mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-24 02:20:09 +08:00
commit
49e710661f
@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
|
||||
申请翻译
|
||||
How to Auto Execute Commands/Scripts During Reboot or Startup
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
Download Your Free eBooks NOW - [10 Free Linux eBooks for Administrators][5] | [4 Free Shell Scripting eBooks][6]
|
||||
|
||||
I am always fascinated by the things going on behind the scenes when I [boot a Linux system and log on][1]. By pressing the power button on a bare metal or starting a virtual machine, you put in motion a series of events that lead to a fully-functional system – sometimes in less than a minute. The same is true when you log off and / or shutdown the system.
|
||||
|
||||
What makes this more interesting and fun is the fact that you can have the operating system execute certain actions when it boots and when you logon or logout.
|
||||
|
||||
In this distro-agnostic article we will discuss the traditional methods for accomplishing these goals in Linux.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: We will assume the use of Bash as main shell for logon and logout events. If you happen to use a different one, some of these methods may or may not work. If in doubt, refer to the documentation of your shell.
|
||||
|
||||
### Executing Linux Scripts During Reboot or Startup
|
||||
|
||||
There are two traditional methods to execute a command or run scripts during startup:
|
||||
|
||||
#### Method #1 – Use a cron Job
|
||||
|
||||
Besides the usual format (minute / hour / day of month / month / day of week) that is widely used to indicate a schedule, [cron scheduler][2] also allows the use of `@reboot`. This directive, followed by the absolute path to the script, will cause it to run when the machine boots.
|
||||
|
||||
However, there are two caveats to this approach:
|
||||
|
||||
1. a) the cron daemon must be running (which is the case under normal circumstances), and
|
||||
2. b) the script or the crontab file must include the environment variables (if any) that will be needed (refer to this StackOverflow thread for more details).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Method #2 – Use /etc/rc.d/rc.local
|
||||
|
||||
This method is valid even for systemd-based distributions. In order for this method to work, you must grant execute permissions to `/etc/rc.d/rc.local` as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and add your script at the bottom of the file.
|
||||
|
||||
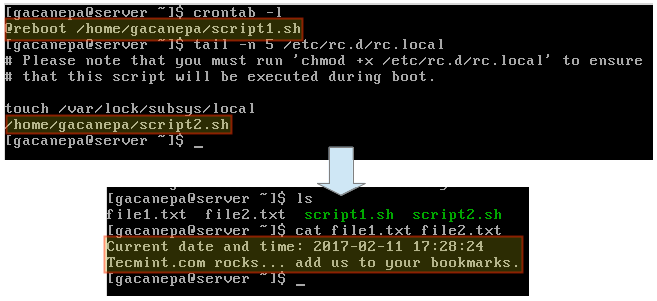
The following image shows how to run two sample scripts (`/home/gacanepa/script1.sh` and `/home/gacanepa/script2.sh`) using a cron job and rc.local, respectively, and their respective results.
|
||||
|
||||
script1.sh:
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
DATE=$(date +'%F %H:%M:%S')
|
||||
DIR=/home/gacanepa
|
||||
echo "Current date and time: $DATE" > $DIR/file1.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
script2.sh:
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
SITE="Tecmint.com"
|
||||
DIR=/home/gacanepa
|
||||
echo "$SITE rocks... add us to your bookmarks." > $DIR/file2.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][3]
|
||||
|
||||
Run Linux Scripts at Startup
|
||||
|
||||
Keep in mind that both scripts must be granted execute permissions previously:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ chmod +x /home/gacanepa/script1.sh
|
||||
$ chmod +x /home/gacanepa/script2.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Executing Linux Scripts at Logon and Logout
|
||||
|
||||
To execute a script at logon or logout, use `~.bash_profile` and `~.bash_logout`, respectively. Most likely, you will need to create the latter file manually. Just drop a line invoking your script at the bottom of each file in the same fashion as before and you are ready to go.
|
||||
|
||||
##### Summary
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we have explained how to run script at reboot, logon, and logout. If you can think of other methods we could have included here, feel free to use the comment form below to point them out. We look forward to hearing from you!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
I am Ravi Saive, creator of TecMint. A Computer Geek and Linux Guru who loves to share tricks and tips on Internet. Most Of My Servers runs on Open Source Platform called Linux. Follow Me: Twitter, Facebook and Google+
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/auto-execute-linux-scripts-during-reboot-or-startup/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ravi Saive ][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/
|
||||
[00]:https://twitter.com/ravisaive
|
||||
[01]:https://www.facebook.com/ravi.saive
|
||||
[02]:https://plus.google.com/u/0/+RaviSaive
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-boot-process/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/11-cron-scheduling-task-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Run-Linux-Commands-at-Startup.png
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,101 @@
|
||||
如何在 Linux 启动时自动执行命令或脚本
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
下载免费电子书 - [给管理员的 10 本 Linux 免费电子书] | [4 本 Shell 脚本免费电子书]
|
||||
|
||||
我一直很好奇,在[启动 Linux 系统并登录][1]的过程中到底发生了什么事情。按下开机键或运行一台虚拟机,经过一系列事件之后,进入到一个完整的系统中,有的时候,都不用一分钟就进入系统了。当你注销或者关机时,也是这样。
|
||||
|
||||
更有意思的是,在登录或注销时,你还可以让系统执行特定的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
本文,我们将探讨一下在 Linux 操作系统中实现这些目标(在登录或注销时,让系统执行特定的操作)的传统方法。
|
||||
|
||||
注意:我们假定使用的是 Bash 作为登录及注销的主 Shell。如果你使用的是其他 Shell,那么有些方法可能会无效。如果有其他的疑问,请参考对应的 Shell 文档。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在启动时执行 Linux 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
有两种传统的方法可以实现在启动时执行命令或脚本:
|
||||
|
||||
#### 方法 #1 - 使用 cron 任务
|
||||
|
||||
除了常用格式(分 / 时 / 日 / 月 / 周)外,[cron 调度器][2]还支持 `@reboot` 指令。这个指令后面的参数是脚本(启动时要执行的那个脚本)的绝对路径。
|
||||
|
||||
然而,这种方法需要注意两点:
|
||||
|
||||
1. a) cron 守护进程必须处于运行状态(通常情况下都会运行),同时
|
||||
2. b) 脚本或 crontab 文件必须包含必要的环境变量(参考 StackOverflow 获取更多详细内容)。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 方法 #2 - 使用 /etc/rc.d/rc.local
|
||||
|
||||
这个方法对于 systemd-based 发行版 Linux 同样有效。不过,使用这个方法,需要授予 `/etc/rc.d/rc.local` 文件执行权限:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后在这个文件底部添加指定的脚本代码。
|
||||
|
||||
下图分别说明如何使用 cron 任务和 rc.local 文件运行两个示例脚本(`/home/gacanepa/script1.sh`、`/home/gacanepa/script2.sh`)。
|
||||
|
||||
script1.sh:
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
DATE=$(date +'%F %H:%M:%S')
|
||||
DIR=/home/gacanepa
|
||||
echo "Current date and time: $DATE" > $DIR/file1.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
script2.sh:
|
||||
```
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
SITE="Tecmint.com"
|
||||
DIR=/home/gacanepa
|
||||
echo "$SITE rocks... add us to your bookmarks." > $DIR/file2.txt
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][3]
|
||||
|
||||
启动时执行 Linux 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
记住,一定要提前给两个示例脚本授予执行权限:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ chmod +x /home/gacanepa/script1.sh
|
||||
$ chmod +x /home/gacanepa/script2.sh
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 在登录或注销时执行 Linux 脚本
|
||||
|
||||
要在登录或注销时执行脚本,分别需要使用 `~.bash_profile` 和 `~.bash_logout` 文件。多数情况下,需要手动创建后一个文件。在每个文件的底部,添加调用脚本代码,就可以实现这个功能。
|
||||
|
||||
##### 总结
|
||||
|
||||
本文主要介绍如何在启动、登录以及注销系统时执行脚本。如果你有其他的方法可以补充,请使用下面的评论表给我们指出,我们期待您的回应!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
作者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
我叫 Ravi Saive,我是 TecMint 的作者。一名喜欢在互联网上分享 Linux 相关技巧的电脑极客和 Linux 大师。我的服务器大多数都是使用 Linux 系统。关注我:Twitter, Facebook, Google+
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/auto-execute-linux-scripts-during-reboot-or-startup/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Ravi Saive ][a]
|
||||
译者:[zhb127](https://github.com/zhb127)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/admin/
|
||||
[00]:https://twitter.com/ravisaive
|
||||
[01]:https://www.facebook.com/ravi.saive
|
||||
[02]:https://plus.google.com/u/0/+RaviSaive
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-boot-process/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/11-cron-scheduling-task-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[3]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/Run-Linux-Commands-at-Startup.png
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-useful-free-linux-ebooks-for-newbies-and-administrators/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/free-linux-shell-scripting-books/
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user