mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-03 23:40:14 +08:00
translating
This commit is contained in:
commit
84dee5a79d
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
Flow 'N Play视频播放器有着独具风格的界面[在Ubuntu上安装]
|
||||
在Ubuntu上安装Flow 'N Play—界面独具风格的视频播放器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
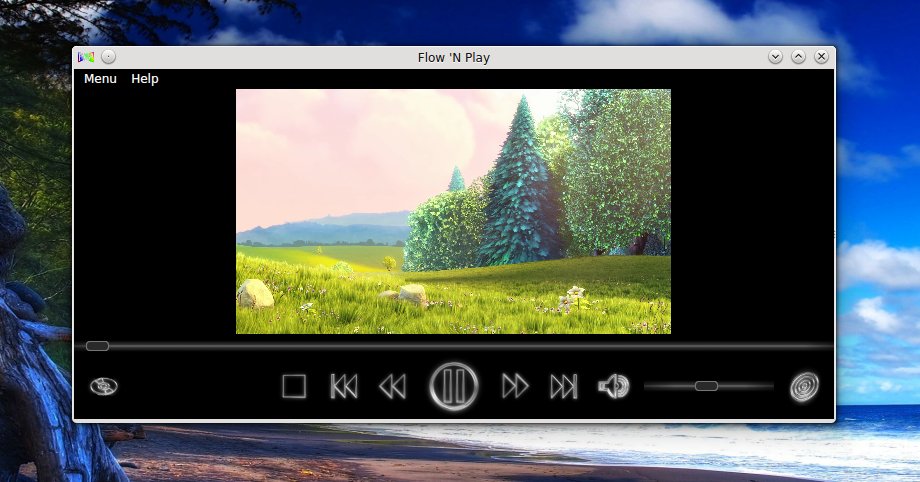
**Flow ‘N Play**是个用Qt编写的新视频播放器。它有着漂亮又简洁的界面,只提供基本播放功能。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[Flow ‘N Play][1]是个比较新的视频播放器,它有着漂亮的界面和简单的操作(今年三月份第一次发行)。其中一个功能就是能通过拖动鼠标滑动视频列表。播放器带有基本功能,一个搜索功能,支持彩色主题。
|
||||
[Flow ‘N Play][1]是个比较新的视频播放器,它有着漂亮的界面和简单的操作(2014年3月份第一次发行)。其中一个功能就是能通过拖动鼠标滑动视频列表。播放器带有基本功能,一个搜索功能,支持彩色主题。
|
||||
|
||||
打开一个新的视频——你还可以在同一个对话框下自定义一个封面:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,128 +0,0 @@
|
||||
CD Audio Grabbers - Graphical Based
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
CD audio grabbers are designed to extract ("rip") the raw digital audio (in a format commonly called CDDA) from a compact disc to a file or other output. This type of software enables a user to encode the digital audio into a variety of formats, and download and upload disc info from freedb, an internet compact disc database.
|
||||
|
||||
Is copying CDs legal? Under US copyright law, converting an original CD to digital files for personal use has been cited as qualifying as 'fair use'. However, US copyright law does not explicitly allow or forbid making copies of a personally-owned audio CD, and case law has not yet established what specific scenarios are permitted as fair use. The copyright position is much clearer in the UK. From 2014 it become legal for UK citizens to make copies of CDs, MP3s, DVD, Blu-rays and e-books. This only applies if the individual owns the physical media being ripped, and the copy is made only for their own private use. For other countries in the European Union, member nations can allow a private copy exception too.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are not sure what the position is for the country you live in, please check your local copyright law to make sure that you are on the right side of the law before using the software featured in this two page article.
|
||||
|
||||
To some extent, it may seem a bit of a chore to rip CDs. Streaming services like Spotify and Google Play Music offer access to a huge library of music in a convenient form, and without having to rip your CD collection. However, if you already have a large CD collection, it is still desirable to be able to convert your CDs to enjoy on mobile devices like smartphones, tablets, and portable MP3 players.
|
||||
|
||||
This two page article highlights my favorite audio CD grabbers. I pick the best four graphical audio grabbers, and the best four console audio grabbers. All of the utilities are released under an open source license.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
fre:ac is an open source audio converter and CD ripper that supports a wide range of popular formats and encoders. The utility currently converts between MP3, MP4/M4A, WMA, Ogg Vorbis, FLAC, AAC, WAV and Bonk formats. It comes with several different presents for the LAME encoder.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Easy to learn and use
|
||||
- Converter for MP3, MP4/M4A, WMA, Ogg Vorbis, FLAC, AAC, WAV and Bonk formats
|
||||
- Integrated CD ripper with CDDB/freedb title database support
|
||||
- Multi-core optimized encoders to speed up conversions on modern PCs
|
||||
- Full Unicode support for tags and file names
|
||||
- Easy to learn and use, still offers expert options when you need them
|
||||
- Joblists
|
||||
- Can use Winamp 2 input plugins
|
||||
- Multilingual user interface available in 41 languages
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [freac.org][1]
|
||||
- Developer: Robert Kausch
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 20141005
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Audex is an easy to use open source audio CD ripping application. Whilst it is in a fairly early stage of development, this KDE desktop tool is stable, slick and simple to use.
|
||||
|
||||
The assistant is able to create profiles for LAME, OGG Vorbis (oggenc), FLAC, FAAC (AAC/MP4) and RIFF WAVE. Beyond the assistant you can define your own profile, which means, that Audex works together with commmand line encoders in general.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Extract with CDDA Paranoia
|
||||
- Extract and encode run parallel
|
||||
- Filename editing with local and remote CDDB/FreeDB database
|
||||
- Submit new entries to CDDB/FreeDB database
|
||||
- Metadata correction tools like capitalize etc
|
||||
- Multi-profile extraction (with one commandline-encoder per profile)
|
||||
- Fetch covers from the internet and store them in the database
|
||||
- Create playlists, cover and template-based-info files in target directory
|
||||
- Create extraction and encoding protocols
|
||||
- Transfer files to a FTP-server
|
||||
- Internationalization support
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [kde.maniatek.com/audex][2]
|
||||
- Developer: Marco Nelles
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.79
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Sound Juicer is a lean CD ripper using GTK+ and GStreamer. It extracts audio from CDs and converts it into audio files. Sound Juicer can also play audio tracks directly from the CD, offering a preview before ripping.
|
||||
|
||||
It supports any audio codec supported by a GStreamer plugin, including MP3, Ogg Vorbis, FLAC, and uncompressed PCM formats.
|
||||
|
||||
It is an established part of the GNOME desktop environment.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Automatic track tagging via CDDB
|
||||
- Encoding to ogg / vorbis, FLAC and raw WAV
|
||||
- Easy to configure encoding path
|
||||
- Multiple genres
|
||||
- Internationalization support
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [burtonini.com][3]
|
||||
- Developer: Ross Burton
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 3.14
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ripperX is an open source graphical interface for ripping CD audio tracks and encoding them to Ogg, MP2, MP3, or FLAC formats. It's goal is to be easy to use, requiring only a few mouse clicks to convert an entire album. It supports CDDB lookups for album and track information.
|
||||
|
||||
It uses cdparanoia to convert (i.e. "rip") CD audio tracks to WAV files, and then calls the Vorbis/Ogg encoder oggenc to convert the WAV to an OGG file. It can also call flac to perform lossless compression on the WAV file, resulting in a FLAC file.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Very simple to use
|
||||
- Rip audio CD tracks into WAV, MP3, OGG, or FLAC files
|
||||
- Supports CDDB lookups
|
||||
- Supports ID3v2 tags
|
||||
- Pause the ripping process
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [sourceforge.net/projects/ripperx][4]
|
||||
- Developer: Marc André Tanner
|
||||
- License: MIT/X Consortium License
|
||||
- Version Number: 2.8.0
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150125043738417/AudioGrabbersGraphical.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.freac.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://kde.maniatek.com/audex/
|
||||
[3]:http://burtonini.com/blog/computers/sound-juicer
|
||||
[4]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/ripperx/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
Pinta 1.6 Released! Install It In Ubuntu And Linux Mint
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Pinta][1] is a free and open source drawing application which is very popular among Linux users. It won’t be incorrect to term it as an **open source alternative to Microsoft Paint**. Pinta is available for all major platforms such as Linux, Windows and Mac OS X.
|
||||
|
||||
While Gimp is popular as full featured image editing software, Pinta is more of a paint and drawing tool. I have used it extensively in my tutorials for drawing arrows and curves on the screenshots and I can say that it’s my favorite drawing app in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### New features in Pinta 1.6 ###
|
||||
|
||||
After over an year, Pinta has released version 1.6, fixing over 50 bugs and introducing some new features. New features are as following:
|
||||
|
||||
- Line tool now supports drawing curves and arrows
|
||||
- Shapes can be edited even after being drawn
|
||||
- All shape tools now support drawing dashed lines
|
||||
- All selection tools now support the Union, Exclude, Xor, and Intersection modes
|
||||
- Add-in manager now consists of ‘add ins’
|
||||
- New options in command line usage
|
||||
|
||||
New version also fixes the annoying bug where you [cannot open a file with Pinta in right click menu option][2]. You can read all the changes in the [release note][3].
|
||||
|
||||
### Install Pinta 1.6 in Ubuntu and Linux Mint ###
|
||||
|
||||
Pinta 1.5 is available in Ubuntu 14.04, 14.10, Linux Mint 17, elementary OS. If you want to install the latest version 1.6, you can use the official PPA from Pinta team. Don’t worry if you have Pinta 1.5 installed already. Installing it again will upgrade the version.
|
||||
|
||||
Open a terminal and use the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:pinta-maintainers/pinta-stable
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install pinta
|
||||
|
||||
To download the source code or to get the installation files for Windows and Mac OS X, check the [download page of Pinta][4]. In a related post, you can also check out [best photo applications for Linux][5].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/pinta-1-6-ubuntu-linux-mint/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://pinta-project.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/add-application-list-open-applications-ubuntu-1310/
|
||||
[3]:http://pinta-project.com/releases/1-6
|
||||
[4]:http://pinta-project.com/releases
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/image-applications-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04 Finally Lets You Set Menus To ‘Always Show’
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**If you hate the way that Unity’s global menus fade out of view after you mouse away, Ubuntu 15.04 has a little extra to win you around.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The latest build of Unity for Ubuntu 15.04, currently sitting in the ‘proposed’ channel, offers an option to **make app menus visible in Ubuntu**.
|
||||
|
||||
No fading, no timeout, no missing menus.
|
||||
|
||||
The drawback for now is that it can currently only be enabled through a dconf switch and not a regular user-facing option.
|
||||
|
||||
I’d hope (if not expect) that an option to set the feature is added to the Ubuntu System Settings > Appearance section as development continues.
|
||||
|
||||
Right now, if you’re on Ubuntu 15.04 and have the “Proposed” update channel enabled, you should find this switch waiting in **com > canonical > unity >** ‘always show menus’.
|
||||
|
||||
### Better Late Than Never? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Developers plan to backport the option to Ubuntu 14.04 LTS in the next SRU (assuming nothing unexpected crops up during testing).
|
||||
|
||||
Locally Integrated Menus (LIM) debuted in Ubuntu 14.04 LTS to much appreciation, being widely seen as the best compromise between those who liked the simplicity of the “hidden” approach and those who disliked the mouse and trackpad aerobics using it required.
|
||||
|
||||
While locally integrated menus brought us half way to silencing the criticisms levelled at this aspect of Unity, the default “fade in/fade out” behaviour left an itch unscratched.
|
||||
|
||||
The past few releases of Ubuntu has seen proactive addressing of concerns and issues experienced by its earlier UX decisions. After several years on the ‘to do’ list [we finally got Locally Integrated Menus last year][1], as well as an unsupported [option to minimise and restore apps to the Unity Launcher][2] by clicking on their icon.
|
||||
|
||||
A year on from that we finally get an option to make application menus always show, no matter where our mouse is. Better late than never, right?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/01/ubuntu-15-04-always-show-menu-bar-option
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/02/locally-integrated-menus-ubuntu-14-04
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/03/minimize-click-launcher-option-ubuntu-14-04
|
||||
@ -1,207 +0,0 @@
|
||||
theo-l translating
|
||||
How to Monitor Network Usage with nload in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
nload is a free linux utility that can help the linux user or sysadmin to monitor network traffic and bandwidth usage in real time by providing two simple graphs: one per incoming traffic and one for outgoing traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
I really like to use **nload** to display information on my screen about the current download speed, the total incoming traffic, and the average download speed. The graphs reported by nload tool are very easy to interpret and what is the most important thing they are very helpful.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the manual pages it monitors all network devices by default, but you can easily specify the device you want to monitor and also switch between different network devices using the arrow keys. There are many options avaliable such as -t to determine refresh interval of the display in milliseconds (the default value of interval is 500), -m to show multiple devices at the same time(traffic graphs are not shown when this option is used), -u to set the type of unit used for the display of traffic numbers and many others that we are going to explore and practise in this tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to install nload on your linux machine ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu** and **Fedora** users can easily install nload from the default repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
Install nload on Ubuntu by using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install nload
|
||||
|
||||
Install nload on Fedora by using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install nload
|
||||
|
||||
What about **CentOS** users? Just type the following command on your machine and you will get nload installed.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install nload
|
||||
|
||||
The following command will help you to install nload on OpenBSD systems.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo pkg_add -i nload
|
||||
|
||||
A very effective way to install software on linux machine is to compile by source as you can download and install the latest version which usually means better performance, cool features and less bugs.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to install nload from source ###
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing you need to do before installing nload from source you need to download it and to do this I like to use the wget uility which is available by default on many linux machines. This free utility helps linux users to download files from the web in a non-interactive way and has support for the following protocols.
|
||||
|
||||
- HTTP
|
||||
- HTTPS
|
||||
- FTP
|
||||
|
||||
Change directory to **/tmp** by using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
cd /tmp
|
||||
|
||||
Now type the following command in your terminal to download the latest version of nload on your linux machine.
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
If you don't like to use the linux wget utility you can easily download it from the [official][1] source by just a mouse click.
|
||||
|
||||
The download will finish in no time as it is a small software. The next step is to untar the file you downloaded with the help of the **tar** utility.
|
||||
|
||||
The tar archiving utility can be used to store and extract files from a tape or disk archive. There are many options available in this tool but we need the followings to perform our operation:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **-x** to extract files from an archive
|
||||
1. **-v** to run in verbose mode
|
||||
1. **-f** to specify the files
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
tar xvf example.tar
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you learned how to use the tar utility I am very sure you know how to untar .tar archives from the commandline.
|
||||
|
||||
tar xvf nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Then use the cd command to change directory to nload*.
|
||||
|
||||
cd nload*
|
||||
|
||||
It looks like this on my system.
|
||||
|
||||
oltjano@baby:/tmp/nload-0.7.4$
|
||||
|
||||
Now run the command
|
||||
|
||||
./configure
|
||||
|
||||
to to configure the package for your system.
|
||||
|
||||
./configure
|
||||
|
||||
Alot of stuff is going to be displayed on your screen. The following screenshot demonstrates how it is going to look like.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then compile the nload with the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
make
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
And finally install nload on your linux machine with the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now that the installation of nload is finished it is time for you to learn how to use it.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to use nload ###
|
||||
|
||||
I like to explore so type the following command on your terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
nload
|
||||
|
||||
What do you see?
|
||||
|
||||
I get the following.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see from the above screenshot I get information on:
|
||||
|
||||
### Incoming Traffic ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### Current download speed ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Average download speed ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Minimum download speed ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Maximum download speed ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Total incoming traffic in bytes by default ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Outgoing Traffic ###
|
||||
|
||||
The same goes for outgoing traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Some useful options of nload ####
|
||||
|
||||
Use the option
|
||||
|
||||
-u
|
||||
|
||||
to set set the type of unit used for the display of traffic numbers.
|
||||
|
||||
The following command will help you to use the MBit/s unit.
|
||||
|
||||
nload -u m
|
||||
|
||||
The following screenshot shows the result of the above command.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Try the following command and see the results.
|
||||
|
||||
nload -u g
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There is also the option **-U**. According to the manual pages it is same as the option -u but only for an amount of data. I tested this option and to be honest it very helpful when you want to check the total amount of traffic be it incoming or outgoing.
|
||||
|
||||
nload -U G
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As you can see from the above screenshot the command **nload -U G** helps to display the total amount of data (incoming or outgoing) in Gbyte.
|
||||
|
||||
Another useful option I like to use with nload is the option **-t**. This option is used to refresh interval of display in milliseconds which is 500 by default.
|
||||
|
||||
I like to experiment a little by using the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
nload -t 130
|
||||
|
||||
So what the above command does is that it sets the display to refresh every 130 milliseconds. It is recommended to no specify refresh intervals shorter than about 100 milliseconds as nload will generate reports with mistakes during the calculations.
|
||||
|
||||
Another option is **-a**. It is used when you want to set the length in seconds of the time window for average calculation which is 300 seconds by default.
|
||||
|
||||
What if you want to monitor a specific network device? It is very easy to do that, just specify the device or the list of devices you want to monitor like shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
nload wlan0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The following syntax can help to monitor specific multiple devices.
|
||||
|
||||
nload [options] device1 device2 devicen
|
||||
|
||||
For example use the following command to monitor eth0 and wlan0.
|
||||
|
||||
nload wlan0 eth0
|
||||
|
||||
And if you run the command nload without any option it will monitor all auto-detected devices, you can display graphs for each one of them by using the right and left arrow keys.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/monitor-network-usage-nload/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Oltjano Terpollari][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/oltjano/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
Translating----geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
How To Fix: Failed to fetch cdrom apt-get update cannot be used to add new CD-ROMs
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by martin.
|
||||
|
||||
How to Setup Passwordless SSH Logon to Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hi all, today we'll gonna learn how we can setup Passwordless SSH Logon to Ubuntu 14.04 "Trusty". Only the workstations having the correct matching key pair (private and public) will be allowed to logon to the SSH server, without the key paring, access will not be allowed.
|
||||
|
||||
Usually, we need to enter username and password combination to connect to an SSH console. If the combination is correct to that of the system's then, we get access to the server else we are denied from the access. But, there is something more secure than Password logon, we have passwordless SSH logon using the encrypted keys.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to enable this secured option, we can simply disable password-logon and only allow logon using an encryption key. When using encryption keys option, the client computer generates a private and public key pair. The client then must upload the public key to the SSH server authorized_key file. Before access is granted, the server and client computer validate the key pair. If the public key on the server matches the private key submitted via the client then access will be granted else will be denied.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a very secure way authenticating to a SSH server and it’s a recommended method if you wish to implement secure logon with single user SSH logon. Here's a quick step-wise process on how to enable Passwordless SSH logon.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Installing Openssh Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
First off all, we'll need to update our local repository index. To do so, we'll first need to run apt-get update as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, we can install openssh-server by running following command.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install openssh-server
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Enabling Openssh Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll want to enable OpenSSH server after we successfully installed it on our Ubuntu 14.04 Operating System. The command to enable/start the server is given as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service ssh start
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh start
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Configuring Key Pair ###
|
||||
|
||||
After we have installed our OpenSSH Server and enabled it. We'll now finally wanna go for generating our Public and Private Key Pair. To do that, run the following command in a terminal or console.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
|
||||
|
||||
After running the above command, we'll be prompted to complete a series of tasks. The first will be where to save the keys, press Enter to choose the default location which is in a hidden .ssh folder in the home directory. The next prompt will be to enter the Paraphrase. I personally leave this blank (just press enter) to continue. It will then create the key pair and we’re done.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After generation of the key pair, we will need to **copy the client’s public key to the SSH server** or host inorder to create trusted relationship with it. We'll need to run the commands below to copy the client public key to the server.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh-copy-id user@ip_address
|
||||
|
||||
After the public key is copied to the server, we can now go and disable password logon via SSH. To do that, we'll need to open **/etc/ssh/ssh_config** via a text editor by run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll need to uncomment the lines and set the values as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Restarting the SSH Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, after we are done configuring SSH Server, we'll want to restart our SSH Server so that all the changes will take affect. To restart one can run the following command in a terminal or the console.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service ssh restart
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we can now ssh in to the server without a password and only from the client having the same key pair not the password.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Hurray! We have successfully enabled Passwordless SSH logon. It is a lot secure to enable Encrypted Key Pair SSH logon . This is a very secure way authenticating to a SSH server and it’s a recommended method if you wish to implement secure logon with single user SSH logon. So, if you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below. Thank you ! Enjoy Encrypted Secure SSH Login :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/setup-passwordless-ssh-logon-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
Translating-------geekpi
|
||||
Translating
|
||||
|
||||
Linux Basics: How To Find Maximum Supported RAM By Your System
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
|
||||
How to Setup lftp - A Simple Command line FTP Program
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hi everyone, this article is about Lftp and how we can install Lftp in our Linux Operating System. [Lftp][1] is a command line based File Transfer Software also known as FTP Client which was developed by Alexander Lukyanov and was distributed as GNU General Public License. Besides FTP, it also supports FTPS, HTTP, HTTPS, HFTP, FISH, and SFTP. The program also supports FXP, allowing for data transfers between two FTP servers bypassing the client machine.
|
||||
|
||||
It has some awesome advanced features such as recursively mirroring entire directory trees and resuming downloads. Transfers can be scheduled for execution at a later time, bandwidth can be throttled, transfer queues can be created, and Unix shell-like job control is supported. The client can also be used interactively or automated with scripts.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Lftp ###
|
||||
|
||||
Before we try to run lftp, we have make sure that it is properly installed in our Linux Distribution. Here are some commands mentioned for installing lftp in the list common distribution of Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
**On Ubuntu 14.04 LTS**
|
||||
|
||||
In Ubuntu 14.04 LTS and its derivatives, we can install lftp using apt manager. So, to install it, we'll need to run the following commands in a shell or a terminal under sudo privilege.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install lftp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**On CentOS/Fedora/RHEL**
|
||||
|
||||
As lftp is also available in the repository of Fedora, CentOS and RHEL, we can use **yum** manager to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install lftp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**On Arch Linux**
|
||||
|
||||
It is also available in Arch Linux Package Repository so, we can simply use pacman to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S lftp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**On OpenSuse**
|
||||
|
||||
Zypper, package management software for OpenSuse can be used to install lftp. Here is the command with which one can install it on their OpenSuse machine.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo zypper install lftp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Logging in ###
|
||||
|
||||
To login to a ftp server or sftp server, we'll first need to know about the required credential for the login like username, password, ports.
|
||||
|
||||
After that, we'll want to login using lftp client as basic usage.
|
||||
|
||||
$ lftp ftp://linoxide@localhost
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If we need to point a port to the login then, we'll need to add port as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
$ lftp ftp://linoxide@localhost:21
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Navigation ###
|
||||
|
||||
We can use **ls** to list files and directories, **cd** to enter into a directory.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Uploading and Download Files ###
|
||||
|
||||
We can use **pget** for downloading files from the remote server.
|
||||
|
||||
> pget linspeed.svg
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We can use **put** for uploading files to the remote server.
|
||||
|
||||
> put linoxide.tar
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To resume partially downloaded files/directories, we will use the -c switch:
|
||||
|
||||
> mirror -c Directory
|
||||
|
||||
>pget -c linoxide.tar
|
||||
|
||||
> put -c upload.tar
|
||||
|
||||
### Using Mirror ###
|
||||
|
||||
We can use mirror to download the whole directory pointed as the source.
|
||||
|
||||
> mirror remote local
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There is also reverse mirror (mirror -R) which uploads or updates a directory tree on server.
|
||||
|
||||
> mirror -R local remote
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
To resume partially downloaded files/directories, we will use the -c switch:
|
||||
|
||||
> mirror -c Directory
|
||||
|
||||
### To Queue Items to Download ###
|
||||
|
||||
We can use queue option with lftp so that we can download selected files in a queue one by one as there is an option in GUI based clients to select and download in a queue. Here's an example on it.
|
||||
|
||||
To prevent queue from auto transferring while you add to it :
|
||||
|
||||
> queue stop
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll add them into queue.
|
||||
|
||||
> queue mirror "directory"
|
||||
|
||||
> queue pget "file.tar"
|
||||
|
||||
After the queue has been added, we should run queue start command.
|
||||
|
||||
> queue start
|
||||
|
||||
To remove the entire queue run the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
> queue -d
|
||||
|
||||
### Segmented Downloading ###
|
||||
|
||||
Here, in this example we are segmenting files into 3 segments, one can change it according to their own need.
|
||||
|
||||
A pget command using segmentation is **pget -n 3 file.tar**, where 3 is the number of segments.
|
||||
|
||||
> pget -n 3 file.tar
|
||||
|
||||
A mirror command using segmentation is **mirror --use-pget-n=3 directory**, where 3 is the number of segments.
|
||||
|
||||
> mirror --use-pget-n=3 linxoxide
|
||||
|
||||
We can use jobs -v to see the speeds of the individual segments as well as the total speed.
|
||||
|
||||
### To Stop, Resume or Kill a Transfer ###
|
||||
|
||||
To cancel a transfer we can press Ctrl+c . And to resume a download we can use the -c (--continue) switch as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
> mirror -c directory
|
||||
|
||||
And to kill an active transfer we should run **kill** and to kill and delete all we'll need to run **kill all** as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
> kill
|
||||
|
||||
> kill all
|
||||
|
||||
### Exiting ###
|
||||
|
||||
To quit from lftp, we should run exit command in the terminal or inside lftp interface.
|
||||
|
||||
> exit
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Hurray! We have successfully installed lftp and learned some basic major ways to use it. lftp is an awesome command line ftp client which supports a lot of additional functionality and cool features. It has a lot stuffs more than the other common ftp client. So, if you have any questions, suggestions, feedback please write them in the comment box below. Thank you ! Enjoy lftp :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/setup-lftp-command-line-ftp/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://lftp.yar.ru/
|
||||
43
sources/tech/20150306 Nmap--Not Just for Evil.md
Normal file
43
sources/tech/20150306 Nmap--Not Just for Evil.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
translating by martin.
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap—Not Just for Evil!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If SSH is the Swiss Army knife of the system administration world, Nmap is a box of dynamite. It's really easy to misuse dynamite and blow your foot off, but it's also a very powerful tool that can do jobs that are impossible without it.
|
||||
|
||||
When most people think of Nmap, they think of scanning servers, looking for open ports to attack. Through the years, however, that same ability is incredibly useful when you're in charge of the server or computer in question. Whether you're trying to figure out what kind of server is using a specific IP address in your network or trying to lock down a new NAS device, scanning networks is incredibly useful.
|
||||
|
||||
Figure 1 shows a network scan of my QNAP NAS. The only thing I use the unit for is NFS and SMB file sharing, but as you can tell, it has a ton of ports wide open. Without Nmap, it would be difficult to figure out what the machine was running.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Figure 1. Network Scan ###
|
||||
|
||||
Another incredibly useful way to use Nmap is to scan a network. You don't even have to have root access for that, and it's as simple as specifying the network block you want to scan. For example, typing:
|
||||
|
||||
nmap 192.168.1.0/24
|
||||
|
||||
will scan the entire range of 254 possible IP addresses on my local network and let me know which are pingable, along with which ports are open. If you've just plugged in a new piece of hardware, but don't know what IP address it grabbed via DHCP, Nmap is priceless. For example, the above command revealed this on my network:
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap scan report for TIVO-8480001903CCDDB.brainofshawn.com (192.168.1.220)
|
||||
Host is up (0.0083s latency).
|
||||
Not shown: 995 filtered ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
443/tcp open https
|
||||
2190/tcp open tivoconnect
|
||||
2191/tcp open tvbus
|
||||
9080/tcp closed glrpc
|
||||
|
||||
This not only tells me the address of my new Tivo unit, but it also shows me what ports it has open. Thanks to its reliability, usability and borderline black hat abilities, Nmap gets this month's Editors' Choice award. It's not a new program, but if you're a Linux user, you should be using it!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/nmap%E2%80%94not-just-evil
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Shawn Powers][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxjournal.com/users/shawn-powers
|
||||
129
translated/share/20150126 CD Audio Grabbers--Graphical Based.md
Normal file
129
translated/share/20150126 CD Audio Grabbers--Graphical Based.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,129 @@
|
||||
|
||||
CD音频抓取器——基于图形界面
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
CD音频抓取器是为了从光盘中提取(“剖出”)原始数字音频(它在一个通常被称为CDDA的格式中)并把它保存成文件或以其他形式输出而设计的。这类软件使用户能把数字音频编码成各种格式,并能下载和上传在线CD目录服务——一个在线的光盘数据库——中的光盘信息。
|
||||
|
||||
复制CD合法吗?在美国版权法中,把一个原始CD转换成数字文件用于个人使用在被引用时等同于‘合理使用’。然而,美国版权法并没有明确的允许或禁止拷贝私人音频CD,而且判例法还没有确立出在具体的哪种情况下可以视为合理使用。在英国版权的位置更清晰一些。从2014年开始,英国公民制造CD,MP3,DVD,蓝光和电子书的行为成为合法行为。这仅适用于这个人拥有被采集的媒体的实体,并且复制品仅用于他们个人使用。对于欧盟的其他国家,成员国可以允许私人复制这种特例。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不确定在你生活的国家里版权处于什么位置,在你使用这两页文章中所列举的软件前请查询本地的版权法以确定你处在合法的一边。
|
||||
|
||||
在某种程度上,提取CD音轨看起来有点多余。如Spotify和Google Play Music这类流服务提供了一个巨大的以通用格式存在的音乐的库,无需采集你的CD集。但是,如果你已将收藏了一个数量巨大的CD集。能把你的CD转换成可以在便携设备如智能手机、平板和便携式MP3播放器上播放的格式仍然是个诱人的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
这两页文章推荐了我最喜欢的音频CD抓取器。我挑了四个最好的图形界面的音频抓取器,四个最好的控制台音频抓取器。所有这些应用程序都是在开源许可下发行的。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
fre:ac是个开源音频转换器和CD提取器,支持很多种流行格式和编码器。目前这个应用可以在MA3、MP4/M4A、WMA、Ogg Vorbis、FLAC、AAC、WAV和Bonk格式间转换。这来源于几种不同形式的LAME编码器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能包括: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 易学易用
|
||||
- MP3、MP4/M4A、WMA、Ogg Vorbis、FLAC、AAC、WAV和Bonk格式转换器
|
||||
- 集成了CDDB/freedb标题数据库支持的CD提取器
|
||||
- 多核优化的编码器加速了现代PC上的转换速度
|
||||
- 对于标签和文件名称的全Unicode支持
|
||||
- 易学易用,当你需要时还提供专家级选项
|
||||
- 任务列表
|
||||
- 可以使用Winamp 2加入附件
|
||||
- 多语言用户界面可以使用41种语言
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址: [freac.org][1]
|
||||
- 开发人员:Robert Kausch
|
||||
- 许可证: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 20141005
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Audex是个简单易用的开源音频CD提取应用。虽然它还处于早期开发阶段,这个KDE桌面工具足够稳定、聪明和简单,可以使用。
|
||||
|
||||
助手可以给LAME、OGG Vorbis(oggenc)、FLAC、FAAC(AAC/MP4)和RIFF WAVE创建配置文件。除去这个助手,你可以定义你自己的配置文件,这意味着,Audex适用于大部分的命令行编码器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能包括: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 可提取CDDA Paranoia
|
||||
- 提取和编码同时进行
|
||||
- 文件名采用本地和远程CDDB/FreeDB数据库
|
||||
- 提供新的CDDB/FreeDB数据库入口
|
||||
- 类似capitalize的元数据纠正工具
|
||||
- 多配置文件提取(每个配置文件文件有一个命令行编码器)
|
||||
- 从互联网上抓取封面并将他们存在数据库中
|
||||
- 在目标目录中创建播放列表、封面和基于模板的信息文件
|
||||
- 创建提取和编码协议
|
||||
- 将文件传送到FTP服务器
|
||||
- 支持国际化
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址: [kde.maniatek.com/audex][2]
|
||||
- 开发人员: Marco Nelles
|
||||
- 许可证: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.79
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Sound Juicer是个使用GTK+和GStreamer的轻量级CD提取器。它从CD中提取音频并把它转换成音频文件。Sound Juicer还可以直接播放CD中的音轨,在提取前提供预览。
|
||||
|
||||
由于GStreamer插件它支持任何音频编码,包括 MP3、Ogg Vorbis、FLAC和未压缩的PCM格式。
|
||||
|
||||
它是GNOME桌面环境已建成的一部分。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能包括: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 自动通过CDDB给音轨加标签
|
||||
- 可编码成ogg/vorbis、FLAC和原始WAV
|
||||
- 编码路径的设置很简单
|
||||
- 多种流派
|
||||
- 国际化支持
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址:[burtonini.com][3]
|
||||
- 开发人员: Ross Burton
|
||||
- 许可证:GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号:3.14
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
ripperX是个开源的图形交互界面,用于提取CD音轨并把他们编码成Ogg、MP2、MP3或FLAC格式。它的目的是容易使用,只需要点几下鼠标就能转换整张专辑。它支持在CDDB寻找专辑和音轨信息。
|
||||
|
||||
他使用cdparanoia把CD音轨转换(也就是“提取”)成WAV文件,然后访问Vorbis/Ogg编码器oggenc把WAV文件转换成OGG文件。它还可以访问flac让WAV文件有无损压缩的表现,制成FLAC文件。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 功能包括: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- 非常简单易用
|
||||
- 可以把CD音轨提取成WAV、MP3、OGG或FLAC文件
|
||||
- 支持CDDB查找
|
||||
- 支持ID3v2标签
|
||||
- 可暂停提取进程
|
||||
|
||||
- 网址:[sourceforge.net/projects/ripperx][4]
|
||||
- 开发人员:Marc André Tanner
|
||||
- 许可证:MIT/X Consortium License
|
||||
- 版本号:2.8.0
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
转自:http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150125043738417/AudioGrabbersGraphical.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[H-mudcup](https://github.com/H-mudcup)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.freac.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://kde.maniatek.com/audex/
|
||||
[3]:http://burtonini.com/blog/computers/sound-juicer
|
||||
[4]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/ripperx/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
Ubuntu 15.04 最终实现你可以设置你的菜单 ‘始终可见’
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**如果你不喜欢 Unity 的全局菜单在你的鼠标离开后就淡出你的视野, Ubuntu 15.04 有一些额外附加去实现这点.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最新的Ubuntu 15.04的Unity界面通过在提议通道提供了一个选项**使应用程序菜单在Ubuntu中可见**.
|
||||
|
||||
不时尚, 不过时, 没有丢失的菜单.
|
||||
|
||||
最大的缺点是它目前只能通过dconf来控制,而不是常规的面向用户的选项设置。
|
||||
|
||||
我希望(如果不是期望)能有一个设置这个特性的选项被加入到Ubuntu的【系统设置】>【外观】部分的开发仍在继续。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,如果你使用的是Ubuntu15.04,并启用“建议”的更新通道后,你会发现这个开关存在于在COM>规范>Unity>“始终显示菜单”。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 迟到总比没有要好? ###
|
||||
|
||||
开发者计划在Ubuntu14.04 LTS的下一个SRU中反向移植这个选项(假设在测试阶段没有任何意外发生)。
|
||||
|
||||
本地集成菜单(LIM)在Ubuntu 14.04 LTS 首次获得了欣赏,被广泛认为在那些喜欢隐藏方式的和那些不喜欢必须使用鼠标和触摸板的人之间的最佳的折衷方法
|
||||
|
||||
虽然本地集成菜单给我们带来了半路上沉默的批评在统一方面,默认的“淡入/淡出”行为给我们留下了令人发痒的伤痕
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu 过去的几个版本中已经能够看到积极的去解决早期UX的经历过的关切的问题。在经过几年“打算去做”的列表[我们去年终于得到了本地集成菜单][1],以及不支持的通过点击图标实现[减少和恢复Unity启动程序中不支持的应用程序的选项]。
|
||||
|
||||
一年以来我们终于得到一个选项以使应用程序菜单始终显示,无论我们的鼠标在哪里。迟来总比没有好,对不对?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2015/01/ubuntu-15-04-always-show-menu-bar-option
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[JeffDing](https://github.com/JeffDing)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/02/locally-integrated-menus-ubuntu-14-04
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/03/minimize-click-launcher-option-ubuntu-14-04
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,196 @@
|
||||
在linux中如何通过nload来监控网络使用情况
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
nload 是一个免费的linux工具,通过提供两个简单的图形化界面来帮助linux用户和系统管理员来实时监控网络流量以及宽带使用情况:一个作为进入流量,一个作为流出流量.
|
||||
|
||||
我是真的很喜欢用**nload**来在屏幕上显示当前的下载速度,总的流入量和平均下载速度等信息。nload工具的报告图非常容易理解,最重要的是这些信息真的非常有用。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在使用手册上说到,在默认情况下会监控所有网络设备。但是你可以轻松地指定你想要监控的设备,而且可以可以通过方向键头在不同的网络设备之间进行转换。另外还有很多的选项可用,例如 ‘-r’选项确定以毫秒来刷新显示时间间隔(默认时间间隔值是500毫秒),‘-m’选项用来实时显示多个设备(流量图在使用该选项时不会显示), ‘-u’选项用来设置显示流量数字的单元类型,另外还有许多其他的选项将会在该教程中探索和练习。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何将 nload安装到你的linux机器上 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu** 和 **Fedora** 用户可以从默认的软件仓库中容易地安装。
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu上使用以下命令进行安装。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install nload
|
||||
|
||||
在Fedora上使用以下命令进行安装。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install nload
|
||||
|
||||
**CentOS**用户该怎么办呢? 只需要在你的机器上输入以下命令,通用能够达到相同的结果--殊途同归。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install nload
|
||||
|
||||
以下的命令会帮助你在OpenBSD系统中安装nload.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo pkg_add -i nload
|
||||
|
||||
linux机器上的另外一个非常有效的安装软件的方式就是编译源代码,通过下载并安装最新的版本意味着能够获得更好地性能,更酷的特性以及越少的bug数。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何通过源代码安装nload ###
|
||||
|
||||
在从源代码安装nload之前,你需要首先下载源代码。 我通常使用wget工具来进行下载--该工具在许多linux机器上默认可用。该免费工具帮助用户以非交互式的方式从网络上下载文件,并支持以下协议:
|
||||
|
||||
- HTTP
|
||||
- HTTPS
|
||||
- FTP
|
||||
|
||||
通过以下命令来进入到**/tmp**目录中。
|
||||
|
||||
cd /tmp
|
||||
|
||||
然后在你的终端中输入以下命令就可以将最新版本的nload下载到你的linux机器上了。
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不喜欢使用wget工具,也可以通过简单的一个鼠标点击轻松地从[官网][1]上下载源代码。
|
||||
|
||||
由于该软件非常轻巧,其下载过程几乎在瞬间就会完成。接下来的步骤就是通过**tar**工具来将下载的源代码包进行解压。
|
||||
|
||||
tar归档工具可以用来从磁带或硬盘文档中存储或解压文件,该工具具有许多可用的选项,但是我们只需要下面的几个选项来执行我们的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
1. **-x** to extract files from an archive
|
||||
1. **-x** 从文档中解压文件
|
||||
1. **-v** to run in verbose mode
|
||||
1. **-v** 使用繁琐模式运行--用来输入详细信息
|
||||
1. **-f** to specify the files
|
||||
1. **-f** 用来指定文件
|
||||
|
||||
例如:
|
||||
|
||||
tar xvf example.tar
|
||||
|
||||
现在你学会了如何使用tar工具,我可以非常肯定你会知道如何从命令行中解压.tar文档。
|
||||
|
||||
tar xvf nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
之后使用cd命令来进入到nload*目录中
|
||||
|
||||
cd nload*
|
||||
|
||||
在我的系统上看起来是这样的
|
||||
|
||||
oltjano@baby:/tmp/nload-0.7.4$
|
||||
|
||||
然后运行下面这个命令来为你的系统配置包
|
||||
|
||||
./configure
|
||||
|
||||
此时会有一大波僵尸会在你的屏幕上显示出来,下面的一个屏幕截图描述了它的样子。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在上述命令完成之后,通过下面的命令来编译nload。
|
||||
|
||||
make
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
好了,终于....,下载通过以下命令可以将nload安装在你的机器上了。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装好nload之后就是时间来让你学习如何使用它了。
|
||||
|
||||
###如何使用nload###
|
||||
|
||||
我喜欢探索,所以在你的终端输入以下命令.
|
||||
|
||||
nload
|
||||
|
||||
看到了什么?
|
||||
|
||||
我得到了下面的结果。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如上述截图可以看到,我得到了以下信息:
|
||||
### 流入量###
|
||||
|
||||
#### 当前下载速度####
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 平均下载速度####
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 最小下载速度####
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 最大下载速度####
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 总的流入量按字节进行显示####
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 流出量 ###
|
||||
|
||||
类似的同样适用于流出量
|
||||
#### 一些nload有用的选项####
|
||||
|
||||
使用选项
|
||||
-u
|
||||
|
||||
用来设置显示流量单元的类型.
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令会帮助你使用MBit/s显示单元
|
||||
nload -u m
|
||||
|
||||
下面的屏幕截图显示了上述命令的结果.
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
尝试以下命令然后看看有什么结果.
|
||||
|
||||
nload -u g
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
同时还有一个**-U**选项.根据手册描述,该选项基本上与-u选项类似,只是用在合计数据. 我测试了这个命令,老实说,当你需要检查总的流入与流出量时非常有用.
|
||||
|
||||
nload -U G
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
从上面的截图中可以看到,**nload -U G** 使用Gbyte来显示数据总量.
|
||||
|
||||
另外一个我喜欢使用的有用选项是 **-t**. 该选项用来设置刷新显示事件间隔为毫秒,默认值为500毫秒.
|
||||
|
||||
我会通过下面的命令做一些小的实验.
|
||||
nload -t 130
|
||||
|
||||
那么上述命令做了什么呢,它讲刷新显示时间间隔设置为130毫秒. 通常推荐不要讲该时间间隔值设置为小于100毫秒,因为nload在计算过程中可能会生成带错的报告.
|
||||
|
||||
另外的一个选项为 **-a**. 在你想要设置计算平均值的时间窗口秒数长度时使用,默认该值为300秒.
|
||||
|
||||
那么当你想要监控指定的网络设备该如何呢? 非常容易, 想下面这样简单地指定设备或者列出想要监控的设备列表.
|
||||
|
||||
nload wlan0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下面的语法可帮助你监控指定的多个设备.
|
||||
|
||||
nload [options] device1 device2 devicen
|
||||
|
||||
例如,使用下面的命令来监控eth0和eth1.
|
||||
|
||||
nload wlan0 eth0
|
||||
|
||||
如果不带选项来运行nload,那么它会监控监控所有自动检测到的设备,你可以通过左右方向键来显示其中的任何一个设备的信息.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/monitoring-2/monitor-network-usage-nload/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Oltjano Terpollari][a]
|
||||
译者:[theo-l](https://github.com/theo-l)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/oltjano/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ Linux有问必答:如何在Debian或Ubuntu上安装完整的内核源码
|
||||
|
||||
只有在你需要生成一个定制的内核,而且内核源码中的一些内核默认设置要被你调整了的情况下,你才需要完整的内核源码树。
|
||||
|
||||
这里将会解答如何**在Debian或Ubuntu的库中下载并安装完整树结构的内核源码**。虽然你可以在这个网站[https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/][2]下载官方的内核源码,但是发行版软件仓库可以允许你下载包含补丁的内核源码。
|
||||
这里将会解答如何**在Debian或Ubuntu的库中下载并安装完整树结构的内核源码**。你可以在[https://www.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/][2]下载官方的内核源码,不过使用发行版软件仓库可以允许你下载包含补丁的内核源码。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Debian上安装完整的内核源码 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ Linux有问必答:如何在Debian或Ubuntu上安装完整的内核源码
|
||||
|
||||
伴随着完整内核源码(linux_X.X.XX.orig.tar.xz)的还有一些可用的内核补丁(linux_X.X.X+XXX.debian.tar.xz)和源码控制文件(linux_XXXX.dsc),这些都将被下载并存储到当前目录。在.dsc文件中会指出如何给内核源码打补丁。
|
||||
|
||||
当下载完成,以上的命令将会自动调用工具dpkg-source将下载的内核源码解压到当前的目录中,与此同时更具.dsc文件来下补丁。
|
||||
当下载完成,以上的命令将会自动调用工具dpkg-source将下载的内核源码解压到当前的目录中,与此同时根据.dsc文件来下补丁。
|
||||
|
||||
最终完整的内核源码树将会以"linux-X.X.XX"的形式呈现在当前目录中。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Linux有问必答:如何在Debian或Ubuntu上安装完整的内核源码
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install git
|
||||
$ git clone git://kernel.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ubuntu-$(lsb_release --codename | cut -f2).git
|
||||
|
||||
举个例子,如果你使用的是Ubuntu14.04,以上的命令将会查看Git的"ubuntu-trusty"仓库中的代码。
|
||||
举个例子,如果你使用的是Ubuntu 14.04,以上的命令将会查看Git的"ubuntu-trusty"仓库中的代码。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-full-kernel-source-debian-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
设置Ubuntu14.04无密码登录SSH
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
大家好,今天我来向大家介绍如何在可信的Ubuntu12.04上设置无密码登录SSH功能。仅在工作站有正确的(公私)密钥以供匹配时SSH服务端才会允许你登录,反之访问将不会被允许。
|
||||
|
||||
正常情况下,我们需要连上SSH的控制台输入用户名和密码,两者结合使用。如果两者全部正确,我们就可以访问,反之访问被服务端拒绝。不过相比而言还有一种比用密码更安全的登录方式,我们用的不是密码在登录SSH我们用的是密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想使用这个安全的方式,我们只需简单的禁用密码登录并只允许密钥即可。使用这种方式时,客户端计算机上会产生公私一对密钥。接着客户端得把公钥上传到SSH服务端的密要验证文件中去。在访问被授予前,服务器及客户端电脑互验密钥对。如果服务器上的公钥与客服端提交的私钥匹配访问开始,否则访问被拒绝。
|
||||
|
||||
这是获取SSH服务器认证中非常安全的一种做法,如果你想为SSH用户登录实施安全的认证,这也是备受推崇的方式。这里快速的过一遍允许无密码登录SSH的配置过程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.安装Openssh服务端 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们需要更新我们的本地库索引。所以如下所见,我们需要先输入“apt-get update”
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在我们可以通过以下命令安装openssh-server:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install openssh-server
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 开启openssh服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在OpenSSH已经成功安装在Ubuntu14.04操作系统上了之后,我们要启动OpenSSH的服务。以下命令让你启动/开启服务。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service ssh start
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh start
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 配置密钥对 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在我们安装并启动了OpenSSH服务以后。现在终于到了要我们搞定公私钥对的时候了,在终端中运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
|
||||
|
||||
在运行完以上命令了以后,我们完成一系列的提示的任务。首先选择保存密钥路径,按回车将会选择默认路径即家目录的一个隐藏的.ssh文件夹。下一个提示是请输入提醒。我个人将此留白(回车过)。之后密钥对就会创建,大功告成。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在密钥对生成以后,我们需要将**客户端的上的公钥复制到SSH服务端**或者宿主来创建对客户端的信任关系。运行以下命令复制客户端的公钥到服务端。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh-copy-id user@ip_address
|
||||
|
||||
在公钥上传之后,我们现在可以不用通过密码登陆SSH了。为此,我们需要通过以下命令用文本编辑器打开**etc/ssh/ssh_config**。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们需要按照下图所示去到几行注释并进行一些赋值。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 重启SSH服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,在我们配置完SSH服务端后,为了使改动生效我们需要重启SSH服务。在终端或控制台运行以下命令重启。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service ssh restart
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们可以试试不用密码仅用密钥配对的方式登录ssh服务端了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
太好了!我们成功的配置了无密码登录SSH。这是获取SSH服务器认证中非常安全的一种做法,如果你想为SSH但用户登录实施安全的认证这也是备受推崇的方式。所以,如果你还有什么问题或建议,请在意见框中向我们反馈。很欣慰你能读完,祝你SSH登录愉快 :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/setup-passwordless-ssh-logon-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user