mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-30 02:40:11 +08:00
[Translated] tech/RHCE/Part 6 - Setting Up Samba and Configure FirewallD and SELinux to Allow File Sharing on Linux or Windows Clients.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
1f8e435781
commit
552e482c8a
@ -1,209 +0,0 @@
|
||||
ictlyh Translating
|
||||
Setting Up Samba and Configure FirewallD and SELinux to Allow File Sharing on Linux/Windows Clients – Part 6
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Since computers seldom work as isolated systems, it is to be expected that as a system administrator or engineer, you know how to set up and maintain a network with multiple types of servers.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article and in the next of this series we will go through the essentials of setting up Samba and NFS servers with Windows/Linux and Linux clients, respectively.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCE: Setup Samba File Sharing – Part 6
|
||||
|
||||
This article will definitely come in handy if you’re called upon to set up file servers in corporate or enterprise environments where you are likely to find different operating systems and types of devices.
|
||||
|
||||
Since you can read about the background and the technical aspects of both Samba and NFS all over the Internet, in this article and the next we will cut right to the chase with the topic at hand.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 1: Installing Samba Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
Our current testing environment consists of two RHEL 7 boxes and one Windows 8 machine, in that order:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Samba / NFS server [box1 (RHEL 7): 192.168.0.18],
|
||||
2. Samba client #1 [box2 (RHEL 7): 192.168.0.20]
|
||||
3. Samba client #2 [Windows 8 machine: 192.168.0.106]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Testing Setup for Samba
|
||||
|
||||
On box1, install the following packages:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install samba samba-client samba-common
|
||||
|
||||
On box2:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install samba samba-client samba-common cifs-utils
|
||||
|
||||
Once the installation is complete, we’re ready to configure our share.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 2: Setting Up File Sharing Through Samba ###
|
||||
|
||||
One of the reason why Samba is so relevant is because it provides file and print services to SMB/CIFS clients, which causes those clients to see the server as if it was a Windows system (I must admit I tend to get a little emotional while writing about this topic as it was my first setup as a new Linux system administrator some years ago).
|
||||
|
||||
**Adding system users and setting up permissions and ownership**
|
||||
|
||||
To allow for group collaboration, we will create a group named finance with two users (user1 and user2) with [useradd command][1] and a directory /finance in box1.
|
||||
|
||||
We will also change the group owner of this directory to finance and set its permissions to 0770 (read, write, and execution permissions for the owner and the group owner):
|
||||
|
||||
# groupadd finance
|
||||
# useradd user1
|
||||
# useradd user2
|
||||
# usermod -a -G finance user1
|
||||
# usermod -a -G finance user2
|
||||
# mkdir /finance
|
||||
# chmod 0770 /finance
|
||||
# chgrp finance /finance
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 3: Configuring SELinux and Firewalld ###
|
||||
|
||||
In preparation to configure /finance as a Samba share, we will need to either disable SELinux or set the proper boolean and security context values as follows (otherwise, SELinux will prevent clients from accessing the share):
|
||||
|
||||
# setsebool -P samba_export_all_ro=1 samba_export_all_rw=1
|
||||
# getsebool –a | grep samba_export
|
||||
# semanage fcontext –at samba_share_t "/finance(/.*)?"
|
||||
# restorecon /finance
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, we must ensure that Samba traffic is allowed by the [firewalld][2].
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=samba
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 4: Configure Samba Share ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now it’s time to dive into the configuration file /etc/samba/smb.conf and add the section for our share: we want the members of the finance group to be able to browse the contents of /finance, and save / create files or subdirectories in it (which by default will have their permission bits set to 0770 and finance will be their group owner):
|
||||
|
||||
**smb.conf**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[finance]
|
||||
comment=Directory for collaboration of the company's finance team
|
||||
browsable=yes
|
||||
path=/finance
|
||||
public=no
|
||||
valid users=@finance
|
||||
write list=@finance
|
||||
writeable=yes
|
||||
create mask=0770
|
||||
Force create mode=0770
|
||||
force group=finance
|
||||
|
||||
Save the file and then test it with the testparm utility. If there are any errors, the output of the following command will indicate what you need to fix. Otherwise, it will display a review of your Samba server configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
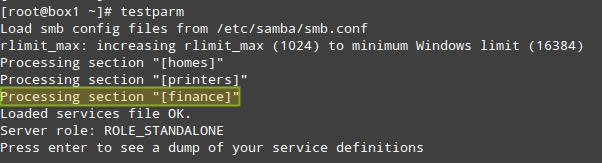
|
||||
|
||||
Test Samba Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Should you want to add another share that is open to the public (meaning without any authentication whatsoever), create another section in /etc/samba/smb.conf and under the new share’s name copy the section above, only changing public=no to public=yes and not including the valid users and write list directives.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 5: Adding Samba Users ###
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you will need to add user1 and user2 as Samba users. To do so, you will use the smbpasswd command, which interacts with Samba’s internal database. You will be prompted to enter a password that you will later use to connect to the share:
|
||||
|
||||
# smbpasswd -a user1
|
||||
# smbpasswd -a user2
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, restart Samba, enable the service to start on boot, and make sure the share is actually available to network clients:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start smb
|
||||
# systemctl enable smb
|
||||
# smbclient -L localhost –U user1
|
||||
# smbclient -L localhost –U user2
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Verify Samba Share
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, the Samba file server has been properly installed and configured. Now it’s time to test this setup on our RHEL 7 and Windows 8 clients.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 6: Mounting the Samba Share in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure the Samba share is accessible from this client:
|
||||
|
||||
# smbclient –L 192.168.0.18 -U user2
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Mount Samba Share on Linux
|
||||
|
||||
(repeat the above command for user1)
|
||||
|
||||
As any other storage media, you can mount (and later unmount) this network share when needed:
|
||||
|
||||
# mount //192.168.0.18/finance /media/samba -o username=user1
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Mount Samba Network Share
|
||||
|
||||
(where /media/samba is an existing directory)
|
||||
|
||||
or permanently, by adding the following entry in /etc/fstab file:
|
||||
|
||||
**fstab**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
//192.168.0.18/finance /media/samba cifs credentials=/media/samba/.smbcredentials,defaults 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
Where the hidden file /media/samba/.smbcredentials (whose permissions and ownership have been set to 600 and root:root, respectively) contains two lines that indicate the username and password of an account that is allowed to use the share:
|
||||
|
||||
**.smbcredentials**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
username=user1
|
||||
password=PasswordForUser1
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, let’s create a file inside /finance and check the permissions and ownership:
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /media/samba/FileCreatedInRHELClient.txt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Create File in Samba Share
|
||||
|
||||
As you can see, the file was created with 0770 permissions and ownership set to user1:finance.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step 7: Mounting the Samba Share in Windows ###
|
||||
|
||||
To mount the Samba share in Windows, go to My PC and choose Computer, then Map network drive. Next, assign a letter for the drive to be mapped and check Connect using different credentials (the screenshots below are in Spanish, my native language):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Mount Samba Share in Windows
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, let’s create a file and check the permissions and ownership:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Create Files on Windows Samba Share
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l /finance
|
||||
|
||||
This time the file belongs to user2 since that’s the account we used to connect from the Windows client.
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we have explained not only how to set up a Samba server and two clients using different operating systems, but also [how to configure the firewalld][3] and [SELinux on the server][4] to allow the desired group collaboration capabilities.
|
||||
|
||||
Last, but not least, let me recommend the reading of the online [man page of smb.conf][5] to explore other configuration directives that may be more suitable for your case than the scenario described in this article.
|
||||
|
||||
As always, feel free to drop a comment using the form below if you have any comments or suggestions.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/setup-samba-file-sharing-for-linux-windows-clients/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/add-users-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/firewalld-vs-iptables-and-control-network-traffic-in-firewall/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/configure-firewalld-in-centos-7/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/selinux-essentials-and-control-filesystem-access/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.samba.org/samba/docs/man/manpages-3/smb.conf.5.html
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,211 @@
|
||||
安装 Samba 并配置 Firewalld 和 SELinux 使得能在 Linux 和 Windows 之间共享文件 - 第六部分
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
由于计算机很少作为一个独立的系统工作,作为一个系统管理员或工程师,就应该知道如何在有多种类型的服务器之间搭设和维护网络。
|
||||
|
||||
在本篇以及该系列后面的文章中,我们会介绍用 Windows/Linux 配置 Samba 和 NFS 服务器以及 Linux 客户端。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
RHCE 系列第六部分 - 设置 Samba 文件共享
|
||||
|
||||
如果有人叫你设置文件服务器用于协作或者配置很可能有多种不同类型操作系统和设备的企业环境,这篇文章就能派上用场。
|
||||
|
||||
由于你可以在网上找到很多关于 Samba 和 NFS 背景和技术方面的介绍,在这篇文章以及后续文章中我们就省略了这些部分直接进入到我们的主题。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤一: 安装 Samba 服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
我们当前的测试环境包括两台 RHEL 7 和一台 Windows 8:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Samba / NFS 服务器 [box1 (RHEL 7): 192.168.0.18],
|
||||
2. Samba 客户端 #1 [box2 (RHEL 7): 192.168.0.20]
|
||||
3. Samba 客户端 #2 [Windows 8 machine: 192.168.0.106]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
测试安装 Samba
|
||||
|
||||
在 box1 中安装以下软件包:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install samba samba-client samba-common
|
||||
|
||||
在 box2:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install samba samba-client samba-common cifs-utils
|
||||
|
||||
安装完成后,就可以配置我们的共享了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤二: 设置通过 Samba 进行文件共享 ###
|
||||
|
||||
Samba 这么重要的原因之一是它为 SMB/CIFS 客户端(译者注:SMB 是微软和英特尔制定的一种通信协议,CIFS 是其中一个版本,更详细的介绍可以参考[Wiki][6])提供了文件和打印设备,这使得客户端看起来服务器就是一个 Windows 系统(我必须承认写这篇文章的时候我有一点激动,因为这是我多年前作为一个新手 Linux 系统管理员的第一次设置)。
|
||||
|
||||
**添加系统用户并设置权限和属性**
|
||||
|
||||
为了允许组协作,我们会在 box1 中用 [useradd 命令][1]创建一个有两个用户(user1 和 user2)的组 finance 和目录 /finance。
|
||||
|
||||
我们同时会把这个目录的组所有者更改为 finance 并把权限设置为 0777(所有者和组属主可读可写可执行):
|
||||
|
||||
# groupadd finance
|
||||
# useradd user1
|
||||
# useradd user2
|
||||
# usermod -a -G finance user1
|
||||
# usermod -a -G finance user2
|
||||
# mkdir /finance
|
||||
# chmod 0770 /finance
|
||||
# chgrp finance /finance
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤三: 配置 SELinux 和 Firewalld ###
|
||||
|
||||
在配置 /finance 作为 Samba 共享目录之前,我们需要像下面那样停用 SELinux 或设置恰当的布尔值和安全选项(否则,SELinux 会阻止客户端访问共享目录):
|
||||
|
||||
# setsebool -P samba_export_all_ro=1 samba_export_all_rw=1
|
||||
# getsebool –a | grep samba_export
|
||||
# semanage fcontext –at samba_share_t "/finance(/.*)?"
|
||||
# restorecon /finance
|
||||
|
||||
另外我们必须确保 [firewalld][2] 允许 Samba 流量通过。
|
||||
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-service=samba
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --reload
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤四: 配置 Samba 共享目录 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们来看看配置文件 /etc/samba/smb.conf 并添加用于共享的章节(section):我们希望组 finance 的成员可以浏览 /finance 的内容,在里面保存/创建文件或者子目录(默认权限为 0777,组所有者为 finance):
|
||||
|
||||
**smb.conf**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[finance]
|
||||
comment=Directory for collaboration of the company's finance team
|
||||
browsable=yes
|
||||
path=/finance
|
||||
public=no
|
||||
valid users=@finance
|
||||
write list=@finance
|
||||
writeable=yes
|
||||
create mask=0770
|
||||
Force create mode=0770
|
||||
force group=finance
|
||||
|
||||
保存文件然后用 testparm 工具进行测试。如果这里有任何错误,命令的输出或提示你需要如何修复。否则,会显示你 Samba 服务器配置的回顾:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
测试 Samba 配置
|
||||
|
||||
如果你要添加另一个公开的共享目录(意味着没有任何验证),在 /etc/samba/smb.conf 中创建另一章节,在共享目录名称下面复制上面的章节,只需要把 public=no 更改为 public=yes 并去掉有效用户和写列表命令。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤五: 添加 Samba 用户 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下一步,你需要添加 user1 和 user2 作为 Samba 的用户。要做到这点,你需要用 smbpasswd 命令,它会和 Samba 的数据库进行交互。会提示你输入一个命令用于你之后和共享目录连接:
|
||||
|
||||
# smbpasswd -a user1
|
||||
# smbpasswd -a user2
|
||||
|
||||
最后,重启 Samda,启用系统启动时自动启动服务,并确保共享目录对网络客户端可用:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start smb
|
||||
# systemctl enable smb
|
||||
# smbclient -L localhost –U user1
|
||||
# smbclient -L localhost –U user2
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
验证 Samba 共享
|
||||
|
||||
到这里,已经正确安装和配置了 Samba 文件服务器。现在让我们在 RHEL 7 和 Windows 8 客户端中测试该配置。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤六: 在 Linux 中挂载 Samba 共享 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,确保客户端可以访问 Samba 共享:
|
||||
|
||||
# smbclient –L 192.168.0.18 -U user2
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 上挂载 Samba 共享
|
||||
|
||||
(为 user1 重复上面的命令)
|
||||
|
||||
正如任何其它存储介质,当你需要的时候你可以挂载(之后卸载)该网络共享:
|
||||
|
||||
# mount //192.168.0.18/finance /media/samba -o username=user1
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
挂载 Samba 网络共享
|
||||
|
||||
(其中 /media/samba 是一个已有的目录)
|
||||
|
||||
或者在 /etc/fstab 文件中添加下面的条目自动挂载:
|
||||
|
||||
**fstab**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
//192.168.0.18/finance /media/samba cifs credentials=/media/samba/.smbcredentials,defaults 0 0
|
||||
|
||||
其中隐藏文件 /media/samba/.smbcredentials(它的权限被设置为 600 和 root:root)有两行,指示允许使用共享的账户的用户名和密码:
|
||||
|
||||
**.smbcredentials**
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
username=user1
|
||||
password=PasswordForUser1
|
||||
|
||||
最后,让我们在 /finance 中创建一个文件并检查权限和属性:
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /media/samba/FileCreatedInRHELClient.txt
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 Samba 共享中创建文件
|
||||
|
||||
正如你看到的,用权限 0770 和属主 user1:finance 创建了文件。
|
||||
|
||||
### 步骤七: 在 Windows 上挂载 Samba 共享 ###
|
||||
|
||||
要在 Windows 上挂载 Samba 共享,进入 ‘我的计算机’ 并选择 ‘计算机’,‘网络驱动映射’。下一步,为要映射的驱动分配一个字母并用不同的认证检查连接(下面的截图使用我的母语西班牙语):
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 Windows 中挂载 Samba 共享
|
||||
|
||||
最后,让我们新建一个文件并检查权限和属性:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 Windows Samba 共享中新建文件
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l /finance
|
||||
|
||||
这次文件属于 user2,因为这是我们用于从 Windows 客户端中连接的账户。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在这篇文章中我们不仅介绍了如何使用不同操作系统设置 Samba 服务器和两个客户端,也介绍了[如何配置 Firewalld][3] 和 [服务器中的 SELinux][4] 以获取所需的组协作功能。
|
||||
|
||||
最后,同样重要的是,我推荐阅读网上的 [smb.conf man 手册][5] 查看其它可能针对你的情况比本文中介绍的场景更加合适的配置命令。
|
||||
|
||||
正如往常,欢迎在下面的评论框中留下你的评论或建议。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/setup-samba-file-sharing-for-linux-windows-clients/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](http://www.mutouxiaogui.cn/blog/)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/add-users-in-linux/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/firewalld-vs-iptables-and-control-network-traffic-in-firewall/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/configure-firewalld-in-centos-7/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/selinux-essentials-and-control-filesystem-access/
|
||||
[5]:https://www.samba.org/samba/docs/man/manpages-3/smb.conf.5.html
|
||||
[6]:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Server_Message_Block
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user