mirror of
https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject.git
synced 2025-02-28 01:01:09 +08:00
Translated tech/20170203 bmon – A Powerful Network Bandwidth Monitoring and Debugging Tool for Linux.md
This commit is contained in:
parent
ea3b12d43c
commit
43ac197757
@ -1,198 +0,0 @@
|
||||
ictlyh Translating
|
||||
bmon – A Powerful Network Bandwidth Monitoring and Debugging Tool for Linux
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
bmon is a simple yet powerful, text-based [network monitoring and debugging tool][1] for Unix-like systems, which captures networking related statistics and displays them visually in a human friendly format. It is a reliable and effective real-time bandwidth monitor and rate estimator.
|
||||
|
||||
It can read input using an assortment of input modules and presents output in various output modes, including an interactive curses user interface as well as a programmable text output for scripting purposes.
|
||||
|
||||
**Suggested Read:** [20 Command Line Tools to Monitor Linux Performance][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### Install bmon Bandwidth Monitoring Tool in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Almost all Linux distributions has bmon package in the default repositories and can be easily install from default package manger, but the available version might be little older.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo yum install bmon [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora]
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install bmon [On Fedora 22+]
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install bmon [On Debian/Ubuntu/Mint]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can get `.rpm` and `.deb` packages for your Linux distribution from [https://pkgs.org/download/bmon][3].
|
||||
|
||||
If you wanted to have a most recent version of bmon (i.e version 4.0), you need to build it from source using following commands.
|
||||
|
||||
#### On CentOS, RHEL and Fedora
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/tgraf/bmon.git
|
||||
$ cd bmon
|
||||
$ sudo yum install make libconfuse-devel libnl3-devel libnl-route3-devel ncurses-devel
|
||||
$ sudo ./autogen.sh
|
||||
$ sudo./configure
|
||||
$ sudo make
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### On Debian, Ubuntu and Linux Mint
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/tgraf/bmon.git
|
||||
$ cd bmon
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential make libconfuse-dev libnl-3-dev libnl-route-3-dev libncurses-dev pkg-config dh-autoreconf
|
||||
$ sudo ./autogen.sh
|
||||
$ sudo ./configure
|
||||
$ sudo make
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Use bmon Bandwidth Monitoring Tool in Linux
|
||||
|
||||
Run it as below (for starters: RX means received bytes per second and TX refers to transmitted bytes per second):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
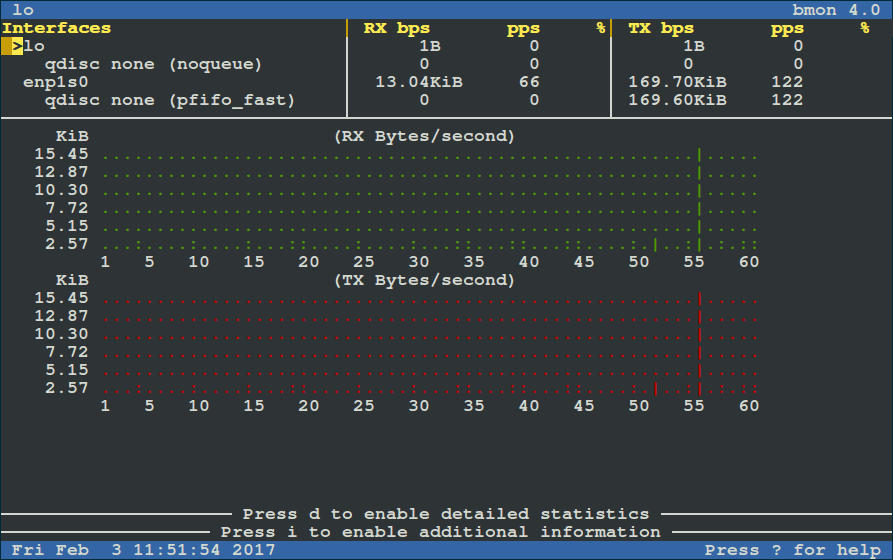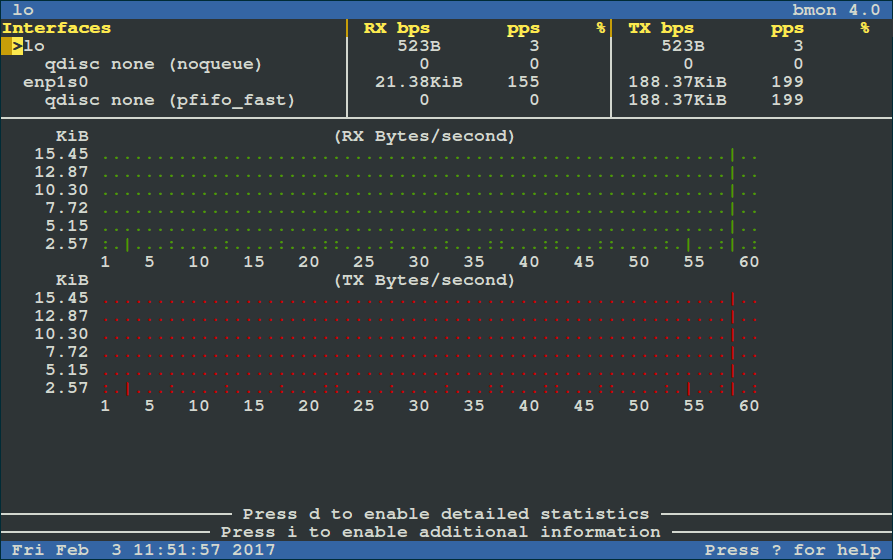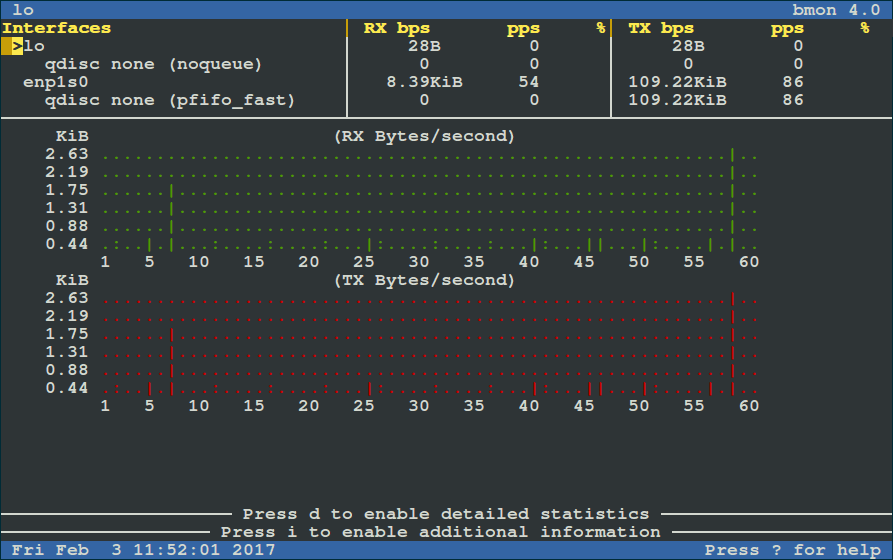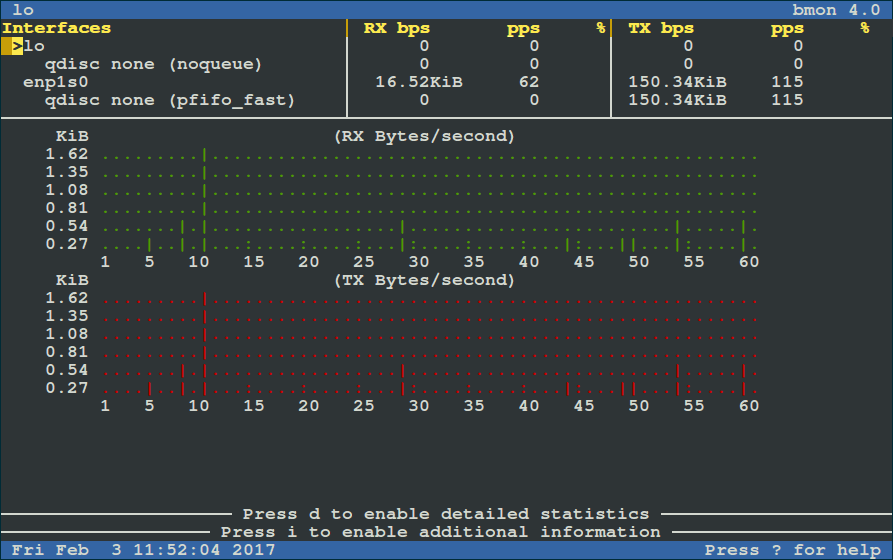
|
||||
][4]
|
||||
|
||||
To view more detailed graphical statistics/information of bandwidth usage, press `d` key and refer screnshot below.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
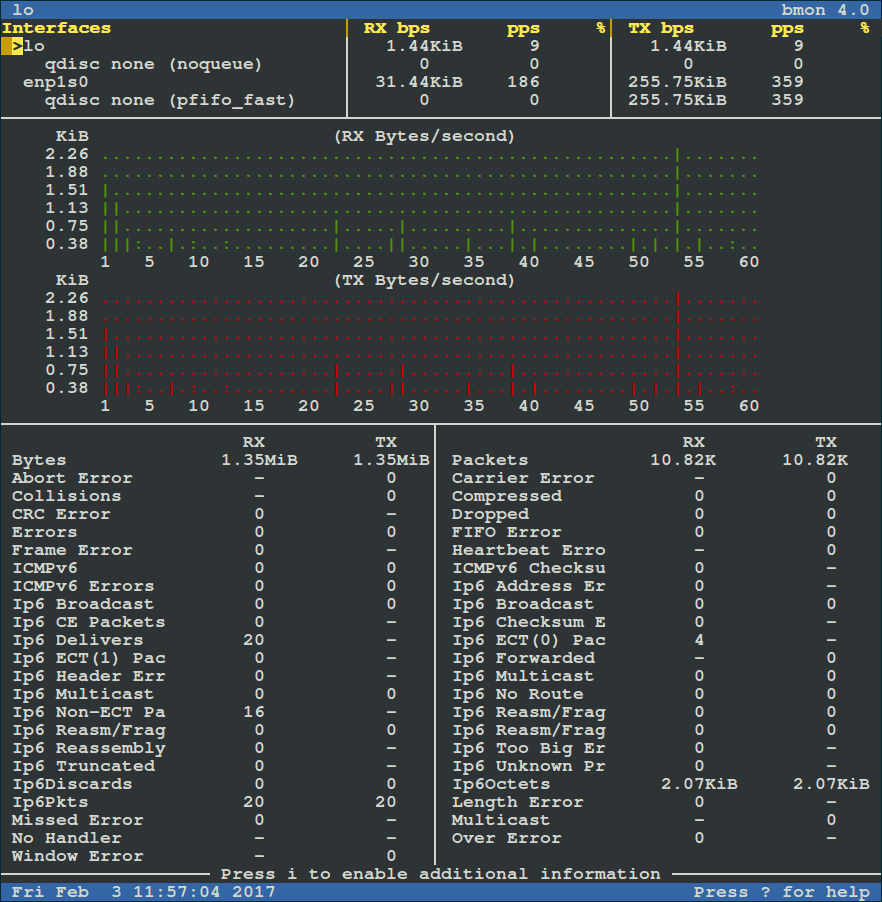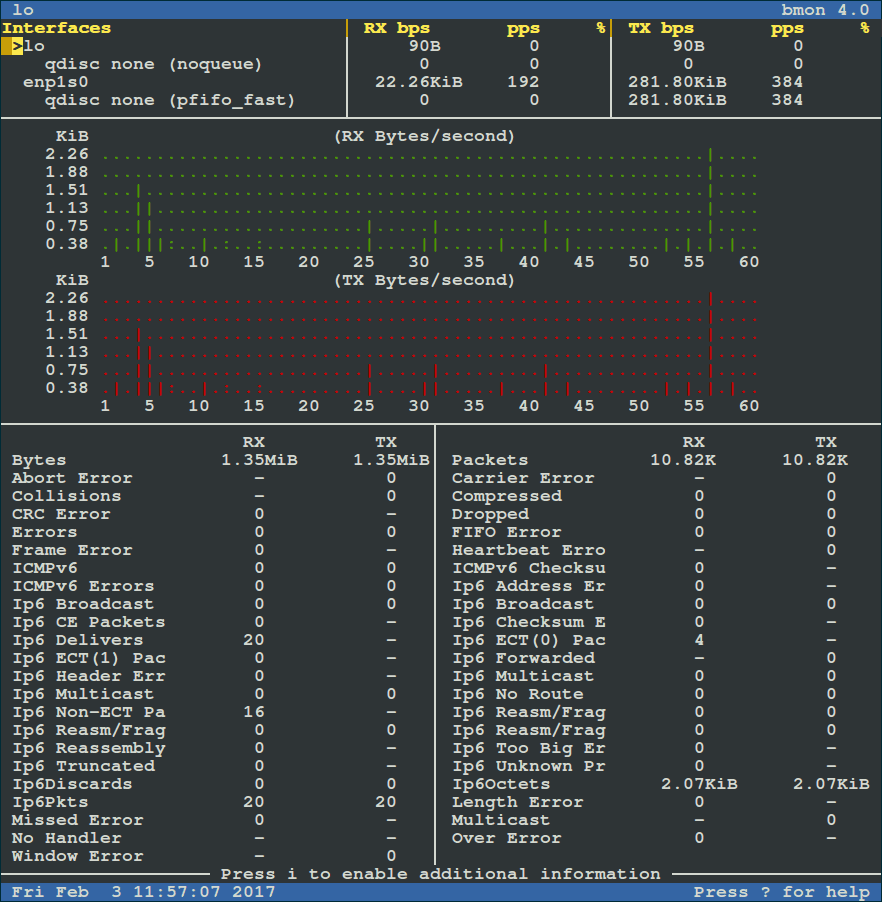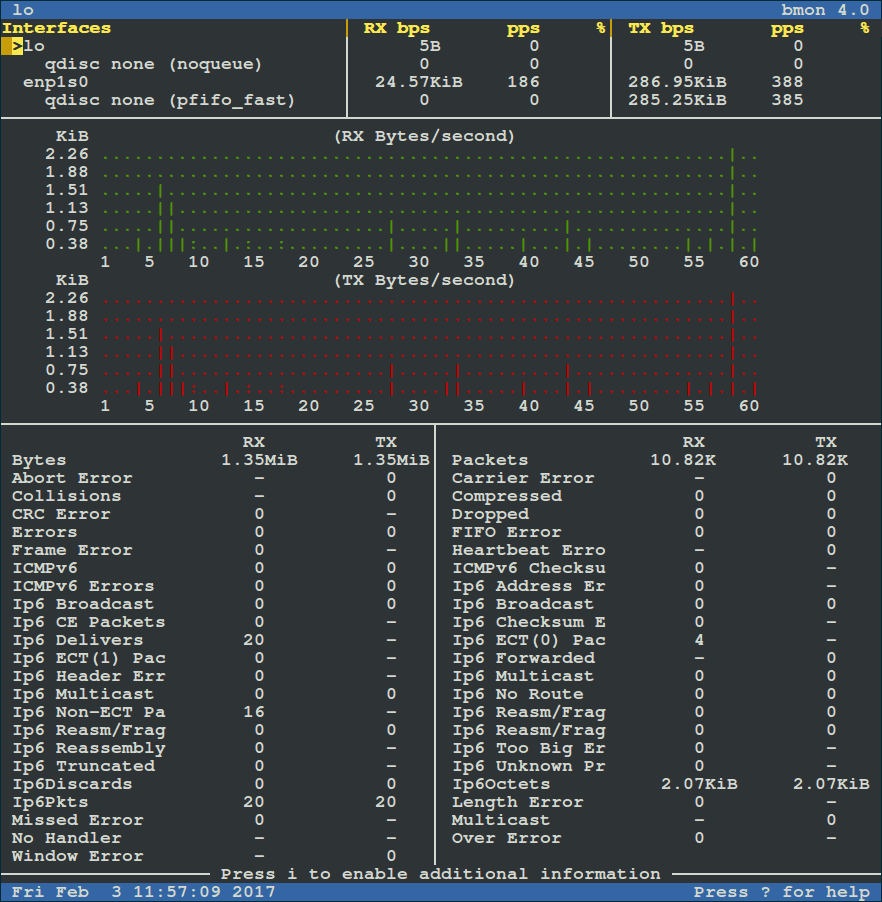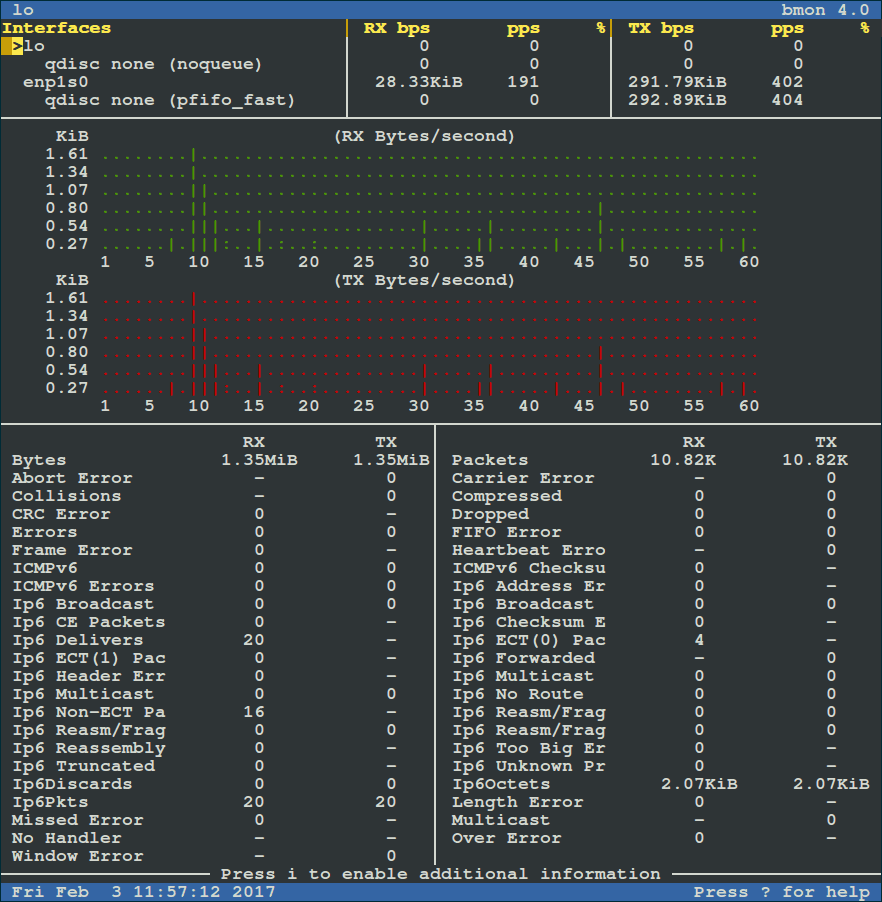
|
||||
][5]
|
||||
|
||||
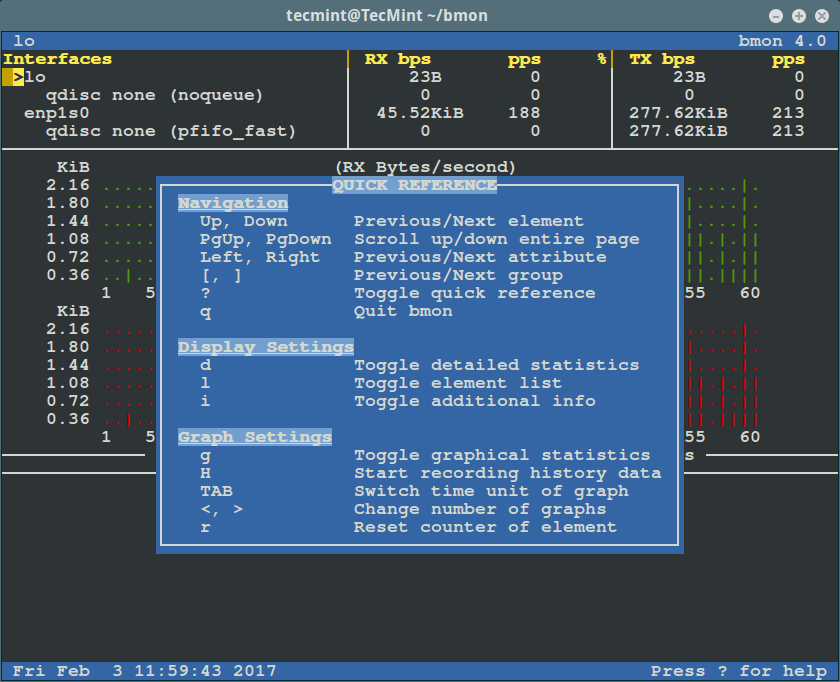
Press `[Shift + ?]` to view the quick reference below. To exit the interface, press [Shift + ?] again.
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
bmon – Quick Reference
|
||||
|
||||
To view statistics of a given interface, select it using the `Up` and `Down` arrows. However, to monitor a specific interface only, specify it as an argument on the command line as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
**Suggested Read:** [13 Tools to Monitor Linux Performance][7]
|
||||
|
||||
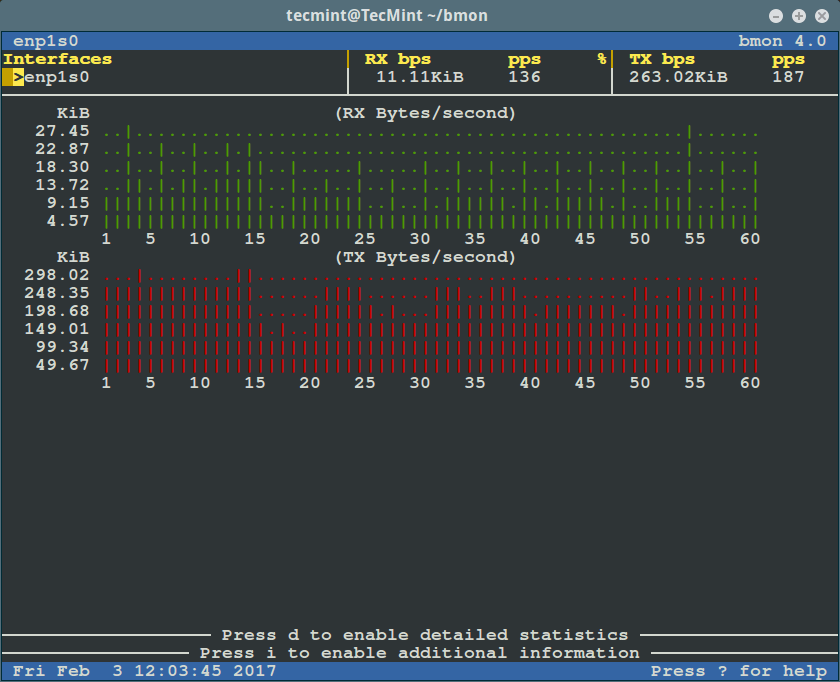
The flag `-p` sets a policy defining which network interfaces to display, in the example below, we will be monitoring the `enp1s0` network interface:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -p enp1s0
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
bmon – Monitor Ethernet Bandwidth
|
||||
|
||||
To use bit per second instead of bytes per second, use the `-b` flag like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -bp enp1s0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can also define the intervals per second with the `-r` flag as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -r 5 -p enp1s0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Use bmon Input Modules
|
||||
|
||||
bmon has a number of input modules that offer statistical data about interfaces, which includes:
|
||||
|
||||
1. netlink – employs the Netlink protocol to collect interface and traffic control statistics from the kernel. This is the default input module.
|
||||
2. proc — reads interface statistics from the /proc/net/dev file. It is considered a legacy interface and offered for backwards compatibly. It is a fallback module in case the Netlink interface is not available.
|
||||
3. dummy – this is a programmable input module for debugging and testing purposes.
|
||||
4. null – disables data collection.
|
||||
|
||||
To find additional info about a module, invoke the it with the “help” option set as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -i netlink:help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The next command will invoke bmon with the proc input module enabled:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -i proc -p enp1s0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How to Use bmon Output Modules
|
||||
|
||||
bmon also uses output modules to display or export the statistical data collected by the input modules above, which includes:
|
||||
|
||||
1. curses – this is an interactive curses based text user interface, it offers real time rate estimations and a graphical representation of each attribute. It is the default output mode.
|
||||
2. ascii – is a straightforward programmable text output meant for human consumption. It can display list of interfaces, detailed counters and graphs to the console. It is the default fallback output mode when curses is not available.
|
||||
3. format – is a fully scriptable output mode, it’s meant for consumption by other programs-meaning we can use its output values at a later time in scripts or programs for analysis and more.
|
||||
4. null – this disables output.
|
||||
|
||||
To get more info concerning a module, run the it with the “help” flag set like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -o curses:help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The command that follows will invoke bmon in ascii output mode:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
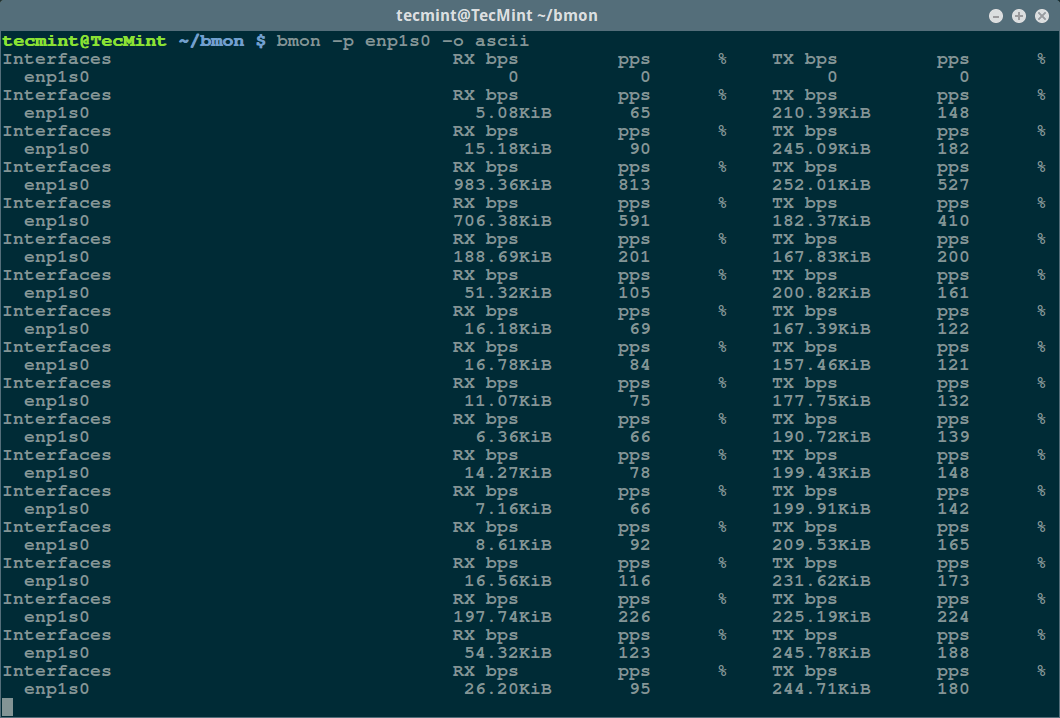
$ bmon -p enp1s0 -o ascii
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||
|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
bmon – Ascii Output Mode
|
||||
|
||||
We can run the format output module as well, then use the values obtained for scripting or in another program:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -p enp1s0 -o format
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][10]
|
||||
|
||||
bmon – Format Output Mode
|
||||
|
||||
For additional usage info, options and examples, read the bmon man page:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man bmon
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Visit the bmon Github repository: [https://github.com/tgraf/bmon][11].
|
||||
|
||||
That’s all for now, test the various features of bmon in different scenarios and share your thoughts about it with us via the comment section below.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
译者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili is a Linux and F.O.S.S enthusiast, an upcoming Linux SysAdmin, web developer, and currently a content creator for TecMint who loves working with computers and strongly believes in sharing knowledge.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/bmon-network-bandwidth-monitoring-debugging-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[译者ID](https://github.com/译者ID)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/bcc-best-linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/command-line-tools-to-monitor-linux-performance/
|
||||
[3]:https://pkgs.org/download/bmon
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/bmon-Linux-Bandwidth-Monitoring.gif
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/bmon-Detailed-Bandwidth-Statistics.gif
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/bmon-Quick-Reference.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/bmon-Monitor-Ethernet-Bandwidth.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/bmon-Ascii-Output-Mode.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/bmon-format-output-mode.png
|
||||
[11]:https://github.com/tgraf/bmon
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,198 @@
|
||||
bmon - Linux 下一个强大的网络带宽监视和调试工具
|
||||
============================================================
|
||||
|
||||
bmon 是类 Unix 系统中一个基于文本,简单但非常强大的 [网络监视和调试工具][1],它能抓取网络相关统计信息并把它们以用户友好的格式展现出来。它是一个可靠高效的带宽监视和网速预估器。
|
||||
|
||||
它能使用各种输入模块读取输入,并以各种输出模式显示输出,包括交互式用户界面和用于脚本编写的可编程文本输出。
|
||||
|
||||
**推荐阅读:** [监控 Linux 性能的20个命令行工具][2]
|
||||
|
||||
### 在 Linux 上安装 bmon 带宽监视工具
|
||||
|
||||
几乎所有 Linux 发行版的默认仓库中都有 bmon 软件包,可以从默认包管理器中轻松安装,但可用的版本可能比较旧。
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo yum install bmon [On RHEL/CentOS/Fedora]
|
||||
$ sudo dnf install bmon [On Fedora 22+]
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install bmon [On Debian/Ubuntu/Mint]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
另外,你也可以从 [https://pkgs.org/download/bmon][3] 获取对应你 Linux 发行版的 `.rpm` 和 `.deb` 软件包。
|
||||
|
||||
如果你想要最新版本(例如版本4.0)的 bmon,你需要通过下面的命令从源码构建。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 CentOS、RHEL 和 Fedora 中
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/tgraf/bmon.git
|
||||
$ cd bmon
|
||||
$ sudo yum install make libconfuse-devel libnl3-devel libnl-route3-devel ncurses-devel
|
||||
$ sudo ./autogen.sh
|
||||
$ sudo./configure
|
||||
$ sudo make
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### 在 Debian、Ubuntu 和 Linux Mint 中
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ git clone https://github.com/tgraf/bmon.git
|
||||
$ cd bmon
|
||||
$ sudo apt-get install build-essential make libconfuse-dev libnl-3-dev libnl-route-3-dev libncurses-dev pkg-config dh-autoreconf
|
||||
$ sudo ./autogen.sh
|
||||
$ sudo ./configure
|
||||
$ sudo make
|
||||
$ sudo make install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何在 Linux 中使用 bmon 带宽监视工具
|
||||
|
||||
通过以下命令运行它(给初学者:RX 表示每秒接收数据,TX 表示每秒发送数据):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][4]
|
||||
|
||||
按 `d` 键可以查看更详细的带宽使用情况的图形化统计信息,参考下面的截图。
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][5]
|
||||
|
||||
按 `[Shift + ?]` 可以查看快速指南。再次按 `[Shift + ?]` 可以退出(指南)界面。
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][6]
|
||||
|
||||
bmon – 快速指南
|
||||
|
||||
通过 `Up` 和 `Down` 箭头键可以查看特定网卡的统计信息。但是,要监视一个特定的网卡,你也可以像下面这样作为命令行参数指定。
|
||||
|
||||
**推荐阅读:** [监控 Linux 性能的13个工具][7]
|
||||
|
||||
标签 `-p` 指定了要显示的网卡,在下面的例子中,我们会监视网卡 `enp1s0`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -p enp1s0
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][8]
|
||||
|
||||
bmon – 监控以太网带宽
|
||||
|
||||
要查看每秒位数而不是字节数,可以像下面这样使用 `-b` 标签:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -bp enp1s0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
我们也可以像下面这样指定每秒的间隔数:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -r 5 -p enp1s0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何使用 bmon 的输入模块
|
||||
### How to Use bmon Input Modules
|
||||
|
||||
bmon 有很多能提供网卡统计数据的输入模块,其中包括:
|
||||
|
||||
1. netlink - 使用 Netlink 协议从内核中收集网卡和流量控制统计信息。这是默认的输入模块。
|
||||
2. proc - 从 /proc/net/dev 文件读取网卡统计信息。它被认为是传统界面,且提供了向后兼容性。它是 Netlink 接口不可用时的备用模块。
|
||||
3. dummy - 这是用于调试和测试的可编程输入模块。
|
||||
4. null - 停用数据收集。
|
||||
|
||||
要查看关于某个模块的其余信息,可以像下面这样使用 “help” 选项调用它:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -i netlink:help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令将启用 proc 输入模块运行 bmon:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -i proc -p enp1s0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何使用 bmon 输出模块
|
||||
|
||||
bmon 也使用输出模块显示或者导出上面输入模块收集的统计数据,输出模块包括:
|
||||
|
||||
1. curses - 这是一个交互式的文本用户界面,它提供实时的网上估计以及每个属性的图形化表示。这是默认的输出模块。
|
||||
2. ascii - 这是用于用户查看的简单可编程文本输出。它能显示网卡列表、详细计数以及图形到控制台。当 curses 不可用时这是默认的备选输出模块。
|
||||
3. format - 这是完全脚本化的输出模式,供其它程序使用 - 意味着我们可以在后面的脚本和程序中使用它的输出值进行分析。
|
||||
4. null - 停用输出。
|
||||
|
||||
像下面这样通过 “help” 标签获取更多的模块信息。
|
||||
To get more info concerning a module, run the it with the “help” flag set like so:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -o curses:help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
下面的命令会用 ascii 输出模式运行 bmon:
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -p enp1s0 -o ascii
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][9]
|
||||
|
||||
bmon – Ascii 输出模式
|
||||
|
||||
我们也可以用 format 输出模式,然后在脚本或者其它程序中使用获取的值:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ bmon -p enp1s0 -o format
|
||||
```
|
||||
[
|
||||

|
||||
][10]
|
||||
|
||||
bmon – Format 输出模式
|
||||
|
||||
想要其它的使用信息、选项和事例,可以阅读 bmon 的 man 手册:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ man bmon
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
访问 bmon 的Github 仓库:[https://github.com/tgraf/bmon][11].
|
||||
|
||||
就是这些,在不同场景下尝试 bmon 的多个功能吧,别忘了在下面的评论部分和我们分享你的想法。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
译者简介:
|
||||
|
||||
Aaron Kili 是一个 Linux 和 F.O.S.S 爱好者、Linux 系统管理员、网络开发人员,现在也是 TecMint 的内容创作者,她喜欢和电脑一起工作,坚信共享知识。
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
via: http://www.tecmint.com/bmon-network-bandwidth-monitoring-debugging-linux/
|
||||
|
||||
作者:[Aaron Kili][a]
|
||||
译者:[ictlyh](https://github.com/ictlyh)
|
||||
校对:[校对者ID](https://github.com/校对者ID)
|
||||
|
||||
本文由 [LCTT](https://github.com/LCTT/TranslateProject) 原创编译,[Linux中国](https://linux.cn/) 荣誉推出
|
||||
|
||||
[a]:http://www.tecmint.com/author/aaronkili/
|
||||
|
||||
[1]:http://www.tecmint.com/bcc-best-linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
|
||||
[2]:http://www.tecmint.com/command-line-tools-to-monitor-linux-performance/
|
||||
[3]:https://pkgs.org/download/bmon
|
||||
[4]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/bmon-Linux-Bandwidth-Monitoring.gif
|
||||
[5]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/bmon-Detailed-Bandwidth-Statistics.gif
|
||||
[6]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/bmon-Quick-Reference.png
|
||||
[7]:http://www.tecmint.com/linux-performance-monitoring-tools/
|
||||
[8]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/bmon-Monitor-Ethernet-Bandwidth.png
|
||||
[9]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/bmon-Ascii-Output-Mode.png
|
||||
[10]:http://www.tecmint.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/02/bmon-format-output-mode.png
|
||||
[11]:https://github.com/tgraf/bmon
|
||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user