mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
commit
74307031bc
@ -1,8 +1,9 @@
|
||||
如何在 Docker 中通过 Kitematic 交互式执行任务
|
||||
如何在 Windows 上通过 Kitematic 使用 Docker
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在本篇文章中,我们会学习如何在 Windows 操作系统上安装 Kitematic 以及部署一个 Hello World Nginx Web 服务器。Kitematic 是一个自由开源软件,它有现代化的界面设计使得允许我们在 Docker 中交互式执行任务。Kitematic 设计非常漂亮、界面也很不错。我们可以简单快速地开箱搭建我们的容器而不需要输入命令,我们可以在图形用户界面中通过简单的点击从而在容器上部署我们的应用。Kitematic 集成了 Docker Hub,允许我们搜索、拉取任何需要的镜像,并在上面部署应用。它同时也能很好地切换到命令行用户接口模式。目前,它包括了自动映射端口、可视化更改环境变量、配置卷、精简日志以及其它功能。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是在 Windows 上安装 Kitematic 并部署 Hello World Nginx Web 服务器的 3 个简单步骤。
|
||||
在本篇文章中,我们会学习如何在 Windows 操作系统上安装 Kitematic 以及部署一个测试性的 Nginx Web 服务器。Kitematic 是一个具有现代化的界面设计的自由开源软件,它可以让我们在 Docker 中交互式执行任务。Kitematic 设计的非常漂亮、界面美观。使用它,我们可以简单快速地开箱搭建我们的容器而不需要输入命令,可以在图形用户界面中通过简单的点击从而在容器上部署我们的应用。Kitematic 集成了 Docker Hub,允许我们搜索、拉取任何需要的镜像,并在上面部署应用。它同时也能很好地切换到命令行用户接口模式。目前,它包括了自动映射端口、可视化更改环境变量、配置卷、流式日志以及其它功能。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是在 Windows 上安装 Kitematic 并部署测试性 Nginx Web 服务器的 3 个简单步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 下载 Kitematic ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,15 +17,15 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 安装 Kitematic ###
|
||||
|
||||
下载好可执行安装程序之后,我们现在打算在我们的 Windows 操作系统上安装 Kitematic。安装程序现在会开始下载并安装运行 Kitematic 需要的依赖,包括 Virtual Box 和 Docker。如果已经在系统上安装了 Virtual Box,它会把它升级到最新版本。安装程序会在几分钟内完成,但取决于你网络和系统的速度。如果你还没有安装 Virtual Box,它会问你是否安装 Virtual Box 网络驱动。建议安装它,因为它有助于 Virtual Box 的网络。
|
||||
下载好可执行安装程序之后,我们现在就可以在我们的 Windows 操作系统上安装 Kitematic了。安装程序现在会开始下载并安装运行 Kitematic 需要的依赖软件,包括 Virtual Box 和 Docker。如果已经在系统上安装了 Virtual Box,它会把它升级到最新版本。安装程序会在几分钟内完成,但取决于你网络和系统的速度。如果你还没有安装 Virtual Box,它会问你是否安装 Virtual Box 网络驱动。建议安装它,因为它用于 Virtual Box 的网络功能。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
需要的依赖 Docker 和 Virtual Box 安装完成并运行后,会让我们登录到 Docker Hub。如果我们还没有账户或者还不想登录,可以点击 **SKIP FOR NOW** 继续后面的步骤。
|
||||
所需的依赖 Docker 和 Virtual Box 安装完成并运行后,会让我们登录到 Docker Hub。如果我们还没有账户或者还不想登录,可以点击 **SKIP FOR NOW** 继续后面的步骤。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你还没有账户,你可以在应用程序上点击注册链接并在 Docker Hub 上创建账户。
|
||||
如果你还没有账户,你可以在应用程序上点击注册(Sign Up)链接并在 Docker Hub 上创建账户。
|
||||
|
||||
完成之后,就会出现 Kitematic 应用程序的第一个界面。正如下面看到的这样。我们可以搜索可用的 docker 镜像。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,7 +51,11 @@
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们终于成功在 Windows 操作系统上安装了 Kitematic 并部署了一个 Hello World Ngnix 服务器。总是推荐下载安装 Kitematic 最新的发行版,因为会增加很多新的高级功能。由于 Docker 运行在 64 位平台,当前 Kitematic 也是为 64 位操作系统构建。它只能在 Windows 7 以及更高版本上运行。在这篇教程中,我们部署了一个 Nginx Web 服务器,类似地我们可以在 Kitematic 中简单的点击就能通过镜像部署任何 docker 容器。Kitematic 已经有可用的 Mac OS X 和 Windows 版本,Linux 版本也在开发中很快就会发布。如果你有任何疑问、建议或者反馈,请在下面的评论框中写下来以便我们更改地改进或更新我们的内容。非常感谢!Enjoy :-)
|
||||
我们终于成功在 Windows 操作系统上安装了 Kitematic 并部署了一个 Hello World Ngnix 服务器。推荐下载安装 Kitematic 最新的发行版,因为会增加很多新的高级功能。由于 Docker 运行在 64 位平台,当前 Kitematic 也是为 64 位操作系统构建。它只能在 Windows 7 以及更高版本上运行。
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇教程中,我们部署了一个 Nginx Web 服务器,类似地我们可以在 Kitematic 中简单的点击就能通过镜像部署任何 docker 容器。Kitematic 已经有可用的 Mac OS X 和 Windows 版本,Linux 版本也在开发中很快就会发布。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有任何疑问、建议或者反馈,请在下面的评论框中写下来以便我们更改地改进或更新我们的内容。非常感谢!Enjoy :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -58,7 +63,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/interactively-docker-kitematic/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
440
published/20150813 Linux file system hierarchy v2.0.md
Normal file
440
published/20150813 Linux file system hierarchy v2.0.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,440 @@
|
||||
Linux 文件系统结构介绍
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
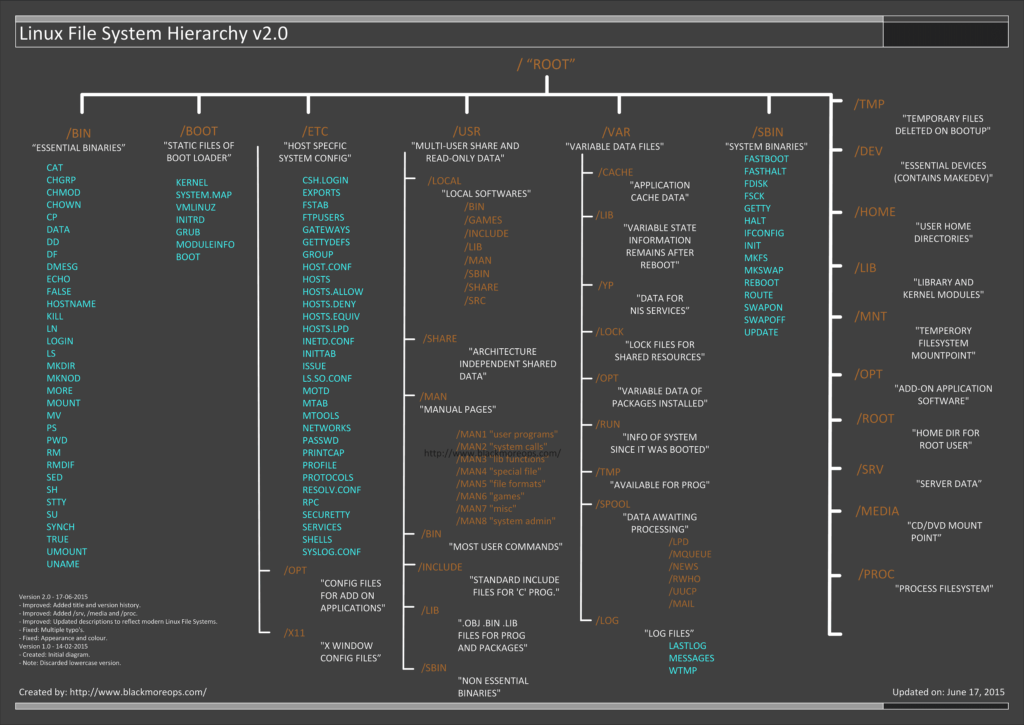
Linux中的文件是什么?它的文件系统又是什么?那些配置文件又在哪里?我下载好的程序保存在哪里了?在 Linux 中文件系统是标准结构的吗?好了,上图简明地阐释了Linux的文件系统的层次关系。当你苦于寻找配置文件或者二进制文件的时候,这便显得十分有用了。我在下方添加了一些解释以及例子,不过“篇幅较长,可以有空再看”。
|
||||
|
||||
另外一种情况便是当你在系统中获取配置以及二进制文件时,出现了不一致性问题,如果你是在一个大型组织中,或者只是一个终端用户,这也有可能会破坏你的系统(比如,二进制文件运行在旧的库文件上了)。若然你在[你的Linux系统上做安全审计][1]的话,你将会发现它很容易遭到各种攻击。所以,保持一个清洁的操作系统(无论是Windows还是Linux)都显得十分重要。
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux的文件是什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
对于UNIX系统来说(同样适用于Linux),以下便是对文件简单的描述:
|
||||
|
||||
> 在UNIX系统中,一切皆为文件;若非文件,则为进程
|
||||
|
||||
这种定义是比较正确的,因为有些特殊的文件不仅仅是普通文件(比如命名管道和套接字),不过为了让事情变的简单,“一切皆为文件”也是一个可以让人接受的说法。Linux系统也像UNIX系统一样,将文件和目录视如同物,因为目录只是一个包含了其他文件名的文件而已。程序、服务、文本、图片等等,都是文件。对于系统来说,输入和输出设备,基本上所有的设备,都被当做是文件。
|
||||
|
||||
题图版本历史:
|
||||
|
||||
- Version 2.0 – 17-06-2015
|
||||
- – Improved: 添加标题以及版本历史
|
||||
- – Improved: 添加/srv,/meida和/proc
|
||||
- – Improved: 更新了反映当前的Linux文件系统的描述
|
||||
- – Fixed: 多处的打印错误
|
||||
- – Fixed: 外观和颜色
|
||||
- Version 1.0 – 14-02-2015
|
||||
- – Created: 基本的图表
|
||||
- – Note: 摒弃更低的版本
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载链接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
以下是大图的下载地址。如果你需要其他格式,请跟原作者联系,他会尝试制作并且上传到某个地方以供下载
|
||||
|
||||
- [大图 (PNG 格式) – 2480×1755 px – 184KB][2]
|
||||
- [最大图 (PDF 格式) – 9919x7019 px – 1686KB][3]
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: PDF格式文件是打印的最好选择,因为它画质很高。
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux 文件系统描述 ###
|
||||
|
||||
为了有序地管理那些文件,人们习惯把这些文件当做是硬盘上的有序的树状结构,正如我们熟悉的'MS-DOS'(磁盘操作系统)就是一个例子。大的分枝包括更多的分枝,分枝的末梢是树的叶子或者普通的文件。现在我们将会以这树形图为例,但晚点我们会发现为什么这不是一个完全准确的一幅图。
|
||||
|
||||
<table cellspacing="2" border="4" style="border-collapse: collapse; width: 731px; height: 2617px;">
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th scope="col">目录</th>
|
||||
<th scope="col">描述</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td><i>主层次</i> 的根,也是整个文件系统层次结构的根目录</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/bin</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>存放在单用户模式可用的必要命令二进制文件,所有用户都可用,如 cat、ls、cp等等</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/boot</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>存放引导加载程序文件,例如kernels、initrd等</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/dev</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>存放必要的设备文件,例如<code>/dev/null</code> </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/etc</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>存放主机特定的系统级配置文件。其实这里有个关于它名字本身意义上的的争议。在贝尔实验室的UNIX实施文档的早期版本中,/etc表示是“其他(etcetera)目录”,因为从历史上看,这个目录是存放各种不属于其他目录的文件(然而,文件系统目录标准 FSH 限定 /etc 用于存放静态配置文件,这里不该存有二进制文件)。早期文档出版后,这个目录名又重新定义成不同的形式。近期的解释中包含着诸如“可编辑文本配置”或者“额外的工具箱”这样的重定义</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/etc/opt</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>存储着新增包的配置文件 <code>/opt/</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/etc/sgml</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>存放配置文件,比如 catalogs,用于那些处理SGML(译者注:标准通用标记语言)的软件的配置文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/etc/X11</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>X Window 系统11版本的的配置文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/etc/xml</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>配置文件,比如catalogs,用于那些处理XML(译者注:可扩展标记语言)的软件的配置文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/home</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>用户的主目录,包括保存的文件,个人配置,等等</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/lib</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td><code>/bin/</code> 和 <code>/sbin/</code>中的二进制文件的必需的库文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/lib<架构位数></code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>备用格式的必要的库文件。 这样的目录是可选的,但如果他们存在的话肯定是有需要用到它们的程序</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/media</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>可移动的多媒体(如CD-ROMs)的挂载点。(出现于 FHS-2.3)</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/mnt</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>临时挂载的文件系统</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/opt</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>可选的应用程序软件包</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/proc</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>以文件形式提供进程以及内核信息的虚拟文件系统,在Linux中,对应进程文件系统(procfs )的挂载点</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/root</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>根用户的主目录</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/sbin</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>必要的系统级二进制文件,比如, init, ip, mount</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/srv</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>系统提供的站点特定数据</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/tmp</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>临时文件 (另见 <code>/var/tmp</code>). 通常在系统重启后删除</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/usr</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td><i>二级层级</i>存储用户的只读数据; 包含(多)用户主要的公共文件以及应用程序</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/usr/bin</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>非必要的命令二进制文件 (在单用户模式中不需要用到的);用于所有用户</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/usr/include</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>标准的包含文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/usr/lib</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>库文件,用于<code>/usr/bin/</code> 和 <code>/usr/sbin/</code>中的二进制文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/usr/lib<架构位数></code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>备用格式库(可选的)</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/usr/local</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td><i>三级层次</i> 用于本地数据,具体到该主机上的。通常会有下一个子目录, <i>比如</i>, <code>bin/</code>, <code>lib/</code>, <code>share/</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/usr/local/sbin</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>非必要系统的二进制文件,比如用于不同网络服务的守护进程</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/usr/share</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>架构无关的 (共享) 数据.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/usr/src</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>源代码,比如内核源文件以及与它相关的头文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/usr/X11R6</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>X Window系统,版本号:11,发行版本:6</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
<code>/var</code>
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>各式各样的(Variable)文件,一些随着系统常规操作而持续改变的文件就放在这里,比如日志文件,脱机文件,还有临时的电子邮件文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/var/cache</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>应用程序缓存数据. 这些数据是由耗时的I/O(输入/输出)的或者是运算本地生成的结果。这些应用程序是可以重新生成或者恢复数据的。当没有数据丢失的时候,可以删除缓存文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/var/lib</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>状态信息。这些信息随着程序的运行而不停地改变,比如,数据库,软件包系统的元数据等等</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/var/lock</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>锁文件。这些文件用于跟踪正在使用的资源</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/var/log</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>日志文件。包含各种日志。</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/var/mail</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>内含用户邮箱的相关文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/var/opt</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>来自附加包的各种数据都会存储在 <code>/var/opt/</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/var/run</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>存放当前系统上次启动以来的相关信息,例如当前登入的用户以及当前运行的<a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Daemon_%28computing%29">daemons(守护进程)</a>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/var/spool</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>该spool主要用于存放将要被处理的任务,比如打印队列以及邮件外发队列</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/var/mail</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>过时的位置,用于放置用户邮箱文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<code>/var/tmp</code>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</td>
|
||||
<td>存放重启后保留的临时文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Linux的文件类型 ###
|
||||
|
||||
大多数文件仅仅是普通文件,他们被称为`regular`文件;他们包含普通数据,比如,文本、可执行文件、或者程序、程序的输入或输出等等
|
||||
|
||||
虽然你可以认为“在Linux中,一切你看到的皆为文件”这个观点相当保险,但这里仍有着一些例外。
|
||||
|
||||
- `目录`:由其他文件组成的文件
|
||||
- `特殊文件`:用于输入和输出的途径。大多数特殊文件都储存在`/dev`中,我们将会在后面讨论这个问题。
|
||||
- `链接文件`:让文件或者目录出现在系统文件树结构上多个地方的机制。我们将详细地讨论这个链接文件。
|
||||
- `(域)套接字`:特殊的文件类型,和TCP/IP协议中的套接字有点像,提供进程间网络通讯,并受文件系统的访问控制机制保护。
|
||||
- `命名管道` : 或多或少有点像sockets(套接字),提供一个进程间的通信机制,而不用网络套接字协议。
|
||||
|
||||
### 现实中的文件系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
对于大多数用户和常规系统管理任务而言,“文件和目录是一个有序的类树结构”是可以接受的。然而,对于电脑而言,它是不会理解什么是树,或者什么是树结构。
|
||||
|
||||
每个分区都有它自己的文件系统。想象一下,如果把那些文件系统想成一个整体,我们可以构思一个关于整个系统的树结构,不过这并没有这么简单。在文件系统中,一个文件代表着一个`inode`(索引节点),这是一种包含着构建文件的实际数据信息的序列号:这些数据表示文件是属于谁的,还有它在硬盘中的位置。
|
||||
|
||||
每个分区都有一套属于他们自己的inode,在一个系统的不同分区中,可以存在有相同inode的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
每个inode都表示着一种在硬盘上的数据结构,保存着文件的属性,包括文件数据的物理地址。当硬盘被格式化并用来存储数据时(通常发生在初始系统安装过程,或者是在一个已经存在的系统中添加额外的硬盘),每个分区都会创建固定数量的inode。这个值表示这个分区能够同时存储各类文件的最大数量。我们通常用一个inode去映射2-8k的数据块。当一个新的文件生成后,它就会获得一个空闲的inode。在这个inode里面存储着以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- 文件属主和组属主
|
||||
- 文件类型(常规文件,目录文件......)
|
||||
- 文件权限
|
||||
- 创建、最近一次读文件和修改文件的时间
|
||||
- inode里该信息被修改的时间
|
||||
- 文件的链接数(详见下一章)
|
||||
- 文件大小
|
||||
- 文件数据的实际地址
|
||||
|
||||
唯一不在inode的信息是文件名和目录。它们存储在特殊的目录文件。通过比较文件名和inode的数目,系统能够构造出一个便于用户理解的树结构。用户可以通过ls -i查看inode的数目。在硬盘上,inodes有他们独立的空间。
|
||||
|
||||
------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.blackmoreops.com/2015/06/18/linux-file-system-hierarchy-v2-0/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[tnuoccalanosrep](https://github.com/tnuoccalanosrep)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.blackmoreops.com/2015/02/15/in-light-of-recent-linux-exploits-linux-security-audit-is-a-must/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.blackmoreops.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/Linux-file-system-hierarchy-v2.0-2480px-blackMORE-Ops.png
|
||||
[3]:http://www.blackmoreops.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/Linux-File-System-Hierarchy-blackMORE-Ops.pdf
|
||||
@ -1,13 +1,10 @@
|
||||
看这些孩子在Ubuntu的Linux终端下玩耍
|
||||
看这些孩子在 Ubuntu 的 Linux 终端下玩耍
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我发现了一个孩子们在他们的计算机教室里玩得很开心的视频。我不知道他们在哪里,但我猜测是在印度尼西亚或者马来西亚。
|
||||
|
||||
注:youtube 视频
|
||||
<iframe width="640" height="390" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="true" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/z8taQPomp0Y?version=3&rel=1&fs=1&showsearch=0&showinfo=1&iv_load_policy=1&wmode=transparent" type="text/html" class="youtube-player"></iframe>
|
||||
我发现了一个孩子们在他们的计算机教室里玩得很开心的视频。我不知道他们在哪里,但我猜测是在印度尼西亚或者马来西亚。视频请自行搭梯子: http://www.youtube.com/z8taQPomp0Y
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux终端下面跑火车 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这里没有魔术。只是一个叫做“sl”的命令行工具。我假定它是在把ls打错的情况下为了好玩而开发的。如果你曾经在Linux的命令行下工作,你会知道ls是一个最常使用的一个命令,也许也是一个最经常打错的命令。
|
||||
这里没有魔术。只是一个叫做“sl”的命令行工具。我想它是在把ls打错的情况下为了好玩而开发的。如果你曾经在Linux的命令行下工作,你会知道ls是一个最常使用的一个命令,也许也是一个最经常打错的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想从这个终端下的火车获得一些乐趣,你可以使用下面的命令安装它。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,7 +27,7 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/ubuntu-terminal-train/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,194 @@
|
||||
5 best open source board games to play online
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I have always had a fascination with board games, in part because they are a device of social interaction, they challenge the mind and, most importantly, they are great fun to play. In my misspent youth, myself and a group of friends gathered together to escape the horrors of the classroom, and indulge in a little escapism. The time provided an outlet for tension and rivalry. Board games help teach diplomacy, how to make and break alliances, bring families and friends together, and learn valuable lessons.
|
||||
|
||||
I had a panache for abstract strategy games such as chess and draughts, as well as word games. I can still never resist a game of Escape from Colditz, a strategy card and dice-based board game, or Risk; two timeless multi-player strategy board games. But Catan remains my favourite board game.
|
||||
|
||||
Board games have seen a resurgence in recent years, and Linux has a good range of board games to choose from. There is a credible implementation of Catan called Pioneers. But for my favourite implementations of classic board games to play online, check out the recommendations below.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### TripleA ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
TripleA is an open source online turn based strategy game. It allows people to implement and play various strategy board games (ie. Axis & Allies). The TripleA engine has full networking support for online play, support for sounds, XML support for game files, and has its own imaging subsystem that allows for customized user editable maps to be used. TripleA is versatile, scalable and robust.
|
||||
|
||||
TripleA started out as a World War II simulation, but now includes different conflicts, as well as variations and mods of popular games and maps. TripleA comes with multiple games and over 100 more games can be downloaded from the user community.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Good interface and attractive graphics
|
||||
- Optional scenarios
|
||||
- Multiplayer games
|
||||
- TripleA comes with the following supported games that uses its game engine (just to name a few):
|
||||
- Axis & Allies : Classic edition (2nd, 3rd with options enabled)
|
||||
- Axis & Allies : Revised Edition
|
||||
- Pact of Steel A&A Variant
|
||||
- Big World 1942 A&A Variant
|
||||
- Four if by Sea
|
||||
- Battle Ship Row
|
||||
- Capture The Flag
|
||||
- Minimap
|
||||
- Hot-seat
|
||||
- Play By EMail mode allows persons to play a game via EMail without having to be connected to each other online
|
||||
- More time to think out moves
|
||||
- Only need to come online to send your turn to the next player
|
||||
- Dice rolls are done by a dedicated dice server that is independent of TripleA
|
||||
- All dice rolls are PGP Verified and email to every player
|
||||
- Every move and every dice roll is logged and saved in TripleA's History Window
|
||||
- An online game can be later continued under PBEM mode
|
||||
- Hard for others to cheat
|
||||
- Hosted online lobby
|
||||
- Utilities for editing maps
|
||||
- Website: [triplea.sourceforge.net][1]
|
||||
- Developer: Sean Bridges (original developer), Mark Christopher Duncan
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.8.0.7
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Domination ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Domination is an open source game that shares common themes with the hugely popular Risk board game. It has many game options and includes many maps.
|
||||
|
||||
In the classic “World Domination” game of military strategy, you are battling to conquer the world. To win, you must launch daring attacks, defend yourself to all fronts, and sweep across vast continents with boldness and cunning. But remember, the dangers, as well as the rewards, are high. Just when the world is within your grasp, your opponent might strike and take it all away!
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Simple to learn
|
||||
- Domination - you must occupy all countries on the map, and thereby eliminate all opponents. These can be long, drawn out games
|
||||
- Capital - each player has a country they have selected as a Capital. To win the game, you must occupy all Capitals
|
||||
- Mission - each player draws a random mission. The first to complete their mission wins. Missions may include the elimination of a certain colour, occupation of a particular continent, or a mix of both
|
||||
- Map editor
|
||||
- Simple map format
|
||||
- Multiplayer network play
|
||||
- Single player
|
||||
- Hotseat
|
||||
- 5 user interfaces
|
||||
- Game types:
|
||||
- Play online
|
||||
- Website: [domination.sourceforge.net][2]
|
||||
- Developer: Yura Mamyrin, Christian Weiske, Mike Chaten, and many others
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.1.1.5
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### PyChess ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
PyChess is a Gnome inspired chess client written in Python.
|
||||
|
||||
The goal of PyChess, is to provide a fully featured, nice looking, easy to use chess client for the gnome-desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
The client should be usable both to those totally new to chess, those who want to play an occasional game, and those who wants to use the computer to further enhance their play.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Attractive interface
|
||||
- Chess Engine Communication Protocol (CECP) and Univeral Chess Interface (UCI) Engine support
|
||||
- Free online play on the Free Internet Chess Server (FICS)
|
||||
- Read and writes PGN, EPD and FEN chess file formats
|
||||
- Built-in Python based engine
|
||||
- Undo and pause functions
|
||||
- Board and piece animation
|
||||
- Drag and drop
|
||||
- Tabbed interface
|
||||
- Hints and spyarrows
|
||||
- Opening book sidepanel using sqlite
|
||||
- Score plot sidepanel
|
||||
- "Enter game" in pgn dialog
|
||||
- Optional sounds
|
||||
- Legal move highlighting
|
||||
- Internationalised or figure pieces in notation
|
||||
- Website: [www.pychess.org][3]
|
||||
- Developer: Thomas Dybdahl Ahle
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.12 Anderssen rc4
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Scrabble ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Scrabble3D is a highly customizable Scrabble game that not only supports Classic Scrabble and Superscrabble but also 3D games and own boards. You can play local against the computer or connect to a game server to find other players.
|
||||
|
||||
Scrabble is a board game with the goal to place letters crossword like. Up to four players take part and get a limited amount of letters (usually 7 or 8). Consecutively, each player tries to compose his letters to one or more word combining with the placed words on the game array. The value of the move depends on the letters (rare letter get more points) and bonus fields which multiply the value of a letter or the whole word. The player with most points win.
|
||||
|
||||
This idea is extended with Scrabble3D to the third dimension. Of course, a classic game with 15x15 fields or Superscrabble with 21x21 fields can be played and you may configure any field setting by yourself. The game can be played by the provided freeware program against Computer, other local players or via internet. Last but not least it's possible to connect to a game server to find other players and to obtain a rating. Most options are configurable, including the number and valuation of letters, the used dictionary, the language of dialogs and certainly colors, fonts etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- Configurable board, letterset and design
|
||||
- Board in OpenGL graphics with user-definable wavefront model
|
||||
- Game against computer with support of multithreading
|
||||
- Post-hoc game analysis with calculation of best move by computer
|
||||
- Match with other players connected on a game server
|
||||
- NSA rating and highscore at game server
|
||||
- Time limit of games
|
||||
- Localization; use of non-standard digraphs like CH, RR, LL and right to left reading
|
||||
- Multilanguage help / wiki
|
||||
- Network games are buffered and asynchronous games are possible
|
||||
- Running games can be kibitzed
|
||||
- International rules including italian "Cambio Secco"
|
||||
- Challenge mode, What-if-variant, CLABBERS, etc
|
||||
- Website: [sourceforge.net/projects/scrabble][4]
|
||||
- Developer: Heiko Tietze
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- Version Number: 3.1.3
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
### Backgammon ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
GNU Backgammon (gnubg) is a strong backgammon program (world-class with a bearoff database installed) usable either as an engine by other programs or as a standalone backgammon game. It is able to play and analyze both money games and tournament matches, evaluate and roll out positions, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to supporting simple play, it also has extensive analysis features, a tutor mode, adjustable difficulty, and support for exporting annotated games.
|
||||
|
||||
It currently plays at about the level of a championship flight tournament player and is gradually improving.
|
||||
|
||||
gnubg can be played on numerous on-line backgammon servers, such as the First Internet Backgammon Server (FIBS).
|
||||
|
||||
Features include:
|
||||
|
||||
- A command line interface (with full command editing features if GNU readline is available) that lets you play matches and sessions against GNU Backgammon with a rough ASCII representation of the board on text terminals
|
||||
- Support for a GTK+ interface with a graphical board window. Both 2D and 3D graphics are available
|
||||
- Tournament match and money session cube handling and cubeful play
|
||||
- Support for both 1-sided and 2-sided bearoff databases: 1-sided bearoff database for 15 checkers on the first 6 points and optional 2-sided database kept in memory. Optional larger 1-sided and 2-sided databases stored on disk
|
||||
- Automated rollouts of positions, with lookahead and race variance reduction where appropriate. Rollouts may be extended
|
||||
- Functions to generate legal moves and evaluate positions at varying search depths
|
||||
- Neural net functions for giving cubeless evaluations of all other contact and race positions
|
||||
- Automatic and manual annotation (analysis and commentary) of games and matches
|
||||
- Record keeping of statistics of players in games and matches (both native inside GNU Backgammon and externally using relational databases and Python)
|
||||
- Loading and saving analyzed games and matches as .sgf files (Smart Game Format)
|
||||
- Exporting positions, games and matches to: (.eps) Encapsulated Postscript, (.gam) Jellyfish Game, (.html) HTML, (.mat) Jellyfish Match, (.pdf) PDF, (.png) Portable Network Graphics, (.pos) Jellyfish Position, (.ps) PostScript, (.sgf) Gnu Backgammon File, (.tex) LaTeX, (.txt) Plain Text, (.txt) Snowie Text
|
||||
- Import of matches and positions from a number of file formats: (.bkg) Hans Berliner's BKG Format, (.gam) GammonEmpire Game, (.gam) PartyGammon Game, (.mat) Jellyfish Match, (.pos) Jellyfish Position, (.sgf) Gnu Backgammon File, (.sgg) GamesGrid Save Game, (.tmg) TrueMoneyGames, (.txt) Snowie Text
|
||||
- Python Scripting
|
||||
- Native language support; 10 languages complete or in progress
|
||||
- Website: [www.gnubg.org][5]
|
||||
- Developer: Joseph Heled, Oystein Johansen, Jonathan Kinsey, David Montgomery, Jim Segrave, Joern Thyssen, Gary Wong and contributors
|
||||
- License: GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.05.000
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150830011533893/BoardGames.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://triplea.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[2]:http://domination.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.pychess.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/scrabble/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.gnubg.org/
|
||||
63
sources/talk/20150901 Is Linux Right For You.md
Normal file
63
sources/talk/20150901 Is Linux Right For You.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
Is Linux Right For You?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Not everyone should opt for Linux -- for many users, remaining with Windows or OSX is the better choice.
|
||||
|
||||
I enjoy using Linux on the desktop. Not because of software politics or because I despise other operating systems. I simply like Linux because it just works.
|
||||
|
||||
It's been my experience that not everyone is cut out for the Linux lifestyle. In this article, I'll help you run through the pros and cons of making the switch to Linux so you can determine if switching is right for you.
|
||||
|
||||
### When to make the switch ###
|
||||
|
||||
Switching to Linux makes sense when there is a decisive reason to do so. The same can be said about moving from Windows to OS X or vice versa. In order to have success with switching, you must be able to identify your reason for jumping ship in the first place.
|
||||
|
||||
For some people, the reason for switching is frustration with their current platform. Maybe the latest upgrade left them with a lousy experience and they're ready to chart new horizons. In other instances, perhaps it's simply a matter of curiosity. Whatever the motivation, you must have a good reason for switching operating systems. If you're pushing yourself in this direction without a good reason, then no one wins.
|
||||
|
||||
However, there are exceptions to every rule. And if you're really interested in trying Linux on the desktop, then maybe coming to terms with a workable compromise is the way to go.
|
||||
|
||||
### Starting off slow ###
|
||||
|
||||
After trying Linux for the first time, I've seen people blast their Windows installation to bits because they had a good experience with Ubuntu on a flash drive for 20 minutes. Folks, this isn't a test. Instead I'd suggest the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- Run the [Linux distro in a virtual machine][1] for a week. This means you are committing to running that distro for all browser work, email and other tasks you might otherwise do on that machine.
|
||||
- If running a VM for a week is too resource intensive, try doing the same with a USB drive running Linux that offers [some persistent storage][2]. This will allow you to leave your main OS alone and intact. At the same time, you'll still be able to "live inside" of your Linux distribution for a week.
|
||||
- If you find that everything is successful after a week of running Linux, the next step is to examine how many times you booted into Windows that week. If only occasionally, then the next step is to look into [dual-booting Windows][3] and Linux. For those of you that only found themselves using their Linux distro, it might be worth considering making the switch full time.
|
||||
- Before you hose your Windows partition completely, it might make more sense to purchase a second hard drive to install Linux onto instead. This allows you to dual-boot, but to do so with ample hard drive space. It also makes Windows available to you if something should come up.
|
||||
|
||||
### What do you gain adopting Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
So what does one gain by switching to Linux? Generally it comes down to personal freedom for most people. With Linux, if something isn't to your liking, you're free to change it. Using Linux also saves users oodles of money in avoiding hardware upgrades and unnecessary software expenses. Additionally, you're not burdened with tracking down lost license keys for software. And if you dislike the direction a particular distribution is headed, you can switch to another distribution with minimal hassle.
|
||||
|
||||
The sheer volume of desktop choice on the Linux desktop is staggering. This level of choice might even seem overwhelming to the newcomer. But if you find a distro base (Debian, Fedora, Arch, etc) that you like, the hard work is already done. All you need to do now is find a variation of the distro and the desktop environment you prefer.
|
||||
|
||||
Now one of the most common complaints I hear is that there isn't much in the way of software for Linux. However, this isn't accurate at all. While other operating systems may have more of it, today's Linux desktop has applications to do just about anything you can think of. Video editing (home and pro-level), photography, office management, remote access, music (listening and creation), plus much, much more.
|
||||
|
||||
### What you lose adopting Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
As much as I enjoy using Linux, my wife's home office relies on OS X. She's perfectly content using Linux for some tasks, however she relies on OS X for specific software not available for Linux. This is a common problem that many people face when first looking at making the switch. You must decide whether or not you're going to be losing out on critical software if you make the switch.
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes the issue is because the software has content locked down with it. In other cases, it's a workflow and functionality that was found with the legacy applications and not with the software available for Linux. I myself have never experienced this type of challenge, but I know those who have. Many of the software titles available for Linux are also available for other operating systems. So if there is a concern about such things, I encourage you to try out comparable apps on your native OS first.
|
||||
|
||||
Another thing you might lose by switching to Linux is the luxury of local support when you need it. People scoff at this, but I know of countless instances where a newcomer to Linux was dismayed to find their only recourse for solving Linux challenges was from strangers on the Web. This is especially problematic if their only PC is the one having issues. Windows and OS X users are spoiled in that there are endless support techs in cities all over the world that support their platform(s).
|
||||
|
||||
### How to proceed from here ###
|
||||
|
||||
Perhaps the single biggest piece of advice to remember is always have a fallback plan. Remember, once you wipe that copy of Windows 10 from your hard drive, you may find yourself spending money to get it reinstalled. This is especially true for those of you who upgrade from other Windows releases. Accepting this, persistent flash drives with Linux or dual-booting Windows and Linux is always a preferable way forward for newcomers. Odds are that you may be just fine and take to Linux like a fish to water. But having that fallback plan in place just means you'll sleep better at night.
|
||||
|
||||
If instead you've been relying on a dual-boot installation for weeks and feel ready to take the plunge, then by all means do it. Wipe your drive and start off with a clean installation of your favorite Linux distribution. I've been a full time Linux enthusiast for years and I can tell you for certain, it's a great feeling. How long? Let's just say my first Linux experience was with early Red Hat. I finally installed a dedicated installation on my laptop by 2003.
|
||||
|
||||
Existing Linux enthusiasts, where did you first get started? Was your switch an exciting one or was it filled with angst? Hit the Comments and share your experiences.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/open-source/is-linux-right-for-you.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matt Hartley][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.datamation.com/author/Matt-Hartley-3080.html
|
||||
[1]:http://www.psychocats.net/ubuntu/virtualbox
|
||||
[2]:http://www.howtogeek.com/howto/14912/create-a-persistent-bootable-ubuntu-usb-flash-drive/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.linuxandubuntu.com/home/dual-boot-ubuntu-15-04-14-10-and-windows-10-8-1-8-step-by-step-tutorial-with-screenshots
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[bazz222]
|
||||
How to filter BGP routes in Quagga BGP router
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In the [previous tutorial][1], we demonstrated how to turn a CentOS box into a BGP router using Quagga. We also covered basic BGP peering and prefix exchange setup. In this tutorial, we will focus on how we can control incoming and outgoing BGP prefixes by using **prefix-list** and **route-map**.
|
||||
@ -198,4 +199,4 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/filter-bgp-routes-quagga-bgp-router.html
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/sarmed
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/centos-bgp-router-quagga.html
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/centos-bgp-router-quagga.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,295 +0,0 @@
|
||||
wyangsun translating
|
||||
How to set up a system status page of your infrastructure
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you are a system administrator who is responsible for critical IT infrastructure or services of your organization, you will understand the importance of effective communication in your day-to-day tasks. Suppose your production storage server is on fire. You want your entire team on the same page in order to resolve the issue as fast as you can. While you are at it, you don't want half of all users contacting you asking why they cannot access their documents. When a scheduled maintenance is coming up, you want to notify interested parties of the event ahead of the schedule, so that unnecessary support tickets can be avoided.
|
||||
|
||||
All these require some sort of streamlined communication channel between you, your team and people you serve. One way to achieve that is to maintain a centralized system status page, where the detail of downtime incidents, progress updates and maintenance schedules are reported and chronicled. That way, you can minimize unnecessary distractions during downtime, and also have any interested party informed and opt-in for any status update.
|
||||
|
||||
One good **open-source, self-hosted system status page solution** is [Cachet][1]. In this tutorial, I am going to describe how to set up a self-hosted system status page using Cachet.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cachet Features ###
|
||||
|
||||
Before going into the detail of setting up Cachet, let me briefly introduce its main features.
|
||||
|
||||
- **Full JSON API**: The Cachet API allows you to connect any external program or script (e.g., uptime script) to Cachet to report incidents or update status automatically.
|
||||
- **Authentication**: Cachet supports Basic Auth and API token in JSON API, so that only authorized personnel can update the status page.
|
||||
- **Metrics system**: This is useful to visualize custom data over time (e.g., server load or response time).
|
||||
- **Notification**: Optionally you can send notification emails about reported incidents to anyone who signed up to the status page.
|
||||
- **Multiple languages**: The status page can be translated into 11 different languages.
|
||||
- **Two factor authentication**: This allows you to lock your Cachet admin account with Google's two-factor authentication.
|
||||
- **Cross database support**: You can choose between MySQL, SQLite, Redis, APC, and PostgreSQL for a backend storage.
|
||||
|
||||
In the rest of the tutorial, I explain how to install and configure Cachet on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step One: Download and Install Cachet ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cachet requires a web server and a backend database to operate. In this tutorial, I am going to use the LAMP stack. Here are distro-specific instructions to install Cachet and LAMP stack.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install curl git apache2 mysql-server mysql-client php5 php5-mysql
|
||||
$ sudo git clone https://github.com/cachethq/Cachet.git /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ cd /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ sudo git checkout v1.1.1
|
||||
$ sudo chown -R www-data:www-data .
|
||||
|
||||
For more detail on setting up LAMP stack on Debian-based systems, refer to [this tutorial][2].
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fedora, CentOS or RHEL ####
|
||||
|
||||
On Red Hat based systems, you first need to [enable REMI repository][3] (to meet PHP version requirement). Then proceed as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install curl git httpd mariadb-server
|
||||
$ sudo yum --enablerepo=remi-php56 install php php-mysql php-mbstring
|
||||
$ sudo git clone https://github.com/cachethq/Cachet.git /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ cd /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ sudo git checkout v1.1.1
|
||||
$ sudo chown -R apache:apache .
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl enable httpd.service; sudo systemctl start httpd.service
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl enable mariadb.service; sudo systemctl start mariadb.service
|
||||
|
||||
For more details on setting up LAMP on Red Hat-based systems, refer to [this tutorial][4].
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure a Backend Database for Cachet ###
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is to configure database backend.
|
||||
|
||||
Log in to MySQL/MariaDB server, and create an empty database called 'cachet'.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mysql -uroot -p
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> create database cachet;
|
||||
mysql> quit
|
||||
|
||||
Now create a Cachet configuration file by using a sample configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ sudo mv .env.example .env
|
||||
|
||||
In .env file, fill in database information (i.e., DB_*) according to your setup. Leave other fields unchanged for now.
|
||||
|
||||
APP_ENV=production
|
||||
APP_DEBUG=false
|
||||
APP_URL=http://localhost
|
||||
APP_KEY=SomeRandomString
|
||||
|
||||
DB_DRIVER=mysql
|
||||
DB_HOST=localhost
|
||||
DB_DATABASE=cachet
|
||||
DB_USERNAME=root
|
||||
DB_PASSWORD=<root-password>
|
||||
|
||||
CACHE_DRIVER=apc
|
||||
SESSION_DRIVER=apc
|
||||
QUEUE_DRIVER=database
|
||||
|
||||
MAIL_DRIVER=smtp
|
||||
MAIL_HOST=mailtrap.io
|
||||
MAIL_PORT=2525
|
||||
MAIL_USERNAME=null
|
||||
MAIL_PASSWORD=null
|
||||
MAIL_ADDRESS=null
|
||||
MAIL_NAME=null
|
||||
|
||||
REDIS_HOST=null
|
||||
REDIS_DATABASE=null
|
||||
REDIS_PORT=null
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Three: Install PHP Dependencies and Perform DB Migration ###
|
||||
|
||||
Next, we are going to install necessary PHP dependencies. For that we will use composer. If you do not have composer installed on your system, install it first:
|
||||
|
||||
$ curl -sS https://getcomposer.org/installer | sudo php -- --install-dir=/usr/local/bin --filename=composer
|
||||
|
||||
Now go ahead and install PHP dependencies using composer.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ sudo composer install --no-dev -o
|
||||
|
||||
Next, perform one-time database migration. This step will populate the empty database we created earlier with necessary tables.
|
||||
|
||||
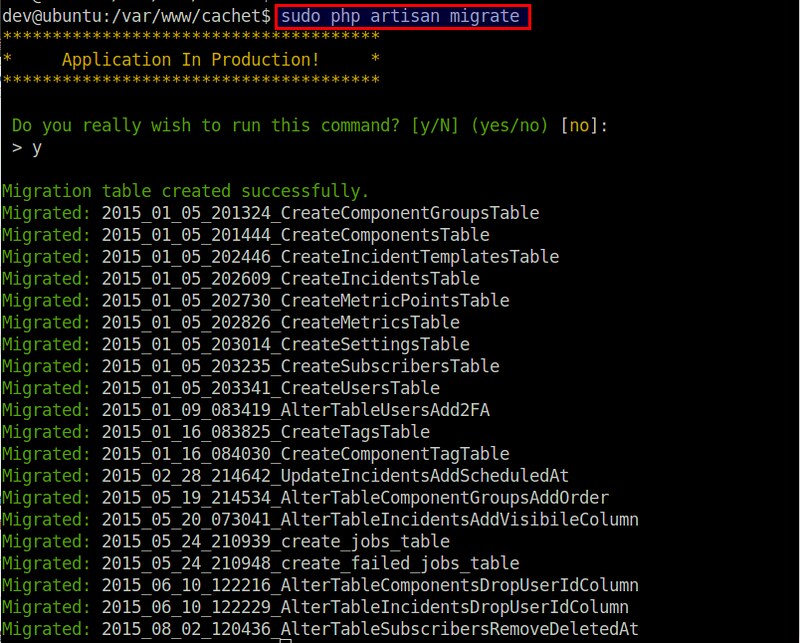
$ sudo php artisan migrate
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming the database config in /var/www/cachet/.env is correct, database migration should be completed successfully as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
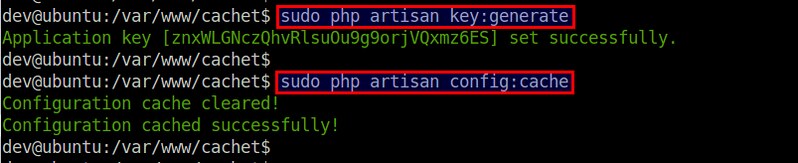
Next, create a security key, which will be used to encrypt the data entered in Cachet.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo php artisan key:generate
|
||||
$ sudo php artisan config:cache
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The generated app key will be automatically added to the APP_KEY variable of your .env file. No need to edit .env on your own here.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Four: Configure Apache HTTP Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now it's time to configure the web server that Cachet will be running on. As we are using Apache HTTP server, create a new [virtual host][5] for Cachet as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/cachet.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerName cachethost
|
||||
ServerAlias cachethost
|
||||
DocumentRoot "/var/www/cachet/public"
|
||||
<Directory "/var/www/cachet/public">
|
||||
Require all granted
|
||||
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow from all
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||
Enable the new Virtual Host and mod_rewrite with:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo a2ensite cachet.conf
|
||||
$ sudo a2enmod rewrite
|
||||
$ sudo service apache2 restart
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fedora, CentOS or RHEL ####
|
||||
|
||||
On Red Hat based systems, create a virtual host file as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/cachet.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerName cachethost
|
||||
ServerAlias cachethost
|
||||
DocumentRoot "/var/www/cachet/public"
|
||||
<Directory "/var/www/cachet/public">
|
||||
Require all granted
|
||||
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow from all
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||
Now reload Apache configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl reload httpd.service
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Five: Configure /etc/hosts for Testing Cachet ###
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, the initial Cachet status page should be up and running, and now it's time to test.
|
||||
|
||||
Since Cachet is configured as a virtual host of Apache HTTP server, we need to tweak /etc/hosts of your client computer to be able to access it. Here the client computer is the one from which you will be accessing the Cachet page.
|
||||
|
||||
Open /etc/hosts, and add the following entry.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/hosts
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
<cachet-server-ip-address> cachethost
|
||||
|
||||
In the above, the name "cachethost" must match with ServerName specified in the Apache virtual host file for Cachet.
|
||||
|
||||
### Test Cachet Status Page ###
|
||||
|
||||
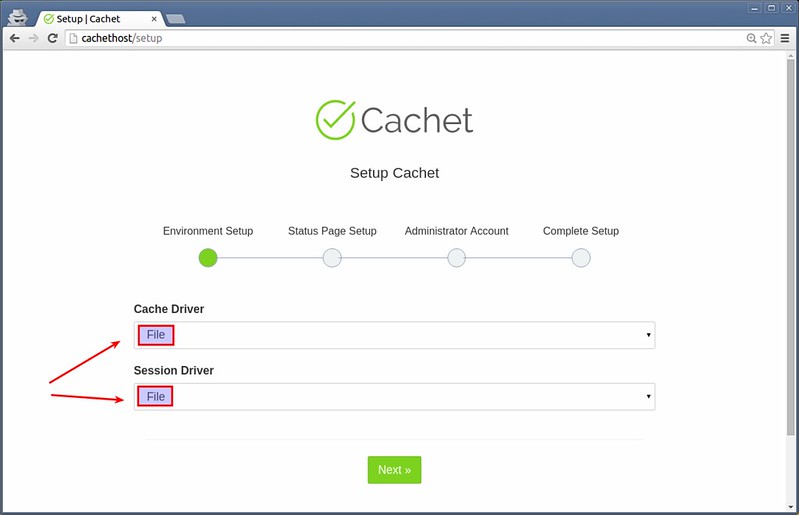
Now you are ready to access Cachet status page. Type http://cachethost in your browser address bar. You will be redirected to the initial Cachet setup page as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Choose cache/session driver. Here let's choose "File" for both cache and session drivers.
|
||||
|
||||
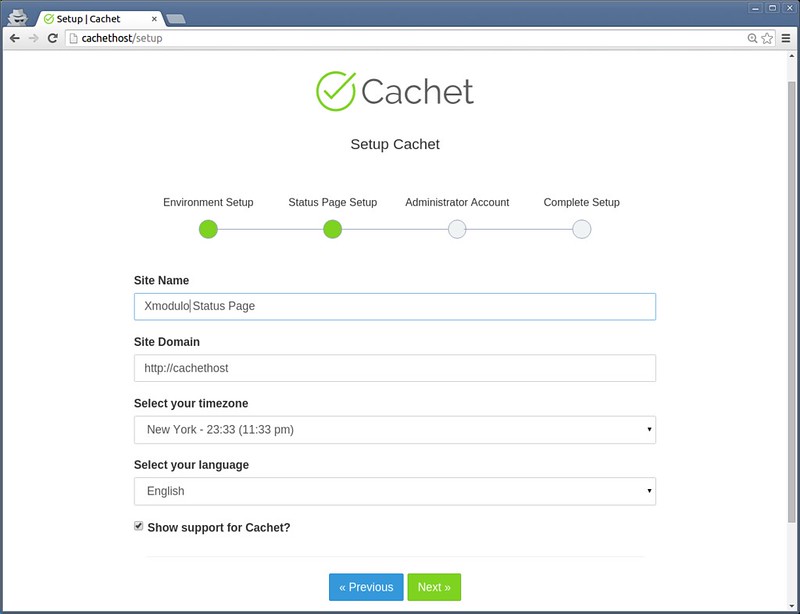
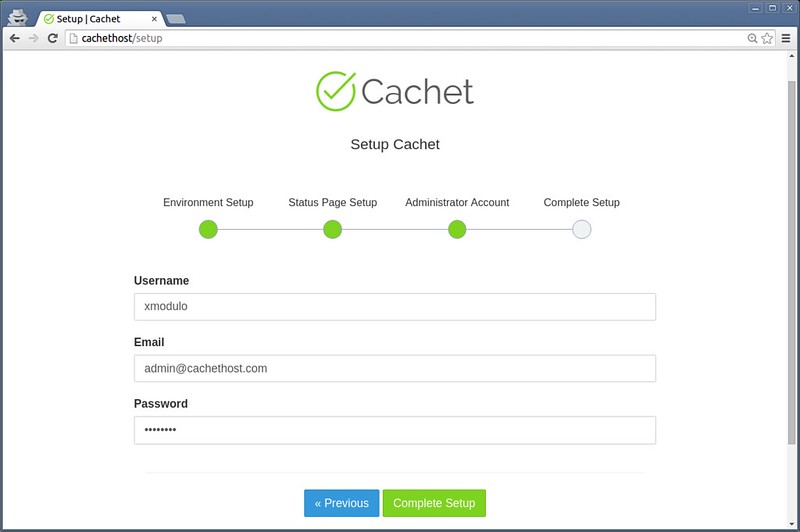
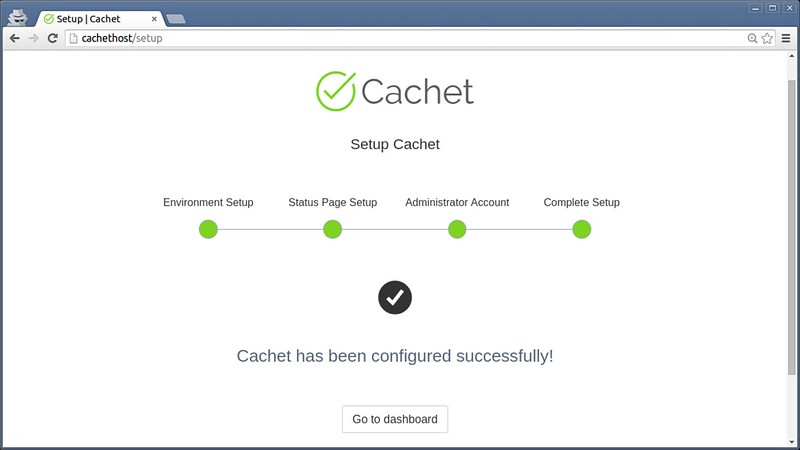
Next, type basic information about the status page (e.g., site name, domain, timezone and language), as well as administrator account.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
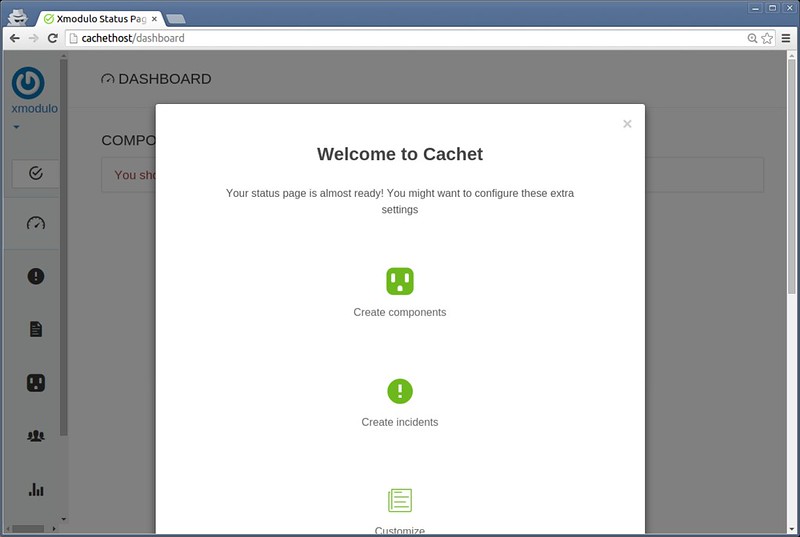
Your initial status page will finally be ready.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Go ahead and create components (units of your system), incidents or any scheduled maintenance as you want.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to add a new component:
|
||||
|
||||
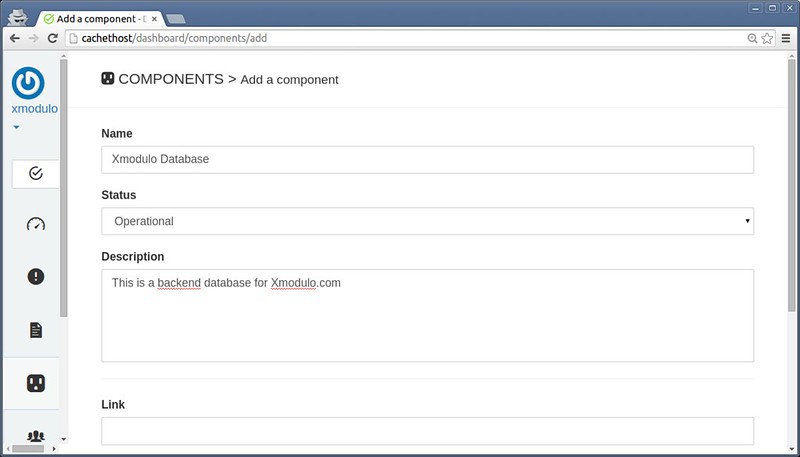
|
||||
|
||||
To add a scheduled maintenance:
|
||||
|
||||
This is what the public Cachet status page looks like:
|
||||
|
||||
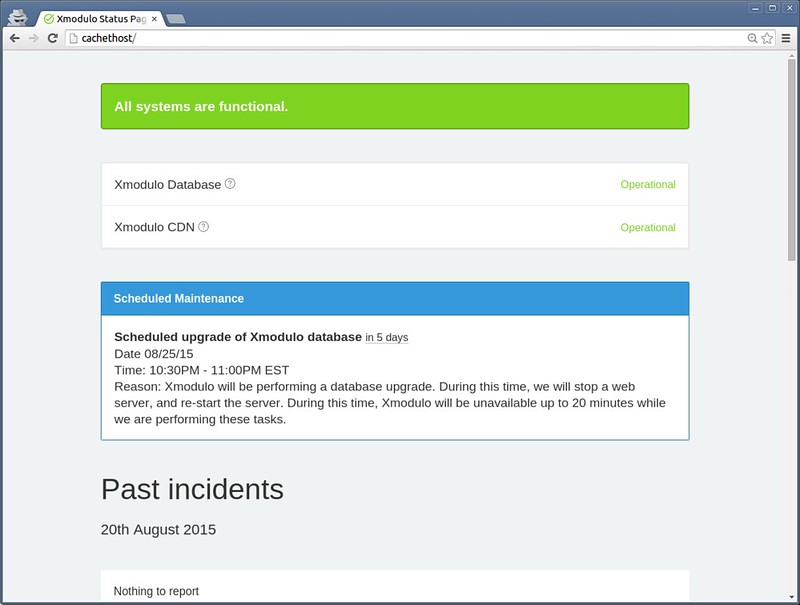
|
||||
|
||||
With SMTP integration, you can send out emails on status updates to any subscribers. Also, you can fully customize the layout and style of the status page using CSS and markdown formatting.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cachet is pretty easy-to-use, self-hosted status page software. One of the nicest features of Cachet is its support for full JSON API. Using its RESTful API, one can easily hook up Cachet with separate monitoring backends (e.g., [Nagios][6]), and feed Cachet with incident reports and status updates automatically. This is far quicker and efficient than manually manage a status page.
|
||||
|
||||
As final words, I'd like to mention one thing. While setting up a fancy status page with Cachet is straightforward, making the best use of the software is not as easy as installing it. You need total commitment from the IT team on updating the status page in an accurate and timely manner, thereby building credibility of the published information. At the same time, you need to educate users to turn to the status page. At the end of the day, it would be pointless to set up a status page if it's not populated well, and/or no one is checking it. Remember this when you consider deploying Cachet in your work environment.
|
||||
|
||||
### Troubleshooting ###
|
||||
|
||||
As a bonus, here are some useful troubleshooting tips in case you encounter problems while setting up Cachet.
|
||||
|
||||
1. The Cachet page does not load anything, and you are getting the following error.
|
||||
|
||||
production.ERROR: exception 'RuntimeException' with message 'No supported encrypter found. The cipher and / or key length are invalid.' in /var/www/cachet/bootstrap/cache/compiled.php:6695
|
||||
|
||||
**Solution**: Make sure that you create an app key, as well as clear configuration cache as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /path/to/cachet
|
||||
$ sudo php artisan key:generate
|
||||
$ sudo php artisan config:cache
|
||||
|
||||
2. You are getting the following error while invoking composer command.
|
||||
|
||||
- danielstjules/stringy 1.10.0 requires ext-mbstring * -the requested PHP extension mbstring is missing from your system.
|
||||
- laravel/framework v5.1.8 requires ext-mbstring * -the requested PHP extension mbstring is missing from your system.
|
||||
- league/commonmark 0.10.0 requires ext-mbstring * -the requested PHP extension mbstring is missing from your system.
|
||||
|
||||
**Solution**: Make sure to install the required PHP extension mbstring on your system which is compatible with your PHP. On Red Hat based system, since we installed PHP from REMI-56 repository, we install the extension from the same repository.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum --enablerepo=remi-php56 install php-mbstring
|
||||
|
||||
3. You are getting a blank page while trying to access Cachet status page. The HTTP log shows the following error.
|
||||
|
||||
PHP Fatal error: Uncaught exception 'UnexpectedValueException' with message 'The stream or file "/var/www/cachet/storage/logs/laravel-2015-08-21.log" could not be opened: failed to open stream: Permission denied' in /var/www/cachet/bootstrap/cache/compiled.php:12851
|
||||
|
||||
**Solution**: Try the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ sudo php artisan cache:clear
|
||||
$ sudo chmod -R 777 storage
|
||||
$ sudo composer dump-autoload
|
||||
|
||||
If the above solution does not work, try disabling SELinux:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo setenforce 0
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/setup-system-status-page.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:https://cachethq.io/
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/install-lamp-stack-ubuntu-server.html
|
||||
[3]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-remi-repository-centos-rhel.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/install-lamp-stack-centos.html
|
||||
[5]:http://xmodulo.com/configure-virtual-hosts-apache-http-server.html
|
||||
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-common-services-nagios.html
|
||||
125
sources/tech/20150901 How to Defragment Linux Systems.md
Normal file
125
sources/tech/20150901 How to Defragment Linux Systems.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,125 @@
|
||||
How to Defragment Linux Systems
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There is a common myth that Linux disks never need defragmentation at all. In most cases, this is true, due mostly to the excellent journaling filesystems Linux uses (ext2, 3, 4, btrfs, etc.) to handle the filesystem. However, in some specific cases, fragmentation might still occur. If that happens to you, the solution is fortunately very simple.
|
||||
|
||||
### What is fragmentation? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Fragmentation occurs when a file system updates files in little chunks, but these chunks do not form a contiguous whole and are scattered around the disk instead. This is particularly true for FAT and FAT32 filesystems. It was somewhat mitigated in NTFS and almost never happens in Linux (extX). Here is why.
|
||||
|
||||
In filesystems such as FAT and FAT32, files are written right next to each other on the disk. There is no room left for file growth or updates:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The NTFS leaves somewhat more room between the files, so there is room to grow. As the space between chunks is limited, fragmentation will still occur over time.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux’s journaling filesystems take a different approach. Instead of placing files beside each other, each file is scattered all over the disk, leaving generous amounts of free space between each file. There is sufficient room for file updates/growth and fragmentation rarely occurs.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, if fragmentation does happen, most Linux filesystems would attempt to shuffle files and chunks around to make them contiguous again.
|
||||
|
||||
### Disk fragmentation on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
Disk fragmentation seldom occurs in Linux unless you have a small hard drive, or it is running out of space. Some possible fragmentation cases include:
|
||||
|
||||
- if you edit large video files or raw image files, and disk space is limited
|
||||
- if you use older hardware like an old laptop, and you have a small hard drive
|
||||
- if your hard drives start filling up (above 85% used)
|
||||
- if you have many small partitions cluttering your home folder
|
||||
|
||||
The best solution is to buy a larger hard drive. If it’s not possible, this is where defragmentation becomes useful.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to check for fragmentation ###
|
||||
|
||||
The `fsck` command will do this for you – that is, if you have an opportunity to run it from a live CD, with **all affected partitions unmounted**.
|
||||
|
||||
This is very important: **RUNNING FSCK ON A MOUNTED PARTITION CAN AND WILL SEVERELY DAMAGE YOUR DATA AND YOUR DISK**.
|
||||
|
||||
You have been warned. Before proceeding, make a full system backup.
|
||||
|
||||
**Disclaimer**: The author of this article and Make Tech Easier take no responsibility for any damage to your files, data, system, or any other damage, caused by your actions after following this advice. You may proceed at your own risk. If you do proceed, you accept and acknowledge this.
|
||||
|
||||
You should just boot into a live session (like an installer disk, system rescue CD, etc.) and run `fsck` on your UNMOUNTED partitions. To check for any problems, run the following command with root permission:
|
||||
|
||||
fsck -fn [/path/to/your/partition]
|
||||
|
||||
You can check what the `[/path/to/your/partition]` is by running
|
||||
|
||||
sudo fdisk -l
|
||||
|
||||
There is a way to run `fsck` (relatively) safely on a mounted partition – that is by using the `-n` switch. This will result in a read only file system check without touching anything. Of course, there is no guarantee of safety here, and you should only proceed after creating a backup. On an ext2 filesystem, running
|
||||
|
||||
sudo fsck.ext2 -fn /path/to/your/partition
|
||||
|
||||
would result in plenty of output – most of them error messages resulting from the fact that the partition is mounted. In the end it will give you fragmentation related information.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If your fragmentation is above 20%, you should proceed to defragment your system.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to easily defragment Linux filesystems ###
|
||||
|
||||
All you need to do is to back up **ALL** your files and data to another drive (by manually **copying** them over), format the partition, and copy your files back (don’t use a backup program for this). The journalling file system will handle them as new files and place them neatly to the disk without fragmentation.
|
||||
|
||||
To back up your files, run
|
||||
|
||||
cp -afv [/path/to/source/partition]/* [/path/to/destination/folder]
|
||||
|
||||
Mind the asterix (*); it is important.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: It is generally agreed that to copy large files or large amounts of data, the dd command might be best. This is a very low level operation and does copy everything “as is”, including the empty space, and even the junk left over. This is not what we want, so it is probably better to use `cp`.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you only need to remove all the original files.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo rm -rf [/path/to/source/partition]/*
|
||||
|
||||
**Optional**: you can fill the empty space with zeros. You could achieve this with formatting as well, but if for example you did not copy the whole partition, only large files (which are most likely to cause fragmentation), this might not be an option.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=[/path/to/source/partition]/temp-zero.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Wait for it to finish. You could also monitor the progress with `pv`.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install pv
|
||||
sudo pv -tpreb | of=[/path/to/source/partition]/temp-zero.txt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
When it is done, just delete the temporary file.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo rm [/path/to/source/partition]/temp-zero.txt
|
||||
|
||||
After you zeroed out the empty space (or just skipped that step entirely), copy your files back, reversing the first cp command:
|
||||
|
||||
cp -afv [/path/to/original/destination/folder]/* [/path/to/original/source/partition]
|
||||
|
||||
### Using e4defrag ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you prefer a simpler approach, install `e2fsprogs`,
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install e2fsprogs
|
||||
|
||||
and run `e4defrag` as root on the affected partition. If you don’t want to or cannot unmount the partition, you can use its mount point instead of its path. To defragment your whole system, run
|
||||
|
||||
sudo e4defrag /
|
||||
|
||||
It is not guaranteed to succeed while mounted (you should also stop using your system while it is running), but it is much easier than copying all files away and back.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Fragmentation should rarely be an issue on a Linux system due to the the journalling filesystem’s efficient data handling. If you do run into fragmentation due to any circumstances, there are simple ways to reallocate your disk space like copying all files away and back or using `e4defrag`. It is important, however, to keep your data safe, so before attempting any operation that would affect all or most of your files, make sure you make a backup just to be on the safe side.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.maketecheasier.com/defragment-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Attila Orosz][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.maketecheasier.com/author/attilaorosz/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
How to automatically dim your screen on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
When you start spending the majority of your time in front of a computer, natural questions start arising. Is this healthy? How can I diminish the strain on my eyes? Why is the sunlight burning me? Although active research is still going on to answer these questions, a lot of programmers have already adopted a few applications to make their daily habits a little healthier for their eyes. Among those applications, there are two which I found particularly interesting: Calise and Redshift.
|
||||
|
||||
### Calise ###
|
||||
|
||||
In and out of development limbo, [Calise][1] stands for "Camera Light Sensor." In other terms, it is an open source program that computes the best backlight level for your screen based on the light intensity received by your webcam. And for more precision, Calise is capable of taking in account the weather in your area based on your geographical coordinates. What I like about it is the compatibility with every desktops, even non-X ones.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It comes with a command line interface and a GUI, supports multiple user profiles, and can even export its data to CSV. After installation, you will have to calibrate it quickly before the magic happens.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
What is less likeable is unfortunately that if you are as paranoid as I am, you have a little piece of tape in front of your webcam, which greatly affects Calise's precision. But that aside, Calise is a great application, which deserves our attention and support. As I mentioned earlier, it has gone through some rough patches in its development schedule over the last couple of years, so I really hope that this project will continue.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Redshift ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you already considered decreasing the strain on your eyes caused by your screen, it is possible that you have heard of f.lux, a free proprietary software that modifies the luminosity and color scheme of your display based on the time of the day. However, if you really prefer open source software, there is an alternative: [Redshift][2]. Inspired by f.lux, Redshift also alters the color scheme and luminosity to enhance the experience of sitting in front of your screen at night. On startup, you can configure it with you geographic position as longitude and latitude, and then let it run in tray. Redshift will smoothly adjust the color scheme or your screen based on the position of the sun. At night, you will see the screen's color temperature turn towards red, making it a lot less painful for your eyes.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Just like Calise, it proposes a command line interface as well as a GUI client. To start Redshift quickly, just use the command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ redshift -l [LAT]:[LON]
|
||||
|
||||
Replacing [LAT]:[LON] by your latitude and longitude.
|
||||
|
||||
However, it is also possible to input your coordinates by GPS via the gpsd module. For Arch Linux users, I recommend this [wiki page][3].
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
To conclude, Linux users have no excuse for not taking care of their eyes. Calise and Redshift are both amazing. I really hope that their development will continue and that they get the support they deserve. Of course, there are more than just two programs out there to fulfill the purpose of protecting your eyes and staying healthy, but I feel that Calise and Redshift are a good start.
|
||||
|
||||
If there is a program that you really like and that you use regularly to reduce the strain on your eyes, please let us know in the comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/automatically-dim-your-screen-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Adrien Brochard][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/adrien
|
||||
[1]:http://calise.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[2]:http://jonls.dk/redshift/
|
||||
[3]:https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/Redshift#Automatic_location_based_on_GPS
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
||||
Install The Latest Linux Kernel in Ubuntu Easily via A Script
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Want to install the latest Linux Kernel? A simple script can always do the job and make things easier in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Michael Murphy has created a script makes installing the latest RC, stable, or lowlatency Kernel easier in Ubuntu. The script asks some questions and automatically downloads and installs the latest Kernel packages from [Ubuntu kernel mainline page][1].
|
||||
|
||||
### Install / Upgrade Linux Kernel via the Script: ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. Download the script from the right sidebar of the [github page][2] (click the “Download Zip” button).
|
||||
|
||||
2. Decompress the Zip archive by right-clicking on it in your user Downloads folder and select “Extract Here”.
|
||||
|
||||
3. Navigate to the result folder in terminal by right-clicking on that folder and select “Open in Terminal”:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
It opens a terminal window and automatically navigates into the result folder. If you **DON’T** find the “Open in Terminal” option, search for and install `nautilus-open-terminal` in Ubuntu Software Center and then log out and back in (or run `nautilus -q` command in terminal instead to apply changes).
|
||||
|
||||
4. When you’re in terminal, give the script executable permission for once.
|
||||
|
||||
chmod +x *
|
||||
|
||||
FINALLY run the script every time you want to install / upgrade Linux Kernel in Ubuntu:
|
||||
|
||||
./*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
I use * instead of the SCRIPT NAME in both commands since it’s the only file in that folder.
|
||||
|
||||
If the script runs successfully, restart your computer when done.
|
||||
|
||||
### Revert back and Uninstall the new Kernel: ###
|
||||
|
||||
To revert back and remove the new kernel for any reason, restart your computer and select boot with the old kernel entry under **Advanced Options** menu when you’re at Grub boot-loader.
|
||||
|
||||
When it boots up, see below section.
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Remove the old (or new) Kernels: ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Synaptic Package Manager from Ubuntu Software Center.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Launch Synaptic Package Manager and do:
|
||||
|
||||
- click the **Reload** button in case you want to remove the new kernel.
|
||||
- select **Status -> Installed** on the left pane to make search list clear.
|
||||
- search **linux-image**- using Quick filter box.
|
||||
- select a kernel image “linux-image-x.xx.xx-generic” and mark for (complete) removal
|
||||
- finally apply changes
|
||||
|
||||
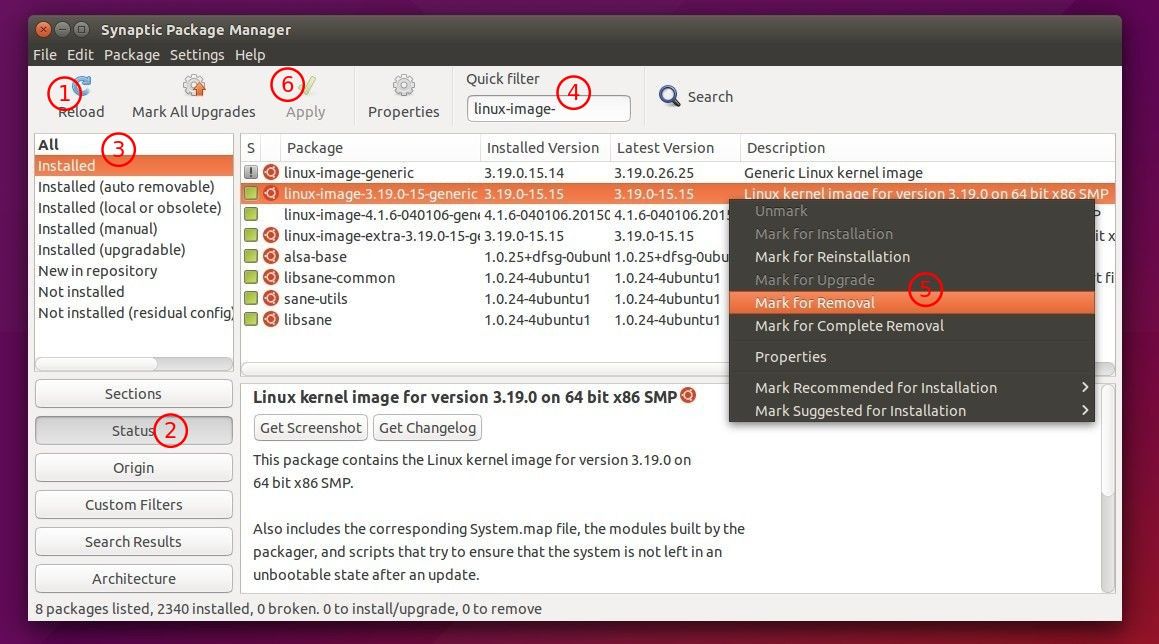
|
||||
|
||||
Repeat until you removed all unwanted kernels. DON’T carelessly remove the current running kernel, check it out via `uname -r` (see below pic.) command.
|
||||
|
||||
For Ubuntu Server, you may run below commands one by one:
|
||||
|
||||
uname -r
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg -l | grep linux-image-
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get autoremove KERNEL_IMAGE_NAME
|
||||
|
||||
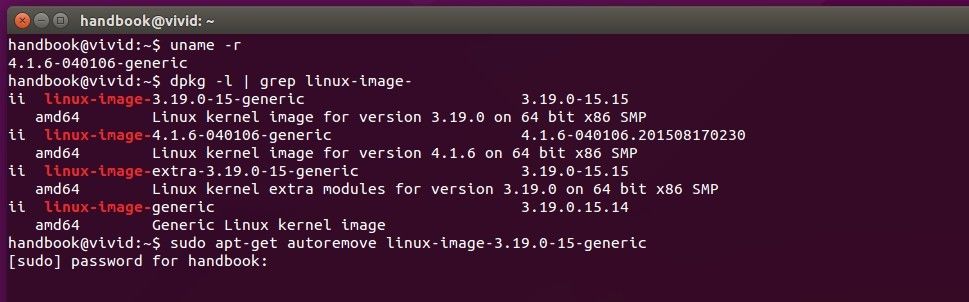
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/2015/08/install-latest-kernel-script/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ji m][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/about/
|
||||
[1]:http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/
|
||||
[2]:https://gist.github.com/mmstick/8493727
|
||||
@ -1,178 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FSSlc Translating
|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA Series: Installing, Configuring and Securing a Web and FTP Server – Part 9
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A web server (also known as a HTTP server) is a service that handles content (most commonly web pages, but other types of documents as well) over to a client in a network.
|
||||
|
||||
A FTP server is one of the oldest and most commonly used resources (even to this day) to make files available to clients on a network in cases where no authentication is necessary since FTP uses username and password without encryption.
|
||||
|
||||
The web server available in RHEL 7 is version 2.4 of the Apache HTTP Server. As for the FTP server, we will use the Very Secure Ftp Daemon (aka vsftpd) to establish connections secured by TLS.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA: Installing, Configuring and Securing Apache and FTP – Part 9
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we will explain how to install, configure, and secure a web server and a FTP server in RHEL 7.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing Apache and FTP Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide we will use a RHEL 7 server with a static IP address of 192.168.0.18/24. To install Apache and VSFTPD, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install httpd vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
When the installation completes, both services will be disabled initially, so we need to start them manually for the time being and enable them to start automatically beginning with the next boot:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start httpd
|
||||
# systemctl enable httpd
|
||||
# systemctl start vsftpd
|
||||
# systemctl enable vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, we have to open ports 80 and 21, where the web and ftp daemons are listening, respectively, in order to allow access to those services from the outside:
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=ftp --permanent
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
To confirm that the web server is working properly, fire up your browser and enter the IP of the server. You should see the test page:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Confirm Apache Web Server
|
||||
|
||||
As for the ftp server, we will have to configure it further, which we will do in a minute, before confirming that it’s working as expected.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring and Securing Apache Web Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
The main configuration file for Apache is located in `/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf`, but it may rely on other files present inside `/etc/httpd/conf.d`.
|
||||
|
||||
Although the default configuration should be sufficient for most cases, it’s a good idea to become familiar with all the available options as described in the [official documentation][1].
|
||||
|
||||
As always, make a backup copy of the main configuration file before editing it:
|
||||
|
||||
# cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf.$(date +%Y%m%d)
|
||||
|
||||
Then open it with your preferred text editor and look for the following variables:
|
||||
|
||||
- ServerRoot: the directory where the server’s configuration, error, and log files are kept.
|
||||
- Listen: instructs Apache to listen on specific IP address and / or ports.
|
||||
- Include: allows the inclusion of other configuration files, which must exist. Otherwise, the server will fail, as opposed to the IncludeOptional directive, which is silently ignored if the specified configuration files do not exist.
|
||||
- User and Group: the name of the user/group to run the httpd service as.
|
||||
- DocumentRoot: The directory out of which Apache will serve your documents. By default, all requests are taken from this directory, but symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations.
|
||||
- ServerName: this directive sets the hostname (or IP address) and port that the server uses to identify itself.
|
||||
|
||||
The first security measure will consist of creating a dedicated user and group (i.e. tecmint/tecmint) to run the web server as and changing the default port to a higher one (9000 in this case):
|
||||
|
||||
ServerRoot "/etc/httpd"
|
||||
Listen 192.168.0.18:9000
|
||||
User tecmint
|
||||
Group tecmint
|
||||
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"
|
||||
ServerName 192.168.0.18:9000
|
||||
|
||||
You can test the configuration file with.
|
||||
|
||||
# apachectl configtest
|
||||
|
||||
and if everything is OK, then restart the web server.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart httpd
|
||||
|
||||
and don’t forget to enable the new port (and disable the old one) in the firewall:
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=80/tcp --permanent
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=9000/tcp --permanent
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
Note that, due to SELinux policies, you can only use the ports returned by
|
||||
|
||||
# semanage port -l | grep -w '^http_port_t'
|
||||
|
||||
for the web server.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to use another port (i.e. TCP port 8100), you will have to add it to SELinux port context for the httpd service:
|
||||
|
||||
# semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 8100
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Add Apache Port to SELinux Policies
|
||||
|
||||
To further secure your Apache installation, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. The user Apache is running as should not have access to a shell:
|
||||
|
||||
# usermod -s /sbin/nologin tecmint
|
||||
|
||||
2. Disable directory listing in order to prevent the browser from displaying the contents of a directory if there is no index.html present in that directory.
|
||||
|
||||
Edit `/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf` (and the configuration files for virtual hosts, if any) and make sure that the Options directive, both at the top and at Directory block levels, is set to None:
|
||||
|
||||
Options None
|
||||
|
||||
3. Hide information about the web server and the operating system in HTTP responses. Edit /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
ServerTokens Prod
|
||||
ServerSignature Off
|
||||
|
||||
Now you are ready to start serving content from your /var/www/html directory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuring and Securing FTP Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
As in the case of Apache, the main configuration file for Vsftpd `(/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf)` is well commented and while the default configuration should suffice for most applications, you should become acquainted with the documentation and the man page `(man vsftpd.conf)` in order to operate the ftp server more efficiently (I can’t emphasize that enough!).
|
||||
|
||||
In our case, these are the directives used:
|
||||
|
||||
anonymous_enable=NO
|
||||
local_enable=YES
|
||||
write_enable=YES
|
||||
local_umask=022
|
||||
dirmessage_enable=YES
|
||||
xferlog_enable=YES
|
||||
connect_from_port_20=YES
|
||||
xferlog_std_format=YES
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES
|
||||
allow_writeable_chroot=YES
|
||||
listen=NO
|
||||
listen_ipv6=YES
|
||||
pam_service_name=vsftpd
|
||||
userlist_enable=YES
|
||||
tcp_wrappers=YES
|
||||
|
||||
By using `chroot_local_user=YES`, local users will be (by default) placed in a chroot’ed jail in their home directory right after login. This means that local users will not be able to access any files outside their corresponding home directories.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, to allow ftp to read files in the user’s home directory, set the following SELinux boolean:
|
||||
|
||||
# setsebool -P ftp_home_dir on
|
||||
|
||||
You can now connect to the ftp server using a client such as Filezilla:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Check FTP Connection
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the `/var/log/xferlo`g log records downloads and uploads, which concur with the above directory listing:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Monitor FTP Download and Upload
|
||||
|
||||
Read Also: [Limit FTP Network Bandwidth Used by Applications in a Linux System with Trickle][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial we have explained how to set up a web and a ftp server. Due to the vastness of the subject, it is not possible to cover all the aspects of these topics (i.e. virtual web hosts). Thus, I recommend you also check other excellent articles in this website about [Apache][3].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/rhcsa-series-install-and-secure-apache-web-server-and-ftp-in-rhel/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/manage-and-limit-downloadupload-bandwidth-with-trickle-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.google.com/cse?cx=partner-pub-2601749019656699:2173448976&ie=UTF-8&q=virtual+hosts&sa=Search&gws_rd=cr&ei=Dy9EVbb0IdHisASnroG4Bw#gsc.tab=0&gsc.q=apache
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
FSSlc Translating
|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA Series: Firewall Essentials and Network Traffic Control Using FirewallD and Iptables – Part 11
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
In simple words, a firewall is a security system that controls the incoming and outgoing traffic in a network based on a set of predefined rules (such as the packet destination / source or type of traffic, for example).
|
||||
@ -188,4 +190,4 @@ via: http://www.tecmint.com/firewalld-vs-iptables-and-control-network-traffic-in
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/configure-iptables-firewall/
|
||||
[4]:https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-US/Red_Hat_Enterprise_Linux/7/html/Security_Guide/sec-Using_Firewalls.html
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/rhcsa-series-install-and-secure-apache-web-server-and-ftp-in-rhel/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/firewalld-rules-for-centos-7/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/firewalld-rules-for-centos-7/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,432 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by tnuoccalanosrep
|
||||
Linux文件系统结构 v2.0
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux中的文件是什么?它的文件系统又是什么?那些配置文件又在哪里?我下载好的程序保存在哪里了?好了,上图简明地阐释了Linux的文件系统的层次关系。当你苦于寻找配置文件或者二进制文件的时候,这便显得十分有用了。我在下方添加了一些解释以及例子,但“篇幅过长,没有阅读”。
|
||||
|
||||
有一种情况便是当你在系统中获取配置以及二进制文件时,出现了不一致性问题,如果你是一个大型组织,或者只是一个终端用户,这也有可能会破坏你的系统(比如,二进制文件运行在就旧的库文件上了)。若然你在你的Linux系统上做安全审计([security audit of your Linux system][1])的话,你将会发现它很容易遭到不同的攻击。所以,清洁操作(无论是Windows还是Linux)都显得十分重要。
|
||||
### What is a file in Linux? ###
|
||||
Linux的文件是什么?
|
||||
对于UNIX系统来说(同样适用于Linux),以下便是对文件简单的描述:
|
||||
> 在UNIX系统中,一切皆为文件;若非文件,则为进程
|
||||
|
||||
> 这种定义是比较正确的,因为有些特殊的文件不仅仅是普通文件(比如命名管道和套接字),不过为了让事情变的简单,“一切皆为文件”也是一个可以让人接受的说法。Linux系统也像UNXI系统一样,将文件和目录视如同物,因为目录只是一个包含了其他文件名的文件而已。程序,服务,文本,图片等等,都是文件。对于系统来说,输入和输出设备,基本上所有的设备,都被当做是文件。
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
- Version 2.0 – 17-06-2015
|
||||
- – Improved: 添加标题以及版本历史
|
||||
- – Improved: 添加/srv,/meida和/proc
|
||||
- – Improved: 更新了反映当前的Linux文件系统的描述
|
||||
- – Fixed: 多处的打印错误
|
||||
- – Fixed: 外观和颜色
|
||||
- Version 1.0 – 14-02-2015
|
||||
- – Created: 基本的图表
|
||||
- – Note: 摒弃更低的版本
|
||||
|
||||
### Download Links ###
|
||||
以下是结构图的下载地址。如果你需要其他结构,请跟原作者联系,他会尝试制作并且上传到某个地方以供下载
|
||||
- [Large (PNG) Format – 2480×1755 px – 184KB][2]
|
||||
- [Largest (PDF) Format – 9919x7019 px – 1686KB][3]
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**: PDF格式文件是打印的最好选择,因为它画质很高。
|
||||
### Linux 文件系统描述 ###
|
||||
为了有序地管理那些文件,人们习惯把这些文件当做是硬盘上的有序的类树结构体,正如我们熟悉的'MS-DOS'(硬盘操作系统)。大的分枝包括更多的分枝,分枝的末梢是树的叶子或者普通的文件。现在我们将会以这树形图为例,但晚点我们会发现为什么这不是一个完全准确的一幅图。
|
||||
注:表格
|
||||
<table cellspacing="2" border="4" style="border-collapse: collapse; width: 731px; height: 2617px;">
|
||||
<thead>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<th scope="col">Directory(目录)</th>
|
||||
<th scope="col">Description(描述)</th>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</thead>
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td><i>主层次</i> 的根,也是整个文件系统层次结构的根目录</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/bin</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>存放在单用户模式可用的必要命令二进制文件,对于所有用户而言,则是像cat,ls,cp等等的文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/boot</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>存放引导加载程序文件,例如kernels,initrd等</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/dev</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>存放必要的设备文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/etc</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>存放主机特定的系统范围内的配置文件。其实这里有个关于它名字本身意义上的的争议。在贝尔实验室的早期UNIX实施文档版本中,/etc表示是“其他目录”,因为从历史上看,这个目录是存放各种不属于其他目录的文件(然而,FSH(文件系统目录标准)限定 /ect是用于存放静态配置文件,这里不该存有二进制文件)。早期文档出版后,这个目录名又重新定义成不同的形式。近期的解释中包含着诸如“可编辑文本配置”或者“额外的工具箱”这样的重定义</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/opt</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>存储着新增包的配置文件 <code>/opt/</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/sgml</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>存放配置文件,比如目录,还有那些处理SGML(译者注:标准通用标记语言)的软件的配置文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/X11</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>X Window系统的配置文件,版本号为11</td>
|
||||
<td></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/xml</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>配置文件,比如目录,处理XML(译者注:可扩展标记语言)的软件的配置文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/home</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>用户的主目录,包括保存的文件, 个人配置, 等等.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/lib</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td><code>/bin/</code> and <code>/sbin/</code>中的二进制文件必不可少的库文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/lib<qual></code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>备用格式的必要的库文件. 这样的目录视可选的,但如果他们存在的话, 他们还有一些要求.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/media</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>可移动的多媒体(如CD-ROMs)的挂载点.(出现于 FHS-2.3)</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/mnt</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>临时挂载的文件系统</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/opt</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>自定义应用程序软件包</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/proc</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>以文件形式提供进程以及内核信息的虚拟文件系统,在Linux中,对应进程文件系统的挂载点</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/root</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>根用户的主目录</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/sbin</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>必要系统二进制文件, <i>比如</i>, init, ip, mount.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/srv</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>系统提供的站点特定数据</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/tmp</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>临时文件 (另见 <code>/var/tmp</code>). 通常在系统重启后删除</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/usr</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td><i>二级层级</i> 存储用户的只读数据; 包含(多)用户主要的公共文件以及应用程序</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/bin</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>非必要的命令二进制文件 (在单用户模式中不需要用到的); 用于所有用户.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/include</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>标准的包含文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/lib</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>库文件,用于<code>/usr/bin/</code> 和 <code>/usr/sbin/</code>.中的二进制文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/lib<qual></code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>备用格式库(可选的).</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/local</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td><i>三级层次</i> 用于本地数据, 具体到该主机上的.通常会有下一个子目录, <i>比如</i>, <code>bin/</code>, <code>lib/</code>, <code>share/</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/sbin</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>非必要系统的二进制文件, <i>比如</i>,用于不同网络服务的守护进程</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/share</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>独立架构的 (共享) 数据.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/src</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>源代码, <i>比如</i>, 内核源文件以及与它相关的头文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/X11R6</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>X Window系统,版本号:11,发行版本:6</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/var</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>各式各样的文件,一些随着系统常规操作而持续改变的文件就放在这里,比如日志文件,脱机文件,还有临时的电子邮件文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/cache</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>应用程序缓存数据. 这些数据是根据I/O(输入/输出)的耗时结果或者是运算生成的.这些应用程序是可以重新生成或者恢复数据的.当没有数据丢失的时候,可以删除缓存文件.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/lib</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>状态信息.这些信息随着程序的运行而不停地改变,比如,数据库,系统元数据的打包等等</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/lock</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>锁文件。这些文件会持续监控正在使用的资源</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/log</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>日志文件. 包含各种日志.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/mail</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>内含用户邮箱的相关文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/opt</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>来自附加包的各种数据都会存储在 <code>/opt/</code>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/run</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>Information about the running system since last boot, <i>e.g.</i>, currently logged-in users and running <a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Daemon_%28computing%29">daemons</a>.</td>
|
||||
<td>存放当前系统上次启动的相关信息, <i>例如</i>, 当前登入的用户以及当前运行的<a href="http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Daemon_%28computing%29">daemons(守护进程)</a>.</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/spool</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>该spool主要用于存放将要被处理的任务, <i>比如</i>, 打印队列以及邮件传出队列</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/mail</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>过时的位置,用于放置用户邮箱文件</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><dl>
|
||||
<dd>
|
||||
<dl>
|
||||
<dd><code>/tmp</code></dd>
|
||||
</dl>
|
||||
</dd>
|
||||
</dl></td>
|
||||
<td>存放重启之前的临时接口</td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
|
||||
### Types of files in Linux ###
|
||||
### Linux的文件类型 ###
|
||||
大多数文件也仅仅是文件,他们被称为`regular`文件;他们包含普通数据,比如,文本,可执行文件,或者程序,程序输入或输出文件等等
|
||||
While it is reasonably safe to suppose that everything you encounter on a Linux system is a file, there are some exceptions.
|
||||
虽然你可以认为“在Linux中,一切你看到的皆为文件”这个观点相当保险,但这里仍有着一些例外。
|
||||
|
||||
- `目录`:由其他文件组成的文件
|
||||
- `特殊文件`:用于输入和输出的途径。大多数特殊文件都储存在`/dev`中,我们将会在后面讨论这个问题。
|
||||
- `链接文件`:让文件或者目录在系统文件树结构上可见的机制。我们将详细地讨论这个链接文件。
|
||||
- `(域)套接字`:特殊的文件类型,和TCP/IP协议中的套接字有点像,提供进程网络,并受文件系统的访问控制机制保护。
|
||||
-`命名管道` : 或多或少有点像sockets(套接字),提供一个进程间的通信机制,而不用网络套接字协议。
|
||||
### File system in reality ###
|
||||
### 现实中的文件系统 ###
|
||||
对于大多数用户和常规系统管理任务而言,"文件和目录是一个有序的类树结构"是可以接受的。然而,对于电脑而言,它是不会理解什么是树,或者什么是树结构。
|
||||
|
||||
每个分区都有它自己的文件系统。想象一下,如果把那些文件系统想成一个整体,我们可以构思一个关于整个系统的树结构,不过这并没有这么简单。在文件系统中,一个文件代表着一个`inode`(索引节点),一种包含着构建文件的实际数据信息的序列号:这些数据表示文件是属于谁的,还有它在硬盘中的位置。
|
||||
|
||||
每个分区都有一套属于他们自己的inodes,在一个系统的不同分区中,可以存在有相同inodes的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
每个inode都表示着一种在硬盘上的数据结构,保存着文件的属性,包括文件数据的物理地址。当硬盘被格式化并用来存储数据时(通常发生在初始系统安装过程,或者是在一个已经存在的系统中添加额外的硬盘),每个分区都会创建关于inodes的固定值。这个值表示这个分区能够同时存储各类文件的最大数量。我们通常用一个inode去映射2-8k的数据块。当一个新的文件生成后,它就会获得一个空闲的indoe。在这个inode里面存储着以下信息:
|
||||
|
||||
- 文件属主和组属主
|
||||
- 文件类型(常规文件,目录文件......)
|
||||
- 文件权限
|
||||
- 创建、最近一次读文件和修改文件的时间
|
||||
- inode里该信息被修改的时间
|
||||
- 文件的链接数(详见下一章)
|
||||
- 文件大小
|
||||
- 文件数据的实际地址
|
||||
|
||||
唯一不在inode的信息是文件名和目录。它们存储在特殊的目录文件。通过比较文件名和inodes的数目,系统能够构造出一个便于用户理解的树结构。用户可以通过ls -i查看inode的数目。在硬盘上,inodes有他们独立的空间。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.blackmoreops.com/2015/06/18/linux-file-system-hierarchy-v2-0/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/tnuoccalanosrep)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.blackmoreops.com/2015/02/15/in-light-of-recent-linux-exploits-linux-security-audit-is-a-must/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.blackmoreops.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/Linux-file-system-hierarchy-v2.0-2480px-blackMORE-Ops.png
|
||||
[3]:http://www.blackmoreops.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/Linux-File-System-Hierarchy-blackMORE-Ops.pdf
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,294 @@
|
||||
如何部署一个你的公共系统状态页面
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如果你是一个系统管理员,负责关键的IT基础设置或你公司的服务,你将明白有效的沟通在日常任务中的重要性。假设你的线上存储服务器故障了。你希望团队所有人达成共识你好尽快的解决问题。当你忙来忙去时,你不想一半的人问你为什么他们不能访问他们的文档。当一个维护计划快到时间了你想在计划前提醒相关人员,这样避免了不必要的开销。
|
||||
|
||||
这一切的要求或多或少改进了你和你的团队,用户和你的服务的沟通渠道。一个实现它方法是维护一个集中的系统状态页面,故障停机详情,进度更新和维护计划会被报告和记录。这样,在故障期间你避免了不必要的打扰,也有一些相关方提供的资料和任何选状态更新择性加入。
|
||||
|
||||
一个不错的**开源, 自承载系统状态页面**是is [Cachet][1]。在这个教程,我将要描述如何用Cachet部署一个自承载系统状态页面。
|
||||
|
||||
### Cachet 特性 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在详细的配置Cachet之前,让我简单的介绍一下它的主要特性。
|
||||
|
||||
- **全JSON API**:Cachet API允许你使用任意外部程序或脚本(例如,uptime脚本)链接到Cachet来报告突发事件或自动更新状态。
|
||||
- **认证**:Cachet支持基础认证和JSON API的API令牌,所以只有认证用户可以更新状态页面。
|
||||
- **衡量系统**:这通常用来展现随着时间推移的自定义数据(例如,服务器负载或者相应时间)。
|
||||
- **通知**:你可以随意的发送通知邮件,报告事件给任一注册了状态页面的人。
|
||||
- **多语言**:状态也可以被转换为11种不同的语言。
|
||||
- **双因子认证**:这允许你使用Google的双因子认证管理账户锁定你的Cachet(什么事Google?呵呵!)。
|
||||
- **支持交叉数据库**:你可以选择MySQL,SQLite,Redis,APC和PostgreSQL作为后端存储。
|
||||
|
||||
剩下的教程,我说明如何在Linux上安装配置Cachet。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一步:下载和安装Cachet ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cachet需要一个web服务器和一个后端数据库来运转。在这个教程中,我将使用LAMP架构。这里有特定发行版安装Cachet和LAMP架构的指令。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Debian, Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install curl git apache2 mysql-server mysql-client php5 php5-mysql
|
||||
$ sudo git clone https://github.com/cachethq/Cachet.git /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ cd /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ sudo git checkout v1.1.1
|
||||
$ sudo chown -R www-data:www-data .
|
||||
|
||||
在基于Debian的系统上更多详细的设置LAMP架构,参考这个[教程][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fedora, CentOS 或 RHEL ####
|
||||
|
||||
在基于Red Hat系统上,你首先需要[设置REMI资源库][3](以满足PHP版本需求)。然后执行下面命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install curl git httpd mariadb-server
|
||||
$ sudo yum --enablerepo=remi-php56 install php php-mysql php-mbstring
|
||||
$ sudo git clone https://github.com/cachethq/Cachet.git /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ cd /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ sudo git checkout v1.1.1
|
||||
$ sudo chown -R apache:apache .
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=http
|
||||
$ sudo firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl enable httpd.service; sudo systemctl start httpd.service
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl enable mariadb.service; sudo systemctl start mariadb.service
|
||||
|
||||
在基于Red Hat系统上更多详细设置LAMP,参考这个[教程][4]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置Cachet的后端数据库###
|
||||
|
||||
下一步是配置后端数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
登陆到MySQL/MariaDB服务,然后创建一个空的数据库称为‘cachet’。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mysql -uroot -p
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> create database cachet;
|
||||
mysql> quit
|
||||
|
||||
现在用一个样本配置文件创建一个Cachet配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ sudo mv .env.example .env
|
||||
|
||||
在.env文件里,填写你自己设置的数据库信息(例如,DB\_\*)。其他的字段先不改变。
|
||||
|
||||
APP_ENV=production
|
||||
APP_DEBUG=false
|
||||
APP_URL=http://localhost
|
||||
APP_KEY=SomeRandomString
|
||||
|
||||
DB_DRIVER=mysql
|
||||
DB_HOST=localhost
|
||||
DB_DATABASE=cachet
|
||||
DB_USERNAME=root
|
||||
DB_PASSWORD=<root-password>
|
||||
|
||||
CACHE_DRIVER=apc
|
||||
SESSION_DRIVER=apc
|
||||
QUEUE_DRIVER=database
|
||||
|
||||
MAIL_DRIVER=smtp
|
||||
MAIL_HOST=mailtrap.io
|
||||
MAIL_PORT=2525
|
||||
MAIL_USERNAME=null
|
||||
MAIL_PASSWORD=null
|
||||
MAIL_ADDRESS=null
|
||||
MAIL_NAME=null
|
||||
|
||||
REDIS_HOST=null
|
||||
REDIS_DATABASE=null
|
||||
REDIS_PORT=null
|
||||
|
||||
### 第三步:安装PHP依赖和执行数据库迁移 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下面,我们将要安装必要的PHP依赖包。所以我们将使用composer。如果你的系统还没有安装composer,先安装它:
|
||||
|
||||
$ curl -sS https://getcomposer.org/installer | sudo php -- --install-dir=/usr/local/bin --filename=composer
|
||||
|
||||
现在开始用composer安装PHP依赖包。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ sudo composer install --no-dev -o
|
||||
|
||||
下面执行一次数据库迁移。这一步将我们早期创建的必要表填充到数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo php artisan migrate
|
||||
|
||||
假设数据库配置在/var/www/cachet/.env是正确的,数据库迁移应该像下面显示一样完成成功。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
下面,创建一个密钥,它将用来加密进入Cachet的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo php artisan key:generate
|
||||
$ sudo php artisan config:cache
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
生成的应用密钥将自动添加到你的.env文件APP\_KEY变量中。你不需要单独编辑.env。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第四步:配置Apache HTTP服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在到了配置web服务的时候,Cachet将运行在上面。我们使用Apache HTTP服务器,为Cachet创建一个新的[虚拟主机][5]如下所述。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Debian, Ubuntu 或 Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/cachet.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerName cachethost
|
||||
ServerAlias cachethost
|
||||
DocumentRoot "/var/www/cachet/public"
|
||||
<Directory "/var/www/cachet/public">
|
||||
Require all granted
|
||||
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow from all
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||
启用新虚拟主机和mod_rewrite:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo a2ensite cachet.conf
|
||||
$ sudo a2enmod rewrite
|
||||
$ sudo service apache2 restart
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fedora, CentOS 或 RHEL ####
|
||||
|
||||
在基于Red Hat系统上,创建一个虚拟主机文件如下所述。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/httpd/conf.d/cachet.conf
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
<VirtualHost *:80>
|
||||
ServerName cachethost
|
||||
ServerAlias cachethost
|
||||
DocumentRoot "/var/www/cachet/public"
|
||||
<Directory "/var/www/cachet/public">
|
||||
Require all granted
|
||||
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
|
||||
AllowOverride All
|
||||
Order allow,deny
|
||||
Allow from all
|
||||
</Directory>
|
||||
</VirtualHost>
|
||||
|
||||
现在重载Apache配置:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo systemctl reload httpd.service
|
||||
|
||||
### 第五步:配置/etc/hosts来测试Cachet ###
|
||||
|
||||
这时候,初始的Cachet状态页面应该启动运行了,现在测试一下。
|
||||
|
||||
由于Cachet被配置为Apache HTTP服务的虚拟主机,我们需要调整你的客户机的/etc/hosts来访问他。你将从这个客户端电脑访问Cachet页面。
|
||||
|
||||
Open /etc/hosts, and add the following entry.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo vi /etc/hosts
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
<cachet-server-ip-address> cachethost
|
||||
|
||||
上面名为“cachethost”必须匹配Cachet的Apache虚拟主机文件的ServerName。
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试Cachet状态页面 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在你准备好访问Cachet状态页面。在你浏览器地址栏输入http://cachethost。你将被转到初始Cachet状态页如下。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
选择cache/session驱动。这里cache和session驱动两个都选“File”。
|
||||
|
||||
下一步,输入关于状态页面的基本信息(例如,站点名称,域名,时区和语言),以及管理员认证账户。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你的初始状态页将要最终完成。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
继续创建组件(你的系统单位),事件或者任意你想要的维护计划。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,增加一个组件:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
增加一个维护计划:
|
||||
|
||||
公共Cachet状态页就像这样:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
集成SMTP,你可以在状态更新时发送邮件给订阅者。并且你可以完全自定义布局和状态页面使用的CSS和markdown格式。
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Cachet是一个相当易于使用,自托管的状态页面软件。Cachet一个高级特性是支持全JSON API。使用它的RESTful API,Cachet可以轻松连接单独的监控后端(例如,[Nagios][6]),然后回馈给Cachet事件报告并自动更新状态。比起手段管理一个状态页它更快和有效率。
|
||||
|
||||
最后一句,我喜欢提及一个事。用Cachet简单的设置一个花哨的状态页面同时,使用最佳的软件不像安装它那么容易。你需要完全保障所有IT团队习惯准确及时的更新状态页,从而建立公共信息的准确性。同时,你需要教用户去查看状态页面。在今天最后,如果不很好的填充,部署状态页面将没有意义,并且/或者没有一个人查看它。记住这个,当你考虑部署Cachet在你的工作环境中时。
|
||||
|
||||
### 故障排查 ###
|
||||
|
||||
作为奖励,万一你安装Cachet时遇到问题,这有一些有用的故障排查的技巧。
|
||||
|
||||
1. Cachet页面没有加载任何东西,并且你看到如下报错。
|
||||
|
||||
production.ERROR: exception 'RuntimeException' with message 'No supported encrypter found. The cipher and / or key length are invalid.' in /var/www/cachet/bootstrap/cache/compiled.php:6695
|
||||
|
||||
**解决方案**:确保你创建了一个应用密钥,以及明确配置缓存如下所述。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /path/to/cachet
|
||||
$ sudo php artisan key:generate
|
||||
$ sudo php artisan config:cache
|
||||
|
||||
2. 调用composer命令时有如下报错。
|
||||
|
||||
- danielstjules/stringy 1.10.0 requires ext-mbstring * -the requested PHP extension mbstring is missing from your system.
|
||||
- laravel/framework v5.1.8 requires ext-mbstring * -the requested PHP extension mbstring is missing from your system.
|
||||
- league/commonmark 0.10.0 requires ext-mbstring * -the requested PHP extension mbstring is missing from your system.
|
||||
|
||||
**解决方案**:确保安装了必要的PHP扩展mbstring到你的系统上,并且兼容你的PHP。在基于Red Hat的系统上,由于我们从REMI-56库安装PHP,要从同一个库安装扩展。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum --enablerepo=remi-php56 install php-mbstring
|
||||
|
||||
3. 你访问Cachet状态页面时得到一个白屏。HTTP日志显示如下错误。
|
||||
|
||||
PHP Fatal error: Uncaught exception 'UnexpectedValueException' with message 'The stream or file "/var/www/cachet/storage/logs/laravel-2015-08-21.log" could not be opened: failed to open stream: Permission denied' in /var/www/cachet/bootstrap/cache/compiled.php:12851
|
||||
|
||||
**解决方案**:尝试如下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /var/www/cachet
|
||||
$ sudo php artisan cache:clear
|
||||
$ sudo chmod -R 777 storage
|
||||
$ sudo composer dump-autoload
|
||||
|
||||
如果上面的方法不起作用,试试禁止SELinux:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo setenforce 0
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/setup-system-status-page.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[wyangsun](https://github.com/wyangsun)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:https://cachethq.io/
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/install-lamp-stack-ubuntu-server.html
|
||||
[3]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/install-remi-repository-centos-rhel.html
|
||||
[4]:http://xmodulo.com/install-lamp-stack-centos.html
|
||||
[5]:http://xmodulo.com/configure-virtual-hosts-apache-http-server.html
|
||||
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/monitor-common-services-nagios.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 中如何安装/升级 Linux 内核到4.2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Linux 内核4.2在昨天中午被公布。Linus Torvalds 写了 [lkml.org][1]:
|
||||
|
||||
> 通过这周的小的变动,4.2版本应该不会有问题,毕竟这是最后一周,但在这里有几个补丁,4.2延迟一个星期也会引发问题。
|
||||
|
||||
>
|
||||
|
||||
> 所以在这里它是,并且4.3的合并窗口现已开放。我已经早期引入了几个悬而未决的请求,但像往常一样,我会从明天开始处理它们,并会发布完成的时间。
|
||||
|
||||
>
|
||||
|
||||
> 从 rc8 中的 shortlog 非常小,并且是追加的。这个补丁也很完美...
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 新内核 4.2 有哪些改进?: ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 英特尔的x86汇编代码重写
|
||||
- 支持新的 ARM 板和 SoCs
|
||||
- 对 F2FS 的 per-file 加密
|
||||
- 有 AMDGPU 内核 DRM 驱动程序
|
||||
- 使用Radeon DRM 来支持 VCE1 视频编码
|
||||
- 初步支持英特尔的 Broxton Atom SoCs
|
||||
- 支持ARCv2和HS38 CPU内核。
|
||||
- 增加了排队自旋锁的支持
|
||||
- 许多其他的改进和驱动更新。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 中如何下载4.2内核 : ###
|
||||
|
||||
此内核版本的二进制包可供下载链接如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载 4.2 内核(.DEB)][1]
|
||||
|
||||
首先检查你的操作系统类型,32位(i386)的或64位(amd64)的,然后使用下面的方式依次下载并安装软件包:
|
||||
|
||||
1. linux-headers-4.2.0-xxx_all.deb
|
||||
1. linux-headers-4.2.0-xxx-generic_xxx_i386/amd64.deb
|
||||
1. linux-image-4.2.0-xxx-generic_xxx_i386/amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
安装内核后,在终端((Ctrl+Alt+T))运行`sudo update-grub`命令来更新 grub boot-loader。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你需要一个低延迟系统(例如用于录制音频),请下载并安装下面的包:
|
||||
|
||||
1. linux-headers-4.2.0_xxx_all.deb
|
||||
1. linux-headers-4.2.0-xxx-lowlatency_xxx_i386/amd64.deb
|
||||
1. linux-image-4.2.0-xxx-lowlatency_xxx_i386/amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
对于没有图形用户界面的 Ubuntu 服务器,你可以运行下面的命令通过 wget 来逐一抓下载,并通过 dpkg 来安装:
|
||||
|
||||
对于64位的系统请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
cd /tmp/
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.2-unstable/linux-headers-4.2.0-040200_4.2.0-040200.201508301530_all.deb
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.2-unstable/linux-headers-4.2.0-040200-generic_4.2.0-040200.201508301530_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.2-unstable/linux-image-4.2.0-040200-generic_4.2.0-040200.201508301530_amd64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i linux-headers-4.2.0-*.deb linux-image-4.2.0-*.deb
|
||||
|
||||
对于32位的系统,请运行:
|
||||
|
||||
cd /tmp/
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.2-unstable/linux-headers-4.2.0-040200_4.2.0-040200.201508301530_all.deb
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.2-unstable/linux-headers-4.2.0-040200-generic_4.2.0-040200.201508301530_i386.deb
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.2-unstable/linux-image-4.2.0-040200-generic_4.2.0-040200.201508301530_i386.deb
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i linux-headers-4.2.0-*.deb linux-image-4.2.0-*.deb
|
||||
|
||||
最后,重新启动计算机才能生效。
|
||||
|
||||
要恢复或删除旧的内核,请参阅[通过脚本安装内核][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/2015/08/upgrade-kernel-4-2-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ji m][a]
|
||||
译者:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/strugglingyouth)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/about/
|
||||
[1]:https://lkml.org/lkml/2015/8/30/96
|
||||
[2]:http://kernel.ubuntu.com/~kernel-ppa/mainline/v4.2-unstable/
|
||||
[3]:http://ubuntuhandbook.org/index.php/2015/08/install-latest-kernel-script/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,188 @@
|
||||
在 Debian 或者 Ubuntu 上配置高性能的 HHVM、Nginx/Apache 和 MariaDB
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
HHVM全称为 HipHop Virtual Machine, 它是一个由 running Hack(一种编程语言)和 PHP的相关应用组成的开源虚拟机。HHVM 在保证了 PHP 程序员最关注的高灵活性的要求下,通过使用最新编译结果的方式来达到一个客观的性能。到目前为止,HHVM 为 FaceBook 在 HTTP 请求的吞吐量上提高了9倍的性能,在内存的占用上,减少了5倍左右的内存占用。
|
||||
|
||||
+ [APC (Alternative PHP Cache)][1].
|
||||
|
||||
HHVM can also be used along with a FastCGI-based web-server like Nginx or Apache.
|
||||
同时,HHVM 也可以通过 FastCGI 接口,与像 Nginx 或者 Apache 进行集成。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装 HHVM,Nginx和 Apache 还有 MariaDB
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我们一起来进行 Nginx/Apache web 服务器、 数据库服务器 MariaDB 和 HHVM 的设置。设置中,我们将使用 Ubuntu 15.04 (64 位),同时,该教程也适用于 Debian 和 Linux Mint。
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: 安装 Nginx 或者 Apache 服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. 首先,先进行一次系统的升级或者更新软件仓库列表.
|
||||
```
|
||||
# apt-get update && apt-get upgrade
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
System Upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
2. 正如我之前说的,HHVM 能和 Nginx 和 Apache 进行集成。所以,究竟使用哪个服务器,这是你的自由,不过,我们会教你如何安装这两个服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 安装 Nginx ####
|
||||
|
||||
我们通过下面的命令安装 Nginx/Apache 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install nginx
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装 Nginx 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
#### 安装 Apache ####
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install apache2
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装 Apache 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
完成这一步,你能通过以下的链接看到 Nginx 或者 Apache 的默认页面
|
||||
|
||||
http://localhost
|
||||
OR
|
||||
http://IP-Address
|
||||
|
||||
#### Nginx 默认页面 ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Nginx 默认页面
|
||||
|
||||
#### Apache 默认页面 ####
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Apache 默认页面
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: 安装和配置 MariaDB ###
|
||||
|
||||
3. 这一步,我们将通过如下命令安装 MariaDB,它是一个比 MySQL 更好的数据库
|
||||
```
|
||||
# apt-get install mariadb-client mariadb-server
|
||||
```
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装 MariaDB
|
||||
|
||||
4. 在 MariaDB 成功安装之后,你可以启动它,并且设置 root 密码来保护数据库:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# systemctl start mysql
|
||||
# mysql_secure_installation
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
回答以下问题,只需要按下`y`或者 `n`并且回车。请确保你仔细的阅读过说明。
|
||||
|
||||
Enter current password for root (enter for none) = press enter
|
||||
Set root password? [Y/n] = y
|
||||
Remove anonymous users[y/n] = y
|
||||
Disallow root login remotely[y/n] = y
|
||||
Remove test database and access to it [y/n] = y
|
||||
Reload privileges tables now[y/n] = y
|
||||
|
||||
5. 在设置了密码之后,你就可以登陆 MariaDB 了。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# mysql -u root -p
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: 安装 HHVM ###
|
||||
|
||||
6. 我们需要添加 HHVM 的仓库到你的`sources.list`文件中,然后更新软件列表。
|
||||
```
|
||||
# wget -O - http://dl.hhvm.com/conf/hhvm.gpg.key | apt-key add -
|
||||
# echo deb http://dl.hhvm.com/ubuntu DISTRIBUTION_VERSION main | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/hhvm.list
|
||||
# apt-get update
|
||||
```
|
||||
**重要**:不要忘记用你的 Ubuntu 发行版型号替换上述的DISTRIBUTION_VERSION (比如:lucid, precise, trusty) 或者是 Debian 的 jessie 或者 wheezy。在 Linux Mint 中也是一样的,不过只支持 petra。
|
||||
|
||||
添加了 HHVM 仓库之后,你就可以安装了。
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install -y hhvm
|
||||
|
||||
安装之后,即可启动它,但是它并没有做到开机启动。可以用如下命令做到开机启动。
|
||||
|
||||
# update-rc.d hhvm defaults
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: 配置 Nginx/Apache 连接 HHVM ###
|
||||
|
||||
7. 现在,nginx/apache 和 HHVM 都已经安装完成了,并且都独立运行起来了,所以我们需要对他们进行设置,来让他们互相关联。这个关键的步骤,就是需要nginx/apache 将所有的 php 文件,都交给 HHVM 进行处理。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你用了 Nginx,请按照如下步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
nginx 的配置文件在 /etc/nginx/sites-available/default, 并且这些配置文件会在 /usr/share/nginx/html 中寻找文件执行,不过,他不知道如何处理 PHP。
|
||||
|
||||
为了确保 Nginx 可以连接 HHVM,我们需要执行如下的脚本。他可以帮助我们正确的配置 Nginx。
|
||||
|
||||
这个脚本可以确保 Nginx 可以对 .hh 和 .php 的做正确的处理,并且通过 fastcgi 与 HHVM 进行通信
|
||||
|
||||
# /usr/share/hhvm/install_fastcgi.sh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
配置 Nginx、HHVM
|
||||
|
||||
**重要**: 如果你使用的是 Apache,这边就不需要进行配置了
|
||||
|
||||
8. 接下来,你需要使用 hhvm 来提供 php 的运行环境。
|
||||
```
|
||||
# /usr/bin/update-alternatives --install /usr/bin/php php /usr/bin/hhvm 60
|
||||
```
|
||||
以上步骤完成之后,你现在可以启动并且测试他了。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start hhvm
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 5: 测试 HHVM 和 Nginx/Apache ###
|
||||
|
||||
9. 为了确认 hhvm 是否工作,你需要在 nginx/apache 的根目录下建立 hello.php。
|
||||
```
|
||||
# nano /usr/share/nginx/html/hello.php [For Nginx]
|
||||
OR
|
||||
# nano /var/www/html/hello.php [For Nginx and Apache]
|
||||
```
|
||||
在文件中添加如下代码:
|
||||
|
||||
<?php
|
||||
if (defined('HHVM_VERSION')) {
|
||||
echo 'HHVM is working';
|
||||
phpinfo();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
echo 'HHVM is not working';
|
||||
}
|
||||
?>
|
||||
|
||||
然后访问如下链接,确认自己能否看到 "hello world"
|
||||
|
||||
http://localhost/info.php
|
||||
OR
|
||||
http://IP-Address/info.php
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
HHVM Page
|
||||
|
||||
如果 “HHVM” 的页面出现了,那就说明你成功了
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
以上的步骤都是非常简单的,希望你能觉得这是一篇有用的教程,如果你在以上的步骤中遇到了问题,给我们留一个评论,我们将全力解决。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-hhvm-and-nginx-apache-with-mariadb-on-debian-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ravi Saive][a]
|
||||
译者:[MikeCoder](https://github.com/MikeCoder)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-apc-alternative-php-cache-in-rhel-centos-fedora/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,175 @@
|
||||
RHCSA 系列: 安装,配置及加固一个 Web 和 FTP 服务器 – Part 9
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Web 服务器(也被称为 HTTP 服务器)是在网络中将内容(最为常见的是网页,但也支持其他类型的文件)进行处理并传递给客户端的服务。
|
||||
|
||||
FTP 服务器是最为古老且最常使用的资源之一(即便到今天也是这样),在身份认证不是必须的情况下,它可使得在一个网络里文件对于客户端可用,因为 FTP 使用没有加密的用户名和密码。
|
||||
|
||||
在 RHEL 7 中可用的 web 服务器是版本号为 2.4 的 Apache HTTP 服务器。至于 FTP 服务器,我们将使用 Very Secure Ftp Daemon (又名 vsftpd) 来建立用 TLS 加固的连接。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCSA: 安装,配置及加固 Apache 和 FTP 服务器 – Part 9
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中,我们将解释如何在 RHEL 7 中安装,配置和加固 web 和 FTP 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 Apache 和 FTP 服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在本指导中,我们将使用一个静态 IP 地址为 192.168.0.18/24 的 RHEL 7 服务器。为了安装 Apache 和 VSFTPD,运行下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install httpd vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
当安装完成后,这两个服务在开始时是默认被禁用的,所以我们需要暂时手动开启它们并让它们在下一次启动时自动地开启它们:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start httpd
|
||||
# systemctl enable httpd
|
||||
# systemctl start vsftpd
|
||||
# systemctl enable vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
另外,我们必须打开 80 和 21 端口,它们分别是 web 和 ftp 守护进程监听的端口,为的是允许从外面访问这些服务:
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-service=ftp --permanent
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
为了确认 web 服务工作正常,打开你的浏览器并输入服务器的 IP,则你应该可以看到如下的测试页面:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
确认 Apache Web 服务器
|
||||
|
||||
对于 ftp 服务器,在确保它如期望中的那样工作之前,我们必须进一步地配置它,我们将在几分钟后来做这件事。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置并加固 Apache Web 服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Apache 的主要配置文件位于 `/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf` 中,但它可能依赖 `/etc/httpd/conf.d` 中的其他文件。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管默认的配置对于大多数的情形是充分的,熟悉描述在 [官方文档][1] 中的所有可用选项是一个不错的主意。
|
||||
|
||||
同往常一样,在编辑主配置文件前先做一个备份:
|
||||
|
||||
# cp /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf.$(date +%Y%m%d)
|
||||
|
||||
然后用你钟爱的文本编辑器打开它,并查找下面这些变量:
|
||||
|
||||
- ServerRoot: 服务器的配置,错误和日志文件保存的目录。
|
||||
- Listen: 通知 Apache 去监听特定的 IP 地址或端口。
|
||||
- Include: 允许包含其他配置文件,这个必须存在,否则,服务器将会崩溃。它恰好与 IncludeOptional 相反,假如特定的配置文件不存在,它将静默地忽略掉它们。
|
||||
- User 和 Group: 运行 httpd 服务的用户/组的名称。
|
||||
- DocumentRoot: Apache 为你的文档服务的目录。默认情况下,所有的请求将在这个目录中被获取,但符号链接和别名可能会被用于指向其他位置。
|
||||
- ServerName: 这个指令将设定用于识别它自身的主机名(或 IP 地址)和端口。
|
||||
|
||||
安全措施的第一步将包含创建一个特定的用户和组(如 tecmint/tecmint)来运行 web 服务器以及更改默认的端口为一个更高的端口(在这个例子中为 9000):
|
||||
|
||||
ServerRoot "/etc/httpd"
|
||||
Listen 192.168.0.18:9000
|
||||
User tecmint
|
||||
Group tecmint
|
||||
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"
|
||||
ServerName 192.168.0.18:9000
|
||||
|
||||
你可以使用下面的命令来测试配置文件:
|
||||
|
||||
# apachectl configtest
|
||||
|
||||
假如一切 OK,接着重启 web 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart httpd
|
||||
|
||||
并别忘了在防火墙中开启新的端口(和禁用旧的端口):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --remove-port=80/tcp --permanent
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=9000/tcp --permanent
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,由于 SELinux 的策略,你只可使用如下命令所返回的端口来分配给 web 服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
# semanage port -l | grep -w '^http_port_t'
|
||||
|
||||
假如你想使用另一个端口(如 TCP 端口 8100)来给 httpd 服务,你必须将它加到 SELinux 的端口上下文:
|
||||
|
||||
# semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 8100
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
添加 Apache 端口到 SELinux 策略
|
||||
|
||||
为了进一步加固你安装的 Apache,请遵循以下步骤:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 运行 Apache 的用户不应该拥有访问 shell 的能力:
|
||||
|
||||
# usermod -s /sbin/nologin tecmint
|
||||
|
||||
2. 禁用目录列表功能,为的是阻止浏览器展示一个未包含 index.html 文件的目录里的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 `/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf` (和虚拟主机的配置文件,假如有的话),并确保 Options 指令在顶级和目录块级别中(注:感觉这里我的翻译不对)都被设置为 None:
|
||||
|
||||
Options None
|
||||
|
||||
3. 在 HTTP 回应中隐藏有关 web 服务器和操作系统的信息。像下面这样编辑文件 `/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf`:
|
||||
|
||||
ServerTokens Prod
|
||||
ServerSignature Off
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你已经做好了从 `/var/www/html` 目录开始服务内容的准备了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置并加固 FTP 服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
和 Apache 的情形类似, Vsftpd 的主配置文件 `(/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf)` 带有详细的注释,且虽然对于大多数的应用实例,默认的配置应该足够了,但为了更有效率地操作 ftp 服务器,你应该开始熟悉相关的文档和 man 页 `(man vsftpd.conf)`(对于这点,再多的强调也不为过!)。
|
||||
|
||||
在我们的示例中,使用了这些指令:
|
||||
|
||||
anonymous_enable=NO
|
||||
local_enable=YES
|
||||
write_enable=YES
|
||||
local_umask=022
|
||||
dirmessage_enable=YES
|
||||
xferlog_enable=YES
|
||||
connect_from_port_20=YES
|
||||
xferlog_std_format=YES
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES
|
||||
allow_writeable_chroot=YES
|
||||
listen=NO
|
||||
listen_ipv6=YES
|
||||
pam_service_name=vsftpd
|
||||
userlist_enable=YES
|
||||
tcp_wrappers=YES
|
||||
|
||||
通过使用 `chroot_local_user=YES`,(默认情况下)本地用户在登陆之后,将马上被置于一个位于用户家目录的 chroot 环境中(注:这里的翻译也不准确)。这意味着本地用户将不能访问除其家目录之外的任何文件。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,为了让 ftp 能够在用户的家目录中读取文件,设置如下的 SELinux 布尔值:
|
||||
|
||||
# setsebool -P ftp_home_dir on
|
||||
|
||||
现在,你可以使用一个客户端例如 Filezilla 来连接一个 ftp 服务器:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
查看 FTP 连接
|
||||
|
||||
注意, `/var/log/xferlog` 日志将会记录下载和上传的情况,这与上图的目录列表一致:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
监视 FTP 的下载和上传情况
|
||||
|
||||
另外请参考: [在 Linux 系统中使用 Trickle 来限制应用使用的 FTP 网络带宽][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在本教程中,我们解释了如何设置 web 和 ftp 服务器。由于这个主题的广泛性,涵盖这些话题的所有方面是不可能的(如虚拟网络主机)。因此,我推荐你也阅读这个网站中有关 [Apache][3] 的其他卓越的文章。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/rhcsa-series-install-and-secure-apache-web-server-and-ftp-in-rhel/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/manage-and-limit-downloadupload-bandwidth-with-trickle-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.google.com/cse?cx=partner-pub-2601749019656699:2173448976&ie=UTF-8&q=virtual+hosts&sa=Search&gws_rd=cr&ei=Dy9EVbb0IdHisASnroG4Bw#gsc.tab=0&gsc.q=apache
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user