mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-28 23:20:10 +08:00
commit
874e11db12
@ -1,26 +1,28 @@
|
||||
‘Unity Greeter标识卡’——将丢失的会话带回Ubuntu登录屏幕
|
||||
‘Unity Greeter Badges’:将丢失的会话图标带回Ubuntu登录屏幕
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu 15.04中的一个新包解决了我对Unity Greeter抱有的微词:缺乏其它像Cinnamon这样的Linux桌面会话的标牌式图标。**
|
||||
新出现在**Ubuntu 15.04中的一个软件包解决了我对Unity 欢迎屏的微词:像Cinnamon这样的其它Linux桌面会话没有徽章图标。**
|
||||
|
||||
我知道这有点吹毛求疵了;这只是对大多数人而言几乎毫无影响的视觉裂痕而已。但是这种不一致性时时刻刻缠绕着我,让我不胜其烦,因为Ubuntu自带了大量的会话,包括Unity、GNOME和KDE。其它桌面环境,包括它自己的一些跳制品,像Xubuntu,都默认在会话切换列表和主用户界面显示了一个朴素的白点。
|
||||
我知道这有点吹毛求疵了;这只是对大多数人而言几乎毫无影响的视觉瑕疵罢了。但是这种不一致性时时刻刻缠绕着我,让我不胜其烦,因为Ubuntu的一些会话带有徽章图标,包括Unity、GNOME和KDE。而剩下的其它桌面环境,包括它自己的一些旁系产品,像Xubuntu,只会在会话切换列表和主用户界面显示了一个不能再简单的白点。
|
||||
|
||||
这些点点们造成的这种不一致性刺激着神经,即使它只是稍纵即逝,但这种刺激不仅仅来自设计,也来自可用性方面。标牌式的标志符号对于让我们知道我们即将登陆到哪个会话很有帮助。
|
||||
这些点点们造成的这种不一致性刺激着我的神经,即使它只是稍纵即逝,但这种刺激不仅仅来自设计,也来自可用性方面。标牌式的标志符号对于让我们知道我们即将登陆到哪个会话很有帮助。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,你能告诉我们这个是个什么会话呢?
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
没有必要这样做啊。构建Unity Greeter,就是为了让桌面环境开发者能够部署标识卡到欢迎屏幕中(有些确实这样做了)。但在许多情况下,像MATE,它的包来自上游的Debian,想要移植一个“Ubuntu专用的补丁包”不太可取,也不太可能。
|
||||
Budgie? 也许是 MATE? 也能是 Cinnamon……我必须点开它才能知道。
|
||||
|
||||
没有必要这样做啊。构建Unity Greeter,就是为了让桌面环境开发者能够部署徽章到欢迎屏幕中(有些确实这样做了)。但在许多情况下,像MATE,它的包来自上游的Debian,想要移植一个“Ubuntu专用的补丁包”不太可取,也不太可能。
|
||||
|
||||
### 一个解决方案出炉了 ###
|
||||
|
||||
有经验的Debian维护者[Doug Torrance][1]得到了修复该可用性裂痕的解决方案。与其依赖桌面制造者自己来添加品牌式标识卡到他们的包中,与其给Ubuntu增加维护它的责任重担,Torrance还不如自己创建了一个独立的‘unity-greeter-badges’包来收容它们。
|
||||
一位有经验的Debian维护者[Doug Torrance][1]有了修复该可用性瑕疵的解决方案。与其依赖桌面制造者自己来添加品牌式徽章到他们的包中,与其给Ubuntu增加维护它的责任重担,Torrance还不如自己创建了一个独立的‘unity-greeter-badges’包来收容它们。
|
||||
|
||||
承担起了直接提供会话标志的假定责任后,该包确保能同时迎合新旧窗口管理器、会话和桌面。
|
||||
|
||||
在30个左右的桌面环境中,它为以下桌面捆绑了新的会话标识卡:
|
||||
在30个左右的桌面环境列表中,它为以下桌面捆绑了新的会话徽章:
|
||||
|
||||
- Xubuntu
|
||||
- Cinnamon
|
||||
@ -46,7 +48,7 @@ via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/01/unity-greeter-badges-brings-missing-sess
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,300 @@
|
||||
指南:使用Trickle限制应用程序带宽占用
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
有没有遇到过系统中的某个应用程序独占了你所有的网络带宽的情形?如果你有过这样的遭遇,那么你就会感受到Trickle这种带宽调整应用的价值。不管你是一个系统管理员还只是普通Linux用户,都需要学习如何控制应用程序的上下行速度,来确保你的网络带宽不会被某个程序霸占。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*在 Linux 上安装 Trickle 带宽限制*
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 Trickle? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Trickle是一个网络带宽调整工具,可以让我们管理应用程序的网络上下行速度,使得可以避免其中的某个应用程序霸占了全部或大部分可用的带宽。换句话说,Trickle可以让你基于单个应用程序来控制网络流量速率,而不是仅仅针对与单个用户——这是在客户端网络环境中经典的带宽调整情况。
|
||||
|
||||
### Trickle 是如何工作的?###
|
||||
|
||||
另外,trickle 可以帮助我们基于应用来定义优先级,所以当对整个系统进行了全局限制设定,高优先级的应用依然会自动地获取更多的带宽。为了实现这个目标,trickle 对 TCP 连接上的套接字的数据发送、接收设置流量限制。我们必须注意到,除了影响传输速率之外,在这个过程中,trickle任何时候都不会以任何方式来改变其中的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
### Trickle不能做什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
这么说吧,唯一的限制就是,trickle不支持静态链接的应用程序或者具有SUID或SGID位设置的二进制程序,因为它使用动态链接的方式将其载入到需要调整的进程和其关联的网络套接字之间。 Trickle此时会在这两种软件组件之间扮演代理的角色。
|
||||
|
||||
由于trickle并不需要超级用户的权限来运行,所以用户可以设置他们自己的流量限制。可能这并不是你想要的,我们会探索如何使用全局设定来限制系统中的所有用户的流量限制。也即是说,此时系统中的每个用户具有管理各自的流量速率,但是无论如何,都会受到系统管理员给他们设置的总体限制。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我们会描述如何通过trickle在linux平台上管理应用程序使用的网络带宽。为了生成所需的流量,在此会在客户端(CentOS 7 server – dev1: 192.168.0.17)上使用 ncftpput 和 ncftpget, 在服务器(Debian Wheezy 7.5 – dev2: 192.168.0.15)上使用vsftpd 来进行演示。 相同的指令也可以在RedHat,Fedora和Ubuntu等系统使用。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 前提条件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
1. 对于 RHEL/CentOS 7/6, [开启EPEL仓库][1]。这些用于企业版 Linux 的额外软件包是一个由Fedora项目维护的高质量、开源的软件仓库,而且百分之百与其衍生产品相兼容,如企业版本Linux和CentOS。 在这个仓库中trickle和ncftp两者都是可用的。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 按照如下方式安装ncftp:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && sudo yum install ncftp [基于 RedHat 的系统]
|
||||
# aptitude update && aptitude install ncftp [基于 Debian 的系统]
|
||||
|
||||
3. 在单独的服务器上设置一个FTP服务器。需要注意的是,尽管FTP天生就不安全,但是仍然被广泛应用在安全性无关紧要的文件上传下载中。 在这篇文章中我们使用它来演示trickle的优点,同时它也会在客户端的标准输出流中显示传输速率。我们将是否在其它时间使用它放在一边讨论。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install vsftpd [基于 RedHat 的系统]
|
||||
# aptitude update && aptitude install vsftpd [基于 Debian 的系统]
|
||||
|
||||
现在,在FTP服务器上按照以下方式编辑 /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
anonymous_enable=NO
|
||||
local_enable=YES
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES
|
||||
allow_writeable_chroot=YES
|
||||
|
||||
在此之后,确保在你的当前会话中启动了vsftpd,并在之后的启动中让其自动启动。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start vsftpd [基于 systemd 的系统]
|
||||
# systemctl enable vsftpd
|
||||
# service vsftpd start [基于 init 的系统]
|
||||
# chkconfig vsftpd on
|
||||
|
||||
4. 如果你选择在一个使用 SSH 密钥进行远程访问的 CentOS/RHEL 7中搭建FTP服务器,你需要一个密码受保护的用户账户,它能访问**root目录之外**的某个目录,并有能在其中上传和下载文件的权限。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过在你的浏览器中输入以下的URL来浏览你的家目录。一个登录窗口会弹出来提示你输入FTP服务器中的有效的用户名和密码。
|
||||
|
||||
ftp://192.168.0.15
|
||||
|
||||
如果验证成功,你就会看到你的家目录中的内容。该教程的稍后部分中,你将可以刷新页面来显示在你之前上传过的文件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*FTP 目录树*
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在Linux中安装 trickle ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. 通过yum或aptitude来安装trickle.
|
||||
|
||||
为了确保能够成功安装,最好在安装工具之前,保证当前的安装包是最新的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# yum -y update && yum install trickle [基于 RedHat 的系统]
|
||||
# aptitude -y update && aptitude install trickle [基于 Debian 的系统]
|
||||
|
||||
2. 确认trickle是否对特定的二进制包有用。
|
||||
|
||||
之前我们解释过,trickle只对使用动态或共享的库的二进制包有用。为了确认我们是否可以对某个特定的应用使用trickle,我们可以使用著名的ldd(列出动态依赖)工具。 特别地,我们会查看任何给定程序的动态依赖中其当前使用的glibc,因为其准确地定义了通过套接字通讯所使用的系统调用。
|
||||
|
||||
对一个给定的二进制包执行以下命令来查看是否能对其使用trickle进行带宽调整:
|
||||
|
||||
# ldd $(which [binary]) | grep libc.so
|
||||
|
||||
例如,
|
||||
|
||||
# ldd $(which ncftp) | grep libc.so
|
||||
|
||||
其输出是:
|
||||
|
||||
# libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007efff2e6c000)
|
||||
|
||||
输出中的括号中的字符可能在不同的系统平台有所不同,甚至相同的命令在不同的时候运行也会不同,因为其代表包加载到物理内存中的地址。
|
||||
|
||||
如果上面的命令没有返回任何的结果,就说明这个二进制包没有使用libc包,因此trickle对其不能起到带宽调整的作用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 学习如何使用Trickle###
|
||||
|
||||
最基本的用法就是使用其独立模式,通过这种方式,trickle用来显式地定义给定应用程序的上传下载速率。如前所述,为了简单,我们会使用相同的应用来进行上传下载测试。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在独立模式下运行trickle####
|
||||
|
||||
我们会比较在有无trickle的情况下的上传下载速率, ‘-d’选项指示下载速率(KB/s单位),而'-u'选项指示相同单位的上传速率。另外我们会使用到‘-s’选项来指定trickle应该以独立模式运行。
|
||||
|
||||
以独立模式运行trickle的基本语法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -s -d [下载速率,KB/s] -u [上传速率,KB/s]
|
||||
|
||||
为了能够让你自己运行以下样例,确保你在自己的客户端安装了trickle和ncftp(我的是192.168.0.17)。
|
||||
|
||||
**样例1:在有无trickle的情况下上传一个2.8 MB的PDF文件。**
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用一个自由发布的[LInux基础知识PDF文件][2]来进行下面的测试。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以首先使用下面的命令将这个文件下载到你当前的工作目录中:
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://linux-training.be/files/books/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
下面是在没有trickle的情况下将一个文件上传到我们的FTP服务器的语法:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /remote_directory local-filename
|
||||
|
||||
其中的 /remote_directory 是相对于该用户的家目录的上传路径,而local-filename是一个你当前工作目录中的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
特别的是,在没有trickle的情形下,我们可以得到上传峰值速率52.02MB/s(请注意,这个不是真正的平均上传速率,而是峰值开始的瞬时值),而且这个文件几乎在瞬间就完成了上传。
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 52.02 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
在使用trickle的情况下,我们会限制上传速率在5KB/s。在第二次上传文件之前,我们需要在目标目录中删除这个文件,否则ncftp就会通知我们在目标目录中已经存在了与上传文件相同的文件,从而不会执行文件的传输:
|
||||
|
||||
# rm /absolute/path/to/destination/directory/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
然后:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -s -u 5 ncftpput -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 /testdir LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 4.94 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的样例中,我们看到平均的上传速率下降到了5KB/s。
|
||||
|
||||
**样例2:在有无trickle的情况下下载相同的2.8MB的PDF文件**
|
||||
|
||||
首先,记得从原来的源目录中删除这个PDF:
|
||||
|
||||
# rm /absolute/path/to/source/directory/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,下面的样例中将远程的文件下载到客户端机器的当前目录下,这是由FTP服务器的IP地址后面的“.”决定的。
|
||||
|
||||
没有trickle的情况下:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 260.53 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
在有trickle的情况下,限制下载速率在20KB/s:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -s -d 30 ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 17.76 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
### 在监督[非托管]模式下运行Trickle ###
|
||||
|
||||
trickle也可以按照/etc/trickled.conf文件中定义的一系列参数运行在非托管模式下。 这个文件定义了守护线程 trickled的行为以及如何管理trickle。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,如果你想要全局设置被所有的应用程序使用的话,我们就会需要使用trickle命令。 这个命令运行守护进程,并允许我们通过trickle定义所有应用程序共享的上传下载限制,不需要我们每次来进行指定。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickled -d 50 -u 10
|
||||
|
||||
会导致任何通过trickle运行的应用程序的上传下载速率分别限制在30kb/s和10kb/s。
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,你可以在任何时间都能确认守护线程trickled是否正在运行以及其运行参数:
|
||||
|
||||
# ps -ef | grep trickled | grep -v grep
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
root 16475 1 0 Dec24 ? 00:00:04 trickled -d 50 -u 10
|
||||
|
||||
**样例3:在使用/不使用trickle的情形下上传一个 19MB 的mp4文件到我们的FTP服务器。**
|
||||
|
||||
在这个样例中,我们会使用“He is the gift”的自由分发视频,可以通过这个[链接][3]下载。
|
||||
|
||||
我们将会在开始时通过以下的命令将这个文件下载到你的当前工作目录中:
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://media2.ldscdn.org/assets/missionary/our-people-2014/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们会使用之前列出的命令来开启守护进程trickled:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickled -d 30 -u 10
|
||||
|
||||
在不使用trickle时:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 36.31 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
在使用trickle时:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 9.51 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以看到上面的输出,上传的速率下降到了约 10KB/s。
|
||||
|
||||
** 样例4:在使用/不使用trickle的情形下下载这个相同的视频 **
|
||||
|
||||
与样例2一样,我们会将该文件下载到当前工作目录中。
|
||||
|
||||
在没有trickle时:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpget -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 . /testdir/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 108.34 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
有trickle的时:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 29.28 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
上面的结果与我们之前设置的下载限速相对应(30KB/s)。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:** 一旦守护进程开启之后,就没有必要使用trickle来为每个应用程序来单独设置限制。
|
||||
|
||||
如前所述,人们可以进一步地通过trickled.conf来客制化trickle的带宽速率调整,该文件的一个典型的分段有以下部分组成:
|
||||
|
||||
[service]
|
||||
Priority = <value>
|
||||
Time-Smoothing = <value>
|
||||
Length-Smoothing = <value>
|
||||
|
||||
其中,
|
||||
|
||||
- [service] 用来指示我们想要对其进行带宽使用调整的应用程序名称
|
||||
- Priority 用来让我们为某个服务制定一个相对于其他服务高的优先级,这样就不允许守护进程管理中的一个单独的应用程序来占用所有的带宽。越小的数字代表更高的优先级。
|
||||
- Time-Smoothing [以秒计]: 定义了trickled让各个应用程序传输或接收数据的时间间隔。小的间隔值(0.1-1秒)对于交互式应用程序是理想的,因为这样会具有一个更加平滑的会话体验,而一个相对较大的时间间隔值(1-10秒)对于需要批量传输应用程序就会显得更好。如果没有指定该值,默认是5秒。
|
||||
- Length-smoothing [KB 单位]: 该想法与Time-Smoothing如出一辙,但是是基于I/O操作而言。如果没有指定值,会使用默认的10KB。
|
||||
|
||||
上述平滑值(Time-Smoothing、 Length-smoothing)的改变会被翻译为将指定的服务的使用一个间隔值而不是一个固定值。不幸的是,没有一个特定的公式来计算间隔值的上下限,主要依赖于特定的应用场景。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个在CentOS 7 客户端中的trickled.conf 样例文件(192.168.0.17):
|
||||
|
||||
[ssh]
|
||||
Priority = 1
|
||||
Time-Smoothing = 0.1
|
||||
Length-Smoothing = 2
|
||||
|
||||
[ftp]
|
||||
Priority = 2
|
||||
Time-Smoothing = 1
|
||||
Length-Smoothing = 3
|
||||
|
||||
使用该设置,trickled会为SSH赋予比FTP较高的传输优先级。值得注意的是,一个交互进程,例如SSH,使用了一个较小的时间间隔值,然而一个处理批量数据传输的服务如FTP,则使用一个较大的时间间隔来控制之前的样例中的上传下载速率,尽管不是百分百的由trickled指定的值,但是也已经非常接近了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在该文章中,我们探索了使用trickle在基于Fedora发行版和Debian衍生版平台上来限制应用程序的带宽使用。也包含了其他的可能用法,但是不对以下情形进行限制:
|
||||
|
||||
- 限制系统工具的下载速度,例如[wget][4],或 BT客户端.
|
||||
- 限制你的系统的包管理工具[`yum`][5]更新的速度 (如果是基于Debian系统的话,其包管理工具为[`aptitude`][6])。
|
||||
- 如果你的服务器是在一个代理或防火墙后面(或者其本身即是代理或防火墙的话),你可以使用trickle来同时设定下载和上传速率,或者客户端或外部通讯的速率。
|
||||
|
||||
欢迎提问或留言。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-and-limit-downloadupload-bandwidth-with-trickle-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[theo-l](https://github.com/theo-l)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:https://linux.cn/article-2324-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://linux-training.be/files/books/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
[3]:http://media2.ldscdn.org/assets/missionary/our-people-2014/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/dpkg-command-examples/
|
||||
@ -1,20 +1,21 @@
|
||||
Linux Email应用 Geary 更新了 — 如何在Ubuntu上安装
|
||||
Linux Email应用 Geary 更新了
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Geary,Linux上流行的桌面email客户端,更新到版本0.10了 — 并且有了很多新的功能。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
elementary OS上运行的旧版本的Geary
|
||||
|
||||
Geary 0.10有一些可惜的用户界面改进以及额外的UI选项,包括:
|
||||
*elementary OS上运行的旧版本的Geary*
|
||||
|
||||
- 新增: 可以对归档,删除以及移动做'Undo'操作
|
||||
Geary 0.10有一些不错的用户界面改进以及额外的UI功能,包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 新增: 可以撤销归档、删除以及移动等操作
|
||||
- 新增: 在2列或者2列布局之间切换
|
||||
- 新的 “split header bar” — 改进邮件列表,发件人布局
|
||||
- 新的快捷键 — 使用j/k切换到上/下一封邮件
|
||||
|
||||
根据Yorba介绍,这次更新还提出了一个 **全新的全文检索算法** ,用来改进Geary的搜索体验。
|
||||
根据Yorba介绍,这次更新还引入了一个**全新的全文检索算法** ,用来改进Geary的搜索体验。
|
||||
|
||||
这个更新应该能平息一下对应用搜索能力的抱怨,那些经常觉得Geary返回的搜索结果仅仅是包装软件自身"看起来和查询语句毫不相关"的观点。
|
||||
这个更新应该能平息一下对该应用的搜索能力的抱怨:Geary返回的搜索结果就如同软件自己所宣称的“看起来和查询语句毫不相关”。
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘Yorba 建议所有这个软件客户端的用户升级到这个版本’
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,7 +37,7 @@ Yorba的最新版本可以从GNOME的Git账户下载可编译的源代码。但
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu用户想知道如何在 **14.04,14.10** 以及 **15.04**(那些更新爱好者) 上安装Geary 0.10。
|
||||
|
||||
官方的Youba PPA包括了 **Geary最新版本** 以及Shotwell(照片管理器)和[California][2](日历应用)。请注意添加这个PPA会使你电脑上任何已经安装的这些应用更新到最近的版本。
|
||||
官方的Youba PPA包括了 **Geary 最新版本** 以及Shotwell(照片管理器)和[California][2](日历应用)。请注意添加这个PPA会使你电脑上任何已经安装的这些应用更新到最近的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
Capiche? Coolio.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,7 +53,7 @@ Capiche? Coolio.
|
||||
|
||||
完成后,打开你的桌面环境应用启动面板并查找‘Geary’图标。点击它,添加你的账户并查看[通过信息高速公路下载了什么][3],开始使用简单的图形界面吧。
|
||||
|
||||
**别忘记:你可以通过电子邮件告诉我们你想看的新闻,应用建议,以及任何你想我们包括的东西,直接点击joey@oho.io**
|
||||
**别忘记:你可以通过电子邮件告诉我们你想看的新闻,应用建议,以及任何你想我们包括的东西。**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,7 +61,7 @@ via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/03/install-geary-ubuntu-linux-email-update
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
sevenot Translating
|
||||
New to Linux? 5 Apps You Didn’t Know You Were Missing
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
translating by wwy-hust
|
||||
|
||||
FAQ: BSD
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by wwy-hust
|
||||
|
||||
Will Ubuntu Linux Hit 200 Million Users This Year?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
It's been four years and two weeks since Mark Shuttleworth expressed his goal of "200 million users of Ubuntu in 4 years." While Ubuntu's presence has continued to increase over the past four years, it doesn't look like that goal has been realized yet or will be by the end of the calendar year.
|
||||
|
||||
It was back at [UDS Budapest][1] in May of 2011 when Shuttleworth expressed a goal of 200 million Ubuntu users in four years.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Last I heard there was "tens of millions" of Ubuntu Linux users, but haven't seen any reliable reports anywhere of the Ubuntu user-base being close to 200 million. The latest monthly statistics from Valve show [the Linux gaming population being below 1%][2] compared to Windows and OS X. Most usage statistics based on web metrics and other data tend to put the total Linux user-base at just a few percent.
|
||||
|
||||
Aside from desktop installations, Ubuntu at least has made substantial inroads with cloud and server deployments over the past four years and have proven to be a contender with Red Hat Enterprise Linux on such fronts. Ubuntu has also proven itself quite well on ARM hardware. When Mark was coming up with his goal in four years, he was probably thinking that Ubuntu Phone/Touch would be much further along than where it is now: just having one device available in the EU and [a second currently in China][3] and [the Ubuntu Touch software stack still maturing][4] with [major work on key apps still needed][5], etc.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It's also been three years since the Canonical claim of [Ubuntu would soon ship on 5% of PCs][6]. The 5% claim was for worldwide PC shipments, but even three years later, I have a hard time believing that... At least in the US and Europe I still very rarely see Ubuntu preloads on systems within brick and mortar stores while the major Internet retailers / OEMs still tend to offer Linux on a few select PC models, sans Chrome OS / Android devices.
|
||||
|
||||
Another lofty, unrelated goal that went unreached by the open-source community was [GNOME owning 10% of the global desktop market by 2010][7]. Five years later, there's no indication they're even close to reaching that 10x10 milestone.
|
||||
|
||||
How large do you think the Ubuntu user-base is today? How large do you think the Ubuntu (or Linux) user-base will grow in the years to come? Share with us your thoughts by commenting on this article.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=2015-200-Million-Goal-Retro
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Michael Larabel][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.michaellarabel.com/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/vr.php?view=16002
|
||||
[2]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Steam-April-2015-1-Drop
|
||||
[3]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Ubuntu-MX4-In-China
|
||||
[4]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Ubuntu-Calculator-Reboot
|
||||
[5]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTgzOTM
|
||||
[6]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTA5ODM
|
||||
[7]:https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Nzg1Mw
|
||||
@ -1,299 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by ZTinoZ
|
||||
15 Things to Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.04 Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
This tutorial is intended for beginners and covers some basic steps on what to do after you have installed Ubuntu 15.04 “Vivid Vervet” Desktop version on your computer in order to customize the system and install basic programs for daily usage.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
15 Things to Do After Installing Ubuntu 15.04
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Enable Ubuntu Extra Repositories and Update the System ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing you should take care of after a fresh installation of Ubuntu is to enable Ubuntu Extra Repositories provided by official Canonical Partners and keep an up-to-date system with the last security patches and software updates.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to accomplish this step, open from the left Launcher System Settings -> Software and Updates utility and check all Ubuntu Software and Other Software (Canonical Partners) repositories. After you finish hit the Close button and wait for the utility to Reload the cache sources tree.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Software Updates
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Other Software (Canonical Partners)
|
||||
|
||||
For a fast and smooth update process, open a Terminal and issue the following command in order to update the system using the new software repositories:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get upgrade
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Ubuntu Upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Install Additional Drivers ###
|
||||
|
||||
In order for the system to scan and install additional hardware proprietary drivers, open Software and Updates utility from System Settings, go to Additional Drivers tab and wait for the utility to scan for drivers.
|
||||
|
||||
If some drivers matching your hardware are found, check the drivers you want to install and hit the Apply Changes button to install it. In case the proprietary drivers are not working as expected, uninstall them using the Revert button or check Do not use the device and Apply Changes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Drivers
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Install Synaptic and Gdebi Package Tools ###
|
||||
|
||||
Besides Ubuntu Software Center, Synaptic is a Graphical utility for apt command line through which you can manage repositories or install, remove, search, upgrade and configure software packages. Similar way, Gdebi has the same functionality for local .deb packages. To install this two package managers on your system issue the following command on Terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install synaptic gdebi
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Synaptic and Gdebi
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Synaptic Package Manager
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Change System Appearance and Behavior ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to change Desktop Background or Launcher Icon Size, open System Settings –> Appearance –> Look and personalize the desktop. To move the menu to window title bar, enable workspaces and desktop icons or auto-hide the Launcher visit Behavior tab.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
System Appearances
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Improve System Security and Privacy ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
System Security Enhancement
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
System Security Options
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Disable Unneeded Startup Applications ###
|
||||
|
||||
To improve system login speed, reveal hidden Startup Applications by issuing the below command on Terminal, open Startup Applications utility by searching it in Dash and uncheck the unneeded applications during login process.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo sed -i ‘s/NoDisplay=true/NoDisplay=false/g’ /etc/xdg/autostart/*.desktop
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Disable Unwanted Applications
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Add Extended Multimedia Support ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Ubuntu comes with a minimal support for media files. In order to play various media formats or manipulate video files, install the following multimedia applications:
|
||||
|
||||
- VLC
|
||||
- Smplayer
|
||||
- Audacious
|
||||
- QMMP
|
||||
- Mixxx
|
||||
- XBMC
|
||||
- Handbrake
|
||||
- Openshot
|
||||
|
||||
Use the following command line to install all with one shot:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install vlc smplayer audacious qmmp mixxx xbmc handbrake openshot
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Media Players
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Media Player Playlist
|
||||
|
||||
Besides this multimedia players also install ubuntu-restricted-extras and Java support packages in order to decode and support other restricted media formats.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras openjdk-8-jdk
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Ubuntu Extras
|
||||
|
||||
To enable DVD Playback and other multimedia codecs issue the following command on Terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install ffmpeg gstreamer0.10-plugins-bad lame libavcodec-extra
|
||||
$ sudo /usr/share/doc/libdvdread4/install-css.sh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enable Video Codes
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Install Image Applications ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you are a photography enthusiast and you want to handle and manipulate images on Ubuntu, probably you want to install the following imaging programs:
|
||||
|
||||
- GIMP (alternative for Adobe Photoshop)
|
||||
- Darktable
|
||||
- Rawtherapee
|
||||
- Pinta
|
||||
- Shotwell
|
||||
- Inkscape (alternative for Adobe Illustrator)
|
||||
- Digikam
|
||||
- Cheese
|
||||
|
||||
This applications can be installed from Ubuntu Software Center or all at once by using the following command line on Terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install gimp gimp-plugin-registry gimp-data-extras darktable rawtherapee pinta shotwell inkscape
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Image Applications
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Rawtherapee Tool
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Install Media Burners ###
|
||||
|
||||
To mount ISO images or burn a CDs or a DVD, you can choose and install from the following software:
|
||||
|
||||
- Brasero Disk Burner
|
||||
- K3b
|
||||
- Xfburn
|
||||
- Furius ISO Mount
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install brasero
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install k3b
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install xfburn
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install furiusisomount
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Media Burners
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Install Archive Applications ###
|
||||
|
||||
To handle most of archive formatted files (zip, tar.gz, zip, 7zip rar etc) install the following packages by issuing the below command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install unace unrar zip unzip p7zip-full p7zip-rar sharutils rar uudeview mpack arj cabextract file-roller
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Archive Applications
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Install Chat Application ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to talk to people all over the world, here is a list of the most popular chat applications for Linux:
|
||||
|
||||
- Pidgin
|
||||
- Skype
|
||||
- Xchat
|
||||
- Telegram
|
||||
- aMSN
|
||||
- Viber
|
||||
|
||||
You can install most of them from Ubuntu Software Center or by using the command line:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install pidgin
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install skype
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install xchat
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install amsn
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:atareao/telegram -y
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install telegram
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Chat Applications
|
||||
|
||||
To install Viber application on Ubuntu visit [Viber official webpage][1], download the Debian package locally and install the viber.deb application using Gdebi package manager (left click – > Open with -> GDebi Package Installer).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Viber
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. Install Torrent Software ###
|
||||
|
||||
The most popular torrent applications and peer-to-peer file sharing programs for Ubuntu are:
|
||||
|
||||
- Deluge
|
||||
- Transmission
|
||||
- Qbittorrent
|
||||
- LinuxDC++
|
||||
|
||||
To install your favorite peer-to-peer file sharing application on Ubuntu issue the following command on Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install deluge
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install transmission
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install qbittorrent
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install linuxdcpp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Torrent
|
||||
|
||||
### 12. Install Windows Emulator -Wine and Gaming Support – Steam ###
|
||||
|
||||
Wine emulator allows you to install and run Windows applications on Linux. On the other hand, Steam is a popular gaming platform for Linux based systems developed by Valve. To install both of them on your machine issue the following command on Terminal or use Ubuntu Software Center.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install steam wine winetricks
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Wine
|
||||
|
||||
### 13. Install Cairo-Dock and Enable Desktop Visual Effects ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cairo-Dock is a beautiful and flexible launcher bar for Linux desktops similar to the Mac OS X dock. To install it on Ubuntu, run the following command on Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install cairo-dock cairo-dock-plug-ins
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Cairo Dock
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Add Cairo Dock at Startup
|
||||
|
||||
To enable a set of Desktop Effects, such as Cube effect, install Compiz package with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install compiz compizconfig-settings-manager compiz-plugins-extra
|
||||
|
||||
To activate the Desktop Cube effect, search for ccsm on Dash, open CompizConfig Settings Manager, go to General Options – > Desktop Size and set Horizontal Virtual Size value to 4 and Vertical Virtual Size to 1. Then go back and check Desktop Cube (Disable Desktop Wall) and Rotate Cube boxes (Resolve Conflicts ->Disable Switch to Viewport 1) and press Ctrl+Alt+Left Mouse Click to view the cube effect.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enable Compiz
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Compiz Settings
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Compiz Settings Addons
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Desktop Window Rotating
|
||||
|
||||
### 14. Add Extra Browser Support ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04 comes by default with Mozilla Firefox Web Browser. To install other browsers such as Google Chrome or Opera, visit their official web pages, download the provided .deb packages and install them on your system using the Gdebi Package Installer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enable Browser Support
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Opera Browser Support
|
||||
|
||||
To install Chromium Open Source browser issue the following command on Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install chromium-browser
|
||||
|
||||
### 15. Install Tweak Tools ###
|
||||
|
||||
Want extra applications for customizing Ubuntu? Then install Unity Tweak Tool and Gnome Tweak Tool by issuing the following commands on Terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install unity-tweak-tool gnome-tweak-tool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Tweak Tool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Tweak Tool Settings
|
||||
|
||||
Another interesting tweak tool is represented by the Ubuntu Tweak package which can be obtained and installed by visiting the webpage: [http://ubuntu-tweak.com/][2].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Tweak Tool: System Information
|
||||
|
||||
After you have installed all this bunch of software, you might want to clean your system in order to free some space on the hard drive, by issuing the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -y autoremove
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -y autoclean
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -y clean
|
||||
|
||||
This are just a few tweaks and programs that an average user might install and use on Ubuntu 15.04 Desktop for daily basic utilization. For more advanced programs, features and utilities use Ubuntu Software Center or consult Ubuntu Wiki webpage.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-15-04-desktop/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.viber.com/en/products/linux
|
||||
[2]:http://ubuntu-tweak.com/
|
||||
@ -1,149 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by goreliu ...
|
||||
|
||||
How to Use Docker Machine with a Cloud Provider
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hi everyone, today we'll learn how we can use Docker Machine to deploy Docker host in various Cloud Provider Platforms. Docker Machine is an application that helps to create Docker hosts on our computer, on cloud providers and inside our own data center. It provides easy solution for creating servers, installing Docker on them and then configuring the Docker client according the users configuration and requirements. The driver APIs works for provisioning Docker on a local machine, on a virtual machine in the data center, or on a public cloud instance. Docker Machine is supported on Windows, OSX, and Linux and is available for installation as one standalone binary. It enables us to take full advantage of ecosystem partners providing Docker-ready infrastructure, while still accessing everything through the same interface. It makes people able to deploy the docker containers in the respective cloud platform pretty fast and in pretty easy way with just a single command.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Installing Docker Machine ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker Machine supports awesome on every Linux Operating System. First of all, we'll need to download the latest version of Docker Machine from the Github site . Here, we'll use curl to download the latest version of Docker Machine ie 0.2.0 .
|
||||
|
||||
For 64 Bit Operating System
|
||||
|
||||
# curl -L https://github.com/docker/machine/releases/download/v0.2.0/docker-machine_linux-amd64 > /usr/local/bin/docker-machine
|
||||
|
||||
For 32 Bit Operating System
|
||||
|
||||
# curl -L https://github.com/docker/machine/releases/download/v0.2.0/docker-machine_linux-i386 > /usr/local/bin/docker-machine
|
||||
|
||||
After downloading the latest release of Docker Machine, we'll make the file named docker-machine under /usr/local/bin/ executable using the command below.
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-machine
|
||||
|
||||
After doing the above, we'll wanna ensure that we have successfully installed docker-machine. To check it, we can run the docker-machine -v which will give output of the version of docker-machine installed in our system.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine -v
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To enable Docker commands on our machines, make sure to install the Docker client as well by running the command below.
|
||||
|
||||
# curl -L https://get.docker.com/builds/linux/x86_64/docker-latest > /usr/local/bin/docker
|
||||
# chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Creating Machine ###
|
||||
|
||||
After finish installing Docker Machine in our Linux box, we'll wanna deploy a docker host into the cloud server. Docker Machine includes drivers for several popular Cloud Platforms such as Digital Ocean, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Computing and many other which enables us to create same interface of docker deployment in different platforms. So, here in this tutorial we'll gonna deploy the Docker Host into the Digital Ocean server using digitalocean driver API. Here, we'll need to run command docker-machine create followed by --driver flag as digitalocean with --digitalocean-access-token flag as the API Token provided by the [Digital Ocean Control Panel][1] and at last the name of the docker host we just created. To do so, we'll need to run the following command as.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine create --driver digitalocean --digitalocean-access-token <API-Token> linux-dev
|
||||
|
||||
# eval "$(docker-machine env linux-dev)"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: Here, linux-dev is the name of the machine we are wanting to create. <API-Token> is a security key which can be generated from the Digital Ocean Control Panel of the account holder of Digital Ocean Cloud Platform. To retrieve that key, we simply need to login to our Digital Ocean Control Panel then click on API, then click on Generate New Token and give it a name tick on both Read and Write. Then we'll get a long hex key, thats the <API-Token> now, simply replace it into the command above.
|
||||
|
||||
After running the above command, we can see in our Digital Ocean Droplet Panel that a droplet has been created with default configuration.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For ease and convenience, docker-machine deploys the droplet with default configuration choosing setting such as images that the VPS is based on we can override the default configuration as our need. We can do that by simply adding the flags respective to our need and requirement of the Droplet. Here are some flags for digitalocean that we can add to override the default configuration of the Docker Machine.
|
||||
|
||||
--digitalocean-image "ubuntu-14-04-x64" for Choosing Droplet Image
|
||||
--digitalocean-ipv6 enable to enable IPv6 Networking
|
||||
--digitalocean-private-networking enable to enable Private Networking
|
||||
--digitalocean-region "nyc3" to choose Region to deploy the Droplet
|
||||
--digitalocean-size "512mb" to select the RAM size and type of deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are wanting to use docker-machine with other cloud providers and need to override the default configuration, we can run following command to get the list of flags for every platforms supported by Docker Machine by default.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine create -h
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Selecting Active Host ###
|
||||
|
||||
After deploying the droplet, we wanna run a docker container straight away but before that, we'll need to check whether the active host is the required machine or not. To see that, we can run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The active host can be identified by "*" in the ACTIVE column.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, if we need to switch the active host to the required machine, we can simply run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine active linux-dev
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**: Here, linux-dev is the Machine name that we are wanting to make as ACTIVE and run Docker Container on top of it.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Running a Docker Container ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, after selecting our active host, we'll wanna finally run a docker container out of the box. Now, to give it a test, we'll run a busybox container out of it by running docker run busybox command with echo hello world so that we can get the output of the container.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run busybox echo hello world
|
||||
|
||||
Note: If you are trying to deploy a docker container using a 32 Bit Operating System running in the host, its good idea to use SSH to run the docker commands. So, you can simply skip this step and follow the SSH step.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. SSH with Docker Machine ###
|
||||
|
||||
If we want to control over the machine or the droplet that we just deployed with Docker Machine, we can ssh into the server using docker-machine ssh as command.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine ssh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, after ssh into the machine, we can run any docker containers into it. Here we'll run an nginx server into it.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -itd -p 80:80 nginx
|
||||
|
||||
After finishing up with SSH, we need to run exit to exit from the droplet or server.
|
||||
|
||||
# exit
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Removing Hosts ###
|
||||
|
||||
In order to remove the active host and all its images, containers, we can use docker-machine rm command as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine rm linux-dev
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To check whether the host has been removed or not, we can run docker-machine ls command.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Adding a host without a driver ###
|
||||
|
||||
We can add a host to Docker which only has a URL and no driver. It can be used an alias for an existing host, so we don’t have to type out the URL every time we run a Docker command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ docker-machine create --url=tcp://104.131.50.36:2376 custombox
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Managing the Hosts ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you are finished working with the running docker, we can simply run **docker-machine stop** command to stop the whole hosts which are Active and if wanna start again, we can run **docker-machine start**.
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine stop
|
||||
# docker-machine start
|
||||
|
||||
You can also specify a machine name to stop or start using the host name as an argument.
|
||||
|
||||
$ docker-machine stop linux-dev
|
||||
$ docker-machine start linux-dev
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker Machine is really and awesome tool for deploying servers with Docker Container running. In this article we demostrated with Digital Ocean Platform but there are other platforms also available like Amazon Web Service, Google Cloud Computing and more which is supported by Docker Machine and includes driver APIs of them. It has made easy for fast and secure deployment of Docker Containers into several different Platforms with Docker Machine. As Docker Machine is still under Beta, so it is recommended not to use docker-machine in production. If you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below so that we can improve or update our contents. Thank you ! Enjoy :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/use-docker-machine-cloud-provider/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://cloud.digitalocean.com/settings/applications
|
||||
300
sources/tech/20150526 20 Useful Terminal Emulators for Linux.md
Normal file
300
sources/tech/20150526 20 Useful Terminal Emulators for Linux.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,300 @@
|
||||
20 Useful Terminal Emulators for Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A Terminal emulator is a computer program that reproduces a video terminal within some other display structure. In other words the Terminal emulator has an ability to make a dumb machine appear like a client computer networked to the server. The terminal emulator allows an end user to access console as well as its applications such as text user interface and command line interface.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
20 Linux Terminal Emulators
|
||||
|
||||
You may find huge number of terminal emulators to choose from this open source world. Some of them offers large range of features while others offers less features. To give a better understanding to the quality of software that are available, we have gathered a list of marvelous terminal emulator for Linux. Each title provides its description and feature along with screenshot of the software with relevant download link.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Terminator ###
|
||||
|
||||
Terminator is an advanced and powerful terminal emulator which supports multiple terminals windows. This emulator is fully customizable. You can change the size, colour, give different shapes to the terminal. Its very user friendly and fun to use.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features of Terminator ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Customize your profiles and colour schemes, set the size to fit your needs.
|
||||
- Use plugins to get even more functionality.
|
||||
- Several key-shortcuts are available to speed up common activities.
|
||||
- Split the terminal window into several virtual terminals and re-size them as needed.
|
||||
|
||||
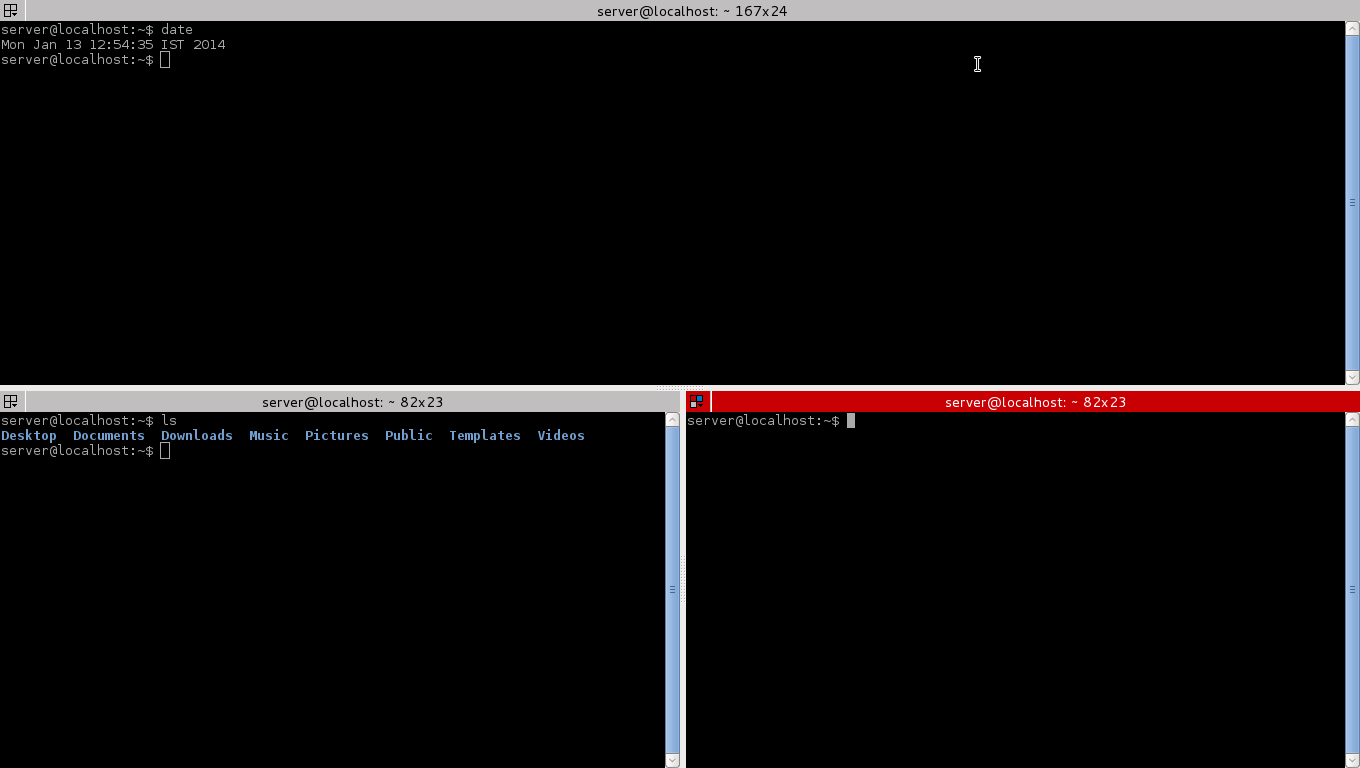
|
||||
|
||||
Terminator Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [Terminator Homepage][1]
|
||||
- [Download and Installation Instructions][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Tilda ###
|
||||
|
||||
Tilda is a stylish drop-down terminal based on GTK+. With the help of a single key press you can launch a new or hide Tilda window. However, you can add colors of your choice to change the look of the text and Terminal background.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features of Tilda ####
|
||||
|
||||
Interface with Highly customization option.
|
||||
You can set the transparency level for Tilda window.
|
||||
Excellent built-in colour schemes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Tilda Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [Tilda Homepage][3]
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Guake ###
|
||||
|
||||
Guake is a python based drop-down terminal created for the GNOME Desktop Environment. It is invoked by pressing a single keystroke, and can make it hidden by pressing same keystroke again. Its design was determined from FPS (First Person Shooter) games such as Quake and one of its main target is be easy to reach.
|
||||
|
||||
Guake is very much similar to Yakuaka and Tilda, but it’s an experiment to mix the best of them into a single GTK-based program. Guake has been written in python from scratch using a little piece in C (global hotkeys stuff).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Guake Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [Guake Homepage][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Yakuake ###
|
||||
|
||||
Yakuake (Yet Another Kuake) is a KDE based drop-down terminal emulator very much similar to Guake terminal emulator in functionality. It’s design was inspired from fps consoles games such as Quake.
|
||||
|
||||
Yakuake is basically a KDE application, which can be easily installed on KDE desktop, but if you try to install Yakuake in GNOME desktop, it will prompt you to install huge number of dependency packages.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Yakuake Features ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Fluently turn down from the top of your screen
|
||||
- Tabbed interface
|
||||
- Configurable dimensions and animation speed
|
||||
- Customizable
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Yakuake Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [Yakuake Homepage][5]
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. ROXTerm ###
|
||||
|
||||
ROXterm is yet another lightweight terminal emulator designed to provide similar features to gnome-terminal. It was originally constructed to have lesser footprints and faster start-up time by not using the Gnome libraries and by using a independent applet to bring the configuration interface (GUI), but over the time it’s role has shifted to bringing a higher range of features for power users.
|
||||
|
||||
However, it is more customizable than gnome-terminal and anticipated more at “power” users who make excessive use of terminals. It is easily integrated with GNOME desktop environment and provides features like drag & drop of items into terminal.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Roxterm Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [ROXTerm Homepage][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Eterm ###
|
||||
|
||||
Eterm is a lightest color terminal emulator designed as a replacement for xterm. It is developed with a Freedom of Choice ideology, leaving as much power, flexibility, and freedom as workable in the hands of the user.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Eterm Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [Eterm Homepage][7]
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Rxvt ###
|
||||
|
||||
Rxvt stands for extended virtual terminal is a color terminal emulator application for Linux intended as an xterm replacement for power users who don’t need to have a feature such as Tektronix 4014 emulation and toolkit-style configurability.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Rxvt Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [Rxvt Homepage][8]
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Wterm ###
|
||||
|
||||
Wterm is a another light weight color terminal emulator based on rxvt project. It includes features such as background images, transparency, reverse transparency and an considerable set or runtime options are accessible resulting in a very high customizable terminal emulator.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
wterm Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [Wterm Homepage][9]
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. LXTerminal ###
|
||||
|
||||
LXTerminal is a default VTE-based terminal emulator for LXDE (Lightweight X Desktop Environment) without any unnecessary dependency. The terminal has got some nice features such as.
|
||||
LXTerminal Features
|
||||
|
||||
- Multiple tabs support
|
||||
- Supports common commands like cp, cd, dir, mkdir, mvdir.
|
||||
- Feature to hide the menu bar for saving space
|
||||
- Change the color scheme.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
lxterminal Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [LXTerminal Homepage][10]
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Konsole ###
|
||||
|
||||
Konsole is yet another powerful KDE based free terminal emulator was originally created by Lars Doelle.
|
||||
Konsole Features
|
||||
|
||||
- Multiple Tabbed terminals.
|
||||
- Translucent backgrounds.
|
||||
- Support for Split-view mode.
|
||||
- Directory and SSH bookmarking.
|
||||
- Customizable color schemes.
|
||||
- Customizable key bindings.
|
||||
- Notification alerts about activity in a terminal.
|
||||
- Incremental search
|
||||
- Support for Dolphin file manager
|
||||
- Export of output in plain text or HTML format.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Konsole Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [Konsole Homepage][11]
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. TermKit ###
|
||||
|
||||
TermKit is a elegant terminal that aims to construct aspects of the GUI with the command line based application using WebKit rendering engine mostly used in web browsers like Google Chrome and Chromium. TermKit is originally designed for Mac and Windows, but due to TermKit fork by Floby which you can now able to install it under Linux based distributions and experience the power of TermKit.
|
||||
|
||||
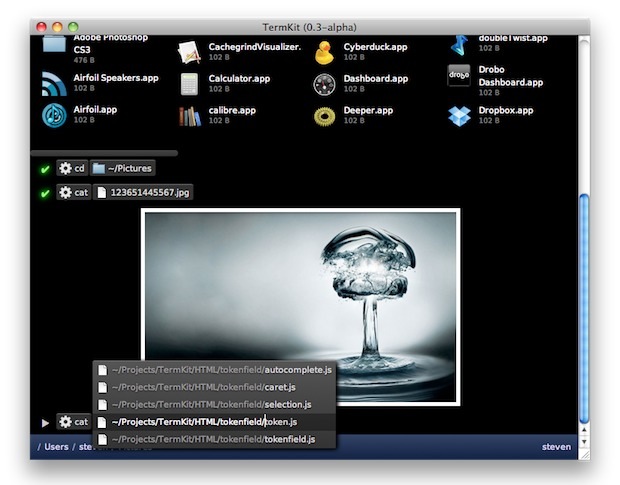
|
||||
|
||||
TermKit Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [TermKit Homepage][12]
|
||||
|
||||
12. st
|
||||
|
||||
st is a simple terminal implementation for X Window.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
st terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [st Homepage][13]
|
||||
|
||||
### 13. Gnome-Terminal ###
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME terminal is a built-in terminal emulator for GNOME desktop environment developed by Havoc Pennington and others. It allow users to run commands using a real Linux shell while remaining on the on the GNOME environment. GNOME Terminal emulates the xterm terminal emulator and brings a few similar features.
|
||||
|
||||
The Gnome terminal supports multiple profiles, where users can able to create multiple profiles for his/her account and can customize configuration options such as fonts, colors, background image, behavior, etc. per account and define a name to each profile. It also supports mouse events, url detection, multiple tabs, etc.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Gnome Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [Gnome Terminal][14]
|
||||
|
||||
### 14. Final Term ###
|
||||
|
||||
Final Term is a open source stylish terminal emulator that has some exciting capabilities and handy features into one single beautiful interface. It is still under development, but provides significant features such as Semantic text menus, Smart command completion, GUI terminal controls, Omnipotent keybindings, Color support and many more. The following animated screen grab demonstrates some of their features. Please click on image to view demo.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
FinalTerm Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [Final Term][15]
|
||||
|
||||
### 15. Terminology ###
|
||||
|
||||
Terminology is yet another new modern terminal emulator created for the Enlightenment desktop, but also can be used in different desktop environments. It has some awesome unique features, which do not have in any other terminal emulator.
|
||||
|
||||
Apart features, terminology offers even more things that you wouldn’t assume from a other terminal emulators, like preview thumbnails of images, videos and documents, it also allows you to see those files directly from Terminology.
|
||||
|
||||
You can watch a following demonstrations video created by the Terminology developer (the video quality isn’t clear, but still it’s enough to get the idea about Terminology).
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe width="630" height="480" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="" src="//www.youtube.com/embed/ibPziLRGvkg"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
- [Terminology][16]
|
||||
|
||||
### 16. Xfce4 terminal ###
|
||||
|
||||
Xfce terminal is a lightweight modern and easy to use terminal emulator specially designed for Xfce desktop environment. The latest release of xfce terminal has some new cool features such as search dialog, tab color changer, drop-down console like Guake or Yakuake and many more.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Xfce Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [Xfce4 Terminal][17]
|
||||
|
||||
### 17. xterm ###
|
||||
|
||||
The xterm application is a standard terminal emulator for the X Window System. It maintain DEC VT102 and Tektronix 4014 compatible terminals for applications that can’t use the window system directly.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
xterm Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [xterm][18]
|
||||
|
||||
### 18. LilyTerm ###
|
||||
|
||||
The LilyTerm is a another less known open source terminal emulator based off of libvte that desire to be fast and lightweight. LilyTerm also include some key features such as:
|
||||
|
||||
- Support for tabbing, coloring and reordering tabs
|
||||
- Ability to manage tabs through keybindings
|
||||
- Support for background transparency and saturation.
|
||||
- Support for user specific profile creation.
|
||||
- Several customization options for profiles.
|
||||
- Extensive UTF-8 support.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Lilyterm Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [LilyTerm][19]
|
||||
|
||||
### 19. Sakura ###
|
||||
|
||||
The sakura is a another less known Unix style terminal emulator developed for command line purpose as well as text-based terminal programs. Sakura is based on GTK and livte and provides not more advanced features but some customization options such as multiple tab support, custom text color, font and background images, speedy command processing and few more.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Sakura Terminal
|
||||
|
||||
- [Sakura][20]
|
||||
|
||||
### 20. rxvt-unicode ###
|
||||
|
||||
The rxvt-unicode (also known as urxvt) is a yet another highly customizable, lightweight and fast terminal emulator with xft and unicode support was developed by Marc Lehmann. It got some outstanding features such as support for international language via Unicode, the ability to display multiple font types and support for Perl extensions.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
rxvt unicode
|
||||
|
||||
- [rxvt-unicode][21]
|
||||
|
||||
If you know any other capable Linux terminal emulators that I’ve not included in the above list, please do share with me using our comment section.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-terminal-emulators/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ravi Saive][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/
|
||||
[1]:https://launchpad.net/terminator
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/terminator-a-linux-terminal-emulator-to-manage-multiple-terminal-windows/
|
||||
[3]:http://tilda.sourceforge.net/tildaabout.php
|
||||
[4]:https://github.com/Guake/guake
|
||||
[5]:http://extragear.kde.org/apps/yakuake/
|
||||
[6]:http://roxterm.sourceforge.net/index.php?page=index&lang=en
|
||||
[7]:http://www.eterm.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/rxvt/
|
||||
[9]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/wterm/
|
||||
[10]:http://wiki.lxde.org/en/LXTerminal
|
||||
[11]:http://konsole.kde.org/
|
||||
[12]:https://github.com/unconed/TermKit
|
||||
[13]:http://st.suckless.org/
|
||||
[14]:https://help.gnome.org/users/gnome-terminal/stable/
|
||||
[15]:http://finalterm.org/
|
||||
[16]:http://www.enlightenment.org/p.php?p=about/terminology
|
||||
[17]:http://docs.xfce.org/apps/terminal/start
|
||||
[18]:http://invisible-island.net/xterm/
|
||||
[19]:http://lilyterm.luna.com.tw/
|
||||
[20]:https://launchpad.net/sakura
|
||||
[21]:http://software.schmorp.de/pkg/rxvt-unicode
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu会在今年达到2亿用户么?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
距离Mark Shuttleworth表达他的目标“在4年内Ubuntu的用户达到2亿”已经过去了四年零两周。尽管Ubuntu的用户数量在过去的四年中一直在上升,但这个目标目前并未实现,并且看起来不会在今年年底实现。
|
||||
|
||||
那是2011年5月在[UDS 布达佩斯][1],Shuttleworth表示Ubuntu将在4年内达到2亿用户。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
上一次我听到Ubuntu有“1千万”用户,但是并没有任何可靠的报道表明Ubuntu的用户数接近2亿。来自Valve最近的统计表明相比于Windows和OS X的用户[使用Linux的游戏用户的比重少于1%][2]。大多数基于Web计量和其他统计方式的数据倾向于表明Linux的用户总数只占很少的部分。
|
||||
|
||||
撇开桌面版不谈,Ubuntu在过去的四年来至少在云和服务器部署方面得到了大量的占有率,并且被证明是Red Hat Enterprise的有力竞争者。Ubuntu还证明了它对基于ARM的硬件十分友好。当Mark在四年前提出他的目标时,他可能考虑到Ubuntu Phone/Touch会比目前的状况更好。可是Ubuntu Phone/Touch目前仅仅在欧洲和[中国][3]可用,并且[Ubuntu Touch软件依旧在成熟的路上][4],[仍需要大量的关键应用程序方面的工作][5]等。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
距离Canonical宣布[Ubuntu不久将登陆5%的PC][6]也已过去了3年。5%的目标是全球的PC装机量,但哪怕再过3年,我依旧很难相信这个目标会实现。至少在美国和欧洲,我仍难以在实体店看到Ubuntu作为预装的系统,主要的网络零售商/OEM厂商仍倾向于在特定的PC型号中提供Linux,比如Chrome OS、Android设备。
|
||||
|
||||
另一个由开源社区提出的高傲地、落空的目标便是[GNOME将在2010年占有全球桌面市场10%的份额][7]。五年前,没有任何迹象表明他们接近了那10%的里程碑。
|
||||
|
||||
在今天,您认为Ubuntu用户有多少呢?在未来的几年里,Ubuntu(或者Linux)的用户会有多大增长呢?通过评论来与我们分享您的想法吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=2015-200-Million-Goal-Retro
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Michael Larabel][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.michaellarabel.com/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/vr.php?view=16002
|
||||
[2]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Steam-April-2015-1-Drop
|
||||
[3]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Ubuntu-MX4-In-China
|
||||
[4]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Ubuntu-Calculator-Reboot
|
||||
[5]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTgzOTM
|
||||
[6]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTA5ODM
|
||||
[7]:https://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=Nzg1Mw
|
||||
@ -1,314 +0,0 @@
|
||||
如何在linux上使用Trickle来限制应用程序的网络宽带使用.
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
有没有遇到过系统中的某个应用程序独占了你所有的网络宽带的情形?如果你有过这样的遭遇,那么你就会感受到Trickle宽带调整应用角色的价值.不管你是一个系统管理员还是仅仅Linux用户,都需要学习如何控制应用程序的上下行速度,来确保你的网络宽带不会被某个程序
|
||||
霸占.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Trickle Bandwidth Limit in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 Trickle? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Trickle是一个网络宽带调整工具,可以让我们管理应用程序的网络上下行速度,使得可以避免其中的某个应用程序吃掉了全部或大部分可用的宽带.换句话说,Trickle可以让你基于单个应用程序来控制
|
||||
网络流量速率,而不是仅仅针对与单个用户--在客户端网络环境中经典的宽带调整样例,
|
||||
|
||||
### Trickle是如何工作的?###
|
||||
|
||||
另外,tricle可以帮助我们基于应用来定义优先级,所以当对整个系统进行了全局限制设定,高优先级的应用依然会自动地获取更多的宽带。为了实现这个目标,tricle设置通过TCP连接的套接字对数
|
||||
据发送、数据接收路径的流量限制。我们必须注意到,除了影响传输速率之外,tricle任何时候都不会以任何方式来改变其处理过程。
|
||||
|
||||
### Trickle不能做什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
这么说吧,唯一的限制就是,tricle静态连接的应用或者具有SUID或SGID位设置的二进制--因为他们使用动态链接并且将其自身加载到调整过程以及其关联的网络套接字之间。 Trickle此时会在这两种软件
|
||||
组件之间扮演代理的角色。
|
||||
|
||||
由于trickle并不会需要超级用户的权限来运行,所以用户可以设置用户独立的流量限制,可能这并不是你想要的,我们会探索如何使用全局设定来限制系统中的所有用户的流量限制。也即是说,此时系统中的每个用户具有管理
|
||||
各自的流量速率,但是无论如何,都会受到系统管理员给他们设置的边界限制。
|
||||
|
||||
在这边文章中,我们会描述如何通过trickle在linux平台上管理应用程序使用的网络宽带。为了生成必要流量,在此会在客户端(CentOS 7 server – dev1: 192.168.0.17)上使用 ncftpput 和
|
||||
ncftpget, 在服务器(Debian Wheezy 7.5 – dev2: 192.168.0.15)上使用vsftpd 来进行演示。 相同的指令也可以在RedHat,Fedora和Ubuntu等系统使用。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 前提条件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
1. 对于 RHEL/CentOS 7/6, [开启EPEL仓库][1]。EPEL的Extra Packages是一个 有Fedora项目维护的高质量、开源的软件仓库,而且百分之百与其衍生产品相兼容,如
|
||||
企业版本Linux和CentOS. 在这个仓库中trickle和ncftp两者都是可用的。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 按照如下方式安装ncftp:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && sudo yum install ncftp [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
# aptitude update && aptitude install ncftp [On Debian based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
3. 在单独的服务器上设置一个FTP服务器。需要注意的是,尽管FTP天生就不安全,但是
|
||||
仍然被广泛应用在安全性无关紧要的文件上传下载中。 在这篇文章中我们使用它来演示
|
||||
trickle的优点,同时它也会在客户端的标准输出流中显示传输速率,我们将是否在另外
|
||||
的日期时间中使用放在一边讨论。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install vsftpd [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
# aptitude update && aptitude install vsftpd [On Debian based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
现在,在FTP服务器上按照以下方式编辑 /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
anonymous_enable=NO
|
||||
local_enable=YES
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES
|
||||
allow_writeable_chroot=YES
|
||||
|
||||
在此之后,确保在你的当前会话中开启了vsftpd,并在之后的启动中让其自动启动。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start vsftpd [For systemd-based systems]
|
||||
# systemctl enable vsftpd
|
||||
# service vsftpd start [For init-based systems]
|
||||
# chkconfig vsftpd on
|
||||
|
||||
4. 如果你选在在一个CentOS/RHEL 7中为FTP服务器的远程访问配备SSH秘钥,你需要
|
||||
一个具有适合访问root目录之外的目录和文件内容上传下载权限并密码受保护的用户账户。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过在你的浏览器中输入以下的URL来浏览你的Home目录。一个登陆窗口会弹出来
|
||||
提示你输入FTP服务器中的有效的用户名和密码。
|
||||
|
||||
ftp://192.168.0.15
|
||||
|
||||
如果验证成功,你就会看到你的home目录中的内容。该教程的稍后部分中,你将可以刷新
|
||||
页面来显示在你之前上传过的文件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
FTP Directory Tree
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在Linux中安装 Tricle ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. 通过yum或aptitude来安装tricle.
|
||||
|
||||
为了确保能够成功安装,最好在安装工具之前,保证当前的安装包是最新的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# yum -y update && yum install trickle [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
# aptitude -y update && aptitude install trickle [On Debian based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
2. 确认trickle是否对特定的二进制包有用。
|
||||
|
||||
之前我们解释过,trickle只对使用动态或共享包的二进制包有用。为了确认我们是否可以对某个特定的应用使用trickle,我们可以使用著名的ldd(
|
||||
列出动态依赖)工具。 特别地,我们会查看任何给定程序的动态依赖中检查其当前使用的glibc,因为其准确地定义了使用套接字交流中使用的系统调用。
|
||||
|
||||
对一个给定的二进制包执行以下命令来查看是否能对其使用trickle进行宽带调整:
|
||||
|
||||
# ldd $(which [binary]) | grep libc.so
|
||||
|
||||
例如,
|
||||
|
||||
# ldd $(which ncftp) | grep libc.so
|
||||
|
||||
其输出是:
|
||||
|
||||
# libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007efff2e6c000)
|
||||
|
||||
输出中的括号中的字符可能在不同的系统平台中发生改变,甚至相同的命令在不同的时候运行也会,因为其代表包加载到物理内存中的地址。
|
||||
|
||||
如果上面的命令没有返回任何的结果,就说明这个二进制包没有使用libc包,因此tricle对其不能起到宽带调整的作用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 学习如何使用Trickle###
|
||||
|
||||
最基本的用法就是使用其单模式,通过这种方式,trickle用来显示地定义给定应用程序的上传下载速率。如前所述,为了简单性,我们会使用相同的应用
|
||||
来进行上传下载测试。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在单模式下运行trickle####
|
||||
|
||||
我们会比较在有无trickle的情况下的上传下载速率, ‘-d’选项指示下载速率(KB/s单位),而'-u'选项指示相同单位的上传速率。另外我们会使用到‘-s’
|
||||
选项来指定trickle应该以单模式运行。
|
||||
|
||||
以单模式运行trickle的基本语法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -s -d [download rate in KB/s] -u [upload rate in KB/s]
|
||||
|
||||
为了能够让你自己运行以下样例,确保你在自己的客户端安装了trickle和ncftp(我的是192.168.0.17)。
|
||||
|
||||
**样例1:在有无trickle的情况下上传一个2.8 MB的PDF文件。**
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用一个自由发布的LInux基础知识PDF文件来进行下面的测试[文件链接][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以首先使用下面的命令将这个文件下载到你当前的工作目录中:
|
||||
# wget http://linux-training.be/files/books/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
下面是在没有trickle的情况下将一个文件上传到我们的FTP服务器的语法:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /remote_directory local-filename
|
||||
|
||||
其中的 /remote_directory 是相对于用户名的Home目录的上传路径,而local-filename是一个你当前工作目录中的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
特别的是,在没有trickle的情形下,我们可以得到上传峰值速率52.02MB/s(请注意,这个不是真正的平均上传速率,而是峰值开始的瞬时值),而且这个文件几乎
|
||||
在瞬间就完成了上传。
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 52.02 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
在使用trickle的情况下,我们会限制上传速率在5KB/s。在第二次上传文件之前,我们需要在目标目录中删除这个文件,否则ncftp就会通知我们在目标
|
||||
目录中已经存在了与上传文件相同的文件,从而不会执行文件的传输:
|
||||
# rm /absolute/path/to/destination/directory/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
然后:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -s -u 5 ncftpput -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 /testdir LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 4.94 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的样例中,我们看到平均的上传速率下降到了5KB/s。
|
||||
|
||||
**样例2:在有无trickle的情况下下载相同过得2.8MB的PDF文件**
|
||||
|
||||
首先,记得从原来的源文目录中删除这个PDF:
|
||||
|
||||
# rm /absolute/path/to/source/directory/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,下面的样例中将远程的文件下载到客户端机器的当前目录下,这是由FTP服务器的IP地址后面的·.·决定的。
|
||||
|
||||
没有trickle的情况下:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 260.53 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
在有trickle的情况下,限制下载速率在20KB/s:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -s -d 30 ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 17.76 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
### 在有监督的模式下运行Trickle [未管理的]###
|
||||
|
||||
Tricle也可以在未管理的模式下运行,通过跟随在/etc/tricled.conf文件中定义的一系列参数。 这个文件定义了守护线程 trickled的行为以及如何管理tricle。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,如果你想要全局设置被所有的应用程序使用的话,我们就会需要使用tricle命令。 这个命令运行守护线程并允许我们通过trickle定义所有应用程序共享的上传下载限制,不需要我们每次来进行指定。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickled -d 50 -u 10
|
||||
|
||||
会导致任何通过tricle运行的应用程序的上传下载速率分别限制在30kb/s和10kb/s。
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,你可以在任何时间都能确认守护线程tricled是否正在运行以及其运行参数:
|
||||
|
||||
# ps -ef | grep trickled | grep -v grep
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
root 16475 1 0 Dec24 ? 00:00:04 trickled -d 50 -u 10
|
||||
|
||||
**样例3:在是否使用tricle的情形下上传一个 19MB 的mp4文件到我们的FTP服务器。**
|
||||
|
||||
在这个样例中,我们会使用“He is the gift”的自由分布视频,可以通过这个[链接][3]下载。
|
||||
|
||||
我们将会在开始通过以下的命令将这个文件下载到你的当前工作目录中:
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://media2.ldscdn.org/assets/missionary/our-people-2014/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们会使用之前列出的命令来开启守护进程trickled:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickled -d 30 -u 10
|
||||
|
||||
在没有trickle时:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 36.31 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
有trickle的时:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 9.51 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以看到上面的输出,上传的速率下降到了约 10KB/s。
|
||||
|
||||
** 样例4:在有无trickle的情形下下载这个相同的视频 **
|
||||
|
||||
与样例2一样,我们会将该文件下载到当前工作目录中。
|
||||
|
||||
在没有trickle时:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpget -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 . /testdir/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 108.34 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
有trickle的时:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 29.28 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
上面的结果与我们之前设置的下载限速相对应(30KB/s)。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:** 一旦守护进程开启之后,没有必要使用trickle来为每个应用程序来单独设置限制。
|
||||
|
||||
如前所述,每个人都可以进一步地通过tricled.conf来客制化tricle的宽带速率调整,该文件的一个典型的分区有以下部分组成:
|
||||
|
||||
[service]
|
||||
Priority = <value>
|
||||
Time-Smoothing = <value>
|
||||
Length-Smoothing = <value>
|
||||
|
||||
其中,
|
||||
|
||||
- [service] 用来指示我们想要对其进行宽带使用调整的应用程序名称
|
||||
- Priority 用来让我们为某个服务制定一个相对于其他服务高的优先级,这样就不允许守护进程管理中的一个单独的应用程序来占用所有的宽带。越小的数字代表更高的优先级。
|
||||
- Time-Smoothing [以秒计]: 定义了trickled让各个应用程序传输或接收数据的时间间隔。小的间隔值(0.1-1秒)对于交互式应用程序是理想的,因为这样会具有一个更加平滑的会话体验,而一个相对较大
|
||||
的时间间隔值(1-10秒)对于需要批量传输应用程序就会显得更好。如果没有指定该值,默认是5秒。
|
||||
- Length-smoothing [KB 单位]: 该想法与Time-Smoothing如出一辙,但是是基于I/O操作而言。如果没有指定值,会使用默认的10KB。
|
||||
|
||||
平滑值的改变会被翻译为将指定的服务的使用一个间隔值而不是一个固定值。不幸的是,没有一个特定的公式来计算间隔值的上下限,主要依赖于特定的应用场景。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个在CentOS 7 客户端中的tricled.conf 样例文件(192.168.0.17):
|
||||
|
||||
[ssh]
|
||||
Priority = 1
|
||||
Time-Smoothing = 0.1
|
||||
Length-Smoothing = 2
|
||||
|
||||
[ftp]
|
||||
Priority = 2
|
||||
Time-Smoothing = 1
|
||||
Length-Smoothing = 3
|
||||
|
||||
使用该设置,tricled会为SSH赋予比FTP较高的传输优先级。值得注意的是,一个交互进程,例如SSH,使用了一个较小的时间间隔值,然而一个处理批量数据传输的服务如FTP使用一个较大的时间
|
||||
间隔来负责之前的样例中的上传下载速率,尽管不是百分百的有trickled指定的值,但是也已经非常接近了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
在该文章中,我们探索了任何使用trickle在基于Fedora发行版和Debian衍生版平台上来限制应用程序的宽带使用.也包含了其他的可能用法,但是不对以下情形进行限制:
|
||||
|
||||
- 限制系统下载工具的下载速度,例如[wget][4],或 BT客户端.
|
||||
|
||||
- 限制你的系统的包管理工具`[yun][5]`更新的速度 (如果是基于Debian系统的话,其包管理工具为`[aptitude][6]`)。
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果你的服务器是在一个代理或防火墙后面(或者其本身即是代理或防火墙的话),你可以使用trickle来同时设定下载和上传速率,或者与客户端或外部交流速率。
|
||||
|
||||
欢迎提问或留言.
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-and-limit-downloadupload-bandwidth-with-trickle-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[theo-l](https://github.com/theo-l)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
[2]:http://linux-training.be/files/books/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
[3]:http://media2.ldscdn.org/assets/missionary/our-people-2014/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/dpkg-command-examples/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,298 @@
|
||||
安装完Ubuntu 15.04桌面后要做的15件事
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
本教程适用于新手和在自己的电脑上安装好Ubuntu 15.04 “Vivid Vervet” 桌面之后为了自定义自己的系统并安装一些基本程序作为日常使用的已经做了一些准备的人。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
安装完Ubuntu 15.04桌面后要做的15件事
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 启用Ubuntu额外软件库并更新系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在刚装好Ubuntu之后你应该要关心的第一件事是启用官方合作伙伴提供的Ubuntu额外软件库并且通过最近一次的安全补丁和软件更新来保持系统是最新状态。
|
||||
|
||||
要完成这一步,依次从左边菜单中打开System Settings -> Software and Updates工具并检查所有Ubuntu软件和其他软件库(官方合作伙伴所提供),点击关闭按钮并等待重新加载缓存源树。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Software Updates
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Other Software (Canonical Partners)
|
||||
|
||||
经过一系列快速平滑的更新过程之后,打开终端并输入以下命令来让系统使用新软件库:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get upgrade
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Ubuntu Upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 安装额外驱动 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了能让系统扫描并安装额外的硬件专有驱动,我们依然从System Settings打开Software and Updates工具,选择Additional Drivers标签并等待该工具扫描驱动。
|
||||
|
||||
如果有驱动匹配到了你的硬件,查看你想要安装的驱动并点击Apply按钮来安装它,以防专有驱动没有如期工作,用Revert按钮就能卸载它们或勾选Do not use the device后点击Apply按钮。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Drivers
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 安装Synaptic和Gdebi工具 ###
|
||||
|
||||
除了Ubuntu Software Center,Synaptic是一个apt图形化工具,通过它你能管理、安装、卸载、搜索和升级软件库并配置软件包。同样的,Gdebi在功能上也有相同的地方。在终端上输入以下命令来安装这两个包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install synaptic gdebi
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Synaptic and Gdebi
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Synaptic Package Manager
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 更改系统外观和运行状态 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要更改桌面背景或图标大小,依次打开System Settings –> Appearance –> Look并对桌面进行个性化设置,把菜单移动到窗口标题栏,在Behavior标签中启动workspaces和desktop icons或开关auto-hide the Launcher。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
System Appearances
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 提升系统安全性和隐私性 ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
System Security Enhancement
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
System Security Options
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 禁用不需要开机自启动的应用程序 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要提高登录系统的速度,通过输入以下命令来显示被隐藏的开机启动应用程序,在Dash中搜索它就能打开Startup Applications工具并反选不需要再登录系统的过程中启动的程序。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo sed -i ‘s/NoDisplay=true/NoDisplay=false/g’ /etc/xdg/autostart/*.desktop
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Disable Unwanted Applications
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 添加扩展多媒体支持 ###
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,Ubuntu对多媒体文件支持不是很好。为了能播放各种不同的多媒体格式或解析视频文件,可以安装以下多媒体应用程序:
|
||||
|
||||
- VLC
|
||||
- Smplayer
|
||||
- Audacious
|
||||
- QMMP
|
||||
- Mixxx
|
||||
- XBMC
|
||||
- Handbrake
|
||||
- Openshot
|
||||
|
||||
用以下命令来一次性安装所有的这些应用程序:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install vlc smplayer audacious qmmp mixxx xbmc handbrake openshot
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Media Players
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Media Player Playlist
|
||||
|
||||
除了多媒体播放器,安装ubuntu-restricted-extras和Java支持包也可以解码并支持其它受约束的多媒体格式。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install ubuntu-restricted-extras openjdk-8-jdk
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Ubuntu Extras
|
||||
|
||||
在终端上输入以下命令来启用DVD Playback和其它多媒体解码器:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install ffmpeg gstreamer0.10-plugins-bad lame libavcodec-extra
|
||||
$ sudo /usr/share/doc/libdvdread4/install-css.sh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enable Video Codes
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. 安装图像处理应用程序 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是一个摄影爱好者,想在Ubuntu上处理调整图像,或许需要安装一下图像处理程序:
|
||||
|
||||
- GIMP (alternative for Adobe Photoshop)
|
||||
- Darktable
|
||||
- Rawtherapee
|
||||
- Pinta
|
||||
- Shotwell
|
||||
- Inkscape (alternative for Adobe Illustrator)
|
||||
- Digikam
|
||||
- Cheese
|
||||
|
||||
这些应用程序能从Ubuntu Software Center中安装或者立刻在终端上使用以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install gimp gimp-plugin-registry gimp-data-extras darktable rawtherapee pinta shotwell inkscape
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Image Applications
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Rawtherapee Tool
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. 安装媒体烧录软件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果要挂载ISO镜像或烧录一张CD或DVD,你可以选择并安装以下软件中的一款:
|
||||
|
||||
- Brasero Disk Burner
|
||||
- K3b
|
||||
- Xfburn
|
||||
- Furius ISO Mount
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install brasero
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install k3b
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install xfburn
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install furiusisomount
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Media Burners
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. 安装压缩应用程序 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果要处理大多数归档格式的文件(zip, tar.gz, zip, 7zip rar等等),输入以下命令来安装这些包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install unace unrar zip unzip p7zip-full p7zip-rar sharutils rar uudeview mpack arj cabextract file-roller
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Archive Applications
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. 安装聊天应用程序 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要和世界各地的人们聊天,这里有一份最流行的Linux聊天应用程序列表:
|
||||
|
||||
- Pidgin
|
||||
- Skype
|
||||
- Xchat
|
||||
- Telegram
|
||||
- aMSN
|
||||
- Viber
|
||||
|
||||
你可以从Ubuntu Software Center中安装它们或使用以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install pidgin
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install skype
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install xchat
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install amsn
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:atareao/telegram -y
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install telegram
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Chat Applications
|
||||
|
||||
想要在Ubuntu上安装Viber可以访问[Viber官方网站][1]下载Debian安装包到本地并用Gdebi包管理工具来安装viber.deb应用程序(右击 –> 打开 -> GDebi Package Installer).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Viber
|
||||
|
||||
### 12. 安装种子软件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu最流行的种子应用程序和P2P文件共享程序是:
|
||||
|
||||
- Deluge
|
||||
- Transmission
|
||||
- Qbittorrent
|
||||
- LinuxDC++
|
||||
|
||||
想要在Ubuntu上安装你最喜欢的P2P文件共享应用程序,可以在终端上输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install deluge
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install transmission
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install qbittorrent
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install linuxdcpp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Torrent
|
||||
|
||||
### 13. 安装Windows仿真器-Wine和游戏支持平台-Steam ###
|
||||
|
||||
Wine仿真器允许你在Linux上安装并运行Window应用程序。在另一方面,Steam是一款Valve开发的流行于Linux系统的游戏平台。想要在你的机器上安装它们,可以输入以下命令或使用Ubuntu Software Center。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install steam wine winetricks
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Wine
|
||||
|
||||
### 14. 安装Cairo-Dock并启用桌面视觉效果 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cairo-Dock是一款漂亮且灵巧的用于Linux桌面上的启动条,类似于Mac OS X dock。想要在Ubuntu上安装它,可以在终端上运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install cairo-dock cairo-dock-plug-ins
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Cairo Dock
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Add Cairo Dock at Startup
|
||||
|
||||
想要启用某一套桌面效果,例如Cube效果,可以使用以下命令来安装Compiz包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install compiz compizconfig-settings-manager compiz-plugins-extra
|
||||
|
||||
想要激活桌面Cube效果,在Dash上查找ccsm,打开CompizConfig Settings Manager,找到General Options – > Desktop Size并设置Horizontal Virtual Size的值为4,Vertical Virtual Size的值为1。然后返回检查Desktop Cube框(禁用Desktop Wall)和Rotate Cube框(解决冲突 -> 禁止切换视图1)并Ctrl+Alt+鼠标左击来查看cube效果。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enable Compiz
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Compiz Settings
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Compiz Settings Addons
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Desktop Window Rotating
|
||||
|
||||
### 15. 添加额外浏览器支持 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04默认浏览器是Mozilla Firefox。想要安装其它浏览器比如Google Chrome或Opera,可以访问它们的官方网站,下载所提供的.deb包并用Gdebi Package Installer在你的系统上安装它们。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Enable Browser Support
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Opera Browser Support
|
||||
|
||||
想要安装Chromium开源浏览器请在终端上输入以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install chromium-browser
|
||||
|
||||
### 16. 安装Tweak工具 ###
|
||||
|
||||
想要用额外的应用程序来自定义Ubuntu吗?在终端上输入以下命令来安装Unity Tweak工具和Gnome Tweak工具:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install unity-tweak-tool gnome-tweak-tool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Tweak Tool
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Tweak Tool Settings
|
||||
|
||||
另一个有趣的tweak工具主要是Ubuntu Tweak包,可以通过访问官方网站来获取并安装: [http://ubuntu-tweak.com/][2].
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Tweak Tool: System Information
|
||||
|
||||
在你安装好这一连串软件之后,你或许想要清理一下你的系统来释放一点硬盘上的空间,输入以下命令即可:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -y autoremove
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -y autoclean
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get -y clean
|
||||
|
||||
这只是tweaks工具中的其中一些和普通用户日常生活中可能会在Ubuntu 15.04桌面上安装使用的程序。想要了解更多高级的程序,特性和功能,请使用Ubuntu Software Center或查阅Ubuntu Wiki主页。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/things-to-do-after-installing-ubuntu-15-04-desktop/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
|
||||
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.viber.com/en/products/linux
|
||||
[2]:http://ubuntu-tweak.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,148 @@
|
||||
如何在云服务提供商的机器使用Docker Machine
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
大家好,今天我们来学习如何使用Docker Machine在各种云服务提供商的平台部署Docker。Docker Machine是一个可以帮助我们在自己的电脑、云服务提供商的机器以及我们数据中心的机器上创建Docker机器的应用程序。它为创建服务器、在服务器中安装Docker、根据用户需求配置Docker客户端提供了简单的解决方案。驱动API对本地机器、数据中心的虚拟机或者公用云机器都适用。Docker Machine支持Windows、OSX和Linux,并且提供一个独立的二进制文件,可以直接使用。它让我们可以充分利用支持Docker的基础设施的生态环境合作伙伴,并且使用相同的接口进行访问。它让人们可以使用一个命令来简单而迅速地在不同的云平台部署Docker容器。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 安装Docker Machine ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker Machine可以很好地支持每一种Linux发行版。首先,我们需要从Github网站下载最新版本的。这里我们使用curl来下载目前最新0.2.0版本的Docker Machine。
|
||||
|
||||
在64位操作系统运行:
|
||||
|
||||
# curl -L https://github.com/docker/machine/releases/download/v0.2.0/docker-machine_linux-amd64 > /usr/local/bin/docker-machine
|
||||
|
||||
在32位操作系统运行:
|
||||
|
||||
# curl -L https://github.com/docker/machine/releases/download/v0.2.0/docker-machine_linux-i386 > /usr/local/bin/docker-machine
|
||||
|
||||
下载最新版本的Docker Machine并将docker-machine文件放到了/usr/local/bin/后,添加执行权限:
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-machine
|
||||
|
||||
完成如上操作后,我们需要确认已经成功安装docker-machine了。可以运行如下命令检查,它会输出系统中docker-machine的版本:
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine -v
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
另外机器上需要有docker命令,可以使用如下命令安装:
|
||||
|
||||
# curl -L https://get.docker.com/builds/linux/x86_64/docker-latest > /usr/local/bin/docker
|
||||
# chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 创建机器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在自己的Linux机器上安装好了Docker Machine之后,我们想要将一个docker虚拟机部署到云服务器上。Docker Machine支持几个流行的云平台,如igital Ocean、Amazon Web Services(AWS)、Microsoft Azure、Google Cloud Computing等等,所以我们可以在不同的平台使用相同的接口来部署Docker。本文中我们会使用digitalocean驱动在Digital Ocean的服务器上部署Docker,--driver选项指定digitalocean驱动,--digitalocean-access-token选项指定[Digital Ocean Control Panel][1]提供的API Token,命令最后的是我们创建的Docker虚拟机的机器名。运行如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine create --driver digitalocean --digitalocean-access-token <API-Token> linux-dev
|
||||
|
||||
# eval "$(docker-machine env linux-dev)"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: 这里linux-dev是我们将要创建的机器的名称。`<API-Token>`是一个安全key,可以在Digtal Ocean Control Panel生成。要找到这个key,我们只需要登录到我们的Digital Ocean Control Panel,然后点击API,再点击Generate New Token,填写一个名称,选上Read和Write。然后我们就会得到一串十六进制的key,那就是`<API-Token>`,简单地替换到上边的命令中即可。
|
||||
|
||||
运行如上命令后,我们可以在Digital Ocean Droplet Panel中看到一个具有默认配置的droplet已经被创建出来了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
简便起见,docker-machine会使用默认配置来部署Droplet。我们可以通过增加选项来定制我们的Droplet。这里是一些digitalocean相关的选项,我们可以使用它们来覆盖Docker Machine所使用的默认配置。
|
||||
|
||||
--digitalocean-image "ubuntu-14-04-x64" 是选择Droplet的镜像
|
||||
--digitalocean-ipv6 enable 是启用IPv6网络支持
|
||||
--digitalocean-private-networking enable 是启用专用网络
|
||||
--digitalocean-region "nyc3" 是选择部署Droplet的区域
|
||||
--digitalocean-size "512mb" 是选择内存大小和部署的类型
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想在其他云服务使用docker-machine,并且想覆盖默认的配置,可以运行如下命令来获取Docker Mackine默认支持的对每种平台适用的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine create -h
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 选择活跃机器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
部署Droplet后,我们想马上运行一个Docker容器,但在那之前,我们需要检查下活跃机器是否是我们需要的机器。可以运行如下命令查看。
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ACTIVE一列有“*”标记的是活跃机器。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,如果我们想将活跃机器切换到需要的机器,运行如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine active linux-dev
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:这里,linux-dev是机器名,我们打算激活这个机器,并且在其中运行Docker容器。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 运行一个Docker容器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们已经选择了活跃机器,就可以运行Docker容器了。可以测试一下,运行一个busybox容器来执行`echo hello word`命令,这样就可以得到输出:
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run busybox echo hello world
|
||||
|
||||
注意:如果你试图在一个装有32位操作系统的宿主机部署Docker容器,使用SSH来运行docker是个好办法。这样你就可以简单跳过这一步,直接进入下一步。
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. SSH到Docker机器中 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果我们想在机器或者Droplet上控制之前部署的Docker机器,可以使用docker-machine ssh命令来SSH到机器上:
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine ssh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
SSH到机器上之后,我们可以在上边运行任何Docker容器。这里我们运行一个nginx:
|
||||
|
||||
# docker run -itd -p 80:80 nginx
|
||||
|
||||
操作完毕后,我们需要运行exit命令来退出Droplet或者服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
# exit
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 删除机器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
删除在运行的机器以及它的所有镜像和容器,我们可以使用docker-machine rm命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine rm linux-dev
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
使用docker-machine ls命令检查是否成功删除了:
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 在不使用驱动的情况新增一个机器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以在不使用驱动的情况往Docker增加一台机器,只需要一个URL。它可以使用一个已有机器的别名,所以我们就不需要每次在运行docker命令时输入完整的URL了。
|
||||
|
||||
$ docker-machine create --url=tcp://104.131.50.36:2376 custombox
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 管理机器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经让Docker运行起来了,可以使用简单的**docker-machine stop**命令来停止所有正在运行的机器,如果需要再启动的话可以运行**docker-machine start**:
|
||||
|
||||
# docker-machine stop
|
||||
# docker-machine start
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以使用如下命令来使用机器名作为参数来将其停止或启动:
|
||||
|
||||
$ docker-machine stop linux-dev
|
||||
$ docker-machine start linux-dev
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Docker Machine是一个非常棒的工具,可以使用Docker容器快速地部署服务。文中我们使用Digital Ocean Platform作演示,但Docker Machine还支持其他平台,如Amazon Web Service、Google Cloud Computing。使用Docker Machine,快速、安全地在几种不同平台部署Docker容器变得很简单了。因为Docker Machine还是Beta版本,不建议在生产环境使用。如果你有任何问题、建议、反馈,请在下方的评论框中写下来,我们会改进或者更新我们的内容。谢谢!享受吧 :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/use-docker-machine-cloud-provider/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[goreliu](https://github.com/goreliu)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:https://cloud.digitalocean.com/settings/applications
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user