mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-12 01:40:10 +08:00
commit
5ad8e212bd
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
保持自由 - GCC应该接受收费插件吗?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
> GCC邮件列表中在争论GCC是否应该接受收费插件,但是认为GCC是一个免费软件开发的媒介的论调占得了上风
|
||||
|
||||
Gcc以及它在模块化方面的缺失又一次作为一个问题被提出来,并且和市场上的新的编译器LLVM做了对比。GCC巨大而古老:5百万行代码,30年研发时间,并且还在继续增长。相比较而言,LLVM更加年轻,更加模块化,并且允许所有的语言都作为一个模块添加进去。
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM的核心是‘开放源代码’。GCC是反著作权(copyleft)代表,是严格的免费软件,她不允许以任何形式收费的插件的代码进入到GCC的代码中。争论的一种意见,正如Eric Raymond说的,“FSF不可能既阻止持有所有权的供应者添加他们的插件到一个免费编译器中,又让这个编译器得到发展。就像马儿已经偏离了跑道,反对插件策略的战略目标已经彻底的失败了”。
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM已经被苹果公司采用作为OS X和苹果硬件上GCC的替代品,并且正在变得流行起来,特别是在BSD系列操作系统的用户中间。LLVM的拥护者推测LLVM将会在更广阔的应用程序和移动设备开发市场上成为GCC的替代者。GCC的反对者们的观点是GCC太过复杂,并且开发者们必须遵守她的‘反著作权(copyleft)’。这限制了那些不想在‘反著作权(copyleft)’许可证下发布他们的语言或者软件产品。作为典型,苹果公司有一个很长的厌恶免费软件的历史。他们也不允许遵守‘反著作权(copyleft)’的软件通过他们的App Store发布。
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM和GCC之间的争论其实是GNU/Linux和BSD系列、开放源代码和免费软件之间历史差异的翻新版。开放源码的开发者允许代码被以任何形式的使用,免费或者维持版权。免费软件则严格地规定,代码或者针对代码做的更新,必须保持永久免费。免费软件的支持者认为完整的‘反著作权’授权有助于GCC的发展,并且已经将Linux和免费软件带到一个其他方式无法到达的高度,同时保证了免费软件不会被收购或者堕落成商业利益。开放源码的支持者则认为开放源码更加的自由,因为使用这没有受到限制,他们可以随意使用,包括开发非开源的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
GNU编译器集合(GCC)一直是免费软件发展的关键。编译器是稀有且昂贵的商品,版权软件公司也充斥着对不符合标准的特性的需求。让软件兼容不同的机器和操作系统是一个非必需的复杂任务。GCC作为第一个真正免费的跨平台编译器,简化了这个过程。
|
||||
|
||||
GCC对于软件开发者和移动设备开发者来说也是一个划时代的产品,而不仅仅对于那些免费软件概念提出者。GCC不但免费和可移植,她跨越不同硬件架构的普遍性和公用性使得更加容易做到软件的兼容性、鲁棒性和一致性。这和John Gilmore,Michael Tiemann和David Henkel-Wallace在开发GCC时发现的一样。这也是Cygnus Solutions公司主要的卖点,Cygnus Solutions是第一家靠卖免费软件赚钱的公司。[译注:Cygnus Solutions是John Gilmore, Michael Tiemann and David Henkel- Wallace创办的公司,同时也是GNU几个主要产品的贡献者]
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM和GCC之间主要的技术差异集中在组成‘前端’,‘中端’,‘后端’的模块分割。‘前端’用来翻译特定的语言。‘中端’对翻译后产生的代码进行优化。‘后端’将优化后的代码转化成特定硬件架构的机器码。LLVM将这些模块分割成不同的实体,但是由于语义的和历史的原因,GCC模糊了这些模块之间的界限。
|
||||
|
||||
对于一个免费软件项目,添加一种新的语言或者架构到GCC也许是一个非常困难的过程,添加有版权的插件也是不允许的。由于模块间界限非常不明确,最容易的添加方法就是让添加的特性遵循免费软件许可证。最初的开发者也许想保持代码的封闭和版权,但最后不得不将代码以免费软件发布。早期的C++以及Objective C就被认为是其中典型的例子。
|
||||
|
||||
与此相反,LLVM允许,甚至也许可以说是鼓励添加和发展版权语言和架构,比如英伟达基于Clang和LLVM的对于GPU开发的NVCC。NVCC的源代码是免费软件或者开源软件开发者获取不到的。
|
||||
|
||||
Richard Stallman[对这方面的演讲中][1]旗帜鲜明地宣布:“在免费软件运动中,我们为自由而战。免费软件的的价值观从根本上就和开源软件不同,后者以写‘更好的代码’为终极目标。如果GCC从免费的编译器变成非免费的编译器,她将不再能够达成自由的目标。
|
||||
|
||||
“Clang和LLVM的开发者不认可我们的价值观和目标,所以得出了跟我们不一样的结论。他们反对我们采取的捍卫自由的措施,因为他们只看到这对他们造成的不便,却没有看到(或者不关心)他们真正的需求。我猜测他们把他们的工作定义为‘开源’,并且漠视自由。”
|
||||
|
||||
GCC开发者们不可能在许可证的条件上妥协。LLVM在某些行业的部门非常流行,因为它很年轻很新,在编程语言的浪潮中跳跃式发展着。流行的风向着更加开放奔跑,GCC决心跟商业利益死磕也许是这个长期演进路上的一大助力。Unix公司们从80和90年代的Unix战争中学到了一些东西。语言和操作系统都是工具,它们最好是开放和共享的。GCC是免费软件,不属于任何人。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxuser.co.uk/features/staying-free-should-gcc-allow-non-free-plug-ins
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[love\_daisy\_love](https://github.com/CNprober) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lwn.net/articles/582241
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
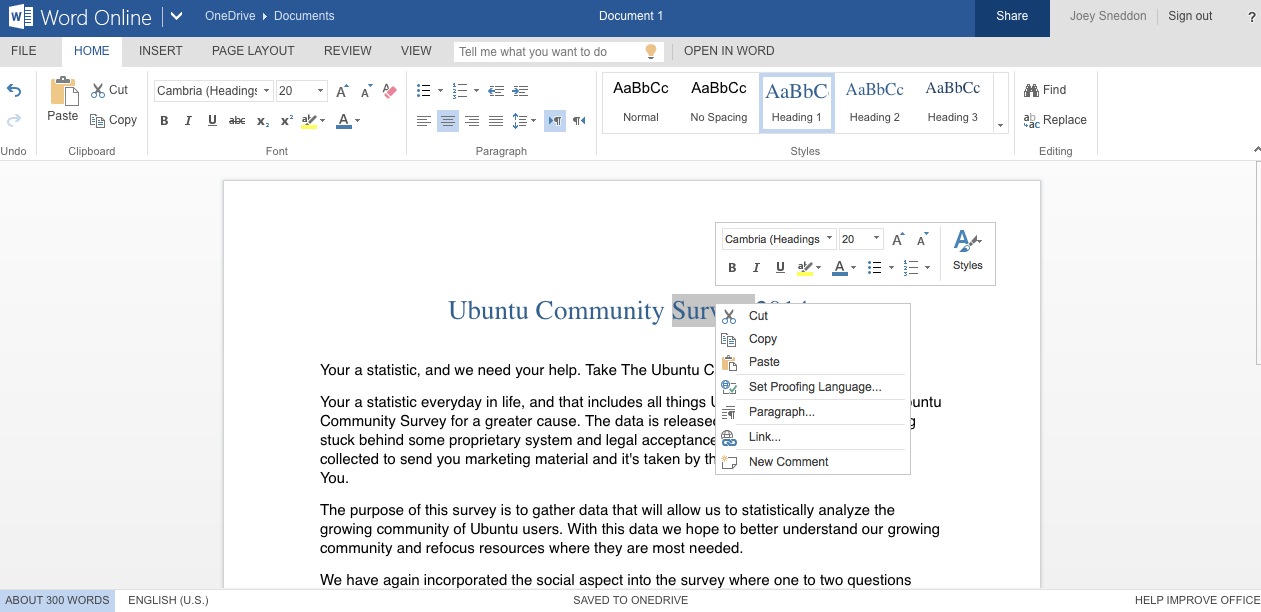
在Ubuntu上要用微软OFFICE?去安装官方的Web应用吧
|
||||
==================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**不论你喜欢与否,微软 Office 及其文件格式是大多数工作和学习环境所必须的,无论是好用还是不好用**
|
||||
|
||||
通过使用[LibreOffice的应用程序套件][1],在Ubuntu上阅读、编辑和保存这些专有文件格式出现是基本可行的。 Writer、Calc和Impress都不同程度的和微软 Office 可以互通,虽然以我的实际经验来看(幸好很短暂),不是很完美。
|
||||
|
||||
有时候你会不得不使用微软Office(虽然我们大多数人都心里向着开放标准,但是我们不应该无视实际问题),但你如果不太想去购买一个完整的微软OFFICE许可证,并通过 WINE来运行它,那么微软的在线网络应用程序就是完美的解决方法。
|
||||
|
||||
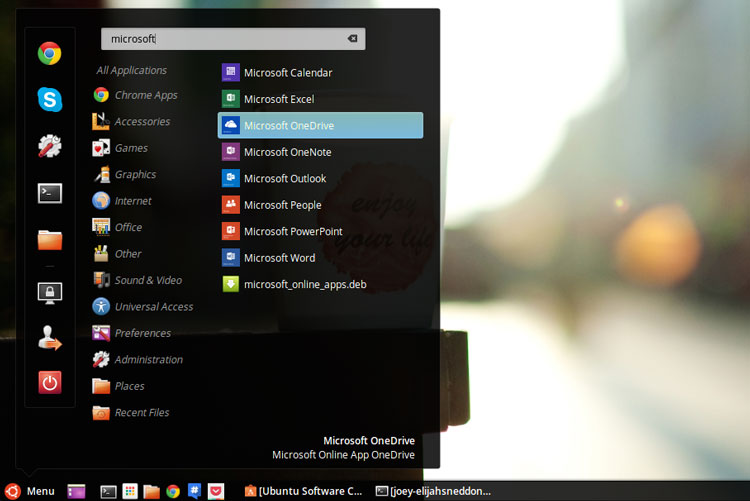
###在Ubuntu安装微软在线办公软件上的应用程序###
|
||||
|
||||
为了更容易地从Ubuntu的桌面访问这些在线版本,“Linux的Web应用项目”创造了一个小的、非官方的安装程序。它可以添加Web应用程序的快捷方式(“漂亮的书签”)到您的应用程序启动器。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
通过快捷方式,可以在你的默认的浏览器中打开相应的Microsoft Web应用,不可能有比这更简单的了。听起来不错吧?你可以找到这些Web 应用的快捷方式:
|
||||
|
||||
- Word
|
||||
- Excel
|
||||
- PowerPoint
|
||||
- Outlook
|
||||
- OneDrive
|
||||
- Calendar
|
||||
- OneNote
|
||||
- People
|
||||
|
||||
该软件包还创建了一个新的应用程序类别来容纳这些链接,不但可以让您把这些快捷方式从其他应用程序单独分开来,而且是直接位于常见的“办公软件”应用程序下。
|
||||
|
||||
这些都是必不可少的吗?不见得。他们有用吗?这取决于你的工作需要。但它是不错的选择吗?一定是的。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以从下面的链接下载.deb文件安装程序。适用于Ubuntu14.04 LTS和更高版本。
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载微软的在线办公应用(.deb)][2]
|
||||
|
||||
###其他可选项###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
类似的替代方案是[安装Chrome官方网上应用商店的在线办公应用程序][3],然后添加应用程序启动器到Linux。这也会在 Dash 中为它们创建启动快捷方式,不过那些可以被设置为打开自己的窗口框架中,而且不需要安装任何第三方软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
同时,谷歌最近在整合完整的Office功能(由于其购买了QuickOffice)[到自己的文档,幻灯片和表单应用][4]。Android应用程序Quickoffice退出了舞台,而以Chrome扩展的方式再次出现。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是一个深度的谷歌网络硬盘/文档的用户,那么这个解决方案可能对你来说更好。
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/run-microsoft-office-web-apps-ubuntu-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[cereuz](https://github.com/cereuz)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.libreoffice.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://docs.google.com/file/d/0ByQnaVw7riBQMjNCUFh4ZlM4Y0E/edit?usp=sharing
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgchrome.com/microsoft-brings-office-online-chrome-web-store/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.omgchrome.com/quickoffice-chrome-extension-gets-name-change/
|
||||
@ -1,22 +1,22 @@
|
||||
diff -u: 内核开发里的新鲜事儿
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
偶尔总会有人指出Linux中的POSIX违规(注:violation此处暂译为违规,若不妥,请修正),通常的回答是修复违规问题,但有时李纳斯·托瓦兹认为POSIX特性是不完整的,至少他们维护Linux特性的情形下是这样的。因此,他们或许应该构建一层POSIX兼容层,即便这个分层会相对较慢和低效。
|
||||
偶尔总会有人指出Linux中的POSIX违规(violation),通常的回答是“修复违规问题”,但有时李纳斯·托瓦兹认为POSIX特性是不完整的,至少他们维护Linux特性的情形下是这样的。因此,他们或许应该构建一层POSIX兼容层,即便这个分层会相对较慢和低效。
|
||||
|
||||
这一次,*迈克尔·凯利斯克*报告了一个影响文件操作的POSIX违规。显然,在多线程操作期间读写文件会导致竞争出现,重写其它操作的改变。
|
||||
这一次,*迈克尔·凯利斯克(Michael Kerrisk)*报告了一个影响文件操作的POSIX违规。显然,在多线程操作期间读写文件会导致竞争出现,重写其它操作的改变。
|
||||
|
||||
关于这是否是POSIX的一个违规存在一些讨论,但到最后又有谁关心呢?数据重写是很糟糕的。在迈克尔提交部分代码去重现这个问题后,讨论的问题集中到该做什么去修复它。但迈克尔确实提出了“Linux从早期开始就与UNIX不一致。(如在1992年版的史蒂夫的APUE的191页讨论到fork()操作后在父进程与子进程之间文件偏移量的共享问题。尽管史蒂夫没有显式地讲清楚一致性的保证,但缺乏这个保证的推论这里的讨论可能有些没意义。)”的观点。
|
||||
关于这是否是POSIX的一个违规存在一些讨论,但到最后又有谁关心呢?数据重写(clobbering)是很糟糕的事情。在迈克尔提交部分代码去重现这个问题后,讨论的问题集中到该做什么去修复它。但迈克尔的观点是:“Linux从早期开始就与UNIX不一致。(如在1992年版的史蒂夫的APUE的191页讨论到fork()操作后在父进程与子进程之间文件偏移量的共享问题。尽管史蒂夫没有显式地讲清楚一致性的保证,但缺乏这个保证的推论这里的讨论可能有些没意义。)”
|
||||
|
||||
艾尔·维洛和李纳斯一起设法解决这个修复。李纳斯尝试引入一个简单的互斥量去锁住文件,以便写操作无法互相重写。艾尔提出了自己的改进以改善李纳斯的补丁。
|
||||
艾尔·维洛(Al Viro)和李纳斯一起设法解决这个修复。李纳斯尝试引入一个简单的互斥量去锁住文件,以便写操作无法互相重写。艾尔提出了自己的改进以改善李纳斯的补丁。
|
||||
|
||||
李纳斯一度解释过这个故障自身的历史。显然,从前这个用来告诉系统去哪里写文件的文件指针已经被锁在一个信号量中,所以只有一个进程可以在某一时刻对这个文件做任何操作。但是,他们从中拿走了这个信号量,以便在任何时候可以适应设备文件和其它非常规文件,因为当用户被禁止写入其中时它们就会陷入竞争状态。
|
||||
|
||||
这就是错误的由来。那时候,它悄悄通过了检查,未被发现。因为实际上对常规文件的读写仍然由内核自动处理。只有文件指针自身可以避免同步。而且,因为高速线程化的文件操作是一个非常罕见的需求,所以对任何人来说都需要很长时间才能遇到这个问题并报告它。
|
||||
这就是错误的由来。那个时候,它悄悄地通过了检查,未被发现。因为实际上对常规文件的读写仍然由内核自动处理。只有文件指针自身可以避免同步。而且,因为高速线程化的文件操作是一个非常罕见的需求,所以对任何人来说都需要很长时间才能遇到这个问题并报告它。
|
||||
|
||||
一个有趣的小细节是当李纳斯和艾尔在寻找一个修复方案时,艾尔一度抱怨李纳斯采用的方法并不能支持确定的架构,包括*ARM*和*PowerPC*。李纳斯的回应是“我怀疑关心这个是否有意义。[...]如果使用ARM/PPC架构的人停止抱怨,他们可以往gcc中加入struct-return的支持。”
|
||||
一个有趣的小细节是当李纳斯和艾尔在寻找一个修复方案时,艾尔一度抱怨李纳斯采用的方法并不能支持一些确定的架构,包括*ARM*和*PowerPC*。李纳斯的回应是“我怀疑关心这个是否有意义。[...]如果使用ARM/PPC架构的人停止抱怨,他们可以往gcc中加入struct-return的支持。”
|
||||
|
||||
看到这些问题突然产生并得到处理通常是很有趣的。在某些情况下,这个修复的部分工作必须在内核中进行,部分在GCC中,部分在其它地方。在这个特例里,艾尔认为整个事情都应该在内核里处理,他在灵感的激发下往补丁中写入了自己的版本,李纳斯也接受了。
|
||||
|
||||
*安迪·克伦*则想为*perf*增加底层CPU事件支持。问题在于这可能会导致大量的底层事件,而且会因CPU的变化而改变。即使为了所有类型的CPU把可能的时间都存储在内存里,也可能会显著地增加内核的运行大小。因此,把这个信息硬编码进内核的方法是有问题的。
|
||||
*安迪·克伦(Andi Kleen)*则想为*perf*增加底层CPU事件支持。问题在于这可能会导致大量的底层事件,而且会因CPU的变化而改变。即使为了所有类型的CPU把可能的时间都存储在内存里,也可能会显著地增加内核的运行大小。因此,把这个信息硬编码进内核的方法是有问题的。
|
||||
|
||||
他也指出*OProfile*工具依赖于这些时间的公开可用列表,尽管他表示OProfile开发者并非总维持他们的列表与最新的可用版本一致。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,20 +24,21 @@ diff -u: 内核开发里的新鲜事儿
|
||||
|
||||
有各种各样对安迪代码的反馈,其中大部分涉及到应该在哪个目录下保存事件列表和文件如何命名。这份代码本身的特性似乎得到了很好的回应。一处细节证明了安迪的代码比其他人的更有争议,就是将列表下载到用户家目录下的一个子目录。安迪表示如果不这样做的话,用户可能会以系统管理员的身份去下载事件列表,这会是危害安全的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
萨沙·莱文最近发布了一个脚本来从堆栈转储中把*十六进制的偏移量*翻译成有意义的指向内核源码文件的行号。因此诸如“ffffffff811f0ec8”形式的十六进制表示可以被翻译成“fs/proc/generic.c:445”。
|
||||
萨沙·莱文(Sasha Levin)最近发布了一个脚本来从堆栈转储中把*十六进制的偏移量*翻译成有意义的指向内核源码文件的行号。因此诸如“ffffffff811f0ec8”形式的十六进制表示可以被翻译成“fs/proc/generic.c:445”。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,结果表明李纳斯·托瓦兹正打算从堆栈转储中移除十六进制偏移量,具体原因是他们难以理解。所以萨沙的代码看起来过时了。【译者注:程序媛,伤不起!】
|
||||
然而,结果表明李纳斯·托瓦兹正打算从堆栈转储中移除十六进制偏移量,具体原因是他们难以理解。所以萨沙的代码看起来过时了。[译者注:程序媛,伤不起!:< ]
|
||||
|
||||
他们在这个问题上纠结了一番。起初,萨沙打算依赖存储在System.map文件里的数据区补偿,但李纳斯指出包括他在内的有些人并不会保留System.map文件。李纳斯推荐使用/usr/bin/nm从编译好的内核文件中提取符号表。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,似乎萨沙的脚本可能确实为调试堆栈转储提供了有意义的文件和行号,假设堆栈转储提供足够的信息去完成计算。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxjournal.com/content/diff-u-whats-new-kernel-development-0
|
||||
|
||||
原文作者:[Zack Brown][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu) 校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,56 +13,56 @@ shell脚本中的变量是用来**调用**一个**数值**或者**字符值**的
|
||||
<table width="100%" cellspacing="1" cellpadding="1">
|
||||
<tbody>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td><strong> System Defined Variables </strong></td>
|
||||
<td><strong> Meaning </strong></td>
|
||||
<td><strong>系统定义的变量 </strong></td>
|
||||
<td><strong>意义 </strong></td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> BASH=/bin/bash </td>
|
||||
<td> Shell Name </td>
|
||||
<td> Bash Shell 名称 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> BASH_VERSION=4.1.2(1) </td>
|
||||
<td> Bash Version </td>
|
||||
<td> Bash 版本 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> COLUMNS=80 </td>
|
||||
<td> No. of columns for our screen </td>
|
||||
<td> 你的屏幕宽度(列数) </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> HOME=/home/linuxtechi </td>
|
||||
<td> Home Directory of the User </td>
|
||||
<td> 用户家目录 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> LINES=25 </td>
|
||||
<td> No. of columns for our screen </td>
|
||||
<td> 你的屏幕高度(行数) </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> LOGNAME=LinuxTechi </td>
|
||||
<td> LinuxTechi Our logging name </td>
|
||||
<td> 当前登录用户的名字 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> OSTYPE=Linux </td>
|
||||
<td> OS type </td>
|
||||
<td> 操作系统类型 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> PATH=/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin </td>
|
||||
<td> Path Settings </td>
|
||||
<td> 可执行文件搜索路径 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> PS1=[\u@\h \W]\$ </td>
|
||||
<td> Prompt Settings </td>
|
||||
<td> 命令行提示符 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> PWD=/home/linuxtechi </td>
|
||||
<td> Current Working Directory </td>
|
||||
<td> 当前工作目录 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> SHELL=/bin/bash </td>
|
||||
<td> Shell Name </td>
|
||||
<td> Shell 名称 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
<tr>
|
||||
<td> USERNAME=linuxtechi </td>
|
||||
<td> User name who is currently login to system </td>
|
||||
<td> 当前登录的用户名 </td>
|
||||
</tr>
|
||||
</tbody>
|
||||
</table>
|
||||
@ -87,7 +87,7 @@ shell脚本中的变量是用来**调用**一个**数值**或者**字符值**的
|
||||
$ echo “The cost of the item is $15”
|
||||
The cost of the item is 5
|
||||
|
||||
很明显,那不是我们说希望的。无论何时,当脚本遇见引号中的美元符号时,它都会认为你是在调用一个变量。在本例中,改脚本试着显示**变量$1**(而这个变量并没有定义),然后显示数字5。要显示实际上的美元符号,你**必须前置**一个**反斜线字符**:
|
||||
很明显,那不是我们说希望的。无论何时,当脚本遇见引号中的美元符号时,它都会认为你是在调用一个变量。在本例中,该脚本试着显示**变量$1**(而这个变量并没有定义),然后显示数字5。要显示实际上的美元符号,你**必须前置**一个**反斜线字符**:
|
||||
|
||||
$ echo “The cost of the item is \$15”
|
||||
The cost of the item is $15
|
||||
@ -98,7 +98,7 @@ shell脚本中的变量是用来**调用**一个**数值**或者**字符值**的
|
||||
|
||||
这些变量由**用户**定义。shell脚本允许我们在脚本中设置并使用我们**自己的变量**。设置变量允许你**临时存储数据**并在脚本中使用,让shell脚本看起来像一个真正的计算机程序。
|
||||
|
||||
**用户变量**可以是任何不超过**20个字母,数字**的文本字符串,或者**一个下划线字符**。用户变量是大小写敏感的,因此,变量Var1和变量var1是不同的变量。这个小规则常常让新手编写脚本时麻烦重重。
|
||||
**用户变量**可以是任何不超过**20个的字母、数字**或者**下划线字符**的文本字符串(LCTT 译注:变量只能以字母或下划线开头)。用户变量是大小写敏感的,因此,变量Var1和变量var1是不同的变量。这个小规则常常让新手编写脚本时麻烦重重。
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以通过**等于号**为变量赋值。变量,等于号和值(对于新手又是个麻烦的地方)之间不能有空格。下面是几个给用户变量赋值的例子:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -130,7 +130,7 @@ shell脚本为变量值**自动确定数据类型**。shell脚本内定义的变
|
||||
Jessica checked in 5 days ago
|
||||
$
|
||||
|
||||
每次变量被**调用**,它都会产生当前分配给它的值。记住这一点很重要,当调用一个变量值时,你使用**美元符号**,但是当调用一个变量来为其分配一个值时,你不能用美元符号。下面用例子来说明:
|
||||
每次变量被**调用**,它都会变成了当前分配给它的值。有一点很重要,当调用一个变量值时,你使用**美元符号**,但是当为一个变量分配一个值时,你不能用美元符号。下面用例子来说明:
|
||||
|
||||
$ cat test4
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
@ -180,7 +180,7 @@ shell会在**反引号**中运行命令,然后将输出结果赋值给变量te
|
||||
$ ./test5
|
||||
The date and time are: Mon Jan 31 20:23:25 EDT 2011
|
||||
|
||||
**注**:在bash中,你也可以选用$(...)语法来替换反引号(`),它有个优点就是可以重用。
|
||||
**注**:在bash中,你也可以选用$(...)语法来替换反引号(`),它有个优点就是可以重用(re-entrant)。
|
||||
|
||||
例:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -192,8 +192,8 @@ shell会在**反引号**中运行命令,然后将输出结果赋值给变量te
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxtechi.com/variables-in-shell-scripting/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Pradeep Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[ ](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQ -- 如何在VMware ESXi虚拟机上设置静态MAC地址。
|
||||
Linux有问必答:如何在VMware ESXi虚拟机上设置静态MAC地址
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:我想给VMware ESXi上的一台虚拟机分配一个静态的MAC地址。然而当我开始这么做的时候,虚拟机就不能启动了不且抛出了一个这样一个错误"00:0c:29:1f:4a:ab is not an allowed static Ethernet address. It conflicts with VMware reserved MACs"(00:0c:29:1f:4a:ab不是一个合法的静态以太网地址。它与VMWare的保留MAC地址冲突)。我该如何在VMware ESXi虚拟机上设置静态MAC地址?
|
||||
> **问题**:我想给VMware ESXi上的一台虚拟机分配一个静态的MAC地址。然而当我开始这么做的时候,虚拟机就不能启动了,并且抛出了一个这样一个错误"00:0c:29:1f:4a:ab is not an allowed static Ethernet address. It conflicts with VMware reserved MACs"(00:0c:29:1f:4a:ab不是一个合法的静态以太网地址。它与VMWare的保留MAC地址冲突)。我该如何在VMware ESXi虚拟机上设置静态MAC地址?
|
||||
|
||||
当你在VMware ESXi上创建虚拟机时,虚拟机的每个网络接口就被分配了一个动态的NAC地址。如果你想要改变默认的行为并给你的虚拟机分配一个静态MAC地址时就这样做
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ Linux FAQ -- 如何在VMware ESXi虚拟机上设置静态MAC地址。
|
||||
|
||||
首先关闭你想要分配静态MAC地址的虚拟机。
|
||||
|
||||
[对你的ESXi主机启用SSH访问][1]如果你还没这么做的话。接着通过SSH登录ESXi主机。
|
||||
[对你的ESXi主机启用SSH访问][1],如果你还没这么做的话。接着通过SSH登录ESXi主机。
|
||||
|
||||
移到你虚拟机的.vmx文件所在目录。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,7 +35,7 @@ Linux FAQ -- 如何在VMware ESXi虚拟机上设置静态MAC地址。
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/static-mac-address-vmware-esxi-virtual-machine.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
|
||||
Linux 下 SSH 命令实例指南
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如果你已经接触计算机比较长时间, 应该对 SSH 这个了不起的工具及其安全特性有所耳闻吧. 本教程可以让你在短时间内掌握通过 SSH 安全便利地连接到远程计算机的技术.
|
||||
如果你已经在IT圈内混了很长时间, 应该对 SSH 这个了不起的工具及其安全特性有所耳闻吧. 本教程可以让你在短时间内掌握通过 SSH 安全便利地连接到远程计算机的技术.
|
||||
|
||||
如果你对 SSH 还没什么概念, 可以先访问 [维基百科][1] 进行了解.
|
||||
|
||||
### 基本用法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
最简单的 SSH 命令只需要提供用户名和主机名参数即可. 主机名可以是 IP 地址或者域名. 命令格式如下:
|
||||
最简单的 SSH 命令只需要指定用户名和主机名参数即可. 主机名可以是 IP 地址或者域名. 命令格式如下:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh user@hostname
|
||||
|
||||
比如要登录到局域网内我的一个树莓派系统, 只需要简单的在命令行输入如下命令:
|
||||
比如要在我的局域网内登录一个树莓派系统, 只需要简单的在命令行输入如下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh pi@10.42.0.47
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ Linux 下 SSH 命令实例指南
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用其他端口 ###
|
||||
|
||||
SSH 默认连接到目标主机的 22 端口上, 但是由于各种原因你可能需要连接到其他端口.
|
||||
SSH 默认连接到目标主机的 22 端口上,但是由于各种原因你可能需要连接到其他端口.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh -p 10022 user@hostname
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ SSH 默认连接到目标主机的 22 端口上, 但是由于各种原因你可
|
||||
|
||||
### 远程执行命令 ###
|
||||
|
||||
有时需要很方便地在远程主机执行一条命令并显示到本地, 然后继续本地工作. SSH 就能满足这个需求:
|
||||
有时在远程主机执行一条命令并显示到本地, 然后继续本地工作是很方便的. SSH 就能满足这个需求:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh pi@10.42.0.47 ls -l
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,9 +38,9 @@ SSH 默认连接到目标主机的 22 端口上, 但是由于各种原因你可
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 挂在远程文件系统 ###
|
||||
### 挂载远程文件系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
有一个很赞的基于 SSH 的工具叫 sshfs. sshfs 可以让你在本地直接挂载远程主机的文件系统.
|
||||
另外一个很赞的基于 SSH 的工具叫 sshfs. sshfs 可以让你在本地直接挂载远程主机的文件系统.
|
||||
|
||||
$ sshfs -o idmap=user user@hostname:/home/user ~/Remote
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ SSH 默认连接到目标主机的 22 端口上, 但是由于各种原因你可
|
||||
|
||||
该命令就将远程主机 pi 用户的主目录挂载到本地主目录下的 Pi 文件夹.
|
||||
|
||||
要详细了解可以参考 [sshfs 入门教程][2].
|
||||
要详细了解可以参考 [sshfs 教程][2].
|
||||
|
||||
### X11 图形界面 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -114,7 +114,7 @@ SSH 提供了多样的转义字符功能. 用 SSH 连接到任意一台远程主
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
通过以上的内容你应该可以很轻松的使用 SSH 了. SSH 还有很多功能值得你去发掘, 这就要看你的想象力了.
|
||||
通过以上的内容你应该可以轻松使用 SSH 了. SSH 还有很多功能值得你去发掘, 这就要看你的想象力了。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
@ -123,7 +123,7 @@ via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/pocket-guide-linux-ssh-command/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Bobbin Zachariah][a]
|
||||
译者:[henryfour](https://github.com/henryfour)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
中国将要改变软件购买和销售的方式
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> 这一切都是关于“开源”.
|
||||
|
||||
**中国并不需要你,也不需要你的软件。具体说来,中国市场并不需要你的工程师日以继夜的工作,也不需要你提供的任何东西。
|
||||
|
||||
中国每年会产生超过100000名新软件工程师。这些工程师会写出一大批令人惊叹的奇妙软件。如果有中国市场上尚未出现的软件,中国的工程师们就会从国外“借鉴”。在2012年,这样的软件掠夺达到了77%之多。对于那些已经面对着开源和云服务的挑战的西方软件卖家来说,中国无疑让他们的日子更苦难了。
|
||||
|
||||
不止是更困难,简直是举步维艰。
|
||||
|
||||
中国正在挑战西方公司在中国及其他地区的赚钱模式。对于那些已经明白如何在中国运营的公司来说,他们的未来看起来一片光明。
|
||||
|
||||
### 抵制中国模式 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当然,并非每家公司都会坐以待毙。以微软为例,微软已经通过[行使美国的国家司法权力来禁止中国公司做生意][1]——除非他们向微软购买许可证。这是一种很聪明的做法,而且它可能会为微软创造数十亿美元的价值,但是最终这一做法看起来与中国市场格格不入。
|
||||
|
||||
原因很简单,中国与微软对待知识产权的态度十分不同。
|
||||
|
||||
正如 [我所提到的][2],“与同在亚洲的印度十分相似,中国的企业更倾向于购买复杂的、面向企业的软件。因为这种软件比服务大众的公司开发出来的更为先进。”但这种形势不会持续太久,因为中国的软件产业正在以一种惊人的速度前进,并毫无颓势。中国将会坚持向西方国家“借鉴”代码,直到有一天有足够的能力可以创造出创新性的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
但即使到那时候,中国的软件公司与美国软件的运营模式还是有所不同,美国的软件大多都已经捆绑在设备、架构在云端或者公司只靠提供软件支持而盈利。而这些运营模式都是无法克隆的。
|
||||
|
||||
不出所料,接下来的问题将是,这些公司将如何通过“开源”来盈利。
|
||||
|
||||
### 开源化中国 ###
|
||||
|
||||
正如CCID的分析师在 [J. Aaron Farr 的关于中国开源化报告][3] 中指出的,中国的开源社区规模很小而且没什么影响力。开源社区中缺少大项目、参与者稀少而且资金匮乏。
|
||||
|
||||
这真是个坏消息。
|
||||
|
||||
而好消息是,华为等公司将开源视为一种战略前景。具体而言,当[华为的开源项目网页][4]过时或疲软之时,就间接显示出了技术大步伐的前进方向。在与参与了开源项目的华为公司内部顾问的谈话中,虽然华为对如何参与到开源社区还处于摸索阶段,但他们总是对华为的开源项目赞不绝口。
|
||||
|
||||
这看起来并不容易坚持长久。
|
||||
|
||||
从一件事就可以看出端倪。中国最大的互联网公司们都纷纷以积极地姿态拥抱开源,这意味着中国开源时代的到来。你若是和任意一位在百度、阿里巴巴、微博的员工谈话,你会发现他们的软件项目都是彻底开源的。这些开源的软件都是运行在这些公司自己研发的硬件上而不是西方的硬件上。
|
||||
|
||||
换句话说,这样的模式已经和美国及西欧的运营模式如出一辙了。
|
||||
|
||||
抬头看看 [现金软件行业内最炙手可热的新公司][5], 你就会知道中国的互联网公司未来的主流趋势,正如发生在西方世界的一样。不出意料的,许多都是关于“开源”。
|
||||
|
||||
### 销售给中国 ###
|
||||
|
||||
所有的一切都表明中国的软件行业不会像美国的软件行业发展历史一般发展。中国不会产生在柜台上卖卖软件就赚上亿美元的公司。因为西方对于知识产权的观念无法简单适用于中国的科技经济。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,商家们需要售卖比软件更丰富的产品。云服务是一大前景。硬件设施看起来也是前途璀璨。软件支持和咨询服务(虽然有一些非主流)也很被公司门看好。总而言之,中国的软件行业将会充满开源味道,而不能靠着简单的售卖专柜软件的形式赚钱。
|
||||
|
||||
图片由 [hackNY.org][6] 提供。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
原文: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/12/china-opensource-software-ip-programmers-united-states
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matt Asay][a]
|
||||
译者:[chi1shi2](https://github.com/chi1shi2)
|
||||
校对:[reinoir](https://github.com/reinoir)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/matt-asay
|
||||
[1]:http://readwrite.com/2014/03/17/microsoft-anti-piracy-strategy-china
|
||||
[2]:http://readwrite.com/2014/04/11/india-starts-paying-for-software-china-it
|
||||
[3]:http://cdn.oreillystatic.com/en/assets/1/event/12/Open%20Source%20in%20China%20Presentation%201.pdf
|
||||
[4]:http://huawei.com/en/about-huawei/Partner/openathuawei/index.htm
|
||||
[5]:http://codingvc.com/which-technologies-do-startups-use-an-exploration-of-angellist-data
|
||||
[6]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/hackny/8675057448/
|
||||
32
published/20140829 Linux Doesn't Need to Own the Desktop.md
Normal file
32
published/20140829 Linux Doesn't Need to Own the Desktop.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
Linux 应当放弃桌面
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linus Torvalds 前不久发布了 Linux 3.17 rc-2,这[偏离了他正常的发布时间表][1],因为8月25日是 Linux 的第23个生日。“Hello 大家好,你还在使用minix吗?”,23年前的8月25日,Torvalds 在 Linux 的第一次发布中这样写道。
|
||||
|
||||
与此同时,最近 PCMag.com 网站声称[Linux 的时间已经不多了][2]。但是你们不觉得这样没玩没了地讨论 Linux 在桌面端是否成功其实是毫无意义的吗?Linux 已经广泛应用于超级计算机和车载系统,它构建了 Android 的基础,同时还是最流行的云整合(例如 OpenStack)的运行平台 —— 以上这些还只是 Linux 的一部分成就。桌面并不是 Linux 唯一的战场。
|
||||
|
||||
Jon Buys 在他[最近的文章][3]中谈到了 Linux 专业化以及与桌面有关的内容:
|
||||
|
||||
> “最近,IT业在追问‘[Linus 是否还在执著于 Linux 桌面?][4]’,来自 Teck Republic 的 Matt Asay 也在说‘[拜托不要再讨论 Linux 桌面了行吗?][5]’。这两篇文章都对 Linux 在个人计算机方面的发展空间持怀疑态度,还拿 Android 的成功故事来说事…… 但是它们都忽略了,Linux的灵活性以及它开源许可证的开放性,也许这两者正是拯救 Linux 桌面的关键。”
|
||||
|
||||
也许这是事实,但是 Linux 对于如此众多的桌面用户来说,还是太多余了。Linux 分享庞大市场的最佳机会已经来也匆匆去也匆匆了。
|
||||
|
||||
事实其实很简单,Linux已经改变了世界,获得了无与伦比的成功 —— 除了桌面系统,这毋庸置疑。Android已经不仅仅是一个基于Linux的平台,它已经成为了一个伟大的标志。Linux在服务器端和嵌入式技术领域占有巨大的份额,同时也为平台整合方面不断提供创新动力。Ubuntu已经成为部署搭建 OpenStack 最流行的平台。全世界的超级计算机都运行着 Linux,Chrome OS 也是基于 Linux。
|
||||
|
||||
因此,Linux 正在不断推动着整个世界的巨变,批评家们是时候停下来执著于 Linux 在桌面端的状态了。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/linux-doesnt-need-to-own-the-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sam Dean][a]
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ostatic.com/member/samdean
|
||||
[1]:http://www.theregister.co.uk/2014/08/26/linux_turns_23_and_linus_torvalds_celebrates_as_only_he_can/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2465125,00.asp
|
||||
[3]:http://ostatic.com/blog/specialization-and-the-linux-desktop
|
||||
[4]:http://www.itworld.com/open-source/432816/does-it-still-make-sense-linus-want-desktop-linux
|
||||
[5]:http://www.techrepublic.com/article/can-we-please-stop-talking-about-the-linux-desktop/
|
||||
@ -1,27 +1,28 @@
|
||||
如何在linux上分享你shell命令的输出
|
||||
如何在linux上分享你shell命令的输出
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
前段时间我发布了一篇关于[shelr.tv][1]这个网站的文章,它提供一个服务允许你从网站上直接分享你的[终端][2]记录。
|
||||
|
||||
现在shelr.tv这个网站似乎关闭了,然后我在周围寻找是否有类似的网站,于是我发现了[commands.com][3]。
|
||||
现在shelr.tv这个网站似乎关闭了,然后我四处寻找是否有类似的网站,于是我发现了[commands.com][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
从它的主页上来看,它的服务和其他网站提供的服务是类似的,因此让我们来测试它。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 1 – 在网站上注册 ###
|
||||
|
||||
只需要[注册][4]一个新的 用户名/密码,或者直接使用你的github账户。
|
||||
只需要[注册][4]一个新的 用户名/密码,或者直接使用你的github账户快速登录。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤 2 – 下载安装monitor程序 ###
|
||||
|
||||
[Monitor][5]是一个命令行工具,它能捕获命令行的输入输出并且发送到commands.com网站上,这个程序是开源的,并托管在github上。
|
||||
|
||||
Monitor使得仓库的设置/安装变得更简单。通过它,你能方便地向人们展示常见错误与命令的输出。
|
||||
Monitor使得仓库的设置/安装变得更简单。通过它,你能方便地向人们展示最常见的错误与命令的输出。
|
||||
|
||||
简而言之,你能方便地和世界分享你的命令及其输出。
|
||||
|
||||
通过如下简单几步来安装它:
|
||||
|
||||
1) 克隆github上的这个项目的仓库,这样你能获得最新的源代码。
|
||||
要完成这步,你需要在系统中已经安装了git命令,如果你获得了错误信息,你可以使用包管理工具来安装它,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
要完成这步,你需要在系统中已经安装了git命令,如果你得到关于这个命令的报错信息,你可以使用包管理工具来安装它,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
基于Debian的发布版:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -48,6 +49,7 @@ Redhat/Centos/Fedora发布版:
|
||||
3) 构建程序:
|
||||
|
||||
要完成这步,你必须进入刚刚用git克隆的目录,然后编译这个c程序:
|
||||
|
||||
cd monitor
|
||||
make
|
||||
sudo make install
|
||||
@ -84,20 +86,20 @@ monitor命令特别简单易用:
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这只是一个简单的安装指南,在这个网站上你能参加更多“社会化”的活动,比如评论脚本/shell会话,派生它们或者选为你的最爱。
|
||||
这只是一个简单的安装指南,在这个网站上你能参加更多“社会化”的活动,比如评论脚本/shell会话,派生它们或者选择你的最爱。
|
||||
|
||||
和github一样,你能派生任何一个公开的脚本/命令并能直接在网站上改变它,然后你也能得到一个公开(或私有)的url。你可以直接运行你脚本,就像这样:
|
||||
|
||||
curl commands.io/JTNSHRLQJA | sh
|
||||
|
||||
在网络上储存一些你在电脑/服务器上经常使用到的脚本,这是极好的,通常不要放置任何密码或敏感信息,这样能保证你足够的安全。
|
||||
在网络上储存一些你在电脑/服务器上经常使用到的脚本,这是极好的,通常不要放置任何密码或敏感信息,这样你的信息才足够安全。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linuxaria.com/article/how-to-share-on-linux-the-output-of-your-shell-commands
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[guodongxiaren](https://github.com/guodongxiaren)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,4 @@
|
||||
2q1w2007翻译中
|
||||
[小贴士] 怎么在Linux发行版下列出所有安装了的包
|
||||
怎么在Linux发行版下列出所有安装了的包
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,7 +38,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
dpkg -l
|
||||
|
||||
祝你有好的一天。
|
||||
祝你一天好心情。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,7 +46,7 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/quick-tip-list-installed-packages-linux-distribution
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Enock Seth Nyamador][a]
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
如何“上手”体验乌托邦独角兽!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**想要知道如何在正式发布前上手体验乌托邦独角兽(Utopic Unicorn)?现在你就可以做到!—— 真的是[“上手”][1]体验哦~!**
|
||||
|
||||
显然是为了庆祝即将发布的同名Ubuntu,Canonical上线了一款“手把手教你独角兽折纸指南”。这一活动作为该公司[2014 Deconstruct][2] 大会的一部分出现,大会于九月上旬在英国Brighton举办。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
供图: Alejandra Obregon
|
||||
|
||||
大会为期一天,为富有创造力的专家以及数字文化狂热者们提供了一个理想的交流场所,Canonical将展示一个正在开发中版本的 Ubuntu Phone,内容包括具体的设计以及用户交互界面,用以满足与会观众。
|
||||
|
||||
人们对这一折纸活动的反响很积极。折纸独角兽作品最棒的人,将会获得一部全新的 Ubuntu 手机,这大大激发了人们的积极性。
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载折纸独角兽 ###
|
||||
|
||||
其余没有获奖的朋友,也不要气馁,下载折纸独角兽还是会有惊喜哦~
|
||||
|
||||
如果你有五分钟的休息时间,为什么不玩玩这个折纸娱乐一下呢?如果你认为自己折出来的独角兽非常非常出(la)色(ji),请在[Twitter][3] 或 [Google+][4]上给我们发照片~(译者表示不爽!这是诚心不给我们天朝百姓获奖的机会吗?)
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载 ‘Make a Unicorn’ 手工折纸][5]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/unicorn-origami-download-pdf-ubuntu-utopic
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://design.canonical.com/2014/09/canonical-and-ubuntu-at-dconstruct/
|
||||
[2]:http://2014.dconstruct.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://twitter.com/omgubuntu
|
||||
[4]:http://plus.google.com/+omgubuntu
|
||||
[5]:http://design.canonical.com/wp-content/uploads/042_CAN_dConstruct_instructions.pdf
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
Potenza 图标主题2.0已可下载
|
||||
=================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Potenza][1]图标主题版本2.0已经发布。Potenza 图标的灵感来自[faenza][2],faenza是我们在[Ubuntu 13.10的最佳图标][3]的列出的一款漂亮的图标主题。
|
||||
|
||||
Potenza 的开发者 Alessandro Bompadre说,他曾试图建立一个适用于Linux的完整图标集,它应该适合各种桌面环境,包括如Unity,Gnome,Cinnamon,KDE等。
|
||||
|
||||
###下载 Potenza 图标###
|
||||
|
||||
Potenza 图标可在 Ubuntu,Linux Mint、Elementary OS、Linux Lite 等环境中通过Noobslab的PPA来安装。只有一点需要提醒你,因为要为所有主要类型的桌面环境提供了大量的图标,所以总下载字节大概是400 MB。
|
||||
|
||||
打开一个终端,使用下面的命令:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:noobslab/potenza
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install potenza-2
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不想使用PPA,您也可以从下面的链接安装该图标主题:
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载 Potenza 图标主题][4]
|
||||
|
||||
解压文件到 ~/.icons 目录。在Ubuntu的Unity环境中,你可以[使用Unity Tweak Tool把当前的图标主题切换][5] 为 Potenza 。
|
||||
|
||||
希望你喜欢Potenza,您也可以试试[Dalisha图标主题][6]或看看我们的[Ubuntu 14.04的最佳图标主题列表][7]。
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/potenza-icon-themes-20-download/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[fbigun](https://github.com/fbigun)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:https://github.com/AlessandroBompadre/Potenza/
|
||||
[2]:http://tiheum.deviantart.com/art/Faenza-Icons-173323228
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1310/
|
||||
[4]:http://gnome-look.org/content/show.php/Potenza+2.0?content=166853
|
||||
[5]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
[6]:http://itsfoss.com/dalisha-icon-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
[7]:http://itsfoss.com/best-icon-themes-ubuntu-1404/
|
||||
@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Go Hands On With the Utopic Unicorn – Literally!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Looking to go hands-on with the Utopic Unicorn ahead of its release? Now you can — [literally][1]!**
|
||||
|
||||
A step-by-step guide to making your own paper Unicorn (to celebrate the upcoming release of the same name, obviously) has been posted online by Canonical. The instructions were offered as part of the company’s presence at the 2014 [deconstruct][2] event held in Brighton, UK in early September.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Image: Alejandra Obregon
|
||||
|
||||
The one-day conference for creative professionals and digital culture enthusiasts served as an ideal place for Canonical to showcase an in-progress version of the upcoming Ubuntu Phone, its design and the user interaction benefits they believe it offers.
|
||||
|
||||
Reaction was positive, they say. That will have made the prize of a brand new Ubuntu phone to the maker of the best origami unicorn all the more tempting!
|
||||
|
||||
### Download Origami Unicorn ###
|
||||
|
||||
No prizes are on offer to the rest of us attempting to fold our way to frustration, but a download of the how-to is.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a spare five hours minutes, why not make one for fun? If you make particularly epic success/fail of it be sure to send us a pic on [Twitter][3] or [Google+][4].
|
||||
|
||||
- [Download ‘Make a Unicorn’ Instructions][5]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/unicorn-origami-download-pdf-ubuntu-utopic
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://design.canonical.com/2014/09/canonical-and-ubuntu-at-dconstruct/
|
||||
[2]:http://2014.dconstruct.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://twitter.com/omgubuntu
|
||||
[4]:http://plus.google.com/+omgubuntu
|
||||
[5]:http://design.canonical.com/wp-content/uploads/042_CAN_dConstruct_instructions.pdf
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
One of the Smallest Distros in the World, Tiny Core, Gets a Fresh Update
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Tiny Core desktop
|
||||
|
||||
**Robert Shingledecker has announced the immediate availability for download of the final version of the Tiny Core 5.4 Linux operating system, which also happens to be one the smaller operating systems in the world.**
|
||||
|
||||
The name of the distro says pretty much everything about the operating system, but the developers have integrated some interesting packages and a very light desktop to match it. This latest iteration only had a single Release Candidate and it's one of the quietest releases made so far.
|
||||
|
||||
"Tiny Core is simply an example of what the Core Project can produce, an 12MB FLTK/FLWM desktop. The user has complete control over which applications and/or additional hardware to have supported, be it for a desktop, a netbook, an appliance, or server, selectable by the user by installing additional applications from online repositories, or easily compiling most anything you desire using tools provided," says the dev on the official website.
|
||||
|
||||
According to the changelog, entries for nfs server have been added, 'Done' is now printed in a new lin, and udev has been updated to version 174 to fix a race condition.
|
||||
|
||||
A complete list of updates and changes can be found in the official [announcement][1].
|
||||
|
||||
You can download Tiny Core Linux 5.4.
|
||||
|
||||
- [Tiny Core Linux 5.4 (ISO)][2][iso] [14 MB]
|
||||
- [Tiny Core Plus 5.4 (ISO)][3][iso] [72 MB]
|
||||
- [Core 5.4 (ISO)][4][iso] [8.90 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
The distribution is Live, so you can test it before installing it.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/One-of-the-Smallest-Distros-in-the-World-Tiny-Core-Gets-a-Fresh-Update-458785.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://forum.tinycorelinux.net/index.php/topic,17487.0.html
|
||||
[2]:http://distro.ibiblio.org/pub/linux/distributions/tinycorelinux/5.x/x86/release/TinyCore-5.4.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://repo.tinycorelinux.net/5.x/x86/release/CorePlus-5.4.iso
|
||||
[4]:http://distro.ibiblio.org/tinycorelinux/5.x/x86/release/Core-current.iso
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
alim0x translating
|
||||
|
||||
GNOME Control Center 3.14 RC1 Corrects Lots of Potential Crashes
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
GNOME Control Center in Arch Linux
|
||||
|
||||
**GNOME Control Center, GNOME's main interface for the configuration of various aspects of your desktop, has been updated to version 3.14 RC1, along with a lot of the packages from the GNOME stack.**
|
||||
|
||||
The GNOME Control Center is a piece of software that's actually very important in the GNOME ecosystem, although not all users are aware of its existence. This is the part that takes care of all the settings in an OS powered by GNOME, as you can see from the screenshot.
|
||||
|
||||
It's not something that's usually advertised and it's actually one of the few packages in the GNOME stack that doesn't have the same name as source and as implementation. The source package is called GNOME Control Center, but users will usually see Settings or System Settings, depending on what the developers choose.
|
||||
|
||||
### What's new in GNOME Control Center 3.14 RC1 ###
|
||||
|
||||
According to the changelog, libgd has been updated in order to fix the GdNotification theming, the background chooser dialog is no longer resizing when switching views, a stack with three views is now used for the chooser dialog, a memory leak in Flickr support has been fixed, the hard-code font size is no longer used for the Date & Time, a crash that occurred if the WM changed (or restarted) has been fixed, a possible crash that occurred when wireless-enabled was changing has been fixed, and more potential crashers for WWAN have been corrected.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, the hotspot is now running only if the device is active, all of the virtualization bridges are now hidden, the underlying device for VPN connections is no longer shown, the empty folder list is no longer shown by default, various UI padding issues have been fixed, the focus is now returned in the account dialog, a crash that occurred when setting year to 0 has been fixed, the "Wi-Fi hotspot" properties are now centered, a warning provided on startup with the hotspot enabled has been fixed, and an error is now provided when turning on the hotspot fails.
|
||||
|
||||
A complete list of changes, updates, and bug fixes can be found in the official [changelog][1].
|
||||
|
||||
You can download GNOME Control Center 3.14 RC1:
|
||||
|
||||
- [tar.xz (3.12.1 Stable)][2][sources] [6.50 MB]
|
||||
- [tar.xz (3.14 RC1 Development)][3][sources] [6.60 MB]
|
||||
|
||||
This is just the source package and you will have to compile it yourself in order to test it. Unless you really know what you are doing, you should wait until the complete GNOME stack is made available through the repositories.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/GNOME-Control-Center-3-14-RC1-Correct-Lots-of-Potential-Crashes-458986.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-control-center/3.13/gnome-control-center-3.13.92.news
|
||||
[2]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-control-center/3.12/gnome-control-center-3.12.1.tar.xz
|
||||
[3]:http://ftp.acc.umu.se/pub/GNOME/sources/gnome-control-center/3.13/gnome-control-center-3.13.92.tar.xz
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
Another Italian City Says Goodbye To Microsoft Office, Will Switch To OpenOffice Soon
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
It seems [Open Source][1] adoption is the latest fad in European countries. Last month only we heard that [Turin became the first Italian city to officially opt for Open Source product][2]. Another city in north-west Italy, [Udine][3], has also announced that it is ditching Microsoft office and will migrate to [OpenOffice][4].
|
||||
|
||||
Udine has a population of 100,000 and the administration has around 900 computers which are running Microsoft Windows as their default productivity suite. As per the [budget document][5], the migration will start somewhere around December with 80 new computers. It will be followed by the migration of older computers to OpenOffice.
|
||||
|
||||
The migration is estimated to save licensing fee which otherwise would have cost around Euro 400 per computer, which makes a total of Euro 360,000. But saving money is not the only goal of this migration, getting regular software update is also one of the factors.
|
||||
|
||||
Of course the transition from Microsoft Office to OpenOffice won’t be smooth. Keeping this in mind, the municipality is planning training sessions for at least first few employees who will get the new machines with OpenOffice.
|
||||
|
||||
As I stated earlier, this seems to be a trend in Europe. [French city Toulouse saved a million euro with LibreOffice][6] earlier this year along with [Canary Islands in Spain][7]. Neighboring Spanish city [Geneva also showed sign of Open Source adoption][8]. In other part of the world, government organizations in [Tamil Nadu][9] and Kerala provinces of India also ditched Microsoft for Open Source.
|
||||
|
||||
I think demise of Windows XP has been a boon for Open Source, along with sluggish economy. Whatever may be the reason, I am happy to see this list growing. What about you?
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/udine-open-source/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://itsfoss.com/category/open-source-software/
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/italian-city-turin-open-source/
|
||||
[3]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Udine
|
||||
[4]:https://www.openoffice.org/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.comune.udine.it/opencms/opencms/release/ComuneUdine/comune/Rendicontazione/PEG/PEG_2014/index.html?lang=it&style=1&expfolder=???+NavText+???
|
||||
[6]:http://itsfoss.com/french-city-toulouse-saved-1-million-euro-libreoffice/
|
||||
[7]:http://itsfoss.com/canary-islands-saves-700000-euro-open-source/
|
||||
[8]:http://itsfoss.com/170-primary-public-schools-geneva-switch-ubuntu/
|
||||
[9]:http://itsfoss.com/tamil-nadu-switches-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
Translating-----geekpi
|
||||
|
||||
Netflix Offers to Work with Ubuntu to Bring Native Playback to All
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**We saw [last month just how close native Netflix support for Linux is][1] to arriving, with now only a few simple steps required to enable HTML5 video streaming on Ubuntu desktops.**
|
||||
|
||||
Now Netflix wants to go one step further. It wants to bring true, out-of-the-box Netflix playback to all Ubuntu users. And all it requires is an update to the **Network Security** Services library.
|
||||
|
||||
### Netflix Natively? Neato. ###
|
||||
|
||||
In [an e-mail][2] sent to the Ubuntu Developer mailing list Netflix’s Paul Adolph explains the current situation:
|
||||
|
||||
> “Netflix will play with Chrome stable in 14.02 if NSS version 3.16.2 or greater is installed. If this version is generally installed across 14.02, Netflix would be able to make a change so users would no longer have to hack their User-Agent to play.”
|
||||
|
||||
While the upcoming release of Ubuntu 14.10 offers the newer [NSS v3.17][3], Ubuntu 14.04 LTS — used by the majority of users — currently offers v3.15.x.
|
||||
|
||||
NSS is a set of libraries that supports a range of security-enabled client and server applications, including SSL, TLS, PKCS and other security standards. Keen to enable native HTML5 Netflix for Ubuntu LTS users, Paul asks:
|
||||
|
||||
> “What is the process of getting a new NSS version into the update stream? Or can somebody please provide me with the right contact?”
|
||||
|
||||
Netflix began offering HTML5 video playback on Windows 8.1 and OS X Yosemite earlier this year, negating the need for any extra downloads or plugins. The switch has been made possible through the [Encrypted Media Extension][4] spec.
|
||||
|
||||
While we wait for the discussions to move forward (and hopefully solve it for all) you can still “hack” HTML5 Netflix on Ubuntu by [following our guide][5].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/09/netflix-linux-html5-nss-change-request
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Joey-Elijah Sneddon][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/117485690627814051450/?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/08/netflix-linux-html5-support-plugins
|
||||
[2]:https://lists.ubuntu.com/archives/ubuntu-devel-discuss/2014-September/015048.html
|
||||
[3]:https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Mozilla/Projects/NSS/NSS_3.17_release_notes
|
||||
[4]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Encrypted_Media_Extensions
|
||||
[5]:http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/08/netflix-linux-html5-support-plugins
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
Red Hat Acquires FeedHenry for $82 Million to Advance Mobile Development
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Red Hat jumps into the mobile development sector with a key acquisition.
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat's JBoss developer tools division has always focused on enterprise development, but hasn't always been focused on mobile. Today that will start to change as Red Hat announced its intention to acquire mobile development vendor [FeedHenry][1] for $82 million in cash. The deal is set to close in the third quarter of Red Hat's fiscal 2015. Red Hat is set to disclose its second quarter fiscal 2015 earning at 4 ET today.
|
||||
|
||||
Mike Piech, general manager of Middleware at Red Hat, told Datamation that upon the deal's closing FeedHenry's employees will become Red Hat employees
|
||||
|
||||
FeedHenry's development platform enables application developers to rapidly build mobile application for Android, IOS, Windows Phone and BlackBerry. The FeedHenry platform leverages Node.js programming architecture, which is not an area where JBoss has had much exposure in the past.
|
||||
|
||||
"The acquisition of FeedHenry significantly expands Red Hat's support for and engagement in Node.js," Piech said.
|
||||
|
||||
Piech Red Hat's OpenShift Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) technology already has a Node.js cartridge. Additionally Red Hat Enterprise Linux ships a tech preview of node.js as part of the Red Hat Software Collections.
|
||||
|
||||
While node.js itself is open source, not all of FeedHenry's technology is currently available under an open source license. As has been Red Hat's policy throughout its entire history, it is now committing to making FeedHenry open source as well.
|
||||
|
||||
"As we've done with other acquisitions, open sourcing the technology we acquire is a priority for Red Hat, and we have no reason to expect that approach will change with FeedHenry," Piech said.
|
||||
|
||||
Red Hat's last major acquisition of a company with non open source technology was with [ManageIQ][2] for $104 million back in 2012. In May of this year, Red Hat launched the ManageIQ open-source project, opening up development and code of the formerly closed-source cloud management technology.
|
||||
|
||||
From an integration standpoint, Red Hat is not yet providing full details of precisely where FeedHenry will fit it.
|
||||
|
||||
"We've already identified a number of areas where FeedHenry and Red Hat's existing technology and products can be better aligned and integrated," Piech said. "We'll share more details as we develop the roadmap over the next 90 days."
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.datamation.com/mobile-wireless/red-hat-acquires-feedhenry-for-82-million-to-advance-mobile-development.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sean Michael Kerner][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.datamation.com/author/Sean-Michael-Kerner-4807810.html
|
||||
[1]:http://www.feedhenry.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.datamation.com/cloud-computing/red-hat-makes-104-million-cloud-management-bid-with-manageiq-acquisition.html
|
||||
@ -1,39 +0,0 @@
|
||||
CNprober translating..
|
||||
|
||||
Staying free – should GCC allow non-free plug ins?
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Arguments in favour of the use of non-free plug-ins in GCC have again been raised on GCC mailing-lists, but are trumped by the arguments for GCC as a vehicle for free software development
|
||||
|
||||
Once again, Gcc and its lack of modularity has been raised as an issue and contrasted with LLVm, the new compiler on the block. GCC is huge and venerable: 5 million lines, 30 years, and growing. LLVM, in contrast, is relatively youthful and modular and allows free and proprietary languages to be added as modules.
|
||||
|
||||
The core of LLVM is ‘open source’. GCC is copyleft and unreservedly free software and doesn’t allow plug-ins or other means to add proprietary extensions to the GCC code. The argument, as delivered by Eric Raymond, is that “FSF can no longer prevent proprietary vendors from plugging into a free compiler to improve their tools. That horse has left the barn; the strategic goal of the anti-plug-in policy has been definitively busted.”
|
||||
|
||||
LLVM has been sponsored by Apple as a replacement for GCC on OS X and Apple hardware and has grown in popularity, especially among users of the BSDs. Advocates of LLVM see it as a putative replacement for GCC in the wider market for applications developers and mobile devices. The argument against GCC is that its complexity, and the commitment of its developers to copyleft licensing, constrains the possibilities for proprietary developers, who do not want to release their language or architectural specifications under a copyleft licence. Apple, of course, has a long history of antipathy to free software, and doesn’t allow applications licensed under copyleft licences to be distributed through its App Store.
|
||||
|
||||
To this extent, the argument between LLVM and GCC is a retread of the historic differences between GNU/Linux and the BSDs, between ‘open source’ and free software. Open source developers allow the code to be reused in any context, free or proprietary. Free software is restrictive in that it insists that the code, and any modifications to the code, must remain free in perpetuity. Advocates of free software would argue that the integrity of copyleft licensing has been instrumental in the spread of GCC, and has taken Linux and free software into places it would not otherwise have reached, and that free software cannot be bought or corrupted by commercial or corporate interests. Open source advocates argue that open source is more free because the user has no restrictions and can do what he or she likes, including developing closed source versions of the code.
|
||||
|
||||
Since the beginning, the GNU Compiler Collection (GCC) was vital to the spread of free software. Compilers were a rare and expensive commodity and the compilers of the proprietary software companies were rife with ‘features’ that were non-compliant with ANSI programming standards. Porting software between different machines and operating systems was an unnecessarily complicated task. GCC, the first truly free cross-platform compiler, commoditised this process.
|
||||
|
||||
GCC was a breakthrough product for applications developers and mobile device developers – not just those who were committed to the idea of free software. Not only was GCC free and portable, its ubiquity and commonality across different architectures made it easier to port software between machines and to expect robust and consistent results – as the likes of John Gilmore, Michael Tiemann and David Henkel- Wallace were to discover when they made GCC and its development the key selling point of Cygnus Solutions, the first company to make money by selling free software.
|
||||
|
||||
The primary technical difference between LLVM and GCC emerges in the separation between the modules that form the ‘front ends’, ‘middle end’ and ‘back ends’ of both GCC and LLVM. ‘Front ends’ are used to interpret the code specific to the translation of a particular language. The ‘middle end’ optimises the translated code. The ‘back ends’ take the optimised code and apply the results to a specific target architecture. LLVM separates these modules into distinct entities, but for semantic and historical reasons, GCC obfuscates the separation between the modules.
|
||||
|
||||
Perhaps untypically for a free software project, it is a difficult process to add a new language or architecture to GCC and the adding of proprietary plug-ins is not allowed. There is little clear separation between the modules, and the path of least resistance is to add any feature under a free software licence. The early ports of C++ and Objective C (via Apple) are cited as examples where the original developers might have preferred to keep the code in-house and proprietary, and instead released the code as free software.
|
||||
|
||||
In contrast, LLVM has allowed, or perhaps even encouraged, the addition and development of proprietary languages and architectures – one example being Nvidia’s NVCC for GPU computing, based on Clang and LLVM. The source code of NVCC is inaccessible to free software or ‘open source’ developers.
|
||||
|
||||
Richard Stallman’s [take on this][1] is characteristically resolute: “In the free software movement, we campaign for the freedom of the users of computing. The values of free software are fundamentally different from the values of open source, which make‘bettercode’theultimategoal. IfGCCwere to change from a free compiler into a platform for non-free compilers, it would no longer serve the goal of freedom very well.
|
||||
|
||||
“The Clang and LLVM developers reach different conclusions from ours because they do not share our values and goals. They object to the measures we have taken to defend freedom because they see the inconvenience of them and do not recognise (or don’t care about) the need for them. I would guess they describe their work as ‘open source’ and do not talk about freedom.”
|
||||
|
||||
The GCC developers are unlikely to compromise on the licensing terms. While LLVM is fashionable among certain sectors of industry, because it is young and new and has been quicker to jump on developing trands in programming languages, the prevailing wind is towards greater openness, and GCC’s resolve to be incorruptible and free from commercial interests, may be the greater asset in the long term. The Unix companies learnt something from the Unix wars of the Eighties and Nineties. Languages and operating systems are tools, and are better open and shared. GCC is free software and belongs to nobody.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxuser.co.uk/features/staying-free-should-gcc-allow-non-free-plug-ins
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://lwn.net/articles/582241
|
||||
@ -1,105 +0,0 @@
|
||||
zpl1025
|
||||
Where And How To Code: Choosing The Best Free Code Editor
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A close look at Cloud9, Koding and Nitrous.IO.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Ready to start your first coding project? Great! Just configure** Terminal or Command Prompt, learn to use it and then install all the languages, add-on libraries and APIs you’ll need. When you're finally through with all that, you can get started with installing [Visual Studio][1] so you can preview your work.
|
||||
|
||||
At least that's how you used to have to do it.
|
||||
|
||||
No wonder beginning coders are increasingly turning to online integrated development environments (IDEs). An IDE is a code editor that comes ready to work with languages and all their dependencies, saving you the hassle of installing them on your computer.
|
||||
|
||||
I wanted to learn more about what constitutes the typical IDE, so I took a look at the free tier for three of the most popular integrated development environments out there: [Cloud9][2], [Koding][3], and [Nitrous.IO][4]. In the process, I learned a lot about the cases in which programmers would and would not want to use IDEs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why Use An IDE? ###
|
||||
|
||||
If a text editor is like Microsoft Word, think of an IDE as Google Drive. You get similar functionality, but it's accessible from any computer and ready to share. As the Internet becomes an increasingly influential part of project workflow, IDEs make life easier.
|
||||
|
||||
I used Nitrous.IO for my last ReadWrite tutorial, the Python app in [Create Your Own Obnoxiously Simple Messaging App Just Like Yo][5]. When you use an IDE, you select the language you want to work in so you can test and preview how it looks on the IDE’s Virtual Machine (VM) designed to run programs written specifically in that language.
|
||||
|
||||
If you read the tutorial, you'll see there are only two API libraries that my app depended on—messaging service Twilio and Python microframework Flask. That would have been easy to build using a text editor and Terminal on my computer, but I chose an IDE for yet another convenience: when everyone is using the same developer environment, it’s easier to follow along with a tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
### What An IDE Is Not ###
|
||||
|
||||
Still, an IDE is not a long term hosting solution.
|
||||
|
||||
When you’re working on an IDE, you’re able to build, test and preview your app in the cloud. You’re even able to share the final draft via link.
|
||||
|
||||
But you can’t use an IDE to store your project permanently. You wouldn't ditch your blog in favor of hosting your posts as Google Drive documents. Like Google Drive, IDEs allow you to link and share content, but neither are equipped to replace real hosting.
|
||||
|
||||
What's more, IDEs aren't designed for wide-spread sharing. Despite the increased functionality IDEs add to the preview capability of most text editors, stick with showing off your app preview to friends and coworkers, not with, say, the front page of Hacker News. In that case, your IDE would probably shut you down for excessive traffic.
|
||||
|
||||
Think of it this way: an IDE is a place to build and test your app; a host is a place for it to live. So once you’ve finalized your app, you’ll want to deploy it on a cloud-based service that lets you host apps long term, preferably one with a free hosting option like [Heroku][6].
|
||||
|
||||
### Choosing An IDE ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As IDEs become more popular, more are popping up all the time. In my opinion, there’s no perfect IDE. However, some IDEs are better for certain work process priorities than others.
|
||||
|
||||
I took a look at the free tier for three of the most popular integrated development environments out there: Cloud9, Koding, and Nitrous.IO. Each has its benefits, depending on what you're working on. Here's what I found.
|
||||
|
||||
### Cloud9: Ready To Collaborate ###
|
||||
|
||||
When I signed up for Cloud9, one of the first things it prompted me to do was integrate my GitHub and BitBucket accounts. Instantly, all my GitHub projects, solo and collaborative, were ready to clone and work on in Cloud9’s development tool. Other IDEs have nowhere near this level of GitHub integration.
|
||||
|
||||
Out of the three IDEs I looked at, Cloud9 seemed most intent on ensuring an environment where I could work seamlessly with co-coders. Here, it’s not just a chat function in the corner. In fact, said CEO Ruben Daniels, Cloud9 collaborators can see each others coding in real time, just like co-authors are able to on Google Drive.
|
||||
|
||||
“Most services’ collaborative features only work on a single file,” said Daniels. “Ours work on multiples throughout the project. Collaboration is fully integrated within the IDE.”
|
||||
|
||||
### Koding: Help When You Need It ###
|
||||
|
||||
IDEs give you the tools you need to build and test applications in the gamut of open source languages. For a beginner, that can be a little bit intimidating. For example, if I’m working on a project with both Python and Ruby components, which VM do I use for testing?
|
||||
|
||||
The answer is both, though on a free account, you can only turn on one VM for testing at a time. I was able to find that out right on my Koding dashboard, which doubles as a place for users to give and get advice on their Koding projects. Of the three, it’s the most transparent when it comes to where you can ask for assistance and hear back in minutes.
|
||||
|
||||
“We have an active community built into the application,” said Nitin Gupta, Chief Business Officer at Koding. “We wanted to create an environment that is extremely attractive to people who need help and who want to help.”
|
||||
|
||||
### Nitrous.IO: An IDE Wherever You Want ###
|
||||
|
||||
The ultimate advantage of using an IDE over your own desktop environment is that it’s self-contained. You don’t have to install anything to use it. On the other hand, the ultimate advantage of using your own desktop environment is that you can work locally, even without Internet.
|
||||
|
||||
Nitrous.IO gives you the best of both worlds. You can use the IDE on the Web, or you can download it to your own computer, said cofounder AJ Solimine. The advantage is that you can merge the integrations of Nitrous with the familiarity of your preferred text editor.
|
||||
|
||||
“You can access Nitrous.IO from any modern web browser via our online Web IDE, but we also have handy desktop applications for Windows and Mac that let you edit with your favorite editor,” he said.
|
||||
|
||||
### The Bottom Line ###
|
||||
|
||||
The most surprising thing I learned from a week of [using][7] three different IDEs? How similar they are. [When it comes to the basics of coding][8], they’re all equally helpful.
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud9, Koding, [and Nitrous.IO all support][9] every major open source language, from Ruby to Python to PHP to HTML5. You can choose from any of those VMs.
|
||||
|
||||
Both Cloud9 and Nitrous.IO have built-in one-click GitHub integration. For Koding there are a [couple more steps][10], but it can be done.
|
||||
|
||||
Each integrated easily with the APIs I needed. Each let me install my preferred package installers, too (and Koding made me do it as a superuser). They all have a built in Terminal for easily testing and deploying projects. All three allow you to easily preview your project. And of course, they all hosted my project in the cloud so I could work on it anywhere.
|
||||
|
||||
On the downside, they all had the same negatives, which is reasonable when you consider they're free. You can only run one VM at a time to test a program written in a particular language. When you’re not using your VM for a while, the IDE preserves bandwidth by putting it into hibernation and you have to wait for it to reload next time you use it (and Cloud9 was especially laborious). None of them make a good permanent host for your finished projects.
|
||||
|
||||
So to answer those who ask me if there’s a perfect free IDE out there, probably not. But depending on your priorities, there might be one that’s perfect for your project.
|
||||
|
||||
Lead image courtesy of [Shutterstock][11]
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/14/cloud9-koding-nitrousio-integrated-development-environment-ide-coding
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Lauren Orsini][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/lauren-orsini
|
||||
[1]:http://www.visualstudio.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://c9.io/
|
||||
[3]:https://koding.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://nitrous.io/
|
||||
[5]:http://readwrite.com/2014/07/11/one-click-messaging-app
|
||||
[6]:http://heroku.com/
|
||||
[7]:http://help.nitrous.io/ide-general/
|
||||
[8]:https://www.nitrous.io/desktop
|
||||
[9]:https://www.nitrous.io/desktop
|
||||
[10]:https://koding.com/Activity/steps-clone-projects-github-koding-1-create-account-github-2-open-your-terminal-3
|
||||
[11]:http://www.shutterstock.com/
|
||||
@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
|
||||
barney-ro translating
|
||||
|
||||
Why Your Company Needs To Write More Open Source Software - ReadWrite
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Real innovation doesn't happen behind closed doors.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**The Wall Street Journal [thinks][1] it's news that Zulily is developing** "more software in-house." It's not. At all. As [Eric Raymond wrote][2] years ago, 95% of the world's software is written for use, not for sale. The reasons are many, but one stands out: as Zulily CIO Luke Friang declares, it's "nearly impossible for a [off the shelf] solution to keep up with our pace."
|
||||
|
||||
True now, just as it was true 20 years ago.
|
||||
|
||||
But one thing is different, and it's something the WSJ completely missed. Historically software developed in-house was zealously kept proprietary because, the reasoning went, it was the source of a firm's competitive advantage. Today, however, companies increasingly realize the opposite: there is far more to be gained by open sourcing in-house software than keeping it closed.
|
||||
|
||||
Which is why your company needs to contribute more open-source code. Much more.
|
||||
|
||||
We've gone through an anomalous time these past 20 years. While most software continued to be written for internal use, most of the attention has been focused on vendors like SAP and Microsoft that build solutions that apply to a wide range of companies.
|
||||
|
||||
That's the theory, anyway.
|
||||
|
||||
In practice, buyers spent a small fortune on license fees, then a 5X multiple on top of that to make the software fit their requirements. For example, a company may spend $100,000 on an ERP system, but they're going to spend another $500,000 making it work.
|
||||
|
||||
One of the reasons open source took off, even in applications, was that companies could get a less functional product for free (or a relatively inexpensive fee) and then spend their implementation dollars tuning it to their needs. Either way, customization was necessary, but the open source approach was less costly and arguably more likely to result in a more tailored result.
|
||||
|
||||
Meanwhile, technology vendors doubled-down on "sameness," as Redmonk analyst [Stephen O'Grady describes][3]:
|
||||
|
||||
> The mainstream technology industry has, in recent years, eschewed specialization. Virtual appliances, each running a version of the operating system customized for an application or purpose, have entirely failed to dent the sales of general purpose alternatives such as RHEL or Windows. For better than twenty years, the answer to any application data persistence requirement has meant one thing: a relational database. If you were talking about enterprise application development, you were talking about Java. And so on.
|
||||
|
||||
Along the way, however, companies discovered that vendors weren't really meeting their needs, even for well-understood product categories like Content Management Systems. They needed different, not same.
|
||||
|
||||
So the customers went rogue. They became vendors. Sort of.
|
||||
|
||||
As is often the case, [O'Grady nails][4] this point. Writing in 2010, O'Grady uncovers an interesting trend: "Software vendors are facing a powerful new market competitor: their customers."
|
||||
|
||||
Think about the most visible technologies today. Most are open source, and nearly all of them were originally written for some company's internal use, or some developer's hobby. Linux, Git, Hadoop, Cassandra, MongoDB, Android, etc. None of these technologies were originally written to be sold as products.
|
||||
|
||||
Instead, they were developed by companies—usually Web companies—building software to "[scratch their own itches][5]," to use the open source phrase. And unlike previous generations of in-house software developed at banks, hospitals and other organizations, they open sourced the code.
|
||||
|
||||
While [some companies eschew developing custom software][6] because they don't want to maintain it, open source (somewhat) mitigates this by letting a community grow up to extend and maintain a project, thereby amortizing the costs of development for the code originators. Yahoo! started Hadoop, but its biggest contributors today are Cloudera and Hortonworks. Facebook kickstarted Cassandra, but DataStax primarily maintains it today. And so on.
|
||||
|
||||
Today real software innovation doesn't happen behind closed doors. Or, if it does, it doesn't stay there. It's open source, and it's upending decades of established software orthodoxy.
|
||||
|
||||
Not that it's for the faint of heart.
|
||||
|
||||
The best open-source projects [innovate very fast][7]. Which is not the same as saying anyone will care about your open-source code. There are [significant pros and cons to open sourcing your code][8]. But one massive "pro" is that the best developers want to work on open code: if you need to hire quality developers, you need to give them an open source outlet for their work. (Just [ask Netflix][9].)
|
||||
|
||||
But that's no excuse to sit on the sidelines. It's time to get involved, and not for the good of some ill-defined "community." No, the primary beneficiary of open-source software development is you and your company. Better get started.
|
||||
|
||||
Lead image courtesy of Shutterstock.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/16/open-source-software-business-zulily-erp-wall-street-journal
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matt Asay][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/matt-asay
|
||||
[1]:http://blogs.wsj.com/cio/2014/08/08/zulily-calls-in-house-software-a-differentiator-for-competitive-advantage/
|
||||
[2]:http://oreilly.com/catalog/cathbazpaper/chapter/ch05.html
|
||||
[3]:http://redmonk.com/sogrady/2010/01/12/roll-your-own/#ixzz3ATBuZsef
|
||||
[4]:http://redmonk.com/sogrady/2010/01/12/roll-your-own/
|
||||
[5]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Cathedral_and_the_Bazaar
|
||||
[6]:http://www.abajournal.com/magazine/article/roll_your_own_software_hidden_dangers_on_the_road_less_traveled/
|
||||
[7]:http://readwrite.com/2013/12/12/open-source-innovation
|
||||
[8]:http://readwrite.com/2014/07/07/open-source-software-pros-cons
|
||||
[9]:http://techblog.netflix.com/2012/07/open-source-at-netflix-by-ruslan.html
|
||||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linus Torvalds Promotes Linux for Desktops, Embedded Computing
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Linux kernel developer and open source leader Linus Torvalds spoke recently about the future of desktop Linux and Linux for embedded devices.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
What's the future of Linux for desktop computers and embedded devices? That's a question up for debate, but Linux founder and open source superstar Linus Torvalds provided some intriguing viewpoints in a discussion at the [Linux Foundation's][1] recent LinuxCon event.
|
||||
|
||||
As the guy who wrote the first Linux kernel code and shared it publicly over the Internet back in 1991, Torvalds is without doubt among the most famous developers of open source software—or any software, really—alive today. And while Torvalds is only one individual among many thousands of people and organizations guiding the development of Linux, his opinions tend to be influential with the open source community, and his role as a lead kernel developer places him in a powerful position for deciding which features and code make it into the operating system.
|
||||
|
||||
So it's worth paying attention when Torvalds says, "I still want the desktop," as he [did last week][2] at LinuxCon. It's a sign that he still sees a future for Linux as an operating system for powering personal PCs, even though desktop Linux market share has remained minuscule and relatively flat for more than a decade, and most of the commercial activity around Linux these days involves servers or Android-powered mobile hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
But, Torvalds added, ensuring a strong future for desktop Linux means solving an "infrastructure problem" that stems, he seems to believe, from the broader open source software ecosystem and the hardware world. It's not the core Linux code itself that's at issue, and making the channel friendly for desktop Linux is a feat Torvalds and his fellow kernel developers probably have little power to achieve on their own. That's up to app developers, hardware manufacturers and other parties who have the power to deliver computing platforms based on Linux that people will readily use.
|
||||
|
||||
On the other hand, Torvalds also mentioned a hope that kernel developers might streamline the Linux code for embedded devices—a task that might be at odds in some ways with making the kernel more desktop-friendly. But that's not necessarily the case, and at any rate, given that Linux is designed to be so modular, there's no reason a single kernel code base can't meet the needs of desktop users and embedded developers equally well, depending on which chunks they choose to use.
|
||||
|
||||
As a longtime desktop Linux user who would also like to see more Linux-powered embedded devices, I'm hoping Torvalds's aspirations in both regards will be realized, and that I will one day be able to do everything I need using only Linux, whether it's on a desktop computer, a mobile phone, the car or anywhere else.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/082514/linus-torvalds-promotes-linux-desktops-and-embedded-compu
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Christopher Tozzi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://thevarguy.com/author/christopher-tozzi
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.eweek.com/enterprise-apps/linux-founder-linus-torvalds-still-wants-the-desktop.html
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
translating by barney-ro
|
||||
|
||||
Interesting facts about Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Today, August, 25th, is the 23rd birthday of Linux. The modest [Usenet post][1] made by a 21 year old student at the University of Helsinki on August 25th, 1991, marks the birth of the venerable Linux as we know it today.
|
||||
@ -49,7 +51,7 @@ Happy birthday, Linux!
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/08/interesting-facts-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux Doesn't Need to Own the Desktop
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Linus Torvalds issued Linux 3.17 rc-2 on Monday of this week, and [he deviated from his normal schedule][1] in doing so, because August 25 happens to mark the 23rd anniversary of the original Linux announcement. "Hello everybody out there using minix," Torvalds wrote.
|
||||
|
||||
Meanwhile, PCMag.com has proclaimed that [Linux has run out of time][2]. But isn't it true that the endless discussions of whether Linux is a success on the desktop are moot? Linux is in supercomputers and cars, it formed the basis for Android and is the most popular platform to run emerging cloud platforms like OpenStack on--just to name a few of its successes. The desktop is not the only battleground for Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Jon Buys took note of specialization and the Linux desktop [in a recent post][3], where he wrote:
|
||||
|
||||
> "Recently, IT World asked “[Does it still make sense for Linus to want the desktop for Linux?][4]”, and Matt Asay from Tech Repubic asked “[Can we please stop talking about the Linux desktop?][5]”. Both publishers are critical of the claim that there is still room for Linux on Personal Computers, and point to Android as a Linux success story...What both articles miss though is that the flexibility of Linux, and the permissiveness of its open source license may be the things that save Linux on the desktop."
|
||||
|
||||
That may be true, but Linux is so much to so many people beyond the desktop. Linux's opportunity for great market share on the desktop has come and gone.
|
||||
|
||||
The simple fact is that Linux has changed the world and been a tremendous success outside the desktop, and there is nothing wrong with that. Android is hardly the only Linux-based platform that has made a big mark. Linux is huge on servers, in embedded technology, and is a constant prompt for innovation on emerging platforms. Ubuntu is the most popular platform for building OpenStack deployments on. Supercomputers all over the world run Linux, and Chrome OS is based on it.
|
||||
|
||||
So Linux is making a huge difference globally, and it is time for detractors to stop focusing exclusively on its status on the desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ostatic.com/blog/linux-doesnt-need-to-own-the-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sam Dean][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ostatic.com/member/samdean
|
||||
[1]:http://www.theregister.co.uk/2014/08/26/linux_turns_23_and_linus_torvalds_celebrates_as_only_he_can/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2465125,00.asp
|
||||
[3]:http://ostatic.com/blog/specialization-and-the-linux-desktop
|
||||
[4]:http://www.itworld.com/open-source/432816/does-it-still-make-sense-linus-want-desktop-linux
|
||||
[5]:http://www.techrepublic.com/article/can-we-please-stop-talking-about-the-linux-desktop/
|
||||
@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Happy Birthday Email
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**An Indian American had the brain to invent electronic mail without which we cannot figure out a single day in this era.**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
30 August, email turned 32. Now we wonder how this fast and quick method of message transfer came into existence. The credit goes to an Indian American, Shiva Ayyadurai. Shiva developed a full-scale software of the interoffice mail system and it was named email.
|
||||
|
||||
He was officially acknowledged as the inventor of the computer programme on 30 August, 1982, by the US government. Born to Tamil family in Bombay, Shiva was just 14 years old when he invented the email system. He was studying at Livingston High School in New Jersey and he began working on this system for the University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey. A copyright was given to the email system as no other way was known to protect software inventions at that time.
|
||||
|
||||
Ayyadurai got the idea of the email system from the way mail was transported internally in offices. He tried to make a copy of ‘Pneumatic Tube System’ which was mostly used to send interoffice mails across offices. This system used a physical network of tubes which used to transport typed mails to secretaries. Each secretary used to have inbox, outbox, drafts, carbon copy paper, folders, address book, paper clips or attachments etc. All these were used to create and process incoming and outgoing mails.
|
||||
|
||||
Shiva also took a note of the common templates like “To”, “From”, “Subject”, “Date”, “Body”, “CC”, “BCC” and so on. All these templates were incorporated in the version of the electronic mail too. Mail was written FORTRAN programming language and Shiva discovered an electronic version of the same. Shiva received many accolades for his extraordinary work and also won a Westinghouse Science Talent Search Award for high school seniors in 1981. Now Smithsonian Institution National Museum of American History (SINMAH) has the official US copyright for “Email”. But there is a controversy that not Ayyadurai but some other people have invented email.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=147170
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Sanchari Banerjee
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
10 Open Source Cloning Software For Linux Users
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> These cloning software take all disk data, convert them into a single .img file and you can copy it to another hard drive.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Disk cloning means copying data from a hard disk to another one and you can do this by simple copy & paste. But you cannot copy the hidden files and folders and not the in-use files too. That's when you need a cloning software which can also help you in saving a back-up image from your files and folders. The cloning software takes all disk data, convert them into a single .img file and you can copy it to another hard drive. Here we give you the best 10 Open Source Cloning software:
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. [Clonezilla][1]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Clonezilla is a Live CD based on Ubuntu and Debian. It clones all your hard drive data and take a backup just like Norton Ghost on Windows but in a more effective way. Clonezilla support many filesystems like ext2, ext3, ext4, btrfs, xfs and others. It also supports BIOS, UEFI, MPR and GPT partitions.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. [Redo Backup][2]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Redo Bakcup is another Live CD tool which clones your drivers easily. It is free and Open Source Live System which has its licence under GPL 3. Its main features include easy GUI boots from CD, no installation, restoration of Linux and Windows systems, access to files with out any log-in, recovery of deleted files and more.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. [Mondo Rescue][3]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Mondo doesn't work like other software. It doesn’t convert your hard drivers into an .img file. It converts them into an .iso image and with Mondo you can also create a custom Live CD using “mindi” which is a special tool developed by Mondo Rescue to clone your data from the Live CD. It supports most Linux distributions, FreeBSD, and it is licensed under GPL.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. [Partimage][4]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
This is an open-source software backup, which works under Linux system, by default. It's also available to install from the package manager for most Linux distributions and if you don’t have a Linux system then you can use “SystemRescueCd”. It is a Live CD which includes Partimage by default to do the cloning process that you want. Partimage is very fast in cloning hard drivers.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 5. [FSArchiver][5]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
FSArchiver is a follow-up to Partimage, and it is again a good tool to clone hard disks. It supports cloning Ext4 partitions and NTFS partitions, basic file attributes like owner, permissions, extended attributes like those used by SELinux, basic file system attributes for all Linux file systems and so on.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. [Partclone][6]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Partclone is a free tool which clones and restores partitions. Written in C it first appeared in 2007 and it supports many filesystems like ext2, ext3, ext4, xfs, nfs, reiserfs, reiser4, hfs+, btrfs. It is very simple to use and it's licensed under GPL.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. [doClone][7]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
doClone is a free software project which is developed to clone Linux system partitions easily. It's written in C++ and it supports up to 12 different filesystems. It can preform Grub bootloader restoration and can also transform the clone image to another computer via LAN. It also provides support to live cloning which means you will eb able to clone from the system even if it's running.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 8. [Macrium Reflect Free Edition][8]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Macrium Reflect Free Edition is claimed to be one of the fastest disk cloning utilities which supports only Windows file systems. It is a fairly straightforward user interface. This software does disk imaging and disk cloning and also allows you to access images from the file manager. It allows you to create a Linux rescue CD and it is compatible with Windows Vista and 7.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 9. [DriveImage XML][9]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
DriveImage XML uses Microsoft VSS for creation of images, quite reliably. With this software you can create "hot" images from a disk, which is still running. XML files store images, which means you can access them from any supporting third-party software. DriveImage XML also allows restoring an image to a machine without any reboot. This software is also compatible with Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Vista, and 7.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 10. [Paragon Backup & Recovery Free][10]: ###
|
||||
|
||||
Paragon Backup & Recovery Free does a great job when it comes to managing scheduled imaging. This is a free software but it's for personal use only.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=148039
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Sanchari Banerjee
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://clonezilla.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://redobackup.org/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.mondorescue.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.partimage.org/Main_Page
|
||||
[5]:http://www.fsarchiver.org/Main_Page
|
||||
[6]:http://www.partclone.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://doclone.nongnu.org/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.macrium.com/reflectfree.aspx
|
||||
[9]:http://www.runtime.org/driveimage-xml.htm
|
||||
[10]:http://www.paragon-software.com/home/br-free/
|
||||
190
sources/talk/20140915 Make Downloading Files Effortless.md
Normal file
190
sources/talk/20140915 Make Downloading Files Effortless.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,190 @@
|
||||
zpl1025
|
||||
Make Downloading Files Effortless
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
A download manager is computer software that is dedicated to the task of downloading files, optimizing bandwidth usage, and operating in a more organized way. Some web browsers, such as Firefox, include a download manager as a feature, but their implementation lacks the sophistication of a dedicated download manager (or add-ons for the web browser), without using bandwidth optimally, and without good file management features.
|
||||
|
||||
Users that regularly download files benefit from using a good download manager. The ability to maximize download speeds (with download acceleration), resume and schedule downloads, make safer and more rewarding downloading. Download managers have lost some of their popularity, but the best of them offer real benefits including tight integration with browsers, support for popular sites such as YouTube and much more.
|
||||
|
||||
There are some sublime open source download managers for Linux, which makes selection somewhat problematic. I have compiled a roundup of my favorite download managers, and add-ons that turn a download manager into an excellent download manager for Firefox. Each application featured here is released under an open source license.
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
uGet is a lightweight, easy-to-use and full-featured open source download manager. uGet allows the user to download in multiple parallel streams for download acceleration, put files in a download queue, pause & resume downloads, offers advanced category management, with browser integration, clipboard monitoring, batch downloads, localized into 26 languages, and many more features.
|
||||
|
||||
uGet is mature software; it has been in developed for more than 11 years. In that time, it has progressed into a highly versatile download manager, with an estimable set of features, yet maintaining ease of use.
|
||||
|
||||
uGet is written in the C language, uses cURL as a backend, and the applicable library, libcurl. uGet has excellent platform compatibility. uGet is primarily a project for Linux, but it also runs on Mac OS X, FreeBSD, Android, and Windows.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Easy to use
|
||||
- Downloads queue place your downloads into a queue to download as many, or as few, downloads as you want simultaneously
|
||||
- Resume downloads
|
||||
- Categorized defaults
|
||||
- Clipboard monitor which is well implemented
|
||||
- Batch downloads
|
||||
- Import downloads import from HTML files
|
||||
- Support for downloading files through HTTP, HTTPS, FTP, BitTorrent & Metalink
|
||||
- Multi-connection (also known as Multi-Segment): up to 20 simultaneous connections per download with adaptive segment management which means that when one segment drops out then the other connections pick up the slack to ensure optimal download speeds at all times
|
||||
- Multi-mirror
|
||||
- FTP login & anonymous FTP
|
||||
- Powerful scheduler
|
||||
- FireFox integration via FlashGot
|
||||
- Aria2 plugin
|
||||
- Theme chameleoning
|
||||
- Quiet mode
|
||||
- Keyboard shortcuts
|
||||
- CLI / Terminal usage support
|
||||
- Folder auto-creation
|
||||
- Download history management
|
||||
- GnuTLS support
|
||||
- Supports 26 languages including: Arabic, Belarusian, Chinese (Simplified), Chinese (Traditional), Czech, Danish, English (default), French, Georgian, German, Hungarian, Indonesian, Italian, Polish, Portuguese (Brazil), Russian, Spanish, Turkish, Ukrainian, and Vietnamese
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [ugetdm.com][1]
|
||||
- Developer: C.H. Huang and contributors
|
||||
- License: GNU LGPL 2.1
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.10.5
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
DownThemAll! is a fast, reliable and easy-to-use, open source download manager/accelerator built inside Firefox. This add-on lets the user download all the links or images contained in a webpage and much more. The add-on gives the user full control over downloads, dedicated speed and number of parallel connections at any time. Use Metalinks or add mirrors manually to download a file from different servers at the same time.
|
||||
|
||||
DownThemAll reads the size of the files you want to download and splits them into multiple sections, which are downloaded in parallel.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Complete integration with Firefox
|
||||
- Multi-part download which allows the user to download the file in pieces, then combining the pieces after a completed download; thus increasing the download speed when connected to a slow server
|
||||
- Metalink support which allows multiple URLs for each file to be passed to DTA, along with checksums and other informatio
|
||||
- Spider a page with a single link
|
||||
- Filtering
|
||||
- Advanced auto-renaming options
|
||||
- Pause and restart downloads
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/downthemall][2]
|
||||
- Developer: Federico Parodi, Stefano Verna, Nils Maier
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 2.0.17
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
JDownloader is a free, open-source download management tool with a large community of developers that makes downloading easy and fast. Users can start, stop or pause downloads, set bandwith limitations, auto-extract archives and much more. It offers an easy-to-extend framework.
|
||||
|
||||
JDownloader simplifies downloading files from One-Click-Hosters. It also offers downloading in multiple parallel streams, captcha recognition, automatic file extraction and much more. Additionally, many "link encryption" sites are supported - so you just paste the "encrypted" links and JDownloader does the rest. JDownloader can import CCF, RSDF and DLC files.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Download several files at once
|
||||
- Download with multiple connections
|
||||
- JD has an own powerful OCR module
|
||||
- Automatic extractor (including password list search) (Rar archives)
|
||||
- Theme Support
|
||||
- Multilingual
|
||||
- About 110 hoster and over 300 decrypt plug-ins
|
||||
- Reconnect with JDLiveHeaderScripts: (1400 router supported)
|
||||
- Webupdate
|
||||
- Integrated package manager for additional modules (eg. Webinterface, Shutdown)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [jdownloader.org][3]
|
||||
- Developer: AppWork UG
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v3
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.9.581
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
FreeRapid Downloader is an easy to use open source downloader that supports downloading from Rapidshare, Youtube, Facebook, Picasa and other file-sharing services. Its engine is based on a list of plugins that make it possible to download from specific websites.
|
||||
|
||||
FreeRapid Downloader is an ideal choice for users needing a download manager specialized in sharing websites.
|
||||
|
||||
FreeRapid Downloader is written in Java. It needs at least Sun Java 7.0 to run.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Easy to use
|
||||
- Supports concurrent downloading from multiple services
|
||||
- Supports resuming downloads
|
||||
- Download using proxy list
|
||||
- Supports streamed videos or pictures
|
||||
- Download history
|
||||
- Smart clipboard monitoring
|
||||
- Automatic checking for file's existence on server
|
||||
- Auto shutdown options
|
||||
- Automatic plugins updates
|
||||
- Simple CAPTCHA recognition
|
||||
- Multi-platform support
|
||||
- Internationalization support: English, Bulgarian, Czech, Finnish, Portugal, Slovak, Hungarian, Simplified Chinese and many others
|
||||
- More than 700 supported sites
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [wordrider.net/freerapid/][4]
|
||||
- Developer: Vity and contributors
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 0.9u4
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
FlashGot is a free add-on for Firefox and Thunderbird, meant to handle single and massive ("all" and "selection") downloads with several external Download Managers.
|
||||
|
||||
FlashGot turns every supported download manager into a download manager for Firefox.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Features include: ####
|
||||
|
||||
- Supports in Linux: Aria, Axel Download Accelerator, cURL, Downloader 4 X, FatRat, GNOME Gwget, FatRat, JDownloader, KDE KGet, pyLoad, SteadyFlow, uGet, wxDFast, and wxDownload Fast)
|
||||
- Build Gallery functionality which helps to synthesize full media galleries in one page, from serial contents originally scattered on several pages, for easy and fast "download all"
|
||||
- FlashGot Link downloads through the default download manager the link under the mouse pointer
|
||||
- FlashGot Selection
|
||||
- FlashGot All
|
||||
- FlashGot Tabs
|
||||
- FlashGot Media
|
||||
- Capture all links from a page
|
||||
- Capture all links from all tabs
|
||||
- Filter the links using a mask (e.g. to download only certain types of files)
|
||||
- Make a selection on a web page and capture all links in that selection
|
||||
- Supports direct and batch download from the most popular link protection and file hosting services
|
||||
- Privacy options
|
||||
- Internationalization support
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Website: [flashgot.net][5]
|
||||
- Developer: Giorgio Maone
|
||||
- License: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- Version Number: 1.5.6.5
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20140913062041384/DownloadManagers.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ugetdm.com/
|
||||
[2]:https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/downthemall/
|
||||
[3]:http://jdownloader.org/
|
||||
[4]:http://wordrider.net/freerapid/
|
||||
[5]:http://flashgot.net/
|
||||
@ -1,132 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Translating by ZTinoZ
|
||||
10 Useful “Squid Proxy Server” Interview Questions and Answers in Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
It’s not only to System Administrator and Network Administrator, who listens the phrase Proxy Server every now and then but we too. Proxy Server is now a corporate culture and is the need of the hour. Proxy server now a days is implemented from small schools, cafeteria to large MNCs. Squid (also known as proxy) is such an application which acts as proxy server and one of the most widely used tool of its kind.
|
||||
|
||||
This Interview article aims at strengthening your base from Interview point on the ground of proxy server and squid.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Squid Interview Questions
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. What do you mean by Proxy Server? What is the use of Proxy Server in Computer Networks? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : A Proxy Server refers to physical machine or Application which acts intermediate between client and resource provider or server. A client seeks for file, page or data from the the proxy server and proxy server manages to get the requested demand of client fulfilled by handling all the complexities in between.
|
||||
|
||||
Proxy servers are the backbone of WWW (World Wide Web). Most of the proxies of today are web proxies. A proxy server handles the complexity in between the Communication of client and Server. Moreover it provides anonymity on the web which simply means your identity and digital footprints are safe. Proxies can be configured to allow which sites client can see and which sites are blocked.
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. What is Squid? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Squid is an Application software released under GNU/GPL which acts as a proxy server as well as web cache Daemon. Squid primarily supports Protocol like HTTP and FTP however other protocols like HTTPS, SSL,TLS, etc are well supported. The feature web cache Daemon makes web surfing faster by caching web and DNS for frequently visited websites. Squid is known to support all major platforms including Linux, UNIX, Microsoft Windows and Mac.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. What is the default port of squid and how to change its operating port? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : The default port on which squid runs is 3128. We can change the operating port of squid from default to any custom unused port by editing its configuration file which is located at /etc/squid/squid.conf as suggested below.
|
||||
|
||||
Open ‘/etc/squid/squid.conf’ file and with your choice of editor.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||||
|
||||
Now change this port to any other unused port. Save the editor and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
http_port 3128
|
||||
|
||||
Restart the squid service as shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. You works for a company the management of which ask you to block certain domains through squid proxy server. What are you going to do? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Blocking domain is a module which is implemented well in the configuration file. We just need to perform a little manual configuration as suggested below.
|
||||
|
||||
a. Create a file say ‘blacklist’ under directory ‘/etc/squid’.
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /etc/squid/blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
b. Open the file ‘/etc/squid/blacklist’ with nano editor.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
c. Add all the domains to the file blacklist with one domain per line.
|
||||
|
||||
.facebook.com
|
||||
.twitter.com
|
||||
.gmail.com
|
||||
.yahoo.com
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
d. Save the file and exit. Now open the Squid configuration file from location ‘/etc/squid/squid.conf’.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||||
|
||||
e. Add the lines below to the Squid configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
acl BLACKLIST dstdom_regex -i “/etc/squid/blacklist”
|
||||
http_access deny blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
f. Save the configuration file and exit. Restart Squid service to make the changes effective.
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. What is Media Range Limitation and partial download in Squid? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Media Range Limitation is a special feature of squid in which just the required data is requested from the server and not the whole file. This feature is very well implemented in various videos streaming websites like Youtube and Metacafe where a user can click on the middle of progress bar hence whole video need not be fetched except for the requested part.
|
||||
|
||||
The squid’s feature of partial download is implemented well within windows update where downloads are requested in the form of small packets which can be paused. Because of this feature a update downloading windows machine can be restarted without any fear of data loss. Squid makes the Media Range Limitation and Partial Download possible only after storing a copy of whole data in it. Moreover the partial download gets deleted and not cached when user points to another page until Squid is specially configured somehow.
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. What is reverse proxy in squid? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Reverse proxy is a feature of Squid which is used to accelerate the web surfing for end user. Say the Real server ‘RS’ contains the resource and ‘PS’ is the proxy Server. The client seek some data which is available at RS. It will rely on RS for the specified data for the first time and the copy of that specified data gets stored on PS for configurable amount of time. For every request for that data from now PS becomes the real source. This results in Less traffic, Lesser CPU usages, Lesser web resource utilization and hence lesser load to actual server RS. But RS has no statistics for the total traffic since PS acted as actual server and no Client reached RS. ‘X-Forwarded-For HTTP’ can be used to log the client IP although on RS.
|
||||
|
||||
Technically it is feasible to use single squid server to act both as normal proxy server and reverse proxy server at the same point of time.
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. Since Squid can be used as web-cache Daemon, is it possible to Clear its Cache? How? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : No Doubt! Squid acts as web-cache Daemon which is used to accelerate web surfing still it is possible to clear its cache and that too very easily.
|
||||
|
||||
a. First stop Squid proxy server and delete cache from the location ‘/var/lib/squid/cache’ directory.
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid stop
|
||||
# rm -rf /var/lib/squid/cache/*<
|
||||
|
||||
b. Create Swap directories.
|
||||
|
||||
# squid -z
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. A client approaches you, who is working. They want the web access time be restricted for their children. How will you achieve this scenario? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Say the web access allow time be 4′o clock to 7′o clock in the evening for three hours, sharply form Monday to Friday.
|
||||
|
||||
a. To restrict web access between 4 to 7 from Monday to Friday, open the Squid configuration file.
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||||
|
||||
b. Add the following lines and save the file and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
acl ALLOW_TIME time M T W H F 16:00-19:00
|
||||
shttp_access allow ALLOW_TIME
|
||||
|
||||
c. Restart the Squid Service.
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Squid stores data in which file format? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : Data stored by Squid is in ufs format. Ufs is the old well-known Squid storage format.
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Where do cache gets stored by squid? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **Answer** : A squid stores cache in special folder at the location ‘/var/spool/squid’.
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now. I’ll be here again with another interesting article soon. Till then stay tuned and connected to Tecmint. Don’t forget to provide us with your valuable feedback the comment section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/squid-interview-questions/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
@ -1,77 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Check how much do you type with WhatPulse on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
If, like me, you are a statistics freak you must install this small application on all your computers: [WhatPulse][1]
|
||||
|
||||
The software tracks a user’s pressed keys, mouse clicks and used [bandwidth][2] and the uptime of the system. Periodically, or by hand, the user can upload to the server the number of keystrokes made; this is called “pulsing”.
|
||||
|
||||
Users can see where they are in a leaderboard of people who have joined the program and compare themselves against people from their own countries. Users can also join teams, which enables them to compare themselves against people with similar interests (Go Linux Users !!).
|
||||
|
||||
There is a basic, and free, version where you can easily see and check all the basic statistics and a premium account where you can see some more stats.
|
||||
|
||||
The software is available for Linux, Windows and Mac.
|
||||
|
||||
### Registration on the website ###
|
||||
|
||||
As first step you have to register your account on the [WhatPulse Website][1] or as alternative when you first start the WhatPulse client there is a practical wizard through which each user has the option to create an account to upload their own statistics (you can also log in with Facebook).
|
||||
|
||||
You will be prompted to login, once you login, you have to search for your computers name, this is because you can login to several computers with this and they’ll all collectively go to the same statistic count. Once you’ve logged in, a small W will appear in your system tray, that’s it, your set up!
|
||||
|
||||
### Installation of WhatPulse on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
The official website offer on the [download page][3] a generic version distributed via a .tar.gz archive (available for 32 and 64 bit) and a debian package.
|
||||
|
||||
Personally I’ve installed the debian package on my Mint Qiana and the [Aur Package][4] on My Arch Linux, no problems at all.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to go with the generic installation please keep in mind that WhatPulse requires several libraries to function. Mainly Qt, because WhatPulse is built on Qt. Here’s a list of requirements:
|
||||
|
||||
- libQtCore
|
||||
- libQtWebKit
|
||||
- libqt4-sql
|
||||
- libqt4-sql-sqlite
|
||||
- openssl-devel (libssl-dev)
|
||||
- libQtScript
|
||||
|
||||
#### Input Statistics ####
|
||||
|
||||
The client needs permissions to be allowed to read your keyboard/mouse input. Run the included interactive .sh script to set up these permissions.
|
||||
|
||||
#### [Network][5] Statistics ####
|
||||
|
||||
To enable the network measurements, you also need the package **libpcap** to allow WhatPulse to hook into the network traffic. If WhatPulse does not find libpcap, it will run but it will not display any network statistics.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Using the Application ###
|
||||
|
||||
By default WhatPulse will start automatically at the login of your graphical session and clicking on the W on your systray you’ll go to the Overview tab that gives a birds-eye view of all the different information gathered about your machine, for instance, the Linux version installed on your PC, processor model, RAM, GPU, total click counts, keystrokes and bandwidth usage. Clicking ‘Pulse’ under these information will upload the gathered data to the main server.
|
||||
|
||||
It’s also possible to select when automatically ‘Pulse’ the data to the server, such as every 50.000 clicks or 1 GB downloaded.
|
||||
|
||||
For further details, you can switch to each category’s pertaining tab. For example, the Input tab shows you the amount of key strokes and clicks your PC has registered during a certain time period. The time period can be sorted on a daily, weekly, monthly, yearly and all-time basis. The ‘all’ setting will show stats since the program was installed.
|
||||
|
||||
Below the keystrokes, you’ll find the keyboard heat map, which basically uses light and warm colors to shows what keys were used more than others during the selected time period, as shown in the screenshot above. Below that, the app displays the total amount of clicks registered in the selected period.
|
||||
|
||||
Under the Network tab, it’s possible to view the daily Internet usage. The application can monitor bandwidth usage of all the network devices, and even shows you bandwidth usage by country. Once again, you can navigate between available data using the arrow buttons at the top-right.
|
||||
|
||||
On the website you’ll see the sum of all your computer statistics with the same information available on the client.
|
||||
|
||||
Disclaimer: The link above to the WhatPulse website contains my referral link, using it when you register will give me a premium account for some time.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linuxaria.com/recensioni/check-how-much-do-you-type-with-whatpulse-on-linux
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[linuxari][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/100563597940685405833?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://whatpulse.org/ref/833872/
|
||||
[2]:http://linuxaria.com/article/tool-command-line-bandwidth-linux
|
||||
[3]:http://www.whatpulse.org/downloads/
|
||||
[4]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/whatpulse/
|
||||
[5]:http://linuxaria.com/tag/network
|
||||
@ -1,112 +0,0 @@
|
||||
8 Options to Trace/Debug Programs using Linux strace Command
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The strace is the tool that helps in debugging issues by tracing system calls executed by a program. It is handy when you want to see how the program interacts with the operating system, like what system calls are executed in what order.
|
||||
|
||||
This simple yet very powerful tool is available for almost all the Linux based operating systems and can be used to debug a large number of programs.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Command Usage ###
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s see how we can use strace command to trace the execution of a program.
|
||||
|
||||
In the simplest form, any command can follow strace. It will list a whole lot of system calls. Not all of it would make sence at first, but if you’re really looking for something particular, then you should be able to figure something out of this output.
|
||||
Lets see the system calls trace for simple ls command.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This output shows the first few lines for strace command. The rest of the output is truncated.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The above part of the output shows the write system call where it outputs to STDOUT the current directory’s listing. Following image shows the listing of the directoy by ls command (without strace).
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.1 Find configuration file read by program ####
|
||||
|
||||
One use of strace (Except debugging some problem) is that you can find out which configuration files are read by a program. For example,
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace php 2>&1 | grep php.ini
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.2 Trace specific system call ####
|
||||
|
||||
The -e option to strace command can be used to display certain system calls only (for example, open, write etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
Lets trace only ‘open’ system call for cat command.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -e open cat dead.letter
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.3 Stracing a process ####
|
||||
|
||||
The strace command can not only be used on the commands, but also on the running processes with -p option.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ sudo strace -p 1846
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.4 Statistical summary of strace ####
|
||||
|
||||
The summary of the system calls, time of execution, errors etc. can be displayed in a neat manner with -c option:
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -c ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.5 Saving output ####
|
||||
|
||||
The output of strace command can be saved into a file with -o option.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ sudo strace -o process_strace -p 3229
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The above command is run with sudo as it will display error in case the user ID does not match with the process owner.
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.6 Displaying timestamp ###
|
||||
|
||||
The timestamp can be displayed before each output line with -t option.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -t ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.7 The Finer timestamp ####
|
||||
|
||||
The -tt option displays timestamp followed by microsecond.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -tt ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The -ttt displays microseconds like above, but instead of printing surrent time, it displays the number of seconds since the epoch.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -ttt ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.8 Relative Time ####
|
||||
|
||||
The -r option displays the relative timestamp between the system calls.
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -r ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-strace-command-examples/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Raghu][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/raghu/
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,6 @@
|
||||
>>Linchenguang is translating
|
||||
|
||||
》》延期申请
|
||||
Linux TCP/IP networking: net-tools vs. iproute2
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Many sysadmins still manage and troubleshoot various network configurations by using a combination of ifconfig, route, arp and netstat command-line tools, collectively known as net-tools. Originally rooted in the BSD TCP/IP toolkit, the net-tools was developed to configure network functionality of older Linux kernels. Its development in the Linux community so far has ceased since 2001. Some Linux distros such as Arch Linux and CentOS/RHEL 7 have already deprecated net-tools in favor of iproute2.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,224 @@
|
||||
|
||||
How to create a software RAID-1 array with mdadm on Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Redundant Array of Independent Disks (RAID) is a storage technology that combines multiple hard disks into a single logical unit to provide fault-tolerance and/or improve disk I/O performance. Depending on how data is stored in an array of disks (e.g., with striping, mirroring, parity, or any combination thereof), different RAID levels are defined (e.g., RAID-0, RAID-1, RAID-5, etc). RAID can be implemented either in software or with a hardware RAID card. On modern Linux, basic software RAID functionality is available by default.
|
||||
|
||||
In this post, we'll discuss the software setup of a RAID-1 array (also known as a "mirroring" array), where identical data is written to the two devices that form the array. While it is possible to implement RAID-1 with partitions on a single physical hard drive (as with other RAID levels), it won't be of much use if that single hard drive fails. In fact, that's why most RAID levels normally use multiple physical drives to provide redundancy. In the event of any single drive failure, the virtual RAID block device should continue functioning without issues, and allow us to replace the faulty drive without significant production downtime and, more importantly, with no data loss. However, it does not replace the need to save periodic system backups in external storage.
|
||||
|
||||
Since the actual storage capacity (size) of a RAID-1 array is the size of the smallest drive, normally (if not always) you will find two identical physical drives in RAID-1 setup.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing mdadm on Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
The tool that we are going to use to create, assemble, manage, and monitor our software RAID-1 is called mdadm (short for **m**ultiple **d**isks **adm**in). On Linux distros such as Fedora, CentOS, RHEL or Arch Linux, mdadm is available by default. On Debian-based distros, mdadm can be installed with aptitude or apt-get.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Fedora, CentOS or RHEL ####
|
||||
|
||||
As mdadm comes pre-installed, all you have to do is to start RAID monitoring service, and configure it to auto-start upon boot:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start mdmonitor
|
||||
# systemctl enable mdmonitor
|
||||
|
||||
For CentOS/RHEL 6, use these commands instead:
|
||||
|
||||
# service mdmonitor start
|
||||
# chkconfig mdmonitor on
|
||||
|
||||
#### Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint ####
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian and its derivatives, mdadm can be installed with **aptitude or apt-get**:
|
||||
|
||||
# aptitude install mdadm
|
||||
|
||||
On Ubuntu, you will be asked to configure postfix MTA for sending out email notifications (as part of RAID monitoring). You can skip it for now.
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, the installation will start with the following explanatory message to help us decide whether or not we are going to install the root filesystem on a RAID array. What we need to enter on the next screen will depend on this decision. Read it carefully:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Since we will not use our RAID-1 for the root filesystem, we will leave the answer blank:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
When asked whether we want to start (reassemble) our array automatically during each boot, choose "Yes". Note that we will need to add an entry to the /etc/fstab file later in order for the array to be properly mounted during the boot process as well.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Partitioning Hard Drives ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now it's time to prepare the physical devices that will be used in our array. For this setup, I have plugged in two 8 GB USB drives that have been identified as /dev/sdb and /dev/sdc from dmesg output:
|
||||
|
||||
# dmesg | less
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[ 60.014863] sd 3:0:0:0: [sdb] 15826944 512-byte logical blocks: (8.10 GB/7.54 GiB)
|
||||
[ 75.066466] sd 4:0:0:0: [sdc] 15826944 512-byte logical blocks: (8.10 GB/7.54 GiB)
|
||||
|
||||
We will use fdisk to create a primary partition on each disk that will occupy its entire size. The following steps show how to perform this task on /dev/sdb, and assume that this drive hasn't been partitioned yet (otherwise, we can delete the existing partition(s) to start off with a clean disk):
|
||||
|
||||
# fdisk /dev/sdb
|
||||
|
||||
Press 'p' to print the current partition table:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
(if one or more partitions are found, they can be deleted with 'd' option. Then 'w' option is used to apply the changes).
|
||||
|
||||
Since no partitions are found, we will create a new primary partition ['n'] as a primary partition ['p'], assign the partition number = ['1'] to it, and then indicate its size. You can press Enter key to accept the proposed default values, or enter a value of your choosing, as shown in the image below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now repeat the same process for /dev/sdc.
|
||||
|
||||
If we have two drives of different sizes, say 750 GB and 1 TB for example, we should create a primary partition of 750 GB on each of them, and use the remaining space on the bigger drive for another purpose, independent of the RAID array.
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a RAID-1 Array ###
|
||||
|
||||
Once you are done with creating the primary partition on each drive, use the following command to create a RAID-1 array:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -Cv /dev/md0 -l1 -n2 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
|
||||
|
||||
Where:
|
||||
|
||||
- **-Cv**: creates an array and produce verbose output.
|
||||
- **/dev/md0**: is the name of the array.
|
||||
- **-l1** (l as in "level"): indicates that this will be a RAID-1 array.
|
||||
- **-n2**: indicates that we will add two partitions to the array, namely /dev/sdb1 and /dev/sdc1.
|
||||
|
||||
The above command is equivalent to:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --create --verbose /dev/md0 --level=1 --raid-devices=2 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
|
||||
|
||||
If alternatively you want to add a spare device in order to replace a faulty disk in the future, you can add '--spare-devices=1 /dev/sdd1' to the above command.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer "y" when prompted if you want to continue creating an array, then press Enter:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
You can check the progress with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# cat /proc/mdstat
|
||||
|
||||
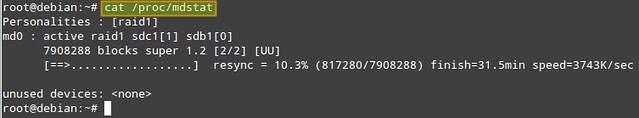
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to obtain more information about a RAID array (both while it's being assembled and after the process is finished) is:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --query /dev/md0
|
||||
# mdadm --detail /dev/md0 (or mdadm -D /dev/md0)
|
||||
|
||||
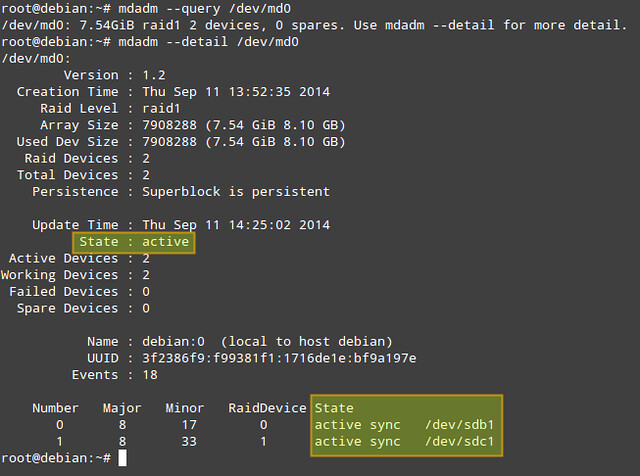
|
||||
|
||||
Of the information provided by 'mdadm -D', perhaps the most useful is that which shows the state of the array. The active state means that there is currently I/O activity happening. Other possible states are clean (all I/O activity has been completed), degraded (one of the devices is faulty or missing), resyncing (the system is recovering from an unclean shutdown such as a power outage), or recovering (a new drive has been added to the array, and data is being copied from the other drive onto it), to name the most common states.
|
||||
|
||||
### Formatting and Mounting a RAID Array ###
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is formatting (with ext4 in this example) the array:
|
||||
|
||||
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/md0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now let's mount the array, and verify that it was mounted correctly:
|
||||
|
||||
# mount /dev/md0 /mnt
|
||||
# mount
|
||||
|
||||
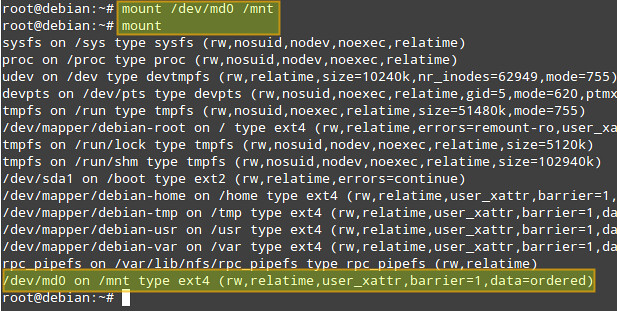
|
||||
|
||||
### Monitor a RAID Array ###
|
||||
|
||||
The mdadm tool comes with RAID monitoring capability built in. When mdadm is set to run as a daemon (which is the case with our RAID setup), it periodically polls existing RAID arrays, and reports on any detected events via email notification or syslog logging. Optionally, it can also be configured to invoke contingency commands (e.g., retrying or removing a disk) upon detecting any critical errors.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, mdadm scans all existing partitions and MD arrays, and logs any detected event to /var/log/syslog. Alternatively, you can specify devices and RAID arrays to scan in mdadm.conf located in /etc/mdadm/mdadm.conf (Debian-based) or /etc/mdadm.conf (Red Hat-based), in the following format. If mdadm.conf does not exist, create one.
|
||||
|
||||
DEVICE /dev/sd[bcde]1 /dev/sd[ab]1
|
||||
|
||||
ARRAY /dev/md0 devices=/dev/sdb1,/dev/sdc1
|
||||
ARRAY /dev/md1 devices=/dev/sdd1,/dev/sde1
|
||||
.....
|
||||
|
||||
# optional email address to notify events
|
||||
MAILADDR your@email.com
|
||||
|
||||
After modifying mdadm configuration, restart mdadm daemon:
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
# service mdadm restart
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora, CentOS/RHEL 7:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl restart mdmonitor
|
||||
|
||||
On CentOS/RHEL 6:
|
||||
|
||||
# service mdmonitor restart
|
||||
|
||||
### Auto-mount a RAID Array ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now we will add an entry in the /etc/fstab to mount the array in /mnt automatically during boot (you can specify any other mount point):
|
||||
|
||||
# echo "/dev/md0 /mnt ext4 defaults 0 2" << /etc/fstab
|
||||
|
||||
To verify that mount works okay, we now unmount the array, restart mdadm, and remount. We can see that /dev/md0 has been mounted as per the entry we just added to /etc/fstab:
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt
|
||||
# service mdadm restart (on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint)
|
||||
or systemctl restart mdmonitor (on Fedora, CentOS/RHEL7)
|
||||
or service mdmonitor restart (on CentOS/RHEL6)
|
||||
# mount -a
|
||||
|
||||
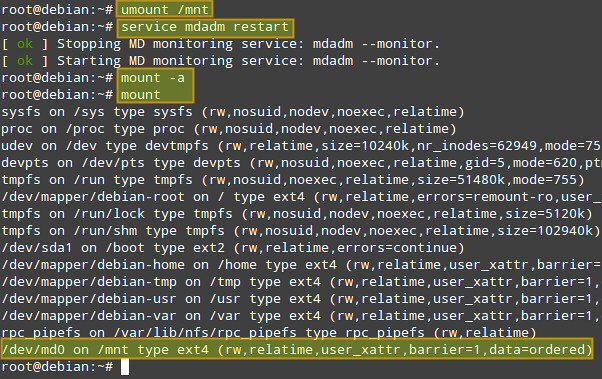
|
||||
|
||||
Now we are ready to access the RAID array via /mnt mount point. To test the array, we'll copy the /etc/passwd file (any other file will do) into /mnt:
|
||||
|
||||
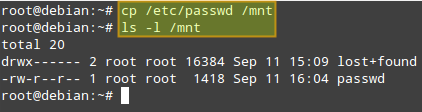
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, we need to tell the mdadm daemon to automatically start the RAID array during boot by setting the AUTOSTART variable to true in the /etc/default/mdadm file:
|
||||
|
||||
AUTOSTART=true
|
||||
|
||||
### Simulating Drive Failures ###
|
||||
|
||||
We will simulate a faulty drive and remove it with the following commands. Note that in a real life scenario, it is not necessary to mark a device as faulty first, as it will already be in that state in case of a failure.
|
||||
|
||||
First, unmount the array:
|
||||
|
||||
# umount /mnt
|
||||
|
||||
Now, notice how the output of 'mdadm -D /dev/md0' indicates the changes after performing each command below.
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm /dev/md0 --fail /dev/sdb1 #Marks /dev/sdb1 as faulty
|
||||
# mdadm --remove /dev/md0 /dev/sdb1 #Removes /dev/sdb1 from the array
|
||||
|
||||
Afterwards, when you have a new drive for replacement, re-add the drive again:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb1
|
||||
|
||||
The data is then immediately started to be rebuilt onto /dev/sdb1:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that the steps detailed above apply for systems with hot-swappable disks. If you do not have such technology, you will also have to stop a current array, and shutdown your system first in order to replace the part:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --stop /dev/md0
|
||||
# shutdown -h now
|
||||
|
||||
Then add the new drive and re-assemble the array:
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm /dev/md0 --add /dev/sdb1
|
||||
# mdadm --assemble /dev/md0 /dev/sdb1 /dev/sdc1
|
||||
|
||||
Hope this helps.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/create-software-raid1-array-mdadm-linux.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/gabriel
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
How to install Arch Linux the easy way with Evo/Lution
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
The one who ventures into an install of Arch Linux and has only experienced installing Linux with Ubuntu or Mint is in for a steep learning curve. The number of people giving up halfway is probably higher than the ones that pull it through. Arch Linux is somewhat cult in the way that you may call yourself a weathered Linux user if you succeed in setting it up and configuring it in a useful way.
|
||||
|
||||
Even though there is a [helpful wiki][1] to guide newcomers, the requirements are still too high for some who set out to conquer Arch. You need to be at least familiar with commands like fdisk or mkfs in a terminal and have heard of mc, nano or chroot to make it through this endeavour. It reminds me of a Debian install 10 years ago.
|
||||
|
||||
For those ambitious souls that still lack some knowledge, there is an installer in the form of an ISO image called [Evo/Lution Live ISO][2] to the rescue. Even though it is booted like a distribution of its own, it does nothing but assist with installing a barebone Arch Linux. Evo/Lution is a project that aims to diversify the user base of Arch by providing a simple way of installing Arch as well as a community that provides comprehensive help and documentation to that group of users. In this mix, Evo is the (non-installable) live CD and Lution is the installer itself. The project's founders see a widening gap between Arch developers and users of Arch and its derivative distributions, and want to build a community with equal roles between all participants.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The software part of the project is the CLI installer Lution-AIS which explains every step of what happens during the installation of a pure vanilla Arch. The resulting installation will have all the latest software that Arch has to offer without adding anything from AUR or any other custom packages.
|
||||
|
||||
After booting up the ISO image, which weighs in at 422 MB, we are presented with a workspace consisting of a Conky display on the right with shortcuts to the options and a LX-Terminal on the left waiting to run the installer.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After setting off the actual installer by either right-clicking on the desktop or using ALT-i, you are presented with a list of 16 jobs to be run. It makes sense to run them all unless you know better. You can either run them one by one or make a selection like 1 3 6 or 1-4 or do them all at once by entering 1-16. Most steps need to be confirmed with a 'y' for yes, and the next task waits for you to hit Enter. This will allow time to read the installation guide which is hidden behind ALT-g or even walking away from it.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The 16 steps are divided in "Base Install" and "Desktop Install". The first group takes care of localization, partitioning, and installing a bootloader.
|
||||
|
||||
The installer leads you through partitioning with gparted, gdisk, and cfdisk as options.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After you have created partitions (e.g., /dev/sda1 for root and /dev/sda2 for swap using gparted as shown in the screenshot), you can choose 1 out of 10 file systems. In the next step, you can choose your kernel (latest or LTS) and base system.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
After installing the bootloader of your choice, the first part of the install is done, which takes approximately 12 minutes. This is the point where in plain Arch Linux you reboot into your system for the first time.
|
||||
|
||||
With Lution you just move on to the second part which installs Xorg, sound and graphics drivers, and then moves on to desktop environments.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The installer detects if an install is done in VirtualBox, and will automatically install and load the right generic drivers for the VM and sets up **systemd** accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
In the next step, you can choose between the desktop environments KDE, Gnome, Cinnamon, LXDE, Enlightenment, Mate or XFCE. Should you not be friends with the big ships, you can also go with a Window manager like Awesome, Fluxbox, i3, IceWM, Openbox or PekWM.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Part two of the installer will take under 10 minutes with Cinnamon as the desktop environment; however, KDE will take longer due to a much larger download.
|
||||
|
||||
Lution-AIS worked like a charm on two tries with Cinnamon and Awesome. After the installer was done and prompted me to reboot, it took me to the desired environments.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
I have only two points to criticize: when the installer offered me to choose a mirror list and when it created the fstab file. In both cases it opened a second terminal, prompting me with an informational text. It took me a while to figure out I had to close the terminals before the installer would move on. When it prompts you after creating fstab, you need to close the terminal, and answer 'yes' when asked if you want to save the file.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
The second of my issues probably has to do with VirtualBox. When starting up, you may see a message that no network has been detected. Clicking on the top icon on the left will open wicd, the network manager that is used here. Clicking on "Disconnect" and then "Connect" and restarting the installer will get it automatically detected.
|
||||
|
||||
Evo/Lution seems a worthwhile project, where Lution works fine. Not much can be said on the community part yet. They started a brand new website, forum, and wiki that need to be filled with content first. So if you like the idea, join [their forum][3] and let them know. The ISO image can be downloaded from [the website][4].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2014/09/install-arch-linux-easy-way-evolution.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ferdinand Thommes][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://xmodulo.com/author/ferdinand
|
||||
[1]:https://wiki.archlinux.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.evolutionlinux.com/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.evolutionlinux.com/forums/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.evolutionlinux.com/downloads.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to create a MySQL database from the command line
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I have a MySQL server up and running somewhere. How can I create and populate a MySQL database from the command line?
|
||||
|
||||
To create a MySQL database from the command line, you can use mysql CLI client. Here is a step-by-step procedure to create and populate a MySQL database using mysql client from the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step One: Install MySQL Client ###
|
||||
|
||||
Of course you need to make sure that MySQL client program is installed. If not, you can install it as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
On Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install mysql-client
|
||||
|
||||
On Fedora, CentOS or RHEL:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum install mysql
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Two: Log in to a MySQL Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
To begin, first log in to your MySQL server as root with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -h <mysql-server-ip-address> -p
|
||||
|
||||
Note that to be able to log in to a remote MySQL server, you need to [enable remote access on the server][1]. If you are invoking mysql command on the same host where the MySQL server is running, you can omit "-h <mysql-server-ip-address>" as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
$ mysql -u root -p
|
||||
|
||||
You will be then asked for the password of the MySQL root user. If the authentication succeeds, the MySQL prompt will appear.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step Three: Create a MySQL Database ###
|
||||
|
||||
Before you start typing commands at the MySQL prompt, remember that each command must end with a semicolon (otherwise it will not execute). In addition, consider using uppercase letters for commands and lowercase letter for database objects. Note that this is not required but helpful for reading.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's create a database named xmodulo_DB:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS xmodulo_DB;
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step Four: Create a MySQL Table ###
|
||||
|
||||
For a demonstration purpose, we will create a tabled called posts_tbl where we want to store the following information about posts:
|
||||
|
||||
- Text of article
|
||||
- Author's first name
|
||||
- Author's last name
|
||||
- Whether the post is enabled (visible) or not
|
||||
- Date when article was posted
|
||||
|
||||
This process is actually performed in two steps:
|
||||
|
||||
First, select the database that we want to use:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> USE xmodulo_DB;
|
||||
|
||||
Then create a new table in the database:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> CREATE TABLE 'posts_tbl' (
|
||||
'post_id' INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
|
||||
'content' TEXT,
|
||||
'author_FirstName' VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
|
||||
'author_LastName' VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL ,
|
||||
'isEnabled' TINYINT(1) NOT NULL DEFAULT 1,
|
||||
'date' TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ,
|
||||
PRIMARY KEY ( 'post_id' )
|
||||
) TYPE = MYISAM;
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### Step Five: Create a User Account and Grant Permissions ###
|
||||
|
||||
When it comes to accessing our newly created database and tables, it's a good idea to create a new user account, so it can access that database (and that database only) without full permissions to the whole MySQL server.
|
||||
|
||||
You can create a new user, grant permissions and apply changes in two easy steps as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON xmodulo_DB.* TO 'new_user'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'new_password';
|
||||
mysql> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
|
||||
|
||||
where 'new_user' and 'new_password' refer to the new user account name and its password, respectively. This information will be stored in the mysql.user table, and the password will be encrypted.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Six: Testing ###
|
||||
|
||||
Let's insert one dummy record to the posts_tbl table:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> USE xmodulo_DB;
|
||||
mysql> INSERT INTO posts_tbl (content, author_FirstName, author_LastName)
|
||||
VALUES ('Hi! This is some dummy text.', 'Gabriel', 'Canepa');
|
||||
|
||||
Then view all the records in posts_tbl table:
|
||||
|
||||
mysql> SELECT * FROM posts_tbl;
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Note that MySQL automatically inserted the proper default values in the fields where we defined them earlier (e.g., 'isEnabled' and 'date').
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/create-mysql-database-command-line.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/2012/06/how-to-allow-remote-access-to-mysql.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
|
||||
Network Installation of “Debian 7 (Whezzy) on Client Machines using DNSMASQ Network Boot Server
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
This tutorial will guide you on how you can install **Debian 7 (Whezzy)** directly from a network location using **DNSMASQ** as a **PXE Server (Preboot eXecution Environment)**, in case your server doesn’t provide any method to boot from a CD/DVD/USB media drive or it just can operate with an attached monitor, keyboard and mouse.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Debian 7 Network Installation on Client Machines
|
||||
|
||||
**DNSMASQ** is a lightweight network infrastructure server which can provide crucial network services such as DNS, DHCP and Network Boot, using a build-in DNS, DHCP and TFTP server.
|
||||
|
||||
Once the PXE server is up and running you can instruct all your clients machines to directly boot from network, with the specifications that your clients must own a network card that supports network booting, which can be enabled from BIOS under Network Boot or Boot Services option.
|
||||
|
||||
### Requirements ###
|
||||
|
||||
- [Debian 7 (Wheezy) Installation Guide][1]
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Install and Configure DNSMASQ Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
**1.** On first hand, after you install Debian Server assure that your system uses a **Static IP Address**, because, besides network booting, will also provide DHCP service for your entire network segment. Once the Static IP Address has been configured run the following command from root account or using a user with root powers to install DNSMASQ server.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install dnsmasq
|
||||
|
||||
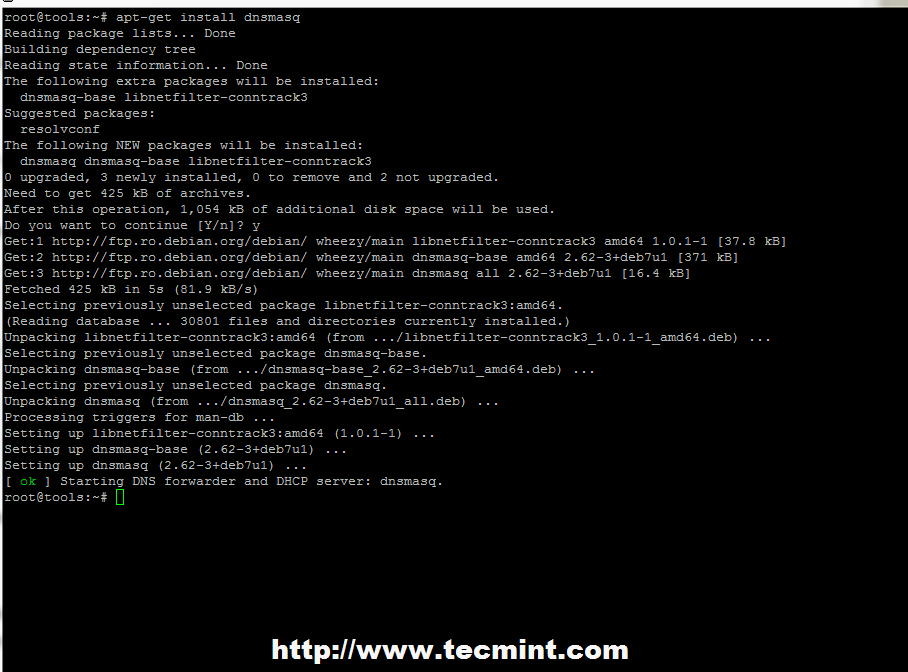
|
||||
|
||||
Install Dnsmasq Package
|
||||
|
||||
**2.** Once DNSMASQ package installed, you can start editing its configuration file. First create a backup of the main configuration and then start editing **dnsmasq.conf** file by issuing the following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
# mv /etc/dnsmasq.conf /etc/dnsmasq.conf.backup
|
||||
# nano /etc/dnsmasq.conf
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Backup Dnsmasq Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
**3.** The above backup process consisted on renaming the main configuration file, so the new file should be an empty one. Use the following excerpt for **DNSMASQ** configuration file as described below.
|
||||
|
||||
interface=eth0
|
||||
domain=debian.lan
|
||||
dhcp-range=192.168.1.3,192.168.1.253,255.255.255.0,1h
|
||||
dhcp-boot=pxelinux.0,pxeserver,192.168.1.100
|
||||
pxe-prompt="Press F8 for menu.", 60
|
||||
#pxe-service types: x86PC, PC98, IA64_EFI, Alpha, Arc_x86, Intel_Lean_Client, IA32_EFI, BC_EFI, Xscale_EFI and X86-64_EFI
|
||||
pxe-service=x86PC, "Install Debian 7 Linux from network server 192.168.1.100", pxelinux
|
||||
enable-tftp
|
||||
tftp-root=/srv/tftp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Configuration of Dnsmasq
|
||||
|
||||
- **interface** – The network interface that the server should listen.
|
||||
- **domain** – Replace it with your domain name.
|
||||
- **dhcp-range** – Replace it with your network IP range defined by your network mask.
|
||||
- **dhcp-boot** – Leave it as default but replace the IP statement with your server IP Address.
|
||||
- **pxe-prompt** – Leave it as default – requires **F8 key strike** to enter menu 60 with seconds wait time.
|
||||
- **pxe=service** – Use **x86PC** for 32-bit/64-bit architectures and enter a menu description prompt under string quotes. Other values types can be: PC98, IA64_EFI, Alpha, Arc_x86, Intel_Lean_Client, IA32_EFI, BC_EFI, Xscale_EFI and X86-64_EFI.
|
||||
- **enable-tftp** – Enables the build-in TFTP server.
|
||||
- **tftp-root** – Use /srv/tftp is the location for Debian netboot files.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Download Debian Netboot Files and Open Firewall Connection ###
|
||||
|
||||
**4.** Now it’s time to download Debian Network Boot files. First, change your current working directory path to **TFTP Root** location defined by the last configuration statement (**/srv/tftp** system path ).
|
||||
|
||||
Go to a offical page mirror of [Debian Netinstall][2] – [Network boot section][3] and grab the following files depending on your system architecture that you want to install it on your clients.
|
||||
|
||||
Once, you download **netboot.tar.gz** file, extract archive at the same time (this procedure describes only for 64-bit but the same procedure applies for other system architectures).
|
||||
|
||||
# cd /srv/tftp/
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-amd64/current/images/netboot/netboot.tar.gz
|
||||
# tar xfz netboot.tar.gz
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-amd64/current/images/SHA256SUMS
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/Release
|
||||
# wget http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/Release.gpg
|
||||
|
||||
Also it may be necessary to make all files in **TFTP** directory readable for TFTP server.
|
||||
|
||||
# chmod -R 755 /srv/tftp/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Download Debian NetBoot Files
|
||||
|
||||
Use the following variables for **Debian Netinstall** mirrors and architectures.
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-"$ARCH"/current/images/netboot/netboot.tar.gz
|
||||
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/main/installer-"$ARCH"/current/images/SHA256SUMS
|
||||
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/Release
|
||||
# wget http://"$YOURMIRROR"/debian/dists/wheezy/Release.gpg
|
||||
|
||||
**5.** On the next step start or restart DNSMASQ daemon and run netstat command to get a list of ports that the server is listening.
|
||||
|
||||
# service dnsmasq restart
|
||||
# netstat -tulpn | grep dnsmasq
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Start Dnsmasq Service
|
||||
|
||||
**6.** Debian based distribution usually ships with **UFW Firewall** package. Use the following commands to open the required **DNSMASQ** port numbers: **67** (Bootps), **69** (TFTP) **53** (DNS), **4011** (proxyDHCP) udp and **53** tcp (DNS).
|
||||
|
||||
# ufw allow 69/udp
|
||||
# ufw allow 4011/udp ## Only if you have a ProxyDHCP on the network
|
||||
# ufw allow 67/udp
|
||||
# ufw allow 53/tcp
|
||||
# ufw allow 53/udp
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Open Dnsmasq Ports
|
||||
|
||||
Now, the PXE loader located on your client network interface will load **pxelinux** configuration files from **/srv/tftp/pxelinux.cfg** directory using this order.
|
||||
|
||||
- GUID files
|
||||
- MAC files
|
||||
- Default file
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Configure Clients to Boot from Network ###
|
||||
|
||||
**7.** To enable network boot for a client computer enter your system **BIOS configuration** (please consult the hardware motherboard vendor documentation for entering BIOS settings).
|
||||
|
||||
Go to **Boot menu** and select **Network boot** as the **primary boot device** (on some systems you can select the boot device without entering BIOS configuration just by pressing a key during **BIOS POST**).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Select BIOS Settings
|
||||
|
||||
**8.** After editing the boot order sequence, usually, press **F10** to save BIOS settings. After reboot, your client computer should boot directly from network and the first **PXE** prompt should appear demanding you to press **F8** key to enter menu.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, hit **F8** key to move forward and a new prompt should appear. Hit **Enter** key again and the main **Debian Installer** prompt should appear on your screen as in the screenshots below.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Boot Menu Selection
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Select Debian Installer Boot
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Select Debian Install
|
||||
|
||||
From here on you can start install Debian on your machine using the Debian 7 Wheezy procedure (installation link given above), but you can also need to make sure that your machine has an active Internet connection in order to be able to finish installation process.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Debug DNSMASQ Server and Enable it System-Wide ###
|
||||
|
||||
**9.** To diagnosticate the server for eventual occurred problems or other information offered to clients run the following command to open log file.
|
||||
|
||||
# tailf /var/log/daemon.log
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Debug DNSMASQ Server
|
||||
|
||||
**10.** If everything is in place during server tests you can now enable **DNSMASQ** daemon to automatically start after system reboot with the help of **sysv-rc-conf** package.
|
||||
|
||||
# apt-get install sysv-rc-conf
|
||||
# sysv-rc-conf dnsmaq on
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Enable DNSMASQ Daemon
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all! Now your **PXE** server is ready to allocate IP addresses (**DHCP**) and to offer the required boot information for all your network segment clients which will be configured to boot and install Debian Wheezy from network.
|
||||
|
||||
Using PXE network boot installation has some advantages on networks with an increased number of server hosts because you can set up the entire network infrastructure in a short period of time or the same time, facilitates the distribution upgrading process, and, can also automate the entire installation process using kickstart files.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/network-installation-of-debian-7-on-client-machines/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matei Cezar][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/cezarmatei/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/debian-gnulinux-7-0-code-name-wheezy-server-installation-guide/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.debian.org/distrib/netinst#netboot
|
||||
[3]:http://ftp.nl.debian.org/debian/dists/wheezy/main/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
来自Ubuntu开发团队关于Mir和Unity 8的状态更新
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 目前Unity 8和Mir的开发进度很慢,但是仍在进行中
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**和其他项目一样,Canonical也在开发Unity桌面环境与Mir显示服务。开发团队刚刚发布了一个小的更新来据此让我们知道发生了些什么**
|
||||
|
||||
Ubuntu开发者可能刚刚集中精力在一些重要的发布上,就像接下来的Ubuntu 14.10(Utopic Unicorn) 或者是新的面向移动设备的Ubuntu Touch,但是他们同样也涉及想Mir以及Unity 8这样的项目。
|
||||
|
||||
目前这代Ubuntu系统使用的是Unity 7桌面环境,但是新一代已经酝酿了很长一段时间。与新的显示服务一起,已经在Ubuntu的移动版中了,但最终也要将它带到桌面上。
|
||||
|
||||
这两个项目的领导Kevin Gunn经常发布一些来自开发者的进度信息以及这周以来的一些改变,虽然这些都很粗略。
|
||||
|
||||
根据 [开发团队][1]的消息, 一些关于触摸/高难度的问题已经修正了,几个翻译问题也已经修复了,一些Dash UI相关的问题已经修复了,目前 团队在开发Mir 0.8,Mir 0.7.2已经推广了,同时一些高优先级的bug也在进行中。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以下载 Ubuntu Next
|
||||
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 14.10 Daily Build (ISO) 64-bit][2]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 14.10 Daily Build (ISO) 32-bit][3]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu 14.10 Daily Build (ISO) 64-bit Mac][4]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Desktop Next 14.10 Daily Build (ISO) 64-bit][5]
|
||||
- [Ubuntu Desktop Next 14.10 Daily Build (ISO) 32-bit][6]
|
||||
|
||||
这个的特性是新的Unity 8以及Mir,但是还不完全。直到有一个明确的方向之前,它还会持续一会。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://news.softpedia.com/news/Mir-and-Unity-8-Update-Arrive-from-Ubuntu-Devs-459263.shtml
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Silviu Stahie][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://news.softpedia.com/editors/browse/silviu-stahie
|
||||
[1]:https://lists.launchpad.net/ubuntu-phone/msg09875.html
|
||||
[2]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/daily-live/current/utopic-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
[3]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/daily-live/current/utopic-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
[4]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/daily-live/current/utopic-desktop-amd64+mac.iso
|
||||
[5]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-desktop-next/daily-live/current/utopic-desktop-amd64.iso
|
||||
[6]:http://cdimage.ubuntu.com/ubuntu-desktop-next/daily-live/current/utopic-desktop-i386.iso
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
|
||||
在哪儿以及怎么写代码:选择最好的免费代码编辑器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
深入了解一下Cloud9,Koding和Nitrous.IO。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**已经准备好开始你的第一个编程项目了吗?很好!只要配置一下**终端或命令行,学习如何使用并安装所有要用到的编程语言,插件库和API函数库。当最终准备好一切以后,再安装好[Visual Studio][1]就可以开始了,然后才可以预览自己的工作。
|
||||
|
||||
至少这是大家过去已经熟悉的方式。
|
||||
|
||||
也难怪初学程序员们逐渐喜欢上在线集成开发环境(IDE)了。IDE是一个代码编辑器,不过已经准备好编程语言以及所有需要的依赖,可以让你避免把它们一一安装到电脑上的麻烦。
|
||||
|
||||
我想搞清楚到底是哪些因素能组成一个典型的IDE,所以我试用了一下免费级别的时下最受欢迎的三款集成开发环境:[Cloud9][2],[Koding][3]和[Nitrous.IO][4]。在这个过程中,我了解了许多程序员应该或不应该使用IDE的各种情形。
|
||||
|
||||
### 为什么要用IDE? ###
|
||||
|
||||
假如有一个像Microsoft Word那样的文字编辑器,想想类似Google Drive那样的IDE吧。你可以拥有类似的功能,但是它还能支持从任意电脑上访问,还能随时共享。因为因特网在项目工作流中的影响已经越来越重要,IDE也让生活更轻松。
|
||||
|
||||
在我最近的一篇ReadWrite教程中我使用了Nitrous.IO,这是在文章[创建一个你自己的像Yo那样的极端简单的聊天应用][5]里的一个Python应用。当使用IDE的时候,你只要选择你要用的编程语言,然后通过IDE特别设计用来运行这种语言程序的虚拟机(VM),你就可以测试和预览你的应用了。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你读过那篇教程,就会知道我的那个应用只用到了两个API库-信息服务Twilio和Python微框架Flask。在我的电脑上就算是使用文字编辑器和终端来做也是很简单的,不过我选择使用IDE还有一个方便的地方:如果大家都使用同样的开发环境,跟着教程一步步走下去就更简单了。
|
||||
|
||||
### IDE不能做的事情 ###
|
||||
|
||||
到目前为止,IDE还不是一个长期托管方案。
|
||||
|
||||
当你使用IDE工作的时候,你可以在云上构建,测试和预览你的应用。你甚至还可以直接通过链接共享你的最终作品。
|
||||
|
||||
但是不能用IDE来永久存储你的整个项目。把帖子保存在Google Drive文件中不会让你的博客丢失。类似Google Drive,IDE可以让你创建链接用于共享内容,但是任何一个都还不足以替代真正的托管服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
还有,IDE并不是设计成方便广泛共享。尽管各种IDE都在不断改善大多数文字编辑器的预览功能,还只能用来给你的朋友或同事展示一下应用预览,而不是,比如说,类似Hacker News的主页。那样的话,占用太多带宽的IDE也许会让你崩溃。
|
||||
|
||||
这样说吧:IDE只是构建和测试你的应用的地方,托管服务器才是它们生存的地方。所以一旦完成了你的应用,你会希望把它布置到能长期托管的云服务器上,最好是能免费托管的那种,例如[Heroku][6]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 选择一个IDE ###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
随着IDE变得越来越流行,选择也越来越多。在我眼里,没有一个是完美的。不过,还是有些IDE在完成某些工作方面相对来说有些优势。
|
||||
|
||||
我尝试了一下免费级别的三个最受欢迎的集成开发环境:Cloud9,Koding和Nitrous.IO。每一个都有自己的优点,当然跟你用来做的事情有关系。下面就是我的发现。
|
||||
|
||||
### Cloud9:乐于协作 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当我完成了Cloud9的注册后,它提示的第一件事情就是添加我的GitHub和BitBucket账号。马上,所有我的GitHub项目,个人的和协作的,都可以直接克隆到本地并使用Cloud9的开发工具开始工作。其他的IDE在和GitHub集成的方面都没有达到这种水准。
|
||||
|
||||
在我测试的这三款IDE中,Cloud9看起来更加侧重于一个可以让协同工作的人们无缝衔接工作的环境。在这里,它并不是角落里放个聊天窗口。实际上,按照CEO Ruben Daniels说的,试用Cloud9的协作者可以互相看到其他人实时的编码情况,就像Google Drive上的合作者那样。
|
||||
|
||||
“大多数IDE服务的协同功能只能操作单一文件”,Daniels说,“而我们的产品可以支持整个项目中的不同文件。协同功能被完美集成到了我们的IDE中。”
|
||||
|
||||
### Koding:在你需要的时候能提供帮助 ###
|
||||
|
||||
IDE可以提供你所需的工具来构建和测试所有开源编程语言的应用。对于初学者来说,看起来有点吓人。举个例子,如果我要做一个项目同时用到Python和Ruby组件,那我要用哪个VM来测试?
|
||||
|
||||
答案是两个都要,尽管使用免费账号的话,只能够同时打开一个VM用于测试。我就在Koding的控制面板里找到了答案,一个折叠起来的地方,用户可以提供或获得他们Koding项目的各种经验。在这三者中间,它是最容易使用的,拥有一个你可以寻求帮助并很快有人回答的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
“我们在这款产品里加入了一个积极的社区功能”,Koding的首席商务官Nitin Gupta说,“我们希望搭建一个环境,真正吸引那些希望得到帮助和愿意提供帮助的人们。”
|
||||
|
||||
### Nitrous.IO: An IDE Wherever You Want ###
|
||||
|
||||
相对于自己的桌面环境,使用IDE的最大优势是它是自包含的。你不需要安装任何其他的就可以使用。而另一方面,使用自己的桌面环境的最大优势就是你可以在本地工作,甚至在没有互联网的情况下。
|
||||
|
||||
Nitrous.IO结合了这两个优势。你可以在网站上在线使用这个IDE,你也可以把它下载到自己的饿电脑上,共同创始人AJ Solimine这样说。优点是你可以结合Nitrous的集成性和你最喜欢的文字编辑器的熟悉。
|
||||
|
||||
他说:“你可以使用任意当代浏览器访问Nitrous.IO的在线IDE网站,但我们仍然提供了方便的Windows和Mac桌面应用,可以让你使用你最喜欢的编辑器来写代码。”
|
||||
|
||||
### 底线 ###
|
||||
|
||||
这一个星期的[使用][7]三个不同IDE的最让我意外的收获?它们是如此相似。[当用来做最基本的代码编辑的时候][8],它们都一样的好用。
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud9,Koding,[和Nitrous.IO都支持][9]所有主流的开源编程语言,从Ruby到Python到PHP到HTML5。你可以选择任何一种VM。
|
||||
|
||||
Cloud9和Nitrous.IO都实现了GitHub的一键集成。Koding需要[多几个步骤][10],不过也是可以实现的。
|
||||
|
||||
每一个都轻松地集成了我需要的API。每一个也都可以让我自己安装喜欢的包(Koding需要超级用户权限)。它们都带有内置的终端,可以用来轻松地测试和布置项目。三个都支持轻松地预览项目。当然,它们也都把我的项目托管在云服务器中,所以我在任意地方都可以在上边工作。
|
||||
|
||||
不好的一面,它们都有相同的缺陷,不过考虑到它们都是免费的也还合理。你每次只能同时运行一个VM来测试特定编程语言写出的程序。而当你一段时间没有使用VM之后,IDE会把VM切换成休眠模式以节省带宽,而下次要用的时候就得等它重新加载(Cloud9在这一点上更加费力)。它们中也没有任何一个为已完成的项目提供像样的永久托管服务。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,对咨询我是否有一个完美的免费IDE的人,答案是可能没有。但是这也要看你侧重的地方,对你的某个项目来说也许有一个完美的IDE。
|
||||
|
||||
图片由[Shutterstock][11]友情提供
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/14/cloud9-koding-nitrousio-integrated-development-environment-ide-coding
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Lauren Orsini][a]
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/lauren-orsini
|
||||
[1]:http://www.visualstudio.com/
|
||||
[2]:http://c9.io/
|
||||
[3]:https://koding.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://nitrous.io/
|
||||
[5]:http://readwrite.com/2014/07/11/one-click-messaging-app
|
||||
[6]:http://heroku.com/
|
||||
[7]:http://help.nitrous.io/ide-general/
|
||||
[8]:https://www.nitrous.io/desktop
|
||||
[9]:https://www.nitrous.io/desktop
|
||||
[10]:https://koding.com/Activity/steps-clone-projects-github-koding-1-create-account-github-2-open-your-terminal-3
|
||||
[11]:http://www.shutterstock.com/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
为什么你的公司需要参与更多开源软件的编写
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
>闭关锁国是产生不了创新的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**华尔街日报 [称][1],有消息表明,Zulily正在开发** 更多的内部软件,但实际上根本不是。多年前[Eric Raymond写道][2],全世界95%的软件写来用的,而不是售卖。原因很多,但是其中有一个比较突出:正如Zulily的CIO Luke Friang所说,几乎没有一个[非定制]软件解决方案能跟上我们的步伐。
|
||||
|
||||
20年前是这样,现在也是这样。
|
||||
|
||||
但是有一点是不同的,这也正是华尔街日报完全忽略的地方。而这也正是历史上开发的内部软件始终保持着专有的原因了,因为她是一个公司的 核心竞争力。然而今天,越来越多的公司意识到另一面:开源内部软件将会比保持专有获益更多。
|
||||
|
||||
这也就是为什么你的公司需要为开源项目做出更多的贡献。记住是更多。
|
||||
|
||||
我们刚刚经历了一个很不一样的20年,那时很多软件的开发都是为了内部的使用,大多数人的精力都放在由SAP和微软这样的厂商建立的应用广泛的企业级解决方案。
|
||||
|
||||
不管怎么说,这都是一个理论。
|
||||
|
||||
在实践中,买方花费很少的钱购买license,然后至少付出5倍以上的代价来使软件符合他们的需求。比如说,一个公司可能在一个ERP系统上花费 100,000美元,但是他们还得继续花费500,000来维持软件正常运行。
|
||||
|
||||
开源软件甚至是应用程序正式发展起来的原因之一是很多公司可以免费获得一些功能性的产品(或者是以一个相对便宜的费用获得产品), 然后定制为他们所需要的。不管怎样,定制是有必要的,而且开源的根本是使成本更低,或许,这样的定制或许能产生更好的结果。
|
||||
|
||||
同时,开发者尽量的减少同类之间的相似之处。作为Redmonk分析师,[Stephen O'Grady认为][3]:
|
||||
|
||||
> 从最近几年看,主流技术产业都有意避开专业化。运行在定制操作系统上的虚拟设备,已经彻底败给了RHEL和Windowns这些通用的操作系统。 最快20年,任何程序的数据保存都意味着一件事:一个关联的数据库,如果你要做的是企业级应用开发,那么你首先要接触的是Java,等等。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,开源的道路上,一些公司也发现,有些销售商不能很好地描述他们所想要的,即便是很好理解的产品类别,如像内容管理系统,他们需要 知道的是产品亮点,而不希望是一个模子刻出来的。
|
||||
|
||||
所以顾客没了,他们中有一部分上转变变成了供应商。
|
||||
|
||||
这也是常有的事,[O'Grady指出了][4]这一点。2010年,O'Grady发现了一个有趣的现象:“软件提供商正面对着一个强有力的市场竞争者:他们 的顾客。”
|
||||
|
||||
回想一下今天的高科技,大多数都是开源的,几乎所有的项目一开始都是某些公司的内部项目,或者仅仅是有些开发者的爱好,Linux,Git,Hadoop,Cassandra,MongDB,Android,等等。没有一个项目起初是为了售卖而产生的。
|
||||
|
||||
相反,这些项目通常是由一些公司维护,他们使用开源的资源来构建软件并[完善软件][5],这主要是一些Web公司。不像以前银行,医院和一些组织开发的软件只供内部使用,他们开源源码。
|
||||
|
||||
虽然,[有些公司避免定制软件][6],因为他们不想自己维护它,开源(稍微)减轻了这些发展中公司来维护一个项目的压力。从而为项目发起人均摊项目的开发成本,Yahoo,开始于Hadoop,但是现在最大的贡献者是Cloudera和Hortonworks。Facebook开始于Cassandra,但是现在主要是靠DataStax在维护。等等。
|
||||
|
||||
今天,真正的软件创新并不是闭门造车能造出来的,即便是可以,它也不会在那儿,开源项目颠覆了几十年的软件开发传统。
|
||||
|
||||
这不仅仅是一个人的一点点力量。
|
||||
|
||||
最好的开源项目都[发展得很快][7],但是这并不意味着别人在乎你的开源代码。[开放你的源码有显著的优缺点][8],其中一个很重要的优点是 很多伟大的开发者都希望为开源做出贡献:如果你也想找一个伟大的开发者跟你一起,你需要给他们一个开放的源代码来让他们工作。([Netflix][9]说)
|
||||
|
||||
但是,我们没有理由站在一边看,现在正是时候参与开源社区了,而不是一些不清楚的社区。是的,开源最大的参与者正是你们和你们的公司。 赶紧开始吧。
|
||||
|
||||
主要图片来自于Shutterstock. (注:Shutterstock是美国的一家摄影图片网站。)
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/16/open-source-software-business-zulily-erp-wall-street-journal
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matt Asay][a]
|
||||
译者:[barney-ro](https://github.com/barney-ro)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/matt-asay
|
||||
[1]:http://blogs.wsj.com/cio/2014/08/08/zulily-calls-in-house-software-a-differentiator-for-competitive-advantage/
|
||||
[2]:http://oreilly.com/catalog/cathbazpaper/chapter/ch05.html
|
||||
[3]:http://redmonk.com/sogrady/2010/01/12/roll-your-own/#ixzz3ATBuZsef
|
||||
[4]:http://redmonk.com/sogrady/2010/01/12/roll-your-own/
|
||||
[5]:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Cathedral_and_the_Bazaar
|
||||
[6]:http://www.abajournal.com/magazine/article/roll_your_own_software_hidden_dangers_on_the_road_less_traveled/
|
||||
[7]:http://readwrite.com/2013/12/12/open-source-innovation
|
||||
[8]:http://readwrite.com/2014/07/07/open-source-software-pros-cons
|
||||
[9]:http://techblog.netflix.com/2012/07/open-source-at-netflix-by-ruslan.html
|
||||
@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
|
||||
中国将要改变软件购买和销售的方式
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
> 这一切都是关于“开源”.
|
||||
|
||||
**中国并不需要开源,也不需要你的软件。具体说来,中国市场并不需要你的工程师日以继夜的工作,也不需要你提供的任何东西。
|
||||
|
||||
中国每年会产生超过100000名新软件工程师们,这些工程师会写出一大批令人惊叹的奇妙软件。如果有中国市场上尚未出现的软件,中国的工程师们就会从国外“借鉴”。在2012年,这样的软件掠夺达到了77%之多。对于那些已经面对着开源和云服务的挑战的软件卖家来说,中国无疑让他们的日子更苦难了。
|
||||
|
||||
不止是更困难,简直是举步维艰。
|
||||
|
||||
中国正在挑战西方公司在中国或者其他地方赚钱的模式。对于那些已经明白如何在中国运营的公司来说,他们的未来看起来一片光明。
|
||||
|
||||
### 抵制中国模式 ###
|
||||
|
||||
当然,并非每家公司都会坐以待毙。以微软为例,微软通用美国的国家司法权力来禁止中国公司做生意——除非他们像微软购买许可证。这是一种很聪明的做法,而且它可能会为微软创造数以十亿计的价值。但是最终这一做法看起来与中国市场格格不入。
|
||||
|
||||
原因很简单,中国与微软对待知识产权的态度十分不同。
|
||||
|
||||
正如 [我所提到的][2],“中国的企业更倾向于购买复杂的,面向企业的软件。因为这种软件比服务大众的公司设计出来的软件更先进,就像同在亚洲的印度。”但这种形势不会持续太久,因为中国的软件产业正在以一种惊人的速度前进,并毫无颓势。中国一定会坚持向西方国家“借鉴”代码直到有一天有足够的能力可以创造出有创新能力的软件。
|
||||
|
||||
但是即使这样,中国的软件公司与美国软件的运营模式还是有所不同,美国的软件大多都已经捆绑在设备、架构在云端或者公司只因为提供软件支持而要价。而这些运营模式中国是无法克隆的。
|
||||
|
||||
不出所料的,每一个收费模式是公司门使用“开源”进行盈利。
|
||||
|
||||
### 开源化中国 ###
|
||||
|
||||
正如CCID的分析师在 [J. Aaron Farr 的关于中国开源化报告][3] 中指出的,中国的开源社区规模很小而且没什么影响力。开源社区们没有大项目、参与者稀少而且资金匮乏。
|
||||
|
||||
这真是个坏消息。
|
||||
|
||||
好消息是,像华为这样的公司就把开源作为一种战略前景。具体而言,当华为的开源项目过时或者不是很强势的时候,这种现象就证明了他们的科技步伐是错误的。在与参与了开源项目的华为公司内部顾问的谈话中,虽然华为对如何参与到开源社区还处于摸索阶段,但他们总是对华为的开源项目赞不绝口。
|
||||
|
||||
这种无人关注开源的现象不会长久地持续下去。
|
||||
|
||||
从一件事就可以看出端倪。中国最大的互联网公司们都纷纷以积极地姿态拥抱开源,这意味着中国开源时代的到来。你若是和任意一位在百度、阿里巴巴、微博的员工谈话,你会发现他们的软件项目都是彻底开源的。这些开源的软件都是运行在这些公司自己研发的硬件上而不是西方的硬件上。
|
||||
|
||||
换句话说,这样的模式已经和西方的运营模式如出一辙了。
|
||||
|
||||
抬头看看 [现金软件行业内最炙手可热的新公司][5], 你就会知道中国的互联网公司未来的主流趋势,正如发生在西方世界的一样。不出意料的,许多都是关于“开源”。
|
||||
|
||||
### 销售给中国 ###
|
||||
|
||||
所有的一切都表明中国的软件行业不会像美国的软件行业发展历史一般发展。中国不会产生在柜台上卖卖软件就赚上亿美元的公司。因为西方对于知识产权的观念就是不适于中国的科技经济。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,软件卖家们需要售卖币软件更丰富的产品。云服务是一大前景。硬件设施看起来也是前途璀璨。软件支持和咨询服务(虽然有一些非主流)也很被公司门看好。总而言之,中国的软件行业会充满了开源味道,而不能靠着简单的售卖专柜软件的形式赚钱。
|
||||
|
||||
图片由 [hackNY.org][6] 提供。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
原文: http://readwrite.com/2014/08/12/china-opensource-software-ip-programmers-united-states
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Matt Asay][a]
|
||||
译者:[chi1shi2](https://github.com/chi1shi2)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://readwrite.com/author/matt-asay
|
||||
[1]:http://readwrite.com/2014/03/17/microsoft-anti-piracy-strategy-china
|
||||
[2]:http://readwrite.com/2014/04/11/india-starts-paying-for-software-china-it
|
||||
[3]:http://cdn.oreillystatic.com/en/assets/1/event/12/Open%20Source%20in%20China%20Presentation%201.pdf
|
||||
[4]:http://huawei.com/en/about-huawei/Partner/openathuawei/index.htm
|
||||
[5]:http://codingvc.com/which-technologies-do-startups-use-an-exploration-of-angellist-data
|
||||
[6]:https://www.flickr.com/photos/hackny/8675057448/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
Linus Torvalds推动Linux的桌面与嵌入式计算的发展
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> Linux的内核开发者和开源领袖Linus Torvalds最近表达了关于Linux桌面和嵌入式设备中Linux的未来的看法。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
什么是Linux桌面和嵌入式设备中Linux的未来?这是个值得讨论的问题,不过Linux的创始人和开源巨人Linus Torvalds在最近一届 [Linux 基金会][1] 的LinuxCon大会上,在一次对话中表达了一些有趣的观点。
|
||||
|
||||
作为敲出第一版Linux内核代码并且在1991年将它们共享在互联网上的家伙,Torvalds毫无疑问是开源软件甚至是任何软件中最著名的开发者,如今他依然活跃在其中。在此期间,Torvalds是许多人和组织中唯一一个引领着Linux发展的个体,它的观点往往能影响着开源社区,而且,作为一个内核开发者的角色赋予了他能决定哪些特点和代码能被放进操作系统内部的强大权利。
|
||||
|
||||
所以说,关注Torvalds所说的话是很值得的, "我还是挺想要桌面的。" [上周他在LinuxCon大会上这样说道][2] 那标志着他仍然着眼于作为使个人机更加强大的操作系统Linux的未来,尽管十年来Linux桌面市场的分享一直很少,而且大部分围绕Linux的商业活动都去涉及服务器或者安卓手机硬件去了。
|
||||
|
||||
但是,Torvalds还说,确保Linux桌面能有个宏伟的未来意味着解决了受阻的 “基础设施问题”,好像庞大的开源软件生态系统和硬件世界让他充满信心。这不是Linux核心代码本身的问题,而是要让Linux桌面渠道友好,这可能是伟大的Torvalds和他开发同伴们所需要花精力去达到的目标。这取决于app的开发者、硬件制造商和其它有志于实现人们能方便使用基于Linux的计算平台的各方力量。
|
||||
|
||||
另一方面,Torvalds也提到了他的憧憬,就是内核开发者们能简化嵌入式装置中的Linux代码——一个在让内核更加桌面友好化上会导致很多分歧的任务。但这也不一定,因为无论如何,Linux都是以模块化设计的,单内核代码库不能同时满足桌面用户和嵌入式开发者的需求,这是没有道理的,因为这取决于他们使用的模块。
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个长时间想看到更多搭载Linux的嵌入式设备出现的Linux桌面用户,我希望Torvalds的所有愿望都可以实现,到那时我就能只用Liunx来做所有我想做的事情,无论是在电脑桌面上、手机上、车上,或者是任何其它的地方。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://thevarguy.com/open-source-application-software-companies/082514/linus-torvalds-promotes-linux-desktops-and-embedded-compu
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Christopher Tozzi][a]
|
||||
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://thevarguy.com/author/christopher-tozzi
|
||||
[1]:http://linuxfoundation.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.eweek.com/enterprise-apps/linux-founder-linus-torvalds-still-wants-the-desktop.html
|
||||
23
translated/talk/20140902 Happy Birthday Email.md
Normal file
23
translated/talk/20140902 Happy Birthday Email.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,23 @@
|
||||
Email生日快乐
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**一个印度裔美国人用他天才的头脑发明了电子邮件,而从此以后我们没有哪一天可以离开电子邮件。**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
8月30日,电子邮件满32岁了。现在让我们一起熟悉一下这个快捷迅速的信息传递方式是怎么诞生的。这要感谢以为印度裔美国人,Shiva Ayyadurai。Shiva开发了一个全功能的办公室间邮件系统软件并命名为email。
|
||||
|
||||
在1982年8月30日,他被美国政府正式承认作为这个电脑程序的发明者。Shiva生于孟买的一个泰米尔家庭,发明email系统的时候只有14岁。当时他还在新泽西的利文斯顿高中学习,并开始为新泽西牙科和医科大学开发这个系统。email系统被授予版权,因为当时还没有其他方式被用来保护软件发明。
|
||||
|
||||
Ayyadurai从日常办公室之间的内部邮件往来方式里找到email系统的点子。他尝试复制普遍用来传送办公室之间邮件的‘气动管道系统’。这个系统使用了一个物理的管道网络来传送打印好的邮件给秘书。每一位秘书都有收件箱,发件箱,草稿箱,复写纸,文件夹,地址本,别针,或是附件等等。所有这些都用作建立和处理接收和发送邮件。
|
||||
|
||||
Shiva也记下了一些常用的模板,像“发给”,“来自”,“主题”,“日期”,“正文”,“抄送”,“密送”等等。所有这些模版也都被纳入电子邮件的版本中。电子邮件系统是用FORTRAN编程语言写的,Shiva发明了一个同样系统的电子版本。因为这件非凡的作品,Shiva获得了无数嘉奖,也赢得了1981年度高中毕业生的西屋科学天才奖。如今,由史密森学会美国历史国家博物馆持有“Email”的正式美国版权。但是,也有争论说不是Ayyadurai而是其他什么人发明了email。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.efytimes.com/e1/fullnews.asp?edid=147170
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Sanchari Banerjee
|
||||
译者:[zpl1025](https://github.com/zpl1025)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
|
||||
需要在Ubuntu上安装微软办公软件?去安装官方的网络应用程序
|
||||
================================================== ==============================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**这是微软办公软件及其一贯繁琐的文件指令,而不是每个人的一杯咖啡。同时这是许多工作和教育环境的主要依靠——无论是好还是坏**
|
||||
|
||||
通过使用[LibreOffice的应用程序套件][1],阅读、编辑和保存这些专有指令出现在Ubuntu上是有着某种程度的可能。在作家中,Calc和Impress都不同程度的夸耀微软办公软件文件的协作性,但在我自己的实际操作经验中(谢天谢地,它很简洁!)它并不完美。
|
||||
|
||||
时不时的,你会不得不使用微软办公软件,(虽然我们大多数人都心里向着开放标准,但是我们不应该无视实际问题)但你已经没有意愿去购买一个完整的微软办公软件许可证来运行这个窗口模拟器,那么微软的在线网络应用程序是完美的解决方法。
|
||||
|
||||
###安装微软在线办公软件上的应用程序在Ubuntu###
|
||||
|
||||
为了使从Ubuntu的桌面访问这些在线版本更容易,“Linux的网络应用程序项目”创造了一个小的、非官方的安装程序。它可以添加网络应用程序的快捷方式(“荣耀书签”)到您的应用程序启动器。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
通过快捷方式,相应的Microsoft Web应用程序在你默认的系统浏览器中打开,不可能有比这更精美的了。听起来漂亮吗?下面是你的应用程序的快捷方式:
|
||||
|
||||
- 文档
|
||||
- 表格
|
||||
- 幻灯片
|
||||
- Outlook
|
||||
- OneDrive
|
||||
- 日历
|
||||
- OneNote
|
||||
- 通讯录
|
||||
|
||||
该软件包还创建了一个新的应用程序类别来容纳这些链接,不但可以让您把这些快捷方式从其他应用程序单独分开来,而且是直接位于常见的“办公软件”应用程序下。
|
||||
|
||||
这些都是必不可少的吗?不见得。他们有用吗?这取决于你的工作流程。但它是不错的选择吗?一定是的。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以从下面的链接保存含有.deb文件安装程序,其中有安装链接。适用于Ubuntu14.04 LTS和更高版本。
|
||||
|
||||
- [下载微软的在线办公应用(.deb)][2]
|
||||
|
||||
###其他可选项###
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
类似的替代方案是[安装Chrome官方网上应用商店的在线办公应用程序][3],然后添加应用程序启动器到Linux。这次短跑中仍然会为它们创建可启动的快捷方式,但那些可以被设置为打开自己的窗框,而且不需要安装任何第三方软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
同时,谷歌最近在整合完整的Office功能(由于其购买了QuickOffice)[到自己的文档,幻灯片和床单应用][4]。Android应用程序Quickoffice退出了舞台,同时Chrome也实现了扩展。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是一个深度的谷歌网络硬盘/文档的用户,那么这个解决方案可能对你是更加好了。
|
||||
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.omgubuntu.co.uk/2014/07/run-microsoft-office-web-apps-ubuntu-desktop
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[cereuz](https://github.com/cereuz)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.libreoffice.org/
|
||||
[2]:https://docs.google.com/file/d/0ByQnaVw7riBQMjNCUFh4ZlM4Y0E/edit?usp=sharing
|
||||
[3]:http://www.omgchrome.com/microsoft-brings-office-online-chrome-web-store/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.omgchrome.com/quickoffice-chrome-extension-gets-name-change/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,131 @@
|
||||
10个实用的关于linux中Squid代理服务器的面试问答
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
不仅是系统管理员和网络管理员时不时会听到“代理服务器”这个词,我们也经常听到。代理服务器已经是一种企业的文化,而且那是需要时间来积累的。它现在也在一些小型的学校或者大型跨国公司的自助餐厅里得到了实现。Squid(也可做代理服务)就是这样一个应用程序,它既可以被作为代理服务器,同时也是在其同类工具中比较被广泛使用的一种。
|
||||
|
||||
本文旨在提高你在遇到关于代理服务器面试点时的一些基本应对能力。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
以下为面试问答的内容
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 什么是代理服务器?代理服务器在计算机网络中有什么用途? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 代理服务器是指那些作为客户端和资源提供商或服务器之间的中间件的物理机或者应用程序。客户端从代理服务器中寻找文件、页面或者是数据而且代理服务器能处理客户端与服务器之间所有复杂事务从而满足客户端的生成的需求。
|
||||
代理服务器是WWW(万维网)的支柱,它们其中大部分都是Web代理。一台代理服务器能处理客户端与服务器之间的复杂通信事务。此外,它在网络上提供的是匿名信息那就意味着你的身份和浏览痕迹都是安全的。代理可以去配置允许哪些网站的客户能看到,哪些网站被屏蔽了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Squid是什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : Squid是一个在GNU/GPL协议下发布的即可作为代理服务器同时也可作为Web缓存守护进程的应用软件。Squid主要是支持像HTTP和FTP那样的协议但是对其它的协议比如HTTPS,SSL,TLS等同样也能支持。其特点是Web缓存守护进程通过从经常上访问的网站里缓存Web和DNS从而让上网速度更快。Squid支持所有的主流平台,包括Linux,UNIX,微软公司的Windows和苹果公司的Mac。
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Squid的默认端口是什么?怎么去修改它的操作端口? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : Squid运行时的默认端口是3128。我们可以通过编辑它的配置文件来把它的默认端口修改成未被用户使用的端口,路径是 /etc/squid/squid.conf ,建议如下。
|
||||
|
||||
用你的编辑器打开 ‘/etc/squid/squid.conf’ 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||||
|
||||
现在把它修改成未被使用的其它端口,并保存退出。
|
||||
|
||||
http_port 3128
|
||||
|
||||
重新启动Squid代理服务,如下显示。
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 你的公司管理层要求你通过Squid代理服务器屏蔽掉一些域名,你怎么做? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 屏蔽域名是一个在配置文件中实现的功能模块。我们只需要执行一个小的手动配置即可,建议如下。
|
||||
|
||||
a. 在 ‘/etc/squid’ 目录下创建一个名为 ‘blacklist’ 的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /etc/squid/blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
b. 用nano编辑器打开这个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
c. 以每行一个域名的方式将想要屏蔽的域名写进这个文件里。
|
||||
|
||||
.facebook.com
|
||||
.twitter.com
|
||||
.gmail.com
|
||||
.yahoo.com
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
d. 保存退出,然后从 ‘/etc/squid/squid.conf’ 打开Squid配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||||
|
||||
e. 在配置文件中添加如下行。
|
||||
|
||||
acl BLACKLIST dstdom_regex -i “/etc/squid/blacklist”
|
||||
http_access deny blacklist
|
||||
|
||||
f. 保存配置文件并退出,重启Squid服务让其生效。
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 在Squid中什么是媒体范围限制和部分下载? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 媒体范围限制是Squid的一种特殊的功能,它只从服务器中获取所需要的数据而不是整个文件。这个功能很好的实现了用户在各种视频流媒体网站如YouTube和Metacafe看视频时,可以点击视频中的进度条来选择进度,因此整个视频不用全部都加载,除了一些需要的部分。
|
||||
|
||||
Squid部分下载功能的特点是很好地实现了在Windows更新时下载的文件能以一个个小数据包的形式暂停。正因为它的这个特点,正在下载文件的Windows机器能不用担心数据会丢失,从而进行恢复下载。Squid让媒体范围限制和部分下载功能只在存储一个完整文件的复件之后实现。此外,当用户指向另一个页面时,Squid要以某种方式进行特殊地配置,部分下载下来的文件才会不被删除且留有缓存。
|
||||
|
||||
### 6. 什么是Squid的反向代理? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 反向代理是Squid的一个特点,这个功能被用来加快最终用户的上网速度。缩写为 ‘RS’ 的原服务器包含了所有资源,而代理服务器则叫 ‘PS’ 。客户端寻找RS所提供的数据,第一次指定的数据和它的复件会经过多次配置从RS上存储在PS上。这样的话每次从PS上请求的数据就等于就是从原服务器上获取的。这样就会减轻网络拥堵,减少CPU使用率,降低网络资源的利用率从而缓解原来实际服务器的负载压力。但是RS统计不了总流量的数据因为PS分担了部分原服务器的任务。‘X-Forwarded-For HTTP’ 就能记录下通过HTTP代理或负载均衡方式连接到RS的客户端最原始的IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
严格意义上来说,用单个Squid服务器同时作为正向代理服务器和反向代理服务器是可行的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 7. 由于Squid能作为一个Web缓存守护进程,那缓存可以删除吗?怎么删除? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : 当然!作为一个Web缓存守护进程,Squid能加快网页的访问速度,清除缓存也是非常简单的。
|
||||
|
||||
a. 首先停止Squid代理服务,然后从这个 ‘/var/lib/squid/cache’ 目录中删除缓存。
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid stop
|
||||
# rm -rf /var/lib/squid/cache/*<
|
||||
|
||||
b. 创建交换分区目录。
|
||||
|
||||
# squid -z
|
||||
|
||||
### 8. 你身边有一台客户机,而你正在工作,如果想要限制儿童的访问时间段,你会怎么去设置那个场景? ###
|
||||
|
||||
把允许访问的时间设置成晚上4点到7点三个小时,跨度为星期一到星期五。
|
||||
|
||||
a. 想要限制Web访问时间在星期一到星期五的晚上4点到7点,要先打开Squid的配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# nano /etc/squid/squid.conf
|
||||
|
||||
b. 在配置文件中添加如下行,保存文件并退出。
|
||||
|
||||
acl ALLOW_TIME time M T W H F 16:00-19:00
|
||||
shttp_access allow ALLOW_TIME
|
||||
|
||||
c. 重启Squid服务。
|
||||
|
||||
# service squid restart
|
||||
|
||||
### 9. Squid存储的数据是什么文件格式? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : Squid存储的数据是UFS文件格式的。UFS是一种老的,使用比较广泛的Squid存储格式
|
||||
|
||||
### 10. Squid的缓存会存储到哪里? ###
|
||||
|
||||
> **回答** : Squid存储的缓存是位于 ‘/var/spool/squid’ 的特殊目录下。
|
||||
|
||||
以上就是全部内容了,很快我还会带着其它有趣的内容回到这里,届时还请继续关注Tecmint。别忘了告诉我们你的反馈和评论。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/squid-interview-questions/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Avishek Kumar][a]
|
||||
译者:[ZTinoZ](https://github.com/ZTinoZ)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/avishek/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
Linux输入统计神器——WhatPulse
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果,你想我这样,是个对统计数据有着狂热癖好的人,那么你必须在你的计算机上安装这个小应用:[WhatPulse][1]
|
||||
|
||||
此软件会追踪用户的击键、鼠标点击以及使用的[带宽][2]和系统开机时间。用户可以周期性地,或者手动上传击键的数量到服务器上,这称之为“脉动”。
|
||||
|
||||
用户可以看到他们在所有加入该程序的人的领先选手排名板的所处位置,并且与他们自己国家的人作比较。用户也可以加入团队,在团队中他们可以和有着相同爱好的人作对比(去吧,Linux用户们!!)。
|
||||
|
||||
软件分为免费的基础版和高级版,在基础版中你可以查看并检查所有的基本统计数据,而在高级版中你可以看到更多。
|
||||
|
||||
该软件可用于Linux,Windows和Mac。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在线注册 ###
|
||||
|
||||
第一步,你必须在[WhatPulse网站][1]注册帐号,或者也可以在你第一次启动WhatPulse客户端时出现的实用向导中创建帐号,以用于上传自己的统计数据(你也可以使用Facebook的帐号登录)。
|
||||
|
||||
你会被提示需要登录,登录之后,你必须搜索你的计算机名,这是因为你可以通过该帐号登录到多台计算机,而它们的数据都会上传到同一统计帐号。一旦你登入后,一个小小的W将出现在你的系统托盘中,那就对了,你已搞定!
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Linux上安装WhatPulse ###
|
||||
|
||||
官方网站在[下载页][3]提供了一个通用版本.tar.gz归档压缩包(用于32位和64位)和一个debian包。
|
||||
|
||||
就我个人而言,我已经在我的Mint Qiana上安装了debian包,在我的Arch Linux[Aur包][4]一点问题都没有。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要使用通用版本安装,请记住:WhatPulse需要几个库文件。最主要的是QT,因为WhatPulse构建于QT平台。下面列出了软件安装需求:
|
||||
|
||||
- libQtCore
|
||||
- libQtWebKit
|
||||
- libqt4-sql
|
||||
- libqt4-sql-sqlite
|
||||
- openssl-devel (libssl-dev)
|
||||
- libQtScript
|
||||
|
||||
#### 输入统计数据 ####
|
||||
|
||||
客户端需要设置相应的权限,以读取键盘/鼠标输入。运行包含的交互脚本.sh来设置这些权限。
|
||||
|
||||
#### [网络][5]统计数据 ####
|
||||
|
||||
要启用网络测量,你也需要**libpcap**包来允许WhatPulse挂钩到网络通信。如果WhatPulse找不到libpcap,它会运行,但不会显示任何网络统计数据。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 使用应用程序 ###
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,WhatPulse会在登入图形会话后自动启动。点击系统托盘上的W图标,你将进入总览标签页,这里显示你机器上收集到的所有不同信息的鸟瞰图。例如,安装在你PC上的Linux版本、处理器型号、RAM、GPU、总点击次数、击键和带宽使用。点击这些信息下面的‘Pulse’,它将会上传这些收集到的数据到主服务器上。
|
||||
|
||||
也可以选择自动‘Pulse’数据到服务器的时间,如每50.000点击,或者1GB下载量。
|
||||
|
||||
要了解深度详情,你可以切换到每个类目的附属标签。例如,Input标签展示给你的是注册后一段时间内的击键的数量和点击次数。时间周期分为每日、每周、每月、每年以及全时。‘all’设置将显示程序安装以来的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
在击键下面,你会找到键盘点击热图,它简单地使用冷暖色显示选定周期内各个键的使用状况,如上述截图所示。在图的下面,应用显示了选定周期内记录的点击总量。
|
||||
|
||||
在Network标签下,可以查看到日常互联网使用情况。应用程序可以监控所有网络设备的带宽使用量,甚至也可以给你展示按国家分布的带宽使用情况。再次提醒,你可以使用顶部右边的箭头按钮浏览可用的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
在网站上,你会看到与客户端上相同的所有统计数据。
|
||||
|
||||
免责声明:上面的WhatPulse网站链接包含了我的参考链接,注册时请使用该链接,这会让我的帐号在某天升级到高级帐号。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linuxaria.com/recensioni/check-how-much-do-you-type-with-whatpulse-on-linux
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[linuxari][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:https://plus.google.com/100563597940685405833?rel=author
|
||||
[1]:http://whatpulse.org/ref/833872/
|
||||
[2]:http://linuxaria.com/article/tool-command-line-bandwidth-linux
|
||||
[3]:http://www.whatpulse.org/downloads/
|
||||
[4]:https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/whatpulse/
|
||||
[5]:http://linuxaria.com/tag/network
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,113 @@
|
||||
8 Options to Trace/Debug Programs using Linux strace Command
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
在调试的时候,strace能帮助你追踪到一个程序所执行的系统调用。当你想知道程序和操作系统如何交互的时候,这是极其方便的,比如你想知道执行了哪些系统调用,并且以何种顺序执行。
|
||||
|
||||
这个简单而又强大的工具几乎在所有的Linux操作系统上可用,并且可被用来调试大量的程序。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 命令用法 ###
|
||||
|
||||
让我们看看strace命令如何追踪一个程序的执行情况。
|
||||
|
||||
最简单的形式,strace后面可以跟任何命令。它将列出许许多多的系统调用。一开始,我们并不能理解所有的输出,但是如果你正在寻找一些特殊的东西,那么你应该能从输出中发现它。
|
||||
让我们来看看简单命令ls的系统调用跟踪情况。
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这是strace命令输出的前几行。其他输出被截去了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
上面的输出部分展示了write系统调用,它把当前目录的列表输出到标准输出。
|
||||
下面的图片展示了使用ls命令列出的目录内容(没有使用strace)。
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.1 寻找被程序读取的配置文件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
一个有用的跟踪(除了调试某些问题以外)是你能找到被一个程序读取的配置文件。例如,
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace php 2>&1 | grep php.ini
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.2 跟踪指定的系统调用 ####
|
||||
|
||||
strace命令的-e选项仅仅被用来展示特定的系统调用(例如,open,write等等)
|
||||
|
||||
让我们跟踪一下cat命令的‘open’系统调用。
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -e open cat dead.letter
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.3 用于进程 ####
|
||||
|
||||
strace不但能用在命令上,而且通过使用-p选项能用在运行的进程上。
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ sudo strace -p 1846
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.4 strace的统计概要 ####
|
||||
|
||||
包括系统调用的概要,执行时间,错误等等。使用-c选项能够以一种整洁的方式展示:
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -c ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.5 保存输出结果 ####
|
||||
|
||||
通过使用-o选项可以把strace命令的输出结果保存到一个文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ sudo strace -o process_strace -p 3229
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
之所以以sudo来运行上面的命令,是为了防止用户ID与所查看进程的所有者ID不匹配的情况。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.6 显示时间戳 ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用-t选项,可以在每行的输出之前添加时间戳。
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -t ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.7 更好的时间戳 ####
|
||||
|
||||
-tt选项可以展示微秒级别的时间戳。
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -tt ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
-ttt也可以向上面那样展示微秒级的时间戳,但是它并不是打印当前时间,而是显示自从epoch(译注:1970年1月1日00:00:00 UTC)以来的所经过的秒数。
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -ttt ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 1.8 Relative Time ####
|
||||
|
||||
-r选项展示系统调用之间的相对时间戳。
|
||||
|
||||
raghu@raghu-Linoxide ~ $ strace -r ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-command/linux-strace-command-examples/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Raghu][a]
|
||||
译者:[guodongxiaren](https://github.com/guodongxiaren)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/raghu/
|
||||
@ -1,7 +1,6 @@
|
||||
2q1w2007翻译中
|
||||
QuiteRSS: Linux桌面的RSS阅读器
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
[QuiteRSS][1]是一个自由而[开源][2]的RSS/Atome阅读器。它可以运行在Windows , Linux和Mac上运行。它用C++/QT编写,所以它会有更好的未来。
|
||||
[QuiteRSS][1]是一个自由[开源][2]的RSS/Atome阅读器。它可以在Windows、Linux和Mac上运行。它用C++/QT编写,所以它有许多的特点。
|
||||
|
||||
QuiteRSS的界面让我想起Lotus Notes mail,会有很多RSS信息排列在大小合适的方块上,你可以通过标签分组。需要查找东西时,只需在下面板上打开RSS信息。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,17 +10,17 @@ QuiteRSS的界面让我想起Lotus Notes mail,会有很多RSS信息排列在
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 上安装 QuiteRSS ###
|
||||
|
||||
QuiteRSS在Ubuntu 14.04 和 Linux Mint 17中可用。你可以很简单的通过以下命令行安装:
|
||||
QuiteRSS在Ubuntu 14.04 和 Linux Mint 17中可用。你可以通过以下命令行轻松安装:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install quiterss
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想安装最新的稳定版本,你可以用官方的[QuiteRSS PPA][4]:
|
||||
如果你想安装最新的稳定版本,你可以使用官方的[QuiteRSS PPA][4]:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:quiterss/quiterss
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
sudo apt-get install quiterss
|
||||
|
||||
上面的命令在所有基于Ubuntu的发行版像 Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Linux Lite, Pinguy OS 都应该好用。在其他Linux发行版和平台上,你可以从 [下载页][5]获得源码来安装.
|
||||
上面的命令在所有基于Ubuntu的发行版都支持,比如Linux Mint, Elementary OS, Linux Lite, Pinguy OS等等。对于其他Linux发行版和平台上,你可以从 [下载页][5]获得源码来安装。
|
||||
|
||||
### 卸载 QuiteRSS ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -29,19 +28,19 @@ QuiteRSS在Ubuntu 14.04 和 Linux Mint 17中可用。你可以很简单的通过
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get remove quiterss
|
||||
|
||||
如果你用了PPA,你还需要从源列表中把仓库删除:
|
||||
如果你使用了PPA,你还需要从源列表中把仓库删除:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:quiterss/quiterss
|
||||
|
||||
QuiteRSS是一个不错的开源RSS阅读器,尽管我更喜欢[Feedly][6]。尽管现在 Feedly 还没有Linux桌面程序,但是你依然可以在网页浏览器中使用。我希望你会认为QuiteRSS值得一试。
|
||||
QuiteRSS是一个不错的开源RSS阅读器,尽管我更喜欢[Feedly][6]。尽管现在 Feedly 还没有Linux桌面程序,但是你依然可以在网页浏览器中使用。希望你会觉得QuiteRSS值得在桌面Linux一试。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/quiterss-rss-reader-desktop-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007(https://github.com/2q1w2007)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[2q1w2007](https://github.com/2q1w2007)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,4 +50,4 @@ via: http://itsfoss.com/quiterss-rss-reader-desktop-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://quiterss.org/en/about
|
||||
[4]:https://launchpad.net/~quiterss/+archive/ubuntu/quiterss/
|
||||
[5]:http://quiterss.org/en/download
|
||||
[6]:http://feedly.com/
|
||||
[6]:http://feedly.com/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
||||
从Windows双启动中卸载Ubuntu Linux
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
我在过去已经多次涉及到[在UEFI模式下安装Ubuntu 14.04与Windows 8/8.1双启动][1]的话题。 但是要怎么从**Windows双启动中卸载Ubuntu呢**?下面我们将看到的教程适用于任意的Linux操作系统,如Ubuntu,Linux Mint,Elementary OS或其它任意Linux发行版。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你认为[在双启动模式下安装Ubuntu与Windows 8共存][2]是件难事,而从Windows双启动中移除Ubuntu将是很简单的,你的想法并不是完全错误的。如果你有个Windows安装介质的话,从Windows双启动中卸载Linux将是轻而易举的。
|
||||
|
||||
这个教程将教你如何在有**Windows 8/8.1安装介质**的情况下将Linux从Windows 8或Windows 8.1双启动中完全移除。
|
||||
|
||||
### 将Ubuntu从Windows 8双启动中安全卸载 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你有没有Windows 8安装介质以及是否已经安装了Windows 8.1在你系统上这都不重要。它同样工作得很好。但是我不能说在Windows 7上也一样。如果你身边有Windows安装盘,让我们开始从Windows双启动中移除Ubuntu的进程吧。
|
||||
|
||||
从双启动中删除Linux分为两部分。第一部分是删除Linux安装的所在分区。第二部分是修复Windows启动引导,因为简单地将Linux分区删除会引起[“Grub rescue”错误][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一部分:在Windows下删除Linux分区 ###
|
||||
|
||||
**第一步:**
|
||||
|
||||
登录Windows。按下 **Windows+R** 然后在其中运行 diskmgmt.msc 命令。它将会打开Windows磁盘管理工具。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第二步:**
|
||||
|
||||
在你安装了Linux之后,就能很容易地从大小上分辨出Linux分区。另一个分辨Linux分区的提示是找没有文件系统以及驱动器卷标的分区。Windows分区通常用卷标进行标记,比如C,D,E等等,而且通常是NTFS或FAT文件系统。
|
||||
|
||||
就像你所能看到的,我在这里有三个Linux分区,因为我在安装Ubuntu时单独地创建了根分区(root),交换分区(swap)和家目录(home)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Step 3:**
|
||||
**第三步:**
|
||||
|
||||
选择Linux分区,右键点击并选择 **删除卷** 选项。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果出现了警告,在这里选择是即可。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**Step 4:**
|
||||
**第四步:**
|
||||
|
||||
被删除的分区会变成一块可用的空闲空间。你可以用它来扩展已有的卷或创建一个新的Windows分区。我会建议你创建一个新的驱动器(或是卷或者分区,随便你怎么叫),因为这样子万一你将来又想将Linux和Winodws双启动时会简单一点。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### 第二部分:修复Windows启动引导 ####
|
||||
|
||||
一旦你删除了Linux分区,就是时候修复Windows启动引导了。这里的图片看起来可能不是很清楚,因为相对于Windows来说[在Ubuntu下对登录画面进行截图][4]要简单的多。我用手机相机拍下了这些照片。
|
||||
|
||||
**第一步:**
|
||||
|
||||
**插入Windows 8安装介质并重启**你的电脑。在启动的时候按下F10或F12进入BIOS/UEFI,选择**从可移除介质启动(boot from removable disk)**。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第二步:**
|
||||
|
||||
选择修复你的计算机(repair your computer):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第三步:**
|
||||
|
||||
在这里选择疑难解答(Troubleshoot):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第四步:**
|
||||
|
||||
在疑难解答页面,选择高级选项(Advanced options):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第五步:**
|
||||
|
||||
找到这里的命令提示符(command prompt):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第六步:**
|
||||
|
||||
在命令行中输入下列命令来修复Windows启动引导:
|
||||
|
||||
bootrec.exe /fixmbr
|
||||
|
||||
正常情况下,它是立即生效的,你甚至都不用等。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
**第七步:**
|
||||
|
||||
一旦完成了这一步,重启你的电脑,这次从硬盘正常启动。你应该能够启动进入Windows。如果你仍然看到Grub rescue错误,试试下面的步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
**第八步:如果第六步中的方法不起作用**
|
||||
|
||||
如果第六步中的命令不起作用,试试高级疑难解答中的自动修复选项。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
它会花点时间查找问题然后修复它。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在如果你重启的话,你应该能够正常进入Windows,不再看到任何的Grub rescue错误提示。
|
||||
|
||||
我希望这个指南能够帮助你**将Ubuntu从Windows 8双启动中完全移除**。欢迎提出任何问题与建议。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://itsfoss.com/uninstall-ubuntu-linux-windows-dual-boot/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Abhishek][a]
|
||||
译者:[alim0x](https://github.com/alim0x)
|
||||
校对:[Caroline](https://github.com/carolinewuyan)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://itsfoss.com/author/Abhishek/
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-3178-1.html
|
||||
[2]:http://itsfoss.com/install-ubuntu-dual-boot-mode-windows/
|
||||
[3]:http://itsfoss.com/solve-error-partition-grub-rescue-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
[4]:http://itsfoss.com/screenshot-login-screen-ubuntu-linux/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——如何使用tcpdump来捕获TCP SYN,ACK和FIN包
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:我想要监控TCP连接活动(如,建立连接的三次握手,以及断开连接的四次握手)。要完成此事,我只需要捕获TCP控制包,如SYN,ACK或FIN标记相关的包。我怎样使用tcpdump来仅仅捕获TCP SYN,ACK和/或FYN包?
|
||||
|
||||
作为事实上的捕获工具,tcpdump提供了强大而又灵活的包过滤功能。作为tcpdump基础的libpcap包捕获引擎支持标准的包过滤规则,如基于5重包头的过滤(如基于源/目的IP地址/端口和IP协议类型)。
|
||||
|
||||
tcpdump/libpcap的包过滤规则也支持更多通用分组表达式,在这些表达式中,包中的任意字节范围都可以使用关系或二进制操作符进行检查。对于字节范围表达,你可以使用以下格式:
|
||||
|
||||
proto [ expr : size ]
|
||||
|
||||
“proto”可以是熟知的协议之一(如ip,arp,tcp,udp,icmp,ipv6),“expr”表示与指定的协议头开头相关的字节偏移量。有我们熟知的直接偏移量如tcpflags,也有取值常量如tcp-syn,tcp-ack或者tcp-fin。“size”是可选的,表示从字节偏移量开始检查的字节数量。
|
||||
|
||||
使用这种格式,你可以像下面这样过滤TCP SYN,ACK或FIN包。
|
||||
|
||||
只捕获TCP SYN包:
|
||||
|
||||
# tcpdump -i <interface> "tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-syn) != 0"
|
||||
|
||||
只捕获TCP ACK包:
|
||||
|
||||
# tcpdump -i <interface> "tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-ack) != 0"
|
||||
|
||||
只捕获TCP FIN包:
|
||||
|
||||
# tcpdump -i <interface> "tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-fin) != 0"
|
||||
|
||||
之捕获TCP SYN或ACK包:
|
||||
|
||||
# tcpdump -r <interface> "tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-syn|tcp-ack) != 0"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/capture-tcp-syn-ack-fin-packets-tcpdump.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[作者名][a]
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——如何在CentOS或RHEL 7上修改主机名
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> 问题:在CentOS/RHEL 7上修改主机名的正确方法是什么(永久或临时)?
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS或RHEL中,有三种定义的主机名:(1)静态的,(2)瞬态的,以及(3)优雅的。“静态”主机名也成为内核主机名,是系统在启动时从/etc/hostname自动初始化的主机名。“瞬态”主机名是在系统运行时临时分配的主机名,例如,通过DHCP或mDNS服务器分配。静态主机名和瞬态主机名都遵从作为互联网域名同样的字符限制规则。而另一方面,“优雅”主机名则被允许使用自由形式(包括特殊/空白字符)的主机名,以展示给终端用户(如Dan's Computer)。
|
||||
|
||||
在CentOS/RHEL 7中,有个叫hostnamectl的命令行工具,它允许你查看或修改与主机名相关的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
要查看主机名相关的设置:
|
||||
|
||||
$ hostnamectl status
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
只查看静态、瞬态或优雅主机名,分别使用“--static”,“--transient”或“--pretty”选项。
|
||||
|
||||
$ hostnamectl status [--static|--transient|--pretty]
|
||||
|
||||
要同时修改所有三个主机名:静态、瞬态和优雅主机名:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo hostnamectl set-hostname <host-name>
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
就像上面展示的那样,在修改静态/瞬态主机名时,任何特殊字符或空白字符会被移除,而提供的参数中的任何大写字母会自动转化为小写。一旦修改了静态主机名,/etc/hostname将被自动更新。然而,/etc/hosts不会更新以对修改作出回应,所以你需要手动更新/etc/hosts。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你只想修改特定的主机名(静态,瞬态或优雅),你可以使用“--static”,“--transient”或“--pretty”选项。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,要永久修改主机名,你可以修改静态主机名:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo hostnamectl --static set-hostname <host-name>
|
||||
|
||||
注意,你不必重启机器以激活永久主机名修改。上面的命令会立即修改内核主机名。注销并重新登入后在命令行提示观察新的静态主机名。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/change-hostname-centos-rhel-7.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——如何创建新的亚马逊AWS访问密钥
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:我在配置一个需要访问我的亚马逊AWS帐号的应用时被要求提供**AWS访问密钥ID**和**秘密访问密钥**,我怎样创建一个新的AWS访问密钥呢?
|
||||
|
||||
亚马逊AWS安全凭证用于验证你以及授权任何第三方应用访问你的AWS帐号,有各种不同的AWS安全凭证可用,如密码、访问密钥、多因素身份验证、X.509证书等。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要创建新的访问密钥(访问密钥ID和秘密访问密钥),请按一下步骤进行。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,登录到[AWS控制台][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
从顶部栏选择“安全凭证”菜单(图中红色方框所示)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在下一页中,选择“访问密钥(访问密钥ID和秘密访问密钥)”选项(图中红色方框所示)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在下一页中,你将看到一个现存访问密钥ID列表(如果有的话)。注意,你不能恢复现存访问密钥ID的“秘密访问密钥”。出于安全的原因,秘密访问密钥只能在你创建新访问密钥时才可见。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
点击“创建新访问密钥”(见图示),将会立即创建一个新的访问密钥ID和密码访问密钥对。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要么下载一个包含有新访问密钥的密钥文件,要么复制并粘贴新访问密钥信息。再次提请牢记,一旦你关闭该窗口,秘密访问密钥将不再可用,除非你下载一个密钥文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 多用户AWS帐号 ###
|
||||
如果你是作为公司身份创建的帐号,多个雇员共享这一公司帐号,你可能想要使用身份和访问管理(IAM)来创建并管理他们的访问密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
IAM是一个web服务,它允许一个公司管理多个用户及其与一个AWS帐号关联的安全凭证。使用IAM,多个用户可以作为不同身份登入单一的AWS帐号,并管理他们的安全凭证而不会相互干预对方的密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
要管理IAM用户,点击“安全凭证”页面上的“用户”菜单(见图示)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
然后,你就可以创建一个新的IAM用户并管理他们的安全凭证,比如访问密钥之类的东西。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/create-amazon-aws-access-key.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://aws.amazon.com/console/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——如何扩展XFS文件系统
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:我的磁盘上有额外的空间,所以我想要扩展其上创建的现存的XFS文件系统,以完全使用额外空间。怎样才是扩展XFS文件系统的正确途径?
|
||||
|
||||
XFS是一个开源的(GPL)日子文件系统,最初由硅谷图形开发,现在被大多数的Linux发行版都支持。事实上,XFS已经被最新的CentOS/RHEL 7采用,成为其默认的文件系统。在其众多的特性中,包含了“在线调整大小”这一特性,使得现存的XFS文件系统在被挂载时可以进行扩展。然而,对于XFS文件系统的缩减确实不被支持的。
|
||||
|
||||
要扩展一个现存的XFS文件系统,你可以使用命令行工具xfs_growfs,这在大多数Linux发行版上都默认可用。由于XFS支持在线调整大小,目标文件系统可以挂在,也可以不挂载。
|
||||
|
||||
下面展示了**xfs_growfs**的基本用法:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
作为目标XFS文件系统来扩展,你可以指定挂载点、磁盘分区或者逻辑卷(在使用LVM时),使用数据块数量来指定新的XFS文件系统的大小。你可以使用xfs_info命令行工具来检查数据块大小和数量:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
要将XFS文件扩展到1986208:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo xfs_growfs /dev/centos/root -D 1986208
|
||||
|
||||
如果你不使用“-D”选项来指定大小,xfs_growfs将会自动扩展XFS文件系统到最大的可用大小。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo xfs_growfs /dev/centos/root
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
注意,当你扩展一个现存的XFS文件系统时,必须准备事先添加用于XFS文件系统扩展的空间。这虽然是十分明了的事,但是如果在潜在的分区或磁盘卷上没有空闲空间可用的话,xfs_growfs不会做任何事情。同时,如果你尝试扩展XFS文件系统大小到超过磁盘分区或卷的大小,xfs_growfs将会失败。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/expand-xfs-file-system.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答——如何查找并移除Ubuntu上陈旧的PPA仓库
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**:我试着通过运行apt-get update命令来再次同步包索引文件,但是却出现了“404 无法找到”的错误,看起来似乎是我不能从先前添加的第三方PPA仓库中获取最新的索引。我怎样才能清楚这些破损而且陈旧的PPA仓库呢?
|
||||
|
||||
Err http://ppa.launchpad.net trusty/main amd64 Packages
|
||||
404 Not Found
|
||||
Err http://ppa.launchpad.net trusty/main i386 Packages
|
||||
404 Not Found
|
||||
W: Failed to fetch http://ppa.launchpad.net/finalterm/daily/ubuntu/dists/trusty/main/binary-amd64/Packages 404 Not Found
|
||||
|
||||
W: Failed to fetch http://ppa.launchpad.net/finalterm/daily/ubuntu/dists/trusty/main/binary-i386/Packages 404 Not Found
|
||||
|
||||
E: Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead.
|
||||
|
||||
但你试着更新APT包索引时,“404 无法找到”错误总是会在版本更新之后发生。就是说,在你升级你的Ubuntu发行版后,你在旧的版本上添加的一些第三方PPA仓库就不再受新版本的支持。在此种情况下,你可以像下面这样来**鉴别并清除那些破损的PPA仓库**。
|
||||
|
||||
首先,找出那些引起“404 无法找到”错误的PPA。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update | grep "Failed"
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在本例中,Ubuntu Trusty不再支持的PPA仓库是“ppa:finalterm/daily”。
|
||||
|
||||
去吧,去[移除PPA仓库][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:finalterm/daily
|
||||
|
||||
你得去重复重复再重复,把上面找到的所有过时的PPA仓库一个一个地移除。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在移除所有过时PPA仓库后,重新运行“apt-get update”命令来检查它们是否都被移除。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/find-remove-obsolete-ppa-repositories-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[GOLinux](https://github.com/GOLinux)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/how-to-remove-ppa-repository-from-command-line-on-ubuntu.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQ - Ubuntu如何使用命令行移除PPA仓库
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **问题**: 前段时间,我的Ubuntu增加了一个第三方的PPA仓库,如何才能移除这个PPA仓库呢?
|
||||
|
||||
个人软件包档案(PPA)是Ubuntu独有的解决方案,允许独立开发者和贡献者构建、贡献任何定制的软件包来作为通过启动面板的第三方APT仓库。如果你是Ubuntu用户,有可能你已经增加一些流行的第三方PPA仓库到你的Ubuntu系统。如果你需要删除掉已经预先配置好的PPA仓库,下面将教你怎么做。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
假如你有一个第三方PPA仓库叫“ppa:webapps/preview”增加到了你的系统中,如下。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webapps/preview
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要 **单独地删除一个PPA仓库**,运行下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo add-apt-repository --remove ppa:someppa/ppa
|
||||
|
||||
注意,上述命令不会同时删除任何已经安装或更新的软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要 **完整的删除一个PPA仓库并包括来自这个PPA安装或更新过的软件包**,你需要ppa-purge命令。
|
||||
|
||||
安装ppa-purge软件包:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install ppa-purge
|
||||
|
||||
删除PPA仓库和与之相关的软件包,运行下列命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo ppa-purge ppa:webapps/preview
|
||||
|
||||
特别滴,在发行版更新后,你需要[分辨和清除已损坏的PPA仓库][1],这个方法特别有用!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/how-to-remove-ppa-repository-from-command-line-on-ubuntu.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[Vic___](http://www.vicyu.net)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/find-remove-obsolete-ppa-repositories-ubuntu.html
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user