mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-03 23:40:14 +08:00
已翻译 by小眼儿
Signed-off-by: tinyeyeser <tinyeyeser@gmail.com>
This commit is contained in:
parent
fca8d1fd6d
commit
4bfea9cd7e
@ -1,124 +0,0 @@
|
|||||||
翻译中 by小眼儿
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
How to set up web-based network traffic monitoring system on Linux
|
|
||||||
================================================================================
|
|
||||||
When you are tasked with monitoring network traffic on the local network, you can consider many different options to do it, depending on the scale/traffic of the local network, monitoring platforms/interface, types of backend database, etc.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[ntopng][1] is an open-source (GPLv3) network traffic analyzer which provides a web interface for real-time network traffic monitoring. It runs on multiple platforms including Linux and MacOS X. ntopng comes with a simple RMON-like agent with built-in web server capability, and uses [Redis][2]-backed key-value server to store time series statistics. You can install ntopng network traffic analyzer on any designated monitoring server connected to your network, and use a web browser to access real-time traffic reports available on the server.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In this tutorial, I will describe **how to set up a web-based network traffic monitoring system on Linux by using ntopng.**
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Features of ntopng ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
- Flow-level, protocol-level real-time analysis of local network traffic.
|
|
||||||
- Domain, AS (Autonomous System), VLAN level statistics.
|
|
||||||
- Geolocation of IP addresses.
|
|
||||||
- Deep packet inspection (DPI) based service discovery (e.g., Google, Facebook).
|
|
||||||
- Historical traffic analysis (e.g., hourly, daily, weekly, monthly, yearly).
|
|
||||||
- Support for sFlow, NetFlow (v5/v9) and IPFIX through nProbe.
|
|
||||||
- Network traffic matrix (who’s talking to who?).
|
|
||||||
- IPv6 support.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Install ntopng on Linux ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
The official website offers binary packages for [Ubuntu][3] and [CentOS][4]. So if you use either platform, you can install these packages.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
If you want to build the latest ntopng from [its source][5], follow the instructions below.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To build ntopng on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo apt-get install libpcap-dev libglib2.0-dev libgeoip-dev redis-server wget
|
|
||||||
$ tar xzf ntopng-1.0.tar.gz
|
|
||||||
$ cd ntopng-1.0/
|
|
||||||
$ ./configure
|
|
||||||
$ make geoip
|
|
||||||
$ make
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
In the above steps, “make geoip” will automatically download a free version of GeoIP databases with wget from maxmind.com. So make sure that your system is connected to the network.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To build ntopng on Fedora:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo yum install libpcap-devel glib2-devel GeoIP-devel
|
|
||||||
libxml2-devel redis wget
|
|
||||||
$ tar xzf ntopng-1.0.tar.gz
|
|
||||||
$ cd ntopng-1.0/
|
|
||||||
$ ./configure
|
|
||||||
$ make geoip
|
|
||||||
$ make
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To install ntopng on CentOS or RHEL, first [set up EPEL repository][6], and then follow the same instructions as in [Fedora][7] above.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Configure ntopng on Linux ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
After building ntopng, create a configuration directory for ntopng, and prepare default configuration files as follows. I assume that “192.168.1.0/24″ is the CIDR address prefix of your local network.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo mkir /etc/ntopng -p
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo -e /etc/ntopng/ntopng.start
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
> --local-networks "192.168.1.0/24"
|
|
||||||
>
|
|
||||||
> --interface 1
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo -e /etc/ntopng/ntopng.conf
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
> -G=/var/run/ntopng.pid
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Before running ntopng, make sure to first start redis, which is a key-value store for ntopng.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To start ntopng on Debian, Ubuntu or Linux Mint:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/redis-server restart
|
|
||||||
$ sudo ./ntopng
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
To start ntopng on Fedora, CentOS or RHEL:
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo service redis restart
|
|
||||||
$ sudo ./ntopng
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
By default, ntopng listens on TCP/3000 port. Verify this is the case using the command below.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo netstat -nap|grep ntopng
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
> tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 29566/ntopng
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
### Monitor Network Traffic in Web-Based Interface ###
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Once ntopng is successfully running, go to http://<ip-address-of-host>:3000 on your web browser to access the web interface of ntopng.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
You will see the login screen of ntopng. Use the default username and password: “admin/admin” to log in.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Here are a few screenshots of ntopng in action.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Real-time visualization of top flows.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[][8]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Live statistics of top hosts, top protocols and top AS numbers.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[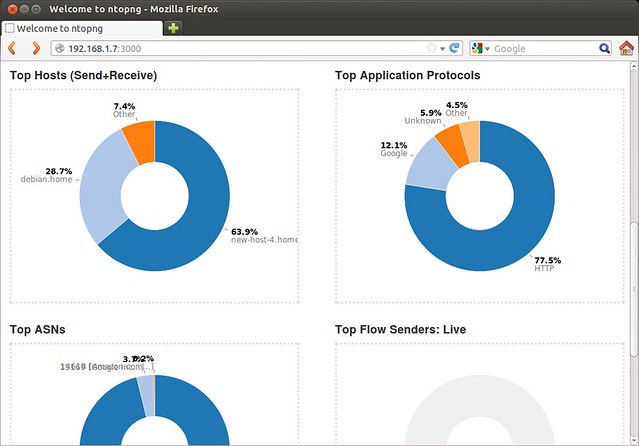][9]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Real time report of active flows with DPI-based automatic application/service discovery.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Historic traffic analysis.
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[][10]
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/10/set-web-based-network-traffic-monitoring-linux.html
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
[1]:http://www.ntop.org/products/ntop/
|
|
||||||
[2]:http://redis.io/
|
|
||||||
[3]:http://apt.ntop.org/
|
|
||||||
[4]:http://rpm.ntop.org/
|
|
||||||
[5]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/ntop/files/ntopng/
|
|
||||||
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
|
||||||
[7]:http://xmodulo.com/go/fedora_guide
|
|
||||||
[8]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10487165303/
|
|
||||||
[9]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10486988416/
|
|
||||||
[10]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10486995114/
|
|
||||||
@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
|
|||||||
|
如何在Linux上配置基于Web的网络流量监控系统
|
||||||
|
================================================================================
|
||||||
|
当你在本地网络监控网络流量,根据流量大小、监控平台/接口、数据库类型等等,可以有许多不同的选择。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[ntopng][1]是一套开源(遵循GPLv3协议)网络流量分析解决方案,提供基于web界面的实时网络流量监控。支持跨平台,包括Linux和MacOS X。ntopng类似于RMON远端网络监控代理,具有内置的Web服务能力,使用[Redis][2]键值服务按时间序列存储统计信息。你可以在任何指定的监控服务器上安装ntopng,只需使用任一web浏览器,就能实时访问服务器上的流量报告了。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本教程就来介绍**如何使用ntopng在Linux上配置基于Web的网络流量监控系统**
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
###ntopng的特性###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
- 从数据流级别与协议级别对本地网络流量进行实时分析
|
||||||
|
- 支持域、AS(自制系统)与VLAN级别的统计分析
|
||||||
|
- 支持IP地址地理定位
|
||||||
|
- 支持基于“服务探索”(例如Google、Facebook)的深度报文检测(DPI)
|
||||||
|
- 历史流量分析(例如分别按照小时、日、周、月、年进行分析)
|
||||||
|
- 支持sFlow、NetFlow(v5/v9版)以及基于nProbe的IPFIX
|
||||||
|
- 网络流量矩阵(谁正在和谁谈话?)
|
||||||
|
- 支持IPv6
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
###在Linux上安装ntopng
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
官方网页上提供了针对[Ubuntu][3]和[CentOS][4]的二进制安装包。如果你使用的恰好是以上二者其一,并且懒得用源码安装,可以直接到官网下载二进制文件包安装,并忽略这一小节下面的内容。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
如果你想通过[源码][5]安装最新的ntopng,请继续往下看
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
如果你是Debian、Ubuntu或Linux Mint,执行以下命令:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo apt-get install libpcap-dev libglib2.0-dev libgeoip-dev redis-server wget
|
||||||
|
$ tar xzf ntopng-1.0.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
$ cd ntopng-1.0/
|
||||||
|
$ ./configure
|
||||||
|
$ make geoip
|
||||||
|
$ make
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
上面的几个步骤中,“make geoip”将会自动通过wget从maxmind.com下载一个免费版的GeoIP数据库,因此,这里最好确保你的系统能联网。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
如果你是Fedora:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo yum install libpcap-devel glib2-devel GeoIP-devel
|
||||||
|
libxml2-devel redis wget
|
||||||
|
$ tar xzf ntopng-1.0.tar.gz
|
||||||
|
$ cd ntopng-1.0/
|
||||||
|
$ ./configure
|
||||||
|
$ make geoip
|
||||||
|
$ make
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
如果你是CentOS或RHEL,首先[设置EPEL repository][6],然后再执行上面和[Fedora][7]一样的命令就可以。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
###在Linux上配置ntopng###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ntopng安装完毕之后,接下来,新建一个ntopng配置目录,然后按照下列命令准备默认的配置文件。这里我假设你的本地网络地址为C类“192.168.1.0/24”。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo mkir /etc/ntopng -p
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo -e /etc/ntopng/ntopng.start
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
> --local-networks "192.168.1.0/24"
|
||||||
|
>
|
||||||
|
> --interface 1
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo -e /etc/ntopng/ntopng.conf
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
> -G=/var/run/ntopng.pid
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在运行ntopng之前,要确认先启动redis,刚才不说了,redis为ntopng提供键值存储嘛~
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在Debian、Ubuntu和Linux Mint上,这样启动:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo /etc/init.d/redis-server restart
|
||||||
|
$ sudo ./ntopng
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
在Fedora、CentOS和RHEL上,这样启动:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo service redis restart
|
||||||
|
$ sudo ./ntopng
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
ntopng默认监听TCP的3000端口,使用下列命令加以确认。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo netstat -nap|grep ntopng
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
> tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:3000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 29566/ntopng
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
###基于Web界面的网络流量监控###
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
一旦ntopng成功运行,就可以打开浏览器,访问地址http://<你的主机IP地址>:3000
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
这时,你会看到ntopng的登录界面。使用默认帐密:“admin/admin”。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
下面是一些截图。
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
top流的实时可视化图像
|
||||||
|
[][8]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
top主机的实时统计,包括top协议和top AS数量
|
||||||
|
[][9]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
基于DPI的自动程序/服务探索生成的的实时数据报告
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
历史流量数据分析
|
||||||
|
[][10]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
via: http://xmodulo.com/2013/10/set-web-based-network-traffic-monitoring-linux.html
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
译者:[Mr小眼儿](http://blog.csdn.net/tinyeyeser) 校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[1]:http://www.ntop.org/products/ntop/
|
||||||
|
[2]:http://redis.io/
|
||||||
|
[3]:http://apt.ntop.org/
|
||||||
|
[4]:http://rpm.ntop.org/
|
||||||
|
[5]:http://sourceforge.net/projects/ntop/files/ntopng/
|
||||||
|
[6]:http://xmodulo.com/2013/03/how-to-set-up-epel-repository-on-centos.html
|
||||||
|
[7]:http://xmodulo.com/go/fedora_guide
|
||||||
|
[8]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10487165303/
|
||||||
|
[9]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10486988416/
|
||||||
|
[10]:http://www.flickr.com/photos/xmodulo/10486995114/
|
||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user