mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-30 02:40:11 +08:00
commit
4f3533f650
published
sources/tech
translated/tech
@ -0,0 +1,219 @@
|
||||
在 Linux 下使用 RAID(一):使用 mdadm 工具创建软件 RAID 0 (条带化)
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
|
||||
RAID 即廉价磁盘冗余阵列,其高可用性和可靠性适用于大规模环境中,相比正常使用,数据更需要被保护。RAID 是一些磁盘的集合,是包含一个阵列的逻辑卷。驱动器可以组合起来成为一个阵列或称为(组的)集合。
|
||||
|
||||
创建 RAID 最少应使用2个连接到 RAID 控制器的磁盘组成,来构成逻辑卷,可以根据定义的 RAID 级别将更多的驱动器添加到一个阵列中。不使用物理硬件创建的 RAID 被称为软件 RAID。软件 RAID 也叫做穷人 RAID。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
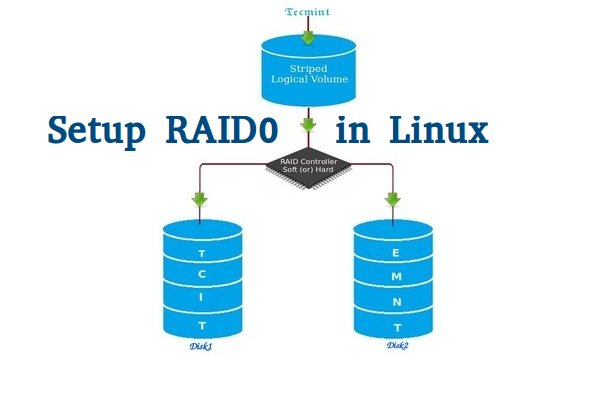
*在 Linux 中创建 RAID0*
|
||||
|
||||
使用 RAID 的主要目的是为了在发生单点故障时保存数据,如果我们使用单个磁盘来存储数据,如果它损坏了,那么就没有机会取回我们的数据了,为了防止数据丢失我们需要一个容错的方法。所以,我们可以使用多个磁盘组成 RAID 阵列。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 RAID 0 中条带是什么 ####
|
||||
|
||||
条带是通过将数据在同时分割到多个磁盘上。假设我们有两个磁盘,如果我们将数据保存到该逻辑卷上,它会将数据保存在两个磁盘上。使用 RAID 0 是为了获得更好的性能,但是如果驱动器中一个出现故障,我们将不能得到完整的数据。因此,使用 RAID 0 不是一种好的做法。唯一的解决办法就是安装有 RAID 0 逻辑卷的操作系统来提高重要文件的安全性。
|
||||
|
||||
- RAID 0 性能较高。
|
||||
- 在 RAID 0 上,空间零浪费。
|
||||
- 零容错(如果硬盘中的任何一个发生故障,无法取回数据)。
|
||||
- 写和读性能都很好。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 要求 ####
|
||||
|
||||
创建 RAID 0 允许的最小磁盘数目是2个,但你可以添加更多的磁盘,不过数目应该是2,4,6,8等的偶数。如果你有一个物理 RAID 卡并且有足够的端口,你可以添加更多磁盘。
|
||||
|
||||
在这里,我们没有使用硬件 RAID,此设置只需要软件 RAID。如果我们有一个物理硬件 RAID 卡,我们可以从它的功能界面访问它。有些主板默认内建 RAID 功能,还可以使用 Ctrl + I 键访问它的界面。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是刚开始设置 RAID,请阅读我们前面的文章,我们已经介绍了一些关于 RAID 基本的概念。
|
||||
|
||||
- [介绍 RAID 的级别和概念][1]
|
||||
|
||||
**我的服务器设置**
|
||||
|
||||
操作系统 : CentOS 6.5 Final
|
||||
IP 地址 : 192.168.0.225
|
||||
两块盘 : 20 GB each
|
||||
|
||||
这是9篇系列教程的第2部分,在这部分,我们将看看如何能够在 Linux 上创建和使用 RAID 0(条带化),以名为 sdb 和 sdc 两个 20GB 的硬盘为例。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第1步:更新系统和安装管理 RAID 的 mdadm 软件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
1、 在 Linux 上设置 RAID 0 前,我们先更新一下系统,然后安装`mdadm` 包。mdadm 是一个小程序,这将使我们能够在Linux下配置和管理 RAID 设备。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum clean all && yum update
|
||||
# yum install mdadm -y
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*安装 mdadm 工具*
|
||||
|
||||
### 第2步:确认连接了两个 20GB 的硬盘 ###
|
||||
|
||||
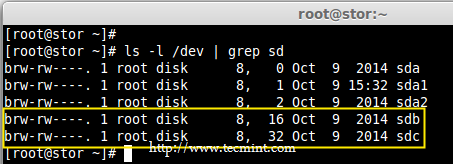
2、 在创建 RAID 0 前,请务必确认两个硬盘能被检测到,使用下面的命令确认。
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l /dev | grep sd
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*检查硬盘*
|
||||
|
||||
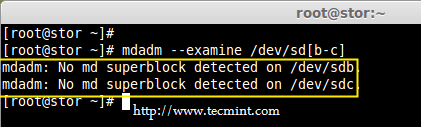
3、 一旦检测到新的硬盘驱动器,同时检查是否连接的驱动器已经被现有的 RAID 使用,使用下面的`mdadm` 命令来查看。
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --examine /dev/sd[b-c]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*检查 RAID 设备*
|
||||
|
||||
从上面的输出我们可以看到,没有任何 RAID 使用 sdb 和 sdc 这两个驱动器。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第3步:创建 RAID 分区 ###
|
||||
|
||||
4、 现在用 sdb 和 sdc 创建 RAID 的分区,使用 fdisk 命令来创建。在这里,我将展示如何创建 sdb 驱动器上的分区。
|
||||
|
||||
# fdisk /dev/sdb
|
||||
|
||||
请按照以下说明创建分区。
|
||||
|
||||
- 按`n` 创建新的分区。
|
||||
- 然后按`P` 选择主分区。
|
||||
- 接下来选择分区号为1。
|
||||
- 只需按两次回车键选择默认值即可。
|
||||
- 然后,按`P` 来显示创建好的分区。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*创建分区*
|
||||
|
||||
请按照以下说明将分区创建为 Linux 的 RAID 类型。
|
||||
|
||||
- 按`L`,列出所有可用的类型。
|
||||
- 按`t` 去修改分区。
|
||||
- 键入`fd` 设置为 Linux 的 RAID 类型,然后按回车确认。
|
||||
- 然后再次使用`p`查看我们所做的更改。
|
||||
- 使用`w`保存更改。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*在 Linux 上创建 RAID 分区*
|
||||
|
||||
**注**: 请使用上述步骤同样在 sdc 驱动器上创建分区。
|
||||
|
||||
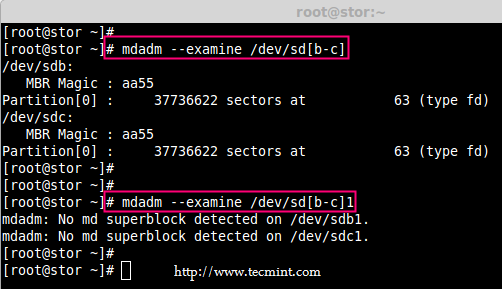
5、 创建分区后,验证这两个驱动器是否正确定义 RAID,使用下面的命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --examine /dev/sd[b-c]
|
||||
# mdadm --examine /dev/sd[b-c]1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*验证 RAID 分区*
|
||||
|
||||
### 第4步:创建 RAID md 设备 ###
|
||||
|
||||
6、 现在使用以下命令创建 md 设备(即 /dev/md0),并选择 RAID 合适的级别。
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -C /dev/md0 -l raid0 -n 2 /dev/sd[b-c]1
|
||||
# mdadm --create /dev/md0 --level=stripe --raid-devices=2 /dev/sd[b-c]1
|
||||
|
||||
- -C – 创建
|
||||
- -l – 级别
|
||||
- -n – RAID 设备数
|
||||
|
||||
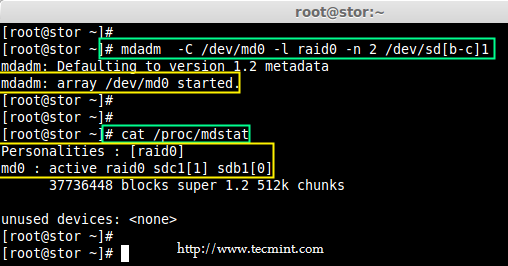
7、 一旦 md 设备已经建立,使用如下命令可以查看 RAID 级别,设备和阵列的使用状态。
|
||||
|
||||
# cat /proc/mdstat
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*查看 RAID 级别*
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -E /dev/sd[b-c]1
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*查看 RAID 设备*
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --detail /dev/md0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*查看 RAID 阵列*
|
||||
|
||||
### 第5步:给 RAID 设备创建文件系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
8、 将 RAID 设备 /dev/md0 创建为 ext4 文件系统,并挂载到 /mnt/raid0 下。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/md0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*创建 ext4 文件系统*
|
||||
|
||||
9、 在 RAID 设备上创建好 ext4 文件系统后,现在创建一个挂载点(即 /mnt/raid0),并将设备 /dev/md0 挂载在它下。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /mnt/raid0
|
||||
# mount /dev/md0 /mnt/raid0/
|
||||
|
||||
10、下一步,使用 df 命令验证设备 /dev/md0 是否被挂载在 /mnt/raid0 下。
|
||||
|
||||
# df -h
|
||||
|
||||
11、 接下来,在挂载点 /mnt/raid0 下创建一个名为`tecmint.txt` 的文件,为创建的文件添加一些内容,并查看文件和目录的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /mnt/raid0/tecmint.txt
|
||||
# echo "Hi everyone how you doing ?" > /mnt/raid0/tecmint.txt
|
||||
# cat /mnt/raid0/tecmint.txt
|
||||
# ls -l /mnt/raid0/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*验证挂载的设备*
|
||||
|
||||
12、 当你验证挂载点后,就可以将它添加到 /etc/fstab 文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/fstab
|
||||
|
||||
添加以下条目,根据你的安装位置和使用文件系统的不同,自行做修改。
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/md0 /mnt/raid0 ext4 deaults 0 0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*添加设备到 fstab 文件中*
|
||||
|
||||
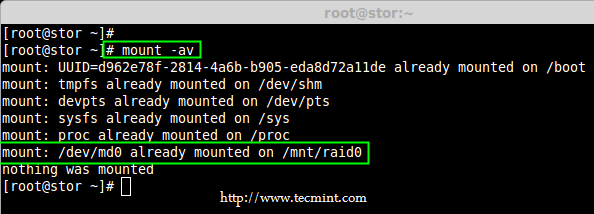
13、 使用 mount 命令的 `-a` 来检查 fstab 的条目是否有误。
|
||||
|
||||
# mount -av
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
*检查 fstab 文件是否有误*
|
||||
|
||||
### 第6步:保存 RAID 配置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
14、 最后,保存 RAID 配置到一个文件中,以供将来使用。我们再次使用带有`-s` (scan) 和`-v` (verbose) 选项的 `mdadm` 命令,如图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -E -s -v >> /etc/mdadm.conf
|
||||
# mdadm --detail --scan --verbose >> /etc/mdadm.conf
|
||||
# cat /etc/mdadm.conf
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
*保存 RAID 配置*
|
||||
|
||||
就这样,我们在这里看到,如何通过使用两个硬盘配置具有条带化的 RAID 0 。在接下来的文章中,我们将看到如何设置 RAID 1。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/create-raid0-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Babin Lonston][a]
|
||||
译者:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/strugglingyouth)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/babinlonston/
|
||||
[1]:https://linux.cn/article-6085-1.html
|
||||
@ -1,74 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to create an AP in Ubuntu 15.04 to connect to Android/iPhone
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I tried creating a wireless access point via Gnome Network Manager in 15.04 and was successful. I’m sharing the steps with our readers. Please note: you must have a wifi card which allows you to create an Access Point. If you want to know how to find that, type iw list in a terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
If you don’t have iw installed, you can install iw in Ubuntu using the command sudo apt-get install iw.
|
||||
|
||||
After you type iw list, look for supported interface section, where it should be a entry called AP like the one shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
Supported interface modes:
|
||||
|
||||
* IBSS
|
||||
* managed
|
||||
* AP
|
||||
* AP/VLAN
|
||||
* monitor
|
||||
* mesh point
|
||||
|
||||
Let’s see the steps in detail
|
||||
|
||||
1. Disconnect WIFI. Get a an internet cable and plug into your laptop so that you are connected to a wired internet connection
|
||||
1. Go to Network Icon on the top panel -> Edit Connections then click the Add button in the pop-up window
|
||||
1. Choose Wi-Fi from the drop-down menu
|
||||
1. Next,
|
||||
|
||||
a. Type in a connection name e.g. Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
b. Type in a SSID e.g. Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
c. Select mode: Infrastructure
|
||||
|
||||
d. Device MAC address: select your wireless card from drop-down menu
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to Wi-Fi Security tab, select security type WPA & WPA2 Personal and set a password
|
||||
1. Go to IPv4 Settings tab, from Method drop-down box, select Shared to other computers
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. Go to IPv6 tab and set Method to ignore (do this only if you do not use IPv6)
|
||||
1. Hit the “Save” button to save the configuration
|
||||
1. Open a terminal from the menu/dash
|
||||
1. Now, edit the connection with you just created via network settings
|
||||
|
||||
VIM editor:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo vim /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
Gedit:
|
||||
|
||||
gksu gedit /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
Replace name Hotspot with the connection name you have given in step 4
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. Change the line mode=infrastructure to mode=ap and save the file
|
||||
1. Once you save the file, you should be able to see the wifi named Hotspot showing up in the list of available wifi networks. (If the network does not show, disable and enable wifi )
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. You can now connect your Android phone. Connection tested using Xioami Mi4i running Android 5.0 (Downloaded 1GB to test speed and reliability)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxveda.com/2015/08/23/how-to-create-an-ap-in-ubuntu-15-04-to-connect-to-androidiphone/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sayantan Das][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxveda.com/author/sayantan_das/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
|
||||
如何在 Ubuntu 15.04 下创建连接至 Android/iOS 的 AP
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
我成功地在 Ubuntu 15.04 下用 Gnome Network Manager 创建了一个无线AP热点. 接下来我要分享一下我的步骤. 请注意: 你必须要有一个可以用来创建AP热点的无线网卡. 如果你不知道如何找到连上了的设备的话, 在终端(Terminal)里输入`iw list`.
|
||||
|
||||
如果你没有安装`iw`的话, 在Ubuntu下你可以使用`udo apt-get install iw`进行安装.
|
||||
|
||||
在你键入`iw list`之后, 寻找可用的借口, 你应该会看到类似下列的条目:
|
||||
|
||||
Supported interface modes:
|
||||
|
||||
* IBSS
|
||||
* managed
|
||||
* AP
|
||||
* AP/VLAN
|
||||
* monitor
|
||||
* mesh point
|
||||
|
||||
让我们一步步看
|
||||
|
||||
1. 断开WIFI连接. 使用有线网络接入你的笔记本.
|
||||
1. 在顶栏面板里点击网络的图标 -> Edit Connections(编辑连接) -> 在弹出窗口里点击Add(新增)按钮.
|
||||
1. 在下拉菜单内选择Wi-Fi.
|
||||
1. 接下来,
|
||||
|
||||
a. 输入一个链接名 比如: Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
b. 输入一个 SSID 比如: Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
c. 选择模式(mode): Infrastructure
|
||||
|
||||
d. 设备 MAC 地址: 在下拉菜单里选择你的无线设备
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入Wi-Fi安全选项卡, 选择 WPA & WPA2 Personal 并且输入密码.
|
||||
1. 进入IPv4设置选项卡, 在Method(方法)下拉菜单里, 选择Shared to other computers(共享至其他电脑).
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. 进入IPv6选项卡, 在Method(方法)里设置为忽略ignore (只有在你不使用IPv6的情况下这么做)
|
||||
1. 点击 Save(保存) 按钮以保存配置.
|
||||
1. 从 menu/dash 里打开Terminal.
|
||||
1. 修改你刚刚使用 network settings 创建的连接.
|
||||
|
||||
使用 VIM 编辑器:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo vim /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
使用Gedit 编辑器:
|
||||
|
||||
gksu gedit /etc/NetworkManager/system-connections/Hotspot
|
||||
|
||||
把名字 Hotspot 用你在第4步里起的连接名替换掉.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. 把 `mode=infrastructure` 改成 `mode=ap` 并且保存文件
|
||||
1. 一旦你保存了这个文件, 你应该能在 Wifi 菜单里看到你刚刚建立的AP了. (如果没有的话请再顶栏里 关闭/打开 Wifi 选项一次)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. 你现在可以把你的设备连上Wifi了. 已经过 Android 5.0的小米4测试.(下载了1GB的文件以测试速度与稳定性)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxveda.com/2015/08/23/how-to-create-an-ap-in-ubuntu-15-04-to-connect-to-androidiphone/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Sayantan Das][a]
|
||||
译者:[jerryling315](https://github.com/jerryling315)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.linuxveda.com/author/sayantan_das/
|
||||
@ -1,218 +0,0 @@
|
||||
在 Linux 上使用 ‘mdadm’ 工具创建软件 RAID0 (条带化)在 ‘两个设备’ 上 - 第2部分
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
RAID 是廉价磁盘的冗余阵列,其高可用性和可靠性适用于大规模环境中,为了使数据被保护而不是被正常使用。RAID 只是磁盘的一个集合被称为逻辑卷。结合驱动器,使其成为一个阵列或称为集合(组)。
|
||||
|
||||
创建 RAID 最少应使用2个磁盘被连接组成 RAID 控制器,逻辑卷或多个驱动器可以根据定义的 RAID 级别添加在一个阵列中。不使用物理硬件创建的 RAID 被称为软件 RAID。软件 RAID 一般都是不太有钱的人才使用的。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 中创建 RAID0
|
||||
|
||||
使用 RAID 的主要目的是为了在单点故障时保存数据,如果我们使用单个磁盘来存储数据,如果它损坏了,那么就没有机会取回我们的数据了,为了防止数据丢失我们需要一个容错的方法。所以,我们可以使用多个磁盘组成 RAID 阵列。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 RAID 0 中条带是什么 ####
|
||||
|
||||
条带是通过将数据在同一时间分割到多个磁盘上。假设我们有两个磁盘,如果我们将数据保存到逻辑卷上,它会将数据保存在两个磁盘上。使用 RAID 0 是为了获得更好的性能,但是如果驱动器中一个出现故障,我们将不能得到完整的数据。因此,使用 RAID 0 不是一种好的做法。唯一的解决办法就是安装有 RAID0 逻辑卷的操作系统来提高文件的安全性。
|
||||
|
||||
- RAID 0 性能较高。
|
||||
- 在 RAID 0 上,空间零浪费。
|
||||
- 零容错(如果硬盘中的任何一个发生故障,无法取回数据)。
|
||||
- 写和读性能得以提高。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 要求 ####
|
||||
|
||||
创建 RAID 0 允许的最小磁盘数目是2个,但你可以添加更多的磁盘,但数目应该是2,4,6,8等的两倍。如果你有一个物理 RAID 卡并且有足够的端口,你可以添加更多磁盘。
|
||||
|
||||
在这里,我们没有使用硬件 RAID,此设置只依赖于软件 RAID。如果我们有一个物理硬件 RAID 卡,我们可以从它的 UI 组件访问它。有些主板默认内建 RAID 功能,还可以使用 Ctrl + I 键访问 UI。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你是刚开始设置 RAID,请阅读我们前面的文章,我们已经介绍了一些关于 RAID 基本的概念。
|
||||
|
||||
- [Introduction to RAID and RAID Concepts][1]
|
||||
|
||||
**我的服务器设置**
|
||||
|
||||
Operating System : CentOS 6.5 Final
|
||||
IP Address : 192.168.0.225
|
||||
Two Disks : 20 GB each
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章是9个 RAID 系列教程的第2部分,在这部分,我们将看看如何能够在 Linux 上创建和使用 RAID0(条带化),以名为 sdb 和 sdc 两个20GB的硬盘为例。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第1步:更新系统和安装管理 RAID 的 mdadm 软件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
1.在 Linux 上设置 RAID0 前,我们先更新一下系统,然后安装 ‘mdadm’ 包。mdadm 是一个小程序,这将使我们能够在Linux下配置和管理 RAID 设备。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum clean all && yum update
|
||||
# yum install mdadm -y
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
安装 mdadm 工具
|
||||
|
||||
### 第2步:检测并连接两个 20GB 的硬盘 ###
|
||||
|
||||
2.在创建 RAID 0 前,请务必确认两个硬盘能被检测到,使用下面的命令确认。
|
||||
|
||||
# ls -l /dev | grep sd
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查硬盘
|
||||
|
||||
3.一旦检测到新的硬盘驱动器,同时检查是否连接的驱动器已经被现有的 RAID 使用,使用下面的 ‘mdadm’ 命令来查看。
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --examine /dev/sd[b-c]
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查 RAID 设备
|
||||
|
||||
从上面的输出我们可以看到,没有任何 RAID 使用 sdb 和 sdc 这两个驱动器。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第3步:创建 RAID 分区 ###
|
||||
|
||||
4.现在用 sdb 和 sdc 创建 RAID 的分区,使用 fdisk 命令来创建。在这里,我将展示如何创建 sdb 驱动器上的分区。
|
||||
|
||||
# fdisk /dev/sdb
|
||||
|
||||
请按照以下说明创建分区。
|
||||
|
||||
- 按 ‘n’ 创建新的分区。
|
||||
- 然后按 ‘P’ 选择主分区。
|
||||
- 接下来选择分区号为1。
|
||||
- 只需按两次回车键选择默认值即可。
|
||||
- 然后,按 ‘P’ 来打印创建好的分区。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建分区
|
||||
|
||||
请按照以下说明将分区创建为 Linux 的 RAID 类型。
|
||||
|
||||
- 按 ‘L’,列出所有可用的类型。
|
||||
- 按 ‘t’ 去修改分区。
|
||||
- 键入 ‘fd’ 设置为Linux 的 RAID 类型,然后按 Enter 确认。
|
||||
- 然后再次使用‘p’查看我们所做的更改。
|
||||
- 使用‘w’保存更改。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在 Linux 上创建 RAID 分区
|
||||
|
||||
**注**: 请使用上述步骤同样在 sdc 驱动器上创建分区。
|
||||
|
||||
5.创建分区后,验证这两个驱动器能使用下面的命令来正确定义 RAID。
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --examine /dev/sd[b-c]
|
||||
# mdadm --examine /dev/sd[b-c]1
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
验证 RAID 分区
|
||||
|
||||
### 第4步:创建 RAID md 设备 ###
|
||||
|
||||
6.现在使用以下命令创建 md 设备(即 /dev/md0),并选择 RAID 合适的级别。
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -C /dev/md0 -l raid0 -n 2 /dev/sd[b-c]1
|
||||
# mdadm --create /dev/md0 --level=stripe --raid-devices=2 /dev/sd[b-c]1
|
||||
|
||||
- -C – create
|
||||
- -l – level
|
||||
- -n – No of raid-devices
|
||||
|
||||
7.一旦 md 设备已经建立,使用如下命令可以查看 RAID 级别,设备和阵列的使用状态。
|
||||
|
||||
# cat /proc/mdstat
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
查看 RAID 级别
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -E /dev/sd[b-c]1
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
查看 RAID 设备
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm --detail /dev/md0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
查看 RAID 阵列
|
||||
|
||||
### 第5步:挂载 RAID 设备到文件系统 ###
|
||||
|
||||
8.将 RAID 设备 /dev/md0 创建为 ext4 文件系统并挂载到 /mnt/raid0 下。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkfs.ext4 /dev/md0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
创建 ext4 文件系统
|
||||
|
||||
9. ext4 文件系统为 RAID 设备创建好后,现在创建一个挂载点(即 /mnt/raid0),并将设备 /dev/md0 挂载在它下。
|
||||
|
||||
# mkdir /mnt/raid0
|
||||
# mount /dev/md0 /mnt/raid0/
|
||||
|
||||
10.下一步,使用 df 命令验证设备 /dev/md0 是否被挂载在 /mnt/raid0 下。
|
||||
|
||||
# df -h
|
||||
|
||||
11.接下来,创建一个名为 ‘tecmint.txt’ 的文件挂载到 /mnt/raid0 下,为创建的文件添加一些内容,并查看文件和目录的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /mnt/raid0/tecmint.txt
|
||||
# echo "Hi everyone how you doing ?" > /mnt/raid0/tecmint.txt
|
||||
# cat /mnt/raid0/tecmint.txt
|
||||
# ls -l /mnt/raid0/
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
验证挂载的设备
|
||||
|
||||
12.一旦你验证挂载点后,同时将它添加到 /etc/fstab 文件中。
|
||||
|
||||
# vim /etc/fstab
|
||||
|
||||
添加以下条目,根据你的安装位置和使用文件系统的不同,自行做修改。
|
||||
|
||||
/dev/md0 /mnt/raid0 ext4 deaults 0 0
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
添加设备到 fstab 文件中
|
||||
|
||||
13.使用 mount ‘-a‘ 来检查 fstab 的条目是否有误。
|
||||
|
||||
# mount -av
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
检查 fstab 文件是否有误
|
||||
|
||||
### 第6步:保存 RAID 配置 ###
|
||||
|
||||
14.最后,保存 RAID 配置到一个文件中,以供将来使用。同样,我们使用 ‘mdadm’ 命令带有 ‘-s‘ (scan) 和 ‘-v‘ (verbose) 选项,如图所示。
|
||||
|
||||
# mdadm -E -s -v >> /etc/mdadm.conf
|
||||
# mdadm --detail --scan --verbose >> /etc/mdadm.conf
|
||||
# cat /etc/mdadm.conf
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
保存 RAID 配置
|
||||
|
||||
就这样,我们在这里看到,如何通过使用两个硬盘配置具有条带化的 RAID0 级别。在接下来的文章中,我们将看到如何设置 RAID5。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/create-raid0-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Babin Lonston][a]
|
||||
译者:[strugglingyouth](https://github.com/strugglingyouth)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/babinlonston/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/understanding-raid-setup-in-linux/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user