mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
Merge pull request #3194 from DongShuaike/master
Translated by DongShuaike 下会不要改文件名哈~~
This commit is contained in:
commit
84565c994d
@ -1,164 +0,0 @@
|
||||
DongShuaike is translating.
|
||||
|
||||
Linux and Unix Test Disk I/O Performance With dd Command
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
How can I use dd command on a Linux to test I/O performance of my hard disk drive? How do I check the performance of a hard drive including the read and write speed on a Linux operating systems?
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the following commands on a Linux or Unix-like systems for simple I/O performance test:
|
||||
|
||||
- **dd command** : It is used to monitor the writing performance of a disk device on a Linux and Unix-like system
|
||||
- **hdparm command** : It is used to get/set hard disk parameters including test the reading and caching performance of a disk device on a Linux based system.
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial you will learn how to use the dd command to test disk I/O performance.
|
||||
|
||||
### Use dd command to monitor the reading and writing performance of a disk device: ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Open a shell prompt.
|
||||
- Or login to a remote server via ssh.
|
||||
- Use the dd command to measure server throughput (write speed) `dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/test1.img bs=1G count=1 oflag=dsync`
|
||||
- Use the dd command to measure server latency `dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/test2.img bs=512 count=1000 oflag=dsync`
|
||||
|
||||
#### Understanding dd command options ####
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, I'm using RAID-10 (Adaptec 5405Z with SAS SSD) array running on a Ubuntu Linux 14.04 LTS server. The basic syntax is
|
||||
|
||||
dd if=/dev/input.file of=/path/to/output.file bs=block-size count=number-of-blocks oflag=dsync
|
||||
## GNU dd syntax ##
|
||||
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/test1.img bs=1G count=1 oflag=dsync
|
||||
## OR alternate syntax for GNU/dd ##
|
||||
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/testALT.img bs=1G count=1 conv=fdatasync
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
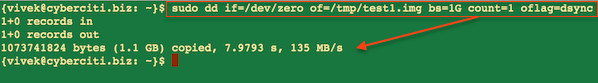
|
||||
Fig.01: Ubuntu Linux Server with RAID10 and testing server throughput with dd
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that one gigabyte was written for the test and 135 MB/s was server throughput for this test. Where,
|
||||
|
||||
- `if=/dev/zero (if=/dev/input.file)` : The name of the input file you want dd the read from.
|
||||
- `of=/tmp/test1.img (of=/path/to/output.file)` : The name of the output file you want dd write the input.file to.
|
||||
- `bs=1G (bs=block-size)` : Set the size of the block you want dd to use. 1 gigabyte was written for the test.
|
||||
- `count=1 (count=number-of-blocks)`: The number of blocks you want dd to read.
|
||||
- `oflag=dsync (oflag=dsync)` : Use synchronized I/O for data. Do not skip this option. This option get rid of caching and gives you good and accurate results
|
||||
- `conv=fdatasyn`: Again, this tells dd to require a complete "sync" once, right before it exits. This option is equivalent to oflag=dsync.
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, 512 bytes were written one thousand times to get RAID10 server latency time:
|
||||
|
||||
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/test2.img bs=512 count=1000 oflag=dsync
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
1000+0 records in
|
||||
1000+0 records out
|
||||
512000 bytes (512 kB) copied, 0.60362 s, 848 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that server throughput and latency time depends upon server/application load too. So I recommend that you run these tests on a newly rebooted server as well as peak time to get better idea about your workload. You can now compare these numbers with all your devices.
|
||||
|
||||
#### But why the server throughput and latency time are so low? ####
|
||||
|
||||
Low values does not mean you are using slow hardware. The value can be low because of the HARDWARE RAID10 controller's cache.
|
||||
|
||||
Use hdparm command to see buffered and cached disk read speed
|
||||
|
||||
I suggest you run the following commands 2 or 3 times Perform timings of device reads for benchmark and comparison purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
### Buffered disk read test for /dev/sda ##
|
||||
hdparm -t /dev/sda1
|
||||
## OR ##
|
||||
hdparm -t /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
To perform timings of cache reads for benchmark and comparison purposes again run the following command 2-3 times (note the -T option):
|
||||
|
||||
## Cache read benchmark for /dev/sda ###
|
||||
hdparm -T /dev/sda1
|
||||
## OR ##
|
||||
hdparm -T /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
OR combine both tests:
|
||||
|
||||
hdparm -Tt /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
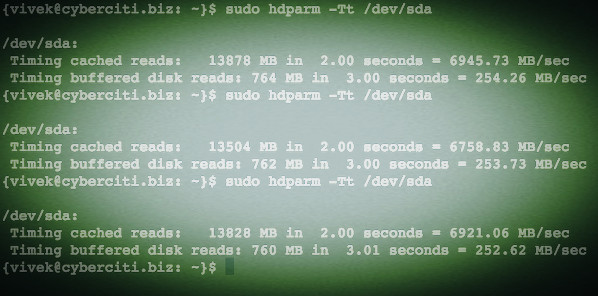
|
||||
Fig.02: Linux hdparm command to test reading and caching disk performance
|
||||
|
||||
Again note that due to filesystems caching on file operations, you will always see high read rates.
|
||||
|
||||
**Use dd command on Linux to test read speed**
|
||||
|
||||
To get accurate read test data, first discard caches before testing by running the following commands:
|
||||
|
||||
flush
|
||||
echo 3 | sudo tee /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
|
||||
time time dd if=/path/to/bigfile of=/dev/null bs=8k
|
||||
|
||||
**Linux Laptop example**
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
### Debian Laptop Throughput With Cache ##
|
||||
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/laptop.bin bs=1G count=1 oflag=direct
|
||||
|
||||
### Deactivate the cache ###
|
||||
hdparm -W0 /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
### Debian Laptop Throughput Without Cache ##
|
||||
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/laptop.bin bs=1G count=1 oflag=direct
|
||||
|
||||
**Apple OS X Unix (Macbook pro) example**
|
||||
|
||||
GNU dd has many more options but OS X/BSD and Unix-like dd command need to run as follows to test real disk I/O and not memory add sync option as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
## Run command 2-3 times to get good results ###
|
||||
time sh -c "dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/testfile bs=100k count=1k && sync"
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
1024+0 records in
|
||||
1024+0 records out
|
||||
104857600 bytes transferred in 0.165040 secs (635346520 bytes/sec)
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m0.241s
|
||||
user 0m0.004s
|
||||
sys 0m0.113s
|
||||
|
||||
So I'm getting 635346520 bytes (635.347 MB/s) write speed on my MBP.
|
||||
|
||||
**Not a fan of command line...?**
|
||||
|
||||
You can use disk utility (gnome-disk-utility) on a Linux or Unix based system to get the same information. The following screenshot is taken from my Fedora Linux v22 VM.
|
||||
|
||||
**Graphical method**
|
||||
|
||||
Click on the "Activities" or press the "Super" key to switch between the Activities overview and desktop. Type "Disks"
|
||||
|
||||
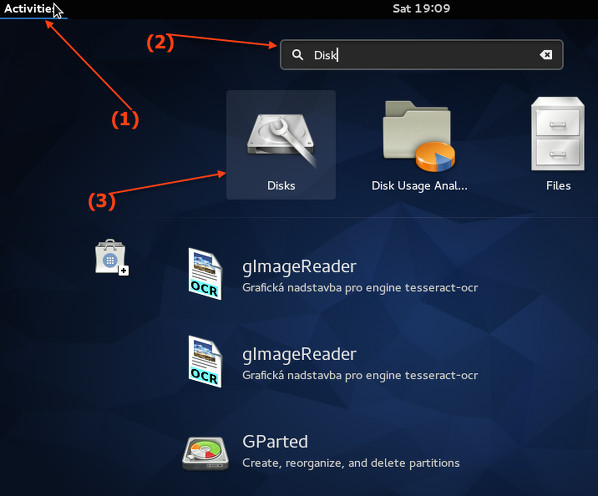
|
||||
Fig.03: Start the Gnome disk utility
|
||||
|
||||
Select your hard disk at left pane and click on configure button and click on "Benchmark partition":
|
||||
|
||||
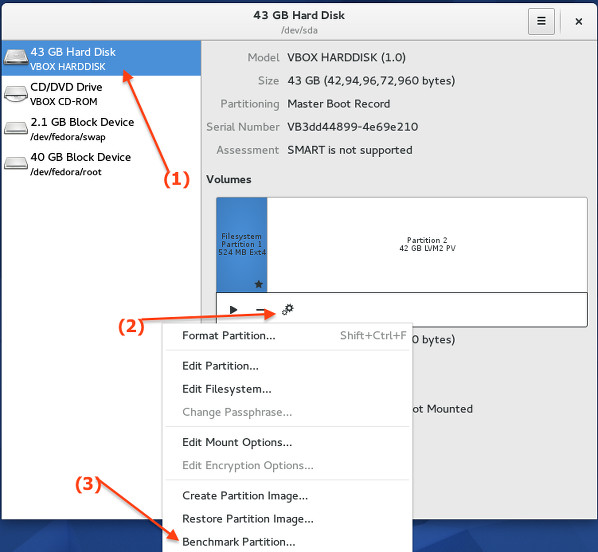
|
||||
Fig.04: Benchmark disk/partition
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, click on the "Start Benchmark..." button (you may be promoted for the admin username and password):
|
||||
|
||||
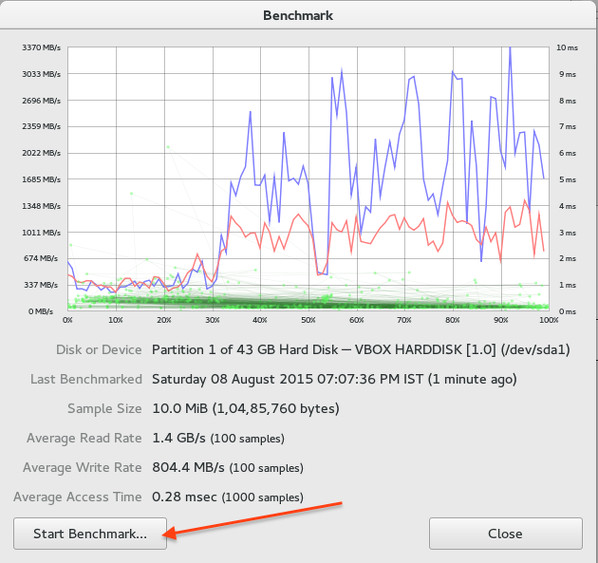
|
||||
Fig.05: Final benchmark result
|
||||
|
||||
Which method and command do you recommend to use?
|
||||
|
||||
- I recommend dd command on all Unix-like systems (`time sh -c "dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/testfile bs=100k count=1k && sync`"
|
||||
- If you are using GNU/Linux use the dd command (`dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/testALT.img bs=1G count=1 conv=fdatasync`)
|
||||
- Make sure you adjust count and bs arguments as per your setup to get a good set of result.
|
||||
- The GUI method is recommended only for Linux/Unix laptop users running Gnome2 or 3 desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-linux-unix-test-disk-performance-with-dd-command/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
|
||||
使用dd命令在Linux和Unix环境下进行硬盘I/O性能检测
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如何使用dd命令测试硬盘的性能?如何在linux操作系统下检测硬盘的读写能力?
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用以下命令在一个Linux或类Unix操作系统上进行简单的I/O性能测试。
|
||||
|
||||
- **dd命令** :它被用来在Linux和类Unix系统下对硬盘设备进行写性能的检测。
|
||||
- **hparm命令**:它被用来获取或设置硬盘参数,包括测试读性能以及缓存性能等。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇指南中,你将会学到如何使用dd命令来测试硬盘性能。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用dd命令来监控硬盘的读写性能:###
|
||||
|
||||
- 打开shell终端(这里貌似不能翻译为终端提示符)。
|
||||
- 通过ssh登录到远程服务器。
|
||||
- 使用dd命令来测量服务器的吞吐率(写速度) `dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/test1.img bs=1G count=1 oflag=dsync`
|
||||
- 使用dd命令测量服务器延迟 `dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/test2.img bs=512 count=1000 oflag=dsync`
|
||||
|
||||
####理解dd命令的选项###
|
||||
|
||||
在这个例子当中,我将使用搭载Ubuntu Linux 14.04 LTS系统的RAID-10(配有SAS SSD的Adaptec 5405Z)服务器阵列来运行。基本语法为:
|
||||
|
||||
dd if=/dev/input.file of=/path/to/output.file bs=block-size count=number-of-blocks oflag=dsync
|
||||
## GNU dd语法 ##
|
||||
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/test1.img bs=1G count=1 oflag=dsync
|
||||
##另外一种GNU dd的语法 ##
|
||||
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/testALT.img bs=1G count=1 conv=fdatasync
|
||||
|
||||
输出样例:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Fig.01: 使用dd命令获取的服务器吞吐率
|
||||
|
||||
请各位注意在这个实验中,我们写入一个G的数据,可以发现,服务器的吞吐率是135 MB/s,这其中
|
||||
|
||||
- `if=/dev/zero (if=/dev/input.file)` :用来设置dd命令读取的输入文件名。
|
||||
- `of=/tmp/test1.img (of=/path/to/output.file)` :dd命令将input.file写入的输出文件的名字。
|
||||
- `bs=1G (bs=block-size)` :设置dd命令读取的块的大小。例子中为1个G。
|
||||
- `count=1 (count=number-of-blocks)`: dd命令读取的块的个数。
|
||||
- `oflag=dsync (oflag=dsync)` :使用同步I/O。不要省略这个选项。这个选项能够帮助你去除caching的影响,以便呈现给你精准的结果。
|
||||
- `conv=fdatasyn`: 这个选项和`oflag=dsync`含义一样。
|
||||
|
||||
在这个例子中,一共写了1000次,每次写入512字节来获得RAID10服务器的延迟时间:
|
||||
|
||||
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/test2.img bs=512 count=1000 oflag=dsync
|
||||
|
||||
输出样例:
|
||||
|
||||
1000+0 records in
|
||||
1000+0 records out
|
||||
512000 bytes (512 kB) copied, 0.60362 s, 848 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
请注意服务器的吞吐率以及延迟时间也取决于服务器/应用的加载。所以我推荐你在一个刚刚重启过并且处于峰值时间的服务器上来运行测试,以便得到更加准确的度量。现在你可以在你的所有设备上互相比较这些测试结果了。
|
||||
|
||||
####为什么服务器的吞吐率和延迟时间都这么差?###
|
||||
|
||||
低的数值并不意味着你在使用差劲的硬件。可能是HARDWARE RAID10的控制器缓存导致的。
|
||||
|
||||
使用hdparm命令来查看硬盘缓存的读速度。
|
||||
|
||||
我建议你运行下面的命令2-3次来对设备读性能进行检测,以作为参照和相互比较:
|
||||
|
||||
### 有缓存的硬盘读性能测试——/dev/sda ###
|
||||
hdparm -t /dev/sda1
|
||||
## 或者 ##
|
||||
hdparm -t /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
然后运行下面这个命令2-3次来对缓存的读性能进行对照性检测:
|
||||
|
||||
## Cache读基准——/dev/sda ###
|
||||
hdparm -T /dev/sda1
|
||||
## 或者 ##
|
||||
hdparm -T /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
或者干脆把两个测试结合起来:
|
||||
|
||||
hdparm -Tt /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
输出样例:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Fig.02: 检测硬盘读入以及缓存性能的Linux hdparm命令
|
||||
|
||||
请再一次注意由于文件文件操作的缓存属性,你将总是会看到很高的读速度。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用dd命令来测试读入速度**
|
||||
|
||||
为了获得精确的读测试数据,首先在测试前运行下列命令,来将缓存设置为无效:
|
||||
|
||||
flush
|
||||
echo 3 | sudo tee /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches
|
||||
time time dd if=/path/to/bigfile of=/dev/null bs=8k
|
||||
|
||||
**笔记本上的示例**
|
||||
|
||||
运行下列命令:
|
||||
|
||||
### Cache存在的Debian系统笔记本吞吐率###
|
||||
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/laptop.bin bs=1G count=1 oflag=direct
|
||||
|
||||
###使cache失效###
|
||||
hdparm -W0 /dev/sda
|
||||
|
||||
###没有Cache的Debian系统笔记本吞吐率###
|
||||
dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/laptop.bin bs=1G count=1 oflag=direct
|
||||
|
||||
**苹果OS X Unix(Macbook pro)的例子**
|
||||
|
||||
GNU dd has many more options but OS X/BSD and Unix-like dd command need to run as follows to test real disk I/O and not memory add sync option as follows:
|
||||
GNU dd命令有其他许多选项但是在 OS X/BSD 以及类Unix中, dd命令需要像下面那样执行来检测去除掉内存地址同步的硬盘真实I/O性能:
|
||||
|
||||
## 运行这个命令2-3次来获得更好地结果 ###
|
||||
time sh -c "dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/testfile bs=100k count=1k && sync"
|
||||
|
||||
输出样例:
|
||||
|
||||
1024+0 records in
|
||||
1024+0 records out
|
||||
104857600 bytes transferred in 0.165040 secs (635346520 bytes/sec)
|
||||
|
||||
real 0m0.241s
|
||||
user 0m0.004s
|
||||
sys 0m0.113s
|
||||
|
||||
本人Macbook Pro的写速度是635346520字节(635.347MB/s)。
|
||||
|
||||
**不喜欢用命令行?^_^**
|
||||
|
||||
你可以在Linux或基于Unix的系统上使用disk utility(gnome-disk-utility)这款工具来得到同样的信息。下面的那个图就是在我的Fedora Linux v22 VM上截取的。
|
||||
|
||||
**图形化方法**
|
||||
|
||||
点击“Activites”或者“Super”按键来在桌面和Activites视图间切换。输入“Disks”
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Fig.03: 打开Gnome硬盘工具
|
||||
|
||||
在左边的面板上选择你的硬盘,点击configure按钮,然后点击“Benchmark partition”:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Fig.04: 评测硬盘/分区
|
||||
|
||||
最后,点击“Start Benchmark...”按钮(你可能被要求输入管理员用户名和密码):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Fig.05: 最终的评测结果
|
||||
|
||||
如果你要问,我推荐使用哪种命令和方法?
|
||||
|
||||
- 我推荐在所有的类Unix系统上使用dd命令(`time sh -c "dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/testfile bs=100k count=1k && sync`)
|
||||
- 如果你在使用GNU/Linux,使用dd命令 (`dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/testALT.img bs=1G count=1 conv=fdatasync`)
|
||||
- 确保你每次使用时,都调整了count以及bs参数以获得更好的结果。
|
||||
- GUI方法只适合桌面系统为Gnome2或Gnome3的Linux/Unix笔记本用户。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/howto-linux-unix-test-disk-performance-with-dd-command/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Vivek Gite
|
||||
译者:[DongShuaike](https://github.com/DongShuaike)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user