mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
translated
This commit is contained in:
parent
98cffc134c
commit
7516d88c77
@ -1,254 +0,0 @@
|
||||
NearTan 认领
|
||||
|
||||
Fabric – Automate Your Linux Administration Tasks and Application Deployments Over SSH
|
||||
===========================
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes to managing remote machines and deployment of applications, there are several command line tools out there in existence though many have a common problem of lack of detailed documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we shall cover the steps to introduce and get started on how to use fabric to improve on administering groups of servers.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Automate Linux Administration Tasks Using Fabric
|
||||
|
||||
Fabric is a python library and a powerful command line tool for performing system administration tasks such as executing SSH commands on multiple machines and application deployment.
|
||||
|
||||
Having a working knowledge of Python can be helpful when using Fabric, but may certainly not be necessary.
|
||||
|
||||
Reasons why you should choose fabric over other alternatives:
|
||||
|
||||
- Simplicity
|
||||
- It is well-documented
|
||||
- You don’t need to learn another language if you’re already a python guy.
|
||||
- Easy to install and use.
|
||||
- It is fast in its operations.
|
||||
- It supports parallel remote execution.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Install Fabric Automation Tool in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
An important characteristic about fabric is that the remote machines which you need to administer only need to have the standard OpenSSH server installed. You only need certain requirements installed on the server from which you are administering the remote servers before you can get started.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Requirements:
|
||||
|
||||
- Python 2.5+ with the development headers
|
||||
- Python-setuptools and pip (optional, but preferred) gcc
|
||||
|
||||
Fabric is easily installed using pip (highly recommended), but you may also prefer to choose your default package manager `yum`, `dnf` or `apt-get` to install fabric package, typically called fabric or python-fabric.
|
||||
|
||||
For RHEL/CentOS based distributions, you must have [EPEL repository][1] installed and enabled on the system to install fabric package.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum install fabric [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
# dnf install fabric [On Fedora 22+ versions]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For Debian and it’s derivatives such as Ubuntu and Mint users can simply do apt-get to install the fabric package as shown:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# apt-get install fabric
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to install development version of fabric, you may use pip to grab the most recent master branch.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum install python-pip [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
# dnf install python-pip [On Fedora 22+ versions]
|
||||
# apt-get install python-pip [On Debian based systems]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once pip has been installed successfully, you may use pip to grab the latest version of fabric as shown:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# pip install fabric
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Use Fabric to Automate Linux Administration Tasks
|
||||
|
||||
So lets get started on how you can use Fabric. During the installation process, a Python script called fab was added to a directory in your path. The `fab` script does all the work when using fabric.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Executing commands on the local Linux machine
|
||||
|
||||
By convention, you need to start by creating a Python file called fabfile.py using your favorite editor. Remember you can give this file a different name as you wish but you will need to specify the file path as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fabric --fabfile /path/to/the/file.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Fabric uses `fabfile.py` to execute tasks. The fabfile should be in the same directory where you run the Fabric tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Example 1: Let’s create a basic `Hello World` first.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# vi fabfile.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Add these lines of code in the file.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def hello():
|
||||
print('Hello world, Tecmint community')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and run the command below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
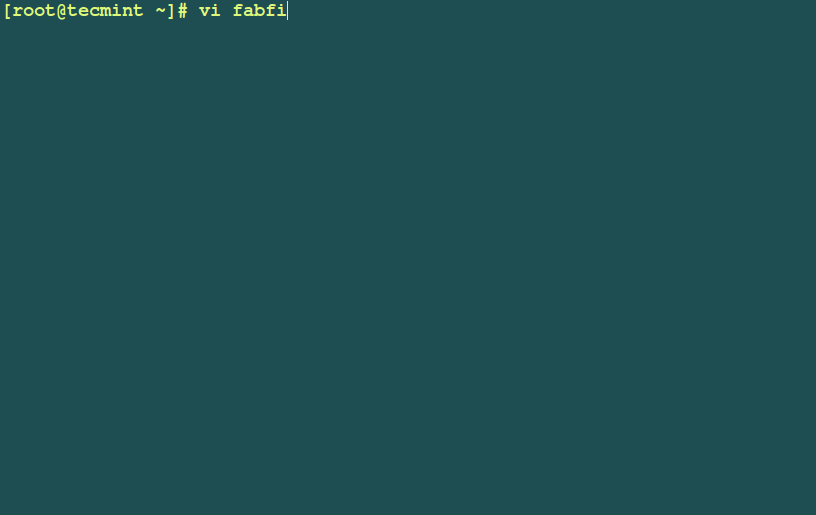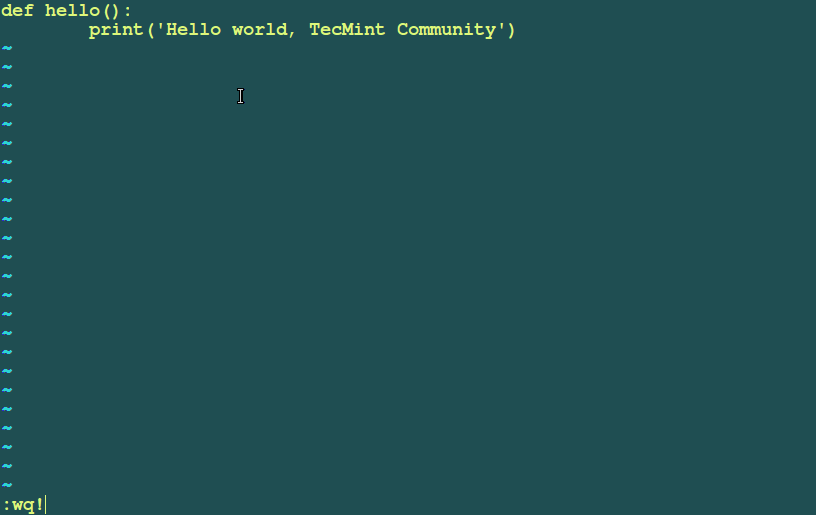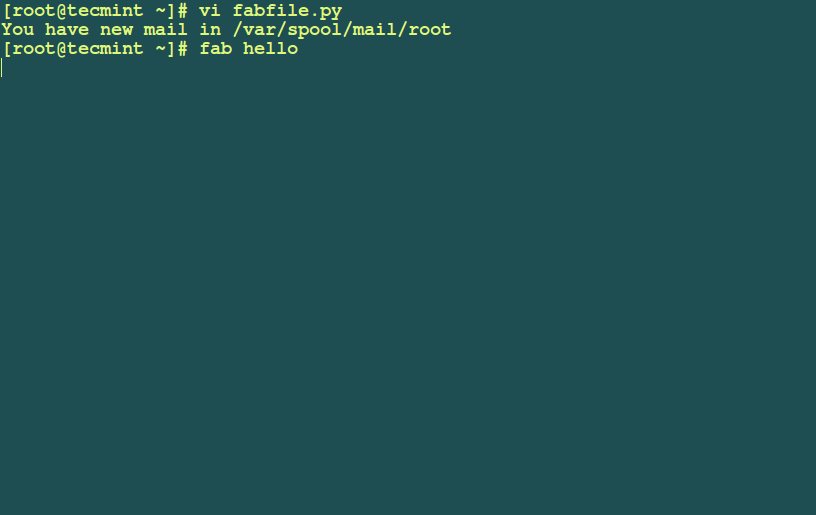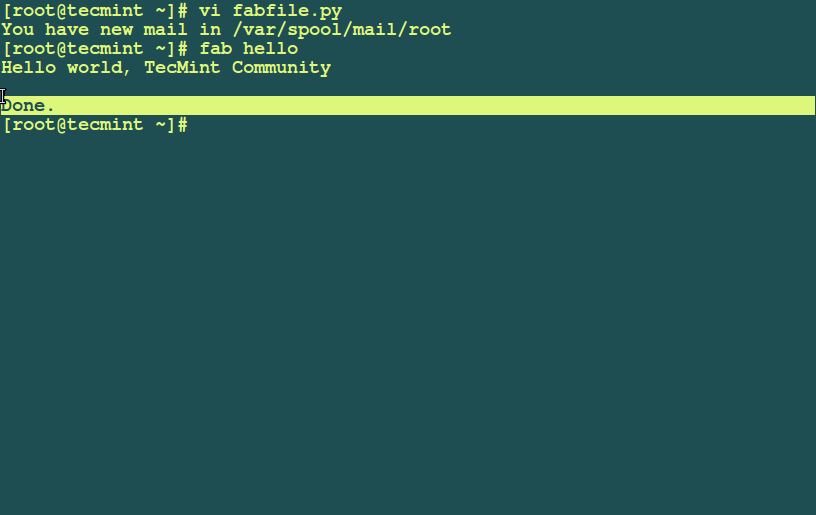
# fab hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Fabric Tool Usage
|
||||
|
||||
And paste the following lines of code in the file.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from fabric.api import local
|
||||
def uptime():
|
||||
local('uptime')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then save the file and run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fab uptime
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Fabric: Check System Uptime
|
||||
|
||||
#### Executing commands on remote Linux machines to automate tasks
|
||||
|
||||
The Fabric API uses a configuration dictionary which is Python’s equivalent of an associative array known as `env`, which stores values that control what Fabric does.
|
||||
|
||||
The `env.hosts` is a list of servers on which you want run Fabric tasks. If your network is 192.168.0.0 and wish to manage host 192.168.0.2 and 192.168.0.6 with your fabfile, you could configure the env.hosts as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from fabric.api import env
|
||||
env.hosts = [ '192.168.0.2', '192.168.0.6' ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above line of code only specify the hosts on which you will run Fabric tasks but do nothing more. Therefore you can define some tasks, Fabric provides a set of functions which you can use to interact with your remote machines.
|
||||
|
||||
Although there are many functions, the most commonly used are:
|
||||
|
||||
- run – which runs a shell command on a remote machine.
|
||||
- local – which runs command on the local machine.
|
||||
- sudo – which runs a shell command on a remote machine, with root privileges.
|
||||
- Get – which downloads one or more files from a remote machine.
|
||||
- Put – which uploads one or more files to a remote machine.
|
||||
|
||||
Example 3: To echo a message on multiple machines create a fabfile.py such as the one below.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from fabric.api import env, run
|
||||
env.hosts = ['192.168.0.2','192.168.0.6']
|
||||
def echo():
|
||||
run("echo -n 'Hello, you are tuned to Tecmint ' ")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To execute the tasks, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fab echo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Fabric: Automate Linux Tasks on Remote Linux
|
||||
|
||||
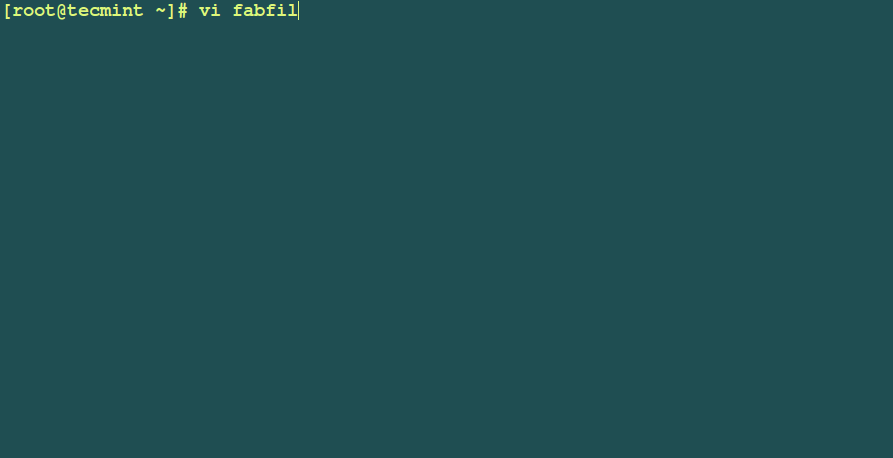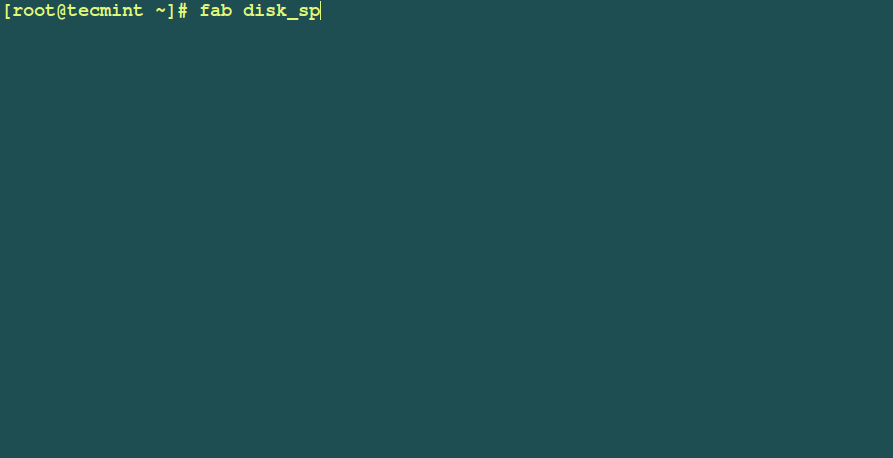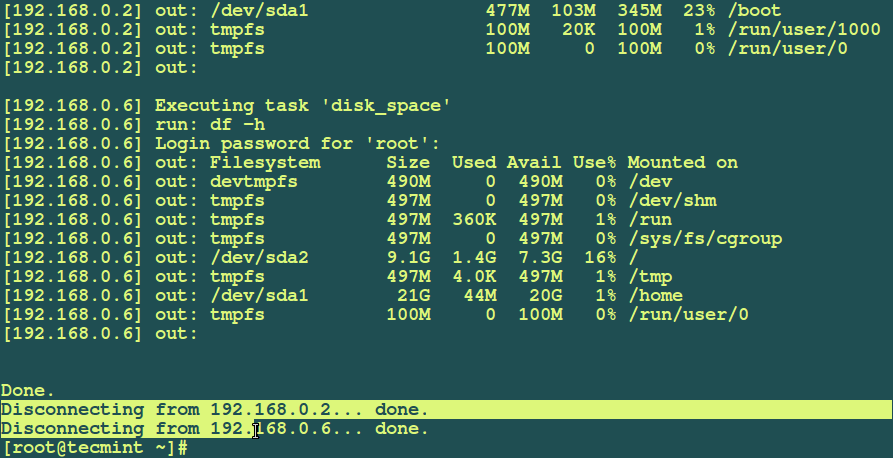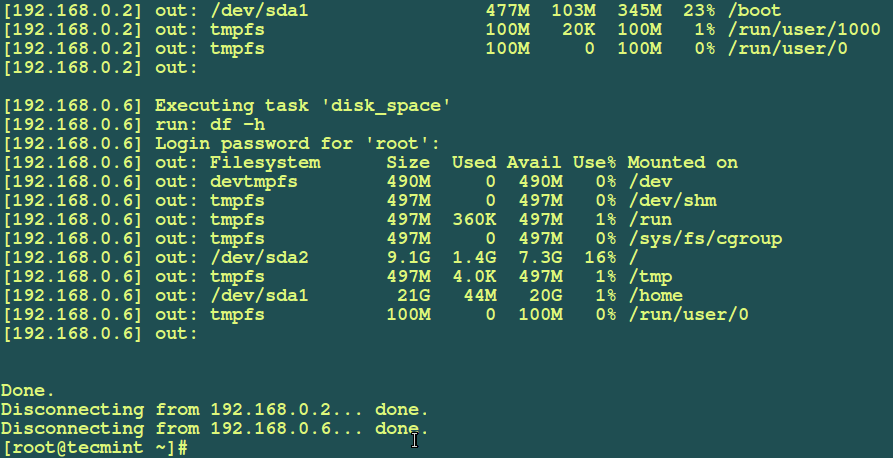
Example 4: You can improve the fabfile.py which you created earlier on to execute the uptime command on the local machine, so that it runs the uptime command and also checks disk usage using the df command on multiple machines as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from fabric.api import env, run
|
||||
env.hosts = ['192.168.0.2','192.168.0.6']
|
||||
def uptime():
|
||||
run('uptime')
|
||||
def disk_space():
|
||||
run('df -h')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fab uptime
|
||||
# fab disk_space
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>Fabric: Automate Tasks on Multiple Linux Systems
|
||||
|
||||
#### Automatically Deploy LAMP Stack on Remote Linux Server
|
||||
|
||||
Example 4: Let us look at an example to deploy LAMP (Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB and PHP) server on a remote Linux server.
|
||||
|
||||
We shall write a function that will allow LAMP to be installed remotely using root privileges.
|
||||
|
||||
##### For RHEL/CentOS and Fedora
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from fabric.api import env, run
|
||||
env.hosts = ['192.168.0.2','192.168.0.6']
|
||||
def deploy_lamp():
|
||||
run ("yum install -y httpd mariadb-server php php-mysql")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### For Debian/Ubuntu and Linux Mint
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from fabric.api import env, run
|
||||
env.hosts = ['192.168.0.2','192.168.0.6']
|
||||
def deploy_lamp():
|
||||
sudo("apt-get install -q apache2 mysql-server libapache2-mod-php5 php5-mysql")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fab deploy_lamp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Due to large output, it’s not possible for us to create a screencast (animated gif) for this example.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can able to [automate Linux server management tasks][2] using Fabric and its features and examples given above…
|
||||
|
||||
#### Some Useful Options to Use with Fabric
|
||||
|
||||
- You can run fab –help to view help information and a long list of available command line options.
|
||||
- An important option is –fabfile=PATH that helps you to specify a different python module file to import other then fabfile.py.
|
||||
- To specify a username to use when connecting to remote hosts, use the –user=USER option.
|
||||
- To use password for authentication and/or sudo, use the –password=PASSWORD option.
|
||||
- To print detailed info about command NAME, use –display=NAME option.
|
||||
- To view formats use –list option, choices: short, normal, nested, use the –list-format=FORMAT option.
|
||||
- To print list of possible commands and exit, include the –list option.
|
||||
- You can specify the location of config file to use by using the –config=PATH option.
|
||||
- To display a colored error output, use –colorize-errors.
|
||||
- To view the program’s version number and exit, use the –version option.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Fabric is a powerful tool and is well documented and provides easy usage for newbies. You can read the full documentation to get more understanding of it. If you have any information to add or incase of any errors you encounter during installation and usage, you can leave a comment and we shall find ways to fix them.
|
||||
|
||||
Reference: [Fabric documentation][3]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/automating-linux-system-administration-tasks/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili ][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]: http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
[2]: http://www.tecmint.com/use-ansible-playbooks-to-automate-complex-tasks-on-multiple-linux-servers/
|
||||
[3]: http://docs.fabfile.org/en/1.4.0/usage/env.html
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,257 @@
|
||||
|
||||
Fabric - 通过 SSH 来自动化管理 Linux 任务和布署应用
|
||||
===========================
|
||||
|
||||
当要管理远程机器或者要布署应用时,你会有多种命令行工具的选择,但是其中很多工具都缺少详细的使用文档。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇教程中,我们将会一步一步地向你介绍如何使用 fabric 来帮助你更好得管理多台服务器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>使用 Fabric 来自动化地管理 Linux 任务
|
||||
|
||||
Fabric 是一个用 Python 编写的命令行工具库,它可以帮助系统管理员高效地执行某些任务,比如 SSH 到多台机器上执行某些命令,远程布署应用等。
|
||||
|
||||
在使用之前,如果你拥有使用 Python 的经验能帮你更好的使用 Fabric。当然,如果没有那也不影响使用 Fabric。
|
||||
|
||||
我们为什么要选择 Fabric
|
||||
|
||||
- 简单
|
||||
- 拥有详细的文档
|
||||
- 如果你会 Python,不用增加学习其他语言的成本
|
||||
- 即插即用
|
||||
- 使用便捷
|
||||
- 支持多台机器并行操作
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 上如何安装 Fabric
|
||||
|
||||
Fabric 有一个特点就是要远程操作的机器只需要支持标准的 OpenSSH 服务即可。只要保证在机器上安装并开启了这个服务就能使用 Fabric 来管理机器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 依赖:
|
||||
|
||||
- Python 2.5 或更新版本,以及对应的开发组件
|
||||
- Python-setuptools 和 pip(可选,但是非常推荐)gcc
|
||||
|
||||
我们推荐使用 pip 安装 Fabric,你可以使用系统自带的包管理器如 `yum`, `dnf` 或 `apt-get` 来安装,包名一般是 `fabric` 或 `python-fabric`。
|
||||
|
||||
如果是基于 RHEL/CentOS 的发行版本的系统,你可以使用系统自带的 [EPEL 源][1] 来安装 fabric
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum install fabric [适用于基于 RedHat 系统]
|
||||
# dnf install fabric [适用于 Fedora 22+ 版本]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是 Debian 或者其派生的系统如 Ubuntu 和 Mint 用户,你可以使用 apt-gte 来安装,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# apt-get install fabric
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你要安装开发版的 Fabric,你应该安装 master 分支上最新版本的 pip
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum install python-pip [适用于基于 RedHat 系统]
|
||||
# dnf install python-pip [适用于Fedora 22+ 版本]
|
||||
# apt-get install python-pip [适用于基于 Debian 系统]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
安装好 pip 后,你可以使用 pip 获取最新版本的 Fabric
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# pip install fabric
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何使用 Fabric 来自动化管理 Linux 任务
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们来开始使用 Fabric,在之前的安装的过程中,Fabric Python 脚本已经被增加到我们的系统目录,当我们要运行 Fabric 时输入 `fab` 命令即可。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在本地 Linux 机器上运行命令行
|
||||
|
||||
按照惯例,先用你最喜欢的编辑器创建一个名为 fabfile.py 的 Python 脚本。你可以使用其他名字来命名脚本,但是需要先声明这个脚本的路径,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fabric --fabfile /path/to/the/file.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你要使用 Fabric 来执行 `fabfile.py` 里面的任务,文件必需在你执行 Fabric 命令下的同一目录
|
||||
|
||||
例 1:创建入门的 `Hello World` 任务:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# vi fabfile.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在文件内输入如下内容:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def hello():
|
||||
print('Hello world, Tecmint community')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存文件并执行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fab hello
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Fabric 工具使用说明
|
||||
|
||||
让我们看看这个例子,fabfile.py 文件在本机执行了 uptime 这个命令
|
||||
|
||||
例子2:新建一个名为 fabfile.py 的文件并打开:
|
||||
|
||||
粘贴以下代码至文件(to 校对:选题时的文章缺少了上面这三句话,译者从原网站补充至本文,请校对注意)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from fabric.api import local
|
||||
|
||||
def uptime():
|
||||
local('uptime')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存文件并执行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fab uptime
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Fabric: 检查系统运行时间
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在远程 Linux 机器上运行命令行来执行自动化任务
|
||||
|
||||
Fabric API 提供了一个名为 `env` 的关联数组(Python 中的词典)来储存 Fabric 要控制的机器的相关信息。
|
||||
|
||||
`env.hosts` 是一个 list 用来存储你要执行 Fabric 任务的机器,如果你的 IP 地址是 192.168.0.0,想要用 Fabric 来管理地址为 192.168.0.2 和 192.168.0.6 的机器,需要的配置如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from fabric.api import env
|
||||
env.hosts = [ '192.168.0.2', '192.168.0.6' ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
上面这几行代码只是声明了你要执行 Fabric 任务的主机地址,但是实际上并没有执行任何任务,下面我们就来定义一些任务。Fabric 提供了一系列可以与远程服务器交互的方法。
|
||||
|
||||
Fabric 提供了众多的方法,这里列出几个经常会用到的:
|
||||
|
||||
- run - 可以在远程机器上运行的 shell 命令
|
||||
- local - 可以在本机上运行的 shell 命令
|
||||
- sudo 使用 root 权限运行的 shell 命令
|
||||
- get - 从远程机器上下载文件
|
||||
- put - 上传文件到远程机器
|
||||
|
||||
例子 3:在多台机子上输出信息,新建新的 fabfile.py 文件如下所示
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from fabric.api import env, run
|
||||
env.hosts = ['192.168.0.2','192.168.0.6']
|
||||
def echo():
|
||||
run("echo -n 'Hello, you are tuned to Tecmint ' ")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
运行以下命令执行 Fabric 任务
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fab echo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>fabric: 自动在远程 Linux 机器上执行任务
|
||||
|
||||
例子 4:你可以继续改进之前创建的执行 uptime 任务的 fabfile.py 文件,让它可以在多台服务器上检查其磁盘使用情况,如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from fabric.api import env, run
|
||||
env.hosts = ['192.168.0.2','192.168.0.6']
|
||||
def uptime():
|
||||
run('uptime')
|
||||
def disk_space():
|
||||
run('df -h')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并执行以下命令
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fab uptime
|
||||
# fab disk_space
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
>Fabric:自动在多台服务器上执行任务
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在远程服务器上自动化布署 LAMP
|
||||
|
||||
Example 4(5?):我们来尝试一下在远程服务器上布署 LAMP(Linux, Apache, MySQL/MariaDB and PHP)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
我们在远程安装 LAMP 时应该使用 root 权限。
|
||||
|
||||
##### 在 RHEL/CentOS 或 Fedora 上
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from fabric.api import env, run
|
||||
env.hosts = ['192.168.0.2','192.168.0.6']
|
||||
def deploy_lamp():
|
||||
run ("yum install -y httpd mariadb-server php php-mysql")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
##### 在 Debian/Ubuntu 或 Linux Mint 上
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
from fabric.api import env, run
|
||||
env.hosts = ['192.168.0.2','192.168.0.6']
|
||||
def deploy_lamp():
|
||||
sudo("apt-get install -q apache2 mysql-server libapache2-mod-php5 php5-mysql")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并执行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# fab deploy_lamp
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
注:由于安装时会输出大量信息,这个例子我们就不提供屏幕 gif 图了
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以使用上文例子所示的功能来[自动化的管理 Linux 服务器上的任务][2]了。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 一些 Fabric 有用的选项
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 你可以运行 `fab -help` 输出帮助信息,里面列出了所有可以使用的命令行信息
|
||||
- `–fabfile=PATH` 选项可以让你定义除了名为 fabfile.py 之外的模块
|
||||
- 如果你想用指定的用户名登录远程主机,请使用 `-user=USER` 选项
|
||||
- 如果你需要密码进行验证或者 sudo 提权,请使用 `–password=PASSWORD` 选项
|
||||
- 如果需要输出某个命令行的详细信息,请使用 `–display=NAME` 选项
|
||||
- 使用 `--list-format=FORMAT` 选项能格式化 `-list` 选项输出的信息,可选的有 short, normal, nested
|
||||
- 使用 `--list` 输出所有可用的任务(to 校对:建议与上一条交换位置)
|
||||
- `--config=PATH` 选项可以指定读取配置文件的地址
|
||||
- `-–colorize-errors` 能显示彩色的错误输出信息
|
||||
- `--version` 输出当前版本
|
||||
(to 校对:以上根据原文格式加了代码标签,并且根据 Fabric 文档修正了命令使用)
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary
|
||||
|
||||
Fabric 是一个强大并且拥有充足文档的工具,对于新手来说也能很快上手,阅读提供的文档能帮助你更好的了解这个它。如果你在安装和使用 Fabric 时发现什么问题可以在评论区留言,我们会及时回复。
|
||||
|
||||
引文:[Fabric 文档][3]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/automating-linux-system-administration-tasks/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili ][a]
|
||||
译者:[NearTan](https://github.com/NearTan)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]: http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
[2]: http://www.tecmint.com/use-ansible-playbooks-to-automate-complex-tasks-on-multiple-linux-servers/
|
||||
[3]: http://docs.fabfile.org/en/1.4.0/usage/env.html
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user