十分有用的。这并不是说以root身份运行二进制测试文件也不是个好主意。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 模块的构造 ####
|
||||
|
||||
由于大多数的Linux内核模块是用C写的(除了底层的特定于体系结构的部分),所以推荐你将你的模块以单一文件形式保存(例如,reverse.c)。我们已经把完整的源代码放在GitHub上——这里我们将看其中的一些片段。开始时,我们先要包含一些常见的文件头,并用预定义的宏来描述模块:
|
||||
|
||||
#include <linux/init.h>
|
||||
#include <linux/kernel.h>
|
||||
#include <linux/module.h>
|
||||
|
||||
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
|
||||
MODULE_AUTHOR("Valentine Sinitsyn <valentine.sinitsyn@gmail.com>");
|
||||
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("In-kernel phrase reverser");
|
||||
|
||||
这里一切都直接明了,除了**MODULE\_LICENSE()**:它不仅仅是一个标记。内核坚定地支持GPL兼容代码,因此如果你把许可证设置为其它非GPL兼容的(如,“Proprietary”[专利]),某些特定的内核功能将在你的模块中不可用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么时候不该写内核模块 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> 内核编程很有趣,但是在现实项目中写(尤其是调试)内核代码要求特定的技巧。通常来讲,在没有其它方式可以解决你的问题时,你才应该在内核级别解决它。以下情形中,可能你在用户空间中解决它更好:
|
||||
|
||||
> - 你要开发一个USB驱动 —— 请查看[libusb][1]。
|
||||
> - 你要开发一个文件系统 —— 试试[FUSE][2]。
|
||||
> - 你在扩展Netfilter —— 那么[libnetfilter\_queue][3]对你有所帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
> 通常,内核里面代码的性能会更好,但是对于许多项目而言,这点性能丢失并不严重。
|
||||
|
||||
由于内核编程总是异步的,没有一个**main()**函数来让Linux顺序执行你的模块。取而代之的是,你要为各种事件提供回调函数,像这个:
|
||||
|
||||
static int __init reverse_init(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printk(KERN_INFO "reverse device has been registered\n");
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static void __exit reverse_exit(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printk(KERN_INFO "reverse device has been unregistered\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
module_init(reverse_init);
|
||||
module_exit(reverse_exit);
|
||||
|
||||
这里,我们定义的函数被称为模块的插入和删除。只有第一个的插入函数是必要的。目前,它们只是打印消息到内核环缓冲区(可以在用户空间通过**dmesg**命令访问);**KERN\_INFO**是日志级别(注意,没有逗号)。**\_\_init**和**\_\_exit**是属性 —— 联结到函数(或者变量)的元数据片。属性在用户空间的C代码中是很罕见的,但是内核中却很普遍。所有标记为**\_\_init**的,会在初始化后释放内存以供重用(还记得那条过去内核的那条“Freeing unused kernel memory…[释放未使用的内核内存……]”信息吗?)。**\_\_exit**表明,当代码被静态构建进内核时,该函数可以安全地优化了,不需要清理收尾。最后,**module\_init()**和**module\_exit()**这两个宏将**reverse\_init()**和**reverse_exit()**函数设置成为我们模块的生命周期回调函数。实际的函数名称并不重要,你可以称它们为**init()**和**exit()**,或者**start()**和**stop()**,你想叫什么就叫什么吧。他们都是静态声明,你在外部模块是看不到的。事实上,内核中的任何函数都是不可见的,除非明确地被导出。然而,在内核程序员中,给你的函数加上模块名前缀是约定俗成的。
|
||||
|
||||
这些都是些基本概念 - 让我们来做更多有趣的事情吧。模块可以接收参数,就像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
# modprobe foo bar=1
|
||||
|
||||
**modinfo**命令显示了模块接受的所有参数,而这些也可以在**/sys/module//parameters**下作为文件使用。我们的模块需要一个缓冲区来存储参数 —— 让我们把这大小设置为用户可配置。在**MODULE_DESCRIPTION()**下添加如下三行:
|
||||
|
||||
static unsigned long buffer_size = 8192;
|
||||
module_param(buffer_size, ulong, (S_IRUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH));
|
||||
MODULE_PARM_DESC(buffer_size, "Internal buffer size");
|
||||
|
||||
这儿,我们定义了一个变量来存储该值,封装成一个参数,并通过sysfs来让所有人可读。这个参数的描述(最后一行)出现在modinfo的输出中。
|
||||
|
||||
由于用户可以直接设置**buffer\_size**,我们需要在**reverse\_init()**来清除无效取值。你总该检查来自内核之外的数据 —— 如果你不这么做,你就是将自己置身于内核异常或安全漏洞之中。
|
||||
|
||||
static int __init reverse_init()
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (!buffer_size)
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
printk(KERN_INFO
|
||||
"reverse device has been registered, buffer size is %lu bytes\n",
|
||||
buffer_size);
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
来自模块初始化函数的非0返回值意味着模块执行失败。
|
||||
|
||||
### 导航 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> 但你开发模块时,Linux内核就是你所需一切的源头。然而,它相当大,你可能在查找你所要的内容时会有困难。幸运的是,在庞大的代码库面前,有许多工具使这个过程变得简单。首先,是Cscope —— 在终端中运行的一个比较经典的工具。你所要做的,就是在内核源代码的顶级目录中运行**make cscope && cscope**。Cscope和Vim以及Emacs整合得很好,因此你可以在你最喜爱的编辑器中使用它。
|
||||
|
||||
> 如果基于终端的工具不是你的最爱,那么就访问[http://lxr.free-electrons.com][4]吧。它是一个基于web的内核导航工具,即使它的功能没有Cscope来得多(例如,你不能方便地找到函数的用法),但它仍然提供了足够多的快速查询功能。
|
||||
|
||||
现在是时候来编译模块了。你需要你正在运行的内核版本头文件(**linux-headers**,或者等同的软件包)和**build-essential**(或者类似的包)。接下来,该创建一个标准的Makefile模板:
|
||||
|
||||
obj-m += reverse.o
|
||||
all:
|
||||
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) modules
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) clean
|
||||
|
||||
现在,调用**make**来构建你的第一个模块。如果你输入的都正确,在当前目录内会找到reverse.ko文件。使用**sudo insmod reverse.ko**插入内核模块,然后运行如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ dmesg | tail -1
|
||||
[ 5905.042081] reverse device has been registered, buffer size is 8192 bytes
|
||||
|
||||
恭喜了!然而,目前这一行还只是假象而已 —— 还没有设备节点呢。让我们来搞定它。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 混杂设备 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux中,有一种特殊的字符设备类型,叫做“混杂设备”(或者简称为“misc”)。它是专为单一接入点的小型设备驱动而设计的,而这正是我们所需要的。所有混杂设备共享同一个主设备号(10),因此一个驱动(**drivers/char/misc.c**)就可以查看它们所有设备了,而这些设备用次设备号来区分。从其他意义来说,它们只是普通字符设备。
|
||||
|
||||
要为该设备注册一个次设备号(以及一个接入点),你需要声明**struct misc\_device**,填上所有字段(注意语法),然后使用指向该结构的指针作为参数来调用**misc\_register()**。为此,你也需要包含**linux/miscdevice.h**头文件:
|
||||
|
||||
static struct miscdevice reverse_misc_device = {
|
||||
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,
|
||||
.name = "reverse",
|
||||
.fops = &reverse_fops
|
||||
};
|
||||
static int __init reverse_init()
|
||||
{
|
||||
...
|
||||
misc_register(&reverse_misc_device);
|
||||
printk(KERN_INFO ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
这儿,我们为名为“reverse”的设备请求一个第一个可用的(动态的)次设备号;省略号表明我们之前已经见过的省略的代码。别忘了在模块卸下后注销掉该设备。
|
||||
|
||||
static void __exit reverse_exit(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
misc_deregister(&reverse_misc_device);
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
‘fops’字段存储了一个指针,指向一个**file\_operations**结构(在Linux/fs.h中声明),而这正是我们模块的接入点。**reverse\_fops**定义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
static struct file_operations reverse_fops = {
|
||||
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
|
||||
.open = reverse_open,
|
||||
...
|
||||
.llseek = noop_llseek
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
另外,**reverse\_fops**包含了一系列回调函数(也称之为方法),当用户空间代码打开一个设备,读写或者关闭文件描述符时,就会执行。如果你要忽略这些回调,可以指定一个明确的回调函数来替代。这就是为什么我们将**llseek**设置为**noop\_llseek()**,(顾名思义)它什么都不干。这个默认实现改变了一个文件指针,而且我们现在并不需要我们的设备可以寻址(这是今天留给你们的家庭作业)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 关闭和打开 ####
|
||||
|
||||
让我们来实现该方法。我们将给每个打开的文件描述符分配一个新的缓冲区,并在它关闭时释放。这实际上并不安全:如果一个用户空间应用程序泄漏了描述符(也许是故意的),它就会霸占RAM,并导致系统不可用。在现实世界中,你总得考虑到这些可能性。但在本教程中,这种方法不要紧。
|
||||
|
||||
我们需要一个结构函数来描述缓冲区。内核提供了许多常规的数据结构:链接列表(双联的),哈希表,树等等之类。不过,缓冲区常常从头设计。我们将调用我们的“struct buffer”:
|
||||
|
||||
struct buffer {
|
||||
char *data, *end, *read_ptr;
|
||||
unsigned long size;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
**data**是该缓冲区存储的一个指向字符串的指针,而**end**指向字符串结尾后的第一个字节。**read_ptr**是**read()**开始读取数据的地方。缓冲区的size是为了保证完整性而存储的 —— 目前,我们还没有使用该区域。你不能假设使用你结构体的用户会正确地初始化所有这些东西,所以最好在函数中封装缓冲区的分配和收回。它们通常命名为**buffer\_alloc()**和**buffer\_free()**。
|
||||
|
||||
static struct buffer *buffer_alloc(unsigned long size)
|
||||
{
|
||||
struct buffer *buf;
|
||||
buf = kzalloc(sizeof(*buf), GFP_KERNEL);
|
||||
if (unlikely(!buf))
|
||||
goto out;
|
||||
...
|
||||
out:
|
||||
return buf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
内核内存使用**kmalloc()**来分配,并使用**kfree()**来释放;**kzalloc()**的风格是将内存设置为全零。不同于标准的**malloc()**,它的内核对应部分收到的标志指定了第二个参数中请求的内存类型。这里,**GFP_KERNEL**是说我们需要一个普通的内核内存(不是在DMA或高内存区中)以及如果需要的话函数可以睡眠(重新调度进程)。**sizeof(*buf)**是一种常见的方式,它用来获取可通过指针访问的结构体的大小。
|
||||
|
||||
你应该随时检查**kmalloc()**的返回值:访问NULL指针将导致内核异常。同时也需要注意**unlikely()**宏的使用。它(及其相对宏**likely()**)被广泛用于内核中,用于表明条件几乎总是真的(或假的)。它不会影响到控制流程,但是能帮助现代处理器通过分支预测技术来提升性能。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,注意**goto**语句。它们常常为认为是邪恶的,但是,Linux内核(以及一些其它系统软件)采用它们来实施集中式的函数退出。这样的结果是减少嵌套深度,使代码更具可读性,而且非常像更高级语言中的**try-catch**区块。
|
||||
|
||||
有了**buffer\_alloc()**和**buffer\_free()**,**open**和**close**方法就变得很简单了。
|
||||
|
||||
static int reverse_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int err = 0;
|
||||
file->private_data = buffer_alloc(buffer_size);
|
||||
...
|
||||
return err;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
**struct file**是一个标准的内核数据结构,用以存储打开的文件的信息,如当前文件位置(**file->f\_pos**)、标志(**file->f\_flags**),或者打开模式(**file->f\_mode**)等。另外一个字段**file->privatedata**用于关联文件到一些专有数据,它的类型是void *,而且它在文件拥有者以外,对内核不透明。我们将一个缓冲区存储在那里。
|
||||
|
||||
如果缓冲区分配失败,我们通过返回否定值(**-ENOMEM**)来为调用的用户空间代码标明。一个C库中调用的**open(2)**系统调用(如 **glibc**)将会检测这个并适当地设置**errno** 。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 学习如何读和写 ####
|
||||
|
||||
“read”和“write”方法是真正完成工作的地方。当数据写入到缓冲区时,我们放弃之前的内容和反向地存储该字段,不需要任何临时存储。**read**方法仅仅是从内核缓冲区复制数据到用户空间。但是如果缓冲区还没有数据,**revers\_eread()**会做什么呢?在用户空间中,**read()**调用会在有可用数据前阻塞它。在内核中,你就必须等待。幸运的是,有一项机制用于处理这种情况,就是‘wait queues’。
|
||||
|
||||
想法很简单。如果当前进程需要等待某个事件,它的描述符(**struct task_struct**存储‘current’信息)被放进非可运行(睡眠中)状态,并添加到一个队列中。然后**schedule()**就被调用来选择另一个进程运行。生成事件的代码通过使用队列将等待进程放回**TASK\_RUNNING**状态来唤醒它们。调度程序将在以后在某个地方选择它们之一。Linux有多种非可运行状态,最值得注意的是**TASK\_INTERRUPTIBLE**(一个可以通过信号中断的睡眠)和**TASK\_KILLABLE**(一个可被杀死的睡眠中的进程)。所有这些都应该正确处理,并等待队列为你做这些事。
|
||||
|
||||
一个用以存储读取等待队列头的天然场所就是结构缓冲区,所以从为它添加**wait\_queue\_head_t read\_queue**字段开始。你也应该包含**linux/sched.h**头文件。可以使用DECLARE\_WAITQUEUE()宏来静态声明一个等待队列。在我们的情况下,需要动态初始化,因此添加下面这行到**buffer\_alloc()**:
|
||||
|
||||
init_waitqueue_head(&buf->read_queue);
|
||||
|
||||
我们等待可用数据;或者等待**read\_ptr != end**条件成立。我们也想要让等待操作可以被中断(如,通过Ctrl+C)。因此,“read”方法应该像这样开始:
|
||||
|
||||
static ssize_t reverse_read(struct file *file, char __user * out,
|
||||
size_t size, loff_t * off)
|
||||
{
|
||||
struct buffer *buf = file->private_data;
|
||||
ssize_t result;
|
||||
while (buf->read_ptr == buf->end) {
|
||||
if (file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) {
|
||||
result = -EAGAIN;
|
||||
goto out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (wait_event_interruptible
|
||||
(buf->read_queue, buf->read_ptr != buf->end)) {
|
||||
result = -ERESTARTSYS;
|
||||
goto out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
我们让它循环,直到有可用数据,如果没有则使用**wait\_event\_interruptible()**(它是一个宏,不是函数,这就是为什么要通过值的方式给队列传递)来等待。好吧,如果**wait\_event\_interruptible()**被中断,它返回一个非0值,这个值代表**-ERESTARTSYS**。这段代码意味着系统调用应该重新启动。**file->f\_flags**检查以非阻塞模式打开的文件数:如果没有数据,返回**-EAGAIN**。
|
||||
|
||||
我们不能使用**if()**来替代**while()**,因为可能有许多进程正等待数据。当**write**方法唤醒它们时,调度程序以不可预知的方式选择一个来运行,因此,在这段代码有机会执行的时候,缓冲区可能再次空出。现在,我们需要将数据从**buf->data** 复制到用户空间。**copy\_to\_user()**内核函数就干了此事:
|
||||
|
||||
size = min(size, (size_t) (buf->end - buf->read_ptr));
|
||||
if (copy_to_user(out, buf->read_ptr, size)) {
|
||||
result = -EFAULT;
|
||||
goto out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
如果用户空间指针错误,那么调用可能会失败;如果发生了此事,我们就返回**-EFAULT**。记住,不要相信任何来自内核外的事物!
|
||||
|
||||
buf->read_ptr += size;
|
||||
result = size;
|
||||
out:
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
为了使数据在任意块可读,需要进行简单运算。该方法返回读入的字节数,或者一个错误代码。
|
||||
|
||||
写方法更简短。首先,我们检查缓冲区是否有足够的空间,然后我们使用**copy\_from\_userspace()**函数来获取数据。再然后**read\_ptr**和结束指针会被重置,并且反转存储缓冲区内容:
|
||||
|
||||
buf->end = buf->data + size;
|
||||
buf->read_ptr = buf->data;
|
||||
if (buf->end > buf->data)
|
||||
reverse_phrase(buf->data, buf->end - 1);
|
||||
|
||||
这里, **reverse\_phrase()**干了所有吃力的工作。它依赖于**reverse\_word()**函数,该函数相当简短并且标记为内联。这是另外一个常见的优化;但是,你不能过度使用。因为过多的内联会导致内核映像徒然增大。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,我们需要唤醒**read\_queue**中等待数据的进程,就跟先前讲过的那样。**wake\_up\_interruptible()**就是用来干此事的:
|
||||
|
||||
wake_up_interruptible(&buf->read_queue);
|
||||
|
||||
耶!你现在已经有了一个内核模块,它至少已经编译成功了。现在,是时候来测试了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 调试内核代码 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> 或许,内核中最常见的调试方法就是打印。如果你愿意,你可以使用普通的**printk()** (假定使用**KERN\_DEBUG**日志等级)。然而,那儿还有更好的办法。如果你正在写一个设备驱动,这个设备驱动有它自己的“struct device”,可以使用**pr\_debug()**或者**dev\_dbg()**:它们支持动态调试(**dyndbg**)特性,并可以根据需要启用或者禁用(请查阅**Documentation/dynamic-debug-howto.txt**)。对于单纯的开发消息,使用**pr\_devel()**,除非设置了DEBUG,否则什么都不会做。要为我们的模块启用DEBUG,请添加以下行到Makefile中:
|
||||
|
||||
> CFLAGS_reverse.o := -DDEBUG
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 完了之后,使用**dmesg**来查看**pr_debug()**或**pr_devel()**生成的调试信息。
|
||||
> 或者,你可以直接发送调试信息到控制台。要想这么干,你可以设置**console_loglevel**内核变量为8或者更大的值(**echo 8 /proc/sys/kernel/printk**),或者在高日志等级,如**KERN_ERR**,来临时打印要查询的调试信息。很自然,在发布代码前,你应该移除这样的调试声明。
|
||||
|
||||
> 注意内核消息出现在控制台,不要在Xterm这样的终端模拟器窗口中去查看;这也是在内核开发时,建议你不在X环境下进行的原因。
|
||||
|
||||
### 惊喜,惊喜! ###
|
||||
|
||||
编译模块,然后加载进内核:
|
||||
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
$ sudo insmod reverse.ko buffer_size=2048
|
||||
$ lsmod
|
||||
reverse 2419 0
|
||||
$ ls -l /dev/reverse
|
||||
crw-rw-rw- 1 root root 10, 58 Feb 22 15:53 /dev/reverse
|
||||
|
||||
一切似乎就位。现在,要测试模块是否正常工作,我们将写一段小程序来翻转它的第一个命令行参数。**main()**(再三检查错误)可能看上去像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
int fd = open("/dev/reverse", O_RDWR);
|
||||
write(fd, argv[1], strlen(argv[1]));
|
||||
read(fd, argv[1], strlen(argv[1]));
|
||||
printf("Read: %s\n", argv[1]);
|
||||
|
||||
像这样运行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./test 'A quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dog'
|
||||
Read: dog lazy the over jumped fox brown quick A
|
||||
|
||||
它工作正常!玩得更逗一点:试试传递单个单词或者单个字母的短语,空的字符串或者是非英语字符串(如果你有这样的键盘布局设置),以及其它任何东西。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,让我们让事情变得更好玩一点。我们将创建两个进程,它们共享一个文件描述符(及其内核缓冲区)。其中一个会持续写入字符串到设备,而另一个将读取这些字符串。在下例中,我们使用了**fork(2)**系统调用,而pthreads也很好用。我也省略打开和关闭设备的代码,并在此检查代码错误(又来了):
|
||||
|
||||
char *phrase = "A quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dog";
|
||||
if (fork())
|
||||
/* Parent is the writer */
|
||||
while (1)
|
||||
write(fd, phrase, len);
|
||||
else
|
||||
/* child is the reader */
|
||||
while (1) {
|
||||
read(fd, buf, len);
|
||||
printf("Read: %s\n", buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
你希望这个程序会输出什么呢?下面就是在我的笔记本上得到的东西:
|
||||
|
||||
Read: dog lazy the over jumped fox brown quick A
|
||||
Read: A kcicq brown fox jumped over the lazy dog
|
||||
Read: A kciuq nworb xor jumped fox brown quick A
|
||||
Read: A kciuq nworb xor jumped fox brown quick A
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
这里发生了什么呢?就像举行了一场比赛。我们认为**read**和**write**是原子操作,或者从头到尾一次执行一个指令。然而,内核确实无序并发的,随便就重新调度了**reverse\_phrase()**函数内部某个地方运行着的写入操作的内核部分。如果在写入操作结束前就调度了**read()**操作呢?就会产生数据不完整的状态。这样的bug非常难以找到。但是,怎样来处理这个问题呢?
|
||||
|
||||
基本上,我们需要确保在写方法返回前没有**read**方法能被执行。如果你曾经编写过一个多线程的应用程序,你可能见过同步原语(锁),如互斥锁或者信号。Linux也有这些,但有些细微的差别。内核代码可以运行进程上下文(用户空间代码的“代表”工作,就像我们使用的方法)和终端上下文(例如,一个IRQ处理线程)。如果你已经在进程上下文中和并且你已经得到了所需的锁,你只需要简单地睡眠和重试直到成功为止。在中断上下文时你不能处于休眠状态,因此代码会在一个循环中运行直到锁可用。关联原语被称为自旋锁,但在我们的环境中,一个简单的互斥锁 —— 在特定时间内只有唯一一个进程能“占有”的对象 —— 就足够了。处于性能方面的考虑,现实的代码可能也会使用读-写信号。
|
||||
|
||||
锁总是保护某些数据(在我们的环境中,是一个“struct buffer”实例),而且也常常会把它们嵌入到它们所保护的结构体中。因此,我们添加一个互斥锁(‘struct mutex lock’)到“struct buffer”中。我们也必须用**mutex\_init()**来初始化互斥锁;**buffer\_alloc**是用来处理这件事的好地方。使用互斥锁的代码也必须包含**linux/mutex.h**。
|
||||
|
||||
互斥锁很像交通信号灯 —— 要是司机不看它和不听它的,它就没什么用。因此,在对缓冲区做操作并在操作完成时释放它之前,我们需要更新**reverse\_read()**和**reverse\_write()**来获取互斥锁。让我们来看看**read**方法 —— **write**的工作原理相同:
|
||||
|
||||
static ssize_t reverse_read(struct file *file, char __user * out,
|
||||
size_t size, loff_t * off)
|
||||
{
|
||||
struct buffer *buf = file->private_data;
|
||||
ssize_t result;
|
||||
if (mutex_lock_interruptible(&buf->lock)) {
|
||||
result = -ERESTARTSYS;
|
||||
goto out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
我们在函数一开始就获取锁。**mutex\_lock\_interruptible()**要么得到互斥锁然后返回,要么让进程睡眠,直到有可用的互斥锁。就像前面一样,**\_interruptible**后缀意味着睡眠可以由信号来中断。
|
||||
|
||||
while (buf->read_ptr == buf->end) {
|
||||
mutex_unlock(&buf->lock);
|
||||
/* ... wait_event_interruptible() here ... */
|
||||
if (mutex_lock_interruptible(&buf->lock)) {
|
||||
result = -ERESTARTSYS;
|
||||
goto out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
下面是我们的“等待数据”循环。当获取互斥锁时,或者发生称之为“死锁”的情境时,不应该让进程睡眠。因此,如果没有数据,我们释放互斥锁并调用**wait\_event\_interruptible()**。当它返回时,我们重新获取互斥锁并像往常一样继续:
|
||||
|
||||
if (copy_to_user(out, buf->read_ptr, size)) {
|
||||
result = -EFAULT;
|
||||
goto out_unlock;
|
||||
}
|
||||
...
|
||||
out_unlock:
|
||||
mutex_unlock(&buf->lock);
|
||||
out:
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
|
||||
最后,当函数结束,或者在互斥锁被获取过程中发生错误时,互斥锁被解锁。重新编译模块(别忘了重新加载),然后再次进行测试。现在你应该没发现毁坏的数据了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 接下来是什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在你已经尝试了一次内核黑客。我们刚刚为你揭开了这个话题的外衣,里面还有更多东西供你探索。我们的第一个模块有意识地写得简单一点,在从中学到的概念在更复杂的环境中也一样。并发、方法表、注册回调函数、使进程睡眠以及唤醒进程,这些都是内核黑客们耳熟能详的东西,而现在你已经看过了它们的运作。或许某天,你的内核代码也将被加入到主线Linux源代码树中 —— 如果真这样,请联系我们!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/be-a-kernel-hacker/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) [disylee](https://github.com/disylee) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.libusb.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://fuse.sf.net/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/be-a-kernel-hacker/www.netfilter.org/projects/libnetfilter_queue
|
||||
[4]:http://lxr.free-electrons.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
在linux桌面上观看2014年巴西世界杯比赛!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
足球是世界上受众最广和观众最多的运动,现代足球起源于英国。足球运动员平均每场比赛要跑6个多英里。上届南非世界杯有近10亿的电视观众,而今年的的观赛数量预计还要增加。
|
||||
|
||||
2014年第20界世界杯在巴西举行,时间安排为从6月12号开始持续到7月13号,共有32个国家参加这项赛事。
|
||||
|
||||
爱足球的小伙子们,我们将要介绍一款可以提供最新的赛况以及你喜欢的球队的进球数信息的应用程序,它叫做“icup 2014 Brazil”。下面让我们介绍它的特点,用法和安装等。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*iCup 2014 Brazil*
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是“icup 2014 Brazil” ###
|
||||
|
||||
“icup 2014 Brazil”简单的说是一个应用程序,在linux桌面为你提供2014年世界杯的最新比赛赛况。
|
||||
|
||||
### “icup 2014 Brazil”的特点###
|
||||
|
||||
- 自适应的用户界面,比如自动缩放
|
||||
- 迅速查看战绩
|
||||
- 支持Facebook、twitter和Google+社交分享功能
|
||||
- 支持Retina显示输出
|
||||
- 实时跟踪比赛结果
|
||||
- 包括32个国家的国歌小工具配合露天广场效果很不错
|
||||
- 内置日历和时区工具,实时的显示当天数据,图像化展示最新的战况和得分
|
||||
- 支持代理
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 平台和框架支持 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这款软件可以运行在Mac、windows和linux上,特别提醒,在Linux上,它是为x86的CPU设计的,虽然它也可以在x64的平台上安装,不过我们需要做一下设置。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在不同平台的技术规范 ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 实时结果,日历,数据分组,第二阶段整合,社交网络连接和多语言支持,这些支持全平台
|
||||
- Retina显示支持,这个不支持windows和linux,仅支持Mac OS
|
||||
- 详细的统计-支持linux。在windows和Mac需要捐赠才行
|
||||
- 声音小工具-支持MAC和linux,windows不确定
|
||||
|
||||
**重要**: 上面的特点都支持,一些具体的特性除了linux外都不是免费提供的,这是为了支付服务器和带宽费用。对于linux用户来说,任何细节不需要关心,高兴的用去吧。
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux下安装“icup 2014 Brazil” ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先去[“icup 2014 Brazil”官方下载页面][1]下载你电脑平台的软件版本
|
||||
|
||||
#### 32位下的安装步骤 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# cd Downloads/
|
||||
# tar xvf iCup_2014_FREE-Brazil_1.1_linux.tar.bz2
|
||||
# cd iCup\ 2014\ FREE\ -\ Brazil\ 1.1/
|
||||
# chmod 755 iCup\ 2014\ FREE\ -\ Brazil
|
||||
|
||||
如上文所说,这个应用程序只为X86架构设计,为了在64位架构下安装32位的软件,我们需要在系统上安装一些软件包:**GTK+2**和**libstdc++.so.6**。
|
||||
|
||||
不只是这款软件,一大堆Linux下的软件不支持64位架构,例如**Skype**,我们也需要这样调整我们的系统来安装这些软件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在64位系统下 ####
|
||||
|
||||
安装**GTK+2**和**libstdc++so.6**,用如下apt或者yum命令
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install libgtk2.0-0 libstdc++6 [在基于Debian系统上执行这个命令]
|
||||
|
||||
如果有报错的话,运行下面的命令来解决
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -f install
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install gtk2 libstdc++ [在基于Redhat系统上执行这个命令]
|
||||
|
||||
需要的软件包安装完后,就可以在64位系统下安装32位的软件了,进入你的下载目录,找到“**icup 2014 Brazil**”安装包然后执行下面的命令
|
||||
|
||||
# cd Downloads/
|
||||
# tar xvf iCup_2014_FREE-Brazil_1.1_linux.tar.bz2
|
||||
# cd iCup\ 2014\ FREE\ -\ Brazil\ 1.1/
|
||||
# chmod 755 iCup\ 2014\ FREE\ -\ Brazil
|
||||
|
||||
然后,进入软件所在目录,双击可执行文件启动软件。下面的截屏图中看不到所有的信息,**因为本文写作时2014年世界杯现在还没开始呢,开始后我们就能看到结果了**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
iCup Brazil 2014
|
||||
|
||||
无具体信息,世界杯尚未开始。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Match Detailed Information
|
||||
|
||||
分组和队伍
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Groups and Teams
|
||||
|
||||
第二阶段详细信息
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2nd stage Detailed Information
|
||||
|
||||
比赛细节,尚未完整
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Match Summary
|
||||
|
||||
集成语言切换和社交分享按钮
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Language Change
|
||||
|
||||
Linux上捐赠是可选的,你可以贡献你的心意。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Donation
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
上面的这个软件有望成为足球粉丝的一大福利,赶快在线试用吧。
|
||||
|
||||
好了,我马上又有一个有趣的文章了。请保持关注Tecmint.com。请在评论区对我们的工作给予反馈。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/view-fifa-world-cup-matche-results/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[jiajia9linuxer](https://github.com/jiajia9linuxer) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.e-link.it/icup/brazil2014/icup-brazil-2014-desktop-app.php
|
||||
@ -1,26 +1,25 @@
|
||||
如何使用ffmpeg从视频中提取图片(有些专业词汇不太懂可能翻译错了,各位校译幸苦了)
|
||||
如何使用ffmpeg从视频中提取图片
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
嗨,unixmen的读者们,
|
||||
|
||||
你曾想过从一个视频文件中提取图片吗?在Linux中做这件事是有可能的,教程中我将使用ffmpeg来从视频中获取图片。
|
||||
你曾想过从一个视频文件中提取图片吗?在Linux下就可以,在这个教程中我将使用ffmpeg来从视频中获取图片。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是ffmpeg?What is ffmpeg? ###
|
||||
|
||||
ffmpeg是一个非常有用的命令行程序,它可以用来转码媒体文件。它是FFmpeg领先的多媒体框架的一部分,其有很多功能,比如解码、编码、转码、混流、分离、转化为流、过滤以及播放几乎所有的的由人和机器创建的媒体文件。
|
||||
ffmpeg是一个非常有用的命令行程序,它可以用来转码媒体文件。它是领先的多媒体框架FFmpeg的一部分,其有很多功能,比如解码、编码、转码、混流、分离、转化为流、过滤以及播放几乎所有的由人和机器创建的媒体文件。
|
||||
|
||||
框架中包含有很多不同的工具,其中每一个都有特定的功能。例如,ffserver能够将多媒体文件转化为用于实时广播的流,ffprobe用于分析多媒体流,ffplay可以当作一个简易的媒体播放器,**ffmpeg**能够转换多媒体文件格式。
|
||||
在这个框架中包含有各种工具,每一个用于完成特定的功能。例如,ffserver能够将多媒体文件转化为用于实时广播的流,ffprobe用于分析多媒体流,ffplay可以当作一个简易的媒体播放器,**ffmpeg**则能够转换多媒体文件格式。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你感兴趣,以下是包括在FFmpeg框架中的开发者库:
|
||||
如果你感兴趣,以下列出的是FFmpeg框架中包含的开发者库:
|
||||
|
||||
- libavutil是一个包含简化编程功能的库,其中包括随机数生成器,数据结构,数学代码,核心多媒体工具等更多东西。
|
||||
- libavcodec是一个包含音频/视频解码器和编码器的库。
|
||||
- libavformat是一个包含了多媒体格式的解析器和产生器的库。
|
||||
- libavdevice是一个包含输入输出设备的库,用于捕捉和渲染很多公共多媒体输入/输出软件框架,包括Video4Linux,Video4Linux2,VfW和ALSA。
|
||||
- libavformat是一个包含了多媒体格式的分离器和混流器的库。
|
||||
- libavdevice是一个包含输入输出设备的库,用于捕捉和渲染很多来自常用的多媒体输入/输出软件框架的数据,包括Video4Linux,Video4Linux2,VfW和ALSA。
|
||||
- libavfilter是一个包含媒体过滤器的库。
|
||||
- libswscale是一个用于执行高度优化的图像缩放和颜色空间/像素格式转换操作的库。
|
||||
- libswresample是一个用于执行高度优化的音频重采样,重新矩阵和样本格式转换操作的库。
|
||||
- libswresample是一个用于执行高度优化的音频重采样,重新矩阵和取样格式转换操作的库。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:ffmpeg和FFmpeg并不一样。FFmpeg是一个框架而ffmpeg是一个FFmpeg中的一个功能。
|
||||
**注意**:ffmpeg和FFmpeg不是同一个东西。FFmpeg是框架,而ffmpeg是一个其中的一个功能。
|
||||
|
||||
### 开始行动 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,9 +56,9 @@ Fedora用户可以从源中直接安装ffmpeg。
|
||||
|
||||
之后我使用以下命令从视频中提取图片。
|
||||
|
||||
ffmpeg -i "Тимати - Рентген ( Альбом '13')-C9Plztvv8ac.mp4" -r 1 -q:v 2 -f image2 image-3%d.jpeg
|
||||
ffmpeg -i "你是我的小呀小苹果儿.mp4" -r 1 -q:v 2 -f image2 image-3%d.jpeg
|
||||
|
||||
**-i**选项用来获取输入文件,在这里是视频文件名**Тимати – Рентген ( Альбом ’13′)-C9Plztvv8ac.mp4**,-r选项设置每秒提取图片的帧数。我想要每秒提取一帧。
|
||||
**-i**选项用来获取输入文件,在这里是视频文件名**你是我的小呀小苹果儿.mp4**,-r选项设置每秒提取图片的帧数。我想要每秒提取一帧。
|
||||
|
||||
之后有一个重要的选项是-q:v,应该留意这个选项并且我很喜欢用它,它用来设置提取到的图片质量。我总是设置值为2来从视频中获取高质量图片。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -67,6 +66,6 @@ Fedora用户可以从源中直接安装ffmpeg。
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/extract-images-videos-using-ffmpeg/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[linuhap](https://github.com/linuhap) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[linuhap](https://github.com/linuhap) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
33
published/20140607 How To Install iCup 2014 In Linux.md
Normal file
33
published/20140607 How To Install iCup 2014 In Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
在Linux上用iCup追世界杯
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
嗨,Linux 极客们,
|
||||
|
||||
在本文简短的叙述中,我将教您如何在Linux中安装一个非常棒的2014FIFA世界杯APP。这个应用叫iCup,支持Windows,Mac以及伟大的Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
我看足球比赛已经有很长的时间了,所以我得在我的电脑上装个这样的应用来保持更新2014世界杯的最新情况。我可不想在我朋友们面前看起来像一无所知的笨货。iCup应用正好提供了每一场赛程、比分、球队教练组等信息。更有提供实时比赛更新,给您提供 正在进行的比赛的最新数据。
|
||||
|
||||
### 支持以下功能: ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 30种语言支持,完全本地化(使用语言菜单选择)
|
||||
- 独家的灵活界面可随意调整窗口大小
|
||||
- 可按日期或阶段检索比赛日历
|
||||
- 可视化分组
|
||||
- 支持自动转变比赛时间来适应本地时间和格式
|
||||
- 一键化社交网络发表比赛评论(支持Facebook,Google+和Twitter)
|
||||
- 支持代理(支持基本认证和摘要认证方法)
|
||||
|
||||
我已经在Ubuntu12.04LTS上用过而且真的很好用!目前为止,这款软件还没有出错或者崩溃过。通过[官方网站][1]您可以下载到压缩包并且十分轻松地安装这个很棒的应用,然后您可以解压到任何您喜欢的地方。解压完成后,双击iCup 2014 FREE- Brazil运行。
|
||||
|
||||
iCup真心好用,我希望您也能用其享受世界杯!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-icup-2014-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic020](http://www.vicyu.net) 校对:[213edu](http://ryanhu.me/)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.e-link.it/icup/brazil2014/icup-brazil-2014-desktop-app.php
|
||||
@ -2,11 +2,12 @@ Linux:使用bash删除目录中的特定文件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我是一个Linux新手用户。现在我需要清理一个下载目录中的文件,其实我就是想删除~/Download/文件夹下面除了以下格式的文件外所以其它文件:
|
||||
*.iso - 所有的iso格式的文件。
|
||||
*.zip - 所有zip格式的文件。
|
||||
我是一名Linux新用户。现在我需要清理一个下载目录中的文件,其实我就是想从~/Download/文件夹删去除了以下格式的文件外所以其它文件:
|
||||
|
||||
我如何在一个基于Linux,OS X 或者Unix-like系统上的bash shell中删除特定的文件呢?
|
||||
- *.iso - 所有的iso格式的文件。
|
||||
- *.zip - 所有zip格式的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
我如何在一个基于Linux,OS X 或者 Unix-like 系统上的bash shell中删除特定的文件呢?
|
||||
|
||||
Bash shell 支持丰富的文件模式匹配符例如:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,13 +19,15 @@ Bash shell 支持丰富的文件模式匹配符例如:
|
||||
|
||||
这里你需要用系统内置的shopt命令来开启shell中的extglob选项,然后你就可以使用扩展的模式符了,这些模式匹配符如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. ?(pattern-list) - 匹配零次或一次给定的模式。
|
||||
1. *(pattern-list) -至少匹配零次给定的模式。
|
||||
1. +(pattern-list) - 至少匹配一次给定的模式。
|
||||
1. @(pattern-list) - 匹配一次给定的模式。
|
||||
1. !(pattern-list) - 匹配所有除给定模式以外的模式。
|
||||
1. ?(模式列表) - 匹配零次或一次给定的模式。
|
||||
1. *(模式列表) - 匹配零次或多次给定的模式。
|
||||
1. +(模式列表) - 至少匹配一次给定的模式。
|
||||
1. @(模式列表) - 匹配一次给定的模式。
|
||||
1. !(模式列表) - 不匹配给定模式。
|
||||
|
||||
一个模式列表就是一个或多个用 | 分开的模式(文件名)。首先打开extgolb选项:
|
||||
一个模式列表就是一个或多个用 | 分开的模式(文件名)。
|
||||
|
||||
首先要打开extgolb选项:
|
||||
|
||||
shopt -s extglob
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,20 +50,21 @@ rm 命令的语法格式为:
|
||||
## 你也可以使用完整的目录 ##
|
||||
rm /Users/vivek/!(*.zip|*.iso|*.mp3)
|
||||
|
||||
## 传递参数 ##
|
||||
rm [options] !(*.zip|*.iso)
|
||||
## 也可以传递参数 ##
|
||||
rm [选项] !(*.zip|*.iso)
|
||||
rm -v !(*.zip|*.iso)
|
||||
rm -f !(*.zip|*.iso)
|
||||
rm -v -i !(*.php)
|
||||
|
||||
最后,关闭 extglob 选项:
|
||||
最后,关闭 extglob 选项方法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
shopt -u extglob
|
||||
|
||||
### 策略 #2: 使用bash的 GLOBIGNORE 变量删除指定文件以外的所有文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
摘自 [bash(1)][1] 手册页:
|
||||
> 一个用冒号分开的模式列表定义了被路径扩展忽略的文件的集合。如果一个文件同时与路径扩展模式和GLOBIGNORE中的模式匹配,那么它就从匹配列表中移除了。
|
||||
|
||||
> 这是一个用冒号分开的模式列表,通过路径展开方式定义了要忽略的文件集合。如果一个匹配到路径展开模式的文件也匹配GLOBIGNORE中的模式,那么它会从匹配列表中移除。
|
||||
|
||||
要删除所有文件只保留 zip 和 iso 文件,应如下设置 GLOBIGNORE:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,16 +79,16 @@ rm 命令的语法格式为:
|
||||
|
||||
如果你正在使用 tcsh/csh/sh/ksh 或者其它shell,你可以在Unix-like系统上试着用下面find命令的语法格式来删除文件:
|
||||
|
||||
find /dir/ -type f -not -name 'PATTERN' -delete
|
||||
find /dir/ -type f -not -name '匹配模式' -delete
|
||||
|
||||
或者
|
||||
|
||||
## 对于怪异的文件名可以使用 xargs ##
|
||||
find /dir/ -type f -not -name 'PATTERN' -print0 | xargs -0 -I {} rm {}
|
||||
find /dir/ -type f -not -name 'PATTERN' -print0 | xargs -0 -I {} rm [options] {}
|
||||
find /dir/ -type f -not -name '匹配模式' -print0 | xargs -0 -I {} rm {}
|
||||
find /dir/ -type f -not -name '匹配模式' -print0 | xargs -0 -I {} rm [选项] {}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
为了删除 ~/source 目录下除 php 以外的文件,键入:
|
||||
想要删除 ~/source 目录下除 php 以外的文件,键入:
|
||||
|
||||
find ~/sources/ -type f -not -name '*.php' -delete
|
||||
|
||||
@ -103,9 +107,9 @@ rm 命令的语法格式为:
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/linux-bash-delete-all-files-in-directory-except-few/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Linchenguang](https://github.com/Linchenguang) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[Linchenguang](https://github.com/Linchenguang) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man1/bash.1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man1/find.1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.manpager.com/linux/man1/find.1.html
|
||||
@ -1,28 +1,30 @@
|
||||
Linux下的在线云音乐播放器 —— Nuvola Player 2.4.0发布
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Nuvola Player**是一个开源的播放器,在它自身的web界面中运行像Amazon云播放器,Bandcamp,Deezer,8tracks,Google Play音乐,Grooveshark,Hyper Machine以及Pandora等等云音乐服务,同时它也能整合到Linux桌面中。
|
||||
**Nuvola Player**是一个开源的播放器,可以在其web界面中运行像Amazon云播放器,Bandcamp,Deezer,8tracks,Google Play音乐,Grooveshark,Hyper Machine以及Pandora等等云音乐服务,同时它也能整合到Linux桌面中。
|
||||
|
||||
该应用程序以插件的形式提供了大量的功能特性,像桌面通知、系统托盘、多媒体键、媒体播放器小程序、停靠栏菜单、歌词、last.fm等等。
|
||||
|
||||
**2014年5月31日**,**Nuvola Player 2.4.0**的一个新版本发布了 —— 它带来了一些新的特性,包括两个新的服务罗技媒体服务器和这是我的果酱,以及众多的bug修复。
|
||||
**2014年5月31日**,**Nuvola Player 2.4.0**的一个新版本发布了 —— 它带来了一些新的特性,包括两个新的服务“Logitech Media Server”和“This is My Jam ”,以及众多的bug修复。
|
||||
|
||||
### 这个发布中有什么新东西 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 删除了破损的隐藏Google+按钮选项,因为Google修改代码过于频繁。
|
||||
- 删除了破损的隐藏Google+按钮选项,因为Google修改代码过于频繁了。
|
||||
- 加快了服务设置的启用速度,不需要再重新加载。
|
||||
- 修复了暂停和播放/暂停动作开关。
|
||||
- 为Chrome添加了兼容问题警告桌面通知。
|
||||
- 提供了页面内导航按钮(现在用户可以在Google Play标识旁边的顶部栏中找到它)。
|
||||
- 添加了罗技媒体服务器和这是我的果酱服务。
|
||||
- 添加了“Logitech Media Server”和“This is My Jam ”服务。
|
||||
- 包含了对鼠标后退/前进按钮的支持。
|
||||
- 修复了对GNOME锁屏通知的支持。
|
||||
|
||||
要查看完整的特性列表,请访问官方发行[声明页面][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Debian, Ubuntu和Linux Mint中安装Nuvola Player ###
|
||||
## 在Debian, Ubuntu和Linux Mint中安装Nuvola Player ##
|
||||
|
||||
官方的Nuvola Player仓库中包含了**Ubuntu 14.04, 13.10, 12.10, 12.04**以及**Linux Mint 17, 16, 15, 14.**可用的二进制包,你可以通过添加Nuvola Player仓库到你的系统中来安装二进制包‘nuvolaplayer’。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu和Linux Mint上 ####
|
||||
### 在Ubuntu和Linux Mint上 ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开终端并运行以下一系列命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:nuvola-player-builders/stable
|
||||
@ -36,7 +38,8 @@ Linux下的在线云音乐播放器 —— Nuvola Player 2.4.0发布
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get --no-install-recommends install nuvolaplayer
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Debian上 ####
|
||||
### 在Debian上 ###
|
||||
|
||||
对于**Debian Wheezy**和**Debian Sid**,可以从官方仓库中获取稳定的Nuvola Player二进制包。你可以使用下面这一堆命令来安装最新的稳定版。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,打开终端并导入公钥,然后添加仓库到‘**sources.list**‘文件,接着像下面这样进行一次系统更新来安装nuvolaplayer。
|
||||
@ -97,7 +100,7 @@ Rdio音乐服务
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-nuvola-player-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 写一个shell脚本来得到当前的日期,时间,用户名和当前工作目录。 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : 将输出用户名,当前日期和时间,以及当前工作目录的命令就是logname,date,who i am和pwd。
|
||||
> **答案** : 输出用户名,当前日期和时间,以及当前工作目录的命令就是logname,date,who i am和pwd。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,创建一个名为**`userstats.sh`**文件,将下面的代码添加到它。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@
|
||||
echo "User is `who i am`"
|
||||
echo "Current directory `pwd`"
|
||||
|
||||
给他添加执行权限,并且执行他。
|
||||
给它添加执行权限,并且执行他。
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod 755 userstats.sh
|
||||
# ./userstats.sh
|
||||
@ -34,10 +34,9 @@
|
||||
User is avi pts/0 2014-06-07 11:59 (:0)
|
||||
Current directory /home/avi/Desktop
|
||||
|
||||
### 2.写一个shell脚本,进行两个数字的相加,如果没有输入参数就输出错误信息和使用说明的###
|
||||
### 2.写一个shell脚本,进行两个数字的相加,如果没有输入参数就输出错误信息和一行使用说明###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** :
|
||||
下面是简单的shell脚本以及描述,如果没有命令行参数,它会抛出错误与如何使用脚本的说明。
|
||||
> **答案** : 下面是简单的shell脚本以及描述,如果没有命令行参数,它会抛出错误与如何使用脚本的说明。
|
||||
|
||||
再创建一个名为**`twonumbers.sh`**文件和下面的内容添加到文件里。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -70,24 +69,24 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod 755 two-numbers.sh
|
||||
|
||||
**Condition 1**: 未输入两个数字作为命令行参数运行脚本,你将得到下面的输出。
|
||||
**情形一**: 未输入两个数字作为命令行参数运行脚本,你将得到下面的输出。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sample Output ####
|
||||
#### 样例输出 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# ./two-numbers.sh
|
||||
|
||||
Usage - ./two-numbers.sh x y
|
||||
Where x and y are two nos for which I will print sum
|
||||
|
||||
**Condition 2**: 当数字存在时,你会得到如图所示的结果。
|
||||
**情形二**: 当数字存在时,你会得到如图所示的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./two-numbers.sh 4 5
|
||||
|
||||
Sum of 4 and 5 is 9
|
||||
|
||||
因此,上述shell脚本满足条件作为问题提出了建议。
|
||||
因此,上述shell脚本满足了问题的要求。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.你需要打印一个给定的数字的反序,如输入10572,输出27501,如果没有输入数据,应该抛出错误和使用脚本说明。在此之前,告诉我,你需要在这里使用的算法。 ###
|
||||
### 3.你需要打印一个给定的数字的反序,如输入10572,输出27501,如果没有输入数据,应该抛出错误和使用脚本说明。在此之前,告诉我你需要在这里使用的算法。 ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 算法 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -95,7 +94,7 @@
|
||||
2. 赋值 rev=0, sd=0 (反向和单个数字设置为0)
|
||||
3. n % 10, 将得到最左边的数字
|
||||
4. 反向数字可以用这个方法生成 rev * 10 + sd
|
||||
5. 对输入数字进行-1操作
|
||||
5. 对输入数字进行右位移操作(除以10)
|
||||
6. 如果n > 0, 进入第三步,否则进行第七步
|
||||
7. 输出rev
|
||||
|
||||
@ -126,9 +125,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod 755 numbers.h
|
||||
|
||||
**Condition 1**: 当输入不包含命令行参数,你将得到下面的输出。
|
||||
**情形一**: 当输入不包含命令行参数,你将得到下面的输出。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Sample Output ####
|
||||
#### 样例输出 ####
|
||||
|
||||
./numbers.sh
|
||||
|
||||
@ -136,7 +135,7 @@
|
||||
I will find reverse of given number
|
||||
For eg. ./2.sh 123, I will print 321
|
||||
|
||||
**Condition 2**: 正常输入
|
||||
**情形二**: 正常输入
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./numbers.sh 10572
|
||||
|
||||
@ -146,9 +145,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 你应该直接用终端,而不是依靠任何shell脚本来进行实数计算。你会怎么做(比如实数7.56+2.453)? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** :
|
||||
|
||||
我们需要用如下所述的特殊方式使用bc命令。将7.56+2.453作为输入通过管道进入bc中。
|
||||
> **答案** : 我们需要用如下所述的特殊方式使用bc命令。将7.56+2.453作为输入通过管道进入bc中。
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo 7.56 + 2.453 | bc
|
||||
|
||||
@ -156,13 +153,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 你需要给出圆周率的值,精度为小数点后100位,什么是最简单的方法。 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : 找圆周率的值最简单的方法,我们只是需要发出以下命令。
|
||||
> **答案** : 找圆周率的值最简单的方法,我们只是需要发出以下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# pi 100
|
||||
|
||||
3.141592653589793238462643383279502884197169399375105820974944592307816406286208998628034825342117067
|
||||
|
||||
很明显!安装我们必须有包**`pi`**。只是一个**apt**或**yum**命令,就能获得所需的软件包,同时用最简单方法来实现这个需求。
|
||||
很明显!安装我们必须有包**`pi`**。只用一个**apt**或**yum**命令,就能获得所需的软件包,同时用最简单方法来实现这个需求。
|
||||
|
||||
就是这样。我会很快在Tecmint.com发表另一个有趣的文章。至此敬请关注。别忘了向我们提供您在的评论和反馈。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -170,7 +167,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/practical-interview-questions-on-linux-shell-scripting/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[MikeCoder](https://github.com/MikeCoder) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[MikeCoder](https://github.com/MikeCoder) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,7 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux中知道你的系统是否有USB 3.0 端口[快速技巧]
|
||||
[小白技巧]如何在Linux中知道你的系统是否有USB 3.0 端口
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Most of the new computers come with USB 3.0 ports these days. But **how can you know if your computer has USB 3.0 port** or not? In this quick tip, we shall see how to find if your system has USB 3 or USB 2 in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
近来的大多数的新计算机都有了USB 3.0接口了。但是**你怎么知道你的计算机有没有USB 3.0接口**?这篇短文中,我们会告诉如何在Linux下知道你的系统上有USB 3还是USB3接口。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux终端中检测是否有USB 3.0 端口 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +17,7 @@ Most of the new computers come with USB 3.0 ports these days. But **how can you
|
||||
|
||||
### 辨别哪个口是USB 3.0 ###
|
||||
|
||||
通常USB 3.0 口被标记为SS(“Super Speed”的缩写)。如果你的系统制造商没有标记SS或者USB 3,那么你可以检查端口的内部通常是颜色的。
|
||||
通常USB 3.0 口被标记为SS(“Super Speed”的缩写)。如果你的系统制造商没有标记SS或者USB 3,那么你可以检查端口的内部通常是蓝色的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,6 +27,6 @@ Most of the new computers come with USB 3.0 ports these days. But **how can you
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/find-usb-3-port-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ LDAP(轻量级目录访问协议)是一个用于访问目录服务的应用
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20140607022012848/LDAPSolutions.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,118 @@
|
||||
怎样使用linux的iptables工具进行网络共享
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我将解释多个设备怎样在linux下共享一个网络连接。目前无线路由器已经成为主流的消费品,从而解决了本文这一问题。这里假设你家中并没有一台无线路由器,不过,你却有一台已经有"猫"和有线网卡的的linux主机。"猫"是以动态公有IP地址的模式连接到互联网,主机的网卡连接到你的交换机或者集线器。其他设备(如linux或者windows的PC或者笔记本)以网桥的形式连接,并且没有连接到互联网。为了共享linux主机的互联网,你必须把主机转换成网关,以便它能实现从其他设备中传送和接受信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 术语字汇 ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- **私有IP地址**(路由不可达地址)是一个被用于本地局域网的IP地址(在互联网中不可见)。
|
||||
- **公用IP地址**(路由可达地址)是一个在互联网中可见的IP地址。
|
||||
- **IP伪装**是一项允许一系列机器通过MASQ网关连接互联网的功能。这些MASQ网关之外的机器在互联网中是不可见的。MASQ之后的机器中任何流入或流出的数据必须经过MASQ网关。
|
||||
- **网络地址转换**(NAT)是一项通过IP伪装技术可以使私有IP地址访问互联网的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
### Hardware Requirements ###
|
||||
|
||||
硬件要求
|
||||
|
||||
- 一台有两个接口(一个公有IP地址和其他的私有IP地址)的linux主机,这个主机将被用作网关。
|
||||
- 一台或者多台拥有私有IP地址的linux/windows系统的PC或者笔记本。
|
||||
- 交换机/集线器(可选)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 教程步骤 ###
|
||||
|
||||
接下来的过程需要在linux主机(用于共享的网关)上完成。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1、激活IP转发 ####
|
||||
|
||||
为了设置网络共享,你需要在linux主机上更改一个内核参数来使能IP转发功能。内核启动参数设定在/etc/sysctl.conf文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
打开这个文件,定位到含有"# net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0"的这一行,移除#号(即取消注释),然后将其值设置为1,改好之后应该和下面的一致。
|
||||
|
||||
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
|
||||
|
||||
你还要使激活IP转发功能生效,通过执行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
|
||||
$ sudo sysctl -p
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2、NAT配置 ####
|
||||
|
||||
另一个网络共享的重要部分是NAT配置,这可以通过使用iptables的命令,iptables包含四个防火墙的规则表:
|
||||
|
||||
- FILTER (默认表格)
|
||||
- NAT
|
||||
- MANGLE
|
||||
- RAW
|
||||
|
||||
这个教程中我们将仅使用两个表格:FILTER和NAT表格。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,刷新所有活跃的防火墙的规则。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -X
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -F
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -t nat -X
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -t nat -F
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在输入表格中,你需要设置转发链(FORWARD)成可接受的(ACCEPT)目的地,因此所有通过主机的数据包将会被正确的处理。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -I INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -I FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在NAT表中,你必须为你的WAN口启用IP伪装功能,我们假设WAN口协议是ppp0。为了在ppp0接口上使能IP伪造技术,我们使用以下的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3、配置私有IP地址 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在linux主机上的所有配置完成后,你需要配置其他设备(linux/windows的PC或笔记本)的DNS服务器以及默认网关,让它们的数据流可以指向linux主机。注意你不需要在linux主机上设置一个DNS服务器,从其他设备发出的每一个DNS请求都会通过上游的ISP自动转发到linux主机上。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的其他设备上用的系统是linux,你可以通过以下命令来更改他们的默认网关和DNS服务器。假设你的网段是192.168.1.0/24的私有IP地址网段,linux主机上绑定的IP地址是192.168.1.1。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ip route del default
|
||||
$ sudo ip route add default via 192.168.1.1
|
||||
$ sudo sh -c "echo 'nameserver 192.168.1.1' > /etc/resolv.conf"
|
||||
|
||||
如果还有其他的linux设备,那么你可以重复以上命令。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有windows设备,你可以通过控制面板的网络连接属性来更改默认网关和DNS服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4、完整的脚本 ####
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个在linux主机上设置网络连接共享的一个完整的脚本。WAN口(ppp0协议)需要根据你具体的网络接口协议来替换。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /usr/local/bin/ishare
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
## Internet connection shating script
|
||||
|
||||
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
|
||||
sysctl -p
|
||||
iptables -X
|
||||
iptables -F
|
||||
iptables -t nat -X
|
||||
iptables -t nat -F
|
||||
iptables -I INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
iptables -I FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE
|
||||
|
||||
保存以上的脚本到/usr/local/bin/ishare,然后添加可执行权限通过执行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo chmox +x /usr/local/bin/ishare
|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要这个脚本开机启动,你需要在/etc/rc.local文件中执行这个脚本,并在该文件中的"exit 0"之前添加下面一行。
|
||||
|
||||
/usr/local/bin/ishare
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/internet-connection-sharing-iptables-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[yujianxuechuan](https://github.com/yujianxuechuan) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,14 +1,14 @@
|
||||
Linux 平台七大桌面环境
|
||||
Linux 平台七大桌面环境通览
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
通常的 Linux 发行版都使用 KDE 或者 GNOME 作为默认的桌面环境。它们都给用户提供了一个原始的并且有吸引力的桌面,并且内置了各式各样的多媒体软件、系统程序、游戏、实用程序、网页开发工具、编程工具等等。这两个桌面致力于提供给用户一个拥有类似于 Windows 操作系统体验的尖端计算环境,而忽略了最小化它们所占用的系统资源。
|
||||
通常的 Linux 发行版都使用 KDE 或者 GNOME 作为默认的桌面环境。它们都给用户提供了一个原始的并且有吸引力的桌面,并且内置了各式各样的多媒体软件、系统程序、游戏、实用程序、网页开发工具、编程工具等等。这两个桌面致力于提供给用户一个拥有类似于 Windows 操作系统体验的尖端计算环境,而不是如何更少的占用系统资源。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你正在使用 Ubuntu (或者其他Linux发行版) 并且厌倦始终使用 Unity 桌面,那么你应该看看这些可以替代 Unity 的选择。我收集了 7 种桌面环境。它们都很棒。在你读完这篇文章之后,请试着使用它们吧。
|
||||
如果你正在使用 Ubuntu (或者其他Linux发行版) 并且厌倦了始终使用 Unity 桌面,那么你应该看看这些可以替代 Unity 的选择。我收集了 7 种桌面环境。它们都很棒。在你读完这篇文章之后,请试着使用它们吧。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Mate][1] ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
MATE 是 GNOME2 的一个分支。它提供了一个自然且吸引人的桌面环境。它是 Linux 和其它类 Unix 工作环境中的传统工作框架的代表。MATE 正在改善以使用新的技术来保留传统的桌面体验。
|
||||
MATE 是 GNOME2 的一个分支。它提供了一个自然且吸引人的桌面环境。它是 Linux 和其它类 Unix 工作环境中的传统工作框架的代表。MATE 在保留传统的桌面体验的同时正在不断进步使用新的技术。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 14.04 中,可以直接从 Ubuntu 软件中心获取 MATE 桌面。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,25 +16,25 @@ MATE 是 GNOME2 的一个分支。它提供了一个自然且吸引人的桌面
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
KDE 是另一个类似于 GNOME 一样的重量级桌面环境。它在本文章所提及的7种桌面环境中被认为是最华丽最重量级的一个。它同样是一个类似于 Windows 的桌面,在这一点上没有什么特殊的变化。不过 KDE 非常有特点,但是随之而来的是大量的设置来提升你的桌面体验。同样的,有很多关于 KDE 的话题。所以真的可以从 KDE 的特点中获益,并且保持你所想的外观。
|
||||
KDE 是另一个类似于 GNOME 一样的重量级桌面环境。它在本文章所提及的7种桌面环境中被认为是最华丽最重量级的一个。它同样是一个类似于 Windows 的桌面,在这一点上没有什么特殊的变化。不过 KDE 非常有特点,但是随之而来的是可以通过大量的设置来提升你的桌面体验。同样的,有很多关于 KDE 的话题,所以你可以很舒服的使用 KDE,并让它以你希望的方式工作。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Cinnamon][3] ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon 是一个基于 Gtk+ 的环境。它最初作为 GNOME Shell 的一个用户界面分支,由 Linux Mint 创造。 Cinnamon 本质上是为了推行使用终端和定点装置。无论是使用鼠标,还是使用触摸屏都可以获得同样便捷的操作。不像 KDE Plasma 工作空间,只有一种 GUI。 当前版本—— Cinnamon 2.0 于2013年10月10日发布。
|
||||
Cinnamon 是一个基于 Gtk+ 的环境。它最初作为 GNOME Shell 的一个用户界面分支,由 Linux Mint 为其创建的。 Cinnamon 的核心设计目标是让桌面终端和触屏设备都能完美操作。无论是使用鼠标,还是使用触摸屏都可以获得同样便捷的操作。不像 KDE Plasma 工作空间,只有一种图形用户体验。当前版本—— Cinnamon 2.0 于2013年10月10日发布。
|
||||
|
||||
### [Unity][4] ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unity 是 GNOME 桌面环境的一个界面,由 Canonical 公司创建,使用于 Ubuntu 系统中。Unity 最初现身于 Ubuntu 10.10 的上网本版本中。它起初打算充分利用上网本的屏幕空间,例如一个被称为启动器的垂直应用切换器(a vertical app switcher called launcher)和一个节省垂直空间的多功能顶部菜单栏。Unity 不像 GNOME、KDE、 Xfce 或者 LXDE 是许多软件的合集,它是作为使用实用功能而开发的。
|
||||
Unity 是 GNOME 桌面环境的一个界面,由 Canonical 公司创建,用于 Ubuntu 系统中。Unity 最初现身于 Ubuntu 10.10 的上网本版本中。它起初打算充分利用上网本的屏幕空间,例如一个竖直的应用启动器和一个节省空间的多功能顶部菜单栏。Unity 不像 GNOME、KDE、 Xfce 或者 LXDE 是许多软件的合集,它是为了可用性而开发的。
|
||||
|
||||
### [GNOME Shell][5] ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
GNOME 提供了桌面核心接口例如交换窗口,启动应用程序以及显示提示。它利用先进图形硬件来实现吸引人的,创新的界面思想,提供了愉悦简单的用户体验。GNOME Shell 定义了 GNOME 3 的客户体验。
|
||||
GNOME 提供了桌面核心接口例如交换窗口,启动应用程序以及显示提示。它利用先进的图形硬件来实现吸引人的、创新的界面思想,提供了愉悦简单的用户体验。GNOME Shell 定义了 GNOME 3 的客户体验。
|
||||
|
||||
作为 GNOME 的一个重要组成部分, GNOME Shell 的稳定版本首次发布于2011年3月3日。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ Xfce 是一个轻量级的桌面环境,围绕 GTK 框架实现。它看起来
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
LXDE 显然是桌面环境中最轻量级的选择,至少在传统的桌面标准中是这样。这个基于 GTK 的桌面环境使用了很多轻量级的选择替代了默认的应用(例如 Abiword, Gnumeric, 而不是 LibreOffice)。它没有提供 flash 视觉冲击 ,总体感觉也不是特别的棒,没有高级的设置。但是,LXDE 仍然提供了漂亮的桌面和完整的功能。当你需要快速简洁时,它就是你的选择。
|
||||
LXDE 显然是桌面环境中最轻量级的选择,至少在传统的桌面标准中是这样。这个基于 GTK 的桌面环境使用了很多轻量级的选择替代了默认的应用(例如 Abiword, Gnumeric, 而不是 LibreOffice)。它没有提供炫目的视觉震撼 ,总体感觉也不是特别的棒,没有高级的设置。但是,LXDE 仍然提供了漂亮的桌面和完整的功能。当你需要快速简洁时,它就是你的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ Numix图标主题张冠李戴,Fedora 20劲爆酷爽
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-numix-icon-theme-fedora-20/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,17 @@
|
||||
用笔记本模式工具1.65来延长电池续航
|
||||
用笔记本模式工具1.65来延长电池续航能力
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
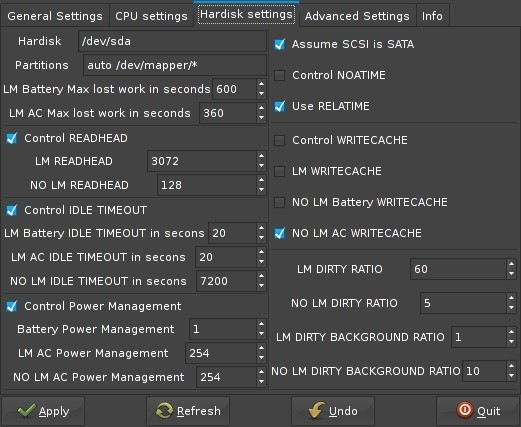
|
||||
|
||||
笔记本模式工具是一个Liunx省电工具包,它可以让用户以多种方式延长笔记本电池续航,现在它已经升级到1.65。
|
||||
笔记本模式工具是一个Liunx电源管理工具包,它可以让用户以多种方式延长笔记本电池续航能力,现在它已经升级到1.65。
|
||||
|
||||
笔记本模式工具的版本曾经很少而且间隔很长,但开发者在最新的版本中做了一些很有意思的改变,虽然此次更新与以前不同。
|
||||
笔记本模式工具的发布的版本曾经很少而且间隔很长,但开发者在最新的版本中做了一些很有意思的改变,虽然此次更新与以前不同。
|
||||
|
||||
根据更新日志,grep找不到$device/uevent的错误已得到修复、 sysfs/enabled已被"ip link down"所取代、 添加了对iwlwifi的支持,运行时电源管理框架现在更健壮,并且usb-autosuspend模块已被去除。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,当笔记本电脑恢复时,笔记本模式工具将强制以初始化模式运行,最新版本已添加英特尔 PState 驱动程序的模块,并已实现挂起/休眠接口。
|
||||
|
||||
用户不须更改自动设置。更改自动设置可能会导致更多的问题但一般准期望他们总是要打开。此外,要注意到每个功能所做的因为你可能会搞出更多问题。
|
||||
用户不须更改自动设置。更改自动设置可能会导致更多的问题,但通常看来他们总是会去动它。此外,要注意到每个功能究竟是做什么的,否则你可能会搞出更多问题。
|
||||
|
||||
看官方[公告][1]来了解更多细节。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +23,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Improve-Battery-Life-with-Laptop-Mode-Tools-1-65-447397.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,26 +1,27 @@
|
||||
红帽携手eNovance,共进OpenStack市场
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
正在OpenStack峰会于亚特兰大举办的同时,红帽确认了数项与OpenStack相关的项目。其中一项是,红帽正与开源云计算市场的领导者eNovance进行 [合作][1] 。双方将推动网络功能虚拟(Network Functions Virtualization)和电信功能融入OpenStack. 红帽 [宣布][2] 将以七千万欧元或九千五百万美金的现金和股票,购买eNovance.
|
||||
正在OpenStack峰会于亚特兰大举办的同时,红帽确认了数项与OpenStack相关的项目。其中一项是,红帽正与开源云计算市场的领导者eNovance进行[合作][1] 。双方将推动网络功能虚拟化(Network Functions Virtualization)及将电信功能融入OpenStack中。红帽[宣布][2]将以七千万欧元或九千五百万美金的现金和股票投资eNovance。
|
||||
|
||||
eNovance 是OpenStack市场上重要的角色, 特别以其和电信公司的合作而为人所知。eNovance帮助服务提供商和大型私企搭建部署云基础架构,快速且成本低廉。这也将为红帽开创新的产品线。
|
||||
|
||||
IDC 分析员 Laura DuBois and Ashish Nadkarni 在2014春季OpenStack 峰会上指出 “像eNovance这样的集成商将继续助力云服务提供商和企业,建立OpenStack云。OpenStack的前景开起来十分光明。"
|
||||
IDC 分析员 Laura DuBois 和 Ashish Nadkarni 在2014春季OpenStack 峰会上指出 “像eNovance这样的集成商将继续助力云服务提供商和企业,建立OpenStack云。OpenStack的前景开起来十分光明。"
|
||||
|
||||
eNovance 是OpenStack十大上游贡献者之一, 也是OpenStack 基金唯一的欧洲金牌合作商。 该公司在全球有超过150家客户,包括 Alcatel-Lucent, AXA, Cisco, Cloudwatt, and Ericsson. 在巴黎、蒙特利尔、班加罗尔、印度,都设有办公室。
|
||||
eNovance 是OpenStack十大上游贡献者之一, 也是OpenStack 基金唯一的欧洲金牌合作商。 该公司在全球有超过150家客户,包括 Alcatel-Lucent、 AXA,、 Cisco、 Cloudwatt 和 Ericsson. 在巴黎、蒙特利尔、班加罗尔、印度,都设有办公室。
|
||||
|
||||
2013年,红帽和 eNovance 第一次展开[合作][3] ,为其共同客户,提供OpenStack 部署和集成服务。该服务基于Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack 平台。 五月的OpenStack峰会上, 两家公司宣布了 [进一步的合作][4] ,推动网络功能虚拟(NFV) 和电信在OpenStack上的创新, 意在提供业界最完整、电信级的 通讯服务,基于Linux, 基于内核的虚拟机 (KVM), 和 OpenStack.
|
||||
2013年,红帽和 eNovance 第一次展开[合作][3] ,为其共同客户提供OpenStack 部署和集成服务。该服务基于Red Hat Enterprise Linux OpenStack 平台。 今年五月的OpenStack峰会上, 两家公司宣布了[进一步的合作][4] ,推动网络功能虚拟(NFV) 和电信在OpenStack上的创新,意在提供业界最完整、电信级的 通讯服务,基于Linux、内核级虚拟机 (KVM)和 OpenStack。
|
||||
|
||||
eNovance的联合创始人、首席执行官Raphaël Ferreira, 在声明中说:
|
||||
eNovance的联合创始人、首席执行官Raphaël Ferreira, 在声明中说:
|
||||
|
||||
> “和红帽一样,eNovance理解OpenStack改变企业市场的力量,当其正确部署且集成时。 我们非常高兴能成为红帽的一部分。红帽不仅仅提供一流的OpenStack发行版本, 也和我们一样坚信: 最好以连续、无缝的方式部署、集成OpenStack."
|
||||
> “和红帽一样,eNovance也认为部署和集成OpenStack已成趋势,这是企业市场上的变革力量。 我们非常高兴能成为红帽的一部分。红帽不仅仅提供一流的OpenStack发行版本,也和我们一样坚信: 最好以连续、无缝的方式部署、集成OpenStack。”
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/red-hat-to-acquire-enovance-focus-together-on-openstack
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[tengpeng](https://github.com/tengpeng) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[tengpeng](https://github.com/tengpeng) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,14 @@
|
||||
庆祝下X已经30岁了!
|
||||
X 窗口系统已经30岁了!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
X.org基金会很自豪地宣布一个特别的日子:30年前,1984年六月19日,Bob Scheifler发布了X窗口系统。
|
||||
|
||||
[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X11#Introduction][1]
|
||||
有关X窗口系统的介绍参见: [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X11#Introduction][1]
|
||||
|
||||
在这30年中,X作为UNIX桌面无处不在。通过使用桌面环境如GNOME,KDE,Xfce,Unity,Enlightenment,在今天,数以百万计的用户使用X作为底层技术。
|
||||
在这30年中,X作为UNIX桌面无处不在。在今天,数以百万计的用户使用着桌面环境如GNOME,KDE,Xfce,Unity,Enlightenment等等,而这些都使用X作为其底层技术。
|
||||
|
||||
X的开发者做出了巨大的突破,把X从运行在VAX VS100 CPU的一个程序发展成为在今天的笔记本电脑上渲染3D界面的程序。事实上,X的出现早于图形处理单元(GPU)概念的出现,甚至是比推广这项技术公司——于1999上市的Nvidia更早。
|
||||
X的开发者们做出了巨大的突破,把X从原本为VAX VS100 CPU编写的一个程序发展成为在今天可在笔记本电脑上进行3D渲染的图形用户界面。事实上,X的出现早于图形处理单元(GPU)概念的出现,甚至是比推广这项技术公司——于1999上市的Nvidia更早。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
尽管X已经服务了很长时间,但是X仍将做出改进并继续陪伴我们。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,18 +16,18 @@ X的开发者做出了巨大的突破,把X从运行在VAX VS100 CPU的一个
|
||||
|
||||
- Linux, FreeBSD, NetBSD, OpenBSD, Solaris, Microsoft Windows
|
||||
- POSIX, C89, C99, C++, Java
|
||||
- 万维网
|
||||
- 互联网
|
||||
- GPL 和 FSF
|
||||
|
||||
X是第一个主要的开源软件项目,比Free Software 和 Open Source Software更早。和我们一起庆祝吧,因为没有X,桌面会不会是今天这个样子。
|
||||
X是第一个主要的开源软件项目,比Free Software 和 Open Source Software更早。和我们一起庆祝吧,因为没有X,桌面就不会是今天这个样子。
|
||||
|
||||
-The X.Org Board of Directors
|
||||
- X.Org 品牌总监
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://comments.gmane.org/gmane.comp.freedesktop.xorg.announce/2177
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
使用DNSCrypt来加密您与OpenDNS之间的通信
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**正如SSL能将HTTP通信变为加密过的HTTPS通信,DNSCrypt, 物如其名, 是一款能加密您电脑与OpenDNS之间的通信的小神器。**
|
||||
|
||||
DNSCrypt刚问世的时候,官方公布它只是一款Mac才能用的工具,但根据最近一篇由OpenDNS发的[文章][1]表明,虽然还没有用户界面,但其实当Mac版DNSCrypt推出的时候源码已经放到了Github上了, Linux的用户也可以安装以及使用哦!
|
||||
|
||||
### 为神马要使用 DNSCrypt? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**DNSCrypt可以加密您电脑与OpenDNS服务器的所有通信,加密可以防止中间人攻击,信息窥觑,DNS劫持。更能防止网络供应商对某些网站的封锁。**
|
||||
|
||||
这是世界上第一款加密DNS通信的工具,虽然TOR可以加密DNS的请求,但毕竟它们只是在出口节点加密而已。
|
||||
|
||||
> 这款工具并不需要对域名或其工作方式做任何的改变,它只是提供了个该工具的用户与机房里的DNS服务器之间的加密方式而已。
|
||||
|
||||
您可以在[GitHub][3]的[OpenSND DNSCrypt][2]页面阅读更多的相关信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在Linux使用DNSCrypt ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先下载安装[Download DNSCrypt][4], 然后在Terminal里输入这个命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo /usr/sbin/dnscrypt-proxy --daemonize
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
然后把您的DNS服务器调成"127.0.0.1" - 在GNOME界面下的话,只要到Network Connections(网络连接)选项然后选择"Edit"并在"DNS servers"输入"127.0.0.1"就好了。如果您用的是DHCP的话,请选择Automatic (DHCP) addresses only", 这样的话才能输入DNS服务器。然后只要重连网络便可。
|
||||
|
||||
您可以访问这条[链接][5]来测试您连接到了OpenDNS了没。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您想设置开机启动DNSCrypt,可以自建一个init的脚本,如果您用的是Ubuntu,可以参考下面的。
|
||||
|
||||
**Arch Linux的用户可以通过[AUR][6]来安装DNSCrypt-proxy** (内含rc.d脚本)
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu下的DNSCrypt ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果您想在Ubuntu设置开机启动,您可以使用这个[Upstart脚本][7]。
|
||||
|
||||
注: 在Ubuntu 12.04版在127.0.0.1有个本地的DNS cache 服务器(dnsmasq)在跑,所以已经把改脚本改成让DNSCrypt使用127.0.0.2了, 所以按照上面的教程,应该把127.0.0.1换成127.0.0.2了。
|
||||
|
||||
要安装此脚本请使用以下的指令(要首先解压下下来的压缩文件):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cp dnscrypt.conf /etc/init/
|
||||
sudo ln -s /lib/init/upstart-job /etc/init.d/dnscrypt
|
||||
|
||||
然后用这个指令来启动:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo start dnscrypt
|
||||
|
||||
现在DNSCrypt就应该是开机自启了,如果您想停止的话,可以使用:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo stop dnscrypt
|
||||
|
||||
[下载DNSCrypt][8] (.deb、 .rpm以及源码都可供下载哦!)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.webupd8.org/2012/02/encrypt-dns-traffic-in-linux-with.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[213edu](https://github.com/213edu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://blog.opendns.com/2012/02/16/tales-from-the-dnscrypt-linux-rising/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.opendns.com/technology/dnscrypt/
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/opendns/dnscrypt-proxy
|
||||
[4]:http://download.dnscrypt.org/dnscrypt-proxy/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.opendns.com/welcome
|
||||
[6]:http://aur.archlinux.org/packages.php?ID=54702
|
||||
[7]:http://webupd8.googlecode.com/files/dnscrypt-0.2.tar.gz
|
||||
[8]:https://github.com/opendns/dnscrypt-proxy/downloads
|
||||
@ -1,20 +1,20 @@
|
||||
戴文的Linux内核专题:25 配置内核 (21)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
大家好!本篇我们将会配置Linux内核的网路文件系统支持。网络文件系统是一个通过网络远程访问计算机的远程文件系统。
|
||||
大家好!本篇我们将会配置Linux内核的网络文件系统支持。网络文件系统是一个可以通过网络远程访问计算机的远程文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,"NFS client support"驱动允许linux系统使用NFS网络文件系统。这里还有3个不同版本的NFS - (NFS client support for NFS version 2)、 (NFS client support for NFS version 3)、 (NFS client support for NFS version 4) 和 (NFS client support for NFSv4.1)。如果你有一个处理NFS的网络,找出你正在使用NFS的版本,或者启用所有的NFS驱动。
|
||||
首先,"NFS client support"驱动允许linux系统使用NFS网络文件系统。这里还有3个不同版本的NFS - (NFS client support for NFS version 2)、 (NFS client support for NFS version 3)、 (NFS client support for NFS version 4) 和 (NFS client support for NFSv4.1)。如果你有一个使用NFS的网络,找出你正在使用NFS的版本,或者启用所有的NFS驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
交换空间并不需要在本地存储单元上。这个驱动允许Linux使用NFS作为远程交换空间(Provide swap over NFS support)。
|
||||
交换空间并不需要总在本地存储单元上。这个驱动允许Linux使用NFS作为远程交换空间(Provide swap over NFS support)。
|
||||
|
||||
NFS系统可以通过缓存系统加速 (Provide NFS client caching support)。这是一个本地缓存。
|
||||
|
||||
启用这个驱动允许DNS对NFS服务器使用主机名(Use the legacy NFS DNS resolver)。
|
||||
启用这个驱动允许NFS服务器使用DNS解析器(Use the legacy NFS DNS resolver)。
|
||||
|
||||
"NFS server support"给予需要满足这个需求的服务器提供了NFS的特性。其他一些NFS驱动包括(NFS server support for NFS version 3) 和 (NFS server support for NFS version 4)。
|
||||
|
||||
"NFS server manual fault injection"驱动是一个调试驱动,它允许开发者让NFS服务器认为在NFS上发生了一个错误。特别地,这是用于测试服务器如何处理NFS错误。
|
||||
"NFS server manual fault injection"驱动是一个调试驱动,它允许开发者让NFS服务器认为在NFS上发生了一个错误。特别地,这用于测试服务器如何处理NFS错误。
|
||||
|
||||
"Secure RPC: Kerberos V mechanism"被用于RPC安全调用。由于安全原因,没有这个特性,NFS无法被加入到内核中。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,8 +26,7 @@ CIFS是一个用于Samba和Windows服务器的虚拟文件系统(CIFS support (a
|
||||
|
||||
有两个特性被用于调试或监视CIFS驱动(CIFS statistics) 和 (Extended statistics)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
一个特殊的需要在有LANMAN安全的服务器上需要(Support legacy servers which use weaker LANMAN security)。LANMAN或者LM哈希是一种有一些弱点的特殊的密码哈希函数。
|
||||
要在服务器上支持LANMAN安全需要一个特定的驱动(Support legacy servers which use weaker LANMAN security)。LANMAN或者LM哈希是一种较弱的特殊的密码哈希函数。
|
||||
|
||||
CIFS在被挂载到安全服务器上之前需要Kerberos票据(Kerberos/SPNEGO advanced session setup)。这个驱动提供了CIFS使用能够提供票据的用户空间工具的能力。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,7 +36,7 @@ CIFS在被挂载到安全服务器上之前需要Kerberos票据(Kerberos/SPNEGO
|
||||
|
||||
CIFS有两个其他的调试工具(Enable CIFS debugging routines) 和 (Enable additional CIFS debugging routines)。
|
||||
|
||||
CIFS有"DFS feature support",它允许共享在被移除后仍可以访问。DFS代表"Distributed FileSystem"(分布式文件系统)。
|
||||
CIFS有"DFS feature support",它允许共享在被移除后仍可以访问。DFS代表"Distributed FileSystem"(分布式文件系统)。
|
||||
|
||||
SMB2是CIFS的一个提升替代品(SMB2 network file system support)。SMB2代表的是"Server Message Block version 2"(服务器消息块第2版)。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,7 +84,7 @@ Linux内核有一个实验性的驱动,通过9P2000协议访问Plan 9资源(Pl
|
||||
|
||||
这个设定分会启用/禁用普遍不需要或者废除的符号 (Enable unused/obsolete exported symbols)。然而,一些模块可能需要这些符号。启用这个会增加内核的大小。Linux用户很少会需要这些符号。通常上,禁用这个特性,除非你了解一个重要的模块需要这个符号。
|
||||
|
||||
如果启用这个shehi,内核会在用户内核头上执行健康检查(Run 'make headers_check' when building vmlinux)。
|
||||
如果启用这个设施,内核会在用户内核头上执行健康检查(Run 'make headers_check' when building vmlinux)。
|
||||
|
||||
在编译期,这个特性会检查无效的引用(Enable full Section mismatch analysis)。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -115,6 +114,6 @@ Linux内核有一个实验性的驱动,通过9P2000协议访问Plan 9资源(Pl
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-21.4988/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
戴文的Linux内核专题:26 配置内核 (22)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你好!本篇我们将继续配置"kernel hacks",接着我们会配置整个安全系统。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ Alpha和s390处理器需要配置下一个特性(Force weak per-cpu definitions)
|
||||
|
||||
"Latency measuring infrastructure"驱动提供了延迟检测工具LatencyTop,以找出用户空间中由于内核执行/任务而被阻碍/干扰的对象。
|
||||
|
||||
下面,我们有一个子菜单名为"Tracers",它包含了不同追踪器的列表。追踪器是一段监视不同内核函数的代码。每次某个特定的函数启动,追踪器将被调用来检测函数。
|
||||
下面,我们有一个子菜单名为"Tracers",它包含了不同追踪器的列表。追踪器是一段监视不同内核函数的代码。每次某个特定的函数启动,追踪器将被调用来检测函数。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的模块用来测试红黑树库的性能(Red-Black tree test)。红黑树是一个排序和搜索算法。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,9 +28,9 @@ printk()函数可以用来打印不同的调试信息,如果这个特性启用
|
||||
|
||||
Atomic64自我测试检查系统是否支持原子操作(Perform an atomic64_t self-test at boot)。这是一个32位系统执行64位操作。
|
||||
|
||||
这个驱动提供了对于所有可能的RAID6恢复系统的自我测试(Self test for hardware accelerated raid6 recovery)。
|
||||
这个驱动提供了对于所有可能的RAID6恢复系统的自检(Self test for hardware accelerated raid6 recovery)。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:自我测试是底层测试并且在绝大多数系统硬件和软件开启和执行前侦查软件。自我测试搜索硬件,失败的设备等等。自我测试也可能被编成应用测试它本身。
|
||||
注意:自检是底层测试并且在绝大多数系统硬件和软件开启和执行前侦查软件。自检搜索硬件,失败的设备等等。自检也可能被编成应用以测试它本身。
|
||||
|
||||
在"Kernel Hacking"菜单中(如果你是用的是像ncurses那样的菜单接口),有一个名为"Sample kernel code"的子菜单。在以后的文章中,我们会讨论如何实现自定义/自制内核模块。只要记住这里是启用你自己的模块。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ printk()打印不同的消息到dmsg的启动界面,但是在串行和控制
|
||||
|
||||
下面的驱动提供了对"copy_from_user()"系统调用的基本测试(Strict copy size checks)。copy_fcrom_user()从用户空间拷贝数据块到内核空间中。
|
||||
|
||||
这里还有一个自我测试;它用于NNI(NMI Selftest)。
|
||||
这里还有一个自检;它用于NMI(NMI Selftest)。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们会进入"Security Options",如果你使用像ncurses的基于菜单的接口时。第一个选项允许访问内核中存储的键和验证令牌(Enable access key retention support)。这有很多原因用到,像访问加密文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -114,6 +114,6 @@ Yama是另外一个LSM(Yama support)。如果启用这个特性Yama可以与另
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linux.org/threads/the-linux-kernel-configuring-the-kernel-part-22.5017/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
Canonical Debuts 'Orange Box' for Ubuntu OpenStack Cloud Demos
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> The Orange Box, a portable server cluster that Canonical will use for Ubuntu-based OpenStack cloud demonstrations and training, is now available.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Canonical's Orange Box, the portable server cluster that the company intends to use to showcase [OpenStack][1], [MAAS][2], [Juju][3] and other aspects of the Ubuntu Linux-based cloud, is out. Here's what it's all about.
|
||||
|
||||
For starters, it's important to understand what the Orange Box is not: A revenue-generating hardware product from Canonical. The company has given no indication so far that it plans to sell these devices on a large scale—although if you truly want you can [buy one][4], for the equivalent of around $12,900, from [TranquilPC Limited][5], the company that has the contract for manufacturing them.
|
||||
|
||||
Primarily, the Orange Box is a tool for convincing enterprises to invest in the Ubuntu-based cloud. It's a key part of the Ubuntu OpenStack strategy that Canonical founder Mark Shuttleworth [outlined last month][6], especially the OpenStack training program the company is offering, called [Jumpstart][7].
|
||||
|
||||
As part of Jumpstart, Canonical will loan an Orange Box to a participating organization so its employees can practice configuring OpenStack and related software on an Ubuntu cluster. Canonical staff also will provide consultation during the training period.
|
||||
|
||||
But training purposes aside, the Orange Box [looks pretty cool][8]. And with 10 [Intel NUCs][9] inside—packing a collective punch of 160GB of RAM, 1,200GB of storage space and 10 i5 CPUs—the device fits quite a bit of computing power into a tiny space.
|
||||
|
||||
Better still, the Orange Box comes preconfigured with software that provides a basis for launching Ubuntu-based cloud technologies.
|
||||
|
||||
For Canonical, however, the real test will be making sure enterprises take advantage of the Orange Boxes that the company lends them not just to poke around an unusual hardware device, but to experience the Ubuntu cloud in a truly compelling way—compelling enough to convince IT decision-makers to ground the next-generation cloud infrastructure that they are building in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/ubuntu/062314/canonical-debuts-orange-box-ubuntu-openstack-cloud-demos
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://openstack.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://maas.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://juju.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tranquilpcshop.co.uk/ubuntu-orange-box/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tranquilpcshop.co.uk/
|
||||
[6]:http://thevarguy.com/ubuntu/051614/shuttleworth-highlights-ubuntu-openstack-cloud-innovations
|
||||
[7]:http://www.ubuntu.com/cloud/tools/jumpstart
|
||||
[8]:http://arstechnica.com/information-technology/2014/06/hands-on-with-canonicals-orange-box-and-a-peek-into-cloud-nirvana/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/nuc/overview.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
Canonical Designers Update Ubuntu Linux Website
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> The website for Canonical's Ubuntu Linux operating system has received several enhancements tailored for Chinese speakers, Ubuntu cloud users and others.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Ubuntu.com][1], the website of [Canonical][2]'s Linux-based operating system for PCs, servers, the cloud and (maybe soon) mobile devices, has received a series of subtle but significant upgrades recently, and more are on the way. Here's a look at the latest site updates and additions for the cloud, Canonical's partner network and more.
|
||||
|
||||
The Ubuntu design team outlined the enhancements to ubuntu.com in a recent [blog post][3]. The full list of changes is available there, but the most significant tweaks and updates include:
|
||||
|
||||
- The creation of a Chinese site for Ubuntu, [ubuntu-china.cn][4], which could help create new inroads for Canonical in the Asian market, where Ubuntu has traditionally taken a backseat to locally grown Linux distributions. The move may also help to strengthen Canonical's relationship with China-based [Meizu][5], one of the two hardware manufacturers with which it has [partnered][6] to deliver mobile phones running Ubuntu by the end of this year.
|
||||
- A new version of [Ubuntu Insights][7], a Web portal where Canonical publishes news about the Ubuntu world.
|
||||
|
||||
Those are only the changes that the design team has already completed. Currently in the works for future implementation are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Updates to the Web interface for Canonical's [Juju][8] cloud orchestration service.
|
||||
- The debut of a series of changes throughout the Ubuntu website that will make it more "[responsive][9]," which means enhancing readability, accessibility and the general visitor experience across different types of devices.
|
||||
- A new [Ubuntu Partners][10] website.
|
||||
- Further development of the Chinese Ubuntu website, including the addition of cloud and server sections.
|
||||
|
||||
All of these updates are good news for Canonical's customers and partners. But what makes the changes truly remarkable is how far Ubuntu's Web presence has evolved since the operating system's debut nearly 10 years ago, when ubuntu.com looked like [this][11], and the landing page primarily featured images of people dressed in workout clothes.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/ubuntu/062314/canonical-designers-update-ubuntu-linux-website
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://canonical.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://design.canonical.com/2014/06/latest-from-the-web-team-june-2014/
|
||||
[4]:http://ubuntu-china.cn/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.meizu.com/
|
||||
[6]:http://thevarguy.com/ubuntu/022014/ubuntu-linux-phones-will-ship-2014-says-canonical
|
||||
[7]:http://insights.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[8]:https://juju.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
[9]:http://design.canonical.com/2014/03/making-ubuntu-com-responsive/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.ubuntu.com/partners
|
||||
[11]:http://web.archive.org/web/20041106014450/http://www.ubuntu.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
Google Forks Open Source OpenSSL Web Security Code
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Google's BoringSSL, a fork of the open source OpenSSL software for encrypting Web data, will spread the open source community's resources thinner.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the wake of [Heartbleed][1], there may soon be as many variants of the open source OpenSSL software for encrypting Web traffic as there are Pokemon characters—or something like that. A few days ago, Google (GOOG) became the latest organization to announce its own OpenSSL spin, which it's calling BoringSSL.
|
||||
|
||||
Google developer Adam Langley announced BoringSSL—a name he described as "aspirational," presumably because Google hopes the new software will prove more drama-free than OpenSSL—in a [blog post][2] on June 20.
|
||||
|
||||
Google has made its own modifications to the OpenSSL code for some time for use in Chrome and other offerings, Langley said. But going forward, the company intends to fork OpenSSL entirely to create a separate solution, a change it hopes will simplify development on Google's end.
|
||||
|
||||
That said, Langley emphasized that Google is "not aiming to replace OpenSSL as an open source project," and will continue sharing code with the OpenSSL developers when it will help them fix bugs in their own software. Those code contributions will be available under an [ISC license][3], a type of open source license that the [GNU folks][4]—who probably spend more time than anyone else worrying about keeping software Free—regard as essentially [kosher][5].
|
||||
|
||||
Yet while BoringSSL may do little to upset the Free Software crowd, it's making a confusing situation worse for the open source community. Previously, OpenSSL was the sole widely used open source solution for encrypting traffic sent to and from Web pages on millions of servers. But following the security fiasco called Heartbleed, when it became apparent that a bug (which has now been fixed) in OpenSSL allowed third parties to snoop data, consensus around OpenSSL as the best solution for implementing this very important piece of Web functionality has evaporated.
|
||||
|
||||
Shortly after Heartbleed, a group of open source developers forked the OpenSSL code into [LibReSSL][6] because they believe the former was "[not developed by a responsible team][7]." At the same time, the [Linux Foundation][8] and its partners are spending potentially millions of dollars trying to inject new life—and public faith—into OpenSSL through the [Core Infrastructure Initiative][9].
|
||||
|
||||
Now Google has gone off on in yet another direction with BoringSSL, a move that does nothing to advance faith in either OpenSSL or LibReSSL. And that means the open source community's development resources are being spread even thinner, a situation that can only be resolved if one OpenSSL-variant emerges to rule them all.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/062314/google-forks-open-source-openssl-web-security-code-boring
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://heartbleed.com/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.imperialviolet.org/2014/06/20/boringssl.html
|
||||
[3]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ISC_license
|
||||
[4]:https://www.gnu.org/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.gnu.org/licenses/license-list.html#ISC
|
||||
[6]:http://www.libressl.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://opensslrampage.org/post/82973312181/openssl-is-not-developed-by-a-responsible-team
|
||||
[8]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/053014/core-infrastructure-initiative-endorses-open-source-netwo
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,26 @@
|
||||
Linux Domination, Ubuntu Uncertainty, and Nerdy Enlightenment
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
here are some interesting stories today in Linuxville. Steven J. Vaughan-Nichols is reporting that Linux dominates on supercomputers more than ever. Arstechnica says "Mint 17 is the perfect place for Linux-ers to wait out Ubuntu uncertainty." Linux Tycoon Bryan Lunduke reviews Enlightenment 17 and Jamie Watson says Makulu Linux 6 makes him smile. This and more in tonight's Linux news recap.
|
||||
|
||||
**Over at ZDNet**, Steven J. [Vaughan-Nichols reports][1] the findings that Linux is once again the fastest operating system on the world's leading supercomputers. But not only that, Vaughan-Nichols says, "In the latest contest, not only did Linux dominate, but Linux showed that is slowly pushing out all its competitors." Linux runs on 97% of them. Only two of the Top 500 run Windows, the other 13 Unix. Despite their speed records, Linux developers are still trying to go even faster because Vaughan-Nichols says, "research and businesses, especially the stock markets and trading companies, not only want but need even faster computers."
|
||||
|
||||
**Another notable** on ZDNet today is Jamie Watson's review of Makulu Linux 6.0 KDE saying it's "guaranteed to make you smile." This release ships with Linux 3.14.7, KDE 4.13.1, and a more modern but cranky installer. He says of this release, "It's big, it's beautiful, it's fun, and it is chock full of just about everything imaginable." [He concludes][2] that it's about as much fun as one can have with a Linux distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
**arstechnica** reviews Mint 17 saying it's an important release because of being based on Ubuntu 14.04 LTS. They contend Mint and its users can sit back and enjoy Mint while Ubuntu suffers the growing pains of Mir and Unity until 2016. Reviewer Scott Gilbertson says Mint 17 is a "great base" to update the next two years. He looks at both the Cinnamon and MATE versions of Mint 17 closely, but touches on the Xfce and Debian editions as well as the common elements of them all. [Gilbertson concludes][3], "Linux Mint 17 makes a fantastic Linux desktop right now. It's stable, familiar enough for Windows refugees to pick it up without missing a beat, and has all the familiar tools Ubuntu fans would expect."
|
||||
|
||||
**Speaking of Ubuntu**, The Var Guy posted of the Ubuntu website updates. Posts from the Design Team have been appearing on the company website on the topic of its designs for a while, but today Christopher [Tozzi summed][4] it all up nicely saying, "All of these updates are good news for Canonical's customers and partners. But what makes the changes truly remarkable is how far Ubuntu's Web presence has evolved since the operating system's debut nearly 10 years ago, when ubuntu.com looked like this, and the landing page primarily featured images of people dressed in workout clothes."
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/linux-domination-ubuntu-uncertainty-and-nerdy-enlightenment
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.zdnet.com/linux-dominates-supercomputers-as-never-before-7000030890/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.zdnet.com/makulu-linux-6-0-kde-guaranteed-to-make-you-smile-7000030833/
|
||||
[3]:http://arstechnica.com/gadgets/2014/06/mint-17-the-perfect-place-for-linux-ers-to-wait-out-ubuntu-uncertainty/
|
||||
[4]:http://thevarguy.com/ubuntu/062314/canonical-designers-update-ubuntu-linux-website
|
||||
@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
|
||||
jiajia translating...
|
||||
Has Microsoft really changed its attitude toward open source?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **In today's open source roundup: Microsoft may or may not have a new attitude toward open source. Plus: Android versus Windows, and Cinnamon versus Unity in Ubuntu 14.04**
|
||||
|
||||
Microsoft became infamous for its very negative early remarks about open source software. But restructuring at the company may be giving it a more positive attitude toward open source. CNet reports on changes in Microsoft's perceptions and behavior when it comes to open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
> According to [CNet][1]:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> But Microsoft's feud with open source has been sputtering for quite some time, and the senior managers who led the anti-open source charge are gone from the scene -- or at least no longer in positions of authority. Open source is now routinely used by corporations around the world, and the company's sniffy put-downs only fed into the perception of Microsoft as out of touch.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Some of that new thinking reflects the change at the top of the corporate pyramid, with Satya Nadella replacing Ballmer as CEO in early February. Since taking over, Nadella has talked up his vision of a Microsoft whose future isn't shackled to its Windows past.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> [More at CNet][2]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Microsoft and Communist Open Source
|
||||
> Image credit: [Curako's Blog][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Okay, I hate to be a Negative Ned here, but I'm firmly in the "trust but verify" camp when it comes to Microsoft and open source. Yes, a new CEO and other changes may be helping Microsoft to adjust to living in an open source world. But change never comes easy or fast in such a large organization, so I think the jury is still out on whether or not Microsoft has really changed for the better when it comes to open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, I've never forgotten the company's "embrace, extend, extinguish" strategy that they used in the past to destroy competitive software products. That alone is reason enough to keep a wary eye on Microsoft's involvement with any open source project. Perhaps the company really has changed, but maybe it hasn't. I think it bears watching for at least another few years to see if enduring change has really set in or not.
|
||||
|
||||
### Android versus Windows ###
|
||||
|
||||
ZDNet has an article that covers the top end-user Linux distributions. It notes that Windows still rules the desktop for now, but Android may eventually be the big kahuna among end-user operating systems by the end of this year.
|
||||
|
||||
> According to [ZDNet][4]:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> If smartphones and tablet sales continue to grow as expected, Android tablet vendors continue to erode Apple's market share, and PCs continue their decline, Android may end up being the top end-user operating system by the end of 2014—regardless of what happens with the proposed Android PCs.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Taken as a whole, Android clearly rules the Linux end-user space. No, you may not think of it as a desktop yet —although AMD and Intel would both like you to change your mind about that — but Android is on its way to being the top end-user operating system of all.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> [More at ZDNet][4]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 
|
||||
> Image credit: [ZDNet][4]
|
||||
|
||||
The numbers mentioned in the article aren't really a surprise, given the mobile revolution that's happened over the last ten years. The desktop just isn't as important as it used to be, and Microsoft just never really mattered in mobile devices. Even now, as they struggle desperately for traction in tablets and phones, Microsoft is still mostly irrelevant in the mobile devices market.
|
||||
|
||||
Google has wreaked absolute havoc on Microsoft's efforts in mobile and is now beginning to be a threat to Microsoft in the desktop market. Between Chrome OS and Android, Google has been battering Microsoft on a number of fronts. If you look at Amazon's list of [top selling desktops][5] and [top selling laptops][6], you see plenty of Chrome OS computers and even some Android PCs. So people are actually buying alternatives to Windows computers and aren't bothered in the least by it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cinnamon versus Unity in Ubuntu 14.04 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Tech Republic takes a look at whether or not Cinnamon is a viable replacement for Unity in Ubuntu 14.04. The article includes instructions on how to install Cinnamon in Ubuntu 14.04.
|
||||
|
||||
> According to [Tech Republic][7]:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> If you want a performance-centric desktop that doesn't toss aside feature and customization, Cinnamon is for you. Cinnamon is a straight-forward desktop interface that pretty much anyone can use -- from your IT staff to your grandmother. It really is that easy to use. Cinnamon doesn't surprise you, it doesn't trick you, but it also (in my opinion) doesn't wow you. But that's not what Cinnamon is about. This take on the desktop is all about functionality -- on a standard level. It doesn't break rules, push envelopes, or have new tricks up its sleeve.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Cinnamon is a fairly pedestrian desktop that takes the bits and pieces of what's worked well over the years and cobbles them together into one, well-designed piece. So, if you're okay with using a desktop that looks and feels a bit long in the tooth (but one that functions very, very well), Cinnamon is for you. If you lean towards the bleeding edge of design and prefer a more modern look and feel, Cinnamon will most likely disappoint.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> [More at Tech Republic][7]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Image credit: [Tech Republic][7]
|
||||
|
||||
I'll have to weigh in on the side of Cinnamon here. While Unity has its pluses, I have never really been able to warm up to it. Cinnamon is closer to a more traditional desktop interface and that seems to work the best for me.
|
||||
|
||||
But as always, beauty is in the eye of the beholder. The great thing about Linux is that it offers so many different choices. So you really can't go wrong with Unity or Cinnamon, just use whichever one you like best.
|
||||
|
||||
What's your take on all this? Tell me in the comments below.
|
||||
|
||||
The opinions expressed by the author do not necessarily reflect the views of ITworld.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.itworld.com/open-source/421894/has-microsoft-really-changed-its-attitude-toward-open-source
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cnet.com/news/dead-and-buried-microsofts-holy-war-on-open-source-software/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cnet.com/news/dead-and-buried-microsofts-holy-war-on-open-source-software/
|
||||
[3]:http://curako.wordpress.com/2010/12/06/the-uneasy-alliance-free-software-vs-open-source/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.zdnet.com/the-five-most-popular-end-user-linux-distributions-7000030058/http://www.zdnet.com/the-five-most-popular-end-user-linux-distributions-7000030058/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.amazon.com/Best-Sellers-Electronics-Desktop-Computers/zgbs/electronics/565098/?_encoding=UTF8&camp=1789&creative=390957&linkCode=ur2&tag=fnh-20&linkId=REWXUPB7SQXPDSOL
|
||||
[6]:http://www.amazon.com/Best-Sellers-Computers-Accessories-Laptop/zgbs/pc/565108/?_encoding=UTF8&camp=1789&creative=390957&linkCode=ur2&tag=fnh-20&linkId=POG3J2CFBHDWBAVL
|
||||
[7]:http://www.techrepublic.com/article/is-cinnamon-a-worthy-replacement-for-ubuntu-unity/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
owen-carter translating
|
||||
14 Apps To Boost Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Making the switch to Ubuntu – or any popular Linux distribution – is more than the mere act of changing operating systems. You must also have apps that allow you to get work done.
|
||||
@ -77,4 +78,4 @@ via: http://www.datamation.com/applications/14-apps-to-boost-ubuntu-1.html
|
||||
[17]:http://www.libreoffice.org/discover/writer/
|
||||
[18]:http://www.maartenbaert.be/simplescreenrecorder/
|
||||
[19]:https://launchpad.net/simple-scan
|
||||
[20]:http://www.marzocca.net/linux/baobab/baobab-getting-started.html
|
||||
[20]:http://www.marzocca.net/linux/baobab/baobab-getting-started.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
(翻译中 by runningwater)
|
||||
Does Linux Lack a Killer App?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
@ -98,7 +99,7 @@ Linux "could be reaching critical mass, and I was only partially joking when I s
|
||||
|
||||
via:
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
|
||||
9 ASCII Games You'll Want to Play Again and Again
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Modern Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) offer exceptional gaming capabilities, and have contributed to the trend of astonishing leaps in graphics fidelity. There is not a year that has gone by without a game being released that makes significant advances in technical graphics wizardry. Computer graphics have been advancing at a staggering pace. At the current rate of progress, in the next 10 years it may not be possible to distinguish computer graphics from reality.
|
||||
|
||||
Personally, these developments do not overly interest me. I find little fascination playing games that focus so much on the visuals they neglect the essential elements. Too often the storyline and game play has been compromised for visual quality. Most of my favourite games are somewhat deficient in the graphics department. Gameplay is always king in my eyes.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux has an excellent library of free games many of which are released under an open source license. The vast majority of these games are aesthetically pleasing. Popular games often have full motion video, vector graphics, 3D graphics, realistic 3D rendering, animation, texturing, a physics engine, and much more. Early computer games did not have these graphic techniques. The earliest video games were text games or text-based games that used text characters rather than vector or bitmapped graphics.
|
||||
|
||||
Text-based games often receive little coverage in the Linux press. However, there are some real ASCII gems out there waiting to be explored which are immensely addictive and great fun to play.
|
||||
|
||||
The idiom 'don't judge a book by its cover' can be extended to 'don't judge a computer game by its graphics'. Whilst the games featured in this article have extremely basic graphics, they have many redeeming qualities beyond evoking fond memories of the early days of computer gaming.
|
||||
|
||||
There are no fancy graphics here, just great gameplay coupled with the urge of always having just one more play.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The first game in this roundup is UnNetHack, a fork of NetHack, originally based on the hugely popular roguelike game NetHack. NetHack was first released in 1987, and is considered by many gamers to be one of the best gaming experiences the computing world offers.
|
||||
|
||||
UnNetHack adds a number of enhancements to NetHack, such as additional monsters, more levels, a few new objects, additional dangers, more challenging gameplay, and most importantly more entertainment than vanilla NetHack. It offers a tutorial to help new players get started.
|
||||
|
||||
Be warned, UnNetHack is fiendishly addictive.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [sourceforge.net/apps/trac/unnethack][1]
|
||||
- Authors: Patric Mueller
|
||||
- License: Nethack General Public License
|
||||
- Version Number: 5.1.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Empire is a simulation of a full-scale war between two emperors, the computer and you. Naturally, there is only room for one, so the object of the game is to destroy the other. The computer plays by the same rules that you do.
|
||||
|
||||
This game is the ancestor of all the multiplayer 4X simulations out there, including Civilization and Master of Orion. The classic game from the 1980s uses text mode graphical output, drawing your units, cities and the world in color. Commands are issued using the keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
The world on which the game takes place is a square rectangle containing cities, land, and water. Cities are used to build armies, planes, and ships which can move across the world destroying enemy pieces, exploring, and capturing more cities. The objective of the game is to destroy all the enemy pieces, and capture all the cities.
|
||||
|
||||
The game starts by assigning you one city and the computer one city. Cities can produce new pieces. Every city that you own produces more pieces for you according to the cost of the desired piece. The typical play of the game is to issue the Automove command until you decide to do something special. During movement in each round, the player is prompted to move each piece that does not otherwise have an assigned function.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.catb.org/~esr/vms-empire][2]
|
||||
- Authors: Chuck Simmons, Eric S. Raymond
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.12
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Intricacy is an addictive, open source, networked, video puzzle game. It is written in Haskell, using the Curses and SDL libraries.
|
||||
|
||||
Intricacy runs directly from the command-line, and provides a turn-based, abstract puzzle game where the players need to pick locks, simply by coordinating a couple of tools in order to manipulate the lock’s mechanism. Constructing and solving difficult puzzles within certain strict design constraints is both challenging and good fun.
|
||||
|
||||
The catch is that you will be able to pick locks that are designed by other players. It has multi-platform support, with binaries for both Linux and Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [mbays.freeshell.org/intricacy][3]
|
||||
- Authors: Chuck Simmons, Eric S. Raymond
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.2.6.3
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
XorCurses is a puzzle game set inside a series of mazes. It is a remake of XOR by Astral Software, a game published in 1987 and released on the popular home computers of the day including the Commodore 64, ZX Spectrum, Atari ST, and Amiga. XOR is a pure puzzle game with no random or arcade elements.
|
||||
|
||||
In some respects, XorCurses is a regression from the graphics of the old 8 bit computers as it uses even more simplistic graphics, with coloured ASCII characters instead of pixel based graphics.
|
||||
|
||||
XorCurses attempts to faithfully recreate that game for Linux, with particular attention placed on the behaviour of the objects within the original game.
|
||||
|
||||
The basic premise of Xor is to roam around a series of mazes collecting all of the blue masks and then finding the exit. You have two player-shields to aid you and you can use either one at any time and switch between them. The first few levels are easy to progress, but the rest are progressively harder to solve. A particularly challenging and difficult puzzle game that will keep you engaged for hours.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [www.jwm-art.net/dark.php?p=XorCurses][4]
|
||||
- Authors: James W. Morris
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.2.2
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Goblin Hack is an open source roguelike OpenGL-based smooth-scrolling ASCII graphics game. The game is inspired by the likes of NetHack, but faster with fewer keys.
|
||||
|
||||
Goblin Hack has a simple interface that appears to appeal to players of all ages, and fires their imagination in today's world of over-rendered games.
|
||||
|
||||
Players can choose one of several classes before being thrown into the first floor of a randomized, ongoing dungeon.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [goblinhack.sourceforge.net][5]
|
||||
- Authors: Neil McGill
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.18
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Curse of War is a fast-paced real time strategy game released under an open source license. It is implemented using C and ncurses. There is also an SDL version available.
|
||||
|
||||
The core game mechanics turns out to be quite close to WWI-WWII type of warfare, however, there is no explicit reference to any historical period.
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike most real time strategy games, in Curse of War players do not control units, but instead they concentrate on high-level strategic planning: Building infrastructure, securing resources, and moving armies.
|
||||
|
||||
A multiplayer mode is available. Computer opponents differ in personality, and it affects the way they fight.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [a-nikolaev.github.io/curseofwar][6]
|
||||
- Authors: Alexey Nikolaev
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.2.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Brogue is an open source Roguelike game for Mac OS X, Windows, Linux, iOS and Android.
|
||||
|
||||
Brogue is a direct descendant of Rogue, a dungeon crawling video game first developed by Michael Toy and Glenn Wichman around 1980. Unlike other popular modern roguelikes, Brogue favors simplicity over complexity, while trying to ensure that the interactions between components are interesting and varied.
|
||||
|
||||
Your goal is to travel to the 26th subterranean floor of the dungeon, retrieve the Amulet of Yendor and return with it to the surface. For the truly skillful who desire further challenge, depths below 26 contain three lumenstones each, items which confer an increased score upon victory.
|
||||
|
||||
Brogue is a challenging game, but still great fun to play. Try not to be disheartened by the difficulty of the game; with some application, Brogue will become very addictive.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [sites.google.com/site/broguegame][7]
|
||||
- Authors: Brian Walker
|
||||
- License: GNU Affero GPL
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.7.3
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
DiabloRL is a roguelike "unmake" of the popular Blizzard game Diablo 1 classic RPG to a turn-based ASCII roguelike.
|
||||
|
||||
The game was created for the 7 Day Roguelike Competition, but has since been expanded with magic items, spells, more classes and levels, as well as fast travelling to known locations, and high scores.
|
||||
|
||||
DiabloRL gives you a choice of classes, the Warrior, Rogue, or Sorcerer. Each of these has different starting and maximum stats, as well as completely different play styles.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [diablo.chaosforge.org][8]
|
||||
- Authors: Kornel Kisielewicz, Chris Johnson and Mel'nikova Anastasia
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.5.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cataclysm is an open source post-apocalyptic roguelike, set in the countryside of fictional New England after a devastating plague of monsters and zombies. It is a continuation of Whale's original Cataclysm, which expands it with numerous new creatures, buildings, gameplay mechanics and many other features.
|
||||
|
||||
While some have described it as a "zombie game", there's far more to Cataclysm than that. Struggle to survive in a harsh, persistent, procedurally generated world. Scavenge the remnants of a dead civilization for for food, equipment, or, if you're lucky, a vehicle with a full tank of gas to get you the hell out of Dodge. Fight to defeat or escape from a wide variety of powerful monstrosities, from zombies to giant insects to killer robots and things far stranger and deadlier, and against the others like yourself, that want what you have...
|
||||
|
||||
Cataclysm is very different from most roguelikes in many ways. Rather than being set in a vertical, linear dungeon, it is set in an unbounded, 3D world. This means that exploration plays a much bigger role than in most roguelikes, and the game is much less linear. As the map is so huge, it is actually completely persistant between games. If you die, and start a new character, your new game will be set in the same game world as your last. Like in many roguelikes, you will be able to loot the dead bodies of previous characters; unlike most roguelikes, you will also be able to retrace their steps completely, and any dramatic changes made to the world will persist into your next game.
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [en.cataclysmdda.com][9]
|
||||
- Authors: Kevin Granade
|
||||
- License: Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.A
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20140621060017503/9ASCIIGames.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://sourceforge.net/apps/trac/unnethack/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.catb.org/~esr/vms-empire/
|
||||
[3]:http://mbays.freeshell.org/intricacy/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.jwm-art.net/dark.php?p=XorCurses
|
||||
[5]:http://goblinhack.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[6]:http://a-nikolaev.github.io/curseofwar/
|
||||
[7]:https://sites.google.com/site/broguegame/
|
||||
[8]:http://diablo.chaosforge.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://en.cataclysmdda.com/
|
||||
94
sources/talk/20140624 Performance benchmarks--KVM vs. Xen.md
Normal file
94
sources/talk/20140624 Performance benchmarks--KVM vs. Xen.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
Performance benchmarks: KVM vs. Xen
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
After having some interesting discussions last week around KVM and Xen performance improvements over the past years, I decided to do a little research on my own. The last complete set of benchmarks I could find were from the [Phoronix Haswell tests in 2013][1]. There were [some other benchmarks from 2011][2] but those were hotly debated due to the Xen patches headed into kernel 3.0.
|
||||
|
||||
The 2011 tests had a [good list of benchmarks][3] and I’ve done my best to replicate that list here three years later. I’ve removed two or three of the benchmark tests because they didn’t run well without extra configuration or they took an extremely long time to run.
|
||||
|
||||
### Testing environment ###
|
||||
|
||||
My testing setup consists of two identical SuperMicro servers. Both have a single [Intel Xeon E3-1220][4] (four cores, 3.10GHz), 24GB Kingston DDR3 RAM, and four Western Digital RE-3 160GB drives in a RAID 10 array. BIOS versions are identical.
|
||||
|
||||
All of the tests were run in Fedora 20 (with SELinux enabled) for the hosts and the virtual machines. Very few services were left running during the tests. Here are the relevant software versions:
|
||||
|
||||
- Kernel: 3.14.8
|
||||
- For KVM: qemu-kvm 1.6.2
|
||||
- For Xen: xen 4.3.2
|
||||
|
||||
All root filesystems are XFS with the default configuration. Virtual machines were created using virt-manager using the default configuration available for KVM and Xen. Virtual disks used raw images and were allotted 8GB RAM with 4 virtual CPU’s. Xen guests used [PVHVM][5].
|
||||
|
||||
### Caveats ###
|
||||
|
||||
One might argue that Fedora’s parent owner, Red Hat, puts a significant amount of effort into maintaining and improving KVM within their distribution. Red Hat hasn’t made significant contributions to Xen in years and they [made the switch to KVM back in 2009][6]. I’ve left this out of scope for these tests, but it’s still something worth considering.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, contention was tightly controlled and minimized. On most virtualized servers, you’re going to have multiple virtual machines fighting for CPU time, disk I/O, and access to the network. These tests didn’t take that type of activity into consideration. One hypervisor might have poor performance at low contention but then perform much better than its competitors when contention for resources is high.
|
||||
|
||||
These tests were performed only on Intel CPU’s. Results may vary on AMD and ARM.
|
||||
|
||||
### Results ###
|
||||
|
||||
The tests against the bare metal servers served as a baseline for the virtual machine tests. The deviation in performance between the two servers without virtualization was at 0.51% or less.
|
||||
|
||||
KVM’s performance fell within 1.5% of bare metal in almost all tests. Only two tests fell outside that variance. One of those tests was the 7-Zip test where KVM was 2.79% slower than bare metal. Oddly enough, KVM was 4.11% faster than bare metal with the PostMark test (which simulates a really busy mail server). I re-ran the PostMark tests again on both servers and those results fell within 1% of my original test results. I’ll be digging into this a bit more as my knowledge of virtio’s internals isn’t terribly deep.
|
||||
|
||||
Xen’s performance varied more from bare metal than KVM. Three tests came within 2.5% of bare metal speeds but the remainder were anywhere from 2-4x slower than KVM. The PostMark test was 14.41% slower in KVM than bare metal and I found that result surprising. I re-ran the test and the results during the second run were within 2% of my original results. KVM’s best performing CPU test, the MAFFT alignment, was Xen’s second worst.
|
||||
|
||||
I’ve provided a short summary table here with the final results:
|
||||
|
||||
<table id="tablepress-3" class="tablepress tablepress-id-3 dataTable">
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr class="row-1 odd" role="row"><th class="column-1 sorting" role="columnheader" tabindex="0" aria-controls="tablepress-3" rowspan="1" colspan="1" aria-label="&nbsp;: activate to sort column ascending" style="width: 261px;"><div> </div></th><th class="column-2 sorting" role="columnheader" tabindex="0" aria-controls="tablepress-3" rowspan="1" colspan="1" aria-label="Best Value: activate to sort column ascending" style="width: 124px;"><div>Best Value</div></th><th class="column-3 sorting" role="columnheader" tabindex="0" aria-controls="tablepress-3" rowspan="1" colspan="1" aria-label="Bare Metal: activate to sort column ascending" style="width: 124px;"><div>Bare Metal</div></th><th class="column-4 sorting" role="columnheader" tabindex="0" aria-controls="tablepress-3" rowspan="1" colspan="1" aria-label="KVM: activate to sort column ascending" style="width: 85px;"><div>KVM</div></th><th class="column-5 sorting" role="columnheader" tabindex="0" aria-controls="tablepress-3" rowspan="1" colspan="1" aria-label="Xen: activate to sort column ascending" style="width: 66px;"><div>Xen</div></th></tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
|
||||
<tbody class="row-hover" role="alert" aria-live="polite" aria-relevant="all"><tr class="row-2 even">
|
||||
<td class="column-1 ">C-Ray</td><td class="column-2 ">lower</td><td class="column-3 ">35.35</td><td class="column-4 ">35.66</td><td class="column-5 ">36.13</td>
|
||||
</tr><tr class="row-3 odd">
|
||||
<td class="column-1 ">POV-Ray</td><td class="column-2 ">lower</td><td class="column-3 ">230.02</td><td class="column-4 ">232.44</td><td class="column-5 ">235.89</td>
|
||||
</tr><tr class="row-4 even">
|
||||
<td class="column-1 ">Smallpt</td><td class="column-2 ">lower</td><td class="column-3 ">160</td><td class="column-4 ">162</td><td class="column-5 ">167.5</td>
|
||||
</tr><tr class="row-5 odd">
|
||||
<td class="column-1 ">John the Ripper (Blowfish)</td><td class="column-2 ">higher</td><td class="column-3 ">3026</td><td class="column-4 ">2991.5</td><td class="column-5 ">2856</td>
|
||||
</tr><tr class="row-6 even">
|
||||
<td class="column-1 ">John the Ripper (DES)</td><td class="column-2 ">higher</td><td class="column-3 ">7374833.5</td><td class="column-4 ">7271833.5</td><td class="column-5 ">6911167</td>
|
||||
</tr><tr class="row-7 odd">
|
||||
<td class="column-1 ">John the Ripper (MD5)</td><td class="column-2 ">higher</td><td class="column-3 ">49548</td><td class="column-4 ">48899.5</td><td class="column-5 ">46653.5</td>
|
||||
</tr><tr class="row-8 even">
|
||||
<td class="column-1 ">OpenSSL</td><td class="column-2 ">higher</td><td class="column-3 ">397.68</td><td class="column-4 ">393.95</td><td class="column-5 ">388.25</td>
|
||||
</tr><tr class="row-9 odd">
|
||||
<td class="column-1 ">7-Zip</td><td class="column-2 ">higher</td><td class="column-3 ">12467.5</td><td class="column-4 ">12129.5</td><td class="column-5 ">11879</td>
|
||||
</tr><tr class="row-10 even">
|
||||
<td class="column-1 ">Timed MAFFT Alignment</td><td class="column-2 ">lower</td><td class="column-3 ">7.78</td><td class="column-4 ">7.795</td><td class="column-5 ">8.42</td>
|
||||
</tr><tr class="row-11 odd">
|
||||
<td class="column-1 ">CLOMP</td><td class="column-2 ">higher</td><td class="column-3 ">3.3</td><td class="column-4 ">3.285</td><td class="column-5 ">3.125</td>
|
||||
</tr><tr class="row-12 even">
|
||||
<td class="column-1 ">PostMark</td><td class="column-2 ">higher</td><td class="column-3 ">3667</td><td class="column-4 ">3824</td><td class="column-5 ">3205</td>
|
||||
</tr></tbody></table>
|
||||
|
||||
If you’d like to see the full data, feel free to review the [spreadsheet on Google Docs][7].
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Based on this testing environment, KVM is almost always within 2% of bare metal performance. Xen fell within 2.5% of bare metal performance in three out of ten tests but often had a variance of up to 5-7%. Although KVM performed much better with the PostMark test, there was only one I/O test run in this group of tests and more testing is required before a clear winner in disk I/O could be found.
|
||||
|
||||
As for me, I’d like to look deeper into how KVM and Xen handle disk I/O and why their results were so different. I may also run some tests under contention to see if one hypervisor can deal with that stress with better performance.
|
||||
|
||||
I’d encourage readers to review the list of benchmark tests available in the [Phoronix test suite][8] and find some that emulate portions of their normal workloads. If your workloads are low CPU and high I/O in nature, look for some of the I/O stress tests in the suite. On the other hand, if you do a lot of audio/video transcoding, try some of the x264 or mp3 tests within the suite.
|
||||
|
||||
UPDATE: [Chris Behrens pointed out][9] that I neglected to mention the type of virtual machine I tested with Xen. I used PVHVM for the tests as it’s the fastest performing option for Linux guests on Xen 4.3. Keep in mind that PVH is available in Xen 4.4 but that version of Xen isn’t available in Fedora 20 at this time.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://major.io/2014/06/22/performance-benchmarks-kvm-vs-xen/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=article&item=intel_haswell_virtualization&num=1
|
||||
[2]:http://blog.xen.org/index.php/2011/11/29/baremetal-vs-xen-vs-kvm-redux/
|
||||
[3]:http://blog.xen.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/11/overview.png
|
||||
[4]:http://ark.intel.com/products/52269/Intel-Xeon-Processor-E3-1220-8M-Cache-3_10-GHz?q=e3-1220
|
||||
[5]:http://wiki.xen.org/wiki/Xen_Linux_PV_on_HVM_drivers
|
||||
[6]:http://www.infoworld.com/d/virtualization/red-hat-releases-first-kvm-support-rhel-54-376
|
||||
[7]:https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1kmudbOjCDUgfw76b8qP2GqNqF1ddlTOKyOjc0GmNOIE/edit?usp=sharing
|
||||
[8]:http://www.phoronix-test-suite.com/
|
||||
[9]:https://twitter.com/comstud/status/480785742730252288
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
Staying free – should GCC allow non-free plug ins?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Arguments in favour of the use of non-free plug-ins in GCC have again been raised on GCC mailing-lists, but are trumped by the arguments for GCC as a vehicle for free software development
|
||||
|
||||
Once again, Gcc and its lack of modularity has been raised as an issue and contrasted with LLVm, the new compiler on the block. GCC is huge and venerable: 5 million lines, 30 years, and growing. LLVM, in contrast, is relatively youthful and modular and allows free and proprietary languages to be added as modules.
|
||||
|
||||
The core of LLVM is ‘open source’. GCC is copyleft and unreservedly free software and doesn’t allow plug-ins or other means to add proprietary extensions to the GCC code. The argument, as delivered by Eric Raymond, is that “FSF can no longer prevent proprietary vendors from plugging into a free compiler to improve their tools. That horse has left the barn; the strategic goal of the anti-plug-in policy has been definitively busted.”
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM has been sponsored by Apple as a replacement for GCC on OS X and Apple hardware and has grown in popularity, especially among users of the BSDs. Advocates of LLVM see it as a putative replacement for GCC in the wider market for applications developers and mobile devices. The argument against GCC is that its complexity, and the commitment of its developers to copyleft licensing, constrains the possibilities for proprietary developers, who do not want to release their language or architectural specifications under a copyleft licence. Apple, of course, has a long history of antipathy to free software, and doesn’t allow applications licensed under copyleft licences to be distributed through its App Store.
|
||||
|
||||
To this extent, the argument between LLVM and GCC is a retread of the historic differences between GNU/Linux and the BSDs, between ‘open source’ and free software. Open source developers allow the code to be reused in any context, free or proprietary. Free software is restrictive in that it insists that the code, and any modifications to the code, must remain free in perpetuity. Advocates of free software would argue that the integrity of copyleft licensing has been instrumental in the spread of GCC, and has taken Linux and free software into places it would not otherwise have reached, and that free software cannot be bought or corrupted by commercial or corporate interests. Open source advocates argue that open source is more free because the user has no restrictions and can do what he or she likes, including developing closed source versions of the code.
|
||||
|
||||
Since the beginning, the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) was vital to the spread of free software. Compilers were a rare and expensive commodity and the compilers of the proprietary software companies were rife with ‘features’ that were non-compliant with ANSI programming standards. Porting software between different machines and operating systems was an unnecessarily complicated task. GCC, the first truly free cross-platform compiler, commoditised this process.
|
||||
|
||||
GCC was a breakthrough product for applications developers and mobile device developers – not just those who were committed to the idea of free software. Not only was GCC free and portable, its ubiquity and commonality across different architectures made it easier to port software between machines and to expect robust and consistent results – as the likes of John Gilmore, Michael Tiemann and David Henkel- Wallace were to discover when they made GCC and its development the key selling point of Cygnus Solutions, the first company to make money by selling free software.
|
||||
|
||||
The primary technical difference between LLVM and GCC emerges in the separation between the modules that form the ‘front ends’, ‘middle end’ and ‘back ends’ of both GCC and LLVM. ‘Front ends’ are used to interpret the code specific to the translation of a particular language. The ‘middle end’ optimises the translated code. The ‘back ends’ take the optimised code and apply the results to a specific target architecture. LLVM separates these modules into distinct entities, but for semantic and historical reasons, GCC obfuscates the separation between the modules.
|
||||
|
||||
Perhaps untypically for a free software project, it is a difficult process to add a new language or architecture to GCC and the adding of proprietary plug-ins is not allowed. There is little clear separation between the modules, and the path of least resistance is to add any feature under a free software licence. The early ports of C++ and Objective C (via Apple) are cited as examples where the original developers might have preferred to keep the code in-house and proprietary, and instead released the code as free software.
|
||||
|
||||
In contrast, LLVM has allowed, or perhaps even encouraged, the addition and development of proprietary languages and architectures – one example being Nvidia’s NVCC for GPU computing, based on Clang and LLVM. The source code of NVCC is inaccessible to free software or ‘open source’ developers.
|
||||
|
||||
Richard Stallman’s [take on this][1] is characteristically resolute: “In the free software movement, we campaign for the freedom of the users of computing. The values of free software are fundamentally different from the values of open source, which make‘bettercode’theultimategoal. IfGCCwere to change from a free compiler into a platform for non-free compilers, it would no longer serve the goal of freedom very well.
|
||||
|
||||
“The Clang and LLVM developers reach different conclusions from ours because they do not share our values and goals. They object to the measures we have taken to defend freedom because they see the inconvenience of them and do not recognise (or don’t care about) the need for them. I would guess they describe their work as ‘open source’ and do not talk about freedom.”
|
||||
|
||||
The GCC developers are unlikely to compromise on the licensing terms. While LLVM is fashionable among certain sectors of industry, because it is young and new and has been quicker to jump on developing trands in programming languages, the prevailing wind is towards greater openness, and GCC’s resolve to be incorruptible and free from commercial interests, may be the greater asset in the long term. The Unix companies learnt something from the Unix wars of the Eighties and Nineties. Languages and operating systems are tools, and are better open and shared. GCC is free software and belongs to nobody.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxuser.co.uk/features/staying-free-should-gcc-allow-non-free-plug-ins
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lwn.net/articles/582241
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
Top500 Supercomputer Remains Stuck at 33.86 Petaflops/s
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The Tianhe-2 first jumped onto the world's supercomputing stage a year ago, taking the crown of world's most powerful computer. At the time, the Tianhe-2 was rated with a performance of 33.86 petaflops per second.
|
||||
|
||||
One full year later and Tianhe-2's performance numbers are unchanged and it still holds down the top spot as the world's most powerful supercomputer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Back in June of 2013 the number two supercomputer in the world was the Cray Titan, at the U.S. Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Lab. A year ago, Titan clocked in at 17.59 petaflops per second. Titan's performance, like that of Tianhe-2, remains unchanced for June 2014 and it still holds down the number two spot.
|
||||
|
||||
In fact, over the course of the last year, very little has changed among the performance rankings for the top 10 supercomputers in the world, as ranked by the Top500 list.
|
||||
|
||||
Looking at the list from the bottom up, the number 500 system on the list, a Cray XC30 at Deutcher Wetterdienst in Germany, clocked in at 133.7 teraflops per second.
|
||||
|
||||
"The last system on the newest list was listed at position 384 in the previous TOP500," the TOP500 site stated. "This represents the lowest turnover rate in the list in two decades."
|
||||
|
||||
Once again, Intel chips dominate the list with 85.4 percent of the supercomputers, and IBM Power processors hold an 8 percent share. AMD's share now stands at 6 percent.
|
||||
|
||||
In terms of chip architectures, 53.6 percent of all systems had 8 or more cores per socket, and 13.4 percent had 10 or more cores.
|
||||
|
||||
Looking at the networking interconnects, Infiniband and Ethernet continue to split the field. On the June 2014 list, Infiniband holds a 44.4 percent share of systems.
|
||||
|
||||
In contrast, Gigabit Ethernet was reported to have a 25.4 percent share and 10 Gigabit Ethernet had 15 percent, for a combined Ethernet share of 40.4 percent.
|
||||
|
||||
HP and IBM once again dominate the list of supercomputing vendors. HP now holds a 36.4 percent share, while IBM holds 35.2 percent. Cray holds down the third spot with a 10.2 percent share.
|
||||
|
||||
While there are competing vendors, chip architectures, core counts and networking fabrics at play in the list of the worlds top 500 supercomputers, when it comes to the operating system of choice, there is no debate. Linux dominates the list with a 97 percent share, being installed on 485 systems on the top 500 list.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.serverwatch.com/server-news/top500-supercomputer-remains-stuck-at-33.86-petaflops.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
||||
Keep an eye on these 5 new features in RHEL 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> RHEL 7 supports Docker containers, systemd, Microsoft-compatible ID management, and XFS for 500TB filesystems
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After six-plus months of [public beta testing][1] and more than three years after its previous major point release, RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux) version 7 is out. The update speaks to Red Hat's interests in outfitting RHEL with many of the latest enterprise and data center features. Here are the five top-of-the-line new additions to RHEL 7 that caught our eyes.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Docker ###
|
||||
|
||||
The biggest new addition to RHEL 7 is [tight integration][2] of [Docker][3], the explosively popular application-virtualization technology. With Docker itself [hitting 1.0 status][4], the timing on RHEL 7 couldn't be more fitting.
|
||||
|
||||
Apps packaged by Docker are isolated from the system and from each other, so they can be moved between systems and still run as expected. RHEL 7 is meant to be able to use Docker as efficiently as possible so that apps don't contend for resources or get confused about which edition of a runtime to use.
|
||||
|
||||
Long-term plans on the road map for Docker in RHEL involve possibly breaking the OS itself into a series of Docker containers, allowing as little or as much of a system to be deployed as needed with minimal overhead. Dubbed "[Project Atomic][5]," the initiative is still in the early stages, with Red Hat planning to deploy it first via its Fedora Linux distribution, nominally used as a testing ground for cutting-edge technologies.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Systemd ###
|
||||
|
||||
The inclusion of the systemd process manager may spark controversy among system administrators and Linux mavens. Systemd was developed to replace the init system in use since the days of proprietary Unix, and it allows, for example, more efficient loading of services during the boot process.
|
||||
|
||||
With systemd as a potential sore spot, Red Hat has not rushed in to add it. Fedora has included systemd as a default since version 15, released in 2010, giving Red Hat good experience with how systemd behaves in the real world. Also, systemd isn't joining RHEL 7 arbitrarily, but as part of larger plans for the OS. Red Hat wants to enhance the way Docker containers are supported in RHEL 7 by using systemd, for example.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. XFS by default ###
|
||||
|
||||
A third major change, though not likely to raise nearly as many eyebrows, applies to the default file system used by RHEL to XFS.
|
||||
|
||||
Originally created by Silicon Graphics International, XFS has long been in production use with Linux systems, and on RHEL 7 it'll support file systems of up to 500TB in size. RHEL 6 used ext4 as the default, although it shipped with XFS as an option. Red Hat competitor Suse Linux [also supports XFS][6], although it [defaults to ext3][7] on installation.
|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, there's no real way to migrate from other file systems currently in use on RHEL -- such as ext4 or btrfs-- other than backing up and restoring.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Microsoft-compatible identity management ###
|
||||
|
||||
Even admins who aren't fans of Microsoft Windows have a grudging respect for Microsoft Active Directory. RHEL 7 improves the way RHEL deals with AD by adding two key new features. Cross-realm trusts can now be established between RHEL 7 and AD, so AD users can access resources on the Linux side without having to go through another sign-on step. The other big AD-related addition to RHEL 7, realmd, automates both the discovery of AD (or other Red Hat identity services) based on DNS information and the process of joining to it.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Performance Co-Pilot ###
|
||||
|
||||
Performance tuning without live statistics is like driving with the windshield painted over, so RHEL 7 introduces a new performance-monitoring system PCP ([Performance Co-Pilot][8]), [originally created][9] by Silicon Graphics International but now available as part of RHEL 7. In addition to monitoring and recording system stats, PCP sports APIs and a tool set for making that data available to other subsystems, such as -- you guessed it -- the newly introduced systemd.
|
||||
|
||||
Another minor addition in this vein: new performance profiles. RHEL 6 already had performance profiles, which are ways to tune RHEL overall to meet specific usage scenarios. RHEL 7 not only defaults to a new profile that emphasizes maximum throughput performance, but includes another new default profile for balancing performance against energy savings.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://www.infoworld.com/t/linux/keep-eye-these-5-new-features-in-rhel-7-244023
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.infoworld.com/t/linux/red-hat-enterprise-linux-7-beta-now-available-232520
|
||||
[2]:http://www.infoworld.com/t/application-virtualization/red-hat-fast-tracks-docker-apps-enterprise-linux-238122
|
||||
[3]:http://www.infoworld.com/t/application-virtualization/docker-unleashed-app-portability-gets-boost-231716
|
||||
[4]:http://www.infoworld.com/d/application-development/review-docker-10-ready-prime-time-243935
|
||||
[5]:http://www.projectatomic.io/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.suse.com/products/server/technical-information/
|
||||
[7]:https://www.suse.com/products/server/technical-information/
|
||||
[8]:http://developerblog.redhat.com/2013/11/19/exploratory-performance-pcp/
|
||||
[9]:http://oss.sgi.com/projects/pcp/index.html
|
||||
58
sources/talk/20140626 Joy of Programming--Fail Fast.md
Normal file
58
sources/talk/20140626 Joy of Programming--Fail Fast.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
Joy of Programming: Fail Fast!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> When a problem occurs in the software, it should fail immediately, in an easily noticeable way. This “fail fast” behaviour is desirable, and we’ll discuss this important concept in this column.
|
||||
|
||||
At first, a “fail fast” might appear to be a bad practice affecting reliability — why should a system crash (or fail), when it can continue execution? For this, we need to understand that fail fast is very relevant in the context of Heisenbugs.
|
||||
|
||||
Consider Bohrbugs, which always crash for a given input, for example, with a null-pointer access. These bugs are easier to test, reproduce and fix. Now, all experienced programmers would have faced situations where the bug that caused the crash just disappears when the software is restarted. No matter how much time and effort is spent to reproduce the problem, the bug eludes us. These bugs are known as Heisenbugs.
|
||||
|
||||
The effort required to find, fix and test Heisenbugs is an order of magnitude more than the effort required for Bohrbugs. One strategy to avoid Heisenbugs is to turn them into Bohrbugs. How? By anticipating the possible cases in which Heisenbugs can arise, and trying to make them Bohrbugs. Yes, it is not easy, and it is also not always possible, but let us look at a specific example where it is useful.
|
||||
|
||||
Concurrent programming is one paradigm where Heisenbugs are common. Our example is a concurrency-related issue in Java. While iterating over a Java collection, we are supposed to modify the collection only through the Iterator methods, such as the remove() method. During iteration, if another thread attempts to modify that underlying collection (because of a programming mistake), the underlying collection will get corrupted (i.e., result in an incorrect state).
|
||||
|
||||
Such an incorrect state can lead to an eventual failure — or if we are fortunate (actually, unfortunate!), the program continues execution without crashing, but gives the wrong results. It is difficult to reproduce and fix these bugs, because such programming mistakes are non-deterministic. In other words, it is a Heisenbug.
|
||||
|
||||
Fortunately, the Java Iterators try to detect such concurrent modifications, and if found, will throw a `ConcurrentModificationException`, instead of failing late — and that too, silently. In other words, the Java Iterators follow the “fail fast” approach.
|
||||
|
||||
What if a `ConcurrentModificationException` is observed in production software? As the Javadoc for this exception observes, it “
should be used only to detect bugs.” In other words, `ConcurrentModificationExceptions` are supposed to be found and fixed during software development, and should not leak to production code.
|
||||
|
||||
Well, if production software does get this exception, it is certainly a bug in the software, and should be reported to the developer and fixed. At least, we know that there was an attempt for concurrent modification of the underlying data structure, and that’s why the software failed (instead of getting wrong results from the software, or failing later with some other symptoms, for which it is not feasible to trace the root cause).
|
||||
|
||||
The “fail-safe” approach is meant for developing robust code. A very good example of writing fail-safe code is using assertions. Unfortunately, there is a lot of unnecessary controversy surrounding the use of asserts. The main criticism is this: the checks are enabled in the development version, and disabled in release versions.
|
||||
|
||||
However, this criticism is wrong: asserts are never meant to replace the defensive checks that should be put in place in the release version of the software. For example, asserts should not be used to check if the argument passed to a function is null or not. Instead, an if condition should be used to check if the argument is passed correctly, or else an exception, or a premature return, should be performed, as appropriate to the context. However, asserts can be used to do additional checks for assumptions that are made in the code, which are supposed to hold true. For example, a condition that checks that the stack is not empty after a push operation is performed on it (i.e., checking for “invariants”).
|
||||
|
||||
So, fail fast, be assertive, and you’re on the way to developing more robust code.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via:http://www.opensourceforu.com/2011/12/joy-of-programming-fail-fast/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
[13]:
|
||||
[14]:
|
||||
[15]:
|
||||
[16]:
|
||||
[17]:
|
||||
[18]:
|
||||
[19]:
|
||||
[20]:
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
Linux Administration: A Smart Career Choice
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> This is a good year for IT professionals with a number of new jobs in emerging technologies like Big Data and Analytics, and Social Mobile Analytics and Cloud (SMAC) as employers look to strengthen their technological force.
|
||||
|
||||
If we were to believe the reports by [Dice.com][1] and Linux foundation released in mid Feb, 2014, this year will be a high octane year for Linux professionals and aspirants particularly. Thus it only makes sense to be future-ready and find out about the details of career opportunities such as that of a Linux administrator.
|
||||
|
||||
Dice.com, the leading job site for tech professionals and Linux Foundation did a comprehensive survey to find out about the advantage Linux professionals have in the current technology landscape. The findings were heavily skewed in favor of those who are looking for a good job opportunity on Linux platform.
|
||||
|
||||
While seventy seven percent of hiring managers surveyed consider hiring Linux talent as one of their top priorities (up from 70 percent in 2013), 64 percent of professionals chose to work with Linux owing to its ubiquitous nature in the present day technology infrastructure. More than nine in ten recruitment manager is planning to hire a Linux professional in the next six months. This demand is surely going to translate in form of a lot of interview calls from employers. Most hiring managers also agree to the fact that it is rather difficult to find experienced professionals, and those who have the right mix of skills, knowledge, certifications and experience are being aggressively recruited.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Linux administration? ###
|
||||
|
||||
The findings of this report make it clear that Linux professionals are amongst the most sought after in the current tech market. However, a more interesting finding of the report is that amongst all the skills, the hiring managers are most actively seeking system administration, with 58 percent confirming they were on look out of professionals with good system administration skills. The reason is quite simple. There aren’t too many good system administrators out there, which is also driving the salaries of system admins northwards.
|
||||
Getting started in Linux administration
|
||||
|
||||
Armed with all this data, it wouldn’t come as surprise if you decide right away to pursue a career in Linux administration. So, how do you become a pro Linux system admin? Well, the right mix of certification, education and experience will obviously land you the perfect Linux job, but if you are clueless about a place to start, then a degree in computers is what you should be looking at. This could be B.Tech with Computer Science or IT as specialisation or Bachelors in Computer Application or even a Bachelor in Science with IT as specialisation will do. This would actually make you familiar with the various aspects of computer science as a subject, likes of programming, hardware, and software. This understanding would come handy in the advancement of your career, when you climb the next ladder through certifications.
|
||||
|
||||
### Certifications ###
|
||||
|
||||
It is widely believed that IT certifications do help one in career advancement. However, it ultimately boils down to selecting the right certification to gain the maximum RoI. There are many Linux based certifications, the most famous of which is Red Hat Certification Program, which teaches general Linux related skills along with specific system administration skills.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the vendor sponsored certifications, there is a vendor-independent Linux Professional Institute Certification offered by Linux Professional Institute, a non-profit organisation based in Toronto, Canada.
|
||||
|
||||
These exams can be taken by anyone irrespective of their nationalities. The LPI programs have three level hierarchies that include LPIC-1: Junior Level Linux Administration, LPIC-2: Advanced Level Linux Administration and LPIC 3: Senior Level Linux Administration. In order to be considered seriously for any system administrator job opportunity in one must possess at least one of the above described certifications. The LPI also has partnerships with SUSE, which is the vendor for a famous enterprise operating system going by the same name. CompTIA, which is a global IT certification agency also provided a Linux+ certification which was phased out after an agreement between LPI and CompTIA.
|
||||
|
||||
### Salaries and Benefits ###
|
||||
|
||||
The compensations for Linux administrators are generally on the higher side. As per PayScale, the annual median salary is around INR 3 lacs for entry level professionals (as updated on 27th March, 2014). With experience, there is an exponential increase in the salary levels as individuals with 5+ years of experience getting annual packages in seven figures.
|
||||
Well, with the grass being greener for Linux professionals this year, you won’t get a better opportunity or time for pursuing career as a Linux system administrator.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.opensourceforu.com/2014/04/career-overview-linux-administrator/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://dice.com/
|
||||
@ -1,127 +0,0 @@
|
||||
jiajia translating...
|
||||
|
||||
Cup 2014 Brazil: Watch FIFA World Cup 2014 Competition in Your Linux Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Football is the most played and most watched sports on Earth. The present form of football originated in Britain. Football players run an average of more than six miles during a single match. Over one billion fans watched last world cup football matches on Television. This figure is estimated to rise on an above note, this year.
|
||||
|
||||
Yeah! 2014 FIFA World Cup is going to start from 12th of June and will last on 13th of July. This will be the 20th FIFA World Cup, which is scheduled to be played in Brazil. A total of 32 countries are participating in this event.
|
||||
|
||||
For the fan-boys of football, here we are going to throw light on an application software called “icup 2014 Brazil”, which will update you with latest scores, keep tracks of the match score of your favourite team. Here in this article we will be discussing its features, usages, installation, etc.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
iCup 2014 Brazil
|
||||
|
||||
### What is icup 2014 Brazil? ###
|
||||
|
||||
icup 2014 Brazil is an application which is capable of keeping a track of match results of the FIFA world cup 2014 into your Linux desktop, starting shortly.
|
||||
|
||||
### Features of icup 2014 Brazil ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Adaptive User Interface, i.e., auto-resize of user interface.
|
||||
- Fast Access to Statistics.
|
||||
- Social Network Sharing Enabled, which extends to Facebook, Twitter and Google+.
|
||||
- Latest one is – Retina display Support.
|
||||
- Detailed data with time events and Statistics related to match and Team.
|
||||
- Audio Kit which comprise of the ‘National-Anthem’ of all the participating countries (32) in high quality effect along with the stadium background sound which makes the whole thing real.
|
||||
- An inbuilt calendar with the support of time zone for better understanding of events in local time zone, grouping of data and statistics for real time comparison groupable by day or stage, Graphical 2nd stage table, Result and Scores of Teams in real time.
|
||||
- Proxy support.
|
||||
|
||||
### Platforms and Architecture Supported ###
|
||||
|
||||
The application is designed to run on all major platforms including **Mac**, **Windows** and **Linux**. For the point of Linux, it is important to mention that the application is designed for **x86** processor only. However installing an **x86** application on **x86_64** architecture is possible. We have to tweak a little to make it work **x86_64** systems.
|
||||
|
||||
#### An insight of the Technical Specification on different Platforms ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Live Result, Calendar, Grouping of Data, 2nd stage Table, Social Network Linking and Multi-language support – Available for all supported platform.
|
||||
- Retina Display – No support in Windows and Linux, however supported in Mac OS.
|
||||
- Detailed Statistics – Supported in Linux. Donation-ware for Windows and Mac.
|
||||
- Audio Kit – Supported in Mac and Linux. Unknown for Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
**Important**: As visible in the above specification, some of the features like detailed specification are not available on platform other than Linux, for free. It is just to support Server and Bandwidth cost. For a Linux user, nothing needs to be cared about as far as detailed statistics are concerned, a proud moment.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing iCup 2014 Brazil in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
First go to official [iCup 2014 Brazil download][1] page and download application according to your platform and architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On 32-Bit System ####
|
||||
|
||||
# cd Downloads/
|
||||
# tar xvf iCup_2014_FREE-Brazil_1.1_linux.tar.bz2
|
||||
# cd iCup\ 2014\ FREE\ -\ Brazil\ 1.1/
|
||||
# chmod 755 iCup\ 2014\ FREE\ -\ Brazil
|
||||
|
||||
As I said above, this application is designed for x86 systems only. In order to Install a 32 bit application on 64 bit architecture, we need to prepare our system by installing some packages – **GTK+2** and **libstdc++.so.6**.
|
||||
|
||||
Well not for this Application only, but there are a whole lot of application in Linux which is not supported in 64-bit e.g., **Skype**. We need to build our System to install those applications.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On 64-Bit Systems ####
|
||||
|
||||
Install **GTK+2** and **libstdc++so.6**, using apt or yum command as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install libgtk2.0-0 libstdc++6 [on Debian based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
If you get any dependency error, run the following command to resolve those dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -f install
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install gtk2 libstdc++ [on RedHat based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
Once all the required packages are installed. Now the System is capable of running 32 bit applications on 64-bit systems, now go the directory where you’ve downloaded ‘**iCup 2014 Brazil**‘ package and run the following commands to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
# cd Downloads/
|
||||
# tar xvf iCup_2014_FREE-Brazil_1.1_linux.tar.bz2
|
||||
# cd iCup\ 2014\ FREE\ -\ Brazil\ 1.1/
|
||||
# chmod 755 iCup\ 2014\ FREE\ -\ Brazil
|
||||
|
||||
Next, move to the directory and double click the executable to start the application. In the below screen-shot you may not get the full information since the FIFA 2014 has not started till now. Although the glimpse of what we can get once the event starts.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
iCup Brazil 2014
|
||||
|
||||
No detailed Information : World cup hasn’t started Yet.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Match Detailed Information
|
||||
|
||||
Groups and Teams
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Groups and Teams
|
||||
|
||||
2nd stage Detailed Information
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
2nd stage Detailed Information
|
||||
|
||||
Match Details. Seems incomplete now.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Match Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Language Change window and Social share button Integrated.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Language Change
|
||||
|
||||
Donation is optional for Linux. You can always contribute.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Donation
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
The above Application seems promising and may prove to be a boon for those Football fan-wall who can now remain connected.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I’ll be here again with another interesting article soon. In that mean keep connected to Tecmint.com. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback in the comment section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/view-fifa-world-cup-matche-results/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.e-link.it/icup/brazil2014/icup-brazil-2014-desktop-app.php
|
||||
@ -1,86 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Managing Vim extensions with NeoBundle
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[NeoBundle][1] is a third-generation extension manager for [Vim][2], building on [Vundle][3], which builds on [Pathogen][4]. In an earlier article, I [advised against using Neobundle][5] because of its rapid development and minimal English documentation. Now, more than a year later, both problems are more manageable.
|
||||
|
||||
Why use an extension manager? Vim supports a healthy number of plugins, but its unmodified structure makes administering them difficult because extension files can be spread over several directories. Vim extension managers simplify things. Pathogen, Vundle, and NeoBundle create the directory ~/.vim/bundle, with a separate subdirectory for all the files of each extension. This structure allows users to easily and thoroughly delete extensions, either manually or via a file manager, and helps minimize potential conflicts when you have a couple of dozen extensions.
|
||||
|
||||
NeoBundle openly models itself on Vundle. Like Vundle, it both installs and updates extensions. However, the help file openly admits that "Neobundle is not a stable plugin manager. If you want [a] stable plugin manager, you should use Vundle." New releases, the help warns, "may break compatibility" – a comment that is less than reassuring, coming from the developers.
|
||||
|
||||
So why should you use NeoBundle? One reason is that Vundle works only with [Git][6], while NeoBundle also supports [Subversion][7] and [Mercurial][8] repositories. Another reason is that, if you want to keep extension updates from breaking your Vim ecosystem, you can lock NeoBundle so that it uses only a specific version of any particular extension.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, NeoBundle's creator, Shougo Matsuishita, is adding its command structures to several other extensions in order to reduce the list of commands they use. Currently, NeoBundle supports three such extensions: [unite.vim][9], a file and buffer manager that works within Vim; [vimshell.vim][10], a scripting shell for Vim; and [vimproc.vim][11], which works within vimshell.vim to allow asynchronous events. That's an idiosyncratic collection, and all three are poorly documented in English, so average users may wish to forgo them. Before tackling any of them, most users should focus on the basics of NeoBundle.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing and initializing NeoBundle ###
|
||||
|
||||
NeoBundle requires Vim 7.2.051 or higher and requires git be installed, and depends on [cURL][12] for downloading files. You can install NeoBundle manually, but the fast way to install it is to clone its repository on GitHub using cURL. From your home directory, enter the following command to copy the files for NeoBundle into .vim/bundle/neobundle.vim, where the extension can manage itself:
|
||||
|
||||
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Shougo/neobundle.vim/master/bin/install.sh | sh
|
||||
|
||||
You also need to modify your .vimrc file. NeoBundle's GitHub page offers a sample .vimrc file, but copying it means installing five plugins you may not want. This is the minimal content that you need:
|
||||
|
||||
if has('vim_starting')
|
||||
set nocompatible
|
||||
set runtimepath+=~/.vim/bundle/neobundle.vim/
|
||||
call neobundle#begin(expand('~/.vim/bundle/'))
|
||||
NeoBundleFetch 'Shougo/neobundle.vim'
|
||||
call neobundle#end()
|
||||
filetype plugin indent on
|
||||
|
||||
These lines set up and start NeoBundle, and set NeoBundle to update itself just like any other plugin. NeoBundle defaults to updating itself from GitHub repositories, so if you use GitHub, all you have to do is specify the maintainer's username and the directory for the plugin; in the lines above, NeoBundleFetch needs to specify only "Shougo/neobundle.vim" instead of the complete path on GitHub. If you want to use another site instead, including one that supports Subversion or Mecurial, you need to add the complete URL to the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to install other NeoBundle plugins, use this generic form:
|
||||
|
||||
curl -k https://github.com/[MAINTAINER]/ [PLUGIN PATH] > ~/.vim/bundle/[PLUGIN PATH]
|
||||
|
||||
or, to give a more specific example, you can install the [vim-abolish plugin][13], a super-charged search and replace extension, with the command
|
||||
|
||||
curl -k https://github.com/tpope/vim-abolish > ~/.vim/bundle/abolish
|
||||
|
||||
To have the extension updated automatically, add a line below the NeoBundleFetch line that gives the path to its repository. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
NeoBundle 'tpope/vim-abolish'
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally, you can specify a particular branch or revision of NeoBundle to use, preventing any updates. This option can be useful if you are using extensions that are in rapid development and you want to avoid having them break when you update any other extensions. For instance:
|
||||
|
||||
NeoBundle 'Shougo/vimshell', { 'rev' : '3787e5' }
|
||||
|
||||
Another option is to place the directive NeoBundleCheck on a line at the end of the NeoBundle stanza in .vimrc. When this line is present, NeoBundle checks for uninstalled bundles and prompts you to install them. You can also run the utility `:NeoBundleInstall` from within NeoBundle to initialize or update installed extensions.
|
||||
|
||||
### NeoBundle utilities ###
|
||||
|
||||
Many of NeoBundle's utilities function similarly to Vundle's, but they are differently named. You use the utilities to administer plugins from within NeoBundle:
|
||||
|
||||
- Run `:NeoBundleUpdate` when you install or update extensions, and when you manually remove an extension's files. It can be followed by a specific plugin, such as "/Shougo/neobundle.vim," or without a plugin name to configure all plugins that are installed but not configured. The command NeoBundleInstall! provides the same functionality.
|
||||
- `:NeoBundle {REPOSITORY URI} [[REVISION}] [,OPTIONS}]]` configures an extension while locking it into a specified version, preventing any updates.
|
||||
- `:NeoBundleList` lists unintialized extensions.
|
||||
- `:NeoBundleClean` runs an interactive utility for removing unused extensions.
|
||||
|
||||
These utilities are also available in slightly different forms when you run NeoBundle with unite.vim. You can learn more about the utilities in all their forms by running the command `:help neobundle`.
|
||||
|
||||
Deciding whether to use NeoBundle
|
||||
|
||||
NeoBundle is a powerful tool, but its seemingly permanent state of rapid development can be a blessing or a curse, depending on your preferences. If you want the latest features and extensions, NeoBundle can make Vundle and Pathogen look decidedly old-fashioned.
|
||||
|
||||
However, with the online help itself warning of instability, ignoring the possibility of the latest version of one extension interfering with the proper functioning of another would be rash. At the very least, you should specify in your .vimrc a version of NeoBundle that you know to be stable. You might also do the same for any extension that you use regularly. With this precaution, you can enjoy following the development of NeoBundle and its related extensions while avoiding the consequence of working on the bleeding edge.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.openlogic.com/wazi/bid/348084/Managing-Vim-extensions-with-NeoBundle
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/Shougo/neobundle.vim
|
||||
[2]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/vim
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/gmarik/Vundle.vim
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/tpope/vim-pathogen
|
||||
[5]:http://www.openlogic.com/wazi/bid/262302/Three-tools-for-managing-Vim-plugins
|
||||
[6]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/git
|
||||
[7]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/subversion
|
||||
[8]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/mercurial
|
||||
[9]:https://github.com/Shougo/unite.vim
|
||||
[10]:https://github.com/Shougo/vimshell.vim/blob/master/doc/vimshell.txt
|
||||
[11]:https://github.com/Shougo/vimproc.vim/blob/master/doc/vimproc.txt
|
||||
[12]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/curl
|
||||
[13]:https://github.com/tpope/vim-abolish
|
||||
@ -1,52 +0,0 @@
|
||||
(翻译中 by runningwater)
|
||||
Make Ubuntu 14.04 Look Like Mac With Zukimac Theme
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Unity itself is a beautiful desktop but people over the world are smitten by the looks of Mac OS X. If you are among one of those, you don’t need to ditch Ubuntu just for the sake of OS X looks. Instead you can give it a makeover and **make Ubuntu 14.04 look like Mac OS X**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Make Ubuntu 14.04 look like Mac OS X ###
|
||||
|
||||
To give Ubuntu a makeover of Mac, we shall be using Zukimac theme.
|
||||
|
||||
- Get Zukimac theme from the link below:[Download Zukimac Theme for Ubuntu 14.04][1]
|
||||
- Extract the downloaded zipped file. You will find two directories in there, Zukimac and Zukimac-ml. Copy these to .themes directory in your home directory. Go to Home and press Ctrl+H to show all the hidden folders. If there is no .themes folder here, create one.
|
||||
- Use [Unity Tweak Tool to change the theme][2].
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it. Zukimac gives some a basic look and feel of Mac OS. Here is what it looks like with default OS X Maveric wallpaper.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Further changes to get Mac feel in Ubuntu 14.04 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, you can **install a dock launcher like Plank** or Docky. To install Plank in Ubuntu 14.04 use the commands below:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ricotz/docky
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install plank
|
||||
|
||||
Along with the dock launcher, you can also install S**ynapse indicator as an alternative of Mac Spotlight**. Use the following PPA from Noobslabs to install Synapse indicator:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install indicator-synapse
|
||||
|
||||
Apart from these two, you can also install **Slingscold launcher, alternative of Mac OS X launchpad**. Use the same Noobslabs PPA as mentioned above to install Slingscold launcher in Ubuntu 14.04:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install slingscold
|
||||
|
||||
Honestly, I am an avid Ubuntu fan and I like Ubuntu’s default Unity looks. In addition, there are plenty of [beautiful icon themes in Ubuntu 14.04][3] to beautify it. But as I mentioned before there are plenty of people who like Mac OS X and I hope this tutorial helped them to make Ubuntu 14.04 look and feel like Mac OS X.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-1404-mac-zukimac-theme/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://gnome-look.org/content/show.php/Zukimac?content=165450
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-themes-in-ubuntu-13-10/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
@ -1,18 +1,16 @@
|
||||
11 Advance MySQL Database “Interview Questions and Answers” for Linux Users
|
||||
translating by johnhoow...
|
||||
给linux用户的11个高级MySQL数据库面试问题和答案
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
We have already published two MySQL articles, well appreciated by Tecmint Community. This is the third article on MySQL Interview series and sixteen in the the Interview Genre Column.
|
||||
我们已经发表了两篇MySQL的文章,非常感谢Tecmint社区的大力支持.这是MySQL面试系列的第三篇文章,并且在面试专栏中排第16.
|
||||
- [15个基本的MySQL面试问题][1]
|
||||
- [给中级人员的10个MySQL面试问题][1]
|
||||
|
||||
- [15 Basic MySQL Interview Questions][1]
|
||||
- [10 MySQL Database Interview Questions for Intermediates][1]
|
||||
注:上面这两篇文章我们都翻译过,可以适当修改成我们的链接
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
感谢你们这一路上对我们的支持.这篇文章主要针对MySQL的实用性,讲面试方面的问题.
|
||||
|
||||
We have reached here all because of yours support and we seek the same in future form your end. Here in this article we will be concentrating on the practical aspect of MySQL, the question relevant for Interview aspect.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Using SELECT statement find the version of the server you are running and print the name of the current database? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**: The below MySQL command will show server version and currently selected Database.
|
||||
### 1. 如何使用SELECT语句找到你正在运行的服务器的版本并打印出当前数据库的名称? ###
|
||||
**答案**:下面的语句的结果会显示服务器的版本和当前的数据库名称
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SELECT VERSION(), DATABASE();
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,7 +21,7 @@ We have reached here all because of yours support and we seek the same in future
|
||||
+-------------------------+------------+
|
||||
1 row in set (0.06 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
In the Database Column it is showing **NULL** value because we have not selected any database. So, select database as shown in the following command.
|
||||
在Database一栏中显示**NULL**是因为我们当前没有选择任何数据库.因此,使用下面的语句先选择一个数据库,就能看到相应的结果.
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> use Tecmint;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -43,9 +41,9 @@ In the Database Column it is showing **NULL** value because we have not selected
|
||||
+-------------------------+------------+
|
||||
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. USE NOT Operator (!) to select all the users except ‘SAM’ from a table say ‘Tecmint’ ###
|
||||
### 2. 使用非运算符(!)从表"Tecmint"中列出除了user等于"SAM"的所有记录
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**: The below statement will show all the columns of all the users from table ‘**Tecmint**‘ except the user ‘**SAM**‘.
|
||||
**答案**:使用下面的语句
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SELECT * FROM Tecmint WHERE user !=SAM;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -56,9 +54,10 @@ In the Database Column it is showing **NULL** value because we have not selected
|
||||
| 2001-05-15 08:50:57 | TIM | venus | phil | venus | 978 |
|
||||
+---------------------+---------+---------+---------+---------+-------+
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Is it possible to implement ‘AND’ with NOT (!) Operator. ###
|
||||
### 3. 是否能够使用非运算符(!)来实现'AND'运算
|
||||
|
||||
**Ans**: The AND operator is used when we use (=) and the operator OR is used when we use (!=). An example of (=) with AND Operator.
|
||||
**答案**: The AND operator is used when we use (=) and the operator OR is used when we use (!=). An example of (=) with AND Operator.
|
||||
**答案**:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SELECT * FROM mail WHERE user = SAM AND root = phil
|
||||
|
||||
@ -201,4 +200,4 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/mysql-advance-interview-questions/
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/basic-mysql-interview-questions-for-database-administrators/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-mysql-database-interview-questions-for-beginners-and-intermediates/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-mysql-database-interview-questions-for-beginners-and-intermediates/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[Tranlation] in progress -- [213edu][https://github.com/213edu]
|
||||
|
||||
ENCRYPT DNS TRAFFIC IN LINUX WITH DNSCRYPT (VIA OPENDNS)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**DNSCrypt, as its name suggests, encrypts DNS traffic between your computer and OpenDNS, in the same way SSL turns HTTP traffic into HTTPS encrypted traffic.**
|
||||
|
||||
Initially, DNSCrypt was announced as being available for Mac only for now, but according to an OpenDNS [article][1] posted yesterday, the source code for DNSCrypt was published on GitHub when they've released the Mac preview and even though there's no user interface yet, Linux users can already install DNSCrypt.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why use DNSCrypt? ###
|
||||
|
||||
**DNSCrypt encrypts all DNS traffic between your computer and the OpenDNS servers (so you'll be using OpenDNS) and can protect you from man-in-the-middle attacks, spying, resolver impersonation, can prevent Internet service providers from blocking various websites and more.**
|
||||
|
||||
This is the first tool that encrypts DNS traffic - for instance, TOR encrypts DNS requests, but they are decrypted at the exit node.
|
||||
|
||||
> It doesn’t require any changes to domain names or how they work, it simply provides a method for securely encrypting communication between our customers and our DNS servers in our data centers.
|
||||
|
||||
You can read more about DNSCrypt @ [OpenSND DNSCrypt][2] page and on [GitHub][3].
|
||||
|
||||
### How to use DNSCrypt in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Download DNSCrypt][4], install it and then run the following command in a terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo /usr/sbin/dnscrypt-proxy --daemonize
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then set your DNS server to "127.0.0.1" - to do this under GNOME, go to your Network Connections and select "Edit" and enter "127.0.0.1" under "DNS servers". If you are using DHCP, just select "Automatic (DHCP) addresses only, so you can enter a DNS server. Then, restart your network connection.
|
||||
|
||||
You can then check if you're using OpenDNS by visiting [THIS][5] link.
|
||||
|
||||
To get DNSCrypt to start automatically, you must create an init script. For Ubuntu, see below.
|
||||
|
||||
**Arch Linux users can install DNSCrypt-proxy via [AUR][6]** (it includes an rc.d script).
|
||||
|
||||
### DNSCrypt in Ubuntu ###
|
||||
|
||||
To make DNSCrypt start automatically in Ubuntu, I've created an Upstart script which you can use if you want - [download it][7].
|
||||
|
||||
Update: Because in Ubuntu 12.04 there is a local DNS cache running on 127.0.0.1 (dnsmasq), I've updated the script to make DNSCrypt use 127.0.0.2, so you should add "**127.0.0.2**" as your DNS and not "127.0.0.1" if you're using this script (for any Ubuntu version). Thanks to zzecool for testing it in Ubuntu 12.04!
|
||||
|
||||
To install the script, use the commands below (firstly extract the downloaded archive):
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cp dnscrypt.conf /etc/init/
|
||||
sudo ln -s /lib/init/upstart-job /etc/init.d/dnscrypt
|
||||
|
||||
And finally, start it with:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo start dnscrypt
|
||||
|
||||
DNSCrypt should now start automatically when you boot. To stop it, you can use:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo stop dnscrypt
|
||||
|
||||
[Download DNSCrypt][8] (.deb, .rpm and source code available)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.webupd8.org/2012/02/encrypt-dns-traffic-in-linux-with.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://blog.opendns.com/2012/02/16/tales-from-the-dnscrypt-linux-rising/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.opendns.com/technology/dnscrypt/
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/opendns/dnscrypt-proxy
|
||||
[4]:http://download.dnscrypt.org/dnscrypt-proxy/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.opendns.com/welcome
|
||||
[6]:http://aur.archlinux.org/packages.php?ID=54702
|
||||
[7]:http://webupd8.googlecode.com/files/dnscrypt-0.2.tar.gz
|
||||
[8]:https://github.com/opendns/dnscrypt-proxy/downloads
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[Translating] --213edu
|
||||
|
||||
How to enable testing and unstable repository on Debian
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Testing/Unstable sources
|
||||
@ -154,4 +156,4 @@ via: http://www.binarytides.com/enable-testing-repo-debian/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://wiki.debian.org/AptPreferences
|
||||
[2]:http://wiki.debian.org/DebianTesting
|
||||
[3]:http://www.debian.org/security/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.debian.org/security/
|
||||
|
||||
70
sources/tech/20140624 Super Pi Brothers.md
Normal file
70
sources/tech/20140624 Super Pi Brothers.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
Super Pi Brothers
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I don't game as much as I used to. Although I've certainly spent countless hours of my life in front of a Nintendo, SNES, or after that, playing a first-person shooter on my computer (Linux only, thank you), these days, my free time tends to go toward one of the many nongaming hobbies I've accumulated. Recently though, I found myself dusting off my Wii console just so I could play an NES and SNES game I re-purchased for it. The thing is, those games require using a somewhat strange controller, and I already have a modified SNES controller that can connect over USB. That was enough to encourage me to search for a better solution. Of course, I simply could connect three or four consoles and stack up games in my living room, but I've grown accustomed to ripping my CDs and DVDs and picking what I want to listen to or watch from a central media center. It would be nice if I didn't have to get up and find a cartridge every time I wanted to switch games. This, of course, means going with emulation, but although in the past I'd had success with a modified classic Xbox, I didn't have that hardware anymore. I figured someone must have gotten this set up on the Raspberry Pi, and sure enough, after a brief search and a few commands, I had a perfect retro-gaming arcade set up on a spare Raspberry Pi.
|
||||
|
||||
One nice thing about the Raspberry Pi project is the large number of people out there with identical hardware. For me, that meant instead of having to go through someone else's instructions, knowing I'd likely have to tweak it to suit my setup, I basically could follow someone else's guide verbatim. In my case, I found the RetroPie project, which wrapped up all of the commands you would need to install everything on a Raspberry Pi into a single large script. At the end, you have the RetroArch project fully installed and configured, which includes all of the major emulators you'd want and a centralized method to configure them, plus an EmulationStation graphical front end the Pi can boot directly into that makes it simple to navigate to the game you want, all from a gamepad.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install RetroPie ###
|
||||
|
||||
Before you install RetroPie, you will want to make sure your Raspbian distribution (the default Linux distribution for a Raspberry Pi, and the one this project assumes you will use) is completely up to date, including any new firmware images. This just means a few common `apt` commands. Although you certainly could connect a keyboard to your Raspberry Pi for this step, I've found it more convenient to `ssh` in to the device so I could copy and paste commands:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -y upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
Now that the Raspberry Pi is up to date, make sure the git and dialog packages are installed, and then use git to download RetroPie:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -y install git dialog
|
||||
$ cd
|
||||
$ git clone --depth=0
|
||||
↪git://github.com/petrockblog/RetroPie-Setup.git
|
||||
|
||||
This will create a RetroPie-Setup directory containing the main setup script. Now you just need to go inside that directory and execute it:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd RetroPie-Setup
|
||||
$ chmod +x retropie_setup.sh
|
||||
$ sudo ./retropie_setup.sh
|
||||
|
||||
This script presents you with an in-terminal menu (Figure 1) where you can choose to perform a binary installation or source installation, set up RetroPie, or perform a series of updates for the RetroPie setup script and binaries. Choose either the binary or source installation. The binary installation won't take as much time, but you may risk running older versions of some of the software. The source installation requires you to compile software, so it takes longer, but at the end, you will have the latest possible versions of everything. Personally, I opted for the binary install, knowing I always could re-run the script and go with the source install if I found any problems.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Figure 1. RetroPie Setup Menu ####
|
||||
|
||||
This part of the process will take quite some time on a vanilla Raspbian image, as there are a lot of different packages to download and install. Once the installation completes, go back to the main RetroPie setup screen and select SETUP from the main menu. In this submenu, you can tweak settings, such as whether to start EmulationStation from boot (recommended) and whether to enable a splash screen. In my case, I enabled both settings as I intended my device to be a standalone emulation machine. Note that if you do allow EmulationStation to start up from boot, you still can always ssh in to the machine and run the original RetroPie configuration script to change the settings.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding ROMs ###
|
||||
|
||||
You also can add ROMs within the RetroPie setup screen. If you choose the Samba method in the menu, you then can locate a local Samba mountpoint on your network, and you can copy ROMs from that. With the USB stick method, RetroPie will generate a directory structure on a USB stick that you plug in to your Raspberry Pi that represents the different emulators it supports. After this point, you can take that USB stick to another computer and copy ROMs over to the appropriate directory, and the next time you plug it in to the Raspberry Pi, it automatically will sync the files over. Finally (and this is what I did), you just can use scp or rsync to copy over ROMs to the appropriate directory under ~/RetroPie/roms/. So for instance, NES games would be copied to ~/RetroPie/roms/nes/.
|
||||
|
||||
Once you are done with the configuration and exit out of the RetroPie setup script, you will want to reboot back into EmulationStation, but before you do, you should reconfigure the memory split on the Raspberry Pi so that it is set to 192 or 128, so run:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo raspi-config
|
||||
|
||||
and go to the Advanced Settings to change the memory split setting. Now you can reboot safely.
|
||||
|
||||
### EmulationStation ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once you reboot, you should be greeted with the initial EmulationStation screen, which will prompt you to set up your joystick, gamepad or keyboard buttons so it can work with the EmulationStation menu. Note that this doesn't affect how your controllers work within games, just within the EmulationStation menu. After your controller or controllers are set up, you should be able to press right and left on your controller to switch between the different emulator menus. In my case, all of the buttons on my gamepad were going to be used within games, so I made a point to bind a key on a separate keyboard to the menu function so I could exit out of games when I was done without having to reboot the Raspberry Pi.
|
||||
|
||||
EmulationStation will show you only menus that represent emulators for which it has detected ROMs, so if you haven't copied ROMs for a particular emulator yet, you will want to do that and potentially restart your Raspberry Pi before you can see them. Also, by default, your controller will not be configured for any games, but if you press the right arrow enough times within EmulationStation, you will get to an input configuration screen that allows you to map keys on your controller to keys inside a game. The nice thing about this setup is that after you configure the keys, it will apply appropriately within each emulator.
|
||||
|
||||
That's it. From this point, you can browse through your collection of games and press whatever button you bound to Accept to start playing. At first I was concerned the Raspberry Pi wouldn't have the horsepower to play my games, but so far, it has been able to play any games I tried without a problem.
|
||||
|
||||
### Resources ###
|
||||
|
||||
The RetroPie Project: [http://blog.petrockblock.com/retropie][1]
|
||||
|
||||
RetroPie Installation Docs: [https://github.com/petrockblog/RetroPie-Setup][2]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/super-pi-brothers
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://blog.petrockblock.com/retropie
|
||||
[2]:https://github.com/petrockblog/RetroPie-Setup
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,202 @@
|
||||
CNprober翻译中。。。619913541
|
||||
|
||||
Betty: Translate English Phrases Into Linux Commands
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Betty** is an open source tool that translates English-like phrases into Linux commands. The main goal of this project is to use the Linux powered systems through natural language input. Let us see some examples how it works.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation ###
|
||||
|
||||
Betty installation is very simple and straight forward. Make sure you’ve installed the following prerequisites packages.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Debian based systems: ####
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install git curl ruby
|
||||
|
||||
On RPM based systems:
|
||||
|
||||
yum install git curl ruby
|
||||
|
||||
Now, git clone the Betty repository to any preferred location. I am going to clone the betty repo in my home directory **i.e /home/sk/**.
|
||||
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/pickhardt/betty
|
||||
|
||||
Add the betty alias in your bashrc file.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo nano ~/.bashrc
|
||||
|
||||
Add the following line at the end:
|
||||
|
||||
alias betty="/home/sk/betty/main.rb"
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure you’ve replaced the correct path of the betty directory.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s done. Now, it’s time to play with betty.
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
You should include the word “betty” in-front of every English phrases. As you may know already, if we want to know the user name of our system, we run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
whoami
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
sk
|
||||
|
||||
As you see above, my current user name is **sk**. Well, now we can get the same result using betty as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
betty whats my username
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
Betty: Running whoami
|
||||
sk
|
||||
|
||||
Cool, isn’t it? Yes. Betty understands the normal English phrase “whats my username” that I entered, and ran the command “whoami” automatically, and finally displayed the correct output.
|
||||
|
||||
Let us see some other commands too.
|
||||
|
||||
Betty will respond in multiple ways if you didn’t enter exactly what you’re looking for. For example, we run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
betty whats my name
|
||||
|
||||
Betty isn’t sure whether she should find the system username or full name. In this case, she will ask you multiple questions to find the exact result. As you see below, Betty asks me which command(whoami or finger $(whoami) | sed ‘s/.*: *//;q’) should I want to execute. I just want it to display my username, so i chose number **1**.
|
||||
|
||||
Betty: Okay, I have multiple ways to respond.
|
||||
Betty: Enter the number of the command you want me to run, or N (no) if you don't want me to run any.
|
||||
[1] whoami
|
||||
Gets your system username.
|
||||
[2] finger $(whoami) | sed 's/.*: *//;q'
|
||||
Gets your full name.
|
||||
1
|
||||
Betty: Running whoami
|
||||
sk
|
||||
|
||||
### Compress And Uncompress Folders ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to compress a file or a folder, use the following command. For example, I want to compress a folder called “test” folder in my home directory.
|
||||
|
||||
betty compress test/ test.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
Betty: Running tar -czvf test.tar.gz test/
|
||||
test/
|
||||
test/home/
|
||||
test/home/sk/
|
||||
test/home/sk/test/
|
||||
test/home/sk/test/sample
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, we can use the following command to uncompress an archive file.
|
||||
|
||||
betty uncompress test.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Sample output:
|
||||
|
||||
Betty: Running mkdir test && tar -zxvf test.tar.gz -C test
|
||||
test/
|
||||
test/home/
|
||||
test/home/sk/
|
||||
test/home/sk/test/
|
||||
test/home/sk/test/sample
|
||||
|
||||
### Complete list of Betty commands ###
|
||||
|
||||
Betty tool has some command formats. It doesn’t understand if you put the command “what is my user name” instead of “whats my username”. So, you have to enter the correct English phrase that supported by Betty.
|
||||
|
||||
The complete list of supported commands are given below.
|
||||
|
||||
Count:
|
||||
betty how many words are in this directory
|
||||
betty how many characters are in myfile.py
|
||||
betty count lines in this folder
|
||||
(Note that there's many ways to say more or less the same thing.)
|
||||
|
||||
Config:
|
||||
betty change your name to Joe
|
||||
betty speak to me
|
||||
betty stop speaking to me
|
||||
|
||||
Datetime:
|
||||
betty what time is it
|
||||
betty what is todays date
|
||||
betty what month is it
|
||||
betty whats today
|
||||
|
||||
Find:
|
||||
betty find me all files that contain california
|
||||
|
||||
Internet:
|
||||
betty download http://www.mysite.com/something.tar.gz to something.tar.gz
|
||||
betty uncompress something.tar.gz
|
||||
betty unarchive something.tar.gz to somedir
|
||||
(You can use unzip, unarchive, untar, uncompress, and expand interchangeably.)
|
||||
betty compress /path/to/dir
|
||||
|
||||
iTunes:
|
||||
betty mute itunes
|
||||
betty unmute itunes
|
||||
betty pause the music
|
||||
betty resume itunes
|
||||
betty stop my music
|
||||
betty next song
|
||||
betty prev track
|
||||
betty what song is playing
|
||||
(Note that the words song, track, music, etc. are interchangeable)
|
||||
|
||||
Fun:
|
||||
betty go crazy
|
||||
betty whats the meaning of life
|
||||
...and more that are left for you to discover!
|
||||
|
||||
Map:
|
||||
betty show me a map of mountain view
|
||||
|
||||
Meta:
|
||||
betty what version are you (or just betty version)
|
||||
betty whats your github again
|
||||
|
||||
Permissions:
|
||||
betty give me permission to this directory
|
||||
betty give anotheruser ownership of myfile.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Process:
|
||||
betty show me all processes by root containing grep
|
||||
betty show me all my processes containing netbio
|
||||
|
||||
Sizes:
|
||||
betty show size for myfile.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Spotify:
|
||||
betty play spotify
|
||||
betty pause spotify
|
||||
betty next spotify
|
||||
betty previous spotify
|
||||
|
||||
User:
|
||||
betty whats my username
|
||||
betty whats my real name
|
||||
betty whats my ip address
|
||||
betty who else is logged in
|
||||
betty whats my version of ruby
|
||||
|
||||
Web queries:
|
||||
betty turn web on
|
||||
betty please tell me what is the weather like in London
|
||||
|
||||
Betty seems very nice tool to Linux novice users. Hope this tool will useful for you too.
|
||||
|
||||
Cheers!
|
||||
|
||||
Source:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Betty Homepage][1]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/betty-translate-english-phrases-linux-commands/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/pickhardt/betty
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
||||
微软真的改变对开源软件的态度了吗?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **在今天的开源软件摘要中:微软或许没有对开源软件有一个新的态度,就像安卓和windows的对抗,Cinnamon和Unity在Ubuntu14.04的对抗。**
|
||||
|
||||
微软因为以前对开源软件的态度而臭名昭著,但是公司改建后对开源软件发出了积极的信号。CNet报道了微软对开源软件认知的行为的改变。
|
||||
|
||||
> [CNet][1]消息:
|
||||
> 微软自助开源软件有一些时间了,那些曾经反对开源软件的领导者们已经退出了或者不在位了。开软软件现在用在遍布全世界的公司当中,这些公司有些自命不凡但这只是在认识到微软帝国之外的事。
|
||||
> 一些新的想法反映了企业顶层的一些变化,今年二月初Satya Nadella代替鲍尔默成为了微软CEO,Nadella已经给微软带来了一些新的东西改变了微软以前的一些束缚。
|
||||
>
|
||||
> [更多报道][2]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 微软和开源社区
|
||||
> Image credit: [Curako's Blog][3]
|
||||
|
||||
我是一个持悲观态度的人,但是我认为微软和开源软件之间的信任关系是有待确定的。一个新的CEO和些许改变或许会改变微软在开源世界中的存在状态,但是对于微软这么大的企业来说改变并不容易,所以对于开源的世界来说微软是否真的改变还有待确定。
|
||||
|
||||
我也从来不会忘记微软“欢迎,扩大,压死”的策略来打翻其他的竞争软件,光这一条凡是微软参合的开源项目就必须多一只谨慎的眼,或许这家公司真的改了,但如果没有呢!我们还是用几年时间来观察下吧。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安卓对抗windows ###
|
||||
|
||||
ZDNet曾经报道过使用数量最多的Linux发行版本,但是现在桌面环境仍然是windows的天下,但是安卓今年很可能会是用户数量最大的用户终端操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
> [ZDNet][4]报道:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 如果桌面和平板依旧像预期增长的销量,安卓平板渐渐蚕食苹果的市场,PC市场继续萎缩,安卓在2014年末很有可能成为终端用户数量最多的操作系统而且不算安卓PC。
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 总而言之,安卓几乎统治了Linux终端用户。你可能不会想到它作为桌面使用,尽管Intel和AMD努力在让它变成现实,但是安卓正在变成使用量第一的终端操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
>
|
||||
> [更多消息][4]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 
|
||||
> Image credit: [ZDNet][4]
|
||||
|
||||
上面提到的并不算真的惊喜,移动终端的革命发展了接近10年了。桌面依然还像原来那样重要,微软也确实没有真正的在乎过移动设备。即使现在,微软在艰难的推他的手机和平板,他仍旧认为移动终端市场并不重要。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
谷歌严重的破坏了微软在移动领域的努力,而现在他在桌面市场又对微软发起了挑战。从chrome OS到安卓,谷歌给微软一连串的打击,如果你查看下Amazon最受欢迎的[台式机][5]和[笔记本][6]的话,你会看到很多chrome OS的电脑甚至是装有安卓的PC。所以人们的购买需求在变得多样化,并不局限在windows一家了。
|
||||
|
||||
### Cinnamon和Unity在Ubuntu14.04上的对抗 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Tech Republic发表了一篇文章介绍了如何在Ubuntu14.04上安装cinnamon,研究了一下Ubuntu14.04上用cinnamon替换unity的可行性。
|
||||
|
||||
> [Tech Republic][7]报道:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 如果你寻求性能为主不需要其他有特色的可自定义的桌面,cinnamon适合你。Cinnamon是一个直观简洁的桌面,任何人都可以使用,不论你是IT工作者还是你的老妈妈。它非常的简单易用。Cinnamon很平淡,不会和你开什么玩笑,也不会让你感到有惊奇的感觉,但这就是它所注重的。它只会给桌面带来在标准层面上带来实用性,它不求突破,不耍花招,不加条条框框。
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Cinnamon是一个很平凡的桌面它只集成了最好的功能并且把它们集成到一起,完美整合到一块。如果你可以用一个看起来和用起来都点老掉牙但是性能很好的桌面的话,cinnamon完全适合你。如果你喜欢各种花哨的界面和看起来很现代的感觉,cinnamon可能就不适合你了。
|
||||
|
||||
> [ 更多消息][7]
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Image credit: [Tech Republic][7]
|
||||
|
||||
我是站在cinnamon这边的,unity有自己的长处,但是我从来没用习惯过。Cinnamon更接近传统桌面,我用起来不错!
|
||||
|
||||
但是在别人眼里,漂亮的桌面总是很受欢迎。Linux最大的特色就是提供很多很多不同的选择,如果你真不知道unity和cinnamon该选择谁,你就用自己最喜欢的就行了。
|
||||
|
||||
你赞成那些呢?请在下方留下你的评论吧
|
||||
|
||||
作者的观点和ITworld无关!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.itworld.com/open-source/421894/has-microsoft-really-changed-its-attitude-toward-open-source
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[jiajia9linuxer](https://github.com/jiajia9linuxer) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cnet.com/news/dead-and-buried-microsofts-holy-war-on-open-source-software/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cnet.com/news/dead-and-buried-microsofts-holy-war-on-open-source-software/
|
||||
[3]:http://curako.wordpress.com/2010/12/06/the-uneasy-alliance-free-software-vs-open-source/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.zdnet.com/the-five-most-popular-end-user-linux-distributions-7000030058/http://www.zdnet.com/the-five-most-popular-end-user-linux-distributions-7000030058/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.amazon.com/Best-Sellers-Electronics-Desktop-Computers/zgbs/electronics/565098/?_encoding=UTF8&camp=1789&creative=390957&linkCode=ur2&tag=fnh-20&linkId=REWXUPB7SQXPDSOL
|
||||
[6]:http://www.amazon.com/Best-Sellers-Computers-Accessories-Laptop/zgbs/pc/565108/?_encoding=UTF8&camp=1789&creative=390957&linkCode=ur2&tag=fnh-20&linkId=POG3J2CFBHDWBAVL
|
||||
[7]:http://www.techrepublic.com/article/is-cinnamon-a-worthy-replacement-for-ubuntu-unity/
|
||||
@ -1,369 +0,0 @@
|
||||
编写属于你的第一个Linux内核模块
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 曾经多少次想要在内核游荡?曾经多少次茫然不知方向?你不要再对着它迷惘,让我们指引你走向前方……
|
||||
内核编程常常看起来像是黑魔法,而在亚瑟 C 克拉克的眼中,它八成就是了。Linux内核和它的用户空间是大不相同的:抛开漫不经心,你必须小心翼翼,因为你编程中的一个bug就会影响到整个系统。浮点数学做起来可不容易,堆栈固定而渺小,而你写的代码总是异步的,因此你需要想想怎样让它并发。而除了所有这一切之外,Linux内核只是一个很大的、很复杂的C程序,它对每个人开放,任何人都去读它、学习它并改进它,而你也可以是其中之一。
|
||||
|
||||
> “开始内核编程的最简单的方式
|
||||
> 是写模块——一段代码
|
||||
> 可以用来动态加载进内核。”
|
||||
|
||||
可能,开始内核编程的最简单的方式,就是写模块——一段可以动态加载进内核并从内核移除的代码。模块所能做的事是有限的——例如,他们不能添加或移除像进程描述符这样的常规数据结构域。但是,在其它方面,他们是成熟的内核级的代码,可以在需要时随时编译进内核(这样就可以摒弃所有的限制了)。完全可以在Linux源代码树以外来开发并编译一个模块(这并不奇怪,它称为树外开发),如果你只是想稍微玩玩,而并不想提交修改以包含到主线内核中去,这样的方式是很方便的。
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我们将开发一个简单的内核模块用以创建一个**/dev/reverse**设备。写入该设备的字符串将以逆序的方式读回(“Hello World”读成“World Hello”)。这是一个流行的节目采访智力游戏,而当你展示能力来实施时,你也可能获得一些奖励分。在开始前,有一句忠告:你的模块中的一个bug会导致系统崩溃(虽然可能性不大,但还是有可能的)和数据丢失。在开始前,请确保你已经将重要数据备份,或者,采用一种更好的方式,在虚拟机中进行试验。
|
||||
### 尽可能避免root身份 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> 默认情况下,**/dev/reverse**只有root可以使用,因此你不得不使用**sudo**来测试该程序。要解决该问题,可以创建一个包含以下内容的**/lib/udev/rules.d/99-reverse.rules**文件:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> SUBSYSTEM=="misc", KERNEL=="reverse", MODE="0666"
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 别忘了重新插入模块。让设备节点让非root用户访问这往往不是一个好主意,但是在开发其间却是十分有用的,这不是说以root身份运行二进制测试文件也不是个好主意。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 模块的构造 ####
|
||||
|
||||
由于大多数的Linux内核模块是用C写的(除了低级别特定架构部分),所以推荐你将模块以单一文件形式保存(例如,reverse.c)。我们已经把完整的源代码放在GitHub上——这里我们将看其中的一些片段。开始时,我们先要包含一些常见的文件头,并用预定义的宏来描述模块:
|
||||
|
||||
#include <linux/init.h>
|
||||
#include <linux/kernel.h>
|
||||
#include <linux/module.h>
|
||||
|
||||
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
|
||||
MODULE_AUTHOR("Valentine Sinitsyn <valentine.sinitsyn@gmail.com>");
|
||||
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("In-kernel phrase reverser");
|
||||
|
||||
这里一切都直接明了,除了**MODULE_LICENSE()**:它不仅仅是一个标记。内核坚定地支持GPL兼容代码,因此如果你把许可证设置为其它非GPL兼容的(如,“专利”),特定的内核功能将在你的模块中不可用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么时候不该写内核模块 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> 内核编程很有趣,但是在现实项目中写(尤其是调试)内核代码要求特定的技巧。通常来讲,在没有其它方式解决你的问题时,你才应该沉入内核级别。可能你可以待在用户空间中,如果:
|
||||
|
||||
> - 你开发一个USB驱动 —— 请查看[libusb][1]。
|
||||
> - 你开发一个文件系统 —— 试试[FUSE][2]。
|
||||
> - 你在扩展Netfilter —— 那么[libnetfilter_queue][3]对你有所帮助。
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 通常,本地内核代码会干得更好,但是对于许多项目而言,这点性能丢失并不严重。
|
||||
由于内核编程总是异步的,没有Linux顺序执行得**main()**函数来运行你的模块。取而代之的是,你为各种事件提供了回调函数,像这个:
|
||||
|
||||
static int __init reverse_init(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printk(KERN_INFO "reverse device has been registered\n");
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
static void __exit reverse_exit(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
printk(KERN_INFO "reverse device has been unregistered\n");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
module_init(reverse_init);
|
||||
module_exit(reverse_exit);
|
||||
|
||||
这儿,我们定义了函数,用来访问模块的插入和移除功能,只有第一个是必要的。目前,它们只是打印消息到内核环缓冲区(可以通过**dmesg**命令从用户空间访问);**KERN_INFO**是日志等级(注意,没有逗号)。**_init**和**_exit**是属性 —— 联结到函数的元数据片(或者变量)。属性在用户空间的C代码中是很罕见的,但是内核中却很普遍。所有标记为**_init**的,会在初始化后再生(还记得那条老旧的“释放未使用的内核内存……”信息?)。**__exit**表明,当代码被静态构建进内核时,该函数可以安全地优化。最后,**module_init()**和**module_exit()**这两个宏将**reverse_init()**和**reverse_exit()**函数设置成为我们模块的生命周期回调函数。实际的函数名称并不重要,你可以称它们为**init()**和**exit()**,或者**start()**和**stop()**,你想叫什么就叫什么吧。在你的模块外,它们被申明成为静态的和不可见的。事实上,内核中的任何函数都是不可见的,除非明确地被导出。然而,在内核程序员中,给你的函数加上模块名前缀是约定俗成的。
|
||||
|
||||
这些是基本要素 —— 让我们把事情变得更有趣些。模块可以接收参数,就像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
# modprobe foo bar=1
|
||||
|
||||
**modinfo**命令显示了所有模块接受的参数,而这些也可以在**/sys/module//parameters**下作为文件使用。我们的模块需要一个缓冲区来存储短语 —— 让我们把这大小设置为用户可配置。添加**MODULE_DESCRIPTION()**以下的三行:
|
||||
|
||||
static unsigned long buffer_size = 8192;
|
||||
module_param(buffer_size, ulong, (S_IRUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH));
|
||||
MODULE_PARM_DESC(buffer_size, "Internal buffer size");
|
||||
|
||||
这儿,我们定义了一个变量来存储该值,将其包裹到一个参数中,并通过sysfs来让所有人可读。参数的描述(最后一行)会出现在modinfo的输出中。
|
||||
|
||||
由于用户可以直接设置**buffer_size**,我们需要在**reverseinit()**来清除它。你总该检查来自内核外的数据 —— 如果你不这么做,你就是会将你自身置于内核异常之中,设置造成安全漏洞。
|
||||
|
||||
static int __init reverse_init()
|
||||
{
|
||||
if (!buffer_size)
|
||||
return -1;
|
||||
printk(KERN_INFO
|
||||
"reverse device has been registered, buffer size is %lu bytes\n",
|
||||
buffer_size);
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
来自模块初始化函数的非0返回值意味着模块执行失败。
|
||||
|
||||
### 导航 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> 但你开发模块时,Linux内核就是你所需一切的源头。然而,它相当大,你可能在查找你所要的内容时会有困难。幸运的是,在浏览庞大的代码库时,有工具可以帮助你干得轻松一点。首先,是Cscope —— 在终端中运行的一个令人肃然起敬的工具。你所要做的,就是在内核源代码的顶级目录中运行**make cscope && cscope**。Cscope和Vim以及Emacs整合得很好,因此你可以在使用你最喜爱的编辑器舒适地工作时来使用它。
|
||||
|
||||
> 如果基于终端的工具不是你的最爱,那么就访问[http://lxr.free-electrons.com][4]吧。它是一个基于web的内核导航工具,即使它的功能没有Cscope来得多(例如,你不能方便地找到函数的用法),但它仍然提供了足够多的快速查询功能。
|
||||
现在是时候来编译模块了。你将需要用于正在运行的内核版本的头文件(**linux-headers**,或者同等软件包)和**build-essential**(或者类似的包)。接下来,该创建一个标准的Makefile模板:
|
||||
|
||||
obj-m += reverse.o
|
||||
all:
|
||||
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) modules
|
||||
clean:
|
||||
make -C /lib/modules/$(shell uname -r)/build M=$(PWD) clean
|
||||
|
||||
现在,调用**make**来构建你的第一个模块。如果你输入的都正确,在当前目录内会发现reverse.ko文件。使用**sudo insmod reverse.ko**插入,然后运行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ dmesg | tail -1
|
||||
[ 5905.042081] reverse device has been registered, buffer size is 8192 bytes
|
||||
|
||||
恭喜了!然而,目前这一行还只是在逗你玩而已 —— 还没有设备节点呢。让我们来修复它。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 混杂设备 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux中,有一种特殊的字符设备类型,叫做“混杂设备”(或者简称为“misc”)。它设计用于只有一个单一接入点的小型设备驱动,而这正是我们所需要的。所有混杂设备共享同一个主设备号(10),因此一个驱动(**drivers/char/misc.c**)就可以查看它们所有设备了,而这些设备用次设备号来区分。在所有其它意义上,它们只是普通字符设备。
|
||||
|
||||
要为该设备注册一个次设备号(以及一个接入点),你需要声明**struct misc_device**,填上所有字段(注意语法),然后使用指针指向该结构函数来调用**misc_register()**。为了这个能工作,你也需要包含**linux/miscdevice.h**头文件:
|
||||
|
||||
static struct miscdevice reverse_misc_device = {
|
||||
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,
|
||||
.name = "reverse",
|
||||
.fops = &reverse_fops
|
||||
};
|
||||
static int __init reverse_init()
|
||||
{
|
||||
...
|
||||
misc_register(&reverse_misc_device);
|
||||
printk(KERN_INFO ...
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
这儿,我们为名为“reverse”的设备请求一个第一个可用的(动态的)次设备号;省略号表明我们已经见过的省略的代码。别忘了在模块卸下后注销掉该设备。
|
||||
|
||||
static void __exit reverse_exit(void)
|
||||
{
|
||||
misc_deregister(&reverse_misc_device);
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
‘fops’字段存储了一个指针,指向结构函数**file_operations**(在Linux/fs.h中已声明),而这真是我们模块的接入点。**reverse_fops**定义如下:
|
||||
|
||||
static struct file_operations reverse_fops = {
|
||||
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
|
||||
.open = reverse_open,
|
||||
...
|
||||
.llseek = noop_llseek
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
再者,**reverse_fops**包含了一系列回调函数(也称之为方法),当用户空间代码打开一个设备时,就会执行。从该设备读取,向该设备写入,或者关闭文件描述符。如果你忽略了所有这些,就会使用一个灵敏的回调函数来替代。这就是为什么我们明确给**noop_llseek()**设置了**llseek**方法,而它却什么也不干(就像名称中暗指的)。默认部署改变了文件指针,我们现在也不想我们的设备被找到(这是你们的今天的回家作业)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 我在关闭时打开 ####
|
||||
|
||||
让我们实施该方法。我们将分配一个新的缓冲区给每个打开的文件描述符,并在它关闭时释放。这事实上并不安全:如果一个用户空间应用程序泄漏了描述符(也许是故意的),它就会霸占RAM,并使系统不可用。在现实世界中,你总得考虑到这些可能性。但在本教程中,这种方法可以接受。
|
||||
|
||||
我们需要一个结构函数来描述缓冲区。内核提供了许多常规的数据结构:链接列表(双联的),哈希表,树等等之类。然而,缓冲区常常从零开始实施。我们将调用我们的“struct buffer”:
|
||||
|
||||
struct buffer {
|
||||
char *data, *end, *read_ptr;
|
||||
unsigned long size;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
**data**是该缓冲区存储的一个指向字符串的指针,而最后部分是字符串结尾后的第一个字节。**read_ptr**是**read()**开始读取数据的地方。缓冲区大小为了完整性而存储 —— 目前,我们还没有使用该区域。你不能假设使用你结构体的用户会正确地初始化所有这些东西,所以最好在函数中封装缓冲区分配和解除。它们通常命名为**buffer_alloc()**和**buffer_free()**。
|
||||
|
||||
static struct buffer *buffer_alloc(unsigned long size)
|
||||
{
|
||||
struct buffer *buf;
|
||||
buf = kzalloc(sizeof(*buf), GFP_KERNEL);
|
||||
if (unlikely(!buf))
|
||||
goto out;
|
||||
...
|
||||
out:
|
||||
return buf;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
内核内存使用**kmalloc()**来分配,并使用**kfree()**来释放;**kzalloc()**的风格是将内存设置为全零。不同于标准的**malloc()**,它的内核对应部分收到的标志指定了第二个参数中请求的内存类型。这里,**GFP_KERNEL**是说我们需要一个普通的内核内存(不是在DMA或高内存中)以及函数可以按需睡眠(重新编排进程)。**sizeof(*buf)**是一种常见的方式,它用来获取可通过指针访问的结构体的大小。
|
||||
|
||||
你应该随时检查**kmalloc()**的返回值:解应用NULL指针将导致内核异常。同时也需要注意**unlikely()**宏的使用。它(及其相对宏**likely()**)被广泛用于内核中,用于表明条件几乎总是真的(或假的)。它不会影响到控制流,但是能帮助现代处理器通过分支预测技术来提升性能。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,注意**gotos**。它们常常为认为是邪恶的,但是,Linux内核(以及一些其它系统软件)采用它们来实施集中式的函数退出。这样的结果是减少嵌套深度,使代码更具可读性,而且非常像更高级语言中的**try-catch**区块。
|
||||
|
||||
有了**buffer_alloc()**和**buffer_free()**,**open**和**close**方法就变得很简单了。
|
||||
|
||||
static int reverse_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
|
||||
{
|
||||
int err = 0;
|
||||
file->private_data = buffer_alloc(buffer_size);
|
||||
...
|
||||
return err;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
**struct file**是一个标准的内核数据结构,用以存储打开的文件的信息,如当前文件位置(**file->fpos**),标志(**file->flags**),或者打开模式(**file->fmode**)。另外一个字段**file->privatedata**用于关联文件到一些专有数据,它的类型是void *,而且它在文件拥有者以外对内核不透明。我们将一个缓冲区存储在那里。
|
||||
|
||||
如果缓冲区分配失败,我们通过返回否定值(**-ENOMEM**)来为调用的用户空间代码标明。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 学会读写 ####
|
||||
|
||||
“read”和“write”方法是真正完成工作的地方。当数据写入到缓冲区时,我们就丢弃它里头先前的内容,并在没有任何临时存储时将短语恢复原状。**read**方法仅仅是从内核缓冲区复制数据到用户空间。但是如果缓冲区还没有数据,**reverseread()**会做什么呢?在用户空间中,**read()**调用会在有可用数据前阻塞它。在内核中,你必须等待。幸运的是,有一项机制用于处理这种情况,就是‘wait queues’。
|
||||
|
||||
想法很简单。如果当前进程需要等待某个事件,它的描述符(**struct task_struct**存储为‘current’)被放进非可运行(睡眠中)状态,并添加到一个队列中。然后**schedule()**就被调用来选择另一个进程运行。生成事件的代码通过使用队列将等待进程放回**TASKRUNNING**状态来唤醒它们。调度程序将在以后在某个地方选择它们之一。Linux有多种非可运行状态,最值得注意的是**TASKINTERRUPTIBLE**(一个可以通过信号中断的睡眠)和**TASKKILLABLE**(一个可被杀死的睡眠中的进程)。所有这些都应该正确处理,并等待队列为你做这些事。
|
||||
|
||||
一个用以存储读取等待队列头的天然场所就是结构缓冲区,所以从为它添加**wait_queue_head_t read_queue**字段开始。你也应该包含**linux/sched.h**。可以使用DECLARE_WAITQUEUE()宏来静态声明一个等待队列。在我们这种情况下,需要动态初始化,因此添加下面这行到**buffer_alloc()**:
|
||||
|
||||
init_waitqueue_head(&buf->read_queue);
|
||||
|
||||
我们等待可用数据;或者等待**read_ptr != end**条件成立。我们也想要让等待操作可以被中断(如,通过Ctrl+C)。因此,“read”方法应该像这样开始:
|
||||
|
||||
static ssize_t reverse_read(struct file *file, char __user * out,
|
||||
size_t size, loff_t * off)
|
||||
{
|
||||
struct buffer *buf = file->private_data;
|
||||
ssize_t result;
|
||||
while (buf->read_ptr == buf->end) {
|
||||
if (file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK) {
|
||||
result = -EAGAIN;
|
||||
goto out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (wait_event_interruptible
|
||||
(buf->read_queue, buf->read_ptr != buf->end)) {
|
||||
result = -ERESTARTSYS;
|
||||
goto out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
我们让它循环,直到有可用数据,如果没有则使用**wait_event_interruptible()**(它是一个宏,不是函数,这就是为什么要给队列传递值)来等待。好吧,如果**wait_event_interruptible()**被中断,它返回一个非0值,这个值代表**-ERESTARTSYS**。这段代码意味着系统调用应该重新启动。**file->f_flags**检查以非阻塞模式打开的文件数:如果没有数据,返回**-EAGAIN**。
|
||||
|
||||
我们不能使用**if()**来替代**while()**,因为可能有许多进程正等待数据。当**write**方法唤醒它们时,调度程序选择一个来以不可预知的方式运行,因此,在这段代码有机会执行的时候,缓冲区可能再次空出。现在,我们需要将数据从**buf->data** 复制到用户空间。**copytouser()**内核函数就干了此事:
|
||||
|
||||
size = min(size, (size_t) (buf->end - buf->read_ptr));
|
||||
if (copy_to_user(out, buf->read_ptr, size)) {
|
||||
result = -EFAULT;
|
||||
goto out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
如果用户空间指针错误,那么调用可能会失败;如果发生了此事,我们就返回**-EFAULT**。记住,不要相信任何来自内核外的事物!
|
||||
|
||||
buf->read_ptr += size;
|
||||
result = size;
|
||||
out:
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
为了让数据能读入到专有组块中,需要进行简单运算。该方法返回读入的字节数,或者一个错误代码。
|
||||
|
||||
写方法更简短。首先,我们检查缓冲区是否有足够的空间,然后我们使用**copy_from_userspace()**函数来获取数据。再然后**read_ptr**和结束指针会被重置,缓冲区内容会被撤销掉:
|
||||
|
||||
buf->end = buf->data + size;
|
||||
buf->read_ptr = buf->data;
|
||||
if (buf->end > buf->data)
|
||||
reverse_phrase(buf->data, buf->end - 1);
|
||||
|
||||
这里, **reverse_phrase()**干了所有吃力的工作。它依赖于**reverse_word()**函数,该函数相当简短并且标记为内联。这是另外一个常见的优化;但是,你不能过度使用。因为积极的内联会导致内核映像徒然增大。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,我们需要唤醒**read_queue**中等待数据的进程,就跟先前讲过的那样。**wake_up_interruptible()**就是用来干此事的:
|
||||
|
||||
wake_up_interruptible(&buf->read_queue);
|
||||
|
||||
唷!你现在已经有了一个内核模块,它至少已经编译成功了。现在,是时候来测试了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 调试内核代码 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> 或许,内核中最常见的调试方法就是打印。如果你愿意,你可以使用普通的**printk()** (假定使用**KERN_DEBUG**日志等级)。然而,那儿还有更好的办法。如果你正在写一个设备驱动,这个设备驱动有它自己的“struct device”,可以使用**pr_debug()**或者**dev_dbg()**:它们支持动态调试(**dyndbg**)特性,并可以根据需要启用或者禁用(请查阅**Documentation/dynamic-debug-howto.txt**)。对于单纯的开发消息,使用**prdevel()**,该函数没有操作符,除非设置了DEBUG。要为我们的模块启用DEBUG,请添加以下行到Makefile中:
|
||||
|
||||
> CFLAGS_reverse.o := -DDEBUG
|
||||
>
|
||||
> 完了之后,使用**dmesg**来查看**pr_debug()**或**pr_devel()**生成的调试信息。
|
||||
> 或者,你可以直接发送调试信息到控制台。要想这么干,你可以设置**console_loglevel**内核变量为8或者更大的值(**echo 8 /proc/sys/kernel/printk**),或者在高日志等级,如**KERN_ERR**,来临时打印要查询的调试信息。很自然,在发布代码前,你应该移除这样的调试声明。
|
||||
|
||||
> 注意出现在控制台的内核消息,而不要在Xterm这样的终端模拟器窗口中去查看;那也是你在内核开发时,经常会建议你不要再X环境下进行的原因。
|
||||
|
||||
### 惊喜,惊喜! ###
|
||||
|
||||
编译模块,然后加载进内核:
|
||||
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
$ sudo insmod reverse.ko buffer_size=2048
|
||||
$ lsmod
|
||||
reverse 2419 0
|
||||
$ ls -l /dev/reverse
|
||||
crw-rw-rw- 1 root root 10, 58 Feb 22 15:53 /dev/reverse
|
||||
|
||||
一切似乎就位。现在,要测试模块是否正常工作,我们将写一段小程序来翻转它的第一个命令行参数。**main()**(没有错误检查)可能看上去像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
int fd = open("/dev/reverse", O_RDWR);
|
||||
write(fd, argv[1], strlen(argv[1]));
|
||||
read(fd, argv[1], strlen(argv[1]));
|
||||
printf("Read: %s\n", argv[1]);
|
||||
|
||||
像这样运行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./test 'A quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dog'
|
||||
Read: dog lazy the over jumped fox brown quick A
|
||||
|
||||
它工作正常!玩得更逗一点:试试传递单个单词或者单个字母的短语,空的字符串或者是非英语字符串(如果你有这样的键盘布局设置),以及其它任何东西。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,让我们让事情变得更好玩一点。我们将创建两个进程,它们共享一个文件描述符(因而还有内核缓冲区)。其中一个会持续写入字符串到设备,而另一个将读取这些字符串。在下例中,我们使用了**fork(2)**系统调用,而pthreads也很好用。我也忽略了打开和关闭设备,以及错误检查部分的代码(又来了):
|
||||
|
||||
char *phrase = "A quick brown fox jumped over the lazy dog";
|
||||
if (fork())
|
||||
/* Parent is the writer */
|
||||
while (1)
|
||||
write(fd, phrase, len);
|
||||
else
|
||||
/* child is the reader */
|
||||
while (1) {
|
||||
read(fd, buf, len);
|
||||
printf("Read: %s\n", buf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
你希望这个程序会输出什么呢?下面就是在我的笔记本上得到的东西:
|
||||
|
||||
Read: dog lazy the over jumped fox brown quick A
|
||||
Read: A kcicq brown fox jumped over the lazy dog
|
||||
Read: A kciuq nworb xor jumped fox brown quick A
|
||||
Read: A kciuq nworb xor jumped fox brown quick A
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
这里发生了什么呢?举行了一场比赛。我们认为**read**和**write**是很小的,或者从头到尾一次执行一个指令。然而,内核是并发的野兽,它可以很容易地重排**reverse_phrase()**函数内部某个地方运行着的内核模式部分的写入操作。如果进行**read()**操作的进程在写入操作结束前就被编排进去,就会产生数据不连续状态。这些bug非常难以排除。但是,怎样来处理这个问题呢?
|
||||
|
||||
基本上,我们需要确保在写方法返回前没有**read**方法能被执行。如果你曾经编写过一个多线程的应用程序,你可能见过同步原语(锁),如互斥锁或者信号。Linux也有这些,但有些细微的差别。内核代码可以运行在进程条件中(“代表”用户空间代码工作,就像我们的方法那样)以及运行在中断条件中(例如,在IRQ处理器中)。如果你的程序处于进程条件中,并且你需要的锁已经被拿走,你的程序就会睡眠并重试直至成功。在中断条件中是无法睡眠的,因此代码在循环中流转,直到有可用的锁为止。关联原语被称为自旋锁,但在我们的环境中,一个简单的互斥锁 —— 在特定时间内只有唯一一个进程能“占有”的对象 —— 就足够了。处于性能方面的考虑,现实的代码可能也会使用读-写信号。
|
||||
|
||||
锁总是保护某些数据(在我们的环境中,是一个“struct buffer”实例),而且也常常会把它们嵌入到它们所保护的结构体中。因此,我们添加一个互斥锁(‘struct mutex lock’)到“struct buffer”中。我们也必须用**mutex_init()**来初始化互斥锁;**buffer_alloc**是用来处理这件事的好地方。使用互斥锁的代码也必须包含**linux/mutex.h**。
|
||||
|
||||
互斥锁很像交通信号灯 —— 除非驱动查看并跟踪信号,否则它没什么用。因此,在对缓冲区做操作并在操作完成时释放它之前,我们需要更新**reverse_read()**和**reverse_write()**来获取互斥锁。让我们来看看**read**方法 —— **write**的工作原理相同:
|
||||
|
||||
static ssize_t reverse_read(struct file *file, char __user * out,
|
||||
size_t size, loff_t * off)
|
||||
{
|
||||
struct buffer *buf = file->private_data;
|
||||
ssize_t result;
|
||||
if (mutex_lock_interruptible(&buf->lock)) {
|
||||
result = -ERESTARTSYS;
|
||||
goto out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
我们在函数一开始就获取锁。**mutex_lock_interruptible()**要么抓取互斥锁然后返回,要么让进程睡眠,直到有可用的互斥锁。就像前面一样,**_interruptible**后缀意味着睡眠可以由信号来中断。
|
||||
|
||||
while (buf->read_ptr == buf->end) {
|
||||
mutex_unlock(&buf->lock);
|
||||
/* ... wait_event_interruptible() here ... */
|
||||
if (mutex_lock_interruptible(&buf->lock)) {
|
||||
result = -ERESTARTSYS;
|
||||
goto out;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
下面是我们的“等待数据”循环。当持有互斥锁,或者发生称之为“死锁”的情境时,不应该让进程睡眠。因此,如果没有数据,我们释放互斥锁并调用**wait_event_interruptible()**。当它返回时,我们重新获取互斥锁并像往常一样继续:
|
||||
|
||||
if (copy_to_user(out, buf->read_ptr, size)) {
|
||||
result = -EFAULT;
|
||||
goto out_unlock;
|
||||
}
|
||||
...
|
||||
out_unlock:
|
||||
mutex_unlock(&buf->lock);
|
||||
out:
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
|
||||
最后,当函数结束,或者在互斥锁被占有过程中发生错误时,互斥锁被解锁。重新编译模块(别忘了重新加载),然后再次进行测试。现在你应该没发现毁坏的数据了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 接下来是什么? ###
|
||||
现在,你体验了一把内核侵入。我们刚刚为你揭开了今天话题的外衣,里面还有更多东西供你探索。我们的第一个模块是有意识地写得简单一点,在从中学到的概念在更复杂的环境中也一样。并发、方法表、注册回调函数、使进程睡眠以及唤醒进程,这些都是内核黑客们耳熟能详的东西,而现在你已经看过了它们的运作。或许某天,你的内核代码也将被加入到主线Linux源代码树中 —— 如果真这样,请联系我们!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxvoice.com/be-a-kernel-hacker/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.libusb.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://fuse.sf.net/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.linuxvoice.com/be-a-kernel-hacker/www.netfilter.org/projects/libnetfilter_queue
|
||||
[4]:http://lxr.free-electrons.com/
|
||||
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
用iCup在linux追世界杯
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
嗨,Linux 极客们,
|
||||
|
||||
在本文简短的叙述中,我将教你如何在Linux中安装一个非常棒的2014FIFA世界杯APP。这个应用叫iCup,支持Windows,Mac以及伟大的Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
我看足球比赛已经有很长的时间了,所以我得我的电脑上安装这样的应用来保持更新2014世界杯的最新情况。我不想在我朋友们面前看起来一无所知。iCup应用正好提供了每一场赛程、比分、球队教练组等信息。更有提供实时比赛更新,给你正在进行的比赛的最新数据。
|
||||
|
||||
### 支持一下功能: ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 30种语言支持,完全本地化(使用语言菜单选择)
|
||||
- 可以随意调整窗口大小的独家灵活的界面
|
||||
- 可按天、阶段检索的比赛日历
|
||||
- 可视化分组
|
||||
- 支持自动转变比赛时间来适应本地时间和格式
|
||||
- 一键化社交网络发表比赛评论(支持Facebook,Google+和Twitter)
|
||||
- 支持代理(支持基本认证和摘要认证方法)
|
||||
|
||||
我已经在Ubuntu12.04LTS上测试并且运很好!目前为止,我没有经历过任何错误或崩溃。你可以十分轻松地安装这个很棒的应用,通过[官方网站][1]你可以得到压缩包,然后你可以解压到任何你喜欢的地方。解压完成后,双击iCup 2014 FREE- Brazil运行。
|
||||
|
||||
iCup 对我非常有用,我希你也能享受到。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-icup-2014-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic020](http://www.vicyu.net) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.e-link.it/icup/brazil2014/icup-brazil-2014-desktop-app.php
|
||||
@ -1,163 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by yujianxuechuan,占坑
|
||||
How to set up Internet connection sharing with iptables on Linux
|
||||
怎样使用linux的iptables工具进行网络共享
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In this tutorial, I'll explain how to share a single Internet connection among multiple devices on Linux. While consumer-grade WiFi routers have become mainstream nowadays, making this problem a non-issue, suppose you don't have one at home. However, say you have a Linux box already assembled with a modem and a LAN card. The modem is connected to the Internet with a dynamic public IP address, and the LAN card connected to your switch/hub. Other devices (Linux/Windows PC, laptop) are connected to the switch without having any Internet connection. To share the Internet connection of the Linux box, you have to turn the box into a gateway, so that it can relay traffic to and from other devices.
|
||||
在本教程中,我将解释多个设备怎样在linux下共享一个网络连接。目前无线路由器已经成为主流的消费品,从而解决了本文这一问题,假设你家中并没有一台无线路由器。然而,你却有一台已经有"猫"和局lan网卡的的linux主机。"猫"是以动态公有IP地址的模式连接的互联网,主机的lan网卡连接到你的交换机或者集线器。其他设备(如linux或者windows的PC或者笔记本)以网桥的形式连接并无互联网连接。为了共享linux主机的互联网,你必须把主机摄制成网关,于是它才能实现从其他设备中传送和接受信息。
|
||||
### Glossary of Terms ###
|
||||
术语字汇
|
||||
- **Private IP address** (non-routeable address) is an IP address used for a Local Area Network (not visible through Internet).
|
||||
- **Public IP address** (routeable address) is an IP address that is visible through Internet.
|
||||
- **IP masquerading** is a function that allows set of machines to reach the Internet via a MASQ gateway. Those machines behind the MASQ gateway is never visible to the Internet. Any outgoing and incoming traffic from and to the machines behind the MASQ gateway must pass through the MASQ gateway.
|
||||
- **Network Address Translation** (NAT) is a function that can make a private IP address reaches the Internet with the help of IP masquerading.
|
||||
-私有IP地址(不可到达地址)是一个被用于本地局域网的IP地址(在互联网中不可见)。
|
||||
-公用IP地址(可到达地址)是一个在互联网中可见的IP地址。
|
||||
IP伪装是一项允许一系列机器通过MASQ网关连接互联网的功能。这些MASQ网关之外的机器在互联网中是不可见的。MASQ之后的机器中任何流入或流出的数据必须经过MASQ网关。
|
||||
-网络地址转换(NAT)是一项通过IP伪装技术可以使私有IP地址访问互联网的功能。
|
||||
### Hardware Requirements ###
|
||||
硬件要求
|
||||
- One Linux box with two interfaces (one public IP address and the other private IP address), which will be used as a gateway.
|
||||
- One or more Linux/Windows PC or laptop with private IP addresses.
|
||||
- Switch/HUB (optional).
|
||||
-一台有两个接口(一个公有IP地址和其他的私有IP地址)的linux主机,这个主机将被用作网关。
|
||||
-一台或者多台拥有私有IP地址的linux/windows系统的PC或者笔记本。
|
||||
-交换机/集线器(可选)。
|
||||
### Step-by-Step Guide ###
|
||||
教程步骤
|
||||
The following procedure is required on the Linux box (the connection sharing gateway).
|
||||
接下来的过程需要在linux主机(用于共享的网关)上完成。
|
||||
#### 1. Activate IP forwarding ####
|
||||
1、激活IP转发
|
||||
In order to set up Internet connection sharing, you need to enable IP forwarding on the Linux box with a kernel parameter. Startup kernel parameters stored in /etc/sysctl.conf.
|
||||
为了设置网络共享,你需要在linux主机上更改一个内核参数来使能IP转发功能。内核启动参数设定在/etc/sysctl.conf文件中。
|
||||
Open the file, and locate line with the following parameter "# net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0". Remove hash mark (i.e., uncomment it), and set the value to 1. It should look like the following:
|
||||
打开这个文件,定位到含有"# net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0"的这一行,移除#号(即取消注释),然后将其值设置为1,改好之后应该和下面的一致。
|
||||
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
|
||||
|
||||
You may also activate IP forwaring at run time by the following command:
|
||||
你还要使激活IP转发功能生效,通过执行下面的命令:
|
||||
$ sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
|
||||
$ sudo sysctl -p
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. NAT configuration ####
|
||||
2、NAT配置
|
||||
Another important part of Internet connection sharing is NAT configuration which can be done using iptables command. iptables maintains four firewall tables:
|
||||
另一个网络共享的重要部分是NAT配置,这可以通过使用iptables的命令,iptables包含四个防火墙的表格:
|
||||
- FILTER (the default table)
|
||||
- NAT
|
||||
- MANGLE
|
||||
- RAW
|
||||
- FILTER (默认表格)
|
||||
- NAT
|
||||
- MANGLE
|
||||
- RAW
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial we will use only two tables: FILTER and NAT tables.
|
||||
这个教程中我们将仅使用两个表格:FILTER和NAT表格。
|
||||
First, flush all active firewall rules.
|
||||
首先,刷新所有活跃的防火墙的规则。
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -X
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -F
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -t nat -X
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -t nat -F
|
||||
|
||||
On the INPUT table, you have to set chain FORWARD to ACCEPT target, so all packets passed through the box will be processed correctly.
|
||||
在输入表格中,你需要设置转发链成可接受的目的地,因此艘游通过主机的数据包将会被正确的处理。
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -I INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -I FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
|
||||
On the NAT table, you have to enable IP masquerading for your WAN interface. We assume that the WAN interface is ppp0. To enable IP masquerading on ppp0 interface, you can use the following command:
|
||||
在NAT表中,你必须为你的WAN口使能IP伪装,我们假设WAN口协议是ppp0。为了在ppp0接口上使能IP伪造技术,我们使用以下的命令:
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Configuring a private IP address ####
|
||||
3、配置私有IP地址
|
||||
After all configuration is completed on the Linux box, you have to configure the DNS server and default gateway of other devices (Linux/Windows PC, laptop), so that they point to the Linux box. Note that you don't need to set up a DNS server on the Linux box. Every DNS request from other devices are automatically forwarded by the Linux box to your upstream ISP.
|
||||
在linux主机上的所有配置完成后,你需要配置其他设备(linux/windows的PC或笔记本)的DNS服务器以及默认网关,因此他们的数据流可以指向linux主机。注意你不需要在linux主机上设置一个DNS服务器,从其他设备发出的每一个DNS请求都会通过上游的ISP自动转发到linux主机上。
|
||||
If you are using Linux on the other devices, you can use the following command to change their default gateway and DNS servers. I assume that you are using 192.168.1.0/24 private IP address segment, and that 192.168.1.1 is the IP address assigned to the Linux box.
|
||||
如果你的其他设备上用的系统是linux,你可以通过以下命令来更改他们的默认网关和DNS服务器。假设你的网段是192.168.1.0/24的私有IP地址网段,linux主机上绑定的IP地址是192.168.1.1。
|
||||
$ sudo ip route del default
|
||||
$ sudo ip route add default via 192.168.1.1
|
||||
$ sudo sh -c "echo 'nameserver 192.168.1.1' > /etc/resolv.conf"
|
||||
|
||||
If you have other Linux devices, you can repeat the command above on other devices.
|
||||
如果还有其他的linux设备,那么你可以重复以上命令。
|
||||
If you have a Windows device, you can change the default gateway and the DNS server via network connection properties on the control panel.
|
||||
如果你有windows设备,你可以通过控制面板的网络连接属性来更改默认网关和DNS服务器。
|
||||
#### 4. The complete script ####
|
||||
4、完整的脚本
|
||||
Here is the complete script which sets up Internet connection sharing on the Linux box. The WAN interface (ppp0) needs to be replaced according to your environment.
|
||||
这是一个在linux主机上设置网络连接共享的一个完整的脚本。WAN口(ppp0协议)需要根据你具体的网络接口协议来替换。
|
||||
$ sudo vi /usr/local/bin/ishare
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial we will use only two tables: FILTER and NAT tables.
|
||||
|
||||
First, flush all active firewall rules.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -X
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -F
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -t nat -X
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -t nat -F
|
||||
|
||||
On the INPUT table, you have to set chain FORWARD to ACCEPT target, so all packets passed through the box will be processed correctly.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -I INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -I FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
|
||||
On the NAT table, you have to enable IP masquerading for your WAN interface. We assume that the WAN interface is ppp0. To enable IP masquerading on ppp0 interface, you can use the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Configuring a private IP address ####
|
||||
|
||||
After all configuration is completed on the Linux box, you have to configure the DNS server and default gateway of other devices (Linux/Windows PC, laptop), so that they point to the Linux box. Note that you don't need to set up a DNS server on the Linux box. Every DNS request from other devices are automatically forwarded by the Linux box to your upstream ISP.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using Linux on the other devices, you can use the following command to change their default gateway and DNS servers. I assume that you are using 192.168.1.0/24 private IP address segment, and that 192.168.1.1 is the IP address assigned to the Linux box.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ip route del default
|
||||
$ sudo ip route add default via 192.168.1.1
|
||||
$ sudo sh -c "echo 'nameserver 192.168.1.1' > /etc/resolv.conf"
|
||||
|
||||
If you have other Linux devices, you can repeat the command above on other devices.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a Windows device, you can change the default gateway and the DNS server via network connection properties on the control panel.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. The complete script ####
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the complete script which sets up Internet connection sharing on the Linux box. The WAN interface (ppp0) needs to be replaced according to your environment.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /usr/local/bin/ishare
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
## Internet connection shating script
|
||||
|
||||
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
|
||||
sysctl -p
|
||||
iptables -X
|
||||
iptables -F
|
||||
iptables -t nat -X
|
||||
iptables -t nat -F
|
||||
iptables -I INPUT -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
iptables -I FORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
|
||||
iptables -t nat -I POSTROUTING -o ppp0 -j MASQUERADE
|
||||
|
||||
Save the above script to /usr/local/bin/ishare, and then change the executable bit by the following command.
|
||||
保存以上的脚本到/usr/local/bin/ishare,然后添加可执行权限通过执行下面的命令。
|
||||
$ sudo chmox +x /usr/local/bin/ishare
|
||||
|
||||
If you want the script executed every startup, you can register the script to /etc/rc.local. Open /etc/rc.local, before statement "exit 0", add the following line:
|
||||
如果你需要这个脚本开机启动,你需要在/etc/rc.local文件中注册这个脚本,在文件中的"exit 0"之前添加下面一行。
|
||||
/usr/local/bin/ishare
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/internet-connection-sharing-iptables-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
教你用NeoBundle管理Vim插件
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[NeoBundle][1] 是一个 [Vim][2] 的插件管理器,以 [Vundle][3] 为基础(Vundle 是一个基于 [Pathogen][4] 的 Vim 插件管理器)。在之前的文章中,我[非常不推荐使用 Neobundle][5],原因是它当时还处于高速开发阶段(LCTT:意味着不稳定、变数大),并且当时它的英文文档很少。现在,已经过了一年多了,这两个问题都早已不再是问题。
|
||||
|
||||
我们为什么要使用插件管理器?Vim 支持大量插件,但是由于它没有严格定义框架,插件的文件可以胡乱分布在不同目录下,导致用户管理起来会很困难(LCTT:当然,前提是你有很多插件,还有点小小的强迫症,觉得理一理这些插件心里会舒服点)。而一款插件管理器能让管理变得简单许多。Pathogen, Vundle 和 NeoBundle 的工作就是为不同插件建立一个目录,然后将这些目录扔到 ~/.vim/bundle 目录下。这个文件整理方法可以让你方便彻底地删除插件,使用 'rm -rf <插件目录>' 或直接 'Ctrl + Del' 组合键把插件所在的目录删除就可以了,绝对绿色环保无残留。同时,这种方法还能最大程度避免插件与插件之间的不兼容性。
|
||||
|
||||
NeoBundle 是一个基于 Vundle 的项目,如同 Vundle,它们都可以安装和升级插件。然而 NeoBundle 的说明文件上明确指出:“NeoBundle 不是一个稳定的插件管理器,如果你想要一个稳定的,请选择 Vundle”。最新的 release-note 上也有警“可能会造成兼容性问题”——这是一个开发者写的注解,说明这个管理器还不能让人放心使用。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,我们为什么要使用 NeoBundle?它都不能保证稳定运行!好吧,它还是有可取之处的。Vundle 只支持 [Git][6] 这种版本控制系统,而 NeoBundle 可以支持 [Subversion][7] 和 [Mercurial][8]。另一个原因是如果你不想插件升级时破坏你的 Vim 生态环境,你可以锁住 NeoBundle,让它只使用某个插件的固定版本。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,NeoBundle 创建者,Shougo Matsuishita(LCTT:名字看着像日本人),正在将它的命令接口添加到其他插件项目,以便减少他们的命令使用量。现在 NeoBundle 支持3种插件:[unite.vim][9],Vim 使用的文件和缓存管理器;[vimshell.vim][10],Vim 使用的脚本程序;[vimproc.vim][11],运行于 vimshell.vim 中,用于对异步事件的支持。上面说的都是特殊案例,缺少英文文档,所以用户希望有人能完善它们。在正式使用它们之前,我们需要把注意力先集中在一些基本操作上。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装并初始化 NeoBundle ###
|
||||
|
||||
NeoBundle 依赖 Vim 7.2.051 或更高版本,依赖 git,依赖 [cURL][12](用于下载文件)。你可以手动下载 NeoBundle,也可以使用 cURL 下载它在 GitHub 上的库。在你的 home 目录下使用如下命令,可以将 NeoBundle 插件下载到 .vim/bundle/neobundle.vim 目录里,然后 NeoBundle 就能管理它自己了。
|
||||
|
||||
curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Shougo/neobundle.vim/master/bin/install.sh | sh
|
||||
|
||||
你还需要修改 .vimrc 文件。NeoBundle 的 GitHub 主页提供一个 .vimrc 范本,使用这个范本后,NeoBundle 会为你下载5个插件。如果不需要它们,你可以使用下面的最小配置:
|
||||
|
||||
if has('vim_starting')
|
||||
set nocompatible
|
||||
set runtimepath+=~/.vim/bundle/neobundle.vim/
|
||||
call neobundle#begin(expand('~/.vim/bundle/'))
|
||||
NeoBundleFetch 'Shougo/neobundle.vim'
|
||||
call neobundle#end()
|
||||
filetype plugin indent on
|
||||
|
||||
上述配置的作用是:启动 NeoBundle 并且像其他插件一样升级自己。NeoBundle 默认从 GitHub 下载并升级,如果你正好在使用 GitHub,你只需要为这个插件指定维护者的用户名和路径。在上面的配置中,NeoBundleFetch 只需要指定为“Shougo/neobundle.vim”,而不是完整的 GitHub 路径。如果你想使用其他网站,比如是 Subversion 或 Mecurial 的网站,你就需要添加完整的 URL。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想安装其他插件,你可以使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
curl -k https://github.com/[项目维护者]/[插件路径] > ~/.vim/bundle/[插件路径]
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子:你想安装 [vim-abolish][13],一个超级 NB 的文本搜索和替换插件,就使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
curl -k https://github.com/tpope/vim-abolish > ~/.vim/bundle/abolish
|
||||
|
||||
如果要让它自动升级,在 NeoBundleFetch 那行下面添加一行:
|
||||
|
||||
NeoBundle 'tpope/vim-abolish'
|
||||
|
||||
再介绍一个小技巧:你可以为插件指定一个分支或版本号。什么意思?NeoBundle 只会关注这个插件的某个分支或版本的更新,而忽略其他更新。如果你使用的某个插件处于高速开发过程,你就可以使用这个技巧,避免用到有 bug 的插件版本。举个例子:
|
||||
|
||||
NeoBundle 'Shougo/vimshell', { 'rev' : '3787e5' }
|
||||
|
||||
还有一个技巧:在 .vimtc 文件内添加一行关于“NeoBundleCheck”的属性。NeoBundle 会检查被卸载的插件,并提示你安装它们。你也可以使用命令“:NeoBundleInstall”(LCTT:这是要在 Vim 编辑器的命令模式下输入)来安装或升级插件。
|
||||
|
||||
### NeoBundle 用法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
很多 NeoBundle 命令用起来和 Vundle 类似,但命令的名字不一样。下面是 NeoBundle 命令的用法:
|
||||
|
||||
- `:NeoBundleUpdate`:安装或升级插件,如果你手动把一个插件的目录删除了,这个命令会重新安装这个插件。在这个命令后面加上插件名称,就只升级一个插件;不加参数,会将所有己安装但没被记录在案的插件给记录下来。“:NeoBundleInstall”命令效果相同。
|
||||
- `:NeoBundle {REPOSITORY URI} [[REVISION}] [,OPTIONS}]]`:将一个插件锁定到固定版本,防止胡乱升级。
|
||||
- `:NeoBundleList`:列出所有未初始化的插件。
|
||||
- `:NeoBundleClean`:进入交互界面,删除插件。
|
||||
|
||||
这些命令在配合 unite.vim (LCTT:就是上面举过的32个例子之一)使用时,效果会稍微有些出入。你可以使用“:help neobundle”命令了解更多信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 是否使用 NeoBundle,自己决定 ###
|
||||
|
||||
NeoBundle 是强大的工具,正处于高速开发状态。任何处于这种状态的项目,都会被帖上“有前途”和“不稳定”两个标签,看你自己怎么选。如果你想要最新的稳定版本的插件,NeoBundle 可以让 Vundle 和 Pathogen 永远保持在老界面。
|
||||
|
||||
然而在线帮助文档已经给出警告,它不是个稳定的产品,不及时更新版本可能造成一些插件运行出错。最后,你需要在 .vimrc 文件为你的 Neoundle 和其他插件指定一个稳定的版本。记住这警告,然后你可以在使用这些尖端技术产品时游刃有余。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.openlogic.com/wazi/bid/348084/Managing-Vim-extensions-with-NeoBundle
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[bazz2](https://github.com/bazz2) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/Shougo/neobundle.vim
|
||||
[2]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/vim
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/gmarik/Vundle.vim
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/tpope/vim-pathogen
|
||||
[5]:http://www.openlogic.com/wazi/bid/262302/Three-tools-for-managing-Vim-plugins
|
||||
[6]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/git
|
||||
[7]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/subversion
|
||||
[8]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/mercurial
|
||||
[9]:https://github.com/Shougo/unite.vim
|
||||
[10]:https://github.com/Shougo/vimshell.vim/blob/master/doc/vimshell.txt
|
||||
[11]:https://github.com/Shougo/vimproc.vim/blob/master/doc/vimproc.txt
|
||||
[12]:http://olex.openlogic.com/packages/curl
|
||||
[13]:https://github.com/tpope/vim-abolish
|
||||
@ -1,13 +1,13 @@
|
||||
-------------translating by tenght~
|
||||
9 commands to check hard disk partitions and disk space on Linux
|
||||
查看Linux硬盘分区和磁盘空间的9个命令
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In this post we are taking a look at some commands that can be used to check up the partitions on your system. The commands would check what partitions there are on each disk and other details like the total size, used up space and file system etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Commands like fdisk, sfdisk and cfdisk are general partitioning tools that can not only display the partition information, but also modify them.
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我们来了解一些用来检查你的系统分区的一些命令,这些命令将检查每个磁盘的分区情况和其它细节,例如总空间容量,已用完的空间和文件系统等。
|
||||
|
||||
像fdisk,sfdisk和cfdisk命令这样的常规分区工具,不仅可以显示分区信息,还可以修改。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. fdisk ###
|
||||
|
||||
Fdisk is the most commonly used command to check the partitions on a disk. The fdisk command can display the partitions and details like file system type. However it does not report the size of each partitions.
|
||||
Fdisk是检查磁盘上分区的最常用命令,fdisk命令可以显示分区和细节,如文件系统类型,但是它并不报告每个分区的大小。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo fdisk -l
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,11 +36,11 @@ Fdisk is the most commonly used command to check the partitions on a disk. The f
|
||||
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
|
||||
/dev/sdb1 * 2048 7907327 3952640 b W95 FAT32
|
||||
|
||||
Each device is reported separately with details about size, seconds, id and individual partitions.
|
||||
单独显示了每个设备的详细信息:大小,秒,ID和单个分区。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. sfdisk ###
|
||||
|
||||
Sfdisk is another utility with a purpose similar to fdisk, but with more features. It can display the size of each partition in MB.
|
||||
Sfdisk是另一种跟fdisk用途相似的实用工具,但具有更多的功能。它能够以MB为单位显示每个分区的大小。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo sfdisk -l -uM
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,20 +75,20 @@ Sfdisk is another utility with a purpose similar to fdisk, but with more feature
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. cfdisk ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cfdisk is a linux partition editor with an interactive user interface based on ncurses. It can be used to list out the existing partitions as well as create or modify them.
|
||||
Cfdisk是一个基于ncurses(提供字符终端处理库,包括面板和菜单)的带有交互式用户界面的Linux分区编辑器,它可以用来列出现有分区以及创建或修改这些分区。
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of how to use cfdisk to list the partitions.
|
||||
下面是一个如何使用Cfdisk来列出分区的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Cfdisk works with one partition at a time. So if you need to see the details of a particular disk, then pass the device name to cfdisk.
|
||||
Cfdisk一次只能列出一个分区,所以如果你需要看某一磁盘的细节,可以把设备名传给Cfdisk。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo cfdisk /dev/sdb
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. parted ###
|
||||
|
||||
Parted is yet another command line utility to list out partitions and modify them if needed.
|
||||
Here is an example that lists out the partition details.
|
||||
Parted是另一个命令行实用程序用来列出分区,如果需要的话,也可进行修改。
|
||||
下面是一个例子,列出了详细的分区信息。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo parted -l
|
||||
Model: ATA ST3500418AS (scsi)
|
||||
@ -115,9 +115,9 @@ Here is an example that lists out the partition details.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. df ###
|
||||
|
||||
Df is not a partitioning utility, but prints out details about only mounted file systems. The list generated by df even includes file systems that are not real disk partitions.
|
||||
Df是不是一个分区工具,但它打印出挂装文件系统的细节,Df可以列出甚至不是真实的磁盘分区的文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a simple example
|
||||
这里是个简单的例子:
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h
|
||||
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
|
||||
@ -131,16 +131,16 @@ Here is a simple example
|
||||
/dev/sda8 196G 154G 33G 83% /media/13f35f59-f023-4d98-b06f-9dfaebefd6c1
|
||||
/dev/sda5 98G 37G 62G 38% /media/4668484A68483B47
|
||||
|
||||
Only the file systems that start with a /dev are actual devices or partitions.
|
||||
文件系统只有以 /dev 开始的,是实际设备或分区。
|
||||
|
||||
Use grep to filter out real hard disk partitions/file systems.
|
||||
使用grep命令来筛选出实际的硬盘分区或文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h | grep ^/dev
|
||||
/dev/sda6 97G 43G 49G 48% /
|
||||
/dev/sda8 196G 154G 33G 83% /media/13f35f59-f023-4d98-b06f-9dfaebefd6c1
|
||||
/dev/sda5 98G 37G 62G 38% /media/4668484A68483B47
|
||||
|
||||
To display only real disk partitions along with partition type, use df like this
|
||||
要只显示真正的磁盘分区与分区类型,可以这样使用Df:
|
||||
|
||||
$ df -h --output=source,fstype,size,used,avail,pcent,target -x tmpfs -x devtmpfs
|
||||
Filesystem Type Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
|
||||
@ -148,11 +148,11 @@ To display only real disk partitions along with partition type, use df like this
|
||||
/dev/sda8 ext4 196G 154G 33G 83% /media/13f35f59-f023-4d98-b06f-9dfaebefd6c1
|
||||
/dev/sda5 fuseblk 98G 37G 62G 38% /media/4668484A68483B47
|
||||
|
||||
Note that df shows only the mounted file systems or partitions and not all.
|
||||
请注意,Df只显示已挂载的文件系统或分区,并不是所有。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. pydf ###
|
||||
|
||||
Improved version of df, written in python. Prints out all the hard disk partitions in a easy to read manner.
|
||||
它是用Python写的Df的改进版本,以一个方便阅读的方式打印出所有磁盘分区。
|
||||
|
||||
$ pydf
|
||||
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
|
||||
@ -160,12 +160,13 @@ Improved version of df, written in python. Prints out all the hard disk partitio
|
||||
/dev/sda8 195G 153G 32G 78.4 [#######..] /media/13f35f59-f023-4d98-b06f-9dfaebefd6c1
|
||||
/dev/sda5 98G 36G 61G 37.1 [###......] /media/4668484A68483B47
|
||||
|
||||
Again, pydf is limited to showing only the mounted file systems.
|
||||
另外,pydf限制为仅显示已挂载的文件系统
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. lsblk ###
|
||||
|
||||
Lists out all the storage blocks, which includes disk partitions and optical drives. Details include the total size of the partition/block and the mount point if any.
|
||||
Does not report the used/free disk space on the partitions.
|
||||
列出了所有的存储块,包括磁盘分区和光盘驱动器。细节包括所有分区/块总大小和挂载点。
|
||||
|
||||
不报告分区上的已使用和空闲磁盘空间。
|
||||
|
||||
$ lsblk
|
||||
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
|
||||
@ -180,13 +181,14 @@ Does not report the used/free disk space on the partitions.
|
||||
└─sdb1 8:17 1 3.8G 0 part
|
||||
sr0 11:0 1 1024M 0 rom
|
||||
|
||||
If there is no MOUNTPOINT, then it means that the file system is not yet mounted. For cd/dvd this means that there is no disk.
|
||||
|
||||
Lsblk is capbale of displaying more information about each device like the label and model. Check out the man page for more information
|
||||
如果没有挂载点,这就意味着文件系统未安装,对于cd/dvd这意味着没有磁盘。
|
||||
|
||||
lsblk能够显示每个设备的更多信息,如标签和模型,更多请查看信息手册。
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. blkid ###
|
||||
|
||||
Prints the block device (partitions and storage media) attributes like uuid and file system type. Does not report the space on the partitions.
|
||||
打印块设备(分区和存储介质)属性,例如UUID和文件系统类型,不报告分区空间。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo blkid
|
||||
/dev/sda1: UUID="5E38BE8B38BE6227" TYPE="ntfs"
|
||||
@ -198,7 +200,7 @@ Prints the block device (partitions and storage media) attributes like uuid and
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. hwinfo ###
|
||||
|
||||
The hwinfo is a general purpose hardware information tool and can be used to print out the disk and partition list. The output however does not print details about each partition like the above commands.
|
||||
hwinfo是一个通用的硬件信息的工具,可以用来打印出磁盘和分区表,但是输出不再像上面的命令那样打印每个分区的详细信息。
|
||||
|
||||
$ hwinfo --block --short
|
||||
disk:
|
||||
@ -215,18 +217,18 @@ The hwinfo is a general purpose hardware information tool and can be used to pri
|
||||
cdrom:
|
||||
/dev/sr0 SONY DVD RW DRU-190A
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
The output of parted is concise and complete to get an overview of different partitions, file system on them and the total space. Pydf and df are limited to showing only mounted file systems and the same on them.
|
||||
parted的输出可以得到简洁而完整的不同分区的概述、上面的文件系统以及总空间。pydf和df被限制为只显示和它们一样的已挂载的文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
Fdisk and Sfdisk show a whole lot of information that can take sometime to interpret whereas, Cfdisk is an interactive partitioning tool that display a single device at a time.
|
||||
fdisk和sfdisk显示完整大量的信息,需要花些时间来解释。cfdisk是一个互动的分区工具,每次显示一个单一的设备。
|
||||
|
||||
So try them out, and do not forget to comment below.
|
||||
来尝试下这些命令吧,别忘了在下面评论哟!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.binarytides.com/linux-command-check-disk-partitions/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[tenght](https://github.com/tenght) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
Zukimac 主题使 Ubuntu 14.04 桌面变成 Mac 桌面
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
虽然 Ubuntu Unity 本身已经是一款很漂亮的桌面了,但世界各地还是有很人被 Mac OS X 的外观所震撼。如果您恰好是其中之一,为了获得 OS X 的主题,是不需要换掉 Ubuntu 的,相反,您可以对它来个美化改造,**使 Ubuntu 14.04 看起来就像 Mac OS X**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 让 Ubuntu 14.04 看起来像 Mac OS X ###
|
||||
|
||||
要使 Ubuntu 美化成 Mac 的样子,我们得使用 Zukimac 主题。
|
||||
|
||||
- 从后面的链接获得 Zukimac 主题包:[下载 Zukimac Theme for Ubuntu 14.04][1]
|
||||
- 解压下载的 Zip 包,解压后会出现 Zukimac 和 Zukimac-ml 两个目录文件。把这些目录拷贝到您的 home 目录下的 .themes 文件夹中。进入 Home 目录中,按下快捷键 Ctrl+H 可以显示所有隐藏的文件,如果没有 .themes 文件夹,需要创建一个。
|
||||
- 使用 [Unity Tweak Tool 来改变主题][2].
|
||||
|
||||
就这些操作。Zukimac 提供了一些基本的 Mac OS 系统的外观和视窗感觉。下面是带有默认的 OS X MaVeric 壁纸的外观。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu 14.04 中获得 Mac 感觉更多的调整###
|
||||
|
||||
通常,您可以**安装像 Plank 或 Docky 这样的 dock 启动面板**。在 Ubuntu 14.04 中要安装 Plank 可以使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ricotz/docky
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install plank
|
||||
|
||||
安装完 dock 启动面板后,您也可以安装 **Synapse indicator 来代替模拟 Mac 中的 Spotlight**。使用来自于 Noobslabs 的 PPA 源来安装 Synapse indicator,如下示:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install indicator-synapse
|
||||
|
||||
不想安装上面的两软件的话,您也可以安装 **Slingscold launcher,用来代替模拟 Mac OS X 的启动面板**。在 Ubuntu 14.04 中,使用上面提到的 Noobslabs 的 PPA 源来安装 Slingscold 启动面板,如下示:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install slingscold
|
||||
|
||||
老实说,我是个狂热的 Ubuntu 迷,我喜欢 Ubuntu 默认的 Unity 主题样式外观。此外,还有很多[关于 Ubuntu 14.04 的漂亮图标主题样式][3] 可用来美化默认的外观。但正如我上面提到的仍有很多用户喜欢 Mac OS X 的主题样式,我希望这篇文章能帮助到他们,使其能把 Ubuntu 14.4 装扮成 Mac OS X 的样式。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-1404-mac-zukimac-theme/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://gnome-look.org/content/show.php/Zukimac?content=165450
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/how-to-install-themes-in-ubuntu-13-10/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
Linux 高级目录导航技巧
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
目录当行是命令行系统的基础概念.虽然不是什么难以理解的东西,但是知道一些技巧能够丰富你的经验并且提高工作效率.在这篇文章中,我们会讨论这些小技巧.
|
||||
|
||||
### 我们已经知道的东西 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在开始高级技巧之前,有一些必须知道的基本命令:
|
||||
|
||||
- ‘pwd’显示当前目录
|
||||
- ‘cd’ 改变当前目录
|
||||
- ‘cd’ 跟两个点(cd ..)能返回父目录
|
||||
- ‘cd’ 跟着相对目录就能直接切换当相对目录下
|
||||
- ‘cd’ 跟着绝对目录就能切换到绝对目录下
|
||||
|
||||
### 高阶技巧 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这节将介绍几个技巧方便你进行目录的切换
|
||||
|
||||
### 从任何地方回到home目录 ###
|
||||
|
||||
虽然使用‘cd /home/<your-home-directory-name>’, 不是什么大麻烦, 但是有一种方法直接打‘cd’ 就能回到home目录.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example :
|
||||
|
||||
$ pwd
|
||||
/usr/include/netipx
|
||||
$ cd
|
||||
$ pwd
|
||||
/home/himanshu
|
||||
|
||||
所以无论你在哪个目录下,都能这么干然后回到home目录.
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**- 如果要切换到确定用户的目录下, 就使用 ‘cd ~user_name'
|
||||
|
||||
### 用cd在目录间切换 - ###
|
||||
|
||||
假设你的工作目录是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
$ pwd
|
||||
/home/himanshu/practice
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想切换到 **/usr/bin/X11**, 然后又想回到之前的目录. 你会怎么做? 最直接的 :
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /usr/bin/X11
|
||||
$ cd /home/himanshu/practice/
|
||||
|
||||
虽然这样行得通,但是要记住这些复杂的目录是个大困难.这种情况下使用 ‘cd -’ 命令就行.
|
||||
|
||||
使用 ‘cd -’的第一步和上面的例子是一样的, 你可以 cd 到你想要切换到的<path>下 , 但是回到之前的目录用 ‘cd -’就可以.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /usr/bin/X11
|
||||
$ cd -
|
||||
/home/himanshu/practice
|
||||
$ pwd
|
||||
/home/himanshu/practice
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想回到最后访问的目录(在这个例子中是/usr/bin/X11),也使用'cd -'就可以.但是这个命令只会记住最后访问的目录,这是一个缺点.
|
||||
|
||||
### 用 pushd 和 popd 来切换目录 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
如果你对'cd -'非常了解了的话,你会发现这个命令只能帮助你在两个目录之间移动,但是很多场景下需要在很多目录之间切换.比如你要从A切换到B再到C然后又想回到A.
|
||||
|
||||
一般来说,你需要打出A的完整路劲,但是如果这个路径非常复杂,将是非常烦人的一件事,热别是你的切换非常频繁的话.
|
||||
|
||||
一些场景下可以使用 ‘pushd’ 还有 ‘popd’ 命令. The ‘pushd’ 将一个目录存到内存中,‘popd’ 将目录从内存中去除,并且转换到那个目录下.
|
||||
|
||||
例如 :
|
||||
|
||||
$ pushd .
|
||||
/usr/include/netipx /usr/include/netipx
|
||||
$ cd /etc/hp/
|
||||
$ cd /home/himanshu/practice/
|
||||
$ cd /media/
|
||||
$ popd
|
||||
/usr/include/netipx
|
||||
$ pwd
|
||||
/usr/include/netipx
|
||||
|
||||
使用‘pushd’ 命令存储当前的工作目录 (用 .表示), 然后切换到各种各样的目录去. 为了返回之前的目录 ,只要使用 ‘popd’命令就行了.
|
||||
使用
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**- 你也可以使用 ‘pushd’ 来切换到之前存储的目录, 但是不会像 ‘popd’ 一样去除这个目录.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/directory-navigations-tips-tricks/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[ggaaooppeenngg](https://github.com/ggaaooppeenngg) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu,Linux Mint,Debian上禁用Ipv6
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Ipv6 ###
|
||||
|
||||
IPv6是寻址方案Ipv4的下一个版本,被用来给如google.com这样的域名分配数字地址。
|
||||
|
||||
Ipv6比Ipv4支持更多的地址。然而,它还没有被广泛支持,还在被接受的过程中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 你的系统支持Ipv6么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了支持Ipv6,需要很多事情。首先你需要系统/操作系统支持Ipv6。Ubuntu,Linux Mint,和大多是现代发行版都支持它。如果你看一下ifconfig指令的输出,你就会看见你的网络接口被分配了ipv6地址。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ifconfig
|
||||
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 00:1c:c0:f8:79:ee
|
||||
inet addr:192.168.1.2 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
|
||||
inet6 addr: fe80::21c:c0ff:fef8:79ee/64 Scope:Link
|
||||
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
|
||||
RX packets:110880 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
|
||||
TX packets:111960 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
|
||||
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
|
||||
RX bytes:62289395 (62.2 MB) TX bytes:25169458 (25.1 MB)
|
||||
Interrupt:20 Memory:e3200000-e3220000
|
||||
|
||||
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
|
||||
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
|
||||
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
|
||||
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
|
||||
RX packets:45258 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
|
||||
TX packets:45258 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
|
||||
collisions:0 txqueuelen:0
|
||||
RX bytes:4900560 (4.9 MB) TX bytes:4900560 (4.9 MB)
|
||||
|
||||
看一下行“inet6 addr”。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来你需要一个支持ipv6的路由器/调制解调器。额外地,你的ISP也必须支持ipv6。
|
||||
|
||||
除了检查网络设备的每一部分,最好查出你是否可以通过ipv6访问网站。
|
||||
|
||||
有很多网站可以检测你的连接是否支持ipv6. 这里就是个例子:[http://testmyipv6.com/][1]
|
||||
|
||||
下面是在内核中启用ipv6的参数:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sysctl net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 0
|
||||
|
||||
$ sysctl net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 0
|
||||
|
||||
$ sysctl net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 0
|
||||
|
||||
同样可以在proc文件中检查
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat /proc/sys/net/ipv6/conf/all/disable_ipv6
|
||||
0
|
||||
|
||||
注意这里的变量是控制ipv6的“禁用”。所以设置1就会禁用ipv6。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如果它不支持就禁用ipv6 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的网络设备中不支持ipv6,那最好就全部禁用它们。为什么?因为这回引起延迟域查询,在网络连接中不必要地尝试连接到ipv6地址导致延迟等等问题。
|
||||
|
||||
我也遇到过像这样的问题,apt-get命令偶尔会尝试连接到ipv6地址失败接着检索ipv4地址。看一下下面的输出。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
Ign http://archive.canonical.com trusty InRelease
|
||||
Ign http://archive.canonical.com raring InRelease
|
||||
Err http://archive.canonical.com trusty Release.gpg
|
||||
Cannot initiate the connection to archive.canonical.com:80 (2001:67c:1360:8c01::1b). - connect (101: Network is unreachable) [IP: 2001:67c:1360:8c01::1b 80]
|
||||
Err http://archive.canonical.com raring Release.gpg
|
||||
Cannot initiate the connection to archive.canonical.com:80 (2001:67c:1360:8c01::1b). - connect (101: Network is unreachable) [IP: 2001:67c:1360:8c01::1b 80]
|
||||
|
||||
.....
|
||||
|
||||
像这样的错误在最近的Ubuntu中更频繁了,或许它比以前更频繁地尝试使用IPv6地址。
|
||||
|
||||
我在其他的应用上也注意到了相似的问题,如Hexchat,同样Google Chrome也会有时会在查询域名的时候花费更长的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
所以最好的方案是完全禁用Ipv6来摆脱这些事情。这只需要一点点配置但可以帮助你解决很多你系统上的很多问题。用户甚至反应这可以加速网络。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 禁用 Ipv6 - 方案1 ####
|
||||
|
||||
编辑文件 - /etc/sysctl.conf
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo gedit /etc/sysctl.conf
|
||||
|
||||
在文件的最后加入下面的行。
|
||||
|
||||
# IPv6 disabled
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6 = 1
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6 = 1
|
||||
net.ipv6.conf.lo.disable_ipv6 = 1
|
||||
|
||||
保存并关闭
|
||||
|
||||
重启sysctl
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo sysctl -p
|
||||
|
||||
再次检查ifconfig的输出,这里应该没有ipv6地址了。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ifconfig
|
||||
eth0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 08:00:27:5f:28:8b
|
||||
inet addr:192.168.1.3 Bcast:192.168.1.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
|
||||
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
|
||||
RX packets:1346 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
|
||||
TX packets:965 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
|
||||
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
|
||||
RX bytes:1501691 (1.5 MB) TX bytes:104883 (104.8 KB)
|
||||
|
||||
If it does not work, then try rebooting the system and check ifconfig again.
|
||||
如果不行,尝试重启系统并再次检查ifconfig
|
||||
|
||||
#### 禁用 ipv6 - GRUB 方案 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Ipv6同样可以通过编辑grub配置文件禁用。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo gedit /etc/default/grub
|
||||
|
||||
查找包含"GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX"的行,并如下编辑:
|
||||
|
||||
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="ipv6.disable=1"
|
||||
|
||||
同样可以加入名为"GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT"的变量,这同样有用。保存并关闭文件,重新生成grub配置。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo update-grub2
|
||||
|
||||
重启,现在ipv应该就已经禁用了。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.binarytides.com/disable-ipv6-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://testmyipv6.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
在Linux终端中加速目录导航
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
与在命令行中导航目录一样令人称道的是,很少有比一遍又一遍重复”cd ls cd ls cd ls……“更令人沮丧的事情了。如果你不是百分百确定你想要进入的下一个目录的名字,那么你不得不使用ls来确认,然后使用cd来进入你想要进的那一个。所幸的是,现在大量的终端和shell语言提供了强大的自动补全功能来处理该问题。但是,你仍然需要一直疯狂地敲击制表键来干这事。如果你和我一样懒惰,你就会对autojump十分痴迷。自动跳转是一个命令行工具,它允许你可以直接跳转到你喜爱的目录,而不用管你现在身在何处。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux上安装autojump ###
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu或Debian上autojump:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install autojump
|
||||
|
||||
要在CentOS或Fedora上安装autojump,请使用yum命令。在CentOS上,你需要先[启用EPEL仓库][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install autojump
|
||||
|
||||
在Archlinux上安装autojump:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S autojump
|
||||
|
||||
如果你找不到适合你的版本的包,你可以从[GitHub][2]上下载源码包来编译。
|
||||
|
||||
### autojump的基本用法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
autojump的工作方式很简单:它会在你每次启动命令时记录你当前位置,并把它添加进它自身的数据库中。那样,某些目录比其它一些目录添加的次数多,这些目录一般就代表你最重要的目录,而它们的“weight”也会增大。
|
||||
|
||||
从那儿,你可以使用下面的语法来直接跳转到这些目录:
|
||||
|
||||
autojump [name or partial name of the directory]
|
||||
|
||||
注意,你不需要输入完整的名称,因为autojump会检索它的数据库,并返回最可能的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,假定我们正在下面的目录结构中工作。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
那么下面的命令将直接让你跳到/root/home/doc下,不管你当前位置在哪里。
|
||||
|
||||
$ autojump do
|
||||
|
||||
如果你也很讨厌打字,那么我推荐你为autojump起个别名,或者使用默认的别名。
|
||||
|
||||
$ j [name or partial name of the directory]
|
||||
|
||||
另外一个引人注目的功能是,autojump支持
|
||||
|
||||
还是同样的例子,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ autojump d
|
||||
|
||||
然后敲击tab键,将会返回/root/home/doc或者/root/home/ddl。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,对于高级用户,你可以访问目录数据库,并修改它的内容。它使得使用下面的命令来手动添加一个目录成为可能:
|
||||
|
||||
$ autojump -a [directory]
|
||||
|
||||
如果你突然想要把它变成你的最爱和使用最频繁的文件夹,你可以通过命令的内部参数来手工增加它的weight
|
||||
|
||||
$ autojump -i [weight]
|
||||
|
||||
这将使得该目录更可能被选择跳转。相反的例子是使用内部参数来减少weight:
|
||||
|
||||
$ autojump -d [weight]
|
||||
|
||||
要跟踪所有这些改变,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ autojump -s
|
||||
|
||||
这会显示数据库中的统计数据,然而:
|
||||
|
||||
$ autojump --purge
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令将会把不再存在的目录从数据库移除。
|
||||
|
||||
简言之,autojump将会受到所有命令行高级用户的欢迎。不管你是在ssh进一台服务器,还是仅仅想要追随复古潮流,敲更少的键来减少导航时间总是件好事。如果你真的热衷于此类工具,你也肯定会看看[Fasd][3],它应该会很称职。
|
||||
|
||||
你觉得autojump怎么样?你会经常用它么?发表一下你的评论吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/speed-up-directory-navigation-linux-terminal.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||
[2]:https://github.com/joelthelion/autojump
|
||||
[3]:https://github.com/clvv/fasd
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux中同步微软 OneDrive
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[OneDrive][1](以前称为SkyDrive)是微软的一个广受欢迎的云存储产品。目前OneDrive为每一个新注册用户提供7GB免费存储空间。正如你所想,OneDrive与微软其他软件产品很好地集成。微软还提供了一个独立的OneDrive客户端,它会自动备份照相机拍摄的图片和视频到OneDrive。但你猜怎么着。该客户端可用于除Linux的各大PC/移动平台。 “OneDrive在任何设备,任何时间”?嗯,这还不存在。
|
||||
|
||||
不要失望。开源社区已经已经拿出了解决方案。 Boilermaker写的[onedrive-d][2]可以完成这项工作。作为监测守护进程运行,onedrive-D可自动将本地文件夹同步到OneDrive云存储。
|
||||
|
||||
I在本教程中,我将介绍**如何在Linux上使用onedrive-d同步微软OneDrive**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在linux上onedrive-d ###
|
||||
|
||||
虽然onedrive-d最初是为Ubuntu/ Debian开发的,但它仍然支持CentOS/ Fedora的/ RHEL。
|
||||
|
||||
安装就像输入下面的命令一样容易。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/xybu92/onedrive-d.git
|
||||
$ cd onedrive-d
|
||||
$ ./inst install
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一次配置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
安装之后,你需要进行一次性配置来授予onedrive-d对您OneDrive账户的读/写权限。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,创建将用于对远程OneDrive账户同步的本地文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mkdir ~/onedrive
|
||||
|
||||
接着运行下面的命令开开启一次性配置。
|
||||
|
||||
$ onedrive-d
|
||||
|
||||
它接着会弹出如下onedrive-d的设置窗口。在“Location”选项中,选择你之前创建的本地文件夹。在“Authentication”选项中,你会看见“You have not authenticated OneDrive-d yet”(“你还没有授权OneDrive-d”)的信息。现在点击"Connect to OneDrive.com"按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
它会弹出一个新窗口来要求你登录OneDrivecom。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
登录OneDrive.com之后,你会被要求授权onedrive-d访问。选择“Yes”。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
回到先前的设置窗口,你会看到之前的状态已经变成了You have connected to OneDrive.com"(“你已经连接到了OneDrive.com”)。点击“OK”完成。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 与OneDrive同步一个本地文件夹 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里有两种方法来使用onedrice-d将本地文件夹与OneDrive存储同步。
|
||||
|
||||
一种是“手动使用命令行来同步OneDrive”。就是当你需要与你的OneDrive账户同步时运行:
|
||||
|
||||
$ onedrive-d
|
||||
|
||||
`onedrive-d`接着将扫描本地文件夹与OneDrive帐户的内容并使两者同步。这意味着要么上传一个在本地文件夹新添加的文件,或者从远程OneDrive帐户下载最新发现的文件。如果你从本地文件夹删除任何文件,相应的文件将自动在与OneDrive帐户同步后被删除。同样的事情也会在相反的方向发生。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦同步完成,你可以使用Ctrl-C杀掉onedirve-d的前台运行进程。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
另一种方法是将onedrive-d作为一个始终运行的守护进程在开机时自动启动。在这种情况下,后台守护进程会同时监视本地文件夹和OneDrive账户,以使它们保持同步。对于这一点,只需将onedrive-D加入到你桌面[自动启动程序列表][3]中就行了。
|
||||
|
||||
当onedrive-D作为守护进程在后台运行,你会在桌面状态栏中看到OneDrive图标,如下图所示。每当同步更新被触发,你就会看到一个桌面通知。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要注意的是:根据作者所言,onedrive-d仍在积极开发中。这并不能用于任何形式的生产环境。如果您遇到任何bug,请随时提交一份[bug报告][4]。你的贡献,笔者将不胜感激。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/06/sync-microsoft-onedrive-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/go/onedrive
|
||||
[2]:http://xybu.me/projects/onedrive-d/
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/12/start-program-automatically-linux-desktop.html
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/xybu92/onedrive-d/issues?state=open
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
开源多媒体转换器Curlew 0.1.22.3发布了
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Curlew是linux下的一款容易使用,开源多媒体转换器,现在的版本是0.1.22.3。**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Curlew可以转换超过100种不同的格式、显示文件的详细信息、转换预览、插入字幕等等。
|
||||
|
||||
根据变更日志,转换前后实例的最后大小和位置会被记住、加入了一些失去对话图标、文件系统会在挂起前同步。
|
||||
|
||||
这个程序有一些依赖:至少Python 2.7 (小于3.0)、python-gobject 3.0、gir1.2-gtk 3.0、 ffmpeg 0.8、libav-tools 0.8、 mencoder、libavcodec-extra、xdg-utils、mediainfo。
|
||||
|
||||
来自noobslab.com的人提供一种通过PPA来简单地安装这个应用的方法。你要做的是在命令行下输入少量的命令(你需要使用root权限来生效)
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/apps
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install curlew
|
||||
|
||||
查看官方[更新日志][1]来获取完整的特性与更新列表。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以下载Curlew 0.1.22.3 的软件包:
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 14.04 DEB ALL][2][ubuntu_deb] [172 KB]
|
||||
- [tar.gz][3][sources] [152 KB]
|
||||
|
||||
记住这是一个开发版因此不应该安装在生产机器上。它只用于测试。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Open-Source-Multimedia-Converter-Curlew-0-1-22-3-Is-Out-448028.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://gtk-apps.org/content/show.php/Curlew?content=155664
|
||||
[2]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/curlew/files/curlew-0.1.22.3/curlew_0.1.22.3ubuntu14.04_all.deb/download
|
||||
[3]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/curlew/files/curlew-0.1.22.3/curlew-0.1.22.3.tar.gz/download
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,201 @@
|
||||
在Ubuntu下使用“Reprepro”工具在Sourceforge.net中创建".deb"包仓库
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Reprepro**是一款小巧的命令行工具来方便地创建并管理**.deb**仓库。今天我们会战士如何人使用reprepro简单地创建一个Debian包仓库,并使用**rsync**上传到Sourceforge.net。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 1: 安装Reprepro并生成key ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,安装所有需要的包,使用下面的apt-get命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install reprepro gnupg
|
||||
|
||||
现在你需要使用hnupg生成一个gpg key,这里使用下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ gpg --gen-key
|
||||
|
||||
它会询问你一些问题,比如你想要哪种key、key的有效期、如果你不知道如何回答,只需点击**Enter** 来选择默认选项(建议)
|
||||
|
||||
当然,它会询问你用户名和密码,在脑海中记住这些,因为我们会在之后需要它。
|
||||
|
||||
gpg (GnuPG) 1.4.14; Copyright (C) 2013 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
|
||||
This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.
|
||||
There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.
|
||||
|
||||
Please select what kind of key you want:
|
||||
(1) RSA and RSA (default)
|
||||
(2) DSA and Elgamal
|
||||
(3) DSA (sign only)
|
||||
(4) RSA (sign only)
|
||||
Your selection?
|
||||
RSA keys may be between 1024 and 4096 bits long.
|
||||
What keysize do you want? (2048)
|
||||
Requested keysize is 2048 bits
|
||||
Please specify how long the key should be valid.
|
||||
0 = key does not expire
|
||||
= key expires in n days
|
||||
w = key expires in n weeks
|
||||
m = key expires in n months
|
||||
y = key expires in n years
|
||||
Key is valid for? (0)
|
||||
Key does not expire at all
|
||||
Is this correct? (y/N) Y
|
||||
|
||||
You need a user ID to identify your key; the software constructs the user ID
|
||||
from the Real Name, Comment and Email Address in this form:
|
||||
"Heinrich Heine (Der Dichter) <heinrichh@duesseldorf.de>"
|
||||
|
||||
Real name: ravisaive
|
||||
Email address: tecmint.com@gmail.com
|
||||
Comment: tecmint
|
||||
You selected this USER-ID:
|
||||
"Ravi Saive (tecmint) <tecmint.com@gmail.com>"
|
||||
|
||||
Change (N)ame, (C)omment, (E)mail or (O)kay/(Q)uit? O
|
||||
You need a Passphrase to protect your secret key.
|
||||
|
||||
We need to generate a lot of random bytes. It is a good idea to perform
|
||||
some other action (type on the keyboard, move the mouse, utilize the
|
||||
disks) during the prime generation; this gives the random number
|
||||
generator a better chance to gain enough entropy.
|
||||
|
||||
+++++
|
||||
gpg: key 2EB446DD marked as ultimately trusted
|
||||
public and secret key created and signed.
|
||||
|
||||
gpg: checking the trustdb
|
||||
gpg: 3 marginal(s) needed, 1 complete(s) needed, PGP trust model
|
||||
gpg: depth: 0 valid: 1 signed: 0 trust: 0-, 0q, 0n, 0m, 0f, 1u
|
||||
pub 2048R/2EB446DD 2014-06-24
|
||||
Key fingerprint = D222 B1C9 342E 5911 02B1 9147 3BD6 7918 2EB4 46DD
|
||||
uid Ravi Saive (tecmint) <tecmint.com@gmail.com>
|
||||
sub 2048R/7EF2F750 2014-06-24
|
||||
|
||||
现在你的key已经生成了,要检查一下,用root权限运行这条命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo gpg --list-keys
|
||||
|
||||
#### 示例输出 ####
|
||||
|
||||
/home/ravisaive/.gnupg/pubring.gpg
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
pub 2048R/2EB446DD 2014-06-24
|
||||
uid ravisaive (tecmint) <tecmint.com@gmail.com>
|
||||
sub 2048R/7EF2F750 2014-06-24
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 2: 创建一个包仓库并导出key ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们现在要开始创建仓库,首先你需要创建一些文件夹,我们的仓库会在**/var/www/apt**目录,让我们先创建这些目录。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo su
|
||||
# cd /var/www
|
||||
# mkdir apt
|
||||
# mkdir -p ./apt/incoming
|
||||
# mkdir -p ./apt/conf
|
||||
# mkdir -p ./apt/key
|
||||
|
||||
你现在需要将key导出到仓库文件夹,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
# gpg --armor --export username yourmail@mail.com >> /var/www/apt/key/deb.gpg.key
|
||||
|
||||
注意:用你之前步骤中输入的用户名代替username,用你的email代替yourmail@mail.com。
|
||||
|
||||
我们需要在**/var/www/apt/conf**创建一个文件“**distributions**”。
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /var/www/apt/conf/distributions
|
||||
|
||||
加入下面这几行到distributions这个文件中并保存。
|
||||
|
||||
Origin: (yourname)
|
||||
Label: (name of repository)
|
||||
Suite: (stable or unstable)
|
||||
Codename: (the codename for the distribution you are using, like trusty)
|
||||
Version: (the version for the distribution you are using, like 14.04)
|
||||
Architectures: (the repository packages architecture, like i386 or amd64)
|
||||
Components: (main restricted universe multiverse)
|
||||
Description: (Some information about the repository)
|
||||
SignWith: yes
|
||||
|
||||
接下来我们会创建仓库树,运行这些命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# reprepro --ask-passphrase -Vb /var/www/apt export
|
||||
|
||||
#### 示例输出 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Created directory "/var/www/apt/db"
|
||||
Exporting Trusty...
|
||||
Created directory "/var/www/apt/dists"
|
||||
Created directory "/var/www/apt/dists/Trusty"
|
||||
Created directory "/var/www/apt/dists/Trusty/universe"
|
||||
Created directory "/var/www/apt/dists/Trusty/universe/binary-i386"
|
||||
FF5097B479C8220C ravisaive (tecmint) <tecmint.com@gmail.com> needs a passphrase
|
||||
Please enter passphrase:
|
||||
Successfully created '/var/www/apt/dists/Trusty/Release.gpg.new'
|
||||
FF5097B479C8220C ravisaive (tecmint) <tecmint.com@gmail.com> needs a passphrase
|
||||
Please enter passphrase:
|
||||
Successfully created '/var/www/apt/dists/Trusty/InRelease.new'
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 3: 在新创建的仓库中加入包 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在准备你的**.deb**包来加入到仓库中。进入 **/var/www/apt**目录,你每次要加包的时候都不得不这么做。
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /var/www/apt
|
||||
# reprepro --ask-passphrase -Vb . includedeb Trusty /home/ravisaive/packages.deb
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:用你在distributions文件中输入的仓库代号来代替**trusty** ,并且用包的路径替换**/home/username/package.deb**,你会被要求输入密码。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 示例输出####
|
||||
|
||||
/home/ravisaive/packages.deb : component guessed as 'universe'
|
||||
Created directory "./pool"
|
||||
Created directory "./pool/universe"
|
||||
Created directory "./pool/universe/o"
|
||||
Created directory "./pool/universe/o/ojuba-personal-lock"
|
||||
Exporting indices...
|
||||
FF5097B479C8220C ravisaive (tecmint) <tecmint.com@gmail.com> needs a passphrase
|
||||
Please enter passphrase:
|
||||
Successfully created './dists/Trusty/Release.gpg.new'
|
||||
FF5097B479C8220C ravisaive (tecmint) <tecmint.com@gmail.com> needs a passphrase
|
||||
Please enter passphrase:
|
||||
Successfully created './dists/Trusty/InRelease.new'
|
||||
|
||||
你的包已经加入了仓库,要移除它:
|
||||
|
||||
# reprepro --ask-passphrase -Vb /var/www/apt remove trusty package.deb
|
||||
|
||||
当然你需要用你的包名与仓库代号来修改命令。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 4: 上传仓库到Sourceforge.net ###
|
||||
|
||||
要上传仓库到**Sourceforge.net**,你当然需要一个活跃账号与一个活跃项目,让我假设你想要上传仓库到**http://sourceforge.net/projects/myfoo/testrepository**,这里的myfoo是项目名(UNIX名称,不是URL,不是标题),testrepository是你想要上传文件到这上面的目录,这里我们会使用[rsync 命令][1]
|
||||
|
||||
# rsync -avP -e ssh /var/www/apt/ username@frs.sourceforge.net:/home/frs/project/myfoo/testrepository/
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:用你在sourceforge.net上的用户名代替username,用你的项目的UNIX类型名称代替myfoo,用你想要存储的文件夹代替testrepository。
|
||||
|
||||
现在你的仓库上传到了**http://sourceforge.net/projects/myfoo/testrepository**,要把它加入到已安装的系统,首先你需要导入仓库key,它会在**/var/www/apt/key/deb.gpg.key**,但是这是一个本地路径,并且你仓库的用户不能添加到他们的系统中,这就是为什么我们要导入来自sourceforge.net的key的原因。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo su
|
||||
# wget -O - http://sourceforge.net/projects/myfoo/testrepository/apt/key/deb.gpg.key | apt-key add -
|
||||
|
||||
你现在可以非常轻松地把仓库加入到系统中了,打开**/etc/apt/sources.list**,并加入下面这行:
|
||||
|
||||
deb http://sourceforge.net/projects/myfoo/testrepository/apt/key/deb.gpg.key trusty main
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**:用你的项目的UNIX类型名称代替myfoo,用你的仓库代码代替trusty,用你上传存储的文件夹代替testrepository,用你在distributionsj加入的仓库组件代替main。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,运行下面的命令来更新仓库列表。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
**祝贺你**! 你的软件仓库已经激活了!你现在可以非常简单地在你需要的时候安装包了。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/create-deb-pacakge-repository-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/rsync-local-remote-file-synchronization-commands/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user