", line 1>
-
->>> hello.__code__.co_consts
-
-(None, 'Hello, World!')
-
->>> hello.__code__.co_varnames
-
-()
-
->>> hello.__code__.co_names
-
-('print',)
-
-```
-
-The code object is accessible as the attribute `__code__` on the function and carries a few important attributes:
-
- * `co_consts` is a tuple of any literals that occur in the function body
- * `co_varnames` is a tuple containing the names of any local variables used in the function body
- * `co_names` is a tuple of any non-local names referenced in the function body
-
-
-
-Many bytecode instructions—particularly those that load values to be pushed onto the stack or store values in variables and attributes—use indices in these tuples as their arguments.
-
-So now we can understand the bytecode listing of the `hello()` function:
-
- 1. `LOAD_GLOBAL 0`: tells Python to look up the global object referenced by the name at index 0 of `co_names` (which is the `print` function) and push it onto the evaluation stack
- 2. `LOAD_CONST 1`: takes the literal value at index 1 of `co_consts` and pushes it (the value at index 0 is the literal `None`, which is present in `co_consts` because Python function calls have an implicit return value of `None` if no explicit `return` statement is reached)
- 3. `CALL_FUNCTION 1`: tells Python to call a function; it will need to pop one positional argument off the stack, then the new top-of-stack will be the function to call.
-
-
-
-The "raw" bytecode—as non-human-readable bytes—is also available on the code object as the attribute `co_code`. You can use the list `dis.opname` to look up the names of bytecode instructions from their decimal byte values if you'd like to try to manually disassemble a function.
-
-### Putting bytecode to use
-
-Now that you've read this far, you might be thinking "OK, I guess that's cool, but what's the practical value of knowing this?" Setting aside curiosity for curiosity's sake, understanding Python bytecode is useful in a few ways.
-
-First, understanding Python's execution model helps you reason about your code. People like to joke about C being a kind of "portable assembler," where you can make good guesses about what machine instructions a particular chunk of C source code will turn into. Understanding bytecode will give you the same ability with Python—if you can anticipate what bytecode your Python source code turns into, you can make better decisions about how to write and optimize it.
-
-Second, understanding bytecode is a useful way to answer questions about Python. For example, I often see newer Python programmers wondering why certain constructs are faster than others (like why `{}` is faster than `dict()`). Knowing how to access and read Python bytecode lets you work out the answers (try it: `dis.dis("{}")` versus `dis.dis("dict()")`).
-
-Finally, understanding bytecode and how Python executes it gives a useful perspective on a particular kind of programming that Python programmers don't often engage in: stack-oriented programming. If you've ever used a stack-oriented language like FORTH or Factor, this may be old news, but if you're not familiar with this approach, learning about Python bytecode and understanding how its stack-oriented programming model works is a neat way to broaden your programming knowledge.
-
-### Further reading
-
-If you'd like to learn more about Python bytecode, the Python virtual machine, and how they work, I recommend these resources:
-
- * [Inside the Python Virtual Machine][3] by Obi Ike-Nwosu is a free online book that does a deep dive into the Python interpreter, explaining in detail how Python actually works.
- * [A Python Interpreter Written in Python][4] by Allison Kaptur is a tutorial for building a Python bytecode interpreter in—what else—Python itself, and it implements all the machinery to run Python bytecode.
- * Finally, the CPython interpreter is open source and you can [read through it on GitHub][1]. The implementation of the bytecode interpreter is in the file `Python/ceval.c`. [Here's that file for the Python 3.6.4 release][5]; the bytecode instructions are handled by the `switch` statement beginning on line 1266.
-
-
-
-To learn more, attend James Bennett's talk, [A Bit about Bytes: Understanding Python Bytecode][6], at [PyCon Cleveland 2018][7].
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/18/4/introduction-python-bytecode
-
-作者:[James Bennett][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/ubernostrum
-[1]:https://github.com/python/cpython
-[2]:https://docs.python.org/3/library/dis.html
-[3]:https://leanpub.com/insidethepythonvirtualmachine
-[4]:http://www.aosabook.org/en/500L/a-python-interpreter-written-in-python.html
-[5]:https://github.com/python/cpython/blob/d48ecebad5ac78a1783e09b0d32c211d9754edf4/Python/ceval.c
-[6]:https://us.pycon.org/2018/schedule/presentation/127/
-[7]:https://us.pycon.org/2018/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180424 Things You Should Know About Ubuntu 18.04.md b/sources/tech/20180424 Things You Should Know About Ubuntu 18.04.md
deleted file mode 100644
index c8f958c900..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180424 Things You Should Know About Ubuntu 18.04.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,155 +0,0 @@
-translating by wyxplus
-Things You Should Know About Ubuntu 18.04
-======
-[Ubuntu 18.04 release][1] is just around the corner. I can see lots of questions from Ubuntu users in various Facebook groups and forums. I also organized Q&A sessions on Facebook and Instagram to know what Ubuntu users are wondering about Ubuntu 18.04.
-
-I have tried to answer those frequently asked questions about Ubuntu 18.04 here. I hope it helps clear your doubts if you had any. And if you still have questions, feel free to ask in the comment section below.
-
-### What to expect in Ubuntu 18.04
-
-![Ubuntu 18.04 Frequently Asked Questions][2]
-
-Just for clarification, some of the answers here are influenced by my personal opinion. If you are an experienced/aware Ubuntu user, some of the questions may sound silly to you. If that’s case, just ignore those questions.
-
-#### Can I install Unity on Ubuntu 18.04?
-
-Yes, you can.
-
-Canonical knows that there are people who simply loved Unity. This is why it has made Unity 7 available in the Universe repository. This is a community maintained edition and Ubuntu doesn’t develop it directly.
-
-I advise using the default GNOME first and if you really cannot tolerate it, then go on [installing Unity on Ubuntu 18.04][3].
-
-#### What GNOME version does it have?
-
-At the time of its release, Ubuntu 18.04 has GNOME 3.28.
-
-#### Can I install vanilla GNOME on it?
-
-Yes, you can.
-
-Existing GNOME users might not like the Unity resembling, customized GNOME desktop in Ubuntu 18.04. There are some packages available in Ubuntu’s main and universe repositories that allows you to [install vanilla GNOME on Ubuntu 18.04][4].
-
-#### Has the memory leak in GNOME fixed?
-
-Yes. The [infamous memory leak in GNOME 3.28][5] has been fixed and [Ubuntu is already testing the fix][6].
-
-Just to clarify, the memory leak was not caused by Ubuntu. It was/is impacting all Linux distributions that use GNOME 3.28. A new patch was released under GNOME 3.28.1 to fix this memory leak.
-
-#### How long will Ubuntu 18.04 be supported?
-
-It is a long-term support (LTS) release and like any LTS release, it will be supported for five years. Which means that Ubuntu 18.04 will get security and maintenance updates until April 2023. This is also true for all participating flavors except Ubuntu Studio.
-
-#### When will Ubuntu 18.04 be released?
-
-Ubuntu 18.04 LTS has been released on 26th April. All the participating flavors like Kubuntu, Lubuntu, Xubuntu, Budgie, MATE etc will have their 18.04 release available on the same day.
-
-It seems [Ubuntu Studio will not have 18.04 as LTS release][7].
-
-#### Is it possible to upgrade to Ubuntu 18.04 from 16.04/17.10? Can I upgrade from Ubuntu 16.04 with Unity to Ubuntu 18.04 with GNOME?
-
-Yes, absolutely. Once Ubuntu 18.04 LTS is released, you can easily upgrade to the new version.
-
-If you are using Ubuntu 17.10, make sure that in Software & Updates -> Updates, the ‘Notify me of a new Ubuntu version’ is set to ‘For any new version’.
-
-![Get notified for a new version in Ubuntu][8]
-
-If you are using Ubuntu 16.04, make sure that in Software & Updates -> Updates, the ‘Notify me of a new Ubuntu version’ is set to ‘For long-term support versions’.
-
-![Ubuntu 18.04 upgrade from Ubuntu 16.04][9]
-
-You should get system notification about the availability of the new versions. After that, upgrading to Ubuntu 18.04 is a matter of clicks.
-
-Even if Ubuntu 16.04 was Unity, you can still [upgrade to Ubuntu 18.04][10] GNOME.
-
-#### What does upgrading to Ubuntu 18.04 mean? Will I lose my data?
-
-If you are using Ubuntu 17.10 or Ubuntu 16.04, sooner or later, Ubuntu will notify you that Ubuntu 18.04 is available. If you have a good internet connection that can download 1.5 Gb of data, you can upgrade to Ubuntu 18.04 in a few clicks and in under 30 minutes.
-
-You don’t need to create a new USB and do a fresh install. Once the upgrade procedure finishes, you’ll have the new Ubuntu version available.
-
-Normally, your data, documents etc are safe in the upgrade procedure. However, keeping a backup of your important documents is always a good idea.
-
-#### When will I get to upgrade to Ubuntu 18.04?
-
-If you are using Ubuntu 17.10 and have correct update settings in place (as mentioned in the previous section), you should be notified for upgrading to Ubuntu 18.04 within a few days of Ubuntu 18.04 release. Since Ubuntu servers encounter heavy load on the release day, not everyone gets the upgrade the same day.
-
-For Ubuntu 16.04 users, it may take some weeks before they are officially notified of the availability of Ubuntu 18.04. Usually, this will happen after the first point release Ubuntu 18.04.1. This point release fixes the newly discovered bugs in 18.04.
-
-#### If I upgrade to Ubuntu 18.04 can I downgrade to 17.10 or 16.04?
-
-No, you cannot. While upgrading to the newer version is easy, there is no option to downgrade. If you want to go back to Ubuntu 16.04, you’ll have to do a fresh install.
-
-#### Can I use Ubuntu 18.04 on 32-bit systems?
-
-Yes and no.
-
-If you are already using the 32-bit version of Ubuntu 16.04 or 17.10, you may still get to upgrade to Ubuntu 18.04. However, you won’t find Ubuntu 18.04 bit ISO in 32-bit format anymore. In other words, you cannot do a fresh install of the 32-bit version of Ubuntu 18.04 GNOME.
-
-The good news here is that other official flavors like Ubuntu MATE, Lubuntu etc still have the 32-bit ISO of their new versions.
-
-In any case, if you have a 32-bit system, chances are that your system is weak on hardware. You’ll be better off using lightweight [Ubuntu MATE][11] or [Lubuntu][12] on such system.
-
-#### Where can I download Ubuntu 18.04?
-
-Once 18.04 is released, you can get the ISO image of Ubuntu 18.04 from its website. You have both direct download and torrent options. Other official flavors will be available on their official websites.
-
-#### Should I do a fresh install of Ubuntu 18.04 or upgrade to it from 16.04/17.10?
-
-If you have a choice, make a backup of your data and do a fresh install of Ubuntu 18.04.
-
-Upgrading to 18.04 from an existing version is a convenient option. However, in my opinion, it still keeps some traces/packages of the older version. A fresh install is always cleaner.
-
-For a fresh install, should I install Ubuntu 16.04 or Ubuntu 18.04?
-
-If you are going to install Ubuntu on a system, go for Ubuntu 18.04 instead of 16.04.
-
-Both of them are long-term support release and will be supported for a long time. Ubuntu 16.04 will get maintenance and security updates until 2021 and 18.04 until 2023.
-
-However, I would suggest that you use Ubuntu 18.04. Any LTS release gets [hardware updates for a limited time][13] (two and a half years I think). After that, it only gets maintenance updates. If you have newer hardware, you’ll get better support in 18.04.
-
-Also, many application developers will start focusing on Ubuntu 18.04 soon. Newly created PPAs might only support 18.04 in a few months. Using 18.04 has its advantages over 16.04.
-
-#### Will it be easier to install printer-scanner drivers instead of using the CLI?
-
-I am not an expert when it comes to printers so my opinion is based on my limited knowledge in this field. Most of the new printers support [IPP protocol][14] and thus they should be well supported in Ubuntu 18.04. I cannot say the same about older printers.
-
-#### Does Ubuntu 18.04 have better support for Realtek and other WiFi adapters?
-
-No specific information on this part.
-
-#### What are the system requirements for Ubuntu 18.04?
-
-For the default GNOME version, you should have [4 GB of RAM for a comfortable use][15]. A processor released in last 8 years will work as well. Anything older than that should use a [lightweight Linux distribution][16] such as [Lubuntu][12].
-
-#### Any other questions about Ubuntu 18.04?
-
-If you have any other doubts regarding Ubuntu 18.04, please feel free to leave a comment below. If you think some other information should be added to the list, please let me know.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-18-04-faq/
-
-作者:[Abhishek Prakash][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
-[1]:https://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-18-04-release-features/
-[2]:https://4bds6hergc-flywheel.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/04/ubuntu-18-04-faq-800x450.png
-[3]:https://itsfoss.com/use-unity-ubuntu-17-10/
-[4]:https://itsfoss.com/vanilla-gnome-ubuntu/
-[5]:https://feaneron.com/2018/04/20/the-infamous-gnome-shell-memory-leak/
-[6]:https://community.ubuntu.com/t/help-test-memory-leak-fixes-in-18-04-lts/5251
-[7]:https://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2018/04/ubuntu-studio-plans-to-reboot
-[8]:https://4bds6hergc-flywheel.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/upgrade-ubuntu-2.jpeg
-[9]:https://4bds6hergc-flywheel.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/ubuntu-18-04-upgrade-settings-800x379.png
-[10]:https://itsfoss.com/upgrade-ubuntu-version/
-[11]:https://ubuntu-mate.org/
-[12]:https://lubuntu.net/
-[13]:https://www.ubuntu.com/info/release-end-of-life
-[14]:https://www.pwg.org/ipp/everywhere.html
-[15]:https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Installation/SystemRequirements
-[16]:https://itsfoss.com/lightweight-linux-beginners/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180427 3 Python template libraries compared.md b/sources/tech/20180427 3 Python template libraries compared.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 18a434150b..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180427 3 Python template libraries compared.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,135 +0,0 @@
-3 Python template libraries compared
-======
-
-
-In my day job, I spend a lot of time wrangling data from various sources into human-readable information. While a lot of the time this just takes the form of a spreadsheet or some type of chart or other data visualization, there are other times when it makes sense to present the data instead in a written format.
-
-But a pet peeve of mine is copying and pasting. If you’re moving data from its source to a standardized template, you shouldn’t be copying and pasting either. It’s error-prone, and honestly, it’s not a good use of your time.
-
-So for any piece of information I send out regularly which follows a common pattern, I tend to find some way to automate at least a chunk of it. Maybe that involves creating a few formulas in a spreadsheet, a quick shell script, or some other solution to autofill a template with information pulled from an outside source.
-
-But lately, I’ve been exploring Python templating to do much of the work of creating reports and graphs from other datasets.
-
-Python templating engines are hugely powerful. My use case of simplifying report creation only scratches the surface of what they can be put to work for. Many developers are making use of these tools to build full-fledged web applications and content management systems. But you don’t have to have a grand vision of a complicated web app to make use of Python templating tools.
-
-### Why templating?
-
-Each templating tool is a little different, and you should read the documentation to understand the exact usage. But let’s create a hypothetical example. Let’s say I’d like to create a short page listing all of the Python topics I've written about recently. Something like this:
-```
-html>
-
- head>
-
- title>/title>
-
- /head>
-
- body>
-
- p>/p>
-
- ul>
-
- li>/li>
-
- li>/li>
-
- li>/li>
-
- /ul>
-
- /body>
-
-/html>My Python articlesThese are some of the things I have written about Python:Python GUIsPython IDEsPython web scrapers
-
-```
-
-Simple enough to maintain when it’s just these three items. But what happens when I want to add a fourth, or fifth, or sixty-seventh? Rather than hand-coding this page, could I generate it from a CSV or other data file containing a list of all of my pages? Could I easily create duplicates of this for every topic I've written on? Could I programmatically change the text or title or heading on each one of those pages? That's where a templating engine can come into play.
-
-There are many different options to choose from, and today I'll share with you three, in no particular order: [Mako][6], [Jinja2][7], and [Genshi][8].
-
-### Mako
-
-[Mako][6] is a Python templating tool released under the MIT license that is designed for fast performance (not unlike Jinja2). Mako has been used by Reddit to power their web pages, as well as being the default templating language for web frameworks like Pyramid and Pylons. It's also fairly simple and straightforward to use; you can design templates with just a couple of lines of code. Supporting both Python 2.x and 3.x, it's a powerful and feature-rich tool with [good documentation][9], which I consider a must. Features include filters, inheritance, callable blocks, and a built-in caching system, which could be import for large or complex web projects.
-
-### Jinja2
-
-Jinja2 is another speedy and full-featured option, available for both Python 2.x and 3.x under a BSD license. Jinja2 has a lot of overlap from a feature perspective with Mako, so for a newcomer, your choice between the two may come down to which formatting style you prefer. Jinja2 also compiles your templates to bytecode, and has features like HTML escaping, sandboxing, template inheritance, and the ability to sandbox portions of templates. Its users include Mozilla, SourceForge, NPR, Instagram, and others, and also features [strong documentation][10]. Unlike Mako, which uses Python inline for logic inside your templates, Jinja2 uses its own syntax.
-
-### Genshi
-
-[Genshi][8] is the third option I'll mention. It's really an XML tool which has a strong templating component, so if the data you are working with is already in XML format, or you need to work with formatting beyond a web page, Genshi might be a good solution for you. HTML is basically a type of XML (well, not precisely, but that's beyond the scope of this article and a bit pedantic), so formatting them is quite similar. Since a lot of the data I work with commonly is in one flavor of XML or another, I appreciated working with a tool I could use for multiple things.
-
-The release version currently only supports Python 2.x, although Python 3 support exists in trunk, I would caution you that it does not appear to be receiving active development. Genshi is made available under a BSD license.
-
-### Example
-
-So in our hypothetical example above, rather than update the HTML file every time I write about a new topic, I can update it programmatically. I can create a template, which might look like this:
-```
-html>
-
- head>
-
- title>/title>
-
- /head>
-
- body>
-
- p>/p>
-
- ul>
-
- %for topic in topics:
-
- li>/li>
-
- %endfor
-
- /ul>
-
- /body>
-
-/html>My Python articlesThese are some of the things I have written about Python:%for topic in topics:${topic}%endfor
-
-```
-
-And then I can iterate across each topic with my templating library, in this case, Mako, like this:
-```
-from mako.template import Template
-
-
-
-mytemplate = Template(filename='template.txt')
-
-print(mytemplate.render(topics=("Python GUIs","Python IDEs","Python web scrapers")))
-
-```
-
-Of course, in a real-world usage, rather than listing the contents manually in a variable, I would likely pull them from an outside data source, like a database or an API.
-
-These are not the only Python templating engines out there. If you’re starting down the path of creating a new project which will make heavy use of templates, you’ll want to consider more than just these three. Check out this much more comprehensive list on the [Python wiki][11] for more projects that are worth considering.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/resources/python/template-libraries
-
-作者:[Jason Baker][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/jason-baker
-[1]:https://opensource.com/resources/python?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ
-[2]:https://opensource.com/resources/python/ides?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ
-[3]:https://opensource.com/resources/python/gui-frameworks?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ
-[4]:https://opensource.com/tags/python?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ
-[5]:https://developers.redhat.com/?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ
-[6]:http://www.makotemplates.org/
-[7]:http://jinja.pocoo.org/
-[8]:https://genshi.edgewall.org/
-[9]:http://docs.makotemplates.org/en/latest/
-[10]:http://jinja.pocoo.org/docs/2.10/
-[11]:https://wiki.python.org/moin/Templating
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180428 How to get a core dump for a segfault on Linux.md b/sources/tech/20180428 How to get a core dump for a segfault on Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..71a272c5d4
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20180428 How to get a core dump for a segfault on Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,194 @@
+How to get a core dump for a segfault on Linux
+============================================================
+
+This week at work I spent all week trying to debug a segfault. I’d never done this before, and some of the basic things involved (get a core dump! find the line number that segfaulted!) took me a long time to figure out. So here’s a blog post explaining how to do those things!
+
+At the end of this blog post, you should know how to go from “oh no my program is segfaulting and I have no idea what is happening” to “well I know what its stack / line number was when it segfaulted at at least!“.
+
+### what’s a segfault?
+
+A “segmentation fault” is when your program tries to access memory that it’s not allowed to access, or tries to . This can be caused by:
+
+* trying to dereference a null pointer (you’re not allowed to access the memory address `0`)
+
+* trying to dereference some other pointer that isn’t in your memory
+
+* a C++ vtable pointer that got corrupted and is pointing to the wrong place, which causes the program to try to execute some memory that isn’t executable
+
+* some other things that I don’t understand, like I think misaligned memory accesses can also segfault
+
+This “C++ vtable pointer” thing is what was happening to my segfaulting program. I might explain that in a future blog post because I didn’t know any C++ at the beginning of this week and this vtable lookup thing was a new way for a program to segfault that I didn’t know about.
+
+But! This blog post isn’t about C++ bugs. Let’s talk about the basics, like, how do we even get a core dump?
+
+### step 1: run valgrind
+
+I found the easiest way to figure out why my program is segfaulting was to use valgrind: I ran
+
+```
+valgrind -v your-program
+
+```
+
+and this gave me a stack trace of what happened. Neat!
+
+But I wanted also wanted to do a more in-depth investigation and find out more than just what valgrind was telling me! So I wanted to get a core dump and explore it.
+
+### How to get a core dump
+
+A core dump is a copy of your program’s memory, and it’s useful when you’re trying to debug what went wrong with your problematic program.
+
+When your program segfaults, the Linux kernel will sometimes write a core dump to disk. When I originally tried to get a core dump, I was pretty frustrated for a long time because – Linux wasn’t writing a core dump!! Where was my core dump????
+
+Here’s what I ended up doing:
+
+1. Run `ulimit -c unlimited` before starting my program
+
+2. Run `sudo sysctl -w kernel.core_pattern=/tmp/core-%e.%p.%h.%t`
+
+### ulimit: set the max size of a core dump
+
+`ulimit -c` sets the maximum size of a core dump. It’s often set to 0, which means that the kernel won’t write core dumps at all. It’s in kilobytes. ulimits are per process – you can see a process’s limits by running `cat /proc/PID/limit`
+
+For example these are the limits for a random Firefox process on my system:
+
+```
+$ cat /proc/6309/limits
+Limit Soft Limit Hard Limit Units
+Max cpu time unlimited unlimited seconds
+Max file size unlimited unlimited bytes
+Max data size unlimited unlimited bytes
+Max stack size 8388608 unlimited bytes
+Max core file size 0 unlimited bytes
+Max resident set unlimited unlimited bytes
+Max processes 30571 30571 processes
+Max open files 1024 1048576 files
+Max locked memory 65536 65536 bytes
+Max address space unlimited unlimited bytes
+Max file locks unlimited unlimited locks
+Max pending signals 30571 30571 signals
+Max msgqueue size 819200 819200 bytes
+Max nice priority 0 0
+Max realtime priority 0 0
+Max realtime timeout unlimited unlimited us
+
+```
+
+The kernel uses the soft limit (in this case, “max core file size = 0”) when deciding how big of a core file to write. You can increase the soft limit up to the hard limit using the `ulimit` shell builtin (`ulimit -c unlimited`!)
+
+### kernel.core_pattern: where core dumps are written
+
+`kernel.core_pattern` is a kernel parameter or a “sysctl setting” that controls where the Linux kernel writes core dumps to disk.
+
+Kernel parameters are a way to set global settings on your system. You can get a list of every kernel parameter by running `sysctl -a`, or use `sysctl kernel.core_pattern` to look at the `kernel.core_pattern` setting specifically.
+
+So `sysctl -w kernel.core_pattern=/tmp/core-%e.%p.%h.%t` will write core dumps to `/tmp/core-`
+
+If you want to know more about what these `%e`, `%p` parameters read, see [man core][1].
+
+It’s important to know that `kernel.core_pattern` is a global settings – it’s good to be a little careful about changing it because it’s possible that other systems depend on it being set a certain way.
+
+### kernel.core_pattern & Ubuntu
+
+By default on Ubuntu systems, this is what `kernel.core_pattern` is set to
+
+```
+$ sysctl kernel.core_pattern
+kernel.core_pattern = |/usr/share/apport/apport %p %s %c %d %P
+
+```
+
+This caused me a lot of confusion (what is this apport thing and what is it doing with my core dumps??) so here’s what I learned about this:
+
+* Ubuntu uses a system called “apport” to report crashes in apt packages
+
+* Setting `kernel.core_pattern=|/usr/share/apport/apport %p %s %c %d %P`means that core dumps will be piped to `apport`
+
+* apport has logs in /var/log/apport.log
+
+* apport by default will ignore crashes from binaries that aren’t part of an Ubuntu packages
+
+I ended up just overriding this Apport business and setting `kernel.core_pattern` to `sysctl -w kernel.core_pattern=/tmp/core-%e.%p.%h.%t` because I was on a dev machine, I didn’t care whether Apport was working on not, and I didn’t feel like trying to convince Apport to give me my core dumps.
+
+### So you have a core dump. Now what?
+
+Okay, now we know about ulimits and `kernel.core_pattern` and you have actually have a core dump file on disk in `/tmp`. Amazing! Now what??? We still don’t know why the program segfaulted!
+
+The next step is to open the core file with `gdb` and get a backtrace.
+
+### Getting a backtrace from gdb
+
+You can open a core file with gdb like this:
+
+```
+$ gdb -c my_core_file
+
+```
+
+Next, we want to know what the stack was when the program crashed. Running `bt` at the gdb prompt will give you a backtrace. In my case gdb hadn’t loaded symbols for the binary, so it was just like `??????`. Luckily, loading symbols fixed it.
+
+Here’s how to load debugging symbols.
+
+```
+symbol-file /path/to/my/binary
+sharedlibrary
+
+```
+
+This loads symbols from the binary and from any shared libraries the binary uses. Once I did that, gdb gave me a beautiful stack trace with line numbers when I ran `bt`!!!
+
+If you want this to work, the binary should be compiled with debugging symbols. Having line numbers in your stack traces is extremely helpful when trying to figure out why a program crashed :)
+
+### look at the stack for every thread
+
+Here’s how to get the stack for every thread in gdb!
+
+```
+thread apply all bt full
+
+```
+
+### gdb + core dumps = amazing
+
+If you have a core dump & debugging symbols and gdb, you are in an amazing situation!! You can go up and down the call stack, print out variables, and poke around in memory to see what happened. It’s the best.
+
+If you are still working on being a gdb wizard, you can also just print out the stack trace with `bt` and that’s okay :)
+
+### ASAN
+
+Another path to figuring out your segfault is to do one compile the program with AddressSanitizer (“ASAN”) (`$CC -fsanitize=address`) and run it. I’m not going to discuss that in this post because this is already pretty long and anyway in my case the segfault disappeared with ASAN turned on for some reason, possibly because the ASAN build used a different memory allocator (system malloc instead of tcmalloc).
+
+I might write about ASAN more in the future if I ever get it to work :)
+
+### getting a stack trace from a core dump is pretty approachable!
+
+This blog post sounds like a lot and I was pretty confused when I was doing it but really there aren’t all that many steps to getting a stack trace out of a segfaulting program:
+
+1. try valgrind
+
+if that doesn’t work, or if you want to have a core dump to investigate:
+
+1. make sure the binary is compiled with debugging symbols
+
+2. set `ulimit` and `kernel.core_pattern` correctly
+
+3. run the program
+
+4. open your core dump with `gdb`, load the symbols, and run `bt`
+
+5. try to figure out what happened!!
+
+I was able using gdb to figure out that there was a C++ vtable entry that is pointing to some corrupt memory, which was somewhat helpful and helped me feel like I understood C++ a bit better. Maybe we’ll talk more about how to use gdb to figure things out another day!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://jvns.ca/blog/2018/04/28/debugging-a-segfault-on-linux/
+
+作者:[Julia Evans ][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://jvns.ca/about/
+[1]:http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man5/core.5.html
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180504 A Beginners Guide To Cron Jobs.md b/sources/tech/20180504 A Beginners Guide To Cron Jobs.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 58cf8611fd..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180504 A Beginners Guide To Cron Jobs.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,231 +0,0 @@
-KevinSJ Translating
-A Beginners Guide To Cron Jobs
-======
-
-
-**Cron** is one of the most useful utility that you can find in any Unix-like operating system. It is used to schedule commands at a specific time. These scheduled commands or tasks are known as “Cron Jobs”. Cron is generally used for running scheduled backups, monitoring disk space, deleting files (for example log files) periodically which are no longer required, running system maintenance tasks and a lot more. In this brief guide, we will see the basic usage of Cron Jobs in Linux.
-
-### The Beginners Guide To Cron Jobs
-
-The typical format of a cron job is:
-```
-Minute(0-59) Hour(0-24) Day_of_month(1-31) Month(1-12) Day_of_week(0-6) Command_to_execute
-
-```
-
-Just memorize the cron job format or print the following illustration and keep it in your desk.
-
-![][2]
-
-In the above picture, the asterisks refers the specific blocks of time.
-
-To display the contents of the **crontab** file of the currently logged in user:
-```
-$ crontab -l
-
-```
-
-To edit the current user’s cron jobs, do:
-```
-$ crontab -e
-
-```
-
-If it is the first time, you will be asked to editor to edit the jobs.
-```
-no crontab for sk - using an empty one
-
-Select an editor. To change later, run 'select-editor'.
- 1. /bin/nano <---- easiest
- 2. /usr/bin/vim.basic
- 3. /usr/bin/vim.tiny
- 4. /bin/ed
-
-Choose 1-4 [1]:
-
-```
-
-Choose any one that suits you. Here it is how a sample crontab file looks like.
-
-![][3]
-
-In this file, you need to add your cron jobs.
-
-To edit the crontab of a different user, for example ostechnix, do:
-```
-$ crontab -u ostechnix -e
-
-```
-
-Let us see some examples.
-
-To run a cron job **every minute** , the format should be like below.
-```
-* * * * *
-
-```
-
-To run cron job every 5 minute, add the following in your crontab file.
-```
-*/5 * * * *
-
-```
-
-To run a cron job at every quarter hour (every 15th minute), add this:
-```
-*/15 * * * *
-
-```
-
-To run a cron job every hour at 30 minutes, run:
-```
-30 * * * *
-
-```
-
-You can also define multiple time intervals separated by commas. For example, the following cron job will run three times every hour, at minutes 0, 5 and 10:
-```
-0,5,10 * * * *
-
-```
-
-Run a cron job every half hour:
-```
-*/30 * * * *
-
-```
-
-Run a job every hour:
-```
-0 * * * *
-
-```
-
-Run a job every 2 hours:
-```
-0 */2 * * *
-
-```
-
-Run a job every day (It will run at 00:00):
-```
-0 0 * * *
-
-```
-
-Run a job every day at 3am:
-```
-0 3 * * *
-
-```
-
-Run a job every sunday:
-```
-0 0 * * SUN
-
-```
-
-Or,
-```
-0 0 * * 0
-
-```
-
-It will run at exactly at 00:00 on Sunday.
-
-Run a job on every day-of-week from Monday through Friday i.e every weekday:
-```
-0 0 * * 1-5
-
-```
-
-The job will start at 00:00.
-
-Run a job every month:
-```
-0 0 1 * *
-
-```
-
-Run a job at 16:15 on day-of-month 1:
-```
-15 16 1 * *
-
-```
-
-Run a job at every quarter i.e on day-of-month 1 in every 3rd month:
-```
-0 0 1 */3 *
-
-```
-
-Run a job on a specific month at a specific time:
-```
-5 0 * 4 *
-
-```
-
-The job will start at 00:05 in April.
-
-Run a job every 6 months:
-```
-0 0 1 */6 *
-
-```
-
-This cron job will start at 00:00 on day-of-month 1 in every 6th month.
-
-Run a job every year:
-```
-0 0 1 1 *
-
-```
-
-This cron job will start at 00:00 on day-of-month 1 in January.
-
-We can also use the following strings to define job.
-
-@reboot Run once, at startup. @yearly Run once a year. @annually (same as @yearly). @monthly Run once a month. @weekly Run once a week. @daily Run once a day. @midnight (same as @daily). @hourly Run once an hour.
-
-For example, to run a job every time the server is rebooted, add this line in your crontab file.
-```
-@reboot
-
-```
-
-To remove all cron jobs for the current user:
-```
-$ crontab -r
-
-```
-
-There is also a dedicated website named [**crontab.guru**][4] for learning cron jobs examples. This site provides a lot of cron job examples.
-
-For more details, check man pages.
-```
-$ man crontab
-
-```
-
-And, that’s all for now. At this point, you might have a basic understanding of cron jobs and how to use them in real time. More good stuffs to come. Stay tuned!!
-
-Cheers!
-
-
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://www.ostechnix.com/a-beginners-guide-to-cron-jobs/
-
-作者:[SK][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
-[1]:data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7
-[2]:http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/cron-job-format-1.png
-[3]:http://www.ostechnix.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/cron-jobs-1.png
-[4]:https://crontab.guru/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180507 4 Firefox extensions to install now.md b/sources/tech/20180507 4 Firefox extensions to install now.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 77032f0345..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180507 4 Firefox extensions to install now.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
-4 Firefox extensions to install now
-======
-
-As I mentioned in my [original article][1] on Firefox extensions, the web browser has become a critical component of the computing experience for many users. Modern browsers have evolved into powerful and extensible platforms, and extensions can add or modify their functionality. Extensions for Firefox are built using the WebExtensions API, a cross-browser development system.
-
-In the first article, I asked readers: "Which extensions should you install?" To reiterate, that decision largely comes down to how you use your browser, your views on privacy, how much you trust extension developers, and other personal preferences. Since that article was published, one extension I recommended (Xmarks) has been discontinued. Additionally, that article received a ton of feedback that has been taken into account for this update.
-
-Once again, I'd like to point out that browser extensions often require the ability to read and/or change everything on the web pages you visit. You should consider the ramifications of this very carefully. If an extension has modify access to all the web pages you visit, it could act as a keylogger, intercept credit card information, track you online, insert advertisements, and perform a variety of other nefarious activities. That doesn't mean every extension will surreptitiously do these things, but you should carefully consider the installation source, the permissions involved, your risk profile, and other factors before you install any extension. Keep in mind you can use profiles to manage how an extension impacts your attack surface—for example, using a dedicated profile with no extensions to perform tasks such as online banking.
-
-With that in mind, here are four open source Firefox extensions you may want to consider.
-
-### uBlock Origin
-
-![ublock origin ad blocker screenshot][2]
-
-My first recommendation remains unchanged. [uBlock Origin][3] is a fast, low memory, wide-spectrum blocker that allows you to not only block ads but also enforce your own content filtering. The default behavior of uBlock Origin is to block ads, trackers, and malware sites using multiple, predefined filter lists. From there it allows you to arbitrarily add lists and rules, or even lock down to a default-deny mode. Despite being powerful, the extension has proven to be efficient and performant. It continues to be updated regularly and is one of the best options available for this functionality.
-
-### Privacy Badger
-
-![privacy badger ad blocker][4]
-
-My second recommendation also remains unchanged. If anything, privacy has been brought even more to the forefront since my previous article, making this extension an easy recommendation. As the name indicates, [Privacy Badger][5] is a privacy-focused extension that blocks ads and other third-party trackers. It's a project of the Electronic Freedom Foundation, which says:
-
-> "Privacy Badger was born out of our desire to be able to recommend a single extension that would automatically analyze and block any tracker or ad that violated the principle of user consent; which could function well without any settings, knowledge, or configuration by the user; which is produced by an organization that is unambiguously working for its users rather than for advertisers; and which uses algorithmic methods to decide what is and isn't tracking."
-
-Why is Privacy Badger on this list when the previous item may seem similar? A couple reasons. The first is that it fundamentally works differently than uBlock Origin. The second is that a practice of defense in depth is a sound policy to follow. Speaking of defense in depth, the EFF also maintains [HTTPS Everywhere][6] to automatically ensure https is used for many major websites. When you're installing Privacy Badger, you may want to consider HTTPS Everywhere as well.
-
-In case you were starting to think this article was simply going to be a rehash of the last one, here's where my recommendations diverge.
-
-### Bitwarden
-
-![Bitwarden][7]
-
-When recommending LastPass in the previous article, I mentioned it was likely going to be a controversial selection. That certainly proved true. Whether you should use a password manager at all—and if you do, whether you should choose one that has a browser plugin—is a hotly debated topic, and the answer very much depends on your personal risk profile. I asserted that most casual computer users should use one because it's much better than the most common alternative: using the same weak password everywhere. I still believe that.
-
-[Bitwarden][8] has really matured since the last time I checked it out. Like LastPass, it is user-friendly, supports two-factor authentication, and is reasonably secure. Unlike LastPass, it is [open source][9]. It can be used with or without the browser plugin and supports importing from other solutions including LastPass. The core functionality is completely free, and there is a premium version that is $10/year.
-
-### Vimium-FF
-
-![Vimium][10]
-
-[Vimium][11] is another open source extension that provides Firefox keyboard shortcuts for navigation and control in the spirit of Vim. They call it "The Hacker's Browser." Modifier keys are specified as **< c-x>**, **< m-x>**, and **< a-x>** for Ctrl+x, Meta+x, and Alt+x, respectively, and the defaults can be easily customized. Once you have Vimium installed, you can see this list of key bindings at any time by typing **?**. Note that if you prefer Emacs, there are also a couple of extensions for those keybindings as well. Either way, I think keyboard shortcuts are an underutilized productivity booster.
-
-### Bonus: Grammarly
-
-Not everyone is lucky enough to write a column on Opensource.com—although you should seriously consider writing for the site; if you have questions, are interested, or would like a mentor, reach out and let's chat. But even without a column to write, proper grammar is beneficial in a large variety of situations. Enter [Grammarly][12]. This extension is not open source, unfortunately, but it does make sure everything you type is clear, effective, and mistake-free. It does this by scanning your text for common and complex grammatical mistakes, spanning everything from subject-verb agreement to article use to modifier placement. Basic functionality is free, with a premium version with additional checks available for a monthly charge. I used it for this article and it caught multiple errors that my proofreading didn't.
-
-Again, Grammarly is the only extension included on this list that is not open source, so if you know of a similar high-quality open source replacement, let us know in the comments.
-
-These extensions are ones I've found useful and recommend to others. Let me know in the comments what you think of the updated recommendations.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/18/5/firefox-extensions
-
-作者:[Jeremy Garcia][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/jeremy-garcia
-[1]:https://opensource.com/article/18/1/top-5-firefox-extensions
-[2]:https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/panopoly_image_original/public/ublock.png?itok=_QFEbDmq (ublock origin ad blocker screenshot)
-[3]:https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/ublock-origin/
-[4]:https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/panopoly_image_original/public/images/life-uploads/privacy_badger_1.0.1.png?itok=qZXQeKtc (privacy badger ad blocker screenshot)
-[5]:https://www.eff.org/privacybadger
-[6]:https://www.eff.org/https-everywhere
-[7]:https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/panopoly_image_original/public/u128651/bitwarden.png?itok=gZPrCYoi (Bitwarden)
-[8]:https://bitwarden.com/
-[9]:https://github.com/bitwarden
-[10]:https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/panopoly_image_original/public/u128651/vimium.png?itok=QRESXjWG (Vimium)
-[11]:https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/vimium-ff/
-[12]:https://www.grammarly.com/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180510 Creating small containers with Buildah.md b/sources/tech/20180510 Creating small containers with Buildah.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 9b8a550e7e..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180510 Creating small containers with Buildah.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,100 +0,0 @@
-pinewall translating
-
-Creating small containers with Buildah
-======
-
-I recently joined Red Hat after many years working for another tech company. In my previous job, I developed a number of different software products that were successful but proprietary. Not only were we legally compelled to not share the software outside of the company, we often didn’t even share it within the company. At the time, that made complete sense to me: The company spent time, energy, and budget developing the software, so they should protect and claim the rewards it garnered.
-
-Fast-forward to a year ago, when I joined Red Hat and developed a completely different mindset. One of the first things I jumped into was the [Buildah project][1]. It facilitates building Open Container Initiative (OCI) images, and it is especially good at allowing you to tailor the size of the image that is created. At that time Buildah was in its very early stages, and there were some warts here and there that weren’t quite production-ready.
-
-Being new to the project, I made a few minor changes, then asked where the company’s internal git repository was so that I could push my changes. The answer: Nothing internal, just push your changes to GitHub. I was baffled—sending my changes out to GitHub would mean anyone could look at that code and use it for their own projects. Plus, the code still had a few warts, so that just seemed so counterintuitive. But being the new guy, I shook my head in wonder and pushed the changes out.
-
-A year later, I’m now convinced of the power and value of open source software. I’m still working on Buildah, and we recently had an issue that illustrates that power and value. The issue, titled [Buildah images not so small?][2] , was raised by Tim Dudgeon (@tdudgeon). To summarize, he noted that images created by Buildah were bigger than those created by Docker, even though the Buildah images didn’t contain the extra "fluff" he saw in the Docker images.
-
-For comparison he first did:
-```
-$ docker pull centos:7
-$ docker images
-REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
-docker.io/centos 7 2d194b392dd1 2 weeks ago 195 MB
-```
-
-He noted that the size of the Docker image was 195MB. Tim then created a minimal (scratch) image using Buildah, with only the `coreutils` and `bash` packages added to the image, using the following script:
-```
-$ cat ./buildah-base.sh
-#!/bin/bash
-
-set -x
-
-# build a minimal image
-newcontainer=$(buildah from scratch)
-scratchmnt=$(buildah mount $newcontainer)
-
-# install the packages
-yum install --installroot $scratchmnt bash coreutils --releasever 7 --setopt install_weak_deps=false -y
-yum clean all -y --installroot $scratchmnt --releasever 7
-
-sudo buildah config --cmd /bin/bash $newcontainer
-
-# set some config info
-buildah config --label name=centos-base $newcontainer
-
-# commit the image
-buildah unmount $newcontainer
-buildah commit $newcontainer centos-base
-
-$ sudo ./buildah-base.sh
-
-$ sudo buildah images
-IMAGE ID IMAGE NAME CREATED AT SIZE
-8379315d3e3e docker.io/library/centos-base:latest Mar 25, 2018 17:08 212.1 MB
-```
-
-Tim wondered why the image was 17MB larger, because `python` and `yum` were not installed in the Buildah image, whereas they were installed in the Docker image. This set off quite the discussion in the GitHub issue, as it was not at all an expected result.
-
-What was great about the discussion was that not only were Red Hat folks involved, but several others from outside as well. In particular, a lot of great discussion and investigation was led by GitHub user @pixdrift, who noted that the documentation and locale-archive were chewing up a little more than 100MB of space in the Buildah image. Pixdrift suggested forcing locale in the yum installer and provided this updated `buildah-bash.sh` script with those changes:
-```
-#!/bin/bash
-
-set -x
-
-# build a minimal image
-newcontainer=$(buildah from scratch)
-scratchmnt=$(buildah mount $newcontainer)
-
-# install the packages
-yum install --installroot $scratchmnt bash coreutils --releasever 7 --setopt=install_weak_deps=false --setopt=tsflags=nodocs --setopt=override_install_langs=en_US.utf8 -y
-yum clean all -y --installroot $scratchmnt --releasever 7
-
-sudo buildah config --cmd /bin/bash $newcontainer
-
-# set some config info
-buildah config --label name=centos-base $newcontainer
-
-# commit the image
-buildah unmount $newcontainer
-buildah commit $newcontainer centos-base
-```
-
-When Tim ran this new script, the image size shrank to 92MB, shedding 120MB from the original Buildah image size and getting closer to the expected size; however, engineers being engineers, a size savings of 56% wasn’t enough. The discussion went further, involving how to remove individual locale packages to save even more space. To see more details of the discussion, click the [Buildah images not so small?][2] link. Who knows—maybe you’ll have a helpful tip, or better yet, become a contributor for Buildah. On a side note, this solution illustrates how the Buildah software can be used to quickly and easily create a minimally sized container that's loaded only with the software that you need to do your job efficiently. As a bonus, it doesn’t require a daemon to be running.
-
-This image-sizing issue drove home the power of open source software for me. A number of people from different companies all collaborated to solve a problem through open discussion in a little over a day. Although no code changes were created to address this particular issue, there have been many code contributions to Buildah from contributors outside of Red Hat, and this has helped to make the project even better. These contributions have served to get a wider variety of talented people to look at the code than ever would have if it were a proprietary piece of software stuck in a private git repository. It’s taken only a year to convert me to the [open source way][3], and I don’t think I could ever go back.
-
-This article was originally posted at [Project Atomic][4]. Reposted with permission.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/18/5/containers-buildah
-
-作者:[Tom Sweeney][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/tomsweeneyredhat
-[1]:https://github.com/projectatomic/buildah
-[2]:https://github.com/projectatomic/buildah/issues/532
-[3]:https://twitter.com/opensourceway
-[4]:http://www.projectatomic.io/blog/2018/04/open-source-what-a-concept/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180514 MapTool- A robust, flexible virtual tabletop for RPGs.md b/sources/tech/20180514 MapTool- A robust, flexible virtual tabletop for RPGs.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..4786da0b50
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20180514 MapTool- A robust, flexible virtual tabletop for RPGs.md
@@ -0,0 +1,216 @@
+MapTool: A robust, flexible virtual tabletop for RPGs
+======
+
+
+
+When I was looking for a virtual tabletop for role-playing games (RPGs), either for local play or for playing on a network with family and friends around the world, I had several criteria. First, I wanted a platform I could use offline while I prepped a campaign. Second, I didn't want something that came with the burden of being a social network. I wanted the equivalent of a [Sword Coast][1] campaign-setting [boxed set][2] that I could put on my digital "shelf" and use when I wanted, how I wanted.
+
+I looked at it this way: I purchased [AD&D 2nd edition][3] as a hardcover book, so even though there have since been many great releases, I can still play AD&D 2nd edition today. The same goes for my digital life. When I want to use my digital maps and tokens or go back to an old campaign, I want access to them regardless of circumstance.
+
+
+
+### Virtual tabletop
+
+[MapTool][4] is the flagship product of the RPTools software suite. It's a Java application, so it runs on any operating system that can run Java, which is basically every computer. It's also open source and costs nothing to use, although RPTools accepts [donations][5] if you're so inclined.
+
+### Installing MapTool
+
+Download MapTool from [rptools.net][6].
+
+It's likely that you already have Java installed; if not, download and install it from [java.net][7]. If you're not sure whether you have it installed or not, you can download MapTool first, try to run it, and install Java if it fails to run.
+
+### Using MapTool
+
+If you're a game master (GM), MapTool is a great way to provide strategic maps for battles and exploration without investing in physical maps, tokens, or miniatures.
+
+MapTool is a full-featured virtual tabletop. You can load maps into it, import custom tokens, track initiative order and health, and save campaigns. You can use it locally at your game table, or you can share your session with remote gamers so they can follow along. There are other virtual tabletops out there, but MapTool is the only one you own, part and parcel.
+
+To load a map into MapTool, all you need is a PNG or JPEG version of a map.
+
+ 1. Launch MapTool, then go to the **Map** menu and select **New Map**.
+ 2. In the **Map Properties** window that appears, click the **Map** button.
+ 3. Click the **Filesystem** button in the bottom-left corner to locate your map graphic on your hard drive.
+
+
+
+If you have no digital maps yet, there are dozens of map packs available from [Open Gaming Store][8], so you're sure to find a map regardless of where your adventure path may take you.
+
+MapTool, like most virtual tabletops, expects a PNG or JPEG. I maintain a simple [Image Magick][9] script to convert maps from PDF to PNG. The script runs on Linux, BSD, or Mac and is probably also easily adapted to PowerShell.
+```
+#!/usr/bin/env bash
+
+#GNU All-Permissive http://www.gnu.org/licenses
+
+
+
+CMD=`which convert` || echo "Image Magick not found in PATH."
+
+ARG=("${@}")
+
+ARRAYSIZE=${#ARG[*]}
+
+
+
+while [ True ]; do
+
+ for item in "${ARG[@]}"; do
+
+$CMD "${item}" `basename "${item}" .pdf`.jpg || \
+
+$CMD "${item}" `basename "${item}" .PDF`.jpg
+
+ done
+
+ done
+
+exit
+
+```
+
+If running code like that scares you, there are plenty of PDF-to-image converters, like [GIMP][10], for manually converting a PDF to PNG or JPEG on an as-needed basis.
+
+#### Adding tokens
+
+Now that you have a map loaded, it's time to add player characters (PCs) and non-player characters (NPCs). MapTool ships with a modest selection of token graphics, but you can always create and use your own or download more from the internet. In fact, the RPTools website recently linked to [ImmortalNights][11], a website by artist Devin Night, with over 100 tokens for free and purchase.
+
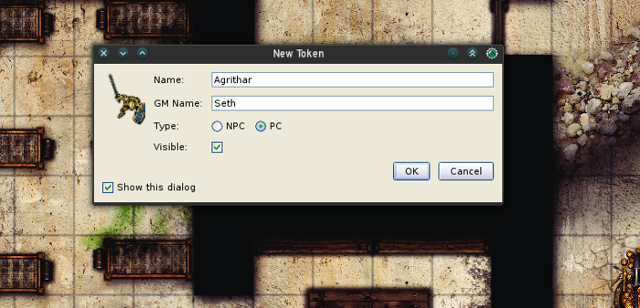
+ 1. Click the **Tokens** folder icon in the MapTool **Resource Library** panel.
+ 2. In the panel just beneath the **Resource Library** panel, the default tokens appear. You can add your own tokens using the **Add resources to library** option in the **File** menu.
+ 3. In the **New token** pop-up dialogue box, give the token a name and PC or NPC designation.
+
+
+
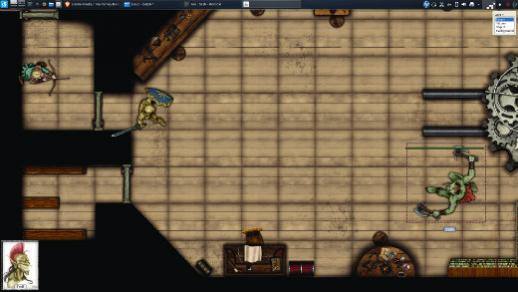
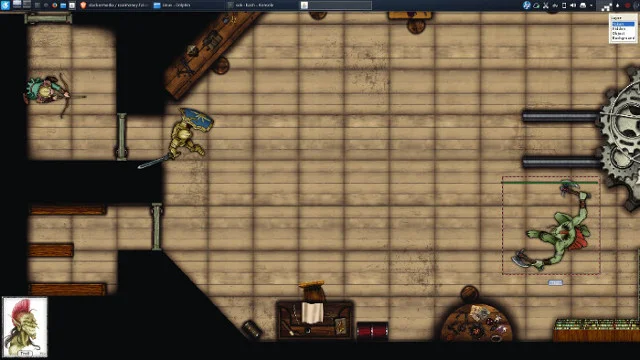
+ 4. Once the token is on the map, it should align perfectly with the map grid. If it doesn't, you can adjust the grid.
+ 5. Right-click on the token to adjust its rotation, size, and other attributes.
+
+
+
+#### Adjusting the grid
+
+By default, MapTool provides an invisible 50x50 square grid over any map. If your map graphic already has a grid on it, you can adjust MapTool's grid to match your graphic.
+
+ 1. Select **Adjust grid** in the **Map** menu. A grid overlay appears over your map.
+ 2. Click and drag the overlay grid so one overlay square sits inside one of your map graphic's grid squares.
+ 3. Adjust the **Grid Size** pixel value in the property box in the top-right corner of the MapTool window.
+ 4. When finished, click the property box's **Close** button.
+
+
+
+You can set the default grid size using the **Preferences** selection in the **Edit** menu. For instance, I do this for [Paizo][12] maps on my 96dpi screen.
+
+MapTool's default assumes each grid block is a five-foot square, but you can adjust that if you're using a wide area representing long-distance travel or if you've drawn a custom map to your own scale.
+
+### Sharing the screen locally
+
+While you can use MapTool solely as a GM tool to help keep track of character positions, you can also share it with your players.
+
+If you're using MapTool as a digital replacement for physical maps at your game table, you can just plug your computer into your TV. That's the simplest way to share the map with everyone at your table.
+
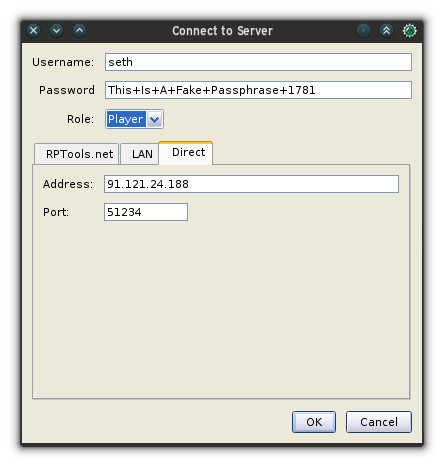
+Another alternative is to use MapTool's built-in server. If your players are physically sitting in the same room and on the same network, select **Start server** from the **File** menu.
+
+The only required field is a name for the GM. The default port is 51234. If you don't know what that means, that's OK; a port is just a flag identifying where a service like MapTool is running.
+
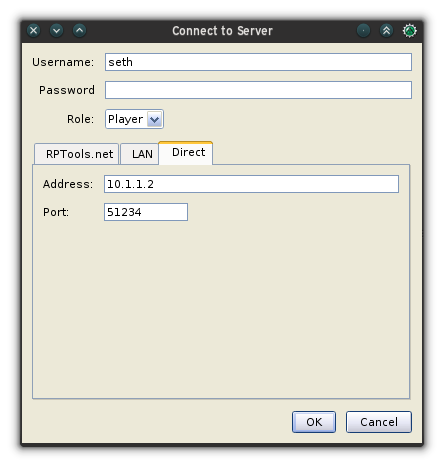
+Once your MapTool server is started, players can connect by selecting **Connect to server** in the **File** menu.
+
+
+
+A name is required, but no password is needed unless the GM has set one when starting the server.
+
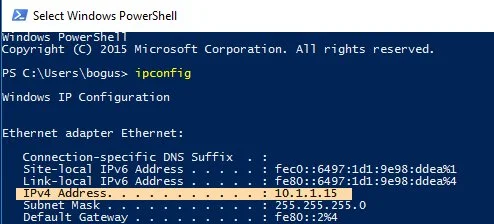
+The IP address is your local IP address, so it starts with either 192.168 or 10. If you don't know your local IP address, you can check it from your computer's networking control panel. On Linux, you can also find it by typing:
+```
+$ ip -4 -ts a
+
+```
+
+And on BSD or Mac:
+```
+$ ifconfig
+
+```
+
+On Windows, open PowerShell from your **Start** menu and type:
+```
+ipconfig
+
+```
+
+
+
+If your players have trouble connecting, there are two likely causes:
+
+ * You forgot to start the server. Start it and have your players try again.
+ * You have a firewall running on your computer. If you're on your home network, it's safe to deactivate your firewall or to tell it to permit traffic on port 51234. If you're in a public gaming space, you should not lower your firewall, but it's safe to permit traffic on port 51234 as long as you have set a password for your MapTool server.
+
+
+
+### Sharing the screen worldwide
+
+If you're playing remotely with people all over the world, letting them into your private MapTool server is a little more complex to set up, but you only have to do it once and then you're set.
+
+#### Router
+
+The first device that needs to be adjusted is your home router. This is the box you got from your internet service provider. You might also call it your modem.
+
+Every device is different, so there's no way for me to definitively tell you what you need to click on to adjust your settings. Generally, you access your home router through a web browser. Your router's address is often printed on the bottom of the router and begins with either 192.168 or 10.
+
+Navigate to the router address and log in with the credentials you were provided when you got your internet service. It's often as simple as `admin` with a numeric password (sometimes this password is printed on the router, too). If you don't know the login, call your internet provider and ask for details.
+
+Different routers use different terms for the same thing; keywords to look for are **Port forwarding** , **Virtual server** , and **Firewall**. Whatever your router calls it, you want to accept traffic coming to port 51234 of your router and forward that traffic to the same port of your personal computer's IP address.
+
+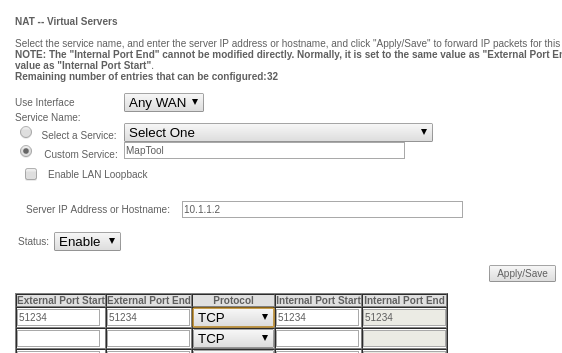
+
+If you're confused, search the internet for the term "port forwarding" and your router's brand name. This isn't an uncommon task for PC gamers, so instructions are out there.
+
+#### Finding your external IP address
+
+Now you're allowing traffic through the MapTool port, so you need to tell your players where to go.
+
+ 1. Get your worldwide IP address at [icanhazip.com][13].
+ 2. Start the MapTool server from the **File** menu. Set a password for safety.
+ 3. Have players select **Connect to server** from the **File** menu.
+ 4. In the **Connect to server** window, have players click the **Direct** tab and enter a username, password, and your IP address.
+
+
+
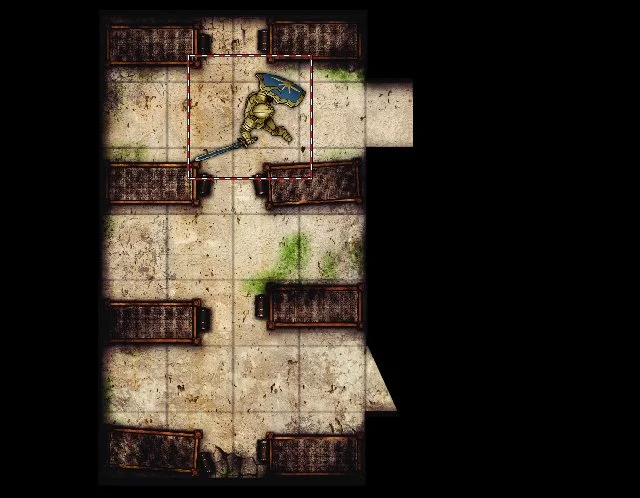
+### Features a-plenty
+
+This has been a brief overview of things you can do with MapTool. It has many other features, including an initiative tracker, adjustable tokens visibility (hide treasure and monsters from your players!), impersonation, line-of-sight (conceal hidden doors behind statues or other structures!), and fog of war.
+
+It can serve just as a digital battle map, or it can be the centerpiece of your tabletop game.
+
+
+
+### Why MapTool?
+
+Before you comment about them: Yes, there are a few virtual tabletop services online, and some of them are very good. They provide a good supply of games looking for players and players looking for games. If you can't find your fellow gamers locally, online tabletops are a great solution.
+
+By contrast, some people are not fans of social networking, so we shy away from sites that excitedly "bring people together." I've got friends to game with, and we're happy to build and set up our own infrastructure. We don't need to sign up for yet another site; we don't need to throw our hats into a great big online bucket and register when and how we game.
+
+Ultimately, I like MapTool because I have it with me whether or not I'm online. I can plan a campaign, populate it with graphics, and set up all my maps in advance without depending on having internet access. It's almost like doing the frontend programming for a video game, knowing that the backend "technology" will all happen in the player's minds on game night.
+
+If you're looking for a robust and flexible virtual tabletop, try MapTool!
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/18/5/maptool
+
+作者:[Seth Kenlon][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://opensource.com/users/seth
+[1]:https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Dungeons_%26_Dragons/Commercial_settings/Forgotten_Realms/Sword_Coast
+[2]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dungeons_%26_Dragons_campaign_settings
+[3]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Editions_of_Dungeons_%26_Dragons#Advanced_Dungeons_&_Dragons_2nd_edition
+[4]:http://www.rptools.net/toolbox/maptool/
+[5]:http://www.rptools.net/donate/
+[6]:http://www.rptools.net/downloadsw/
+[7]:http://jdk.java.net/8
+[8]:https://www.opengamingstore.com/search?q=map
+[9]:http://www.imagemagick.org/script/index.php
+[10]:http://gimp.org
+[11]:http://immortalnights.com/tokenpage.html
+[12]:http://paizo.com/
+[13]:http://icanhazip.com/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180515 Give Your Linux Desktop a Stunning Makeover With Xenlism Themes.md b/sources/tech/20180515 Give Your Linux Desktop a Stunning Makeover With Xenlism Themes.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f76a483199
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20180515 Give Your Linux Desktop a Stunning Makeover With Xenlism Themes.md
@@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
+Give Your Linux Desktop a Stunning Makeover With Xenlism Themes
+============================================================
+
+
+ _Brief: Xenlism theme pack provides an aesthetically pleasing GTK theme, colorful icons, and minimalist wallpapers to transform your Linux desktop into an eye-catching setup._
+
+It’s not every day that I dedicate an entire article to a theme unless I find something really awesome. I used to cover themes and icons regularly. But lately, I preferred having lists of [best GTK themes][6] and icon themes. This is more convenient for me and for you as well as you get to see many beautiful themes in one place.
+
+After [Pop OS theme][7] suit, Xenlism is another theme that has left me awestruck by its look.
+
+
+
+Xenlism GTK theme is based on the Arc theme, an inspiration behind so many themes these days. The GTK theme provides Windows buttons similar to macOS which I neither like nor dislike. The GTK theme has a flat, minimalist layout and I like that.
+
+There are two icon themes in the Xenlism suite. Xenlism Wildfire is an old one and had already made to our list of [best icon themes][8].
+
+
+Xenlism Wildfire Icons
+
+Xenlsim Storm is the relatively new icon theme but is equally beautiful.
+
+
+Xenlism Storm Icons
+
+Xenlism themes are open source under GPL license.
+
+### How to install Xenlism theme pack on Ubuntu 18.04
+
+Xenlism dev provides an easier way of installing the theme pack through a PPA. Though the PPA is available for Ubuntu 16.04, I found the GTK theme wasn’t working with Unity. It works fine with the GNOME desktop in Ubuntu 18.04.
+
+Open a terminal (Ctrl+Alt+T) and use the following commands one by one:
+
+```
+sudo add-apt-repository ppa:xenatt/xenlism
+sudo apt update
+```
+
+This PPA offers four packages:
+
+* xenlism-finewalls: for a set of wallpapers that will be available directly in the wallpaper section of Ubuntu. One of the wallpapers has been used in the screenshot.
+
+* xenlism-minimalism-theme: GTK theme
+
+* xenlism-storm: an icon theme (see previous screenshots)
+
+* xenlism-wildfire-icon-theme: another icon theme with several color variants (folder colors get changed in the variants)
+
+You can decide on your own what theme component you want to install. Personally, I don’t see any harm in installing all the components.
+
+```
+sudo apt install xenlism-minimalism-theme xenlism-storm-icon-theme xenlism-wildfire-icon-theme xenlism-finewalls
+```
+
+You can use GNOME Tweaks for changing the theme and icons. If you are not familiar with the procedure already, I suggest reading this tutorial to learn [how to install themes in Ubuntu 18.04 GNOME][9].
+
+### Getting Xenlism themes in other Linux distributions
+
+You can install Xenlism themes on other Linux distributions as well. Installation instructions for various Linux distributions can be found on its website:
+
+[Install Xenlism Themes][10]
+
+### What do you think?
+
+I know not everyone would agree with me but I loved this theme. I think you are going to see the glimpse of Xenlism theme in the screenshots in future tutorials on It’s FOSS.
+
+Did you like Xenlism theme? If not, what theme do you like the most? Share your opinion in the comment section below.
+
+#### 关于作者
+
+I am a professional software developer, and founder of It's FOSS. I am an avid Linux lover and Open Source enthusiast. I use Ubuntu and believe in sharing knowledge. Apart from Linux, I love classic detective mysteries. I'm a huge fan of Agatha Christie's work.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://itsfoss.com/xenlism-theme/
+
+作者:[Abhishek Prakash ][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[1]:https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[2]:https://itsfoss.com/xenlism-theme/#comments
+[3]:https://itsfoss.com/category/desktop/
+[4]:https://itsfoss.com/tag/themes/
+[5]:https://itsfoss.com/tag/xenlism/
+[6]:https://itsfoss.com/best-gtk-themes/
+[7]:https://itsfoss.com/pop-icon-gtk-theme-ubuntu/
+[8]:https://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-16-04/
+[9]:https://itsfoss.com/install-themes-ubuntu/
+[10]:http://xenlism.github.io/minimalism/#install
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180517 How to find your IP address in Linux.md b/sources/tech/20180517 How to find your IP address in Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index ff523101d2..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180517 How to find your IP address in Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
-translating---geekpi
-
-How to find your IP address in Linux
-======
-
-Internet Protocol (IP) needs no introduction—we all use it daily. Even if you don't use it directly, when you type website-name.com on your web browser, it looks up the IP address of that URL and then loads the website.
-
-Let's divide IP addresses into two categories: private and public. Private IP addresses are the ones your WiFi box (and company intranet) provide. They are in the range of 10.x.x.x, 172.16.x.x-172.31.x.x, and 192.168.x.x, where x=0 to 255. Public IP addresses, as the name suggests, are "public" and you can reach them from anywhere in the world. Every website has a unique IP address that can be reached by anyone and from anywhere; that is considered a public IP address.
-
-Furthermore, there are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6.
-
-IPv4 addresses have the format x.x.x.x, where x=0 to 255. There are 2^32 (approximately 4 billion) possible IPv4 addresses.
-
-IPv6 addresses have a more complex format using hex numbers. The total number of bits is 128, which means there are 2^128—340 undecillion!—possible IPv6 addresses. IPv6 was introduced to tackle the foreseeable exhaustion of IPv4 addresses in the near future.
-
-As a network engineer, I recommend not sharing your machine’s public IP address with anyone. Your WiFi router has a public IP, which is the WAN (wide-area network) IP address, and it will be the same for any device connected to that WiFi. All the devices connected to the same WiFi have private IP addresses locally identified by the range provided above. For example, my laptop is connected with the IP address 192.168.0.5, and my phone is connected with 192.168.0.8. These are private IP addresses, but both would have the same public IP address.
-
-The following commands will get you the IP address list to find public IP addresses for your machine:
-
- 1. `ifconfig.me`
- 2. `curl -4/-6 icanhazip.com`
- 3. `curl ipinfo.io/ip`
- 4. `curl api.ipify.org`
- 5. `curl checkip.dyndns.org`
- 6. `dig +short myip.opendns.com @resolver1.opendns.com`
- 7. `host myip.opendns.com resolver1.opendns.com`
- 8. `curl ident.me`
- 9. `curl bot.whatismyipaddress.com`
- 10. `curl ipecho.net/plain`
-
-
-
-The following commands will get you the private IP address of your interfaces:
-
- 1. `ifconfig -a`
- 2. `ip addr (ip a)`
- 3. `hostname -I | awk ‘{print $1}’`
- 4. `ip route get 1.2.3.4 | awk '{print $7}'`
- 5. `(Fedora) Wifi-Settings→ click the setting icon next to the Wifi name that you are connected to → Ipv4 and Ipv6 both can be seen`
- 6. `nmcli -p device show`
-
-
-
-_Note: Some utilities need to be installed on your system based on the Linux distro you are using. Also, some of the noted commands use a third-party website to get the IP_
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://opensource.com/article/18/5/how-find-ip-address-linux
-
-作者:[Archit Modi][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://opensource.com/users/architmodi
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180517 What You Need to Know About Cryptocurrency ‘Malware- Found on Ubuntu-s Snap Store.md b/sources/tech/20180517 What You Need to Know About Cryptocurrency ‘Malware- Found on Ubuntu-s Snap Store.md
deleted file mode 100644
index dae40507ac..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180517 What You Need to Know About Cryptocurrency ‘Malware- Found on Ubuntu-s Snap Store.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,107 +0,0 @@
-What You Need to Know About Cryptocurrency ‘Malware’ Found on Ubuntu’s Snap Store
-======
-Recently, it was discovered that a couple of apps in the Ubuntu Snaps store contained cryptocurrency mining software. Canonical swiftly removed the offending apps, but several questions are left unanswered.
-
-### Discovery of Crypto Miner on Snap Store
-
-![Crypto Miner Malware on Ubuntu Snap Store][1]
-
-On May 11, a user named [tarwirdur][2] opened a new issue on the [snapcraft.io repository][3]. In the issue, he noted that a snap entitled 2048buntu created by Nicolas Tomb contained a cryptocurrency miner. He asked how he could “complain about the application” for security reasons. tarwirdur later posted to say that all the others snaps created by Nicolas Tomb also contained cryptocurrency miners.
-
-It appears that the snaps used systemd to automatically launch the code at boot and run it in the background with the user none the wiser.
-
-{For those unfamiliar with the terminology, a cryptocurrency miner is a piece of software that uses a computer’s main processor or graphics processor to “mine” digital currency. “Mining” usually involves solving a mathematical equation. In this case, if you were running the 2048buntu game, the game used additional processing power for cryptocurrency mining.}
-
-The Snapcraft team responded by quickly removing all apps created by the offender. They also started an investigation.
-
-### The Man Behind the Mask Speaks
-
-On May 13, a Disqus user named Nicolas Tomb [posted a comment][4] on OMGUbuntu’s coverage of the news. In this comment, he stated that he added the cryptocurrency miner to monetize the snaps. He apologized for his actions and promised to send any funds that had been mined to the Ubuntu foundation.
-
-We can’t say for sure if this comment was posted by the same Nicolas Tomb since the Disqus account was just recently created and only has one comment associated with it. For now, we’ll assume that it is.
-
-### Canonical Makes a Statement
-
-On May 15, Canonical issued a statement on the situation. Entitled [“Trust and security in the Snap Store”][5], the post starts out by restating the situation. They add that the snaps have been [reissued with the cryptocurrency mining code removed][6].
-
-Canonical then attempts to examine the motives of Nicolas Tomb. They note that he told them he did it in an attempt to monetize the apps (as stated above) and stopped doing it when confronted. They also note that “mining cryptocurrency is not illegal or unethical by itself”. They are however unhappy about the fact that he did not disclose the cryptocurrency miner in the snap description.
-
-From there Canonical moves to the subject of reviewing software. According to the post, the Snap Store uses a quality control system similar to iOS, Android, and Windows: “automated checkpoints that packages must go through before they are accepted, and manual reviews by a human when specific issues are flagged”.
-
-However, Canonical says “it’s impossible for a large scale repository to only accept software after every individual file has been reviewed in detail”. Therefore, they need to trust the source, not the content. After all, that is what the current Ubuntu repo system is based on.
-
-Canonical follows this up by talking about the future of snaps. They acknowledge that the current system is not perfect. They are continually working to improve it. They have “very interesting security features in the works that will improve the safety of the system and also the experience of people handling software deployments in servers and desktops”.
-
-One of the features they are working on is the ability to see if a publisher is verified. Other improvements include: “upstreaming of all the AppArmor kernel patches” and other under-the-hood fixes.
-
-### Thoughts on the ‘Snap store malware’
-
-Based on all that I’ve read, I’ve got a few thoughts and questions of my own.
-
-#### How Long Was This Running?
-
-First of all, how long have these mining snaps been available on the Snap Store? Since they have all been removed, we don’t have that data. I was able to grab an image of the 2048buntu page from the Google cache, but it doesn’t show much of anything. Depending on how long it ran, how many systems it got installed on, and what cryptocurrency was being mined, we could either be talks about a little bit of money or a pile. A further question is: would Canonical have been able to catch this in the future?
-
-#### Was it Really a Malware?
-
-A lot of news sites are reporting this as a malware infection. I think I might have even seen this incident referred to as Linux’s first malware. I’m not sure that term is accurate. Dictionary.com defines [malware][7] as: “software intended to damage a computer, mobile device, computer system, or computer network, or to take partial control over its operation”.
-
-The snaps in question did not damage or take control of the computers involved. it also did not infect other computers. It couldn’t have because all snaps are sandboxed. At the most, they leached processor power, that’s about it. So, I wouldn’t call it malware.
-
-#### Nothing Like a Loophole
-
-The one defense that Nicolas Tomb uses is that the Snap Store didn’t have any rules against cryptocurrency mining when he uploaded the snaps. {I can bet you that they are rectifying that problem right now.} They didn’t have that rule for the simple reason that no one had done it before. If Tomb was trying to do things correctly, he should have asked if this kind of behavior was allowed. The fact that he didn’t seems to point to the fact that he knew they would probably say no. At the very least, they would have told him to put it in the description.
-
-![][8]
-
-#### Something Looks Hinkey
-
-As I said before, I got a screenshot of the 2048buntu page from Google cache. Just looking at it raises several red flags. First, there is almost no real description. This is all it says “Game like 2048. This game is clone popular game – 2048 with ubuntu colors.” Wow. {That’ll bring in the suckers.} When I read something as empty as that, I get nervous.
-
-Another thing to notice is the size of it. Version 1.0 of the 2048buntu snap weighs almost 140 MB. Why would a game this simple need that much space? There are browser versions written in Javascript that probably use less than a quarter of that. There other snaps of 2048 games on the Snap Store and none of them has half the file size.
-
-Then, you have the license. This is a clone of a popular game using Ubuntu colors. How can it be considered proprietary? I’m sure that legit devs in the audience would have uploaded it with a FOSS (Free and Open Source Software) license just because of the content.
-
-These factors alone should have made this snap, in particular, stand out and call for a review.
-
-#### Who is Nicolas Tomb?
-
-After first reading about this, I decided to see what I could find out about the guy who started this mess. When I searched for Nicolas Tomb, I found nothing, zip, nada, zilch. All I found were a bunch of news articles about the cryptocurrency mining snaps and information about taking a trip to the tomb of St. Nicolas. There is no sign of Nicolas Tomb on Twitter or Github either. This seems like a name created just to upload these snaps.
-
-This also leads to a point in the Canonical blog post about verifying publishers. The last time I looked, quite a few snaps were not published by the maintainers of the applications. This makes me nervous. I would be more willing to trust a snap of say Firefox if it was published by Mozilla, instead of Leonard Borsch. If it’s too much work for the application maintainer to also take care of the snap, there should be a way for the maintainer to put their stamp of approval on the snap for their program. Something like Firefox snap published by Fredrick Ham, approved by Mozilla Foundation. Just something to give the user more confidence in what they are downloading.
-
-#### Snap Store Definitely has Room to Improve
-
-It seems to me that one of the first features that the Snap Store team should have implemented was a way to report suspicious snaps. tarwirdur had to find the site’s Github page. The average user would not have thought of that. If the Snap Store can’t review every line of code, enabling the users to reports problems is the next best thing. Even rating system would not be a bad addition. I’m sure there would have been a couple people who would have given 2048buntu a low rating for using too many system resources.
-
-#### Conclusion
-
-From all the I have seen, I think that someone created a number of simple apps, embedded a cryptocurrency miner in each, and uploaded them to the Snap Store with the goal of raking in piles of money. Once they got caught, they claimed it was only to monetize the snaps. If that was true, they would have mentioned it in the snap description. Hidden crypto miners are nothing [new][9]. They are generally a method of computing power theft.
-
-I wish that Canonical already have features in place to combat this problem and I hope they appear quickly.
-
-What do you think of the Snap Store ‘malware episode’? What would you do to improve it? Let us know in the comments below.
-
-If you found this article interesting, please take a minute to share it on social media.
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://itsfoss.com/snapstore-cryptocurrency-saga/
-
-作者:[John Paul][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]: https://itsfoss.com/author/john/
-[1]:https://4bds6hergc-flywheel.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/ubuntu-snap-malware-800x450.jpeg
-[2]:https://github.com/tarwirdur
-[3]:https://github.com/canonical-websites/snapcraft.io/issues/651
-[4]:https://disqus.com/home/discussion/omgubuntu/malware_found_on_the_ubuntu_snap_store/#comment-3899153046
-[5]:https://blog.ubuntu.com/2018/05/15/trust-and-security-in-the-snap-store
-[6]:https://forum.snapcraft.io/t/action-against-snap-store-malware/5417/8
-[7]:http://www.dictionary.com/browse/malware?s=t
-[8]:https://4bds6hergc-flywheel.netdna-ssl.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/2048buntu.png
-[9]:https://krebsonsecurity.com/2018/03/who-and-what-is-coinhive/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180518 How To Install Ncurses Library In Linux.md b/sources/tech/20180518 How To Install Ncurses Library In Linux.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 472d389a11..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180518 How To Install Ncurses Library In Linux.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,92 +0,0 @@
-translating---geekpi
-
-How To Install Ncurses Library In Linux
-======
-
-
-**GNU Ncurses** is a programming library that allows the users to write text-based user interfaces(TUI). Many text-based games are created using this library. One popular example is [**PacVim**][1], a CLI game to learn VIM commands. In this brief guide, I will be explaining how to install Ncurses library in Unix-like operating systems.
-
-### Install Ncurses Library In Linux
-
-Ncurses is available in the default repositories of most Linux distributions. For instance, you can install it on Arch-based systems using the following command:
-```
-$ sudo pacman -S ncurses
-
-```
-
-On RHEL, CentOS:
-```
-$ sudo yum install ncurses-devel
-
-```
-
-On Fedora 22 and newer versions:
-```
-$ sudo dnf install ncurses-devel
-
-```
-
-On Debian, Ubuntu, Linux Mint:
-```
-$ sudo apt-get install libncurses5-dev libncursesw5-dev
-
-```
-
-The GNU ncureses might be bit old in the default repositories. If you want a most recent stable version, you can compile and install from the source as shown below.
-
-Download the latest ncurses version from [**here**][2]. As of writing this guide, the latest version was 6.1.
-```
-$ wget https://ftp.gnu.org/pub/gnu/ncurses/ncurses-6.1.tar.gz
-
-```
-
-Extract the tar file:
-```
-$ tar xzf ncurses-6.1.tar.gz
-
-```
-
-This will create a folder named ncurses-6.1 in the current directory. Cd to the directory:
-```
-$ cd ncurses-6.1
-
-$ ./configure --prefix=/opt/ncurses
-
-```
-
-Finally, compile and install using the following commands:
-```
-$ make
-
-$ sudo make install
-
-```
-
-Verify the installation using command:
-```
-$ ls -la /opt/ncurses
-
-```
-
-That’s it. Ncurses have been installed on the Linux distribution. Go ahead and create your nice looking TUIs using Ncurses.
-
-More good stuffs to come. Stay tuned!
-
-Cheers!
-
-
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://www.ostechnix.com/how-to-install-ncurses-library-in-linux/
-
-作者:[SK][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/
-[1]:https://www.ostechnix.com/pacvim-a-cli-game-to-learn-vim-commands/
-[2]:https://ftp.gnu.org/pub/gnu/ncurses/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180521 Audacity quick tip- quickly remove background noise.md b/sources/tech/20180521 Audacity quick tip- quickly remove background noise.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 25ca446a9d..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180521 Audacity quick tip- quickly remove background noise.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,53 +0,0 @@
-Audacity quick tip: quickly remove background noise
-======
-
-
-When recording sounds on a laptop — say for a simple first screencast — many users typically use the built-in microphone. However, these small microphones also capture a lot of background noise. In this quick tip, learn how to use [Audacity][1] in Fedora to quickly remove the background noise from audio files.
-
-### Installing Audacity
-
-Audacity is an application in Fedora for mixing, cutting, and editing audio files. It supports a wide range of formats out of the box on Fedora — including MP3 and OGG. Install Audacity from the Software application.
-
-![][2]
-
-If the terminal is more your speed, use the command:
-```
-sudo dnf install audacity
-
-```
-
-### Import your Audio, sample background noise
-
-After installing Audacity, open the application, and import your sound using the **File > Import** menu item. This example uses a [sound bite from freesound.org][3] to which noise was added:
-
-Next, take a sample of the background noise to be filtered out. With the tracks imported, select an area of the track that contains only the background noise. Then choose **Effect > Noise Reduction** from the menu, and press the **Get Noise Profile** button.
-
-![][4]
-
-### Filter the Noise
-
-Next, select the area of the track you want to filter the noise from. Do this either by selecting with the mouse, or **Ctrl + a** to select the entire track. Finally, open the **Effect > Noise Reduction** dialog again, and click OK to apply the filter.
-
-![][5]
-
-Additionally, play around with the settings until your tracks sound better. Here is the original file again, followed by the noise reduced track for comparison (using the default settings):
-
-https://ryanlerch.fedorapeople.org/sidebyside.ogg?_=2
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://fedoramagazine.org/audacity-quick-tip-quickly-remove-background-noise/
-
-作者:[Ryan Lerch][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]: https://fedoramagazine.org/introducing-flatpak/
-[1]:https://www.audacityteam.org/
-[2]:https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/audacity-software.jpg
-[3]:https://freesound.org/people/levinj/sounds/8323/
-[4]:https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/select-noise-profile.gif
-[5]:https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/apply-filter.gif
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180521 Starting user software in X.md b/sources/tech/20180521 Starting user software in X.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 148127c817..0000000000
--- a/sources/tech/20180521 Starting user software in X.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
-translating---geekpi
-
-Starting user software in X
-======
-
-There are currently many ways of starting software when a user session starts.
-
-This is an attempt to collect a list of pointers to piece the big picture together. It's partial and some parts might be imprecise or incorrect, but it's a start, and I'm happy to keep it updated if I receive corrections.
-
-### x11-common
-
-`man xsession`
-
- * Started by the display manager for example, `/usr/share/lightdm/lightdm.conf.d/01_debian.conf` or `/etc/gdm3/Xsession`
- * Debian specific
- * Runs scripts in `/etc/X11/Xsession.d/`
- * `/etc/X11/Xsession.d/40x11-common_xsessionrc` sources `~/.xsessionrc` which can do little more than set env vars, because it is run at the beginning of X session startup
- * At the end, it starts the session manager (`gnome-session`, `xfce4-session`, and so on)
-
-
-
-### systemd --user
-
- *
- * Started by `pam_systemd`, so it might not have a DISPLAY variable set in the environment yet
- * Manages units in:
- * `/usr/lib/systemd/user/` where units provided by installed packages belong.
- * `~/.local/share/systemd/user/` where units of packages that have been installed in the home directory belong.
- * `/etc/systemd/user/` where system-wide user units are placed by the system administrator.
- * `~/.config/systemd/user/` where the users put their own units.
- * A trick to start a systemd user unit when the X session has been set up and the DISPLAY variable is available, is to call `systemctl start` from a `.desktop` autostart file.
-
-
-
-### dbus activation
-
- *
- * A user process making a dbus request can trigger starting a server program
- * For systems debugging, is there a way of monitoring what services are getting dbus activated?
-
-
-
-### X session manager
-
- *
- * Run by `x11-common`'s `Xsession.d`
- * Runs freedesktop autostart .desktop files
- * Runs Desktop Environment specific software
-
-
-
-### xdg autostart
-
- *
- * Run by the session manager
- * If `/etc/xdg/autostart/foo.desktop` and `~/.config/autostart/foo.desktop` exist then only the file `~/.config/autostart/foo.desktop` will be used because `~/.config/autostart/` is more important than `/etc/xdg/autostart/`
- * Is there an ordering or is it all in parallel?
-
-
-
-### Other startup notes
-
-#### ~/.Xauthority
-
-To connect to an X server, a client needs to send a token from `~/.Xauthority`, which proves that they can read the user's provate data.
-
-`~/.Xauthority` contains a token generated by display manager and communicated to X at startup.
-
-To view its contents, use `xauth -i -f ~/.Xauthority list`
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: http://www.enricozini.org/blog/2018/debian/starting-user-software/
-
-作者:[Enrico Zini][a]
-选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:http://www.enricozini.org/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180522 How to Enable Click to Minimize On Ubuntu.md b/sources/tech/20180522 How to Enable Click to Minimize On Ubuntu.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..50d68ad445
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20180522 How to Enable Click to Minimize On Ubuntu.md
@@ -0,0 +1,102 @@
+How to Enable Click to Minimize On Ubuntu
+============================================================
+
+
+ _Brief: This quick tutorial shows you how to enable click to minimize option on Ubuntu 18.04 and Ubuntu 16.04._
+
+The launcher at the left hand side in [Ubuntu][7] is a handy tool for quickly accessing applications. When you click on an icon in the launcher, the application window appears in focus.
+
+If you click again on the icon of an application already in focus, the default behavior is to do nothing. This may bother you if you expect the application window to be minimized on the second click.
+
+Perhaps this GIF will be better in explaining the click on minimize behavior on Ubuntu.
+
+[video](https://giphy.com/gifs/linux-ubuntu-itsfoss-52FlrSIMxnZ1qq9koP?utm_source=iframe&utm_medium=embed&utm_campaign=Embeds&utm_term=https%3A%2F%2Fitsfoss.com%2Fclick-to-minimize-ubuntu%2F%3Futm_source%3Dnewsletter&%3Butm_medium=email&%3Butm_campaign=new_linux_laptop_ubuntu_1804_flavor_reviews_meltdown_20_and_other_linux_stuff&%3Butm_term=2018-05-23)
+
+In my opinion, this should be the default behavior but apparently Ubuntu doesn’t think so. So what? Customization is one of the main reason [why I use Linux][8] and this behavior can also be easily changed.
+
+In this quick tutorial, I’ll show you how to enable click to minimize on Ubuntu 18.04 and 16.04\. I’ll show both command line and the GUI methods here.
+
+
+### Enable click to minimize on Ubuntu using command line (recommended)
+
+ _This method is for Ubuntu 18.04 and 17.10 users with [GNOME desktop environment][1]_ .
+
+The first option is using the terminal. I recommend this way to ‘minimize on click’ even if you are not comfortable with the command line.
+
+It’s not at all complicated. Open a terminal using Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut or searching for it in the menu. All you need is to copy paste the command below in the terminal.
+
+```
+gsettings set org.gnome.shell.extensions.dash-to-dock click-action 'minimize'
+```
+
+No need of restarting your system or any thing of that sort. You can test the minimize on click behavior immediately after it.
+
+If you do not like ‘click to minimize’ behavior, you can set it back to default using the command below:
+
+```
+gsettings reset org.gnome.shell.extensions.dash-to-dock click-action
+```
+
+### Enable click to minimize on Ubuntu using GUI tool
+
+You can do the same steps mentioned above using a GUI tool called [Dconf Editor][10]. It is a powerful tool that allows you to change many hidden aspects of your Linux desktop. I avoid recommending it because one wrong click here and there may screw up your desktop settings. So be careful while using this tool keeping in mind that it works on single click and changes are applied immediately.
+
+You can find and install Dconf Editor in the Ubuntu Software Center.
+
+
+
+Once installed, launch Dconf Editor and go to org -> gnome -> shell -> extensions -> dash-to-dock. Scroll down a bit until you find click-action. Click on it to access the click action settings.
+
+In here, turn off the Use default value option and change the Custom Valueto ‘minimize’.
+
+
+
+You can see that the minimize on click behavior has been applied instantly.
+
+### Enable click to minimize on Ubuntu 16.04 Unity
+
+If you are using Unity desktop environment, you can easily d it using Unity Tweak Tool. If you have not installed it already, look for Unity Tweak Tool in Software Center and install it.
+
+Once installed, launch Unity Tweak Tool and click on Launcher here.
+
+
+
+Check the “Minimize single window application on click” option here.
+
+
+
+That’s all. The change takes into effect right away.
+
+### Did it work for you?
+
+I hope this quick tip helped you to enable the minimize on click feature in Ubuntu. If you are using Ubuntu 18.04, I suggest reading [GNOME customization tips][11] for more such options.
+
+If you have any questions or suggestions, please leave a comment. If it helped you, perhaps you could share this article on various social media platforms such as Reddit and Twitter.
+
+
+#### 关于作者
+
+I am a professional software developer, and founder of It's FOSS. I am an avid Linux lover and Open Source enthusiast. I use Ubuntu and believe in sharing knowledge. Apart from Linux, I love classic detective mysteries. I'm a huge fan of Agatha Christie's work.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://itsfoss.com/click-to-minimize-ubuntu/
+
+作者:[Abhishek Prakash ][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[1]:https://www.gnome.org/
+[2]:https://itsfoss.com/author/abhishek/
+[3]:https://itsfoss.com/click-to-minimize-ubuntu/#comments
+[4]:https://itsfoss.com/category/how-to/
+[5]:https://itsfoss.com/tag/quick-tip/
+[6]:https://itsfoss.com/tag/ubuntu-18-04/
+[7]:https://www.ubuntu.com/
+[8]:https://itsfoss.com/reasons-switch-linux-windows-xp/
+[9]:https://itsfoss.com/how-to-know-ubuntu-unity-version/
+[10]:https://wiki.gnome.org/Projects/dconf
+[11]:https://itsfoss.com/gnome-tricks-ubuntu/
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180522 How to Run Your Own Git Server.md b/sources/tech/20180522 How to Run Your Own Git Server.md
index bb2d6bfe1f..9a1ee8509a 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20180522 How to Run Your Own Git Server.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20180522 How to Run Your Own Git Server.md
@@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
+translating by wyxplus
How to Run Your Own Git Server
======
**Learn how to set up your own Git server in this tutorial from our archives.**
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180522 Using Stratis to manage Linux storage from the command line.md b/sources/tech/20180522 Using Stratis to manage Linux storage from the command line.md
index 2bed178d85..9d1919c689 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20180522 Using Stratis to manage Linux storage from the command line.md
+++ b/sources/tech/20180522 Using Stratis to manage Linux storage from the command line.md
@@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
+translating----geekpi
+
Using Stratis to manage Linux storage from the command line
======
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180524 How CERN Is Using Linux and Open Source.md b/sources/tech/20180524 How CERN Is Using Linux and Open Source.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..fd2437f251
--- /dev/null
+++ b/sources/tech/20180524 How CERN Is Using Linux and Open Source.md
@@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
+KevinSJ translating
+
+How CERN Is Using Linux and Open Source
+============================================================
+
+
+>CERN relies on open source technology to handle huge amounts of data generated by the Large Hadron Collider. The ATLAS (shown here) is a general-purpose detector that probes for fundamental particles. (Image courtesy: CERN)[Used with permission][2]
+
+[CERN][3]
+
+[CERN][6] really needs no introduction. Among other things, the European Organization for Nuclear Research created the World Wide Web and the Large Hadron Collider (LHC), the world’s largest particle accelerator, which was used in discovery of the [Higgs boson][7]. Tim Bell, who is responsible for the organization’s IT Operating Systems and Infrastructure group, says the goal of his team is “to provide the compute facility for 13,000 physicists around the world to analyze those collisions, understand what the universe is made of and how it works.”
+
+CERN is conducting hardcore science, especially with the LHC, which [generates massive amounts of data][8] when it’s operational. “CERN currently stores about 200 petabytes of data, with over 10 petabytes of data coming in each month when the accelerator is running. This certainly produces extreme challenges for the computing infrastructure, regarding storing this large amount of data, as well as the having the capability to process it in a reasonable timeframe. It puts pressure on the networking and storage technologies and the ability to deliver an efficient compute framework,” Bell said.
+
+### [tim-bell-cern.png][4]
+
+
+Tim Bell, CERN[Used with permission][1]Swapnil Bhartiya
+
+The scale at which LHC operates and the amount of data it generates pose some serious challenges. But CERN is not new to such problems. Founded in 1954, CERN has been around for about 60 years. “We've always been facing computing challenges that are difficult problems to solve, but we have been working with open source communities to solve them,” Bell said. “Even in the 90s, when we invented the World Wide Web, we were looking to share this with the rest of humanity in order to be able to benefit from the research done at CERN and open source was the right vehicle to do that.”
+
+### Using OpenStack and CentOS
+
+Today, CERN is a heavy user of OpenStack, and Bell is one of the Board Members of the OpenStack Foundation. But CERN predates OpenStack. For several years, they have been using various open source technologies to deliver services through Linux servers.
+
+“Over the past 10 years, we've found that rather than taking our problems ourselves, we find upstream open source communities with which we can work, who are facing similar challenges and then we contribute to those projects rather than inventing everything ourselves and then having to maintain it as well,” said Bell.
+
+A good example is Linux itself. CERN used to be a Red Hat Enterprise Linux customer. But, back in 2004, they worked with Fermilab to build their own Linux distribution called [Scientific Linux][9]. Eventually they realized that, because they were not modifying the kernel, there was no point in spending time spinning up their own distribution; so they migrated to CentOS. Because CentOS is a fully open source and community driven project, CERN could collaborate with the project and contribute to how CentOS is built and distributed.
+
+CERN helps CentOS with infrastructure and they also organize CentOS DoJo at CERN where engineers can get together to improve the CentOS packaging.
+
+In addition to OpenStack and CentOS, CERN is a heavy user of other open source projects, including Puppet for configuration management, Grafana and influxDB for monitoring, and is involved in many more.
+
+“We collaborate with around 170 labs around the world. So every time that we find an improvement in an open source project, other labs can easily take that and use it,” said Bell, “At the same time, we also learn from others. When large scale installations like eBay and Rackspace make changes to improve scalability of solutions, it benefits us and allows us to scale.”
+
+### Solving realistic problems
+
+Around 2012, CERN was looking at ways to scale computing for the LHC, but the challenge was people rather than technology. The number of staff that CERN employs is fixed. “We had to find ways in which we can scale the compute without requiring a large number of additional people in order to administer that,” Bell said. “OpenStack provided us with an automated API-driven, software-defined infrastructure.” OpenStack also allowed CERN to look at problems related to the delivery of services and then automate those, without having to scale the staff.
+
+“We're currently running about 280,000 cores and 7,000 servers across two data centers in Geneva and in Budapest. We are using software-defined infrastructure to automate everything, which allows us to continue to add additional servers while remaining within the same envelope of staff,” said Bell.
+
+As time progresses, CERN will be dealing with even bigger challenges. Large Hadron Collider has a roadmap out to 2035, including a number of significant upgrades. “We run the accelerator for three to four years and then have a period of 18 months or two years when we upgrade the infrastructure. This maintenance period allows us to also do some computing planning,” said Bell. CERN is also planning High Luminosity Large Hadron Collider upgrade, which will allow for beams with higher luminosity. The upgrade would mean about 60 times more compute requirement compared to what CERN has today.
+
+“With Moore's Law, we will maybe get one quarter of the way there, so we have to find ways under which we can be scaling the compute and the storage infrastructure correspondingly and finding automation and solutions such as OpenStack will help that,” said Bell.
+
+“When we started off the large Hadron collider and looked at how we would deliver the computing, it was clear that we couldn't put everything into the data center at CERN, so we devised a distributed grid structure, with tier zero at CERN and then a cascading structure around that,” said Bell. “There are around 12 large tier one centers and then 150 small universities and labs around the world. They receive samples at the data from the LHC in order to assist the physicists to understand and analyze the data.”
+
+That structure means CERN is collaborating internationally, with hundreds of countries contributing toward the analysis of that data. It boils down to the fundamental principle that open source is not just about sharing code, it’s about collaboration among people to share knowledge and achieve what no single individual, organization, or company can achieve alone. That’s the Higgs boson of the open source world.
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.linux.com/blog/2018/5/how-cern-using-linux-open-source
+
+作者:[SWAPNIL BHARTIYA ][a]
+译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.linux.com/users/arnieswap
+[1]:https://www.linux.com/licenses/category/used-permission
+[2]:https://www.linux.com/licenses/category/used-permission
+[3]:https://home.cern/about/experiments/atlas
+[4]:https://www.linux.com/files/images/tim-bell-cernpng
+[5]:https://www.linux.com/files/images/atlas-cernjpg
+[6]:https://home.cern/
+[7]:https://home.cern/topics/higgs-boson
+[8]:https://home.cern/about/computing
+[9]:https://www.scientificlinux.org/
diff --git a/translated/talk/20180107 7 leadership rules for the DevOps age.md b/translated/talk/20180107 7 leadership rules for the DevOps age.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..587d7761fb
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/20180107 7 leadership rules for the DevOps age.md
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
+DevOps时代的7个领导准则
+======
+
+
+
+如果[DevOps]最终更多的是关于文化而不是任何其他的技术或者平台,那么请记住:没有终点线。而是继续改变和提高--而且最高管理层并没有通过。
+
+然而,如果期望DevOps能够帮助获得更多的成果,领导者需要[修订他们的一些传统的方法][2]让我们考虑7个在DevOps时代更有效的IT领导的想法。
+
+### 1. 向失败说“是的”
+
+“失败”这个词在IT领域中一直包含着特殊的内涵,而且通常是糟糕的意思:服务器失败,备份失败,硬盘驱动器失败-你得了解这些情况。
+
+然而一种健康的DevOps文化取决于重新定义失败-IT领导者在他们的字典里应该重新定义这个单词将它的含义和“机会”对等起来。
+
+“在DevOps之前,我们曾有一种惩罚失败者的文化,”罗伯特·里夫斯说,[Datical][3]的首席技术官兼联合创始人。“我们学到的仅仅是去避免错误。在IT领域避免错误的首要措施就是不要去改变任何东西:不要加速版本迭代的日程,不要迁移到云中,不要去做任何不同的事”
+
+那是过去的一个时代的剧本,里夫斯坦诚的说,它已经不起作用了,事实上,那种停滞是失败的。
+
+“那些缓慢的释放并逃避云的公司被恐惧所麻痹-他们将会走向失败,”里夫斯说道。“IT领导者必须拥抱失败并把它当做成一个机遇。人们不仅仅从他们的过错中学习,也会从其他的错误中学习。一种开放和[安全心里][4]的文化促进学习和提高”
+**[相关文章:[为什么敏捷领导者谈论“失败”必须超越它本义]]
+### 2. 在管理层渗透开发运营的理念
+
+尽管DevOps文化可以在各个方向有机的发展,那些正在从整体中转变,孤立的IT实践,而且可能遭遇逆风的公司-需要执行领导层的全面支持。你正在传达模糊的信息
+而且可能会鼓励那些愿意推一把的人,这是我们一贯的做事方式。[改变文化是困难的][6];人们需要看到领导层完全投入进去并且知道改变已经实际发生了。
+
+“为了成功的实现利益的兑现高层管理必须全力支持DevOps,”来自[Rainforest QA][7]的首席技术官说道。
+
+成为一个DevOps商店。德里克指出,涉及到公司的一切,从技术团队到工具到进程到规则和责任。
+
+"没有高层管理的统一赞助支持,DevOps的实施将很难成功,"德里克说道。"因此,在转变到DevOps之前在高层中有支持的领导同盟是很重要的。"
+
+### 3. 不要只是声明“DevOps”-要明确它
+即使IT公司也已经开始拥抱欢迎DevOps,每个人可能不是在同一个进程上。
+**[参考我们的相关文章,**][**3 阐明了DevOps和首席技术官们必须在同一进程上**][8] **.]**
+
+造成这种脱节的一个根本原因是:人们对这个术语的有着不同的定义理解。
+
+“DevOps 对不同的人可能意味着不同的含义,”德里克解释道。“对高管层和副总裁层来说,执行明确的DevOps的目标,清楚的声明期望的成果,充分理解带来的成果将如何使公司的商业受益并且能够衡量和报告成功的过程。”
+
+事实上,在基线和视野之上,DevOps要求正在进行频繁的交流,不是仅仅在小团队里,而是要贯穿到整个组织。IT领导者必须为它设置优先级。
+
+“不可避免的,将会有些阻碍,在商业中将会存在失败和破坏,”德里克说道。“领导者名需要清楚的将这个过程向公司的其他人阐述清楚告诉他们他们作为这个过程的一份子能够期待的结果。”
+
+### 4. DevOps和技术同样重要
+
+IT领导者们成功的将DevOps商店的这种文化和实践当做一项商业策略,与构建和运营软件的方法相结合。DevOps是将IT从支持部门转向战略部门的推动力。
+
+IT领导者们必须转变他们的思想和方法,从成本和服务中心转变到驱动商业成果,而且DevOps的文化能够通过自动化和强大的协作加速收益。来自[CYBRIC][9]的首席技术官和联合创始人迈克说道。
+
+事实上,这是一个强烈的趋势通过更多的这些规则在DevOps时代走在前沿。
+
+“促进创新并且鼓励团队成员去聪明的冒险是DevOps文化的一个关键部分,IT领导者们需要在一个持续的基础上清楚的和他们交流,”凯尔说道。
+
+“一个高效的IT领导者需要比以往任何时候都要积极的参与到商业中去,”来自[West Monroe Partners][10]的性能服务部门的主任埃文说道。“每年或季度回顾的日子一去不复返了-你需要欢迎每两周一次的待办事项。[11]你需要有在年度水平上的思考战略能力,在冲刺阶段的互动能力,在商业期望满足时将会被给予一定的奖励。”
+
+### 5. 改变妨碍DevOps目标的任何事情
+
+虽然DevOps的老兵们普遍认为DevOps更多的是一种文化而不是技术,成功取决于通过正确的过程和工具激活文化。当你声称自己的部门是一个DevOps商店却拒绝对进程或技术做必要的改变,这就是你买了辆法拉利却使用了用过20年的引擎,每次转动钥匙都会冒烟。
+
+展览 A: [自动化][12].这是DevOps成功的重要并行策略。
+
+“IT领导者需要重点强调自动化,”卡伦德说。“这将是DevOps的前期投资,但是如果没有它,DevOps将会很容易被低效吞噬自己而且将会无法完整交付。”
+
+自动化是基石,但改变不止于此。
+
+“领导者们需要推动自动化,监控和持续的交付过程。这意着对现有的实践,过程,团队架构以及规则的很多改变,”Choy说。“领导者们需要改变一切会阻碍隐藏团队去全利实现自动化的因素。”
+
+### 6. 重新思考团队架构和能力指标
+
+当你想改变时...如果你桌面上的组织结构图和你过去大部分时候嵌入的名字都是一样的,那么你是时候该考虑改革了。
+
+“在这个DevOps的新时代文化中,IT执行者需要采取一个全新的方法来组织架构。”Kail说。“消除组织的边界限制,它会阻碍团队间的合作,允许团队自我组织,敏捷管理。”
+
+Kail告诉我们在DevOps时代,这种反思也应该拓展应用到其他领域,包括你怎样衡量个人或者团队的成功,甚至是你和人们的互动。
+
+“根据业务成果和总体的积极影响来衡量主动性,”Kail建议。“最后,我认为管理中最重要的一个方面是:有同理心。”
+
+注意很容易收集的到测量值不是DevOps真正的指标,[Red Hat]的技术专员Gardon Half写到,“DevOps应该把指标以某种形式和商业成果绑定在一起,”他指出。“你可能真的不在乎开发者些了多少代码,是否有一台服务器在深夜硬件损坏,或者是你的测试是多么的全面。你甚至都不直接关注你的网站的响应情况或者是你更新的速度。但是你要注意的是这些指标可能和顾客放弃购物车去竞争对手那里有关,”参考他的文章,[DevOps 指标:你在测量什么?]
+
+### 7. 丢弃传统的智慧
+
+如果DevOps时代要求关于IT领导能力的新的思考方式,那么也就意味着一些旧的方法要被淘汰。但是是哪些呢?
+
+“是实话,是全部,”Kail说道。“要摆脱‘因为我们一直都是以这种方法做事的’的心态。过渡到DevOps文化是一种彻底的思维模式的转变,不是对瀑布式的过去和变革委员会的一些细微改变。”
+
+事实上,IT领导者们认识到真正的变革要求的不只是对旧方法的小小接触。它更多的是要求对之前的进程或者策略的一个重新启动。
+
+West Monroe Partners的卡伦德分享了一个阻碍DevOps的领导力的例子:未能拥抱IT混合模型和现代的基础架构比如说容器和微服务
+
+“我所看到的一个大的规则就是架构整合,或者认为在一个同质的环境下长期的维护会更便宜,”卡伦德说。
+
+**想要更多像这样的智慧吗?[注册我们的每周邮件新闻报道][15].**
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2018/1/7-leadership-rules-devops-age
+
+作者:[Kevin Casey][a]
+译者:[译者FelixYFZ](https://github.com/FelixYFZ)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://enterprisersproject.com/user/kevin-casey
+[1]:https://enterprisersproject.com/tags/devops
+[2]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/7/devops-requires-dumping-old-it-leadership-ideas
+[3]:https://www.datical.com/
+[4]:https://rework.withgoogle.com/guides/understanding-team-effectiveness/steps/foster-psychological-safety/
+[5]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/10/why-agile-leaders-must-move-beyond-talking-about-failure?sc_cid=70160000000h0aXAAQ
+[6]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/10/how-beat-fear-and-loathing-it-change
+[7]:https://www.rainforestqa.com/
+[8]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2018/1/3-areas-where-devops-and-cios-must-get-same-page
+[9]:https://www.cybric.io/
+[10]:http://www.westmonroepartners.com/
+[11]:https://www.scrumalliance.org/community/articles/2017/february/product-backlog-grooming
+[12]:https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/automation?intcmp=701f2000000tjyaAAA
+[13]:https://www.redhat.com/en?intcmp=701f2000000tjyaAAA
+[14]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/7/devops-metrics-are-you-measuring-what-matters
+[15]:https://enterprisersproject.com/email-newsletter?intcmp=701f2000000tsjPAAQ
diff --git a/translated/talk/20180305 What-s next in IT automation- 6 trends to watch.md b/translated/talk/20180305 What-s next in IT automation- 6 trends to watch.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..f5e93d0a0c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/talk/20180305 What-s next in IT automation- 6 trends to watch.md
@@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
+IT自动化的下一步是什么: 6 大趋势
+======
+
+
+
+我们最近介绍了 [促进自动化的因素][1] ,目前正在被人们采用的 [趋势][2], 以及那些刚开始使用自动化部分流程组织 [有用的技巧][3] 。
+
+噢, 我们也分享了在你的公司[如何使用自动化的案例][4] , 以及 [长期成功的关键][5].
+
+现在, 只有一个问题: 自动化的下一步是什么? 我们邀请一系列专家分享一下 [自动化][6]不远的将来。 以下是他们建议IT领域领导需密切关注的六大趋势。
+
+### 1. 机器学习的成熟
+
+对于关于 [机器学习][7]的讨论 (与“自我学习系统”相似的定义),对于绝大多数组织的项目来说,实际执行起来它仍然为时过早。但预计这将发生变化,机器学习将在下一次IT自动化浪潮中将扮演着至关重要的角色。
+
+[Advanced Systems Concepts, Inc.][8]公司工程总监 Mehul Amin 指出机器学习是IT自动化下一个关键增长领域之一。
+
+“随着数据化的发展, 自动化软件理应可以自我决策,否则这就是开发人员的责任了”, Amin 说。 “例如, 开发者需要执行构建内容, 但是识别系统最佳执行流程的,可能是由系统内软件分析完成。”
+
+假设将这个系统延伸到其他地方中。Amin 指出,机器学习可以使自动化系统在必要的时候提供额外的资源,以需要满足时间线或SLA,同样在不需要资源的时候退出以及其他的可能性。
+
+显然不只有 Amin 一个人这样认为。
+
+[Sungard Availability Services][9] 公司首席架构师 Kiran Chitturi 表示,“IT自动化正在走向自我学习的方向” 。“系统将会能测试和监控自己,加强业务流程和软件交付能力。”
+
+Chitturi 指出自动化测试就是个例子。脚本测试已经被广泛采用,但很快这些自动化测试流程将会更容易学习,更快发展,例如开发出新的代码或将更为广泛地影响生产环境。
+
+### 2. 人工智能催生的自动化
+
+上述原则同样适合 [人工智能][10](但是为独立)的领域。假定新兴的人工智能技术将也会产生新的自动化机会。根据对人工智能的定义,机器学习在短时间内可能会对IT领域产生巨大的影响(并且我们可能会看到这两个领域的许多重叠的定义和理解)。
+
+[SolarWinds][11]公司技术负责人 Patrick Hubbard说,“人工智能(AI)和机器学习的整合普遍被认为对未来几年的商业成功起至关重要的作用。”
+
+### 3. 这并不意味着不再需要人力
+
+让我们试着安慰一下那些不知所措的人:前两种趋势并不一定意味着我们将失去工作。
+
+这很可能意味着各种角色的改变以及[全新角色][12]的创造。
+
+但是在可预见的将来,至少,你不必需要机器人鞠躬。
+
+“一台机器只能运行在给定的环境变量中它不能选择包含新的变量,在今天只有人类可以这样做,” Hubbard 解释说。“但是,对于IT专业人员来说,这将是需要培养AI和自动化技能的时代。如对程序设计、编程、管理人工智能和机器学习功能算法的基本理解,以及用强大的安全状态面对更复杂的网络攻击。”
+
+Hubbard 分享一些新的工具或功能例子,例如支持人工智能的安全软件或机器学习的应用程序,这些应用程序可以远程发现石油管道中的维护需求。两者都可以提高效益和效果,自然不会代替需要信息安全或管道维护的人员。
+
+“许多新功能仍需要人工监控,”Hubbard 说。“例如,为了让机器确定一些‘预测’是否可能成为‘规律’,人为的管理是必要的。”
+
+即使你把机器学习和AI先放在一边,看待一般地IT自动化,同样原理也是成立的,尤其是在软件开发生命周期中。
+
+[Juniper Networks][13]公司自动化首席架构师 Matthew Oswalt ,指出IT自动化增长的根本原因是它通过减少操作基础设施所需的人工工作量来创造直接价值。
+
+在代码上,操作工程师可以使用事件驱动的自动化提前定义他们的工作流程,而不是在凌晨3点来应对基础设施的问题。
+
+“它也将操作工作流程作为代码而不再是容易过时的文档或系统知识阶段,”Oswalt解释说。“操作人员仍然需要在[自动化]工具响应事件方面后发挥积极作用。采用自动化的下一个阶段是建立一个能够跨IT频谱识别发生的有趣事件的系统,并以自主方式进行响应。在代码上,操作工程师可以使用事件驱动的自动化提前定义他们的工作流程,而不是在凌晨3点来应对基础设施的问题。他们可以依靠这个系统在任何时候以同样的方式作出回应。”
+
+### 4. 对自动化的焦虑将会减少
+
+SolarWinds公司的 Hubbard 指出,“自动化”一词本身就产生大量的不确定性和担忧,不仅仅是在IT领域,而且是跨专业领域,他说这种担忧是合理的。但一些随之而来的担忧可能被夸大了,甚至是科技产业本身。现实可能实际上是这方面的镇静力:当自动化的实际实施和实践帮助人们认识到这个列表中的“3”时,我们将看到“4”的出现。
+
+“今年我们可能会看到对自动化焦虑的减少,更多的组织开始接受人工智能和机器学习作为增加现有人力资源的一种方式,”Hubbard说。“自动化历史上的今天为更多的工作创造了空间,通过降低成本和时间来完成较小任务,并将劳动力重新集中到无法自动化并需要人力的事情上。人工智能和机器学习也是如此。”
+
+自动化还将减少IT领导者神经紧张主题的一些焦虑:安全。正如[红帽][14]公司首席架构师 Matt Smith 最近[指出][15]的那样,自动化将越来越多地帮助IT部门降低与维护任务相关的安全风险。
+
+他的建议是:“首先在维护活动期间记录和自动化IT资产之间的交互。通过依靠自动化,您不仅可以消除历史上需要大量手动操作和手术技巧的任务,还可以降低人为错误的风险,并展示当您的IT组织采纳变更和新工作方法时可能发生的情况。最终,这将迅速减少对应用安全补丁的抵制。而且它还可以帮助您的企业在下一次重大安全事件中摆脱头条新闻。”
+
+**[ 阅读全文: [12个企业安全坏习惯要打破。][16] ] **
+
+### 5. 脚本和自动化工具将持续发展
+
+看到许多组织增加自动化的第一步 - 通常以脚本或自动化工具(有时称为配置管理工具)的形式 - 作为“早期”工作。
+
+但是随着各种自动化技术的使用,对这些工具的观点也在不断发展。
+
+[DataVision][18]首席运营官 Mark Abolafia 表示:“数据中心环境中存在很多重复性过程,容易出现人为错误,[Ansible][17]等技术有助于缓解这些问题。“通过 Ansible ,人们可以为一组操作编写特定的步骤,并输入不同的变量,例如地址等,使过去长时间的过程链实现自动化,而这些过程以前都需要人为触摸和更长的交货时间。”
+
+**[想了解更多关于Ansible这个方面的知识吗?阅读相关文章:[使用Ansible时的成功秘诀][19]。 ]**
+
+另一个因素是:工具本身将继续变得更先进。
+
+“使用先进的IT自动化工具,开发人员将能够在更短的时间内构建和自动化工作流程,减少易出错的编码,” ASCI 公司的 Amin 说。“这些工具包括预先构建的,预先测试过的拖放式集成,API作业,丰富的变量使用,参考功能和对象修订历史记录。”
+
+### 6. 自动化开创了新的指标机会
+
+正如我们在此前所说的那样,IT自动化不是万能的。它不会修复被破坏的流程,或者以其他方式为您的组织提供全面的灵丹妙药。这也是持续不断的:自动化并不排除衡量性能的必要性。
+
+**[ 参见我们的相关文章 [DevOps指标:你在衡量什么重要吗?][20] ]**
+
+实际上,自动化应该打开新的机会。
+
+[Janeiro Digital][21]公司架构师总裁 Josh Collins 说,“随着越来越多的开发活动 - 源代码管理,DevOps管道,工作项目跟踪 - 转向API驱动的平台 - 将这些原始数据拼接在一起以描绘组织效率提升的机会和图景”。
+
+Collins 认为这是一种可能的新型“开发组织度量指标”。但不要误认为这意味着机器和算法可以突然预测IT所做的一切。
+
+“无论是衡量个人资源还是整体团队,这些指标都可以很强大 - 但应该用大量的背景来衡量。”Collins说,“将这些数据用于高层次趋势并确认定性观察 - 而不是临床评级你的团队。”
+
+**想要更多这样知识, IT领导者?[注册我们的每周电子邮件通讯][22]。**
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2018/3/what-s-next-it-automation-6-trends-watch
+
+作者:[Kevin Casey][a]
+译者:[MZqk](https://github.com/MZqk)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://enterprisersproject.com/user/kevin-casey
+[1]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/12/5-factors-fueling-automation-it-now
+[2]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/12/4-trends-watch-it-automation-expands
+[3]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2018/1/getting-started-automation-6-tips
+[4]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2018/1/how-make-case-it-automation
+[5]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2018/1/it-automation-best-practices-7-keys-long-term-success
+[6]:https://enterprisersproject.com/tags/automation
+[7]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2018/2/how-spot-machine-learning-opportunity
+[8]:https://www.advsyscon.com/en-us/
+[9]:https://www.sungardas.com/en/
+[10]:https://enterprisersproject.com/tags/artificial-intelligence
+[11]:https://www.solarwinds.com/
+[12]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/12/8-emerging-ai-jobs-it-pros
+[13]:https://www.juniper.net/
+[14]:https://www.redhat.com/en?intcmp=701f2000000tjyaAAA
+[15]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2018/2/12-bad-enterprise-security-habits-break
+[16]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2018/2/12-bad-enterprise-security-habits-break?sc_cid=70160000000h0aXAAQ
+[17]:https://opensource.com/tags/ansible
+[18]:https://datavision.com/
+[19]:https://opensource.com/article/18/2/tips-success-when-getting-started-ansible?intcmp=701f2000000tjyaAAA
+[20]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/7/devops-metrics-are-you-measuring-what-matters?sc_cid=70160000000h0aXAAQ
+[21]:https://www.janeirodigital.com/
+[22]:https://enterprisersproject.com/email-newsletter?intcmp=701f2000000tsjPAAQ
diff --git a/translated/tech/20171009 What-s next in DevOps- 5 trends to watch.md b/translated/tech/20171009 What-s next in DevOps- 5 trends to watch.md
deleted file mode 100644
index d6d7ecce7f..0000000000
--- a/translated/tech/20171009 What-s next in DevOps- 5 trends to watch.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
-DevOps 接下来会发生什么:观察到的 5 个趋势
-======
-
-
-
-"DevOps" 一词通常认为是来源于 [2008 年关于敏捷基础设施和运营的介绍][1]。现在的 IT 词汇中,它无处不在,这个“混搭”的词汇出现还不到 10 年:我们还在研究它在 IT 中更现代化的工作方法。
-
-当然,多年来一直在 “从事 DevOps" 的人积累了丰富的知识。但是大多数的 DevOps 环境 —— 人与 [文化][2] 、流程与方法、工具与技术的融合 —— 还远远没有成熟。
-
-更多的变化即将到来。Robert Reeves 说 ”DevOps 是一个过程,一种算法“,他是 [Datical][3] 的 CTO, "它的绝对目标就是随着时间进行改变和演进”,这就是重点。
-
-那我们预计接下来会发生什么呢?这里有一些专家们观察到的重要趋势。
-
-### 1. 预计 DevOps、容器、以及微服务之间的相互依赖会增强
-
-驱动 DevOps 发展的文化本身可能会演进。当然,DevOps 仍然将在根本上摧毁传统的 IT 站点和瓶颈,但这样做的理由可能会变得更加急迫。展示(证据) A & B: [对容器和微服务的兴趣][4] 与日俱增。这个技术组合很强大、可连续扩展、与规划和 [持续进行的管理][5]配合最佳。
-
-Arvind Soni 说 "影响 DevOps 的其中一个主要因素是向微服务转变“,它是 [Netsil][6] 的产品副总裁,添加容器和业务流程,使开发者打包和交付的速度越来越快。DevOps 团队的任务可能是帮助去加速打包并管理越来越复杂的微服务弹性架构。
-
-### 2. 预计 ”安全网“ 更少
-
-DevOps 使团队可以更快更敏捷地去构建软件,部署速度也更快更频繁、同时还能提升软件质量和稳定性。但是好的 IT 领导通常都不会忽视管理风险,因此,早期大量的 DevOps 迭代都是使用了安全防护 —— 从后备的不重要业务开始的。为了实现更快的速度和敏捷性,越来越多的团队将抛弃他们的 ”辅助轮“(译者注:意思说减少了安全防护措施)。
-
-Nic Grange 说 "随着团队的成熟,他们决定不再需要一些早期增加的安全 ”防护栏“ 了”,他是 [Retriever Communications][7] 的 CTO。Grange 给出了一个展示服务器的示例:随着 DevOps 团队的成熟,他们决定不再需要了,尤其是他们很少在试生产环境中发现问题。(Grange 指出,这一举措对于缺乏 DevOps 经验的团队来说,不可轻易效仿)
-
-Grange 说 "这个团队可能在监视和发现并解决生产系统中出现的问题的能力上有足够的信心“,"部署过程和测试阶段,如果没有任何证据证明它的价值,那么它可能会把整个进度拖慢”。
-
-### 3. 预计 DevOps 将在其它领域大面积展开
-
-DevOps 将两个传统的 IT 组(开发和运营)结合的更紧密。越来越多的公司看到了这种结合的好处,这种文化可能会传播开来。这种情况在一些组织中已经出现,在 “DevSecOps” 一词越来越多出现的情况下,它反映出了在软件开发周期中有意地、越来越早地包含了安全性。
-
-Derek Weeks 说 "DevSecOps 不仅是一个工具,它是将安全思维更早地集成到开发实践中“,它是 [Sonatype][8] 的副总裁和 DevOps 拥挤者。
-
- [Red Hat][9] 的安全策略师 Kirsten Newcomer 说,这种做法并不是一个技术挑战,而是一个文化挑战。
-
-Newcomer 说 "从历史来看,安全团队都是从开发团队中分离出来的 —— 每个团队在它们不同的 IT 领域中形成了各自的专长” ,"它并不需要这种方法。每个关心安全性的企业也关心他们通过软件快速交付业务价值的能力,这些企业正在寻找方法,将安全放进应用程序的开发周期中。它们采用 DevSecOps 通过 CI/CD 流水线去集成安全实践、工具、和自动化。为了做的更好,他们整合他们的团队 —— 将安全专家整合到应用程序开发团队中,参与到从设计到产品部署的全过程中。这种做法使双方都看到了价值 —— 每个团队都扩充了它们的技能和知识,使他们成为更有价值的技术专家。DevOps 做对了—— 或者说是 DevSecOps —— 提升了 IT 安全性。“
-
-除了安全以外,让 DevOps 扩展到其它领域,比如数据库团队、QA、甚至是 IT 以外的潜在领域。
-
-Datical 的 Reeves 说 "这是一件非常 DevOps 化的事情:发现相互掣肘的地方并解决它们”,"对于以前采用 DevOps 的企业来说,安全和数据库是他们面临的最大瓶颈。“
-
-### 4. 预计 ROI 将会增加
-
-Eric Schabell 说,”由于公司深入推进他们的 DevOps 工作,IT 团队在方法、流程、容器、和微服务方面的投资将得到更多的回报。“ 他是 Red Hat 的全球技术传播总监,Schabell 说 "Holy Grail 将移动的更快、完成的更多、并且变得更灵活。由于这些组件找到了更宽阔的天地,组织在应用程序中更有归属感时,结果就会出现。”
-
-"每当新兴技术获得我们的关注时,任何事都有一个令人兴奋的学习曲线,但当认识到它应用很困难的时候,同时也会经历一个从兴奋到幻灭的低谷。最终,我们将开始看到从低谷中爬出来,并收获到应用 DevOps、容器、和微服务的好处。“
-
-### 5. 预计成功的指标将持续演进
-
-Mike Kail 说 "我相信 DevOps 文化的两个核心原则 —— 自动化和可衡量是从来不会变的”,它是 [CYBRIC][10] 的 CTO,也是 Yahoo 前 CIO。“总是有办法去自动化一个任务,或者提升一个已经自动化的解决方案,而随着时间的推移,重要的事情是测量可能的变化和扩展。这个成熟的过程是一个永不停步的旅行,而不是一个目的地或者已完成的任务。”
-
-在 DevOps 的精神中,成熟和学习也与协作者和分享精神有关。Kail 认为,对于敏捷方法和 DevOps 文化来说,它仍然为时尚早,这意味着它们还有足够的增长空间。
-
-Kail 说 "随着越来越多的成熟组织持续去测量可控指标,我相信(希望) —— 这些经验应该被广泛的分享,以便我们去学习并改善它们。“
-
-作为 Red Hat 技术传播专家 [Gordon Haff][11] 最近注意到,组织使用业务成果相关的因素去改善他们的 DevOps 指标的工作越来越困难。 [Haff 写道][12] "你或许并不真正关心你的开发者写了多少行代码、服务器是否在一夜之间出现了硬件故障、或者你的测试覆盖面是否全面”。事实上,你可能并不直接关心你的网站的响应速度和更新快慢。但是你要注意的是,这些指标可能与消费者放弃购物车或者转到你的竞争对手那里有关。“
-
-与业务成果相关的一些 DevOps 指标的例子包括,消费者交易金额(作为消费者花销统计的指标)和净推荐值(消费者推荐公司产品和服务的意愿)。关于这个主题更多的内容,请查看这篇完整的文章—— [DevOps 指标:你是否测量了重要的东西 ][12]。
-
-### 唯一不变的就是改变
-
-顺利说一句,如果你希望这件事一蹴而就,那你就要倒霉了。
-
-Reeves 说 "如果你认为今天发布非常快,那你就什么也没有看到”,“这就是为什么要让相关者包括数据库团队进入到 DevOps 中的重要原因。因为今天这两组人员的冲突会随着发布速度的提升而呈指数级增长。”
-
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
-via: https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/10/what-s-next-devops-5-trends-watch
-
-作者:[Kevin Casey][a]
-译者:[qhwdw](https://github.com/qhwdw)
-校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
-
-本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
-
-[a]:https://enterprisersproject.com/user/kevin-casey
-[1]:http://www.jedi.be/presentations/agile-infrastructure-agile-2008.pdf
-[2]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/9/5-ways-nurture-devops-culture
-[3]:https://www.datical.com/
-[4]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/9/microservices-and-containers-6-things-know-start-time
-[5]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/10/microservices-and-containers-6-management-tips-long-haul
-[6]:https://netsil.com/
-[7]:http://retrievercommunications.com/
-[8]:https://www.sonatype.com/
-[9]:https://www.redhat.com/en/
-[10]:https://www.cybric.io/
-[11]:https://enterprisersproject.com/user/gordon-haff
-[12]:https://enterprisersproject.com/article/2017/7/devops-metrics-are-you-measuring-what-matters
diff --git a/translated/tech/20171121 How To Kill The Largest Process In An Unresponsive Linux System.md b/translated/tech/20171121 How To Kill The Largest Process In An Unresponsive Linux System.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..042cd39684
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20171121 How To Kill The Largest Process In An Unresponsive Linux System.md
@@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
+如何在无响应的 Linux 系统中杀掉最大的进程
+======
+
+
+作为一名博客作者,我收藏了很多博客、网站和论坛用来标记 Linux 和 Unix 相关的内容。有时候,我在浏览器中开启了非常多的标签页,导致操作系统会无响应好几分钟。我不能移动我的鼠标去杀掉一个进程或关闭任何开启的标签页。在这种情况下,我别无选择,只能强制重启系统。当然我也用了 **OneTab** (译者注:OneTab 是一个 Chrome 的 Extension, 可以将标签页转化成一个列表保存。)和 **Greate Suspender** (译者注:Great Suspender 是一个 Chrome 的 Extension, 可以自动冻结标签页)这样浏览器拓展,但它们在这里也起不到太大的作用。 我经常耗尽我的内存。而这就是 **Early OOM** 起作用的时候了。在情况严重,它会杀掉一个未响应系统中的最大的进程。Early OOM 每秒会检测可用内存和空余交换区 10 次,一旦两者都低于 10%,它就会把最大的进程杀死。
+
+### 为什么用 Early OOM?为什么不用系统内置的 OOM killer?
+
+在继续讨论下去之前,我想先简短的介绍下 OOM killer,也就是 **O** ut **O** f **M** emory killer。OOM killer 是一个由内核在可用内存非常低的时候使用的进程。它的主要任务是不断的杀死进程,直到释放出足够的内存,是内核正在运行的进程的其余部分能顺利运行。OOM killer 会找到系统中最不重要并且能释放出最多内存的进程,然后杀掉他们。在 **/proc** 目录下的 **pid** 目录中,我们可以看到每个进程的 oom_score。
+
+示例:
+```
+$ cat /proc/10299/oom_score
+1
+```
+
+一个进程的 oom_score 的值越高,这个进程越有可能在系统内存耗尽的时候被 OOM killer 杀死。
+
+Early OOM 的开发者表示,相对于内置的 OOM killer,Early OOM 有一个很大的优点。就像我之前说的那样,OOM killer 会杀掉 oom_score 最高的进程,而这也导致 Chrome 浏览器总是会成为第一个被杀死的进程。为了避免这种情况发生,Early OOM 使用 **/proc/*/status** 而不是 **echo f > /proc/sysrq-trigger**(译者注:这条命令会调用 OOM killer 杀死进程)。开发者还表示,手动触发 OOM killer 在最新版本的 Linux 内核中很可能不会起作用。
+
+### 安装 Early OOM
+
+Early OOM 在AUR(Arch User Repository)中可以被找到,所以你可以在 Arch 和它的衍生版本中使用任何 AUR 工具安装它。
+
+使用 [**Pacaur**][1]:
+```
+pacaur -S earlyoom
+```
+
+使用 [**Packer**][2]:
+```
+packer -S earlyoom
+```
+
+使用 [**Yaourt**][3]:
+```
+yaourt -S earlyoom
+```
+
+启用并启动 Early OOM daemon:
+```
+sudo systemctl enable earlyoom
+```
+```
+sudo systemctl start earlyoom
+```
+
+在其它的 Linux 发行版中,可以按如下方法编译安装它
+```
+git clone https://github.com/rfjakob/earlyoom.git
+cd earlyoom
+make
+sudo make install
+```
+
+### Early OOM - Kill The Largest Process In An Unresponsive Linux System杀掉无响应 Linux 系统中的最大的进程
+
+运行如下命令启动 Early OOM:
+```
+earlyoom
+```
+
+如果是通过编译源代码安装的, 运行如下命令启动 Early OOM:
+```
+./earlyoom
+```
+
+示例输出:
+```
+earlyoom 0.12
+mem total: 3863 MiB, min: 386 MiB (10 %)
+swap total: 2047 MiB, min: 204 MiB (10 %)
+mem avail: 1770 MiB (45 %), swap free: 2047 MiB (99 %)
+mem avail: 1773 MiB (45 %), swap free: 2047 MiB (99 %)
+mem avail: 1772 MiB (45 %), swap free: 2047 MiB (99 %)
+mem avail: 1773 MiB (45 %), swap free: 2047 MiB (99 %)
+mem avail: 1772 MiB (45 %), swap free: 2047 MiB (99 %)
+mem avail: 1773 MiB (45 %), swap free: 2047 MiB (99 %)
+mem avail: 1771 MiB (45 %), swap free: 2047 MiB (99 %)
+mem avail: 1773 MiB (45 %), swap free: 2047 MiB (99 %)
+mem avail: 1784 MiB (46 %), swap free: 2047 MiB (99 %)
+[...]
+```
+
+就像你在上面的输出中可以看到的,Early OOM 将会显示你有多少内存和交换区,以及有多少可用的内存和交换区。记住它会一直保持运行,直到你按下 CTRL+C。
+
+如果可用的内存和交换区大小都低于 10%,Early OOM 将会自动杀死最大的进程,直到系统有足够的内存可以流畅的运行。你也可以根据你的需求配置最小百分比值。
+
+设置最小的可用内存百分比,运行:
+```
+earlyoom -m
+```
+
+设置最小可用交换区百分比, 运行:
+```
+earlyoom -s
+```
+
+在帮助部分,可以看到更多详细信息:
+```
+$ earlyoom -h
+earlyoom 0.12
+Usage: earlyoom [OPTION]...
+
+ -m PERCENT set available memory minimum to PERCENT of total (default 10 %)
+ -s PERCENT set free swap minimum to PERCENT of total (default 10 %)
+ -M SIZE set available memory minimum to SIZE KiB
+ -S SIZE set free swap minimum to SIZE KiB
+ -k use kernel oom killer instead of own user-space implementation
+ -i user-space oom killer should ignore positive oom_score_adj values
+ -d enable debugging messages
+ -v print version information and exit
+ -r INTERVAL memory report interval in seconds (default 1), set to 0 to
+ disable completely
+ -p set niceness of earlyoom to -20 and oom_score_adj to -1000
+ -h this help text
+```
+
+现在,你再也不用担心内存消耗最高的进程了。希望这能给你帮助。更多的好内容将会到来,敬请期待。
+
+谢谢!
+
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.ostechnix.com/kill-largest-process-unresponsive-linux-system/
+
+作者:[Aditya Goturu][a]
+译者:[cizezsy](https://github.com/cizezsy)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.ostechnix.com
+[1]:https://www.ostechnix.com/install-pacaur-arch-linux/
+[2]:https://www.ostechnix.com/install-packer-arch-linux-2/
+[3]:https://www.ostechnix.com/install-yaourt-arch-linux/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180404 Containerization, Atomic Distributions, and the Future of Linux.md b/translated/tech/20180404 Containerization, Atomic Distributions, and the Future of Linux.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..2a75db4754
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180404 Containerization, Atomic Distributions, and the Future of Linux.md
@@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
+容器化,原子化发行版以及 Linux 的未来
+======
+
+
+自从 Linus Torvalds 在 1991 年发布 Linux 以来,Linux 已历经漫长的岁月。它已经成为企业级领域的主流操作系统。同时,我们看到桌面级领域出现了很多改进和调整,但在过去的 25+ 年,主流 Linux 发行版的模式很大程度上保持不变。基于软件包管理的传统模式依然统治着桌面级和服务器级市场。
+
+但随着 Google 发布了基于 Linux 的 Chrome-OS,情况出现了微妙的转变,Chrome-OS 采用镜像模式。Core OS (目前归属于 Red Hat) 受 Google 启发推出了一款操作系统 Container Linux,主要面向企业级用户。
+
+Container Linux 改变了操作系统更新的方式,也改变了应用分发和更新的方式。这会是 Linux 发行版的未来吗?这是否会取代基于软件包的传统发行版模式呢?
+
+### 三种模式
+
+SLE (SUSE Linux Enterprise) 的产品管理总监 Matthias Eckermann 认为目前存在 3 种模式,而不是 2 种。Eckermann 提到:“除了传统模式 (RHEL/SLE) 和镜像模式 (RH Atomic Host),还存在第三种模型:事务模式。[SUSE CaaS 平台][1] 及 SUSE MicroOS 就采用这种模型。”
+
+### 差异有哪些
+
+Linux 用户对传统模式非常熟悉,它由独立的软件包和共享库组成。这种模式有独特的优势,让应用开发者无需将共享库捆绑在应用中。由于库不会多次引入,使得系统简洁和轻便。这也让用户无需下载很多软件包,节省了带宽。发行版对软件包全权负责,通过推送系统级别的更新,可以轻松地解决安全隐患。
+
+RHEL (Red Hat Enterprise Linux) 的产品管理总监 Ron Pacheco 表示,“传统的打包方式继续为我们提供精心构建和优化操作系统的机会,以便支持需要经过时间考验的任务关键型工作负载。”
+
+但传统模式也有一些弊端。应用开发者受限使用发行版包含的库,使其无法从发行版不支持的新软件中获益。这也可能导致不同版本之间相互冲突。最终,传统模式给管理员增加了挑战,使其难以让软件包一直处于最新版本状态。
+
+### 镜像模式
+
+镜像模式应运而生。Eckermann 表示,“镜像模式解决了传统模式遇到的问题,它在每次迭代更新时替换整个操作系统,其中也不包含独立的软件包”。
+
+Pacheco 表示,“当我们用镜像作为操作系统的代名词进行讨论时,我们真正关心的是可编程式的开发部署以及更好的集成式生命周期管理”,基于 RHEL 搭建的 OpenShift 被他用作示例。
+
+Pacheco 认为基于镜像的操作系统是一种延续,从手工打造并部署镜像,到可大规模管理的高度自动化基础设施;无论客户使用哪种类型,都需要运行同样的应用。他说,“你肯定不希望使用一个完全不同的部署模式,这需要重做很多工作”。
+
+镜像模式替代了使用新库和软件包的完整操作系统,但也面临一系列问题。在镜像模式中,需要重建镜像才能适应特殊环境的需求。例如,用户有特殊需求,需要安装特定硬件的驱动或安装底层监控功能,镜像模式无法满足,需要重新设计功能以实现细粒度操作。
+
+### 事务模式
+
+第三种模式采用事务更新,基于传统的软件包更新,但将全部的软件包视为一个镜像,就像镜像那样在一次操作中更新全部软件包。
+
+Eckermann 表示,“由于安装或回滚时操作对象是打包在一起的独立软件包,用户在需要时能够做相应的调整,这就是差别所在。结合传统模式和镜像模式的优点,避免两种模式的缺点,事务模式给用户提供了额外的灵活性。”
+
+Pacheco 表示,将精心构造的工作负载部署成镜像的做法越来越成为主流,因为这种部署方式具有一致性和可靠性,而且可以弹性部署。“这正是我们用户目前的做法,部署环境包括在预置设备或公有/私有云上创建并部署的虚拟机,或在传统的裸机上”
+
+Pacheco 建议我们将这几种模式视为操作系统角色的进化和扩展,而不是仅仅“使用场景的比较和对比“。
+
+### 原子化更新的问世
+
+Google 的 Chrome OS 和 Core OS 为我们普及了事务更新的概念,该模型也被 Red Hat 和 SUSE 采用。
+
+Eckermann 表示,”我们必须认识到,用于容器主机的操作系统已经不再是关注点 —— 至少不是管理员的关注点。RH Atomic 主机和 SUSE CaaS 平台都解决了该问题,实现方式在用户看来很相似。“
+
+SUSE CaaS 平台、Red Hat Atomic Host和 Container Linux (前身是 Core OS)提供的[不可变基础设施][2] 推广了事务更新的使用。Red Hat 高级技术产品经理 Ben Breard 表示,”在事务模式中,主机总是会变更到已确认正确的新状态,这让我们更有信心执行更新,进而实现更快速的功能流、安全优势以及易于采用的操作模式“。
+
+这些新型操作系统使用 Linux 容器将应用与底层系统隔离,解除了传统模式中基础设施更新的诸多限制。
+
+Breard 补充道,“当编排层可以智能处理更新、部署,甚至最终实现无缝操作时,我们才会真正意识到该模式的威力和好处”。
+
+### 展望未来
+
+Linux 的未来会是什么样子?不同的人会给出不同的回答。容器支持者认为未来属于容器化的操作系统,但依然拥有庞大市场的 Linux 供应商显然不这么认为。
+
+当被问到原子化发行版是否在很久以后将替换传统发行版时,Eckermann 表示,“如果我回答肯定的,那么表示我顺应潮流;如果回答是否的的,意味着我还是站在传统阵营。然而,我的回答是否定的,即 atomic 发行版在很久以后也不会替换传统发行版,传统负载和容器化负载将在数据中心、私有云以及公有云环境中共存。”
+
+Pacheco 认为,从 Linux 的部署增长情况来看,一般情况下很难想象一种模式替换另一种模式。与其将多种模式视为相互竞争的关系,不如将原子化发行版视为操作系统进化和部署的一部分。
+
+此外,在一些使用案例中,我们需要同时使用多种 Linux 发行版。Eckermann 表示,“想一想银行和保险公司中大量的 PL/1 和 Cobol 系统。再想一想内存数据库和核心数据总线系统”。
+
+这些应用大多数无法进行容器化。就我们目前来看,容器化不是解决所有问题的万金油。总是会同时存在多种不同的技术。
+
+Eckermann 相信,随着时间的推移,大量新的开发和部署将采用容器化,但仍然有不错的理由,促使我们在企业级环境中保留传统的部署方式和应用。
+
+Pacheco 认为,“用户需要经历业务、设计和文化的转型,才能最大化基于容器的部署带来的优势。好消息是业界已经认识到并开始大规模转变,就像历史上大型机转变成 UNIX,UNIX 转变成 x86,x86 转变成虚拟化那样”。
+
+### 结论
+
+很明显,未来容器化负载的使用量会持续增长,也就意味着原子化发行版的需求量持续增长。与此同时,仍会有不少工作负载运行在传统发行版中。重要的是,这两类用户都在新模式上大规模投入,以便市场改变时可以做相应的策略改变。从外部观察者的视角来看,未来属于事务/原子化模式。我们已经见证了数据中心的发展,我们花了很长时间完成了从每个服务器一个应用到函数即服务模型的转变。Linux 发行版进入原子化时代的日子也不会太远了。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://www.linux.com/blog/2018/4/containerization-atomic-distributions-and-future-linux
+
+作者:[SWAPNIL BHARTIYA][a]
+译者:[pinewall](https://github.com/pinewall)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://www.linux.com/users/arnieswap
+[1]:https://www.suse.com/products/caas-platform/
+[2]:https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/what-is-immutable-infrastructure
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180406 How To Register The Oracle Linux System With The Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN).md b/translated/tech/20180406 How To Register The Oracle Linux System With The Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN).md
similarity index 75%
rename from sources/tech/20180406 How To Register The Oracle Linux System With The Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN).md
rename to translated/tech/20180406 How To Register The Oracle Linux System With The Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN).md
index 34e6c36401..92c8407884 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20180406 How To Register The Oracle Linux System With The Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN).md
+++ b/translated/tech/20180406 How To Register The Oracle Linux System With The Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN).md
@@ -1,58 +1,57 @@
-Translating by qhwdw
-How To Register The Oracle Linux System With The Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN)
+Oracle Linux 系统如何去注册使用坚不可摧 Linux 网络(ULN)
======
-Most of us knows about RHEL subscription but only few of them knows about Oracle subscription and its details.
+大多数人都知道 RHEL 的订阅 ,但是知道 Oracle 订阅及细节的人却很少。
-Even i don’t know the information about this and i recently came to know about this and wants to share this with others so, i’m going to write a article which will guide you to register the Oracle Linux system with the Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN).
+甚至我也不知道关于它的信息,我是最近才了解了有关它的信息,想将这些内容共享给其他人。因此写了这篇文章,它将指导你去注册 Oracle Linux 系统去使用坚不可摧 Linux 网络(ULN) 。
-This allows the register systems to get software update and other patches ASAP.
+这将允许你去注册系统以获得软件更新和其它的 ASAP 补丁。
-### What Is Unbreakable Linux Network
+### 什么是坚不可摧 Linux 网络
-ULN stands for Unbreakable Linux Network which is owned by Oracle. If you have a active subscription to Oracle OS Support, you can register your system with Unbreakable Linux Network (ULN).
+ULN 代表坚不可摧 Linux 网络,它是由 Oracle 所拥有的。如果你去 Oracle OS 支持中去激活这个订阅,你就可以注册你的系统去使用坚不可摧 Linux 网络(ULN)。
-ULN offers software patches, updates, and fixes for Oracle Linux and Oracle VM, as well as information on yum, Ksplice, and support policies. You can also download useful packages that are not included in the original distribution.
+ULN 为 Oracle Linux 和 Oracle VM 提供软件补丁、更新、以及修复,此外还有在 yum、Ksplice、以及支持策略上的信息。你也可以通过它来下载原始发行版中没有包含的有用的安装包。
-The ULN Alert Notification Tool periodically checks with ULN and alerts you when updates are available.
+ULN 的告警提示工具周期性地使用 ULN 去检查,当有更新的时候它给你发送警报信息。
-If you want to use ULN repository with yum to manage your systems, make sure your system should registered with ULN and subscribe each system to one or more ULN channels. When you register a system with ULN, automatically it will choose latest version of channel based on the system architecture and OS.
+如果你想在 yum 上使用 ULN 仓库去管理你的系统,需要确保你的系统已经注册到 ULN 上,并且订阅了一个或多个 ULN 频道。当你注册一个系统使用 ULN,它将基于你的系统架构和操作系统去自动选择频道中最新的版本。
-### How To Register As A ULN User
+### 如何注册为一个 ULN 用户
-To register as a ULN user, make sure you have a valid customer support identifier (CSI) for Oracle Linux support or Oracle VM support.
+去注册为一个 ULN 用户,需要你有一个 Oracle Linux 支持或者 Oracle VM 支持的有效客户支持代码(CSI)。
-Follow the below steps to register as a ULN user.
+请按以下步骤去注册为一个 ULN 用户。
-Visit @ [linux.oracle.com][1]
+请访问 [linux.oracle.com][1]
![][3]
-If you already have an SSO account, click Sign On.
+如果你已经有一个 SSO 帐户,请点击 “Sign On”。
![][4]
-If you don’t have a account, click Create New Single Signon Account and follow the onscreen instructions to create one.
+如果你没有帐户,点击 “Create New Single Signon Account” 然后按屏幕上的要求去创建一个帐户。
![][5]
-Verify your email address to complete your account setup.
+验证你的电子邮件地址以完成帐户设置。
-Log in using your SSO user name and password. On the Create New ULN User page, enter your CSI and click Create New User.
+使用你的 SSO 帐户的用户名和密码去登入。在 “Create New ULN User” 页面上,输入你的 CSI 然后点击 “Create New User”。
![][6]
-**Note :**
+**注意:**
- * If no administrator is currently assigned to manage the CSI, you are prompted to click Confirm to become the CSI administrator.
- * If your user name already exists on the system, you are prompted to proceed to ULN by clicking the link Unbreakable Linux Network.
+ * 如果当前没有分配管理员去管理 CSI,将会提示你去点击确认让你成为 CSI 管理员。
+ * 如果你的用户名已经在系统上存在,你将被提示通过点击坚不可摧 Linux 网络的链接去操作 ULN。
-### How To Register The Oracle Linux 6/7 System With ULN
+### 如何注册 Oracle Linux 6/7 系统使用 ULN
-Just run the below command and follow the instruction to register the system.
+只需要运行下列的命令,并按随后的指令提示去注册系统。
```
# uln_register
```
-Make sure your system is having active internet connection. Also keep ready your Oracle Single Sign-On Login & password (SSO) details then hit `Next`.
+确保你的系统有一个活动的因特网连接。同时准备好你的 Oracle 单点登陆帐户(SSO)的用户名和密码,然后点击 `Next`。
```
Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
@@ -78,7 +77,7 @@ Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
```
-Input your login information for Unbreakable Linux Network, then hit `Next`.
+输入你的 ULN 登陆信息,然后点击 `Next`。
```
Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
@@ -101,7 +100,7 @@ Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
```
-Register a System Profile – Hardware information, then hit `Next`.
+注册一个系统概要 – 硬件信息,然后点击 `Next`。
```
Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
@@ -130,7 +129,7 @@ Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
```
-Register a System Profile – Packages configuration, then hit `Next`.
+注册一个系统概要 – 包配置,然后点击 `Next`。
```
Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
@@ -168,7 +167,7 @@ Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
```
-Press “Next” to send this System Profile to Unbreakable Linux Network.
+按下 “Next” 去发送系统概要到 ULN。
```
Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
@@ -188,7 +187,7 @@ Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
```
-Sending Profile to Unbreakable Linux Network is under processing.
+发送概要到 ULN 是如下的一个过程。
```
Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
@@ -202,7 +201,7 @@ Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
```
-ULN registration has been done and review system subscription details. If everything is fine, then hit `ok`.
+ULN 注册做完后,重新回顾系统订阅的详细情况。如果一切正确,然后点击 `ok`。
```
Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
@@ -237,7 +236,7 @@ Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
```
-Finally hit `Finish` to complete the registration.
+最后点击 `Finish` 完成注册。
```
Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
@@ -256,7 +255,7 @@ Copyright © 2006--2010 Red Hat, Inc. All rights reserved.
```
-ULN registration has been done successfully, in order to get repository from ULN run the following command.
+ULN 注册已经成功,为了从 ULN 中得到仓库,运行如下的命令。
```
# yum repolist
Loaded plugins: aliases, changelog, presto, refresh-packagekit, rhnplugin, security, tmprepo, ulninfo, verify, versionlock
@@ -271,13 +270,13 @@ repolist: 40,966
```
-Also, you can check the same in ULN website. Go to the `System` tab to view the list of registered systems.
+另外,你也可以在 ULN 网站上查看到相同的信息。转到 `System` 标签页去查看已注册的系统列表。
![][7]
-To view list of the enabled repositories. Go to the `System` tab then hit the corresponding system. Also, you can able to see the available updates for the system for errata.
+去查看已经启用的仓库列表。转到 `System` 标签页,然后点击相应的系统。另外,你也能够看到系统勘误及可用更新。
![][8]
-To manage subscription channel. Go to the `System` tab, then hit appropriate `system name` and finally hit `Manage Subscriptions`.
+去管理订阅的频道。转到 `System` 标签页,然后点击有关的 `system name`,最后点击 `Manage Subscriptions`。
![][9]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -285,7 +284,7 @@ To manage subscription channel. Go to the `System` tab, then hit appropriate `sy
via: https://www.2daygeek.com/how-to-register-the-oracle-linux-system-with-the-unbreakable-linux-network-uln/
作者:[Vinoth Kumar][a]
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+译者:[qhwdw](https://github.com/qhwdw)
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180410 Top 9 open source ERP systems to consider - Opensource.com.md b/translated/tech/20180410 Top 9 open source ERP systems to consider - Opensource.com.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..d992352a2c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180410 Top 9 open source ERP systems to consider - Opensource.com.md
@@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
+可以考虑的 9 个开源 ERP 系统
+======
+
+拥有一定数量员工的企业就需要大量的协调工作,包括价格、生产计划、帐务和财务、管理支出、管理存货等等。把一套截然不同的工具拼接到一起去处理这些工作,是一种粗制滥造和无价值的做法。
+
+那种方法没有任何弹性。并且那样在各种各样的自组织系统之间高效移动数据是非常困难的。同样,它也很难维护。
+
+因此,大多数成长型企业都转而使用一个 [企业资源计划][1] (ERP) 系统。
+
+在这个行业中的大咖有 Oracle、SAP、以及 Microsoft Dynamics。它们都提供了一个综合的系统,但同时也很昂贵。如果你的企业支付不起如此昂贵的大系统,或者你仅需要一个简单的系统,怎么办呢?你可以使用开源的产品来作为替代。
+
+### 一个 ERP 系统中有什么东西
+
+显然,你希望有一个满足你需要的系统。基于那些需要,更多的功能并不意味着就更好。但是,你的需要会根据你的业务的增长而变化的,因此,你希望能够找到一个 ERP 系统,它能够根据你新的需要而扩展它。那就意味着系统有额外的模块或者支持插件和附加功能。
+
+大多数的开源 ERP 系统都是 web 应用程序。你可以下载并将它们安装到你的服务器上。但是,如果你不希望(或者没有相应技能或者人员)自己去维护系统,那么应该确保它们的应用程序提供托管版本。
+
+最后,你还应该确保应用程序有良好的文档和支持 —— 要么是付费支持或者有一个活跃的用户社区。
+
+有很多弹性很好的、功能丰富的、很划算的开源 ERP 系统。如果你正打算购买这样的系统,这里有我们挑选出来的 9 个。
+
+### ADempiere
+
+像大多数其它开源 ERP 解决方案,[ADempiere][2] 的目标客户是中小企业。它已经存在一段时间了— 这个项目出现于 2006,它是 Compiere ERP 软件的一个分支。
+
+它的意大利语名字的意思是“实现”或者“满足”,它“涉及多个方面”的 ERP 特性旨在帮企业去满足各种需求。它在 ERP 中增加了供应链管理(SCM)和客户关系管理(CRM)功能,能够让 ERP 套件在一个软件中去管理销售、采购、库存、以及帐务处理。它的最新版本是 v.3.9.0,更新了用户界面、销售点、人力资源、工资、以及其它的特性。
+
+因为是一个跨平台的、基于 Java 的云解决方案,ADempiere 可以运行在Linux、Unix、Windows、MacOS、智能手机、平板电脑上。它使用 [GPLv2][3] 授权。如果你想了解更多信息,这里有一个用于测试的 [demo][4],或者也可以在 GitHub 上查看它的 [源代码][5]。
+
+### Apache OFBiz
+
+[Apache OFBiz][6] 的业务相关的套件是构建在通用的架构上的,它允许企业根据自己的需要去定制 ERP。因此,它是有内部开发资源的大中型企业去修改和集成它到它们现有的 IT 和业务流程的最佳套件。
+
+OFBiz 是一个成熟的开源 ERP 系统;它的网站上说它是一个有十年历史的顶级 Apache 项目。可用的 [模块][7] 有帐务、生产制造、人力资源、存货管理、目录管理、客户关系管理、以及电子商务。你可以在它的 [demo 页面][8] 上试用电子商务的网上商店以及后端的 ERP 应用程序。
+
+Apache OFBiz 的源代码能够在它的 [项目仓库][9] 中找到。它是用 Java 写的,它在 [Apache 2.0 license][10] 下可用。
+
+### Dolibarr
+
+[Dolibarr][11] 提供了中小型企业端到端的业务管理,从发票跟踪、合同、存货、订单、以及支付,到文档管理和电子化 POS 系统支持。它的全部功能封装在一个清晰的界面中。
+
+如果你担心不会使用 Dolibarr,[这里有一些关于它的文档][12]。
+
+另外,还有一个 [在线演示][13],Dolibarr 也有一个 [插件商店][14],你可以在那是购买一些软件来扩展它的功能。你可以在 GitHub 上查看它的 [源代码][15];它在 [GPLv3][16] 或者任何它的最新版本许可下面使用。
+
+### ERPNext
+
+[ERPNext][17] 是这类开源项目中的其中一个;实际上它最初 [出现在 Opensource.com][18]。它被设计用于打破一个陈旧而昂贵的专用 ERP 系统的垄断局面。
+
+ERPNext 适合于中小型企业。它包含的模块有帐务、存货管理、销售、采购、以及项目管理。ERPNext 是表单驱动的应用程序 — 你可以在一组字段中填入信息,然后让应用程序去完成剩余部分。整个套件非常易用。
+
+如果你感兴趣,在你考虑参与之前,你可以请求获取一个 [demo][19],去 [下载它][20] 或者在托管服务上 [购买一个订阅][21]。
+
+### Metasfresh
+
+[Metasfresh][22] 的名字表示它承诺软件的代码始终保持“新鲜”。它自 2015 年以来每周发行一个更新版本,那时,它的代码是由创始人从 ADempiere 项目中 fork 的。与 ADempiere 一样,它是一个基于 Java 的开源 ERP,目标客户是中小型企业。
+
+虽然,相比在这里介绍的其它软件来说,它是一个很 “年青的” 项目,但是它早早就引起了一起人的注意,获得很多积极的评价,比如,被提名为“最佳开源”的 IT 创新奖入围者。
+
+Metasfresh 在自托管系统上或者在云上单用户使用时是免费的,或者可以按月交纳订阅费用。它的 [源代码][23] 在 GitHub 上,可以在遵守 [GPLv2][24] 许可的情况下使用,它的云版本是以 GPLv3 方式授权使用。
+
+### Odoo
+
+[Odoo][25] 是一个应用程序集成解决方案,它包含的模块有项目管理、帐单、存货管理、生产制造、以及采购。这些模块之间可以相互通讯,实现高效平滑地信息交换。
+
+虽然 ERP 可能很复杂,但是,Odoo 通过简单的,甚至是简洁的界面使它变得很友好。这个界面让人联想到谷歌云盘,它只让你需要的功能可见。在你决定签定采购合同之前,你可以 [得到一个 Odoo 去试用][26]。
+
+Odoo 是基于 web 的工具。按单个模块来订阅的话,每个模块每月需要支付 20 美元。你也可以 [下载它][27],或者可以从 GitHub 上获得 [源代码][28],它以 [LGPLv3][29] 方式授权。
+
+### Opentaps
+
+[Opentaps][30] 是专为大型业务设计的几个开源 ERP 解决方案之一,它的功能强大而灵活。这并不奇怪,因为它是在 Apache OFBiz 基础之上构建的。
+
+你可以得到你所希望的模块组合,来帮你管理存货、生产制造、财务、以及采购。它也有分析功能,帮你去分析业务的各个方面。你可以借助这些信息让未来的计划做的更好。Opentaps 也包含一个强大的报表功能。
+
+在它的基础之上,你还可以 [购买一些插件和附加模块][31] 去增强 Opentaps 的功能。包括与 Amazon Marketplace Services 和 FedEx 的集成等。在你 [下载 Opentaps][32] 之前,你可以到 [在线 demo][33] 上试用一下。它遵守 [GPLv3][34] 许可。
+
+### WebERP
+
+[WebERP][35] 是一个如它的名字所表示的那样:一个通过 Web 浏览器来使用的 ERP 系统。另外还需要的其它软件只有一个,那就是查看报告所使用的 PDF 阅读器。
+
+具体来说,它是一个面向批发、分销、生产制造业务的账务和业务管理解决方案。它也可以与 [第三方的业务软件][36] 集成,包括多地点零售管理的销售点系统、电子商务模块、以及构建业务知识库的 wiki 软件。它是用 PHP 写的,并且它致力于成为低资源占用、高效、快速、以及平台无关的、普通商业用户易于使用的 ERP 系统。
+
+WebERP 正在积极地进行开发,并且它有一个活跃的 [论坛][37],在那里你可以咨询问题或者学习关于如何使用这个应用程序的相关知识。你也可以试用一个 [demo][38],或者在 GitHub 上下载它的 [源代码][39](遵守 [GPLv2][40] 许可)
+
+### xTuple PostBooks
+
+如果你的生产制造、分销、电子商务业务已经从小规模业务成长起来了,并且正在寻找一个适合你的成长型企业的 ERP 系统,那么,你可以去了解一下 [xTuple PostBooks][41]。它是围绕核心 ERP 功能、帐务、以及可以添加存货、分销、采购、以及供应商报告等 CRM 功能构建的全面解决方案的系统。
+
+xTuple 在通用公共属性许可证([CPAL][42])下使用,并且这个项目欢迎开发者去 fork 它,然后为基于存货的生产制造型企业开发其它的业务软件。它的基于 web 的核心是用 JavaScript 写的,它的 [源代码][43] 可以在 GitHub 上找到。你可以去在 xTuple 的网站上注册一个免费的 [demo][44] 去了解它。
+
+还有许多其它的开源 ERP 可供你选择 — 另外你可以去了解的还有 [Tryton][45],它是用 Python 写的,并且使用的是 PostgreSQL 数据库引擎,或者基于 Java 的 [Axelor][46],它的好处是用户可以使用拖放界面来创建或者修改业务应用。如果还有在这里没有列出的你喜欢的开源 ERP 解决方案,请在下面的评论区共享出来。你也可以去查看我们的 [供应链管理工具][47] 榜单。
+
+这篇文章是 [以前版本][48] 的一个更新版,它是由 Opensource.com 的主席 [Scott Nesbitt][49] 所写。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/tools/enterprise-resource-planning
+
+作者:[Opensource.com][a]
+译者:[qhwdw](https://github.com/qhwdw)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com
+[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enterprise_resource_planning
+[2]:http://www.adempiere.net/welcome
+[3]:http://wiki.adempiere.net/License
+[4]:http://www.adempiere.net/web/guest/demo
+[5]:https://github.com/adempiere/adempiere
+[6]:http://ofbiz.apache.org/
+[7]:https://ofbiz.apache.org/business-users.html#UsrModules
+[8]:http://ofbiz.apache.org/ofbiz-demos.html
+[9]:http://ofbiz.apache.org/source-repositories.html
+[10]:http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+[11]:http://www.dolibarr.org/
+[12]:http://wiki.dolibarr.org/index.php/What_Dolibarr_can%27t_do
+[13]:http://www.dolibarr.org/onlinedemo
+[14]:http://www.dolistore.com/
+[15]:https://github.com/Dolibarr/dolibarr
+[16]:https://github.com/Dolibarr/dolibarr/blob/develop/COPYING
+[17]:https://erpnext.com/
+[18]:https://opensource.com/business/14/11/building-open-source-erp
+[19]:https://frappe.erpnext.com/request-a-demo
+[20]:https://erpnext.com/download
+[21]:https://erpnext.com/pricing
+[22]:http://metasfresh.com/en/
+[23]:https://github.com/metasfresh/metasfresh
+[24]:https://github.com/metasfresh/metasfresh/blob/master/LICENSE.md
+[25]:https://www.odoo.com/
+[26]:https://www.odoo.com/page/start
+[27]:https://www.odoo.com/page/download
+[28]:https://github.com/odoo
+[29]:https://github.com/odoo/odoo/blob/11.0/LICENSE
+[30]:http://www.opentaps.org/
+[31]:http://shop.opentaps.org/
+[32]:http://www.opentaps.org/products/download
+[33]:http://www.opentaps.org/products/online-demo
+[34]:https://www.gnu.org/licenses/agpl-3.0.html
+[35]:http://www.weberp.org/
+[36]:http://www.weberp.org/Links.html
+[37]:http://www.weberp.org/forum/
+[38]:http://www.weberp.org/weberp/
+[39]:https://github.com/webERP-team/webERP
+[40]:https://github.com/webERP-team/webERP#legal
+[41]:https://xtuple.com/
+[42]:https://xtuple.com/products/license-options#cpal
+[43]:http://xtuple.github.io/
+[44]:https://xtuple.com/free-demo
+[45]:http://www.tryton.org/
+[46]:https://www.axelor.com/
+[47]:https://opensource.com/tools/supply-chain-management
+[48]:https://opensource.com/article/16/3/top-4-open-source-erp-systems
+[49]:https://opensource.com/users/scottnesbitt
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180415 Some Common Concurrent Programming Mistakes.md b/translated/tech/20180415 Some Common Concurrent Programming Mistakes.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9b47185d88
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180415 Some Common Concurrent Programming Mistakes.md
@@ -0,0 +1,429 @@
+一些常见的并发编程错误
+============================================================
+
+Go 是一个内置支持并发编程的语言。借助使用 `go` 关键字去创建 goroutines(轻量级线程)和在 Go 中提供的 [使用][8] [信道][9] 和 [其它的并发][10] [同步方法][11],使得并发编程变得很容易、很灵活和很有趣。
+
+另一方面,Go 并不会阻止一些因 Go 程序员粗心大意或者缺乏经验而造成的并发编程错误。在本文的下面部分将展示一些在 Go 编程中常见的并发编程错误,以帮助 Go 程序员们避免再犯类似的错误。
+
+### 需要同步的时候没有同步
+
+代码行或许 [没有按出现的顺序运行][2]。
+
+在下面的程序中有两个错误。
+
+* 第一,在 main goroutine 中读取 `b` 和在新的 goroutine 中写入 `b` 可能导致数据争用。
+
+* 第二,条件 `b == true` 并不能保证在 main goroutine 中的 `a != nil`。在新的 goroutine 中编译器和 CPU 可能会通过 [重排序指令][1] 进行优化,因此,在运行时 `b` 赋值可能发生在 `a` 赋值之前,在 main goroutine 中当 `a` 被修改后,它将会让部分 `a` 一直保持为 `nil`。
+
+```
+package main
+
+import (
+ "time"
+ "runtime"
+)
+
+func main() {
+ var a []int // nil
+ var b bool // false
+
+ // a new goroutine
+ go func () {
+ a = make([]int, 3)
+ b = true // write b
+ }()
+
+ for !b { // read b
+ time.Sleep(time.Second)
+ runtime.Gosched()
+ }
+ a[0], a[1], a[2] = 0, 1, 2 // might panic
+}
+
+```
+
+上面的程序或者在一台计算机上运行的很好,但是在另一台上可能会引发异常。或者它可能运行了 _N_ 次都很好,但是可能在第 _(N+1)_ 次引发了异常。
+
+我们将使用 `sync` 标准包中提供的信道或者同步方法去确保内存中的顺序。例如,
+
+```
+package main
+
+func main() {
+ var a []int = nil
+ c := make(chan struct{})
+
+ // a new goroutine
+ go func () {
+ a = make([]int, 3)
+ c <- struct{}{}
+ }()
+
+ <-c
+ a[0], a[1], a[2] = 0, 1, 2
+}
+
+```
+
+### 使用 `time.Sleep` 调用去做同步
+
+我们先来看一个简单的例子。
+
+```
+ppackage main
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "time"
+)
+
+func main() {
+ var x = 123
+
+ go func() {
+ x = 789 // write x
+ }()
+
+ time.Sleep(time.Second)
+ fmt.Println(x) // read x
+}
+
+```
+
+我们预期程序将打印出 `789`。如果我们运行它,通常情况下,它确定打印的是 `789`。但是,这个程序使用的同步方式好吗?No!原因是 Go 运行时并不保证 `x` 的写入一定会发生在 `x` 的读取之前。在某些条件下,比如在同一个操作系统上,大部分 CPU 资源被其它运行的程序所占用的情况下,写入 `x` 可能就会发生在读取 `x` 之后。这就是为什么我们在正式的项目中,从来不使用 `time.Sleep` 调用去实现同步的原因。
+
+我们来看一下另外一个示例。
+
+```
+package main
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "time"
+)
+
+var x = 0
+
+func main() {
+ var num = 123
+ var p = &num
+
+ c := make(chan int)
+
+ go func() {
+ c <- *p + x
+ }()
+
+ time.Sleep(time.Second)
+ num = 789
+ fmt.Println(<-c)
+}
+
+```
+
+你认为程序的预期输出是什么?`123` 还是 `789`?事实上它的输出与编译器有关。对于标准的 Go 编译器 1.10 来说,这个程序很有可能输出是 `123`。但是在理论上,它可能输出的是 `789`,或者其它的随机数。
+
+现在,我们来改变 `c <- *p + x` 为 `c <- *p`,然后再次运行这个程序。你将会发现输出变成了 `789` (使用标准的 Go 编译器 1.10)。这再次说明它的输出是与编译器相关的。
+
+是的,在上面的程序中存在数据争用。表达式 `*p` 可能会被先计算、后计算、或者在处理赋值语句 `num = 789` 时计算。`time.Sleep` 调用并不能保证 `*p` 发生在赋值语句处理之前进行。
+
+对于这个特定的示例,我们将在新的 goroutine 创建之前,将值保存到一个临时值中,然后在新的 goroutine 中使用临时值去消除数据争用。
+
+```
+...
+ tmp := *p + x
+ go func() {
+ c <- tmp
+ }()
+...
+
+```
+
+### 使 Goroutines 挂起
+
+挂起 goroutines 是指让 goroutines 一直处于阻塞状态。导致 goroutines 被挂起的原因很多。比如,
+
+* 一个 goroutine 尝试从一个 nil 信道中或者从一个没有其它 goroutines 给它发送值的信道中检索数据。
+
+* 一个 goroutine 尝试去发送一个值到 nil 信道,或者发送到一个没有其它的 goroutines 接收值的信道中。
+
+* 一个 goroutine 被它自己死锁。
+
+* 一组 goroutines 彼此死锁。
+
+* 当运行一个没有 `default` 分支的 `select` 代码块时,一个 goroutine 被阻塞,以及在 `select` 代码块中 `case` 关键字后的所有信道操作保持阻塞状态。
+
+除了有时我们为了避免程序退出,特意让一个程序中的 main goroutine 保持挂起之外,大多数其它的 goroutine 挂起都是意外情况。Go 运行时很难判断一个 goroutine 到底是处于挂起状态还是临时阻塞。因此,Go 运行时并不会去释放一个挂起的 goroutine 所占用的资源。
+
+在 [谁先响应谁获胜][12] 的信道使用案例中,如果使用的 Future 信道容量不够大,当尝试向 Future 信道发送结果时,一些响应较慢的信道将被挂起。比如,如果调用下面的函数,将有 4 个 goroutine 处于永远阻塞状态。
+
+```
+func request() int {
+ c := make(chan int)
+ for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
+ i := i
+ go func() {
+ c <- i // 4 goroutines will hang here.
+ }()
+ }
+ return <-c
+}
+
+```
+
+为避免这 4 个 goroutines 一直处于挂起状态, `c` 信道的容量必须至少是 `4`。
+
+在 [实现谁先响应谁获胜的第二种方法][13] 的信道使用案例中,如果将 future 信道用做非缓冲信道,那么有可能这个信息将永远也不会有响应并挂起。例如,如果在一个 goroutine 中调用下面的函数,goroutine 可能会挂起。原因是,如果接收操作 `<-c` 准备就绪之前,五个发送操作全部尝试发送,那么所有的尝试发送的操作将全部失败,因此那个调用者 goroutine 将永远也不会接收到值。
+
+```
+func request() int {
+ c := make(chan int)
+ for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
+ i := i
+ go func() {
+ select {
+ case c <- i:
+ default:
+ }
+ }()
+ }
+ return <-c
+}
+
+```
+
+将信道 `c` 变成缓冲信道将保证五个发送操作中的至少一个操作会发送成功,这样,上面函数中的那个调用者 goroutine 将不会被挂起。
+
+### 在 `sync` 标准包中拷贝类型值
+
+在实践中,`sync` 标准包中的类型值不会被拷贝。我们应该只拷贝这个值的指针。
+
+下面是一个错误的并发编程示例。在这个示例中,当调用 `Counter.Value` 方法时,将拷贝一个 `Counter` 接收值。作为接收值的一个字段,`Counter` 接收值的各个 `Mutex` 字段也会被拷贝。拷贝不是同步发生的,因此,拷贝的 `Mutex` 值可能会出错。即便是没有错误,拷贝的 `Counter` 接收值的访问保护也是没有意义的。
+
+```
+import "sync"
+
+type Counter struct {
+ sync.Mutex
+ n int64
+}
+
+// This method is okay.
+func (c *Counter) Increase(d int64) (r int64) {
+ c.Lock()
+ c.n += d
+ r = c.n
+ c.Unlock()
+ return
+}
+
+// The method is bad. When it is called, a Counter
+// receiver value will be copied.
+func (c Counter) Value() (r int64) {
+ c.Lock()
+ r = c.n
+ c.Unlock()
+ return
+}
+
+```
+
+我们只需要改变 `Value` 接收类型方法为指针类型 `*Counter`,就可以避免拷贝 `Mutex` 值。
+
+在官方的 Go SDK 中提供的 `go vet` 命令将会报告潜在的错误值拷贝。
+
+### 在错误的地方调用 `sync.WaitGroup` 的方法
+
+每个 `sync.WaitGroup` 值维护一个内部计数器,这个计数器的初始值为 0。如果一个 `WaitGroup` 计数器的值也是 0,调用 `WaitGroup` 值的 `Wait` 方法不会被阻塞,否则,在计数器值为 0 之前,这个调用会一直被阻塞。
+
+为了让 `WaitGroup` 值的使用有意义,当一个 `WaitGroup` 计数器值为 0 时,必须在相应的 `WaitGroup` 值的 `Wait` 方法调用之前,去调用 `WaitGroup` 值的 `Add` 方法。
+
+例如,下面的程序中,在不正确位置调用了 `Add` 方法,这将使最后打印出的数字不总是 `100`。事实上,这个程序最后打印的数字可能是在 `[0, 100)` 范围内的一个随意数字。原因就是 `Add` 方法的调用并不保证一定会发生在 `Wait` 方法调用之前。
+
+```
+package main
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "sync"
+ "sync/atomic"
+)
+
+func main() {
+ var wg sync.WaitGroup
+ var x int32 = 0
+ for i := 0; i < 100; i++ {
+ go func() {
+ wg.Add(1)
+ atomic.AddInt32(&x, 1)
+ wg.Done()
+ }()
+ }
+
+ fmt.Println("To wait ...")
+ wg.Wait()
+ fmt.Println(atomic.LoadInt32(&x))
+}
+
+```
+
+为让程序的表现符合预期,在 `for` 循环中,我们将把 `Add` 方法的调用移动到创建的新 goroutines 的范围之外,修改后的代码如下。
+
+```
+...
+ for i := 0; i < 100; i++ {
+ wg.Add(1)
+ go func() {
+ atomic.AddInt32(&x, 1)
+ wg.Done()
+ }()
+ }
+...
+
+```
+
+### 不正确使用 Futures 信道
+
+在 [信道使用案例][14] 的文章中,我们知道一些函数将返回 [futures 信道][15]。假设 `fa` 和 `fb` 就是这样的两个函数,那么下面的调用就使用了不正确的 future 参数。
+
+```
+doSomethingWithFutureArguments(<-fa(), <-fb())
+
+```
+
+在上面的代码行中,两个信道接收操作是顺序进行的,而不是并发的。我们做如下修改使它变成并发操作。
+
+```
+ca, cb := fa(), fb()
+doSomethingWithFutureArguments(<-c1, <-c2)
+
+```
+
+### 没有等 Goroutine 的最后的活动的发送结束就关闭信道
+
+Go 程序员经常犯的一个错误是,还有一些其它的 goroutine 可能会发送值到以前的信道时,这个信道就已经被关闭了。当这样的发送(发送到一个已经关闭的信道)真实发生时,将引发一个异常。
+
+这种错误在一些以往的著名 Go 项目中也有发生,比如在 Kubernetes 项目中的 [这个 bug][3] 和 [这个 bug][4]。
+
+如何安全和优雅地关闭信道,请阅读 [这篇文章][5]。
+
+### 在值上做 64 位原子操作时没有保证值地址 64 位对齐
+
+到目前为止(Go 1.10),在标准的 Go 编译器中,在一个 64 位原子操作中涉及到的值的地址要求必须是 64 位对齐的。如果没有对齐则导致当前的 goroutine 异常。对于标准的 Go 编译器来说,这种失败仅发生在 32 位的架构上。请阅读 [内存布局][6] 去了解如何在一个 32 位操作系统上保证 64 位对齐。
+
+### 没有注意到大量的资源被 `time.After` 函数调用占用
+
+在 `time` 标准包中的 `After` 函数返回 [一个延迟通知的信道][7]。这个函数在某些情况下用起来很便捷,但是,每次调用它将创建一个 `time.Timer` 类型的新值。这个新创建的 `Timer` 值在通过传递参数到 `After` 函数指定期间保持激活状态,如果在这个期间过多的调用了该函数,可能会有太多的 `Timer` 值保持激活,这将占用大量的内存和计算资源。
+
+例如,如果调用了下列的 `longRunning` 函数,将在一分钟内产生大量的消息,然后在某些周期内将有大量的 `Timer` 值保持激活,即便是大量的这些 `Timer` 值已经没用了也是如此。
+
+```
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "time"
+)
+
+// The function will return if a message arrival interval
+// is larger than one minute.
+func longRunning(messages <-chan string) {
+ for {
+ select {
+ case <-time.After(time.Minute):
+ return
+ case msg := <-messages:
+ fmt.Println(msg)
+ }
+ }
+}
+
+```
+
+为避免在上述代码中创建过多的 `Timer` 值,我们将使用一个单一的 `Timer` 值去完成同样的任务。
+
+```
+func longRunning(messages <-chan string) {
+ timer := time.NewTimer(time.Minute)
+ defer timer.Stop()
+
+ for {
+ select {
+ case <-timer.C:
+ return
+ case msg := <-messages:
+ fmt.Println(msg)
+ if !timer.Stop() {
+ <-timer.C
+ }
+ }
+
+ // The above "if" block can also be put here.
+
+ timer.Reset(time.Minute)
+ }
+}
+
+```
+
+### 不正确地使用 `time.Timer` 值
+
+在最后,我们将展示一个符合语言使用习惯的 `time.Timer` 值的使用示例。需要注意的一个细节是,那个 `Reset` 方法总是在停止或者 `time.Timer` 值释放时被使用。
+
+在 `select` 块的第一个 `case` 分支的结束部分,`time.Timer` 值被释放,因此,我们不需要去停止它。但是必须在第二个分支中停止定时器。如果在第二个分支中 `if` 代码块缺失,它可能至少在 `Reset` 方法调用时,会(通过 Go 运行时)发送到 `timer.C` 信道,并且那个 `longRunning` 函数可能会早于预期返回,对于 `Reset` 方法来说,它可能仅仅是重置内部定时器为 0,它将不会清理(耗尽)那个发送到 `timer.C` 信道的值。
+
+例如,下面的程序很有可能在一秒内而不是十秒时退出。并且更重要的是,这个程序并不是 DRF 的(译者注:data race free,多线程程序的一种同步程度)。
+
+```
+package main
+
+import (
+ "fmt"
+ "time"
+)
+
+func main() {
+ start := time.Now()
+ timer := time.NewTimer(time.Second/2)
+ select {
+ case <-timer.C:
+ default:
+ time.Sleep(time.Second) // go here
+ }
+ timer.Reset(time.Second * 10)
+ <-timer.C
+ fmt.Println(time.Since(start)) // 1.000188181s
+}
+
+```
+
+当 `time.Timer` 的值不再被其它任何一个东西使用时,它的值可能被停留在一种非停止状态,但是,建议在结束时停止它。
+
+在多个 goroutines 中如果不按建议使用 `time.Timer` 值并发,可能会有 bug 隐患。
+
+我们不应该依赖一个 `Reset` 方法调用的返回值。`Reset` 方法返回值的存在仅仅是为了兼容性目的。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://go101.org/article/concurrent-common-mistakes.html
+
+作者:[go101.org ][a]
+译者:[qhwdw](https://github.com/qhwdw)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:go101.org
+[1]:https://go101.org/article/memory-model.html
+[2]:https://go101.org/article/memory-model.html
+[3]:https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/pull/45291/files?diff=split
+[4]:https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/pull/39479/files?diff=split
+[5]:https://go101.org/article/channel-closing.html
+[6]:https://go101.org/article/memory-layout.html
+[7]:https://go101.org/article/channel-use-cases.html#timer
+[8]:https://go101.org/article/channel-use-cases.html
+[9]:https://go101.org/article/channel.html
+[10]:https://go101.org/article/concurrent-atomic-operation.html
+[11]:https://go101.org/article/concurrent-synchronization-more.html
+[12]:https://go101.org/article/channel-use-cases.html#first-response-wins
+[13]:https://go101.org/article/channel-use-cases.html#first-response-wins-2
+[14]:https://go101.org/article/channel-use-cases.html
+[15]:https://go101.org/article/channel-use-cases.html#future-promise
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180423 An introduction to Python bytecode.md b/translated/tech/20180423 An introduction to Python bytecode.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..c27346bc91
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180423 An introduction to Python bytecode.md
@@ -0,0 +1,155 @@
+Python 字节码介绍
+======
+
+如果你从没有写过 Python,或者甚至只是使用过 Python,你或许已经习惯于看 Python 源代码文件;它们的名字以 `.py` 结尾。你可能还看到过其它类型的文件,比如使用 `.pyc` 结尾的文件,或许你可能听说过,它们就是 Python 的 "字节码" 文件。(在 Python 3 上这些可能不容易看到 — 因为它们与你的 `.py` 文件不在同一个目录下,它们在一个叫 `__pycache__` 的子目录中)或者你也听说过,这是节省时间的一种方法,它可以避免每次运行 Python 时去重新解析源代码。
+
+但是,除了 “噢,原来这就是 Python 字节码” 之外,你还知道这些文件能做什么吗?以及 Python 是如何使用它们的?
+
+如果你不知道,那你走运了!今天我将带你了解 Python 的字节码是什么,Python 如何使用它去运行你的代码,以及知道它是如何帮助你的。
+
+### Python 如何工作
+
+Python 经常被介绍为它是一个解释型语言 — 其中一个原因是程序运行时,你的源代码被转换成 CPU 的原生指令 — 但这样认为只是部分正确。Python 与大多数解释型语言一样,确实是将源代码编译为一组虚拟机指令,并且 Python 解释器是针对相应的虚拟机实现的。这种中间格式被称为 “字节码”。
+
+因此,这些 `.pyc` 文件是 Python 悄悄留下的,是为了让它们运行的 “更快”,或者是针对你的源代码的 “优化” 版本;它们是你的程序在 Python 虚拟机上运行的字节码指令。
+
+我们来看一个示例。这里是用 Python 写的经典程序 "Hello, World!":
+```
+def hello()
+
+ print("Hello, World!")
+
+```
+
+下面是转换后的字节码(转换为人类可读的格式):
+```
+2 0 LOAD_GLOBAL 0 (print)
+
+ 2 LOAD_CONST 1 ('Hello, World!')
+
+ 4 CALL_FUNCTION 1
+
+```
+
+如果你输入那个 `hello()` 函数,然后使用 [CPython][1] 解释器去运行它,上面的 Python 程序将会运行。它看起来可能有点奇怪,因此,我们来深入了解一下它都做了些什么。
+
+### Python 虚拟机内幕
+
+CPython 使用一个基于栈的虚拟机。也就是说,它完全面向栈数据结构的(你可以 “推入” 一个东西到栈 “顶”,或者,从栈 “顶” 上 “弹出” 一个东西来)。
+
+CPython 使用三种类型的栈:
+
+ 1. **调用栈**。这是运行 Python 程序的主要结构。它为每个当前活动的函数调用使用了一个东西 — "帧“,栈底是程序的入口点。每个函数调用推送一个新帧到调用栈,每当函数调用返回后,这个帧被销毁。
+ 2. 在每个帧中,有一个 **计算栈** (也称为 **数据栈**)。这个栈就是 Python 函数运行的地方,运行的 Python 代码大多数是由推入到这个栈中的东西组成的,操作它们,然后在返回后销毁它们。
+ 3. 在每个帧中,还有一个 **块栈**。它被 Python 用于去跟踪某些类型的控制结构:loops、`try`/`except` 块、以及 `with` 块,全部推入到块栈中,当你退出这些控制结构时,块栈被销毁。这将帮助 Python 了解任意给定时刻哪个块是活动的,比如,一个 `continue` 或者 `break` 语句可能影响正确的块。
+
+
+
+大多数 Python 字节码指令操作的是当前调用栈帧的计算栈,虽然,还有一些指令可以做其它的事情(比如跳转到指定指令,或者操作块栈)。
+
+为了更好地理解,假设我们有一些调用函数的代码,比如这个:`my_function(my_variable, 2)`。Python 将转换为一系列字节码指令:
+
+ 1. 一个 `LOAD_NAME` 指令去查找函数对象 `my_function`,然后将它推入到计算栈的顶部
+ 2. 另一个 `LOAD_NAME` 指令去查找变量 `my_variable`,然后将它推入到计算栈的顶部
+ 3. 一个 `LOAD_CONST` 指令去推入一个实整数值 `2` 到计算栈的顶部
+ 4. 一个 `CALL_FUNCTION` 指令
+
+
+
+这个 `CALL_FUNCTION` 指令将有 2 个参数,它表示那个 Python 需要从栈顶弹出两个位置参数;然后函数将在它上面进行调用,并且它也同时被弹出(对于函数涉及的关键字参数,它使用另一个不同的指令 — `CALL_FUNCTION_KW`,但使用的操作原则类似,以及第三个指令 — `CALL_FUNCTION_EX`,它适用于函数调用涉及到使用 `*` 或 `**` 操作符的情况)。一旦 Python 拥有了这些之后,它将在调用栈上分配一个新帧,填充到函数调用的本地变量上,然后,运行那个帧内的 `my_function` 字节码。运行完成后,这个帧将被调用栈销毁,最初的帧内返回的 `my_function` 将被推入到计算栈的顶部。
+
+### 访问和理解 Python 字节码
+
+如果你想玩转字节码,那么,Python 标准库中的 `dis` 模块将对你有非常大的帮助;`dis` 模块为 Python 字节码提供了一个 "反汇编",它可以让你更容易地得到一个人类可读的版本,以及查找各种字节码指令。[`dis` 模块的文档][2] 可以让你遍历它的内容,并且提供一个字节码指令能够做什么和有什么样的参数的完整清单。
+
+例如,获取上面的 `hello()` 函数的列表,可以在一个 Python 解析器中输入如下内容,然后运行它:
+```
+import dis
+
+dis.dis(hello)
+
+```
+
+函数 `dis.dis()` 将反汇编一个函数、方法、类、模块、编译过的 Python 代码对象、或者字符串包含的源代码,以及显示出一个人类可读的版本。`dis` 模块中另一个方便的功能是 `distb()`。你可以给它传递一个 Python 追溯对象,或者发生预期外情况时调用它,然后它将反汇编发生预期外情况时在调用栈上最顶端的函数,并显示它的字节码,以及插入一个指向到引发意外情况的指令的指针。
+
+它也可以用于查看 Python 为每个函数构建的编译后的代码对象,因为运行一个函数将会用到这些代码对象的属性。这里有一个查看 `hello()` 函数的示例:
+```
+>>> hello.__code__
+
+", line 1>
+
+>>> hello.__code__.co_consts
+
+(None, 'Hello, World!')
+
+>>> hello.__code__.co_varnames
+
+()
+
+>>> hello.__code__.co_names
+
+('print',)
+
+```
+
+代码对象在函数中可以作为属性 `__code__` 来访问,并且携带了一些重要的属性:
+
+ * `co_consts` 是存在于函数体内的任意实数的元组
+ * `co_varnames` 是函数体内使用的包含任意本地变量名字的元组
+ * `co_names` 是在函数体内引用的任意非本地名字的元组
+
+
+
+许多字节码指令 — 尤其是那些推入到栈中的加载值,或者在变量和属性中的存储值 — 在这些用作它们参数的元组中使用索引。
+
+因此,现在我们能够理解 `hello()` 函数中所列出的字节码:
+
+ 1. `LOAD_GLOBAL 0`:告诉 Python 通过 `co_names` (它是 `print` 函数)的索引 0 上的名字去查找它指向的全局对象,然后将它推入到计算栈
+ 2. `LOAD_CONST 1`:带入 `co_consts` 在索引 1 上的实数值,并将它推入(索引 0 上的实数值是 `None`,它表示在 `co_consts` 中,因为 Python 函数调用有一个隐式的返回值 `None`,如果没有显式的返回表达式,就返回这个隐式的值 )。
+ 3. `CALL_FUNCTION 1`:告诉 Python 去调用一个函数;它需要从栈中弹出一个位置参数,然后,新的栈顶将被函数调用。
+
+
+
+"原始的" 字节码 — 是非人类可读格式的字节 — 也可以在代码对象上作为 `co_code` 属性可用。如果你有兴趣尝试手工反汇编一个函数时,你可以从它们的十进制字节值中,使用列出 `dis.opname` 的方式去查看字节码指令的名字。
+
+### 字节码的用处
+
+现在,你已经了解的足够多了,你可能会想 ” OK,我认为它很酷,但是知道这些有什么实际价值呢?“由于对它很好奇,我们去了解它,但是除了好奇之外,Python 字节码在几个方面还是非常有用的。
+
+首先,理解 Python 的运行模型可以帮你更好地理解你的代码。人们都开玩笑说,C 将成为一个 ”便携式汇编器“,在那里你可以很好地猜测出一段 C 代码转换成什么样的机器指令。理解 Python 字节码之后,你在使用 Python 时也具备同样的能力 — 如果你能预料到你的 Python 源代码将被转换成什么样的字节码,那么你可以知道如何更好地写和优化 Python 源代码。
+
+第二,理解字节码可以帮你更好地回答有关 Python 的问题。比如,我经常看到一些 Python 新手困惑为什么某些结构比其它结构运行的更快(比如,为什么 `{}` 比 `dict()` 快)。知道如何去访问和阅读 Python 字节码将让你很容易回答这样的问题(尝试对比一下: `dis.dis("{}")` 与 `dis.dis("dict()")` 就会明白)。
+
+最后,理解字节码和 Python 如何运行它,为 Python 程序员不经常使用的一种特定的编程方式提供了有用的视角:面向栈的编程。如果你以前从来没有使用过像 FORTH 或 Fator 这样的面向栈的编程语言,它们可能有些古老,但是,如果你不熟悉这种方法,学习有关 Python 字节码的知识,以及理解面向栈的编程模型是如何工作的,将有助你开拓你的编程视野。
+
+### 延伸阅读
+
+如果你想进一步了解有关 Python 字节码、Python 虚拟机、以及它们是如何工作的更多知识,我推荐如下的这些资源:
+
+ * [Python 虚拟机内幕][3],它是 Obi Ike-Nwosu 写的一本免费在线电子书,它深入 Python 解析器,解释了 Python 如何工作的细节。
+ * [一个用 Python 编写的 Python 解析器][4],它是由 Allison Kaptur 写的一个教程,它是用 Python 构建的 Python 字节码解析器,并且它实现了运行 Python 字节码的全部构件。
+ * 最后,CPython 解析器是一个开源软件,你可以在 [GitHub][1] 上阅读它。它在文件 `Python/ceval.c` 中实现了字节码解析器。[这是 Python 3.6.4 发行版中那个文件的链接][5];字节码指令是由第 1266 行开始的 `switch` 语句来处理的。
+
+
+
+学习更多内容,参与到 James Bennett 的演讲,[有关字节的知识:理解 Python 字节码][6],将在 [PyCon Cleveland 2018][7] 召开。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/18/4/introduction-python-bytecode
+
+作者:[James Bennett][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[qhwdw](https://github.com/qhwdw)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/ubernostrum
+[1]:https://github.com/python/cpython
+[2]:https://docs.python.org/3/library/dis.html
+[3]:https://leanpub.com/insidethepythonvirtualmachine
+[4]:http://www.aosabook.org/en/500L/a-python-interpreter-written-in-python.html
+[5]:https://github.com/python/cpython/blob/d48ecebad5ac78a1783e09b0d32c211d9754edf4/Python/ceval.c
+[6]:https://us.pycon.org/2018/schedule/presentation/127/
+[7]:https://us.pycon.org/2018/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180427 3 Python template libraries compared.md b/translated/tech/20180427 3 Python template libraries compared.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..cae93421c1
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180427 3 Python template libraries compared.md
@@ -0,0 +1,112 @@
+3 个 Python 模板库比较
+=====
+
+
+在我的日常工作中,我花费大量的时间将各种来源的数据转化为可读的信息。虽然很多时候这只是电子表格或某种类型的图表或其他数据可视化的形式,但也有其他时候,将数据以书面形式呈现是有意义的。
+
+但我的一个 pet peeve (to 校正:不知道该怎么翻译)正在复制和粘贴。如果你要将数据从源头移动到标准化模板,则不应该复制和粘贴。这很容易出错,说实话,这会浪费你的时间。
+
+因此,对于我定期发送的任何信息都遵循一个共同的模式,我倾向于找到某种方法来自动化至少一部分信息。也许这涉及到在电子表格中创建一些公式,一个快速 shell 脚本或其他解决方案,以便使用从外部源提取的信息自动填充模板。
+
+但最近,我一直在探索 Python 模板来完成从其他数据集创建报告和图表的大部分工作。
+
+Python 模板引擎非常强大。我简化创建报告的使用案例仅仅触及了它们可以用来工作的皮毛。许多开发人员正在利用这些工具来构建完整的 web 应用程序和内容管理系统。但是,你不需要有一个复杂的 web 应用程序来使用 Python 模板工具。
+
+### 为什么选择模板?
+
+每个模板工具都不甚相同,你应该阅读文档以了解其确切的用法。但让我们创建一个假设的例子。假设我想创建一个简短的页面,列出我最近编写的所有 Python 主题。就像这样:
+```
+
+
+ My Python articles
+
+
+
+ These are some of the things I have written about Python:
+
+ - Python GUIs
+ - Python IDEs
+ - Python web scrapers
+
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+当它仅仅是这三个项目时,足够简单地维护它。但是当我想添加第四个,第五个或第六十七个时会发生什么?我可以从包含我所有页面列表的 CSV 文件或其他数据文件生成它,而不是手动编码此页面吗?我可以轻松地为我写的每个主题创建重复内容吗?我可以以编程方式更改每个页面上的文本标题吗?这就是模板引擎可以发挥作用的地方。
+
+有许多不同的选择,今天我将与你其中分享三个,顺序不分先后:[Mako][6], [Jinja2][7] 和 [Genshi][8]。
+
+### Mako
+
+[Mako][6] 是根据 MIT 许可证发布的 Python 模板工具,专为快速展现而设计的(与Jinja2不同)。Reddit 已经使用 Mako 为他们的网页提供动力,它同时也是 Pyramid 和 Pylons 等 web 框架的默认模板语言。它相当简单且易于使用。你可以使用几行代码来设计模板;支持Python 2.x 和 3.x,它是一个功能强大且功能丰富的工具,具有[良好的文档][9],这一点我认为是必须的。其功能包括过滤器,继承,可调用块和内置缓存系统,这些系统可以被大型或复杂的 web 项目导入。
+
+### Jinja2
+
+Jinja2 是另一个快速且功能全面的选项,可用于 Python 2.x 和 3.x,遵循 BSD 许可证。Jinja2 从功能角度与 Mako 有很多重叠,因此对于新手来说,你在两者之间的选择可能会归结为你喜欢的格式化风格。Jinja2 还将模板编译为字节码,并具有 HTML 转义,沙盒,模板继承和模板沙盒部分的功能。其用户包括 Mozilla, SourceForge, NPR, Instagram 等,并且还具有[强大的文档][10]。与 Mako 在模板内部使用 Python 逻辑不同的是,Jinja2 使用自己的语法。
+
+### Genshi
+
+[Genshi][8] 是我会提到的第三个选项。它是一个 XML 工具,具有强大的模板组件,所以如果你使用的数据已经是 XML 格式,或者你需要使用网页以外的格式,Genshi 可能成为你的一个很好的解决方案。HTML 基本上是一种 XML(好吧,不是精确的,但这超出了本文的范围,有点卖弄学问了),因此格式化它们非常相似。由于我通常使用的很多数据都是 XML 或其他类型的数据,因此我非常喜欢使用我可以用于多种事物的工具。
+
+发行版目前仅支持 Python 2.x,尽管 Python 3 支持存在于主干中,但我提醒你,它看起来并没有得到有效的开发。Genshi 遵循 BSD 许可证提供。
+
+### 示例
+
+因此,在上面的假设示例中,我不会每次写新主题时都更新 HTML 文件,而是通过编程方式对其进行更新。我可以创建一个模板,如下所示:
+```
+
+
+ My Python articles
+
+
+
+ These are some of the things I have written about Python:
+
+ %for topic in topics:
+ - ${topic}
+ %endfor
+
+
+
+
+```
+
+然后我可以使用我的模板库来迭代每个主题,比如使用 Mako,像这样:
+```
+from mako.template import Template
+
+mytemplate = Template(filename='template.txt')
+print(mytemplate.render(topics=("Python GUIs","Python IDEs","Python web scrapers")))
+
+```
+
+当然,在现实世界的用法中,我不会将这些内容手动地列在变量中,而是将它们从外部数据源(如数据库或API)中提取出来。
+
+这些不是唯一的 Python 模板引擎。如果你正在开始创建一个将大量使用模板的新项目,那么你考虑的可能不仅仅是这三种选择。在[ Python 维基][11]上查看更全面的列表,以获得更多值得考虑的项目。
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/resources/python/template-libraries
+
+作者:[Jason Baker][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/jason-baker
+[1]:https://opensource.com/resources/python?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ
+[2]:https://opensource.com/resources/python/ides?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ
+[3]:https://opensource.com/resources/python/gui-frameworks?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ
+[4]:https://opensource.com/tags/python?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ
+[5]:https://developers.redhat.com/?intcmp=7016000000127cYAAQ
+[6]:http://www.makotemplates.org/
+[7]:http://jinja.pocoo.org/
+[8]:https://genshi.edgewall.org/
+[9]:http://docs.makotemplates.org/en/latest/
+[10]:http://jinja.pocoo.org/docs/2.10/
+[11]:https://wiki.python.org/moin/Templating
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180507 4 Firefox extensions to install now.md b/translated/tech/20180507 4 Firefox extensions to install now.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..db97507357
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180507 4 Firefox extensions to install now.md
@@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
+4 个 Firefox 扩展
+=====
+
+
+正如我在关于 Firefox 扩展的[原创文章][1]中提到的,web 浏览器已成为许多用户计算(机)验的关键组件。现代浏览器已经发展成为功能强大且可扩展的平台,扩展可以添加或修改其功能。Firefox 的扩展是使用 WebExtensions API(一种跨浏览器开发系统)构建的。
+
+在第一篇文章中,我问读者:“你应该安装哪些扩展?” 重申一下,这一决定主要取决于你如何使用浏览器,你对隐私的看法,你对扩展程序开发人员的信任程度以及其他个人偏好。自文章发表以来,我推荐的一个扩展(Xmarks)已经停止。另外,该文章收到了大量的反馈,在这篇更新中,这些反馈已经被考虑到。
+
+我想再次指出,浏览器扩展通常需要能够阅读和(或)更改你访问的网页上的所有内容。你应该仔细考虑这一点。如果扩展程序修改了你访问的所有网页的访问权限,那么它可能充当键盘记录程序,拦截信用卡信息,在线跟踪,插入广告以及执行各种其他恶意活动。这并不意味着每个扩展程序都会暗中执行这些操作,但在安装任何扩展程序之前,你应该仔细考虑安装源,涉及的权限,风险配置文件以及其他因素。请记住,你可以使用配置文件来管理扩展如何影响你的攻击面 - 例如,使用没有扩展的专用配置文件来 执行网上银行等任务。
+
+考虑到这一点,这里有你可能想要考虑的四个开源 Firefox 扩展。
+
+### uBlock Origin
+
+![ublock origin ad blocker screenshot][2]
+
+我的第一个建议保持不变。[uBlock Origin][3] 是一款快速,低内存,广泛的拦截器,它不仅可以拦截广告,而且还可以执行你自己的内容过滤。 uBlock Origin 的默认行为是使用多个预定义的过滤器列表来拦截广告,跟踪器和恶意软件站点。它允许你任意添加列表和规则,甚至可以锁定到默认拒绝模式。尽管它很强大,但它已被证明是高效和高性能的。它将继续定期更新,并且是该功能的最佳选择之一。
+
+### Privacy Badger
+
+![privacy badger ad blocker][4]
+
+我的第二个建议也保持不变。如果说有什么区别的话,那就是自从我上一篇文章发表以来,隐私问题就一直被带到最前沿,这使得这个扩展成为一个简单的建议。顾名思义,[Privacy Badger][5] 是一个专注于隐私的扩展,可以拦截广告和其他第三方跟踪器。这是 Electronic Freedom (to 校正者:这里 Firefox 添加此扩展后,弹出页面译为电子前哨基金会)基金会的一个项目,他们说:
+
+> Privacy Badger 诞生于我们希望能够推荐一个单独的扩展,它可以自动分析和拦截任何违反用户同意原则的追踪器或广告;在用户没有任何设置、有关知识或配置的情况下,它可以很好地运行;它是由一个明确为其用户而不是为广告商工作的组织所产生的;它使用了算法的方法来决定什么是什么,什么是不跟踪的。”
+
+为什么 Privacy Badger 会出现在这个列表上,它的功能与上一个扩展看起来很类似?因为一些原因。首先,它从根本上工作原理与 uBlock Origin 不同。其次,深度防御的实践是一项合理的策略。说到深度防御,EFF 还维护着 [HTTPS Everywhere][6] 扩展,它自动确保 https 用于许多主流网站。当你安装 Privacy Badger 时,你也可以考虑使用 HTTPS Everywhere。
+
+如果你开始认为这篇文章只是对上一篇文章的重新讨论,那么以下是我的建议分歧。
+
+### Bitwarden
+
+![Bitwarden][7]
+
+在上一篇文章中推荐 LastPass 时,我提到这可能是一个有争议的选择。这无疑属实。无论你是否应该使用密码管理器 - 如果你使用,那么是否应该选择带有浏览器插件的密码管理器 - 这是一个备受争议的话题,答案很大程度上取决于你的个人风险状况。我认为大多数普通的计算机用户应该使用一个,因为它比最常见的选择要好得多:在任何地方都使用相同的弱密码。我仍然相信这一点。
+
+[Bitwarden][8] 自从我上次审视以后确实成熟了。像 LastPass 一样,它对用户友好,支持双因素身份验证,并且相当安全。与 LastPass 不同的是,它是[开源的][9]。它可以使用或不使用浏览器插件,并支持从其他解决方案(包括 LastPass)导入。它的核心功能完全免费,它还有一个 10 美元/年的高级版本。
+
+### Vimium-FF
+
+![Vimium][10]
+
+[Vimium][11] 是另一个开源的扩展,它为 Firefox 键盘快捷键提供了类似 Vim 一样的导航和控制,其称之为“黑客的浏览器”。对于 Ctrl+x, Meta+x 和 Alt+x,分别对应 **< c-x>**, **< m-x>** 和 **< a-x>**,默认值可以轻松定制。一旦你安装了 Vimium,你可以随时键入 **?** 来查看键盘绑定列表。请注意,如果你更喜欢 Emacs,那么也有一些针对这些键绑定的扩展。无论哪种方式,我认为键盘快捷键是未充分利用的生产力推动力。
+
+### 额外福利: Grammarly
+
+不是每个人都有幸在 Opensource.com 上撰写专栏 - 尽管你应该认真考虑为网站撰写文章;如果你有问题,有兴趣,或者想要一个导师,伸出手,让我们聊天吧。但是,即使没有专栏撰写,正确的语法在各种各样的情况下都是有益的。试一下 [Grammarly][12]。不幸的是,这个扩展不是开源的,但它确实可以确保你输入的所有东西都是清晰的,有效的并且没有错误。它通过扫描你文本中的常见的和复杂的语法错误来实现这一点,涵盖了从主谓一致到文章使用到修饰词的放置这些所有内容。它的基本功能是免费的,它有一个高级版本,每月收取额外的费用。我在这篇文章中使用了它,它发现了许多我的校对没有发现的错误。
+
+再次说明,Grammarly 是这个列表中包含的唯一不是开源的扩展,因此如果你知道类似的高质量开源替代品,请在评论中告诉我们。
+
+这些扩展是我发现有用并推荐给其他人的扩展。请在评论中告诉我你对更新建议的看法。
+
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/18/5/firefox-extensions
+
+作者:[Jeremy Garcia][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[MjSeven](https://github.com/MjSeven)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/jeremy-garcia
+[1]:https://opensource.com/article/18/1/top-5-firefox-extensions
+[2]:https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/panopoly_image_original/public/ublock.png?itok=_QFEbDmq (ublock origin ad blocker screenshot)
+[3]:https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/ublock-origin/
+[4]:https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/panopoly_image_original/public/images/life-uploads/privacy_badger_1.0.1.png?itok=qZXQeKtc (privacy badger ad blocker screenshot)
+[5]:https://www.eff.org/privacybadger
+[6]:https://www.eff.org/https-everywhere
+[7]:https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/panopoly_image_original/public/u128651/bitwarden.png?itok=gZPrCYoi (Bitwarden)
+[8]:https://bitwarden.com/
+[9]:https://github.com/bitwarden
+[10]:https://opensource.com/sites/default/files/styles/panopoly_image_original/public/u128651/vimium.png?itok=QRESXjWG (Vimium)
+[11]:https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/vimium-ff/
+[12]:https://www.grammarly.com/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180510 Creating small containers with Buildah.md b/translated/tech/20180510 Creating small containers with Buildah.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..9e15770d4f
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180510 Creating small containers with Buildah.md
@@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
+使用 Buildah 创建小体积的容器
+======
+
+我最近加入了 Red Hat,在这之前我在另外一家科技公司工作了很多年。在我的上一份工作岗位上,我开发了不少不同类型的软件产品,这些产品是成功的,但都有版权保护。不仅法规限制了我们不能在公司外将软件共享,而且我们在公司内部也基本不进行共享。在那时,我觉得这很有道理:公司花费了时间、精力和预算用于开发软件,理应保护并要求软件涉及的利益。
+
+时间如梭,去年我加入 Red Hat 并培养出一种完全不同的理念。[Buildah 项目][1]是我最早加入的项目之一,该项目用于构建 OCI (Open Container Initiative) 标准的镜像,特别擅长让你精简已创建镜像的体积。那时 Buildah 还处于非常早期的阶段,包含一些瑕疵,不适合用于生产环境。
+
+刚接触项目不久,我做了一些小变更,然后询问公司内部 git 仓库地址,以便提交我做的变更。收到的回答是:没有内部仓库,直接将变更提交到 GitHub 上。这让我感到困惑,将我的变更提交到 GitHub 意味着:任何人都可以查看这部分代码并在他们自己的项目中使用。况且代码还有一些瑕疵,这样做简直有悖常理。但作为一个新人,我只是惊讶地摇了摇头并提交了变更。
+
+一年后,我终于相信了开源软件的力量和价值。我仍为 Buildah 项目工作,我们最近遇到的一个主题很形象地说明了这种力量和价值。标题为 [Buildah 镜像体积并不小?][2] 的主题由 Tim Dudgeon (@tdudgeon) 提出。简而言之,他发现使用 Buildah 创建的镜像比使用 Docker 创建的镜像体积更大,而且 Buildah 镜像中并不包含一些额外应用,但 Docker 镜像中却包含它们。
+
+为了比较,他首先操作如下:
+```
+$ docker pull centos:7
+$ docker images
+REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
+docker.io/centos 7 2d194b392dd1 2 weeks ago 195 MB
+```
+
+他发现 Docker 镜像的体积为 195MB。Tim 接着使用 Buildah 创建了一个(基于 scratch 的)最小化镜像,仅仅将 `coreutils` 和 `bash` 软件包加入到镜像中,使用的脚本如下:
+```
+$ cat ./buildah-base.sh
+#!/bin/bash
+
+set -x
+
+# build a minimal image
+newcontainer=$(buildah from scratch)
+scratchmnt=$(buildah mount $newcontainer)
+
+# install the packages
+yum install --installroot $scratchmnt bash coreutils --releasever 7 --setopt install_weak_deps=false -y
+yum clean all -y --installroot $scratchmnt --releasever 7
+
+sudo buildah config --cmd /bin/bash $newcontainer
+
+# set some config info
+buildah config --label name=centos-base $newcontainer
+
+# commit the image
+buildah unmount $newcontainer
+buildah commit $newcontainer centos-base
+
+$ sudo ./buildah-base.sh
+
+$ sudo buildah images
+IMAGE ID IMAGE NAME CREATED AT SIZE
+8379315d3e3e docker.io/library/centos-base:latest Mar 25, 2018 17:08 212.1 MB
+```
+
+Tim 想知道为何 Buildah 镜像体积反而大 17MB,毕竟 `python` 和 `yum` 软件包都没有安装到 Buildah 镜像中,而这些软件已经安装到 Docker 镜像中。这个结果并不符合预期,在 Github 的相关主题中引发了广泛的讨论。
+
+不仅 Red Hat 的员工参与了讨论,还有不少公司外人士也加入了讨论,这很有意义。值得一提的是,GitHub 用户 @pixdrift 主导了很多重要的讨论并提出很多发现,他指出在 Buildah 镜像中文档和语言包就占据了比 100MB 略多一点的空间。Pixdrift 建议在 yum 安装器中强制指定语言,据此提出如下修改过的 `buildah-bash.sh` 脚本:
+```
+#!/bin/bash
+
+set -x
+
+# build a minimal image
+newcontainer=$(buildah from scratch)
+scratchmnt=$(buildah mount $newcontainer)
+
+# install the packages
+yum install --installroot $scratchmnt bash coreutils --releasever 7 --setopt=install_weak_deps=false --setopt=tsflags=nodocs --setopt=override_install_langs=en_US.utf8 -y
+yum clean all -y --installroot $scratchmnt --releasever 7
+
+sudo buildah config --cmd /bin/bash $newcontainer
+
+# set some config info
+buildah config --label name=centos-base $newcontainer
+
+# commit the image
+buildah unmount $newcontainer
+buildah commit $newcontainer centos-base
+```
+
+Tim 运行这个新脚本,得到的镜像体积缩减至 92MB,相比之前的 Buildah 镜像体积减少了 120MB,这比较接近我们的预期;然而,c出于工程师的天性,56% 的体积缩减不能让他们满足。讨论继续深入下去,涉及如何移除个人语言包以节省更多空间。如果想了解讨论细节,点击 [Buildah 镜像体积并不小?][2] 链接。说不定你也能给出有帮助的点子,甚至更进一步成为 Buildah 项目的贡献者。这个主题的解决从一个侧面告诉我们,Buildah 软件可以多么快速和容易地创建体积最小化的容器,该容器仅包含你高效运行任务所需的软件。额外的好处是,你无需运行一个守护进程。
+
+这个镜像体积缩减的主题让我意识到开源软件的力量。来自不同公司的大量开发者,在一天多的时间内,以开放讨论的形式进行合作解决问题。虽然解决这个具体问题并没有修改已有代码,但 Red Hat 公司外开发者对 Buildah 做了很多代码贡献,进而帮助项目变得更好。这些贡献也吸引了更多人才关注项目代码;如果像之前那样,代码作为版权保护软件的一部分放置在私有 git 仓库中,不会获得上述好处。我只用了一年的时间就转向拥抱 [开源方式][3],而且可能不会再转回去了。
+
+文章最初发表于 [Project Atomic][4],已获得转载许可。
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://opensource.com/article/18/5/containers-buildah
+
+作者:[Tom Sweeney][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[pinewall](https://github.com/pinewall)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]:https://opensource.com/users/tomsweeneyredhat
+[1]:https://github.com/projectatomic/buildah
+[2]:https://github.com/projectatomic/buildah/issues/532
+[3]:https://twitter.com/opensourceway
+[4]:http://www.projectatomic.io/blog/2018/04/open-source-what-a-concept/
diff --git a/translated/tech/20180521 Audacity quick tip- quickly remove background noise.md b/translated/tech/20180521 Audacity quick tip- quickly remove background noise.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..0765199582
--- /dev/null
+++ b/translated/tech/20180521 Audacity quick tip- quickly remove background noise.md
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
+Audacity 快速指南:快速消除背景噪音
+======
+
+
+当在笔记本电脑上录制声音时 - 比如首次简单地录屏 - 许多用户通常使用内置麦克风。但是,这些小型麦克风也会捕获很多背景噪音。在这个快速指南中,我们会学习如何使用 Fedora 中的 [Audacity][1] 快速移除音频文件中的背景噪音。
+
+### 安装 Audacity
+
+Audacity 是 Fedora 中用于混合、剪切和编辑音频文件的程序。在 Fedora 上它支持各种开箱即用的格式 - 包括 MP3 和 OGG。从软件中心安装 Audacity。
+
+![][2]
+
+如果你更喜欢终端,请使用以下命令:
+```
+sudo dnf install audacity
+
+```
+
+### 导入您的音频、样本背景噪音
+
+安装 Audacity 后,打开程序,使用 **File > Import** 菜单项导入你的声音。这个例子使用了一个[来自 freesound.org 添加了噪音的声音][3]:
+
+接下来,采样要滤除的背景噪音。导入音轨后,选择仅包含背景噪音的音轨区域。然后从菜单中选择 **Effect > Noise Reduction**,然后按下 **Get Noise Profile** 按钮。
+
+![][4]
+
+### 过滤噪音
+
+接下来,选择你要过滤噪音的音轨区域。通过使用鼠标进行选择,或者按 **Ctrl + a** 来选择整个音轨。最后,再次打开 **Effect > Noise Reduction** 对话框,然后单击确定以应用滤镜。
+
+![][5]
+
+此外,调整设置,直到你的音轨听起来更好。这里是原始文件,接下来是用于比较的降噪音轨(使用默认设置):
+
+https://ryanlerch.fedorapeople.org/sidebyside.ogg?_=2
+
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
+
+via: https://fedoramagazine.org/audacity-quick-tip-quickly-remove-background-noise/
+
+作者:[Ryan Lerch][a]
+选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
+译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
+校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
+
+本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
+
+[a]: https://fedoramagazine.org/introducing-flatpak/
+[1]:https://www.audacityteam.org/
+[2]:https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/audacity-software.jpg
+[3]:https://freesound.org/people/levinj/sounds/8323/
+[4]:https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/select-noise-profile.gif
+[5]:https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/apply-filter.gif
diff --git a/sources/tech/20180521 How to Install and Configure KVM on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server.md b/translated/tech/20180521 How to Install and Configure KVM on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server.md
similarity index 50%
rename from sources/tech/20180521 How to Install and Configure KVM on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server.md
rename to translated/tech/20180521 How to Install and Configure KVM on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server.md
index 051ca46bc1..a39d5be591 100644
--- a/sources/tech/20180521 How to Install and Configure KVM on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server.md
+++ b/translated/tech/20180521 How to Install and Configure KVM on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server.md
@@ -1,14 +1,17 @@
-How to Install and Configure KVM on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS Server
+如何在 Ubuntu 18.04 服务器上安装和配置 KVM
+
======
-**KVM** (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is an open source full virtualization solution for Linux like systems, KVM provides virtualization functionality using the virtualization extensions like **Intel VT** or **AMD-V**. Whenever we install KVM on any linux box then it turns it into the hyervisor by loading the kernel modules like **kvm-intel.ko** ( for intel based machines) and **kvm-amd.ko** ( for amd based machines).
-KVM allows us to install and run multiple virtual machines (Windows & Linux). We can create and manage KVM based virtual machines either via **virt-manager** graphical user interface or **virt-install** & **virsh** cli commands.
+**KVM**(基于内核的虚拟机)是一款为类 Linux 系统提供的开源全虚拟化解决方案,KVM 使用虚拟化扩展(如 **Intel VT** 或 **AMD-V**)提供虚拟化功能。无论何时我们在任何 Linux 机器上安装 KVM,都会通过加载诸如 kvm-intel.ko(基于 Intel 的机器)和 kvm-amd.ko(基于 amd 的机器)的内核模块,使其成为管理程序(LCTT 译者注:一种监控和管理虚拟机运行的核心软件层)。
-In this article we will discuss how to install and configure **KVM hypervisor** on Ubuntu 18.04 LTS server. I am assuming you have already installed Ubuntu 18.04 LTS server on your system. Login to your server and perform the following steps.
+KVM 允许我们安装和运行多个虚拟机(Windows 和 Linux)。我们可以通过 **virt-manager** 的图形用户界面或使用 **virt-install** 和 **virsh** 命令在命令行界面来创建和管理基于 KVM 的虚拟机。
-### Step:1 Verify Whether your system support hardware virtualization
+在本文中,我们将讨论如何在Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 服务器上安装和配置 **KVM 管理程序**。我假设你已经在你的服务器上安装了 Ubuntu 18.04 LTS 。接下来登录到您的服务器执行以下步骤。
+
+### 第一步:确认您的硬件是否支持虚拟化
+
+执行 egrep 命令以验证您的服务器的硬件是否支持虚拟化,
-Execute below egrep command to verify whether your system supports hardware virtualization or not,
```
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ egrep -c '(vmx|svm)' /proc/cpuinfo
1
@@ -16,15 +19,17 @@ linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$
```
-If the output is greater than 0 then it means your system supports Virtualization else reboot your system, then go to BIOS settings and enable VT technology.
+如果输出结果大于 0,就意味着您的硬件支持虚拟化。重启,进入 BIOS 设置中启用 VT 技术。
+
+现在使用下面的命令安装“ **kvm-ok** ”实用程序,该程序用于确定您的服务器是否能够运行硬件加速的 KVM 虚拟机
-Now Install “ **kvm-ok** ” utility using below command, it is used to determine if your server is capable of running hardware accelerated KVM virtual machines
```
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo apt install cpu-checker
```
-Run kvm-ok command and verify the output,
+运行 kvm-ok 命令确认输出结果,
+
```
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo kvm-ok
INFO: /dev/kvm exists
@@ -33,41 +38,44 @@ linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$
```
-### Step:2 Install KVM and its required packages
+### 第二步:安装 KVM 及其依赖包
-Run the below apt commands to install KVM and its dependencies
+
+运行下面的 apt 命令安装 KVM 及其依赖项
```
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo apt update
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo apt install qemu qemu-kvm libvirt-bin bridge-utils virt-manager
-
```
-Once the above packages are installed successfully, then your local user (In my case linuxtechi) will be added to the group libvirtd automatically.
+只要上图相应的软件包安装成功,那么你的本地用户(对于我来说是 linuxtechi)将被自动添加到 libvirtd 群组。
-### Step:3 Start & enable libvirtd service
+### 第三步:启动并启用 libvirtd 服务
+
+我们在 Ubuntu 18.04 服务器上安装 qemu 和 libvirtd 软件包之后,它就会自动启动并启用 libvirtd 服务,如果 libvirtd 服务没有开启,则运行以下命令开启,
-Whenever we install qemu & libvirtd packages in Ubuntu 18.04 Server then it will automatically start and enable libvirtd service, In case libvirtd service is not started and enabled then run beneath commands,
```
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo service libvirtd start
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo update-rc.d libvirtd enable
```
-Now verify the status of libvirtd service using below command,
+现在使用下面的命令确认 libvirtd 服务的状态,
+
```
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ service libvirtd status
```
-Output would be something like below:
+输出结果如下所示:
[![libvirtd-command-ubuntu18-04][1]![libvirtd-command-ubuntu18-04][2]][3]
-### Step:4 Configure Network Bridge for KVM virtual Machines
+### 第四步:为 KVM 虚拟机配置桥接网络
-Network bridge is required to access the KVM based virtual machines outside the KVM hypervisor or host. In Ubuntu 18.04, network is managed by netplan utility, whenever we freshly installed Ubuntu 18.04 server then a file with name “ **/etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml** ” is created automatically, to configure static IP and bridge, netplan utility will refer this file.
+只有通过桥接网络,KVM 虚拟机才能访问外部的 KVM 管理程序或主机。在Ubuntu 18.04中,网络由 netplan 实用程序管理,每当我们新安装一个 Ubuntu 18.04 系统时,会自动创建一个名称为 “**/etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml**” 文件,其配置了静态 IP 和桥接网络,netplan 实用工具将引用这个文件。
+
+截至目前,我已经在此文件配置了静态 IP,文件的具体内容如下:
-As of now I have already configured the static IP via this file and content of this file is below:
```
network:
ethernets:
@@ -82,7 +90,8 @@ network:
```
-Let’s add the network bridge definition in this file,
+我们在这个文件中添加桥接网络的配置信息,
+
```
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo vi /etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml
@@ -104,20 +113,23 @@ network:
```
-As you can see we have removed the IP address from interface(ens33) and add the same IP to the bridge ‘ **br0** ‘ and also added interface (ens33) to the bridge br0. Apply these changes using below netplan command,
+正如你所看到的,我们已经从接口(ens33)中删除了 IP 地址,并将该 IP 添加到 '**br0**' 中,并且还将接口(ens33)添加到 br0。使用下面的 netplan 命令使更改生效,
+
```
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo netplan apply
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$
```
-If you want to see the debug logs then use the below command,
+如果您想查看 debug 日志请使用以下命令,
+
```
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo netplan --debug apply
```
-Now Verify the bridge status using following methods:
+现在使用以下方法确认网络桥接状态:
+
```
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo networkctl status -a
@@ -131,18 +143,18 @@ linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ ifconfig
[![ifconfig-command-output-ubuntu18-04][1]![ifconfig-command-output-ubuntu18-04][5]][5]
-### Start:5 Creating Virtual machine (virt-manager or virt-install command )
+### 第五步:创建虚拟机(使用 virt-manager 或 virt-install 命令)
-There are two ways to create virtual machine:
+有两种方式创建虚拟机:
- * virt-manager (GUI utility)
- * virt-install command (cli utility)
+ * virt-manager(图形化工具)
+ * virt-install(命令行工具)
+**使用 virt-manager 创建虚拟机:**
-**Creating Virtual machine using virt-manager:**
+通过执行下面的命令启动 virt-manager,
-Start the virt-manager by executing the beneath command,
```
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo virt-manager
@@ -150,39 +162,42 @@ linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo virt-manager
[![Start-Virt-Manager-Ubuntu18-04][1]![Start-Virt-Manager-Ubuntu18-04][6]][6]
-Create a new virtual machine
+创建一个新的虚拟机
[![ISO-file-Virt-Manager][1]![ISO-file-Virt-Manager][7]][7]
-Click on forward and select the ISO file, in my case I am using RHEL 7.3 iso file.
+点击下一步然后选择 ISO 镜像文件,我使用的是 RHEL 7.3 iso 镜像。
[![Select-ISO-file-virt-manager-Ubuntu18-04-Server][1]![Select-ISO-file-virt-manager-Ubuntu18-04-Server][8]][8]
-Click on Forward
+点击下一步
-In the next couple of windows, you will be prompted to specify the RAM, CPU and disk for the VM.
+在接下来的几个窗口中,系统会提示要求您为 VM 分配内存,处理器数量和磁盘空间。
-Now Specify the Name of the Virtual Machine and network,
+并指定虚拟机名字和桥接网络名,
[![VM-Name-Network-Virt-Manager-Ubuntu18-04][1]![VM-Name-Network-Virt-Manager-Ubuntu18-04][9]][9]
-Click on Finish
+点击结束
[![RHEL7-3-Installation-Virt-Manager][1]![RHEL7-3-Installation-Virt-Manager][10]][10]
-Now follow the screen instruction and complete the installation,
+接下来只需要按照屏幕指示安装系统,
-**Creating Virtual machine from CLI using virt-install command,**
+**使用virt-install命令从命令行界面创建虚拟机,**
+
+使用下面的 virt-install 命令从终端创建一个虚拟机,它将在命令行界面中开始安装,并根据您对虚拟机的名字,说明,ISO 文件位置和桥接配置的设置创建虚拟机。
-Use the below virt-install command to create a VM from terminal, it will start the installation in CLI, replace the name of the VM, description, location of ISO file and network bridge as per your setup.
```
linuxtechi@kvm-ubuntu18-04:~$ sudo virt-install -n DB-Server --description "Test VM for Database" --os-type=Linux --os-variant=rhel7 --ram=1096 --vcpus=1 --disk path=/var/lib/libvirt/images/dbserver.img,bus=virtio,size=10 --network bridge:br0 --graphics none --location /home/linuxtechi/rhel-server-7.3-x86_64-dvd.iso --extra-args console=ttyS0
```
-That’s conclude the article, I hope this article help you to install KVM on your Ubuntu 18.04 Server. Apart from this, KVM is the default hypervisor for Openstack.
+本文到此为止,我希望这篇文章能帮助你能够在 Ubuntu 18.04 服务器上成功安装 KVM。 除此之外,KVM 也是 Openstack 默认的管理程序。
+
+
+阅读更多:“[**如何使用 virsh 命令创建,还原和删除 KVM 虚拟机快照**][11]”
-Read More On : “[ **How to Create, Revert and Delete KVM Virtual machine (domain) snapshot with virsh command**][11]“
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@@ -190,7 +205,7 @@ via: https://www.linuxtechi.com/install-configure-kvm-ubuntu-18-04-server/
作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
选题:[lujun9972](https://github.com/lujun9972)
-译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
+译者:[wyxplus](https://github.com/wyxplus)
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出