mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
Merge remote-tracking branch 'LCTT/master'
This commit is contained in:
commit
7dcfcb5ab6
@ -1,21 +1,21 @@
|
||||
如何用 Python 编写你喜爱的 R 函数
|
||||
======
|
||||
R 还是 Python ? Python 脚本模仿易使用的 R 风格函数,使得数据统计变得简单易行。
|
||||
> R 还是 Python ? Python 脚本模仿易使用的 R 风格函数,使得数据统计变得简单易行。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
“Python vs. R” 是数据科学和机器学习的现代战争之一。毫无疑问,近年来这两者发展迅猛,成为数据科学,预测分析和机器学习领域的顶级编程语言。事实上,根据 IEEE 最近的一篇文章,Python 已在 [最受欢迎编程语言排行榜][1] 中超越 C++ 并且 R 语言也稳居前 10 位。
|
||||
“Python vs. R” 是数据科学和机器学习的现代战争之一。毫无疑问,近年来这两者发展迅猛,成为数据科学、预测分析和机器学习领域的顶级编程语言。事实上,根据 IEEE 最近的一篇文章,Python 已在 [最受欢迎编程语言排行榜][1] 中超越 C++ 成为排名第一的语言,并且 R 语言也稳居前 10 位。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,这两者之间存在一些根本区别。[R][2] 语言设计的初衷主要是作为统计分析和数据分析问题的快速原型设计的工具,另一方面,Python 是作为一种通用的,现代的面向对象语言而开发的,类似 C++ 或 Java,但具有更简单的学习曲线和更灵活的语言风格。因此,R 仍在统计学家,定量生物学家,物理学家和经济学家中备受青睐,而 Python 已逐渐成为日常脚本,自动化,后端 Web 开发,分析和通用机器学习框架的顶级语言,拥有广泛的支持基础和开源开发社区。
|
||||
但是,这两者之间存在一些根本区别。[R][2] 语言设计的初衷主要是作为统计分析和数据分析问题的快速原型设计的工具,另一方面,Python 是作为一种通用的、现代的面向对象语言而开发的,类似 C++ 或 Java,但具有更简单的学习曲线和更灵活的语言风格。因此,R 仍在统计学家、定量生物学家、物理学家和经济学家中备受青睐,而 Python 已逐渐成为日常脚本、自动化、后端 Web 开发、分析和通用机器学习框架的顶级语言,拥有广泛的支持基础和开源开发社区。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Python 环境中模仿函数式编程
|
||||
|
||||
[R 作为函数式编程语言的本质][3]为用户提供了一个极其简洁的用于快速计算概率的接口,还为数据分析问题提供了必不可少的描述统计和推论统计方法(译者注:统计学从功能上分为描述统计学和推论统计学)。例如,只用一个简洁的函数调用来解决以下问题难道不是很好吗?
|
||||
[R 作为函数式编程语言的本质][3]为用户提供了一个极其简洁的用于快速计算概率的接口,还为数据分析问题提供了必不可少的描述统计和推论统计方法(LCTT 译注:统计学从功能上分为描述统计学和推论统计学)。例如,只用一个简洁的函数调用来解决以下问题难道不是很好吗?
|
||||
|
||||
* 如何计算数据向量的平均数 / 中位数 / 众数。
|
||||
* 如何计算某些服从正态分布的事件的累积概率。如果服<ruby>从泊松分布<rt>Poisson distribution</rt></ruby>又该怎样计算呢?
|
||||
* 如何计算一系列数据点的四分位距。
|
||||
* 如何生成服从学生 t 分布的一些随机数(译者注: 在概率论和统计学中,学生 t -分布(Student's t*-*distribution)可简称为t 分布,用于根据小样本来估计呈正态分布且方差未知的总体的均值)。
|
||||
* 如何生成服从学生 t 分布的一些随机数(LCTT 译注: 在概率论和统计学中,学生 t-分布(Student's t-distribution)可简称为 t 分布,用于根据小样本来估计呈正态分布且方差未知的总体的均值)。
|
||||
|
||||
R 编程环境可以完成所有这些工作。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,16 +23,15 @@ R 编程环境可以完成所有这些工作。
|
||||
|
||||
要结合二者的优势,你只需要一个简单的 Python 封装的库,其中包含与 R 风格定义的概率分布和描述性统计相关的最常用函数。 这使你可以非常快速地调用这些函数,而无需转到正确的 Python 统计库并理解整个方法和参数列表。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 便于调用 R 函数的 Python 包装脚本
|
||||
|
||||
[我编写了一个Python脚本][4] ,用 Python 简单统计分析定了义最简洁和最常用的 R 函数。导入此脚本后,你将能够自然地使用这些R函数,就像在R编程环境中一样。
|
||||
[我编写了一个 Python 脚本][4] ,用 Python 简单统计分析定义了最简洁和最常用的 R 函数。导入此脚本后,你将能够原生地使用这些 R 函数,就像在 R 编程环境中一样。
|
||||
|
||||
此脚本的目标是提供简单的 Python 函数,模仿 R 风格的统计函数,以快速计算密度估计和点估计,累积分布和分位数,并生成重要概率分布的随机变量。
|
||||
此脚本的目标是提供简单的 Python 函数,模仿 R 风格的统计函数,以快速计算密度估计和点估计、累积分布和分位数,并生成重要概率分布的随机变量。
|
||||
|
||||
为了延续 R 风格,脚本不使用类结构,并且只在文件中定义原始函数。 因此,用户可以导入这个 Python 脚本,并在需要单个名称调用时使用所有功能。
|
||||
为了延续 R 风格,脚本不使用类结构,并且只在文件中定义原始函数。因此,用户可以导入这个 Python 脚本,并在需要单个名称调用时使用所有功能。
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,我使用 mimic 这个词。 在任何情况下,我都声称要模仿 R 的真正的函数式编程范式,该范式包括深层环境设置以及这些环境和对象之间的复杂关系。 这个脚本允许我(我希望无数其他的 Python 用户)快速启动P ython 程序或 Jupyter 笔记本程序,导入脚本,并立即开始进行简单的描述性统计。 这就是目标,仅此而已。
|
||||
请注意,我使用 mimic 这个词。 在任何情况下,我都声称要模仿 R 的真正的函数式编程范式,该范式包括深层环境设置以及这些环境和对象之间的复杂关系。 这个脚本允许我(我希望无数其他的 Python 用户)快速启动 Python 程序或 Jupyter 笔记本程序、导入脚本,并立即开始进行简单的描述性统计。这就是目标,仅此而已。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经写过 R 代码(可能在研究生院)并且刚刚开始学习并使用 Python 进行数据分析,那么你将很高兴看到并在 Jupyter 笔记本中以类似在 R 环境中一样使用一些相同的知名函数。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -48,7 +47,7 @@ lst=[20,12,16,32,27,65,44,45,22,18]
|
||||
<more code, more statistics...>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
假设你想从数据向量计算[ Tuckey 五数][5]摘要。 你只需要调用一个简单的函数 **fivenum**,然后将向量传进去。 它将返回五数摘要,存在 NumPy 数组中。
|
||||
假设你想从数据向量计算 [Tuckey 五数][5]摘要。 你只需要调用一个简单的函数 `fivenum`,然后将向量传进去。 它将返回五数摘要,存在 NumPy 数组中。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
lst=[20,12,16,32,27,65,44,45,22,18]
|
||||
@ -56,25 +55,26 @@ fivenum(lst)
|
||||
> array([12. , 18.5, 24.5, 41. , 65. ])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
或许你想要知道下面问题的答案
|
||||
或许你想要知道下面问题的答案:
|
||||
|
||||
假设一台机器平均每小时输出 10 件成品,标准偏差为 2。输出模式遵循接近正态的分布。 机器在下一个小时内输出至少 7 个但不超过 12 个单位的概率是多少?
|
||||
> 假设一台机器平均每小时输出 10 件成品,标准偏差为 2。输出模式遵循接近正态的分布。 机器在下一个小时内输出至少 7 个但不超过 12 个单位的概率是多少?
|
||||
|
||||
答案基本上是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
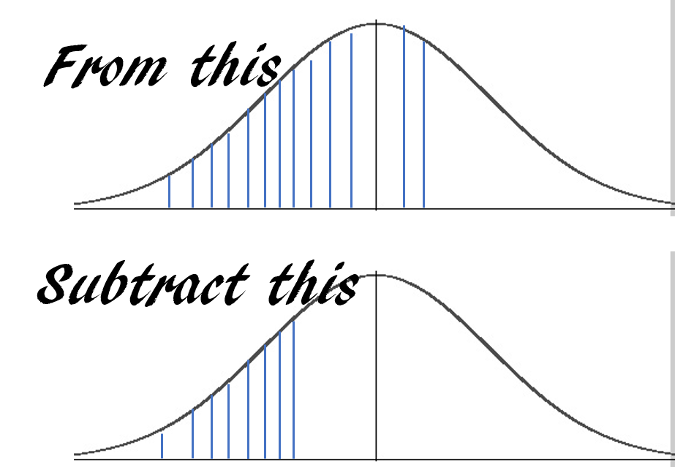
|
||||
|
||||
使用 **pnorm** ,你可以只用一行代码就能获得答案:
|
||||
使用 `pnorm` ,你可以只用一行代码就能获得答案:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pnorm(12,10,2)-pnorm(7,10,2)
|
||||
> 0.7745375447996848
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
或者你可能需要回答以下问题:
|
||||
|
||||
假设你有一个不公平硬币,每次投它时有 60% 可能正面朝上。 你正在玩 10 次投掷游戏。 你如何绘制并给出这枚硬币所有可能的胜利数(从0到10)的概率?
|
||||
> 假设你有一个不公平硬币,每次投它时有 60% 可能正面朝上。 你正在玩 10 次投掷游戏。 你如何绘制并给出这枚硬币所有可能的胜利数(从 0 到 10)的概率?
|
||||
|
||||
只需使用一个函数 **dbinom** 就可以获得一个只有几行代码的美观条形图:
|
||||
只需使用一个函数 `dbinom` 就可以获得一个只有几行代码的美观条形图:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
probs=[]
|
||||
@ -93,8 +93,8 @@ plt.show()
|
||||
R 提供了一个非常简单直观的接口,可以从基本概率分布中快速计算。 接口如下:
|
||||
|
||||
* **d** 分布:给出点 **x** 处的密度函数值
|
||||
* **p** 分布:给出 **x**点的累积值
|
||||
* **q** 分布:以概率 **p**给出分位数函数值
|
||||
* **p** 分布:给出 **x** 点的累积值
|
||||
* **q** 分布:以概率 **p** 给出分位数函数值
|
||||
* **r** 分布:生成一个或多个随机变量
|
||||
|
||||
在我们的实现中,我们坚持使用此接口及其关联的参数列表,以便你可以像在 R 环境中一样执行这些函数。
|
||||
@ -103,16 +103,16 @@ R 提供了一个非常简单直观的接口,可以从基本概率分布中快
|
||||
|
||||
脚本中实现了以下 R 风格函数,以便快速调用。
|
||||
|
||||
* 平均数,中位数,方差,标准差
|
||||
* Tuckey 五数摘要,<ruby>四分位距<rt>interquartile range</rt></ruby>IQR
|
||||
* 矩阵的协方差或两个向量之间的协方差
|
||||
* 以下分布的密度,累积概率,分位数函数和随机变量生成:正态,均匀,二项式,<ruby>泊松<rt>Poisson</rt></ruby>,F,<ruby>学生 t<rt>Student's t</rt></ruby>,<ruby>卡方<rt>Chi-square</rt></ruby>,<ruby>贝塔<rt>beta</rt></ruby>和<ruby>伽玛<rt>gamma</rt></ruby>
|
||||
* 平均数、中位数、方差、标准差
|
||||
* Tuckey 五数摘要、<ruby>四分位距<rt>interquartile range</rt></ruby>(IQR)
|
||||
* 矩阵的协方差或两个向量之间的协方差
|
||||
* 以下分布的密度、累积概率、分位数函数和随机变量生成:正态、均匀、二项式、<ruby>泊松<rt>Poisson</rt></ruby>、F、<ruby>学生 t<rt>Student's t</rt></ruby>、<ruby>卡方<rt>Chi-square</rt></ruby>、<ruby>贝塔<rt>beta</rt></ruby>和<ruby>伽玛<rt>gamma</rt></ruby>
|
||||
|
||||
### 进行中的工作
|
||||
|
||||
显然,这是一项正在进行的工作,我计划在此脚本中添加一些其他方便的R函数。 例如,在 R 中,单行命令 **lm** 可以为数字数据集提供一个简单的最小二乘拟合模型,其中包含所有必要的推理统计(P 值,标准误差等)。 这非常简洁! 另一方面,Python 中的标准线性回归问题经常使用 [Scikit-learn][6] 库来处理,此用途需要更多的脚本,所以我打算使用 Python 的 [statsmodels][7] 库合并这个单函数线性模型来拟合功能。
|
||||
显然,这是一项正在进行的工作,我计划在此脚本中添加一些其他方便的R函数。 例如,在 R 中,单行命令 `lm` 可以为数字数据集提供一个简单的最小二乘拟合模型,其中包含所有必要的推理统计(P 值,标准误差等)。 这非常简洁! 另一方面,Python 中的标准线性回归问题经常使用 [Scikit-learn][6] 库来处理,此用途需要更多的脚本,所以我打算使用 Python 的 [statsmodels][7] 库合并这个单函数线性模型来拟合功能。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你喜欢这个脚本,并且愿意在工作中使用,请 [GitHub 仓库][8]点个 star 或者 fork 帮助其他人找到它。 另外,你可以查看我其他的 [GitHub 仓库][9],了解 Python,R 或 MATLAB 中的有趣代码片段以及一些机器学习资源。
|
||||
如果你喜欢这个脚本,并且愿意在工作中使用,请在 [GitHub 仓库][8]点个 star 或者 fork 帮助其他人找到它。 另外,你可以查看我其他的 [GitHub 仓库][9],了解 Python、R 或 MATLAB 中的有趣代码片段以及一些机器学习资源。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有任何问题或想法要分享,请通过 [tirthajyoti [AT] gmail.com][10] 与我联系。 如果你像我一样热衷于机器学习和数据科学,请 [在 LinkedIn 上加我为好友][11]或者[在 Twitter 上关注我][12]。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,15 +54,23 @@ rule_translation_revised() {
|
||||
&& [ "$TOTAL" -eq 1 ] && echo "匹配规则:校对译文"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# 发布译文:发布多篇译文
|
||||
# 发布译文:发布一篇译文
|
||||
rule_translation_published() {
|
||||
[ "$TSL_D" -ge 1 ] && [ "$PUB_A" -ge 1 ] && [ "$TSL_D" -eq "$PUB_A" ] \
|
||||
&& ensure_identical SRC D TSL A 1 \
|
||||
[ "$TSL_D" -eq 1 ] && [ "$PUB_A" -eq 1 ] \
|
||||
&& ensure_identical TSL D PUB A 1 \
|
||||
&& check_category TSL D \
|
||||
&& check_category PUB A \
|
||||
&& [ "$TOTAL" -eq $((TSL_D + PUB_A)) ] \
|
||||
&& echo "匹配规则:发布译文 ${PUB_A} 篇"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# 校对已发布:只能校对一篇
|
||||
rule_published_revised() {
|
||||
[ "$PUB_M" -eq 1 ] \
|
||||
&& check_category PUB M \
|
||||
&& [ "$TOTAL" -eq 1 ] && echo "匹配规则:校对已发布"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# 定义常见错误
|
||||
|
||||
# 未知错误
|
||||
@ -76,6 +84,12 @@ error_translation_requested_multiple() {
|
||||
&& echo "匹配错误:申领多篇,请一次仅申领一篇"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# 提交多篇
|
||||
error_translation_completed_multiple() {
|
||||
[ "$TSL_A" -gt 1 ] \
|
||||
&& echo "匹配错误:提交多篇,请一次仅提交一篇"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# 执行检查并输出匹配项目
|
||||
do_check() {
|
||||
rule_bypass_check \
|
||||
@ -84,8 +98,10 @@ do_check() {
|
||||
|| rule_translation_completed \
|
||||
|| rule_translation_revised \
|
||||
|| rule_translation_published \
|
||||
|| rule_published_revised \
|
||||
|| {
|
||||
error_translation_requested_multiple \
|
||||
|| error_translation_completed_multiple \
|
||||
|| error_undefined
|
||||
exit 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,327 +0,0 @@
|
||||
ScarboroughCoral translating!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Top 30 OpenStack Interview Questions and Answers
|
||||
======
|
||||
Now a days most of the firms are trying to migrate their IT infrastructure and Telco Infra into private cloud i.e OpenStack. If you planning to give interviews on Openstack admin profile, then below list of interview questions might help you to crack the interview.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Q:1 Define OpenStack and its key components?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: It is a bundle of opensource software, which all in combine forms a provide cloud software known as OpenStack.OpenStack is known as Stack of Open source Software or Projects.
|
||||
|
||||
Following are the key components of OpenStack
|
||||
|
||||
* **Nova** – It handles the Virtual machines at compute level and performs other computing task at compute or hypervisor level.
|
||||
* **Neutron** – It provides the networking functionality to VMs, Compute and Controller Nodes.
|
||||
* **Keystone** – It provides the identity service for all cloud users and openstack services. In other words, we can say Keystone a method to provide access to cloud users and services.
|
||||
* **Horizon** – It provides a GUI (Graphical User Interface), using the GUI Admin can all day to day operations task at ease.
|
||||
* **Cinder** – It provides the block storage functionality, generally in OpenStack Cinder is integrated with Chef and ScaleIO to service block storage to Compute & Controller nodes.
|
||||
* **Swift** – It provides the object storage functionality. Generally, Glance images are on object storage. External storage like ScaleIO can work as Object storage too and can easily be integrated with Glance Service.
|
||||
* **Glance** – It provides Cloud image services, using glance admin used to upload and download cloud images.
|
||||
* **Heat** – It provides an orchestration service or functionality. Using Heat admin can easily VMs as stack and based on requirements VMs in the stack can be scale-in and Scale-out
|
||||
* **Ceilometer** – It provides the telemetry and billing services.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:2 What are services generally run on a controller node?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Following services run on a controller node:
|
||||
|
||||
* Identity Service ( KeyStone)
|
||||
* Image Service ( Glance)
|
||||
* Nova Services like Nova API, Nova Scheduler & Nova DB
|
||||
* Block & Object Service
|
||||
* Ceilometer Service
|
||||
* MariaDB / MySQL and RabbitMQ Service
|
||||
* Management services of Networking (Neutron) and Networking agents
|
||||
* Orchestration Service (Heat)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:3 What are the services generally run on a Compute Node?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Following services run on a compute node,
|
||||
|
||||
* Nova-Compute
|
||||
* Networking Services like OVS
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:4 What is the default location of VMs on the Compute Nodes?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: VMs in the Compute node are stored at “ **/var/lib/nova/instances** ”
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:5 What is default location of glance images?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: As the Glance service runs on a controller node, all the glance images are store under the folder “ **/var/lib/glance/images** ” on a controller node.
|
||||
|
||||
Read More : [**How to Create and Delete Virtual Machine(VM) from Command line in OpenStack**][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:6 Tell me the command how to spin a VM from Command Line?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: We can easily spin a new VM using the following openstack command,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# openstack server create --flavor {flavor-name} --image {Image-Name-Or-Image-ID} --nic net-id={Network-ID} --security-group {Security_Group_ID} –key-name {Keypair-Name} <VM_Name>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:7 How to list the network namespace of a tenant in OpenStack?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Network namespace of a tenant can be listed using “ip net ns” command
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# ip netns list
|
||||
qdhcp-a51635b1-d023-419a-93b5-39de47755d2d
|
||||
haproxy
|
||||
vrouter
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:8 How to execute command inside network namespace in openstack?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Let’s assume we want to execute “ifconfig” command inside the network namespace “qdhcp-a51635b1-d023-419a-93b5-39de47755d2d”, then run the beneath command,
|
||||
|
||||
Syntax : ip netns exec {network-space} <command>
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# ip netns exec qdhcp-a51635b1-d023-419a-93b5-39de47755d2d "ifconfig"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:9 How to upload and download a cloud image in Glance from command line?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: A Cloud image can be uploaded in glance from command using beneath openstack command,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack image create --disk-format qcow2 --container-format bare --public --file {Name-Cloud-Image}.qcow2 <Cloud-Image-Name>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use below openstack command to download a cloud image from command line,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# glance image-download --file <Cloud-Image-Name> --progress <Image-ID>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:10 How to reset error state of a VM into active in OpenStack env?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: There are some scenarios where some VMs went to error state and this error state can be changed into active state using below commands,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# nova reset-state --active {Instance_id}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:11 How to get list of available Floating IPs from command line?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Available floating ips can be listed using the below command,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~]# openstack ip floating list | grep None | head -10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:12 How to provision a virtual machine in specific availability zone and compute Host?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Let’s assume we want to provision a VM on the availability zone NonProduction in compute-02, use the beneath command to accomplish this,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~]# openstack server create --flavor m1.tiny --image cirros --nic net-id=e0be93b8-728b-4d4d-a272-7d672b2560a6 --security-group NonProd_SG --key-name linuxtec --availability-zone NonProduction:compute-02 nonprod_testvm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:13 How to get list of VMs which are provisioned on a specific Compute node?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Let’s assume we want to list the vms which are provisioned on compute-0-19, use below
|
||||
|
||||
Syntax: openstack server list –all-projects –long -c Name -c Host | grep -i {Compute-Node-Name}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack server list --all-projects --long -c Name -c Host | grep -i compute-0-19
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:14 How to view the console log of an openstack instance from command line?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Console logs of an instance can be viewed from the command line using the following commands,
|
||||
|
||||
First get the ID of an instance and then use the below command,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack console log show {Instance-id}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:15 How to get console URL of an openstack instance?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Console URL of an instance can be retrieved from command line using the below openstack command,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack console url show {Instance-id}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:16 How to create a bootable cinder / block storage volume from command line?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: To Create a bootable cinder or block storage volume (assume 8 GB) , refer the below steps:
|
||||
|
||||
* Get Image list using below
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack image list | grep -i cirros
|
||||
| 89254d46-a54b-4bc8-8e4d-658287c7ee92 | cirros | active |
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Create bootable volume of size 8 GB using cirros image
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# cinder create --image-id 89254d46-a54b-4bc8-8e4d-658287c7ee92 --display-name cirros-bootable-vol 8
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:17 How to list all projects or tenants that has been created in your opentstack?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Projects or tenants list can be retrieved from the command using the below openstack command,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack project list --long
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:18 How to list the endpoints of openstack services?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Openstack service endpoints are classified into three categories,
|
||||
|
||||
* Public Endpoint
|
||||
* Internal Endpoint
|
||||
* Admin Endpoint
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Use below openstack command to view endpoints of each openstack service,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack catalog list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To list the endpoint of a specific service like keystone use below,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack catalog show keystone
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Read More : [**Step by Step Instance Creation Flow in OpenStack**][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:19 In which order we should restart nova services on a controller node?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Following order should be followed to restart the nova services on openstack controller node,
|
||||
|
||||
* service nova-api restart
|
||||
* service nova-cert restart
|
||||
* service nova-conductor restart
|
||||
* service nova-consoleauth restart
|
||||
* service nova-scheduler restart
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:20 Let’s assume DPDK ports are configured on compute node for data traffic, now how you will check the status of dpdk ports?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: As DPDK ports are configured via openvSwitch (OVS), use below commands to check the status,
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:21 How to add new rules to the existing SG(Security Group) from command line in openstack?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: New rules to the existing SG in openstack can be added using the neutron command,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# neutron security-group-rule-create --protocol <tcp or udp> --port-range-min <port-number> --port-range-max <port-number> --direction <ingress or egress> --remote-ip-prefix <IP-address-or-range> Security-Group-Name
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:22 How to view the OVS bridges configured on Controller and Compute Nodes?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: OVS bridges on Controller and Compute nodes can be viewed using below command,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~]# ovs-vsctl show
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:23 What is the role of Integration Bridge(br-int) on the Compute Node ?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: The integration bridge (br-int) performs VLAN tagging and untagging for the traffic coming from and to the instance running on the compute node.
|
||||
|
||||
Packets leaving the n/w interface of an instance goes through the linux bridge (qbr) using the virtual interface qvo. The interface qvb is connected to the Linux Bridge & interface qvo is connected to integration bridge (br-int). The qvo port on integration bridge has an internal VLAN tag that gets appended to packet header when a packet reaches to the integration bridge.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:24 What is the role of Tunnel Bridge (br-tun) on the compute node?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: The tunnel bridge (br-tun) translates the VLAN tagged traffic from integration bridge to the tunnel ids using OpenFlow rules.
|
||||
|
||||
br-tun (tunnel bridge) allows the communication between the instances on different networks. Tunneling helps to encapsulate the traffic travelling over insecure networks, br-tun supports two overlay networks i.e GRE and VXLAN
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:25 What is the role of external OVS bridge (br-ex)?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: As the name suggests, this bridge forwards the traffic coming to and from the network to allow external access to instances. br-ex connects to the physical interface like eth2, so that floating IP traffic for tenants networks is received from the physical network and routed to the tenant network ports.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:26 What is function of OpenFlow rules in OpenStack Networking?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: OpenFlow rules is a mechanism that define how a packet will reach to destination starting from its source. OpenFlow rules resides in flow tables. The flow tables are part of OpenFlow switch.
|
||||
|
||||
When a packet arrives to a switch, it is processed by the first flow table, if it doesn’t match any flow entries in the table then packet is dropped or forwarded to another table.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:27 How to display the information about a OpenFlow switch (like ports, no. of tables, no of buffer)?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Let’s assume we want to display the information about OpenFlow switch (br-int), run the following command,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
root@compute-0-15# ovs-ofctl show br-int
|
||||
OFPT_FEATURES_REPLY (xid=0x2): dpid:0000fe981785c443
|
||||
n_tables:254, n_buffers:256
|
||||
capabilities: FLOW_STATS TABLE_STATS PORT_STATS QUEUE_STATS ARP_MATCH_IP
|
||||
actions: output enqueue set_vlan_vid set_vlan_pcp strip_vlan mod_dl_src mod_dl_dst mod_nw_src mod_nw_dst mod_nw_tos mod_tp_src mod_tp_dst
|
||||
1(patch-tun): addr:3a:c6:4f:bd:3e:3b
|
||||
config: 0
|
||||
state: 0
|
||||
speed: 0 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
|
||||
2(qvob35d2d65-f3): addr:b2:83:c4:0b:42:3a
|
||||
config: 0
|
||||
state: 0
|
||||
current: 10GB-FD COPPER
|
||||
speed: 10000 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
|
||||
………………………………………
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:28 How to display the entries for all the flows in a switch?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Flows entries of a switch can be displayed using the command ‘ **ovs-ofctl dump-flows** ‘
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s assume we want to display flow entries of OVS integration bridge (br-int),
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:29 What are Neutron Agents and how to list all neutron agents?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: OpenStack neutron server acts as the centralized controller, the actual network configurations are executed either on compute and network nodes. Neutron agents are software entities that carry out configuration changes on compute or network nodes. Neutron agents communicate with the main neutron service via Neuron API and message queue.
|
||||
|
||||
Neutron agents can be listed using the following command,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack network agent list -c ‘Agent type’ -c Host -c Alive -c State
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:30 What is CPU pinning?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: CPU pinning refers to reserving the physical cores for specific virtual machine. It is also known as CPU isolation or processor affinity. The configuration is in two parts:
|
||||
|
||||
* it ensures that virtual machine can only run on dedicated cores
|
||||
* it also ensures that common host processes don’t run on those cores
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
In other words we can say pinning is one to one mapping of a physical core to a guest vCPU.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.linuxtechi.com/openstack-interview-questions-answers/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/create-delete-virtual-machine-command-line-openstack/
|
||||
[2]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/step-by-step-instance-creation-flow-in-openstack/
|
||||
@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: ( geekpi)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: subject: (Standalone web applications with GNOME Web)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://fedoramagazine.org/standalone-web-applications-gnome-web/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Ryan Lerch https://fedoramagazine.org/introducing-flatpak/)
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
|
||||
Standalone web applications with GNOME Web
|
||||
======
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Do you regularly use a single-page web application, but miss some of the benefits of a full-fledged desktop application? The GNOME Web browser, simply named Web (aka Epiphany) has an awesome feature that allows you to ‘install’ a web application. By doing this, the web application is then presented in the applications menus, GNOME shell search, and is a separate item when switching windows. This short tutorial walks you through the steps of ‘installing’ a web application with GNOME Web.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install GNOME Web
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME Web is not included in the default Fedora install. To install, search in the Software application for ‘web’, and install.
|
||||
|
||||
![][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, use the following command in the terminal:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo dnf install epiphany
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Install as Web Application
|
||||
|
||||
Next, launch GNOME Web, and browse to the web application you wish to install. Connect to the application using the browser, and choose ‘Install site as Web Application’ from the menu:
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME Web next presents a dialog to edit the name of the application. Either leave it as the default (the URL) or change to something more descriptive:
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, press **Create** to ‘install’ your new web application. After creating the web application, close GNOME Web.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using the new web application
|
||||
|
||||
Launch the web application as you would with any typical desktop application. Search for it in the GNOME Shell Overview:
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, the web application will appear as a separate application in the alt-tab application switcher:
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
One additional feature this adds is that all web notifications from the ‘installed’ web application are presented as regular GNOME notifications.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://fedoramagazine.org/standalone-web-applications-gnome-web/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ryan Lerch][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://fedoramagazine.org/introducing-flatpak/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/gnome-web-in-gnome-software.png
|
||||
[2]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/freenode-page-in-gnome-web.png
|
||||
[3]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/edit-web-application-in-GNOME-web.png
|
||||
[4]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/web-application-in-overview.jpg
|
||||
[5]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/web-app-in-app-switcher.jpg
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: ( )
|
||||
[#]: translator: (geekpi)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: subject: (Easily Convert Audio File Formats with SoundConverter in Linux)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,339 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Openstack 30个经典面试问题和解答
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
现在,大多数公司都试图将它们的 IT 基础设施和 Telco Infra 迁移到私有云,即OpenStack。如果你打算面试 OpenStack 管理员这个岗位,那么下面列出的这些面试问题可能会帮助你通过面试。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Q:1 说一下 OpenStack 及其主要组件?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: OpenStack 是一系列开源软件,这些软件组成了一个云提供软件,也就是 OpenStack,被称为开源软件或项目栈。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是 OpenStack 的主要关键组件:
|
||||
|
||||
* **Nova** – 用于计算级别管理虚拟机,并在计算或管理程序级别执行其他计算任务。
|
||||
* **Neutron** – 为虚拟机、计算和控制节点提供网络功能。
|
||||
* **Keystone** – 为所有云用户和 OpenStack 云服务提供身份认证服务。换句话说,我们可以说 Keystone 是一个提供给云用户和云服务访问权限的方法。
|
||||
* **Horizon** – 用于提供图形用户界面。使用图形化管理界面可以很轻松地完成各种日常操作任务。
|
||||
* **Cinder** – 用于提供块存储功能。通常来说 OpenStack 的 Cinder 中集成了 Chef 和 ScaleIO 来共同为计算和控制节点提供块存储服务。
|
||||
* **Swift** – 用于提供对象存储功能。通常来说,Glance 管理的镜像是存储在对象存储空间的。扩展存储就像 ScaleIO 也可以提供对象存储,可以很容易的集成 Glance 服务。
|
||||
* **Glance** – 用于提供镜像服务。使用 Glance 的管理平台来上传和下载云镜像。
|
||||
* **Heat** – 用于提供编排服务或功能。使用 Heat 管理平台可以轻松地将虚拟机作为堆栈,并且根据需要可以将虚拟机扩展或收缩。
|
||||
* **Ceilometer** – 用于提供计量与监控功能。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:2 什么服务通常在控制节点上运行?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 以下服务通常在控制节点上运行:
|
||||
|
||||
* 认证服务 ( KeyStone)
|
||||
* 镜像服务 ( Glance)
|
||||
* Nova 服务比如 Nova API, Nova Scheduler 和 Nova DB
|
||||
* 块存储和对象存储服务
|
||||
* Ceilometer 服务
|
||||
* MariaDB / MySQL 和 RabbitMQ 服务
|
||||
* 网络(Neutron)和网络代理的管理服务
|
||||
* 编排服务 (Heat)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:3 什么服务通常在计算节点上运行?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 以下服务通常在计算节点运行:
|
||||
|
||||
* Nova 计算
|
||||
* 网络服务,比如 OVS
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:4 计算节点上虚拟机的默认地址是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 虚拟机存储在计算节点的 “ **/var/lib/nova/instances** ”
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:5 Glance 镜像的默认地址是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 因为Glance 服务运行在控制节点上,所以 Glance 镜像都被存储在控制节点的“ **/var/lib/glance/images** ”文件夹下。
|
||||
|
||||
想了解更多请访问 : [**在 OpenStack 中如何使用命令行创建和删除虚拟机**][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:6 说一下如何使用命令行启动一个虚拟机?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 我们可以使用如下 OpenStack 命令来启动一个新的虚拟机:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# openstack server create --flavor {flavor-name} --image {Image-Name-Or-Image-ID} --nic net-id={Network-ID} --security-group {Security_Group_ID} –key-name {Keypair-Name} <VM_Name>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:7 如何在 OpenStack 中显示用户的网络命名空间列表?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 可以使用 “ip net ns” 命令来列出用户的网络命名空间。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# ip netns list
|
||||
qdhcp-a51635b1-d023-419a-93b5-39de47755d2d
|
||||
haproxy
|
||||
vrouter
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:8 如何在 OpenStack 中执行网络命名空间内的命令?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 假设我们想在 “qdhcp-a51635b1-d023-419a-93b5-39de47755d2d” 网络命名空间中执行 “ifconfig” 命令,我们可以执行如下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
命令格式 : ip netns exec {network-space} <command>
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# ip netns exec qdhcp-a51635b1-d023-419a-93b5-39de47755d2d "ifconfig"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:9 在 Glance 服务中如何使用命令行上传和下载镜像?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: Glance 服务中云镜像上传可以使用如下 OpenStack 命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack image create --disk-format qcow2 --container-format bare --public --file {Name-Cloud-Image}.qcow2 <Cloud-Image-Name>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下载云镜像则使用如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# glance image-download --file <Cloud-Image-Name> --progress <Image-ID>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:10 OpenStack 如何将虚拟机从错误状态转换为活动状态?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 在某些情况下虚拟机可能会进入错误状态,可以使用如下命令将错误状态转换为活动状态:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# nova reset-state --active {Instance_id}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:11 如何使用命令行来获取可使用的浮动 IP 列表?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 可使用如下命令来显示可用浮动 IP 列表:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~]# openstack ip floating list | grep None | head -10
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:12 如何在特定可用区域中或在计算主机上配置虚拟机?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 假设我们想在 compute-02 中的可用区 NonProduction 上配置虚拟机,可以使用如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~]# openstack server create --flavor m1.tiny --image cirros --nic net-id=e0be93b8-728b-4d4d-a272-7d672b2560a6 --security-group NonProd_SG --key-name linuxtec --availability-zone NonProduction:compute-02 nonprod_testvm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:13 如何在特定计算节点上获取配置的虚拟机列表?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 假设我们想要获取在 compute-0-19 中配置的虚拟机列表,可以使用如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
命令格式: openstack server list –all-projects –long -c Name -c Host | grep -i {Compute-Node-Name}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack server list --all-projects --long -c Name -c Host | grep -i compute-0-19
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:14 如何使用命令行查看 OpenStack 实例的打印信息?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 使用如下命令可查看实例的命令行打印信息:
|
||||
|
||||
首先获取实例的 ID,然后使用如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack console log show {Instance-id}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:15 如何获取 OpenStack 实例的控制台的 URL 地址?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 可以使用以下 OpenStack 命令从命令行检索实例的控制台 URL 地址:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack console url show {Instance-id}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:16 如何使用命令行创建可启动的 cinder / block 存储卷?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 假设创建一个 8GB 可启动存储卷,可参考如下步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
* 使用如下命令获取镜像列表
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack image list | grep -i cirros
|
||||
| 89254d46-a54b-4bc8-8e4d-658287c7ee92 | cirros | active |
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* 使用 cirros 镜像创建 8GB 的可启动存储卷
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# cinder create --image-id 89254d46-a54b-4bc8-8e4d-658287c7ee92 --display-name cirros-bootable-vol 8
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:17 如何列出所有在你的 OpenStack 中创建的项目或用户?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 可以使用如下命令来检索所有项目和用户:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack project list --long
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:18 如何显示 OpenStack 服务端点列表?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: OpenStack 服务端点被分为 3 类:
|
||||
|
||||
* 公共端点
|
||||
* 内部端点
|
||||
* 管理端点
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下 OpenStack 命令来查看各种 OpenStack 服务端点:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack catalog list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
可通过以下命令来显示特定服务端点(比如说 keystone)列表:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack catalog show keystone
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
想了解更多请访问 : [**OpenStack 中的实例创建流程**][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:19 在控制节点上你应该按照什么步骤来重启 nova 服务?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 应该按照如下步骤来重启 OpenStack 控制节点的 nova 服务:
|
||||
|
||||
* service nova-api restart
|
||||
* service nova-cert restart
|
||||
* service nova-conductor restart
|
||||
* service nova-consoleauth restart
|
||||
* service nova-scheduler restart
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:20 假如计算节点上为数据流量配置了一些 DPDK 端口,你如何检查 DPDK 端口的状态呢?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 因为我们使用 openvSwitch (OVS) 来配置 DPDK 端口,因此可以使用如下命令来检查端口的状态:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
root@compute-0-15:~# ovs-appctl bond/show | grep dpdk
|
||||
active slave mac: 90:38:09:ac:7a:99(dpdk0)
|
||||
slave dpdk0: enabled
|
||||
slave dpdk1: enabled
|
||||
root@compute-0-15:~#
|
||||
root@compute-0-15:~# dpdk-devbind.py --status
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:21 How to add new rules to the existing SG(Security Group) from command line in openstack?如何使用命令行在 OpenStack 中向存在的安全组 SG(Security Group)中添加新规则?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 可以使用 neutron 命令向 OpenStack 已存在的安全组中添加新规则:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# neutron security-group-rule-create --protocol <tcp or udp> --port-range-min <port-number> --port-range-max <port-number> --direction <ingress or egress> --remote-ip-prefix <IP-address-or-range> Security-Group-Name
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:22 如何查看控制节点和计算节点的 OVS 桥配置?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 控制节点和计算节点的 OVS 桥配置可使用以下命令来查看:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~]# ovs-vsctl show
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:23 计算节点上的集成桥(br-int)的作用是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 集成桥(br-int)对来自和运行在计算节点上的实例的流量执行 VLAN 标记和取消标记。
|
||||
|
||||
数据包从实例的 n/w 接口发出使用虚拟接口 qvo 通过 linux 桥(qbr)。qvb接口是用来连接 Linux 桥的,qvo 接口是用来连接集成桥(br-int)的。集成桥上的 qvo 端口有一个内部 VLAN 标签,这个标签是用于当数据包到达集成桥的时候贴到数据包头部的。
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:24 隧道桥(br-tun)在计算节点上的作用是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 隧道网桥(br-tun)根据 OpenFlow 规则将 VLAN 标记的流量从集成网桥转换为隧道 ID。
|
||||
|
||||
br-tun(tunnel bridge,即隧道桥)允许不同网络的实例彼此进行通信。隧道有利于封装在非安全网络上传输的流量,br-tun 支持两层网络,即 GRE 和 VXLAN。
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:25 外部 OVS 桥(br-ex)的作用是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 顾名思义,此网桥转发来往网络的流量,以允许外部访问实例。br-ex 连接物理接口比如 eth2,这样用户网络的浮动 IP 数据从物理网络接收并路由到用户网络端口。
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:26 OpenStack 网络中 OpenFlow 规则的作用是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: OpenFlow 规则是一种机制,这种机制定义了一个数据包如何从源到达目的地。OpenFlow 规则存储在 flow 表中。flow 表是 OpenFlow 交换机的一部分。
|
||||
|
||||
当一个数据包到达交换机就会被第一个 flow 表检查,如果不匹配 flow 表中的任何入口,那这个数据包就会被丢弃或者转发到其他 flow 表中。
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:27 怎样查看 OpenFlow 交换机的信息(比如端口、表编号、缓存编号等)?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 假如我们要显示 OpenFlow 交换机的信息(br-int),需要执行如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
root@compute-0-15# ovs-ofctl show br-int
|
||||
OFPT_FEATURES_REPLY (xid=0x2): dpid:0000fe981785c443
|
||||
n_tables:254, n_buffers:256
|
||||
capabilities: FLOW_STATS TABLE_STATS PORT_STATS QUEUE_STATS ARP_MATCH_IP
|
||||
actions: output enqueue set_vlan_vid set_vlan_pcp strip_vlan mod_dl_src mod_dl_dst mod_nw_src mod_nw_dst mod_nw_tos mod_tp_src mod_tp_dst
|
||||
1(patch-tun): addr:3a:c6:4f:bd:3e:3b
|
||||
config: 0
|
||||
state: 0
|
||||
speed: 0 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
|
||||
2(qvob35d2d65-f3): addr:b2:83:c4:0b:42:3a
|
||||
config: 0
|
||||
state: 0
|
||||
current: 10GB-FD COPPER
|
||||
speed: 10000 Mbps now, 0 Mbps max
|
||||
………………………………………
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:28 如何显示交换机中的所有 flow 的入口?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: 可以使用命令 ‘ **ovs-ofctl dump-flows** ‘ 来查看交换机的 flow 入口
|
||||
|
||||
假设我们想显示 OVS 集成桥(br-int)的所有 flow 入口,可以使用如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[root@compute01 ~]# ovs-ofctl dump-flows br-int
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:29 什么是 Neutron 代理?如何显示所有 Neutron 代理?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: OpenStack Neutron 服务器充当中心控制器,实际网络配置是在计算节点或者网络节点上执行的。Neutron 代理是计算节点或者网络节点上进行配置更新的软件实体。Neutron 代理通过 Neuron 服务和消息队列来和中心 Neutron 服务通信。
|
||||
|
||||
可通过如下命令查看 Neutron 代理列表:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
~# openstack network agent list -c ‘Agent type’ -c Host -c Alive -c State
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Q:30 CPU Pinning 是什么?
|
||||
|
||||
Ans: CPU Pinning 是指为某个虚拟机保留物理核心。它也称为 CPU 隔离或处理器关联。有两个目的:
|
||||
|
||||
* 它确保虚拟机只能在专用核心上运行
|
||||
* 它还确保公共主机进程不在这些核心上运行
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们也可以认为 Pinning 是物理核心到一个用户虚拟 CPU(vCPU) 的一对一映射。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.linuxtechi.com/openstack-interview-questions-answers/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[ScarboroughCoral](https://github.com/ScarboroughCoral)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.linuxtechi.com/author/pradeep/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/create-delete-virtual-machine-command-line-openstack/
|
||||
[2]: https://www.linuxtechi.com/step-by-step-instance-creation-flow-in-openstack/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: (geekpi)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: subject: (Standalone web applications with GNOME Web)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://fedoramagazine.org/standalone-web-applications-gnome-web/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Ryan Lerch https://fedoramagazine.org/introducing-flatpak/)
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
|
||||
使用 GNOME Web 的独立 Web 应用
|
||||
======
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你是否经常使用单页 Web 应用,但失去了一些完整桌面应用的好处? GNOME Web 浏览器,简称为 Web(又名 Epiphany)有一个非常棒的功能,它允许你“安装” 一个 Web 应用。安装完成后,Web 应用将显示在应用菜单、GNOME shell 搜索中,并且它在切换窗口时是一个单独的项目。这个简短的教程将引导你完成使用 GNOME Web “安装” Web 应用的步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 GNOME Web
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME Web 未包含在默认的 Fedora 安装中。要安装它,请在软件中心搜索 “web”,然后安装。
|
||||
|
||||
![][1]
|
||||
|
||||
或者,在终端中使用以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo dnf install epiphany
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装为 Web 应用
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,启动 GNOME Web,然后选择要安装的 Web 应用。使用浏览器连接到应用,然后从菜单中选择“将站点安装为 Web 应用”:
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME Web 接下来会出现一个用于编辑应用名称的对话框。将其保留为默认值 (URL) 或更改为更具描述性的内容:
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
最后,按下**创建**以 “安装” 你的新 Web 应用。创建 Web 应用后,关闭 GNOME Web。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用新的 Web 应用
|
||||
|
||||
像使用任何典型的桌面应用一样启动 Web 应用。在 GNOME Shell Overview 中搜索它:
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
此外,Web 应用将在 alt-tab 应用切换器中显示为单独的应用:
|
||||
|
||||
![][5]
|
||||
|
||||
另一个额外的功能是来自“已安装”的 Web 应用的所有 Web 通知都显示为常规 GNOME 通知。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://fedoramagazine.org/standalone-web-applications-gnome-web/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ryan Lerch][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://fedoramagazine.org/introducing-flatpak/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/gnome-web-in-gnome-software.png
|
||||
[2]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/freenode-page-in-gnome-web.png
|
||||
[3]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/edit-web-application-in-GNOME-web.png
|
||||
[4]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/web-application-in-overview.jpg
|
||||
[5]: https://fedoramagazine.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/web-app-in-app-switcher.jpg
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user