mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
translated
This commit is contained in:
parent
c6ff7fc459
commit
6c146196cb
@ -1,42 +1,40 @@
|
||||
translating----geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to find information about built-in kernel modules on Linux
|
||||
Linux有问必答--如何找出Linux中内置模块的信息
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I would like to know what modules are built into the kernel of my Linux system, and what parameters are available in each module. Is there a way to get a list of all built-in kernel modules and device drivers, and find detailed information about them?
|
||||
> **提问**:我想要知道Linux系统中内核内置的模块,以及每个模块的参数。有什么方法可以得到内置模块和设备驱动的列表,以及它们的详细信息呢?
|
||||
|
||||
The modern Linux kernel has been growing significantly over the years to support a wide variety of hardware devices, file systems and networking functions. During this time, "loadable kernel modules (LKM)" came into being in order to keep the kernel from getting bloated, while flexibly extending its capabilities and hardware support under different environments, without having to rebuild it.
|
||||
现代Linux内核正在随着时间迅速地增长来支持大量的硬件、文件系统和网络功能。在此期间,“可加载模块”的引入防止内核变得越来越臃肿,以及在不同的环境中灵活地扩展功能及硬件支持,而不必重新构建内核。
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux kernel shipped with the latest Linux distributions comes with relatively a small number of "built-in modules", while the rest of hardware-specific drivers or custom capabilities exist as "loadable modules" which you can selectively load or unload.
|
||||
最新的Linux发型版的内核只带了相对较小的“内置模块”,其余的特定硬件驱动或者自定义功能作为“可加载模块”来让你选择地加载或卸载。
|
||||
|
||||
The built-in modules are statically compiled into the kernel. Unlike loadable kernel modules which can be dynamically loaded, unloaded, looked up or listed using commands like modprobe, insmod, rmmod, modinfo or lsmod, built-in kernel modules are always loaded in the kernel upon boot-up, and cannot be managed with these commands.
|
||||
内置模块被静态地编译进了内核。不像可加载内核模块可以动态地使用modprobe、insmod、rmmod、modinfo或者lsmod等命令地加载、卸载、查询模块,内置的模块总是在启动是就加载进了内核,不会被这些命令管理。
|
||||
|
||||
### Find a List of Built-in Kernel Modules ###
|
||||
### 找出内置模块列表 ###
|
||||
|
||||
To get a list of all built-in modules, run the following command.
|
||||
要得到内置模块列表,运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/modules.builtin
|
||||
|
||||
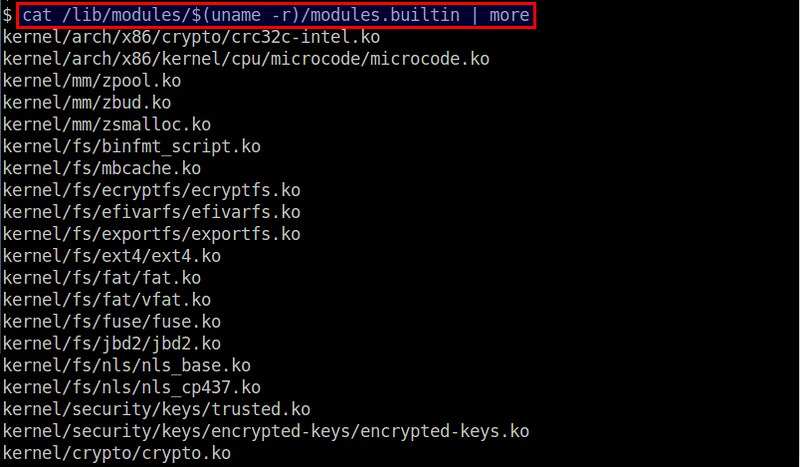
|
||||
|
||||
You can also get a hint on what modules are built-in by running:
|
||||
你也可以用下面的命令来查看有哪些内置模块:
|
||||
|
||||
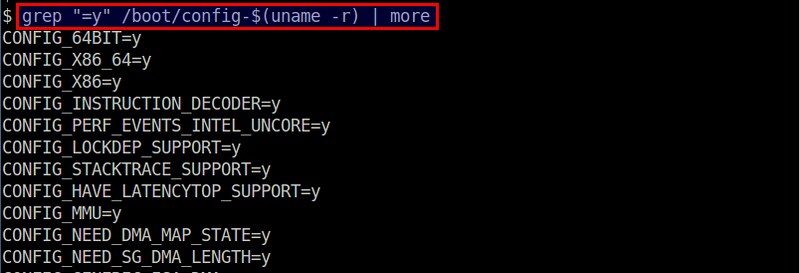
|
||||
|
||||
### Find Parameters of Built-in Kernel Modules ###
|
||||
### 找出内置模块参数 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Each kernel module, whether it's built-in or loadable, comes with a set of parameters. For loadable kernel modules, the modinfo command will show parameter information about them. However, this command will not work with built-in modules. You will simply get the following error.
|
||||
每个内核模块无论是内置的还是可加载的都有一系列的参数。对于可加载模块,modinfo命令显示它们的参数信息。然而这个命令不对内置模块管用。你会得到下面的错误。
|
||||
|
||||
modinfo: ERROR: Module XXXXXX not found.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to check what parameters are available in a given built-in module, and what their values are, you can instead examine the content in **/sys/module** directory.
|
||||
如果你想要查看内置模块的参数,以及它们的值,你可以在**/sys/module** 下检查它们的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
Under /sys/module directory, you will find sub-directories named after existing kernel modules (both built-in and loadable). Then in each module directory, there is a directory named "parameters", which lists all available parameters for the module.
|
||||
在 /sys/module目录下,你可以找到内核模块(包含内置和可加载的)命名的子目录。结合则进入每个模块目录,这里有个“parameters”目录,列出了这个模块所有的参数。
|
||||
|
||||
For example, let's say you want to find out parameters of a built-in module called tcp_cubic (the default TCP implementation of the kernel). Then you can do this:
|
||||
比如你要找出tcp_cubic(内核默认的TCP实现)模块的参数。你可以这么做:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls /sys/module/tcp_cubic/parameters
|
||||
|
||||
And check the value of each parameter by reading a corresponding file.
|
||||
接着阅读这个文件查看每个参数的值。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat /sys/module/tcp_cubic/parameters/tcp_friendliness
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,7 +45,7 @@ And check the value of each parameter by reading a corresponding file.
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/find-information-builtin-kernel-modules-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user