mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-25 00:50:15 +08:00
Finish 20161102 How to Convert Files to UTF-8 Encoding in Linux
This commit is contained in:
parent
9947157991
commit
88e7633e10
@ -1,148 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by StdioA
|
||||
|
||||
# How to Convert Files to UTF-8 Encoding in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we will describe what character encoding and cover a few examples of converting files from one character encoding to another using a command line tool. Then finally, we will look at how to convert several files from any character set (charset) to UTF-8 encoding in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
As you may probably have in mind already, a computer does not understand or store letters, numbers or anything else that we as humans can perceive except bits. A bit has only two possible values, that is either a `0` or `1`, `true` or `false`, `yes` or `no`. Every other thing such as letters, numbers, images must be represented in bits for a computer to process.
|
||||
|
||||
In simple terms, character encoding is a way of informing a computer how to interpret raw zeroes and ones into actual characters, where a character is represented by set of numbers. When we type text in a file, the words and sentences we form are cooked-up from different characters, and characters are organized into a charset.
|
||||
|
||||
There are various encoding schemes out there such as ASCII, ANSI, Unicode among others. Below is an example of ASCII encoding.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Character bits
|
||||
A 01000001
|
||||
B 01000010
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In Linux, the iconv command line tool is used to convert text from one form of encoding to another.
|
||||
|
||||
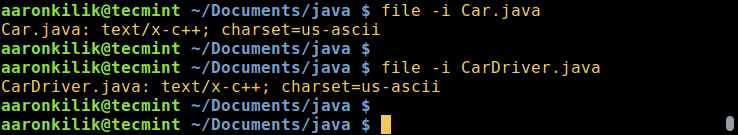
You can check the encoding of a file using the file command, by using the `-i` or `--mime` flag which enables printing of mime type string as in the examples below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ file -i Car.java
|
||||
$ file -i CarDriver.java
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Check File Encoding in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
The syntax for using iconv is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ iconv option
|
||||
$ iconv options -f from-encoding -t to-encoding inputfile(s) -o outputfile
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where `-f` or `--from-code` means input encoding and `-t` or `--to-encoding` specifies output encoding.
|
||||
|
||||
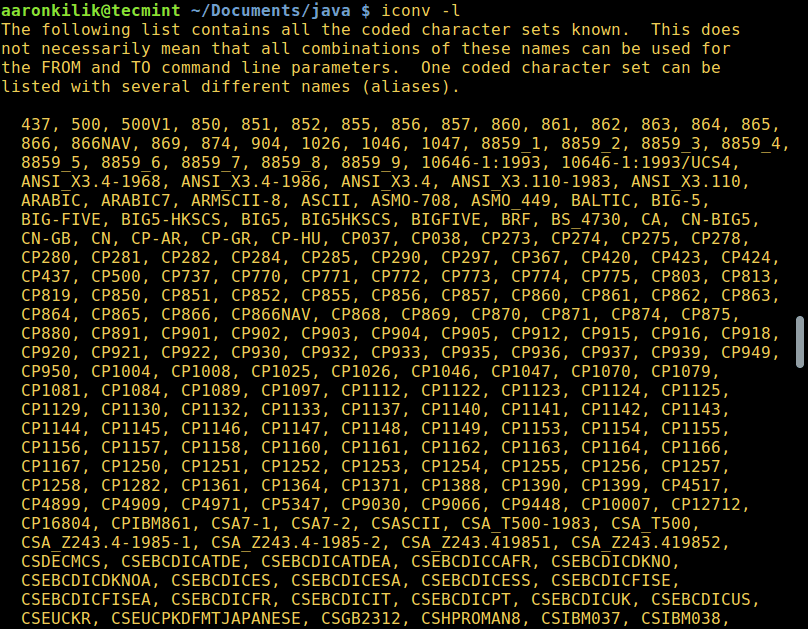
To list all known coded character sets, run the command below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ iconv -l
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][2]
|
||||
|
||||
List Coded Charsets in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
### Convert Files from UTF-8 to ASCII Encoding
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we will learn how to convert from one encoding scheme to another. The command below converts from ISO-8859-1 to UTF-8 encoding.
|
||||
|
||||
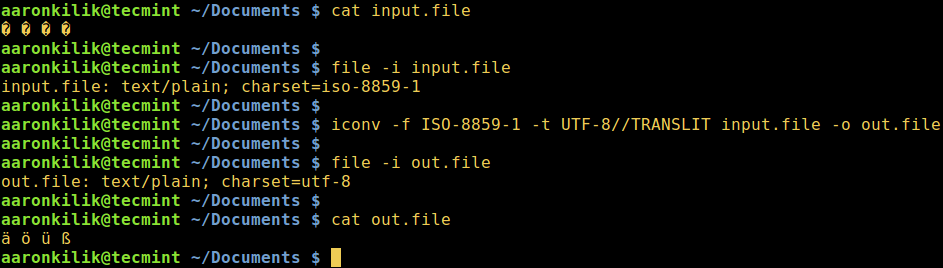
Consider a file named `input.file` which contains the characters:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<EFBFBD> <20> <20> <20>
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let us start by checking the encoding of the characters in the file and then view the file contents. Closely, we can convert all the characters to ASCII encoding.
|
||||
|
||||
After running the iconv command, we then check the contents of the output file and the new encoding of the characters as below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ file -i input.file
|
||||
$ cat input.file
|
||||
$ iconv -f ISO-8859-1 -t UTF-8//TRANSLIT input.file -o out.file
|
||||
$ cat out.file
|
||||
$ file -i out.file
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Convert UTF-8 to ASCII in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Note: In case the string `//IGNORE` is added to to-encoding, characters that can’t be converted and an error is displayed after conversion.
|
||||
|
||||
Again, supposing the string `//TRANSLIT` is added to to-encoding as in the example above (ASCII//TRANSLIT), characters being converted are transliterated as needed and if possible. Which implies in the event that a character can’t be represented in the target character set, it can be approximated through one or more similar looking characters.
|
||||
|
||||
Consequently, any character that can’t be transliterated and is not in target character set is replaced with a question mark `(?)` in the output.
|
||||
|
||||
### Convert Multiple Files to UTF-8 Encoding
|
||||
|
||||
Coming back to our main topic, to convert multiple or all files in a directory to UTF-8 encoding, you can write a small shell script called encoding.sh as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
#enter input encoding here
|
||||
FROM_ENCODING="value_here"
|
||||
#output encoding(UTF-8)
|
||||
TO_ENCODING="UTF-8"
|
||||
#convert
|
||||
CONVERT=" iconv -f $FROM_ENCODING -t $TO_ENCODING"
|
||||
#loop to convert multiple files
|
||||
for file in *.txt; do
|
||||
$CONVERT "$file" -o "${file%.txt}.utf8.converted"
|
||||
done
|
||||
exit 0
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file, then make the script executable. Run it from the directory where your files (`*.txt`) are located.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ chmod +x encoding.sh
|
||||
$ ./encoding.sh
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Important: You can as well use this script for general conversion of multiple files from one given encoding to another, simply play around with the values of the `FROM_ENCODING` and `TO_ENCODING`variable, not forgetting the output file name `"${file%.txt}.utf8.converted"`.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, look through the iconv man page.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man iconv
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To sum up this guide, understanding encoding and how to convert from one character encoding scheme to another is necessary knowledge for every computer user more so for programmers when it comes to dealing with text.
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, you can get in touch with us by using the comment section below for any questions or feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/convert-files-to-utf-8-encoding-in-linux/#
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Converts-UTF8-to-ASCII-in-Linux.png
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/List-Coded-Charsets-in-Linux.png
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Check-File-Encoding-in-Linux.png
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
|
||||
# 如何在 Linux 中将文件编码转换为 UTF-8
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇教程中,我们将解释字符编码的含义,然后给出一些使用命令行工具将使用某种字符编码的文件转化为另一种编码的例子。最后,我们将一起看一看如何在 Linux 下将使用各种字符编码的文件转化为 UTF-8 编码。
|
||||
|
||||
你可能已经知道,计算机是不会理解和存储字符、数字或者任何人类能够理解的东西的,除了二进制数据。一个二进制位只有两种可能的值,也就是 `0` 或 `1`,`真`或`假`,`对`或`错`。其它的任何事物,比如字符、数据和图片,必须要以二进制的形式来表现,以供计算机处理。
|
||||
|
||||
简单来说,字符编码是一种可以指示电脑来将原始的 0 和 1 解释成实际字符的方式,在这些字符编码中,字符都可以用数字串来表示。
|
||||
|
||||
字符编码方案有很多种,比如 ASCII, ANCI, Unicode 等等。下面是 ASCII 编码的一个例子。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
字符 二进制
|
||||
A 01000001
|
||||
B 01000010
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中,命令行工具 `iconv` 用来将使用一种编码的文本转化为另一种编码。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用 `file` 命令,并添加 `-i` 或 `--mime` 参数来查看一个文件的字符编码,这个参数可以让程序像下面的例子一样输出字符串的 mime (Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) 数据:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ file -i Car.java
|
||||
$ file -i CarDriver.java
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][3]
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中查看文件的编码
|
||||
|
||||
iconv 工具的使用方法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ iconv option
|
||||
$ iconv options -f from-encoding -t to-encoding inputfile(s) -o outputfile
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在这里,`-f` 或 `--from-code` 标明了输入编码,而 `-t` 或 `--to-encoding` 指定了输出编码。
|
||||
|
||||
为了列出所有已有编码的字符集,你可以使用以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ iconv -l
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][2]
|
||||
|
||||
列出所有已有编码字符集
|
||||
|
||||
### 将文件从 ISO-8859-1 编码转换为 UTF-8 编码
|
||||
|
||||
下面,我们将学习如何将一种编码方案转换为另一种编码方案。下面的命令将会将 ISO-8859-1 编码转换为 UTF-8 编码。
|
||||
|
||||
Consider a file named `input.file` which contains the characters:
|
||||
考虑如下文件 `input.file`,其中包含这几个字符:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
<EFBFBD> <20> <20> <20>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们从查看这个文件的编码开始,然后来查看文件内容。最后,我们可以把所有字符转换为 UTF-8 编码。
|
||||
|
||||
在运行 `iconv` 命令之后,我们可以像下面这样检查输出文件的内容,和它使用的字符编码。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ file -i input.file
|
||||
$ cat input.file
|
||||
$ iconv -f ISO-8859-1 -t UTF-8//TRANSLIT input.file -o out.file
|
||||
$ cat out.file
|
||||
$ file -i out.file
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][1]
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中将 ISO-8859-1 转化为 UTF-8
|
||||
|
||||
注意:如果输出编码后面添加了 `//IGNORE` 字符串,那些不能被转换的字符将不会被转换,并且在转换后,程序会显示一条错误信息。
|
||||
|
||||
好,如果字符串 `//TRANSLIT` 被添加到了上面例子中的输出编码之后 (UTF-8//TRANSLIT),待转换的字符会尽量采用形译原则。也就是说,如果某个字符在输出编码方案中不能被表示的话,它将会被替换为一个形状比较相似的字符。
|
||||
|
||||
而且,如果一个字符不在输出编码中,而且不能被形译,它将会在输出文件中被一个问号标记 `(?)` 代替。
|
||||
|
||||
### 将多个文件转换为 UTF-8 编码
|
||||
|
||||
回到我们的主题。如果你想将多个文件甚至某目录下所有文件转化为 UTF-8 编码,你可以像下面一样,编写一个简单的 shell 脚本,并将其命名为 `encoding.sh`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
# 将 values_here 替换为输入编码
|
||||
FROM_ENCODING="value_here"
|
||||
# 输出编码 (UTF-8)
|
||||
TO_ENCODING="UTF-8"
|
||||
# 转换命令
|
||||
CONVERT=" iconv -f $FROM_ENCODING -t $TO_ENCODING"
|
||||
# 使用循环转换多个文件
|
||||
for file in *.txt; do
|
||||
$CONVERT "$file" -o "${file%.txt}.utf8.converted"
|
||||
done
|
||||
exit 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存文件,然后为它添加可执行权限。在待转换文件 (*.txt) 所在的目录中运行这个脚本。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ chmod +x encoding.sh
|
||||
$ ./encoding.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
重要事项:你也可以使这个脚本变得更通用,比如转换任意特定的字符编码到另一种编码。为了达到这个目的,你只需要改变 `FROM_ENCODING` 及 `TO_ENCODING` 变量的值。别忘了改一下输出文件的文件名 `"${file%.txt}.utf8.converted"`.
|
||||
|
||||
若要了解更多信息,可以查看 `iconv` 的手册页 (man page)。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man iconv
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
将这篇指南总结一下,理解字符编码的概念、了解如何将一种编码方案转换为另一种,是一个电脑用户处理文本时必须要掌握的知识,程序员更甚。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,你可以在下面的评论部分中与我们联系,提出问题或反馈。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/convert-files-to-utf-8-encoding-in-linux/#
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[StdioA](https://github.com/StdioA)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Converts-UTF8-to-ASCII-in-Linux.png
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/List-Coded-Charsets-in-Linux.png
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/Check-File-Encoding-in-Linux.png
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user