mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-30 02:40:11 +08:00
translated
This commit is contained in:
parent
a30b9412c1
commit
513234f106
@ -1,233 +0,0 @@
|
||||
ivo-wang translating
|
||||
Setting Up Real-Time Monitoring with ‘Ganglia’ for Grids and Clusters of Linux Servers
|
||||
===========
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Ever since system administrators have been in charge of managing servers and groups of machines, tools like monitoring applications have been their best friends. You will probably be familiar with tools like [Nagios][11], [Zabbix][10], [Icinga][9], and Centreon. While those are the heavyweights of monitoring, setting them up and fully taking advantage of their features may be somewhat difficult for new users.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we will introduce you to Ganglia, a monitoring system that is easily scalable and allows to view a wide variety of system metrics of Linux servers and clusters (plus graphs) in real time.
|
||||
|
||||
[][8]
|
||||
|
||||
Install Gangila Monitoring in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Ganglia lets you set up grids (locations) and clusters (groups of servers) for better organization.
|
||||
|
||||
Thus, you can create a grid composed of all the machines in a remote environment, and then group those machines into smaller sets based on other criteria.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, Ganglia’s web interface is optimized for mobile devices, and also allows you to export data en `.csv`and `.json` formats.
|
||||
|
||||
Our test environment will consist of a central CentOS 7 server (IP address 192.168.0.29) where we will install Ganglia, and an Ubuntu 14.04 machine (192.168.0.32), the box that we want to monitor through Ganglia’s web interface.
|
||||
|
||||
Throughout this guide we will refer to the CentOS 7 system as the master node, and to the Ubuntu box as the monitored machine.
|
||||
|
||||
### Installing and Configuring Ganglia
|
||||
|
||||
To install the monitoring utilities in the the master node, follow these steps:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. Enable the [EPEL repository][7] and then install Ganglia and related utilities from there:
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum update && yum install epel-release
|
||||
# yum install ganglia rrdtool ganglia-gmetad ganglia-gmond ganglia-web
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The packages installed in the step above along with ganglia, the application itself, perform the following functions:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `rrdtool`, the Round-Robin Database, is a tool that’s used to store and display the variation of data over time using graphs.
|
||||
2. `ganglia-gmetad` is the daemon that collects monitoring data from the hosts that you want to monitor. In those hosts and in the master node it is also necessary to install ganglia-gmond (the monitoring daemon itself):
|
||||
3. `ganglia-web` provides the web frontend where we will view the historical graphs and data about the monitored systems.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. Set up authentication for the Ganglia web interface (/usr/share/ganglia). We will use basic authentication as provided by Apache.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to explore more advanced security mechanisms, refer to the [Authorization and Authentication][6]section of the Apache docs.
|
||||
|
||||
To accomplish this goal, create a username and assign a password to access a resource protected by Apache. In this example, we will create a username called `adminganglia` and assign a password of our choosing, which will be stored in /etc/httpd/auth.basic (feel free to choose another directory and / or file name – as long as Apache has read permissions on those resources, you will be fine):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# htpasswd -c /etc/httpd/auth.basic adminganglia
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Enter the password for adminganglia twice before proceeding.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. Modify /etc/httpd/conf.d/ganglia.conf as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Alias /ganglia /usr/share/ganglia
|
||||
<Location /ganglia>
|
||||
AuthType basic
|
||||
AuthName "Ganglia web UI"
|
||||
AuthBasicProvider file
|
||||
AuthUserFile "/etc/httpd/auth.basic"
|
||||
Require user adminganglia
|
||||
</Location>
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. Edit /etc/ganglia/gmetad.conf:
|
||||
|
||||
First, use the gridname directive followed by a descriptive name for the grid you’re setting up:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
gridname "Home office"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, use data_source followed by a descriptive name for the cluster (group of servers), a polling interval in seconds and the IP address of the master and monitored nodes:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
data_source "Labs" 60 192.168.0.29:8649 # Master node
|
||||
data_source "Labs" 60 192.168.0.32 # Monitored node
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. Edit /etc/ganglia/gmond.conf.
|
||||
|
||||
a) Make sure the cluster block looks as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cluster {
|
||||
name = "Labs" # The name in the data_source directive in gmetad.conf
|
||||
owner = "unspecified"
|
||||
latlong = "unspecified"
|
||||
url = "unspecified"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
b) In the udp_send_chanel block, comment out the mcast_join directive:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
udp_send_channel {
|
||||
#mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
|
||||
host = localhost
|
||||
port = 8649
|
||||
ttl = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
c) Finally, comment out the mcast_join and bind directives in the udp_recv_channel block:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
udp_recv_channel {
|
||||
#mcast_join = 239.2.11.71 ## comment out
|
||||
port = 8649
|
||||
#bind = 239.2.11.71 ## comment out
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Save the changes and exit.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6. Open port 8649/udp and allow PHP scripts (run via Apache) to connect to the network using the necessary SELinux boolean:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --add-port=8649/udp
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --add-port=8649/udp --permanent
|
||||
# setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect 1
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7. Restart Apache, gmetad, and gmond. Also, make sure they are enabled to start on boot:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# systemctl restart httpd gmetad gmond
|
||||
# systemctl enable httpd gmetad httpd
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
At this point, you should be able to open the Ganglia web interface at `http://192.168.0.29/ganglia` and login with the credentials from #Step 2.
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Gangila Web Interface
|
||||
|
||||
#### 8. In the Ubuntu host, we will only install ganglia-monitor, the equivalent of ganglia-gmond in CentOS:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo aptitude update && aptitude install ganglia-monitor
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 9. Edit the /etc/ganglia/gmond.conf file in the monitored box. This should be identical to the same file in the master node except that the commented out lines in the cluster, udp_send_channel, and udp_recv_channelshould be enabled:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cluster {
|
||||
name = "Labs" # The name in the data_source directive in gmetad.conf
|
||||
owner = "unspecified"
|
||||
latlong = "unspecified"
|
||||
url = "unspecified"
|
||||
}
|
||||
udp_send_channel {
|
||||
mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
|
||||
host = localhost
|
||||
port = 8649
|
||||
ttl = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
udp_recv_channel {
|
||||
mcast_join = 239.2.11.71 ## comment out
|
||||
port = 8649
|
||||
bind = 239.2.11.71 ## comment out
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, restart the service:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo service ganglia-monitor restart
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 10. Refresh the web interface and you should be able to view the statistics and graphs for both hosts inside the Home office grid / Labs cluster (use the dropdown menu next to to Home office grid to choose a cluster, Labsin our case):
|
||||
|
||||
[][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Ganglia Home Office Grid Report
|
||||
|
||||
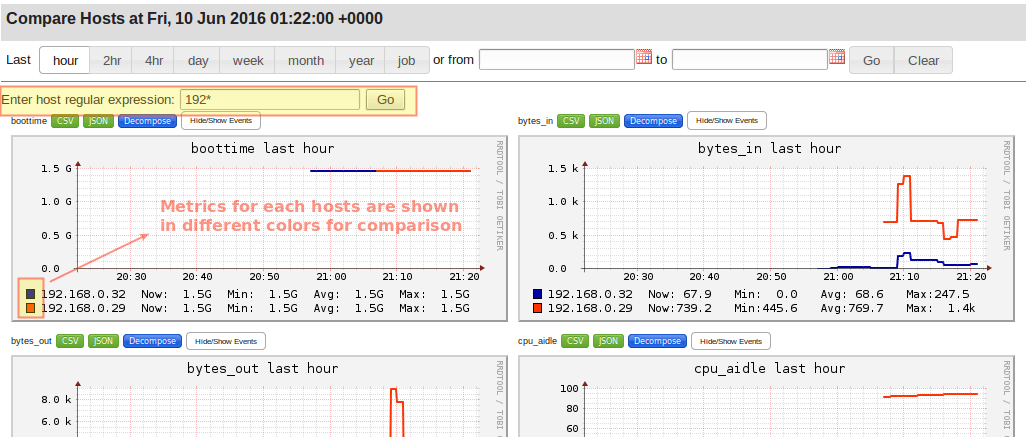
Using the menu tabs (highlighted above) you can access lots of interesting information about each server individually and in groups. You can even compare the stats of all the servers in a cluster side by side using the Compare Hosts tab.
|
||||
|
||||
Simply choose a group of servers using a regular expression and you will be able to see a quick comparison of how they are performing:
|
||||
|
||||
[][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Ganglia Host Server Information
|
||||
|
||||
One of the features I personally find most appealing is the mobile-friendly summary, which you can access using the Mobile tab. Choose the cluster you’re interested in and then the individual host:
|
||||
|
||||
[][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Ganglia Mobile Friendly Summary View
|
||||
|
||||
### Summary
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we have introduced Ganglia, a powerful and scalable monitoring solution for grids and clusters of servers. Feel free to install, explore, and play around with Ganglia as much as you like (by the way, you can even try out Ganglia in a demo provided in the project’s [official website][1].
|
||||
|
||||
While you’re at it, you will also discover that several well-known companies both in the IT world or not use Ganglia. There are plenty of good reasons for that besides the ones we have shared in this article, with easiness of use and graphs along with stats (it’s nice to put a face to the name, isn’t it?) probably being at the top.
|
||||
|
||||
But don’t just take our word for it, try it out yourself and don’t hesitate to drop us a line using the comment form below if you have any questions.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-configure-ganglia-monitoring-centos-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://ganglia.info/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Ganglia-Mobile-View.png
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Ganglia-Server-Information.png
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Ganglia-Home-Office-Grid-Report.png
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Gangila-Web-Interface.png
|
||||
[6]:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/current/howto/auth.html
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Install-Gangila-Monitoring-in-Linux.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-icinga-in-centos-7/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-and-configure-zabbix-monitoring-on-debian-centos-rhel/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-nagios-in-linux/
|
||||
226
translated/tech/20160610 Setting Up Real-Time Monitoring with Ganglia.md
Executable file
226
translated/tech/20160610 Setting Up Real-Time Monitoring with Ganglia.md
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,226 @@
|
||||
使用Ganglia来监控linux类型的网格和集群服务器
|
||||
===========
|
||||
自从SA接手服务和主机管理以后,监控类的工具就成了他们的好帮手。其中比较有名的有[Nagios][11], [Zabbix][10], [Icinga][9], 和 Centreon.以上这些重量级的监控工具,让一个新手SA来设置,并使用其中的高级特性是非常困难的。
|
||||
本文将向你介绍Ganglia,它是一个容易扩展配置的监控系统。它可以查看服务器中的各项性能指标,也可以实时图形化的展示集群配置。
|
||||
[][8]
|
||||
|
||||
在Linux上安装Ganglia
|
||||
Ganglia能够让集群和网格服务器更加容易管理。
|
||||
我们可以远程创建一个包含所有主机的网格配置,其中的成员主机可以使用模板设置。
|
||||
|
||||
此外Ganglia对移动设备进行过页面优化,排版非常人性化。当然你还可以导出`csv`和 `.json`格式的数据。
|
||||
|
||||
我们的测试环境包括一个安装Ganglia的主节点服务器CentOS7(IP 地址 192.168.0.29)和一个作为被监控端的Ubuntu 14.04主机 (192.168.0.32)。我们将通过Ganglia Web的页面来监控这台Ubuntu主机。
|
||||
|
||||
下面的例子可以给大家提供参考,CentOS7作为主节点,Ubuntu作为被监控对象。
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装和配置 Ganglia
|
||||
|
||||
请遵循以下步骤在主节点服务器安装监控工具。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 1. 1. 使用yum源 [EPEL repository][7] ,然后安装 Ganglia和相关工具:
|
||||
命令如下
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# yum update && yum install epel-release
|
||||
# yum install ganglia rrdtool ganglia-gmetad ganglia-gmond ganglia-web
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Ganglia将附加安装一些应用,它们的功能如下:
|
||||
|
||||
1. `rrdtool`, 轮询数据库,它是一个储存以及用图形化显示变化数据的工具
|
||||
2. `ganglia-gmetad` 一个守护进程,用来收集被监控主机的数据。被监控主机与主节点主机都要安装Ganglia-gmond(监控守护进程自己)
|
||||
3. `ganglia-web` 提供Web前端用于显示监控系统的历史数据
|
||||
|
||||
#### 2. 使用Apache为Ganglia配置Web身份认证
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想了解更多的高级认证机制,请参阅[Authorization and Authentication][6]选择Apache部分。
|
||||
|
||||
为完成这部分的任务,我们需要用Apache来创建一个用户名和对应的密码,下面的例子我们先来创建一个叫`adminganglia`的用户名,然后给他分配一个密码,它将被储存在 /etc/httpd/auth.basic(如果随便选择根目录或其他Apache没有权限读取的目录,这项配置最终将会以失败告终。)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# htpasswd -c /etc/httpd/auth.basic adminganglia
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
给adminganglia添加密码,需要经过2次确认
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3. 修改配置文件 /etc/httpd/conf.d/ganglia.conf
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Alias /ganglia /usr/share/ganglia
|
||||
<Location /ganglia>
|
||||
AuthType basic
|
||||
AuthName "Ganglia web UI"
|
||||
AuthBasicProvider file
|
||||
AuthUserFile "/etc/httpd/auth.basic"
|
||||
Require user adminganglia
|
||||
</Location>
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 4. 编辑 /etc/ganglia/gmetad.conf:
|
||||
|
||||
首先, 使用gridname命令来设置集群的名称。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
gridname "Home office"
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后, 使用data_source命令根据集群的名称来设置主节点主机和被监控节点的轮询时间
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
data_source "Labs" 60 192.168.0.29:8649 # Master node
|
||||
data_source "Labs" 60 192.168.0.32 # Monitored node
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 5. 编辑 /etc/ganglia/gmond.conf.
|
||||
|
||||
a)确保集群的配置和下面的一样。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cluster {
|
||||
name = "Labs" # The name in the data_source directive in gmetad.conf
|
||||
owner = "unspecified"
|
||||
latlong = "unspecified"
|
||||
url = "unspecified"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
b) 在udp_send_chanel 中,注释掉 mcast_join directive:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
udp_send_channel {
|
||||
# mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
|
||||
host = localhost
|
||||
port = 8649
|
||||
ttl = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
c)在udp_recv_channel 中:注释掉mcast_join 和bind部分
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
udp_recv_channel {
|
||||
# mcast_join = 239.2.11.71 ## comment out
|
||||
port = 8649
|
||||
# bind = 239.2.11.71 ## comment out
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
保存并退出
|
||||
|
||||
#### 6.打开8649/udp端口,更改SELinux确保php脚本能够连接:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --add-port=8649/udp
|
||||
# firewall-cmd --add-port=8649/udp --permanent
|
||||
# setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect 1
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 7.重启Apache,gmetad,gmond并确保他们在开机启动里面。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# systemctl restart httpd gmetad gmond
|
||||
# systemctl enable httpd gmetad httpd
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
至此,我们现在能够打开并登录Ganglia的Web页面 `http://192.168.0.29/ganglia`
|
||||
|
||||
[][5]
|
||||
|
||||
Gangila Web Interface
|
||||
|
||||
#### 8. 在Ubuntu上安装Ganglia-monitor:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo aptitude update && aptitude install ganglia-monitor
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 9. 编辑被监控主机的配置文件/etc/ganglia/gmond.conf,在主节点主机上也是相同的文件,注释掉网格里面不在线的主机。需要编辑udp_send_channel和udp_recv_channelshould这两项
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
cluster {
|
||||
name = "Labs" # The name in the data_source directive in gmetad.conf
|
||||
owner = "unspecified"
|
||||
latlong = "unspecified"
|
||||
url = "unspecified"
|
||||
}
|
||||
udp_send_channel {
|
||||
mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
|
||||
host = localhost
|
||||
port = 8649
|
||||
ttl = 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
udp_recv_channel {
|
||||
mcast_join = 239.2.11.71 ## comment out
|
||||
port = 8649
|
||||
bind = 239.2.11.71 ## comment out
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then, restart the service:
|
||||
之后重启服务
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo service ganglia-monitor restart
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 10. 刷新页面你将看到各种状态以及图形化的展示集群或网格的配置情况(用下拉菜单选择我们想查看的集群或网格):
|
||||
|
||||
[][4]
|
||||
|
||||
Ganglia中网格的报告
|
||||
|
||||
使用菜单按钮你可以选择组里面的节点主机,这将非常容易的获取到你感兴趣的信息。可以使用对比选项来查看集群中所有主机的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
当然你也可以使用正则表达式来快速对比一组主机
|
||||
|
||||
[][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Ganglia Host Server Information
|
||||
|
||||
One of the features I personally find most appealing is the mobile-friendly summary, which you can access using the Mobile tab. Choose the cluster you’re interested in and then the individual host:
|
||||
能够使用移动设备管理,对于移动端有友好界面,这是一个非常吸引人的特点。在集群中选中一个主机,点击它。
|
||||
|
||||
[][2]
|
||||
|
||||
Ganglia 移动端截图
|
||||
### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
本篇文章向大家介绍了Ganglia,他是一个功能强大扩展性很好的监控工具,主要用来监控集群和网格。它可以随意安装,便捷的组合各种功能(你甚至可以尝试一下官方提供的demo网站[official website][1])。
|
||||
此时你可能会发现许多知名的it企业或许并不使用Ganglia来监控作为监控工具。他们有自己更好的工具去实现,除了那些工具以外,我们这篇文章里面提到的Ganglia可能是最方便的图形化(在图示主机上显示对应的名字)工具。
|
||||
但是请不要拘泥于本篇文章,尝试一下自己去做,不必犹豫不敢尝试。如果你有任何问题也欢迎给我留言。
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/install-configure-ganglia-monitoring-centos-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[ivo-wang](https://github.com/ivo-wang)
|
||||
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 组织编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]: http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://ganglia.info/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Ganglia-Mobile-View.png
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Ganglia-Server-Information.png
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Ganglia-Home-Office-Grid-Report.png
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.co m/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/Gangila-Web-Interface.png
|
||||
[6]:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/current/howto/auth.html
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/ Install-Gangila-Monitoring-in-Linux.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-icinga-in-centos-7/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-and-configure-zabbix-monitoring-on-debian-centos-rhel/
|
||||
[11]:http://www.tecmint.com/install-nagios-in-linux/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user