mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-01-13 22:30:37 +08:00
20131106-1 选题
This commit is contained in:
parent
238520a9ba
commit
6d3c40465b
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
|||||||
|
How to add kernel boot parameters via GRUB on Linux
|
||||||
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
|
The Linux kernel can be supplied with various parameters during boot time or at run time. These parameters customize the default behavior of the kernel, or inform the kernel about hardware configuration. Kernel parameters can be changed at run time by modifying files in /proc or /sys, while certain kernel parameters need be passed to the kernel at boot time by a boot loader such as GRUB or LILO.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In this tutorial, I will describe **how to add kernel boot parameters via GRUB on Linux**.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If you want to change or add kernel parameters when you are using GRUB boot loader, you can edit GRUB config file. The following are distro-specific ways to add kernel boot parameters to a GRUB config file.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Add Kernel Boot Parameters on Debian or Ubuntu ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If you want to add kernel parameters during boot time on a Debian based system, edit GRUB config template at /etc/default/grub. Add a kernel parameter in the form of “name=value” in GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT variable.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo -e /etc/default/grub
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
> GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="...... name=value"
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Then run the following command to actually generate a GRUB config file.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo update-grub
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If the command update-grub is not found, you can install it as follows.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo apt-get install grub2-common
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Add Kernel Boot Parameters on Fedora ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To add kernel parameters during boot time on Fedora, edit GRUB config template at /etc/default/grub. Add a kernel parameter in the form of “name=value” in GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX variable.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo -e /etc/default/grub
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
> GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="...... name=value"
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Then run the following command to generate a GRUB2 config file.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Add Kernel Boot Parameters on CentOS ###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
To add kernel parameters during boot on CentOS, directly edit a GRUB config file located at /boot/grub/grub.conf. In the config file, look for the entry describing the default Linux image used. The string “default=N” at the top of the config file indicates which entry is the default image.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[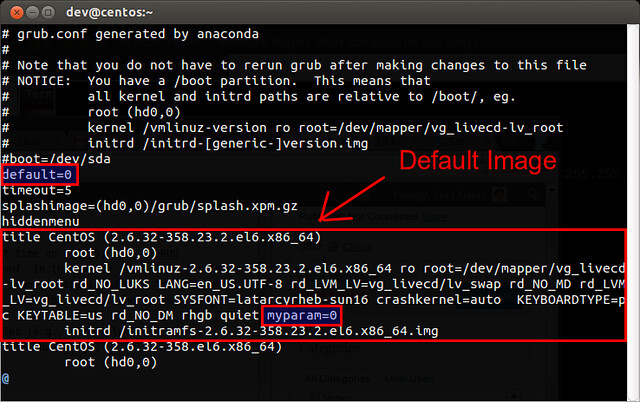][1]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Under the default image entry, append a kernel parameter to the line starting with “kernel /vmlinuz-”. A kernel parameter should be formatted as “name=value”.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/11/add-kernel-boot-parameters-via-grub-linux.html
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[1]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10618657834/
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user