mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-15 01:50:08 +08:00
commit
897a7ea4b6
@ -1,12 +1,13 @@
|
||||
优秀的开源合作编辑工具
|
||||
六款优秀的开源协作编辑工具
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
一句话,合作编著就是多个人进行编著。合作有好处也有风险。好处包括更加全面/协调的方式,更好的利用现有资源和一个更加有力的、团结的声音。对于我来说,最大的好处是极大的透明度。那是当我需要采纳同事的观点。同事之间来来回回地传文件效率非常低,导致不必要的延误还让人(比如,我)对整个合作这件事都感到不满意。有个好的合作软件,我就能实时地或异步地分享笔记,数据和文件,并用评论来分享自己的想法。这样在文档、图片、视频、演示文稿上合作就不会那么的琐碎而无聊。
|
||||
|
||||
有很多种方式能在线进行合作,简直不能更简便了。这篇文章表明了我最喜欢的开源实时文档合作编辑工具。
|
||||
简而言之,协作编辑(Collaborative Edit)就是多个人进行编辑。协作有好处也有风险。好处之一是更加全面/协调的方式,更好的利用现有资源和一个更加有力一致的声音。对于我来说,最大的好处是极大的透明度。那是当我需要采纳同事的观点。同事之间来来回回地传文件效率非常低,导致不必要的延误还让人(比如,我)对整个协作这件事都感到不满意。有个好的协作软件,我就能实时地或异步地分享笔记,数据和文件,并用评论来分享自己的想法。这样在文档、图片、视频、演示文稿上协作就不会那么的琐碎而无聊。
|
||||
|
||||
Google Docs 是个非常好的高效应用,有着大部分我所需要的功能。它可以作为一个实时地合作编辑文档的工具提供服务。文档可以被分享、打开并被多位用户同时编辑,用户还能看见其他合作者一个字母一个字母的编辑过程。虽然 Google Docs 对个人是免费的,但并不开源。
|
||||
有很多种方式能在线进行协作,简直不能更简便了。这篇文章展示了我最喜欢的开源的实时文档协作编辑工具。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是我带来的最棒的开源合作编辑器,它们能帮你不被打扰的集中精力进行写作,而且是和其他人协同完成。
|
||||
Google Docs 是个非常好的高效应用,有着大部分我所需要的功能。它可以作为一个实时地协作编辑文档的工具提供服务。文档可以被分享、打开并被多位用户同时编辑,用户还能看见其他协作者一个字母一个字母的编辑过程。虽然 Google Docs 对个人是免费的,但并不开源。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是我带来的最棒的开源协作编辑器,它们能帮你不被打扰的集中精力进行写作,而且是和其他人协同完成。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,17 +15,17 @@ Google Docs 是个非常好的高效应用,有着大部分我所需要的功
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Hackpad 是个开源的基于网页的实时 wiki,基于开源 EtherPad 合作文档编辑器。
|
||||
Hackpad 是个开源的基于网页的实时 wiki,基于开源 EtherPad 协作文档编辑器。
|
||||
|
||||
Hackpad 允许用户实时分享你的文档,它还用彩色编码显示各个作者分别贡献了哪部分。它还允许插入图片、清单,由于提供了语法高亮功能,它还能用来写代码。
|
||||
|
||||
当2014年4月 Dropbox 获得了 Hackpad 后,这款软件就以开源的形式在本月发行。让我们经历的等待非常值得。
|
||||
当2014年4月 Dropbox 收购了 Hackpad 后,就在这个月这款软件以开源的形式发布。让我们经历的等待非常值得。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 有类似 wiki 所提供的,一套非常完善的功能
|
||||
- 实时或者异步地记合作笔记,共享数据和文件,或用评论分享你们的想法
|
||||
- 细致的隐私许可让你可以邀请单个朋友,一个十几人的团队或者上千的 Twitter 粉丝
|
||||
- 实时或者异步地记录协作笔记,共享数据和文件,或用评论分享你们的想法
|
||||
- 细致的隐私许可让你可以邀请单个朋友、一个十几人的团队或者上千的 Twitter 粉丝
|
||||
- 智能执行
|
||||
- 直接从流行的视频分享网站上插入视频
|
||||
- 表格
|
||||
@ -42,9 +43,9 @@ Hackpad 允许用户实时分享你的文档,它还用彩色编码显示各个
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Etherpad 是个基于网页的开源实时合作编辑器,允许多个作者同时编辑一个文本文档,写评论,并与其他作者用群聊方式进行交流。
|
||||
Etherpad 是个基于网页的开源实时协作编辑器,允许多个作者同时编辑一个文本文档,写评论,并与其他作者用群聊方式进行交流。
|
||||
|
||||
Etherpad 是用 JavaScript 运行的,在 AppJet 平台的顶端,通过 Comet 流实现实时的功能。
|
||||
Etherpad 是用 JavaScript 编写的,运行在 AppJet 平台之上,通过 Comet 流实现实时的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -55,9 +56,9 @@ Etherpad 是用 JavaScript 运行的,在 AppJet 平台的顶端,通过 Comet
|
||||
- 每隔一段很短的时间就会自动保存
|
||||
- 可个性化程度高
|
||||
- 有客户端插件可以扩展编辑的功能
|
||||
- 几百个支持 Etherpad 的扩展包括支持 email 提醒,pad 管理,授权
|
||||
- 几百个支持 Etherpad 的扩展,包括支持 email 提醒,pad 管理,授权
|
||||
- 可访问性开启
|
||||
- 可从 Node 里或通过 CLI(命令行界面)和 Pad 目录实时交互
|
||||
- 可从 Node 里或通过 CLI(命令行界面)和 EtherPad 的内容交互
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [etherpad.org][4]
|
||||
- 源代码:[github.com/ether/etherpad-lite][5]
|
||||
@ -71,7 +72,7 @@ Etherpad 是用 JavaScript 运行的,在 AppJet 平台的顶端,通过 Comet
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Firepad 是个开源的合作文本编辑器。它的设计目的是被嵌入到更大的网页应用中对几天内新加入的代码进行批注。
|
||||
Firepad 是个开源的协作文本编辑器。它的设计目的是被嵌入到更大的网页应用中对几天内新加入的代码进行批注。
|
||||
|
||||
Firepad 是个全功能的文本编辑器,有解决冲突,光标同步,用户属性,用户在线状态检测功能。它使用 Firebase 作为后台,而且不需要任何服务器端的代码。他可以被加入到任何网页应用中。Firepad 可以使用 CodeMirror 编辑器或者 Ace 编辑器提交文本,它的操作转换代码是从 ot.js 上借鉴的。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -81,7 +82,7 @@ Firepad 已被多个编辑器使用,包括Atlassian Stash Realtime Editor、Ni
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 纯正的合作编辑
|
||||
- 纯正的协作编辑
|
||||
- 基于 OT 的智能合并及解决冲突
|
||||
- 支持多种格式的文本和代码的编辑
|
||||
- 光标位置同步
|
||||
@ -106,13 +107,13 @@ Firepad 已被多个编辑器使用,包括Atlassian Stash Realtime Editor、Ni
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ownCloud Documents 是个可以单独并/或合作进行办公室文档编辑 ownCloud 应用。它允许最多5个人同时在网页浏览器上合作进行编辑 .odt 和 .doc 文件。
|
||||
ownCloud Documents 是个可以单独并/或协作进行办公室文档编辑 ownCloud 应用。它允许最多5个人同时在网页浏览器上协作进行编辑 .odt 和 .doc 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
ownCloud 是个自托管文件同步和分享服务器。他通过网页界面,同步客户端或 WebDAV 提供你数据的使用权,同时提供一个容易在设备间进行浏览、同步和分享的平台。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 合作编辑,多个用户同时进行文件编辑
|
||||
- 协作编辑,多个用户同时进行文件编辑
|
||||
- 在 ownCloud 里创建文档
|
||||
- 上传文档
|
||||
- 在浏览器里分享和编辑文件,然后在 ownCloud 内部或通过公共链接进行分享这些文件
|
||||
@ -131,16 +132,16 @@ ownCloud 是个自托管文件同步和分享服务器。他通过网页界面
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Gobby 是个支持在一个会话内进行多个用户聊天并打开多个文档的合作编辑器。所有的用户都能同时在文件上进行工作,无需锁定。不同用户编写的部分用不同颜色高亮显示,它还支持多个编程和标记语言的语法高亮。
|
||||
Gobby 是个支持在一个会话内进行多个用户聊天并打开多个文档的协作编辑器。所有的用户都能同时在文件上进行工作,无需锁定。不同用户编写的部分用不同颜色高亮显示,它还支持多个编程和标记语言的语法高亮。
|
||||
|
||||
Gobby 允许多个用户在互联网上实时共同编辑同一个文档。他很好的整合了 GNOME 环境。它拥有一个客户端-服务端结构,这让它能支持一个会话开多个文档,文档同步请求,密码保护和 IRC 式的聊天方式可以在多个频道进行交流。用户可以选择一个颜色对他们在文档中编写的文本进行高亮。
|
||||
Gobby 允许多个用户在互联网上实时共同编辑同一个文档。它很好的整合了 GNOME 环境。它拥有一个客户端-服务端结构,这让它能支持一个会话开多个文档,文档同步请求,密码保护和 IRC 式的聊天方式可以在多个频道进行交流。用户可以选择一个颜色对他们在文档中编写的文本进行高亮。
|
||||
|
||||
还供有一个叫做 infinoted 的专用服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
特性:
|
||||
|
||||
- 成熟的文本编辑能力包括使用 GtkSourceView 的语法高亮功能
|
||||
- 实时、无需锁定、通过加密(包括PFS)连接的合作文本编辑
|
||||
- 实时、无需锁定、通过加密(包括PFS)连接的协作文本编辑
|
||||
- 整合了群聊
|
||||
- 本地组撤销:撤销不会影响远程用户的修改
|
||||
- 显示远程用户的光标和选择区域
|
||||
@ -170,9 +171,9 @@ Gobby 允许多个用户在互联网上实时共同编辑同一个文档。他
|
||||
|
||||
ONLYOFFICE(从前叫 Teamlab Office)是个多功能云端在线办公套件,整合了 CRM(客户关系管理)系统、文档和项目管理工具箱、甘特图以及邮件整合器
|
||||
|
||||
它能让你整理商业任务和时间表,保存并分享你的合作或个人文档,使用网络社交工具如博客和论坛,还可以和你的队员通过团队的即时聊天工具进行交流。
|
||||
它能让你整理商业任务和时间表,保存并分享你的协作或个人文档,使用网络社交工具如博客和论坛,还可以和你的队员通过团队的即时聊天工具进行交流。
|
||||
|
||||
能在同一个地方管理文档、项目、团队和顾客关系。OnlyOffice 结合了文本,电子表格和电子幻灯片编辑器,他们的功能跟微软桌面应用(Word、Excel 和 PowerPoint)的功能相同。但是他允许实时进行合作编辑、评论和聊天。
|
||||
能在同一个地方管理文档、项目、团队和顾客关系。OnlyOffice 结合了文本,电子表格和电子幻灯片编辑器,他们的功能跟微软桌面应用(Word、Excel 和 PowerPoint)的功能相同。但是他允许实时进行协作编辑、评论和聊天。
|
||||
|
||||
OnlyOffice 是用 ASP.NET 编写的,基于 HTML5 Canvas 元素,并且被翻译成21种语言。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -182,7 +183,7 @@ OnlyOffice 是用 ASP.NET 编写的,基于 HTML5 Canvas 元素,并且被翻
|
||||
- 文档可以在浏览/编辑模式下分享
|
||||
- 文档嵌入
|
||||
- 电子表格和电子幻灯片编辑器
|
||||
- 合作编辑
|
||||
- 协作编辑
|
||||
- 评论
|
||||
- 群聊
|
||||
- 移动应用
|
||||
@ -209,7 +210,7 @@ via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150823085112605/CollaborativeEditing.ht
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[H-mudcup](https://github.com/H-mudcup)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,25 +1,24 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux系统上安装Suricata入侵检测系统
|
||||
如何在 Linux 系统上安装 Suricata 入侵检测系统
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
随着安全威胁的不断发生,入侵检测系统(IDS)在如今的数据中心环境中显得尤为必要。然而,随着越来越多的服务器将他们的网卡升级到10GB/40GB网络,对如此线路上的硬件进行计算密集型的入侵检测越来越困难。其中一种扩展入侵检测系统性能的途径是**多线程入侵检测系统**,它将CPU密集型的深度包检测工作并行的分配给多个并发任务来完成。这样的并行检测可以充分利用多核硬件的优势来轻松扩展入侵检测系统的吞吐量。在这方面有两个知名的开源项目,分别是[Suricata][1] 和 [Bro][2]。
|
||||
随着安全威胁的不断发生,入侵检测系统(IDS)在如今的数据中心环境中显得尤为必要。然而,随着越来越多的服务器将他们的网卡升级到10GB/40GB以太网,对如此线路上的硬件进行计算密集型的入侵检测越来越困难。其中一种提升入侵检测系统性能的途径是**多线程入侵检测系统**,它将 CPU 密集型的深度包检测工作并行的分配给多个并发任务来完成。这样的并行检测可以充分利用多核硬件的优势来轻松提升入侵检测系统的吞吐量。在这方面有两个知名的开源项目,分别是 [Suricata][1] 和 [Bro][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
这个教程里,我会向大家演示**如何在Linux服务器上安装和配置Suricata入侵检测系统**
|
||||
这个教程里,我会向大家演示**如何在 Linux 服务器上安装和配置 Suricata 入侵检测系统**
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux上安装Suricata IDS ###
|
||||
### 在 Linux 上安装 Suricata IDS ###
|
||||
|
||||
让我们从源文件来构建 Suricata,但在此之前,需要按如下所示安装几个依赖包先。
|
||||
让我们从源文件来构建 Suricata,但在此之前,需要按如下所示先安装几个依赖包。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Debian, Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint 操作系统上安装依赖包 ####
|
||||
#### 在 Debian, Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint 操作系统上安装依赖包 ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install wget build-essential libpcre3-dev libpcre3-dbg automake autoconf libtool libpcap-dev libnet1-dev libyaml-dev zlib1g-dev libcap-ng-dev libjansson-dev
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在CentOS, Fedora 或者 RHEL 操作系统上安装依赖包 ####
|
||||
#### 在 CentOS, Fedora 或者 RHEL 操作系统上安装依赖包 ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install wget libpcap-devel libnet-devel pcre-devel gcc-c++ automake autoconf libtool make libyaml-devel zlib-devel file-devel jansson-devel nss-devel
|
||||
|
||||
一旦将所有依赖包安装完毕,我们就可以继续安装 Suricata 了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
首先从 [http://suricata-ids.org/download/][3] 下载 Suricata 源代码,然后构建它。撰写这篇文章的时候,其最新版本号为 2.0.8 。
|
||||
|
||||
$ wget http://www.openinfosecfoundation.org/download/suricata-2.0.8.tar.gz
|
||||
@ -61,12 +60,11 @@ Suricata 源代码带有默认的配置文件。按照如下方法安装这些
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make install-conf
|
||||
|
||||
正如你所料,如果没有IDS规则集的话,Suricata 毛用没有。幸好 Makefile 为我们提供了 IDS 规则集的安装选项。安装方法如下。
|
||||
|
||||
正如你所料,如果没有IDS规则集的话,Suricata 什么用也没有。幸好 Makefile 为我们提供了 IDS 规则集的安装选项。安装方法如下。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make install-rules
|
||||
|
||||
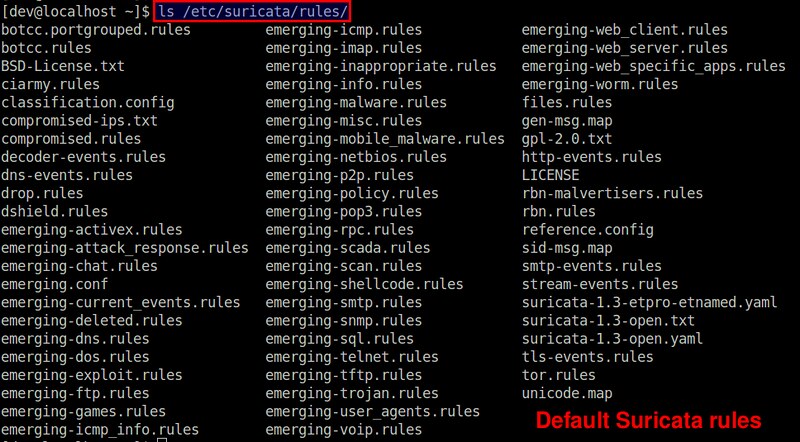
以上的规则安装命令会从 [EmergingThreats.net][4] 上下载可用的现存社区规则集快照,并且将其存储在 /etc/suricata/rules 目录下。
|
||||
以上的规则安装命令会从 [EmergingThreats.net][4] 上下载可用的社区规则集快照,并且将其存储在 /etc/suricata/rules 目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -76,14 +74,13 @@ Suricata 源代码带有默认的配置文件。按照如下方法安装这些
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/suricata/suricata.yaml
|
||||
|
||||
文件中有一些基本的配置供你使用。
|
||||
文件中有一些运行所需的基本配置。
|
||||
|
||||
为"default-log-dir"关键字指定Suricata日至文件所在的位置。
|
||||
为`default-log-dir`关键字指定 Suricata 日志文件所在的位置。
|
||||
|
||||
default-log-dir: /var/log/suricata/
|
||||
|
||||
在"vars"部分下方,你会发现几项对 Suricata 来说很重要变量。"HOME_NET"变量需要指定 Suricata 检查的网络。被分配给 EXTERNAL_NET 变量的 "!$HOME_NET" 代表除本地网络之外的其他网络。"XXX_PORTS"变量用来辨别不同服务所用到的端口号。需要注意的是无论使用什么端口,Suricata 都可以自动检测HTTP流量。所以是不是正确指定端口就显得没那么重要了。
|
||||
|
||||
在`vars`部分下方,你会发现几项对 Suricata 来说很重要变量。`HOME_NET`变量需要指定 Suricata 检查的网络。被分配给 `EXTERNAL_NET` 变量的 `!$HOME_NET` 代表除本地网络之外的其他网络。`XXX_PORTS`变量用来辨别不同服务所用到的端口号。需要注意的是无论使用什么端口,Suricata 都可以自动检测 HTTP 流量。所以是不是正确指定端口就显得没那么重要了。
|
||||
|
||||
vars:
|
||||
HOME_NET: "[192.168.122.0/24]"
|
||||
@ -92,7 +89,7 @@ Suricata 源代码带有默认的配置文件。按照如下方法安装这些
|
||||
SHELLCODE_PORTS: "!80"
|
||||
SSH_PORTS: 22
|
||||
|
||||
"host-os-policy" 部分用于防御利用操作系统网络栈(例如:TCP reassembly)的自身行为来逃避检测的一些知名攻击手段。作为对策,通过针对目标操作系统而对检测引擎算法进行微调,现代IDC提供了“基于目标”的检测手段。因此,如果你知道某台主机运行了什么操作系统的话,将这个信息提供给 Suricata 就可以大幅提高检测的成功率。这就是 "host-os-policy" 存在的意义。本例中,默认的IDC对策是Linux系统。如果针对某个IP地址没有指定操作系统信息,Suricata 会默认应用基于Linux系统的检测策略。当捕获到对192.168.122.0/28 和 192.168.122.155通讯时,Suricata就会应用基于Windows系统的检测策略。
|
||||
`host-os-policy` 部分用于防御利用操作系统网络栈的自身行为来逃避检测的一些知名攻击手段(例如:TCP reassembly)。作为对策,通过针对目标操作系统而对检测引擎算法进行微调,现代 IDC 提供了“基于目标”的检测手段。因此,如果你知道某台主机运行了什么操作系统的话,将这个信息提供给 Suricata 就可以大幅提高检测的成功率。这就是 `host-os-policy` 存在的意义。本例中,默认的 IDC 策略是 Linux 系统。如果针对某个 IP 地址没有指定操作系统信息,Suricata 会默认应用基于 Linux 系统的检测策略。如下,当捕获到对 192.168.122.0/28 和 192.168.122.155通讯时,Suricata 就会应用基于 Windows 系统的检测策略。
|
||||
|
||||
host-os-policy:
|
||||
# These are Windows machines.
|
||||
@ -111,38 +108,37 @@ Suricata 源代码带有默认的配置文件。按照如下方法安装这些
|
||||
vista: []
|
||||
windows2k3: []
|
||||
|
||||
在 "threading" 部分下,你可以为不同的 Suricata 线程指定CPU关联。默认状态下,[CPU 关联][5] 是被禁止使用的 ("set-cpu-affinity: no"),这意味着 Suricata 会分配其线程到所有可用的CPU核心上。Suricata 会默认为每一个CPU核心创建一个检测线程。你可以通过指定 "detect-thread-ratio: N" 来调整此行为。此处会创建 N*M 个检测线程,M代表CPU核心总数。
|
||||
在 `threading` 部分下,你可以为不同的 Suricata 线程指定 CPU 关联。默认状态下,[CPU 关联][5] 是被禁止使用的 (`set-cpu-affinity: no`),这意味着 Suricata 会分配其线程到所有可用的 CPU 核心上。Suricata 会默认为每一个 CPU 核心创建一个检测线程。你可以通过指定 `detect-thread-ratio: N` 来调整此行为。此处会创建 N*M 个检测线程,M 代表 CPU 核心总数。
|
||||
|
||||
threading:
|
||||
set-cpu-affinity: no
|
||||
detect-thread-ratio: 1.5
|
||||
|
||||
通过以上对线程的设置,Suricata会创建 1.5*M 个检测线程,M是系统的CPU核心总数。
|
||||
通过以上对线程的设置,Suricata 会创建 1.5*M 个检测线程,M 是系统的 CPU 核心总数。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想对Suricata配置有更多的了解,可以去翻阅默认配置文件。里边配有有大量的注释以供你清晰理解。
|
||||
如果你想对 Suricata 配置有更多的了解,可以去翻阅默认配置文件。里边配有有大量的注释以供你清晰理解。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用Suricata进行入侵监控 ###
|
||||
### 使用 Suricata 进行入侵监控 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在是时候让 Suricata 跑起来了,但在这之前还有一个步骤需要去完成。
|
||||
|
||||
当你使用 pcap捕获模式 的时候,强烈建议关闭Suricata监听网卡上的任何的包卸载(例如 LRO/GRO)功能。这些功能会干扰包的实时捕获行为。
|
||||
当你使用 pcap 捕获模式的时候,强烈建议关闭 Suricata 监听网卡上的任何的包卸载(例如 LRO/GRO)功能。这些功能会干扰包的实时捕获行为。
|
||||
|
||||
按照以下方法关闭 eth0 接口的 LRO/GRO 功能。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ethtool -K eth0 gro off lro off
|
||||
|
||||
这里要注意,在使用部分网卡的情况下,你会看到如下警告信息。忽略它们就行了,这些信息只不过告诉你你的网卡不支持LRO功能而已。
|
||||
这里要注意,在使用某些网卡的情况下,你会看到如下警告信息。忽略它们就行了,这些信息只不过告诉你你的网卡不支持 LRO 功能而已。
|
||||
|
||||
Cannot change large-receive-offload
|
||||
|
||||
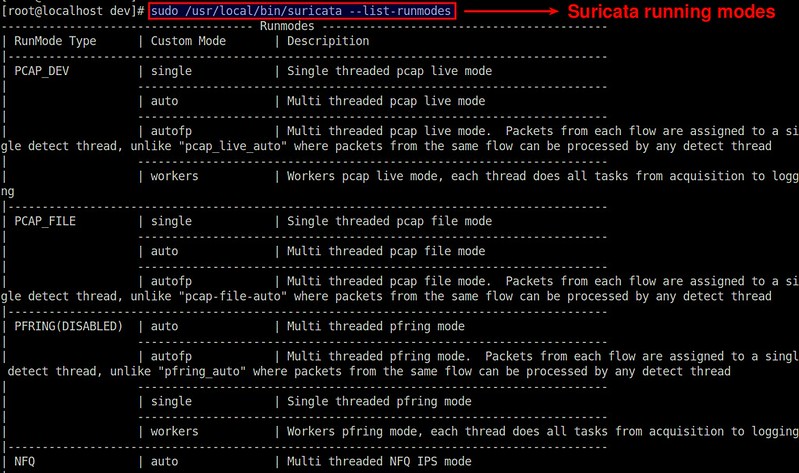
Suricata 支持许多运行模式。运行模式决定着IDC会使用何种线程。以下命令可以查看所有 [可用的运行模式][6]。
|
||||
Suricata 支持许多运行模式。运行模式决定着 IDC 会使用何种线程。以下命令可以查看所有 [可用的运行模式][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /usr/local/bin/suricata --list-runmodes
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Suricata 使用的默认运行模式是autofp("auto flow pinned load balancing"==“自动流绑定负载均衡” 的缩写)。这个模式下,来自某一个流的包会被分配到一个单独的检测线程中。这些流会根据未被处理的包的最低数量来分配相应的线程。
|
||||
Suricata 使用的默认运行模式是 autofp("auto flow pinned load balancing"==“自动流绑定负载均衡” 的缩写)。这个模式下,来自某一个流的包会被分配到一个单独的检测线程中。这些流会根据未被处理的包的最低数量来分配相应的线程。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,让我们将 Suricata 运行起来,看看它表现如何。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -150,14 +146,13 @@ Suricata 使用的默认运行模式是autofp("auto flow pinned load balancing
|
||||
|
||||
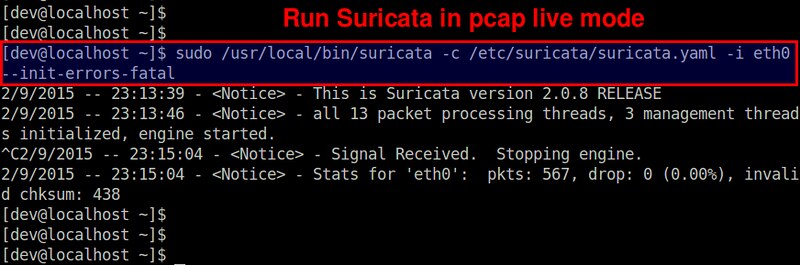
|
||||
|
||||
本例中,我们在一个8核心系统中监控eth0网络接口。如上所示,Suricata 创建了13个包处理线程和3个管理线程。包处理线程中包括一个PCAP包捕获线程,12个检测线程(由8*1.5得出)。这表示IDS内的1个包捕获线程均衡负载到12个检测线程中。管理线程包括1个流管理和2个计数/统计相关线程。
|
||||
本例中,我们在一个8核心系统中监控 eth0 网络接口。如上所示,Suricata 创建了13个包处理线程和3个管理线程。包处理线程中包括一个 PCAP 包捕获线程,12个检测线程(由8*1.5得出)。这表示 IDS 内的1个包捕获线程均衡负载到12个检测线程中。管理线程包括1个流管理和2个计数/统计相关线程。
|
||||
|
||||
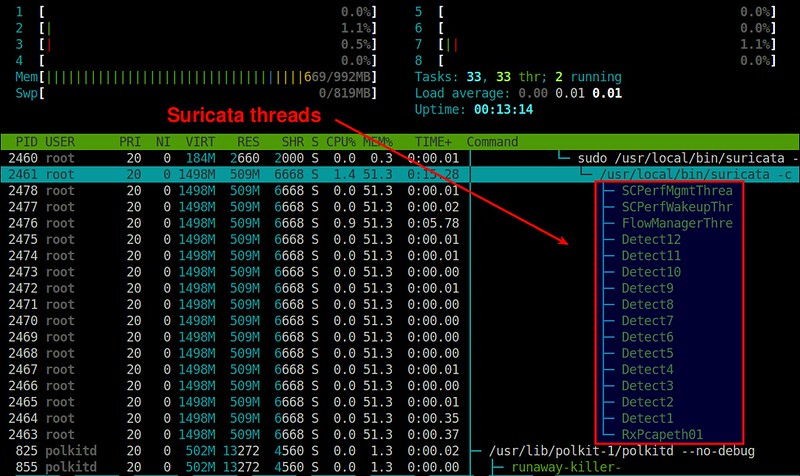
Here is a thread-view of Suricata process (plotted by [htop][7]).
|
||||
以下是一个关于Suricata处理的线程截图(由 [htop][7] 绘制)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Suricata检测日志存储在 /var/log/suricata 目录下。
|
||||
Suricata 检测日志存储在 /var/log/suricata 目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
$ tail -f /var/log/suricata/fast.log
|
||||
|
||||
@ -167,7 +162,7 @@ Suricata检测日志存储在 /var/log/suricata 目录下。
|
||||
04/01/2015-15:49:06.565901 [**] [1:2200074:1] SURICATA TCPv4 invalid checksum [**] [Classification: (null)] [Priority: 3] {TCP} 172.16.253.158:22 -> 172.16.253.1:46317
|
||||
04/01/2015-15:49:06.566759 [**] [1:2200074:1] SURICATA TCPv4 invalid checksum [**] [Classification: (null)] [Priority: 3] {TCP} 172.16.253.158:22 -> 172.16.253.1:46317
|
||||
|
||||
日志也可以提供Json格式,被当做引用实例去使用:
|
||||
日志也可以提供 Json 格式以便导入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ tail -f /var/log/suricata/eve.json
|
||||
|
||||
@ -177,9 +172,9 @@ Suricata检测日志存储在 /var/log/suricata 目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这篇教程中,我为大家演示了如何在一台多核Linux服务器上安装Suricata入侵检测系统。不同于单线程的 [Snort IDS][8] ,Suricata 可以很容易的从多核硬件的多进程特性所带来的红利中获益。定制Suricata来最大化其效能和检测范围是一个很好的主意。Suricata的粉丝们维护着一个 [在线 Wiki][9],如果你打算将Suricata部署到你的环境中,我强烈建议你去那儿取取经。
|
||||
这篇教程中,我为大家演示了如何在一台多核 Linux 服务器上安装 Suricata 入侵检测系统。不同于单线程的 [Snort IDS][8] ,Suricata 可以很容易的从多核硬件的多进程特性所带来的好处中获益。定制 Suricata 来最大化其效能和检测范围是一个很好的主意。Suricata 的粉丝们维护着一个 [在线 Wiki][9],如果你打算将 Suricata 部署到你的环境中,我强烈建议你去那儿取取经。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你现在已经开始使用Suricata了的话,把你的经验也分享出来吧。
|
||||
如果你现在已经开始使用 Suricata 了的话,把你的经验也分享出来吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -187,7 +182,7 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/install-suricata-intrusion-detection-system-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[mr-ping](https://github.com/mr-ping)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,52 +1,52 @@
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8 评论
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8 新变化一览
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
除了Gnome和KDE外,Cinnamon是另一个很多人使用的桌面环境。它是由创作Linux Mint的团队制作的,并且可以被安装在许多其他发行版上。该桌面环境的最新版本 - Cinnamon 2.8 - 于本月早些时间发布,此版本修复了许多的Bug、做了许多改进并添加了一些新功能。
|
||||
除了Gnome和KDE外,Cinnamon是另一个很多人使用的桌面环境。它是由创作Linux Mint的团队制作的,并且可以被安装在许多其他发行版上。该桌面环境的最新版本 - Cinnamon 2.8 - 于去年底发布,此版本修复了许多的Bug、做了许多改进并添加了一些新功能。
|
||||
|
||||
我将仔细介绍该发行版本的主要改进,以及如何更新到Cinnamon 2.8或者第一次安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 对Applets的改进 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在此版本中,对已经在面板中存在的Applets做了若干的改进。
|
||||
在此版本中,对面板中已有的Applets做了若干的改进。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 声音 Applet ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
声音Applet经过修订,目前可以显示音轨信息并且可以在音频文件的艺术家封面上面进行媒体控制。对于支持拖动的音乐播放器来说(例如Banshee),会有一个进度条在同样的位置,您可以用它来改变音轨位置。在applet的面板上右击将显示对输入和输出静音的选项。
|
||||
声音Applet经过修正,目前可以显示音轨信息并且可以在音频文件的艺术家封面上面进行媒体控制。对于支持拖动的音乐播放器来说(例如Banshee),会有一个进度条显示同样的播放进度,您可以用它来改变音轨位置。在applet的面板上右击将显示对输入和输出设备静音的选项。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 电源 Applet ####
|
||||
|
||||
电源applet则会使用制造商的数据而不是通用名称显示每一个连接的电池和设备。
|
||||
电源applet则会使用电池制造商的数据而不是通用名称来显示每一个连接的电池和设备。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 窗口缩略图 ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8带来了可以在鼠标悬停于面板里窗口列表中的窗口时展示窗口缩略图的选项。如果您不喜欢该功能,您还可以关闭它。
|
||||
在Cinnamon 2.8中,可以在鼠标悬停于面板里窗口列表时展示窗口缩略图。如果您不喜欢该功能,您还可以关闭该选项。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 工作区切换 Applet ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
添加工作区切换applet到您的面板将为您显示一个代表工作区的可视化的图像,一些矩形嵌套在其中,代表您的窗口的位置。
|
||||
添加工作区切换applet到您的面板将为您显示一个代表该工作区的可视化图像,一些矩形嵌套显示在其中,代表您的窗口的位置。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 系统托盘 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8带来了对系统托盘中的应用程序指示器的支持。您可以很容易地在设置中禁用它,这将强制应用程序回滚以使用状态图标作为替代。
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8支持在系统托盘中显示应用程序指示器。您可以很容易地在设置中禁用它,这将强制应用程序到以前使用状态图标的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 视觉改进 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8还做了很多视觉上的改进。经典的切换器和Alt + Tab预览切换器都被细细打磨,有了显著的改进,同时修复了Alt + F2对话框的bug,并赋予了它更好的命令自动补全功能。
|
||||
Cinnamon 2.8还做了很多视觉上的改进。经典的切换器和Alt + Tab预览切换器都被精细打磨,有了显著的改进,同时修复了Alt + F2对话框的bug,并赋予了它更好的命令自动补全功能。
|
||||
|
||||
而且,在于最小化窗口时的存在的传统的动画效果中的问题现已被解决并可用于多个面板。
|
||||
而且,传统的最小化窗口时动画效果的问题现已被解决,并可用于多个面板。
|
||||
|
||||
### Nemo 的改进 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cinnamon默认的文件管理器也修复了一些bug,并有了新的“快速重命名”的功能,用于重命名文件和文件夹。可以通过两次点击文件或文件夹并在两次点击之前进行简短的停顿以重命名文件。
|
||||
Cinnamon默认的文件管理器也修复了一些bug,并有了新的“快速重命名”的功能,用于重命名文件和文件夹。可以通过两次点击文件或文件夹并在两次点击之间进行简短的停顿以重命名文件。
|
||||
|
||||
Nemo也会自动地检测缩略图存在的问题,并提示您快速地修复它们。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ Nemo也会自动地检测缩略图存在的问题,并提示您快速地修复
|
||||
|
||||
- Applets如今会在它们被更新的时候自动地重新加载一次。
|
||||
- 对于多个监视器的支持有了显著的提高。
|
||||
- 对话框窗口有了提高,并且会附加到它的父窗口上。
|
||||
- 对话框窗口有了改进,并且会附加到它的父窗口上。
|
||||
- HiDPI检测有了改进。
|
||||
- QT5应用程序现在看起来更加原生并使用了默认的GTK主题。
|
||||
- 窗口管理和渲染性能有了提升。
|
||||
@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/cinnamon-2-8-review/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ayo Isaiah][a]
|
||||
译者:[wwy-hust](https://github.com/wwy-hust)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
51
published/20151206 Supporting secure DNS in glibc.md
Normal file
51
published/20151206 Supporting secure DNS in glibc.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,51 @@
|
||||
通过修改 glibc 支持 DNS 加密
|
||||
========================
|
||||
|
||||
域名解析系统(DNS)是互联网安全的许多薄弱环节之一;可以将应用程序所访问的主机对应的 IP 地址误导到其它地方。也就是说,会连接到错误的位置,从而引发中间人(man-in-the-middle )攻击等等。而 [DNSSEC][1] 扩展协议则通过为 DNS 信息建立一条加密的可信通道来解决这个漏洞。在正确地配置好 DNSSEC 后,应用程序将可以得到可靠的主机查询信息。通过关于[尝试将 DNSSEC 更好地集成到 GNU C 库里][2]的讨论,我们知道,确保 DNS 查询信息安全这件事并不是那么简单。
|
||||
|
||||
从某种意义上来说,这个问题多年以前就解决了,我们可以配置一个本地域名服务实现完整的 DNSSEC 校验(verification)并允许应用程序通过 glibc 函数来使用该服务。DNSSEC 甚至还可以用于提高其他领域的安全性,比如,它可以携带 SSH 或 TLS 密钥指纹,让应用程序可以确认其在与正确的服务器对话。不过,当我们希望确认这条自称带有 DNSSEC 校验的 DNS 结果是不是真的已通过认证的时候 - 也就是说,当我们想依赖 DNSSEC 所承诺的安全的时候,事情变得有点复杂。
|
||||
|
||||
### /etc/resolv.conf 问题
|
||||
|
||||
从 glibc 的角度来看,这个问题一部分是因为 glibc 本身并没有做 DNSSEC 校验,而是引用 /etc/resolv.conf 文件,从该文件里读出的服务器来做解析以及校验,再将结果返回给应用程序。如果应用程序使用底层 res_query() 接口,那结果中将会包含“已认证数据(authenticated data)”(AD)标识(如果域名服务器设定了的话)以表示 DNSSEC 校验已经成功。但是 glibc 却完全不知道提供这些结果的域名服务器的信用,所以它其实并不能告诉应用程序结果是否真的可靠。
|
||||
|
||||
由 glibc 的维护者 Carlos O'Donell 提出的建议是在 resolv.conf 文件里增加一个选项(dns-strip-dnssec-ad-bit)告诉 glibc 无条件移除 AD 标识。这个选项可以由各发行版设定,表示 DNSSEC 级别的 DNS 查询结果并不可靠。而一旦建立好合适的环境可以获得可靠的查询结果后,再移除这个选项。这样一来,虽然问题还没有完全解决,至少应用程序有依据来评价从 glibc 获取的 DNS 查询结果的可靠性。
|
||||
|
||||
一个可靠的环境配置应该是什么样?标准情况应该和这个差不太多:有一个本地域名服务器,通过环路(loopback)接口访问,作为访问 /etc/resolv.conf 文件的唯一条目。这个域名服务器应该配置来做校验,而在校验失败后就只是简单地不返回任何结果。绝大多数情况下,应用程序就不再需要关心 AD 标识,如果结果不可靠,应用程序就根本看不到。一些发行版已经倾向于这种模型,不过情况仍然不像一些人所设想的那么简单。
|
||||
|
||||
其中一个问题是,这种方式将 /etc/resolv.conf 文件放到整个系统可信任度的中心。但是,在一个典型的 Linux 系统里,有无数的 DHCP 客户端、网络脚本以及其他更多的程序可以修改这个文件。就像 Paul Wouters 所[指出][3]的,在短时间内锁定这个文件是不可能的。有时候这种修改是必须的:在一个无盘系统启动的时候,在自身的域名服务器启动之前也是需要域名服务的;一个系统的整个 DNS 环境也会根据所连接的网络不同而有所改变;运行在容器里的系统也最好是配置成使用宿主机的域名服务器;等等。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,现在一般认为,现有系统里的 /etc/resolv.conf 文件并不可信。于是有人提出增加另一个配置文件(/etc/secure-resolv.conf 或其他什么),但这并没有从根本上解决问题。除此之外,有些参与者觉得就算有一个运行在环路接口上的域名服务器也不是真正可靠,比如 Zack Weinberg 甚至[建议][4]系统管理员可以有意禁用 DNSSEC 确认(validation)。
|
||||
|
||||
既然当前系统里的配置不足以信任,那可以这样推断,在情况有改善能够取得可信的结果后,glibc 需要有一种方式来通知应用程序。可以是上面讨论的屏蔽 AD 标识的方式(或者与之相反,增加一个显示的“此域名服务器可以信任”选项);当然,这都需要一定程度上锁定系统以免 /etc/resolv.conf 受到任何不可预计的修改。按 Petr Spacek 的[建议][5],还有一种引申方式,就是提供一种途径允许应用程序查询 glibc 当前通讯的是不是本地域名服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 glibc 里来处理?
|
||||
|
||||
另一种方式是不管域名服务器,而是让 glibc 本身来做 DNSSEC 确认。不过,把这么大一坨加密相关代码放进 glibc 也是有很大阻力。这样将增加库本身的大小,从而感觉会增加使用它的应用程序的受攻击可能性。这个方向再引申一下,由 Zack 提出的[建议][6],可以把确认相关代码放到域名服务缓冲守护进程(nscd)里。因为 nscd 也是 glibc 的一部分,由 glibc 开发人员维护,因此在一定程度上可以相信能正确执行 DNSSEC 确认。而且 nscd 的通讯 socket 所在位置也是公开的,所以可以不考虑 /etc/resolv.conf 问题。不过,Carlos [担心][7]这种方式不能让那些不想使用 nscd 缓存功能的用户所接受;在他看来,基本可以排除 nscd 的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,至少近期内,glibc 不太可能全部执行 DNSSEC 确认了的整个查询过程。这意味着,如果一个有安全考虑的应用要使用 glibc 库来查询域名,该库将需要提供一个标识来评价从独立域名服务器返回的结果有多大程度的可靠性。这几乎肯定需要发行版或系统管理员做出一些明确的改动。就像 Simo Sorce [说的][8]那样:
|
||||
|
||||
> 如果 glibc 不使用明确的配置选项来通知应用程序它所用的域名解析是可信的,不会有什么用……不改一下还有很大弊端,因为应用程序开发者将马上认识到他们不能信任从 glibc 获取的任何信息,从而在处理 DNSSEC 相关信息时就简单地不用它。
|
||||
|
||||
要配置一个系统能正常使用 DNSSEC 需要改动该系统的很多组件 - 这是一个发行版范围的问题,需要时间来完全解决。在这个转变过程中 glibc 所扮演的角色很可能会比较小,但是很重要的一部分:如果应用程序不实现一套自己的域名解析代码,glibc 很可能是保证 DNS 结果可信的唯一方式。在一个系统中运行多个 DNSSEC 实现方式看起来不像是一种安全的方式,所以最好还是把事情做对了。
|
||||
|
||||
glibc 项目目前并没有确定用哪种方式来做这个事情,虽然从 /etc/resolv.conf 文件里的某些标记看上去快好了。这种改动应该需要发布新版本;考虑到 glibc 开发的保守天性,很可能来不及加入预计二月份发布的 2.23 版本了。所以 glibc 中暂时还不会有更高安全性的 DNSSEC ,不过在这个方向上也有一些进展了。
|
||||
|
||||
---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://lwn.net/Articles/664776/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Jonathan Corbet
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domain_Name_System_Security_Extensions
|
||||
[2]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664790/
|
||||
[3]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664794/
|
||||
[4]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664782/
|
||||
[5]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664784/
|
||||
[6]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664796/
|
||||
[7]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664786/
|
||||
[8]: http://lwn.net/Articles/664787/
|
||||
@ -2,6 +2,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Automatic bug-repair system fixes 10 times as many errors as its predecessors.
|
||||
------
|
||||
DongShuaike is translating.
|
||||
|
||||
MIT researchers have developed a machine-learning system that can comb through repairs to open-source computer programs and learn their general properties, in order to produce new repairs for a different set of programs.
|
||||
|
||||
The researchers tested their system on a set of programming errors, culled from real open-source applications, that had been compiled to evaluate automatic bug-repair systems. Where those earlier systems were able to repair one or two of the bugs, the MIT system repaired between 15 and 18, depending on whether it settled on the first solution it found or was allowed to run longer.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
chisper 翻译中
|
||||
How to Install Pure-FTPd with TLS on FreeBSD 10.2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
FTP or File Transfer Protocol is application layer standard network protocol used to transfer file from the client to the server, after user logged in to the FTP server over the TCP-Network, such as internet. FTP has been round long time ago, much longer then P2P Program, or World Wide Web, and until this day it was a primary method for sharing file with other over the internet and it it remain very popular even today. FTP provide an secure transmission, that protect username, password and encrypt the content with SSL/TLS.
|
||||
@ -151,4 +152,4 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-pure-ftpd-tls-freebsd-10-2/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arulm/
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arulm/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,242 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Install Revive Adserver on Ubuntu 15.04 / CentOS 7
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Revive AdserverHow to Install Revive Adserver on Ubuntu 15.04 / CentOS 7 is a free and open source advertisement management system that enables publishers, ad networks and advertisers to serve ads on websites, apps, videos and manage campaigns for multiple advertiser with many features. Revive Adserver is licensed under GNU Public License which is also known as OpenX Source. It features an integrated banner management interface, URL targeting, geo-targeting and tracking system for gathering statistics. This application enables website owners to manage banners from both in-house advertisement campaigns as well as from paid or third-party sources, such as Google's AdSense. Here, in this tutorial, we'll gonna install Revive Adserver in our machine running Ubuntu 15.04 or CentOS 7.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Installing LAMP Stack ###
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, as Revive Adserver requires a complete LAMP Stack to work, we'll gonna install it. LAMP Stack is the combination of Apache Web Server, MySQL/MariaDB Database Server and PHP modules. To run Revive properly, we'll need to install some PHP modules like apc, zlib, xml, pcre, mysql and mbstring. To setup LAMP Stack, we'll need to run the following command with respect to the distribution of linux we are currently running.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 15.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install apache2 mariadb-server php5 php5-gd php5-mysql php5-curl php-apc zlibc zlib1g zlib1g-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev libapache2-mod-php5 zip
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install httpd mariadb php php-gd php-mysql php-curl php-mbstring php-xml php-apc zlibc zlib1g zlib1g-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev zip
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Starting Apache and MariaDB server ###
|
||||
|
||||
We’ll now start our newly installed Apache web server and MariaDB database server in our linux machine. To do so, we'll need to execute the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 15.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04 is shipped with Systemd as its default init system, so we'll need to execute the following commands to start apache and mariadb daemons.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start apache2 mysql
|
||||
|
||||
After its started, we'll now make it able to start automatically in every system boot by running the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable apache2 mysql
|
||||
|
||||
Synchronizing state for apache2.service with sysvinit using update-rc.d...
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d apache2 defaults
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d apache2 enable
|
||||
Synchronizing state for mysql.service with sysvinit using update-rc.d...
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d mysql defaults
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d mysql enable
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Also in CentOS 7, systemd is the default init system so, we'll run the following command to start them.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start httpd mariadb
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we'll enable them to start automatically in every startup of init system using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable httpd mariadb
|
||||
|
||||
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service'
|
||||
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service'
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Configuring MariaDB ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7/Ubuntu 15.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
Now, as we are starting MariaDB for the first time and no password has been assigned for MariaDB so, we’ll first need to configure a root password for it. Then, we’ll gonna create a new database so that it can store data for our Revive Adserver installation.
|
||||
|
||||
To configure MariaDB and assign a root password, we’ll need to run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
|
||||
This will ask us to enter the password for root but as we haven’t set any password before and its our first time we’ve installed mariadb, we’ll simply press enter and go further. Then, we’ll be asked to set root password, here we’ll hit Y and enter our password for root of MariaDB. Then, we’ll simply hit enter to set the default values for the further configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
….
|
||||
so you should just press enter here.
|
||||
|
||||
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
|
||||
OK, successfully used password, moving on…
|
||||
|
||||
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
|
||||
root user without the proper authorisation.
|
||||
|
||||
Set root password? [Y/n] y
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Re-enter new password:
|
||||
Password updated successfully!
|
||||
Reloading privilege tables..
|
||||
… Success!
|
||||
…
|
||||
installation should now be secure.
|
||||
Thanks for using MariaDB!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Creating new Database ###
|
||||
|
||||
After we have assigned the password to our root user of mariadb server, we'll now create a new database for Revive Adserver application so that it can store its data into the database server. To do so, first we'll need to login to our MariaDB console by running the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# mysql -u root -p
|
||||
|
||||
Then, it will ask us to enter the password of root user which we had just set in the above step. Then, we'll be welcomed into the MariaDB console in which we'll create our new database, database user and assign its password and grant all privileges to create, remove and edit the tables and data stored in it.
|
||||
|
||||
> CREATE DATABASE revivedb;
|
||||
> CREATE USER 'reviveuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Pa$$worD123';
|
||||
> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON revivedb.* TO 'reviveuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
|
||||
> EXIT;
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Downloading Revive Adserver Package ###
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we'll download the latest release of Revive Adserver ie version 3.2.2 in the time of writing this article. So, we'll first get the download link from the official Download Page of Revive Adserver ie [http://www.revive-adserver.com/download/][1] then we'll download the compressed zip file using wget command under /tmp/ directory as shown bellow.
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /tmp/
|
||||
# wget http://download.revive-adserver.com/revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip
|
||||
|
||||
--2015-11-09 17:03:48-- http://download.revive-adserver.com/revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip
|
||||
Resolving download.revive-adserver.com (download.revive-adserver.com)... 54.230.119.219, 54.239.132.177, 54.230.116.214, ...
|
||||
Connecting to download.revive-adserver.com (download.revive-adserver.com)|54.230.119.219|:80... connected.
|
||||
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
|
||||
Length: 11663620 (11M) [application/zip]
|
||||
Saving to: 'revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip'
|
||||
revive-adserver-3.2 100%[=====================>] 11.12M 1.80MB/s in 13s
|
||||
2015-11-09 17:04:02 (906 KB/s) - 'revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip' saved [11663620/11663620]
|
||||
|
||||
After the file is downloaded, we'll simply extract its files and directories using unzip command.
|
||||
|
||||
# unzip revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll gonna move the entire Revive directories including every files from /tmp to the default webroot of Apache Web Server ie /var/www/html/ directory.
|
||||
|
||||
# mv revive-adserver-3.2.2 /var/www/html/reviveads
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Configuring Apache Web Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
We'll now configure our Apache Server so that revive will run with proper configuration. To do so, we'll create a new virtualhost by creating a new configuration file named reviveads.conf . The directory here may differ from one distribution to another, here is how we create in the following distributions of linux.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 15.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /etc/apache2/sites-available/reviveads.conf
|
||||
# ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/reviveads.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/reviveads.conf
|
||||
# nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/reviveads.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll gonna add the following lines of configuration into this file using our favorite text editor.
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerAdmin info@reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/reviveads/
|
||||
ServerName reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
ServerAlias www.reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
<Directory /var/www/html/reviveads/>
|
||||
Options FollowSymLinks
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/reviveads.linoxide.com-error_log
|
||||
CustomLog /var/log/apache2/reviveads.linoxide.com-access_log common
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After done, we'll gonna save the file and exit our text editor. Then, we'll restart our Apache Web server.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart apache2
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
In CentOS, we'll directly create the file reviveads.conf under /etc/httpd/conf.d/ directory using our favorite text editor.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/reviveads.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Then, we'll gonna add the following lines of configuration into the file.
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerAdmin info@reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/reviveads/
|
||||
ServerName reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
ServerAlias www.reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
<Directory /var/www/html/reviveads/>
|
||||
Options FollowSymLinks
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/reviveads.linoxide.com-error_log
|
||||
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/reviveads.linoxide.com-access_log common
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once done, we'll simply save the file and exit the editor. And then, we'll gonna restart our apache web server.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart httpd
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Fixing Permissions and Ownership ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll gonna fix some file permissions and ownership of the installation path. First, we'll gonna set the ownership of the installation directory to Apache process owner so that apache web server will have full access of the files and directories to edit, create and delete.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 15.04 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# chown www-data: -R /var/www/html/reviveads
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# chown apache: -R /var/www/html/reviveads
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Allowing Firewall ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll gonna configure our firewall programs to allow port 80 (http) so that our apache web server running Revive Adserver will be accessible from other machines in the network across the default http port ie 80.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Ubuntu 15.04/CentOS 7 ####
|
||||
|
||||
As CentOS 7 and Ubuntu 15.04 both has systemd installed by default, it contains firewalld running as firewall program. In order to open the port 80 (http service) on firewalld, we'll need to execute the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Web Installation ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, after everything is done as expected, we'll now be able to access the web interface of the application using a web browser. We can go further towards the web installation, by pointing the web browser to the web server we are running in our linux machine. To do so, we'll need to point our web browser to http://ip-address/ or http://domain.com assigned to our linux machine. Here, in this tutorial, we'll point our browser to http://reviveads.linoxide.com/ .
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we'll see the Welcome page of the installation of Revive Adserver with the GNU General Public License V2 as Revive Adserver is released under this license. Then, we'll simply click on I agree button in order to continue the installation.
|
||||
|
||||
In the next page, we'll need to enter the required database information in order to connect Revive Adserver with the MariaDB database server. Here, we'll need to enter the database name, user and password that we had set in the above step. In this tutorial, we entered database name, user and password as revivedb, reviveuser and Pa$$worD123 respectively then, we set the hostname as localhost and continue further.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We'll now enter the required information like administration username, password and email address so that we can use these information to login to the dashboard of our Adserver. After done, we'll head towards the Finish page in which we'll see that we have successfully installed Revive Adserver in our server.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we'll be redirected to the Adverstiser page where we'll add new Advertisers and manage them. Then, we'll be able to navigate to our Dashboard, add new users to the adserver, add new campaign for our advertisers, banners, websites, video ads and everything that its built with.
|
||||
|
||||
For enabling more configurations and access towards the administrative settings, we can switch our Dashboard user to the Administrator account. This will add new administrative menus in the dashboard like Plugins, Configuration through which we can add and manage plugins and configure many features and elements of Revive Adserver.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we learned some information on what is Revive Adserver and how we can setup on linux machine running Ubuntu 15.04 and CentOS 7 distributions. Though Revive Adserver's initial source code was bought from OpenX, currently the code base for OpenX Enterprise and Revive Adserver are completely separate. To extend more features, we can install more plugins which we can also find from [http://www.adserverplugins.com/][2] . Really, this piece of software has changed the way of managing the ads for websites, apps, videos and made it very easy and efficient. If you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below so that we can improve or update our contents. Thank you !
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-revive-adserver-ubuntu-15-04-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.revive-adserver.com/download/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.adserverplugins.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,237 @@
|
||||
在Ubuntu 15.04 / CentOS 7上安装Revive Adserver
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Revive Adserver是一个免费且开源的广告管理系统,能使出版商,广告平台和广告商把广告投放在网页,应用,视频上并且管理的系统。Revive Adserver又名OpenX,遵循GNU通用公共授权协议。它集广告管理、网站定位、地理定位和跟踪系统于一体
|
||||
,用于数据收集。能使网站站长管理内部,付费以及第三方来源的广告,如谷歌的AdSense。本教程中,将会教会你在Ubuntu 15.04或CentOS 7安装并运行Revive Adserver。
|
||||
### 1. 安装LAMP###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,Revive Adserver需要完整的LAMP环境才能运行,所以我们先安装LAMP。LAMP是Apache网页服务器,MySQL/MariaDB数据库和PHP模块的集合。要使Revive正常运行,需要安装PHP的众多模块,如apc,zlib,xml,pcre,mysql和mbstring。在不同的Linux发行版中,我们可以用下列命令进行LAMP的配置:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu 15.04下####
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install apache2 mariadb-server php5 php5-gd php5-mysql php5-curl php-apc zlibc zlib1g zlib1g-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev libapache2-mod-php5 zip
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在CentOS 7下 ####
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install httpd mariadb php php-gd php-mysql php-curl php-mbstring php-xml php-apc zlibc zlib1g zlib1g-dev libpcre3 libpcre3-dev zip
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 启动Apache Web和MariaDB服务
|
||||
|
||||
可以用下列命令启动刚刚安装好的Apache Web服务和MariaDB数据库服务。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu 15.04下####
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu15.04使用Systemd作为默认初始系统,所以用下列命令启动Apache和MariaDB进程:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start apache2 mysql
|
||||
|
||||
可以用下列命令使其开机自动运行:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable apache2 mysql
|
||||
|
||||
Synchronizing state for apache2.service with sysvinit using update-rc.d...
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d apache2 defaults
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d apache2 enable
|
||||
Synchronizing state for mysql.service with sysvinit using update-rc.d...
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d mysql defaults
|
||||
Executing /usr/sbin/update-rc.d mysql enable
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在CentOS 7下
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS 7同样是以Systemd作为默认初始系统,可以用下列命令启动:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start httpd mariadb
|
||||
|
||||
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service'
|
||||
ln -s '/usr/lib/systemd/system/mariadb.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/mariadb.service'
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 配置MariaDB
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在CentOS 7/Ubuntu 15.04下 ####
|
||||
|
||||
当我们第一次启动MariaDB时,MariaDB是没有分配密码的,所以要先设置一个root密码。之后再创建一个新的数据库用来储存Revive Adserver的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
使用以下命令配置MariaDB并设置其root密码:
|
||||
|
||||
# mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
|
||||
这时会要我们输入root密码,但我们之前什么密码都没设置,所以按回车下一步。之后,要求设置root密码,这时我们输入Y,然后输入自己想要的密码。回车继续下一步。
|
||||
|
||||
….
|
||||
so you should just press enter here.
|
||||
|
||||
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
|
||||
OK, successfully used password, moving on…
|
||||
|
||||
Setting the root password ensures that nobody can log into the MariaDB
|
||||
root user without the proper authorisation.
|
||||
|
||||
Set root password? [Y/n] y
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Re-enter new password:
|
||||
Password updated successfully!
|
||||
Reloading privilege tables..
|
||||
… Success!
|
||||
…
|
||||
installation should now be secure.
|
||||
Thanks for using MariaDB!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 创建新的数据库 ###
|
||||
为MariaDB的root用户设置了密码之后,就可以创建用来储存Revive Adserver应用数据的数据库。首先通过以下命令登陆MariaDB控制台:
|
||||
|
||||
# mysql -u root -p
|
||||
|
||||
这时要求输入root用户的密码,我们只要输入上一步设置好的密码。然后进入MariaDB控制台创建新的数据库,数据库用户及其密码,并且授予其创建、删除、编辑和存储表与数据的全部权限。
|
||||
|
||||
> CREATE DATABASE revivedb;
|
||||
> CREATE USER 'reviveuser'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'Pa$$worD123';
|
||||
> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON revivedb.* TO 'reviveuser'@'localhost';
|
||||
> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
|
||||
> EXIT;
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 下载Revive Adserver
|
||||
|
||||
接下来下载Revive Adserver的最新版本Revive Adserver.3.2.2(写本文时)。可以使用wget命令从Revive Adserverde 官方网站下载压缩包,网址是:[http://www.revive-adserver.com/download/][1] 。命令如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /tmp/
|
||||
# wget http://download.revive-adserver.com/revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip
|
||||
|
||||
--2015-11-09 17:03:48-- http://download.revive-adserver.com/revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip
|
||||
Resolving download.revive-adserver.com (download.revive-adserver.com)... 54.230.119.219, 54.239.132.177, 54.230.116.214, ...
|
||||
Connecting to download.revive-adserver.com (download.revive-adserver.com)|54.230.119.219|:80... connected.
|
||||
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
|
||||
Length: 11663620 (11M) [application/zip]
|
||||
Saving to: 'revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip'
|
||||
revive-adserver-3.2 100%[=====================>] 11.12M 1.80MB/s in 13s
|
||||
2015-11-09 17:04:02 (906 KB/s) - 'revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip' saved [11663620/11663620]
|
||||
|
||||
解压到临时目录下:
|
||||
|
||||
# unzip revive-adserver-3.2.2.zip
|
||||
|
||||
把解压后的整个文件夹移动到Apache Web服务器的默认根目录/var/www/html/下:
|
||||
|
||||
# mv revive-adserver-3.2.2 /var/www/html/reviveads
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 配置Apache Web服务
|
||||
|
||||
现在配置Apache服务使Revive正常运行。通过创建配置文件reviveads.conf来创建一个新的虚拟主机。这个目录在不同的Linux发行版上有所不同。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu 15.04下
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /etc/apache2/sites-available/reviveads.conf
|
||||
# ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/reviveads.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/reviveads.conf
|
||||
# nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/reviveads.conf
|
||||
|
||||
在这个文件中添加下列几行文本:
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerAdmin info@reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/reviveads/
|
||||
ServerName reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
ServerAlias www.reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
<Directory /var/www/html/reviveads/>
|
||||
Options FollowSymLinks
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
ErrorLog /var/log/apache2/reviveads.linoxide.com-error_log
|
||||
CustomLog /var/log/apache2/reviveads.linoxide.com-access_log common
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
保存并退出,重启Apache Web服务:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart apache2
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在CentOS 7下 ####
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS下,我们直接在/etc/httpd/conf.d/ 目录下创建reviveads.conf :
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/httpd/conf.d/reviveads.conf
|
||||
|
||||
在这个文件中添加下列几行文本:
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerAdmin info@reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/reviveads/
|
||||
ServerName reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
ServerAlias www.reviveads.linoxide.com
|
||||
<Directory /var/www/html/reviveads/>
|
||||
Options FollowSymLinks
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
ErrorLog /var/log/httpd/reviveads.linoxide.com-error_log
|
||||
CustomLog /var/log/httpd/reviveads.linoxide.com-access_log common
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出,重启Apache Web服务:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart httpd
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 修复权限和所有权
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们修改安装路径下文件的权限和所有权。把安装目录的所有权改成Apache进程所有以便Apache Web服务有文件和目录的编辑,创建和删除的完全权限。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu 15.04下####
|
||||
|
||||
# chown www-data: -R /var/www/html/reviveads
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在CentOS 7下
|
||||
|
||||
# chown apache: -R /var/www/html/reviveads
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. 设置防火墙
|
||||
|
||||
现在要配置防火墙,打开80端口使Apache Web服务运行的Revive Adserver能够被网络上的其他机器所访问。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在Ubuntu 15.04/CentOS 7下
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu15.04/CentOS 7都使用Systemd作为默认初始系统,使用firewalld作为其防火墙。要打开80端口(http服务端口),执行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=http
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
success
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. 网站的安装
|
||||
|
||||
顺利的话我们能够使用浏览器进行交互,并可以将浏览器指向正在运行的网络服务器。只要在浏览器输入http://ip-address/ 或者 http://domain.com 。这里我们要访问 http://reviveads.linoxide.com/
|
||||
|
||||
打开后可以看到Revive Adserver的欢迎页面,上面还有作为它发行许可证的GNU通用公共许可证V2。点击 I agree 继续下一步安装。
|
||||
|
||||
在下一页中,我们要输入数据库信息以便把Revive Adserver和MariaDB数据库服务连接起来。要输入之前设置的数据库名称,用户名以及密码。在本教程中,我们分别输入数据库名称为revivedb,用户名为reviveuser,密码为Pa$$worD123,并且令主机名为localhost,点击continue继续。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
输入要填的信息,如:管理员用户名,密码和邮箱。可以以这些信息登录Adserver的控制界面。然后跳到最后一页,可以看到Revive Adserver已经安装成功了。
|
||||
|
||||
接着,转到Adverstiser页面,添加新的广告管理。在控制界面添加新用户到adserver,为广告库户添加标题,网页,视频
|
||||
广告。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
本文中,我们学习了如何在Ubuntu 15.04和CentOS 7上安装并配置Revive Adserver。尽管Revive Adserver的原始代码是从OpenX那买的,但现在它们已经完全分开了。可以从[http://www.adserverplugins.com/][2] 获得更多插件来扩展新特性。讲真,这个软件确实让网页,应用,视频上的广告管理变得容易了许多。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-revive-adserver-ubuntu-15-04-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[chisper](https://github.com/chisper)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.revive-adserver.com/download/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.adserverplugins.com/
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
通过修改 glibc 支持 DNS 加密
|
||||
========================
|
||||
|
||||
感谢:Jonathan Corbet
|
||||
|
||||
域名解析系统(DNS)是因特网安全许多薄弱环节之一;可以误导应用程序所访问的主机相应的 IP 地址。也就是说,会连接到错误的位置,可以引发中间人攻击以及更多攻击。而 DNSSEC 扩展协议是通过为 DNS 信息建立一条加密的可信通道来解决这个漏洞。在正确地配置好 DNSSEC 后,应用程序将可以得到可靠的主机查询信息。通过关于尝试将 DNSSEC 更好地集成到 GNU C 库里的讨论,确保 DNS 查询信息安全并不是那么简单。
|
||||
|
||||
某种意义上来说,这个问题多年以前就解决了,我们可以配置一个本地域名服务实现完整的 DNSSEC 认证并允许应用程序通过 glibc 函数来使用该服务。DNSSEC 甚至还可以用于提高其他领域的安全性,比如,它可以携带 SSH 或 TLS 密钥指纹,让应用程序可以确认其在与正确的服务器通话。不过,当我们希望确认这条自称带有 DNSSEC 认证的 DNS 结果是不是真的已通过认证的时候 - 也就是说,当我们想依赖 DNSSEC 所承诺的安全的时候,事情变得有点复杂。
|
||||
|
||||
/etc/resolv.conf 问题
|
||||
|
||||
从 glibc 的角度来看,这个问题一部分是因为 glibc 本身并没有做 DNSSEC 认证。而是引用 /etc/resolv.conf 文件,从该文件里读出的服务器来做解析以及认证,再将结果返回给应用程序。如果应用程序使用底层 res_query() 接口,那结果中将会包含“已认证数据”(AD)标识(如果域名服务器设定了的话)以表示 DNSSEC 认证已经成功。但是 glibc 却完全不知道提供这些结果的域名服务器的信用,所以它其实并不能告诉应用程序结果是否真的可靠。
|
||||
|
||||
由 glibc 的维护者 Carlos O'Donell 提出的建议是在 resolv.conf 文件里增加一个选项(dns-strip-dnssec-ad-bit)告诉 glibc 无条件移除 AD 标识。这个选项可以由各发行版设定,表示 DNSSEC 级别的 DNS 查询结果并不可靠。而一旦建立好合适的环境可以获得可靠的查询结果后,再移除这个选项。这样一来,虽然问题还没有完全解决,至少应用程序有依据来评价从 glibc 获取的 DNS 查询结果的可靠性。
|
||||
|
||||
一个可靠的环境配置应该是什么样?标准情况应该和这个差不太多:有一个本地域名服务器,通过环路接口访问,作为访问 /etc/resolv.conf 文件的唯一入口。这个域名服务器应该配置来做认证,而在认证失败后就只是简单地不返回任何结果。绝大多数情况下,应用程序就不再需要关心 AD 标识,如果结果不可靠,应用程序就根本看不到。一些发行版已经偏向这种模型,不过情况仍然不像一些人所设想的没那么简单。
|
||||
|
||||
其中一个问题是,这种方式将 /etc/resolv.conf 文件放到整个系统可信任度的中心。但是,在一个典型的 Linux 系统里,有无数的 DHCP 客户端、网络脚本以及其他更多,可以修改这个文件。就像 Paul Wouters 所指出的,在短时间内锁定这个文件是不可能的。有时候这种改变是必须的:在一个无盘系统启动的时候,在自身的域名服务器启动之前也是需要域名服务的;一个系统的整个 DNS 环境也会根据所连接的网络不同而有所改变;运行在容器里的系统也最好是配制成使用宿主机的域名服务器;等等。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,现在一般认为,现有系统里的 /etc/resolv.conf 文件并不可信。于是有人提出增加另一个配置文件(/etc/secure-resolv.conf 或其他什么),但这并没有从根本上解决问题。除此之外,有些参与人员觉得就算有一个运行在环路接口上的域名服务器也不是真正可靠,比如 Zack Weinberg 甚至建议系统管理员可以有意禁用 DNSSEC 认证。
|
||||
|
||||
既然当前系统里的配置不足以信任,那可以这样推断,在情况有改善能够取得可信的结果后,glibc 需要有一种方式来通知应用程序。可以是上面讨论的屏蔽 AD 标识的方式(或者与之相反,增加一个显示的“此域名服务器可以信任”选项);当然,这都需要一定程度上锁定系统以免 /etc/resolv.conf 受到任何不可预计的修改。按 Petr Spacek 的建议,还有一种引申方式,就是提供一种途径允许应用程序查询 glibc 当前通讯的是不是本地域名服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
在 glibc 里来处理?
|
||||
|
||||
另一种方式是去掉域名服务器,而是让 glibc 本身来做 DNSSEC 认证。不过,把这么大一坨加密相关代码放进 glibc 也是有很大阻力。这样将增加库本身的大小,从而感觉会增加使用它的应用程序的受攻击面积。这个方向再引申一下,由 Zack 提出的建议,可以把认证相关代码放到域名服务缓冲守护进程(nscd)里。因为 nscd 也是 glibc 的一部分,由 glibc 开发人员维护,因此在一定程度上可以相信能正确执行 DNSSEC 认证。而且 nscd 的通讯 socket 所在位置也是公开的,所以可以不考虑 /etc/resolv.conf 问题。不过,Carlos 担心这种方式不能让那些不想使用 nscd 缓存功能的用户所接受;在他看来,基本可以排除 nscd 的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,至少近期内,glibc 不太可能全部执行带 DNSSEC 认证的整个查询过程。这意味着,如果一个有安全考虑的应用要使用 glibc 库来查询域名,库将需要提供一个标识来评价从独立域名服务器返回的结果有多大程度的可靠性。这几乎肯定需要发行商或系统管理员做出一些明确的改动。就像 Simo Sorce 说的那样:
|
||||
|
||||
如果 glibc 不使用明确的配置选项来通知应用程序它所用的域名解析是可信的,不会有什么用。。。不改一下还有很大弊端,因为应用程序开发者将马上认识到他们不能信任从 glibc 获取的任何信息,从而在处理 DNSSEC 相关信息时就简单地不用它。
|
||||
|
||||
要配置一个系统能正常使用 DNSSEC 需要改动该系统的很多组件 - 这是一个发行版范围的问题,需要时间来完全解决。在这个转变过程中 glibc 所扮演的角色很可能会比较小,但是很重要的一部分:如果应用程序不实现一套自己的域名解析代码,glibc 很可能是保证 DNS 结果可信的唯一方式。在一个系统中运行多个 DNSSEC 实现方式看起来不像是一种安全的方式,所以最好还是把事情做对了。
|
||||
|
||||
glibc 项目目前并没有确定用哪种方式来做这个事情,虽然从 /etc/resolv.conf 文件里的某些标记看上去快好了。这种改动应该需要发布新版本;考虑到 glibc 开发的保守天性,很可能来不及加入预计二月份发布的 2.23 版本了。所以 glibc 中暂时还不会有更高安全性的 DNSSEC ,不过在这个方向上也有一些进展了。
|
||||
|
||||
---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://lwn.net/Articles/663474/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Jonathan Corbet
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user