mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-13 22:30:37 +08:00
20140325-1 选题
This commit is contained in:
parent
7c6ce30688
commit
7892623206
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
|||||||
|
Red Hat Updates Open Source Software Development Tools
|
||||||
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
|
[Red Hat][1] (RHT) has updated its lineup of open source programming languages and development tools known as Red Hat Software Collections, which are now available in a beta release of version 1.1 The development suite complements (but is released independently of) the company's flagship [Red Hat Enterprise Linux][2] (RHEL) product.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Red Hat Software Collections, which [debuted][3] in fall 2013, are targeted at open source software developers who want a single source for deploying the most up-to-date stable versions of leading open source programming languages, databases and toolsets. Red Hat offers the suite as a subscription service with the promise of providing more frequent updates to the software than it offers for RHEL, where software packages generally receive updates only when the company rolls out a new release of the operating system itself.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Red Hat plans to offer a new base release of Red Hat Software Collections every 18 months, but it will provide incremental updates more frequently. Version 1.1 of the platform, which is the first update to appear since Red Hat introduced the service several months ago, is one of those more minor updates. It includes the following changes, [according to Red Hat][4]:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- Two new open source HTTP server options in the form of Apache HTTP Server and Nginx (available as a Technology Preview)
|
||||||
|
- PHP 5.5, a server-side scripting language designed for web development
|
||||||
|
- Ruby 2.0 and Rails 4.0, which for the first time will be packaged separately, providing developers with access to an updated version of Ruby without requiring the installation of Rails
|
||||||
|
- MongoDB, a high-performance open source document database and leading NoSQL database that provides high availability and easy scalability
|
||||||
|
- Thermostat 1.0, a tool for monitoring Java virtual machine instances on multiple hosts
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Although the Software Collections are currently a much less important part of Red Hat's business than RHEL, they're a good example to the open source community of how an organization can reconcile users' demand for stable yet current software with the rapid pace and decentralized nature of open source development. Open source vendors such as Red Hat rely heavily on code produced by third parties who rarely issue new releases of their software at the same time—and often don't even stick to a regular release schedule—which is why it is so difficult to keep an open source platform fully up to date. But Red Hat does the dirty work of amalgamating the most recent stable releases of far-flung open source projects into an integrated software suite, which can save developers a lot of time and hassle—if they subscribe to the Software Collections, of course.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/032414/red-hat-updates-open-source-software-development-tools
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[1]:http://redhat.com/
|
||||||
|
[2]:http://www.redhat.com/products/enterprise-linux/
|
||||||
|
[3]:http://developerblog.redhat.com/2013/09/12/rhscl1-ga/
|
||||||
|
[4]:http://www.redhat.com/about/news/archive/2014/3/red-hat-software-collections-1-1-beta-now-available
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
|||||||
|
Linux 3.15 Will Dramatically Reduce Suspend And Resume Times!
|
||||||
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
|
The upcoming Linux 3.15 kernel that is anticipated for release in mid-2014 will come with a large number of ACPI and power management updates. Thanks to the update, Linux systems will suspend and resume faster in the days to come.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Pointing out to a list of changes posted by Rafael Wysocki, an Intel employee who maintains the Linux kernel's core power management code, the report by Phoronix quotes that "visible to users with the Linux 3.15 kernel should be reduced time for system suspend and resuming, thanks to the enabling of more asynchronous threads." Linux 3.15 might also come with basic support for Nvidia's Maxwell architecture. Further details are awaited.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Meanwhile, the latest stable release of Linux was version 3.13.6. Linux founder, Linus Torvalds officially announced the sixth Release Candidate (RC) version of the upcoming Linux kernel 3.14. The RC6 is a successor to Linux 3.14-rc5. It is now available for download and testing. However, since it is a development version, it should not be installed on production machines.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
"We're getting closer to the end of the rc cycle, and I have to admit that I would have wished for a less bumpy ride. There haven't been any huge problems, but there's been quite a few small bumps that shouldn't happen this late in the release cycle. And rc6 is noticeably bigger than rc5 was, as well." Torvalds said in the release note. Torvalds said that he would have wished for things to go calm by now, but there have been quite a few small issues including 'small stupid mistakes', and a few late reverts of commits. Torvalds has hinted at rc8 and rc9 if things don’t calm down. Linux 3.14-rc6 consists of a number of trivial fixes.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=133613
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
|||||||
|
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Install NetBeans IDE 8.0 In Ubuntu
|
||||||
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
|
NetBeans 8.0 has just been released and this brief tutorial is going to show you how to easily install it in Ubuntu if you haven’t already done so. For developers who need help installing NetBeans in Ubuntu, this post will guide you.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For those who don’t know what NetBeans is, it’s an IDE application that allows users to quickly and efficiently develop and build desktop, mobile and web applications.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
It’s free and open-source and is supported by a vast community of users and developers.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Some of the features that were released in version 8 are, support for JDK 8 editor and tools enhancements, Tomcat 8.0 support, enhanced CDI integration, a new Maven graph layout switcher, new editor for supporting and creating JQuery widgets and plugins, and HTML 5, PHP 5.5 support.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For more about this release, [check out its release page][1].
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
There are two primary ways to download and install NetBeans IDE. One is downloading a package file that combines JDK 8 and NetBeans. This combination allows for the development of applications on the Java platform.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To get this package, [download it from here][2].
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Another way to get NetBeans is go download and install it directly from its download page. There, you have the option to download the complete package which contains, NetBeans Platform SDK, Java SE, Java FX, Java EE, Java ME, HTML5, C/C++, Groovy, PHP and Apache Tomcat 8.0.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
There are five options of the package to download. Choose the package you wish to download and click the Download button.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To get these packages, visit [NetBeans download page][3].
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Install Java JDK first before installing NetBeans ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Before you can install NetBeans, you must first install Java JDK. Without it, NetBeans won’t install. To lean how to install Java JDK, read [this post][4].
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
After installing Java JDK, continue below to install NetBeans.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If you chose the Oracle version, then JDK is already packaged into the file. All you have to do is run the executable to install both JDK and NetBeans.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Once you’ve downloaded the package you want, run the commands below to make the package executable.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
chmod +x ~/Downloads/netbeans-8.0-linux*.sh
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
the commands above assume that the file was downloaded in your Downloads folder in Ubuntu
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Next, run the commands below to begin the installation.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
sh -c " ~/Downloads/netbeans-8.0-linux*.sh"
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Follow the wizard until the installation is complete.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Enjoy!
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2014/03/daily-ubuntu-tips-install-netbeans-ide-8-0-in-ubuntu/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[1]:https://netbeans.org/community/releases/80/index.html
|
||||||
|
[2]:http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk-netbeans-jsp-142931.html
|
||||||
|
[3]:https://netbeans.org/downloads/
|
||||||
|
[4]:http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/netbeans-ide-7-4-released-heres-install-ubuntu/
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
|||||||
|
Daily Ubuntu Tips – Manually Install Oracle Java JDK 8 In Ubuntu
|
||||||
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
|
This brief tutorial is going to show you how to manually install Oracle Java JDK 8, which was just recently released in Ubuntu. This method will show you how to download the package from its download page and install it in Ubuntu without using external PPAs or third party sources.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
This method doesn’t depend on third-party repository. You download it directly from Oracle’s download page and install in Ubuntu.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
JDK 8 is a major release and the latest which features a new language called Lambda Expressions “enables you to treat functionality as a method argument, or code as date”
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Also released with this version are collection of classes in the new java.util.stream package that provide a Stream API to support functional-style operations.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
For more about this release, please visit the release page @ [http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/8-whats-new-2157071.html][1]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To get started with downloading and installing Java JDK8 in Ubuntu, visit the [download page][2] and get the latest version from there. You can to download the 32-bit or 64-bit version for you Ubuntu machine.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Here’s [download page][3]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
You must accept the license agreement before downloading.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
When you download the file, choose to save it. By default Firefox saves it downloads in the **~/Downloads** folder in Ubuntu.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Next, open the terminal and run the commands below to extract the downloaded file.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
tar -xvf ~/Downloads/jdk-8-linux-x64.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Then run the commands below to create a folder for Java JDK 8 files in the /usr/lib directory.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
sudo mkdir -p /usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.8.0/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Then run the commands below to move JDK content to the new folder.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
sudo mv jdk1.8.0/* /usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.8.0/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Next, run the commands below to begin configuring Java
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
sudo update-alternatives --install "/usr/bin/java" "java" "/usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.8.0/bin/java" 1
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Then copy and paste the line below enable Javac module
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
sudo update-alternatives --install "/usr/bin/javac" "javac" "/usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.8.0/bin/javac" 1
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Finally, copy and paste the commands below to complete the installation.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
sudo update-alternatives --install "/usr/bin/javaws" "javaws" "/usr/lib/jvm/jdk1.8.0/bin/javaws" 1
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To verify if Java is fully installed, run the commands below to test it.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
java –version
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Enjoy!
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2014/03/daily-ubuntu-tips-manually-install-oracle-java-jdk-8-in-ubuntu/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[1]:http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/8-whats-new-2157071.html
|
||||||
|
[2]:http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html
|
||||||
|
[3]:http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/jdk8-downloads-2133151.html
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
|||||||
|
Linux and Unix nload App: Monitor Network Traffic and Bandwidth Usage In Real Time
|
||||||
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
|
If you want to monitor network throughput on the command line interface, use nload application. It is a console application which monitors network traffic and bandwidth usage in real time. It visualizes the in and outgoing traffic using two graphs and provides additional info like total amount of transferred data and min/max network usage.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Install nload on a CentOS/RHEL/Red Hat/Fedora Linux ####
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
First, [turn on EPEL repo on a CentOS or RHEL][1] based system. Type the following [yum command][2] to install nload:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# yum install nload
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Install nload on a Debian or Ubuntu Linux ####
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Type the following [apt-get command][3]:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo apt-get install nload
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Install nload on a FreeBSD system ####
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To install the nload via port, type:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# cd /usr/ports/net/nload/ && make install clean
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Or add the package
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# pkg install net/nload
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Install nload on a OpenBSD system ####
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Type the following command:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo pkg_add -i nload
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Install nload using a source code on a Unix-like systems ####
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
First, grab the source code using either wget command or curl command:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ cd /tmp
|
||||||
|
$ wget http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To [untar a tar file called nload-0.7.4.tar.gz, use tar command][4], enter:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ tar xvf nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Cd to the directory containing the nloads's source code using cd command:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ cd nload*
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
And type ./configure to configure the package for your system:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sh ./configure
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
OR
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ ./configure
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Running configure takes a while. Type make command to compile the nload:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ make
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Finally, type make install to install the nload programs and related files as root user:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo make install
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
OR
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# make install
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
How do I use nload to display the current network usage?
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The basic syntax is:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
nload
|
||||||
|
nload device
|
||||||
|
nload [options] device1 device2
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Just type the following command:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ nload
|
||||||
|
$ nload eth0
|
||||||
|
$ nload em0 em2
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Sample outputs:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
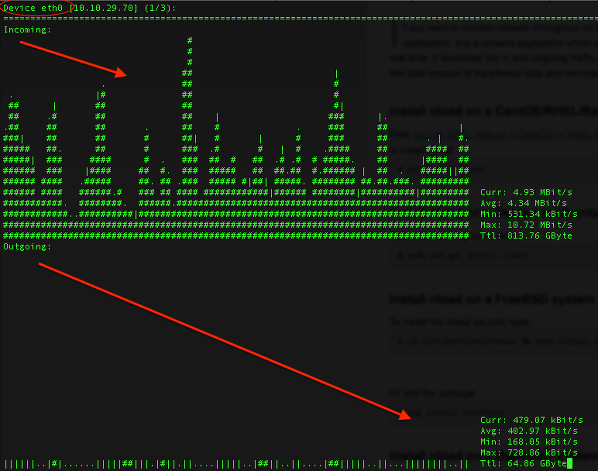
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Fig. 01: nload command in action
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Controlling nload app ####
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Once nload command executed, it begins to monitor the network devices. You can control nload with the following key shortcuts:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
1. You can switch between the devices by pressing the left and right arrow keys or Enter/Tab key.
|
||||||
|
1. Press F2 to show the option window
|
||||||
|
1. Press F5 to save current settings to the user’s config file.
|
||||||
|
1. Press F6 reload settings from the config files.
|
||||||
|
1. Press q or hit Ctrl+C to quit nload.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Setting the refresh interval of the display ####
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The default value of interval is 100 milliseconds to refresh interval of the display. In this example, change to 500 milliseconds:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ nload -t {interval_number_in_millisec}
|
||||||
|
$ nload -t 500
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Sample outputs:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Animated gif 01 - nload command in action
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
#### Setting the type of unit used for the display of traffic numbers ####
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The syntax is:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ nload -u h|H|b|B|k|K|m|M|g|G
|
||||||
|
$ nload -U h|H|b|B|k|K|m|M|g|G
|
||||||
|
$ nload -u h
|
||||||
|
$ nload -u G
|
||||||
|
$ nload -U G
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Where,
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- The lower case -u option: h means human readable (auto), b Bit/s, k kBit/s, m MBit/s and g GBit/s. The upper case letters mean the corresponding units in Bytes (instead of Bits). The default is k.
|
||||||
|
- The upper case -U option is same as lower case -u option, but for an amount of data, e.g. Bit, kByte, GBit etc. (without "/s"). The default is M.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Conclusion ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
I found nload to be reliable and stable application. If you enjoyed nload, you might also like to try out vnstat and iftop tools on Linux/Unix-like systems.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/networking/nload-linux-command-to-monitor-network-traffic-bandwidth-usage/
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/fedora-sl-centos-redhat6-enable-epel-repo/
|
||||||
|
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/rhel-centos-fedora-linux-yum-command-howto/
|
||||||
|
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-debian-package-management-cheat-sheet.html
|
||||||
|
[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/tar-extract-linux/
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user