mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
translated
This commit is contained in:
parent
00f4e1ddba
commit
75a960b591
@ -1,230 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating---geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
Learn The Basics of How Linux I/O (Input/Output) Redirection Works
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most important and [interesting topics under Linux administration][4] is I/O redirection. This feature of the command line enables you to redirect the input and/or output of commands from and/or to files, or join multiple commands together using pipes to form what is known as a “command pipeline”.
|
||||
|
||||
All the commands that we run fundamentally produce two kinds of output:
|
||||
|
||||
1. the command result – data the program is designed to produce, and
|
||||
2. the program status and error messages that informs a user of the program execution details.
|
||||
|
||||
In Linux and other Unix-like systems, there are three default files named below which are also identified by the shell using file descriptor numbers:
|
||||
|
||||
1. stdin or 0 – it’s connected to the keyboard, most programs read input from this file.
|
||||
2. stdout or 1 – it’s attached to the screen, and all programs send their results to this file and
|
||||
3. stderr or 2 – programs send status/error messages to this file which is also attached to the screen.
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, I/O redirection allows you to alter the input source of a command as well as where its output and error messages are sent to. And this is made possible by the `“<”` and `“>”` redirection operators.
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Redirect Standard Output to File in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
You can redirect standard output as in the example below, here, we want to store the output of the [top command][5]for later inspection:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ top -bn 5 >top.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Where the flags:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `-b` – enables top to run in batch mode, so that you can redirect its output to a file or another command.
|
||||
2. `-n` – specifies the number of iterations before the command terminates.
|
||||
|
||||
You can view the contents of `top.log` file using [cat command][6] as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat top.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To append the output of a command, use the `“>>”` operator.
|
||||
|
||||
For instance to append the output of [top command][7] above in the top.log file especially within a script (or on the command line), enter the line below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ top -bn 5 >>top.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Using the file descriptor number, the output redirect command above is the same as:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ top -bn 5 1>top.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Redirect Standard Error to File in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
To redirect standard error of a command, you need to explicitly specify the file descriptor number, `2` for the shell to understand what you are trying to do.
|
||||
|
||||
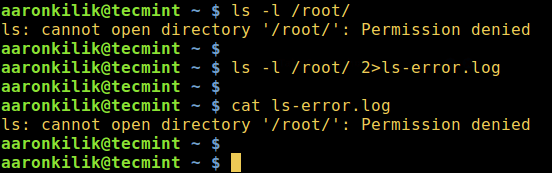
For example the [ls command][8] below will produce an error when executed by a normal system user without root privileges:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -l /root/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can redirect the standard error to a file as below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -l /root/ 2>ls-error.log
|
||||
$ cat ls-error.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
Redirect Standard Error to File
|
||||
|
||||
In order to append the standard error, use the command below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -l /root/ 2>>ls-error.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Redirect Standard Output/ Error To One File
|
||||
|
||||
It is also possible to capture all the output of a command (both standard output and standard error) into a single file. This can be done in two possible ways by specifying the file descriptor numbers:
|
||||
|
||||
1. The first is a relatively old method which works as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -l /root/ >ls-error.log 2>&1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The command above means the shell will first send the output of the [ls command][10] to the file ls-error.log (using `>ls-error.log`), and then writes all error messages to the file descriptor 2 (standard output) which has been redirected to the file ls-error.log (using `2>&1`). Implying that standard error is also sent to the same file as standard output.
|
||||
|
||||
2. The second and direct method is:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -l /root/ &>ls-error.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can as well append standard output and standard error to a single file like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -l /root/ &>>ls-error.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Redirect Standard Input to File
|
||||
|
||||
Most if not all commands get their input from standard input, and by default standard input is attached to the keyboard.
|
||||
|
||||
To redirect standard input from a file other than the keyboard, use the `“<”` operator as below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat <domains.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
Redirect Standard Input to File
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Redirect Standard Input/Output to File
|
||||
|
||||
You can perform standard input, standard output redirection at the same time using [sort command][12] as below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sort <domains.list >sort.output
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Use I/O Redirection Using Pipes
|
||||
|
||||
To redirect the output of one command as input of another, you can use pipes, this is a powerful means of building useful command lines for complex operations.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, the command below will [list the top five recently modified files][13].
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -lt | head -n 5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here, the options:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `-l` – enables long listing format
|
||||
2. `-t` – [sort by modification time with the newest files][1] are shown first
|
||||
3. `-n` – specifies the number of header lines to show
|
||||
|
||||
### Important Commands for Building Pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
Here, we will briefly review two important commands for building command pipelines and they are:
|
||||
|
||||
xargs which is used to build and execute command lines from standard input. Below is an example of a pipeline which uses xargs, this command is used to [copy a file into multiple directories in Linux][14]:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ echo /home/aaronkilik/test/ /home/aaronkilik/tmp | xargs -n 1 cp -v /home/aaronkilik/bin/sys_info.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][15]
|
||||
|
||||
Copy Files to Multiple Directories
|
||||
|
||||
And the options:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `-n 1` – instructs xargs to use at most one argument per command line and send to the [cp command][2]
|
||||
2. `cp` – copies the file
|
||||
3. `-v` – [displays progress of copy command][3].
|
||||
|
||||
For more usage options and info, read through the xargs man page:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man xargs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
A tee command reads from standard input and writes to standard output and files. We can demonstrate how teeworks as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ echo "Testing how tee command works" | tee file1
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][16]
|
||||
|
||||
tee Command Example
|
||||
|
||||
[File or text filters][17] are commonly used with pipes for [effective Linux file operations][18], to process information in powerful ways such as restructuring output of commands (this can be vital for [generation of useful Linux reports][19]), modifying text in files plus several other [Linux system administration tasks][20].
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about Linux filters and pipes, read this article [Find Top 10 IP Addresses Accessing Apache Server][21], shows a useful example of using filters and pipes.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we explained the fundamentals of I/O redirection in Linux. Remember to share your thoughts via the feedback section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-io-input-output-redirection-operators/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-and-sort-files-modification-date-and-time-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/progress-monitor-check-progress-of-linux-commands/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/monitor-copy-backup-tar-progress-in-linux-using-pv-command/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-setup-and-configure-static-network-routing-in-rhel/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/tag/linux-ls-command/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Redirect-Standard-Error-in-Linux.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/15-basic-ls-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Redirect-Standard-Input-to-File.png
|
||||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/sort-command-linux/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-recent-modified-files-in-linux/
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/copy-file-to-multiple-directories-in-linux/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Copy-Files-to-Multiple-Directories.png
|
||||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/tee-command-example.png
|
||||
[17]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-file-operations-commands/
|
||||
[18]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-file-operations-commands/
|
||||
[19]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-and-file-system-statistics-reports/
|
||||
[20]:http://www.tecmint.com/automating-linux-system-administration-tasks/
|
||||
[21]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-top-ip-address-accessing-apache-web-server/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,229 @@
|
||||
了解基础的 Linux I/O (输入/输出) 重定向原理
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Linux 管理的一个最重要并且[有趣的话题][4]是 I/O 重定向。此功能在命令行中使你能够将命令的输入以及/或者输出输入或者输出到文件中,或使用管道将多个命令连接在一起以形成所谓的“命令管道”。
|
||||
|
||||
我们运行的所有命令基本上产生两种输出:
|
||||
|
||||
1.命令结果 - 程序设计产生的数据
|
||||
2.程序状态和错误消息,用来通知用户程序的执行细节。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 和其他类 Unix 系统中,有三个默认文件,这些文件也由 shell 使用文件描述符号标识:
|
||||
|
||||
1. stdin 或 0 - 它连接到键盘,大多数程序从此文件读取输入。
|
||||
2. stdout 或 1 - 它连接到屏幕,并且所有程序将其结果发送到此文件
|
||||
3. stderr 或 2 - 程序将状态/错误消息发送到此文件,该文件也发送到屏幕上。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,I/O 重定向允许你更改命令的输入源以及将输出和错误消息发送到其他地方。这可以通过 `“<”` 和 `“>”` 重定向操作符来实现。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在 Linux 中重定向标准输出到文件中
|
||||
|
||||
如下面的示例所示,你可以重定向标准输出,这里,我们要存储[ top 命令][5]的输出以供以后检查:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ top -bn 5 >top.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
有这些标志:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `-b` - 让 top 以批处理模式运行,以便你可以将其输出重定向到一个文件或另一个命令。
|
||||
2. `-n` - 指定命令终止前的迭代次数。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用[ cat 命令][6]来查看 `top.log` 文件的内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat top.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要附加命令的输出,请使用 `“>>”` 操作符。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,在 top.log 文件中,特别是在脚本(或命令行)中追加上面的[ top 命令][7]的输出,请输入下面的那行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ top -bn 5 >>top.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注意: 使用文件描述符数字,上面的重定向命令等同于:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ top -bn 5 1>top.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在 Linux 中重定向标准错误到文件中
|
||||
|
||||
要重定向命令的标准错误,你需要明确指定文件描述符 `2`,以便让 shell 了解你正在尝试做什么。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,下面的[ ls 命令][8]将在没有 root 权限的普通系统用户执行时产生错误:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -l /root/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你可以重定向标准错误到文件中:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -l /root/ 2>ls-error.log
|
||||
$ cat ls-error.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
重定向标准到文件中
|
||||
|
||||
为了附加到标准错误,使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -l /root/ 2>>ls-error.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何重定向标准输出/错误到一个文件中
|
||||
|
||||
还可以将命令的所有输出(标准输出和标准错误)捕获到单个文件中。这可以用两种可能的方式通过指定文件描述符来完成:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 第一种是相对较旧的方法,其工作方式如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -l /root/ >ls-error.log 2>&1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令意思是 shell 首先将[ ls 命令][10]的输出发送到文件 ls-error.log(使用 `> ls-error.log`),然后将所有错误消息写入文件描述符 2(标准输出),它已被重定向到文件 ls-error.log(使用`2>&1`)中。这表示标准错误也被发送到与标准输出相同的文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 第二种直接的方法是:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -l /root/ &>ls-error.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你也可以这样将标准输出和标准错误附加到单个文件中:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -l /root/ &>>ls-error.log
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何将标准输入重定向到文件中
|
||||
|
||||
大多数(如果不是全部)命令从标准输入获得其输入,并且默认标准输入连接到键盘。
|
||||
|
||||
要从键盘以外的文件重定向标准输入,请使用 `“<”` 操作符,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat <domains.list
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][11]
|
||||
|
||||
重定向文件到标准输入中
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何重定向标准输入/输出到文件中
|
||||
|
||||
你可以如下在[ sort 命令中][12] 同时执行标准输入、标准输出重定向:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sort <domains.list >sort.output
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何使用管道进行 I/O 重定向
|
||||
|
||||
要将一个命令的输出重定向为另一个命令的输入,你可以使用管道,这是用于构建具有复杂操作命令的有力方法。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,以下命令将[列出前五个最近修改的文件][13]。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ls -lt | head -n 5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
选项的意思是:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `-l` - 启用长列表格式
|
||||
2. `-t` - [最新修改的文件][1]首先显示
|
||||
3. `-n` - 指定要显示的标题行数
|
||||
|
||||
### 构建管道的重要命令
|
||||
|
||||
在这里,我们将简要回顾一下构建命令管道的两个重要命令,它们是:
|
||||
|
||||
xargs 用于从标准输入构建和执行命令行。下面是使用 xargs 的管道示例,此命令用于[将文件复制到 Linux 中的多个目录][14]:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ echo /home/aaronkilik/test/ /home/aaronkilik/tmp | xargs -n 1 cp -v /home/aaronkilik/bin/sys_info.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][15]
|
||||
|
||||
复制文件到多个目录
|
||||
|
||||
添加选项:
|
||||
|
||||
1. -n 1` - 让 xargs 对每个命令行最多使用一个参数,并发送到[cp命令][2]
|
||||
2. `cp` - 复制文件
|
||||
3. `-v` - [显示 copy 命令的进度][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
有关更多的使用选项和信息,请阅读 xargs 手册页:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man xargs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
tee 命令从标准输入读取,并写入到标准输出和文件中。我们可以演示 tee 如何工作:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ echo "Testing how tee command works" | tee file1
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][16]
|
||||
|
||||
tee 命令示例
|
||||
|
||||
[文件或文本过滤器][17]通常与管道一起用于[有效地操作 Linux 文件][18],用强大的方式来处理信息,例如命令的重组输出(这对于[生成有用的 Linux 报告][19]是必不可少的)、修改文件中的文本和其他的[ Linux 系统管理任务][20]。
|
||||
|
||||
要了解有关 Linux 过滤器和管道的更多信息,请阅读这篇文章[查找前十个访问 Apache 服务器的 IP 地址][21],这里展示了使用过滤器和管道的一个例子。
|
||||
|
||||
在本文中,我们解释了 Linux 中 I/O 重定向的基本原理。请通过下面的反馈栏分享你的想法。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili 是 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者,将来的 Linux SysAdmin、web 开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创建者,他喜欢用电脑工作,并坚信分享知识。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-io-input-output-redirection-operators/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-and-sort-files-modification-date-and-time-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/progress-monitor-check-progress-of-linux-commands/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/monitor-copy-backup-tar-progress-in-linux-using-pv-command/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-setup-and-configure-static-network-routing-in-rhel/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/13-basic-cat-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/12-top-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/tag/linux-ls-command/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Redirect-Standard-Error-in-Linux.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/15-basic-ls-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Redirect-Standard-Input-to-File.png
|
||||
[12]:http://www.tecmint.com/sort-command-linux/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-recent-modified-files-in-linux/
|
||||
[14]:http://www.tecmint.com/copy-file-to-multiple-directories-in-linux/
|
||||
[15]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Copy-Files-to-Multiple-Directories.png
|
||||
[16]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/tee-command-example.png
|
||||
[17]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-file-operations-commands/
|
||||
[18]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-file-operations-commands/
|
||||
[19]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-and-file-system-statistics-reports/
|
||||
[20]:http://www.tecmint.com/automating-linux-system-administration-tasks/
|
||||
[21]:http://www.tecmint.com/find-top-ip-address-accessing-apache-web-server/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user