mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-21 02:10:11 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of github.com:LCTT/TranslateProject
This commit is contained in:
commit
6b628b5341
@ -0,0 +1,111 @@
|
||||
Linux 面试基础问题 - 3
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
在有关**面试问题**的这一系列话题的前两篇文章中,我们收到了许多好的反馈,在此表示极大的感谢,同时,我们将延续这一系列话题。在这里,我们将再次展示**10个问题**来进行相互学习。
|
||||
|
||||
- [11个基本的Linux面试问题及答案 – 第一部分][1]
|
||||
- [10个基本的Linux面试问题及答案 – 第二部分][2]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Q.1. 你如何向你的系统中添加一个新的用户(例如,tux)? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用useradd指令
|
||||
- 使用adduser 指令
|
||||
- 使用linuxconf指令
|
||||
- 以上全是
|
||||
- 以上答案全都不对
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : 以上全是,即useradd, adduser 和 linuxconf 都可向你的linux系统添加新用户。
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.2. 在一个硬盘上,可能有多少主分区? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
- 2
|
||||
- 4
|
||||
- 16
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : 一个硬盘上最多可能有4个主分区。
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.3. Apache/Http 的默认端口号是多少? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 8080
|
||||
- 80
|
||||
- 8443
|
||||
- 91
|
||||
- 以上答案全都不对
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : Apache/Http默认配置是**80**端口
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.4. GNU代表什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- GNU's not Unix
|
||||
- General Unix
|
||||
- General Noble Unix
|
||||
- Greek Needed Unix
|
||||
- 以上答案全都不对
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : GNU意为**GNU's not Unix**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.5. 如果你在shell提示符中输入mysql并得到“can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/mysql/mysql.sock’ ”的提示,你首先应该检查什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : 看到这条错误消息,我首先会使用**service mysql status**或者**service mysqld status**指令来检查mysql服务是否正在运行。如果mysql服务没有运行,就启动所需服务。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意**:上面的错误消息可能是由于**my.cnf**或者mysql的**用户权限**错误配置导致的。如果启动mysql服务之后仍不管用,你需要检查这两项。
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.6. 如何将windows ntfs分区挂载到Linux上面? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : 首先,使用**apt**或者**yum**工具安装ntfs3g包,然后使用
|
||||
“**sudo mount t ntfs3g /dev/<Windows ntfs的分区号> /<挂载点>**” 命令来将windows分区挂载到Linux上面
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.7. 下面哪一个不是基于RPM的操作系统? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- RedHat Linux
|
||||
- Centos
|
||||
- Scientific Linux
|
||||
- Debian
|
||||
- Fedora
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : ‘**Debian**’ 系统不是基于**RPM**的,其它的几个都是
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.8. Linux中,哪一个指令用来重命名文件? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- mv
|
||||
- ren
|
||||
- rename
|
||||
- change
|
||||
- 以上答案全都不对
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : 在Linux中,**mv** 指令用来重命名一个文件。例如:**mv /path_to_File/original_file_name.extension /Path_to_File/New_name.extension**
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.9. 在Linux中,哪个命令用来创建并显示文件? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- ed
|
||||
- vi
|
||||
- cat
|
||||
- nano
|
||||
- 以上答案全都不对
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : ‘**cat**‘ 命令用来创建并且显示文件
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. 哪层协议用于支持用户和程序,如支持密码、资源分享、文件传输和网络管理? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 第四层协议
|
||||
- 第五层协议
|
||||
- 第六层协议
|
||||
- 第七层协议
|
||||
- 以上答案全都不对
|
||||
|
||||
> **答** : ‘**第七层协议**‘
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-interview-questions-and-answers-for-linux-beginners/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[tomatoKiller](https://github.com/tomatoKiller) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-2315-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://linux.cn/article-2370-1.html
|
||||
@ -2,25 +2,25 @@ ps命令的10个例子
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Linux ps 命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
linux的ps命令是一个浏览系统运行的进程的一个最基础的工具。它提供了一个当前进程的快照,还带有一些具体的信息,比如用户id,cpu使用率,内存使用,命令名等它不会像top或者htop一样实时显示数据。虽然它在功能和输出上更加简单,但它仍然是每个linux新手需要了解和学好的必要进程管理/检测工具。
|
||||
linux的ps命令是一个查看系统运行的进程的一个最基础的工具。它提供了一个当前进程的快照,还带有一些具体的信息,比如用户id,cpu使用率,内存使用,命令名等,它不会像top或者htop一样实时显示数据。虽然它在功能和输出上更加简单,但它仍然是每个linux新手需要了解和学好的必要进程管理/检测工具。
|
||||
|
||||
在本篇中,我门会复习ps命令基本的用法:检测、过滤、以不同的方式排序进程来更好地适应。
|
||||
在本篇中,我们会学习ps命令基本的用法:查找、过滤,以不同的方式排序。
|
||||
|
||||
### 语法说明 ###
|
||||
|
||||
ps命令有两种不同风格的语法规则。它们是BSD和UNIX。Linux新手经常感到困惑并会误解这两种风格。所以在继续下一步之前,我们来弄清楚一些基本的信息。
|
||||
ps命令有两种不同风格的语法规则:BSD风格和UNIX风格。Linux新手经常感到困惑并会误解这两种风格,所以在继续下一步之前,我们来弄清楚一些基本的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
> 注意: "ps aux"不等同于"ps -aux"。比如"-u"用于显示用户的进程,但是"u"意味着显示具体信息。
|
||||
|
||||
BSD 形式 - BSD形式的语法的选项前没有破折号。
|
||||
BSD 形式 - BSD形式的语法的选项前没有破折号,如:
|
||||
|
||||
ps aux
|
||||
|
||||
UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号,如:
|
||||
|
||||
ps -ef
|
||||
|
||||
> 在linux系统上混合这两种语法是可以的。比如 "ps ax -f"。但是本章中我们主要讨论unix形式语法。
|
||||
> 在linux系统上混合这两种语法是可以的。比如 "ps ax -f"。但是本章中我们主要讨论UNIX形式语法。
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何使用ps命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,16 +31,15 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
$ ps ax
|
||||
$ ps -ef
|
||||
|
||||
通过管道输出到"less"可以使它滚动。
|
||||
通过管道输出到"less"可以分页。
|
||||
|
||||
使用"u"或者"-f"选项可以显示进程的具体信息。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps aux
|
||||
$ ps -ef -f
|
||||
|
||||
> 为什么USER列显示的不是我的用户名而是其他的像root,www-data等等?
|
||||
|
||||
对于所有的用户(包括你们的),如果长度大于8个字符,那么ps只会显示你的UID而不是用户名。
|
||||
> 为什么USER列显示的不是我的用户名,但是其他的像root,www-data等却显示?
|
||||
> 对于所有的用户(包括你们的),如果长度大于8个字符,那么ps只会显示你的UID而不是用户名。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 显示用户进程 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -68,9 +67,9 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
4525 ? 00:00:00 apache2
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
要通过进程id显示进程,就使用"-p"选项,并且它还提供使用逗号来分割进程id。
|
||||
要通过进程id显示进程,就使用"-p"选项,并且还可以通过逗号分隔来指定多个进程id。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps -f -p 3150,7298,6544
|
||||
$ ps -f -p 3150,7298,6544
|
||||
|
||||
"-C"必须提供精确的进程名,并且它并不能通过部分名字或者通配符查找。为了更灵活地搜索进程列表,通常使用grep命令。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,10 +77,9 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. 通过cpu或者内存使用排序进程 ####
|
||||
|
||||
系统管理员通常想要找出那些消耗最多内存或者CPU的进程。排序选项会基于特性的字段或者参数排序进程列表。
|
||||
|
||||
多个字段可以用'--sort'指定,并用逗号分割。除此之外,字段前面还可以跟上'-'或者'+'的前缀来相应地表示递减和递增排序。这里有很多的用于排序的选项。通过man页来获取完整的列表。
|
||||
系统管理员通常想要找出那些消耗最多内存或者CPU的进程。排序选项会基于特定的字段或者参数来排序进程列表。
|
||||
|
||||
可以用'--sort'指定多个字段,并用逗号分割。除此之外,字段前面还可以跟上'-'或者'+'的前缀来相应地表示递减和递增排序。这里有很多的用于排序的选项,通过man页来获取完整的列表。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ps aux --sort=-pcpu,+pmem
|
||||
|
||||
@ -109,7 +107,7 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
www-data 4527 2359 0 10:03 ? 00:00:00 \_ /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
|
||||
www-data 4528 2359 0 10:03 ? 00:00:00 \_ /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
|
||||
|
||||
> 尽量不要在排序中使用树状显示,因为两者都会以不同方式影响显示的顺序。
|
||||
> 不要在排序中使用树状显示,因为两者都会以不同方式影响显示的顺序。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. 显示父进程的子进程 ####
|
||||
|
||||
@ -123,11 +121,9 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
4526 www-data apache2
|
||||
4527 www-data apache2
|
||||
4528 www-data apache2
|
||||
[term]
|
||||
|
||||
第一个属于root的进程是apache2的主进程,其他的apache进程都是从主进程fork出来的。下面的命令使用apache2主进程的pid列出了所有的apache2的子进程。
|
||||
第一个属于root的进程是apache2的主进程,其他的apache进程都是从主进程fork出来的。下面的命令使用apache2主进程的pid列出了所有的apache2的子进程。
|
||||
|
||||
[term]
|
||||
$ ps --ppid 2359
|
||||
PID TTY TIME CMD
|
||||
4524 ? 00:00:00 apache2
|
||||
@ -138,7 +134,7 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7. 显示进程的线程 ####
|
||||
|
||||
"-L"选项会随着进程一起显示线程。它可用于显示所有特定进程或者所有进程的线程。
|
||||
"-L"选项会随着进程一起显示线程。它可用于显示所有指定进程或者所有进程的线程。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令会显示进程id为3150的进程的所有线程。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -146,7 +142,7 @@ UNIX/LINUX 形式 - linux形式的语法的选项前有破折号。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 8. 改变显示的列 ####
|
||||
|
||||
ps命令可以被配置用来只显示被选中的列。很多列可以被用来显示,并且完整的列表在man页中。
|
||||
ps命令可以被配置用来只显示被选中的列。很多列可以被用来显示,完整的列表可以查看man页。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令会只显示pid、用户名、cpu、内存、命令列。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -176,7 +172,6 @@ ps命令可以被配置用来只显示被选中的列。很多列可以被用来
|
||||
|
||||
#### 10. 将ps转换为实时进程查看器 ####
|
||||
|
||||
As usual, the watch command can be used to turn ps into a realtime process reporter. Simple example is like this
|
||||
通常上,watch命令可将ps命令变成实时进程查看器。像这个简单的命令
|
||||
|
||||
$ watch -n 1 'ps -e -o pid,uname,cmd,pmem,pcpu --sort=-pmem,-pcpu | head -15'
|
||||
@ -201,11 +196,9 @@ As usual, the watch command can be used to turn ps into a realtime process repor
|
||||
3677 1000 /opt/google/chrome/chrome - 1.5 0.4
|
||||
3639 1000 /opt/google/chrome/chrome - 1.4 0.4
|
||||
|
||||
输出会每秒刷新状态。但不要认为这和top相似。
|
||||
输出会每秒刷新状态,但是这其实很top不同。你会发现top/htop命令的输出相比上面的ps命令刷新得更频繁。
|
||||
|
||||
你会发现top/htop命令的输出相比上面的ps命令刷新得更频繁。
|
||||
|
||||
这是因为top输出是结合了cup使用值和内存使用值后的排序值。但是上面的ps命令是一个更简单的行为的排序,每次获取一列(像学校的数学)。因此它不会像top那样快速更新。
|
||||
这是因为top输出是结合了cup使用值和内存使用值后的排序值。但是上面的ps命令是一个更简单的行为的排序,每次获取一列(像学校的数学),因此它不会像top那样快速更新。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,164 @@
|
||||
Linux 面试基础问题 - 2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
继续我们这面试系列,在这篇文章里我们给出了10个问题。这些问题或者是在以后的文章中出现的问题不一定在面试中会被问到。然而通过这些文章我们呈现出的是一个交互的学习平台,这必将会对你有很大的帮助。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
自本系列的上一篇文章[11个基本的 Linux 面试问题][1],我们分析了不同论坛对此作出的评论,这对我们将更好的文章提供给我们的读者是很重要的。我们付出了时间和金钱,那我们又渴望从你们身上得到什么回报呢?答案是没有的。如果你不能赞扬我们的工作,但恳请不要在评论中诋毁我们的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在文章中没有找到什么新的东西,但也请不要忘记它对某些人却是非常有用的,并且他或她会非常感激我们的工作。我们不能够让每一篇文章都使大家高兴。但我希望读者们能够尽量理解。
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.1:哪一条命令用于把用户登录会话记录在文件中? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- macro
|
||||
- read
|
||||
- script
|
||||
- record
|
||||
- sessionrecord
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:‘script’ 命令是用来把用户登录的会话信息记录在文件里。这条命令能够用在 shell 脚本里面,或者直接在终端中使用。下面是一个例子,它记录了开始用 script 到输入 exit 结束之间的所有东西。
|
||||
|
||||
如下命令记录用户登录会话到一个文件中:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# script my-session-record.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Script started, file is my-session-record.txt
|
||||
|
||||
记录的文件“my-session-record.txt”可以通过下述方式查看:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# nano my-session-record.txt
|
||||
|
||||
script started on Friday 22 November 2013 08:19:01 PM IST
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# ls
|
||||
^[[0m^[[01;34mBinary^[[0m ^[[01;34mDocuments^[[0m ^[[01;34mMusic^[[0m $
|
||||
^[[01;34mDesktop^[[0m ^[[01;34mDownloads^[[0m my-session-record.txt ^[[01;34$
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.2:以下那一条命令可以用来查看内核日志信息 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- dmesg
|
||||
- kernel
|
||||
- ls -i
|
||||
- uname
|
||||
- 以上全不是
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:执行 'dmesg' 命令可以查看内核的日志信息。在上面的命令中,kernel 不是一个有效的命令,'ls -i' 是用来列出工作目录中文件的索引节点,而 'uname' 是用来显示操作系统信息的。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# dmesg
|
||||
|
||||
Initializing cgroup subsys cpuset
|
||||
Initializing cgroup subsys cpu
|
||||
Linux version 2.6.32-279.el6.i686 (mockbuild@c6b9.bsys.dev.centos.org) (gcc version 4.4.6 20120305 (Red Hat 4.4.6-4) (GCC) ) #1 SMP Fri Jun 22 10:59:55 UTC 2012
|
||||
KERNEL supported cpus:
|
||||
Intel GenuineIntel
|
||||
AMD AuthenticAMD
|
||||
NSC Geode by NSC
|
||||
Cyrix CyrixInstead
|
||||
Centaur CentaurHauls
|
||||
Transmeta GenuineTMx86
|
||||
Transmeta TransmetaCPU
|
||||
UMC UMC UMC UMC
|
||||
Disabled fast string operations
|
||||
BIOS-provided physical RAM map:
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.3:哪一条命令是用来显示 Linux 内核发行信息的? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- uname -v
|
||||
- uname -r
|
||||
- uname -m
|
||||
- uname -n
|
||||
- uname -o
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:‘uname -r’是用来显示内核的发行信息。其它参数‘-v’、‘-m’、‘-n’、‘o’分别显示内核版本、机器硬件名称、网络节点、主机名和操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# uname -r
|
||||
|
||||
2.6.32-279.el6.i686
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.4:那一条命令是被用来识别文件类型的? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- type
|
||||
- info
|
||||
- file
|
||||
- which
|
||||
- ls
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:‘file’命令是用来识别文件类型的。其语法是‘file [选项] 文件名’。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# file wtop
|
||||
|
||||
wtop: POSIX shell script text executable
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.5:哪一条命令是被用来找一条命令的二进制文件、源和手册的所在的路径? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:‘whereis’驾到!‘whereis’命令是用来找一条命令的二进制文件、源和手册的所在的路径。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# whereis /usr/bin/ftp
|
||||
|
||||
ftp: /usr/bin/ftp /usr/share/man/man1/ftp.1.gz
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.6:当用户登录时,默认情况下哪些文件会被调用作为用户配置? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:在用户的目录下‘.profile’和‘.bashrc’会默认地被调用作为用户配置。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# ls -al
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 tecmint tecmint 176 May 11 2012 .bash_profile
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 tecmint tecmint 124 May 11 2012 .bashrc
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.7:‘resolve.conf’文件是什么的配置文件? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:‘/etc/resolve.conf’ 是 DNS 客户端的配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
|
||||
|
||||
nameserver 172.16.16.94
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.8:哪一条命令是用来创建一个文件的软链接的? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- ln
|
||||
- ln -s
|
||||
- link
|
||||
- link -soft
|
||||
- 以上都不是
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:在 Linux 环境下,‘ls -s’是被用来创建一个文件的软链接的。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# ln -s /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf httpd.original.conf
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.9:在Linux下,‘pwd’命令是‘passwd’命令的别名吗? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:不是!默认情况下‘pwd’命令不是‘passwd’命令的别名。‘pwd’是‘print working directory’(显示工作目录)的缩写,也就是输出当前的工作目录,而‘passwd’在 Linux 中是被用来更改用户的帐号密码。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# pwd
|
||||
|
||||
/home/tecmint
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# passwd
|
||||
Changing password for user root.
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Retype new password:
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.10:在 Linux 中,你会怎样检测 pci 设备的厂商和版本。 ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **答**:我们用的 Linux 命令是‘lspci’。
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# lspci
|
||||
|
||||
00:00.0 Host bridge: Intel Corporation 5000P Chipset Memory Controller Hub (rev b1)
|
||||
00:02.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset PCI Express x8 Port 2-3 (rev b1)
|
||||
00:04.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset PCI Express x8 Port 4-5 (rev b1)
|
||||
00:06.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset PCI Express x8 Port 6-7 (rev b1)
|
||||
00:08.0 System peripheral: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset DMA Engine (rev b1)
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
现在就到这里。我希望以上的问题也许对你很有用。在下星期我会再想出一些新的问题。到时请保持好的健康,继续关注我们并且与 Tecmint 保持联系喔!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/basic-linux-interview-questions-and-answers-part-ii/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-2315-1.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧 - 使用TeamViewer连接远程桌面
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
TeamViewer,是一款热门的远程支持和桌面共享工具,并且它的Windows版、Mac OS X版和Linux版(包含Ubuntu)已经更新到版本 9 了。TeamViewer 允许你在任何地方通过网络控制任何电脑。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在谈一桩生意或者帮助别人解决一些与电脑相关的问题,例如杀毒,又或者远程共享你的屏幕内容,那同样,它是一款功能强大的工具,值得拥有。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是这个支持工具如何使用的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
最近,我妈妈打电话给我说她想弄清楚如何安装一个程序。当我在电话中花了几分钟尝试帮她弄那个程序,不过都失败后,我决定自己来。
|
||||
|
||||
因此我们两个人都花了几分钟下载了 TeamViewer,我连接上了她的电脑并且帮她安装了那个程序。
|
||||
|
||||
这是一个 TeamViewer 如何帮助你解决问题的例子,如果你准备使用 TeamViewer 来帮助你的顾客或者是客户的话,你可能需要购买一个授权许可来遵守公司的政策。
|
||||
|
||||
我宁愿选择 TeamViewer 而不选择其它远程支持工具的另外一个原因是它允许你直接使用,无需安装,至少在 Windows 上是这样。如果你只使用一次的话,那么你只需要运行它,而它却不会占用你的磁盘空间。
|
||||
|
||||
现在 TeamViewer 能够在几乎所有操作系统上运行,包括 Android 和 IOS。
|
||||
|
||||
Windows 用户可以 [从这里下载 TeamViewer][1]
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu 用户可以 [从这链接下载并运行 TeamViewer][2]
|
||||
|
||||
在 Ubuntu 轻松安装 TeamViewer,运行下面的命令来下载安装程序
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://download.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux.deb
|
||||
|
||||
对于 **64位操作系统**, 使用下面的链接.
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://download.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux_x64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
最后,运行下面的命令来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_linux*.deb; sudo apt-get -f install
|
||||
|
||||
去试试吧!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果上述的命令不能成功运行的话,那么就去 TeamViewer [下载页面来下载][2].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/12/daily-ubuntu-tips-teamviewer-9-is-available-for-download/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.teamviewer.com/en/download/windows.aspx
|
||||
[2]:http://www.teamviewer.com/en/download/linux.aspx
|
||||
23
published/GCC 4.9 Is Now In Bug-Fixes-Only Stage 3 Mode.md
Normal file
23
published/GCC 4.9 Is Now In Bug-Fixes-Only Stage 3 Mode.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
GCC 4.9现在处于修复BUG的第三阶段
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
拥有很多[新功能][2]的[GCC 4.9][1]将定于2014年上半年发布。这个GCC的基础代码将不会增加新的功能,目前将只修改大的BUG。
|
||||
|
||||
Richard Biener宣称代码主干目前处于第三阶段,因此在之后的八个月这些功能将融入到4.9版本,除非有发布主管认可的特例发生,不然不会增加新的功能了。第三阶段只做普通BUG的修复工作,将在2个月内完成,而后到达只编写文档和回归测试的第四阶段。
|
||||
|
||||
目前GCC4.9有63个P1 回归测试(最严重的回归测试)其次是136个P2回归测试,14个P3回归测试,88个P4回归测试 以及60个P5回归测试。直到P1阶段的63个回归测试完成,GCC4.9才接近发布。GCC 4.9.0发布版将可能在2014第二季度左右到来!
|
||||
|
||||
GCC 4.9.0状态报告可以在[GCC mailing list][3]中被找到。GCC 4.9将会是一个非常棒的更新,并会挑战下个月发布的[LLVM3.4][4]。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTUyMjk
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic___](http://blog.csdn.net/Vic___) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=GCC+4.9
|
||||
[2]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTUxNzQ
|
||||
[3]:http://gcc.gnu.org/ml/gcc/2013-11/msg00435.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=LLVM+3.4
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,98 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux上制作一个屏幕录像视频教程
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
一图胜千言,一个精心设计的指导视频更是能给你带来良好体验。Linux上有你需要的制作有用且高质量教学视频的所有工具。我们将用强大的kdenlive视频编辑器和Audacity音频录制器和编辑器制作一个简单的屏幕录像,并学习如何在YouTube上分享精彩的屏幕录像。
|
||||
|
||||
一台安装了Kdenlive和Audacit软件的Linux系统PC,一个质量好的麦克风或耳机,和一个YouTube的帐号就是你需要准备的全部。(是的,除了Youtube还有很多其他的免费视频共享服务,你也可以使用它们。)YouTube属于Google,Google想让你与全世界共享任何人和事。如果这不是你想做的,请说no。
|
||||
|
||||
我们的工作流程是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
- 用Kdenlive录制屏幕录像
|
||||
- 用Audacity录制音轨
|
||||
- 添加音轨到Kdenlive
|
||||
- 上传到YouTube
|
||||
- 全世界看你的视频,好开心
|
||||
|
||||
kdenlive支持最流行的数字视频格式,包括AVI,MP4,H.264,和MOV。它支持的图像文件包括GIF,PNG,SVG和TIFF;支持的音频文件格式,包括非压缩的PCM,Vorbis,WAV,MP3和 AC3。你甚至可以阅读和编辑Flash文件。总之,它可以处理很多东西。
|
||||
|
||||
你的配音与你的视频一样重要。请一定要重视你的音频。使音频保持干净和简单,去除杂乱的题外话、方言,并将背景噪声降到最低点。我喜欢用一个质量好的耳麦做讲述,这样你不必担心话筒位置,你可以反复听你自己的讲述而不会影响到你身边的人。
|
||||
|
||||
Kdenlive的文档已过期,它会告诉你制作屏幕录像需要RecordMyDesktop软件。我用的是kdenlive 0.9.4,其实不需要Recordmydesktop。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*图 1:默认配置*
|
||||
|
||||
### 制作屏幕录像 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首次安装kdenlive,第一次运行时会启动配置向导。不必在意默认设置,因为你随时都可以改变它们。
|
||||
|
||||
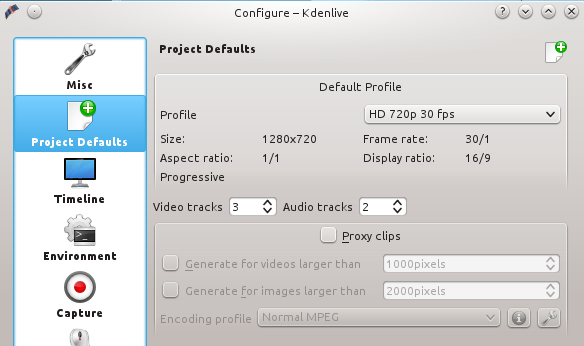
这是我的屏幕录像的设置:高清720p每秒30帧,1280x720的屏幕尺寸。如何知道该使用什么设置项? [Google上有一些说明][1]。设置这些值可到Settings > Configure Kdenlive > Project Defaults > Default Profile > HD 720p 30fps(图1)。
|
||||
|
||||
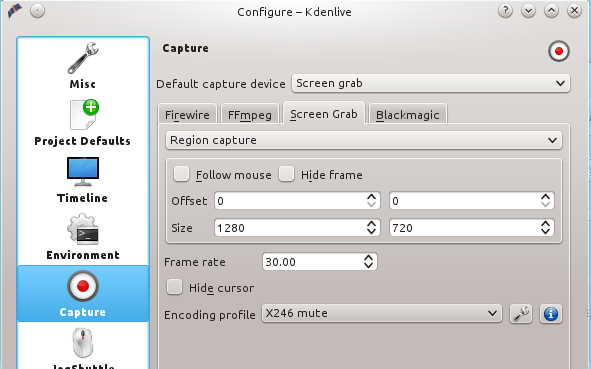
设置捕捉屏幕的大小到 Settings > Configure Kdenlive > Capture > Screen Grab(图2)。虽然你也可以选择捕捉全屏幕,但最好还是坚持用YouTube规定的尺寸。因为如果使用的尺寸与YouTube规定的不一样,则YouTube将增加黑边来达到合适的尺寸。热切的观众会更加希望看到一个充满生动的内容的屏幕,而不是黑边。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*图 2:屏幕录像的屏幕大小*
|
||||
|
||||
默认的YouTube视频播放器的大小是640x360标清320p,又小又模糊。播放器有小屏,大屏,全屏,和多个质量等级的控制。这些设置只有你的观众会使用,640x360标清320p看起来真的不咋样,但郁闷的是你无法改变这个缺陷。尽管如此,你仍然想制作高质量视频的话,你可以添加一些文字来提醒观众尝试更好的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 保存你的项目 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在你做任何其他事情之前,点击 File->Save as 保存您的项目,并记住周期性地保存它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 抓取屏幕 ###
|
||||
|
||||
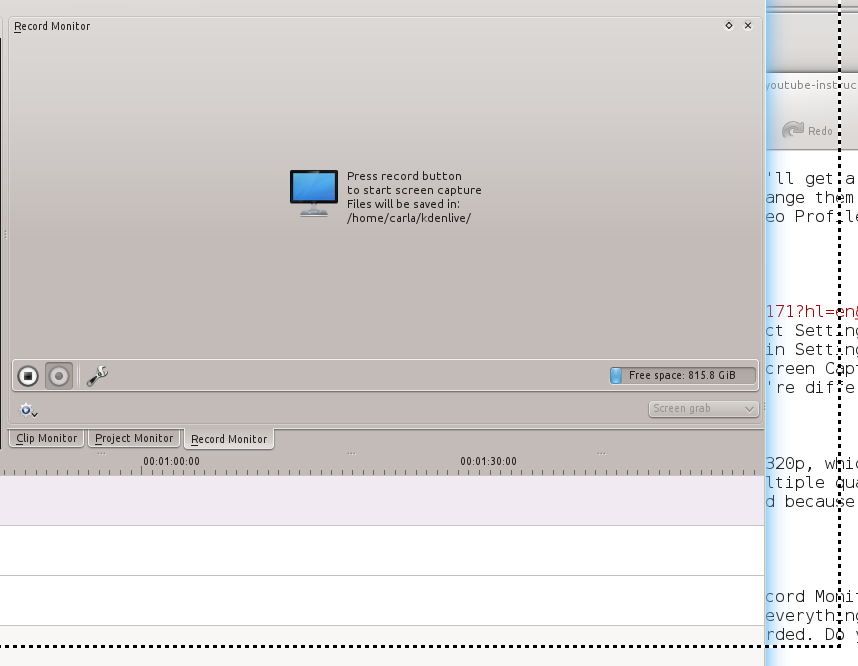
抓屏小菜一碟。到Record Monitor,选择Screen Grab,然后点击Record按钮。屏幕上将打开一个带虚线的框,框里面的所有内容都将被录制下来。因此,你需要做的所有事就是移动框并调整框的大小到你想要l录制的范围。完成后点击停止按钮(图3)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*图 3:屏幕抓取*
|
||||
|
||||
单击Stop,自动打开Clip Monitor,你可以预览你的裁剪效果。如果你觉得不错,把它从Project Tree中拖到Video 1轨道。现在你可以编辑你的视频了。总会有需要你修剪的地方;一个快速的方法是,你在Project Monitor里播放你的剪辑片,直到播放到你需要移除部分的末尾。然后暂停,然后按下Shift+r。你的剪辑片将会在你按下停止的时间轴上的点上被切割为两个剪辑。点击你要删除的片断,按下Delete键,噗!它就消失了。
|
||||
|
||||
对于剩下的剪辑片断,可能你想要从时间轴上的某一点开始播放,也可能你想要加入一些好的变换。比如一些简单的渐变就相当不错;右键点击你的剪辑片断,点击Add Effect > Fade > Fade from black 和 Fade to black,然后Kdenlive将自动将这两个效果放到开头和末尾。
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加配音 ###
|
||||
|
||||
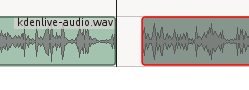
请参阅[Whirlwind Intro to Audacity on Linux: From Recording to CD in One Lesson][2]来学习使用Audacity录音的基础操作。以16bit的wav格式导出你的音频文件,然后通过Project > Add Clip导入到Kdenlive。然后将你的新音频剪辑拖到Audio tracks。一个简单的制作视频讲述的方式是边播视频边说。运气好的话,你不需要做很多的清理工作,你的讲述就会与视频同步。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*图 4:用Shift+r切割音轨,然后将其中一个剪辑片从切割点拖离,创建一个静音间隙*
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的语速比视频快,你可以在音轨中添加空档时间.很简单,用Shift+r切割音轨,然后将其中一个剪辑片从切割点拖离,创建一个静音间隙。(图4)。
|
||||
|
||||
### Rendering Your Project ### 渲染你的项目
|
||||
|
||||
当你满意自己的编辑,并准备导出你的最终格式时,点击Render按钮。这需要几分钟的时间,取决于你的电脑速度和项目大小。已有为网站预先设定的值,如果你选择File Rendering, 你可以调整你的设置(图5)。我用File Rendering中的H.264,Video比特率12000, Audio比特率384取得了不错的效果。H.264是一种超压缩格式,使用这种格式发布的文件小但质量好。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
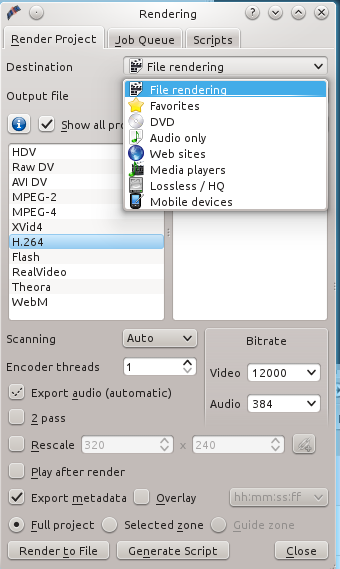
|
||||
|
||||
*图 5:选择文件渲染,调整你的网页设置*
|
||||
|
||||
### 发布到YouTube ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以在VLC或MPlayer或你喜欢的任何播放器中播放你的视频了,如果它看起来很好,那么你就可以将它上传到你的YouTube帐户里了。YouTube是典型的Google风格,信息中心和视频管理器会混乱又复杂,不过请坚持多研究下,你会理出头绪的。在你做任何事情之前,你必须对你的账户做资格认证,也就是通过短信和邮件获得一个验证码。通过输入验证码证明你不是一个网络爬虫后,你就能上传你的视频了。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以上传你的视频,然后标记它们为私人可见或所有人可见。Google有一些编辑工具,你可能会喜欢,比如自动纠错和配背景音乐。不过以我的拙见,几乎没有人是这样子做背景音乐的,所以这种工具只会令人讨厌。不过你有可能是第一个正确使用这个工具的人哦。
|
||||
|
||||
最有用的编辑工具是自动字幕。我推荐在你所有的视频上使用此功能,不光是为了那些听觉障碍的人,也为了那些需要保持低音量观看的人,确保所有的人都明白你在说什么。字幕工具也能创建副本。
|
||||
|
||||
另一个有用的工具是注释工具,它支持对话气泡,标题,聚光灯和标签。当然,在Kdenlive中,这些你都可以做到,所以都可以尝试一下。
|
||||
|
||||
好吧,到这里就结束了,但似乎我们刚刚开始。请分享你的视频,并在评论中添加Youtube的小建议和技巧。如果可以的话,请在[video.linux.com][3]分享你的新的视频教程,并参加100个Linux教程比赛。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
来源于: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/745745-how-to-make-a-youtube-instructional-screencast-video-on-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[coolpigs](https://github.com/coolpigs) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://support.google.com/youtube/answer/1722171?hl=en&ref_topic=2888648
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/422799-whirlwind-intro-to-audacity-on-linux
|
||||
[3]:http://video.linux.com/100-linux-tutorials
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
KVM,Xen与VirtualBox在Intel Haswell上的Linux虚拟化性能比较
|
||||
==============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们做的是[Intel Haswell][1]的虚拟化基准测试。我们在Intel酷睿i7 4770K的“Haswell”处理器上使用搭载了最新软件组件的Fedora 19,来进行KVM,Xen和VirtualBox的基准测试。
|
||||
|
||||
自从上个月推出Haswell以来,我们已经发布了许多和这款全新的英特尔处理器相关的基准测试,但我们直到这篇文章发布前,一直没有涵盖虚拟化方面的性能测试。这里,启用了英特尔硬件虚拟化后,将在一个纯净的Fedora 19 的64位操作系统上,分别安装KVM,Xen和Virtualbox,并进行比较。
|
||||
|
||||
目前Fedora 19拥有搭载GCC 4.8.1的Linux 3.9.8版本内核,Mesa 9.2.0开发库和一个EXT4文件系统。所有的虚拟化组件都从Fedora 19的仓库中获取的,包括QEMU 1.4.2,Xen 4.2.2和libvirt/virt-manager组件。Xen和KVM的虚拟化通过virt-manager来建立。VirtualBox 4.2.16则是通过VirtualBox.org获取并安装在Fedora 19中。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这个英特尔酷睿i7 4770K机器拥有16GB的内存和240GB的OCZ Vertex 3 固态硬盘。在测试中,每一个虚拟机能够使用全部八个逻辑核心(四个物理核心加上超线程)、16GB内存中的12GB以及16GB的虚拟磁盘。
|
||||
|
||||
在采用英特尔酷睿i7 “Haswell”处理器的Linux 3.9版本内核的Fedora 19上安装的KVM,Xen和VirtualBox的性能也和在没有任何形式的虚拟化或其它抽象层上运行基准测试的“裸机(Bare Metal)”的性能进行了对比。VMWare的产品没有在这篇文章里被测试,因为它们的EULA特性限制了这种公开基准测试(尽管VMware在过去可以让我们正常地做这样的基准测试),并且它们的试用软件只能限制运行在四核CPU上。但以后的另外一篇文章会比较下在其它硬件上XEN/KVM/VMware的性能。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
全部的Linux虚拟化基准测试采用完全自动化和可重复的方式进行处理,使用开源软件[Phoronix Test Suite][3]并由[OpenBenchmarking.org][4]支持。在使用虚拟磁盘而且Xen/KVM都没有一个可靠的访问主机驱动或GPU的方法以使用3D功能的情况下,这篇文章里的大部分基准测试都是集中在不同Linux虚拟化方法计算性能开销上。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
磁盘测试在这里并不是虚拟化测试的一个重点,因为只有一个虚拟磁盘被主机的文件系统使用。然而,当把这三种Linux虚拟化方法与裸机结果进行比较时,运行在Linux 3.9内核上的KVM性能最好,其次是Xen。Oracle的Virtual仅仅跑出了主机上PostMark邮件服务器性能的66%,而KVM跑出了性能的96%,Xen是83%。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
对于Dolfyn计算流体动力学的工作量,当运行在KVM或Xen上时,和裸机的运行结果相比并没有任何重大的变化。然而,VirtualBox则是明显变慢了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
FFTE和HMMer的结果和Dolfyn类似:Xen和KVM用很小的开销获得很好的性能,但Oracle的VirtualBox则慢得多。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当John The Ripper这个破解密码的程序在VirtualBox中运行时,则直接崩溃了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
运行TTSIOD渲染器时,在Linux 3.9 内核的Fedora 19上运行的Xen虚拟化方法获得了它的第一次性能比拼的胜利。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
总之,运行在搭载英特尔酷睿i7 4770K处理器Fedora 19上的Xen和KVM虚拟化技术工作良好。这些虚拟化方法在Haswell处理器上的性能开销是最小的。当Xen和KVM在这款全新的英特尔处理器上运行良好的时候,Oracle的VirtualBox(最新版本,v4.2.16)相对慢得多。虽然VirtualBox的一个优点是支持客户机3D加速,但这会在未来的一篇Phoronix文章中再次进行测试。而把Haswell和前几代的英特尔处理器和AMD处理器比较不同虚拟化方法的性能开销也会在不久之后在Phoronix上进行测试。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=article&item=intel_haswell_virtualization
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](http://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=Haswell
|
||||
[2]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTM5MzU
|
||||
[3]:http://www.phoronix-test-suite.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://openbenchmarking.org/
|
||||
|
||||
94
published/Interview with Ding Zhou of Ubuntu Tweak.md
Normal file
94
published/Interview with Ding Zhou of Ubuntu Tweak.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,94 @@
|
||||
专访Ubuntu Tweak的作者周鼎
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
[Ubuntu tweak][1] 是一款知名度很高的应用程序软件,Ubuntu 用户可以用它来调整系统的性能、功能等各个细节。项目的创始人,周鼎又名 Tualatrix Chou ,正与我们分享 Ubuntu Tweak 的特性、使用感觉以及它跟 Canonical 的关系,并且勾勒了项目的未来计划蓝图。享受吧!
|
||||
|
||||
**你什么时候开始使用 Linux 的,并基于什么使你决定开发 Ubuntu tweak ?**
|
||||
|
||||
我开始使用 Linux 是在2006年底,那时刚开始我的大学生活。当时我正在学 C 编程语言,一个朋友建议说要学习编程的话 Linux 是最好的平台环境,所以我就开始了我的 Linux 生涯,是从 Fedora Core 6 开始的。但用了仅仅只有一周的时间,我就换成 Ubuntu 6.10,因为Ubuntu在中国有更好的社区,也有更好更快的源库/镜像。我立马就爱上了 Ubuntu,就一周时间,就从 Windows 环境完全切换到 Ubuntu 环境。
|
||||
|
||||
在苦乐参半的半年使用时间后,我意识到 Ubuntu 对中国用户来说不是太友好,因为全新安装系统后,用户必须得自己配置字体、输入法以及其它很多很多设置。所以,我决定开发出一款应用程序来帮助新手,让他们很简单的就可以对系统做相应配置。
|
||||
|
||||
因此在2007年7月,我就开始开发 Ubuntu Tweak,刚开始的时候,仅仅提供了汉语版本的,但很快就考虑了 Ubuntu Tweak 的国际版本,并且在2007年9月份就发布了首个国际版本。
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu tweak 已经是非常成功的项目了。很多 Ubuntu 用户用它来调整系统的性能、功能等各个细节。能给我们谈论下 Ubuntu Tweak 能做些什么吗?**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Tweak 可以用来切换桌面图标的显示方式、设置字体、启用/禁用多用户切换功能以及登陆的标识(logo)等等。
|
||||
|
||||
在最新的 Ubuntu Tweak 0.6版本中,你也可以调整你的 Unity 桌面以及关机功能。
|
||||
|
||||
你也能使用 Ubuntu Tweak 来清理系统的垃圾以释放空间和使系统保持干净。
|
||||
|
||||
**Canonical 在他们的默认发布源中不考虑加入 Ubuntu Tweak。这意味着什么?这对那些没有经验,但又想要使用你的应用程序来调整他们的系统的用户来说,存在某些风险吗?**
|
||||
|
||||
对的。因为在以前的 Ubuntu Tweak 发布版本中,为流行的 PPA 都提供了可用源,但我不能保证所有的 PPA 都是安全的,所以 Ubuntu Tweak 会有一些安全风险。
|
||||
|
||||
如你们所见,从0.6版本后 Ubuntu Tweak 就已经移除了源中心(Source Center)。但请不要混淆“Ubuntu默认包含”和“加入源仓库”这两个概念。Ubuntu Tweak 首先应该要被加入通用资源仓库,然后才能被 Ubuntu 默认包含。
|
||||
|
||||
从错误报告和用户反馈来看,Ubuntu Tweak 已经比老版本更加稳定及更易使用。
|
||||
|
||||
**你有收到来自 Canonical 和 Ubuntu 开发者的支持或有跟他们合作(不论什么)的事项吗,是哪些方面的?**
|
||||
|
||||
当然,我得到 Canonical 公司的一些帮助,他们试着帮我把 Ubuntu Tweak 放入源仓库。这工作现在仍然在进行。
|
||||
|
||||
也得到社区的很多热心帮助,他们帮我翻译、设计、测试、报告错误,甚至提交代码分支。
|
||||
|
||||
**开发 Ubuntu Tweak 的有多少人?**
|
||||
|
||||
如果你说的是“代码开发者”,就仅仅我一个,但我们有很多设计人员:logo 是M.Sharp设计的,Kevin Chou 帮助设计了 Ubuntu Tweak 的用户界面(UI)原型,就是0.6版本的样子。现在 Jeonkwan Chan 正在帮我重新美化用户界面,将会用在0.7版本上。任何人,只要愿意就可以加入到 Ubuntu Tweak 的开发中来:)
|
||||
|
||||
**在Ubuntu11.04版本中当 Unity 出现时,许多 Ubuntu 用户抱怨其可配置性不好,您对这个怎么看的?这个特殊的桌面环境能有些什么多适用性的配置能力呢?**
|
||||
|
||||
我喜欢桌面系统的可配置高适应性,这是 Linux 系统的优点,不是吗?
|
||||
|
||||
例如,我不喜欢 Unity Launcher 的自动隐藏功能,所以我设置让他不会隐藏。
|
||||
|
||||
事实上,Unity 是可配置的,仅仅是它缺少 CompizConfig 设置管理器,所以你不能把 Unity Launcher 放到桌面底部或右面,这对左撇子来说很不友好。哈哈,开玩笑的。
|
||||
|
||||
如大家所见,Ubuntu 12.04已经增加了隐藏/显示切换功能,Launcher 的大小在系统设置中也可以自定义设置。我认为 Unity 将会有更多的可配置功能。
|
||||
|
||||
**一般来说,你认为 Canonical 公司开发 Unity 桌面环境是正确的决策吗?他们与 Gnome 开发者之间有合作争议,这有些是不可避免的吗?**
|
||||
|
||||
是的,对于 Canonical 公司来说,我觉得他们的决策很正确。回顾三年前,当 Ubuntu 首次引入基于 GNOME Panel 的Indicator ,它的设计就要比原来直接的 GNOME Panel 小程序更优雅。但 Canonical 开发者和 GNOME 开发者之间合作有些问题,因为他们从来没有着眼于 GNOME。直到 GNOME 3 的面世,情况才有所好转,它的 GNOME Shell 已经从 GNOME Panel 移出来了,并且 GNOME Shell 的面板已经和上面提到的 Indicator 用的是同一套设计方式。如果他们之间共用相同的 API 的话,桌面Linux应该会更好用。
|
||||
|
||||
所以来自于公司、社区、GNOME 桌面等的不同的关于用户界面的见解,综合起来最终就形成了 Unity。
|
||||
|
||||
我认为这是好事。至少,到目前为至,比起 GNOME Shell 来说,我更喜欢 Unity。
|
||||
|
||||
**虽然你正在开发的是一款 Ubuntu 系统专用的程序,但我假设你为了使用更多的高级用户功能,会使用其它的发行版本。你会选择哪些发行版本呢?为什么?**
|
||||
|
||||
当然,我已经玩过 Fedora、Arch、 OpenSUSE,特别是 Gentoo,我已经整整使用了一年。它是我第二喜欢的 Linux 发行系统,因为它拥有一个最先进的包管理系统。
|
||||
|
||||
但现在我仅仅只使用 Ubuntu 的桌面版本和服务版,也使用 Mac OS X,很多的设计灵感就来自于它 :)
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu Tweak 能被优化或做几个分支或者改变一点点,以便能在其它的 linux 发行版本比如 Fedora、OpenSue 或者 Debian 上使用吗?有做成统一的一个叫做“Linux Tweak”的应用程序,用户不管选择什么样的发布版本或桌面环境都可以用这种想法吗?不知道是否可行?**
|
||||
|
||||
可以的,要让 Ubuntu Tweak 在其它发行版本中运行非常容易。它是模块化的,很轻松的就可以改造(hack)。
|
||||
|
||||
2008年的时候,我就发布了一版 Fedora 的“Ubuntu Tweak for Fedora”,但最终我放弃维护这个版本了,因为我主要关注 Ubuntu 版本的,所以没有那么多精力。
|
||||
|
||||
**那 Ubuntu Tweak 的未来计划是什么?也许 Canonical 公司会内嵌进系统,然后把它做为发布版本默认的工具或者他们会基于他们自己的系统调整工具来使用它。您认为呢?您的下一步计划会是什么的呢?**
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Tweak 的未来当然会一片光明。哈哈。
|
||||
|
||||
我已经开始实现把 Ubuntu Tweak 加入软件中心这个工作了。如果用户能从软件中心直接安装 Ubuntu Tweak,它会更容易。
|
||||
|
||||
现在我正在开发0.7版本的,它将更美观,并且与 Unity 桌面的集成度更好,也加入了一些很有用的新功能。我想使Ubuntu Tweak 在 Unity 桌面环境下尽可能的发挥作用。
|
||||
|
||||
跟随着 Ubuntu 12.04的发布,我也计划发布新的版本,希望大家喜欢 :)
|
||||
|
||||
还有一件事要透露下,我已经加入 Canonical 北京公司,负责处理 OEM 的事情。虽然 Ubuntu Tweak 仍是一个个人项目,我还没有参与进 Ubuntu 的开发任务,但有可能话我会试着加入开发团队 :)
|
||||
|
||||
**太伟大了!谢谢 Tualatrix。**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/interview-with-ding-zhou-of-ubuntu-tweak/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ubuntu-tweak.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,86 @@
|
||||
Linux领袖说:‘开源很安全,Linux比其它任何系统都安全’
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在对Linux基金会执行官,Jim Zemlin 的采访中,VentureBeat 展望了2014年开源操作系统的未来。
|
||||
|
||||
访谈中我们也探讨了争议性的话题,就是政府部门的监听事件以及‘后门’-那些邪恶的窗口,窥探我们网上的私生活,最近公众发现我们经常使用的大多数服务都有类似的遭遇。
|
||||
|
||||
Zemlin 为我们解释了 GNU/Linux 为什么以及如何使它成为内心有些担忧的消费者的最安全的选择。还有就是为什么选择GNU/Linux作为能源汽车、手机、TV以及其它新兴设备的操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是我们完整的e-mail访谈实录
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 安全和隐私一直是本年度最热门的话题,我们听到的谣言,Linus[Torvalds, Linux 创始人]对政府部门是否有植入后门的要求点头称是。**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 如果Linux真有后门,你应该知道的。
|
||||
|
||||
全世界的用户都可以看到Linux的每一行代码。这也是linux要比其他操作系统更安全、开源整体要比闭源更安全的原因之一。代码的透明度保证了它的安全性。
|
||||
|
||||
必须明确指出:Linux没有后门。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: Linux基金会如何保证Linux用户的隐私和自由,使其免于遭受追踪和监视?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 对此,我们一以贯之。向内核插入违反隐私权和背离自由精神的代码而不被成千上万的开发者注意到,这是很难的。Linux的本性就是自我定制。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 今年的隐私/安全/监视事件会不会促使, 或者将会促使更多的消费者倾向于Linux,对此你作何感想?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 世界范围内,我听到人们都在说,“用开源保证隐私是必须的。”的确,那会促使更多的使用者选择Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
除了他们对linux平台下的隐私和安全持自信、信任的态度以外, 我认为消费者会基于多种原因选择Linux。
|
||||
代码的透明性以及开发过程逐渐给予日渐博学和警觉的消费者一个选择,一个会让他们对linux感觉良好的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
[视频游戏发行商] Valve [及其SteamOS下的工作][1] 正在促使更多的消费者走进Linux,就像逐渐占据主导地位的Android和其他运行Linux的电子设备一样,比如电视、家电、汽车等,当然还有更多。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 针对手机的Ubuntu Edge, 对它有何看法? 对于2014-2015年Linux/Ubuntu手机市场走势,你作何预测?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**:我希望看到潜在的有趣的新产品进入市场,尤其是基于Linux的产品。很难说每年哪款产品会成为手机市场的新宠。
|
||||
|
||||
我认为预测基于Linux的手机将占据主导地位,不算夸大事实。Android, Tizen, Ubuntu, Firefox,等等等等,都显示出Linux可以驱动手机市场的创新,并且为消费者创造新的体验,为开发者和OEMs创造机会。
|
||||
|
||||
明年令人振奋的发展,也是我所关注的就是linux和开源界如何把这些设备、对象和服务关联到一起。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 目前为止,你看到的linux嵌入式车载系统的最令人激动的使用案例是什么?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 毫无疑问,就是,Cadillac, Tesla, Toyota, Jaguar, Land Rover等都搭建了车载信息娱乐系统。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,今年赢得了 “年度汽车族”奖项的Tesla Model S,装备了一个17英寸平面、运行着定制Linux的电脑。这真的是太酷了。
|
||||
|
||||
2014年度汽车族刚刚揭晓 -- Cadillac CTS sedan, 也是使用linux作为车载信息娱乐系统。汽车制造商有能力使用linux进行创新并区别使用这些系统。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux的成功也能从来自IHS汽车的最新数据上看到,IHS本月报告称,在全球车载信息娱乐市场,基于linux的汽车销量2020年有望达到5370万,超过微软和黑莓QNX。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux基金会协同汽车级Linux工作组在该领域做了许多工作。通过在Linux内核社区,其他开源社区,以及汽车行业,营造一个中立、支持性的环境,我们能够帮助一些世界级巨头汽车制造商提高汽车Linux技术,如日产,捷豹,路虎,丰田,等等。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 在硬核开发者市场以外,Linux是如何发展壮大的,尤其是考虑到消费者和游戏玩家?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**:可以肯定的是,对游戏玩家来说,今年确实是linux的一个转折点。Valve, 一个基于Steam网络平台的一个游戏厂商,在linux上构建并运行所有的源代码和动画。Valve的CEO Gabe Newell 称,今年的LinuxCon大会上他们在linux平台运行了198个游戏,随着引进基于linux的Steam,这个数字还会上升。这是Linux和游戏界新趋势的开端。
|
||||
|
||||
用户每天都在用linux。软件支撑着我们的日常生活。像Google,Facebook还有Twitter等公司,都建立在Linux和开源软件之上。去年10月份LinuxCon欧洲大会上,来自Twitter的Chris Aniszczyk告诉听众:
|
||||
“Twitter 理所当然完全运行在linux上。为什么你们还需要其他的东西?”(译注:言外之意就是有linux就够了,不需要别的什么东西了。)
|
||||
|
||||
如今Linux驱动着130万台日常所用Android手机,每天近60万基于linux的新电视售出。新的家电以及汽车都建立在linux之上。主要交通系统也都在使用linux。最受欢迎的[GoPro 使用linux和开源软件][2]。这样的例子层出不穷。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux和开源理念将会逐渐融入主流消费者的生活。三星使用linux内核以及基于linux的产品充实它的产品线,从电视机到手机,再到家电,等等等等。
|
||||
|
||||
敬请关注 - 未来你将看到更多实例,展现了Linux和开源软件,以及协同开发在日常生活中发挥越来越大的作用。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 在你看来,到2014年,免费和开源软件最大的机遇会是什么?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 我们已经谈到游戏和电子设备,但是企业将会继续为linux呈现更多的机会。云计算的兴起为开发者带来新的机遇和挑战。你可以试着去找找不运行在linux上的公共云。
|
||||
|
||||
软件定义的网络(SDN)实现将成为2014年的主要活动之一。人们并没有期望着软件定义网络以及网络功能虚拟化变得多么大。想想吧。数十亿美元花费在硬件上,交换机,路由,负载均衡器,防火墙等等。这些都抽象成了软件。更更重要的是,它是在开源软件的基础架构甜蜜点OSS层被抽象。我认为你会看到,像OpenDaylight项目以及其他项目,在2014年都会有大的突破。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,这只是实现协同发展的大趋势的一部分,你的读者应该会对此感兴趣。我的推测是再过一个20年,几乎所有的基础软件都会以协同开发的方式进行构建。2014年开发者需要学习如何以协同方式构建软件,要学会如何参与开源项目并且贡献代码。如果开发者能够理解协同开发和开源的原则和理念,那么他们职业生涯中的机遇将会是无穷的。
|
||||
|
||||
参与到linux的世界中来是一个激动人心的时刻。从智能手表到电视机,到汽车,只要你能想到,Linux就能为你实现。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://venturebeat.com/2013/11/26/linux-chief-open-source-is-safer-and-linux-is-more-secure-than-any-other-os-exclusive/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[l3b2w1](https://github.com/l3b2w1) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://venturebeat.com/2013/09/23/steamos-valves-linux-based-operating-system-for-the-tv-and-living-room/
|
||||
[2]:http://gopro.com/support/open-source
|
||||
@ -1,110 +0,0 @@
|
||||
tomatoKiller 翻译中
|
||||
|
||||
10 Linux Interview Questions and Answers for Linux Beginners – Part 3
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Continuing the **Interview Questions** series, with a big thanks for the nice feedback on last two articles of this series, we are here presenting **10 questions** again for interactive learning.
|
||||
|
||||
- [11 Basic Linux Interview Questions and Answers – Part 1][1]
|
||||
- [10 Basic Linux Interview Questions and Answers – Part II][2]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 1. How will you add a new user (say, tux) to your system.? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- useradd command
|
||||
- adduser command
|
||||
- linuxconf command
|
||||
- All of the above
|
||||
- None of the above
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : All of the above commands i.e., **useradd, adduser** and **linuxconf** will add an user to the Linux system.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. How many primary partition is possible on one drive? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 1
|
||||
- 2
|
||||
- 4
|
||||
- 16
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : There are a maximum of ‘**4**‘ primary partition possible on a drive.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. The default port for Apache/Http is? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 8080
|
||||
- 80
|
||||
- 8443
|
||||
- 91
|
||||
- None of the above.
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : By default Apache/Http is configured on port **80**.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. What does GNU stand for? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- GNU’s not Unix
|
||||
- General Unix
|
||||
- General Noble Unix
|
||||
- Greek Needed Unix
|
||||
- None of the above
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : GNU stands for ‘**GNU**‘s not **Unix**‘.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. You typed at shell prompt “mysql” and what you got in return was “can’t connect to local MySQL server through socket ‘/var/mysql/mysql.sock’”, what would you check first. ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Seeing the error message, I will first check if mysql is running or not using commands **service mysql status** or **service mysqld status**. If mysql service is not running, starting of the service is required.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**:The above error message can be the result of ill configured **my.cnf** or mysql **user permission**. If mysql service starting doesn’t help, you need to see into the above said issues.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. How to Mount a windows ntfs partition on Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : First install **ntfs3g** pack on the system using **apt** or **yum** tool and then use “**mount sudo mount t ntfs3g /dev/<Windowspartition>/<Mountpoint>**” command to mount Windows partition on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. From the following which is not an RPM based OS.? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- RedHat Linux
|
||||
- Centos
|
||||
- Scientific Linux
|
||||
- Debian
|
||||
- Fedora
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘**Debian**‘ operating system is not an **RPM** based and all listed above are ‘**RPM**‘ based except Debian.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Which command can be used to rename a file in Linux.? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- mv
|
||||
- ren
|
||||
- rename
|
||||
- change
|
||||
- None of the Above
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The **mv** command is used to rename a file in Linux. For example, **mv /path_to_File/original_file_name.extension /Path_to_File/New_name.extension**.
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Which command is used to create and display file in Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- ed
|
||||
- vi
|
||||
- cat
|
||||
- nano
|
||||
- None of the above
|
||||
|
||||
Answer : The ‘**cat**‘ command can be used to create and display file in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. What layer protocol is responsible for user and the application program support such as passwords, resource sharing, file transfer and network management? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Layer 4 protocols
|
||||
- Layer 5 protocols
|
||||
- Layer 6 protocols
|
||||
- Layer 7 protocols
|
||||
- None of the above
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘**Layer 7 Protocol**‘ is responsible for user and the application program support such as passwords, resource sharing, file transfer and network management.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/linux-interview-questions-and-answers-for-linux-beginners/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/basic-linux-interview-questions-and-answers/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/basic-linux-interview-questions-and-answers-part-ii/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,645 @@
|
||||
29 Practical Examples of Nmap Commands for Linux System/Network Administrators
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The **Nmap** aka **Network Mapper** is an open source and a very versatile tool for Linux system/network administrators. **Nmap** is used for **exploring networks, perform security scans, network audit** and **finding open ports** on remote machine. It scans for Live hosts, Operating systems, packet filters and open ports running on remote hosts.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*Nmap Commands and Examples*
|
||||
|
||||
I’ll be covering most of **NMAP** usage in two different parts and this is the first part of nmap serious. Here in this setup, I have used two servers without firewall to test the working of the Nmap command.
|
||||
|
||||
- 192.168.0.100 – server1.tecmint.com
|
||||
- 192.168.0.101 – server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
### Nmap command usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
# nmap [Scan Type(s)] [Options] {target specification}
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Install NMAP in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the today’s Linux distributions like **Red Hat, CentOS, Fedoro, Debian** and **Ubuntu** have included **Nmap** in their default package management repositories called [Yum][1] and [APT][2]. The both tools are used to install and manage software packages and updates. To install **Nmap** on distribution specific use the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install nmap [on Red Hat based systems]
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install nmap [on Debian based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
Once you’ve install latest nmap application, you can follow the example instructions provided in this article.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Scan a System with Hostname and IP Address ###
|
||||
|
||||
The **Nmap** tool offers various methods to scan a system. In this example, I am performing a scan using hostname as **server2.tecmint.com** to find out all open ports, services and MAC address on the system.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Scan using Hostname ####
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 15:42 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.415 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
#### Scan using IP Address ####
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-18 11:04 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
958/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.465 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Scan using “-v” option ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can see that the below command with “**-v**” option is giving more detailed information about the remote machine.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -v server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 15:43 EST
|
||||
Initiating ARP Ping Scan against 192.168.0.101 [1 port] at 15:43
|
||||
The ARP Ping Scan took 0.01s to scan 1 total hosts.
|
||||
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan against server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101) [1680 ports] at 15:43
|
||||
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 192.168.0.101
|
||||
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 192.168.0.101
|
||||
Discovered open port 8888/tcp on 192.168.0.101
|
||||
Discovered open port 111/tcp on 192.168.0.101
|
||||
Discovered open port 3306/tcp on 192.168.0.101
|
||||
Discovered open port 957/tcp on 192.168.0.101
|
||||
The SYN Stealth Scan took 0.30s to scan 1680 total ports.
|
||||
Host server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101) appears to be up ... good.
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.485 seconds
|
||||
Raw packets sent: 1681 (73.962KB) | Rcvd: 1681 (77.322KB)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Scan Multiple Hosts ####
|
||||
|
||||
You can scan multiple hosts by simply writing their IP addresses or hostnames with Nmap.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap 192.168.0.101 192.168.0.102 192.168.0.103
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:06 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
Nmap finished: 3 IP addresses (1 host up) scanned in 0.580 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Scan a whole Subnet ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can scan a whole subnet or IP range with Nmap by providing *** wildcard** with it.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap 192.168.0.*
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:11 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server1.tecmint.com (192.168.0.100):
|
||||
Not shown: 1677 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
851/tcp open unknown
|
||||
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 256 IP addresses (2 hosts up) scanned in 5.550 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
On above output you can see that nmap scanned a whole subnet and gave the information about those hosts which are **Up** in the **Network**.
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Scan Multiple Servers using last octet of IP address ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can perform scans on multiple IP address by simple specifying last octet of IP address. For example, here I performing a scan on IP addresses 192.168.0.101, 192.168.0.102 and 192.168.0.103.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap 192.168.0.101,102,103
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:09 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 3 IP addresses (1 host up) scanned in 0.552 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. Scan list of Hosts from a File ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you have more hosts to scan and all host details are written in a file , you can directly ask nmap to read that file and perform scans. Let’s see how to do that.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a text file called “**nmaptest.txt**” and define all the IP addresses or hostname of the server that you want to do a scan.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# cat > nmaptest.txt
|
||||
|
||||
localhost
|
||||
server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Next, run the following command with “**iL**” option with nmap command to scan all listed IP address in the file.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -iL nmaptest.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-18 10:58 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on localhost.localdomain (127.0.0.1):
|
||||
Not shown: 1675 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
25/tcp open smtp
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
631/tcp open ipp
|
||||
857/tcp open unknown
|
||||
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
958/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
958/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 3 IP addresses (3 hosts up) scanned in 2.047 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Scan an IP Address Range ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify an IP range while performing scan with Nmap.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap 192.168.0.101-110
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:09 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 10 IP addresses (1 host up) scanned in 0.542 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. Scan Network Excluding Remote Hosts ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can exclude some hosts while performing a full network scan or when you are scanning with wildcards with “**–exclude**” option.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap 192.168.0.* --exclude 192.168.0.100
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:16 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 255 IP addresses (1 host up) scanned in 5.313 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Scan OS information and Traceroute ###
|
||||
|
||||
With Nmap, you can detect which OS and version is running on the remote host. To enable OS & version detection, script scanning and traceroute, we can use “**-A**” option with NMAP.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -A 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:25 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 4.3 (protocol 2.0)
|
||||
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.3 ((CentOS))
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind 2 (rpc #100000)
|
||||
957/tcp open status 1 (rpc #100024)
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql MySQL (unauthorized)
|
||||
8888/tcp open http lighttpd 1.4.32
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see http://www.insecure.org/cgi-bin/nmap-submit.cgi).
|
||||
TCP/IP fingerprint:
|
||||
SInfo(V=4.11%P=i686-redhat-linux-gnu%D=11/11%Tm=52814B66%O=22%C=1%M=080027)
|
||||
TSeq(Class=TR%IPID=Z%TS=1000HZ)
|
||||
T1(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=16A0%ACK=S++%Flags=AS%Ops=MNNTNW)
|
||||
T2(Resp=N)
|
||||
T3(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=16A0%ACK=S++%Flags=AS%Ops=MNNTNW)
|
||||
T4(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=O%Flags=R%Ops=)
|
||||
T5(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=S++%Flags=AR%Ops=)
|
||||
T6(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=O%Flags=R%Ops=)
|
||||
T7(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=S++%Flags=AR%Ops=)
|
||||
PU(Resp=Y%DF=N%TOS=C0%IPLEN=164%RIPTL=148%RID=E%RIPCK=E%UCK=E%ULEN=134%DAT=E)
|
||||
|
||||
Uptime 0.169 days (since Mon Nov 11 12:22:15 2013)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 22.271 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
In above Output, you can see that nmap is came up with TCP/IP fingerprint of the OS running on remote hosts and being more specific about the port and services running on the remote hosts.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Enable OS Detection with Nmap ###
|
||||
|
||||
Use the option “-O” and “-osscan-guess” also helps to discover OS information.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -O server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:40 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
No exact OS matches for host (If you know what OS is running on it, see http://www.insecure.org/cgi-bin/nmap-submit.cgi).
|
||||
TCP/IP fingerprint:
|
||||
SInfo(V=4.11%P=i686-redhat-linux-gnu%D=11/11%Tm=52815CF4%O=22%C=1%M=080027)
|
||||
TSeq(Class=TR%IPID=Z%TS=1000HZ)
|
||||
T1(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=16A0%ACK=S++%Flags=AS%Ops=MNNTNW)
|
||||
T2(Resp=N)
|
||||
T3(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=16A0%ACK=S++%Flags=AS%Ops=MNNTNW)
|
||||
T4(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=O%Flags=Option -O and -osscan-guess also helps to discover OSR%Ops=)
|
||||
T5(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=S++%Flags=AR%Ops=)
|
||||
T6(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=O%Flags=R%Ops=)
|
||||
T7(Resp=Y%DF=Y%W=0%ACK=S++%Flags=AR%Ops=)
|
||||
PU(Resp=Y%DF=N%TOS=C0%IPLEN=164%RIPTL=148%RID=E%RIPCK=E%UCK=E%ULEN=134%DAT=E)
|
||||
|
||||
Uptime 0.221 days (since Mon Nov 11 12:22:16 2013)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 11.064 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 11. Scan a Host to Detect Firewall ###
|
||||
|
||||
The below command will perform a scan on a remote host to detect if any packet filters or Firewall is used by host.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sA 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:27 EST
|
||||
All 1680 scanned ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101) are UNfiltered
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.382 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 12. Scan a Host to check its protected by Firewall ###
|
||||
|
||||
To scan a host if it is protected by any packet filtering software or Firewalls.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -PN 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:30 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.399 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 13. Find out Live hosts in a Network ###
|
||||
|
||||
With the help of “**-sP**” option we can simply check which hosts are live and up in Network, with this option nmap skips port detection and other things.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sP 192.168.0.*
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-18 11:01 EST
|
||||
Host server1.tecmint.com (192.168.0.100) appears to be up.
|
||||
Host server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101) appears to be up.
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
Nmap finished: 256 IP addresses (2 hosts up) scanned in 5.109 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 14. Perform a Fast Scan ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can perform a fast scan with “**-F**” option to scans for the ports listed in the nmap-services files and leaves all other ports.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -F 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:47 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1234 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.322 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 15. Find Nmap version ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can find out Nmap version you are running on your machine with “**-V**” option.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -V
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap version 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ )
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 16. Scan Ports Consecutively ###
|
||||
|
||||
Use the “**-r**” flag to don’t randomize.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -r 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 16:52 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.363 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
17. Print Host interfaces and Routes
|
||||
|
||||
You can find out host interface and route information with nmap by using “**–iflist**” option.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap --iflist
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:07 EST
|
||||
************************INTERFACES************************
|
||||
DEV (SHORT) IP/MASK TYPE UP MAC
|
||||
lo (lo) 127.0.0.1/8 loopback up
|
||||
eth0 (eth0) 192.168.0.100/24 ethernet up 08:00:27:11:C7:89
|
||||
|
||||
**************************ROUTES**************************
|
||||
DST/MASK DEV GATEWAY
|
||||
192.168.0.0/0 eth0
|
||||
169.254.0.0/0 eth0
|
||||
|
||||
In above output, you can see that map is listing interfaces attached to your system and their respective routes.
|
||||
|
||||
### 18. Scan for specific Port ###
|
||||
|
||||
There are various options to discover ports on remote machine with Nmap. You can specify the port you want nmap to scan with “**-p**” option, by default nmap scans only **TCP** ports.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -p 80 server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:12 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) sca
|
||||
|
||||
### 19. Scan a TCP Port ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can also specify specific port types and numbers with nmap to scan.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -p T:8888,80 server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:15 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.157 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 20. Scan a UDP Port ###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sU 53 server2.tecmint.com
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:15 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
53/udp open http
|
||||
8888/udp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.157 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 21. Scan Multiple Ports ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can also scan multiple ports using option “**-p**“.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -p 80,443 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-18 10:56 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
443/tcp closed https
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.190 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
### 22. Scan Ports by Network Range ###
|
||||
|
||||
You can scan ports with ranges using expressions.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -p 80-160 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
### 23. Find Host Services version Numbers ###
|
||||
|
||||
We can find out service’s versions which are running on remote hosts with “**-sV**” option.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sV 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:48 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 4.3 (protocol 2.0)
|
||||
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.2.3 ((CentOS))
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind 2 (rpc #100000)
|
||||
957/tcp open status 1 (rpc #100024)
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql MySQL (unauthorized)
|
||||
8888/tcp open http lighttpd 1.4.32
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 12.624 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
#### 24. Scan remote hosts using TCP ACK (PA) and TCP Syn (PS) ####
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes packet filtering firewalls blocks standard **ICMP** ping requests, in that case, we can use **TCP ACK** and **TCP Syn** methods to scan remote hosts.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -PS 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 17:51 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.360 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 25. Scan Remote host for specific ports with TCP ACK ###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -PA -p 22,80 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 18:02 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.166 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 26. Scan Remote host for specific ports with TCP Syn ###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -PS -p 22,80 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 18:08 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.165 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 27. Perform a stealthy Scan ###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sS 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 18:10 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.383 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 28. Check most commonly used Ports with TCP Syn ###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sT 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 18:12 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open http
|
||||
111/tcp open rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 0.406 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
### 29. Perform a tcp null scan to fool a firewall ###
|
||||
|
||||
[root@server1 ~]# nmap -sN 192.168.0.101
|
||||
|
||||
Starting Nmap 4.11 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ ) at 2013-11-11 19:01 EST
|
||||
Interesting ports on server2.tecmint.com (192.168.0.101):
|
||||
Not shown: 1674 closed ports
|
||||
PORT STATE SERVICE
|
||||
22/tcp open|filtered ssh
|
||||
80/tcp open|filtered http
|
||||
111/tcp open|filtered rpcbind
|
||||
957/tcp open|filtered unknown
|
||||
3306/tcp open|filtered mysql
|
||||
8888/tcp open|filtered sun-answerbook
|
||||
MAC Address: 08:00:27:D9:8E:D7 (Cadmus Computer Systems)
|
||||
|
||||
Nmap finished: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 1.584 seconds
|
||||
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it with **NMAP** for now, I’ll be coming up more creative options of **NMAP** in our second part of this serious. Till then, stay tuned with us and don’t forget to share your valuable comments.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/nmap-command-examples/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/useful-basic-commands-of-apt-get-and-apt-cache-for-package-management/
|
||||
@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
|
||||
7 Tips For Becoming A Linux Terminal Power User
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The Linux terminal is much more than merely entering commands into it. If you master the basic tricks, it will assist you in mastering the Bash shell that is used as default on a number of Linux distributions.
|
||||
|
||||
As stated on howtogeek.com, here are some tips for new users as well as advanced users who may have missed out on something along the way-
|
||||
|
||||
**1. Tab Completion** – This saves time and is also handy if you’re unsure of a file or command’s exact name. For instance, there’s a file named “really long file name” in the current directory and you wish to delete it. You can type the entire file name, however, you will have to ensure that you escape the space characters properly. In case of multiple files in the current directory which start with the letter r, Bash will not be aware of the one you want.
|
||||
|
||||
In the event you have another file named “really very long file name” in the current directory and you hit Tab. Bash will fill in the “really\ “ part for both the files start with that. Post that press Tab again and you’ll find a list of matching file names.
|
||||
|
||||
**2. Pipes** – This permits you to transmit the output of a command to another command. In the UNIX philosophy, every program is a small utility that performs one thing well. For instance, the ls command lists out the files in the current directory and the grep command searches its input for a specified term.
|
||||
|
||||
You can combine these with pipes (the | character) and search for a file in the current directory. The command given below searches for the word “word”:
|
||||
|
||||
ls | grep word
|
||||
|
||||
**3. Wild Cards** - The * (asterisk) character is a wild card for matching anything. For instance, if you want to delete both “really long file name” and “really very long file name” from the current directory, you can run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
rm really*name
|
||||
|
||||
This command deletes all files with file names starting with “really” and ending with “name.” However, in case you ran rm * instead, you would end up deleting every file in the current directory.
|
||||
|
||||
**4. Output Redirection** - The > character redirects a command’s output to a file in place of another command. For instance, the following line runs the ls command to list the files in the current directory and in lieu of printing that list to the terminal, it prints to a file named “file1” in the current directory:
|
||||
|
||||
ls > file1
|
||||
|
||||
**5. Command History** – Bash memorizes history of the commands you enter into it. The up and down arrow keys can be used to scroll through recent commands used by you. The history command prints out a list of these commands for piping it to grep in order to search for commands used by you recently.
|
||||
|
||||
~, . & ..
|
||||
|
||||
The ~ character also called the tilde is used to show the current user’s home directory. So in lieu of typing cd /home/name for going to your home directory, you can type cd ~. This also functions with relative paths – cd ~/Desktop to go to the current user’s desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
In the same way, the . is for the current directory and the .. is for the directory above the current directory. So, cd .. goes up a directory. It functions with relative paths for instance when you are in your Desktop folder and wish to go to the Documents folder, that is in the same directory as the Desktop folder, you can make use of the cd ../Documents command.
|
||||
|
||||
**6. Running a Command in the Background** – Bash by default executes every command that is run by you in the current terminal. It’s normally okay but what if you wish to launch an application and maintain utilizing the terminal? By typing firefox for launching Firefox, it will take charge of your terminal and show error messages and other output till you have closed it. You can use the & operator to the end of the command for Bash to execute the program in the backdrop.
|
||||
|
||||
firefox &
|
||||
|
||||
**7. Conditional Execution** – Bash can also run two commands sequentially. The second command can only execute when the first command is completed with success. For doing this, you can put both commands on the same line segregated by a &&, or double ampersand. The command given below will wait for five seconds, and start the gnome-screenshot tool:
|
||||
|
||||
sleep 5 && gnome-screenshot
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=123564
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
@ -1,166 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translated by coolpigs
|
||||
|
||||
Basic Linux Interview Questions and Answers – Part II
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Continuing the Interview Series, we are giving 10 Questions here, in this article. These questions and the questions in the future articles doesn’t necessarily means they were asked in any interview. We are presenting you an interactive learning platform through these kind of posts, which surely will be helpful.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Upon the analysis of comments in different forums on last article [11 Basic Linux Interview Questions][1] of this series, it is important to mention here that to bring up a quality article to our readers. We give our time and money, and in return what we expect from you? Nothing. If you can’t praise our work, please don’t demoralize us from your negative comments.
|
||||
|
||||
If you find nothing new in a post, don’t forget that for someone it was helpful, and for that he/she was thankful. We can’t make everyone happy in each of our article. Hope you readers would take pain to understand this.
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.1: Which command is used to record a user login session in a file? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- macro
|
||||
- read
|
||||
- script
|
||||
- record
|
||||
- sessionrecord
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘script’ command is used to record a user’s login session in a file. Script command can be implemented in a shell script or can directly be used in terminal. Here is an example which records everything between script and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s record the user’s login session with script command as shown.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# script my-session-record.txt
|
||||
|
||||
Script started, file is my-session-record.txt
|
||||
|
||||
The content of log file ‘my-session-record.txt’ can be views as:
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# nano my-session-record.txt
|
||||
|
||||
script started on Friday 22 November 2013 08:19:01 PM IST
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# ls
|
||||
^[[0m^[[01;34mBinary^[[0m ^[[01;34mDocuments^[[0m ^[[01;34mMusic^[[0m $
|
||||
^[[01;34mDesktop^[[0m ^[[01;34mDownloads^[[0m my-session-record.txt ^[[01;34$
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.2: The kernel log message can be viewed using which of the following command? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- dmesg
|
||||
- kernel
|
||||
- ls -i
|
||||
- uname
|
||||
- None of the above
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The kernel log message can be viewed by executing 'dmesg' command. In the list kernel is not a valid Linux command, 'ls -i' lists the file with inode within the working directory and 'uname' command shows os.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# dmesg
|
||||
|
||||
Initializing cgroup subsys cpuset
|
||||
Initializing cgroup subsys cpu
|
||||
Linux version 2.6.32-279.el6.i686 (mockbuild@c6b9.bsys.dev.centos.org) (gcc version 4.4.6 20120305 (Red Hat 4.4.6-4) (GCC) ) #1 SMP Fri Jun 22 10:59:55 UTC 2012
|
||||
KERNEL supported cpus:
|
||||
Intel GenuineIntel
|
||||
AMD AuthenticAMD
|
||||
NSC Geode by NSC
|
||||
Cyrix CyrixInstead
|
||||
Centaur CentaurHauls
|
||||
Transmeta GenuineTMx86
|
||||
Transmeta TransmetaCPU
|
||||
UMC UMC UMC UMC
|
||||
Disabled fast string operations
|
||||
BIOS-provided physical RAM map:
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.3: Which command is used to display the release of Linux Kernel? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- uname -v
|
||||
- uname -r
|
||||
- uname -m
|
||||
- uname -n
|
||||
- uname -o
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The command ‘uname -r’ display the kernel release information. The switch ‘-v’ , ‘-m’ , ‘-n’ , ‘o’ display kernel version, machine hardware name, network node, hostname and operating system, respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# uname -r
|
||||
|
||||
2.6.32-279.el6.i686
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.4: Which command is used to identify the types of file? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- type
|
||||
- info
|
||||
- file
|
||||
- which
|
||||
- ls
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘file’ command is used to identify the types of file. The syntax is ‘file [option] File_name’.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# file wtop
|
||||
|
||||
wtop: POSIX shell script text executable
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.5: Which command locate the binary, source and man page of a command? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘whereis’ command comes to rescue here. The ‘whereis’ command locate the binary, source, and manual page files for a command.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# whereis /usr/bin/ftp
|
||||
|
||||
ftp: /usr/bin/ftp /usr/share/man/man1/ftp.1.gz
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.6: When a user login, which files are called for user profile, by default?? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘.profile’ and ‘.bashrc’ present under home directory are called for user profile by default.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# ls -al
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 tecmint tecmint 176 May 11 2012 .bash_profile
|
||||
-rw-r--r--. 1 tecmint tecmint 124 May 11 2012 .bashrc
|
||||
|
||||
### ###Q.7: The ‘resolve.conf’ file is a configuration file for?
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘/etc/resolve.conf’ is the configuration file for DNS at client side.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# cat /etc/resolv.conf
|
||||
|
||||
nameserver 172.16.16.94
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.8: Which command is used to create soft link of a file? ###
|
||||
|
||||
- ln
|
||||
- ln -s
|
||||
- link
|
||||
- link -soft
|
||||
- None of the above
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The ‘ln -s’ command is used to create soft link of a file in Linux Environment.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# ln -s /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf httpd.original.conf
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.9: The command ‘pwd’ is an alias of command ‘passwd’ in Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : No! The command ‘pwd’ is not an alias of command ‘passwd’ by default. ‘pwd’ stands for ‘print working directory’, which shows current directory and ‘passwd is used to change the password of user account in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# pwd
|
||||
|
||||
/home/tecmint
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# passwd
|
||||
Changing password for user root.
|
||||
New password:
|
||||
Retype new password:
|
||||
|
||||
### Q.10: How will you check pci devices vendor and version on a Linux? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The Linux command ‘lspci’ comes to rescue here.
|
||||
|
||||
[root@tecmint ~]# lspci
|
||||
|
||||
00:00.0 Host bridge: Intel Corporation 5000P Chipset Memory Controller Hub (rev b1)
|
||||
00:02.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset PCI Express x8 Port 2-3 (rev b1)
|
||||
00:04.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset PCI Express x8 Port 4-5 (rev b1)
|
||||
00:06.0 PCI bridge: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset PCI Express x8 Port 6-7 (rev b1)
|
||||
00:08.0 System peripheral: Intel Corporation 5000 Series Chipset DMA Engine (rev b1)
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I hope these above questions might be very helpful to you. In our next weekend we again come-up with some new set of questions. Till then stay healthy, tuned and connected to Tecmint.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/basic-linux-interview-questions-and-answers-part-ii/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/basic-linux-interview-questions-and-answers/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
(whatever1992 ing)
|
||||
Built in Audit Trail Tool – Last Command in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
@ -177,4 +178,4 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-last-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Canonical Dev Calls Linux Mint ‘Vulnerable’, Wouldn’t Use it For Online Banking
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Linux Mint has since responded to the comments by Oliver Grawert. [You can read them here][1].
|
||||
|
||||
**Users of the popular Ubuntu-based operating system Linux Mint should not use it for online banking, a Canonical [engineer has advised][2].**
|
||||
|
||||
Mint’s decision to prevent packages with known security issues from updating – from the kernel and browser to the boot-loader and Xorg display server – leaves its users with a “vulnerable system”, says *Oliver Grawert*.
|
||||
|
||||
> “Instead of just integrating changes properly with the packages in the ubuntu archive they instead suppress doing (security) updates at all for them. i would say forcefully keeping a vulnerable kernel browser or xorg in place instead of allowing the provided security updates to be installer makes it a vulnerable system, (sic)”.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> “I personally wouldn’t do online banking with it.”
|
||||
|
||||
Grawert certainly isn’t alone in considering Mint a sub-par choice for the security conscious. Mozilla contributor and former Ubuntu member Benjamin **Kerensa* feels the same:**
|
||||
|
||||
> “It is unclear why Linux Mint disables all of their security updates. I can say that it took them many months to get a fixed version of Firefox packaged while Ubuntu and Debian had already had security fixes in their package.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> This puts Linux Mint users at risk and is one of the key reasons I never suggest Linux Mint to anyone as an alternative to Ubuntu.”
|
||||
|
||||
Oliver Grawert is no fly-by-night contributor. As one of Canonical’s Ubuntu Engineering bods he’s better placed than most to know what he’s talking about.
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘But are Mint users in actual risk? Yes and no…’
|
||||
|
||||
But are Mint users in actual risk?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes and no. The majority of security “holes” (for want of a better word) of the kind present in the packages that Mint’s developers steadfastly refuse to update are both documented and known, but rarely exploited by those of a nefarious breed. As such the “actual threat” posed to users remains, at least for now, largely a theoretical one.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s to say that there are no known incidents of identify theft or worse resulting from use of Mint (or any other Ubuntu-based distribution with unpatched packages) through any of the exploits referenced by Grawert on the Ubuntu Dev Mailing List.
|
||||
|
||||
But just because no-one has entered through the window left ajar thus far, isn’t to say someone won’t ever do it.
|
||||
|
||||
**After seeing Ubuntu given a long and sustained kicking about its own (largely theoretical) privacy issues, it will be interesting to see if, now the boot is placed firmly on the other foot, the vehement concern for users’ wellbeing will extend to other distributions. **
|
||||
|
||||
Notice: We reached out to Linux Mint for comment & clarification but received no reply.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/canonical-dev-dont-use-linux-mint-online-banking-unsecure
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:这个地址在发布的时候填写成“Linux Mint Respond to Ubuntu Developer’s ‘Vulnerable’ Claim”这篇文章的发布的地址
|
||||
[2]:https://lists.ubuntu.com/archives/ubuntu-devel-discuss/2013-November/014770.html
|
||||
65
sources/Command Line Basics – watch.md
Normal file
65
sources/Command Line Basics – watch.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,65 @@
|
||||
Command Line Basics – watch
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
There are several log files in a Linux system. Keeping an eye on these log files can be one of the important tasks of a Linux System administrator. You can easily view the end of a log file [using the tail command][1]. But if you want to monitor that file all day long it's pretty tedious to enter the tail command every few minutes to check on that log file. You could write a short [script with an infinite loop][2] to check the file periodically, but it turns out that there is already a program to handle repetitive tasks for you.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Linux watch Command ###
|
||||
|
||||
The **watch** command in Linux provides a way to handle repetitive tasks. By default **watch** will repeat the command that follows it every two seconds. As you can imagine, watch is a great tool to keep an eye on log files. Here's an example.
|
||||
|
||||
watch tail /var/log/syslog
|
||||
|
||||
In order to stop the command execution, just use the standard kill sequence, **[Ctrl]+C**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*Using the Linux watch command to monitor the syslog*
|
||||
|
||||
You can change the time interval by issuing the **-n** switch and specifying the interval in seconds. To check the log file every 10 seconds, try this.
|
||||
|
||||
watch -n 10 tail /var/log/syslog
|
||||
|
||||
### The Linux watch Command with a Pipe ###
|
||||
|
||||
The **watch** command isn't limited to viewing log files. It can be used to repeat any command you give it. If you have your system [set up to monitor the CPU temperature][3], you can use **watch** to view that with the **sensors** command.
|
||||
|
||||
watch -n 1 sensors
|
||||
|
||||
The output on my netbook looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
acpitz-virtual-0
|
||||
Adapter: Virtual device
|
||||
temp1: +45.0°C (crit = +100.0°C)
|
||||
|
||||
I'd like to filter this output to only show the temperature output without all of the rest.
|
||||
|
||||
I can use this command to view it one time.
|
||||
|
||||
sensors | grep temp | awk '{ print $2 }'
|
||||
|
||||
Keep in mind that the watch command will repeat the first command that is sees. Care must be taken when pipelining one command to the next. This can be managed by placing your command pipeline inside quotes.
|
||||
|
||||
watch -n1 "sensors | grep temp | awk '{ print $2 }'"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
*Using the Linux watch command with a pipe*
|
||||
|
||||
### Use watch as a clock ###
|
||||
|
||||
As you've probably noticed by now, the **watch** command shows the time that the command was executed in the upper right corner of the terminal window. We can use **watch** as a simple clock by passing an empty command line argument. We can just enclose a space in quotes to act as the empty command.
|
||||
|
||||
watch -n 1 " "
|
||||
|
||||
So you can see, this gives another meaning for the command name, **watch**. You can use it just like your wrist watch.
|
||||
|
||||
So now you know how to use the Linux watch command. What repetitive tasks will you use it to handle?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://tuxtweaks.com/2013/12/linux-watch-command/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://tuxtweaks.com/2011/02/command-line-basics-head-and-tail/
|
||||
[2]:http://tuxtweaks.com/2012/01/creating-a-terminal-window-clock/
|
||||
[3]:http://tuxtweaks.com/2008/08/how-to-control-fan-speeds-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips – TeamViewer 9 Is Available For Download
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
TeamViewer, the popular remote support and desktop sharing tool has been updated to version 9 for Windows, Mac OS X and Linux computers, including Ubuntu. TeamViewer allows you to control any computer over the internet from anywhere.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s a also a great tool to have if you’re in the business or helping folks troubleshoot computer related issues such as virus removal and/or sharing your screen with someone who is at a remote location.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of how this support tool can be used.
|
||||
|
||||
I recently got a call from my mother who was trying to figure out how to get a program installed. After spending few minutes over the phone trying to help her get the program without success, I decided to do it myself.
|
||||
|
||||
So we both download TeamViewer and within minutes, I was connected to her computer and installing the program myself.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s an example of how TeamViewer helps you get stuff done. If you’re going to be using TeamViewer to help your customers or clients, you may have to purchase a license to comply with the company’s policy.
|
||||
|
||||
Another reason I prefer TeamViewer over all other remote support tools is that it allows you to use the program without actually installing it, at least on Windows machines. If you only need to use it once, then just run it without taking up valuable disk space.
|
||||
|
||||
Now TeamViewer works on almost all operating systems, including Android and IOS.
|
||||
|
||||
Windows users can [download TeamViewer from here][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu users can [download and run TeamViewer from this link][2].
|
||||
|
||||
To easily install TeamViewer in Ubuntu, run the commands below to download the installer.
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://download.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux.deb
|
||||
|
||||
For **64-bit systems**, use the link below.
|
||||
|
||||
wget http://download.teamviewer.com/download/teamviewer_linux_x64.deb
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, run the commands below to install it.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo dpkg -i teamviewer_linux*.deb; sudo apt-get -f install
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If the commands above don’t work for you, then go to TeamViewer [download page and download a copy][2].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/12/daily-ubuntu-tips-teamviewer-9-is-available-for-download/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.teamviewer.com/en/download/windows.aspx
|
||||
[2]:http://www.teamviewer.com/en/download/linux.aspx
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips — Install VMware Workstation In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
VMware Workstation is a Type-2 commercial virtualization software. It’s Type-2 because is runs on top of existing operation systems and the computer it’s running on is known as the host computer.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use VMware Workstation to run multiple guest machines simultaneously running individual operating systems on the host machine. A guest machine can either be a 32-bit or 64-bit of supported operating systems. VMware Workstation supports Windows, Mac OS X, Solaris and many others.
|
||||
|
||||
This brief tutorial is going to show you how to install VMware Workstation in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
Since this program is a commercial program, you must have a valid license to use it. You could also [download the 30-day free trial version][1] from the download page to test it. If you want to register it, get a license key and validate it.
|
||||
|
||||
To get started installing VMware Workstation in Ubuntu, first update Ubuntu. To do that, run the commands below.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade && sudo apt-get autoremove
|
||||
|
||||
After updating your computer, run the commands below to prepare Ubuntu before the installation.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install build-essential linux-headers-`uname -r`
|
||||
|
||||
After that, download VMware Workstation. Next, change into the **~/Downloads** folder since Firefox saves files in the Downloads folder.
|
||||
|
||||
cd Downloads
|
||||
|
||||
Next, run the commands below to extract the download package if it came in a .zip archive. If not, go to the next line.
|
||||
|
||||
unzip VMware-Workstation-Full*.zip
|
||||
|
||||
Next, run the commands below to make the file executable.
|
||||
|
||||
chmod +x VMware-Workstation-Full*.bundle
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, run the commands below to begin the installation.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo ./VMware-Workstation-Full*.bundle
|
||||
|
||||
ollow the wizard until the installation is complete. When it’s done, open it from Dash and begin creating guest machines.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You should be able to create many guest machines of all types, including Windows, Linux, Novell, Solaris and others.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/12/daily-ubuntu-tips-install-vmware-workstation-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://my.vmware.com/web/vmware/info/slug/desktop_end_user_computing/vmware_workstation/10_0
|
||||
@ -1,33 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Daily Ubuntu Tips–Change The Language You Use In Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu, a modern and powerful operating system also allows you to use your desktop in dozens of other languages. By default, there are few language packs installed when you first setup Ubuntu. If you want Ubuntu to support more languages, you must install additional language packs. Not all languages are support, but most languages that are in used and written are supported. This brief tutorial is going to show you how to make this happen.
|
||||
|
||||
After installing a language pack, you can also rename standard folders like music, pictures and documents according to your language. You must log off and log back in for the changes to apply. When you log back in, you’ll prompted and asked if you want to rename these standard folders to match the names for your selected language.
|
||||
|
||||
To change which language you use in Ubuntu, click the top right **gear** of the menu bar and select **System Settings**. When the System Settings opens, select **Language Support**.
|
||||
|
||||
If prompted to install additional language support, do it. If not, click Install / Remove to install new language packs, then select the language you which to install and install it. Finally, drag the language at the top of the list and save. This change will only apply to your profile. If you which to apply the language settings system-wide, click **Apply System-Wide**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Drag the new language at the top of the list. When done, click Close.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Close out and log out. Then log back in and enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
Again, changing the language pack will only apply to your profile. If you want it globally, you must click Apply System-Wide.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If you choose to rename standard folders to your native language, you’ll see folders name changed after you sign on.
|
||||
|
||||
Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tipschange-the-language-you-use-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Repack Deb Files on Debian and Ubuntu
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The following tutorial will teach Ubuntu, Linux Mint and Debian GNU/Linux users how to easily unpack and repack a .deb file on their Debian-based Linux operating system.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Once in a while you reach a moment in life when, among other things, you want to modify a .deb file, to change something in it and repackage it back. But, only if you are truly into computing and hacking.
|
||||
|
||||
The following example is a true story, as it happen to me a while ago. A Linux developer created a Debian package (.deb) for a software, which I’ve install on my Ubuntu powered computer with success.
|
||||
|
||||
Apparently, the software did not worked correctly, as it was always stuck when it tried to retrieve some files from a Git repository. So, I knew where the files where installed (in the /opt directory), I’ve searched the code, found the issue and repair it in place. After that, the program was no longer stuck when it tried to retrieve the packages it needed.
|
||||
|
||||
So, long story short, I wanted to unpack the .deb file, replace the file I’ve patched in it, and repackage it back so I can install it on other computers or give it to my friends. How do I do that?
|
||||
|
||||
After searching the Internet for an answer to my problem, I’ve found a small blog called [ailoo.net][1] where it was explained like this:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p extract/DEBIAN
|
||||
dpkg-deb -x package.deb extract/
|
||||
dpkg-deb -e package.deb extract/DEBIAN [...do something, e.g. edit the control file...]
|
||||
mkdir build
|
||||
dpkg-deb -b extract/ build/
|
||||
|
||||
These five commands will do the job like a charm. Let me explain them to you: the first one creates a folder called “extract” and a subfolder called “DEBIAN”; the second command will extract some files from your .deb package in the “extract” folder; the third command will extract the content of the .deb package in the “DEBIAN” subfolder, where you can modify/patch the files you want; the fourth command will create a folder called “build”; and the fifth command will repack the modified files into a new .deb package, which will be generated in the “build” folder.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it! Just remember to stick with the commands above, and modify the files visually with a graphical text editor via your default file manager, after you’ve executed the third command. Do not hesitate to comment below if you run into problems during this tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Repack-Deb-Files-on-Debian-and-Ubuntu-404930.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ailoo.net/2009/06/repack-a-deb-archive-with-dpkg-deb/
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[翻译中] by KayGuowhu
|
||||
Intel Haswell Linux Virtualization: KVM vs. Xen vs. VirtualBox
|
||||
==============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
The latest chapter to our lengthy [Intel Haswell][1] on [Linux saga][2] is virtualization benchmarks. From Fedora 19 with the very latest software components for Linux virtualization, the performance of KVM, Xen, and VirtualBox were benchmarked from the Intel Core i7 4770K "Haswell" CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
Since last month's Haswell launch we have published many benchmarks of the new Intel CPUs but not being covered at Phoronix until today is the Linux virtualization performance for Haswell. With Intel hardware virtualization enabled, KVM, Xen, and VirtualBox were compared from a clean Fedora 19 64-bit installation.
|
||||
|
||||
Fedora 19 presently has the Linux 3.9.8 kernel with GCC 4.8.1, Mesa 9.2.0-devel, and an EXT4 file-system. All of the virtualization components were obtained from the Fedora 19 repository, including QEMU 1.4.2, Xen 4.2.2, and the libvirt / virt-manager components. Xen and KVM virtualization were setup through virt-manager. VirtualBox 4.2.16 was obtained from VirtualBox.org and installed on Fedora 19.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The Intel Core i7 4770K system had 16GB of RAM and a 240GB OCZ Vertex 3 SSD. During testing, each VM had access to all eight logical cores (four physical cores + Hyper Threading), access to 12GB of the system's 16GB of RAM, and a 16GB virtual disk.
|
||||
|
||||
The KVM, Xen, and VirtualBox performance from Fedora 19 Linux 3.9 with the Intel Core i7 "Haswell" processor were also compared to the "bare metal" results when the benchmarks were running on the host without any form of virtualization or other means of abstraction. VMware's products weren't benchmarked in this article since their EULA restricts public benchmarking (though VMware has been okay with us running such benchmarks in the past) and their trial software being limited to running on four CPU cores, but a separate article will look at the Xen/KVM/VMware performance on other hardware in the future.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
All of this Linux virtualization benchmarking was handled in a fully automated and reproducible manner using the open-source [Phoronix Test Suite][3] software and hosting by [OpenBenchmarking.org][4]. With using a virtual disk and with Xen/KVM not having a reliable means of shared 3D access to the host's driver/GPU, most of the benchmarks within this article are computational focused to look at the performance overhead for the different Linux virtualization methods.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Disk benchmarking wasn't a main focus of this virtualization testing since only a virtual disk was being used on the host's file-system. However, when comparing these three Linux virtualization methods against the bare metal results, KVM on the Linux 3.9 kernel was performing the best followed by Xen. Oracle's VirtualBox was running just 66% the speed of the host's PostMark mail server performance while KVM was at 96% the performance and Xen at 83% the host's speed.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For the Dolfyn Computational Fluid Dynamics workload, there aren’t any major changes in performance against the bare metal results when running on KVM or Xen. However, VirtualBox is noticeably slower.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The FFTE and HMMer results were similar to Dolfyn where Xen and KVM were leading to great performance results with very little overhead, but Oracle VM VirtualBox was much slower.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
John The Ripper was crashing when being run under VirtualBox.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Xen virtualization on the Linux 3.9 kernel with Fedora 19 strikes its first performance win when running the TTSIOD renderer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Overall, Xen and KVM virtualization worked out great on Fedora 19 in conjunction with the Intel Core i7 4770K CPU. The performance overhead of these virtualization methods were minimal on the Haswell processor. While Xen and KVM were running great on the new Intel CPU, Oracle's VirtualBox (the latest release, v4.2.16) was much slower than Xen and KVM. The benefit VirtualBox has though is means of guest 3D acceleration, which will be benchmarked again in a future Phoronix article. Also to be benchmarked soon on Phoronix will be the relative overhead of the different virtualization methods when comparing Haswell to previous generations of Intel processors as well as AMD's competition.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=article&item=intel_haswell_virtualization
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](http://blog.csdn.net/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=Haswell
|
||||
[2]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTM5MzU
|
||||
[3]:http://www.phoronix-test-suite.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://openbenchmarking.org/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
|
||||
专访Ubuntu Tweak的作者周鼎
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[Ubuntu tweak][1]是一款知名度很高的应用程序软件,Ubuntu用户可以用它来调整系统的性能、功能等各个细节。项目的创始人,周鼎又名Tualatrix Chou,正与我们分享Ubuntu Tweak的特性、使用感觉以及它跟Canonical的关系,并且勾勒了项目的未来计划蓝图。享受吧!
|
||||
|
||||
**你什么时候开始使用linux的,并基于什么使你决定开发Ubuntu tweak?**
|
||||
|
||||
我开始使用Linux是在2006年底,那时刚开始我的大学生活。当时我正在学C编程语言,一个朋友建议说要学习编程的话Linux是最好的平台环境,所以我就开始了我的Linux生涯,是从Fedora Core 6开始的。但用了仅仅只有一周的时间,我就换成Ubuntu 6.10,因为Ubuntu在中国有更好的社区,也有更好更快的源库/镜像。我立马就爱上了Ubuntu,就一周时间,就从Windows环境完全切换到Ubuntu环境。
|
||||
|
||||
在苦乐参半的半年使用时间后,我意识到Ubuntu对中国用户来说不是太友好,因为全新安装系统后,用户必须得自己配置字体、输入法以及其它很多很多设置。所以,我决定开发出一款应用程序来帮助新手,让他们很简单的就可以对系统做相应配置。
|
||||
|
||||
因此在2007年7月,我就开始开发Ubuntu Tweak,刚开始的时候,仅仅提供了汉语版本的,但很快就考虑了Ubuntu Tweak的国际版本,并且在2007年9月份就发布了首个国际版本。
|
||||
|
||||
**Ubuntu tweak已经是非常成功的项目了。很多Ubutu用户用它来调整系统的性能、功能等各个细节。能给我们谈论下Ubuntu Tweak能做些什么吗?**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu Tweak可以用来切换桌面图表的显示方式、设置字体、启用/禁用多用户切换功能以及登陆的标识(logo)等等。
|
||||
|
||||
在最新的Ubuntu Tweak 0.6版本中,你也可以调整你的Unity桌面以及关机功能。
|
||||
|
||||
你也能使用Ubuntu Tweak来清理系统的垃圾以释放空间和使系统保持干净。
|
||||
|
||||
**Canonical在他们的默认发布源中不考虑加入Ubuntu Tweak。这意味着什么?这对那些没有经验,但又想要使用你的应用程序来调整他们的系统的用户来说,存在某些风险吗?**
|
||||
|
||||
对的。因为在以前的Ubuntu Tweak发布版本中,为流行的PPA都提供了可用源,但我不能保证所有的PPA都是安全的,所以Ubuntu Tweak会有一些安全风险。
|
||||
|
||||
As you see, Source Center has been removed since 0.6. But please don’t mix the “include default by Ubuntu” and “put into the repository”, Ubuntu Tweak first should be put into the universal repository, then can be included by default in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
From the bug reports and user feedback, Ubuntu Tweak has became a lot more stable and easy to use than the old versions.
|
||||
|
||||
**What kind of support or collaboration (if any) you have from/with Canonical and the Ubuntu developers?**
|
||||
|
||||
Of course I received some help from the company, they helped me try to put Ubuntu Tweak into repository. It is still a work in progress.
|
||||
|
||||
I also received a lot of help from community, people help to translate, design, test and report bugs, and some of them even submitted patch for it.
|
||||
|
||||
**How many people are involved in the development of Ubuntu Tweak?**
|
||||
|
||||
If you say “programmer”, I’m the only one. But we have designers: the logo was designed by M.Sharp, Kevin Chou helped to design the mockup UI of Ubuntu Tweak, it became the 0.6. And currently Jeonkwan Chan are helping me polish the UI, it will become 0.7. Anyone can be involved in the development of Ubuntu Tweak, if they like :)
|
||||
|
||||
**When Unity came out on 11.04, a lot of Ubuntu users complained about the lack of configurability. What is your opinion on that, and what are the adaptability-configurability that this particular desktop environment can have?**
|
||||
|
||||
I’d like a desktop to have adaptability-configurability, that’s the advantage of Linux, isn’t it?
|
||||
|
||||
For example, I don’t like the auto-hide feature of Unity Launcher, so I set it to never hide.
|
||||
|
||||
Actually, Unity is configurable, the only thing that Unity is missing (through the ccsm) is that you can’t place Launcher to bottom or right – that’s maybe unfriendly for the left-handedness. Hah, just a joke.
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, Ubuntu 12.04 has already added the hide/show toggle, Launcher size setting in system settings, I think Unity will be more configurable in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
**In general, do you think that the development of the Unity desktop environment was the right decision for Canonical? Was it something inevitable because of the problematic collaboration they had with the Gnome developers?**
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, I think it’s the right decision for Canonical. If you look back three years, when Ubuntu first introduced the Indicator for GNOME Panel, it was a better design than the original GNOME Panel applet. But there’s some problematic collaboration between Canonical and GNOME Developers, so it has never landed in GNOME, until in GNOME 3, the GNOME Shell itself removed the GNOME Panel, and the design of GNOME Shell panel is almost the same as that of the Indicator. If they could share the same API, the desktop Linux world would be better.
|
||||
|
||||
So, between the company, community and GNOME, the different opinions for user interface finally made the Unity desktop out.
|
||||
|
||||
I think it’s a good thing, at least I like Unity more than GNOME Shell right now.
|
||||
|
||||
**Although you are developing an Ubuntu specialized application, I suppose you are using another distro for more advanced users. What is your distro of choice and why?**
|
||||
|
||||
Of course, I had played with Fedora, Arch, OpenSUSE, especially with Gentoo, I had been using it for one year long. It’s my second favourite Linux distribution, because it has one of the most advanced package management systems.
|
||||
|
||||
But now I only use Ubuntu for desktop and server, I also use Mac OS X. I got many design inspiration from it :)
|
||||
|
||||
**Can Ubuntu Tweak, be tweaked or forked or changed a little bit, in order to become useful in other linux distributions like Fedora, or OpenSuse, or Debian? Is the idea of a “Linux Tweak” application that people would choose distro and desktop environment plausible or not?**
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, Ubuntu Tweak can be easily adapted to be used under other distributions. Ubuntu Tweak is modular and very easy to hack.
|
||||
|
||||
In 2008, I released an “Ubuntu Tweak for Fedora”, but finally I gave up the maintenance of this version cause I should keep focus on Ubuntu, and I also don’t have that much energy.
|
||||
|
||||
**So what is the future of Ubuntu Tweak? Maybe Canonical will embrace it making it a default part of their distro, or they could use it to base their own tweaking tool. What do you think and what will be your next steps?**
|
||||
|
||||
Of course the future of Ubuntu Tweak will be bright. Hah.
|
||||
|
||||
I have already started the process of putting Ubuntu Tweak to the Software Center, it would be easier if users can install Ubuntu Tweak from the Software Center.
|
||||
|
||||
Now I’m focusing on developing the 0.7 version, It will be a better polished and well integrated version for Unity desktop than ever before, and it will also introduce some useful new features. I’d like to adapt Ubuntu Tweak to work better under Unity desktop as much as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
I plan to release the new version along with Ubuntu 12.04, hope everyone will like it :)
|
||||
|
||||
And one more thing to tell, I’ve already joined Canonical, in Beijing, and response for OEM things. Although Ubuntu Tweak is still a personal project and I’m not involved in the development of Ubuntu, I will try to move to the development team when possible :)
|
||||
|
||||
**That was great! Thanks Tualatrix.**
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/interview-with-ding-zhou-of-ubuntu-tweak/
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ubuntu-tweak.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
Linux Foundation Gains New Cloud, Open Hardware and Gaming Members
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Cloudius Systems, HSA Foundation and Valve have become the newest members of the Linux Foundation, bringing strengths in the open source cloud, open-standard hardware and gaming.
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud computing, open-standard hardware and gaming: These are all areas in which the [Linux Foundation][1] has recently forged important new connections, announcing the addition of [Cloudius Systems][2], [HSA Foundation][3] and [Valve Software][4] as the newest members of the organization. Together, these collaborations highlight the continuing dynamism of the open source world, and provide hints into where it is headed next.
|
||||
|
||||
The Linux Foundation, a non-profit consortium that promotes the interests of [Linux][6] and related open source projects, detailed the signing-on of these three companies in an [announcement][5] that highlighted the particular strengths they stand to contribute to the open source ecosystem.
|
||||
|
||||
First, Cloudius Systems will help to advance the open source cloud. Its major product is [OSv][7], a sleek operating system that the company recently introduced and designed specifically for the cloud. Interestingly, OSv—which runs as a guest virtual machine on top of the open source [KVM][8] and [Xen][9] hypervisors—could be considered a competitor with Linux, which forms the basis for many other cloud-oriented virtualization platforms. But Cloudious's entry into the Linux Foundation is a sign that the future of the open cloud is about more than Linux itself, and that open source innovators recognize that the Linux kernel, which was built for desktops and servers, can only go so far in the cloud.
|
||||
|
||||
Meanwhile, the non-profit HSA Foundation aims to advance open hardware standards—a key interest for open source developers whether they focus on desktops, servers, the cloud or mobile. Lack of hardware compatibility due to proprietary, undocumented standards has been a thorn in Linux's side from day one, and investing in collaboration to help overcome that barrier is in the interest of virtually everyone within the open source ecosystem.
|
||||
|
||||
Last but not least, Valve, which develops the popular [Steam][10] platform for cloud-based games and other content, injects the Linux world with new energy in the gaming realm, an area that has traditionally been very unwelcoming to Linux users. Valve could be on the forefront of a major shift in open source entertainment that will use the power of the cloud to bring Linux into the mainstream fold—while also promoting Linux as the basis for specialized gaming hardware such as Valve's [Steam Machines][11], home gaming devices that run on Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/linux-foundation-gains-new-cloud-open-hardware-and-gaming
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cloudius-systems.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://hsafoundation.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.valvesoftware.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.linuxfoundation.org/news-media/announcements/2013/12/cloudius-systems-hsa-foundation-and-valve-join-linux-foundation
|
||||
[6]:http://kernel.org/
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/cloudius-systems/osv
|
||||
[8]:http://www.linux-kvm.org/page/Main_Page
|
||||
[9]:http://www.xenproject.org/
|
||||
[10]:http://store.steampowered.com/
|
||||
[11]:http://store.steampowered.com/livingroom/SteamMachines/
|
||||
@ -1,142 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux date command – Display and Set System Date and Time
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Date on the operating system may only be considered as a timepiece. Especially on console mode, we do generally not see date as an important think. But for Administrator, this assumption is false. Do you know that a wrong date and time can make you can’t compile an application?
|
||||
|
||||
Because date and time is important, this is may be the reason why Network Time Protocol is developed. Let’s start to see what date command do for you.
|
||||
|
||||
### Display system date ###
|
||||
|
||||
To display your system date, just type
|
||||
|
||||
$ date
|
||||
Thu Dec 5 22:55:41 WIB 2013
|
||||
|
||||
### Formatting Date ###
|
||||
|
||||
Date come with many formats. If you are unhappy with default format you can change it. You may think “Why I need to change the format? A default output is enough for me”.
|
||||
Yes. It is true. But when you do programming, default output may not meet the user need. So here’s some custom outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Output date and time in RFC 2822 format ###
|
||||
|
||||
$ date -R
|
||||
Thu, 05 Dec 2013 23:40:53 +0700
|
||||
|
||||
**RFC 2822** has a format like this : **day, date-month-year, hours:minutes:second timezone**
|
||||
Timezone +0700 is same with GMT +7
|
||||
|
||||
By default **date** is using the timezone which defined in **/etc/localtime**. Valid timezones data are defined in **/usr/share/timezones**
|
||||
|
||||
### Print or set Coordinated Universal Time ###
|
||||
|
||||
From [Wikipedia][1], UTC means
|
||||
|
||||
> The primary standard which the world regulates clocks and time. It is one several closely related successors to Greenwich Mean Time.
|
||||
|
||||
To display your date and time with UTC format, use -u parameter
|
||||
|
||||
$ date -u
|
||||
Thu Dec 5 16:45:58:UTC 2013
|
||||
|
||||
### Using formatting options ###
|
||||
|
||||
To custom your date format, **use a plus sign (+)**
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”Day : %d Month : %m Year : %Y”
|
||||
Day: 05 Month: 12 Year: 2013
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +%D
|
||||
12/05/13
|
||||
|
||||
**%D** format follows **Year/Month/Day format**.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also put the day name if you want. Here’s some examples :
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”%a %b %d %y”
|
||||
Fri 06 Dec 2013
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”%A %B %d %Y”
|
||||
Friday December 06 2013
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”%A %B %d %Y %T”
|
||||
Friday December 06 2013 00:30:37
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”%A %B-%d-%Y %c”
|
||||
Friday December-06-2013 12:30:37 AM WIB
|
||||
|
||||
There are still a lot of format options available. Just type
|
||||
|
||||
$ date –help
|
||||
|
||||
Or
|
||||
|
||||
$ man date
|
||||
|
||||
To show date command syntax and parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
So basically, date command will interpret all percent sign (%) and print anything inside a quotes sign (“ “)
|
||||
|
||||
### Set system date and time ###
|
||||
|
||||
Generally, you want your system date and time is set automatically. If for some reason you have to change it manually, we can use this command :
|
||||
|
||||
# date –set=”20140125 09:17:00”
|
||||
|
||||
It will **set** your current date and time of your system into **January 25, 2014 and 09:17:00 AM. Please note**, that you **must** have root privilege to do this. Otherwise you will have an error message like this :
|
||||
|
||||
date: cannot set date: Operation not permitted
|
||||
Sat Jan 25 09:17:00 WIB 2014
|
||||
|
||||
### Reset your time back ###
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to reset your system date and time back to the original, you can do this trick.
|
||||
|
||||
# hwclock
|
||||
Fri 06 Dec 2013 03:44:10 AM WIB -0.314082 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
And set your system date and time to the output of hwclock command.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using date command on a script ###
|
||||
|
||||
Remember when I said before about why you may need to change the date output? One of the answer may be because you do programming. Let’s see an example on bash script.
|
||||
|
||||
$ vi display.date
|
||||
|
||||
#! /bin/bash
|
||||
DATETIME=$(date +”DATE: %a %b-%d-%Y TIME: %T WEEK NUMBER: %W”)
|
||||
echo $DATETIME
|
||||
|
||||
Save it and run it using :
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./display.date
|
||||
DATE : Fri Dec-06-2013 TIME: 03:08:19 WEEK Number :40
|
||||
|
||||
If you find error permission denied error message, type :
|
||||
|
||||
$ chmod 755 display.date
|
||||
|
||||
### Using date on a backup procedure ###
|
||||
|
||||
Another example is when you are using date on a backup procedure.
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +%F
|
||||
2013-12-06
|
||||
|
||||
$ tar zcfv /daily_backup/backup-`date +%F`.tar.gz /home/pungki/Documents
|
||||
|
||||
It will compress folder **/home/pungki/Documents** into a a file with name **backup-2013-12-06.tar.gz** which located in **/daily_backup folder**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Date may be seen as something that is not important. But dates play an important role. As usual, to have more detail in using date command, please visit date manual page by typing man date in your console.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/date-command-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coordinated_Universal_Time
|
||||
136
sources/Our Top 10 Linux Applications of 2013.md
Normal file
136
sources/Our Top 10 Linux Applications of 2013.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
||||
Our Top 10 Linux Applications of 2013
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*2013 – What A Year, Right?*
|
||||
|
||||
**This time last year we knew nothing of Ubuntu Touch; Canonical attempting to raise $32 million for a cutting-edge smartphone would’ve sounded insane; Mir was a space station while Wayland was the future; and as far as Saucy Salamanders and Trusty Tahrs are concerned, they were nothing but adjunct words on the pages of untroubled thesaurus.**
|
||||
|
||||
It’s been a busy year. Canonical continue to stride forwards towards a converged future for the OS, while an estimated 25 million people continue to use the regular desktop version for their day-to-day computing needs.
|
||||
|
||||
But key to both experiences are apps. Last year we rounded up 10 of our favourite apps that debuted on the desktop. This year we’re doing things a little differently by also including updates released during the course of the year.
|
||||
|
||||
We’ve opted to exclude ‘obvious’ choices like Firefox, Chrome, LibreOffice and Steam (because we all know they’re awesome anyway) to highlight lesser-known apps and utilities that, this year, made the desktop experience all the more awesome.
|
||||
|
||||
What did we pick? Read on.
|
||||
|
||||
### Geary ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
2013 saw Yorba, the non-profit behind Geary, try, [and fail][1], to secure a future for the app through crowd funding. That could’ve been where things ended for the app; a dour footnote in the history of apps failing to reach their true potential. Thankfully it wasn’t.
|
||||
|
||||
The release of Geary 0.4.x a few months after that disappointing set-up later proved a testament to the dedication and patience of its development team. Building on a strong release from earlier in the year, Geary 0.4 arrived in October with improved stability and performance and a veritable stuffed envelope of new improvements and features in tow.
|
||||
|
||||
Those who insist that the days of desktop mail clients are over are fast being made to eat their words by Yorba. Right now, Geary is one of the the best mail apps on any platform, Linux or otherwise.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Install Geary from Ubuntu Software Center][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### Birdie Twitter App ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Twitter apps for Linux are a bit of an anomaly. While there are a good number of them, few seem to work as efficiently as proprietary apps on other operating systems. That all changed with the hatching of **Birdie** back in March of this year. As the year passed we got to see it grow from an unstable, crash-prone chick to a mature and confident app sure of its direction.
|
||||
|
||||
While it remains far from being the full plumed wonder I’d like, it makes this list because it does what it aims to, looks good doing it, and holds a lot of promise for the future.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Read more about Birdie’s Latest Release][3]
|
||||
|
||||
### Springseed ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For obsessive note-takers 2013 wasn’t short of options – from GNOME’s obtusely named *Bijiben*, to the powerful *Nitro*. But, for me, it was the nimble *Springseed* that grabbed my attention.
|
||||
|
||||
Having been built from the ground-up to be resource-friendly, the app feels responsive and light. The feature set includes all of the vital ones needed to get organised – notebook creation, text formatting, markdown support and drobox sync, etc – all presented within an attractive interface that’s free of needless cruft.
|
||||
|
||||
Springseed is a free and open-source and available to download directly from the project website.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download Springseed for Ubuntu][4]
|
||||
|
||||
### Unity Tweak Tool ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
First released in the beginning of the year, *Unity Tweak Tool* has grown to become the ’*must have*’ app name falling off the lips of anyone offering post-Ubuntu install advice. With a smorgasbord of settings and customisation tools on-hand, the utility makes tailoring the Unity experience to suit your own tastes a [doddle][5].
|
||||
|
||||
Routinely updated to take advantage of the latest options in each new release of Ubuntu, and offering the safety net of an ‘undo’ button should anything go wayward, it’s easy to see why the app has become a favourite tool for so many.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Install Unity Tweak Tool on Ubuntu][6]
|
||||
|
||||
### Intel Graphics Driver Installer ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Intel (specifically Intel’s *Open Source Technology Centre*) made installing the latest and greatest Intel graphics drivers easier on Linux this year with the release of the Intel Driver Manager. The utility automate the entire detection, download and install process for the user, requiring only a couple of clicks and the bit of patience.
|
||||
|
||||
Initial releases of the manager were not without issue. Thankfully, subsequent releases have seen bugs fixed and quirks ironed out. If you tried it earlier in the year without success it might be well worth trying it again.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Intel Driver Manager for Linux][7]
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu SDK ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
A left-field choice, but an important one. The Ubuntu SDK arrived this year primed with everything developers need to create apps for Ubuntu Touch, both on phone and tablet.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s hard to wax too lyrical about a tool that few desktop users will appreciate, but July’s update in particular added some great functionality – including a unified actions API, Ubuntu One database syncing and support for creating converged layouts.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Learn more about the Ubuntu SDK][8]
|
||||
|
||||
### VoD Enablement App ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Arguably this entry is not so much an app as a hack dressed up to look like one. Regardless, thanks to some clever packaging foo of Erich Hoover, Netflix, LoveFilm and a host of other Silverlight-based video streaming sites are now *easily* viewable on Ubuntu for the first time – albeit unofficially, of course!
|
||||
|
||||
For the full skinny on what’s supported, what it install, and how to get it you’ll want to check out our article from January.
|
||||
|
||||
- [How to Watch Netflix & Others on Ubuntu][9]
|
||||
|
||||
### VLC ###
|
||||
|
||||
Everyone’s (cue someone saying ‘not mine!’ – ed) favourite media player received a number of updates over the course of 2013, with its most recent major update landing back in September.
|
||||
|
||||
Amongst the slew of features and refinements shipped with its Linux build was support for 4K video streams; VDPAU hardware decoding; tweaks to .MKV file playback and improved DBus and MPRIS interfaces.
|
||||
|
||||
### Lightworks for Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Lightworks has an odd, but rather brilliant, claim to fame: it’s too featured, too powerful, and too professional-orientated for most desktop users to get to grips with. Addmittedly that’s hardly a shock given the pedigree of the app (used to edit many an Oscar-winning Hollywood film, dontcha’ know).
|
||||
|
||||
Editshare, the company behind the app, took their time publishing a Linux Beta (having delayed its arrival on numerous occasions). But, since its release back in April, they’ve been fastidious in ensuring that it maintains feature parity with the Windows builds – a feat only achieved in the most recent set of updates.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, with new features and tweaks arriving by the week, there’s never been a better time for those who fancy themselves as the next great movie maker to try it out.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Latest Lightworks for Linux Update][10]
|
||||
|
||||
### GNOME Music Preview ###
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Alright, alright: it’s not finished. In fact, if you’re not running a pair of highly unstable GNOME PPAs you can’t even use it in Ubuntu.
|
||||
|
||||
But that’s beside the point; GNOME Music is one of my stand out apps of this year. For some it’s simple to the point of uselessness, for others the beauty lies in its simplicity. Sure, it doesn’t stack up well against apps tasked with doing ‘all the things!’, but that rather misses the point.
|
||||
|
||||
The attention to detail in design and user experience is second to none.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/12/top-10-linux-apps-of-2013
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/04/geary-fundraiser-fails-at-half-way-mark
|
||||
[2]:apt:geary
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/07/birdie-twitter-app-updates-with-conversations
|
||||
[4]:http://getspringseed.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.thefreedictionary.com/doddle
|
||||
[6]:apt://unity-tweak-tool
|
||||
[7]:https://01.org/linuxgraphics/downloads/2013/intelr-graphics-installer-1.0.2-linux
|
||||
[8]:http://developer.ubuntu.com/apps/create/get-the-sdk/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/01/how-to-watch-lovefilm-redbox-instant-or-netflix-on-ubuntu
|
||||
[10]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/lightworks-for-linux-beta-updated
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
(申领 by runningwater)
|
||||
Proprietary Unix Continues to Fall
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Analysts at International Data Corporation (IDC) posted a [press release][1] Wednesday highlighting the rapid decline of IBM's AIX and P-Series hardware. Along side the drop in proprietary Unix systems is an associated rise in sales of X86 servers running Linux. IBM has clearly identified this as a long term trend, investing $1 billion dollars in Linux development on Power systems. With the reported 20% drop in sales, the writing my finally be on the wall for AIX.
|
||||
@ -16,7 +17,7 @@ IBM may not be able to turn things around for AIX, but they could prolong its li
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/proprietary-unix-continues-to-fall
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[runningwater](https://github.com/runningwater) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Security Headers on the Top 1,000,000 Websites: November 2013 Report
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
It has been almost exactly a year since we conducted the first top 1 million security headers report so it is a great time to re-run the analysis and see how well security header adoption is growing. As before, the latest Chrome and Firefox User-Agent strings were used to make requests to the top 1 million sites over both HTTP and HTTPS. Out of the 2,589,918 responses we had over 100,000 distinct security headers and values to analyze.
|
||||
|
||||
Comparing with previous scans, we had 514,288 URLs that matched the first run we did in November 2012 and 1,207,169 URLs that matched from March 2013. This time around we added yet another security header “X-XSS-Protection” due to a request from a commenter on this blog. Unfortunately, we did not store this header in any of the prior scans so we are unable to compare its adoption rate.
|
||||
|
||||
### Changes, Additions and Removals Yearly Review ###
|
||||
|
||||
A total of 7,258 new security headers were added over the course of a year to the 514,288 URLs that existed in both data sets. As before, we see the largest increase in additions to X-Frame-Options and CORS headers. In a not so distant fourth we see Strict-Transport-Security steadily climbing with 538 new sites using the header. Even though X-Content-Security-Policy and X-WebKit-CSP are deprecated, we still see a small increase in their additions. Once again the highest used headers also end up having the highest number of removals with X-Frame-Options being removed from 365 sites over the course of the year.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You may notice that the Content-Security-Policy header is missing from the yearly review, this is because it was not standardized when we first started this analysis. To see the adoption rate of the standardized CSP, we need to look at a comparison of the scan that was conducted in March 2013.
|
||||
|
||||
### Changes, Additions and Removals from March 2013 ###
|
||||
|
||||
We have a lot more URLs that matched since last March, yet surprisingly, the charts look extremely similar. 7,099 new security headers were added for the 1,207,169 URLs that matched between this run and March 2013. Of these sites, a disappointingly small number of 62 sites enabled Content-Security-Policy with 47 sites enabling the soon to be disabled X-Content-Security-Policy header.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
While it would be nice to see CSP’s adoption rates increase more, it is quite understandable as it is such a large undertaking for any website to create a compliant policy.
|
||||
|
||||
### November 2013 Results ###
|
||||
|
||||
#### X-XSS-Protection ####
|
||||
|
||||
This time around another header was added to the analysis. The Microsoft endorsed header was built to allow sites to control how Internet Explorer’s XSS Filtering feature is to be handled on a resource by resource basis. Valid values for X-XSS-Protection are as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
1. 0 – Disables XSS protections
|
||||
1. 1 – Enables XSS protections, in IE the filter will attempt to sanitize potential malicious characters.
|
||||
1. 1; mode=block – Enables XSS protections and instructs IE to block the response instead of sanitizing.
|
||||
1. 1; report=[url] – Allows reports to be sent to the specified URL of potential XSS attempts.
|
||||
|
||||
It should be noted that Google Chrome’s XSS Auditor will also be disabled if a resource responds with 0 as the value for the X-XSS-Protection header.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As previous readers will remember, invalid header values are a serious problem and X-XSS-Protection is no exception. Almost 480 sites incorrectly specified the value of “0; mode=block”. This means that 477 sites who think they are blocking XSS attacks are actively disabling the XSS protections built in to IE and Chrome. Please note that [YouTube][1] and [Blogspot][2] make up the majority of URLs using X-XSS-Protection with 14,210 for YouTube and 18,587 for Blogspot.
|
||||
|
||||
### X-Frame-Options ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
X-Frame-Options is still holding strong with SAMEORIGIN being by far the largest setting with YouTube again taking up the majority with 14,178 URLs all of which are set to SAMEORIGIN. Along with the jump in sites using X-Frame-Options we are also seeing an increase in invalid values being configured.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cross Origin Request Sharing (CORS) Headers ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once again we looked at the two CORS headers Access-Control-Allow-Origin and Access-Control-Allow-Credentials.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unfortunately, we are still seeing a large number of sites incorrectly configuring Access-Control-Allow-Origin by specifying wildcards or multiple origins separated by various characters. As a reminder Access-Control-Allow-Origin only allows either * (wildcard value) or a single origin with a valid scheme specified.
|
||||
|
||||
As for Access-Control-Allow-Credentials, 1388 sites have set the value to true, 51 for false. Surprisingly, we identified 196 sites setting wildcard origin access but setting Access-Control-Allow-Credentials to true which is an invalid combination of settings.
|
||||
|
||||
### Strict-Transport-Security ###
|
||||
|
||||
Due to readers suggestions we have changed the long max-age value to be anything greater than 604800 seconds, or 7 days. Likewise, values below are considered to be a short max-age. [Facebook][3] and [Etsy][4] comprise 74 and 61 URLs respectively in the Max Age of 0 column. As a reminder, a header value of 0 clears the domain from the browser’s Strict Transport Security cache. Of the more interesting invalid values, a large number of sites incorrectly use ‘,’ as a delimiter between the max-age value and includeSubDomains directives. Unfortunately, both Firefox and Chrome are extremely strict in this regard and will refuse to add the site to the STS cache if the ‘,’ character is used instead of the RFC defined token of ‘;’. Once again, please check the RFCs before implementing any of these security headers.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Content-Security-Policy ####
|
||||
|
||||
Content Security Policy continues to grow in usage but extremely slowly. Only 269 sites are using the [w3 specification’s Content-Security-Policy][5] header, with 95 of these URLs coming from Facebook. Interestingly, 584 sites are using X-Content-Security-Policy and 487 sites are using X-Webkit-CSP. It should be noted that these two headers are already considered deprecated but have yet to be disabled. Only an extremely small number of sites using the report-only versions of the CSP headers were observed. It would be expected that web site operators wishing to test out CSP would use the report only mode to determine how Content Security Policy would impact their site, yet we only see 24 sites using Content-Security-Policy-Report-Only.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The most interesting result of the CSP analysis is the large number of sites which use CSP with the unsafe directives. It is assumed the reason unsafe-inline has such a high rate of usage is due to how extremely hard it is for developers to remove all inline script from web page elements. While disappointing to see, it is understandable to anyone who has attempted to enact a strict CSP policy.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
It is safe to say that we have a long way to go to making sure our sites use all available means to protect themselves. While security headers are only a small part of defense, applied appropriately they can and do help us all be more secure internet users. While encouraging to see the numbers increasing, we must keep in mind that less than 10% (199,350) of the 2,589,918 URLs analyzed have security headers. While strict adherence to RFCs is necessary, typos, combined with the rigidness of directive parsing, do not help site administrators or users when encountering these headers. While hope should not be given up on CSP, it’s extremely low adoption rate is rather concerning and it may be worth considering creation of tools to help create, verify and support site administrators that wish to adopt CSP.
|
||||
|
||||
As before, Veracode has released the raw data from this analysis, so feel free to download the November 2013 results here.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.veracode.com/blog/2013/11/security-headers-on-the-top-1000000-websites-november-2013-report/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.youtube.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.blogspot.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.facebook.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.etsy.com/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.w3.org/TR/CSP/
|
||||
@ -1,191 +0,0 @@
|
||||
translating by zsJacky
|
||||
|
||||
Setup FTP Server On openSUSE 13.1
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**vsftpd** (**V**ery **S**ecure **F**ile **T**ransport **P**rotocol **D**aemon) is a secure, fast FTP server for Unix/Linux systems. In this how-to article, let us see how to setup a basic FTP server using vsftpd on openSUSE 13.1.
|
||||
|
||||
### Install vsftpd ###
|
||||
|
||||
Login as root user and Enter the following the following command.
|
||||
|
||||
# zypper in vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
Start vsftpd service and make it to start automatically on every reboot.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable vsftpd.service
|
||||
# systemctl start vsftpd.service
|
||||
|
||||
### Configure vsftpd ###
|
||||
|
||||
Create a folder for ftp users.
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /srv/ftp
|
||||
|
||||
Create a group called **ftp-users**.
|
||||
|
||||
# groupadd ftp-users
|
||||
|
||||
Let us create a sample user called unixmen with home directory **/srv/ftp** and group **ftp-users**.
|
||||
|
||||
# useradd -g ftp-users -d /srv/ftp/ unixmen
|
||||
|
||||
Set password for the new user.
|
||||
|
||||
# passwd unixmen
|
||||
|
||||
Make the ftp home directory **/srv/ftp/** accessible by ftp users.
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod 750 /srv/ftp/
|
||||
# chown unixmen:ftp-users /srv/ftp/
|
||||
|
||||
Edit file vsftpd.conf,
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/vsftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Make the changes as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
#Uncomment and Set YES to enable write.
|
||||
write_enable=YES
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment and Set banner name for your website
|
||||
ftpd_banner=Welcome to Unixmen FTP service.
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment
|
||||
ls_recurse_enable=YES
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment and set YES to allow local users to log in.
|
||||
local_enable=YES
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# To disable anonymous access, set NO.
|
||||
anonymous_enable=NO
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment to enable ascii download and upload.
|
||||
ascii_upload_enable=YES
|
||||
ascii_download_enable=YES
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
## Add at the end of this file ##
|
||||
use_localtime=YES
|
||||
|
||||
Save and exit file.
|
||||
|
||||
### Test FTP Server Locally ###
|
||||
|
||||
First let us try to login to our FTP server as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# ftp localhost
|
||||
Trying ::1:21 ...
|
||||
Connected to localhost.
|
||||
220 (vsFTPd 3.0.2)
|
||||
Name (localhost:root): unixmen
|
||||
331 Please specify the password.
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
230 Login successful.
|
||||
Remote system type is UNIX.
|
||||
Using binary mode to transfer files.
|
||||
ftp>
|
||||
|
||||
As you in the above output, we will be able to login to ftp server using unixmen user.
|
||||
|
||||
### Test FTP Server Remotely ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default openSUSE built-in firewall won’t allow to login to FTP from remote systems. So let us allow vsftpd service through suse firewall. To do that go to **Yast -> Security and Users -> Firewall**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
In the Firewall section, go to **Allowed Services**. In the zone selection drop down box, select **External Zone** and in Service to Allow drop-down box, select **vsftpd server** and click add.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Click Next and close Yast Control center.
|
||||
|
||||
Now try to connect from a remote system.
|
||||
|
||||
I tried to login to FTP server from my ubuntu desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
sk@sk:~$ ftp 192.168.1.53
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.1.53.
|
||||
220 (vsFTPd 3.0.2)
|
||||
Name (192.168.1.53:sk): unixmen
|
||||
331 Please specify the password.
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
230 Login successful.
|
||||
Remote system type is UNIX.
|
||||
Using binary mode to transfer files.
|
||||
ftp>
|
||||
|
||||
As you see in the above output, I will be able to connect to FTP server. If you doesn’t allow the vsftpd service through firewall you will get a Connection timed out error.
|
||||
|
||||
### Connect from Browser ###
|
||||
|
||||
Open up your browser and Navigate to **ftp://ip-address/**. Enter the ftp user name and password.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Connect to FTP server using FileZilla ###
|
||||
|
||||
Working from command-line mode might be little bit annoying to newbies. So let us install a graphical FTP client called [**Filezilla**][1] to get things done quite easier:
|
||||
|
||||
Mostly all distribution will have filezilla client in their official repository. To install filezilla on Linux based systems enter the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
On Ubuntu based systems:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install filezilla
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora/Redhat systems:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install filezilla
|
||||
|
||||
On openSUSE:
|
||||
|
||||
# zypper in filezilla
|
||||
|
||||
After installing filezilla open it. Enter the ftp server IP address, user name and password and click quickconnect.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
For added security, you can restrict FTP access to certain users by adding them to **/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list** file.
|
||||
|
||||
Edit vsftpd.conf file,
|
||||
|
||||
nano /etc/vsftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Make the changes as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment and set YES
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES
|
||||
chroot_list_enable=YES
|
||||
chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
Create **file /etc/vsftpd.chroot_list**,
|
||||
|
||||
nano /etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
|
||||
|
||||
Add the users that you want to give access to FTP server. I added the user **unixmen**.
|
||||
|
||||
unixmen
|
||||
|
||||
Restart ftp service.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart vsftpd.service
|
||||
|
||||
Now you will be able to connect to FTP server with users who are listed in the chroot list file.
|
||||
|
||||
If users other than in the chroot list want to access FTP server, they will get the following error.
|
||||
|
||||
500 OOPS: could not read chroot() list file:/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
|
||||
ftp: Login failed
|
||||
|
||||
That’s it for now. Your FTP server is ready to use. Enjoy!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/setup-ftp-server-opensuse-13-1/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[zsJacky](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://filezilla-project.org/
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
SuperTuxKart 0.8.1 Release Candidate Revved Up And Ready for Testing
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Hands up if you don’t like open-source racing game SuperTuxKart? You, folks, are strange.**
|
||||
|
||||
As kart-racers go, it’s one of the most popular freely available. And for good reason: it’s fun, easy to play and has a dedicated team of developers who are continually adding to and improving what is already a really polished game.
|
||||
|
||||
But it’s getting even better. The first release candidate of build 0.8.1 – the first update since last year’s 0.8 build – [has been made available for testing][1] (for ‘testing’ see ‘excuse to play it for hours and not feel guilty’).
|
||||
|
||||
SuperTuxKart 0.8.1 adds a number of improvements, including:
|
||||
|
||||
- A new Star Trek themed track “STK Enterprise”
|
||||
- Three tracks updated (‘Old Mines’, ‘Lighthouse’ & ‘Zen Garden’)
|
||||
- New ‘Egg Hunt’ and ‘Soccer’ modes
|
||||
- New and updated karts
|
||||
- New difficulty level
|
||||
- Bubblegum shield weapon
|
||||
- Option to save and resume Grand Prix mode
|
||||
- [WiiMote Support][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### Geting SuperTuxKart 0.8.1 ###
|
||||
|
||||
No release date has been given on when to expect the final, stable release of 0.8.1 but I’d expect it to land sometime in December – marking one year from the previous release in the 0.8.x series.
|
||||
|
||||
In the meantime, if you’re okay with “Release Candidate”-quality software, you’ll find a pre-compiled binary for Linux over on the project’s Sourceforge Page.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download SuperTuxKart 0.8.1 Release Candidate][3]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/supertux-kart-0-8-1-release-candidate
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://supertuxkart.blogspot.co.uk/2013/11/supertuxkart-081-rc1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://supertuxkart.net/Wiimote
|
||||
[3]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/supertuxkart/files/SuperTuxKart/0.8.1-rc1/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[Translating by SteveArcher]
|
||||
Top Email Encryption Tools
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Email continues to be one of the most popular and useful functions of a Linux system. Being able to keep in touch with your friends, family, and colleagues is essential for any platform. As the scope of email threats keeps increasing, systems for email security and encryption have become more complex and more of a necessity. Protecting email from unauthorized access and inspection is important particularly because the protocols that govern email do not include encryption. Email was not designed with any privacy or security in mind. The consequence of the lack of security is that email can be compromised on the sender's device, on a network, on a server, and on the recipient's device.
|
||||
@ -31,4 +32,4 @@ via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/2013120707481589/EmailEncryption.html
|
||||
[1]:http://www.enigmail.net/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.mailvelope.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.gnupg.org/
|
||||
[4]:https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/mymail-crypt-for-gmail/jcaobjhdnlpmopmjhijplpjhlplfkhba
|
||||
[4]:https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/mymail-crypt-for-gmail/jcaobjhdnlpmopmjhijplpjhlplfkhba
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
UNIGINE Is Probably the Best Gaming Engine on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**The UNIGINE, a real-time 3D engine built to run on all major platforms, including Linux, has just received another update, bringing some important new features.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unigine Engine is built by non-other than Unigine Corp., the company behind the Heaven DX11 Benchmark software. The technology they develop is getting better all the time, and with their recent expansion on the Linux platform, we’re all too glad to see that major updates have been implemented in the engine.
|
||||
|
||||
Amongst the biggest changes in the latest Unigine update is the Common Image Generator Interface (CIGI) protocol.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the developers, this interface is a standard way for a host device to communicate with an image generator (IG) in the simulation industry.
|
||||
|
||||
### Highlights of the new Unigine Engine: ###
|
||||
|
||||
- Support has been added for the conversion of WGS84, ECF and NED coordinate systems into Cartesian one (this will help developers to made better use of real-world GIS data in UNIGINE-powered projects);
|
||||
- The Game Framework has been implemented, making it easier to create games with features such as automatic link between Entity and Node, automatic link between Level and World, object management for Entities, Global Game context across all Levels, events handling system, optimal updating of Entities, and more;
|
||||
- The FPS stability for the rendered has been increased;
|
||||
- Two new options, a 2D noise and 3D noise (States tab in the editor), have been added to the mesh_leaf_base material;
|
||||
- A new parameter, Occlusion mask, has been added to all of the materials;
|
||||
- Heights of clutters and grass are synchronized now;
|
||||
- A few crashes on rendering of non-Flash splash screens have been fixed.
|
||||
|
||||
A complete list of new features, for all the platforms, is available in the official [announcement][1].
|
||||
|
||||
Keep in mind that the UNIGINE graphics engine is only aimed at commercial enterprises and that not even a trial version is available for the general public.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/UNIGINE-Is-Probably-the-Best-Gaming-Engine-on-Linux-404484.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unigine.com/devlog/2013/11/27/113
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
@ -1,48 +0,0 @@
|
||||
‘Household Brands’ Interested In Ubuntu for Phones and Tablets, Says Shuttleworth
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Mark Shuttleworth has said that an ‘interesting set of household brands’ are looking at putting Ubuntu Touch on their own phones and tablets.**
|
||||
|
||||
The Ubuntu founder was speaking in the [keynote address][1] at the Ubuntu Developer Summit which kicked off this week.
|
||||
|
||||
No specific names, details or dates were offered up alongside the tantalising tidbit, though Mark did hint at one point that he expects Ubuntu Touch devices to be available to buy within the next couple of years.
|
||||
|
||||
### Ubuntu Tablets = Renewed Opportunity ###
|
||||
|
||||
[As mentioned by Jono Bacon recently][2], honing the Ubuntu Tablet experience will be the ‘key focus’ of the Ubuntu 14.04 development cycle. This was touched upon by Shuttleworth in response to a question on whether Ubuntu plan to make dual-booting Touch with Android easier (they are):
|
||||
|
||||
> “I’m excited about the tablet form-factor because I think it’s going to be a lot easier for people to enjoy Ubuntu on a tablet [because] doing it on a phone full time is a bit of a deep-device commitment – [though] we’ve heard some interesting reports of government departments using it because we don’t work for the NSA!”
|
||||
|
||||
Other notable points mentioned in the keynote included:
|
||||
|
||||
- Helping developers tailor Ubuntu Touch apps for the desktop
|
||||
- Stable, dependable and performant desktop experience based on Unity 7
|
||||
- Point releases of Ubuntu 14.04 LTS won’t be introducing Mir or Unity 8
|
||||
- Ubuntu on ARM x64
|
||||
- Sidestage to be re-introduced to tablet
|
||||
- Supporting Android apps on Ubuntu ‘is a goal – but not a focus’ right now
|
||||
|
||||
> ‘Shuttleworth must be hoping that some of those interested household names make a firm commitment soon…’
|
||||
|
||||
This latter point appears to represent an about-turn, if true. Earlier in the year Canonical’s Richard Collins [told Engadget][1] that there were no plans to “engineer middleware for running Android apps [on Ubuntu Touch]“.
|
||||
|
||||
Android apps or not, Shuttleworth must be hoping that some of those interested household names make a firm commitment soon. The longer the gap the more ground competitors are gaining.
|
||||
|
||||
Samsung and Intel’s open-source mobile OS ‘Tizen’ [recently gained the backing of a further 36 companies][4], including an array of mobile networks, electronics bigwigs and game publishers.
|
||||
|
||||
Elsewhere, Mozilla’s Firefox OS continues to grow its users, OEM and carrier base; while [Jolla’s first Sailfish OS-powered handset ships later this month][5]. And although Ubuntu Touch isn’t aiming for the low-end segment, Android 4.4 debuted with a number of performance optimisations when used on hardware with limited resources.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/household-brands-ubuntu-phone-tablets
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D4kHQeu4SJk
|
||||
[2]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2013/11/ubuntu-tablet-will-key-focus-ubuntu-14-04-lts-cycle
|
||||
[3]:http://www.engadget.com/2013/01/25/canonical-richard-collins-interview/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.theverge.com/2013/11/12/5093588/tizen-open-operating-system-partners-with-36-companies
|
||||
[5]:http://www.theregister.co.uk/2013/11/15/jolla_phones_to_ship_in_november/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
成为 Linux 终端高手的 7 个基本点
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linux 终端不仅是一个键入命令的地方。如若你能熟谙基本操作,那么你将掌握绝大多数 Linux 发行版的默认配置 Bash shell。
|
||||
|
||||
howtogeek.com 对初级用户,以及那些学习过程中或多或少有一些遗漏的高级用户提出几个基本点——
|
||||
|
||||
**1.Tab 补全** – 这样能节省时间,并且对于输入那些你不确定其具体名称的文件和命令来说很方便。比如,当前目录下有一个名为“really long file name”的文件,你想要删除它。你可以输入完整的文件名,但是你必须确保正确地输入了空格。若当前目录下还有许多以字母“r”开头的文件,(如果你没有正确地输入空格) Bash 将不知道你想要删除哪一个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
如果在当前目录下存在着另一个名为“really very long file name”的文件,你敲击了Tab键。Bash
|
||||
将为所有以“r”开头的文件自动填充“really\”部分。此时继续敲击Tab键,你将得到匹配所有文件名的列表。
|
||||
|
||||
**2.管道机制** – 这种机制允许你把一条命令的输出传送到另一条命令。按照 UNIX 哲学,每个程序都足够小,只做一件事并将之做到最好。例如,ls命令列出当前目录下的所有文件,grep命令搜索输入其中的指定检索项。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过管道机制(|字符)把二者结合起来,在当前目录下搜索文件。以下给出的命令(在当前文件夹下)搜索关键字为“word”的文件:
|
||||
|
||||
ls | grep word
|
||||
|
||||
**3.通配符** – “*”(星号)字符是一种匹配任意长度字符的通配符。比如,你想删除当前文件夹下名为“really long file name”和“really very long file name”的文件,你可以运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
rm really*name
|
||||
|
||||
这条命令会删除所有以“really”开头以“name”结尾的文件。但是,如果你运行的是 rm * 这条命令,你将会删除文件夹下的所有文件。
|
||||
|
||||
**4.输出重定向** – “>”字符可以把一条命令的输出重定向到一个文件或另一条命令。比如,下面这行命令执行完 ls 后会列出当前文件夹下的所有文件,其结果不是在终端显示,而是输出到当前文件夹下一个名为“file1”的文件中去:
|
||||
|
||||
ls > file1
|
||||
|
||||
**5.历史记录** – Bash 能记住你以前输入过的命令,上、下方向键可以逐行调出它们。使用 history 命令打印历史记录,以管道机制 grep 选择性地输出你想要的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
~, . & ..
|
||||
|
||||
“~”,也叫做波浪符,用来表示当前用户的主目录。相比通过 cd /home/name 到达你的主目录,你可以输入 cd ~ 来达到相同效果。这点也可以在相关路径上使用 – 比如 cd ~/Desktop 能够到达当前用户的 Desktop 目录。
|
||||
|
||||
同样,“.”代表当前目录,“..”代表当前目录的父目录。使用 cd .. 可以返回上一级目录。它们也可以用在相关路径上,举例说明:你当前处在 Desktop 文件夹下,通过 cd ../Documents 命令,你可以转到与 Desktop 共有同一父文件夹的 Documents 文件夹去。
|
||||
|
||||
**6.后台命令** – Bash 默认会在当前终端执行你键入的每条命令。通常没有问题,但是如果你想要在启动应用后继续使用终端呢?通过输入 firefox 启动火狐浏览器,你的终端将被错误提示等各种信息输出占据,直到你关闭火狐浏览器为止。在 Bash 中你可以通过在命令结尾添加“&”操作符来后台执行程序。
|
||||
|
||||
firefox &
|
||||
|
||||
**7.条件执行** – Bash 也可以连续执行两条命令。 第二条命令仅在第一条命令成功执行后才会开始执行。如若如此,你可以通过键入“&&”,也就是两个与字符进行分隔,在同一行输入两条命令。下面给出的命令会在等待 5 秒后运行 gnome-screenshot 工具:
|
||||
|
||||
sleep 5 && gnome-screenshot
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=123564
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[SteveArcher](https://github.com/SteveArcher) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
每日Ubuntu小技巧 - 使用Ubuntu拷贝CD和DVD光盘
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu,一个功能强大的现代操作系统,可以执行很多任务。你可以使用Ubuntu创建文档,浏览网页,聆听音乐,以及烧录或拷贝媒体光盘。
|
||||
|
||||
就像Windows和Max OS X一样,Ubuntu是无所不能的!
|
||||
|
||||
这篇简单的手册将告诉你如何使用Ubuntu拷贝,翻录或烧录一张CD/DVD光盘。如果你有一张包含音频文件(音乐)或视频文件(电影)的光盘,并且你想要复制这张光盘(创建多个副本),使用Ubuntu会使你很容易做到。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你已经准备好想要拷贝进一张媒体光盘(CD/DVD)的音频或视频文件,Ubuntu也可以处理它。你可以在Ubuntu上安装很多的免费软件用于烧录或翻录一张CD/DVD光盘,但Ubuntu已经安装好一款默认的相关软件。接下来我们会使用这款默认软件去拷贝或翻录CD/DVD光盘。
|
||||
|
||||
Brasero光盘烧录机安装在UBuntu的每一个版本上。它是Ubuntu上默认的光盘烧录机。它被设计得足够简单,拥有诸多独特的特性来使得用户能够快速简便地创建光盘。
|
||||
|
||||
下面列出来的是Brasero的一些特性:
|
||||
- 创建数据CD/DVD时自动过滤隐藏和损坏的文件
|
||||
- 同时支持多个绘画,可以执行磁盘文件的完整性
|
||||
- 可以在忙碌中烧录视频CD/DVD[on the fly翻译不合适]
|
||||
- 可以拷贝CD/DVD到系统硬盘
|
||||
- 可以擦除CD/DVD
|
||||
|
||||
还有很多其它的功能。如果你想找一个Ubuntu上简便的磁盘刻录机,在做任何操作前请先检查这个软件。
|
||||
|
||||
为了开始使用Brasero去烧录CD/DVD光盘,请确保你的电脑安装了CD/DVD烧录机。如果没有,你将无法成功烧录。如果你的电脑符合要求,将你想要翻录的数据插入CD/DVD,然后进入Dash,搜索Brasero。
|
||||
|
||||
当Brasero打开后,选择磁盘拷贝。这个功能会拷贝一个光盘里的内容,然后将其写入到另一个光盘中。如果这是你想要的,请继续。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果Ubuntu能够访问你的CD/DVD烧录机,Brasero会打开并自动识别光盘内容。在这里,你可以单击 **复制** 从源光盘创建一个拷贝。如果你希望创建多个拷贝,单击按钮 **创建多个拷贝**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
当系统提示安装所需的软件包时,单击 **安装**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,Brasero会开始拷贝光盘。如果最终光盘完成拷贝,系统会提示你插入一张空白的可写入的CD/DVD光盘以便写入拷贝。插入它然后等待完成将内容写入光盘的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
当你完成以上操作时,移除光盘,就可以使用烧录好的光盘了!
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/12/daily-ubuntu-tips-copy-cd-dvd-discs-using-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
每日 Ubuntu 小技巧 - 更改 Ubuntu 使用语言
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Ubuntu 是一个功能强大的现代化操作系统,并且它还允许你使用多种语言的桌面。在默认情况下,在你第一次安装 Ubuntu 的时候会预装几个语言包。但如果你想要你的 Ubuntu 能够支持更多语言的话,那你就必须安装额外的语言包。通常不是所有的语言都是支持的,但是大多数使用中的语言以及书面语言都能够被支持。下面是一个是简短教程,它将会展示如何去实现。
|
||||
|
||||
在安装语言包之后,你可以根据你的语言重命名标准文件夹,例如音乐、图片和文档。你必须注销系统然后重新登录来使变更生效。当你重新登录之后,你会看到一个弹窗并且询问你是否愿意重命名这些标准文件夹,从而使得文件名满足你的所选择的语言要求。
|
||||
|
||||
要想更改 Ubuntu 的使用语言,单击菜单栏右上角的 **gear**,并且选择 **System Settings**。在打开 System Settings 之后,选择 **Language Support**。
|
||||
|
||||
如果提示要你安装额外的语言支持,那就直接安装。如果没有,那么就单击 Install / Remove 去安装新的语言包,然后,选择你想安装的语言来安装。最后,拖动新的语言到列表的顶端并且保存。这些更改只会应用在你的个人帐号上。如果你想应用在全局范围内,单击 **Apply System-Wide** 。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
拖动新的语言到列表的顶端。之后单击 Close。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
关闭之后注销系统。然后重新登录,你就会看到更改生效了。
|
||||
|
||||
同样,语言包的更改只是应用在你的个人帐号上。如果你想全局更改的话,你必须单击 Apply System-Wide。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你选择了重命名标准文件夹,你必须重新登录才能看到变更。
|
||||
|
||||
好好享受吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.liberiangeek.net/2013/10/daily-ubuntu-tipschange-the-language-you-use-in-ubuntu/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,28 +0,0 @@
|
||||
GCC 4.9现在处于修复BUG的第3阶段
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
[GCC 4.9][1]将拥有很多[新功能][2]将定于2014年上半年发布。早先的GCC代码基础将不会支持新的功能,因为它是一个大修复的标记。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Richard Biener今早宣称分支已经发展到了阶段三,因此在之后的八月将这些功能融入4.9版本,除非发布经理授权的异常发生,不然毫无变化。阶段三只允许一般BUG的修复工作,将在2个月内完成而到达只允许文档和回归的阶段四。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
目前GCC4.9有63 P1 回归(最严重的回归)其次是136 P2回归,14 P3回归,88 P4 回归 以及 60 P5回归。直到63回归的P1阶段被清零,GCC4.9才会被关闭去发布。GCC 4.9.0 发布版将可能在2014第二季度左右到来!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
早先的GCC 4.9.0状态报告可以在[GCC mailing list][3]中被找到。GCC 4.9将会是一个美好的编译器更新,并会挑战下个月发布的[LLVM3.4][4]。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTUyMjk
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic___](http://blog.csdn.net/Vic___) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=GCC+4.9
|
||||
[2]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=news_item&px=MTUxNzQ
|
||||
[3]:http://gcc.gnu.org/ml/gcc/2013-11/msg00435.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.phoronix.com/scan.php?page=search&q=LLVM+3.4
|
||||
@ -1,95 +0,0 @@
|
||||
如何在Linux上制作一个YouTube屏幕录像视频教程
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
一幅画胜过一千句话,一个精心设计的指导视频几乎无价。Linux有你需要的制作有用且高质量教学视频的所有工具。我们将用强大的kdenlive视频编辑器和Audacity音频录制器和编辑器制作一个简单的屏幕录像,并学习如何在YouTube上分享精彩的屏幕录像。
|
||||
|
||||
一台安装了Kdenlive和Audacit软件的Linux系统PC,一个质量好的麦克风或耳机,和一个YouTube的帐号就是你需要准备的全部。(是的,除了Youtube还有很多其他的免费视频共享服务,欢迎您来探索它们。)YouTube属于Google,因此Google试图诱导你与全世界共享任何人和事。如果这不是你想做的,请说no。
|
||||
|
||||
我们的工作流程是这样的:
|
||||
|
||||
- 用Kdenlive录制屏幕录像
|
||||
- 用Audacity录制音轨
|
||||
- 添加音轨到Kdenlive
|
||||
- 上传到YouTube
|
||||
- 全世界看你的视频,好开心
|
||||
|
||||
kdenlive支持最流行的数字视频格式,包括AVI,MP4,H.264,和MOV。它支持的图像文件,如GIF,PNG,SVG和TIFF;支持的音频文件格式,包括非压缩的PCM,Vorbis,WAV,MP3和 AC3。你甚至可以阅读和编辑Flash文件。总之,它可以处理很多东西。
|
||||
|
||||
你的配音与你的视频一样重要。请一定要重视你的音频。使音频保持干净和简单,保持杂乱的题外话,方言,和去除背景噪声降到最低点。我喜欢用一个质量好的耳机做陈述,因为你不必担心话筒位置,你可以听你自己反复地诉说而不影响到你身边的人。
|
||||
|
||||
Kdenlive的文档已过期,它会告诉你制作屏幕录像需要RecordMyDesktop软件。我用的是kdenlive 0.9.4,其实不需要Recordmydesktop。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*图 1:默认配置*
|
||||
|
||||
### 制作屏幕录像 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首次安装kdenlive,第一次运行时会启动配置向导。不必在意默认设置,因为你随时都可以改变它们。这是我的屏幕录像的设置:高清720p每秒30帧,1280x720的屏幕尺寸。如何知道使用什么设置项? [YouTube tells you][1]。设置这些值可到Settings > Configure Kdenlive > Project Defaults > Default Profile > HD 720p 30fps(图1),设置捕捉屏幕的大小到 Settings > Configure Kdenlive > Capture > Screen Grab(图2)。虽然你也可以选择捕捉全屏幕,但最好还是坚持用YouTube规定的尺寸。因为如果使用的尺寸与YouTube规定的不一样,则YouTube将增加Pillarboxes来达到合适的尺寸。热切的观众会更加希望看到一个充满生动的内容的屏幕,而不是Pillarboxes。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*Figure 2: Screencast screen size.*图 2:屏幕录像的屏幕大小
|
||||
|
||||
默认的YouTube视频播放器的大小是640x360标清320p,又小又模糊。播放器控制着小屏,大屏,全屏,和多个质量等级。这些设置只有你的观众会使用,640x360标清320p看起来真的不咋样,但郁闷的是你无法改变这个缺陷。尽管如此,你仍然想制作高质量视频的话,你可以添加一些文字来提醒观众尝试更好的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 保存你的项目 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在你做任何其他事情之前,点击 File->Save as 保存您的项目,并记住周期性地保存它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 抓取屏幕 ###
|
||||
|
||||
抓屏小菜一碟。到Record Monitor,选择Screen Grab,然后点击Record按钮。屏幕上将打开一个带虚线的框,框里面的所有内容都将被录制下来。因此,你需要做的所有事就是移动框并调整框的大小到你想要l录制的范围。完成后点击停止按钮(图3)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*图 3:屏幕抓取*
|
||||
|
||||
单击Stop,自动打开Clip Monitor,你可以预览你的裁剪效果。如果你喜欢它,把它从Project Tree中拖到Video 1轨道。现在你可以编辑你的视频了。总会有需要你修剪的地方;一个快速的方法是,你在Project Monitor里播放你的剪辑片,直到播放到你需要移除部分的末尾。然后暂停,然后按下Shift+r。你的剪辑片将会在你按下停止的时间轴上的点上被切割为两个剪辑。点击你要删除的片断,按下Delete键,噗!它就消失了。
|
||||
|
||||
对于剩下的剪辑片断,可能你想要从时间轴上的某一点开始播放,也可能你想要加入一些好的变换。比如一些简单的渐变就相当不错;右键点击你的剪辑片断,点击Add Effect > Fade > Fade from black 和 Fade to black,然后Kdenlive将自动将这两个效果放到开头和末尾。
|
||||
|
||||
### 添加配音 ###
|
||||
|
||||
请参阅[Whirlwind Intro to Audacity on Linux: From Recording to CD in One Lesson][2]来学习使用Audacity录音的基础。以16bit的wav格式导出你的音频文件,然后通过Project > Add Clip导入到Kdenlive。然后将你的新音频剪辑拖到Audio tracks。一个简单的制作视频陈述的方式是边播视频边说。运气好的话,你不需要做很多的清理工作,你的评述就会与视频同步。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*图 4:用Shift+r切割音轨,然后将其中一个剪辑片从切割点拖离,创建一个静音间隙*
|
||||
|
||||
如果你的语速比视频快,你可以在音轨中添加空档时间.很简单,用Shift+r切割音轨,然后将其中一个剪辑片从切割点拖离,创建一个静音间隙。(图4)。
|
||||
|
||||
### Rendering Your Project ### 渲染你的项目
|
||||
|
||||
当你满意自己的编辑,并准备导出你的最终格式时,点击Render按钮。这需要几分钟的时间,取决于你的电脑速度和项目大小。网页已有预先设定的值,如果你选择File Rendering, 你可以调整你的设置(图5)。我用File Rendering中的H.264,Video比特率12000, Audio比特率384取得了不错的效果。H.264是一种超压缩格式,使用这种格式发布的文件小但质量好。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*图 5:选择文件渲染,调整你的网页设置*
|
||||
|
||||
### YouTube Bound ###YouTube的装订
|
||||
|
||||
现在你可以在VLC或MPlayer或你喜欢的任何播放器中播放你的视频了,如果它看起来很好,那么你就可以将它上传到你的YouTube帐户里了。以典型的Google风格,你的信息中心和视频管理器会混乱又复杂,不过请坚持到处瞅瞅,你会理出头绪的。在你做任何事情之前,你必须对你的账户做资格认证,也就是通过短信和邮件获得一个验证码。通过输入验证码证明你不是一个网络爬虫后,你就能上传你的视频了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
你可以上传你的视频,然后标记它们为私人可见或所有人可见。Google有一些编辑工具,你可能会喜欢,比如自动纠错和配背景音乐。不过以我的拙见,几乎没有人是这样子做背景音乐的,所以这种工具只会令人讨厌。不过你有可能是第一个正确使用这个工具的人哦。
|
||||
|
||||
最有用的编辑工具是自动闭路字幕。我推荐在你所有的视频上使用此功能,不光是为了那些听觉障碍的人,也为了那些需要保持低音量观看的人,确保所有的人都明白你在说什么。字幕工具还创建一个副本。
|
||||
|
||||
另一个有用的工具是注释工具,它支持言语泡沫,标题,聚光灯和标签。当然,在Kdenlive中,这些你都可以做到,所以都可以尝试一下。
|
||||
|
||||
好吧,到这里就结束了,但似乎我们刚刚开始。请分享你的视频,并在评论中添加Youtube的小建议和技巧。如果可以的话,请在[video.linux.com][3]分享你的新的视频教程,并加入100个Linux教程活动。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
来源于: http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/745745-how-to-make-a-youtube-instructional-screencast-video-on-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[coolpigs](https://github.com/coolpigs) 校对:[jasminepeng](https://github.com/jasminepeng)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://support.google.com/youtube/answer/1722171?hl=en&ref_topic=2888648
|
||||
[2]:http://www.linux.com/learn/tutorials/422799-whirlwind-intro-to-audacity-on-linux
|
||||
[3]:http://video.linux.com/100-linux-tutorials
|
||||
52
translated/How to Repack Deb Files on Debian and Ubuntu.md
Normal file
52
translated/How to Repack Deb Files on Debian and Ubuntu.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
如何在Debian和Ubuntu下重新打包Deb文件
|
||||
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
**以下教程会教导Ubuntu,Linux Mint和Debian GUN/Linux用户,如何在它们基于Debian的Linux操作系统上轻松的解开和重建.deb文件。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
有时候你会碰到这样或那样的问题,你想要修改.deb文件的部分内容,然后重新打包。但是,也只有你真正的进入计算机世界之中。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的例子是刚发生在我身上真实的经历。一位Linux的开发者为一个软件构建了一个Debian包(.deb),我也成功得将它安装在我的装载Ubuntu的电脑上。
|
||||
|
||||
当我试图从一个Git库中检索一些文件时,它总是卡顿,佷显然,该软件并没有正常工作。我知道安装的文件在哪里(/opt目录),所以,我搜查了代码并适当的将部分问题修复。之后,当程序试图检索需要的包时不再卡顿。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,长话短说,我要将.deb文件解包,替换上我的补丁文件,然后再重新打包回来。这样我可以其他电脑上安装,或者将有效的包文件给我的朋友。我要怎么做呢?
|
||||
|
||||
在网络上搜索问题的答案,我发现一个名叫[ailoo.net][1]的小型博客,类似这样解释:
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir -p extract/DEBIAN
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg-deb -x package.deb extract/
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg-deb -e package.deb extract/DEBIAN [...do something, e.g. edit the control file...]
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir build
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg-deb -b extract/ build/
|
||||
|
||||
这五个命令像一个魔法来完成工作。让我向你解释:第一条命令创建了一个名为“extract”文件夹和一个名为“DEBIAN”的子文件夹;第二条命令会从你的.deb包提取程序文件到“extract”文件夹;第三条命令会解压.deb包的控制文件到“DEBIAN”子文件夹,在那里你就可以 修改/补丁 你想要的文件;第四条命令建立一个名为“build”的文件夹;而第五条命令会将修改后的文件重新构建到一个新的.deb包中,并在 “build” 文件夹中生成。
|
||||
|
||||
这就是本次的教程!牢牢地记住上面的命令吧,在你执行第三条命令后,可以通过你默认的文件管理器用一个图形化的文本编辑器,可视化的修改文件。如果你在这个教程上遇到问题,你可以毫不犹豫的评论给我们。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/How-to-Repack-Deb-Files-on-Debian-and-Ubuntu-404930.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Luoxcat](https://github.com/Luoxcat) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ailoo.net/2009/06/repack-a-deb-archive-with-dpkg-deb/
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
@ -1,91 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux 宗旨:‘开源很安全,Linux比其它任何系统都安全’
|
||||
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在对Linux基金会执行官,Jim Zemlin 的采访中,VentureBeat 展望了2014开源操作系统的未来。
|
||||
|
||||
We also addressed the controversial issues of government spying and “backdoors” — those nefarious windows into our personal online lives that the public recently discovered in most of the services we use every day.
|
||||
|
||||
我们也探讨了争议性的话题,就是政府部门的监听事件以及‘后门’-那些邪恶的窗口,窥探我们网上的私生活,最近公众发现我们经常使用的大多数服务都有类似的遭遇。
|
||||
|
||||
Zemlin gave us the skinny on how and why GNU/Linux remains the most secure option for concerned consumers — and why it’s becoming the OS of choice for powering cars, phones, TVs, and all kinds of emerging devices.
|
||||
Zemlin 为我们解释了 GNU/Linux 为什么以及如何使自身成为内心有些担忧的消费者的最安全的选择。还有就是为什么选择GNU/Linux作为车载操作系统,TVs以及其他新兴设备的操作系统。
|
||||
|
||||
以下是我们e-mail问答形式的实录。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 安全和隐私成为今年的热门话题,我们听到的谣言,Linus[Torvalds, Linux 创始人]对政府部门是否有安装后门的要求点头称是。**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: Linux是否有后门,你是可以知道的.
|
||||
|
||||
世界上所有人都可以看到Linux的每一行代码。这也是linux要比其他操作系统更安全、开源整体要比闭源更安全的原因之一。代码的透明度保证了它的安全性。
|
||||
|
||||
And for the record: He wasn’t approached.
|
||||
记录在案的是:后门并没有进入到linux。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: Linux基金会如何保证Linux用户的隐私和自由,使其免于遭受追踪和监视?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 对此,我们一以贯之。向内核插入违反隐私权和背离自由精神的代码而不被成千上万的开发者注意到,这是很难的。Linux的本性就是自我定制。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 今年的隐私/安全/监视事件会不会促使, 或者将会促使更多的消费者倾向于Linux,对此你作何感想?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 世界范围内,我听到人们都在说,“用开源保证隐私是必须的。”的确,那会促使更多的使用者选择Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
除了他们对linux平台下的隐私和安全持自信、信任的态度以外, 我认为消费者会基于多种原因选择Linux。
|
||||
代码的透明性以及开发过程逐渐给予博学和警觉的消费者一个选择,一个会让他们对linux感觉良好的选择。
|
||||
|
||||
[视频游戏发行商] Valve [及其SteamOS下的工作][1] 正在促使更多的消费者走进Linux,就像逐渐占据主导的Android和其他运行Linux的电子设备一样,比如电视、家电、汽车等,当然还有更多。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 针对手机的Ubuntu Edge, 对它有何看法? 对于2014-2015年Linux/Ubuntu手机市场走势,你作何预测?*
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**:我希望看到潜在的有趣的新产品进入市场,尤其是基于Linux的产品。很难说每年哪款产品会成为手机市场的新宠。
|
||||
|
||||
我认为预测基于Linux的手机将占据主导地位,不算夸大事实。Android, Tizen, Ubuntu, Firefox,等等等等,都显示出Linux可以驱动手机市场的创新,并且为消费者创造新的体验,为开发者和OEMs创造机会。
|
||||
|
||||
明年令人振奋的及我所关注的,就是,linux和开源界如何把这些设备、对象和服务关联到一起。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: What’s the most exciting use case you’ve seen so far for Linux embedded in automobile systems?**
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 目前为止,你看到的linux嵌入式车载系统的最令人激动的使用案例是什么?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 毫无疑问,就是,Cadillac, Tesla, Toyota, Jaguar, Land Rover等都搭建了车载信息娱乐系统。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,今年赢得了 “年度汽车族”奖项的Tesla Model S,装备了一个17英寸平面、运行着定制Linux的电脑。这真的是太酷了。
|
||||
|
||||
2014年度汽车族刚刚揭晓 -- Cadillac CTS sedan, 也是使用linux作为车载信息娱乐系统。汽车制造商有能力使用linux进行创新并区别使用这些系统。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux的成功也能从来自IHS汽车的最新数据上看到,IHS本月报告称,在全球车载信息娱乐市场,基于linux的汽车销量2020年有望达到5.37千万,超过微软和黑莓QNX。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux基金会协同汽车级Linux工作组在该领域做了许多工作。通过在Linux内核社区,其他开源社区,以及汽车行业,营造一个中立、支持性的环境,针对一些世界上大的汽车制造商如日产,捷豹,路虎,丰田,等等,我们可以帮助其推动汽车linux技术。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 在硬核开发者市场以外,Linux是如何发展壮大的,尤其是考虑到消费者和游戏玩家?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**:可以肯定的是,对游戏玩家来说,今年是linux的一个转折点。Valve, 基于Steam网络平台的一个游戏厂商,在linux上构建并运行所有的源代码和动画。Valve CEO Gabe Newell 称,今年的LinuxCon大会上他们在linux平台运行了198个游戏,随着引进基于linux的Stream,这个数字还会上升。这是Linux和游戏界新趋势的开端。
|
||||
|
||||
用户每天都在用linux。软件支撑着我们的日常生活。像Google,Facebook还有Twitter等公司,都建立在Linux和开源软件之上。去年10月份LinuxCon欧洲大会上,来自Twitter的Chris Aniszczyk告诉观众:
|
||||
“Twitter 理所当然完全运行在linux上。为什么你们还需要其他的东西?”(言外之意就是有linux就够了,不需要别的什么东西了。)
|
||||
|
||||
如今Linux驱动着130万台日常用Android手机,每天近60万基于linux的新电视售出。新的家电以及汽车都建立在linux之上。主要交通系统也都在使用linux。最受欢迎的[GoPro 使用linux和开源软件][2]。举不完的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
Linux和开源理念将会逐渐融入主流消费者的生活。三星使用linux内核以及基于linux的产品充实它的产品线,从电视机到手机,再到家电,等等等等。
|
||||
|
||||
敬请关注 - 你会看到更多的实例,无不展现出Linux和开源软件以及协同开发在日常生活中发挥越来越大的作用。
|
||||
|
||||
**VentureBeat: 在你看来,到2014年,免费和开源软件最大的机遇会是什么?**
|
||||
|
||||
**Zemlin**: 我们已经谈到游戏和电子设备,但是企业将会继续为linux呈现更多的机会。云计算的兴起为开发者带来新的机遇和挑战。你试着去找找没有运行在linux上的公共云。
|
||||
|
||||
软件定义的网络实现将成为2014年的主要活动之一。人们并没有期望着软件定义网络以及网络功能虚拟化变得多么大。想想吧。数十亿美元花费在硬件上,交换机,路由,负载均衡器,防火墙等等。这些都抽象成了软件。更更重要的是,它是在开源软件的基础架构甜蜜点OSS层被抽象。我认为你会看到,像OpenDaylight项目以及其他项目,在2014年都会有大的突破。
|
||||
|
||||
当然,这只是实现协同发展的大趋势的一部分,你的读者应该会对此感兴趣。我的推测是再过一个20年,几乎所有的基础软件都会议协同开发的方式进行构建。2014年开发者需要学习如何以协同方式构建软件,要学会如何参与开源项目并且贡献代码。如果开发者能够理解协同开发和开源的原则和理念,那么他们职业生涯中的机遇将会是无穷的。
|
||||
|
||||
参与到linux的世界中来,这是一个激动人心的时刻。从智能手表到电视机,到汽车,所有你能想到的,Linux成为事实上的平台。
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://venturebeat.com/2013/11/26/linux-chief-open-source-is-safer-and-linux-is-more-secure-than-any-other-os-exclusive/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/l3b2w1) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://venturebeat.com/2013/09/23/steamos-valves-linux-based-operating-system-for-the-tv-and-living-room/
|
||||
[2]:http://gopro.com/support/open-source
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,142 @@
|
||||
Linux date命令 - 显示和设置系统日期与时间
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
操作系统上的时间或许只被认为是时钟。特别在控制台下, 我们通常不认为date重要。但是对于管理员,这个假设是错误的。你知道错误的日期和时间会使你不能编译程序么?
|
||||
|
||||
因为日期和时间的重要,这或许就是开发网络时间协议(Network Time Protocol)的原因。让我们开始了解date命令是如何工作的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 显示系统日期 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要显示系统日期,只要输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ date
|
||||
Thu Dec 5 22:55:41 WIB 2013
|
||||
|
||||
### 格式化日期 ###
|
||||
|
||||
日期有很多格式。如果你不喜欢默认的格式,你可以转换它。你可能会想"为什么我需要改变格式? 默认的输出对我足够了。" 是这样的。但是当你在编程时,默认输出或许无法满足用户的需求。因此这里有一些自定义输出。
|
||||
|
||||
### RFC 2822 的日期与时间输出格式 ###
|
||||
|
||||
$ date -R
|
||||
Thu, 05 Dec 2013 23:40:53 +0700
|
||||
|
||||
**RFC 2822** 的格式像这样 : **星期, 日-月-年, 小时:分钟:秒 时区**
|
||||
时区 +0700 等同于 GMT +7。
|
||||
|
||||
默认上**date**使用的是定义在**/etc/localtime**的时区。有效时区数据定义在**/usr/share/timezones**。
|
||||
|
||||
### 打印或者设置协调世界时 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在 [Wikipedia][1]上, UTC 意思是
|
||||
|
||||
> 主要的调节世界时钟和时间的标准。这是格林位置标准时间几个非常相近的继任者之一。
|
||||
|
||||
以UTC形式显示日期和时间, 使用 -u 参数
|
||||
|
||||
$ date -u
|
||||
Thu Dec 5 16:45:58:UTC 2013
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用格式化选项 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要自定义你的日期格式, **使用加号 (+)**
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”Day : %d Month : %m Year : %Y”
|
||||
Day: 05 Month: 12 Year: 2013
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +%D
|
||||
12/05/13
|
||||
|
||||
**%D** 格式遵循 **年/月/日 的格式**.
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想的话,你可以输出日期的名字。下面是一些例子:
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”%a %b %d %y”
|
||||
Fri 06 Dec 2013
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”%A %B %d %Y”
|
||||
Friday December 06 2013
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”%A %B %d %Y %T”
|
||||
Friday December 06 2013 00:30:37
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +”%A %B-%d-%Y %c”
|
||||
Friday December-06-2013 12:30:37 AM WIB
|
||||
|
||||
还有很多的日期格式。只要输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ date –help
|
||||
|
||||
或者
|
||||
|
||||
$ man date
|
||||
|
||||
来显示date命令的语法和参数。
|
||||
|
||||
基本上,date命令会翻译所有所有的百分号(%)和打印打印在引号("")内所有的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
### 设置系统日期和时间 ###
|
||||
|
||||
通常地,你希望你的系统日期和时间是自动设置的。如果由于一些原因,你想要手动修改它,我们可以使用这个命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# date –set=”20140125 09:17:00”
|
||||
|
||||
这会**设置**你当前的系统日期和时间到**一月 25, 2014 and 09:17:00 AM。请注意**,你**必须**拥有特权来这么做。不然你会得到这样一个错误。
|
||||
|
||||
date: cannot set date: Operation not permitted
|
||||
Sat Jan 25 09:17:00 WIB 2014
|
||||
|
||||
### 重置你的时间 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果你希望重置你的系统日期和时间到原始值,你可以用这个技巧。
|
||||
|
||||
# hwclock
|
||||
Fri 06 Dec 2013 03:44:10 AM WIB -0.314082 seconds
|
||||
|
||||
这回设置你的系统日期和时间到hwclock命令的输出的样子
|
||||
|
||||
### 在脚本中使用date命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
还记得我之前说为什么你需要改变date的输出么?一个答案是你或许需要编程。让我们看下bash脚本下的一个例子。
|
||||
|
||||
$ vi display.date
|
||||
|
||||
#! /bin/bash
|
||||
DATETIME=$(date +”DATE: %a %b-%d-%Y TIME: %T WEEK NUMBER: %W”)
|
||||
echo $DATETIME
|
||||
|
||||
保存并运行它:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./display.date
|
||||
DATE : Fri Dec-06-2013 TIME: 03:08:19 WEEK Number :40
|
||||
|
||||
如果你发现权限拒绝错误信息,输入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ chmod 755 display.date
|
||||
|
||||
### 在备份流程中使用date ###
|
||||
|
||||
另外一个例子是子你备份流程中使用date。
|
||||
|
||||
$ date +%F
|
||||
2013-12-06
|
||||
|
||||
$ tar zcfv /daily_backup/backup-`date +%F`.tar.gz /home/pungki/Documents
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
它会压缩文件夹**/home/pungki/Documents**到一个位于**/daily_backup folder**的文件**backup-2013-12-06.tar.gz**中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
date可能被认为在某些方面不重要。但是date扮演了一个重要的角色。通常上,要想知道关于date命令更多的细节,在你的控制台下输入man date访问man页面。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/date-command-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coordinated_Universal_Time
|
||||
189
translated/Setup FTP Server On openSUSE 13.1.md
Normal file
189
translated/Setup FTP Server On openSUSE 13.1.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,189 @@
|
||||
translating by zsJacky
|
||||
|
||||
在openSUSE 13.1中配置FTP服务器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**vsftpd** (**非常****安全的****文件****传输****协议****守护进程**) 是Unix/Linux系统中的一个安全快速的FTP服务器。 在这篇 how-to 文章中,让我们看看在openSUSE 13.1中怎样使用vsftpd来配置一个基本的FTP服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 vsftpd ###
|
||||
|
||||
作为root用户登录然后输入以下的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# zypper in vsftpd
|
||||
|
||||
启动 vsftpd 服务然后设置让它在每次系统重启时自动启动
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable vsftpd.service
|
||||
# systemctl start vsftpd.service
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置 vsftpd ###
|
||||
|
||||
为ftp用户新建一个文件夹。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /srv/ftp
|
||||
|
||||
创建一个叫 **ftp-users** 的组。
|
||||
|
||||
# groupadd ftp-users
|
||||
|
||||
让我们来创建一个叫unixmen的示例用户 并设置其主目录为 **/srv/ftp** 组为**ftp-users**。
|
||||
|
||||
# useradd -g ftp-users -d /srv/ftp/ unixmen
|
||||
|
||||
为新用户设置密码。
|
||||
|
||||
# passwd unixmen
|
||||
|
||||
使ftp主目录 **/srv/ftp/** 可以被ftp用户所访问。
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod 750 /srv/ftp/
|
||||
# chown unixmen:ftp-users /srv/ftp/
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 vsftpd.conf 文件
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/vsftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
设置如下的更改。
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
#Uncomment and Set YES to enable write.
|
||||
write_enable=YES
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment and Set banner name for your website
|
||||
ftpd_banner=Welcome to Unixmen FTP service.
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment
|
||||
ls_recurse_enable=YES
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment and set YES to allow local users to log in.
|
||||
local_enable=YES
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# To disable anonymous access, set NO.
|
||||
anonymous_enable=NO
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment to enable ascii download and upload.
|
||||
ascii_upload_enable=YES
|
||||
ascii_download_enable=YES
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
## Add at the end of this file ##
|
||||
use_localtime=YES
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 测试本地FTP服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先 让我们按如下步骤尝试登陆FTP服务器
|
||||
|
||||
# ftp localhost
|
||||
Trying ::1:21 ...
|
||||
Connected to localhost.
|
||||
220 (vsFTPd 3.0.2)
|
||||
Name (localhost:root): unixmen
|
||||
331 Please specify the password.
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
230 Login successful.
|
||||
Remote system type is UNIX.
|
||||
Using binary mode to transfer files.
|
||||
ftp>
|
||||
|
||||
正如你在上面所输出的那样, 我们将能够用unixmen用户登录到ftp服务器。
|
||||
### 测试远程FTP服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
默认地 openSUSE内置的防火墙不允许从远程系统登陆FTP。所以让我们允许vsftpd服务通过suse的防火墙。然后我们需要打开: **Yast -> 安全性与用户 -> 防火墙**.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在防火墙界面,进入 **允许服务**. 在区域选择下拉框中,选择 **外部区域** 在服务允许下拉框中,选择 **vsftpd 服务器** 然后点击添加。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
单击下一步并关闭Yast控制中心
|
||||
|
||||
现在尝试从远程系统连接FTP。
|
||||
|
||||
我试着从我的ubuntu桌面系统登录FTP服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
sk@sk:~$ ftp 192.168.1.53
|
||||
Connected to 192.168.1.53.
|
||||
220 (vsFTPd 3.0.2)
|
||||
Name (192.168.1.53:sk): unixmen
|
||||
331 Please specify the password.
|
||||
Password:
|
||||
230 Login successful.
|
||||
Remote system type is UNIX.
|
||||
Using binary mode to transfer files.
|
||||
ftp>
|
||||
|
||||
正如你在上面输出中所看到的,我将能够连接到ftp服务器。如果不允许vsftpd服务通过防火墙, 你将会得到一个连接超时的错误。
|
||||
|
||||
### 从浏览器连接 ###
|
||||
|
||||
打开你的浏览器并导航到**ftp://ip-address/**。输入ftp用户名和密码。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 使用FileZilla连接到FTP服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
对于新手来说,在命令行模式下工作可能会很烦恼。所以让我们来安装一个叫[**Filezilla**][1]的图形化的FTP客户端。它可以让我们登陆FTP变得更加简单:
|
||||
|
||||
几乎所有的发行版在他们的官方软件仓库中都有filezilla客户端。 为了在基于Linux的系统上安装filezilla 需要键入以下的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
在基于Ubuntu的系统中:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install filezilla
|
||||
|
||||
在Fedora/Redhat系统中:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install filezilla
|
||||
在openSUSE中:
|
||||
|
||||
# zypper in filezilla
|
||||
|
||||
安装完fielzilla后打开它。输入ftp服务器的IP地址,用户名和密码,然后点击快速链接。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
为了增加安全性,你可以通过将用户添加到 **/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list**文件中来限制特定用户对FTP服务器的访问。
|
||||
|
||||
编辑 vsftpd.conf 文件,
|
||||
|
||||
nano /etc/vsftpd.conf
|
||||
|
||||
设置如下的更改.
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
# Uncomment and set YES
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES
|
||||
chroot_list_enable=YES
|
||||
chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
创建 **文件 /etc/vsftpd.chroot_list**,
|
||||
|
||||
nano /etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
|
||||
|
||||
添加你希望其能够访问FTP服务器的用户。我添加了用户**unixmen**。
|
||||
|
||||
unixmen
|
||||
|
||||
重启ftp服务.
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart vsftpd.service
|
||||
|
||||
现在你将能够使用chroot_list文件中列出的用户来连接到FTP服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
如果chroot_list以外的用户想访问FTP服务器, 他们将得到如下的错误。
|
||||
|
||||
500 OOPS: could not read chroot() list file:/etc/vsftpd.chroot_list
|
||||
ftp: Login failed
|
||||
|
||||
现在就是这样。 你的FTP服务器已经可以使用了。 享受吧!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.unixmen.com/setup-ftp-server-opensuse-13-1/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[zsJacky](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:https://filezilla-project.org/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
UNIGINE 可能是 Linux 上最好的游戏引擎
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**UNIGINE,是一个实时的 3D 引擎,它能够在所有主流的平台上运行,包括 Linux,并刚刚升级到新的版本,带给了我们一些重要的新特性。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Unigine 引擎正是由 Unigine 公司开发的, 同时这公司还开发了 Heaven DX11 基准测试软件。 这公司开发的技术总是越来越好,并且随着他们最近在 Linux 平台上的扩展,我们真的很高兴看到这引擎在最近时间作出的重大的更新。
|
||||
|
||||
在 UNIGINE 引擎最近作出的更新中,最大的更新是通用图像生成器接口 (Common Image Generator Interface/CIGI) 协议。
|
||||
|
||||
据引擎的开发者说,这个接口在模拟行业中,是一种用于主机设备与图像生成器 (IG) 之间通信的标准方法来的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 新款 UNIGINE 引擎的亮点 ###
|
||||
|
||||
- 在笛卡尔坐标系中增加了对 WGS84,ECF 和 NED 坐标系的支持(这会帮助开发者更好地在用 Unigine 开发的项目中使用实时的 GIS 数据);
|
||||
- 实施了游戏框架,这样使得游戏更加容易地创建,同时这种特性包括实体与节点的自动链接、层次与世界的自动链接、实体对象管理、贯穿所有层次的游戏全局上下文、事件处理系统、最佳的实体更新等等。
|
||||
- 增加渲染时帧率的稳定性。
|
||||
- 两个新的选项,2D 噪音和 3D 噪音(编辑器中的状态选项卡),已被添加到 mesh_leaf_base 材质中。
|
||||
- 一个新的参数,遮挡屏蔽,已经被添加到所有的材质中。
|
||||
- 密杂草丛的高度现已实现同步。
|
||||
- 修复了在渲染非 Flash 闪屏时崩溃的漏洞。
|
||||
|
||||
所有平台的完整新特性列表,可以在官方的[公告]中找到。[1].
|
||||
|
||||
要记住 UNIGINE 引擎只针对商业企业,并不向广大用户提供试用版。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/UNIGINE-Is-Probably-the-Best-Gaming-Engine-on-Linux-404484.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[hyaocuk](https://github.com/hyaocuk) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unigine.com/devlog/2013/11/27/113
|
||||
[2]:
|
||||
[3]:
|
||||
[4]:
|
||||
[5]:
|
||||
[6]:
|
||||
[7]:
|
||||
[8]:
|
||||
[9]:
|
||||
[10]:
|
||||
[11]:
|
||||
[12]:
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,3 @@
|
||||
[翻译中] by KayGuoWhu
|
||||
Unvanquished 可能成为Linux上最好的免费多人游戏
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Unvanquished,一款免费的、开源的并将实时策略元素和未来科幻设定相结合的第一人称视角的射击游戏,已经收到了它的第22次更新。事实上,版本是22.1,但是是谁在计数呢?**
|
||||
@ -39,4 +38,4 @@ via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Unvanquished-Will-Probably-Be-the-Best-Free-
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unvanquished.net/news/111-it-s-release-time-again-alpha-22
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unvanquished.net/download#linux
|
||||
[2]:http://www.unvanquished.net/download#linux
|
||||
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user