mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-24 02:20:09 +08:00
Merge pull request #854 from blueabysm/apply
[translating] & [translated]
This commit is contained in:
commit
6658fde976
@ -1,141 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux and Unix nload App: Monitor Network Traffic and Bandwidth Usage In Real Time
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
If you want to monitor network throughput on the command line interface, use nload application. It is a console application which monitors network traffic and bandwidth usage in real time. It visualizes the in and outgoing traffic using two graphs and provides additional info like total amount of transferred data and min/max network usage.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install nload on a CentOS/RHEL/Red Hat/Fedora Linux ####
|
||||
|
||||
First, [turn on EPEL repo on a CentOS or RHEL][1] based system. Type the following [yum command][2] to install nload:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install nload
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install nload on a Debian or Ubuntu Linux ####
|
||||
|
||||
Type the following [apt-get command][3]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install nload
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install nload on a FreeBSD system ####
|
||||
|
||||
To install the nload via port, type:
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /usr/ports/net/nload/ && make install clean
|
||||
|
||||
Or add the package
|
||||
|
||||
# pkg install net/nload
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install nload on a OpenBSD system ####
|
||||
|
||||
Type the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pkg_add -i nload
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install nload using a source code on a Unix-like systems ####
|
||||
|
||||
First, grab the source code using either wget command or curl command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /tmp
|
||||
$ wget http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
To [untar a tar file called nload-0.7.4.tar.gz, use tar command][4], enter:
|
||||
|
||||
$ tar xvf nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
Cd to the directory containing the nloads's source code using cd command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd nload*
|
||||
|
||||
And type ./configure to configure the package for your system:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sh ./configure
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./configure
|
||||
|
||||
Running configure takes a while. Type make command to compile the nload:
|
||||
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, type make install to install the nload programs and related files as root user:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
# make install
|
||||
|
||||
How do I use nload to display the current network usage?
|
||||
|
||||
The basic syntax is:
|
||||
|
||||
nload
|
||||
nload device
|
||||
nload [options] device1 device2
|
||||
|
||||
Just type the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ nload
|
||||
$ nload eth0
|
||||
$ nload em0 em2
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
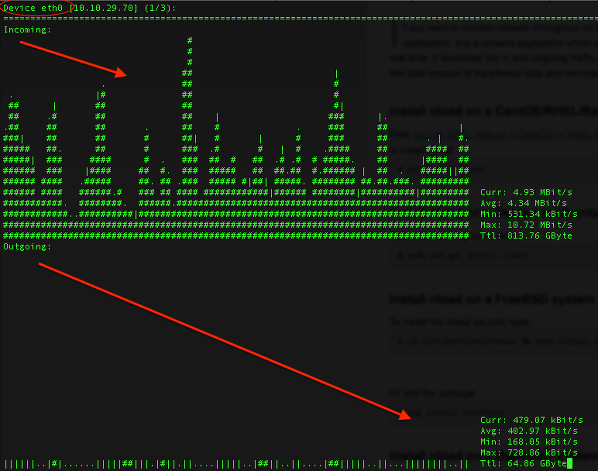
|
||||
|
||||
Fig. 01: nload command in action
|
||||
|
||||
#### Controlling nload app ####
|
||||
|
||||
Once nload command executed, it begins to monitor the network devices. You can control nload with the following key shortcuts:
|
||||
|
||||
1. You can switch between the devices by pressing the left and right arrow keys or Enter/Tab key.
|
||||
1. Press F2 to show the option window
|
||||
1. Press F5 to save current settings to the user’s config file.
|
||||
1. Press F6 reload settings from the config files.
|
||||
1. Press q or hit Ctrl+C to quit nload.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Setting the refresh interval of the display ####
|
||||
|
||||
The default value of interval is 100 milliseconds to refresh interval of the display. In this example, change to 500 milliseconds:
|
||||
|
||||
$ nload -t {interval_number_in_millisec}
|
||||
$ nload -t 500
|
||||
|
||||
Sample outputs:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Animated gif 01 - nload command in action
|
||||
|
||||
#### Setting the type of unit used for the display of traffic numbers ####
|
||||
|
||||
The syntax is:
|
||||
|
||||
$ nload -u h|H|b|B|k|K|m|M|g|G
|
||||
$ nload -U h|H|b|B|k|K|m|M|g|G
|
||||
$ nload -u h
|
||||
$ nload -u G
|
||||
$ nload -U G
|
||||
|
||||
Where,
|
||||
|
||||
- The lower case -u option: h means human readable (auto), b Bit/s, k kBit/s, m MBit/s and g GBit/s. The upper case letters mean the corresponding units in Bytes (instead of Bits). The default is k.
|
||||
- The upper case -U option is same as lower case -u option, but for an amount of data, e.g. Bit, kByte, GBit etc. (without "/s"). The default is M.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
I found nload to be reliable and stable application. If you enjoyed nload, you might also like to try out vnstat and iftop tools on Linux/Unix-like systems.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.cyberciti.biz/networking/nload-linux-command-to-monitor-network-traffic-bandwidth-usage/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/fedora-sl-centos-redhat6-enable-epel-repo/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/rhel-centos-fedora-linux-yum-command-howto/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-debian-package-management-cheat-sheet.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/tar-extract-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
||||
Linux 和 Unix 下 nload 应用程序:实时监控网络流量和带宽使用
|
||||
=================================================================================
|
||||
如果你想在命令行界面监控网络吞吐量,nload 应用程序是个不错的选择。它是一个实时监控网络流量和带宽使用的控制台应用程序,使用两个图表可视化地展示接收和发送的流量,并提供诸如数据交换总量、最小/最大网络带宽使用量等附加信息。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 CentOS/RHEL/Red Hat/Fedora Linux 上安装 nload ####
|
||||
|
||||
首先在 CentOS 或者基于 RHEL 的操作系统上[启用 EPEL 仓库][1],然后键入 [yum 命令][2]安装 nload:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install nload
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Debian 或者 Ubuntu Linux 上安装 nload ####
|
||||
|
||||
键入 [apt-get 命令][3]:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install nload
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 FreeBSD 操作系统上安装 nload ####
|
||||
|
||||
通过 port 安装 nload,键入:
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /usr/ports/net/nload/ && make install clean
|
||||
|
||||
或者添加包
|
||||
|
||||
# pkg install net/nload
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 OpenBSD 操作系统上安装 nload ####
|
||||
|
||||
键入下列命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo pkg_add -i nload
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在类 Unix 操作系统上从源代码安装 nload ####
|
||||
|
||||
首先,使用 wget 或者 curl 命令获取源代码:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /tmp
|
||||
$ wget http://www.roland-riegel.de/nload/nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
[使用 tar 命令解压缩名为 nload-0.7.4.tar.gz 的 tar 包][4],键入:
|
||||
|
||||
$ tar xvf nload-0.7.4.tar.gz
|
||||
|
||||
使用 cd 命令进入 nload 源代码所在目录:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd nload*
|
||||
|
||||
然后键入 ./configure 为你的操作系统配置安装包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sh ./configure
|
||||
|
||||
或者
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./configure
|
||||
|
||||
运行 configure 命令需要一点时间。完成后,使用 make 命令编译 nload:
|
||||
|
||||
$ make
|
||||
|
||||
最后,键入 make install 命令以 root 用户身份安装 nload 应用程序和相关文件:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
|
||||
或者
|
||||
|
||||
# make install
|
||||
|
||||
如何使用 nload 显示当前网络使用量呢?
|
||||
|
||||
基本语法是:
|
||||
|
||||
nload
|
||||
nload device
|
||||
nload [options] device1 device2
|
||||
|
||||
键入下列命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ nload
|
||||
$ nload eth0
|
||||
$ nload em0 em2
|
||||
|
||||
会得到输出:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
图01: 使用 nload 命令
|
||||
|
||||
#### 操控 nload 应用程序 ####
|
||||
|
||||
nload 命令一旦执行就会开始监控网络设备,你可以使用下列快捷键操控 nload 应用程序。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 你可以按键盘上的 ← → 或者 Enter/Tab 键在设备间切换。
|
||||
1. 按 F2 显示选项窗口。
|
||||
1. 按 F5 将当前设置保存到用户配置文件。
|
||||
1. 按 F6 从配置文件重新加载设置。
|
||||
1. 按 q 或者 Ctrl+C 退出 nload。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 设置显示刷新间隔 ####
|
||||
|
||||
默认每 100 毫秒刷新一次显示数值,下面的例子将时间间隔设置成 500 毫秒:
|
||||
|
||||
$ nload -t {interval_number_in_millisec}
|
||||
$ nload -t 500
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
GIF 动画 01 - 使用 nload 命令
|
||||
|
||||
#### 设置流量数值显示的单位 ####
|
||||
|
||||
语法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
$ nload -u h|H|b|B|k|K|m|M|g|G
|
||||
$ nload -U h|H|b|B|k|K|m|M|g|G
|
||||
$ nload -u h
|
||||
$ nload -u G
|
||||
$ nload -U G
|
||||
|
||||
释义:
|
||||
|
||||
- 小写选项 -u: h 意为自动格式化为人类易读的单位,b 意为 Bit/s,k 意为 kBit/s,m 意为 MBit/s,g 意为 GBit/s。大写字母意为使用 Byte 替代 Bit。默认为 k。
|
||||
- 大写选项 -U 与小写选项 -u 非常相似,不同之处在于它展示的是数据量,比如 Bit, kByte, GBit 等等。(没有 "/s")。默认值是 M。
|
||||
|
||||
### 结论 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我觉得 nload 是一个稳定可靠的应用程序,如果你喜欢 nload,你可能也想试试 Linux 和其他类 Unix 操作系统环境下的 vnstat 与 iftop 工具。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
译自: http://www.cyberciti.biz/networking/nload-linux-command-to-monitor-network-traffic-bandwidth-usage/
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[blueabysm](https://github.com/blueabysm) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/fedora-sl-centos-redhat6-enable-epel-repo/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/rhel-centos-fedora-linux-yum-command-howto/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/tips/linux-debian-package-management-cheat-sheet.html
|
||||
[4]:http://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/tar-extract-linux/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user