mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-18 02:00:18 +08:00
Merge branch 'master' of git://github.com/ch-cn/TranslateProject into ch-cn-master
This commit is contained in:
commit
681adea294
@ -1,178 +0,0 @@
|
||||
ch-cn translating
|
||||
10 Useful Tips for Writing Effective Bash Scripts in Linux
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
[Shell scripting][4] is the easiest form of programming you can learn/do in Linux. More so, it is a required skill for [system administration for automating tasks][5], developing new simple utilities/tools just to mention but a few.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article, we will share 10 useful and practical tips for writing effective and reliable bash scripts and they include:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1\. Always Use Comments in Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
This is a recommended practice which is not only applied to shell scripting but all other kinds of programming. Writing comments in a script helps you or some else going through your script understand what the different parts of the script do.
|
||||
|
||||
For starters, comments are defined using the `#` sign.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#TecMint is the best site for all kind of Linux articles
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2\. Make a Script exit When Fails
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes bash may continue to execute a script even when a certain command fails, thus affecting the rest of the script (may eventually result in logical errors). Use the line below to exit a script when a command fails:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#let script exit if a command fails
|
||||
set -o errexit
|
||||
OR
|
||||
set -e
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3\. Make a Script exit When Bash Uses Undeclared Variable
|
||||
|
||||
Bash may also try to use an undeclared script which could cause a logical error. Therefore use the following line to instruct bash to exit a script when it attempts to use an undeclared variable:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#let script exit if an unsed variable is used
|
||||
set -o nounset
|
||||
OR
|
||||
set -u
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4\. Use Double Quotes to Reference Variables
|
||||
|
||||
Using double quotes while referencing (using a value of a variable) helps to prevent word splitting (regarding whitespace) and unnecessary globbing (recognizing and expanding wildcards).
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the example below:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
#let script exit if a command fails
|
||||
set -o errexit
|
||||
#let script exit if an unsed variable is used
|
||||
set -o nounset
|
||||
echo "Names without double quotes"
|
||||
echo
|
||||
names="Tecmint FOSSMint Linusay"
|
||||
for name in $names; do
|
||||
echo "$name"
|
||||
done
|
||||
echo
|
||||
echo "Names with double quotes"
|
||||
echo
|
||||
for name in "$names"; do
|
||||
echo "$name"
|
||||
done
|
||||
exit 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and exit, then run it as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./names.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
[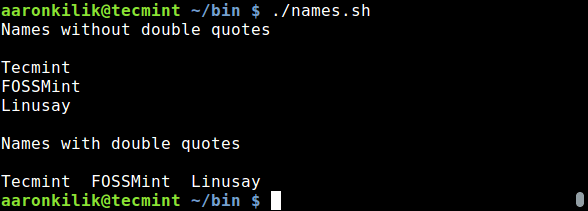][6]
|
||||
|
||||
Use Double Quotes in Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
### 5\. Use functions in Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
Except for very small scripts (with a few lines of code), always remember to use functions to modularize your code and make scripts more readable and reusable.
|
||||
|
||||
The syntax for writing functions is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
function check_root(){
|
||||
command1;
|
||||
command2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
OR
|
||||
check_root(){
|
||||
command1;
|
||||
command2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For single line code, use termination characters after each command like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
check_root(){ command1; command2; }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 6\. Use = instead of == for String Comparisons
|
||||
|
||||
Note that `==` is a synonym for `=`, therefore only use a single `=` for string comparisons, for instance:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
value1=”tecmint.com”
|
||||
value2=”fossmint.com”
|
||||
if [ "$value1" = "$value2" ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 7\. Use $(command) instead of legacy ‘command’ for Substitution
|
||||
|
||||
[Command substitution][7] replaces a command with its output. Use `$(command)` instead of backquotes ``command`` for command substitution.
|
||||
|
||||
This is recommended even by [shellcheck tool][8] (shows warnings and suggestions for shell scripts). For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
user=`echo “$UID”`
|
||||
user=$(echo “$UID”)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 8\. Use Read-only to Declare Static Variables
|
||||
|
||||
A static variable doesn’t change; its value can not be altered once it’s defined in a script:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
readonly passwd_file=”/etc/passwd”
|
||||
readonly group_file=”/etc/group”
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 9\. Use Uppercase Names for ENVIRONMENT Variables and Lowercase for Custom Variables
|
||||
|
||||
All bash environment variables are named with uppercase letters, therefore use lowercase letters to name your custom variables to avoid variable name conflicts:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#define custom variables using lowercase and use uppercase for env variables
|
||||
nikto_file=”$HOME/Downloads/nikto-master/program/nikto.pl”
|
||||
perl “$nikto_file” -h “$1”
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 10\. Always Perform Debugging for Long Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
If you are writing bash scripts with thousands of lines of code, finding errors may become a nightmare. To easily fix things before executing a script, perform some debugging. Master this tip by reading through the guides provided below:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [How To Enable Shell Script Debugging Mode in Linux][1]
|
||||
|
||||
2. [How to Perform Syntax Checking Debugging Mode in Shell Scripts][2]
|
||||
|
||||
3. [How to Trace Execution of Commands in Shell Script with Shell Tracing][3]
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all! Do you have any other best bash scripting practices to share? If yes, then use the comment form below to do that.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
|
||||
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.tecmint.com/useful-tips-for-writing-bash-scripts-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.tecmint.com/enable-shell-debug-mode-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.tecmint.com/check-syntax-in-shell-script/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.tecmint.com/trace-shell-script-execution-in-linux/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.tecmint.com/category/bash-shell/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.tecmint.com/using-shell-script-to-automate-linux-system-maintenance-tasks/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Use-Double-Quotes-in-Scripts.png
|
||||
[7]:https://www.tecmint.com/assign-linux-command-output-to-variable/
|
||||
[8]:https://www.tecmint.com/shellcheck-shell-script-code-analyzer-for-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,177 @@
|
||||
Linux 中编写有效的 Bash 脚本的 10 个有用技巧
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
[Shell 脚本编程][4] 是你在 Linux 下学习或练习编程的最简单的方式。尤其对 [系统管理员要处理着自动化任务][5],且要开发新的简单的实用程序或工具等(这里只是仅举几例)更是必备技能。
|
||||
|
||||
本文中,我们将分享 10 个写出高效可靠的 bash 脚本的实用技巧,它们包括:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1\. 脚本中常用注释
|
||||
|
||||
这是不仅可应用于 shell 脚本程序中也可用在其他所有类型的编程中的一种推荐做法。在脚本中作注释能帮你或别人翻阅你的脚本了解脚本的不同部分所做的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
对于刚入门的人来说,注释用 `#` 号来定义。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#TecMint 是浏览各类 Linux 文章的最佳站点
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 2\. 当运行失败时使脚本退出
|
||||
|
||||
有时即使某些命令运行失败,bash 可能继续去执行脚本,这样就影响到脚本的其余部分(会最终导致逻辑错误)。用下面的行的方式在遇到命令失败时来退出脚本执行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#如果命令运行失败让脚本退出执行
|
||||
set -o errexit
|
||||
或
|
||||
set -e
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 3\. 当 Bash 用未声明变量时使脚本退出
|
||||
|
||||
Bash 也会尝试用会引起逻辑错误的未声明的脚本。因此用下面行的方式去通知 bash 当它尝试去用一个未声明变量时就退出脚本执行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#若有用未设置的变量即让脚本退出执行
|
||||
set -o nounset
|
||||
或
|
||||
set -u
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 4\. 使用双引号来引用变量
|
||||
|
||||
当引用时(使用一个变量的值)用双引号有助于防止单词分割开(由于空白)和不必要的匹配(识别和扩展通配符)
|
||||
|
||||
看看下面的例子:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
#若命令失败让脚本退出
|
||||
set -o errexit
|
||||
#若未设置的变量被使用让脚本退出
|
||||
set -o nounset
|
||||
echo "Names without double quotes"
|
||||
echo
|
||||
names="Tecmint FOSSMint Linusay"
|
||||
for name in $names; do
|
||||
echo "$name"
|
||||
done
|
||||
echo
|
||||
echo "Names with double quotes"
|
||||
echo
|
||||
for name in "$names"; do
|
||||
echo "$name"
|
||||
done
|
||||
exit 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存文件并退出,接着如下运行一下:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ ./names.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
[][6]
|
||||
|
||||
在脚本中用双引号
|
||||
|
||||
### 5\. 在脚本中使用函数
|
||||
|
||||
除了非常小的脚本(只有几行代码),总是记得用函数来使代码模块化且使得脚本更可读和可重用。
|
||||
|
||||
写函数的语法如下所示:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
function check_root(){
|
||||
command1;
|
||||
command2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
或
|
||||
check_root(){
|
||||
command1;
|
||||
command2;
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
写成单行代码,每个命令后要用终止符号:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
check_root(){ command1; command2; }
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 6\. 字符串比较时用 = 替换 ==
|
||||
|
||||
注意 `==` 是 `=` 的同义词,因此仅用个单 `=` 来做字符串比较,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
value1=”tecmint.com”
|
||||
value2=”fossmint.com”
|
||||
if [ "$value1" = "$value2" ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 7\. 用 $(command) 替换老旧的 ‘command’ 来做代用
|
||||
|
||||
[Command substitution(命令代换)][7] 是用这个命令的输出结果取代命令本身。用 `$(command)` 而不是引号 ``command`` 来做命令代换。
|
||||
|
||||
这种做法也是 [shellcheck tool][8] (可针对 shell 脚本显示警告和建议)所建议的。例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
user=`echo “$UID”`
|
||||
user=$(echo “$UID”)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 8\. 用 Read-only 来声明静态变量
|
||||
|
||||
静态变量不会改变;它的值一旦在脚本中定义后不能被修改:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
readonly passwd_file=”/etc/passwd”
|
||||
readonly group_file=”/etc/group”
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 9\. 环境变量用大写字母命名且自定义变量用小写
|
||||
|
||||
所有的 bash 环境变量用大写字母去命名,因此用小写字母来命名你的自定义变量以避免变量名冲突:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
#定义自定义变量用小写且环境变量用大写
|
||||
nikto_file=”$HOME/Downloads/nikto-master/program/nikto.pl”
|
||||
perl “$nikto_file” -h “$1”
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 10\. 总是对长脚本进行调试
|
||||
|
||||
如果你在写有数千行代码的 bash 脚本,排错可能变成噩梦。为了在脚本执行前易于修正一些错误,要进行一些调试。通过阅读下面给出的指南来掌握此技巧:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [如何在 Linux 中启用 Shell 脚本调试模式][1]
|
||||
|
||||
2. [如何在 Shell 脚本中执行语法检查调试模式][2]
|
||||
|
||||
3. [如何在 Shell 脚本中用 Shell Tracing 来跟踪命令的执行情况][3]
|
||||
|
||||
本文到这就结束了,你是否有一些其他更好的 bash 脚本编程经验想要分享?若是的话,在下面评论框分享出来吧。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S(Free and Open-Source Software,自由及开放源代码软件)爱好者,未来的 Linux 系统管理员、Web 开发人员,目前是 TecMint 的内容创作者,他喜欢用电脑工作,且崇尚分享知识。
|
||||
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.tecmint.com/useful-tips-for-writing-bash-scripts-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[ Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[ch-cn](https://github.com/ch-cn)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
[1]:https://www.tecmint.com/enable-shell-debug-mode-linux/
|
||||
[2]:https://www.tecmint.com/check-syntax-in-shell-script/
|
||||
[3]:https://www.tecmint.com/trace-shell-script-execution-in-linux/
|
||||
[4]:https://www.tecmint.com/category/bash-shell/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.tecmint.com/using-shell-script-to-automate-linux-system-maintenance-tasks/
|
||||
[6]:https://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/05/Use-Double-Quotes-in-Scripts.png
|
||||
[7]:https://www.tecmint.com/assign-linux-command-output-to-variable/
|
||||
[8]:https://www.tecmint.com/shellcheck-shell-script-code-analyzer-for-linux/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user