mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-30 02:40:11 +08:00
commit
6754f48711
@ -1,91 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating----geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to mount an LVM partition on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I have an external USB drive which contains several LVM partitions on it. I want to access some of those LVM partitions on my Linux. How can I mount an LVM partition on Linux?
|
||||
|
||||
LVM is a logical volume management tool which allows you to manage disk space using the notion of logical volumes and volume groups. The biggest benefit of using LVM over classic partitions is the flexibility in allocating storage for users and applications without being constrained by the size of individual physical disks.
|
||||
|
||||
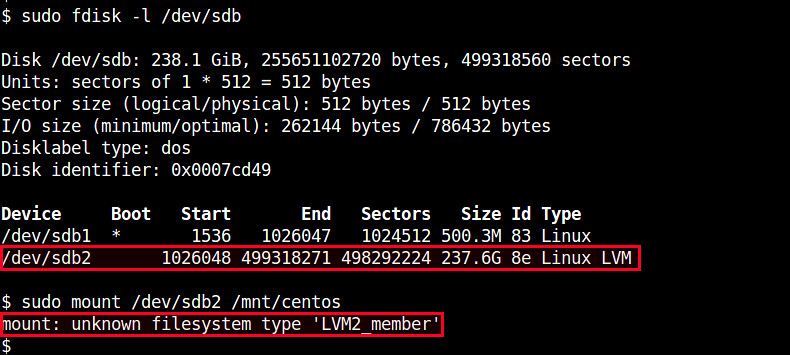
In LVM, the physical storage, on which logical volumes are created, is traditional partitions (e.g., /dev/sda2, /dev/sdb1). These partitions must be initialized as "physical volumes" and labeled so (e.g., "Linux LVM") in order for them to be used in LVM. Once the partitions are labeled as LVM volumes, you cannot mount them directly with mount command.
|
||||
|
||||
If you attempt to mount an LVM partition (e.g., /dev/sdb2), you will get the following error.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mount /dev/sdb2 /mnt
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
mount: unknown filesystem type 'LVM2_member'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to mount an LVM partition properly, you must instead mount "logical volumes" created inside the partition. Here is how to to it.
|
||||
|
||||
First, examine a list of available volume groups by running:
|
||||
|
||||
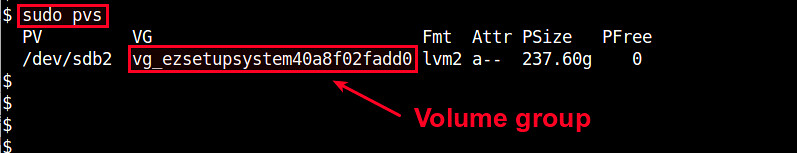
$ sudo pvs
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree
|
||||
/dev/sdb2 vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0 lvm2 a-- 237.60g 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The names of available physical volumes and volume groups are listed under PV and VG columns, respectively. In this example, there is a single volume group named "vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0" created on /dev/sdb2.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, let's check what logical volumes exist inside this volume group. For that, use lvdisplay command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo lvdisplay <volume-group-name>
|
||||
|
||||
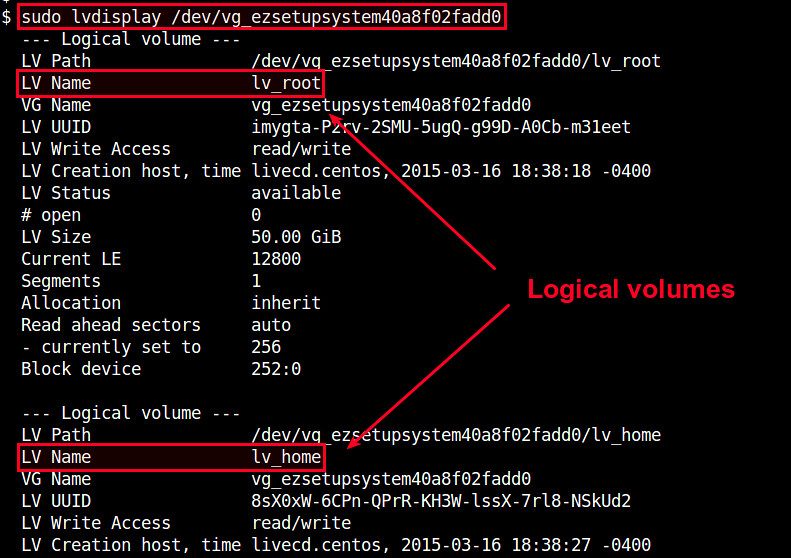
Running lvdisplay shows information about available logical volumes (e.g., device name, volume name, volume size, etc) as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo lvdisplay /dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
--- Logical volume ---
|
||||
LV Path /dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0/lv_root
|
||||
LV Name lv_root
|
||||
VG Name vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0
|
||||
LV UUID imygta-P2rv-2SMU-5ugQ-g99D-A0Cb-m31eet
|
||||
LV Write Access read/write
|
||||
LV Creation host, time livecd.centos, 2015-03-16 18:38:18 -0400
|
||||
LV Status available
|
||||
# open 0
|
||||
LV Size 50.00 GiB
|
||||
Current LE 12800
|
||||
Segments 1
|
||||
Allocation inherit
|
||||
Read ahead sectors auto
|
||||
- currently set to 256
|
||||
Block device 252:0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to mount a particular logical volume, use its device name shown in "LV Path" (e.g., /dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0/lv_home) as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mount /dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0/lv_home /mnt
|
||||
|
||||
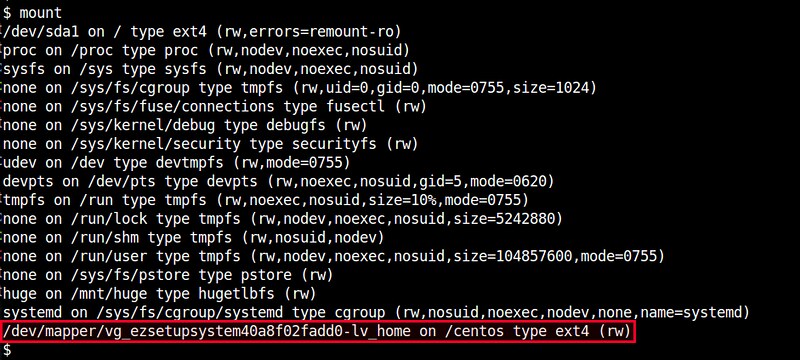
You can check the mount status by running mount command without any argument, which will show you a list of all mounted filesystems.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mount
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to have a logical volume to be mounted automatically on boot, add the following line in /etc/fstab. You need to specify the file system type (e.g., EXT4) of the volume, which you can find out from the output of mount command above.
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0/lv_home /mnt ext4 defaults 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
Now the logical volume will be automatically mounted at /mnt upon boot.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/mount-lvm-partition-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答 -- 如何在Linux中挂载LVM分区
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**: 我有一个USB盘包含了LVM分区。 我想要在Linux中访问这些LVM分区。我该如何在Linux中挂载LVM分区?
|
||||
|
||||
】LVM是逻辑卷管理工具,它允许你使用逻辑卷和卷组的概念来管理磁盘空间。使用LVM相比传统分区最大的好处是弹性地位用户和程序分配空间而不用考虑每个物理磁盘的大小。
|
||||
|
||||
在LVM中,那些创建了逻辑分区的物理存储是传统的分区(比如:/dev/sda2,/dev/sdb1)。这些分区必须被初始化位“物理卷”并被标签(如,“Linux LVM”)来使它们可以在LVM中使用。一旦分区被标记被LVM分区,你不能直接用mount命令挂载。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你尝试挂载一个LVM分区(比如/dev/sdb2), 你会得到下面的错误。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mount /dev/sdb2 /mnt
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
mount: unknown filesystem type 'LVM2_member'
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要正确地挂载LVM分区,你必须挂载分区创建的“逻辑分区”。下面就是如何做的。
|
||||
|
||||
=首先,用下面的命令检查可用的卷组:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pvs
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
PV VG Fmt Attr PSize PFree
|
||||
/dev/sdb2 vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0 lvm2 a-- 237.60g 0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
物理卷的名字和卷组的名字分别在PV和VG列的下面。本例中,只有一个创建在dev/sdb2下的组“vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0”。
|
||||
|
||||
接下来检查卷组中存在的逻辑卷,使用lvdisplay命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo lvdisplay <volume-group-name>
|
||||
|
||||
使用lvdisplay显示了可用卷的信息(如:设备名、卷名、卷大小等等)。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo lvdisplay /dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
--- Logical volume ---
|
||||
LV Path /dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0/lv_root
|
||||
LV Name lv_root
|
||||
VG Name vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0
|
||||
LV UUID imygta-P2rv-2SMU-5ugQ-g99D-A0Cb-m31eet
|
||||
LV Write Access read/write
|
||||
LV Creation host, time livecd.centos, 2015-03-16 18:38:18 -0400
|
||||
LV Status available
|
||||
# open 0
|
||||
LV Size 50.00 GiB
|
||||
Current LE 12800
|
||||
Segments 1
|
||||
Allocation inherit
|
||||
Read ahead sectors auto
|
||||
- currently set to 256
|
||||
Block device 252:0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要挂载一个特定的逻辑卷,使用“LV Path”下面的设备名(如:/dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0/lv_home)。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo mount /dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0/lv_home /mnt
|
||||
|
||||
你可以用mount命令不带任何参数检查挂载状态,这会显示所有已挂载的文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
$ mount
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你想在每次启动时自动挂载逻辑卷,在/etc/fstab中添加下面的行,你可以指定卷的文件系统类型(如 ext4),它可以从mount命令的输出中找。
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/vg_ezsetupsystem40a8f02fadd0/lv_home /mnt ext4 defaults 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
现在逻辑卷会在每次启动时挂载到/mnt。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/mount-lvm-partition-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user