mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-03-12 01:40:10 +08:00
commit
4434dc0e36
@ -0,0 +1,401 @@
|
||||
想找点激烈的游戏?那就试试这 13 款 Roguelike 游戏吧!
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Roguelike 是角色扮演游戏的一个子类。从字面上看,它的意思是 “像 Rogue 的游戏”。Rogue 是一个关于地下城冒险的视频游戏,于 1980 年第一次发行,以极其上瘾而著称。这个游戏的目标是取得深藏于第 26 层的 "Amulet of Yendor",再返回到顶层逃出生天。
|
||||
|
||||
Roguelike 的准确定义并不存在,但这类游戏通常具有下面的特点:
|
||||
|
||||
- 奇幻的叙事背景;
|
||||
- 用程序产生关卡。游戏中的绝大多数场景在开始新的游戏时由游戏自动创建。这样做是为了鼓励玩家不断重玩;
|
||||
- 回合制的地下城探险和战斗;
|
||||
- 随机生成的基于贴片的图形环境;
|
||||
- 随机发生战斗;
|
||||
- 永久死亡 :在游戏中,死亡真的存在,一旦你的角色死了,那就真的结束了;
|
||||
- 高难度。
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章精心挑选了一些可运行在 Linux 平台下的 roguelike 游戏。假如你喜欢激烈、易上瘾的游戏,可以尝试这 13 款游戏。不要因它们原始的画质而退缩,一旦你沉浸其中,你将很快忘记画面的简陋。所有的这些都可以免费下载,并且几乎所有的游戏都是在开源协议下发行的。
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Dungeon Crawl Stone Soup
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Dungeon Crawl Stone Soup 是一个开源的,单用户角色扮演类的 roguelike 游戏,玩家要在遍布危险而充满敌意的怪兽的地下城中进行探险和寻找宝藏,并在任务中拯救传说中的神秘 Zot 宝珠。
|
||||
|
||||
Dungeon Crawl Stone Soup 是 Linley 开发的 Dungeon Crawl 游戏的延续。它是公开开发的,并邀请 Crawl 社区的人员来参与其中。
|
||||
|
||||
Dungeon Crawl 有着超棒且深层次的战术游戏环节,创新的魔法和信仰系统,以及数量宏大的和你战斗的怪兽。Crawl 也是最难以攻陷的 roguelike 游戏之一。当你最终在游戏中通关,将胜利宣言张贴在 rec.games.roguelike.misc 时,你才会知道这有多么令人骄傲!
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 丰富多彩的、富含深层次战术的 roguelike 游戏;
|
||||
- 手绘地图;
|
||||
- 无数的金库;
|
||||
- 漂亮的界面;
|
||||
- 创新的魔法和信仰系统;
|
||||
- 各种神灵,角色,物品和聪明的怪兽;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [crawl.develz.org][1]
|
||||
- 开发者: Stone Soup 开发小组
|
||||
- 协议: Crawl General Public License
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.15.2
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Dwarf Fortress
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Dwarf Fortress 是一个单人魔幻游戏,与 NetHack 类似。你可以在一个随机生成的持久的世界中,控制一个矮人哨兵或一个冒险者。
|
||||
|
||||
这个游戏的特色有:三种游戏模式(矮人要塞,冒险者,传说模式),一个独特的随机生成的世界(由地形,野生生物和传奇生物等组成), 阴森的战斗机制以及各种邪恶鱼群。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 在这个世界里,你想玩多久都可以。可以经历许多次游戏,记录历史事件,对更改进行跟踪等;
|
||||
- 当你扮演的矮人在山群中寻找宝藏时,你可以对他们下达命令
|
||||
- 用各种材料来手工制作珍宝、物品,并可以用贵重金属、宝石等来改进它们;
|
||||
- 通过各种手段保护你自己,防御来自敌对文明的袭击;
|
||||
- 支持贵族,他们会管理你的民众
|
||||
- 让你的矮人高兴起来,了解他们工作和休闲时的想法;
|
||||
- 不同的 Z 坐标可以使你在多个层级上建造你的堡垒。建立塔台或征服地下深处;
|
||||
- 建立水闸来灌溉作物或用水淹没你的对手;
|
||||
- 扮演一个探险者并进行探索,为荣誉而战或复仇
|
||||
- 与以前的游戏中的对手相遇;
|
||||
- 在你经过的旅途中营救小城里的人们;
|
||||
- 没有繁琐的情节,只需要探索;
|
||||
- 无缝连接的漫游游戏世界-总共达到 197376 x 197376 平方 -可以在区域地图上更快速地穿行;
|
||||
- 接受小镇或文明社会的领导所委托的任务;
|
||||
- 可以找到你以前的角色,以一个新的角色带上他们来一场新的冒险,或者直接重新激活并使用他们;
|
||||
- 通过 Z 轴使得你可以在各个地下城的不同层级间和结构间平滑的上下移动来和对手战斗;
|
||||
- 战斗模式是通过技巧、身体部位、搏斗、在不同区域间蓄势和躲避,体验流血、疼痛,恶心及其他感受;
|
||||
- 一个动态的天气模型跟踪风,湿度及空气流动,以创造冷暖气流锋面、风、暴风雨雪;
|
||||
- 超过 200 种岩石和矿物类型被引入到了游戏世界,它们被放置在合适的地理环境中;
|
||||
- 通过可更改的文本文件来添加生物,武器,植物,金属和其他对象;
|
||||
- 以 16 色(包括黑色)渲染的扩展 ASCII 字符集,以及 8 种背景颜色(包括黑色);
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.bay12games.com/dwarves/][2]
|
||||
- 开发者: Tarn Adams
|
||||
- 协议: 免费软件
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.40.19
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Ancient Domains of Mystery
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ancient Domains of Mystery (ADOM) 是一个 rogue-like 游戏,从 1994 年至今一直在不断开发。
|
||||
|
||||
它是一个包含复杂地下城的单用户游戏。你控制一个用种族、类别、属性、技巧和装备等描述的虚构角色。这个虚构角色正尝试着达到一个特定的目标(参考下面的介绍)并在一个困难的任务中取胜。为了完成任务,你必须在以前没有发现的隧道和地下城中探险,和丑陋的怪兽战斗,解开一系列遗忘的秘密,并找到宝藏。
|
||||
|
||||
在游戏期间,你在每次游戏时随机生成的各层地下城中探索。你也可能遇到某个特定的关卡,其中有着特定的挑战或者围绕某个特定主题而生成。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 拥有上百个地点的巨大游戏世界,例如城堡、随机生成的地下城、主题寺庙、墓地、古代遗迹、塔台和其他名胜;
|
||||
- 各种各样的种族(矮人、drakeling、雾精灵、hurthling、兽人、巨魔、ratling 等等)(LCTT注:种族信息可以参考[这里](http://ancardia.wikia.com/wiki/Race) 和丰富的职业(战士、 元素法师、 刺客、 混沌骑士,决斗士等等)带来无限的游戏乐趣;
|
||||
- 上百个怪兽和物品,其中的许多带有随机的增强特性;
|
||||
- 迫使你在对力量的欲望和对诅咒的恐惧之间进行权衡的腐败体系;
|
||||
- 法术、祈祷、思想技艺、炼金术、手工艺和更多;
|
||||
- 多样的任务和分支故事主线;
|
||||
- 许多完全不同的结局,可能改变现实本身。
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.adom.de][3]
|
||||
- 开发者: Thomas Biskup
|
||||
- 协议: Postcardware
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.20 Prelease 20
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Tales of Maj’Eyal (ToME)
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Tales of Maj’Eyal (ToME) (注:中文译名为 马基埃亚尔的传说) 是一个免费、开源的 roguelike 角色扮演游戏,包含特色的战术回合制战役和先进角色构建。它作为运行在 T-Engine 4.0 中的一个模块而被创造。
|
||||
|
||||
现在处于王权世纪(Age of Ascendancy),在长达一万年的冲突痛苦和混乱之后,我们所知的世界终于进入了一个相对和平的时期。 “魔法大爆裂(Spellblaze)” 留下的影响已经大为减缓, 大地的伤痕也慢慢地开始愈合。在薪火世纪(Age of Pyre)之后,各个文明也纷纷开始重建家园。(注:翻译来源于 [这里](http://www.qiyun.org/zhuanti/majiaiyaerdechuanshuo.htm))
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 适合于那些没有 rogueline 体验的玩家;
|
||||
- 同时支持图形界面和 ASCII 模式;
|
||||
- 某些角色拥有多达 40 种的能力;
|
||||
- 天赋系统;
|
||||
- 战役引擎;
|
||||
- 在线的持久状态/成就追踪;
|
||||
- IRC 聊天客户端;
|
||||
- 可扩展,可修改;
|
||||
- 充满激情的音乐;
|
||||
- 可解锁新的种族,类别,起始点,游戏模式和特点等;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [te4.org][4]
|
||||
- 开发者: ToME 开发团队
|
||||
- 协议: GNU GPL v3.0
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.2.5
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Cataclysm Dark Days Ahead
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cataclysm 是一个开源的 “后末世” roguelike 游戏,背景设定在由怪兽和僵尸带来的毁灭性的瘟疫后虚构的新英格兰(New England) 乡村。它是 Whale 开发的原有 Cataclysm 的继续,拓展了更多新的生物,建筑,游戏机制和其他特点。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管有些人描述它为一个 “僵尸游戏”,但 Cataclysm 远比一个“僵尸游戏”包含更多内容。玩家要在一个由程序生成的严酷、持久的世界中艰难生存下去。在一个死寂的文明世界中搜寻剩下的食物和装备,或者假如你足够幸运,搞到一辆装满汽油的汽车逃离 Dodge --这个如地狱一般的地方。从僵尸到巨型昆虫或机器人杀手以及更加奇怪和致命的东西,你要通过战斗来击败它们或逃离,以及和那些想要抢夺你的东西的那些同你一样的人战斗。
|
||||
|
||||
在许多方面上, Cataclysm 与大多数的 roguelike 游戏不同。它被设定在一个没有边界的三维世界里,而不是设定在一个垂直、线性的地下城中。这意味着相比于大多数的 roguel 游戏,探险将占一个更大的比重,而且这个游戏将具有更大的自由度。由于地图是如此的巨大,在每次游戏之间,它可以完全保持原样。假如你死了,并以一个新的角色开始,你的新游戏将会设定在同你最近呆过的游戏世界相同的世界里。同许多 roguelike 游戏一样,你可以获得先前角色的战利品;而与大多数 roguelike 不同的是,你也可以重新踏上先前角色的轨迹,并且对世界做出的任何戏剧性改变将会维持到你的下一次游戏。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 详细的角色创建,提供了数量众多的特性来选择;
|
||||
- 防御模式,这是一个有着快节奏作战的休息模式;
|
||||
- Bionics;类似于在许多其他游戏里的魔法系统;
|
||||
- 基因突变, 有好的和坏的变化;
|
||||
- 无界的,完全随机的世界地图,可以在角色交替时保持不变;
|
||||
- 创造物品
|
||||
- 新的制作方法可能需要通过练习或从书本中获得来磨练你的知识;
|
||||
- 逼真的火、烟和其他动态的地图特效;
|
||||
- 昼/夜循环,需要睡觉。假如你必须的话,可以使用咖啡因来保持更长时间的清醒,但这不健康;
|
||||
- 超过 300 种物品类型,包括众多的现实世界的枪支,药品和工具;
|
||||
- 许多药品是上瘾的,并需要持续使用来避免负面效果;
|
||||
- 通过修补门、窗、建造陷阱和巩固你的家的基石来防止一个僵尸的突然造访;
|
||||
- 能够构建你自己的木屋,包括墙和屋顶;
|
||||
- 可以驾驶在“后末世”发现的汽车兜风;
|
||||
- 这个可以根据你的需求来修改,或甚至你可以自己制造一辆;
|
||||
- 温度系统,太冷或太热都非常危险;
|
||||
- 初步支持贴片界面;
|
||||
- 根据选项生成世界,以及各种编辑方式;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [en.cataclysmdda.com][5]
|
||||
- 作者: Kevin Granade 及其他
|
||||
- 协议: Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.B
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Goblin Hack
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Goblin Hack 是一个开源 roguelike 游戏,基于 OpenGL 的平滑滚动的ASCII 图形界面。这个游戏受 NetHack 外观的启发,但更加快速且使用更少的按键。
|
||||
|
||||
Goblin Hack 有一个简洁的界面,在今天这个过度强调渲染的游戏世界中,似乎它对所有年龄段的玩家都有吸引力,并启发了这些玩家的想象力。
|
||||
|
||||
在被投进一个随机的正在生成的地下城之前,玩家可以从几个角色类别中选择一个角色。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 令人印象深刻的界面(相比于许多其他的 roguelike 游戏);
|
||||
- 简洁的界面;
|
||||
- 在被投进一个随机的正在生成的第一层地下城之前,玩家可以从几个角色类别中选择一个角色;
|
||||
- 手动保存游戏;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [goblinhack.sourceforge.net][6], [github.com/goblinhack/goblinhack][7]
|
||||
- 作者: Neil McGill
|
||||
- 协议: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.19
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###SLASH'EM
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Super Lotsa Added Stuff Hack - Extended Magic (SLASH'EM) 是一个角色扮演游戏,在其中你控制一个单独的角色。SLASH'EM 是 NetHack 的一个变种。它拥有一个和 Rogue、ADOM、Anghand 及 NetHack 相似的界面和游戏玩法。你通过键盘来控制角色的动作,以一个俯视的视角来查看这个世界。
|
||||
|
||||
背景: Amulet of Yendor 已被偷走,不仅如此,偷走 amulet 的 Wizard of Yendor(坏蛋)似乎深藏于 Dungeons of Doom(危险的地方)。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 提供额外的特色、怪兽和项目;
|
||||
- 新颖的特点包括僧人职业和类似推箱子的关卡;
|
||||
- 主地下城比在 NetHack 中的要大很多;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.slashem.org][8]
|
||||
- 开发者: Slash'EM 开发团队
|
||||
- 协议: MIT License, NetHack General Public License
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.0.7E7F3
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###NetHack
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
NetHack 是一个极简,但又非常吸引人的具有地下城与龙风格的冒险游戏。“net”元素指的是它的发展已经根据网络进行了调整,“hack”元素指的是角色扮演游戏的一种类型,以乱砍、猛砍著称,着眼于战斗。
|
||||
|
||||
在 NetHack 中,你扮演凶猛的战士、巫师或许多其他职业中的一种,一路战斗着,为你的神灵获取 Amulet of Yendor(可以说这是一个倒退!)。在这个过程中,你可能会遇到一个或两个 quantum mechanic(LCTT 译注:从[这里](http://nethack.wikia.com/wiki/Quantum_mechanic)得知,这指的是一种怪兽),或者可能遇到一个小型的太空舰队,抑或是 —— 假如你*足够*幸运会遇到 —— Ravenous Bugblatter Beast of Traal。(LCTT 译注:我参考了[这里](http://nethack.wikia.com/wiki/Douglas_Adams))。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 45-50 个关卡, 其中的大多数随机生成;
|
||||
- 各种各样的物品:武器、盔甲、卷轴、药水、戒指、宝石和各种各样的工具,如钥匙和灯;
|
||||
- 祝福和诅咒;
|
||||
- 永久死亡: 若没有对当前的保存文件进行备份,失效的角色就找不回来了;
|
||||
- 界面:
|
||||
- 文本模式;
|
||||
- 图形化界面, 使用 X、Qt 工具集或 GNOME 库;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.nethack.org][9]
|
||||
- 开发者: NetHack 开发团队
|
||||
- 协议: NetHack 通用公共许可证
|
||||
- 版本号: 3.4.3
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Ascii Sector
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ascii Sector 是一个免费的太空战斗/探险/交易游戏,它基于经典的电脑游戏 `Wing Commander: Privateer`,后者由 Origine Systems 公司于 1993 年发布。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Ascii Sector 中,刚开始你将驾驶一艘简易的飞船,然后可以通过接受任务或者贩卖物品来挣得足够多的钱以升级你的飞船或重新再买一艘。不管是在太空中,还是在地面上,抑或是在飞船上,你可以专注于致命的战斗;并且通过使用 Ascii Sector 的脚本语言,你还可以为游戏创造自己的任务或享受其他玩家创造的任务。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 使用 ANSI 字符集生成图形界面;
|
||||
- 真正的深入到游戏中;
|
||||
- 提供各种基地,任务,商品和飞船;
|
||||
- 飞船型号包括: Broadsword, Centurion, Demon, Dralthi, Drayman, Galaxy, Gladius, Gothri, Kamekh, Nexus, Orion, Paradign, Stileto, Talon, Tarsus 和 Ulysses;
|
||||
- 四个象限: Alizarin, Crimson, Mauve, 和 Viridian;
|
||||
- 可下载的任务;
|
||||
- 任务可用脚本编辑;
|
||||
- Ascii Sector 任务语言,在 Ascii Sector 宇宙中创造你自己的故事;
|
||||
- 可以袭击或抢劫星球上的 NPC(非玩家控制角色);
|
||||
- 可以到处移动的持久性舰队、可以改变系统的控制、引来敌人的舰队、回基地修复或重建;
|
||||
- 可以登录系统受损的飞船;
|
||||
- 可下载高质量的音乐文件;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.asciisector.net][10]
|
||||
- 开发者: Christian Knudsen
|
||||
- 协议: 免费软件
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.7.1.4
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Angband
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Angband 是一个免费、单用户、使用 ASCII 字符图形化的地下城探险游戏,在其中你将以一个冒险者的角色探索一个深深的地下城,与怪兽战斗,获得你能取得的最好武器,准备着与黑暗之主 Morgoth 的最后决战。从上世纪九十年代开始,它一直在持续地开发着。
|
||||
|
||||
Angband 沿袭了 Rogue 和 NetHack 的风格路线。它由 Moria 和 Umoria 游戏衍生而来,基于 Rogue 回合制。它经常被描述为一个 “roguelike”游戏,因为它的外观和游戏体验与 Rogue 非常相似。很多游戏中的新生物、物品都来自 J.R.R Tolkien 的画作,尽管有些野兽直接来源于经典的神话、龙与地下城、Rolemaster,或 Angband 的原开发者的脑海中。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 100 层地下城;
|
||||
- 随机产生的新关卡;
|
||||
- 可以选择成为人类、半精灵、精灵、霍比特人、地精、矮人,半兽人,半巨魔, 登丹人 ,高等精灵,或者狗头人;
|
||||
- 神器;
|
||||
- 施法;
|
||||
- 怪物;
|
||||
- 怪物坑;
|
||||
- 怪物巢穴;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [rephial.org][11]
|
||||
- 开发者: Angband 开发小组
|
||||
- 协议: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 3.5.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###UnNetHack
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
UnNetHack 是 NetHack 的一个分支版本。NetHack 最开始于 1987 年发行,并且许多游戏玩家认为它是计算机世界所能提供的最好游戏体验的游戏之一。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 增加了许多针对 NetHack 的增强,如额外的怪兽、更多的关卡、许多新的元素、更多的危险、更具挑战性的游戏,以及最重要的,相比普通的 NetHack,它更具娱乐性;
|
||||
- 帮助新手开始的教程;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [sourceforge.net/apps/trac/unnethack][12]
|
||||
- 作者: Patric Mueller
|
||||
- 协议: Nethack General Public License
|
||||
- 版本号: 5.1.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Hydra Slayer
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Hydra Slayer 是一个专注于杀死九头蛇的开源 Roguelike 游戏。它受到了希腊神话、地下城探险、MathRL seven day roguelike ,和一些关于勇者杀死多头野兽的数字谜题等启发。
|
||||
|
||||
特点如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 独特的游戏机制;
|
||||
- 混合希腊神话和数字迷宫的主题;
|
||||
- 传统的 roguelike ASCII 字符界面或贴片/3D 界面;
|
||||
- 5 种人物角色,具有极为不同的战术、力量及弱点;
|
||||
- 28 种敌人类型:
|
||||
- 10 种基本的九头蛇类型(每种类型都有两种变种);
|
||||
- 8 种特殊类型的敌人;
|
||||
- 可用作战术工具的无害蘑菇;
|
||||
- 28 种装备(并包括材料和装备的大小/力量的变种);
|
||||
- 15 种武器材料;
|
||||
- 18 种非装备物品;
|
||||
- 3 种可供选择的地图;
|
||||
- 8 种关卡拓扑结构(包括莫比乌斯带和克莱因瓶);
|
||||
- 11 个关卡生成器;
|
||||
- 2 种结局;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.roguetemple.com/z/hydra][13]
|
||||
- 开发者: Zeno Rogue
|
||||
- 协议: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 16.1
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
###Brogue
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Brogue 是一个开源的 Roguelike 游戏,它可以运行在 Mac OS X, Windows, Linux, iOS 和 Android 等平台下。
|
||||
|
||||
Brogue 是 Rogue 的一个直系分支,后者是一个最早由 Michael Toy 和 Glenn Wichman 于 1980 年左右开发的地下城探险视频游戏。与其他受欢迎的现代 Roguelike 游戏不同, Brogue 追求简单而不是复杂性,同时尽力确保游戏的不同组成之间的联系是有趣且纷繁多彩。
|
||||
|
||||
这个游戏的目标是取得深藏于地下第 26 层的 "Amulet of Yendor",再返回到地面逃出生天。对于那些技术娴熟且想进一步探险的人来说,位于 26 层之下的每层均包含 3 颗 lumenstone (流明石)(LCTT 译注:此处与我在[这里](http://brogue.wikia.com/wiki/Lumenstone)看到的有些出入),获得它们,将在胜利的基础上被授予额外的得分。
|
||||
|
||||
Brogue 是一个富有挑战性的游戏,但玩起来非常有趣。尽量不要因游戏的高难度而灰心;试玩一段时间之后,你会发现它变得非常吸引人。
|
||||
|
||||
特点如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 追求简单而非复杂;
|
||||
- 对用户友好;
|
||||
- 相比于 Rogue, Brogue 关卡生成更加复杂;
|
||||
- 移除了 XP 和 水平系统 ;
|
||||
- 陷阱,防护性物品;
|
||||
- 额外的怪兽类型和魔法物品;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [sites.google.com/site/broguegame][14]
|
||||
- 作者: Brian Walker
|
||||
- 协议: GNU Affero GPL
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.7.3
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/201412031524381/RoguelikeGames.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://crawl.develz.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.bay12games.com/dwarves/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.adom.de/
|
||||
[4]:http://te4.org/
|
||||
[5]:http://en.cataclysmdda.com/
|
||||
[6]:http://goblinhack.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/goblinhack/goblinhack
|
||||
[8]:http://www.slashem.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.nethack.org/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.asciisector.net/
|
||||
[11]:http://rephial.org/
|
||||
[12]:http://sourceforge.net/apps/trac/unnethack/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.roguetemple.com/z/hydra/
|
||||
[14]:lhttps://sites.google.com/site/broguegame/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,83 @@
|
||||
如何在Ubuntu 14.04上安装轻量级web服务器Cherokee
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Cherokee** 是一个免费,开源,高性能轻量级的全功能web服务器,支持大部分主流操作系统(Linux、 Mac OS X、 Solaris 和 BSD)。它支持TLS/SSL、FastCGI、 SCGI、 PHP、 uWSGI、 SSI、 CGI、 LDAP、 HTTP代理、 视频流处理、 内容缓存、 流量控制、 虚拟主机、Apache兼容的日志文件,以及负载均衡等功能。
|
||||
|
||||
今天我们介绍一下怎样在Ubuntu Server 14.04 LTS安装和配置轻量级的web服务器Cherokee,只需要注意修改软件源列表,同样适用于Ubuntu12.04,12.10和13.04。
|
||||
|
||||
在Ubuntu Server上逐步安装和配置Cherokee
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 更新Ubuntu软件包索引 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先登陆Ubuntu Server,执行以下命令,更新Ubuntu Server的软件源并安装可用的更新。
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 加入 PPA ###
|
||||
|
||||
通过运行以下命令增加Cherokee的PPA
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:cherokee-webserver
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
对于运行14.04版本的服务器还需要执行以下步骤
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/apt/sources.list.d
|
||||
|
||||
nano cherokee-webserver-ppa-trusty.list
|
||||
|
||||
用`deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/cherokee-webserver/ppa/ubuntu saucy main` 替换 `deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/cherokee-webserver/ppa/ubuntu trusty main`
|
||||
|
||||
**再次运行命令:**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 使用apt-get安装Cherokee ###
|
||||
|
||||
使用如下命令安装Cherokee和SSL模块
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install cherokee cherokee-admin cherokee-doc libcherokee-mod-libssl libcherokee-mod-streaming libcherokee-mod-rrd
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 配置Cherokee ###
|
||||
|
||||
重启Cherokee服务:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo service cherokee start
|
||||
|
||||
使用Cherokee最大的好处就是能通过一个简单易用的web界面 cherokee-admin 来管理所有的配置选项。推荐通过浏览器来管理Cherokee。使用如下命令启动cherokee-admin
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cherokee-admin
|
||||
|
||||
**注意: cherokee-admin 会显示用户名,一次性密码和web管理界面地址。**
|
||||
|
||||
**请记录下这个一次性密码,登录到管理界面时需要它。**
|
||||
|
||||
默认情况下,只能通过localhost访问Cherokee-admin,如果需要通过其它网络地址来访问,可以使用‘**-b**’参数。如果不指定任何IP地址,Cherokee-admin会自动监听所有网络端口。然后就可以通过网络访问Cherokee-admin
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cherokee-admin -b
|
||||
|
||||
通过指定IP地址访问Cherokee-admin
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cherokee-admin -b 192.168.1.102
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. 浏览cherokee-admin面板 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在你喜欢的浏览器中输入地址`http://主机名或 IP 地址:9090/`就可以进入控制面板了。例如我的是http://127.0.0.1:9090/,在浏览器中显示如下图
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
好了,到这里我们已经成功地在Ubuntu Server上安装和配置了Cherokee。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-cherokee-lightweight-web-server-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -1,15 +1,15 @@
|
||||
C语言数据类型是如何被大多数计算机系统所支持?
|
||||
---------
|
||||
========================
|
||||
|
||||
#问题:
|
||||
###问题:
|
||||
|
||||
在读K&R版的*The C Programming Language*一书时,我在[介绍,第3页]看到这样一条说明:
|
||||
在读K&R版的*The C Programming Language*一书时,我在[介绍,第3页]看到这样一条说明:
|
||||
|
||||
>因为C语言提供的数据类型和控制结构可以直接被大部分计算机系统所支持,所以在实现自包含程序时所需要的运行库文件一般很小。
|
||||
>**因为C语言提供的数据类型和控制结构可以直接被大部分计算机系统所支持,所以在实现自包含程序时所需要的运行库文件一般很小。**
|
||||
|
||||
这段黑体说明了什么?能找到一个例子来说明C语言中的某种数据类型或控制结构并不能被一种计算机系统所支持呢?
|
||||
这段黑体说明了什么?能否找到一个例子来说明C语言中的某种数据类型或控制结构不被某种计算机系统直接支持呢?
|
||||
|
||||
#回答:
|
||||
###回答:
|
||||
|
||||
事实上,C语言中确实有不被直接支持的数据类型。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,13 +31,13 @@ return _float_add(x, y);
|
||||
|
||||
另一个常见的例子是64位整型数(C语言标准中'long long'类型是1999年之后才出现的),这种类型在32位系统上也不能直接使用。古董级的SPARC系统则不支持整型乘法,所以在运行时必须提供乘法的实现。当然,还有一些其它例子。
|
||||
|
||||
##其它语言
|
||||
####其它语言
|
||||
|
||||
相比起来,其它编程语言有更加复杂的基本类型。
|
||||
|
||||
比如,Lisp中的symbol需要大量的运行时实现支持,就像Lua中的tables、Python中的strings、Fortran中的arrays,等等。在C语言中等价的类型通常要么不属于标准库(C语言没有标准symbols或tables),要么更加简单,而且并不需要那么多的运行时支持(C语言中的array基本上就是指针,以NULL结尾的字符串实现起来也很简单)。
|
||||
比如,Lisp中的symbol需要大量的运行时实现支持,就像Lua中的table、Python中的string、Fortran中的array,等等。在C语言中等价的类型通常要么不属于标准库(C语言没有标准symbol或table),要么更加简单,而且并不需要那么多的运行时支持(C语言中的array基本上就是指针,以NULL结尾的字符串实现起来也很简单)。
|
||||
|
||||
##控制结构
|
||||
####控制结构
|
||||
|
||||
异常处理是C语言中没有的一种控制结构。非局部的退出只有'setjmp()'和'longjmp()'两种,只能提供保存和恢复某些部分的处理器状态。相比之下,C++运行时环境必须先遍历函数调用栈,然后调用析构函数和异常处理函数。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ via:[stackoverflow](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/27977522/how-are-c-data-t
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dietrich Epp][a]
|
||||
译者:[KayGuoWhu](https://github.com/KayGuoWhu)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,13 +1,13 @@
|
||||
如何在CentOS/RHEL中安装机遇Web监控的Linux-dash
|
||||
如何在CentOS/RHEL中安装基于Web的监控系统 linux-dash
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Linux-dash**是一款为Linux设计的基于web的轻量级监控面板。这个程序会显示实时时间、不同的系统属性,比如CPU负载、RAM使用率、磁盘使用率、网速、网络连接、RX/TX带宽、登录用户、运行的进程等等。它不会存储长期的统计。因为它没有后端数据库。
|
||||
**Linux-dash**是一款为Linux设计的基于web的轻量级监控面板。这个程序会实时显示各种不同的系统属性,比如CPU负载、RAM使用率、磁盘使用率、网速、网络连接、RX/TX带宽、登录用户、运行的进程等等。它不会存储长期的统计。因为它没有后端数据库。
|
||||
|
||||
本篇文章将会向你展示如何安装和设置Linux dash,这里的web服务器是**Nginx**.
|
||||
本篇文章将会向你展示如何安装和设置Linux dash,这里所使用的web服务器是**Nginx**.
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先我们要启用[EPEL 仓库][1]。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**接下来,我们需要用下面的命令安装nginx。**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo yum install nginx
|
||||
@ -59,7 +59,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
sudo vim /etc/php-fpm.d/www.conf
|
||||
|
||||
**确保设置了“listn”,“user”和“group”字段。你可以保留下面的配置不变。**
|
||||
**确保设置了如下的“listen”,“user”和“group”字段。你可以保留其它的配置不变。**
|
||||
|
||||
. . .
|
||||
listen = /var/run/php-fpm.sock
|
||||
@ -73,25 +73,25 @@
|
||||
sudo cp -r linux-dash/ /var/www/
|
||||
sudo chown -R nginx:nginx /var/www
|
||||
|
||||
**接下来,重启 Nginx和php-fpm**
|
||||
**接下来,重启 Nginx和php-fpm。**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo service nginx restart
|
||||
sudo service php-fpm restart
|
||||
|
||||
**设置nginx和php-fpm开机自动启动**
|
||||
**设置nginx和php-fpm开机自动启动。**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo chkconfig nginx on
|
||||
sudo chkconfig php-fpm on
|
||||
|
||||
在本例中,我们使用TCP端口8080配置linux-dash。因此确保防火墙没有阻止8080 TCP端口。
|
||||
在本例中,我们使用TCP端口8080配置linux-dash。因此需确保防火墙没有阻止8080 TCP端口。
|
||||
|
||||
### 用linux-dash监控Linux服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
你现在可以在浏览器中输入**http://<linux-IP-address>:8080/linux-dash/**来访问Linux-dash。
|
||||
你现在可以在浏览器中输入**http://\<IP地址>:8080/linux-dash/**来访问Linux-dash。
|
||||
|
||||
web面板包含了不同的组件,每个都显示独特的系统属性。你可以自定义web面板的外观也可以关闭一些组件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
美好的一天!
|
||||
|
||||
@ -104,9 +104,9 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/install-linux-dash-web-based-monitoring-system-cento
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Jijo][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.unixmen.com/author/jijo/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.unixmen.com/install-epel-repository-centos-rhel-7/
|
||||
[1]:http://linux.cn/article-2324-1.html
|
||||
@ -8,7 +8,7 @@ Linux 有问必答:如何在Linux 中修复“fatal error: x264.h: No such fil
|
||||
|
||||
[x264][1]是GNU GPL授权的H.264/MPEG-4 AVC编码库。x264库被广泛用于视频编码/转码程序比如Avidemux、[FFmpeg][2]、 [HandBrake][3]、 OpenShot、 MEncode等等。
|
||||
|
||||
要解决这个问题,你需要安装x264的开发库文件。你可以这么做。
|
||||
要解决这个问题,你需要安装x264的开发库文件。你可以如下做。
|
||||
|
||||
###在 Debian、 Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint 中安装像x264库和开发文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ RPM Fusion设置完成后,你可以使用下面的命令安装x264开发文件
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo yum --enablerepo=rpmfusion-free install x264-devel
|
||||
|
||||
注意RPM Fusion仓库在CentOS 7中还没有,因此上面的方法在CentOS 7中还不可行。万一是CentOS 7 ,你可以从源码编译并安装x264,下面会解释的。
|
||||
注意RPM Fusion仓库在CentOS 7中还没有,因此上面的方法在CentOS 7中还不可行。万一是CentOS 7 ,你可以从源码编译并安装x264,下面会解释的。
|
||||
|
||||
### 在Debian、 Ubuntu 或者 Linux Mint中源码编译x264库 ###
|
||||
|
||||
@ -81,7 +81,7 @@ x264库将会安装在/usr/local/lib。要让其他程序可以使用这个库
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/fatal-error-x264-h-no-such-file-or-directory.html
|
||||
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
如何使用btsync通过网络实现电脑间文件共享
|
||||
如何使用btsync通过网络实现计算机间的文件共享
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
如果你是使用各式设备在网上工作的这类人,我相信你肯定需要一个在不同设备间同步文件及目录的方法,至少是非常渴望有这种功能。
|
||||
如果你是那种使用各式设备在网上工作的人,我相信你肯定需要一个在不同设备间同步文件及目录的方法,至少是非常渴望有这种功能。
|
||||
|
||||
BitTorrent Sync简称btsync,是一个基于BitTorrent(著名P2P文件分享协议)的免费跨平台同步工具。与传统BitTorrent客户端不同的是btsync用于传输加密和访问授权的是不同操作系统及设备中自动生成的键。
|
||||
BitTorrent Sync简称btsync,是一个基于BitTorrent(著名P2P文件分享协议)的免费跨平台同步工具。与传统BitTorrent客户端不同的是,btsync可以在不同操作系统及设备之间加密数据传输和基于自动生成的密钥来授予访问共享文件的权限。
|
||||
|
||||
更具体点,当你想要通过btsync共享一些文件或文件夹,相应的读/写键(所谓的秘密编码)已经创建。这些键将会通过不同的途径例如HTTPS链接,电子邮件,二维码等被分享。一旦两台设备通过一个键配对成功,链接内容将会直接在其间同步。如果没有事先设置,传输将不会有文件大小和速度的限制。你可以在btsync中创建账号,以此来创建和管理通过网络分享的键和文件。
|
||||
更具体点,当你想要通过btsync共享一些文件或文件夹,相应的读/写密钥(所谓的密码)就创建好了。这些密钥可以通过HTTPS链接,电子邮件,二维码等在不同的设备间共享传递。一旦两台设备通过一个密钥配对成功,其所对应的内容将会直接在其间同步。如果没有事先设置,传输将不会有文件大小和速度的限制。你可以在btsync中创建账号,这样你可以通过 web 界面来创建和管理通过网络分享的密钥和文件。
|
||||
|
||||
BitTorrent Sync可以在许多的操作系统上运行,包括Linux,MacOS X,Windows,在 [Android][1]和[iOS][2]上也可以使用。在这里,我们将教你在Linux环境(一台家用服务器)与Windows环境(一台笔记本电脑)之间如何使用BitTorrent Sync来同步文件。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ BitTorrent Sync可以在许多的操作系统上运行,包括Linux,MacOS X
|
||||
|
||||
BitTorrent Sync可以在[项目主页][3]直接下载。由于Windows版本的BitTorrent Syn安装起来十分简单,所以我们假设笔记本上已经安装了。我们把焦点放到Linux服务器上的安装和配置。
|
||||
|
||||
在下载页面中选择你的系统架构,右键相应链接,选择复制连接地址(或者简单的依靠浏览器判断),将链接粘贴到在终端中用wget下载,如下:
|
||||
在下载页面中选择你的系统架构,右键相应链接,复制连接地址(或者类似的功能,不同浏览器可能不同),将链接粘贴到在终端中用wget下载,如下:
|
||||
|
||||
**64位Linux:**
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,11 +36,11 @@ BitTorrent Sync可以在[项目主页][3]直接下载。由于Windows版本的Bi
|
||||
|
||||
export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/bin/btsync
|
||||
|
||||
或者在在该文件夹中运行btsync的二进制文件。我们推荐使用第一种方式,虽需要少量的输入但更容易记忆。
|
||||
或者在该文件夹中运行btsync的二进制文件。我们推荐使用第一种方式,虽需要少量的输入但更容易记忆。
|
||||
|
||||
### 配置Btsync ###
|
||||
### 配置btsync ###
|
||||
|
||||
Btsync带有一个内置的网络服务器被用作其管理接口。想要使用这个接口你需要创建一个配置文件。你可以使用以下命令来创建:
|
||||
btsync带有一个内置的网络服务器,用作其管理接口。想要使用这个接口你需要创建一个配置文件。你可以使用以下命令来创建:
|
||||
|
||||
# btsync --dump-sample-config > btsync.config
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,19 +54,21 @@ Btsync带有一个内置的网络服务器被用作其管理接口。想要使
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如果你将来想要优化一下它的配置,可以看一下 /usr/local/bin/btsync 目录下的 README 文件,不过现在我们先继续下面的步骤。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一次运行btsync ###
|
||||
|
||||
作为一个系统的最高执行者我们需要依赖日志文件!所以在我们启动btsync之前,我们将先为btsync创建一个日志文件。
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /var/log/btsync.log
|
||||
|
||||
最后,让我们开启btsync:
|
||||
最后,让我们启动btsync:
|
||||
|
||||
# btsync --config /usr/local/bin/btsync/btsync.config --log /var/log/btsync.log
|
||||
|
||||
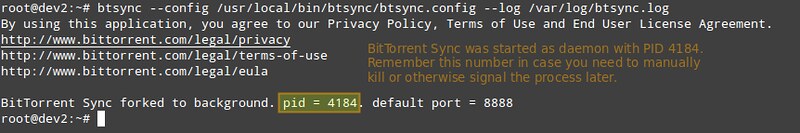
|
||||
|
||||
现在在你的浏览器中输入正在运行btsync监听的服务器IP地址和端口(我这是192.168.0.15:8888),同意隐私政策,条款和最终用户许可协议:
|
||||
现在在你的浏览器中输入正在运行的btsync所监听的服务器IP地址和端口(我这是192.168.0.15:8888),同意其隐私政策,条款和最终用户许可协议:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -80,33 +82,29 @@ Btsync带有一个内置的网络服务器被用作其管理接口。想要使
|
||||
|
||||
现在这样就够了。在运行接下来的步骤之前,请先在Windows主机(或你想使用的其他Linux设备)上安装BitTorrent Sync。
|
||||
|
||||
### Btsync分享文件 ###
|
||||
### btsync分享文件 ###
|
||||
|
||||
下方的视频将会展示如何在安装Windows8的电脑[192.168.0.106]上分享现有的文件夹。在添加好想要同步的文件夹后,你会得到它的键,通过“Enter a key or link”菜单(上面的图已经展示过了)添加到你安装到的Linux机器上,并开始同步:
|
||||
这个[视频][5](需要翻墙)展示了如何在安装Windows8的电脑[192.168.0.106]上分享现有的文件夹。在添加好想要同步的文件夹后,你会得到它的密钥,通过“Enter a key or link”菜单(上面的图已经展示过了)添加到你安装到的Linux机器上,并开始同步。
|
||||
|
||||
注释:youtube视频
|
||||
<iframe width="615" height="346" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen="" src="http://www.youtube.com/embed/f7kLM0lAqF4?feature=oembed"></iframe>
|
||||
现在用别的设备试试吧;找一个想要分享的文件夹或是一些文件,并通过Linux服务器的网络接口将密钥导入到你安装的“中央”btsync中。
|
||||
|
||||
现在用别的设备试试吧;找一个想要分享的文件夹或是一些文件,并通过Linux服务器的网络接口将键导入到你安装的“核心”btsync中。
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用常规用户开机自动运行btsync ###
|
||||
### 以常规用户开机自动运行btsync ###
|
||||
|
||||
你们可能注意到了,视频中在同步文件时是使用'root'组的用户创建/btsync目录的。那是因为我们使用超级用户手动启动BitTorrent Sync的原因。在通常情况下,你会希望它开机自动使用无权限用户(www_data或是专门为此创建的账户,例如btsync)启动。
|
||||
|
||||
所以,我们创建了一个叫做btsync的用户,并在/etc/rc.local文件(exit 0行前)添加如下字段:
|
||||
所以,我们创建了一个叫做btsync的用户,并在/etc/rc.local文件(exit 0 这一行前)添加如下字段:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo -u btsync /usr/local/bin/btsync/btsync --config /usr/local/bin/btsync/btsync.config --log /var/log/btsync.log
|
||||
|
||||
最后,创建pid文件:
|
||||
|
||||
# touch /usr/local/bin/btsync/.sync//sync.pid
|
||||
# touch /usr/local/bin/btsync/.sync/sync.pid
|
||||
|
||||
并递归更改/usr/local/bin/btsync的所属用户:
|
||||
并递归更改 /usr/local/bin/btsync的所属用户:
|
||||
|
||||
# chown -R btsync:root /usr/local/bin/btsync
|
||||
|
||||
现在重启试试,看看btsync是否正在由预期中的用户运行:
|
||||
Now reboot and verify that btsync is running as the intended user:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
@ -114,7 +112,7 @@ Now reboot and verify that btsync is running as the intended user:
|
||||
|
||||
### 尾注 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如你所见,BitTorrent Sync对你几乎就像一个无服务器的Dropbox。我说“几乎”的原因是:当你在局域网内同步数据时,同步在两个设备之间直接进行。然而如果你想要跨网段同步数据,并且你的设备可能要穿过防火墙的限制来配对,那就只能通过一个提供BitTorrent的第三方中继服务器来完成同步传输。虽然声称传输经过 [AES加密][4],你还是可能遇到不想放生的状况。为了你的隐私着想,务必在你共享的每个文件夹中关掉中继/跟踪选项。
|
||||
如你所见,BitTorrent Sync对你而言几乎就像一个无服务器的Dropbox。我说“几乎”的原因是:当你在局域网内同步数据时,同步在两个设备之间直接进行。然而如果你想要跨网段同步数据,并且你的设备可能要穿过防火墙的限制来配对,那就只能通过一个提供BitTorrent的第三方中继服务器来完成同步传输。虽然声称传输经过 [AES加密][4],你还是可能会遇到不想发生的状况。为了你的隐私着想,务必在你共享的每个文件夹中关掉中继/跟踪选项。
|
||||
|
||||
希望这些对你有用!分享愉快!
|
||||
|
||||
@ -123,8 +121,8 @@ Now reboot and verify that btsync is running as the intended user:
|
||||
via: http://xmodulo.com/share-files-between-computers-over-network.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
译者:[martin2011qi](https://github.com/martin2011qi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
@ -133,3 +131,4 @@ via: http://xmodulo.com/share-files-between-computers-over-network.html
|
||||
[2]:https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/bittorrent-sync/id665156116
|
||||
[3]:http://www.getsync.com/
|
||||
[4]:http://www.getsync.com/tech-specs
|
||||
[5]:https://youtu.be/f7kLM0lAqF4
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
如何设置Ubuntu14.04 的 SSH 无密码登录
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
大家好,今天我来向大家介绍如何在 Ubuntu12.04 上设置 SSH 的无密码登录功能。仅在工作站上有正确的(公私)密钥对以供匹配时SSH服务端才会允许你登录,反之访问将不会被允许。
|
||||
|
||||
正常情况下,我们需要连上SSH的控制台输入用户名及其密码才行。如果两者全部正确,我们就可以访问,反之访问被服务端拒绝。不过相比而言还有一种比用密码更安全的登录方式,我们可以在登录SSH时通过加密密钥进行无密码登录。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想启用这个安全的方式,我们只需简单的禁用密码登录并只允许加密密钥登录即可。使用这种方式时,客户端计算机上会产生一对私钥和公钥。接着客户端得把公钥上传到SSH服务端的authorized_key文件中去。在授予访问前,服务器及客户端电脑会校验这个密钥对。如果服务器上的公钥与客服端提交的私钥匹配则授予访问权限,否则访问被拒绝。
|
||||
|
||||
这是认证到SSH服务器的非常安全的一种做法,如果你想为单一的SSH用户登录实现安全登录,这也是备受推崇的方式。这里快速的过一遍如何启用无密码登录SSH的配置过程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.安装Openssh服务端 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们需要更新我们的本地库索引。所以如下所见,我们需要先输入“apt-get update”
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在我们可以通过以下命令安装openssh-server:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install openssh-server
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 开启openssh服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在OpenSSH已经成功安装在Ubuntu14.04操作系统上了之后,我们要启动OpenSSH的服务。以下命令让你启动/开启服务。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service ssh start
|
||||
|
||||
或
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh start
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 配置密钥对 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在我们安装并启动了OpenSSH服务以后。现在终于到了要我们搞定公私钥对的时候了,在终端中运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
|
||||
|
||||
在运行完以上命令了以后,我们需要回答一系列的问题。首先选择保存密钥的路径,按回车将会选择默认路径即家目录的一个隐藏的.ssh文件夹。下一个提示是请输入口令提醒。我个人将此留空(直接回车)。之后密钥对就会创建,大功告成。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在密钥对生成以后,我们需要将**客户端上的公钥复制到SSH服务端**或者主机,来创建对客户端的信任关系。运行以下命令复制客户端的公钥到服务端。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh-copy-id user@ip_address
|
||||
|
||||
在公钥上传之后,我们现在可以禁用通过密码登陆SSH的方式了。为此,我们需要通过以下命令用文本编辑器打开**/etc/ssh/ssh_config**。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们需要按照下图所示去掉几行注释并进行一些赋值。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 重启SSH服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,在我们配置完SSH服务端后,为了使改动生效我们需要重启SSH服务。在终端或控制台运行以下命令重启。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service ssh restart
|
||||
|
||||
或
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们可以试试不用密码仅用密钥对的方式登录ssh服务端了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
太好了!我们成功的配置了无密码登录SSH。使用加密密钥对进行SSH服务器认证是非常安全的一种做法,如果你想为SSH的单一用户登录实施安全的认证这也是备受推崇的方式。所以,如果你还有什么问题或建议,请在意见框中向我们反馈。很欣慰你能读完,希望你能喜欢加密的SSH安全登录 :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/setup-passwordless-ssh-logon-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[martin2011qi](https://github.com/martin2011qi)
|
||||
校对:[wxy](https://github.com/wxy)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
The VirtualBox 5.0 beta is finally here
|
||||
=======================================
|
||||
**Oracle's desktop virtualization software gets its first major point revision in almost five years, but the changes are more evolutionary than revolutionary.**
|
||||
|
||||
VirtualBox, the open source virtualization system originally created by Sun and now under Oracle's stewardship, has released its first revision to the left of the decimal point in nearly five years.
|
||||
|
||||
Don't expect anything truly revolutionary, though, judging from the release notes for and the behavior of the beta itself. With this release, VirtualBox picks up a bit more polish, both visually and technologically, but its main advantage over VMware remains with its offer of a free incarnation of many of the same core features.
|
||||
|
||||
The last major version of VirtualBox 4.0 was released in December 2010, and it delivered a heavily reworked version of the program with a new GUI, new virtual hardware, and a reorganized project design. But the pace of major releases for the project was slow, with the last major release (version 4.3) arriving in late 2013. Everything since then has been officially designated as a "maintenance" release.
|
||||
|
||||
**VirtualBox 5.0**
|
||||
|
||||
*The first beta of VirtualBox 5.0 adds features like the ability to edit the menus and shortcut icons for VM windows, as shown here.*
|
||||
|
||||
Among the biggest changes for VirtualBox 5.0 is support for more instruction set extensions that run with hardware-assisted virtualization. The AES-NI instruction set, typically used for hardware acceleration of encryption, and the SSE 4.1 and SSE 4.2 instructions sets were included among them. Also new is paravirtualization support for Windows and Linux guests, a new architecture for abstracting host audio, and support for USB 3 (xHCI) controller in guests.
|
||||
|
||||
Most of the usability updates are improvements to the VirtualBox GUI. One big change is the ability to customize the menus and the toolbar for individual virtual machines so that little- or never-used options can be removed entirely. Another major addition is the ability to encrypt virtual volumes from within the VirtualBox interface, rather than relying on the guest OS's own disk-encryption system (assuming it has one).
|
||||
|
||||
Oracle warns that this is beta software and should be treated accordingly. Sure enough, the main GUI and the guest OS windows all sport black-and-red Beta warnings in one corner. But a Windows 10 VM created with the previous VirtualBox release (4.3.26) booted and ran fine, and the 5.0 version of the VirtualBox Guest Additions -- for better video support, bidirectional copy and paste, and other features -- installed without issues. (Fixes to better support Windows 10 have been showing up since version 4.3.18.)
|
||||
|
||||
No word has been given yet on when the final version of 5.0 will be out, but Oracle [encourages users][1] to download and try out the beta -- in a nonproduction environment -- and file bug reports with their [beta feedback forum][2].
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.infoworld.com/article/2905098/virtualization/oracle-virtualbox-5-0-beta-is-finally-here.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Serdar Yegulalp][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.infoworld.com/author/Serdar-Yegulalp/
|
||||
[1]:https://forums.virtualbox.org/viewtopic.php?f=15&t=66904
|
||||
[2]:https://forums.virtualbox.org/viewforum.php?f=15
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,5 @@
|
||||
Translating by FSSlc
|
||||
|
||||
Chess in a Few Bytes
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
I am showing my age by mentioning that my introduction to computing was a ZX81, a home computer produced by a UK developer (Sinclair Research) which had a whopping 1KB of RAM. The 1KB is not a typographical error, the home computer really shipped with a mere 1KB of onboard memory. But this memory limitation did not prevent enthusiasts producing a huge variety of software. In fact the machine sparked a generation of programming wizards who were forced to get to grips with its workings. The machine was upgradable with a 16KB RAM pack which offered so many more coding possibilities. But the unexpanded 1KB machine still inspired programmers to release remarkable software.
|
||||
@ -111,4 +113,4 @@ via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/20150222033906262/ChessBytes.html
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://nanochess.org/chess6.html
|
||||
[2]:http://www.pouet.net/prod.php?which=64962
|
||||
[3]:http://home.hccnet.nl/h.g.muller/max-src2.html
|
||||
[3]:http://home.hccnet.nl/h.g.muller/max-src2.html
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,87 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Install Cherokee Lightweight Web Server on Ubuntu 14.04
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
**Cherokee** is an free and open source high performance, lightweight, full-featured web server and running on major platform (Linux, Mac OS X, Solaris, and BSD). It is compatible with TLS/SSL,FastCGI, SCGI, PHP, uWSGI, SSI, CGI, LDAP, HTTP proxying, video streaming, content caching, traffic shaping, virtual hosts, Apache compatible log files, and load balancing.
|
||||
|
||||
Today we'll explains how to install and configure the Light Weight Cherokeeweb server on Ubuntu Server edition 14.04 LTS (Trusty) and should also work with 12.04, 12.10 and 13. 04, just skip the modification of source list.
|
||||
|
||||
Step by step install and configure the Cherokee web server on Ubuntu Server edition
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Updating Ubuntu Package Index ###
|
||||
|
||||
First, Login into Ubuntu Server and make sure your ubuntu server update, run the following commands one by one, and install any available updates:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get upgrade
|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Adding PPA ###
|
||||
|
||||
Add the PPA cherokee webserver. by running the following commands
|
||||
|
||||
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:cherokee-webserver
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
Now, only for servers running Ubuntu 14.04 LTS (Trusty) follow this step below
|
||||
|
||||
cd /etc/apt/sources.list.d
|
||||
|
||||
nano cherokee-webserver-ppa-trusty.list
|
||||
|
||||
replace:
|
||||
|
||||
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/cherokee-webserver/ppa/ubuntu trusty main
|
||||
|
||||
to:
|
||||
|
||||
deb http://ppa.launchpad.net/cherokee-webserver/ppa/ubuntu saucy main
|
||||
|
||||
**then again run:**
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Installing Cherokee Web Server using apt-get ###
|
||||
|
||||
Enter the following command to install the Cherokee web server including Module SSL
|
||||
|
||||
sudo apt-get install cherokee cherokee-admin cherokee-doc libcherokee-mod-libssl libcherokee-mod-streaming libcherokee-mod-rrd
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Configuring Cherokee ###
|
||||
|
||||
sudo service cherokee start
|
||||
|
||||
The best part about using its Web Server is being able to manage all of its configurations through a simple to use web interface. This interface, known as cherokee-admin, is the recommended means of administering cherokee web server through web browser. Start cherokee-admin by running the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cherokee-admin
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: The cherokee-admin will display the administration user name, One-time Password and administration web interface.**
|
||||
|
||||
**Note down your One-Time password. You will need this when you login to its admin web interface.**
|
||||
|
||||
By default, cherokee-admin can only accessed from localhost. If you need to access the admin for other network address using the parameter ‘**-b**’. If you doesn’t mention any ip address, it will automatically listen to all network interfaces. Then you can connect to cherokee-admin from other network address.
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cherokee-admin -b
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to access its admin from specific network address
|
||||
|
||||
sudo cherokee-admin -b 192.168.1.102
|
||||
|
||||
### 5. Browse your Cherokee Admin Panel ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can access the administration panel from you favorite browser by typing http://hostname_or_IP:9090/ for me its http://127.0.0.1:9090/, it will appear on your browser like this:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Hurray, we have successfully installed and configured Cherokee Web Server in our Ubuntu Server.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/install-cherokee-lightweight-web-server-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -1,79 +0,0 @@
|
||||
How to Bind Apache Tomcat to IPv4 in Centos / Redhat
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Hi all, today we'll learn how to bind tomcat to ipv4 in CentOS 7 Linux Distribution.
|
||||
|
||||
**Apache Tomcat** is an open source web server and servlet container developed by the [Apache Software Foundation][1]. It implements the Java Servlet, JavaServer Pages (JSP), Java Unified Expression Language and Java WebSocket specifications from Sun Microsystems and provides a web server environment for Java code to run in.
|
||||
|
||||
Binding Tomcat to IPv4 is necessary if we have our server not working due to the default binding of our tomcat server to IPv6. As we know IPv6 is the modern way of assigning IP address to a device and is not in complete practice these days but may come into practice in soon future. So, currently we don't need to switch our tomcat server to IPv6 due to no use and we should bind it to IPv4.
|
||||
|
||||
Before thinking to bind to IPv4, we should make sure that we've got tomcat installed in our CentOS 7. Here's is a quick tutorial on [how to install tomcat 8 in CentOS 7.0 Server][2].
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. Switching to user tomcat ###
|
||||
|
||||
First of all, we'll gonna switch user to **tomcat** user. We can do that by running **su - tomcat** in a shell or terminal.
|
||||
|
||||
# su - tomcat
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. Finding Catalina.sh ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll First Go to bin directory inside the directory of Apache Tomcat installation which is usually under **/usr/share/apache-tomcat-8.0.x/bin/** where x is sub version of the Apache Tomcat Release. In my case, its **/usr/share/apache-tomcat-8.0.18/bin/** as I have version 8.0.18 installed in my CentOS 7 Server.
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /usr/share/apache-tomcat-8.0.18/bin
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: Please replace 8.0.18 to the version of Apache Tomcat installed in your system. **
|
||||
|
||||
Inside the bin folder, there is a script file named catalina.sh . Thats the script file which we'll gonna edit and add a line of configuration which will bind tomcat to IPv4 . You can see that file by running **ls** into a terminal or shell.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. Configuring Catalina.sh ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll add **JAVA_OPTS= "$JAVA_OPTS -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true -Djava.net.preferIPv4Addresses"** to that scripting file catalina.sh at the end of the file as shown in the figure below. We can edit the file using our favorite text editing software like nano, vim, etc. Here, we'll gonna use nano.
|
||||
|
||||
$ nano catalina.sh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Then, add to the file as shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
**JAVA_OPTS= "$JAVA_OPTS -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true -Djava.net.preferIPv4Addresses"**
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Now, as we've added the configuration to the file, we'll now save and exit nano.
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. Restarting ###
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we'll restart our tomcat server to get our configuration working. We'll need to first execute shutdown.sh and then startup.sh .
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./shutdown.sh
|
||||
|
||||
Now, well run execute startup.sh as:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./startup.sh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
This will restart our tomcat server and the configuration will be loaded which will ultimately bind the server to IPv4.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
Hurray, finally we'have got our tomcat server bind to IPv4 running in our CentOS 7 Linux Distribution. Binding to IPv4 is easy and is necessary if your Tomcat server is bind to IPv6 which will infact will make your tomcat server not working as IPv6 is not used these days and may come into practice in coming future. If you have any questions, comments, feedback please do write on the comment box below and let us know what stuffs needs to be added or improved. Thank You! Enjoy :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/bind-apache-tomcat-ipv4-centos/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.apache.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-tomcat-8-centos-7/
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
[boredivan翻译中]
|
||||
How To Scan And Check A WordPress Website Security Using WPScan, Nmap, And Nikto
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
### Introduction ###
|
||||
@ -421,4 +422,4 @@ via: http://www.unixmen.com/scan-check-wordpress-website-security-using-wpscan-n
|
||||
[4]:http://www.unixmen.com/install-nikto-web-scanner-check-vulnerabilities
|
||||
[5]:https://cirt.net/nikto/
|
||||
[6]:http://osvdb.org/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.unixmen.com/secure-wordpress-website/
|
||||
[7]:http://www.unixmen.com/secure-wordpress-website/
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,298 +0,0 @@
|
||||
theo-l translating
|
||||
|
||||
How to Limit the Network Bandwidth Used by Applications in a Linux System with Trickle
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Have you ever encountered situations where one application dominated you all network bandwidth? If you have ever been in a situation where one application ate all your traffic, then you will value the role of the trickle bandwidth shaper application. Either you are a system admin or just a Linux user, you need to learn how to control the upload and download speeds for applications to make sure that your network bandwidth is not burned by a single application.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Trickle Bandwidth Limit in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
### What is Trickle? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Trickle is a network bandwidth shaper tool that allows us to manage the upload and download speeds of applications in order to prevent any single one of them to hog all (or most) of the available bandwidth. In few words, trickle lets you control the network traffic rate on a per-application basis, as opposed to per-user control, which is the classic example of bandwidth shaping in a client-server environment, and is probably the setup we are more familiar with.
|
||||
|
||||
### How Trickle Works? ###
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, trickle can help us to define priorities on a per-application basis, so that when overall limits have been set for the entire system, priority apps will still get more bandwidth automatically. To accomplish this task, trickle sets traffic limits to the way in which data is sent to, and received from, sockets using TCP connections. We must note that, other than the data transfer rates, trickle does not modify in any way the behavior of the process it is shaping at any given moment.
|
||||
|
||||
### What Can’t Trickle do? ###
|
||||
|
||||
The only limitation, so to speak, is that trickle will not work with statically linked applications or binaries with the SUID or SGID bits set since it uses dynamic linking and loading to place itself between the shaped process and its associated network socket. Trickle then acts as a proxy between these two software components.
|
||||
|
||||
Since trickle does not require superuser privileges in order to run, users can set their own traffic limits. Since this may not be desirable, we will explore how to set overall limits that system users cannot exceed. In other words, users will still be able to manage their traffic rates, but always within the boundaries set by the system administrator.
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we will explain how to limit the network bandwidth used by applications in a Linux server with trickle. To generate the necessary traffic, we will use ncftpput and ncftpget (both tools are available by installing ncftp) on the client (CentOS 7 server – dev1: 192.168.0.17), and vsftpd on the server (Debian Wheezy 7.5 – dev2: 192.168.0.15) for demonstration purposes. The same instructions also works on RedHat, Fedora and Ubuntu based systems.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Prerequisites ####
|
||||
|
||||
1. For RHEL/CentOS 7/6, [enable the EPEL repository][1]. Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux (EPEL) is a repository of high-quality free and open-source software maintained by the Fedora project and is 100% compatible with its spinoffs, such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux and CentOS. Both trickle and ncftp are made available from this repository.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Install ncftp as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && sudo yum install ncftp [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
# aptitude update && aptitude install ncftp [On Debian based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
3. Set up a FTP server in a separate server. Please note that although FTP is inherently insecure, it is still widely used in cases when security in uploading or downloading files is not needed. We are using it in this article to illustrate the bounties of trickle and because it shows the transfer rates in stdout on the client, and we will leave the discussion of whether it should or should not be used for another date and time :).
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install vsftpd [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
# aptitude update && aptitude install vsftpd [On Debian based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
Now, edit the /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf file on the FTP server as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
anonymous_enable=NO
|
||||
local_enable=YES
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES
|
||||
allow_writeable_chroot=YES
|
||||
|
||||
After that, make sure to start vsftpd for your current session and to enable it for automatic start on future boots:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start vsftpd [For systemd-based systems]
|
||||
# systemctl enable vsftpd
|
||||
# service vsftpd start [For init-based systems]
|
||||
# chkconfig vsftpd on
|
||||
|
||||
4. If you chose to set up the FTP server in a CentOS/RHEL 7 droplet with SSH keys for remote access, you will need a password-protected user account with the appropriate directory and file permissions for uploading and downloading the desired content OUTSIDE root’s home directory.
|
||||
|
||||
You can then browse to your home directory by entering the following URL in your browser. A login window will pop up prompting you for a valid user account and password on the FTP server.
|
||||
|
||||
ftp://192.168.0.15
|
||||
|
||||
If the authentication succeeds, you will see the contents of your home directory. Later in this tutorial you will be able to refresh that page to display the files that have been uploaded during previous steps.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
FTP Directory Tree
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Install Trickle in Linux ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install trickle via yum or aptitude.
|
||||
|
||||
To ensure a successful installation, it is considered good practice to make sure the currently installed packages are up-to-date (using yum update) before installing the tool itself.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum -y update && yum install trickle [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
# aptitude -y update && aptitude install trickle [On Debian based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
2. Verify whether trickle will work with the desired binary.
|
||||
|
||||
As we explained earlier, trickle will only work with binaries using dynamic, or shared, libraries. To verify whether we can use this tool with a certain application, we can use the well-known ldd utility, where ldd stands for list dynamic dependencies. Specifically, we will look for the presence of glibc (the GNU C library) in the list of dynamic dependencies of any given program because it is precisely that library which defines the system calls involved in communication through sockets.
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command against a given binary to see if trickle can be used to shape its bandwidth:
|
||||
|
||||
# ldd $(which [binary]) | grep libc.so
|
||||
|
||||
For example,
|
||||
|
||||
# ldd $(which ncftp) | grep libc.so
|
||||
|
||||
whose output is:
|
||||
|
||||
# libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007efff2e6c000)
|
||||
|
||||
The string between brackets in the output may change from system to system and even between subsequent runs of the same command, since it represents the load address of the library in physical memory.
|
||||
|
||||
If the above command does not return any results, it means that the binary it was run against does not use libc and thus trickle cannot be used as bandwidth shaper in that case.
|
||||
|
||||
### Learn How to Use Trickle ###
|
||||
|
||||
The most basic usage of trickle is in standalone mode. Using this approach, trickle is used to explicitly define the download and upload speeds of a given application. As we explained earlier, for the sake of brevity, we will use the same application for download and upload tests.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Running Trickle in Standalone Mode ####
|
||||
|
||||
We will compare the download and upload speeds with and without using trickle. The -d option indicates the download speed in KB/s, while the -u flag tells trickle to limit the upload speed by the same unit. In addition, we will use the -s flag, which specifies that trickle should run in standalone mode.
|
||||
|
||||
The basic syntax to run trickle in standalone mode is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -s -d [download rate in KB/s] -u [upload rate in KB/s]
|
||||
|
||||
In order to perform the following examples on your own, make sure to have trickle and ncftp installed on the client machine (192.168.0.17 in my case).
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 1: Uploading a 2.8 MB PDF file with and without trickle.**
|
||||
|
||||
We are using the freely-distributable Linux Fundamentals PDF file (available from [here][2]) for the following tests.
|
||||
|
||||
You can initially download this file to your current working directory with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://linux-training.be/files/books/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
The syntax to upload a file to our FTP server without trickle is as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /remote_directory local-filename
|
||||
|
||||
Where /remote_directory is the path of the upload directory relative to username’s home, and local-filename is a file in your current working directory.
|
||||
|
||||
Specifically, without trickle we get a peak upload speed of 52.02 MB/s (please note that this is not the real average upload speed, but an instant starting peak), and the file gets uploaded almost instantly:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 52.02 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
With trickle, we will limit the upload transfer rate at 5 KB/s. Before uploading the file for the second time, we need to delete it from the destination directory; otherwise, ncftp will inform us that the file at the destination directory is the same that we are trying to upload, and will not perform the transfer:
|
||||
|
||||
# rm /absolute/path/to/destination/directory/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
Then:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -s -u 5 ncftpput -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 /testdir LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 4.94 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
In the example above, we can see that the average upload speed dropped to ~5 KB/s.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 2: Downloading the same 2.8 MB PDF file with and without trickle**
|
||||
|
||||
First, remember to delete the PDF from the original source directory:
|
||||
|
||||
# rm /absolute/path/to/source/directory/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that the following cases will download the remote file to the current directory in the client machine. This fact is indicated by the period (‘.‘) that appears after the IP address of the FTP server.
|
||||
|
||||
Without trickle:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 260.53 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
With trickle, limiting the download speed at 20 KB/s:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -s -d 30 ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 17.76 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
### Running Trickle in Supervised [unmanaged] Mode ###
|
||||
|
||||
Trickle can also run in unmanaged mode, following a series of parameters defined in /etc/trickled.conf. This file defines how trickled (the daemon) behaves and manages trickle.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition, if we want to set global settings to be used, overall, by all applications, we will need to use the trickled command. This command runs the daemon and allows us to define download and upload limits that will be shared by all the applications run through trickle without us needing to specify limits each time.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, running:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickled -d 50 -u 10
|
||||
|
||||
Will cause that the download and upload speeds of any application run through trickle be limited to 30 KB/s and 10 KB/s, respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
Please note that you can check at any time whether trickled is running and with what arguments:
|
||||
|
||||
# ps -ef | grep trickled | grep -v grep
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
root 16475 1 0 Dec24 ? 00:00:04 trickled -d 50 -u 10
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 3: Uploading a 19 MB mp4 file to our FTP server using with and without trickle.**
|
||||
|
||||
In this example we will use the freely-distributable “He is the gift” video, available for download from [this link][3].
|
||||
|
||||
We will initially download this file to your current working directory with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://media2.ldscdn.org/assets/missionary/our-people-2014/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
First off, we will start the trickled daemon with the command listed above:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickled -d 30 -u 10
|
||||
|
||||
Without trickle:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 36.31 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
With trickle:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 9.51 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
As we can see in the output above, the upload transfer rate dropped to ~10 KB/s.
|
||||
|
||||
**Example 4: Downloading the same video with and without trickle**
|
||||
|
||||
As in Example 2, we will be downloading the file to the current working directory.
|
||||
|
||||
Without trickle:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpget -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 . /testdir/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 108.34 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
With trickle:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 29.28 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
Which is in accordance with the download limit set earlier (30 KB/s).
|
||||
|
||||
**Note:** That once the daemon has been started, there is no need to set individual limits for each application that uses trickle.
|
||||
|
||||
As we mentioned earlier, one can further customize trickle’s bandwidth shaping through trickled.conf. A typical section in this file consists of the following:
|
||||
|
||||
[service]
|
||||
Priority = <value>
|
||||
Time-Smoothing = <value>
|
||||
Length-Smoothing = <value>
|
||||
|
||||
Where,
|
||||
|
||||
- [service] indicates the name of the application whose bandwidth usage we intend to shape.
|
||||
- Priority allows us to specify a service to have a higher priority relative to another, thus not allowing a single application to hog all the bandwidth which the daemon is managing. The lower the number, the more bandwidth that is assigned to [service].
|
||||
- Time-Smoothing [in seconds]: defines with what time intervals trickled will try to let the application transfer and / or receive data. Smaller values (something between the range of 0.1 – 1s) are ideal for interactive applications and will result in a more continuous (smooth) session while slightly larger values (1 – 10 s) are better for applications that need bulk transfer. If no value is specified, the default (5 s) is used.
|
||||
- Length-Smoothing [in KB]: the idea is the same as in Time-Smoothing, but based on the length of an I/O operation. If no value is specified, the default (10 KB) is used.
|
||||
|
||||
Changing the smoothing values will translate into the application specified by [service] using transfer rates within an interval instead of a fixed value. Unfortunately, there is no formula to calculate the lower and upper limits of this interval as it mainly depends of each specific case scenario.
|
||||
|
||||
The following is a trickled.conf sample file in the CentOS 7 client (192.168.0.17):
|
||||
|
||||
[ssh]
|
||||
Priority = 1
|
||||
Time-Smoothing = 0.1
|
||||
Length-Smoothing = 2
|
||||
|
||||
[ftp]
|
||||
Priority = 2
|
||||
Time-Smoothing = 1
|
||||
Length-Smoothing = 3
|
||||
|
||||
Using this setup, trickled will prioritize SSH connections over FTP transfers. Note that an interactive process, such as SSH, uses smaller time-smoothing values, whereas a service that performs bulk data transfers (FTP) uses a greater value. The smoothing values are responsible for the download and upload speeds in our previous example not matching the exact value specified by the trickled daemon but moving in an interval close to it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Conclusion ###
|
||||
|
||||
In this article we have explored how to limit the bandwidth used by applications using trickle on Fedora-based distributions and Debian / derivatives. Other possible use cases include, but are not limited to:
|
||||
|
||||
- Limiting the download speed via a system utility such as [wget][4], or a torrent client, for example.
|
||||
- Limiting the speed at which your system can be updated via `[yum][5]` (or `[aptitude][6]`, if you’re in a Debian-based system), the package management system.
|
||||
- If your server happens to be behind a proxy or firewall (or is the proxy or firewall itself), you can use trickle to set limits on both the download and upload, or communication speed with the clients or the outside.
|
||||
|
||||
Questions and comments are most welcome. Feel free to use the form below to send them our way.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-and-limit-downloadupload-bandwidth-with-trickle-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
[2]:http://linux-training.be/files/books/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
[3]:http://media2.ldscdn.org/assets/missionary/our-people-2014/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/dpkg-command-examples/
|
||||
@ -1,121 +0,0 @@
|
||||
Linux FAQs with Answers--How to install and access CentOS remote desktop on VPS
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **Question**: I want to install CentOS desktop on VPS, and be able to access the desktop GUI remotely from home. What is a recommended way to set up and access CentOS-based remote desktop on VPS?
|
||||
|
||||
Nowadays teleworking or remote working with flexible hours is increasingly popular in tech industry. One of the enabling technologies behind this trend is remote desktop. Your desktop environment is in the cloud, and you can access the remote desktop anywhere you go, either from home or at your workplace.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial describes how you can set up CentOS based remote desktop on VPS. Here we are going to demonstrate CentOS 7 based environment.
|
||||
|
||||
We assume that you already created a CentOS 7 VPS instance somewhere (e.g., using [DigitalOcean][1] or Amazon EC2). Make sure that the VPS instance has at least 1GB memory. Otherwise, CentOS desktop will crash when you try to access remote desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step One: Install CentOS Desktop ###
|
||||
|
||||
If an available CentOS image is a minimal version of CentOS without desktop, you will need to install desktop (e.g., GNOME) on your CentOS VPS before proceeding. For example, DigitalOcean's CentOS image is such a minimal version, which requires [desktop GUI installation][2] as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum groupinstall "GNOME Desktop"
|
||||
|
||||
Reboot a VPS after finishing installation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Two: Install and Configure VNC Server ###
|
||||
|
||||
The next step is to install and configure VNC server. We are going to use TigerVNC, an open-source VNC server implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install tigervnc-server
|
||||
|
||||
Now create a user account (e.g., xmodulo) which will be used to access remote desktop.
|
||||
|
||||
# useradd xmodulo
|
||||
# passwd xmodulo
|
||||
|
||||
When a user tries to access remote desktop using VNC, a dedicated VNC server daemon will be launched to handle its requests. This means that you will need to create a separate VNC server configuration for each user.
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS 7 relies on systemd to manage and configure system services. So we are going to configure VNC server for xmodulo user using systemd.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's first check the status of VNC server by running either command below:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl status vncserver@:.service
|
||||
# systemctl is-enabled vncserver@.service
|
||||
|
||||
By default, freshly installed VNC service is not active (disabled).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Now create a VNC service configuration for xmodulo user by copying a generic VNC service unit file as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
# cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service
|
||||
|
||||
Open the configuration file with a text editor, and replace <USER> with an actual user name (e.g., xmodulo) under [Service] section. Also, append "-geometry <resolution>" parameter in ExecStart. In the end, the following two lines with bold font will be modified.
|
||||
|
||||
# vi /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[Service]
|
||||
Type=forking
|
||||
# Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment
|
||||
ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
|
||||
ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l xmodulo -c "/usr/bin/vncserver %i -geometry 1024x768"
|
||||
PIDFile=/home/xmodulo/.vnc/%H%i.pid
|
||||
ExecStop=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
|
||||
|
||||
Now set up (optional) VNC password for xmodulo user for security. For this, switch to the user, and run vncserver command.
|
||||
|
||||
# su - xmodulo
|
||||
# vncserver
|
||||
|
||||
You will be prompted to enter a VNC password for the user. Once the password is set, you will need to use this password to gain access to remote desktop.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Finally, reload services to activate the new VNC configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl daemon-reload
|
||||
|
||||
and enable VNC service to make it start automatically upon boot:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable vncserver@:1.service
|
||||
|
||||
Check the port number that a VNC server is listening on by running:
|
||||
|
||||
# netstat -tulpn | grep vnc
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Port 5901 is the default port number for VNC client to connect to a VNC server.
|
||||
|
||||
### Step Three: Connect to Remote Desktop over SSH ###
|
||||
|
||||
By design, Remote Frame Buffer (RFB) protocol used by VNC is not a secure protocol. Thus it is not a good idea to directly connect to a remote VNC server running on VPS using a VNC client. Any sensitive information such as password could easily be leaked from VNC traffic. So instead, I strongly recommend that you [tunnel VNC traffic][3] over a secure SSH tunnel, as described here.
|
||||
|
||||
On a local host where you want to run VNC client, create an SSH tunnel to a remote VPS using the following command. When prompted for SSH password, type the password of the user.
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh xmodulo@<VPS-IP-address> -L 5901:127.0.0.1:5901
|
||||
|
||||
Replace "xmodulo" with your own VNC user, and fill in the IP address of your VPS instance.
|
||||
|
||||
Once an SSH tunnel is established, remote VNC traffic will be routed over the SSH tunnel, and be sent to 127.0.0.1:5901.
|
||||
|
||||
Now go ahead and launch your favorite VNC client (e.g., vinagre), and connect to 127.0.0.1:5901.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You will be asked to enter a VNC password. When you type a correct VNC password, you will finally be able to CentOS remote desktop on VPS securely.
|
||||
|
||||
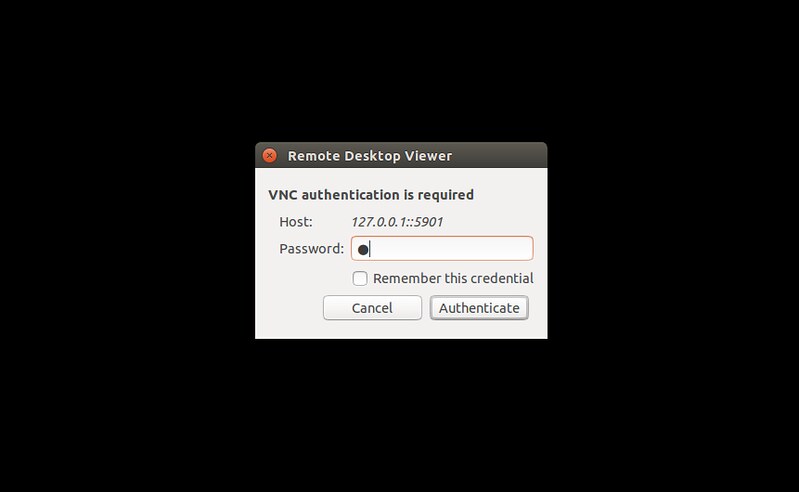
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/centos-remote-desktop-vps.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/go/digitalocean
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-gnome-desktop-on-centos.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-vnc-over-ssh.html
|
||||
@ -1,400 +0,0 @@
|
||||
寻求激烈的游戏玩法?那就试试这 13 款 Roguelike 游戏吧
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
Roguelike 是角色扮演游戏的一个子类。从字面上看,它的意思是 “像 Rogue 的游戏”。Rogue 是一个关于地下城冒险的视频游戏,于 1980 年第一次发行,以友好、易上瘾而著称。这个游戏的目标是取得深藏于第 26 层的 "Amulet of Yendor",再返回到顶层逃出生天。
|
||||
|
||||
Roguelike 的准确定义并不存在,但这类游戏通常具有下面的特点:
|
||||
|
||||
- 奇幻的叙事背景;
|
||||
- 程序性的关卡产生。每个新的游戏环节中的游戏世界均由游戏产生。这样做是为了鼓励玩家重玩;
|
||||
- 回合制的地下城探险和战斗;
|
||||
- 随机生成的基于瓷砖的(Tile-based)图形环境;
|
||||
- 随机的冲突生成;
|
||||
- 永久死亡 。在游戏中,死亡真的存在,一旦你死了,就代表你真的结束了。
|
||||
- 高难度。
|
||||
|
||||
这篇文章精心挑选了一些可运行在 Linux 平台下的 roguelike 游戏。假如你喜欢激烈、易上瘾的游戏,可以尝试这 13 款游戏。不要因它们原始的画质而退步,一旦你沉浸其中,你将很快忘记画面的简陋。所有的这些都可以免费下载,并且几乎所有的游戏都是在开源协议下发行的。
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Dungeon Crawl Stone Soup 是一个开源的,单用户角色扮演类的 roguelike 游戏,玩家要在充满危险和不友好的怪兽的地下城中进行探险和寻找宝藏,并在任务中拯救 mystifyingly fabulous Orb of Zot(注:这里我不知如何翻译)
|
||||
|
||||
Dungeon Crawl Stone Soup 是 Linley 开发的 Dungeon Crawl 游戏的延续。它被公开地开发并邀请 Crawl 社区的人员来参与其中。
|
||||
|
||||
Dungeon Crawl 有着超棒且深层次的战术游戏环节,创新的魔法和信仰系统,以及数量宏大的可供战斗的怪兽。Crawl 也是最难以攻陷的 roguelike 游戏之一。当你最终在游戏中通关并将你的胜利宣言张贴在 rec.games.roguelike.misc ,这时在你心中,你知道你已经取得了什么。
|
||||
|
||||
特点有:
|
||||
|
||||
- 丰富多彩的, 富含深层次战术的 roguelike 游戏;
|
||||
- 手绘地图;
|
||||
- 无数的金库;
|
||||
- 漂亮的界面;
|
||||
- 创新的魔法和信仰系统;
|
||||
- 广泛的神灵,角色,物品和聪明的怪兽;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [crawl.develz.org][1]
|
||||
- 开发者: Stone Soup 开发小组
|
||||
- 协议: Crawl General Public License
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.15.2
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Dwarf Fortress 是一个绝妙的单人游戏,与 NetHack 类似。你可以在一个随机生成的持久的世界中,控制一个矮人哨兵或一个冒险者。
|
||||
|
||||
这个游戏的特色有:三种游戏模式(矮人要塞,冒险者,传说模式),一个独特的随机生成的世界(由地形,野生生物和传说等组成), 阴森的战斗机制以及各种恶性的鲤鱼。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 在这个世界里,你想持续多久都可以。可以经历许多次游戏,记录历史事件,对更改进行跟踪等;
|
||||
- 当你的矮人在山群中寻找宝藏时,你可以对它们下达命令
|
||||
- 用各种材料来手工制作珍宝、家具,并可以用贵重金属,宝石等来改进这些珍宝、家具;
|
||||
- 在广度和深度上保护你自己,防御来自敌对文明的袭击;
|
||||
- 当他们有求于你的民众时,支持贵族(注:感觉自己翻译错了这句)
|
||||
- 维持你的矮人的高兴状态,在它们工作和休闲时读取它们的思想;
|
||||
- Z 坐标可以使你在多个层级上建造你的堡垒,建立塔台或征服深处;
|
||||
- 建立水闸来为耕种调水或水淹你的对手;
|
||||
- 扮演一个探险者并进行探索,为荣誉而战或复仇
|
||||
- 与以前的游戏中的对手相遇;
|
||||
- 在你经过的旅途中营救小城里的人群
|
||||
- 在没有笨重的绘画限制下探险;
|
||||
- 无缝的漫游游戏世界-总共达到 197376 x 197376 平方 -或者在区域地图上更快速地穿行;
|
||||
- 接受小城或文明社会的领导委托的任务
|
||||
- 收回并与你扮演的老角色相遇,在一次探险中,以一个新的角色带上它们或者直接使用它们;
|
||||
- Z 轴使得你可以在各个地牢层级间无缝地上下移动以及调整结构的尺寸来和对手战斗;
|
||||
- 战斗模型的使用技巧,身体组成,搏斗,在方块之间进行操作和躲避,流血,疼痛,恶心及其他;
|
||||
- 一个动态的天气模型用来跟踪风,湿度及空气的动向,用来创造前线,风,暴风雨和暴风雪
|
||||
- 超过 200 种岩石和矿物类型被引入游戏世界,它们被放置在合适的地理环境中;
|
||||
- 通过可更改的文本文件来添加生物,武器,植物,金属和其他对象;
|
||||
- 扩展的以 16 色(包括黑色)渲染的 ASCII 角色集合,以及 8 种背景颜色(包括黑色);
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.bay12games.com/dwarves/][2]
|
||||
- 开发者: Tarn Adams
|
||||
- 协议: 免费软件
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.40.19
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ancient Domains of Mystery (ADOM) 是一个 rogue-like 游戏,自从 1994 年开始,它一直在开发。
|
||||
|
||||
它是一个包含复杂地牢的单用户游戏。你控制一个用种族,类别,属性,技巧和装备等描述的虚构角色。这个虚构角色正尝试着达到一个特定的目标(参考下面的介绍)并在一个困难的任务中取胜。为了完成任务,你必须在以前没有发现的隧道和地牢中探险,和丑陋的怪兽战斗,解开一系列遗忘的秘密,并找到宝藏。
|
||||
|
||||
在游戏期间,你在每次游戏时随机生成的各层地牢中探索。你也可能遇到某个特定的关卡,其中有着特定的挑战或者围绕某个特定主题而生成。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 拥有上百个地点的巨大游戏世界,例如城堡,随机生成的地牢,主题寺庙,墓地,古代遗迹,塔台和其他名胜;
|
||||
- 各种各样的种族(dwarves, drakelings, mist elves, hurthlings, orcs, trolls, ratlings and many others)(注:种族信息可以参考[这里](http://ancardia.wikia.com/wiki/Race) 和更多的类别 (fighters, elementalists, assassins, chaos knights, duelists and much more),允许无限的游戏风格;
|
||||
- 上百个怪兽和物品,其中的许多拥有增强的随机特性;
|
||||
- 一个堕落系统,迫使你在对力量的欲望和对诅咒的恐惧之间进行权衡;
|
||||
- 法术,祈祷,思想技艺,炼金术,手工艺和更多;
|
||||
- 多样的任务和分支故事主线;
|
||||
- 许多完全不同的结局,可能改变现实本身
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.adom.de][3]
|
||||
- 开发者: Thomas Biskup
|
||||
- 协议: Postcardware
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.20 Prelease 20
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Tales of Maj’Eyal (ToME) (注:中文翻译为 马基埃亚尔的传说) 是一个免费,开源的 roguelike 角色扮演游戏,包含特色的战术回合制战役和先进的建筑。它作为运行在 T-Engine 4.0 中的一个模块而被创造。
|
||||
|
||||
现在处于王权世纪(Age of Ascendancy),在长达一万年的冲突痛苦和混乱之后,我们所知的世界终于进入了一个相对和平的时期。 “魔法大爆裂(Spellblaze)” 留下的影响已经大为减缓, 大地的伤痕也慢慢地开始愈合。在薪火世纪(Age of Pyre)之后,各个文明也纷纷开始重建家园。(注:翻译来源于 [这里](http://www.qiyun.org/zhuanti/majiaiyaerdechuanshuo.htm))
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 适合于那些没有 rogueline 体验的玩家;
|
||||
- 同时支持图形界面和 ASCII 模式;
|
||||
- 某些角色拥有超过 40 种能力;
|
||||
- 天赋系统;
|
||||
- 战役引擎;
|
||||
- 在线的持久状态/成就追踪;
|
||||
- IRC 聊天客户端;
|
||||
- 可扩展,可修改;
|
||||
- 充满激情的音乐;
|
||||
- 解锁新的种族,类别,起始点,游戏模式和特点等;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [te4.org][4]
|
||||
- 开发者: ToME 开发团队
|
||||
- 协议: GNU GPL v3.0
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.2.5
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Cataclysm 是一个开源的 “后末世” roguelike 游戏,背景设定在由怪兽和僵尸带来的毁灭性的瘟疫后虚构的新英格兰(New England) 乡村。它是 Whale 开发的原有 Cataclysm 的继续,拓展了更多新的生物,建筑,游戏机制和其他特点。
|
||||
|
||||
尽管有些人描述它为一个 “僵尸游戏”,但 Cataclysm 远比一个“僵尸游戏”包含更多内容。玩家要在一个由程序生成的严酷,持久的世界中艰难生存下去。在一个死寂的文明世界中为了食物,装备或者假如你足够幸运,一辆装满汽油的汽车来逃离 Dodge --这个如地狱一般的地方-- 而苦苦寻觅。通过战斗来击败或从一系列强大的怪兽底下逃离,从僵尸到巨型昆虫或机器人杀手以及更加奇怪和致命的东西中逃离,以及和那些想要得到你拥有的东西的同你一样的人战斗。
|
||||
|
||||
在许多方面上, Cataclysm 同大多数的 roguelike 游戏有很大的不同。它被设定在一个无界的三维世界里,而不是设定在一个垂直、线性的地牢。这意味着相比于大多数的 roguel 游戏,探险将占一个更大的比重,而且这个游戏将具有更少的线性性。由于地图是如此的巨大,在每次游戏之间,它可以完全保持原样。假如你死了,并以一个新的角色开始,你的新游戏将会设定在同你最近呆过的游戏世界相同的世界里。同许多 roguelike 游戏一样,你可以获得先前角色的战利品;而与大多数 roguelike 不同的是,你也可以重新踏上先前角色的轨迹,并且对世界做出的任何戏剧性改变将会维持到你的下一次游戏。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 详细的角色创造,提供了数量众多的特性来选择;
|
||||
- 防御模式, 一个休息模式和快节奏作战;
|
||||
- Bionics; 类似于在许多其他游戏里的 魔法系统;
|
||||
- 基因突变, 有好的和坏的;
|
||||
- 无界的, 完全随机的世界地图,可以在角色交替时保持不变;
|
||||
- 创造物品
|
||||
- 新的制作方法可能需要通过练习或从书本中获得来磨练你的知识;
|
||||
- 逼真的火,烟和其他动态的地图特效;
|
||||
- 一个昼/夜循环,需要睡觉。假如你必须的话,可以使用咖啡因来保持更长时间的清醒,但这不健康;
|
||||
- 超过 300 种物品类型,包括众多的现实世界的枪支,药品和工具;
|
||||
- 许多药品是上瘾的,并需要持续使用来避免负面效果;
|
||||
- 通过修补门,窗,建造陷阱和巩固你的家的基石来防止一个僵尸的突然造访;
|
||||
- 拥有构建你自己的木质建筑,包括墙和屋顶的能力;
|
||||
- 使用汽车在“后末世”发现的景观中兜风;
|
||||
- 这个可以根据你的需求来修改,或甚至你可以从底层建造一个景观;
|
||||
- 一个温度系统,太冷或太热都非常危险;
|
||||
- 初步支持 tile 界面;
|
||||
- 一个类似于 World Gen 一样的选项和多彩的编辑方法;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [en.cataclysmdda.com][5]
|
||||
- 作者: Kevin Granade 及其他
|
||||
- 协议: Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 Unported License
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.B
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Goblin Hack 是一个拥有基于 OpenGL 的平滑滚动的图形界面的开源 roguelike 游戏。这个游戏受 NetHack 外观的启发,但更加快速且使用更少的按键。
|
||||
|
||||
Goblin Hack 有一个简洁的界面,在今天这个过度渲染的游戏世界中,似乎它对所有年龄段的玩家都有吸引力,并启发了这些玩家的想象力。
|
||||
|
||||
在被投进一个随机的正在生成的地牢之前,玩家可以从几个角色类别中选择一个角色。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 令人印象深刻的界面(相比于许多其他的 roguelike 游戏);
|
||||
- 简洁的界面;
|
||||
- 在被投进一个随机的正在生成的第一层地牢之前,玩家可以从几个角色类别中选择一个角色;
|
||||
- 手动保存游戏;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [goblinhack.sourceforge.net][6], [github.com/goblinhack/goblinhack][7]
|
||||
- 作者: Neil McGill
|
||||
- 协议: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.19
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Super Lotsa Added Stuff Hack - Extended Magic (SLASH'EM) 是一个角色扮演游戏,在其中你控制一个单独的角色。SLASH'EM 是 NetHack 的一个变种。它拥有一个和 Rogue, ADOM, Anghand 及 NetHack 相似的界面和游戏玩法。你通过键盘来控制角色的动作,以一个俯视的视角来查看这个世界。
|
||||
|
||||
背景: Amulet of Yendor 已被偷走,不仅如此,偷走 amulet 的 Wizard of Yendor(不是一个好人)似乎深藏于 Dungeons of Doom(不是一个友好的地方)。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 提供额外的特点、怪兽和项目;
|
||||
- 新颖的特点包括僧人种类和类似推箱子的关卡;
|
||||
- 主要的地牢比在 NetHack 中的要大很多;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.slashem.org][8]
|
||||
- 开发者: Slash'EM 开发团队
|
||||
- 协议: MIT License, NetHack General Public License
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.0.7E7F3
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
NetHack 是一个绝妙的简洁,但又非常吸引人的具有地下城与龙风格的冒险游戏。“net”元素指的是它的发展已经根据网络进行了协调,“hack”元素指的是角色扮演游戏的一种体裁,以乱砍、猛砍著称,着眼于战斗。
|
||||
|
||||
在 NetHack 中,你扮演激烈的战士、精灵或许多其他种类的一部分角色,一路战斗着,为你的神灵获取 Amulet of Yendor(可以说这是一个倒退!)。在这个过程中,你可能会遇到一个或两个 quantum mechanic(注:从[这里](http://nethack.wikia.com/wiki/Quantum_mechanic)得知,这指的是一种怪兽),或者可能遇到一个小型的太空舰队,抑或是 --假如你*足够*幸运 -- Ravenous Bugblatter Beast of Traal。(注:我参考了[这里](http://nethack.wikia.com/wiki/Douglas_Adams))。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 45-50 个关卡, 其中的大多数随机生成
|
||||
- 各种各样的物品:武器、盔甲、卷轴、药水、戒指、宝石和各种各样的工具,如钥匙和灯
|
||||
- 祝福和诅咒
|
||||
- Permadeath永久死亡: 若没有对当前的保存文件进行备份,过期的角色不能再找回;
|
||||
- 界面:
|
||||
- 控制台;
|
||||
- 图形化界面, 使用 X、Qt 工具集或 GNOME 库
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.nethack.org][9]
|
||||
- 开发者: NetHack 开发团队
|
||||
- 协议: NetHack 通用公共许可证
|
||||
- 版本号: 3.4.3
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Ascii Sector 是一个免费的太空战斗/探险/交易游戏,它基于经典的电脑游戏 `Wing Commander: Privateer`,后者由 Origine Systems 公司于 1993 年发布。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Ascii Sector 中,刚开始你将驾驶一艘简易的飞船,然后可以通过接受任务或者贩卖物品来挣得足够多的钱以升级你的飞船或重新再买一艘。不管是在太空中,还是在地面上,抑或是在飞船上,你可以专注于致命的战斗;并且通过使用 Ascii Sector 的脚本语言,你还可以为游戏创造自己的任务或享受其他玩家创造的任务。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 图像界面使用 ANSI 人物集;
|
||||
- 真正的深入到游戏中;
|
||||
- 提供各种基地,任务,商品和飞船;
|
||||
- 飞船型号包括: Broadsword, Centurion, Demon, Dralthi, Drayman, Galaxy, Gladius, Gothri, Kamekh, Nexus, Orion, Paradign, Stileto, Talon, Tarsus 和 Ulysses;
|
||||
- 四个象限: Alizarin, Crimson, Mauve, and Viridian;
|
||||
- 可下载的任务;
|
||||
- 任务可用脚本编辑;
|
||||
- Ascii Sector 任务语言,在 Ascii Sector 宇宙中创造你自己的故事;
|
||||
- 可以袭击或抢劫位于星球上的 NPCs(指非玩家控制角色);
|
||||
- 可以到处移动的持久性舰队、可以改变系统的控制、玩弄敌人的舰队、回基地修复或重建;
|
||||
- 可以登录系统受损的飞船;
|
||||
- 可下载高质量的音乐文件;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.asciisector.net][10]
|
||||
- 开发者: Christian Knudsen
|
||||
- 协议: 免费软件
|
||||
- 版本号: 0.7.1.4
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Angband 是一个免费、单用户、图形界面的地下城探险游戏,它使用 ASCII 字符的角色,在其中你将以一个冒险者的角色探索一个深深的地下城,与怪兽战斗,获得你能取得的最好武器,准备着与黑暗之主 Morgoth 的最后绝战。从上世纪九十年代开始,它一直在持续地开发着。
|
||||
|
||||
Angband 沿袭了 Rogue 和 NetHack 的风格路线。它由 Moria 和 Umoria 游戏衍生而来,反过来这两个游戏都以 Rogue 为基础。它经常被描述为一个 “roguelike”游戏,因为它的外观和游戏体验与 Rogue 非常相似。很多游戏中的新生物、物品都来自 J.R.R Tolkien 的画作,尽管有些野兽直接来源于经典的神话、Dungeons & Dragons, Rolemaster(根据wikipedia,这两个都是角色扮演游戏的名称)、或原来 Angband 开发者的脑海中。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 100 层地牢;
|
||||
- 随机产生的新关卡;
|
||||
- 可以选择成为人类、半精灵、精灵、霍比特人、地精、矮人,半兽人,半巨魔, 登丹人 ,高等精灵,或者狗头人;
|
||||
- 神器;
|
||||
- 施法;
|
||||
- 怪物;
|
||||
- 怪物坑;
|
||||
- 怪物巢穴;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [rephial.org][11]
|
||||
- 开发者: Angband 开发小组
|
||||
- 协议: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 3.5.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
UnNetHack 是 NetHack 的一个分支。NetHack 最开始于 1987 年发行,并且许多游戏玩家认为它是计算机世界所能提供的最好游戏体验的游戏之一。
|
||||
|
||||
特点包括:
|
||||
|
||||
- 增加了许多针对 NetHack 的增强,如额外的怪兽、更多的关卡、许多新的元素、更多的危险、更具挑战性的游戏,以及最重要的,相比普通的 NetHack,它更具娱乐性;
|
||||
- 帮助新手开始的教程;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [sourceforge.net/apps/trac/unnethack][12]
|
||||
- 作者: Patric Mueller
|
||||
- 协议: Nethack General Public License
|
||||
- 版本号: 5.1.0
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Hydra Slayer 是一个专注于杀死九头蛇的开源 Roguelike 游戏。它受希腊神话、地下城探险、MathRL 七日 rouguelike,和一些关于勇敢的英雄杀死多头野兽的数字谜题等启发。
|
||||
|
||||
特点如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 独特的游戏机制;
|
||||
- 混合希腊神话和数字迷宫的主题;
|
||||
- 传统的 roguelike ASSCII 字符界面或 砖块/3D 界面;
|
||||
- 5 种人物角色,具有极为不同的战术、力量及弱点;
|
||||
- 28 种敌人类型:
|
||||
- 10 种基本的九头蛇类型(每种类型都有两种变种);
|
||||
- 8 种特殊类型的敌人;
|
||||
- 无害的蘑菇可用作战术工具;
|
||||
- 28 种装备(并包括材料和装备的大小/力量的变种);
|
||||
- 15 种武器材料;
|
||||
- 18 种不可装备项;
|
||||
- 3 种可供选择的地图;
|
||||
- 8 种层级拓扑结构(包括莫比乌斯带和克莱因瓶);
|
||||
- 11 个等级;
|
||||
- 2 种胜利结局;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [www.roguetemple.com/z/hydra][13]
|
||||
- 开发者: Zeno Rogue
|
||||
- 协议: GNU GPL v2
|
||||
- 版本号: 16.1
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
Brogue 是一个开源的 Roguelike 游戏,它可以运行在 Mac OS X, Windows, Linux, iOS 和 Android 等平台下。
|
||||
|
||||
Brogue 是 Rogue 的一个直系分支,后者是一个由 Michael Toy 和 Glenn Wichman 于 1980 年左右最先开发的地下城探险视频游戏。与其他受欢迎的现代 Roguelike 游戏不同, Brogue 追求简单而不是复杂性,同时尽力确保游戏的不同组成之间的联系是有趣且纷繁多彩的。
|
||||
|
||||
这个游戏的目标是取得深藏于地下第 26 层的 "Amulet of Yendor",再返回到顶层逃出生天。对于那些技术娴熟且想进一步探险的人来说,位于 26 层之下的每层均包含 3 颗 lumenstone (流明石)(注:这里与我在[这里](http://brogue.wikia.com/wiki/Lumenstone)看到的有些出入),获得它们,将在胜利的基础上被授予额外的得分。
|
||||
|
||||
Brogue 是一个富有挑战性的游戏,但玩着仍有许多趣味。尽量不要因游戏的高难度而灰心;试玩一段时间之后,你会发现它变得非常吸引人。
|
||||
|
||||
特点如下:
|
||||
|
||||
- 追求简单而非复杂;
|
||||
- 对用户友好;
|
||||
- 相比于 Rogue, Brogue 有一个更加复杂的层级划分;
|
||||
- 移除了 XP 和 水平系统 ;
|
||||
- 陷阱,保护项目;
|
||||
- 额外的怪兽类型和魔法项目;
|
||||
|
||||
- 网站: [sites.google.com/site/broguegame][14]
|
||||
- 作者: Brian Walker
|
||||
- 协议: GNU Affero GPL
|
||||
- 版本号: 1.7.3
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.linuxlinks.com/article/201412031524381/RoguelikeGames.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:Frazer Kline
|
||||
译者:[FSSlc](https://github.com/FSSlc)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://crawl.develz.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.bay12games.com/dwarves/index.html
|
||||
[3]:http://www.adom.de/
|
||||
[4]:http://te4.org/
|
||||
[5]:http://en.cataclysmdda.com/
|
||||
[6]:http://goblinhack.sourceforge.net/
|
||||
[7]:https://github.com/goblinhack/goblinhack
|
||||
[8]:http://www.slashem.org/
|
||||
[9]:http://www.nethack.org/
|
||||
[10]:http://www.asciisector.net/
|
||||
[11]:http://rephial.org/
|
||||
[12]:http://sourceforge.net/apps/trac/unnethack/
|
||||
[13]:http://www.roguetemple.com/z/hydra/
|
||||
[14]:levelling system
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
在CentOS或者Redhat中如何为Apache Tomcat绑定IPv4
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
今天我们来学习一下如何在CentOS 7 Linux分布式系统中为Tomcat绑定IPv4
|
||||
|
||||
**Apache Tomcat** 是由[Apache Software Foundation][1] 开发的开源web服务器和servlet容器。它实现了Java Servlet,JavaServer页面(JSP),Java的统一表达式语言,以及Sun Microsystems的Java的WebSocket规范,并提供了一个运行java代码的web服务器环境。
|
||||
|
||||
如果由于默认绑定tomcat到IPv6而导致我们的web服务器不能正常工作,就有必要将tomcat绑定到IPv4。众所周知,IPv6是为设备分配IP地址的现代方法,虽然在不久的将来也许会得到应用,但是现在并没有得到完全应用。由于没有用处,目前我们并不需要将我们的Tomcat服务器向IPv6转换,我们应该将其绑定到IPv4。
|
||||
|
||||
在开始将tomcat绑定到IPv4之前,我们应该确保在我们的CentOS 7中已经安装了tomcat。这是一个[如何在CentOS 7.0服务器中安装tomcat 8][2]的指导。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1. 切换到tomcat用户 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们要切换到 **tomcat** 用户。我们可以通过在shell或者终端中运行 **su tomcat** 命令完成。
|
||||
|
||||
# su tomcat
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 找到文件 Catalina.sh ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在我们要进入Apache Tomcat安装目录下的bin文件夹,通常是 **/usr/share/apache-tomcat-8.0.x/bin/**, 这里的x是 Apache Tomcat发行版的子版本号。因为我的CentOS 7服务器中安装的版本是8.0.18,这里我的目录是 **/usr/share/apache-tomcat-8.0.18/bin/**。
|
||||
|
||||
$ cd /usr/share/apache-tomcat-8.0.18/bin
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:请用你系统中安装的Apache Tomcat的版本号替换8.0.18。**
|
||||
|
||||
在bin目录中,有一个名字是catalina.sh的脚本文件。这就是我们要编辑的文件,我们将在里面增加一行将tomcat绑定到IPv4的配置信息。你可以通过在shell或者终端中运行命令 **ls** 来查看这个文件。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ls
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 配置 Catalina.sh ###
|
||||
|
||||
如图所示,我们将在catalina.sh脚本文件的最后增加一行 **JAVA_OPTS= "$JAVA_OPTS -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true -Djava.net.preferIPv4Addresses"**。我们可以使用我们喜欢的文本编辑器来编辑这个文件,例如nano,vim等等。这里我们使用nano。
|
||||
|
||||
$ nano catalina.sh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
然后,如下图所示,将 **JAVA_OPTS= "$JAVA_OPTS -Djava.net.preferIPv4Stack=true -Djava.net.preferIPv4Addresses"** 增加到文件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们已经将配置信息增加到文件中。保存文件并退出nano。
|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 重启 ###
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们通过重启tomcat服务器使配置生效。我们要先运行shutdown.sh,然后运行startup.sh。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./shutdown.sh
|
||||
|
||||
运行可执行文件startup.sh:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ./startup.sh
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
这将重启我们的tomcat服务器并加载将服务器绑定到IPv4的配置信息。
|
||||
|
||||
### 结尾 ###
|
||||
|
||||
好了,我们终于将我们运行在CentOS 7 Linux分布式系统上的tomcat服务器绑定到IPv4上了。尽管IPv6在不久的将来也许会得到应用,但由于现在还没有使用,如果因为将你的Tomcat服务器绑定到IPv6上而使得你的tomcat服务器不工作,就有必要将tomcat绑定到IPv4上,这也很简单。如果你有任何疑问,建议,反馈,请在下面的评论框中写下来,让我们知道有什么需要增加或者改进。非常感谢!
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/bind-apache-tomcat-ipv4-centos/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.apache.org/
|
||||
[2]:http://linoxide.com/linux-how-to/install-tomcat-8-centos-7/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,314 @@
|
||||
如何在linux上使用Trickle来限制应用程序的网络宽带使用.
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
有没有遇到过系统中的某个应用程序独占了你所有的网络宽带的情形?如果你有过这样的遭遇,那么你就会感受到Trickle宽带调整应用角色的价值.不管你是一个系统管理员还是仅仅Linux用户,都需要学习如何控制应用程序的上下行速度,来确保你的网络宽带不会被某个程序
|
||||
霸占.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
Install Trickle Bandwidth Limit in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是 Trickle? ###
|
||||
|
||||
Trickle是一个网络宽带调整工具,可以让我们管理应用程序的网络上下行速度,使得可以避免其中的某个应用程序吃掉了全部或大部分可用的宽带.换句话说,Trickle可以让你基于单个应用程序来控制
|
||||
网络流量速率,而不是仅仅针对与单个用户--在客户端网络环境中经典的宽带调整样例,
|
||||
|
||||
### Trickle是如何工作的?###
|
||||
|
||||
另外,tricle可以帮助我们基于应用来定义优先级,所以当对整个系统进行了全局限制设定,高优先级的应用依然会自动地获取更多的宽带。为了实现这个目标,tricle设置通过TCP连接的套接字对数
|
||||
据发送、数据接收路径的流量限制。我们必须注意到,除了影响传输速率之外,tricle任何时候都不会以任何方式来改变其处理过程。
|
||||
|
||||
### Trickle不能做什么? ###
|
||||
|
||||
这么说吧,唯一的限制就是,tricle静态连接的应用或者具有SUID或SGID位设置的二进制--因为他们使用动态链接并且将其自身加载到调整过程以及其关联的网络套接字之间。 Trickle此时会在这两种软件
|
||||
组件之间扮演代理的角色。
|
||||
|
||||
由于trickle并不会需要超级用户的权限来运行,所以用户可以设置用户独立的流量限制,可能这并不是你想要的,我们会探索如何使用全局设定来限制系统中的所有用户的流量限制。也即是说,此时系统中的每个用户具有管理
|
||||
各自的流量速率,但是无论如何,都会受到系统管理员给他们设置的边界限制。
|
||||
|
||||
在这边文章中,我们会描述如何通过trickle在linux平台上管理应用程序使用的网络宽带。为了生成必要流量,在此会在客户端(CentOS 7 server – dev1: 192.168.0.17)上使用 ncftpput 和
|
||||
ncftpget, 在服务器(Debian Wheezy 7.5 – dev2: 192.168.0.15)上使用vsftpd 来进行演示。 相同的指令也可以在RedHat,Fedora和Ubuntu等系统使用。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 前提条件 ####
|
||||
|
||||
1. 对于 RHEL/CentOS 7/6, [开启EPEL仓库][1]。EPEL的Extra Packages是一个 有Fedora项目维护的高质量、开源的软件仓库,而且百分之百与其衍生产品相兼容,如
|
||||
企业版本Linux和CentOS. 在这个仓库中trickle和ncftp两者都是可用的。
|
||||
|
||||
2. 按照如下方式安装ncftp:
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && sudo yum install ncftp [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
# aptitude update && aptitude install ncftp [On Debian based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
3. 在单独的服务器上设置一个FTP服务器。需要注意的是,尽管FTP天生就不安全,但是
|
||||
仍然被广泛应用在安全性无关紧要的文件上传下载中。 在这篇文章中我们使用它来演示
|
||||
trickle的优点,同时它也会在客户端的标准输出流中显示传输速率,我们将是否在另外
|
||||
的日期时间中使用放在一边讨论。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum update && yum install vsftpd [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
# aptitude update && aptitude install vsftpd [On Debian based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
现在,在FTP服务器上按照以下方式编辑 /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf 文件。
|
||||
|
||||
anonymous_enable=NO
|
||||
local_enable=YES
|
||||
chroot_local_user=YES
|
||||
allow_writeable_chroot=YES
|
||||
|
||||
在此之后,确保在你的当前会话中开启了vsftpd,并在之后的启动中让其自动启动。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl start vsftpd [For systemd-based systems]
|
||||
# systemctl enable vsftpd
|
||||
# service vsftpd start [For init-based systems]
|
||||
# chkconfig vsftpd on
|
||||
|
||||
4. 如果你选在在一个CentOS/RHEL 7中为FTP服务器的远程访问配备SSH秘钥,你需要
|
||||
一个具有适合访问root目录之外的目录和文件内容上传下载权限并密码受保护的用户账户。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以通过在你的浏览器中输入以下的URL来浏览你的Home目录。一个登陆窗口会弹出来
|
||||
提示你输入FTP服务器中的有效的用户名和密码。
|
||||
|
||||
ftp://192.168.0.15
|
||||
|
||||
如果验证成功,你就会看到你的home目录中的内容。该教程的稍后部分中,你将可以刷新
|
||||
页面来显示在你之前上传过的文件。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
FTP Directory Tree
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在Linux中安装 Tricle ###
|
||||
|
||||
1. 通过yum或aptitude来安装tricle.
|
||||
|
||||
为了确保能够成功安装,最好在安装工具之前,保证当前的安装包是最新的版本。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# yum -y update && yum install trickle [On RedHat based systems]
|
||||
# aptitude -y update && aptitude install trickle [On Debian based systems]
|
||||
|
||||
2. 确认trickle是否对特定的二进制包有用。
|
||||
|
||||
之前我们解释过,trickle只对使用动态或共享包的二进制包有用。为了确认我们是否可以对某个特定的应用使用trickle,我们可以使用著名的ldd(
|
||||
列出动态依赖)工具。 特别地,我们会查看任何给定程序的动态依赖中检查其当前使用的glibc,因为其准确地定义了使用套接字交流中使用的系统调用。
|
||||
|
||||
对一个给定的二进制包执行以下命令来查看是否能对其使用trickle进行宽带调整:
|
||||
|
||||
# ldd $(which [binary]) | grep libc.so
|
||||
|
||||
例如,
|
||||
|
||||
# ldd $(which ncftp) | grep libc.so
|
||||
|
||||
其输出是:
|
||||
|
||||
# libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007efff2e6c000)
|
||||
|
||||
输出中的括号中的字符可能在不同的系统平台中发生改变,甚至相同的命令在不同的时候运行也会,因为其代表包加载到物理内存中的地址。
|
||||
|
||||
如果上面的命令没有返回任何的结果,就说明这个二进制包没有使用libc包,因此tricle对其不能起到宽带调整的作用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 学习如何使用Trickle###
|
||||
|
||||
最基本的用法就是使用其单模式,通过这种方式,trickle用来显示地定义给定应用程序的上传下载速率。如前所述,为了简单性,我们会使用相同的应用
|
||||
来进行上传下载测试。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在单模式下运行trickle####
|
||||
|
||||
我们会比较在有无trickle的情况下的上传下载速率, ‘-d’选项指示下载速率(KB/s单位),而'-u'选项指示相同单位的上传速率。另外我们会使用到‘-s’
|
||||
选项来指定trickle应该以单模式运行。
|
||||
|
||||
以单模式运行trickle的基本语法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -s -d [download rate in KB/s] -u [upload rate in KB/s]
|
||||
|
||||
为了能够让你自己运行以下样例,确保你在自己的客户端安装了trickle和ncftp(我的是192.168.0.17)。
|
||||
|
||||
**样例1:在有无trickle的情况下上传一个2.8 MB的PDF文件。**
|
||||
|
||||
我们使用一个自由发布的LInux基础知识PDF文件来进行下面的测试[文件链接][2]。
|
||||
|
||||
你可以首先使用下面的命令将这个文件下载到你当前的工作目录中:
|
||||
# wget http://linux-training.be/files/books/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
下面是在没有trickle的情况下将一个文件上传到我们的FTP服务器的语法:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /remote_directory local-filename
|
||||
|
||||
其中的 /remote_directory 是相对于用户名的Home目录的上传路径,而local-filename是一个你当前工作目录中的文件。
|
||||
|
||||
特别的是,在没有trickle的情形下,我们可以得到上传峰值速率52.02MB/s(请注意,这个不是真正的平均上传速率,而是峰值开始的瞬时值),而且这个文件几乎
|
||||
在瞬间就完成了上传。
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 52.02 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
在使用trickle的情况下,我们会限制上传速率在5KB/s。在第二次上传文件之前,我们需要在目标目录中删除这个文件,否则ncftp就会通知我们在目标
|
||||
目录中已经存在了与上传文件相同的文件,从而不会执行文件的传输:
|
||||
# rm /absolute/path/to/destination/directory/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
然后:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -s -u 5 ncftpput -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 /testdir LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 4.94 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
在上面的样例中,我们看到平均的上传速率下降到了5KB/s。
|
||||
|
||||
**样例2:在有无trickle的情况下下载相同过得2.8MB的PDF文件**
|
||||
|
||||
首先,记得从原来的源文目录中删除这个PDF:
|
||||
|
||||
# rm /absolute/path/to/source/directory/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,下面的样例中将远程的文件下载到客户端机器的当前目录下,这是由FTP服务器的IP地址后面的·.·决定的。
|
||||
|
||||
没有trickle的情况下:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 260.53 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
在有trickle的情况下,限制下载速率在20KB/s:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle -s -d 30 ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
LinuxFun.pdf: 2.79 MB 17.76 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
### 在有监督的模式下运行Trickle [未管理的]###
|
||||
|
||||
Tricle也可以在未管理的模式下运行,通过跟随在/etc/tricled.conf文件中定义的一系列参数。 这个文件定义了守护线程 trickled的行为以及如何管理tricle。
|
||||
|
||||
另外,如果你想要全局设置被所有的应用程序使用的话,我们就会需要使用tricle命令。 这个命令运行守护线程并允许我们通过trickle定义所有应用程序共享的上传下载限制,不需要我们每次来进行指定。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,运行:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickled -d 50 -u 10
|
||||
|
||||
会导致任何通过tricle运行的应用程序的上传下载速率分别限制在30kb/s和10kb/s。
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,你可以在任何时间都能确认守护线程tricled是否正在运行以及其运行参数:
|
||||
|
||||
# ps -ef | grep trickled | grep -v grep
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
root 16475 1 0 Dec24 ? 00:00:04 trickled -d 50 -u 10
|
||||
|
||||
**样例3:在是否使用tricle的情形下上传一个 19MB 的mp4文件到我们的FTP服务器。**
|
||||
|
||||
在这个样例中,我们会使用“He is the gift”的自由分布视频,可以通过这个[链接][3]下载。
|
||||
|
||||
我们将会在开始通过以下的命令将这个文件下载到你的当前工作目录中:
|
||||
|
||||
# wget http://media2.ldscdn.org/assets/missionary/our-people-2014/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们会使用之前列出的命令来开启守护进程trickled:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickled -d 30 -u 10
|
||||
|
||||
在没有trickle时:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 36.31 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
有trickle的时:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle ncftpput -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 /testdir 2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 9.51 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
我们可以看到上面的输出,上传的速率下降到了约 10KB/s。
|
||||
|
||||
** 样例4:在有无trickle的情形下下载这个相同的视频 **
|
||||
|
||||
与样例2一样,我们会将该文件下载到当前工作目录中。
|
||||
|
||||
在没有trickle时:
|
||||
|
||||
# ncftpget -u username -p password 192.168.0.15 . /testdir/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 108.34 MB/s
|
||||
|
||||
有trickle的时:
|
||||
|
||||
# trickle ncftpget -u username -p password 111.111.111.111 . /testdir/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4: 18.53 MB 29.28 kB/s
|
||||
|
||||
上面的结果与我们之前设置的下载限速相对应(30KB/s)。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意:** 一旦守护进程开启之后,没有必要使用trickle来为每个应用程序来单独设置限制。
|
||||
|
||||
如前所述,每个人都可以进一步地通过tricled.conf来客制化tricle的宽带速率调整,该文件的一个典型的分区有以下部分组成:
|
||||
|
||||
[service]
|
||||
Priority = <value>
|
||||
Time-Smoothing = <value>
|
||||
Length-Smoothing = <value>
|
||||
|
||||
其中,
|
||||
|
||||
- [service] 用来指示我们想要对其进行宽带使用调整的应用程序名称
|
||||
- Priority 用来让我们为某个服务制定一个相对于其他服务高的优先级,这样就不允许守护进程管理中的一个单独的应用程序来占用所有的宽带。越小的数字代表更高的优先级。
|
||||
- Time-Smoothing [以秒计]: 定义了trickled让各个应用程序传输或接收数据的时间间隔。小的间隔值(0.1-1秒)对于交互式应用程序是理想的,因为这样会具有一个更加平滑的会话体验,而一个相对较大
|
||||
的时间间隔值(1-10秒)对于需要批量传输应用程序就会显得更好。如果没有指定该值,默认是5秒。
|
||||
- Length-smoothing [KB 单位]: 该想法与Time-Smoothing如出一辙,但是是基于I/O操作而言。如果没有指定值,会使用默认的10KB。
|
||||
|
||||
平滑值的改变会被翻译为将指定的服务的使用一个间隔值而不是一个固定值。不幸的是,没有一个特定的公式来计算间隔值的上下限,主要依赖于特定的应用场景。
|
||||
|
||||
下面是一个在CentOS 7 客户端中的tricled.conf 样例文件(192.168.0.17):
|
||||
|
||||
[ssh]
|
||||
Priority = 1
|
||||
Time-Smoothing = 0.1
|
||||
Length-Smoothing = 2
|
||||
|
||||
[ftp]
|
||||
Priority = 2
|
||||
Time-Smoothing = 1
|
||||
Length-Smoothing = 3
|
||||
|
||||
使用该设置,tricled会为SSH赋予比FTP较高的传输优先级。值得注意的是,一个交互进程,例如SSH,使用了一个较小的时间间隔值,然而一个处理批量数据传输的服务如FTP使用一个较大的时间
|
||||
间隔来负责之前的样例中的上传下载速率,尽管不是百分百的有trickled指定的值,但是也已经非常接近了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
在该文章中,我们探索了任何使用trickle在基于Fedora发行版和Debian衍生版平台上来限制应用程序的宽带使用.也包含了其他的可能用法,但是不对以下情形进行限制:
|
||||
|
||||
- 限制系统下载工具的下载速度,例如[wget][4],或 BT客户端.
|
||||
|
||||
- 限制你的系统的包管理工具`[yun][5]`更新的速度 (如果是基于Debian系统的话,其包管理工具为`[aptitude][6]`)。
|
||||
|
||||
- 如果你的服务器是在一个代理或防火墙后面(或者其本身即是代理或防火墙的话),你可以使用trickle来同时设定下载和上传速率,或者与客户端或外部交流速率。
|
||||
|
||||
欢迎提问或留言.
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/manage-and-limit-downloadupload-bandwidth-with-trickle-in-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Gabriel Cánepa][a]
|
||||
译者:[theo-l](https://github.com/theo-l)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/gacanepa/
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/how-to-enable-epel-repository-for-rhel-centos-6-5/
|
||||
[2]:http://linux-training.be/files/books/LinuxFun.pdf
|
||||
[3]:http://media2.ldscdn.org/assets/missionary/our-people-2014/2014-00-1460-he-is-the-gift-360p-eng.mp4
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/10-wget-command-examples-in-linux/
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/20-linux-yum-yellowdog-updater-modified-commands-for-package-mangement/
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/dpkg-command-examples/
|
||||
@ -1,85 +0,0 @@
|
||||
设置Ubuntu14.04无密码登录SSH
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
大家好,今天我来向大家介绍如何在可信的Ubuntu12.04上设置无密码登录SSH功能。仅在工作站有正确的(公私)密钥以供匹配时SSH服务端才会允许你登录,反之访问将不会被允许。
|
||||
|
||||
正常情况下,我们需要连上SSH的控制台输入用户名和密码,两者结合使用。如果两者全部正确,我们就可以访问,反之访问被服务端拒绝。不过相比而言还有一种比用密码更安全的登录方式,我们用的不是密码在登录SSH我们用的是密钥。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想使用这个安全的方式,我们只需简单的禁用密码登录并只允许密钥即可。使用这种方式时,客户端计算机上会产生公私一对密钥。接着客户端得把公钥上传到SSH服务端的密要验证文件中去。在访问被授予前,服务器及客户端电脑互验密钥对。如果服务器上的公钥与客服端提交的私钥匹配访问开始,否则访问被拒绝。
|
||||
|
||||
这是获取SSH服务器认证中非常安全的一种做法,如果你想为SSH用户登录实施安全的认证,这也是备受推崇的方式。这里快速的过一遍允许无密码登录SSH的配置过程。
|
||||
|
||||
### 1.安装Openssh服务端 ###
|
||||
|
||||
首先,我们需要更新我们的本地库索引。所以如下所见,我们需要先输入“apt-get update”
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get update
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在我们可以通过以下命令安装openssh-server:
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install openssh-server
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 2. 开启openssh服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在OpenSSH已经成功安装在Ubuntu14.04操作系统上了之后,我们要启动OpenSSH的服务。以下命令让你启动/开启服务。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service ssh start
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh start
|
||||
|
||||
### 3. 配置密钥对 ###
|
||||
|
||||
在我们安装并启动了OpenSSH服务以后。现在终于到了要我们搞定公私钥对的时候了,在终端中运行以下命令:
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa
|
||||
|
||||
在运行完以上命令了以后,我们完成一系列的提示的任务。首先选择保存密钥路径,按回车将会选择默认路径即家目录的一个隐藏的.ssh文件夹。下一个提示是请输入提醒。我个人将此留白(回车过)。之后密钥对就会创建,大功告成。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
在密钥对生成以后,我们需要将**客户端的上的公钥复制到SSH服务端**或者宿主来创建对客户端的信任关系。运行以下命令复制客户端的公钥到服务端。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh-copy-id user@ip_address
|
||||
|
||||
在公钥上传之后,我们现在可以不用通过密码登陆SSH了。为此,我们需要通过以下命令用文本编辑器打开**etc/ssh/ssh_config**。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config
|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们需要按照下图所示去到几行注释并进行一些赋值。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
### 4. 重启SSH服务 ###
|
||||
|
||||
最后,在我们配置完SSH服务端后,为了使改动生效我们需要重启SSH服务。在终端或控制台运行以下命令重启。
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo service ssh restart
|
||||
|
||||
OR
|
||||
|
||||
$ sudo /etc/init.d/ssh restart
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在,我们可以试试不用密码仅用密钥配对的方式登录ssh服务端了。
|
||||
|
||||
### 总结 ###
|
||||
|
||||
太好了!我们成功的配置了无密码登录SSH。这是获取SSH服务器认证中非常安全的一种做法,如果你想为SSH但用户登录实施安全的认证这也是备受推崇的方式。所以,如果你还有什么问题或建议,请在意见框中向我们反馈。很欣慰你能读完,祝你SSH登录愉快 :-)
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://linoxide.com/ubuntu-how-to/setup-passwordless-ssh-logon-ubuntu-14-04/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Arun Pyasi][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://linoxide.com/author/arunp/
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
|
||||
Linux有问必答-- 如何在VPS上安装和访问CentOS远程桌面
|
||||
================================================================================
|
||||
> **提问**: 我想在VPS中安装CentOS桌面,并可以直接从我家远程访问GUI桌面。有什么建议可以在VPS上设置和访问CentOS远程桌面?
|
||||
|
||||
如何远程办公或者远程弹性化工作制在技术领域正变得越来越流行。这个趋势背后的一个技术就是远程桌面。你的桌面环境在云中,你可以在任何你去的地方,或者在家或者工作场所访问你的远程桌面。
|
||||
|
||||
这个教程介绍如何VPS中设置基于CentOS的远程桌面。现在,我们会先展示CentOS的基础环境。
|
||||
|
||||
我们假设你已经创建了CentOS 7的VPS实例(比如,使用[DigitalOcean][1] 或者 Amazon EC2)。请确保你的VPS实例有至少1GB的内存。不然,CentOS将会在你访问远程桌面的时候回崩溃。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第一步: 安装CentOS桌面 ###
|
||||
|
||||
如果现在的CentOS版本是没有桌面的最小版本,你需要先在VPS上安装桌面(比如GNOME)。比如,DigitalOcean的镜像就是最小版本,它需要如下安装[桌面GUI][2]
|
||||
|
||||
# yum groupinstall "GNOME Desktop"
|
||||
|
||||
在安装完成之后重启VPS。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第二步:安装和配置VNC服务器 ###
|
||||
|
||||
接下来就是安装和配置VNC服务器。我们使用的是TigerVNC,一个开源的VNC服务实现。
|
||||
|
||||
# yum install tigervnc-server
|
||||
|
||||
现在创建一个用户账户(比如:xmodulo)用来访问远程桌面。
|
||||
|
||||
# useradd xmodulo
|
||||
# passwd xmodulo
|
||||
|
||||
当一个用户尝试使用VNC访问远程桌面时,VNC守护进程就会启动来处理这个请求。这意味着你需要为每个用户创建一个独立的VNC配置文件。
|
||||
|
||||
CentOS依靠systemd来管理和配置系统服务。所以我们将使用systemd来为用户xmodulo配置VNC服务器。
|
||||
|
||||
首先让我们使用下面任意一条命令来检查VNC服务器的状态。
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl status vncserver@:.service
|
||||
# systemctl is-enabled vncserver@.service
|
||||
|
||||
默认上,刚安装的VNC服务并没有激活(禁用)。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
现在服务一份通用的VNC服务文件来位用户xmodulo创建一个VNC服务配置。
|
||||
|
||||
# cp /lib/systemd/system/vncserver@.service /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service
|
||||
|
||||
用本文编辑器来打开配置文件,用实际的用户名(比如:xmodulo)来替换[Service]下面的<USER>。同样。在ExecStart后面追加 "-geometry <resolution>" 参数。最后,要修改下面两行加粗字体的两行。
|
||||
|
||||
# vi /etc/systemd/system/vncserver@:1.service
|
||||
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
[Service]
|
||||
Type=forking
|
||||
# Clean any existing files in /tmp/.X11-unix environment
|
||||
ExecStartPre=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
|
||||
ExecStart=/sbin/runuser -l xmodulo -c "/usr/bin/vncserver %i -geometry 1024x768"
|
||||
PIDFile=/home/xmodulo/.vnc/%H%i.pid
|
||||
ExecStop=/bin/sh -c '/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i > /dev/null 2>&1 || :'
|
||||
|
||||
现在为用户xmodulo设置密码(可选)。首先切换到该用户,并运行vncserver命令。
|
||||
|
||||
# su - xmodulo
|
||||
# vncserver
|
||||
|
||||
你会被提示输入用户的VNC密码。密码设置完成后,你下次需要用这个密码来访问你的远程桌面。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
最后,重新加载服务来使新的VNC配置生效:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl daemon-reload
|
||||
|
||||
在启动时自动启动VNC服务:
|
||||
|
||||
# systemctl enable vncserver@:1.service
|
||||
|
||||
检查vnc服务正在监听的端口:
|
||||
|
||||
# netstat -tulpn | grep vnc
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
端口5901是VNC默认的客户端连接到VNC服务器使用的端口。
|
||||
|
||||
### 第三步:通过SSH连接到远程桌面 ###
|
||||
|
||||
设计上,VNC使用的远程帧缓存(RFB)并不是一种安全的协议。那么在VNC客户端上直接连接到VNC服务器上并不是一个好主意。任何敏感信息比如密码都可以在VNC流量中被轻易地泄露。因此,我强烈建议使用SSH隧道来[加密你的VNC流量][3]。
|
||||
|
||||
在你要运行VNC客户端的本机上,使用下面的命令来创建一个连接到远程VPS的SSH通道。当被要输入SSH密码时,输入用户的密码。
|
||||
|
||||
$ ssh xmodulo@<VPS-IP-address> -L 5901:127.0.0.1:5901
|
||||
|
||||
用你自己的VNC用户名来替换“xmodulo”,并填上你自己的VPS IP地址。
|
||||
|
||||
一旦SSH通道建立之后,远程VNC流量就会通过ssh通道路由并发送到127.0.0.1:5901。
|
||||
|
||||
现在启动你最爱的VNC客户端(比如:vinagre),来连接到127.0.0.1:5901。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
你将被要求输入VNC密码。当你输入VNC密码时,你就可以安全地连接到CentOS的远程桌面了.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://ask.xmodulo.com/centos-remote-desktop-vps.html
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Dan Nanni][a]
|
||||
译者:[geekpi](https://github.com/geekpi)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创翻译,[Linux中国](http://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://ask.xmodulo.com/author/nanni
|
||||
[1]:http://xmodulo.com/go/digitalocean
|
||||
[2]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-install-gnome-desktop-on-centos.html
|
||||
[3]:http://xmodulo.com/how-to-set-up-vnc-over-ssh.html
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user