mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-27 02:30:10 +08:00
Merge remote-tracking branch 'LCTT/master'
This commit is contained in:
commit
56f2a3e277
@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: (FSSlc)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: (wxy)
|
||||
[#]: publisher: (wxy)
|
||||
[#]: url: (https://linux.cn/article-10641-1.html)
|
||||
[#]: subject: (Run Particular Commands Without Sudo Password In Linux)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://www.ostechnix.com/run-particular-commands-without-sudo-password-linux/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (SK https://www.ostechnix.com/author/sk/)
|
||||
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@
|
||||
在 Linux 中运行特定命令而无需 sudo 密码
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
我有一台部署在 AWS 上的 Ubuntu 系统,在它的里面有一个脚本,这个脚本的原有目的是以一定间隔(准确来说是每隔 1 分钟)去检查某个特定服务是否正在运行,如果这个服务因为某些原因停止了,就自动重启这个服务。 但问题是我需要 sudo 权限来开启这个服务。正如你所知道的那样,当我们以 sudo 用户运行命令时,我们应该提供密码,但我并不想这么做,实际上我想做的是以 sudo 用户的身份运行这个服务但无需提供密码。假如你曾经经历过这样的情形,那么我知道一个简单的方法来做到这点。今天,在这个简短的指南中,我将教你如何在类 Unix 的操作系统中运行特定命令而无需 sudo 密码。
|
||||
我有一台部署在 AWS 上的 Ubuntu 系统,在它的里面有一个脚本,这个脚本的原有目的是以一定间隔(准确来说是每隔 1 分钟)去检查某个特定服务是否正在运行,如果这个服务因为某些原因停止了,就自动重启这个服务。但问题是我需要 sudo 权限来开启这个服务。正如你所知道的那样,当我们以 sudo 用户运行命令时,我们应该提供密码,但我并不想这么做,实际上我想做的是以 sudo 用户的身份运行这个服务但无需提供密码。假如你曾经经历过这样的情形,那么我知道一个简单的方法来做到这点。今天,在这个简短的指南中,我将教你如何在类 Unix 的操作系统中运行特定命令而无需 sudo 密码。
|
||||
|
||||
就让我们看看下面的例子吧。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,15 +21,15 @@ $ sudo mkdir /ostechnix
|
||||
|
||||
![][2]
|
||||
|
||||
正如上面的截图中看到的那样,当我在根目录(`/`)中创建一个名为 `ostechnix` 的目录时,我需要提供 sudo 密码。每当我们尝试以 sudo 特权执行一个命令时,我们必须输入密码。而在我的预想中,我不想提供 sudo 密码。下面的内容便是我如何在我的 Linux 机子上运行一个 sudo 命令而无需输入密码的过程。
|
||||
正如上面的截图中看到的那样,当我在根目录(`/`)中创建一个名为 `ostechnix` 的目录时,我需要提供 sudo 密码。每当我们尝试以 sudo 特权执行一个命令时,我们必须输入密码。而在我的预想中,我不想提供 sudo 密码。下面的内容便是我如何在我的 Linux 机子上运行一个 `sudo` 命令而无需输入密码的过程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 中运行特定命令而无需 sudo 密码
|
||||
|
||||
基于某些原因,假如你想允许一个用户运行特定命令而无需提供 sudo 密码,则你需要在 **sudoers** 文件中添加上这个命令。
|
||||
基于某些原因,假如你想允许一个用户运行特定命令而无需提供 sudo 密码,则你需要在 `sudoers` 文件中添加上这个命令。
|
||||
|
||||
假如我想让名为 **sk** 的用户去执行 **mkdir** 而无需提供 sudo 密码,下面就让我们看看该如何做到这点。
|
||||
假如我想让名为 `sk` 的用户去执行 `mkdir` 而无需提供 sudo 密码,下面就让我们看看该如何做到这点。
|
||||
|
||||
使用下面的命令来编辑 sudoers 文件:
|
||||
使用下面的命令来编辑 `sudoers` 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo visudo
|
||||
@ -43,15 +43,15 @@ sk ALL=NOPASSWD:/bin/mkdir
|
||||
|
||||
![][3]
|
||||
|
||||
其中 **sk** 是用户名。根据上面一行的内容,用户 **sk** 可以从任意终端执行 `mkdir` 命令而不必输入 sudo 密码。
|
||||
其中 `sk` 是用户名。根据上面一行的内容,用户 `sk` 可以从任意终端执行 `mkdir` 命令而不必输入 sudo 密码。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以用逗号分隔的值来添加额外的命令(例如 **chmod**),正如下面展示的那样。
|
||||
你可以用逗号分隔的值来添加额外的命令(例如 `chmod`),正如下面展示的那样。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sk ALL=NOPASSWD:/bin/mkdir,/bin/chmod
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并关闭这个文件,然后注销(或重启)你的系统。现在以普通用户 `sk` 登录,然后试试使用 sudo 来运行这些命令,看会发生什么。
|
||||
保存并关闭这个文件,然后注销(或重启)你的系统。现在以普通用户 `sk` 登录,然后试试使用 `sudo` 来运行这些命令,看会发生什么。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo mkdir /dir1
|
||||
@ -59,11 +59,11 @@ $ sudo mkdir /dir1
|
||||
|
||||
![][4]
|
||||
|
||||
看到了吗?即便我以 sudo 特权运行 `mkdir` 命令,也不会弹出提示让我输入密码。从现在开始,当用户 **sk** 运行 `mkdir` 时,就不必输入 sudo 密码了。
|
||||
看到了吗?即便我以 sudo 特权运行 `mkdir` 命令,也不会弹出提示让我输入密码。从现在开始,当用户 `sk` 运行 `mkdir` 时,就不必输入 sudo 密码了。
|
||||
|
||||
当运行除了添加到 sudoers 文件之外的命令时,你将被提示输入 sudo 密码。
|
||||
当运行除了添加到 `sudoers` 文件之外的命令时,你将被提示输入 sudo 密码。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们用 sudo 来运行另一个命令。
|
||||
让我们用 `sudo` 来运行另一个命令。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt update
|
||||
@ -73,16 +73,16 @@ $ sudo apt update
|
||||
|
||||
看到了吗?这个命令将提示我输入 sudo 密码。
|
||||
|
||||
假如你不想让这个命令提示你输入 sudo 密码,请编辑 sudoers 文件:
|
||||
假如你不想让这个命令提示你输入 sudo 密码,请编辑 `sudoers` 文件:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo visudo
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
像下面这样将 `apt` 命令添加到 visudo 文件中:
|
||||
像下面这样将 `apt` 命令添加到 `sudoers` 文件中:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sk ALL=NOPASSWD: /bin/mkdir,/usr/bin/apt
|
||||
sk ALL=NOPASSWD:/bin/mkdir,/usr/bin/apt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
你注意到了上面命令中 `apt` 二进制执行文件的路径与 `mkdir` 的有所不同吗?是的,你必须提供一个正确的可执行文件路径。要找到任意命令的可执行文件路径,例如这里的 `apt`,可以像下面这样使用 `whichis` 命令来查看:
|
||||
@ -92,11 +92,11 @@ $ whereis apt
|
||||
apt: /usr/bin/apt /usr/lib/apt /etc/apt /usr/share/man/man8/apt.8.gz
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如你所见,`apt` 命令的可执行文件路径为 **/usr/bin/apt**,所以我将这个路径添加到了 sudoers 文件中。
|
||||
如你所见,`apt` 命令的可执行文件路径为 `/usr/bin/apt`,所以我将这个路径添加到了 `sudoers` 文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
正如我前面提及的那样,你可以添加任意多个以逗号分隔的命令。一旦你做完添加的动作,保存并关闭你的 sudoers 文件,接着注销,然后重新登录进你的系统。
|
||||
正如我前面提及的那样,你可以添加任意多个以逗号分隔的命令。一旦你做完添加的动作,保存并关闭你的 `sudoers` 文件,接着注销,然后重新登录进你的系统。
|
||||
|
||||
现在就检验你是否可以直接运行以 sudo 开头的命令而不必使用密码:
|
||||
现在就检验你是否可以直接运行以 `sudo` 开头的命令而不必使用密码:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt update
|
||||
@ -104,9 +104,9 @@ $ sudo apt update
|
||||
|
||||
![][6]
|
||||
|
||||
看到了吗?`apt` 命令没有让我输入 sudo 密码,即便我用 sudo 来运行它。
|
||||
看到了吗?`apt` 命令没有让我输入 sudo 密码,即便我用 `sudo` 来运行它。
|
||||
|
||||
下面展示另一个例子。假如你想运行一个特定服务,例如 `apache2`,那么就添加下面这条命令到 sudoers 文件中:
|
||||
下面展示另一个例子。假如你想运行一个特定服务,例如 `apache2`,那么就添加下面这条命令到 `sudoers` 文件中:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sk ALL=NOPASSWD:/bin/mkdir,/usr/bin/apt,/bin/systemctl restart apache2
|
||||
@ -116,24 +116,23 @@ sk ALL=NOPASSWD:/bin/mkdir,/usr/bin/apt,/bin/systemctl restart apache2
|
||||
|
||||
我可以再次让一个特别的命令提醒输入 sudo 密码吗?当然可以!只需要删除添加的命令,注销然后再次登录即可。
|
||||
|
||||
除了这种方法外,你还可以在命令的前面添加 **`PASSWD:`** 指令。让我们看看下面的例子:
|
||||
除了这种方法外,你还可以在命令的前面添加 `PASSWD:` 指令。让我们看看下面的例子:
|
||||
|
||||
在 sudoers 文件中添加或者修改下面的一行:
|
||||
在 `sudoers` 文件中添加或者修改下面的一行:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
sk ALL=NOPASSWD:/bin/mkdir,/bin/chmod,PASSWD:/usr/bin/apt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在这种情况下,用户 **sk** 可以运行 `mkdir` 和 `chmod` 命令而不用输入 sudo 密码。然而,当他运行 `apt` 命令时,就必须提供 sudo 密码了。
|
||||
在这种情况下,用户 `sk` 可以运行 `mkdir` 和 `chmod` 命令而不用输入 sudo 密码。然而,当他运行 `apt` 命令时,就必须提供 sudo 密码了。
|
||||
|
||||
**免责声明:** 本篇指南仅具有教育意义。在使用这个方法的时候,你必须非常小心。这个命令既可能富有成效但也可能带来摧毁性效果。例如,假如你允许用户执行 `rm` 命令而不输入 sudo 密码,那么他们可能无意或有意地删除某些重要文件。我警告过你了!
|
||||
免责声明:本篇指南仅具有教育意义。在使用这个方法的时候,你必须非常小心。这个命令既可能富有成效但也可能带来摧毁性效果。例如,假如你允许用户执行 `rm` 命令而不输入 sudo 密码,那么他们可能无意或有意地删除某些重要文件。我警告过你了!
|
||||
|
||||
那么这就是全部的内容了。希望这个能够给你带来帮助。更多精彩内容即将呈现,请保持关注!
|
||||
|
||||
干杯!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.ostechnix.com/run-particular-commands-without-sudo-password-linux/
|
||||
@ -141,7 +140,7 @@ via: https://www.ostechnix.com/run-particular-commands-without-sudo-password-lin
|
||||
作者:[SK][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: (geekpi)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
[#]: subject: (Get started with Freeplane, an open source mind mapping application)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/19/1/productivity-tool-freeplane)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Kevin Sonney https://opensource.com/users/ksonney (Kevin Sonney))
|
||||
|
||||
Get started with Freeplane, an open source mind mapping application
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Map your brainstorming sessions with Freeplane, the 13th in our series on open source tools that will make you more productive in 2019.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
There seems to be a mad rush at the beginning of every year to find ways to be more productive. New Year's resolutions, the itch to start the year off right, and of course, an "out with the old, in with the new" attitude all contribute to this. And the usual round of recommendations is heavily biased towards closed source and proprietary software. It doesn't have to be that way.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's the 13th of my picks for 19 new (or new-to-you) open source tools to help you be more productive in 2019.
|
||||
|
||||
### Freeplane
|
||||
|
||||
[Mind maps][1] are one of the more valuable tools I've used for quickly brainstorming ideas and capturing data. Mind mapping is a versatile process that helps show how things are related and can be used to quickly organize interrelated information. From a planning perspective, mind mapping allows you to quickly perform a brain dump around a single concept, idea, or technology.
|
||||
|
||||
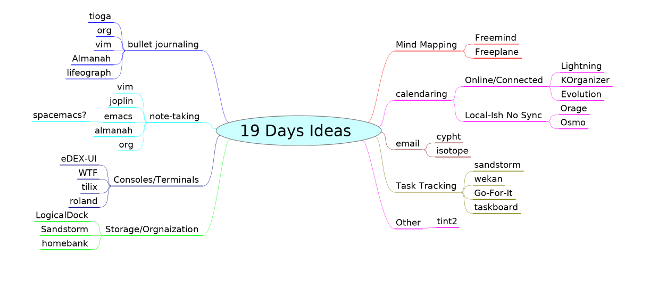
|
||||
|
||||
[Freeplane][2] is a desktop application that makes it easy to create, view, edit, and share mind maps. It is a redesign of [FreeMind][3], which was the go-to mind-mapping application for quite some time.
|
||||
|
||||
Installing Freeplane is pretty easy. It is a [Java][4] application and distributed as a ZIP file with scripts to start the application on Linux, Windows, and MacOS. At its first startup, its main window includes an example mind map with links to documentation about all the different things you can do with Freeplane.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You have a choice of templates when you create a new mind map. The standard template (likely at the bottom of the list) works for most cases. Just start typing the idea or phrase you want to start with, and your text will replace the center text. Pressing the Insert key will add a branch (or node) off the center with a blank field where you can fill in something associated with the idea. Pressing Insert again will add another node connected to the first one. Pressing Enter on a node will add a node parallel to that one.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
As you add nodes, you may come up with another thought or idea related to the main topic. Using either the mouse or the Arrow keys, go back to the center of the map and press Insert. A new node will be created off the main topic.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to go beyond Freeplane's base functionality, right-click on any of the nodes to bring up a Properties menu for that node. The Tool pane (activated under the View–>Controls menu) contains customization options galore, including line shape and thickness, border shapes, colors, and much, much more. The Calendar tab allows you to insert dates into the nodes and set reminders for when nodes are due. (Note that reminders work only when Freeplane is running.) Mind maps can be exported to several formats, including common images, XML, Microsoft Project, Markdown, and OPML.
|
||||
|
||||
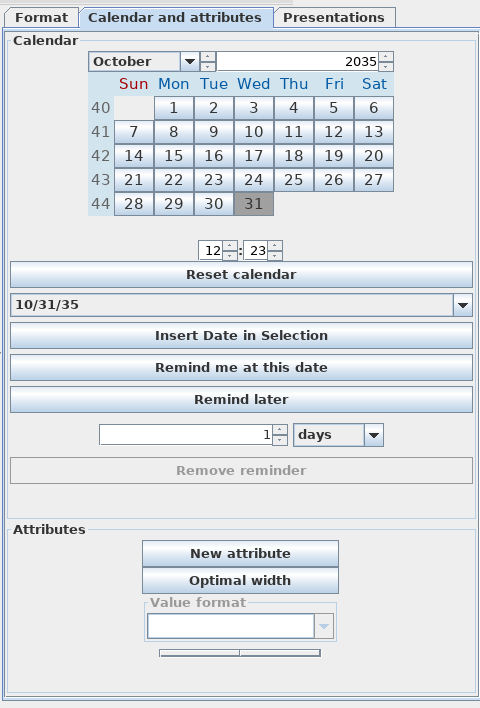
|
||||
|
||||
Freeplane gives you all the tools you'll need to create vibrant and useful mind maps, getting your ideas out of your head and into a place where you can take action on them.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/19/1/productivity-tool-freeplane
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kevin Sonney][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/ksonney (Kevin Sonney)
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mind_map
|
||||
[2]: https://www.freeplane.org/wiki/index.php/Home
|
||||
[3]: https://sourceforge.net/projects/freemind/
|
||||
[4]: https://java.com
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: (sndnvaps)
|
||||
[#]: translator: ( )
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: ( )
|
||||
[#]: translator: (qhwdw)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,366 +0,0 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: (leommxj)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
[#]: subject: (5 Ways To Generate A Random/Strong Password In Linux Terminal)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://www.2daygeek.com/5-ways-to-generate-a-random-strong-password-in-linux-terminal/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Magesh Maruthamuthu https://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/)
|
||||
|
||||
5 Ways To Generate A Random/Strong Password In Linux Terminal
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
Recently we had written an article about **[password strength and password score check][1]** in our website.
|
||||
|
||||
It will help you to validate your password strength and score.
|
||||
|
||||
We can manually create few passwords which we required but if you would like to generate a password for multiple users or servers, what will be the solution.
|
||||
|
||||
Yes, there are many utilities are available in Linux to fulfill this requirements. However, I’m going to include the best five password generators in this article.
|
||||
|
||||
These tools are generates a strong random passwords for you. Navigate to the following article if you would like to update the password on multiple users and servers.
|
||||
|
||||
These tools are easy to use, that’s why i preferred to go with it. By default it will generate a strong password and if you would like to generate a super strong password then use the available options.
|
||||
|
||||
It will help you to generate a super strong password in the following combination. It should have minimum 12-15 characters length, that includes Alphabets (Lower case & Upper case), Numbers and Special Characters.
|
||||
|
||||
These tools are below.
|
||||
|
||||
* `pwgen:` The pwgen program generates passwords which are designed to be easily memorized by humans, while being as secure as possible.
|
||||
* `openssl:` The openssl program is a command line tool for using the various cryptography functions of OpenSSL’s crypto library from the shell.
|
||||
* `gpg:` OpenPGP encryption and signing tool
|
||||
* `mkpasswd:` generate new password, optionally apply it to a user
|
||||
* `makepasswd:` makepasswd generates true random passwords using /dev/urandom, with the emphasis on security over pronounceability.
|
||||
* `/dev/urandom file:` The character special files /dev/random and /dev/urandom (present since Linux 1.3.30) provide an interface to the kernel’s random number generator.
|
||||
* `md5sum:` md5sum is a computer program that calculates and verifies 128-bit MD5 hashes.
|
||||
* `sha256sum:` The program sha256sum is designed to verify data integrity using the SHA-256 (SHA-2 family with a digest length of 256 bits).
|
||||
* `sha1pass:` sha1pass creates a SHA1 password hash. In the absence of a salt value on the command line, a random salt vector will be generated.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Generate A Random Strong Password In Linux Using pwgen Command?
|
||||
|
||||
The pwgen program generates passwords which are designed to be easily memorized by humans, while being as secure as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
Human-memorable passwords are never going to be as secure as completely completely random passwords.
|
||||
|
||||
Use `-s` option to generate completely random, hard-to-memorize passwords. These should only be used for machine passwords as we can’t memorize.
|
||||
|
||||
For **`Fedora`** system, use **[DNF Command][2]** to install pwgen.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install pwgen
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For **`Debian/Ubuntu`** systems, use **[APT-GET Command][3]** or **[APT Command][4]** to install pwgen.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install pwgen
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For **`Arch Linux`** based systems, use **[Pacman Command][5]** to install pwgen.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S pwgen
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For **`RHEL/CentOS`** systems, use **[YUM Command][6]** to install pwgen.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo yum install pwgen
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For **`openSUSE Leap`** system, use **[Zypper Command][7]** to install pwgen.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo zypper install pwgen
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Use pwgen Command In Linux?
|
||||
|
||||
It’s a simple and straight forward method. Use one of the below preferred examples for you. By default, it generates a human memorable password.
|
||||
|
||||
To do so, simple run the `pwgen` command on your terminal. It generates 160 passwords in a single shot. These 160 passwords are printer with 20 rows and 8 columns.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ pwgen
|
||||
ameiK2oo aibi3Cha EPium0Ie aisoh1Ee Nidee9ae uNga0Bee uPh9ieM1 ahn1ooNg
|
||||
oc5ooTea tai7eKid tae2yieS hiecaiR8 wohY2Ohk Uab2maed heC4aXoh Ob6Nieso
|
||||
Shaeriu3 uy9Juk5u hoht7Doo Fah6yah3 faz9Jeew eKiek4ju as0Xuosh Eiwo4epo
|
||||
oot8teeZ Ui1yoohi Aechae7A Ohdi2ael cae5Thoh Au1aeTei ais0aiC2 Cai2quin
|
||||
Oox9ohz4 neev0Che ahza8AQu Ahz7eica meiBeeW0 Av3bo7ah quoiTu3f taeNg3ae
|
||||
Aiko7Aiz SheiGh8E aesaeSh7 haet6Loo AeTel3oN Ath7zeer IeYah4ie UG3ootha
|
||||
Ohch9Och Phuap6su iel5Xu7s diqui7Bu ieF2dier eeluHa1u Thagei0i Ceeth3oh
|
||||
OCei1ahj zei2aiYo Jahgh1ia ooqu1Cej eez2aiPo Wahd5soo noo7Mei9 Hie5ashe
|
||||
Uith4Or2 Xie3uh2b fuF9Eilu eiN2sha9 zae2YaSh oGh5ephi ohvao4Ae aixu6aeM
|
||||
fo4Ierah iephei6A hae9eeGa eiBeiY3g Aic8Kee9 he8AheCh ohM4bid9 eemae3Zu
|
||||
eesh2EiM cheiGa4j PooV2vii ahpeeg5E aezauX2c Xe7aethu Ahvaph7a Joh2heec
|
||||
Ii5EeShi aij7Uo8e ooy2Ahth mieKe2ni eiQuu8fe giedaQu0 eiPhob3E oox1uo2U
|
||||
eehia4Hu ga9Ahw0a ohxuZei7 eV4OoXio Kid2wu1n ku4Ahf5s uigh8uQu AhWoh0po
|
||||
vo1Eeb2u Ahth7ve5 ieje4eiL ieci1Ach Meephie9 iephieY8 Eesoom7u eakai2Bo
|
||||
uo8Ieche Zai3aev5 aGhahf0E Wowoo5th Oraeb0ah Gah3nah0 ieGhah0p aeCh0OhJ
|
||||
ahQu2feZ ahQu0gah foik7Ush cei1Wai1 Aivi3ooY eephei5U MooZae3O quooRoh7
|
||||
aequae5U pae6Ceiv eizahF1k ohmi7ETa ahyaeK1N Mohw2no8 ooc8Oone coo7Ieve
|
||||
eePhei9h Weequ8eV Vie4iezu neeMiim4 ie6aiZoh Queegh2E shahwi3N Inichie8
|
||||
Sid1aeji mohj4Ko7 lieDi0pe Zeemah6a thuevu2E phi4Ohsh paiKeix1 ooz1Ceph
|
||||
ahV4yore ue2laePh fu1eThui qui7aePh Fahth1nu ohk9puLo aiBeez0b Neengai5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To generate a secure random password, use `-s` option with pwgen command.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ pwgen -s
|
||||
CU75lgZd 7HzzKgtA 2ktBJDpR F6XJVhBs UjAm3bNL zO7Dw7JJ pxn8fUvp Ka3lLilG
|
||||
ywJX7iJl D9ajxb6N 78c1HOg2 g8vtWCra Jp6pBGBw oYuev9Vl gbA6gHV8 G6XQoVO5
|
||||
uQN98IU4 50GgQfrX FrTsou2t YQorO4x6 UGer8Yi2 O7DB5nw1 1ax370UR 1xVRPkA1
|
||||
RVaGDr2i Nt11ekUd 9Vm3D244 ck8Lnpd0 SjDt8uWn 5ERT4tf8 4EONFzyY Jc6T83jg
|
||||
WZa6bKPW H4HMo1YU bsDDRik3 gBwV7LOW 9H1QRQ4x 3Ak7RcSe IJu2RBF9 e508xrLC
|
||||
SzTrW191 AslxDa6E IkWWov2b iOb6EmTy qHt82OwG 5ZFO7B53 97zmjOPu A4KZuhYV
|
||||
uQpoJR4D 0eKyOiUr Rz96smeO 3HTABu3N 6W0VmEls uPsp5zpw 8UD3VkMG YTct6Rd4
|
||||
VKo0cVmq E07ZX7j9 kQSlvA69 Nm3fpv3i xWvF2xMu yEfcw8uA oQGVX3l9 grTzx7Xj
|
||||
s4GVEYtM uJl5sYMe n3icRPiY ED3Mup4B k3M9KHI7 IkxqoSM0 dt2cxmMU yb2tUkut
|
||||
2Q9wGZQx 8Rpo11s9 I13siOHu 7GV64Fjv 3VONzD8i SCDfVD3F oiPTx239 6BQakoiJ
|
||||
XUEokiC4 ybL7VGmL el2RfvWk zKc7CLcE 3FqNBSyA NjDWrvZ5 KI3NSX4h VFyo6VPr
|
||||
h4q3XeqZ FDYMoX6f uTU5ZzU3 6u4ob4Ep wiYPt05n CZga66qh upzH6Z9y RuVcqbe8
|
||||
taQv11hq 1xsY67a8 EVo9GLXA FCaDLGb1 bZyh0YN8 0nTKo0Qy RRVUwn9t DuU8mwwv
|
||||
x96LWpCb tFLz3fBG dNb4gCKf n6VYcOiH 1ep6QYFZ x8kaJtrY 56PDWuW6 1R0If4kV
|
||||
2XK0NLQK 4XQqhycl Ip08cn6c Bnx9z2Bz 7gjGlON7 CJxLR1U4 mqMwir3j ovGXWu0z
|
||||
MfDjk5m8 4KwM9SAN oz0fZ5eo 5m8iRtco oP5BpLh0 Z5kvwr1W f34O2O43 hXao1Sp8
|
||||
tKoG5VNI f13fuYvm BQQn8MD3 bmFSf6Mf Z4Y0o17U jT4wO1DG cz2clBES Lr4B3qIY
|
||||
ArKQRND6 8xnh4oIs nayiK2zG yWvQCV3v AFPlHSB8 zfx5bnaL t5lFbenk F2dIeBr4
|
||||
C6RqDQMy gKt28c9O ZCi0tQKE 0Ekdjh3P ox2vWOMI 14XF4gwc nYA0L6tV rRN3lekn
|
||||
lmwZNjz1 4ovmJAr7 shPl9o5f FFsuNwj0 F2eVkqGi 7gw277RZ nYE7gCLl JDn05S5N
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you would like to generate a strong five passwords with 14 characters length, use the following format.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ pwgen -s 14 5
|
||||
7YxUwDyfxGVTYD em2NT6FceXjPfT u8jlrljbrclcTi IruIX3Xu0TFXRr X8M9cB6wKNot1e
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you really want to generate a super strong random twenty passwords, use the following format.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ pwgen -cnys 14 20
|
||||
mQ3E=vfGfZ,5[B #zmj{i5|ZS){jg Ht_8i7OqJ%N`~2 443fa5iJ\W-L?] ?Qs$o=vz2vgQBR
|
||||
^'Ry0Az|J9p2+0 t2oA/n7U_'|QRx EsX*%_(4./QCRJ ACr-,8yF9&eM[* !Xz1C'bw?tv50o
|
||||
8hfv-fK(VxwQGS q!qj?sD7Xmkb7^ N#Zp\_Y2kr%!)~ 4*pwYs{bq]Hh&Y |4u=-Q1!jS~8=;
|
||||
]{$N#FPX1L2B{h I|01fcK.z?QTz" l~]JD_,W%5bp.E +i2=D3;BQ}p+$I n.a3,.D3VQ3~&i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Generate A Random Strong Password In Linux Using openssl Command?
|
||||
|
||||
The openssl program is a command line tool for using the various cryptography functions of OpenSSL’s crypto library from the shell.
|
||||
|
||||
Run the openssl command with the following format to generate a random strong password with 14 characters.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ openssl rand -base64 14
|
||||
WjzyDqdkWf3e53tJw/c=
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you would like to generate ten random strong password with 14 characters using openssl command then use the following for loop.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ for pw in {1..10}; do openssl rand -base64 14; done
|
||||
6i0hgHDBi3ohZ9Mil8I=
|
||||
gtn+y1bVFJFanpJqWaA=
|
||||
rYu+wy+0nwLf5lk7TBA=
|
||||
xrdNGykIzxaKDiLF2Bw=
|
||||
cltejRkDPdFPC/zI0Pg=
|
||||
G6aroK6d4xVVYFTrZGs=
|
||||
jJEnFoOk1+UTSx/wJrY=
|
||||
TFxVjBmLx9aivXB3yxE=
|
||||
oQtOLPwTuO8df7dIv9I=
|
||||
ktpBpCSQFOD+5kIIe7Y=
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Generate A Random Strong Password In Linux Using gpg Command?
|
||||
|
||||
gpg is the OpenPGP part of the GNU Privacy Guard (GnuPG). It is a tool to provide digital encryption and signing services using the OpenPGP standard. gpg features complete key management and all the bells and whistles you would expect from a full OpenPGP implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
Run the gpg command with the following format to generate a random strong password with 14 characters.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ gpg --gen-random --armor 1 14
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ gpg2 --gen-random --armor 1 14
|
||||
jq1mtY4gBa6gIuJrggM=
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you would like to generate ten random strong password with 14 characters using gpg command then use the following for loop.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ for pw in {1..10}; do gpg --gen-random --armor 1 14; done
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ for pw in {1..10}; do gpg2 --gen-random --armor 1 14; done
|
||||
F5ZzLSUMet2kefG6Ssc=
|
||||
8hh7BFNs8Qu0cnrvHrY=
|
||||
B+PEt28CosR5xO05/sQ=
|
||||
m21bfx6UG1cBDzVGKcE=
|
||||
wALosRXnBgmOC6+++xU=
|
||||
TGpjT5xRxo/zFq/lNeg=
|
||||
ggsKxVgpB/3aSOY15W4=
|
||||
iUlezWxL626CPc9omTI=
|
||||
pYb7xQwI1NTlM2rxaCg=
|
||||
eJjhtA6oHhBrUpLY4fM=
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Generate A Random Strong Password In Linux Using mkpasswd Command?
|
||||
|
||||
mkpasswd generates passwords and can apply them automatically to users. With no arguments, mkpasswd returns a new password. It’s part of an expect package so, you have to install expect package to use mkpasswd command.
|
||||
|
||||
For **`Fedora`** system, use **[DNF Command][2]** to install mkpasswd.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install expect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For **`Debian/Ubuntu`** systems, use **[APT-GET Command][3]** or **[APT Command][4]** to install mkpasswd.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install expect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For **`Arch Linux`** based systems, use **[Pacman Command][5]** to install mkpasswd.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S expect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For **`RHEL/CentOS`** systems, use **[YUM Command][6]** to install mkpasswd.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo yum install expect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For **`openSUSE Leap`** system, use **[Zypper Command][7]** to install mkpasswd.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo zypper install expect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run the `mkpasswd` command in terminal to generate a random password.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ mkpasswd
|
||||
37_slQepD
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run the mkpasswd command with the following format to generate a random strong password with 14 characters.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ mkpasswd -l 14
|
||||
W1qP1uv=lhghgh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run the mkpasswd command with the following format to generate a random strong password with 14 characters. It combinations of alphabetic (Lower & Upper case), Numeric number and special characters.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ mkpasswd -l 14 -d 3 -C 3 -s 3
|
||||
3aad!bMWG49"t,
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you would like to generate ten random strong password with 14 characters (It combination of alphabetic (Lower & Upper case), Numeric number and special characters) using mkpasswd command then use the following for loop.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ for pw in {1..10}; do mkpasswd -l 14 -d 3 -C 3 -s 3; done
|
||||
zmSwP[q9;P1r6[
|
||||
E42zcvzM"i3%B\
|
||||
8}1#[email protected]
|
||||
0X:zB(mmU22?nj
|
||||
0sqqL44M}ko(O^
|
||||
43tQ(.6jG;ceRq
|
||||
-jB6cp3x1GZ$e=
|
||||
$of?Rj9kb2N(1J
|
||||
9HCf,nn#gjO79^
|
||||
Tu9m56+Ev_Yso(
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Generate A Random Strong Password In Linux Using makepasswd Command?
|
||||
|
||||
makepasswd generates true random passwords using /dev/urandom, with the emphasis on security over pronounceability. It can also encrypt plaintext passwords given on the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
Run the `makepasswd` command in terminal to generate a random password.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ makepasswd
|
||||
HdCJafVaN
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run the makepasswd command with the following format to generate a random strong password with 14 characters.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ makepasswd --chars 14
|
||||
HxJDv5quavrqmU
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run the makepasswd command with the following format to generate ten random strong password with 14 characters.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ makepasswd --chars 14 --count 10
|
||||
TqmKVWnRGeoVNr
|
||||
mPV2P98hLRUsai
|
||||
MhMXPwyzYi2RLo
|
||||
dxMGgLmoFpYivi
|
||||
8p0G7JvJjd6qUP
|
||||
7SmX95MiJcQauV
|
||||
KWzrh5npAjvNmL
|
||||
oHPKdq1uA9tU85
|
||||
V1su9GjU2oIGiQ
|
||||
M2TMCEoahzLNYC
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Generate A Random Strong Password In Linux Using Multiple Commands?
|
||||
|
||||
Still if you are looking other options then you can use the following utilities to generate a random password in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
**Using md5sum:** md5sum is a computer program that calculates and verifies 128-bit MD5 hashes.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ date | md5sum
|
||||
9baf96fb6e8cbd99601d97a5c3acc2c4 -
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Using /dev/urandom:** The character special files /dev/random and /dev/urandom (present since Linux 1.3.30) provide an interface to the kernel’s random number generator. File /dev/random has major device number 1 and minor device number 8. File /dev/urandom has major device number 1 and minor device number 9.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | head -c 14
|
||||
15LQB9J84Btnzz
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Using sha256sum:** The program sha256sum is designed to verify data integrity using the SHA-256 (SHA-2 family with a digest length of 256 bits).
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ date | sha256sum
|
||||
a114ae5c458ae0d366e1b673d558d921bb937e568d9329b525cf32290478826a -
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Using sha1pass:** sha1pass creates a SHA1 password hash. In the absence of a salt value on the command line, a random salt vector will be generated.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sha1pass
|
||||
$4$9+JvykOv$e7U0jMJL2yBOL+RVa2Eke8SETEo$
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.2daygeek.com/5-ways-to-generate-a-random-strong-password-in-linux-terminal/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Magesh Maruthamuthu][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[leommx](https://github.com/leommxj)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://www.2daygeek.com/how-to-check-password-complexity-strength-and-score-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]: https://www.2daygeek.com/dnf-command-examples-manage-packages-fedora-system/
|
||||
[3]: https://www.2daygeek.com/apt-get-apt-cache-command-examples-manage-packages-debian-ubuntu-systems/
|
||||
[4]: https://www.2daygeek.com/apt-command-examples-manage-packages-debian-ubuntu-systems/
|
||||
[5]: https://www.2daygeek.com/pacman-command-examples-manage-packages-arch-linux-system/
|
||||
[6]: https://www.2daygeek.com/yum-command-examples-manage-packages-rhel-centos-systems/
|
||||
[7]: https://www.2daygeek.com/zypper-command-examples-manage-packages-opensuse-system/
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: ( )
|
||||
[#]: translator: (qhwdw)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: ( )
|
||||
[#]: translator: (geekpi)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: (geekpi)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
[#]: subject: (Get started with Freeplane, an open source mind mapping application)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://opensource.com/article/19/1/productivity-tool-freeplane)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Kevin Sonney https://opensource.com/users/ksonney (Kevin Sonney))
|
||||
|
||||
开始使用 Freeplane,一款开源思维导图
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
使用 Freeplane 进行头脑风暴,这是我们开源工具系列中的第 13 个,它将使你在 2019 年更高效。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
每年年初似乎都有疯狂的冲动,想方设法提高工作效率。新年的决议,开始一年的权利,当然,“与旧的,与新的”的态度都有助于实现这一目标。通常的一轮建议严重偏向封闭源和专有软件。它不一定是这样。
|
||||
|
||||
这是我挑选出的 19 个新的(或者对你而言新的)开源工具中的第 13 个工具来帮助你在 2019 年更有效率。
|
||||
|
||||
### Freeplane
|
||||
|
||||
[思维导图][1]是我用于快速头脑风暴和捕捉数据的最有价值的工具之一。思维导图是一个灵活的过程,有助于显示事物的相关性,并可用于快速组织相互关联的信息。从规划角度来看,思维导图让你快速将大脑中的单个概念,想法或技术表达除了。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
[Freeplane][2] 是一款桌面应用,可以轻松创建、查看、编辑和共享思维导图。它是 [FreeMind][3] 这款很长时间内都是思维导图首选应用的重新设计。
|
||||
|
||||
安装 Freeplane 非常简单。它是一个 [Java][4] 应用,并使用 ZIP 文件分发,可使用脚本在 Linux、Windows 和 MacOS 上启动。在第一次启动它时,主窗口会包含一个示例思维导图,其中包含指向你可以使用 Freeplane 执行的所有不同操作的文档的链接。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建新思维导图时,你可以选择模板。标准模板(可能位于列表底部)适用于大多数情况。你只需开始输入开头的想法或短语,你的文本就会替换中心的文本。按“插入”键将从中心添加一个分支(或节点),其中包含一个空白字段,你可以在其中填写与该想法相关的内容。再次按“插入”将添加另一个节点到第一个上。在节点上按“回车”键将添加与该节点平行的节点。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在添加节点时,你可能会想到与主题相关的另一个想法。使用鼠标或箭头键,返回到导图的中心,然后按“插入”键。这将在主题之外创建一个新节点。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想使用 Freeplane 其他功能,请右键单击任何节点以显示该节点的“属性”菜单。工具窗口(在视图 ->控制菜单下激活)包含丰富的自定义选项,包括线条形状和粗细、边框形状、颜色等等。“日历”选项允许你在节点中插入日期,并为节点设置到期提醒。 (请注意,提醒仅在 Freeplane 运行时有效。)思维导图可以导出为多种格式,包括常见的图像、XML、Microsoft Project、Markdown 和 OPML。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Freeplane 为你提供了创建生动和实用的思维导图所需的所有工具,让你表达头脑中的想法,并可采取行动。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://opensource.com/article/19/1/productivity-tool-freeplane
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Kevin Sonney][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://opensource.com/users/ksonney (Kevin Sonney)
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mind_map
|
||||
[2]: https://www.freeplane.org/wiki/index.php/Home
|
||||
[3]: https://sourceforge.net/projects/freemind/
|
||||
[4]: https://java.com
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,367 @@
|
||||
[#]: collector: (lujun9972)
|
||||
[#]: translator: (leommxj)
|
||||
[#]: reviewer: ( )
|
||||
[#]: publisher: ( )
|
||||
[#]: url: ( )
|
||||
[#]: subject: (5 Ways To Generate A Random/Strong Password In Linux Terminal)
|
||||
[#]: via: (https://www.2daygeek.com/5-ways-to-generate-a-random-strong-password-in-linux-terminal/)
|
||||
[#]: author: (Magesh Maruthamuthu https://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/)
|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 终端下生成随机/强密码的五种方法
|
||||
======
|
||||
|
||||
最近我们在网站上发表过一篇关于 **[密码强度与密码分数检查][1]** 的文章。
|
||||
|
||||
它可以帮助你检查你的密码的强度和分数。
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以手工创建我们需要的密码。但如果你想要为多个用户或服务器生成密码,解决方案是什么呢?
|
||||
|
||||
是的,Linux 中有许多可用的工具能满足这个需求。本文中我将会介绍五种最好的密码生成器。
|
||||
|
||||
这些工具可以为你生成高强度随机密码。如果你想要为多个用户和服务器更新密码,请继续读下去。
|
||||
|
||||
这些工具易于使用,这也是我喜欢用它们的原因。默认情况下它们会生成一个足够强壮的密码,你也可以通过使用其他可用的选项来生成一个超强的密码。
|
||||
|
||||
它会帮助你生成符合下列要求的超强密码。密码长度至少有 12-15 个字符,包括字母(大写及小写),数字及特殊符号。
|
||||
|
||||
工具如下:
|
||||
|
||||
* `pwgen:` pwgen 程序生成易于人类记忆并且尽可能安全的密码。
|
||||
* `openssl:` openssl 是一个用来从 shell 中调用 OpenSSL 加密库提供的多种密码学函数的命令行工具。
|
||||
* `gpg:` OpenPGP 加密/签名工具。
|
||||
* `mkpasswd:` 生成新密码,可以选择直接应用给一名用户。
|
||||
* `makepasswd:` makepasswd 使用 /dev/urandom 生成真随机密码,比起好记它更重视安全性。
|
||||
* `/dev/urandom file` 两个特殊的字符文件 /dev/random 和 /dev/urandom (自 Linux 1.3.30 起) 提供了内核随机数生成器的接口。
|
||||
* `md5sum:` md5sum 是一个用来计算及校验 128-bit MD5 哈希的程序。
|
||||
* `sha256sum:` sha256sum 被设计用来使用 SHA-256 算法(SHA-2系列,摘要长度为256位)校验数据完整性。
|
||||
* `sha1pass:` sha1pass 生成一个 SHA1 密码哈希。在命令缺少盐值的情况下,将会生成一个随机的盐值向量。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 怎么用 pwgen 命令在 linux 下生成一个随机的强壮密码?
|
||||
|
||||
pwgen 程序生成易于人类记忆并且尽可能安全的密码。
|
||||
|
||||
易于人类记忆的密码永远都不会像完全随机的密码一样安全。
|
||||
|
||||
使用 `-s` 选项来生成完全随机,难于记忆的密码。由于我们记不住,这些密码应该只用于机器。
|
||||
|
||||
在 **`Fedora`** 系统中,使用 **[DNF 命令][2]** 来安装 pwgen。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install pwgen
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 **`Debian/Ubuntu`** 系统中,使用 **[APT-GET 命令][3]** 或 **[APT 命令][4]** 来安装 pwgen。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install pwgen
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 **`Arch Linux`** 系统中,使用 **[Pacman 命令][5]** 来安装 pwgen。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S pwgen
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 **`RHEL/CentOS`** 系统中,使用 **[YUM 命令][6]** 来安装 pwgen。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo yum install pwgen
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 **`openSUSE Leap`** 系统中,使用 **[Zypper 命令][7]** 来安装pwgen。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo zypper install pwgen
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 下如何使用 pwgen 命令?
|
||||
|
||||
使用方法非常简单直接。使用下列示例中更适合你的那种。默认情况下,它会生成一个方便记忆的密码。
|
||||
|
||||
想要这样做,只要在你的终端中运行 `pwgen` 命令。将会一下生成160个密码以8列20行打印出来。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ pwgen
|
||||
ameiK2oo aibi3Cha EPium0Ie aisoh1Ee Nidee9ae uNga0Bee uPh9ieM1 ahn1ooNg
|
||||
oc5ooTea tai7eKid tae2yieS hiecaiR8 wohY2Ohk Uab2maed heC4aXoh Ob6Nieso
|
||||
Shaeriu3 uy9Juk5u hoht7Doo Fah6yah3 faz9Jeew eKiek4ju as0Xuosh Eiwo4epo
|
||||
oot8teeZ Ui1yoohi Aechae7A Ohdi2ael cae5Thoh Au1aeTei ais0aiC2 Cai2quin
|
||||
Oox9ohz4 neev0Che ahza8AQu Ahz7eica meiBeeW0 Av3bo7ah quoiTu3f taeNg3ae
|
||||
Aiko7Aiz SheiGh8E aesaeSh7 haet6Loo AeTel3oN Ath7zeer IeYah4ie UG3ootha
|
||||
Ohch9Och Phuap6su iel5Xu7s diqui7Bu ieF2dier eeluHa1u Thagei0i Ceeth3oh
|
||||
OCei1ahj zei2aiYo Jahgh1ia ooqu1Cej eez2aiPo Wahd5soo noo7Mei9 Hie5ashe
|
||||
Uith4Or2 Xie3uh2b fuF9Eilu eiN2sha9 zae2YaSh oGh5ephi ohvao4Ae aixu6aeM
|
||||
fo4Ierah iephei6A hae9eeGa eiBeiY3g Aic8Kee9 he8AheCh ohM4bid9 eemae3Zu
|
||||
eesh2EiM cheiGa4j PooV2vii ahpeeg5E aezauX2c Xe7aethu Ahvaph7a Joh2heec
|
||||
Ii5EeShi aij7Uo8e ooy2Ahth mieKe2ni eiQuu8fe giedaQu0 eiPhob3E oox1uo2U
|
||||
eehia4Hu ga9Ahw0a ohxuZei7 eV4OoXio Kid2wu1n ku4Ahf5s uigh8uQu AhWoh0po
|
||||
vo1Eeb2u Ahth7ve5 ieje4eiL ieci1Ach Meephie9 iephieY8 Eesoom7u eakai2Bo
|
||||
uo8Ieche Zai3aev5 aGhahf0E Wowoo5th Oraeb0ah Gah3nah0 ieGhah0p aeCh0OhJ
|
||||
ahQu2feZ ahQu0gah foik7Ush cei1Wai1 Aivi3ooY eephei5U MooZae3O quooRoh7
|
||||
aequae5U pae6Ceiv eizahF1k ohmi7ETa ahyaeK1N Mohw2no8 ooc8Oone coo7Ieve
|
||||
eePhei9h Weequ8eV Vie4iezu neeMiim4 ie6aiZoh Queegh2E shahwi3N Inichie8
|
||||
Sid1aeji mohj4Ko7 lieDi0pe Zeemah6a thuevu2E phi4Ohsh paiKeix1 ooz1Ceph
|
||||
ahV4yore ue2laePh fu1eThui qui7aePh Fahth1nu ohk9puLo aiBeez0b Neengai5
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成安全的随机密码,使用 pwgen 命令的 `-s` 选项。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ pwgen -s
|
||||
CU75lgZd 7HzzKgtA 2ktBJDpR F6XJVhBs UjAm3bNL zO7Dw7JJ pxn8fUvp Ka3lLilG
|
||||
ywJX7iJl D9ajxb6N 78c1HOg2 g8vtWCra Jp6pBGBw oYuev9Vl gbA6gHV8 G6XQoVO5
|
||||
uQN98IU4 50GgQfrX FrTsou2t YQorO4x6 UGer8Yi2 O7DB5nw1 1ax370UR 1xVRPkA1
|
||||
RVaGDr2i Nt11ekUd 9Vm3D244 ck8Lnpd0 SjDt8uWn 5ERT4tf8 4EONFzyY Jc6T83jg
|
||||
WZa6bKPW H4HMo1YU bsDDRik3 gBwV7LOW 9H1QRQ4x 3Ak7RcSe IJu2RBF9 e508xrLC
|
||||
SzTrW191 AslxDa6E IkWWov2b iOb6EmTy qHt82OwG 5ZFO7B53 97zmjOPu A4KZuhYV
|
||||
uQpoJR4D 0eKyOiUr Rz96smeO 3HTABu3N 6W0VmEls uPsp5zpw 8UD3VkMG YTct6Rd4
|
||||
VKo0cVmq E07ZX7j9 kQSlvA69 Nm3fpv3i xWvF2xMu yEfcw8uA oQGVX3l9 grTzx7Xj
|
||||
s4GVEYtM uJl5sYMe n3icRPiY ED3Mup4B k3M9KHI7 IkxqoSM0 dt2cxmMU yb2tUkut
|
||||
2Q9wGZQx 8Rpo11s9 I13siOHu 7GV64Fjv 3VONzD8i SCDfVD3F oiPTx239 6BQakoiJ
|
||||
XUEokiC4 ybL7VGmL el2RfvWk zKc7CLcE 3FqNBSyA NjDWrvZ5 KI3NSX4h VFyo6VPr
|
||||
h4q3XeqZ FDYMoX6f uTU5ZzU3 6u4ob4Ep wiYPt05n CZga66qh upzH6Z9y RuVcqbe8
|
||||
taQv11hq 1xsY67a8 EVo9GLXA FCaDLGb1 bZyh0YN8 0nTKo0Qy RRVUwn9t DuU8mwwv
|
||||
x96LWpCb tFLz3fBG dNb4gCKf n6VYcOiH 1ep6QYFZ x8kaJtrY 56PDWuW6 1R0If4kV
|
||||
2XK0NLQK 4XQqhycl Ip08cn6c Bnx9z2Bz 7gjGlON7 CJxLR1U4 mqMwir3j ovGXWu0z
|
||||
MfDjk5m8 4KwM9SAN oz0fZ5eo 5m8iRtco oP5BpLh0 Z5kvwr1W f34O2O43 hXao1Sp8
|
||||
tKoG5VNI f13fuYvm BQQn8MD3 bmFSf6Mf Z4Y0o17U jT4wO1DG cz2clBES Lr4B3qIY
|
||||
ArKQRND6 8xnh4oIs nayiK2zG yWvQCV3v AFPlHSB8 zfx5bnaL t5lFbenk F2dIeBr4
|
||||
C6RqDQMy gKt28c9O ZCi0tQKE 0Ekdjh3P ox2vWOMI 14XF4gwc nYA0L6tV rRN3lekn
|
||||
lmwZNjz1 4ovmJAr7 shPl9o5f FFsuNwj0 F2eVkqGi 7gw277RZ nYE7gCLl JDn05S5N
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
假设你想要生成五个14字符长的密码,方法如下。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ pwgen -s 14 5
|
||||
7YxUwDyfxGVTYD em2NT6FceXjPfT u8jlrljbrclcTi IruIX3Xu0TFXRr X8M9cB6wKNot1e
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你真的想要生成20个超强随机密码,方法如下。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ pwgen -cnys 14 20
|
||||
mQ3E=vfGfZ,5[B #zmj{i5|ZS){jg Ht_8i7OqJ%N`~2 443fa5iJ\W-L?] ?Qs$o=vz2vgQBR
|
||||
^'Ry0Az|J9p2+0 t2oA/n7U_'|QRx EsX*%_(4./QCRJ ACr-,8yF9&eM[* !Xz1C'bw?tv50o
|
||||
8hfv-fK(VxwQGS q!qj?sD7Xmkb7^ N#Zp\_Y2kr%!)~ 4*pwYs{bq]Hh&Y |4u=-Q1!jS~8=;
|
||||
]{$N#FPX1L2B{h I|01fcK.z?QTz" l~]JD_,W%5bp.E +i2=D3;BQ}p+$I n.a3,.D3VQ3~&i
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在 Linux 下使用 openssl 命令生成随机强密码?
|
||||
|
||||
openssl 是一个用来从 shell 中调用 OpenSSL 加密库提供的多种密码学函数的命令行工具。
|
||||
|
||||
像下面这样运行 openssl 命令可以生成一个14字符长的随机强密码。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ openssl rand -base64 14
|
||||
WjzyDqdkWf3e53tJw/c=
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要生成十个14字符长的随机强密码,将 openssl 命令与 for 循环结合起来使用。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ for pw in {1..10}; do openssl rand -base64 14; done
|
||||
6i0hgHDBi3ohZ9Mil8I=
|
||||
gtn+y1bVFJFanpJqWaA=
|
||||
rYu+wy+0nwLf5lk7TBA=
|
||||
xrdNGykIzxaKDiLF2Bw=
|
||||
cltejRkDPdFPC/zI0Pg=
|
||||
G6aroK6d4xVVYFTrZGs=
|
||||
jJEnFoOk1+UTSx/wJrY=
|
||||
TFxVjBmLx9aivXB3yxE=
|
||||
oQtOLPwTuO8df7dIv9I=
|
||||
ktpBpCSQFOD+5kIIe7Y=
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在 Linux 下使用 gpg 命令生成随机强密码?
|
||||
|
||||
gpg 是 Gnu Privacy Guard (GnuPG) 中的 OpenPGP 实现部分。它是一个提供 OpenPGP 标准的数字加密与签名服务的工具。gpg 具有完整的密钥管理功能和其他完整 OpenPGP 实现应该具备的全部功能。
|
||||
|
||||
下面这样执行 gpg 命令来生成一个14字符长的随机强密码。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ gpg --gen-random --armor 1 14
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ gpg2 --gen-random --armor 1 14
|
||||
jq1mtY4gBa6gIuJrggM=
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果想要使用 gpg 生成十个14字符长的随机强密码,像下面这样使用 for 循环。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ for pw in {1..10}; do gpg --gen-random --armor 1 14; done
|
||||
or
|
||||
$ for pw in {1..10}; do gpg2 --gen-random --armor 1 14; done
|
||||
F5ZzLSUMet2kefG6Ssc=
|
||||
8hh7BFNs8Qu0cnrvHrY=
|
||||
B+PEt28CosR5xO05/sQ=
|
||||
m21bfx6UG1cBDzVGKcE=
|
||||
wALosRXnBgmOC6+++xU=
|
||||
TGpjT5xRxo/zFq/lNeg=
|
||||
ggsKxVgpB/3aSOY15W4=
|
||||
iUlezWxL626CPc9omTI=
|
||||
pYb7xQwI1NTlM2rxaCg=
|
||||
eJjhtA6oHhBrUpLY4fM=
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在 Linux 下使用 mkpasswd 命令生成随机强密码?
|
||||
|
||||
mkpasswd 生成密码并可以自动将其应用在用户上。不加任何参数的情况下,mkpasswd 返回一个新的密码。它是 expect 软件包的一部分,所以想要使用 mkpasswd 命令,你需要安装 expect 软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
在 **`Fedora`** 系统中,使用 **[DNF 命令][2]** 来安装 mkpasswd。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install expect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 **`Debian/Ubuntu`** 系统中,使用 **[APT-GET 命令][3]** 或 **[APT 命令][4]** 来安装 mkpasswd。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo apt install expect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 **`Arch Linux`** 系统中,使用 **[Pacman 命令][5]** 来安装 mkpasswd。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo pacman -S expect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 **`RHEL/CentOS`** 系统中,使用 **[YUM 命令][6]** 来安装 mkpasswd。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo yum install expect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在 **`openSUSE Leap`** 系统中,使用 **[Zypper 命令][7]** 来安装 mkpasswd。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo zypper install expect
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在终端中执行 `mkpasswd` 命令来生成一个随机密码。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ mkpasswd
|
||||
37_slQepD
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
像下面这样执行 mkpasswd 命令可以生成一个14字符长的随机强密码。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ mkpasswd -l 14
|
||||
W1qP1uv=lhghgh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
像下面这样执行 mkpasswd 命令 来生成一个14字符长,包含大小写字母、数字和特殊字符的随机强密码。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ mkpasswd -l 14 -d 3 -C 3 -s 3
|
||||
3aad!bMWG49"t,
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要生成十个14字符长的随机强密码(包括大小写字母、数字和特殊字符),使用 for 循环和 mkpasswd 命令。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ for pw in {1..10}; do mkpasswd -l 14 -d 3 -C 3 -s 3; done
|
||||
zmSwP[q9;P1r6[
|
||||
E42zcvzM"i3%B\
|
||||
8}1#[email protected]
|
||||
0X:zB(mmU22?nj
|
||||
0sqqL44M}ko(O^
|
||||
43tQ(.6jG;ceRq
|
||||
-jB6cp3x1GZ$e=
|
||||
$of?Rj9kb2N(1J
|
||||
9HCf,nn#gjO79^
|
||||
Tu9m56+Ev_Yso(
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How To Generate A Random Strong Password In Linux Using makepasswd Command?
|
||||
### 如何在 Linux 下使用 makepasswd 命令生成随机强密码?
|
||||
|
||||
makepasswd 使用 /dev/urandom 生成真随机密码,跟易于记忆相比它更注重安全性。它也可以加密命令行中给出的明文密码。
|
||||
|
||||
在终端中执行 `makepasswd` 命令来生成一个随机密码。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ makepasswd
|
||||
HdCJafVaN
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在终端中像下面这样执行 makepasswd 命令来生成14字符长的随机强密码。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ makepasswd --chars 14
|
||||
HxJDv5quavrqmU
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
像下面这样执行 makepasswd 来生成十个14字符长的随机强密码。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ makepasswd --chars 14 --count 10
|
||||
TqmKVWnRGeoVNr
|
||||
mPV2P98hLRUsai
|
||||
MhMXPwyzYi2RLo
|
||||
dxMGgLmoFpYivi
|
||||
8p0G7JvJjd6qUP
|
||||
7SmX95MiJcQauV
|
||||
KWzrh5npAjvNmL
|
||||
oHPKdq1uA9tU85
|
||||
V1su9GjU2oIGiQ
|
||||
M2TMCEoahzLNYC
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在 Linux 系统中使用多个命令生成随机强密码?
|
||||
|
||||
如果你还在寻找其他的方案,下面的工具也可以用来在 Linux 中生成随机密码。
|
||||
|
||||
**使用 md5sum** md5sum 是一个用来计算及校验 128-bit MD5 哈希的程序。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ date | md5sum
|
||||
9baf96fb6e8cbd99601d97a5c3acc2c4 -
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**使用 /dev/urandom:** 两个特殊的字符文件 /dev/random 和 /dev/urandom (自 Linux 1.3.30 起) 提供了内核随机数生成器的接口。/dev/random 的主设备号为1,次设备号为8。/dev/urandom 主设备号为1,次设备号为9。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ cat /dev/urandom | tr -dc 'a-zA-Z0-9' | head -c 14
|
||||
15LQB9J84Btnzz
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**使用 sha256sum:** sha256sum 被设计用来使用 SHA-256 算法(SHA-2系列,摘要长度为256位)校验数据完整性。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ date | sha256sum
|
||||
a114ae5c458ae0d366e1b673d558d921bb937e568d9329b525cf32290478826a -
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**使用 sha1pass:** sha1pass 生成一个 SHA1 密码哈希。在命令缺少盐值的情况下,将会生成一个随机的盐值向量。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sha1pass
|
||||
$4$9+JvykOv$e7U0jMJL2yBOL+RVa2Eke8SETEo$
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: https://www.2daygeek.com/5-ways-to-generate-a-random-strong-password-in-linux-terminal/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Magesh Maruthamuthu][a]
|
||||
选题:[lujun9972][b]
|
||||
译者:[leommx](https://github.com/leommxj)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: https://www.2daygeek.com/author/magesh/
|
||||
[b]: https://github.com/lujun9972
|
||||
[1]: https://www.2daygeek.com/how-to-check-password-complexity-strength-and-score-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]: https://www.2daygeek.com/dnf-command-examples-manage-packages-fedora-system/
|
||||
[3]: https://www.2daygeek.com/apt-get-apt-cache-command-examples-manage-packages-debian-ubuntu-systems/
|
||||
[4]: https://www.2daygeek.com/apt-command-examples-manage-packages-debian-ubuntu-systems/
|
||||
[5]: https://www.2daygeek.com/pacman-command-examples-manage-packages-arch-linux-system/
|
||||
[6]: https://www.2daygeek.com/yum-command-examples-manage-packages-rhel-centos-systems/
|
||||
[7]: https://www.2daygeek.com/zypper-command-examples-manage-packages-opensuse-system/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user